Canon iR1600, iR2000 NETWORK GUIDE [UK]

Network Guide
Network Guide
Series
Please read this guide before operating this equipment.
After you finish reading this guide, store it in a safe place for future reference.
ENG
About the Manuals for the Machine
The manuals for this machine are divided as follows. Please read them to suit your needs.
For Basic Use ................................................
Troubleshooting .............................................
For Basic Copying ...........................................
For Convenient Copying ....................................
For Remote UI Use ..........................................
For Setting Up the Network Connection..................
For Printer Use...............................................
For Installing Printer Driver ...............................
For Connecting and Setting the Network.................
Reference Guide
Copying Guide
Remote UI Guide
Setup Guide
PS/PCL Printer Guide
PS Driver Guide
PCL Driver Guide
Network Guide
(This Document)
CD-ROM
CD-ROM
CD-ROM
CD-ROM
•
The product illustration on the cover may differ slightly from your product.
The volumes marked with this symbol are PDF manuals included in accompanying CD-ROMs.
CD-ROM
How This Manual Is Organized
Chap 1
Chap 2
Chap 3
Chap 4
Chap 5
Chap 6
Before You Start
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
Using a NetWare Network (Windows)
Using a NetBIOS Network (Windows 95/98/Me)
Using an AppleTalk Network (Macintosh)
Appendix
Describes troubleshooting procedures and methods for checking the machine's
network settings, provides lists of network menus accessed from the control panel,
and lists the principal network specifications of the machine.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
•
Some of the data contained herein may not exactly reflect the current model of the particular product with which this manual has been included. If you
have a need for an exact specification, please contact Canon for the current specification.
No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without prior written consent of Canon Inc.
•
10
11
12
13
14

iii

Table of Contents
How to Use This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vi
Symbols Used in This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vi
Abbreviations Used in This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vi
Trademarks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Chapter 1 Before You Start
System Environment Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
System Environment Requirements for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Checking Your Network Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Sample Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000 Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
With a NetWare Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Without a NetWare Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-5
Sample Macintosh Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Sample UNIX Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Using a Network with Various Types of Computers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Chapter 2 Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Preparation for Protocol Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Settings from the Control Panel of the Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-3
Checking the current network settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-5
Settings Using ARP/PING Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-6
Protocol Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
Settings Using a Web Browser (Remote UI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
Settings Using the FTP Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Setting Up a Computer for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Printer Connection Method (LPD/Raw) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-15
Windows 95/98/Me. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Windows NT 4.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
UNIX. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-22
Printer Connection Method (IPP). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Windows 95/98/Me. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Print Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
iii

Printer Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
Printer Management Using Web Browser (Remote UI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
Printer Management Using the FTP Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
Chapter 3 Using a NetWare Network (Windows)
NetWare Network Setup Operating Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
NetWare Print Service Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Types of Print Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Setup Using NetWare Administrator or PCONSOLE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Using NetWare Administrator in NDS Queue Server Mode or Remote Printer
Mode (NetWare 4.x or Later) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Using PCONSOLE with the Bindery Mode in the Queue Server Mode or
Remote Printer Mode (NetWare 3.x). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Protocol Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Printer Protocol Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
Setting Up a Computer for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Connecting to a NetWare Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Installing Printer Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Setting the Printer Destination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Chapter 4 Using a NetBIOS Network (Windows 95/98/Me)
NetBIOS Network Setup Operating Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Setting Up a Computer for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
NetBIOS Network Connection Method. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Installing the Printer Driver. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Setting the Printer Destination . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Chapter 5 Using an AppleTalk Network (Macintosh)
AppleTalk Network Setup Operating Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Macintosh Network Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Protocol Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Settings Using a Web Browser (Remote UI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Installing Printer Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
iv

Chapter 6 Appendix
Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-2
How to Delete Software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
LPR Port Utility Deletion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-6
NetBIOS/NetBEUI Port Monitor Utility Deletion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-7
Network Setting Items. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-8
Network Setting Item Using the Control Panel of the Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
Network Setting Items Using a web Browser (Remote UI)
or FTP Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
The Available Software for Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-13
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6-14
v
Preface
Thank you for purchasing the Canon iR2000/iR1600 Series. Please read this manual
thoroughly before operating the iR2000/iR1600 Series in order to familiarize yourself with its
capabilities, and to make the most of its many functions. After reading this manual store it in
a safe place for future reference.
How to Use This Manual
Symbols Used in This Manual
The following marks are used in this manual to indicate safety precautions,
restrictions and notices for handling the product.
IMPORTANT
NOTE
Key and button names are shown in this manual as follows:
Keys on the printer control panel............... [Go]
Tool buttons on the tool bar
Indicates operational warnings and restrictions. Be certain to read
these items to operate the machine correctly, and to avoid damage to
the machine.
Indicates notes for operation or additional explanations. Reading
these is recommended.
.................................
(Print)
Abbreviations Used in This Manual
In this guide:
Microsoft® Windows® 95 is referred to as Windows 95.
Microsoft® Windows® 98 is referred to as Windows 98.
Microsoft® Windows® Millennium Edition is referred to as Windows Me.
Microsoft® Windows NT® is referred to as Windows NT.
Microsoft® Windows® 2000 is referred to as Windows 2000/XP.
Microsoft® Windows® Operating System is referred to as Windows.
PostScript® 3 emulation is referred to as PS.
Novell NetWare® is referred to as NetWare.
vi

Trademarks
Canon, the Canon logo and NetSpot are trademarks of Canon Inc.
Adobe, Acrobat, PostScript, and PostScript 3 are trademarks of Adobe Systems
Incorporated.
Apple, AppleTalk, Macintosh, and Mac OS are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc.
PCL, HP, and HP-UX are trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company.
IBM is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
Linux is a trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Microsoft, MS-DOS, the Windows logo, Windows, and Windows NT are registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Netscape is a trademark of Netscape Communications Corp.
NetWare® and Novell are registered trademarks of Novell, Inc.
IPX/SPX, NDS, NDPS, and Novell Client are trademarks of Novell Inc.
©1996 Novell, Inc., all rights reserved.
Red Hat is a trademark of Red Hat Software, Inc.
Solaris, Sun, SunOS, and Sun Microsystems are trademarks of Sun Microsystems
in the United States and/or other countries.
Turbolinux and its logo are trademarks of Turbolinux, Inc.
UNIX is a registered trademark exclusively licensed to X/Open Company, Ltd. in the
United States and/or other countries.
Ethernet is a trademark of Xerox Corporation.
Other product and company names herein may be the trademarks of their
respective owners.
Copyright 2001 by Canon, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any
means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and recording, or by any
information storage or retrieval system without the prior written permission of
Canon, Inc.
vii

viii
Before You Start
CHAPTER
This chapter describes what you need to know before you start using the machine, including
the network environments with which the machine is compatible, and how to check the
network environment you are using.
System Environment Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
System Environment Requirements for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-2
Checking Your Network Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Sample Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-4
Sample Macintosh Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Sample UNIX Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-6
Using a Network with Various Types of Computers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-7
1
1-1

System Environment Requirements
1
compatible.
System Environment Requirements for Printing
The following network and system environments are compatible when printing with
the machine.
Before You Start
■
Printing with a TCP/IP Network:
Compatible OS: Microsoft Windows 95/98/Me
Microsoft Windows NT Server 4.0
Microsoft Windows NT Workstation 4.0
Microsoft Windows 2000 Server
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional
Microsoft Windows XP
Solaris Version 1.1x (SunOS Version 4.1x) or later
Solaris Version 2.5x (SunOS Version 5.5x) or later
HP-UX Version 10.x or later
IBM-AIX Version 4.x or later
Red Hat Linux 6.1 or later
Compatible Computers: Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000; IBM PC/compatibles
■
Printing with a NetWare Network:
Compatible Servers: Novell NetWare Version 3.2/4.1/4.11/4.2/5.0/5.1
Compatible Clients: Microsoft Windows 95/98/Me
Microsoft Windows NT Server 4.0
Microsoft Windows NT Workstation 4.0
Microsoft Windows 2000 Server
Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional
Compatible Computers: IBM PC/compatibles
This section describes the system environments with which the machine is
1-2
■
Printing with a NetBIOS Network:
Compatible OS: Microsoft Windows 95/98/Me
Compatible Computers: IBM PC/compatibles
Required Memory for Computers: More than 16MB
■
Printing with an AppleTalk Network:
Compatible OS: Mac OS 7.5 or later
Compatible AppleTalk: EtherTalk Phase 2
System Environment Requirements
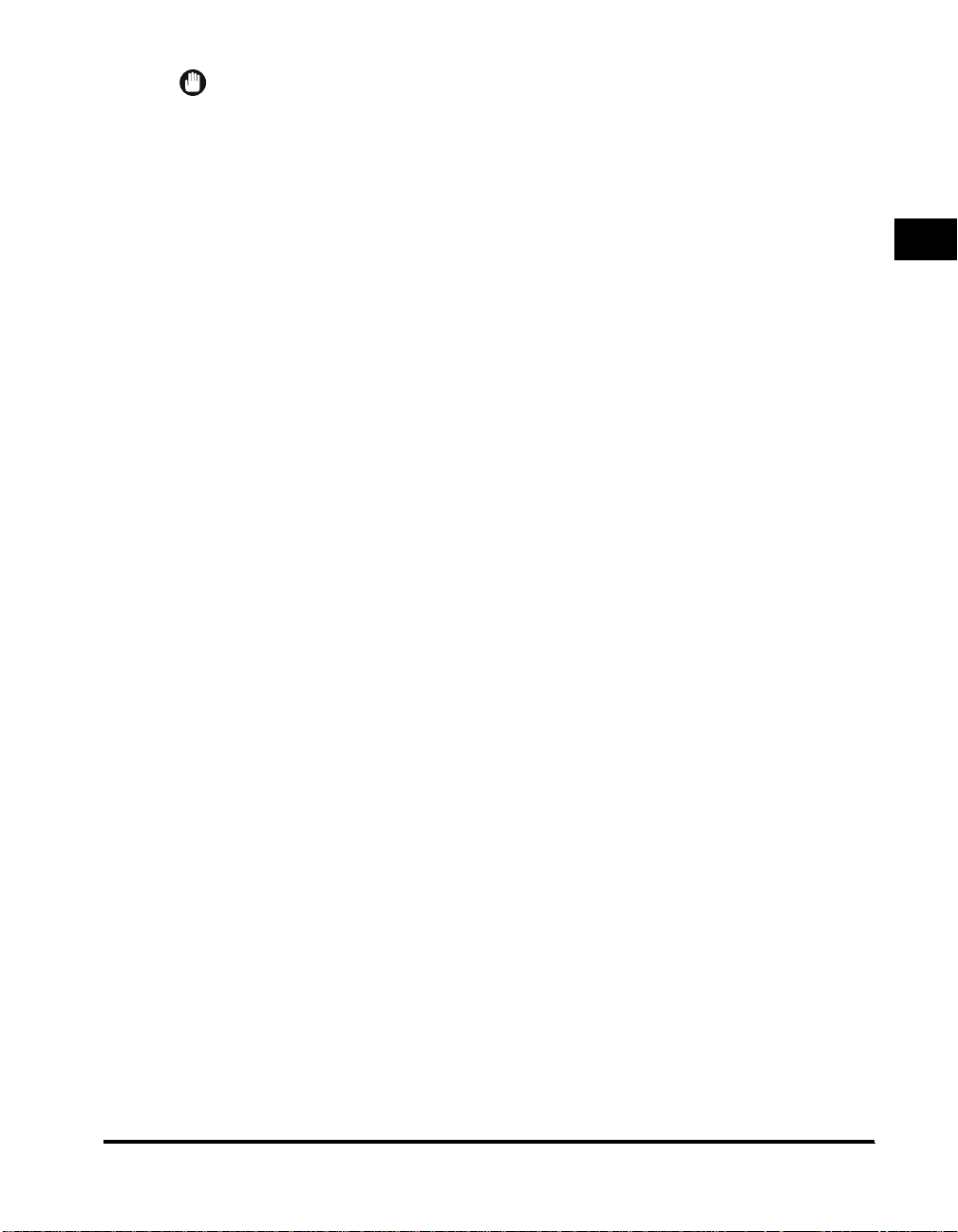
IMPORTANT
•
If you are using Windows NT 4.0, install Service Pack 5 or later.
•
To use the Remote UI on Machintosh, the optional Canon PS Module-B1 should be
installed.
1
Before You Start
System Environment Requirements
1-3
Checking Your Network Environment
1
Refer to the following diagram example to confirm the network environment that is
connected to the machine, and then perform the necessary operations.
Sample Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP Network
With a NetWare Server
Before You Start
In a network environment like the one below, a NetWare, TCP/IP, or NetBIOS
protocol can be used for printing. Multiple protocols can also be used at the same
time. NetBIOS is available only for Windows 95/98/Me.
Windows 95
Windows 98 Windows NT
Protocol: NetWare, TCP/IP, NetBIOS
1-4
NetWare Server
Depending on the protocol, see the following:
•
Chapter 2 Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
•
Chapter 3 Using a NetWare Network (Windows)
•
Chapter 4 Using a NetBIOS Network (Windows 95/98/Me)
Checking Your Network Environment
iR2000/iR1600 Series
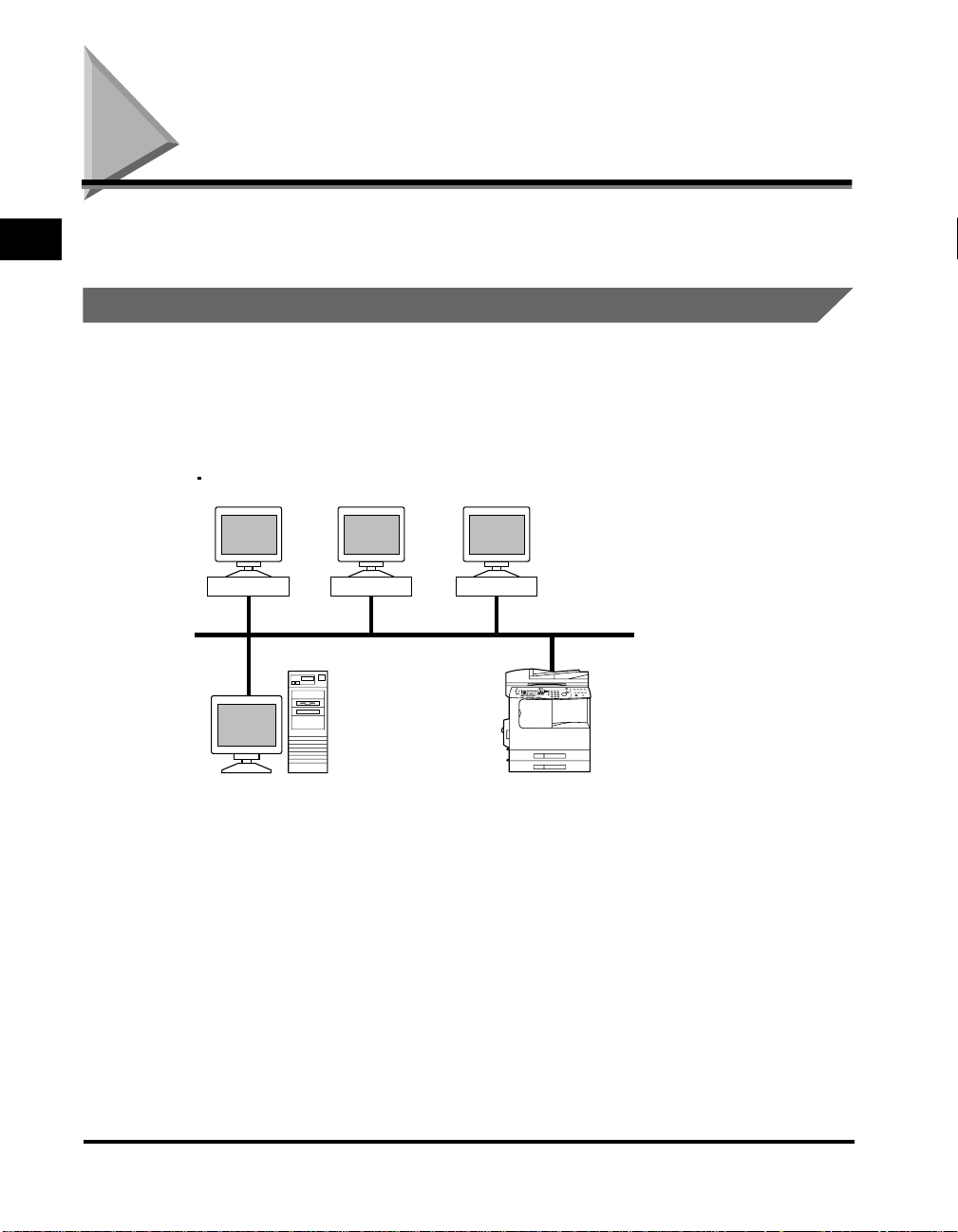
Without a NetWare Server
In a network environment like the one below, either TCP/IP or NetBIOS protocol
can be used. Multiple protocols can also be used at the same time. NetBIOS is
available only for Windows 95/98/Me.
Windows 95 Windows 98 Windows NT
Protocol: TCP/IP, NetBIOS
iR2000/iR1600 Series
Depending on the protocol, see the following:
Chapter 2 Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
•
Chapter 4 Using a NetBIOS Network (Windows 95/98/Me)
•
NOTE
•
Once you set up a network printer, each computer can output directly to it. Using TCP/IP
protocol with Windows 2000 or Windows NT as a print server provides efficient
management of your network printer. For the detailed procedure, see “Print Server
Settings,” on p.2-29.
•
In a network comprising only Windows 95/98/Me that does not use the TCP/IP protocol,
you can only use NetBIOS protocol to specify basic settings.
1
Before You Start
Checking Your Network Environment
1-5
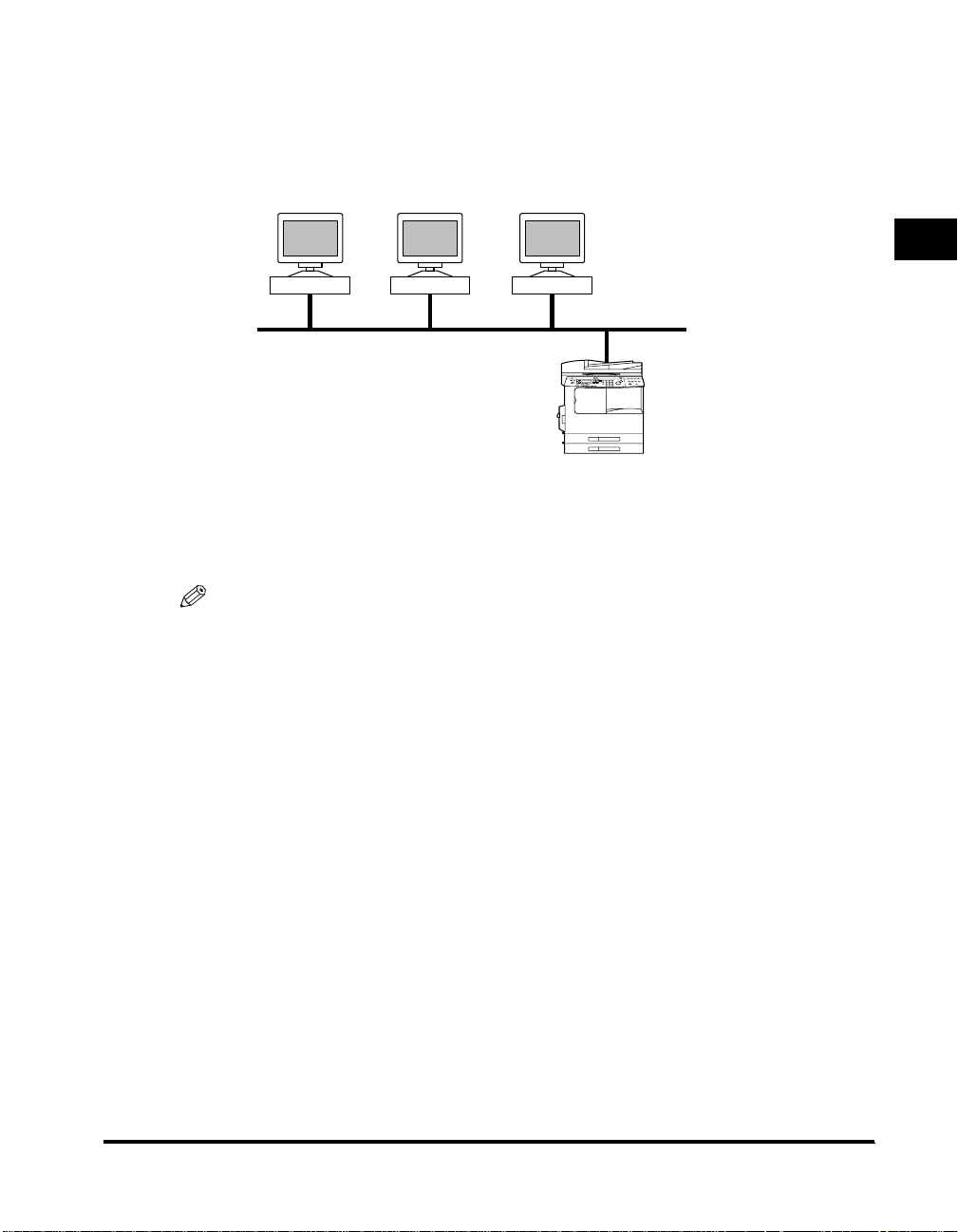
Sample Macintosh Network
With Macintosh computers, the AppleTalk (EtherTalk) protocol is used for printing.
(See “Chapter 5 Using an AppleTalk Network (Macintosh).”)
Macintosh
1
Protocol: AppleTalk
Before You Start
iR2000/iR1600 Series
Sample UNIX Network
With UNIX computers, the TCP/IP protocol is used. (See “Chapter 2 Using a TCP/
IP Network (Windows/UNIX).”)
1-6
Solaris (Sun OS) IBM-AIX HP-UX Linux
Protocol: TCP/IP
iR2000/iR1600 Series
Checking Your Network Environment

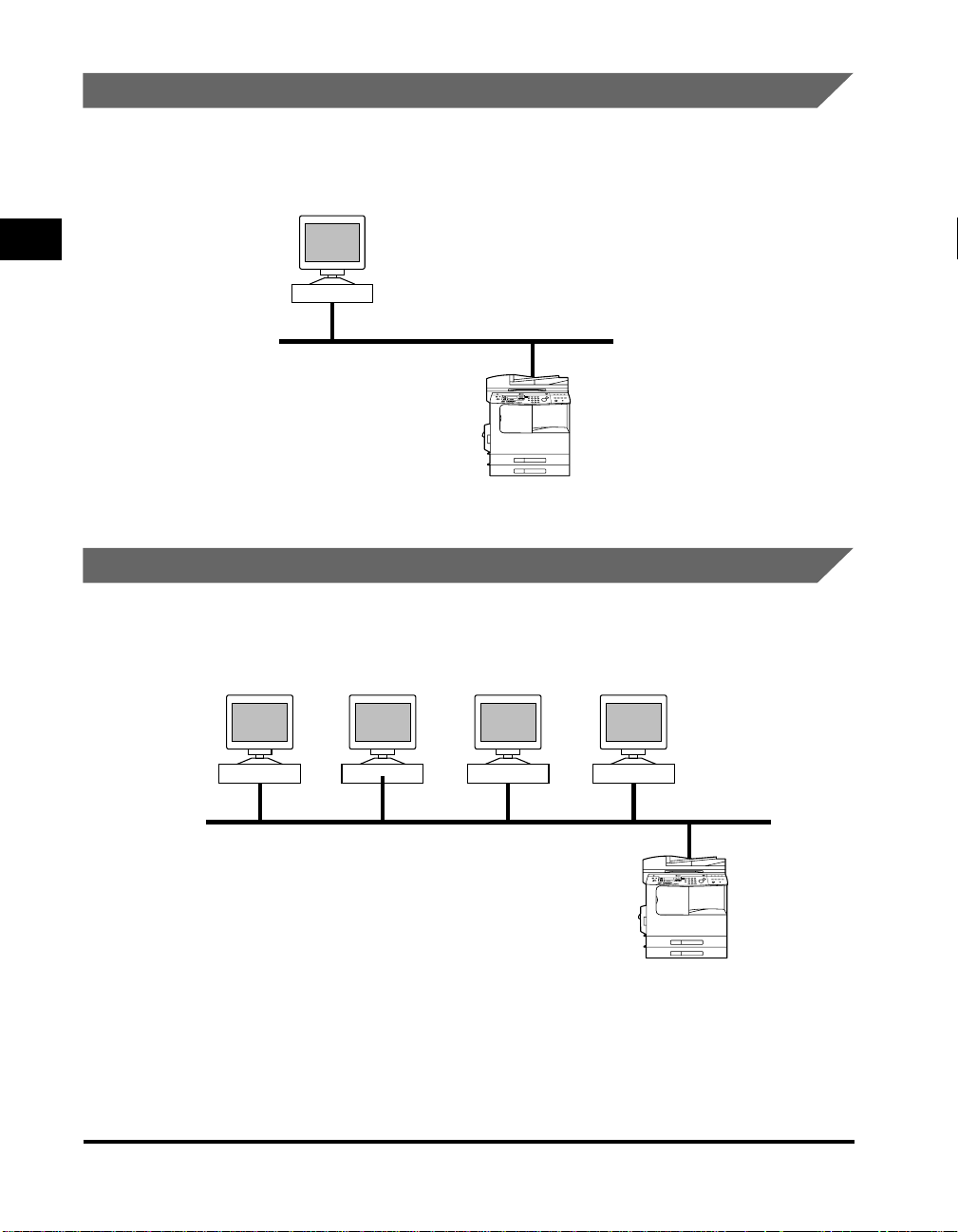
Using a Network with Various Types of Computers
When there are various types of computers on the network, network operations
depend on the type of computer being used.
For example, if you are using Windows 98 and UNIX computers, specify the
settings described in both “Sample Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP Network,” on
p.1-4 and “Sample UNIX Network,” on p.1-6.
Windows Solaris
1
Protocol: TCP/IP, NetWare, NetBIOS
NetWare Server
iR2000/iR1600 Series
Depending on the protocol, see the following:
•
Chapter 2 Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
•
Chapter 3 Using a NetWare Network (Windows)
•
Chapter 4 Using a NetBIOS Network (Windows 95/98/Me)
Before You Start
Checking Your Network Environment
1-7
1
Before You Start
1-8
Checking Your Network Environment
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
This chapter describes the settings and procedures necessary to connect and use the
machine with a TCP/IP network.
TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-2
Preparation for Protocol Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Settings from the Control Panel of the Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-3
Settings Using ARP/PING Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-7
Protocol Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Settings Using a Web Browser (Remote UI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-8
Settings Using the FTP Client. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-13
Setting Up a Computer for Printing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Printer Connection Method (LPD/Raw) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-16
Printer Connection Method (IPP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-26
Print Server Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-29
Printer Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-31
Printer Management Using Web Browser (Remote UI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-31
Printer Management Using the FTP Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2-31
2
CHAPTER
2-1

TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures
To use a TCP/IP network, it is necessary to perform the following procedure.
Network Cable Connection (See the PS/PCL Printer Guide)
1
2
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
Connect the network cables in accordance with the PS/PCL Printer Guide.
Preparation for Protocol Settings (See “Preparation for Protocol Settings,” on
2
p. 2-3.)
Specify the machine’s protocol settings for communication between the machine and computers using the
machine. Any of the following can be used to specify the settings.
• ARP/PING commands
• Machine’s control panel (Additional Functions menu)
Protocol Settings (See “Protocol Settings,” on p. 2-8.)
3
Specify the machine’s protocol settings. Use any of the following software to specify the settings on the
computer.
• Web browser (Remote UI)
• FTP client
2-2
Computer Settings for Printing (See “Setting Up a Computer for Printing,” on
4
p. 2-15.)
Specify the settings for each computer you use for printing.
IMPORTANT
•
It is recommended that the network manager perform steps 1, 2, and 3 above.
•
If you are printing using a TCP/IP network, you can use the following print applications.
- LPD
- FTP
- Raw (Windows 2000/XP only)
- IPP (Windows 95/98/Me/2000/XP only)
•
This machine does not come with printer driver software that can be used for each UNIX
platform.
TCP/IP Network Setup Operating Procedures
Preparation for Protocol Settings
Before you specify the machine’s protocol settings, it is necessary to specify the
machine IP address to enable communication between the machine and your
computers. You can use either of the following to specify the settings. Specify the
settings using the easiest method.
•
Machine’s control panel (Additional Functions menu)
•
ARP/PING commands
IMPORTANT
In the following operations in this section, the machine’s MAC address is necessary. For
•
checking the MAC address, from the printer control panel, follow the procedure below to
make a test print.
1. Press [Go] on the printer control panel; the Online indicator goes off.
2. Press [Menu] several times until <TEST MENU> appears.
3. Press [Item] several times until <PRINT EN CONFIG> appears in the second line in
the display.
4. Press [Enter].
Before you perform the following operations in this section, check that the machine is on
•
and connected to the network.
If you are using ARP/PING commands, the following steps directly allocate the IP
•
address to the machine. For this machine, in addition to direct allocation of the IP
address to the machine, you can use DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP to specify the IP address.
When the machine is started or reset, it checks whether DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP is
being used, and then allocates the IP address using the first available setting method.
Because the machine IP address is automatically allocated at this time, it is not
necessary for you to perform the following operations in this section. However if you are
reallocating the IP address, or if DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP cannot be used, perform the
following operations in this section.
2
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
Settings from the Control Panel of the Machine
IMPORTANT
Settings specified from the control panel become effective after the machine is restarted
•
after the procedure.
Press (Additional Functions) on the control panel.
1
The Additional Functions menu appears and the indicator blinks.
Preparation for Protocol Settings
2-3

2
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
Press or to select <4. SYSTEM SETTINGS>, and press
2
[OK].
The <SYSTEM SETTINGS> menu appears.
Press or to select <3. NETWORK SETTINGS>, and
3
press [OK].
The <NETWORK SETTINGS> menu appears.
Set <IP ADDRESS AUTO.> to <FIXED> or <AUTO>, and press
4
[OK].
NOTE
•
If you have set <IP ADDRESS AUTO> to <FIXED>, go to Step 6.
If you have set <IP ADDRESS AUTO.> to <AUTO>, select
5
<DHCP>, <BOOTP> and <RARP> to <ON> or <OFF>.
Set the items according to the IP ADDRESS AUTO setting.
1.Press or to select the item, if necessary.
2.Select <ON> or <OFF>.
3.Press [OK].
2-4
6
If you have set <IP ADDRESS AUTO.> to <FIXED>, specify <IP
ADDRESS>, <SUBNET MASK> and <DEFAULT GATEWAY> as
follows:
1. Press or to display the item, then press [OK].
2. Enter the number using the numeric keys.
3. Press [OK].
You can delete the number you entered by pressing (Clear).
NOTE
If the number has been previously entered, press (Clear) before entering a
•
new number.
Display <DNS SERVER ADD>, by pressing or if
7
necessary, enter the DNS server address using the numeric
keys, then press [OK].
Preparation for Protocol Settings
C
C
Set <DNS DYNAMIC SET> to <ON> or <OFF>, then press [OK].
8
2
Preparation for Protocol Settings
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
2-5

Checking the current network settings
You can check the network settings of the machine. Settings specified from the
Control panel become effective after the machine is restarted.
1
Press (Additional Functions) on the control panel.
The Additional Functions menu appears and the indicator blinks.
2
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
2
Press or to select <4. SYSTEM SETTINGS>, and press
[OK].
The <SYSTEM SETTINGS> menu appears.
3
Press or to select <3. NETWORK SETTINGS>, and
press [OK].
The <NETWORK SETTINGS> menu appears.
4
Press or repeatedly until <VIEW IP ADDRESS>
appears, and press [OK].
Press repeatedly to display the setting you want check.
5
By pressing , IP ADDRESS, SUBNET MASK, DEFAULT GATEWAY, DNS
SERVER ADD, HOST NAME and DOMAIN NAME are displayed in sequence.
2-6
Preparation for Protocol Settings

Settings Using ARP/PING Commands
Start up the MS-DOS prompt or the Command prompt.
1
If you are using UNIX, display the console screen, and then log in as a
superuser.
Execute the following command to add a static entry to the
2
arp table.
arp -s
<IP Address> <MAC Address>
IP Address: Specify the IP Address you want to allocate to the machine.
The IP address consists of 4 numbers ranging from 0 to 255
with “.” as the breakpoint.
MAC Address: Specify the MAC Address of the machine. Every second digit
is separated by “-” (“:” for UNIX).
Input Example (Windows):
Input Example (UNIX):
NOTE
•
If you are using IBM-AIX, enter "arp -s ether <IP Address> <MAC Address>."
arp -s 172.20.88.125 00-00-85-05-70-31
arp -s 172.20.88.125 00:00:85:05:70:31
2
3
Execute the applicable command below to set the IP address
to the network board.
ping
<IP Address>
ping -s
ping
ping <IP Address> 487 (for HP-UX)
ping -s 479 <IP Address> (for Red Hat Linux)
ping -s 480 <IP Address> (for Turbolinux)
IP Address: Specify the same address as the IP address as you specified
Input Example (Windows): ping 172.20.88.125 -l 479
NOTE
•
•
The preparation for machine protocol settings are completed.
<IP Address>
<IP Address> 479 (for IBM-AIX)
The character in “-l” is the alphabet letter “l.”
The Subnet Mask and Gateway Address are set as <0.0.0.0>.
-l 479
in step 2 above.
(for Windows)
479
(for Solaris 1.x/2.x)
Preparation for Protocol Settings
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
2-7

Protocol Settings
You can specify the machine’s protocol settings on the computer using any of the
following software. Specify the settings using the easiest method.
2
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
• Web browser (Remote UI)
• FTP client
Settings Using a Web Browser (Remote UI)
1
Start the web browser, enter the URL below in Location or
Address, and then press the Enter key.
http://<machine host name or IP address >/
Input Example: http://172.20.88.125/
IMPORTANT
•
For your web browser, use Netscape Navigator/Communicator 4.04 or later, or
Internet Explorer 4.01SP1 or later.
•
Turbolinux 4.0, you cannot set this machine’s protocol settings through Netscape
Communicator 4.08. Use a different version web browser.
•
If you are using a connection via a proxy server, use the following settings. (The
settings differ depending on the network environment.)
- When configuring your web browser to use the proxy server, add the IP address
of the machine to Exception (the address not using the proxy server).
•
Set up the web browser to accept cookies.
•
If you are starting more than one Remote UI at the same time, only the last setting
specified will be valid. It is recommended that you start only one Remote UI.
2-8
Protocol Settings

2
Select Administrator Mode, and then click the OK button.
The Remote UI starts.
NOTE
•
If a password has been set for the machine, enter the password, and then click the
OK button. If no password has been set, it is not necessary to enter a password.
2
Protocol Settings
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
2-9

3
Under Device Manager on the left side of the screen, click
Network.
2
The Network page is displayed.
4
Click the Edit... button at the right of TCP/IP.
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
2-10
The Edit TCP/IP Protocol Settings page is displayed.
Protocol Settings

5
From Frame Type, select Ethernet II.
NOTE
•
If you select Disabled, the network board is not recognized by the TCP/IP network.
•
To use the machine set as Off, see “Preparation for Protocol Settings,” on p.2-3.
2
6
Specify the setting method for the machine IP address.
▼ Under Use DHCP, Use BOOTP, and Use RARP, select On to use for the IP
address setting.
When selecting Off for Use DHCP, Use BOOTP, and Use RARP, the machine does not
check the protocols.
If neither DHCP, BOOTP, nor RARP can be used, the IP address specified in IP Address
is allocated.
IMPORTANT
•
For this machine, in addition to direct allocation of the IP address to the machine,
you can use DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP to specify the IP address. When the
machine is started or reset, it checks whether DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP is being
used, and then allocates the IP address using the first available setting method.
NOTE
•
Checking whether DHCP, BOOTP or RARP can be used takes about 1 to 2
minutes; it is recommended you set unused protocols to <Off>.
•
Depending on whether you use DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP to allocate the IP
address, you need to start the DHCP server, BOOTP daemon, or RARP daemon.
Protocol Settings
Using a TCP/IP Network (Windows/UNIX)
2-11
 Loading...
Loading...