Canon H323 User Manual

IP Office Release 6
H323 IP Telephone Installation
15-601046 Issue 16a - (15 March 2010)

© 2010 AVAYA All Rights Reserved.
Notices
While reasonable efforts have been made to ensure that the information in
this document is complete and accurate at the time of printing, Avaya
assumes no liability for any errors. Avaya reserves the right to make changes
and corrections to the information in this document without the obligation to
notify any person or organization of such changes.
Documentation disclaimer
Avaya shall not be responsible for any modifications, additions, or deletions
to the original published version of this documentation unless such
modifications, additions, or deletions were performed by Avaya.
End User agree to indemnify and hold harmless Avaya, Avaya's agents,
servants and employees against all claims, lawsuits, demands and judgments
arising out of, or in connection with, subsequent modifications, additions or
deletions to this documentation, to the extent made by End User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked Web sites
referenced within this site or documentation(s) provided by Avaya. Avaya is
not responsible for the accuracy of any information, statement or content
provided on these sites and does not necessarily endorse the products,
services, or information described or offered within them. Avaya does not
guarantee that these links will work all the time and has no control over the
availability of the linked pages.
Warranty
Avaya provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to your sales
agreement to establish the terms of the limited warranty. In addition, Avaya’s
standard warranty language, as well as information regarding support for this
product, while under warranty, is available to Avaya customers and other
parties through the Avaya Support Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support.
Please note that if you acquired the product from an authorized Avaya reseller
outside of the United States and Canada, the warranty is provided to you by
said Avaya reseller and not by Avaya.
Licenses
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS AVAILABLE ON THE AVAYA WEBSITE,
HTTP://SUPPORT.AVAYA.COM/LICENSEINFO/ ARE APPLICABLE TO ANYONE
WHO DOWNLOADS, USES AND/OR INSTALLS AVAYA SOFTWARE,
PURCHASED FROM AVAYA INC., ANY AVAYA AFFILIATE, OR AN AUTHORIZED
AVAYA RESELLER (AS APPLICABLE) UNDER A COMMERCIAL AGREEMENT
WITH AVAYA OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER. UNLESS OTHERWISE
AGREED TO BY AVAYA IN WRITING, AVAYA DOES NOT EXTEND THIS
LICENSE IF THE SOFTWARE WAS OBTAINED FROM ANYONE OTHER THAN
AVAYA, AN AVAYA AFFILIATE OR AN AVAYA AUTHORIZED RESELLER, AND
AVAYA RESERVES THE RIGHT TO TAKE LEGAL ACTION AGAINST YOU AND
ANYONE ELSE USING OR SELLING THE SOFTWARE WITHOUT A LICENSE. BY
INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, OR AUTHORIZING
OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU, ON BEHALF OF YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR
WHOM YOU ARE INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE
(HEREINAFTER REFERRED TO INTERCHANGEABLY AS “YOU” AND “END
USER”), AGREE TO THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS AND CREATE A
BINDING CONTRACT BETWEEN YOU AND AVAYA INC. OR THE APPLICABLE
AVAYA AFFILIATE (“AVAYA”).
Avaya grants End User a license within the scope of the license types
described below. The applicable number of licenses and units of capacity for
which the license is granted will be one (1), unless a different number of
licenses or units of capacity is specified in the Documentation or other
materials available to End User. "Designated Processor" means a single
stand-alone computing device. "Server" means a Designated Processor that
hosts a software application to be accessed by multiple users. "Software"
means the computer programs in object code, originally licensed by Avaya
and ultimately utilized by End User, whether as stand-alone products or
pre-installed on Hardware. "Hardware" means the standard hardware
originally sold by Avaya and ultimately utilized by End User.
License types
Designated System(s) License (DS). End User may install and use each copy
of the Software on only one Designated Processor, unless a different number
of Designated Processors is indicated in the Documentation or other materials
available to End User. Avaya may require the Designated Processor(s) to be
identified by type, serial number, feature key, location or other specific
designation, or to be provided by End User to Avaya through electronic means
established by Avaya specifically for this purpose.
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, no use should be made of materials
on this site, the Documentation(s) and Product(s) provided by Avaya. All
content on this site, the documentation(s) and the product(s) provided by
Avaya including the selection, arrangement and design of the content is
owned either by Avaya or its licensors and is protected by copyright and other
intellectual property laws including the sui generis rights relating to the
protection of databases. You may not modify, copy, reproduce, republish,
upload, post, transmit or distribute in any way any content, in whole or in
part, including any code and software. Unauthorized reproduction,
transmission, dissemination, storage, and or use without the express written
consent of Avaya can be a criminal, as well as a civil, offense under the
applicable law.
Third Party Components
Certain software programs or portions thereof included in the Product may
contain software distributed under third party agreements ("Third Party
Components"), which may contain terms that expand or limit rights to use
certain portions of the Product ("Third Party Terms"). Information regarding
distributed Linux OS source code (for those Products that have distributed the
Linux OS source code), and identifying the copyright holders of the Third
Party Components and the Third Party Terms that apply to them is available
on the Avaya Support Web site: http://support.avaya.com/Copyright.
Preventing toll fraud
"Toll fraud" is the unauthorized use of your telecommunications system by an
unauthorized party (for example, a person who is not a corporate employee,
agent, subcontractor, or is not working on your company's behalf). Be aware
that there can be a risk of toll fraud associated with your system and that, if
toll fraud occurs, it can result in substantial additional charges for your
telecommunications services.
Avaya fraud intervention
If you suspect that you are being victimized by toll fraud and you need
technical assistance or support, call Technical Service Center Toll Fraud
Intervention Hotline at +1-800-643-2353 for the United States and Canada.
For additional support telephone numbers, see the Avaya Support Web site:
http://support.avaya.com
Suspected security vulnerabilities with Avaya products should be reported to
Avaya by sending mail to: securityalerts@avaya.com.
Trademarks
Avaya and Aura are trademarks of Avaya, Inc.
The trademarks, logos and service marks (“Marks”) displayed in this site, the
documentation(s) and product(s) provided by Avaya are the registered or
unregistered Marks of Avaya, its affiliates, or other third parties. Users are
not permitted to use such Marks without prior written consent from Avaya or
such third party which may own the Mark. Nothing contained in this site, the
documentation(s) and product(s) should be construed as granting, by
implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license or right in and to the Marks
without the express written permission of Avaya or the applicable third party.
Avaya is a registered trademark of Avaya Inc. All non-Avaya trademarks are
the property of their respective owners.
Downloading documents
For the most current versions of documentation, see the Avaya Support Web
site: http://www.avaya.com/support
Contact Avaya Support
Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report problems or to
ask questions about your product. The support telephone number is
1-800-242-2121 in the United States. For additional support telephone
numbers, see the Avaya Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 2
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

Contents
Contents
IP Office H323 IP Phones1.
..................................................................... 81.1 What is New
..................................................................... 101.2 Supported Phones
..................................................................... 111.3 System Capacity
..................................................................... 121.4 Phone Firmware
..................................................................... 131.5 Simple Installation
..................................................................... 141.6 Installation Requirements
..................................................................... 151.7 Licenses
..................................................................... 161.8 Network Assessment
..................................................................... 171.9 Voice Compression
..................................................................... 191.10 QoS
..................................................................... 191.11 Potential VoIP Problems
..................................................................... 201.12 User PC Connection
..................................................................... 211.13 Power Supply Options
..................................................................... 231.14 File Server Options
..................................................................... 241.15 File Auto Generation
..................................................................... 251.16 Control Unit Memory Card
Installation2.
..................................................................... 302.1 Adding Licenses
..................................................................... 312.2 Creating/Editing the Settings File
..................................................................... 332.3 Manually Creating Extensions
..................................................................... 342.4 Phone Connection
..................................................................... 352.5 Static Address Installation
..................................................................... 362.6 Phone Registration
..................................................................... 372.7 Extension & User Setup
..................................................................... 372.8 Phone Security
..................................................................... 382.9 Backup Restore
..................................................................... 412.10 Listing Registered Phones
..................................................................... 422.11 Error Messages
Alternate DHCP Server Setup7.
..................................................................... 717.1 Using a Windows DHCP Server
..................................................................... 747.2 Alternate Options
WML Server Setup8.
..................................................................... 778.1 Testing 4620 WML Browsing Using Xitami
..................................................................... 798.2 Setting the Home Page
..................................................................... 808.3 Apache Web Server WML Configuration
..................................................................... 808.4 Microsoft IIS Web Server WML Configuration
..................................................................... 818.5 Open URL Entry
...............................................................................83Index
Other Installation Options3.
..................................................................... 443.1 VPN Remote Phones
..................................................................... 473.2 VLAN and IP Phones
Static Administration Options4.
..................................................................... 554.1 QOS Option Settings
4.2 Secondary Ethernet (Hub)/IR Interface
Enable/Disable
..................................................................... 55
..................................................................... 564.3 View Details
..................................................................... 574.4 Self-Test Procedure
..................................................................... 584.5 Resetting a Phone
..................................................................... 594.6 Site Specific Option Number
..................................................................... 604.7 Automatic Gain Control
Restart Scenarios5.
..................................................................... 635.1 Boot File Needs Upgrading
5.2 No Application File or Application File Needs
Upgrading
5.3 Correct Boot File and Application File Already
Loaded
..................................................................... 63
..................................................................... 63
Infrared Dialling6.
..................................................................... 676.1 Enabling the IR Port
..................................................................... 676.2 Dialling Phone Numbers
..................................................................... 686.3 Beaming Files During a Call
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 3
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6


Chapter 1.
IP Office H323 IP Phones
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 5
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

1. IP Office H323 IP Phones
IP Office H323 IP Phones:
This documentation provides notes for the installation of supported Avaya 1600, 4600 and 5600 IP phones onto IP
Office phone systems. It should be used in conjunction with the existing installation documentation for those series of
phones, especially the following:
· 9600 Series IP Telephones Administrator Guide (16-300698)
· 4600 Series IP Telephone LAN Administrator Guide (555-233-507).
· 1600 Series IP Telephones Administrators Guide (16-601443).
10
· DHCP versus Static IP Installation
Though static IP installation of H323 IP phones is possible, installation using DHCP is strongly recommended. The
use of DHCP eases both the installation process and future maintenance and administration. For static installations,
following a boot file upgrade, all static address settings are lost and must be re-entered.
· Network Assessment
High quality voice transmission across an IP network requires careful assessment of many factors. Therefore:
· We strongly recommend that IP phone installation is only done by installers with VoIP experience.
· The whole customer network must be assessed for its suitability for VoIP, before installation. Avaya may refuse
to support any installation where the results of a network assessment cannot be supplied. See Network
Assessment for further details.
16
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 7
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

1.1 What is New
IP Office Release 6
The following changes specific to Avaya H323 IP phone support have been made as part of the IP Office 5.0 release.
· Avaya IP Phone Licenses
On IP500 and IP500 V2 systems, Avaya 1600, 4600, 5600, 9600, IP DECT, DECT R4, T3 IP, Spectralink and VPN
phones are licensed by Avaya IP Endpoint licenses. These licenses are consumed by each phone as it registers
with the IP Office system. Existing VCM channel resources and VCM Channel licenses enable a number of unlicensed
phone registrations.
· Existing VPN Remote licenses are no longer used. Phones using VPNremote client software require an Avaya IP
Phones license.
· Licenses are used on a first come first served basis as phones register with the IP Office system. Phones that
register but cannot get a license will only be able to make emergency calls. Through the IP Office configuration,
it is possible to pre-allocate available license capacity to selected extensions.
· 9600 Series Phones
IP Office Release 6 supports a number of phones from the 9600 Series of phones. Supported phones are the 9620L,
9620C, 9630G, 9640, 9640G, 9650 and 9650C.
IP Office Release 5
The following changes specific to Avaya H323 IP phone support have been made as part of the IP Office 5.0 release.
· Embedded Memory Card Usage
In order to simplify H323 phone installation and maintenance, a number of changes have been made, employing
the Embedded Voicemail memory card supported by IP406 V2 and IP500 control units.
· Automatic File Loading
Using the Embedded File Management option within IP Office Manager, the option File | Upload Phone Files
will transfer all necessary phone firmware files required for phones supported by IP Office 5.0 to the memory
card. Those files are then available to the phones if the IP Office is configured as the HTTP/TFTP server for
phones.
· Auto-Generated File Operation
If the IP Office is configured as the HTTP/TFTP file server for H323 phones, the Embedded Voicemail memory
card is used as the file store. The file server normally requires copies of various .scr and .txt files to be present.
For IP Office 5.0, if those files are not present on the memory card, the IP Office will auto-generate a suitable
file when it is requested by a phone.
· Extension Quality of Service Measurement
Through the IP Office configuration, H323 IP phones (1600 Series, 4600 Series and 5600 Series) can be enabled to
send QoS information to the IP Office system. For other types of extension, when their call involves a VCM channel,
QoS information is available. The QoS information is round trip delay, jitter and packet loss. This information is
used in a number of ways.
· QoS Display
Within the IP Office System Status Application (SSA), the current QoS measurements are shown for calls. This
is in addition to the QoS measurement already displayed by SSA for IP trunks.
· QoS Alarms
QoS alarms thresholds can be set within the IP Office configuration. On calls where a threshold is exceeded, an
alarm is generated at the end of the call. The alarm will contain the maximum value of all the QoS
measurements. QoS alarms are shown in SSA. They can also be specified for output as alarms via SNMP,
Syslog and/or email.
· Resilience
IP Office 5.0 includes support for a number of 'resilience' features within an IP Office Small Community Network.
This includes support for registered H323 phones and their users if the IP Office with which they are registered
should not be available on the network. For details of resilience operation refer to the IP Office 5.0 Manager
manual.
· VLAN Setting
This option within the IP Office configuration (System | LAN1/LAN2 | VoIP) is applied to H323 phones using the IP
Office for DHCP support. If set to Disabled, the L2Q value indicated to phones in the DHCP response is 2
(disabled). If set to Not Present, no L2Q value is included in the DHCP response.
24
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 8
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

IP Office H323 IP Phones: What is New
IP Office 4.2
The following changes specific to H323 IP phone support have been made as part of the IP Office 4.2 release.
· Support for 1600 Series Phones
IP Office 4.2 Q4 2008+ supports the 1603, 1608, 1616 IP phones.
· HTTP Server Support
For Avaya IP phones using IP Office DHCP, the address of the HTTP server from which those phones should
download their software and settings files can now be specified in the IP Office configuration. 4600 Series and 5600
Series phones attempt to load files via HTTPS and then HTTP before falling back to TFTP. 1600 Series IP phones
only support HTTPS or HTTP.
· HTTP-TFTP Relay
The IP Office control unit supports HTTP-TFTP relay for HTTP file requests from phones.
· HTTP-TFTP Using an Embedded Memory Card
For IP Office 4.2, using the Embedded Voicemail memory card is also supported for HTTP file requests for
up to 50 IP phones. This is done by setting the TFTP Server IP Address and HTTP Server IP Address
to the control unit IP address. This method is supported for up to 50 IP phones.
· HTTP-TFTP Using IP Office Manager
For the IP Office 4.2 Q4 2008 maintenance release, HTTP-TFTP Relay is support using IP Office Manager as
the TFTP server. This is done by setting the TFTP Server IP Address to the address of the Manager PC
and the HTTP Server IP Address to the control unit IP address. This method is supported for up to 5 IP
phones.
· HTTP User Backup and Restore
The HTTP file support methods detailed in this manual are for the download of phone firmware, settings and
language files to phones. HTTP support for phone user settings backup and restore requires a separate HTTP
server, the address of which is defined with the phone settings files rather than through the DHCP server
configuration settings.
· Secondary Site Specific Options Number
A Site Specific Option Number (SSON) is used by Avaya IP phones when requesting phone specific settings from a
DHCP server. When the IP Office is acting as the DHCP server, the matching number must be set in the IP Office
configuration. IP Office 4.2 now provides two fields for settings SSON numbers in order to support Avaya 4600 and
5600 Series IP Phones (which use a default SSON of 176) and Avaya 1600 Series phones (which use a default
SSON of 242).
· IP Phone Restart using System Status Application
Individual Avaya IP phones or groups of phones can be selected and then restarted remotely using the System
Status Application. This allows individual phones or groups of phones to be restarted in order to upgrade their
firmware.
· IP500 DHCP Enhancements
The scope of DHCP support on IP500 has been enhanced in a number of areas.
· Full Avaya IP Phone Support
Previous only a maximum of 5 IP phones have been supported if using the IP Office for DHCP and TFTP
functions. An external DHCP server is required to support more than 5 Avaya IP Phones. For IP Office 4.2+, the
IP500 supports the fill extension capacity of the IP500 control unit.
· Multiple DHCP IP Address Pools
On each IP Office LAN interface, up to 8 DHCP address ranges (called 'pools') can be specified. These pools do
not have to be on the same subnet as the IP Office itself. This allows devices being supported by IP Office
DHCP to be given addresses on a different subnet than the IP Office.
· DHCP for Avaya IP Phones Only
The DHCP pools provided by the IP Office can be restricted for use by Avaya IP phones only. The IP Office will
then not respond to DHCP request from other devices.
· Embedded Card File Management
For systems with a compact flash memory card installed, the contents of the card can be viewed through Manager.
This mode is accessed through the File | Advanced | Embedded File Management option. This view can also
be used to add and remove files from the card. This may be useful when the memory card is being used to store
music on hold files and or phone firmware files.
· IP500 VCM Controls
For IP Office 4.2+, the VCM controls for echo and comfort noise supported in the IP Office configuration (System |
VCM) are now also applied to IP500 VCM cards.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 9
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6
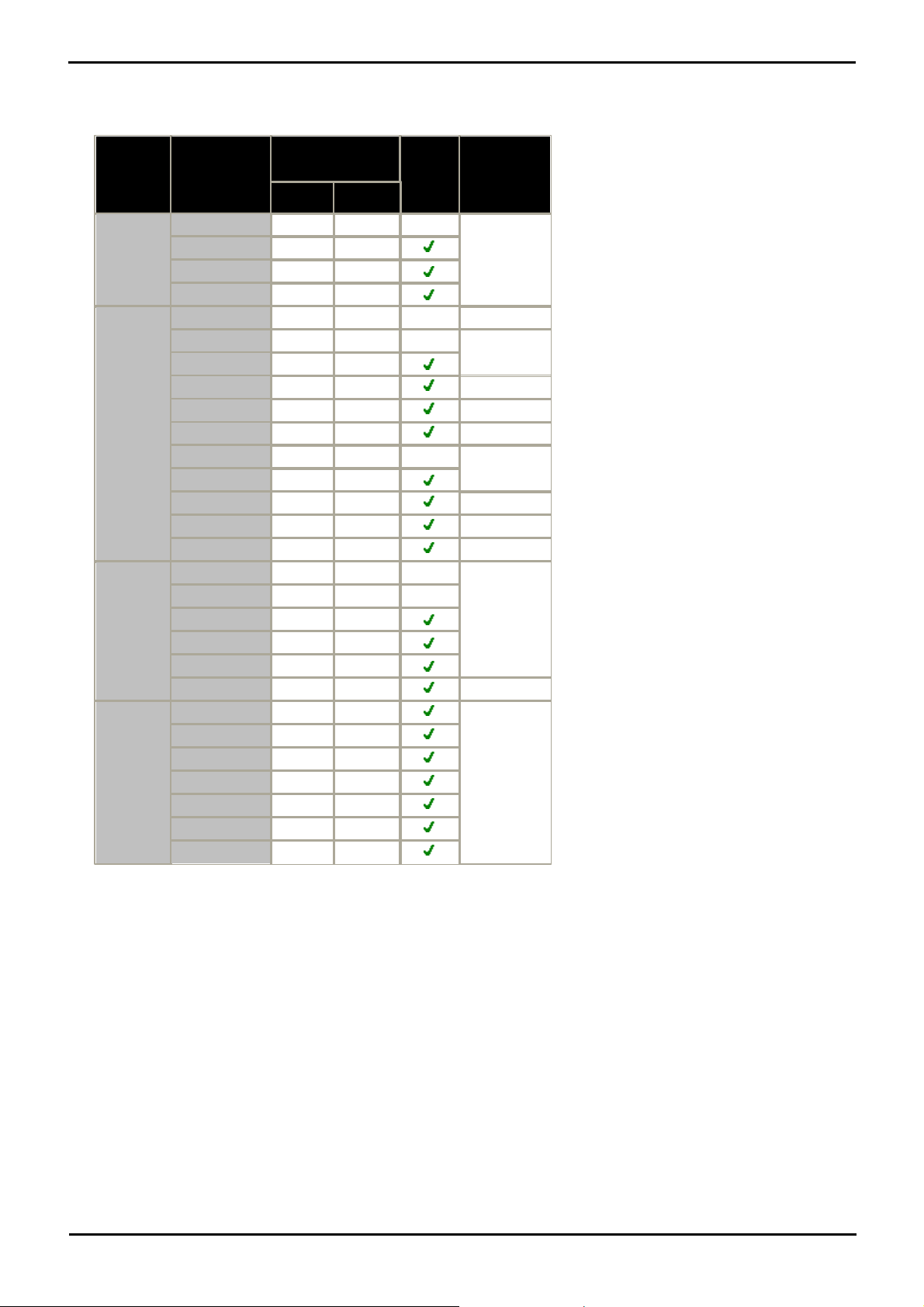
1.2 Supported Phones
H323 IP
Phones
Supported
Models
802.3af PoE
Class
PC Port
IP Office
Core
Software
Class
Idle
1600
Series
160324.4W
–
4.2 Q4 2008
+.
1603SW
2
4.4W
160823.7W
161622.7W
4600
Series
460123.5W
–
3.0+
46021–
–
2.1+.
4602SW
2
3.5W
460604.1W
Up to 3.2.
4610SW
[1]
2
4.0W
3.0+.
461204.1W
Up to 3.2.
462034.0W
–
2.0+.
4620SW
2
–
4621SW
[1]
2
5.75W
3.0+.
462404.1W
Up to 3.2.
462536.45W
3.2+
5600
Series
560123.5W
–
3.0+.
56021–
–
5602SW
2
4.1W
5610SW
[1]
2
3.1W
562033.6W
5621SW
[1]
2
–
3.2+.
9600
Series
9620L12.0W
6+
9620C23.9W
9630G
2
4.6W
964023.9W
9640G
2
3.9W
965024.7W
9650C23.7W
This documentation provides installation notes for the following Avaya IP phone supported by IP Office. Other Avaya IP
phones, for example 3600 Series and IP DECT are covered by separate installation documentation.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 10
VPNremote Support
1.
These phones can also be used with VPNremote firmware.
1603/1603SW
2.
These phones require a PoE Splitter unit in order to user PoE.
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

IP Office H323 IP Phones: Supported Phones
IP Office Unit
Maximum
Extensions
Maximum VCM
Channels
IP406 V2
190
30
IP412
360
60
IP500
384
128
IP500 V2
384
148
1.3 System Capacity
System capacity can be separated into two aspects; the number of configurable phone extensions and the number of
simultaneous IP phone calls.
Extension Capacity
The maximum number of H323 IP phones supported by an IP Office system is based on that system's maximum capacity
for extensions of any type as listed in the table below. To find the capacity for IP phones remove the number of physical
non-IP extensions installed on the system, ie. extension ports on the IP Office control unit and any external expansion
modules.
Call Capacity
There are a number of situations where the IP Office system needs to provide a voice compression channel in order for an
IP phone to make calls. These channels are provided by Voice Compression Modules (VCMs) installed in the IP Office
system. The number of VCM channels required and how long the channel is required will depend on a number of factors.
For further details see Voice Compression .
A simple summary is:
· A VCM channel is required during call setup.
· The VCM channel is released if the call is to/from another IP device using the same compression codec (the
supported VCM codecs are G711, G729 and G723a).
· The VCM channel is used for the duration of the call when the call is to/from/via a non-IP device (extension or trunk
line).
· It should be remembered that VCM channels are also used for calls from non-IP devices to IP lines if those are
configured in the IP Office system (IP, SIP and SES lines).
· Calls from IP phones to the IP Office voicemail server use a VCM channel.
· Note that on Small Office Edition systems with Embedded Voicemail, an additional channel is used for every call
to voicemail.
17
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 11
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

1.4 Phone Firmware
The firmware in Avaya IP phones is upgradeable and different releases of firmware are made available via the Avaya
support website. However H323 IP phones used on an IP Office system must only use the IP Phone software supplied with
the IP Office Manager application. Other versions of IP Phone software may not have been tested with IP Office and so
should not be used unless IP Office support is specifically mentioned in their accompanying documentation.
The phone firmware files are installed as part of the IP Office Manager application and are found in the applications
installation directory. By default this is c:\Program Files\Avaya\IP Office\Manager.
For IP Office 4.2+, they firmware files are also available on the IP Office Administrator Applications CD from which IP
Office Manager is installed. The files are located in the \program files\Avaya\IP Office\Manager folder of the
installation files. This makes it easier to locate all the files needed for IP phone installation though it also includes the .bin
files used for IP Office control and external expansion units.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 12
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6
IP Office H323 IP Phones: Phone Firmware
1.5 Simple Installation
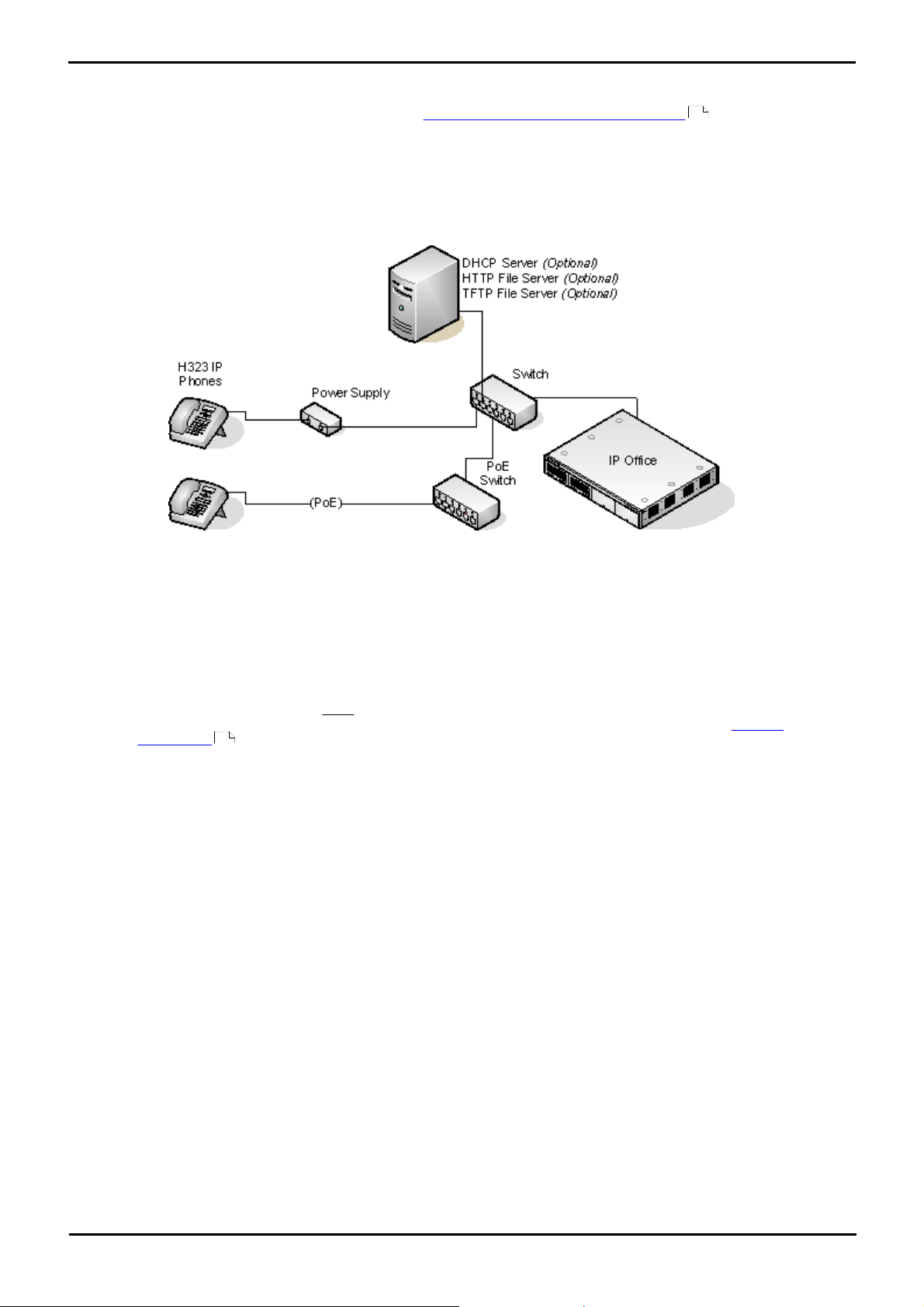
The diagram below shows a simple installation scenario that can be supported by all IP Office systems running IP Office
Release 6.
This type of installation uses the following equipment:
· IP Office
The IP Office control unit is performing a number of roles for the phones:
· DHCP Server
The IP Office unit is acting as the DHCP server for the Avaya IP phones. Key settings such as the file server
address are entered into the IP Office configuration and then provided to the phones in addition to their IP
address.The IP Office DHCP server can be configured to provide DHCP addresses only in response to requests
from Avaya IP phones. This allows an alternate DHCP server to be used for other devices that use DHCP.
· The IP Office control unit can provide DHCP support for up to 272 phones. Alternatively a separate DHCP
server can be used.
· H323 Gatekeeper
IP phones require an H323 gatekeeper to which they register. The gatekeeper then controls connecting calls to
the phone. In this scenario the IP Office control unit acts as the H323 Gatekeeper.
· File Server
During installation the IP phones need to download software and settings files for a file server. If the IP Office
control unit is fitted with a memory card (mandatory on IP500 v2 control units), that card can be used as the
file source.
· The IP Office control unit with memory card can act as the file server for up to 50 phones. Alternatively a
3rd-party HTTP server can be used.
· Switch
The IP Office control units have limited numbers of LAN connection ports. They are intended to be connected to a
LAN switch with port capacity for the customers network equipment.
· Power Supplies
Each H323 IP phone requires a power supply.
· Individual Power Supply Units
An individual power supply unit can be used with each phone. This will require a power supply socket at each
phone location. Note that for phones using a button module add-on, for example a EU24 or BM32, an individual
power supply unit is a requirement.
· Power over Ethernet Supply
Most Avaya IP phones can be powered from an 802.3af Power over Ethernet (PoE) power supply. The IP Office
system does not provide PoE ports so a separate PoE switch or PoE injector devices will be required to power a
phone using PoE.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 13
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

1.6 Installation Requirements
To install an IP phone on IP Office, the following items are required:
· o Extension Number and User Details
A full listing of the planned extension number and user name details is required. The planned extension number
must be unused and is requested by the phone during installation.
· o Power Supplies
Each phone requires a power supply. Avaya IP phones do not draw power from the IP Office. A number of options
exist for how power is supplied to the phones. See Power Supply Options .
· o LAN Socket
An RJ45 Ethernet LAN connection point is required for each phone.
· o Category 5 Cabling
All LAN cables and LAN cable infrastructure used with H323 IP phones should use CAT5 cabling. Existing CAT3
cabling may be used but will be limited to 10Mbps (maximum).
· o LAN Cables
Check that an RJ45 LAN cable has been supplied with the IP phone for connection to the power supply unit. You will
also need an additional RJ45 LAN cable for connection from the power unit to the customer LAN.
· A further RJ45 LAN cable can be used to connect the user's PC to the LAN via the IP phone [not supported on
4601, 4602, 5601 and 5602 H323 IP phones].
· o Voice Compression Channels
The IP Office Unit must have voice compression channels installed. Channels are required during the connection if
calls involving IP phones and may also be required during the call. See Voice Compression Channels for full
details.
· For Small Office Edition units, either 3 or 16 voice compression channels are pre-built into the unit.
· For IP400 control units, voice compression channels are provided by fitting a Voice Compression Module .
· For IP500 control units, channels are installed using a IP500 VCM base card and licenses or using IP400 VCM
modules on an IP500 Legacy Card.
· o DHCP Server
The IP Office Unit can perform this role for up to 5 IP phone devices. If another DHCP server already exists, this
may be able to do DHCP for the H323 IP phones, see Alternate DHCP Servers . Static IP addressing can also be
used, if required, but is not recommended.
· For IP500 IP Office 4.2+ systems, up to 272 IP phones are supported using the IP Office Manager.
· o HTTP/TFTP File Server
A PC running the IP Office Manager application can perform this role for up to 5 H323 IP phones. An IP Office
control unit with a memory card can use that memory card as the source for up to 50 phones. Otherwise an
alternate HTTP file server is required.
· o H323 Gatekeeper
The IP Office Unit performs this role.
· o IP Office Manager PC
A PC running Manager is required for IP Office Unit configuration changes. This PC should have a static IP address.
· o IP Telephone Software
The software for IP phone installation is installed into the IP Office Manager program folder during Manager
installation.
· o Licence Keys
For IP Office Release 6, licenses Avaya IP Endpoint licenses are required on IP500 and IP500 V2 systems. Refer to
Licenses.
21
70
17
17
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 14
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

IP Office H323 IP Phones: Installation Requirements
1.7 Licenses
The following licensing rules apply to the support of Avaya H323 IP phones on IP Office Release 6 systems.
IP500 and IP500 V2 IP Office Systems
On IP500 and IP500 V2 systems, Avaya IP Endpoint license are these licenses are required for Avaya H323 IP phones.
This includes all 1600, 4600, 5600, 9600, IP DECT, DECT R4, T3 IP, Spectralink and VPN phones supported by IP Office
Release 6.
· The system will automatically license 12 Avaya IP phones for each IP500 VCM 32 or VCM 64 card installed in the
system without requiring additional licenses to be added to the configuration.
· Additional Avaya IP phones are licensed either by the addition of Avaya IP Endpoints licenses above or the
conversion of legacy IP500 VCM Channels licenses to Channel Migration licenses (see below).
· By default licenses are consumed by each Avaya IP phone that registers with the IP Office in the order that they
register. The license is released if the phone unregisters. However, it is possible to reserve a license for particular
phones in order to ensure that they phones always obtain a license. This is done through the Reserve Avaya IP
Endpoint Licence setting of each IP extension.
· Avaya IP phones without a license will still be able to register but will be limited to making emergency calls only
(Dial Emergency short code calls). The associated user will be treated as if logged off and the phone will display
"No license available". If a license becomes available, it will be assigned to any unlicensed DECT handsets first and
then to any other unlicensed Avaya IP phone in the order that the phones registered.
· For existing IP500 systems being upgraded to IP Office Release 6, the existing VCM channels and IP500 VCM
Channels license are treated as follows:
· For each IP400 VCM card installed in the system, each VCM channel supported by the card allows support for 3
Avaya IP phones.
· For each IP500 VCM32 and IP500 VCM64 card installed in the system, the 4 unlicensed VCM channels
previously provided by each card are converted to allow unlicensed support of 12 Avaya IP phones.
· For each legacy IP500 VCM Channels license, the license are converted Channel Migration licenses supporting 3 Avaya IP phones. See the Channel Migration license below.
· The IP500 VCM 32 and IP500 VCM 64 cards will provide their full capacity of VCM channels, ie. providing up to
32 or 64 channels depending on the card type and the codecs being used.
Other IP Office Systems
On other IP Office systems, licenses are only required for phones using VPNremote firmware.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 15
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

1.8 Network Assessment
· WARNING: A Network Assessment is Mandatory
When installing H323 IP phones on an IP Office system, it is assumed by Avaya that a network assessment has
been performed. If a support issue is escalated to Avaya, Avaya may request to see the results of the network
assessment and may refuse to provide support if a suitable network assessment was not performed.
Current technology allows optimum network configurations to deliver VoIP with voice quality close to that of the public
phone network. However, few networks are optimum and so care should be taken assessing the VoIP quality achievable
across a customer network.
Not every network is able to carry voice transmissions. Some data networks have insufficient capacity for voice traffic or
have data peaks that will impact voice traffic on occasion. In addition, the usual history of growing and developing
networks by integrating products from many vendors makes it necessary to test all the network components for
compatibility with VoIP traffic.
A network assessment should include a determination of the following:
· A network audit to review existing equipment and evaluate its capabilities, including its ability to meet both current
and planned voice and data needs.
· A determination of network objectives, including the dominant traffic type, choice of technologies and setting voice
quality objectives.
· The assessment should leave you confident that the network will have the capacity for the foreseen data and voice
traffic, and can support H323, DHCP, TFTP and jitter buffers in H323 applications.
The network assessment targets are:
· Latency: Less than 180ms for good quality. Less than 80ms for toll quality.
This is the measurement of packet transfer time in one direction. The range 80ms to 180ms is generally acceptable.
Note that the different audio codecs used each impose a fixed delay caused by the codec conversion as follows:
· G711: 20ms.
· G723a: 80ms.
· G729: 40ms.
· Packet Loss: Less than 3% for good quality. Less than 1% for toll quality.
Excessive packet loss will be audible as clipped words and may also cause call setup delays.
· Jitter: Less than 20ms.
Jitter is a measure of the variance in the time for different packets in the same call to reach their destination.
Excessive jitter will become audible as echo.
· Duration: Monitor statistics once every minute for a full week.
The network assessment must include normal hours of business operation.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 16
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6
IP Office H323 IP Phones: Network Assessment
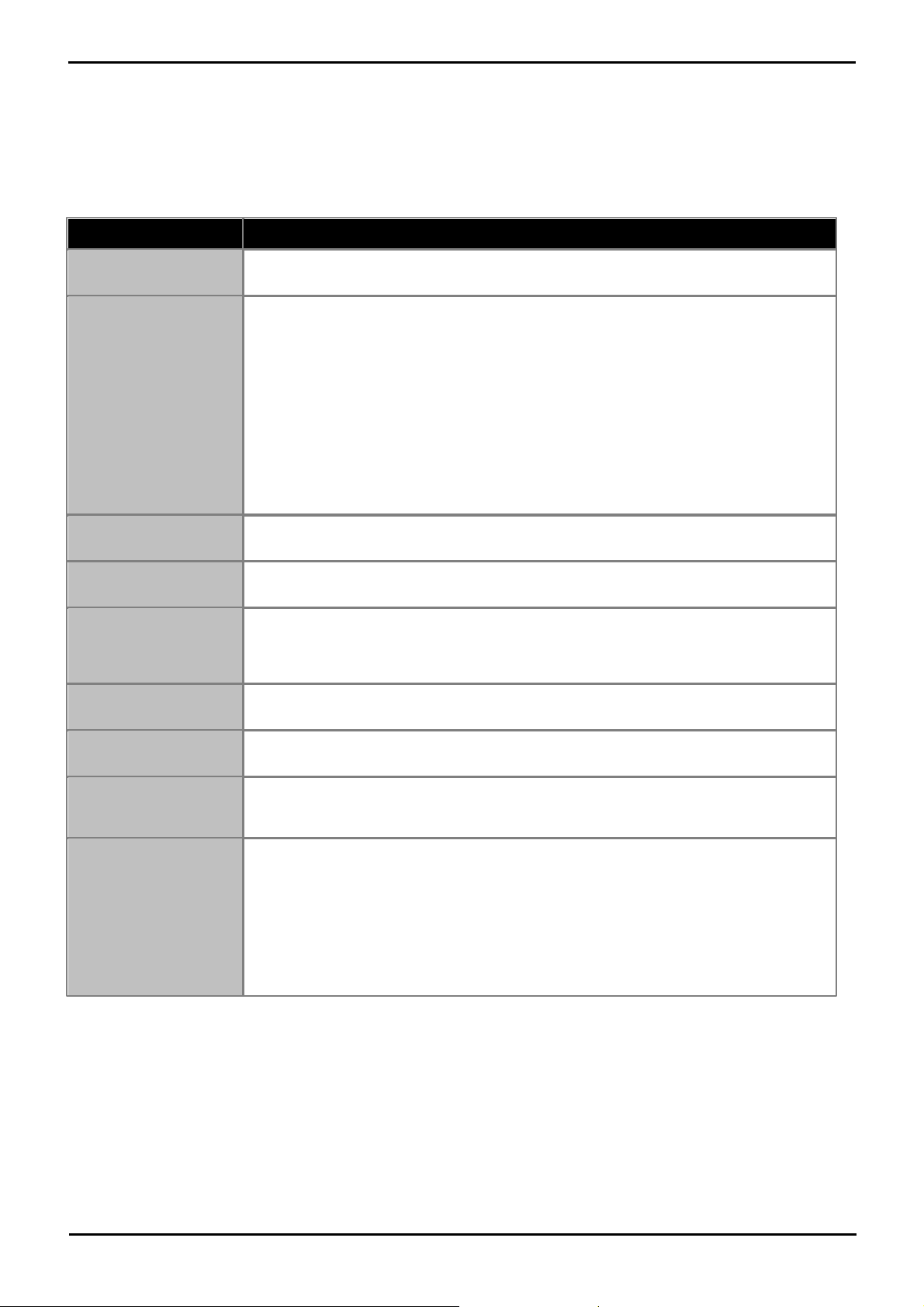
Call Type
Voice Compression Channel Usage
IP Device to Non-IP
Device
These calls require a voice compression channel for the duration of the call. If no channel is
available, busy indication is returned to the caller.
IP Device to IP Device
Call progress tones (for example dial tone, secondary dial tone, etc) do not require voice
compression channels with the following exceptions:
· Short code confirmation, ARS camp on and account code entry tones require a voice
compression channel.
· Devices using G723 require a voice compression channel for all tones except call
waiting.
When a call is connected:
· If the IP devices use the same audio codec no voice compression channel is used.
· If the devices use differing audio codecs, a voice compression channel is required for
each.
Non-IP Device to NonIP Device
No voice compression channels are required.
Music on Hold
This is provided from the IP Office's TDM bus and therefore requires a voice compression
channel when played to an IP device.
Conference Resources
and IP Devices
Conferencing resources are managed by the conference chip which is on the IP Office's TDM
bus. Therefore, a voice compression channel is required for each IP device involved in a
conference. This includes services that use conference resources such as call listen, intrusion,
call recording and silent monitoring.
Page Calls to IP Device
IP Office 4.0 and higher only uses G729a for page calls, therefore only requiring one channel
but also only supporting pages to G729a capable devices.
Voicemail Services and
IP Devices
Calls to the IP Office voicemail servers are treated as data calls from the TDM bus. Therefore
calls from an IP device to voicemail require a voice compression channel.
Fax Calls
These are voice calls but with a slightly wider frequency range than spoken voice calls. IP
Office only supports fax across IP between IP Office systems with the Fax Transport option
selected. It does not currently support T38.
T38 Fax Calls
IP Office 5.0+ supports T38 fax on SIP trunks and SIP extensions. Each T38 fax call uses a
VCM channel.
Within a Small Community Network, a T38 fax call can be converted to a call across an H323
SCN lines using the IP Office Fax Transport Support protocol. This conversion uses 2 VCM
channels.
In order use T38 Fax connection, the Equipment Classification of an analog extension
connected to a fax machine can be set Fax Machine. Additionally, a new short code feature
Dial Fax is available.
1.9 Voice Compression
Calls to and from IP devices can require conversion to the audio codec format being used by the IP device. For IP Office
systems this conversion is done by voice compression channels. These support the common IP audio codecs G711, G723
and G729a.
For IP400 control units channels can be added by fitting IP400 Voice Compression Modules (VCMs). For the IP500 control
units, channels can be added using IP500 VCM cards, IP500 Combination Cards and or IP400 Voice Compression Modules.
The voice compression channels are used as follows:
Note: T3 IP devices must be configured to 20ms packet size for the above conditions to apply. If left configured for 10ms
packet size, a voice compression channel is needed for all tones and for non-direct media calls.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 17
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

Measuring Channel Usage
The IP Office System Status Application can be used to display voice compression channel usage. Within the Resources
section it displays the number of channel in use. It also displays how often there have been insufficient channels available
and the last time such an event occurred.
The IP500 VCM cards, the level of channel usage is also indicated by the LEDs (1 to 8) on the front of the IP500 VCM
card.
Installing VCM Cards
Refer to the IP Office Installation manual.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 18
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

IP Office H323 IP Phones: Voice Compression
1.10 QoS
When transporting voice over low speed links it is possible for normal data packets (1500 byte packets) to prevent or
delay voice packets (typically 67 or 31 bytes) from getting across the link. This can cause unacceptable speech quality.
Therefore, it is vital that all traffic routers and switches in the network to have some form of Quality of Service (QoS)
mechanism. QoS routers are essential to ensure low speech latency and to maintain sufficient audible quality.
IP Office supports the DiffServ (RFC2474) QoS mechanism. This is based upon using a Type of Service (ToS) field in the IP
packet header. On its WAN interfaces, IP Office uses this to prioritize voice and voice signalling packets. It also fragments
large data packets and, where supported, provides VoIP header compression to minimize the WAN overhead.
Note
· IP Office does not perform QoS for its Ethernet ports including the WAN Ethernet port on the Small Office Edition.
1.11 Potential VoIP Problems
It is likely that any fault on a network, regardless of its cause, will initially show up as a degradation in the quality of VoIP
operation. This is regardless of whether the fault is with the VoIP telephony equipment. Therefore, by installing a VoIP
solution, you must be aware that you will become the first point of call for diagnosing and assessing all potential customer
network issues.
Potential Problems
· End-to-End Matching Standards
VoIP depends upon the support and selection of the same voice compression, header compression and QoS
standards throughout all stages of the calls routing. The start and end points must be using the same compression
methods. All intermediate points must support DiffServ QoS.
· Avoid Hubs
Hubs introduce echo and congestion points. If the customer network requires LAN connections beyond the capacity
of the IP Office Unit itself, Ethernet switches should be used. Even if this is not the case, Ethernet switches are
recommended as they allow traffic prioritization to be implemented for VoIP devices and for other device such as
the Voicemail Server PC.
· Power Supply Conditioning, Protection and Backup
Traditional phone systems provide power to all their attached phone devices from a single source. In a VoIP
installation, the same care and concern that goes into providing power conditioning, protection and backup to the
central phone system, must now be applied to all devices on the IP network.
· Multicasting
In a data only network, it is possible for an incorrectly installed printer or hub card to multicast traffic without that
fault being immediately identified. On a VoIP network incorrect multicasting will quickly affect VoIP calls and
features.
· Duplicate IP Addressing
Duplicate addresses is a frequent issue.
· Excessive Utilization
A workstation that constantly transmits high traffic levels can flood a network, causing VoIP service to disappear.
· Network Access
An IP network is much more open to users connecting a new device or installing software on existing devices that
then impacts on VoIP.
· Cabling Connections
Technically VoIP can (bandwidth allowing) be run across any IP network connection. In practice, Cat5 cabling is
essential.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 19
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

1.12 User PC Connection
To simplify the number of LAN connections from the user's desk, it is possible to route their PC Ethernet LAN cable via
some H323 IP phones. The LAN cable should be connected from the PC to the socket with a PC symbol ( ) at the back of
the IP phone. The PC's network configuration does not need to be altered from that which it previously used for direct
connection to the LAN.
Except for phones with a G suffix this port supports 10/100Mbps ethernet connections. Phones with a G suffix also support
1000Mbps Gigabit connections. For other phones a separate Gigabit Adapter (SAP 700416985) must be used. This device
splits the data and voice traffic before it reaches the phone, providing a 10/100Mbps output for the phone and a
10/100/1000Mbps output for the PC. The adapter is powered from the phone's existing PoE supply or 1151 type power
supply unit. Refer to the "Gigabit Ethernet Adapter Installation and Safety Instructions" (16-601543).
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 20
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

IP Office H323 IP Phones: User PC Connection
1.13 Power Supply Options
Each H323 IP phone requires a power supply. They do not draw power from the IP Office phone system. Listed below are
the power supply options that can be used.
Spare Wire Power Options
The following power supplies use the normally unused pin 7 & 8 connections in the CAT3 or CAT5 network cable. This is
referred to as "spare wire" or "mid-span" power supply units. They can be used with 4600 Series and 5600 Series IP
phones.
· Avaya 1151D1 Power Supply Unit (PSU)
A power supply unit for a single IP phone. Has a LINE port for the LAN cable from the IP Office, and a PHONE port
for the LAN cable to the IP phone. Power into the PSU requires a 90 to 264V AC, 47 to 63HZ mains supply. A green
LED indicates when power is available.
· Avaya 1151D2 Power Supply Unit
Same as the 1151C1 above but with integral battery backup. When AC mains supply is removed, the battery will
power the IP phone for between 8 hours at light load (2 Watts) and 15 minutes at full load (20 Watts). A green LED
indicates when power is available. A yellow LED indicates when the backup is charging. The green LED flashes when
the phone is running from the backup battery.
Dedicated Plug-Top Power Supply Units
1600 Series IP phones can be powered using plug-top PSU's. Different models of PSU exist for various power outlet
sockets. These connect to the phone using a barrel connector.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 21
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

802.3af Power over Ethernet (PoE) Options
IEEE 802.3af is a standard commonly known as Power over Ethernet (PoE). It allows network devices to receive power via
the network cable using the same wires as the data signals. All the H323 IP phones supported on IP Office also support
this standard. Note that for phones being used with an add-on unit such as an EU24, EU24BL or BM32, an individual power
supply must be used rather than PoE.
· Exceeding the Class limit of a PoE port or the total Class support of a PoE switch may cause incorrect operation.
· Avaya 1152A1 Power Distribution Unit (Mid-Span Power Unit)
This is a 1U high 19-inch rack mountable unit. It is available in models to support 6, 12 or 24 PoE devices including
H323 IP phones. For each device, it provides a RJ45 data in ports and a matching RJ45 data and power out port. It
can support a maximum of 200 Watts or a peak of 16.8 Watts per port.
· Power of Ethernet (POE) Switch
The Avaya P333T-PWR Switch is a Ethernet LAN switch which also provides PoE input for up to 24 devices including
H323 IP phones.
· IP Phone Inline Adaptor
This adaptor allows 4602, 4602SW, 4620, 4621 and 4625 H323 IP phones and 5600 Series equivalents to be
powered from a Cisco Catalyst power blade. Using these adaptors, up to 24 H323 IP phones can be supported on a
single power blade. The phones do not provide the Catalyst switch with information on their power requirements
and future changes to Catalyst switch software may affect operation.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 22
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6
IP Office H323 IP Phones: Power Supply Options
File Server
Description
Up to X
Phones
TFTP
HTTP
HTTPS
IP Office Manager
When running, the IP Office Manager acts as a
HTTP/TFTP server for file requests from
phones.
5
–
IP Office Unit
Memory Card
For IP Office control units fitted with an
additional memory card, that card can be used
to provided the software files. Various other
files can be auto-generated
by the IP
Office if not present on the memory card.
50
–
3rd Party
Software
3rd Party HTTP and TFTP file server software is
available from many sources including Avaya.
–
1.14 File Server Options
During installation and maintenance, the phones download software and settings files. In order to do this a phone first
request files for an HTTPS server. If it gets no response it then tries to obtain the files from an HTTP server. 4600 and
5600 Series phones will then try TFTP. The address of the server to use is provided through DHCP or entered during static
phone installation.
· The phones will check the file server every time they are restarted. However if they do not find it they will continue
by using the existing files they have. Therefore there is no requirement for the file sever to be permanently
available. The file server is only required during phone installation and maintenance.
The following options are available for the file server for IP phones being installed on an IP Office system.
24
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 23
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

1.15 File Auto Generation
For IP Office 5.0+, for systems configured to use the IP Office control unit's memory card as the file server source, the IP
Office is able to auto-generate the necessary file in response to a phone request if the specific file is not present on the
card. This operation is supported for the following files:
· 16xxupgrade.txt
This file will list the the firmware files for 1600 Series series phones supported by the IP Office. The last line will
contain the filename 46xxsettings.txt.
· 46xxupgrade.scr
This file will list the firmware files for 4600 Series and 5600 Series phones supported by the IP Office. The last line
will contain the filename 46xxsettings.txt.
· 96xxupgrade.txt
This file will list the the firmware files for 1600 Series series phones supported by the IP Office. The last line will
contain the filename 46xxsettings.txt.
· For both the files above, the appropriate .bin files must be manually copied to the memory card. The IP Office
5.0 Manager application provides controls for this.
· The contents of the files above are System Locale dependant as different firmware files are required to
support certain language locales (for example Russia).
· 46xxsettings.txt
This file will match the file supplied with the IP Office 5.0+ Manager application except as follows:
· The BRIURI value will be set to indicate the IP Office memory card as location for backup and restore actions.
· The LANG1FILE to LANG4FILE values for 1600 Series phone non-English language files will be determined
from the best match to the system locale and the most common user locales. Languages supported are Dutch,
French, French (Canadian), German, Italian, Latin Spanish, Portuguese, Russian, Spanish.
· 1600 Series Language files
If the 46xxsettings.txt file is auto-generated, the matching 1600 Series phone languages specified in that file will
also be auto-generated.
· <ext>_16xxdata.txt
If the 46xxsettings.txt file is auto-generated, it will specify the IP Office memory card as the location for phones
to backup and restore user settings. If no file exists for a user, a file will be auto-generated.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 24
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6

IP Office H323 IP Phones: File Auto Generation
1.16 Control Unit Memory Card
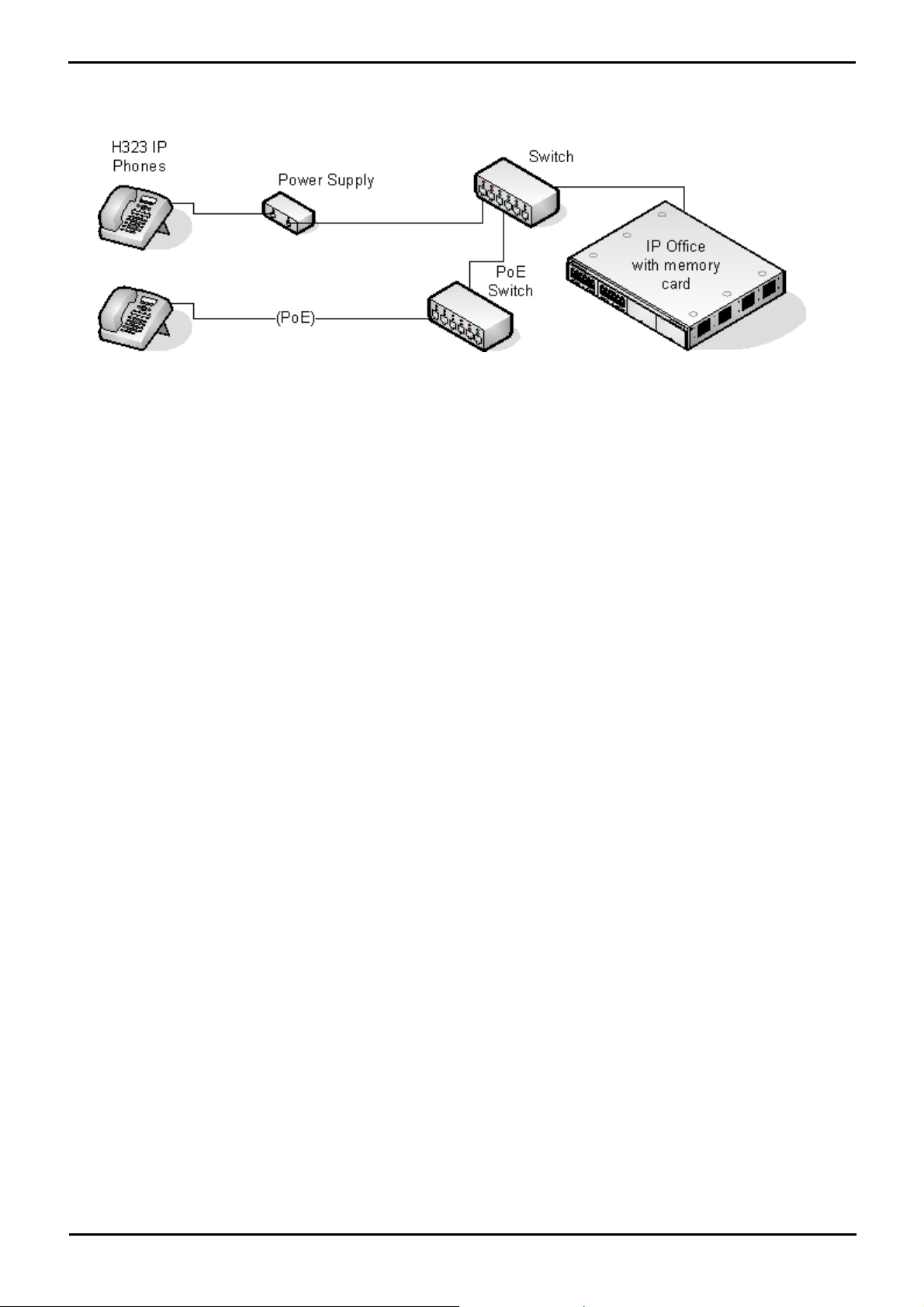
The memory card used with IP406 V2, IP500 and IP500 V2 systems can be used to store files including those used by
Avaya IP Phones.
· Non-Avaya supplied Compact Flash memory cards can be used for this type of file storage. However, they will not
support embedded voicemail.
· If an Avaya supplied memory card is used, any files stored in this way will reduce the message storage capacity of
the Compact Flash memory card.
· The IP500 V2 control unit requires a System SD card at all times and this card normally holds a full set of IP Office
firmware files including those used by Avaya IP phones.
Transferring Files Using IP Office Manager
IP Office 4.2+ allows the contents of the memory card in a system to be viewed and updated. This is done using IP Office
Manager and requires the same user name and password access as used for configuration changes.
Within IP Office Manager, select File | Advanced | Embedded File Management.
1.
The Select IP Office discovery menu is shown. Select the IP Office systems whose memory card you want to view
2.
and click OK.
Enter a user name and password for configuration access to that system.
3.
· TFTP: Received TFTP Error "Not Found" in the Manager status bar indicates that no card was detected in
the selected system. To select another system use File | Open File Settings. To return Manager to normal
configuration mode select File | Configuration.
The contents of the card are shown in Manager.
4.
· For IP Office 5.0+, all the phone firmware files can be transferred by selecting File | Upload Phone Files or
for IP500 V2 systems File | Upload System Files. This will automatically select the phone firmware files that
Manager has available and transfer them to the memory card.
· New files can be drag and dropped to the Files section of the currently selected folder or transferred using File
| Upload File.... The transfer is serial and can be interrupted by other activities on the IP Office system.
Therefore it is recommended that files are transferred in small batches.
· Existing files can be deleted by right-clicking on the file and selecting Delete.
· Files can be downloaded from the card by right-clicking on the file and selecting Download. The file is
downloaded to the Manager applications working directory.
When transfers have been completed, to select another system use File | Open File Settings. To return Manager
5.
to normal configuration mode select File | Configuration.
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 25
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6


Chapter 2.
Installation
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 27
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6
2. Installation
Check the following before beginning installation:
o IP Office Manager PC
1.
Check that the applications for configuring and monitoring an IP Office system are available and able to connect to
that system.
· o Check that IP Office Manager and IP Office System Status Application (SSA) or System Monitor are installed
and can be used to connect to the IP Office system.
· o Verify that you can receive the configuration from the system and send it back to the IP Office.
· o Ensure that the Manager PC has been given a static IP address.
o Voice Compression Channels
2.
The IP Office Unit must be fitted with a voice compression channels . Use either SSA or System Monitor
application to verify that the voice compression channels are available. SSA list the VCM channels on the
Resources screen. The initial lines of Monitor output include the item VCOMP= which will state the number of
channels installed in the control unit.
o Avaya IP Endpoint Licenses
3.
If installing onto an IP500 or IP500 V2 system, each phone requires a license.
o File Server Settings
4.
Using Manager, receive the configuration from the IP Office. Select System and then select the System tab. Check
the following:
· o System Name
On the System tab ensure that a Name for the IP Office Unit has been entered.
· o TFTP Server IP Address
If using TFTP to download software file to the phones, enter the TFTP server address here. This address is used
by the IP phones (excluding 1600 Series) being supported by IP Office DHCP. If another DHCP server is being
used, that address must be set via the DHCP settings on that server, see Alternate DHCP Setup .
· The default 0.0.0.0 will cause the phones to broadcast for any TFTP server available on the same subnet
as themselves.
· To use the memory card installed in the system, enter the LAN1 IP address of the IP Office system (the
address is shown on the LAN1 tab). To use this option the card must be loaded with the IP phone software
files, see Control Unit Memory Card .
· If a 3rd-party TFTP server is being used, set the IP address to the address of the PC running that
software.
· o HTTP Server IP Address
IP Office 4.2+ supports the use of HTTP for file requests from IP phones. This is necessary for 1600 Series
phones and is supported by all other Avaya IP phones. This address is used by the IP phones being supported
by IP Office DHCP. If another DHCP server is being used, that address must be set via the DHCP settings on
that server, see Alternate DHCP Setup .
· The default 0.0.0.0 disables HTTP support.
· For IP Office 4.2, using the Embedded Voicemail memory card is also supported for HTTP file requests for
up to 50 IP phones. This is done by setting the TFTP Server IP Address and HTTP Server IP Address
to match the control units IP address. This is supported for up to 50 IP phones.
· If a 3rd-party HTTP server is being used, set the IP address to the address of the PC running that
software.
o H323 Gatekeeper Settings
5.
Select System and then select the LAN1 tab. Select the Gatekeeper sub tab. Check the following settings:
· o H323 Gatekeeper Enabled
Ensure that this option is enabled.
· o H323 Auto-created Extn
This installation process assumes that this option is enabled until after installation of the phones has been
completed. If not enabled the you must manually add extensions to the IP Office configuration before
installation. See Manually Creating Extensions .
· o H323 Auto-create User
This installation process assumes that this option is enabled until after installation of the phones has been
completed. If not enabled the you must manually add users to the IP Office configuration before installation.
· o Primary Site Specific Option Number
Devices being supported by DHCP can request device specific information using a site specific option number
(SSON). This method is used for Avaya IP phones to request phone specific information from a DHCP server.
For IP phones beign supported by IP Office DHCP, the SSON set here should match that being used by the
phones. By default Avaya 4600 and 5600 Series IP phones use the 176 as their SSON.
25
70
33
17
70
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 28
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6
Installation:
· Secondary Site Specific Option Number (IP Office 4.2+)
This field allows a second SSON to be specified for use by IP phones. By default Avaya 1600 Series IP phones
use 242 as their SSON.
o DHCP Server
6.
If not using the IP Office for DHCP, check that the alternate DHCP server has been configured for the IP phones. It
will need to include details of the files server and gateway settings. See Alternate DHCP Setup . If using the IP
Office for DHCP, select System and then the LAN1 or LAN2 tab.
· o DHCP Mode
Check that the IP Office is set as Server. This allows it to respond to DHCP requests on its subnet.
· o Number of DHCP IP Addresses
Set this to a number sufficient for all the IP devices, including phones, that will be supported by the IP Office
DHCP.
· o Advanced/DHCP Pools (IP500 4.2+)
For IP Office 4.2+ on IP500 systems, multiple ranges of IP addresses can be configured for use by IP Office
DHCP. In addition, the IP Office DHCP can be restricted to Avaya IP phones only by selecting Apply to Avaya
IP Phones Only.
o IP Phone Software and Settings Files
7.
The software for IP phone installation is supplied on the IP Office Administrator Applications CD. Those files must be
placed on the file server. The files are automatically installed as part of the IP Office Manager application and so are
already present if IP Office Manager is used as the file server.
· If another source is used as the file server, the software and settings files must be copied to that server. For
pre-IP Office 4.2 system the files must be copied from the Manager application folder. For IP Office 4.2+ the
files can be copied from the location program files\Avaya\IP Office\Manager on the installation CD.
· If it does not exist already an additional file, 46xxsettings.txt, is also required. See Creating a 46xxsettings.
txt File .
o Extension Number and User Name Details
8.
31
A full listing of the planned extension number and user name details is required. The planned extension number
must be unused and is requested by the phone during installation.
70
H323 IP Telephone Installation Page 29
15-601046 Issue 16a (15 March 2010)IP Office Release 6
 Loading...
Loading...