
Service Bulletin
Issued by Canon Europa N.V.
COPIER
Model : No.:
GP160 series, GP405 series, GP605 series,
CP600IR, CLC1100 series
DATE:
Location :
Subject :
Reason :
Details :
INTRODUCING A NEW TOOL
WRITING TO DIMM, USING ROM WRI TER A ND PC
This bulletin communicates an outline of how to write data to a DIMM using a ROM writer and a PC
and how to go about the work.
The contents of this bulleti n applies to models equipped with flash ROMs/DIMMs; e. g., GP160 Series,
GP405 Series, GP605 Series, CP600IR, CLC1100 Series.
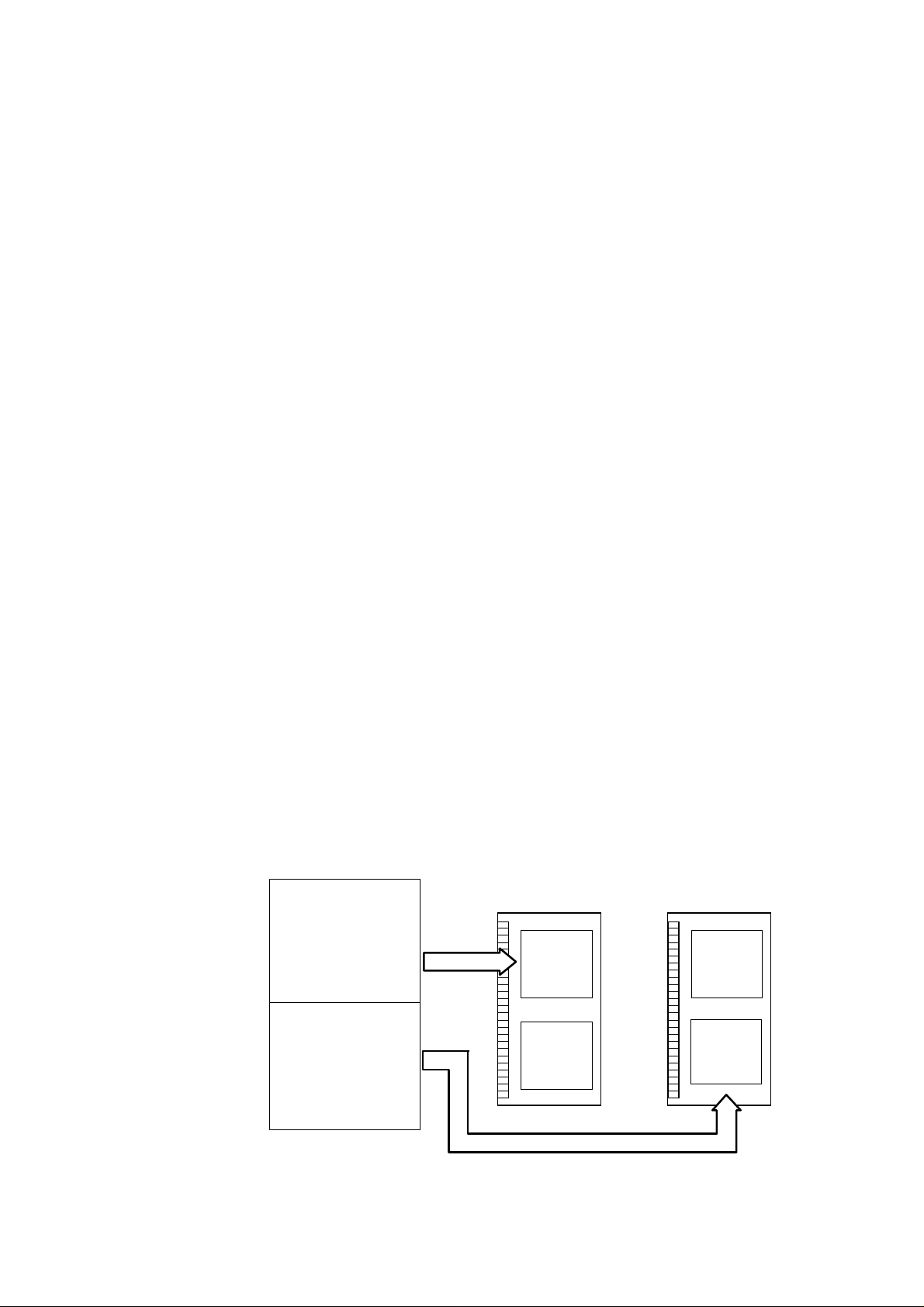
1. Outline
< Upgrading a Copier's DIMM>
You can upgrade a copier's DIMM by any o f the follo wing ways:
a. Downloading data provided by Canon Inc. to the copier from a PC (do es not apply to GP160
Series).
b. Transferring data provided by Canon I nc. to a ROM writer f r om a PC; writing the data to a DIMM
using the ROM writer; and then replacing the existing DIMM with the DIMM.
This bulletin explains method b.
Note that specific data contents will be communicated separately when they have been finalized.
GEN-620
(FF-T01-F-000010-01)
09.04.99
Server at
Canon Inc.
2. Points to Note
a. Exercise care, as this method differs from the way writing is done from a m aster ROM to a DIMM.
b. Whenever you must hold the DIMM, be sure to avoid touching the terminals (gold-plated).
Otherwise, the resulting poor contact or static electricity can damage the DIMM.
PC
ROM writer
Figure 1
DIMM
-
1 / 8 -
GEN-620
3. Writing to a DIMM Using a ROM Writer
3-1. Outline
You can use a RO M writer ( MODEL 1930 from Minato) to write ROM data to a 1-MB, 2-MB, or 4MB DIMM.
A DIMM is equipped with two flash ROM chips. Since they will require separate writing, you will be
repeating the same work.
a. Registering the Flash ROM to the ROM Writer
The ROM writer can deal with different types of ROMs. When the power is turned on, it is for the
previous writing operation, requiring you to r eset it so that it will be able to recognize the type of
the flash ROM mounted on the DIMM you will be writing to.
b. Transferring ROM Data from a PC to the ROM Writer
ROM data is transferred from a PC to the ROM writer using a parallel port (printer port). To do
so, you must select the appropriate format of the data file.
The ROM data files are binary files consisting only of the data written to the ROM. Select "NO
FORMAT" as the format setting.
The ROM writer is equipped with both parallel and serial interfaces. Select the appropriate
interface, and start transfer.
Data may be transferred from a PC either by opening the DOS window and using the Copy
command (binary mode) or by using the GP/PDL downloader that comes with the printer board.
Here, we will discuss the use of the GP/PDL downloader, which can be operated more easily and
provides a higher data speed than the DOS Copy command.
When you double -click the file (GPDL105.e xe or PDLd1115.exe), which has been dist ributed
previously, installation will start automatically and the appropriate icon will be stored as part of
the Startup programs.
c. Writing to the DIMM Flash ROM
The ROM data file is in the form of 16-bit data for DIMMs. The DIMM data bus operates on a
16-bit basis, and addresses are in uni t s of bytes.
A 16-bit data item is given an ev en-numbered address (most significant) or an o dd-numbered
address (least significant bytes).
The DIMM is equipped with two flash ROMs whose data bus operates on an 8-bit basis: one of
the flash ROM s is given even-numbered addresses, w hi le the other flash ROM is g i ven oddnumbered addr esses.
Here, you will make settings to enable writing by dividing the ROM data units stored in the ROM
writer int o ones in even-numbered bytes and ones in odd-numbered bytes.
You will be writing to the flash ROMs in units of chips, requiring you to perform deleting and
writing operations twice to complete the two flash ROMs on the DIMM.
ROM data file
Most significant bytes
(even-numbered
address)
Least significant bytes
(odd-numbered
address)
(odd-numbered socket)
DIMM
Flash ROM
(even-
numbered
address)
Flash ROM
(odd-
numbered
address)
(even-numbered socket)
DIMM
Flash ROM
(even-
numbered
address)
Flash ROM
(odd-
numbered
address)
Figure 2
-
2 / 8 -
3-2. Getting Ready
a. PC
Be sure to store the data to write to the DIMM.
Since you will be using the GP/PDL downloader when transferring ROM data from the PC to the
ROM writer, be sure to install the downloader to the PC in advance.
b. Bi-Centronics Cable
Obtain a cable with the indicati on "IEE1284-compliant." Choose the shortest cable you can wor k
with without a problem.
3-3. Starting Up the PC
1) Connect the PC and the ROM writer with the Centronics cable.
2) Start the PC.
3) Start the GP/PDL downloader using Wi ndows' S tartup Menu pr ogram.
3-4. Registering the Flash ROM to the ROM W r iter
a. Turning On the ROM Writer
1) Turn on the po wer switch found on the back of the ROM writer.
2) Wait until self diagnosis ends.
b. Mounting the DIMM Adapter
Mount the DIMM adapter to the socket in the ROM writer.
Match the DIMM adapter against the front of the socket.
GEN-620
DIMM adapter
Figure 3
c. Setting the DIM Adapter Switch
Be sure to set the switch of the DIMM adapter as shown in the following figure.
Caution:
ROM writer socket
Keep in mind that the switch settings differ between the DIMM adapter to be mounted
to the even-numbered socket and the DIMM adapter to be mounted to the oddnumbered socket.
If you have made a mistake, although an error will not occur during writing operation,
the copier will not work normally after you have installed the completed DIMM to
it.aution:
-
3 / 8 -
 Loading...
Loading...