Canon 162 Users Manual

Linked Shooting
With linked shooting, up to 10 slave cameras can be linked in a wireless
network (via IEEE 802.11g in ad hoc mode) to the master camera on which
you will release the shutter. Any cameras compatible with linked shooting,
when they have WFT series transmitters attached, can be used as slave
cameras, regardless of model.
Note that there will be a slight delay after you release the master camera
shutter before the slave cameras shoot. Movie shooting is not supported.
Slave camera
Master camera
61
Setting Up Linked Shooting
First, establish a connection from the slave cameras to the master camera. Because linked
shooting utilizes a wireless connection via IEEE 802.11g in ad hoc mode, it is not available over
wired LANs.
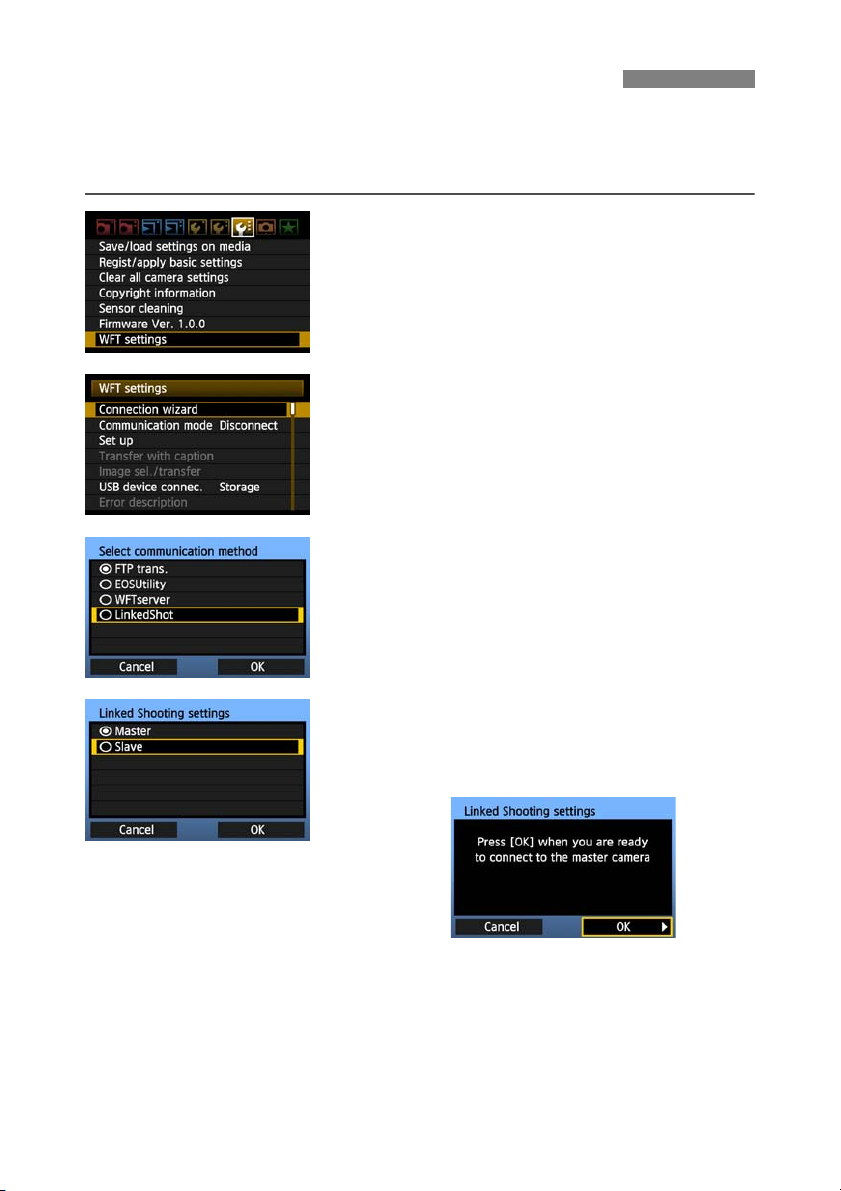
Display the transmitter menu.
1
On the camera, press the <7> button.
On the [7] tab, select [WFT settings] and press
<0>. [WFT settings] is added to the tab after
you attach the transmitter.
Select [Connection wizard].
2
Select [LinkedShot].
3
62
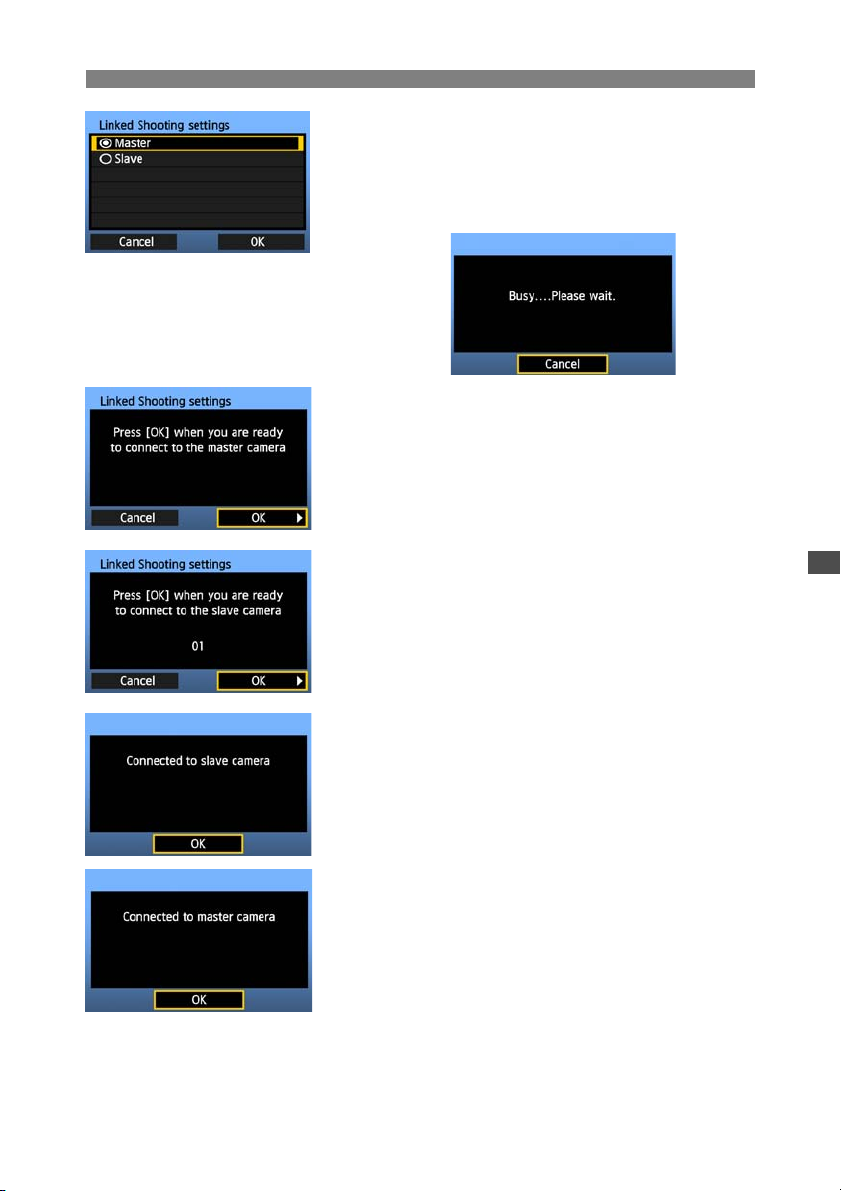
Set up the slave cameras.
4
Select [Slave].
X The slave cameras are now ready, with the
following screen displayed.
When using multiple slave cameras, set up all
slave cameras to slave state.
Once the settings are complete, slaves cannot be
added or removed. You must repeat the setup
process from step 1.
Setting Up Linked Shooting
Set up the master camera.
5
Configure the settings on the master camera
following steps 1-3 on the previous page, and then
select [Master].
X The following screen is displayed.
At this point, switch to setting up the
slave cameras.
6
On the slave cameras, select [OK].
Check the number of slave cameras.
7
X On the master camera LCD monitor, the number of
slave cameras detected is displayed.
Establish the connection.
8
On the master camera and all slave cameras,
select [OK].
X A screen is displayed as the connection is tested.
The information you specified is stored on the
cameras. It is not stored on the transmitters.
63
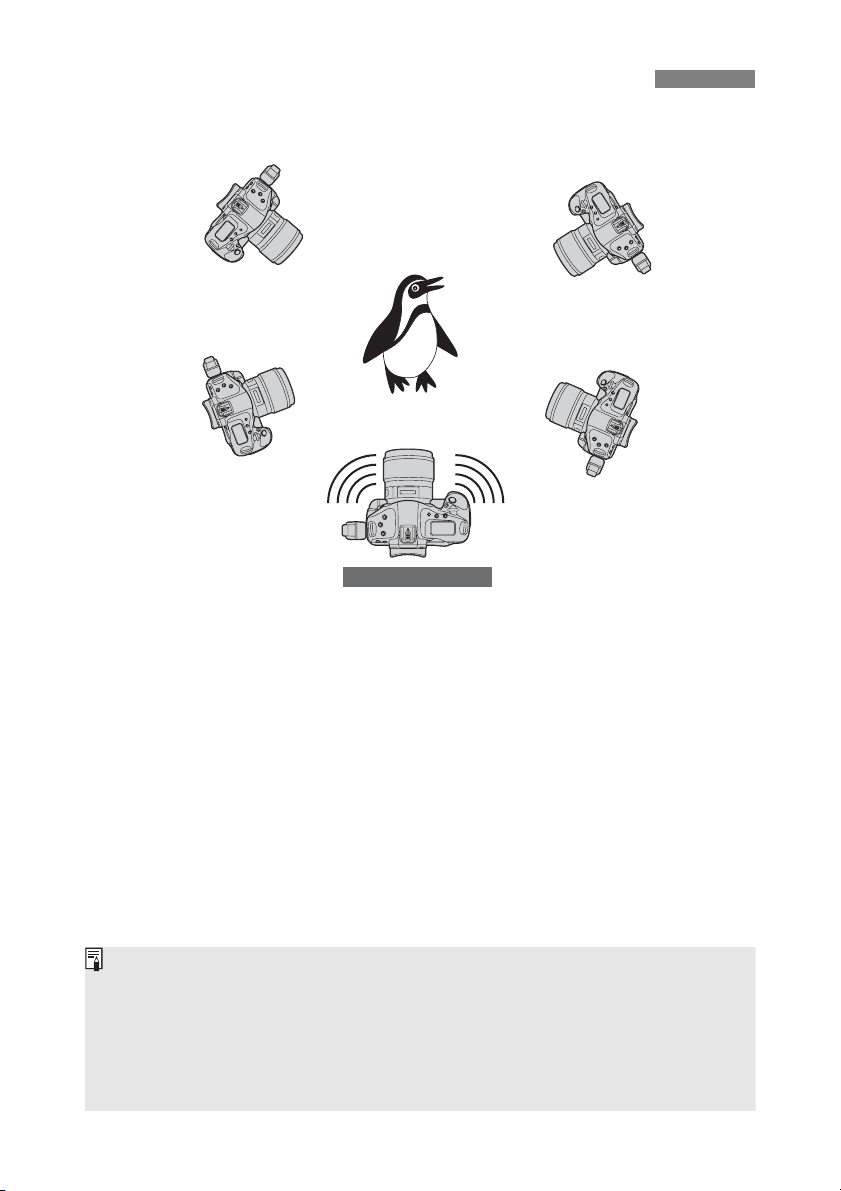
Arranging the Slave Cameras
Slave camera
Master camera
Arrange the slave cameras in clear view of the master camera, without objects between
them.
You can arrange master camera in an overall circumference of up to approximately 100 m /
328 ft. However, the distance supported for linked shooting may be shorter depending on
the wireless communication conditions, which are affected by how the cameras are
arranged, the environment of use, and weather conditions.
Pressing the shutter button halfway on the master camera puts slave cameras in the same
state, as if the shutter buttons were pressed halfway. Similarly, fully pressing the shutter
button on the master camera has the same effect on slave cameras, which respond as if the
shutter buttons were fully pressed.
There will be a slight delay after you release the master camera shutter until the slave
camera shutters are released. (Simultaneous capture is not possible.)
Slave camera
Slave cameraSlave camera
During linked shooting, when you press the AE lock or depth-of-field preview button, the camera
focuses and meters as if you had pressed the shutter button halfway.
Once you have established a connection between the master camera and slave cameras, the
settings are retained even after you replace the batteries.
If you will no longer use a slave camera in linked shooting, set [Communication mode] to
[Disconnect] on that slave camera.
Any cameras compatible with linked shooting, when they have WFT series transmitters attached,
can be used as slave cameras, regardless of model.
64
Managing
Settings Information
65
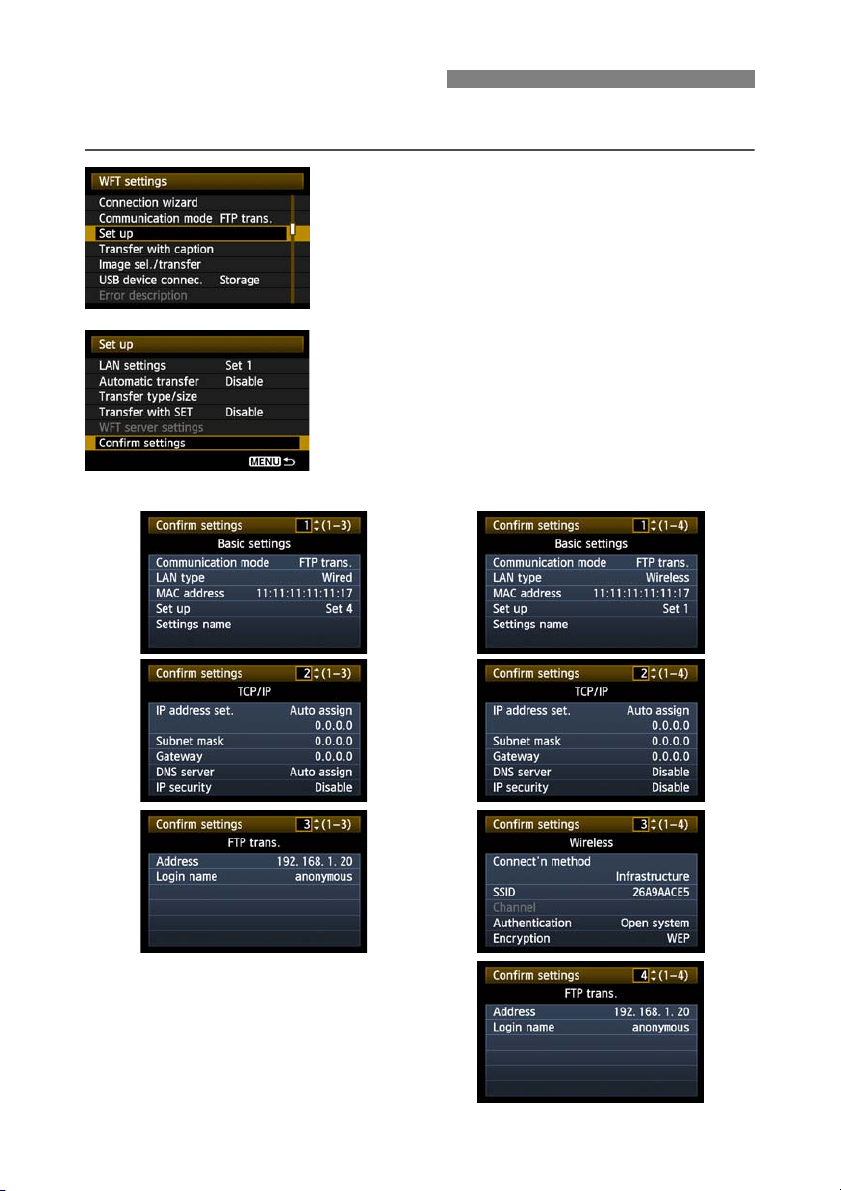
Checking Settings
E
FTP t
LAN
tti
E
FTP t
LAN
tti
Check the network settings as follows.
In [WFT settings], select [Set up].
1
Select [Confirm settings].
2
X The settings are displayed.
xample of
ransfer and wired
se
ngs
xample of
ransfer and wireless
se
ngs
66
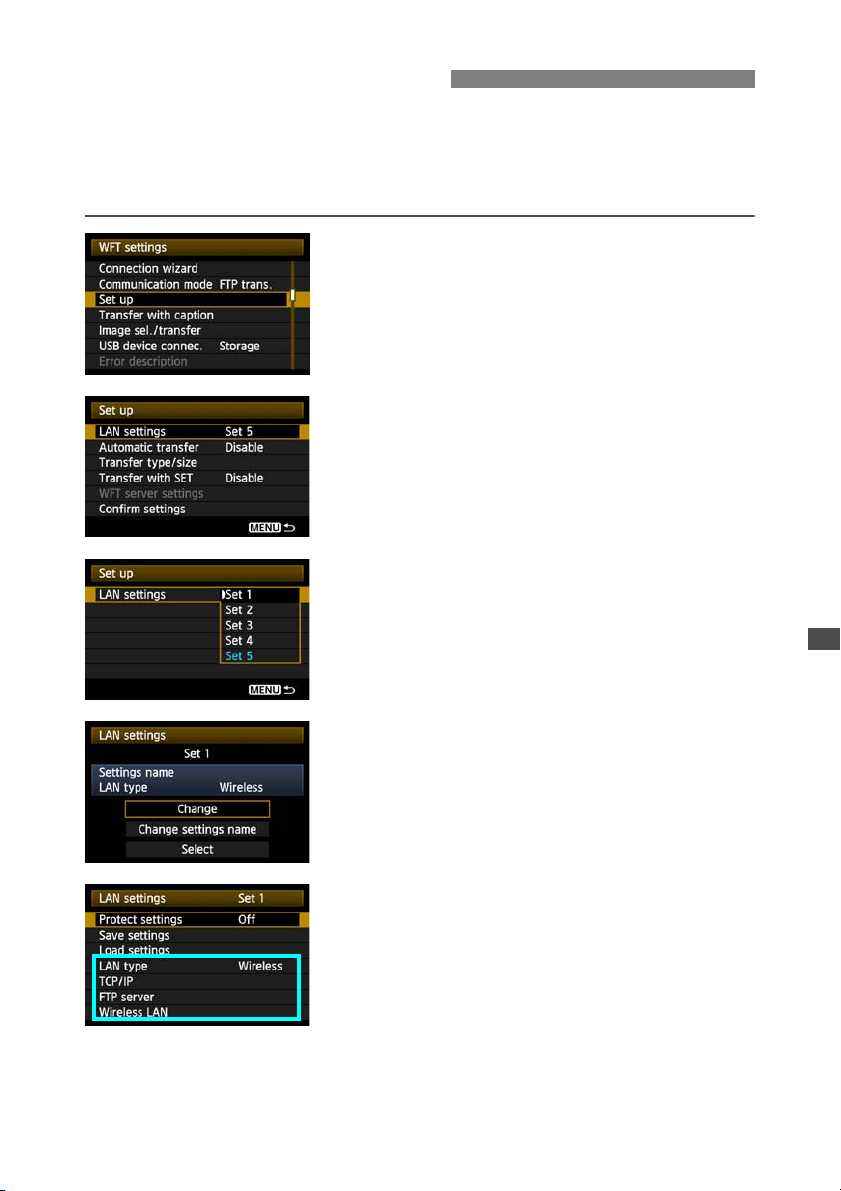
Changing Settings
Settings originally completed using the connection wizard can be changed as follows. You can
also change IP security settings (IPsec) not completed using the connection wizard, as well as
other settings, such as the setting that determines what happens if an image of the same file
name as an existing file is sent to the FTP server. (p.68)
In [WFT settings], select [Set up].
1
Select [LAN settings].
2
Select the settings number.
3
Here, select the settings number that identifies the
LAN settings.
Select [Change].
4
After selecting [Change settings name], you can
rename the settings.
Select the item to change.
5
Select the desired item from [LAN type], [TCP/IP],
[FTP server], or [Wireless LAN] and change the
setting.
67

Changing Settings
IP Security (IPsec)
Configured in [TCP/IP] [Security].
IPsec is a set of standards for encrypted communication over the Internet. It provides effective
security for both wireless and wired LANs. To use this function, you must enable IPsec in the
network settings of your computer. When IPsec is employed, only transport mode is supported,
and DES encryption and SHA1 authentication are used. Note that the IP address of the
computer for communication with the transmitter must be entered in [Destination address] on
the settings screen.
Directory Structure of the Target Folder
Configured in [FTP server] [Directory structure].
Selecting [Camera] automatically creates a folder structure matching that of the camera’s (such
as A/DCIM/100EOS1D) in the server’s root folder for image storage. If you have created a
subfolder in the root folder by changing the [Target folder] setting, a folder structure such as A/
DCIM/100EOS1D is automatically created in that folder for image storage.
Selecting [Default] will use the root folder for image storage. If you have created a subfolder in
the root folder by changing the [Target folder] setting, images are saved in that folder.
Overwriting Files of the Same Name
Configured in [FTP server] [Overwrite same file].
When the transmitter is configured to prevent overwriting
If there is already a file of the same name in the target folder on the FTP server, the new file is
saved with an extension consisting of an underline and a number, as in IMG_0003_1.JPG.
When you resend images if initial transfer fails
Even if the transmitter is configured to overwrite files of the same name, if you resend an image
file that could not be transferred initially, the existing file may not be overwritten in some cases.
If this happens, the new file is saved with an extension consisting of an underline, a letter, and
a number, as in IMG_0003_a1.JPG.
Passive Mode
Configured in [FTP server] [Passive mode].
Enable this setting in network environments protected by a firewall. If an Error 41 occurs
(“Cannot connect to FTP server”), setting passive mode to [Enable] may enable access to the
FTP server.
Preventing Changes to Settings
To prevent accidental changes to LAN settings, set [Protect
settings] to [On].
68
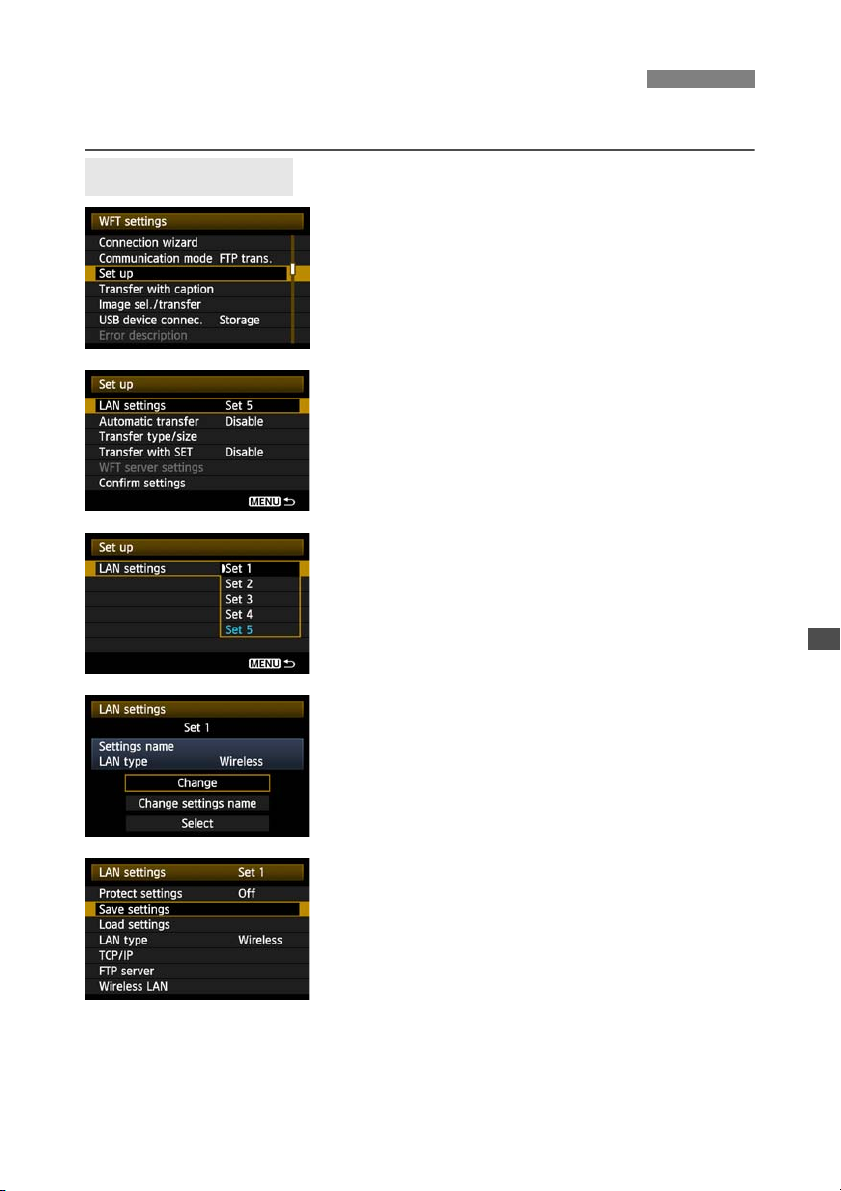
Saving and Loading Settings
Network settings can be saved on a memory card for use with other cameras.
Saving Settings
In [WFT settings], select [Set up].
1
Select [LAN settings].
2
Select the settings number.
3
Here, select the settings number that identifies the
LAN settings.
Select [Change].
4
Select [Save settings].
5
69
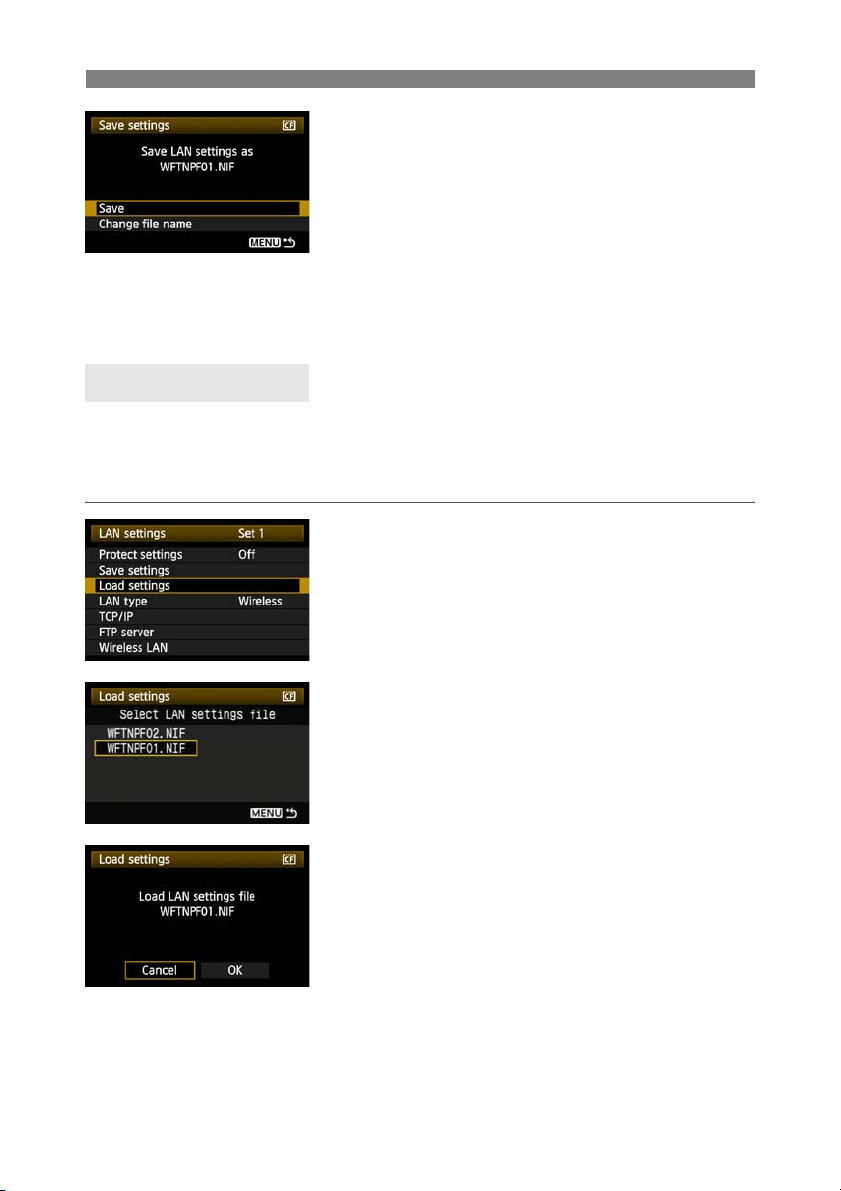
Saving and Loading Settings
Select [Save].
6
X The settings are now saved as a file on the
memory card.
The settings are saved as a file (WFTNPF**.NIF)
in the area of the memory card shown when the
card is opened (in the root directory).
The file name is determined automatically by the
camera: WFTNPF, followed by a number (01 to
99) and the extension NIF. You can rename the file
as desired by selecting [Change file name].
Loading Settings
Load settings files stored on a memory card as follows. Also use this procedure when loading
settings files created on a computer.
Make sure the settings file is saved in the folder shown when the memory card is opened (that
is, the root directory).
Select [Load settings].
1
70
Select the settings file.
2
X Select a settings file that matches your network
environment.
Load the settings file.
3
X Information from the settings file is loaded into the
selected settings number.
Using External Media
Commercially available external media, connected via USB, can be used
the same way as CF and SD cards. You can also back up images from CF
and SD cards onto external media.
Note that external media must meet the following requirements.
Use media conforming to the USB Mass Storage Class Specification.
If an external hard disk drive is used, use a self-powered drive. Bus-
powered drives do not work in some situations.
The main image storage area must be formatted with a FAT16 or
FAT32 file system.
Use media with a main image storage area of less than 1 TB
(terabyte), with 512 bytes per sector.
Do not use external media equipped with a card slot.
71
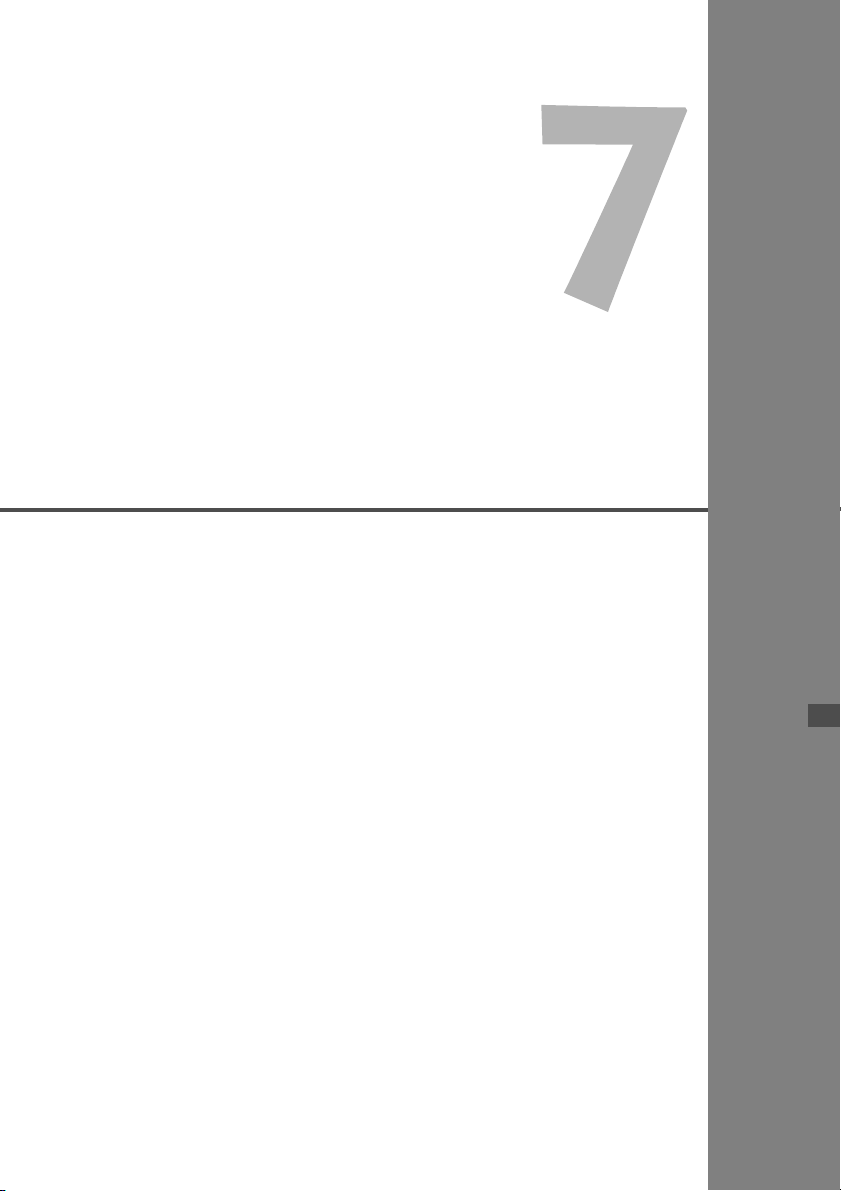
Connecting External Media
Before connecting external media to the transmitter, switch the camera’s power switch to
<
OFF
>. Also turn off external media that has its own power supply.
When connecting external media, be sure to use the USB cable provided with the camera.
The transmitter USB port is not hot-pluggable. USB cables cannot be connected or
disconnected at any time. Follow the instructions in this section when connecting or
disconnecting USB cables.
Plug the external media into the USB
port.
1
Open the port cover and connect the external
media.
Do not connect external media via a USB hub.
If the external media is self-powered, turn it on
after connecting it.
In [WFT settings], select [USB device
connec.].
2
If you will not use a wireless or wired LAN at the
same time as the external media, set
[Communication mode] to [Disconnect].
Select [Storage].
3
72
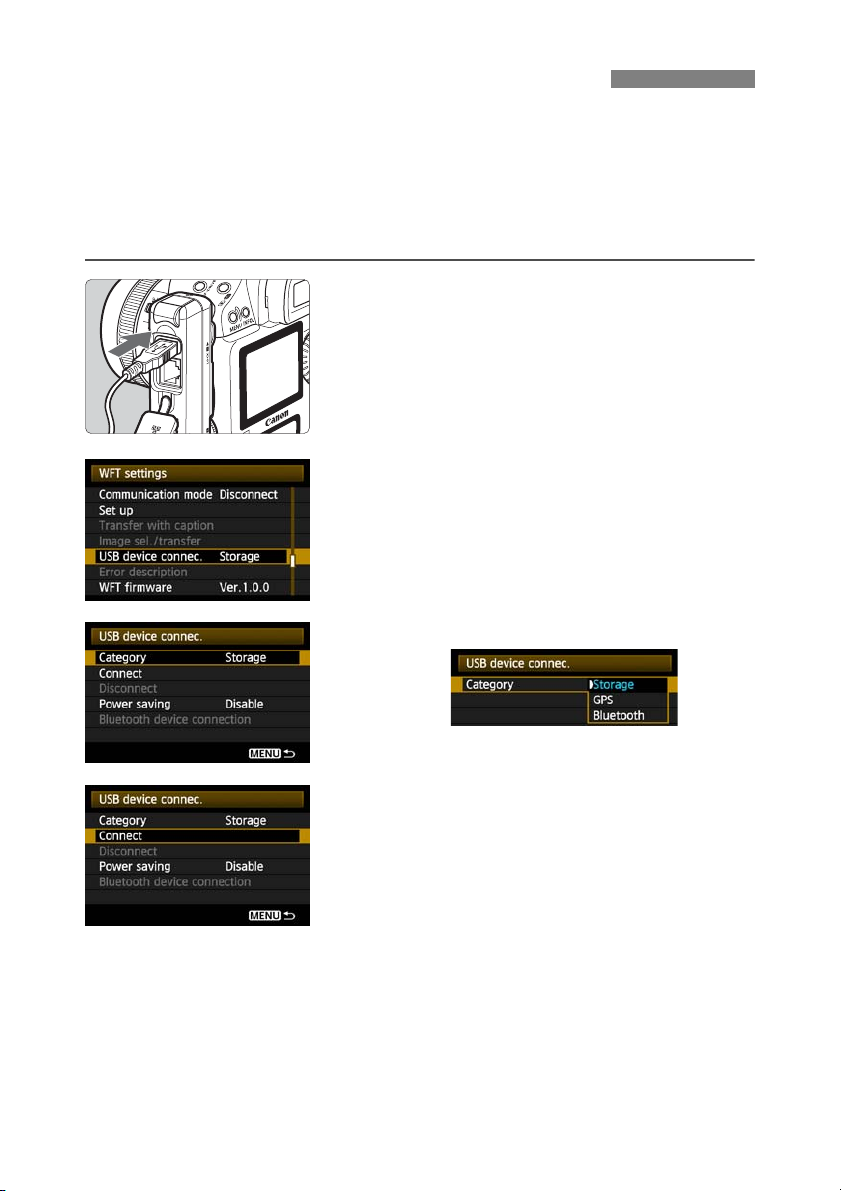
Select [Connect].
4
Connecting External Media
Select [OK].
5
Camera operations such as shooting, menu
display, or image playback are not possible
until the connection is established.
When the transmitter is connected to the external
media, the transmitter’s <
and a message is displayed indicating that a
connection has been established.
When the confirmation message is displayed,
select [OK].
X At this point, the menu option [Disconnect]
becomes available. Select this option before
disconnecting the external media.
USB
> lamp is lit in green
X After you exit the menu, the rear LCD panel
indicates that external media is connected.
External media cannot be formatted using the camera. Format it with a FAT16 or FAT32 file system
using the computer.
73
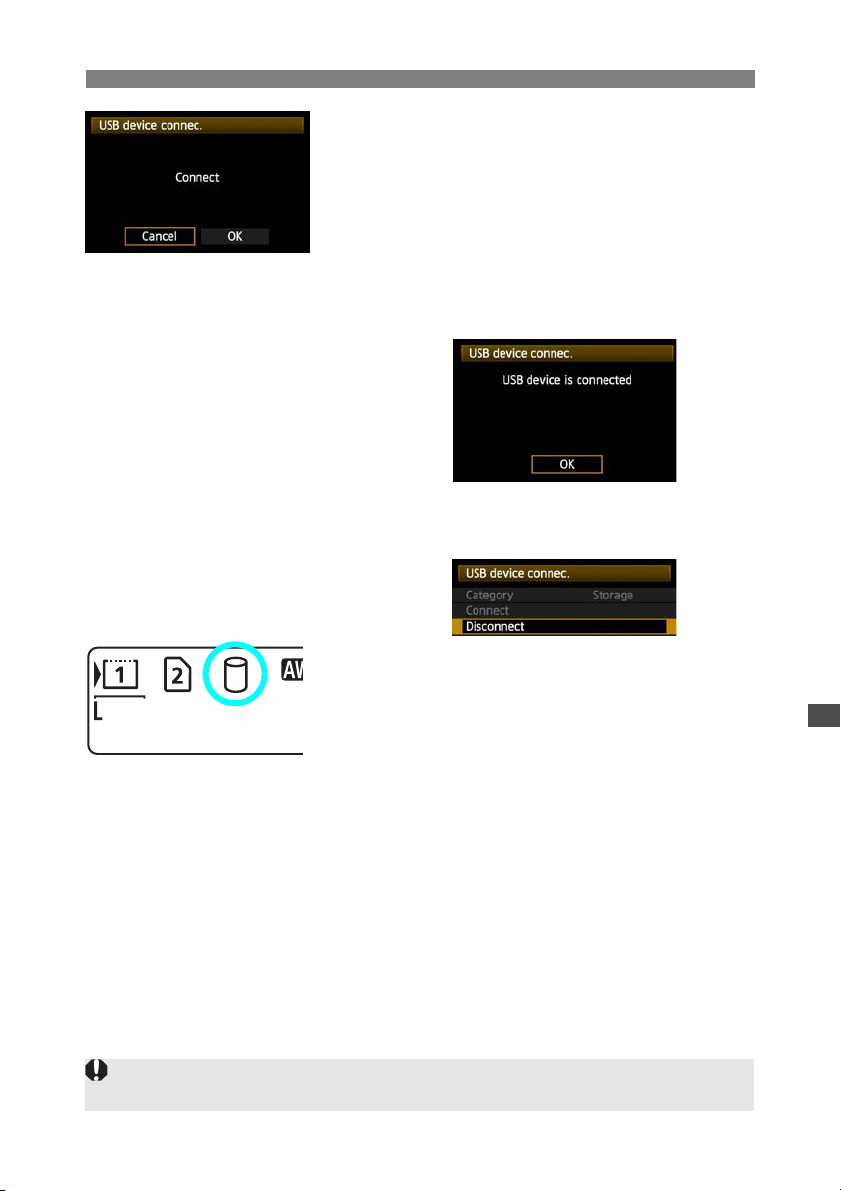
Connecting External Media
Unplugging External Media from the USB Port
Before unplugging external media from the USB port, always select [Disconnect] as shown in
step 5. Follow the instructions displayed to terminate the connection.
The connection will not be terminated if you simply turn off the camera and external media. If
you unplug external media while the connection is still active, plug the external media into the
USB port again and follow the preceding steps to terminate the connection.
Power Supply to External Media
External media is powered via the transmitter’s USB port as needed. However, external hard
disk drives may not work after connection in some cases.
Power Management
If you will not use a wireless or wired LAN at the
same time as the external media, set
[Communication mode] to [Disconnect]. The
camera battery drains faster under settings other
than [Disconnect] because power saving is
disabled.
Setting [Power saving] to [Enable] enables the
power supply to external media to be stopped
automatically, conserving the camera battery.
Power is supplied again automatically during
shooting, when captured images are stored.
Before shooting movie, set [Power saving] to [Disable] and make sure the transmitter’s <
is lit in green. If you start shooting movie when the <
recorded to external media.
USB
> lamp is out or blinking, the movie may not be
74
USB
> lamp
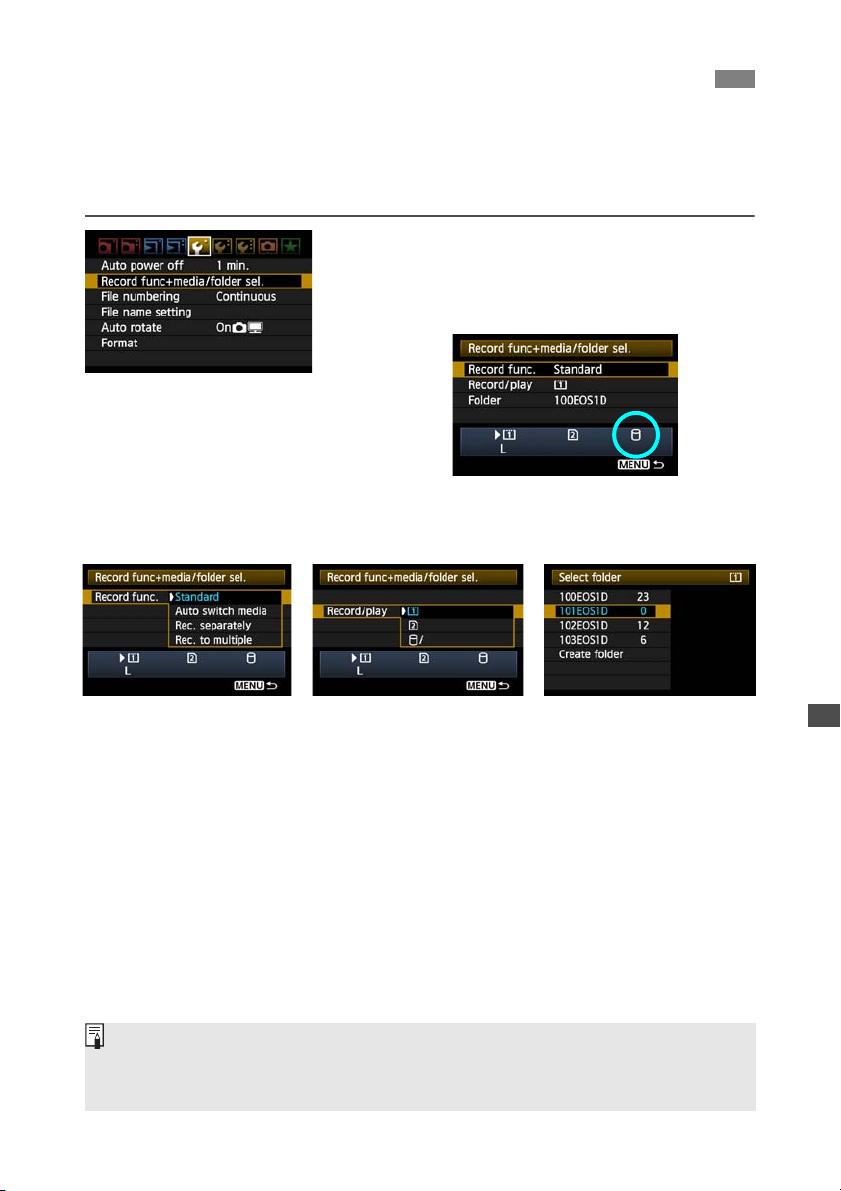
Choosing Recording Media When Shooting
Images can be stored on external media connected via USB just as on CF and SD cards.
You can also configure [Record func.], [Record/play], and [Folder] settings (described below)
to use the external media. For details, refer to the Camera Instruction Manual (page 56).
When recording movies to a hard disk, use a hard disk with fast write speeds.
On the [5] tab, select [Record
func+media/folder sel.].
X The icon for external media is displayed next to
icons for the CF and SD cards.
Complete the following settings, as needed. For
details on using [Record/play] with external
media, refer to the next page.
Although the <
power off, shooting is still possible. Any images captured at this time are stored temporarily in the
camera's internal memory and then recorded on external media when the <
green.
USB
> lamp will blink in green briefly if the camera is restarted or recovering from auto
USB
> lamp remains lit in
75
Choosing Recording Media When Shooting
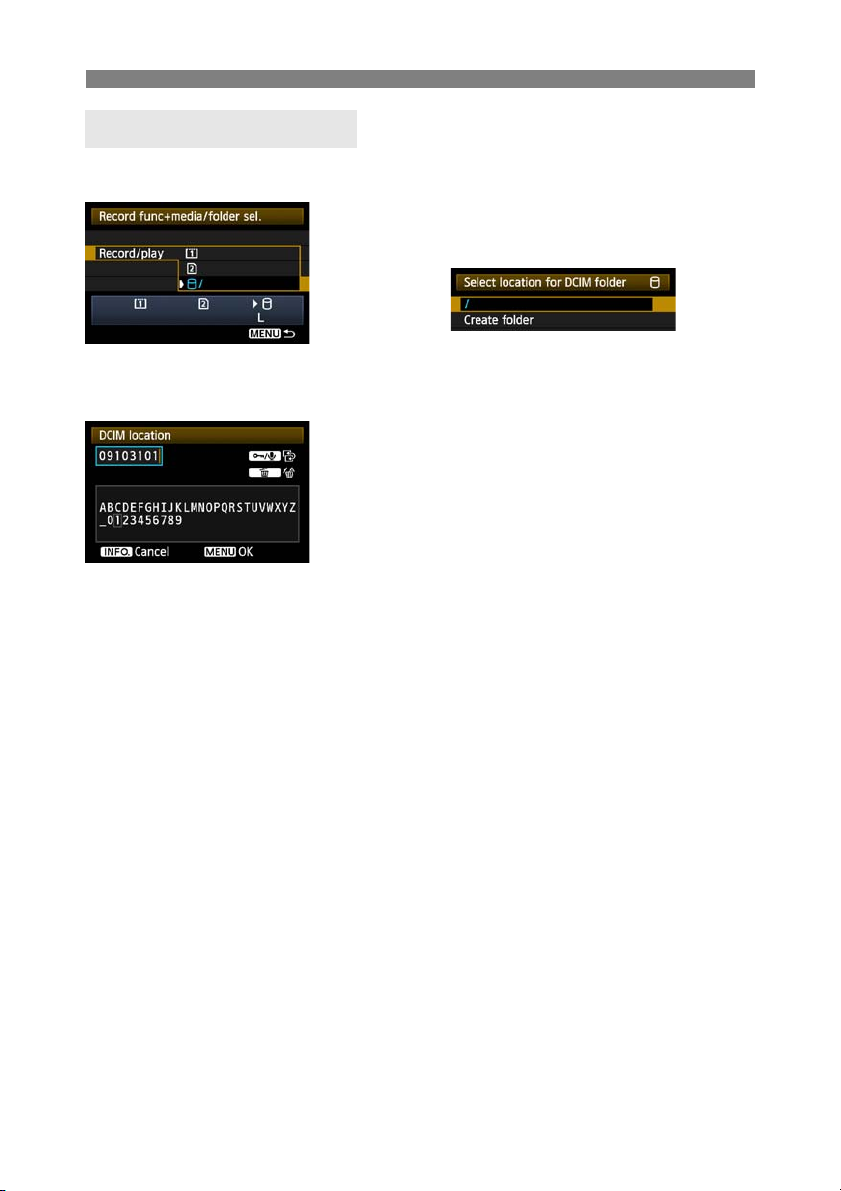
[Record/play] Setting
When you select external media in [Record/play], the [Select location for DCIM folder]
screen is displayed. The DCIM folder contains the EOS1D folder, where images are stored.
To create the DCIM folder in the first folder
displayed when the external media is opened (that
is, the root directory), select the default setting of [/].
To create another parent folder for the DCIM
folder, select [Create folder]. A screen is
displayed for entering the folder name.
By default, the folder name comprises the current
date (last two digits of the year, in addition to the
month and day) and numbers representing the
order the folder was created, in a range of 01 to
99.
Always use 8 characters for the folder name.
For instructions on entering the folder name, refer to
“Virtual Keyboard Operation” (p.27).
76
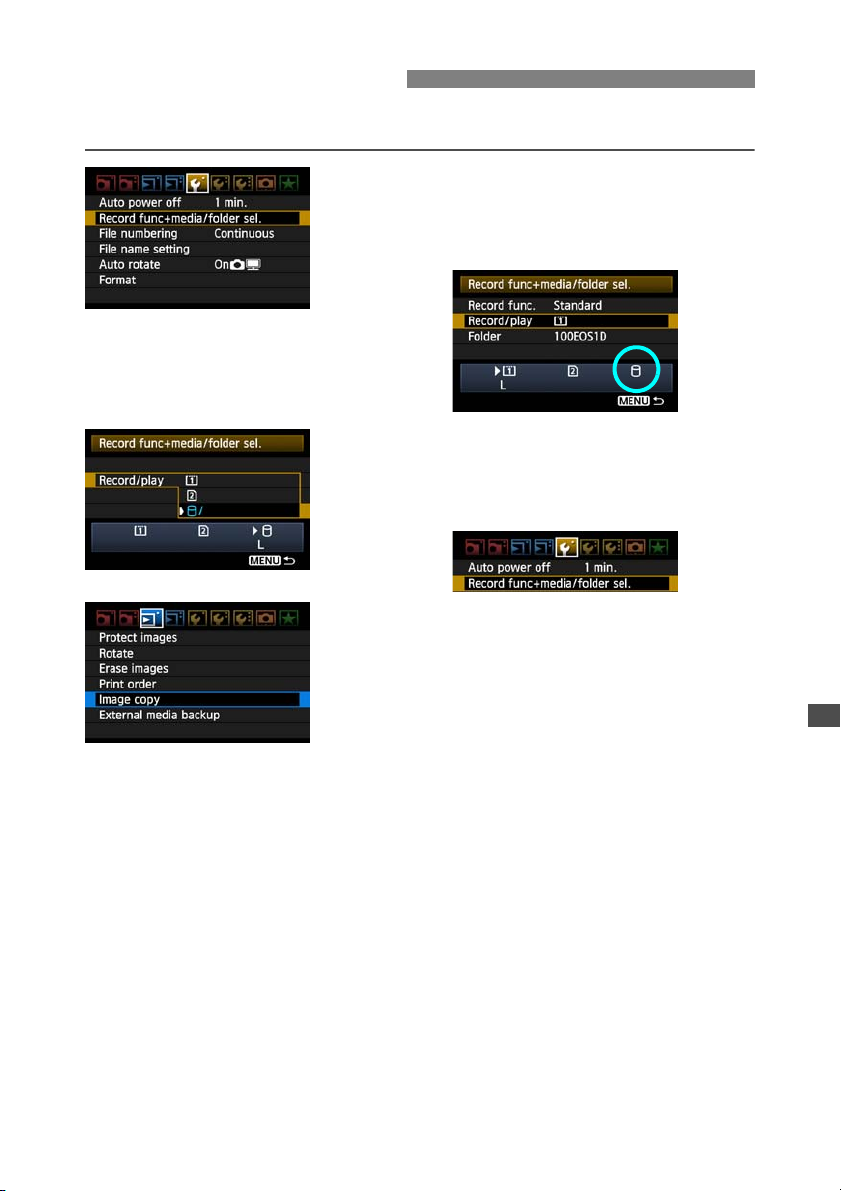
Copying Images
Images can be copied to external media connected via USB just as to CF and SD cards.
On the [5] tab, select [Record
func+media/folder sel.].
1
X The icon for external media is displayed next to
icons for the CF and SD cards.
Select the source media in [Record/
play].
2
After selection, press the <7> button to return
to the menu screen.
On the [3] tab, select [Image copy].
3
For subsequent instructions, refer to the Camera
Instruction Manual (page 176). Operations are the
same as when using a CF or SD card, except that
the external media icon <u> is displayed.
77
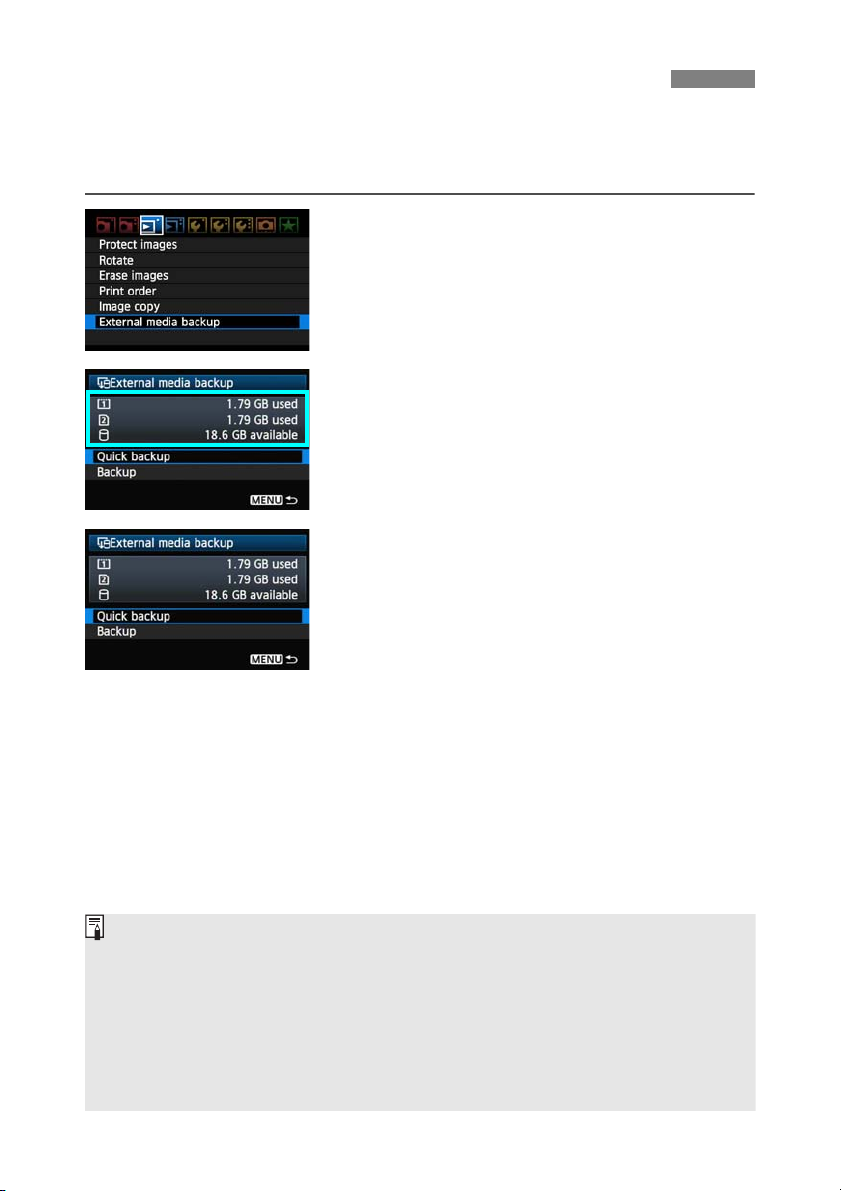
Backing Up on External Media
Images stored on CF or SD cards can be backed up on external media.
Initially, captured images are stored in the DCIM folder on CF or SD cards. Selecting [External
media backup] backs up this DCIM folder to external media.
On the [3] tab, select [External media
backup].
1
Check the free space on the media.
2
Make sure more space is available on the external
media than the amount used on the memory card.
If less free space is available on the external
media, backup is not possible.
Select the method of backup.
3
Select [Quick backup] or [Backup].
You can also backup the MISC folder, where printing and transfer instructions are stored.
External media cannot be backed up onto memory cards.
If the backup destination already has a folder of the same number containing images of the same
number, [Skip image and continue], [Replace existing image], and [Cancel backup] are
displayed. Select the backup method and press <0>.
•[Skip image and continue]: All images are backed up except for images of the same number as
existing images
•[Replace existing image]: All images are backed up, including images of the same number as
existing images
Shooting is not possible during backup. Press [Cancel] before shooting.
78
 Loading...
Loading...