Brawa 0612 BR 65, 0613 BR 65 User Manual [de]

Betriebsanleitung
Dampflokomotive BR 6510 – H0
Ausführung Gleichstrom 0612
Ausführung Wechselstrom 0613
Die Deutsche Reichsbahn in der DDR plante ab 1951, ihren überalterten Lokpark langfristig zu erneuern. Dabei sollten auch Dampflokomotiven den alten Bestand ergänzen. 1952 wurde ein Bauprogramm aufgestellt, das sieben verschiedene Loktypen enthielt.
Vier Typen des Programms wurden tatsächlich realisiert. In der Leistungsklasse der ehemals preußischen P 8 und T 18 entstand die Tenderlok der Baureihe 6510.
1954 verließ die erste Lokomotive 65 1001 die Werkhallen von LEW Hennigsdorf. Da ihre Konstruktion letztlich auf einem Entwurf der Firma Borsig aus dem Jahr 1946 basierte, erhielt sie eine Borsig Fabriknummer. Parallel zu den Versuchsfahrten der ersten Prototypen lief bereits der Serienbau bei Lokomotivbau „Karl Marx“ in Babelsberg. Diese Situation erschwerte das Ausmerzen von konstruktionsbedingten „Kinderkrankheiten“ erheblich.
Bis 1957 wurden insgesamt 93 Lokomotiven gebaut. Dann begann sich der Strukturwandel zur elektrischen – und Dieseltraktion auch in der DDR abzuzeichnen.
Die Lokomotiven blieben bis auf wenige Ausnahmen bis 1975 im Einsatz. Sie fuhren besonders häufig im Berufsverkehr mit kurzen Haltestellenabständen, da sie hier mit ihrer guten Beschleunigung überzeugten. Die maximale Höchstgeschwindigkeit betrug 90 km/h, das Dienstgewicht 113 t. Nur drei Exemplare der Baureihe haben bis heute überlebt. Das direkte Vorbild des Brawa-Modells ist die BR 65 1016.
1

Locomotive BR 6510 – H0
Locomotive BR 6510 – H0
Operating Instructions
Direct current model 0612
Alternating current model 0613
From 1951 onwards Deutsche Reichsbahn – the German State Railway of the GDR (former East Germany) – planned the long-term renewal of its stock of locomotives. The old stock was also to be complemented with steam engines. In 1952 a programme was set up that envisaged seven different types of locomotives.
Four types from this programme were actually built. The 6510 series tank locomotive was based on the former Prussian P 8 and T 18 performance class.
The first locomotive, the 65 1001, left the LEW Hennigsdorf works in 1954. It was given a Borsig factory number because its design was based on a concept of the Borsig company dating back to 1946. Series production at Lokomotivbau “Karl Marx” in Babelsberg proceeded parallel with the trial runs of the first prototypes. This situation made it more difficult to eradicate design-based “teething problems”.
A total of 93 locomotives were built up to 1957. At this point a structural change towards electrical and diesel traction became apparent in the GDR.
With a few exceptions all locomotives remained in service right up to 1975. On account of their excellent acceleration characteristics, they were often used on commuter routes where the distances between the individual stations were short. The locomotive’s maximum speed was 90 km/h, and it had a service weight of 113 t. Only three models of this series have survived to this day. The Brawa version was directly modelled on the basis of the BR 65 1016 concept.
Instructions de service
Modèle à courant continu 0612 Modèle à courant alternativ 0613
Les Chemins de fer allemands (Deutsche Reichsbahn) de l’ex-R.D.A. avaient prévu à partir de 1951 le renouvellement à long terme de leur parc de locomotives qui était vétuste. Ce faisant, on pensait compléter également le vieux parc de locomotives à vapeur. Un programme de construction a été élaboré en 1952. Il se composait de sept types de locomotives différentes.
Quatre types du programme ont abouti et furent réalisés. Dans la catégorie des anciennes locomotives prussiennes P 8 et T 18, on créa la locomotive-tender de la série de fabrication 6510.
La première locomotive 65 1001 quitta en 1954 les halles d’usine de LEW Hennigsdorf. Puisque sa construction partait d’un plan issu de l’entreprise Borsig de l’année 1946, elle reçut un numéro d’usine Borsig. Parallèlement aux essais effectués sur les premiers prototypes, la construction en série commençait déjà dans l’usine de construction de locomotives “Karl Marx” à Babelsberg. Cette situation compliqua considérablement l’élimination des “défauts de jeunesse” dus à la construction.
On construisit 93 locomotives au total jusque 1957. C’est alors que le changement structurel s’annonça en R.D.A. aussi, on passa à la traction électrique – et au moteur à diesel.
Les locomotives furent mobilisées, à part quelques exceptions, jusque
2

Locomotiva BR 6510 – H0
1975. Elles circulaient assez souvent aux heures de pointe, s’arrêtant
àde courtes distances, car leur bonne capacité d’accélération était convaincante dans ces cas-là. La vitesse maximale atteinte s’élevait
à90 km/h, son poids de service était de 113 t. Trois exemplaires seulement de cette série ont survécu jusque de nos jours. Le modèle dont cette locomotive Brawa est directement inspirée, est la locomotive BR 65 1016.
Istruzioni sul funzionamento
Versione a corrente continua 0612 Versione a corrente alternata 0613
Nella Repubblica Democratica Tedesca, a partire dal 1951 le Deutsche Reichsbahn programmarono di rinnovare a lunga scadenza il loro obsoleto parco locomotive. In questa occasione il vecchio parco doveva essere integrato anche da locomotive a vapore. Nel 1952 venne stabilito un programma di produzione contenente sette diversi tipi di locomotive.
Quattro modelli furono effettivamente costruiti. Nell’ordine delle prestazioni delle ex prussiane P 8 e T 18, fu costruita la locomotivatender serie 6510.
Nel 1954, la prima locomotiva 65 1001 lasciò le officine della LEW di Hennigsdorf. Poiché la sua struttura in fondo era basata su un progetto della ditta Borsig dell’anno 1946, essa ricevette un numero di costruzione della Borsig. Contemporaneamente alle corse di prova dei primi prototipi, presso la fabbrica di locomotive “Karl Marx” di Babelsberg era già in corso la produzione in serie. Questa situazione rese notevolmente difficile l’eliminazione delle “malattie infantili” dovute alla costruzione.
Fino al 1957 furono costruite in totale 93 locomotive. Successivamente anche nella RDT iniziò a delinearsi il passaggio alla trazione elettrica e Diesel.
Escluse poche eccezioni, le locomotive rimasero in servizio fino al 1975. Vennero impiegate molto spesso nel trasporto dei pendolari con brevi distanze tra le fermate, poiché convincevano per la loro buona accelerazione. La velocità massima era di 90 km/h e il peso in esercizio di 113 t. Solo 3 esemplari della serie sono sopravvissuti fino ad oggi. Il modello Brawa ha preso direttamente spunto dalla BR 65 1016.
3

Inhaltsverzeichnis
Contents
Benennung |
|
Seite |
||
Allgemeine Hinweise ..................................................................... |
|
5 |
||
Entnahme der Lok aus der Verpackung ......................................... |
|
6 |
||
Zusatzbauteile montieren ............................................................... |
|
7 |
||
Wartungsarbeiten |
|
|
||
• |
1. |
Ölen ....................................................................................... |
|
8 |
• 2. Seuthe Raucheinsatz montieren ............................................ |
|
8 |
||
• 3. Umrüsten auf Digitalbetrieb .................................................. |
|
9 |
||
• |
4. |
Gehäuse demontieren ......................................................... |
|
10 |
• |
5. |
Platine tauschen .................................................................. |
|
10 |
• |
6. |
Motor tauschen ................................................................... |
|
10 |
• |
7. |
Umschaltrelais tauschen ..................................................... |
|
10 |
• |
8. |
Haftreifen tauschen ............................................................. |
|
10 |
• 9. Schleifer tauschen bei Wechselstrom-Ausführung |
.............. 10 |
|||
• |
10. Glühbirne tauschen ........................................................... |
|
10 |
|
• 11. Wartungsarbeiten am Kupplungsnormschacht ................. |
|
10 |
||
• 12. Wartungsarbeiten an Radsätze und Getriebe ..................... |
|
10 |
||
Ersatzteilliste |
|
|
||
Gleichstromund Wechselstrom-Ausführung ........... |
14, 15, 16, 17 |
|||
Bestellbeispiel ........................................................................ |
|
15, 17 |
||
Description |
|
Page |
General information ....................................................................... |
|
5 |
Removing the locomotive from the packaging .............................. |
|
6 |
Fitting additional parts ................................................................... |
|
7 |
Maintenance works |
|
|
• 1. Lubricating ............................................................................ |
|
8 |
• 2. Mounting the Seuthe smoke insert ....................................... |
|
8 |
• 3. Conversion to digital operating ............................................. |
|
9 |
• 4. Dismantling the housing ..................................................... |
|
12 |
• 5. Exchanging the circuit board ............................................... |
|
12 |
• 6. Exchanging the engine ........................................................ |
|
12 |
• 7. Exchanging the change-over relay ...................................... |
|
12 |
• 8. Exchanging the traction tires ............................................... |
|
12 |
• 9. Exchanging the sliding contact, alternating current |
............. 12 |
|
• 10. Exchanging the bulb .......................................................... |
|
12 |
• 11. Maintenance work on the front |
|
|
standard coupling shaft ..................................................... |
|
12 |
• 12. Maintenance work on wheelsets and gear ......................... |
|
12 |
Spare parts list |
|
|
direct current and alternating current ........................ |
14, 15, 18, 19 |
|
Order example ....................................................................... |
|
15, 19 |
4

Allgemeine Montageund Sicherheitshinweise
•Diese Bedienungsanleitung beschreibt sämtliche Arbeitsvorgänge die zur Wartung und Instandhaltung notwendig sind.
Bitte lesen Sie diese Bedienungsanleitung bevor Sie mit den Arbeiten beginnen.
•Bei unsachgemäßem Umgang mit elektrischen Bauteilen können diese zerstört werden. Für entsprechende Arbeiten
(z.B. Platinenwechsel) können Sie sich an Ihren Fachhändler oder den Hersteller wenden.
•Bei den folgenden Wartungsarbeiten ist die jeweilige Demontage beschrieben, der Zusammenbau ist in umgekehrter Reihenfolge auszuführen.
•Die folgenden Wartungsarbeiten sind bei Gleichund Wechsel- strom-Ausführungen fast identisch. Im Ausnahmefall wird im entsprechenden Textabschnitt Bezug genommen.
General assembly and safety information
•These operating instructions describe all work steps necessary for maintenance and repair. Please read these operating instructions carefully before you start with your work.
•In the case of incorrect handling of electrical components, they may be destroyed. Please ask your specialist dealer to help with the necessary work (e.g. changing circuit boards).
•In the case of maintenance work, the disassembly is described below, to re-assemble the tractor reverse the work steps.
•The maintenance work described below is virtually identical for direct current and alternating current models. If there are any differences these will be pointed out specifically.
5
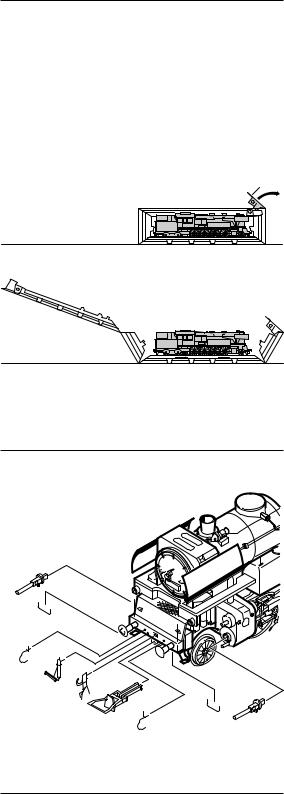
Arbeiten vor der Inbetriebnahme
Work to be performed before starting up
Entnahme der Lok aus der Verpackung (Fig. 1)
Deckel der Verpackung öffnen. Kunststoff-Schutzverpackung mit Lok entnehmen und auf einen Tisch oder ähnliches abstellen. Lasche (1) lösen, Deckel und Seitenteile der Schutzverpackung wegklappen, Lok entnehmen.
Withdrawal of Engine from Packaging (Fig. 1)
Open package lid. Take out plastics protecting package with engine and put it down on a table or similar item. Loosen latch (1), fold away lid and side parts of protecting package, take out engine.
Fig. 1
1
Fig. 2
8
7
4
6
5
1 |
7 |
8
3
6
 Loading...
Loading...