Page 1

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FOR
DGC-2020HD
Digital Genset Controller
Modbus™ Protocol
Publication: 9469300991
Revision: A Nov-13
Page 2

Page 3

9469300991 Rev A i
Preface
This instruction manual provides information about the installation and operation of the DGC-2020HD
Digital Genset Controllers with the Modbus™ protocol. To accomplish this, the following information is
provided:
• General information
• Register table
Conventions Used in this Manual
Important safety and procedural information is emphasized and presented in this manual through
warning, caution, and note boxes. Each type is illustrated and defined as follows.
Warning!
Warning boxes call attention to conditions or actions that may cause
personal injury or death.
Caution
Caution boxes call attention to operating conditions that may lead to
equipment or property damage.
Note
Note boxes emphasize important information pertaining to installation
or operation.
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Preface
Page 4

ii 9469300991 Rev A
This publication contains confidential information of Basler Electric Company, an Illinois corporation. It is loaned for
12570 State Route 143
Highland IL 62249-1074 USA
www.basler.com
info@basler.com
Tel: +1 618.654.2341
Fax: +1 618.654.2351
© 2013 by Basler Electric
All rights reserved
First printing: November 2013
Warning!
READ THIS MANUAL. Read this manual before installing, operating, or maintaining the DGC-2020HD
Note all warnings, cautions, and notes in this manual as well as on the product. Keep this manual with
the product for reference. Only qualified personnel should install, operate, or service this system.
Failure to follow warning and cautionary labels may result in personal injury or property damage.
Exercise caution at all times.
Basler Electric does not assume any responsibility to compliance or noncompliance with national code, local code,
or any other applicable code. This manual serves as reference material that must be well understood prior to
installation, operation, or maintenance.
For terms of service relating to this product and software, see the Commercial Terms of Products and Services
document available at www.basler.com/terms.
confidential use, subject to return on request, and with the mutual understanding that it will not be used in any
manner detrimental to the interests of Basler Electric Company and used strictly for the purpose intended.
It is not the intention of this manual to cover all details and variations in equipment, nor does this manual provide
data for every possible contingency regarding installation or operation. The availability and design of all features
and options are subject to modification without notice. Over time, improvements and revisions may be made to this
publication. Before performing any of the following procedures, contact Basler Electric for the latest revision of this
manual.
The English-language version of this manual serves as the only approved manual version.
Preface DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 5

9469300991 Rev A iii
Contents
General Information .................................................................................................................................... 1
Message Structure .................................................................................................................................... 1
Device Address Field ................................................................................................................................. 1
Function Code Field .................................................................................................................................. 1
Data Block Field ........................................................................................................................................ 2
Error Check Field ....................................................................................................................................... 2
Modbus Modes of Operation ..................................................................................................................... 2
Modbus Over Serial Line ........................................................................................................................... 2
Modbus on TCP/IP .................................................................................................................................... 3
Error Handling and Exception Responses ................................................................................................ 4
DGC-2020HD Modbus via Ethernet .......................................................................................................... 5
Detailed Message Query and Response for RTU Transmission Mode .................................................... 5
Read Holding Registers............................................................................................................................. 5
Return Query Data .................................................................................................................................... 5
Restart Communications Option ............................................................................................................... 6
Listen Only Mode ....................................................................................................................................... 6
Preset Multiple Registers........................................................................................................................... 6
Preset Single Register ............................................................................................................................... 7
Data Formats ............................................................................................................................................. 8
Floating Point Data Format (Float) ............................................................................................................ 8
Long Integer Data Format (Uint32, Int32, and IP Address) ....................................................................... 9
Integer Data Format (Uint16) or Bit-Mapped Variables in Uint16 Format ................................................. 9
Short Integer Data Format/Byte Character Data Format (Uint8)............................................................... 9
String Data Format (String) ....................................................................................................................... 9
CRC Error Check ..................................................................................................................................... 10
Default Register Table .............................................................................................................................. 11
General .................................................................................................................................................... 11
Binary Points ........................................................................................................................................... 21
Bias Control ............................................................................................................................................. 50
Breaker Settings ...................................................................................................................................... 53
Bus Condition .......................................................................................................................................... 56
DGC Settings ........................................................................................................................................... 60
Pulse Outputs .......................................................................................................................................... 62
Control Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 62
Global Settings ........................................................................................................................................ 63
Configuration ........................................................................................................................................... 64
Remote Module Settings ......................................................................................................................... 69
Metering ................................................................................................................................................. 124
Protection Settings ................................................................................................................................ 133
Legacy Register Table ............................................................................................................................ 229
Breaker Management ............................................................................................................................ 229
Bias Control Settings ............................................................................................................................. 230
Pulse Outputs ........................................................................................................................................ 233
Bus Condition Detection ........................................................................................................................ 233
Senders ................................................................................................................................................. 234
System Configuration and Status .......................................................................................................... 235
Control ................................................................................................................................................... 238
Communication ...................................................................................................................................... 239
Protection .............................................................................................................................................. 239
Alarms.................................................................................................................................................... 243
Metering ................................................................................................................................................. 244
Revision History ...................................................................................................................................... 309
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Contents
Page 6

iv 9469300991 Rev A
Contents DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 7

9469300991 Rev A 1
General Information
This document describes the Modbus communications protocol employed by DGC-2020HD systems and
how to exchange information with DGC-2020HD systems over a Modbus network. DGC-2020HD systems
communicate by emulating a subset of the Modicon 984 Programmable Controller.
Modbus communications use a master-slave technique in which only the master can initiate a transaction.
This transaction is called a query. When appropriate, a slave (DGC-2020HD) responds to the query.
When a Modbus master communicates with a slave, information is provided or requested by the master.
Information residing in the DGC-2020HD is grouped categorically as follows:
• General
• Global Settings
• Configuration
• Binary Points
• Metering
• Breaker Settings
• Bias Control
• Pulse Outputs
• Bus Condition
• DGC Settings
• Control Settings
• Protection Settings
• Remote Module Settings
All supported data can be read as specified in the Register Table. Abbreviations are used in the Register
Table to indicate the register type. Register types are:
• Read/Write = RW
• Read Only = R
When a slave receives a query, the slave responds by either supplying the requested data to the master
or performing the requested action. A slave device never initiates communications on the Modbus and will
always generate a response to the query unless certain error conditions occur. The DGC-2020HD is
designed to communicate on the Modbus network only as a slave device.
Refer to the Instruction Manual for Digital Genset Controller DGC-2020HD (Basler Publication
9469300990) for Modbus communication setup and wiring.
Message Structure
Device Address Field
The device address field contains the unique Modbus address of the slave being queried. The addressed
slave repeats the address in the device address field of the response message. This field is 1 byte.
Although Modbus protocol limits a device address from 1 - 247. The address is user-selectable at
installation and can be altered during real-time operation.
Function Code Field
The function code field in the query message defines the action to be taken by the addressed slave. This
field is echoed in the response message and is altered by setting the most significant bit (MSB) of the
field to 1 if the response is an error response. This field is 1 byte in length.
The DGC-2020HD maps all available data into the Modicon 984 holding register address space supports
the following function codes:
• Function 03 (03 hex) - read holding registers
• Function 06 (06 hex) - preset single register
• Function 08 (08 hex), subfunction 00 - diagnostics: return query data
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol General Information
Page 8

2 9469300991 Rev A
PDU
Function code
Data
Additional address
Error Check
• Function 08 (08 hex), subfunction 01 - diagnostics: restart communications option
• Function 08 (08 hex), subfunction 04 - diagnostics: force listen only mode
• Function 16 (10 hex) - preset multiple registers
Data Block Field
The query data block contains additional information needed by the slave to perform the requested
function. The response data block contains data collected by the slave for the queried function. An error
response will substitute an exception response code for the data block. The length of this field varies with
each query.
Error Check Field
The error check field provides a method for the slave to validate the integrity of the query message
contents and allows the master to confirm the validity of response message contents. This field is 2 bytes.
Modbus Modes of Operation
A standard Modbus network offers the remote terminal unit (RTU) transmission mode and Modbus/TCP
mode for communication. DGC-2020HD systems support the Modbus/TCP mode and RS-485 mode at
the same time. To enable editing over Modbus TCP, or RS-485, the unsecured access level for the port
must be configured to the appropriate access level. See the Instruction Manual for Digital Genset
Controller DGC-2020HD (Basler Publication 9469300990) for more information on security and access
levels. These two modes of operation are described below.
A master can query slaves individually or universally. A universal ("broadcast") query, when allowed,
evokes no response from any slave device. If a query to an individual slave device requests actions
unable to be performed by the slave, the slave response message contains an exception response code
defining the error detected. Exception response codes are quite often enhanced by the information found
in the "Error Details" block of holding registers.
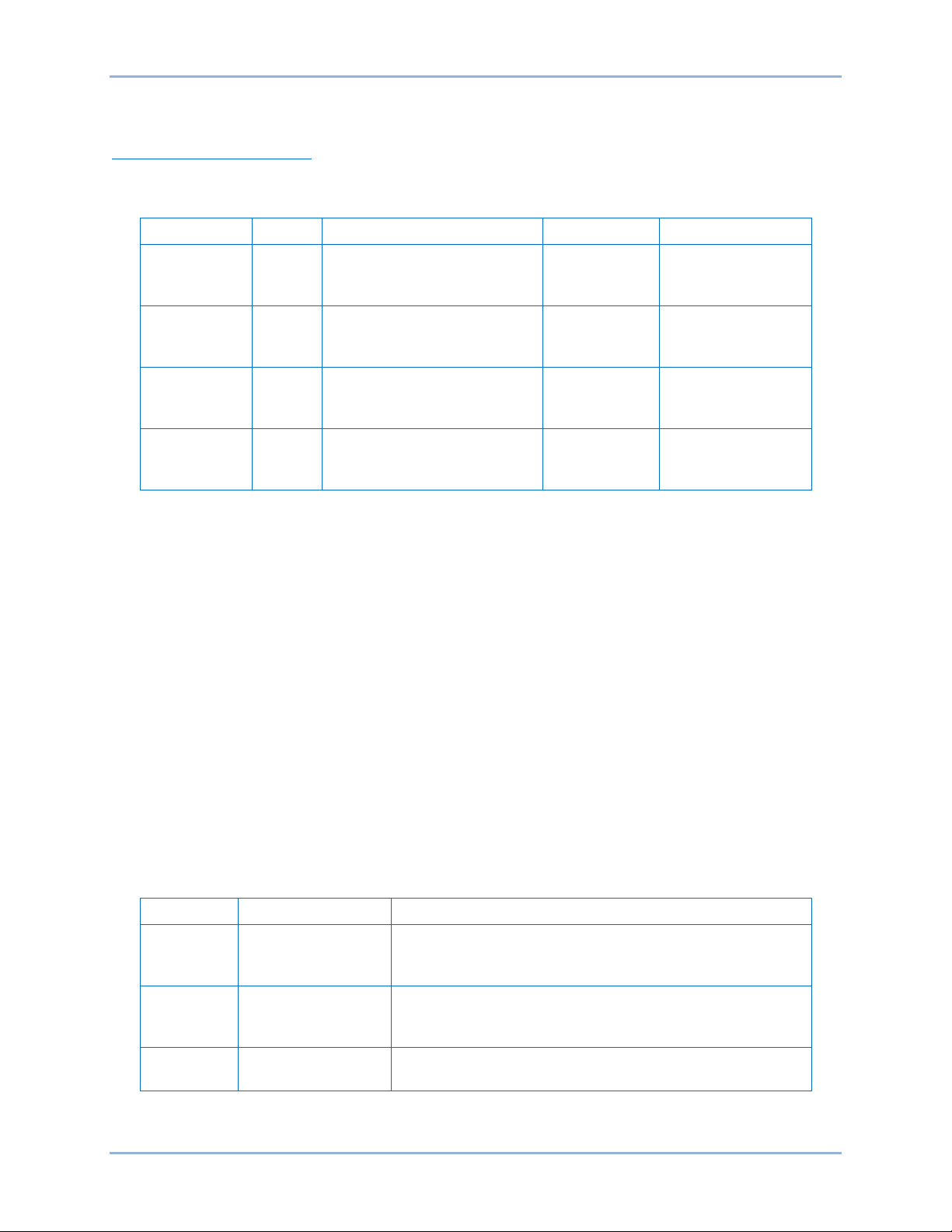
The Modbus protocol defines a simple Protocol Data Unit (PDU) independent of the underlying
communication layers. The mapping of the Modbus protocol on specific buses or networks can introduce
some additional fields on the Application Data Unit (ADU). See Figure 1.
ADU
Figure 1. General Modbus Frame
The client that initiates a Modbus transaction builds the Modbus Application Data Unit. The function code
indicates to the server which kind of action to perform.
Modbus Over Serial Line
Message Structure
Master initiated queries and DGC-2020HD responses share the same message structure. Each message
is comprised of four message fields. They are:
• Device Address (1 byte)
• Function Code (1 byte)
• Data Block (n bytes)
• Error Check field (2 bytes)
Each 8-bit byte in a message contains two 4-bit hexadecimal characters. The message is transmitted in a
continuous stream with the LSB of each byte of data transmitted first. Transmission of each 8-bit data
byte occurs with one start bit and either one or two stop bits. Parity checking is performed, when enabled,
General Information DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 9
9469300991 Rev A 3
PDU
Function code
Data
MBAP Header
and can be either odd or even. The transmission baud rate is user-selectable, and can be set at
installation and altered during real-time operation. DGC-2020HD Modbus supports baud rates up to
115200. The factory default baud rate is 19200.
DGC-2020HD systems support RS-485 compatible serial interfaces. This interface is accessible from the
left side panel of the DGC-2020HD.
Message Framing and Timing Considerations
When receiving a message via the RS-485 communication port, the DGC-2020HD requires an inter-byte
latency of 3.5 character times before considering the message complete.
Once a valid query is received, the DGC-2020HD waits a specified amount of time before responding.
This time delay is set on the Modbus Setup screen under Communications in BESTCOMSPlus
®
. This
parameter contains a value from 10 - 10,000 milliseconds. The default value is 10 milliseconds.
Table 1 provides the response message transmission time (in seconds) and 3.5 character times (in
milliseconds) for various message lengths and baud rates.
Table 1. Timing Considerations
Baud Rate
3.5 Character Time
(ms)
Message Tx Time(s)
128 Bytes 256 Bytes
2400 16.04 0.59 1.17
4800 8.021 0.29 0.59
9600 4.0104 0.15 0.29
19200 2.0052 0.07 0.15
Modbus on TCP/IP
Application Data Unit
The following describes the encapsulation of a Modbus request or response when it is carried on a
Modbus TCP/IP network. See Figure 2.
Modbus TCP/IP ADU
Figure 2. Modbus Request/Response Over TCP/IP
A dedicated header is used on TCP/IP to identify the Modbus Application Data Unit. It is called the MBAP
header (Modbus Application Protocol header).
This header provides some differences compared to the Modbus RTU application data unit used on a
serial line:
• The Modbus ‘slave address’ field usually used on Modbus Serial Line is replaced by a single byte
‘Unit Identifier’ within the MBAP header. The ‘Unit Identifier’ is used to communicate via devices
such as bridges, routers, and gateways that use a single IP address to support multiple
independent Modbus end units.
• All Modbus requests and responses are designed in such a way that the recipient can verify that
a message is finished. For function codes where the Modbus PDU has a fixed length, the function
code alone is sufficient. For function codes carrying a variable amount of data in the request or
response, the data field includes a byte count.
• When Modbus is carried over TCP, additional length information is carried in the MBAP header to
allow the recipient to recognize message boundaries even if the message has been split into
multiple packets for transmission. The existence of explicit and implicit length rules and use of a
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol General Information
Page 10
4 9469300991 Rev A
CRC-32 error check code (on Ethernet) results in an infinitesimal chance of undetected corruption
to a request or response message.
MBAP Header Description
The MBAP Header contains the fields listed in Table 2.
Table 2. MBAP Header Fields
Fields Length Description Client Server
Transaction
Identifier
Protocol
Identifier
Length 2 Bytes Number of following bytes. Initialized by
Unit Identifier 1 Byte Identification of a remote
The header is 7 bytes long:
2 Bytes Identification of a Modbus
request/response
transaction.
2 Bytes 0 = Modbus protocol. Initialized by
slave connected on a serial
line or on other buses.
Initialized by
the client.
the client.
the client
(request).
Initialized by
the client.
Recopied by the
server from the
received request.
Recopied by the
server from the
received request.
Initialized by the
server (response).
Recopied by the
server from the
received request.
• Transaction Identifier – Used for transaction pairing, the Modbus server copies in the response
the transaction identifier of the request.
• Protocol Identifier – Used for intra-system multiplexing. The Modbus protocol is identified by the
value 0.
• Length – A byte count of the following fields, including the Unit Identifier and data fields.
• Unit Identifier – Used for intra-system routing purpose. It is typically used to communicate to a
Modbus or a Modbus serial line slave through a gateway between an Ethernet TCP/IP network
and a Modbus serial line. This field is set by the Modbus Client in the request and must be
returned with the same value in the response by the server.
Note: All Modbus/TCP ADU are sent via TCP on registered port 502.
Error Handling and Exception Responses
Any query received that contains a non-existent device address, a framing error, or CRC error is ignored.
No response is transmitted. Queries addressed to the DGC-2020HD with an unsupported function or
illegal values in the data block result in an error response message with an exception response code. The
exception response codes supported by the DGC-2020HD are provided in Table 3.
Table 3. Supported Exception Response Codes
Code Name Description
01 Illegal Function The query Function/Subfunction Code is unsupported;
query read of more than 125 registers; query preset of
more than 100 registers.
02 Illegal Data
Address
03 Illegal Data Value A preset register data block contains an incorrect number
A register referenced in the data block does not support
queried read/write; query preset of a subset of a numerical
register group.
of bytes or one or more data values out of range.
General Information DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 11

9469300991 Rev A 5
DGC-2020HD Modbus via Ethernet
Modbus can communicate through Ethernet if the IP address of the DGC-2020HD is configured as
described in the Instruction Manual for Digital Genset Controller DGC-2020HD (Basler Publication
9469300990).
Detailed Message Query and Response for RTU Transmission Mode
A detailed description of DGC-2020HD supported message queries and responses is provided in the
following paragraphs.
Read Holding Registers
Query
This query message requests a register or block of registers to be read. The data block contains the starting
register address and the quantity of registers to be read. A register address of N will read holding register
N+1. If the query is a broadcast (device address = 0), no response message is returned.
Device Address
Function Code = 03 (hex)
Starting Address Hi
Starting Address Lo
No. of Registers Hi
No. of Registers Lo
CRC Hi error check
CRC Lo error check
The number of registers cannot exceed 125 without causing an error response with the exception code
for an illegal function.
Response
The response message contains the data queried. The data block contains the block length in bytes
followed by the data (one Data Hi byte and one Data Lo byte) for each requested register.
Reading an unassigned holding register returns a value of zero.
Device Address
Function Code = 03 (hex)
Byte Count
Data Hi (For each requested register, there is one Data Hi and one Data Lo.)
Data Lo
.
.
Data Hi
Data Lo
CRC Hi error check
CRC Lo error check
Return Query Data
This query contains data to be returned (looped back) in the response. The response and query
messages should be identical. If the query is a broadcast (device address = 0), no response message is
returned.
Device Address
Function Code = 08 (hex)
Subfunction Hi = 00 (hex)
Subfunction Lo = 00 (hex)
Data Hi = xx (don't care)
Data Lo = xx (don't care)
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol General Information
Page 12

6 9469300991 Rev A
CRC Hi error check
CRC Lo error check
Restart Communications Option
This query causes the remote communications function of the DGC-2020HD to restart, terminating an
active listen only mode of operation. No effect is made upon primary relay operations. Only the remote
communications function is affected. If the query is a broadcast (device address = 0), no response
message is returned.
If the DGC-2020HD receives this query while in the listen only mode, no response message is generated.
Otherwise, a response message identical to the query message is transmitted prior to the
communications restart.
Device Address
Function Code = 08 (hex)
Subfunction Hi = 00 (hex)
Subfunction Lo = 01 (hex)
Data Hi = xx (don't care)
Data Lo = xx (don't care)
CRC Hi error check
CRC Lo error check
Listen Only Mode
This query forces the addressed DGC-2020HD to the listen only mode for Modbus communications,
isolating it from other devices on the network. No responses are returned.
While in the listen only mode, the DGC-2020HD continues to monitor all queries. The DGC-2020HD does
not respond to any other query until the listen only mode is removed. All write requests with a query to
Preset Multiple Registers (Function Code = 16) are also ignored. When the DGC-2020HD receives the
restart communications query, the listen only mode is removed.
Device Address
Function Code = 08 (hex)
Subfunction Hi = 00 (hex)
Subfunction Lo = 04 (hex)
Data Hi = xx (don't care)
Data Lo = xx (don't care)
CRC Hi error check
CRC Lo error check
Preset Multiple Registers
A preset multiple registers query could address multiple registers in one slave or multiple slaves. If the
query is a broadcast (device address = 0), no response message is returned.
Query
A Preset Multiple Register query message requests a register or block of registers to be written. The data
block contains the starting address and the quantity of registers to be written, followed by the Data Block
byte count and data. The DGC-2020HD will perform the write when the device address in query is a
broadcast address or the same as the DGC-2020HD Modbus Unit ID (device address).
A register address of N will write Holding Register N+1.
Data will cease to be written if any of the following exceptions occur.
• Queries to write to Read Only registers result in an error response with Exception Code of “Illegal
Data Address”.
• Queries attempting to write more than 100 registers cause an error response with Exception
Code “Illegal Function”.
General Information DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 13

9469300991 Rev A 7
• An incorrect Byte Count will result in an error response with Exception Code of “Illegal Data
Value”.
• There are several instances of registers that are grouped together to collectively represent a
single numerical DGC-2020HD data value (i.e. - floating point data, 32-bit integer data, and
strings). A query to write a subset of such a register group will result in an error response with
Exception Code “Illegal Data Address”.
• A query to write a not allowed value (out of range) to a register results in an error response with
Exception Code of “Illegal Data Value”.
Device Address
Function Code = 10 (hex)
Starting Address Hi
Starting Address Lo
No. of Registers Hi
No. of Registers Lo
Byte Count
Data Hi
Data Lo
.
.
Data Hi
Data Lo
CRC Hi error check
CRC Lo error check
Response
The response message echoes the starting address and the number of registers. There is no response
message when the query is a broadcast (device address = 0).
Device Address
Function Code = 10 (hex)
Starting Address Hi
Starting Address Lo
No. of Registers Hi
No. of Registers Lo
CRC Hi Error Check
CRC Lo Error Check
Preset Single Register
A Preset Single Register query message requests a single register to be written. If the query is a
broadcast (device address = 0), no response message is returned.
Note: Only data types INT16, INT8, UINT16, UINT8, and String (not longer than 2 bytes), can be preset
by this function.
Query
Data will cease to be written if any of the following exceptions occur.
• Queries to write to Read Only registers result in an error response with Exception Code of “Illegal
Data Address”.
• A query to write an unallowed value (out of range) to a register results in an error response with
Exception Code of “Illegal Data Value”.
Device Address
Function Code = 06 (hex)
Address Hi
Address Lo
Data Hi
Data Lo
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol General Information
Page 14
8 9469300991 Rev A
CRC Hi error check
CRC Lo error check
Response
The response message echoes the Query message after the register has been altered.
Data Formats
DGC-2020HD systems support the following data types:
• Data types mapped to 2 registers
o Signed Integer 32 (Int32)
o Unsigned Integer 32 (Uint32)
o Floating Point (Float)
o IP Address (IP Address)
o Strings maximum 4 characters long (String)
• Data types mapped to 1 register
o Unsigned Integer 16 (Uint16)
o Unsigned Integer 8 (Uint8)
o Strings maximum 2 characters long (String)
• Data types mapped to more than 2 registers
o Strings longer than 4 characters (String)
Floating Point Data Format (Float)
The Modbus floating point data format uses two consecutive holding registers to represent a data value.
The first register contains the low-order 16 bits of the following 32-bit format:
• MSB is the sign bit for the floating-point value (0 = positive).
• The next 8 bits are the exponent biased by 127 decimal.
• The 23 LSBs comprise the normalized mantissa. The most-significant bit of the mantissa is
always assumed to be 1 and is not explicitly stored, yielding an effective precision of 24 bits.
The value of the floating-point number is obtained by multiplying the binary mantissa times two raised to
the power of the unbiased exponent. The assumed bit of the binary mantissa has the value of 1.0, with
the remaining 23 bits providing a fractional value. Table 4 shows the floating-point format.
Table 4. Floating Point Format
Sign Exponent + 127 Mantissa
1 Bit 8 Bits 23 Bits
The floating-point format allows for values ranging from approximately 8.43X10^
floating-point value of all zeroes is the value zero. A floating-point value of all ones (not a number)
signifies a value currently not applicable or disabled.
Example
will read from two consecutive holding registers as follows:
Holding Register Value
K (Hi Byte) hex 1C
K (Lo Byte) hex 00
K+1 (Hi Byte) hex 47
K+1 (Lo Byte) hex BB
: The value 95,800 represented in floating-point format is hexadecimal 47BB1C00. This number
-37
to 3.38X10^38. A
The same byte alignments are required to write.
General Information DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 15

9469300991 Rev A 9
Long Integer Data Format (Uint32, Int32, and IP Address)
The Modbus long integer data format uses two consecutive holding registers to represent a 32-bit data
value. The first register contains the low-order 16 bits and the second register contains the high-order 16
bits.
Example
will read from two consecutive holding registers as follows:
Holding Register Value
K (Hi Byte) hex 76
K (Lo Byte) hex 38
K+1 (Hi Byte) hex 00
K+1 (Lo Byte) hex 01
The same byte alignments are required to write.
: The value 95,800 represented in long integer format is hexadecimal 0x00017638. This number
Integer Data Format (Uint16) or Bit-Mapped Variables in Uint16 Format
The Modbus integer data format uses a single holding register to represent a 16-bit data value.
Example
a holding register as follows:
Holding Register Value
K (Hi Byte) hex 12
K (Lo Byte) hex 34
The same byte alignments are required to write.
The Uint16 Data Format is listed in Binary Points below.
Example:
specific bit-mapped data such as 1100-0 indicates bit 0 of register 1100 is mapped to RF-TRIG.
: The value 4660 represented in integer format is hexadecimal 0x1234. This number will read from
Register 1100 occupies 16 rows in the Register Table where each row gives the name of
Short Integer Data Format/Byte Character Data Format (Uint8)
The Modbus short integer data format uses a single holding register to represent an 8-bit data value. The
holding register high byte will always be zero.
Example
from a holding register as follows:
Holding Register Value
K (Hi Byte) hex 00
K (Lo Byte) hex 84
The same byte alignments are required to write.
: The value 132 represented in short integer format is hexadecimal 0x84. This number will read
String Data Format (String)
The Modbus string data format uses one or more holding registers to represent a sequence, or string, of
character values. If the string contains a single character, the holding register high byte will contain the
ASCII character code and the low byte will be zero.
Example
Holding Register Value
K (Hi Byte) ‘P’
K (Lo Byte) ‘A’
K+1 (Hi Byte) ‘S’
K+1 (Lo Byte) ‘S’
K+2 (Hi Byte) ‘W’
K+2 (Lo Byte) ‘O’
: The string “PASSWORD” represented in string format will read as follows:
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol General Information
Page 16

10 9469300991 Rev A
K+3 (Hi Byte) ‘R’
K+3 (Lo Byte) ‘D’
Example
Holding Register Value
K (Hi Byte) ‘P’
K (Lo Byte) hex 00
K+1 (Hi Byte) hex 00
K+1 (Lo Byte) hex 00
K+2 (Hi Byte) hex 00
K+2 (Lo Byte) hex 00
K+3 (Hi Byte) hex 00
K+3 (Lo Byte) hex 00
The same byte alignments are required to write.
: If the above string is changed to “P”, the new string will read as follows:
CRC Error Check
This field contains a two-byte CRC value for transmission error detection. The master first calculates the
CRC and appends it to the query message. The DGC-2020HD system recalculates the CRC value for the
received query and performs a comparison to the query CRC value to determine if a transmission error
has occurred. If so, no response message is generated. If no transmission error has occurred, the slave
calculates a new CRC value for the response message and appends it to the message for transmission.
The CRC calculation is performed using all bytes of the device address, function code, and data block
fields. A 16-bit CRC-register is initialized to all 1's. Then each eight-bit byte of the message is used in the
following algorithm:
First, exclusive-OR the message byte with the low-order byte of the CRC-register. The result, stored in
the CRC-register, will then be right-shifted eight times. The CRC-register MSB is zero-filled with each
shift. After each shift, the CRC-register LSB is examined. If the LSB IS a 1, the CRC-register is then
exclusive-ORed with the fixed polynomial value A001 (hex) prior to the next shift. Once all bytes of the
message have undergone the above algorithm, the CRC-register will contain the message CRC value to
be placed in the error check field.
General Information DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 17
9469300991 Rev A 11
Time
Date
GG
0136
String
16 R n/a
0 - 16
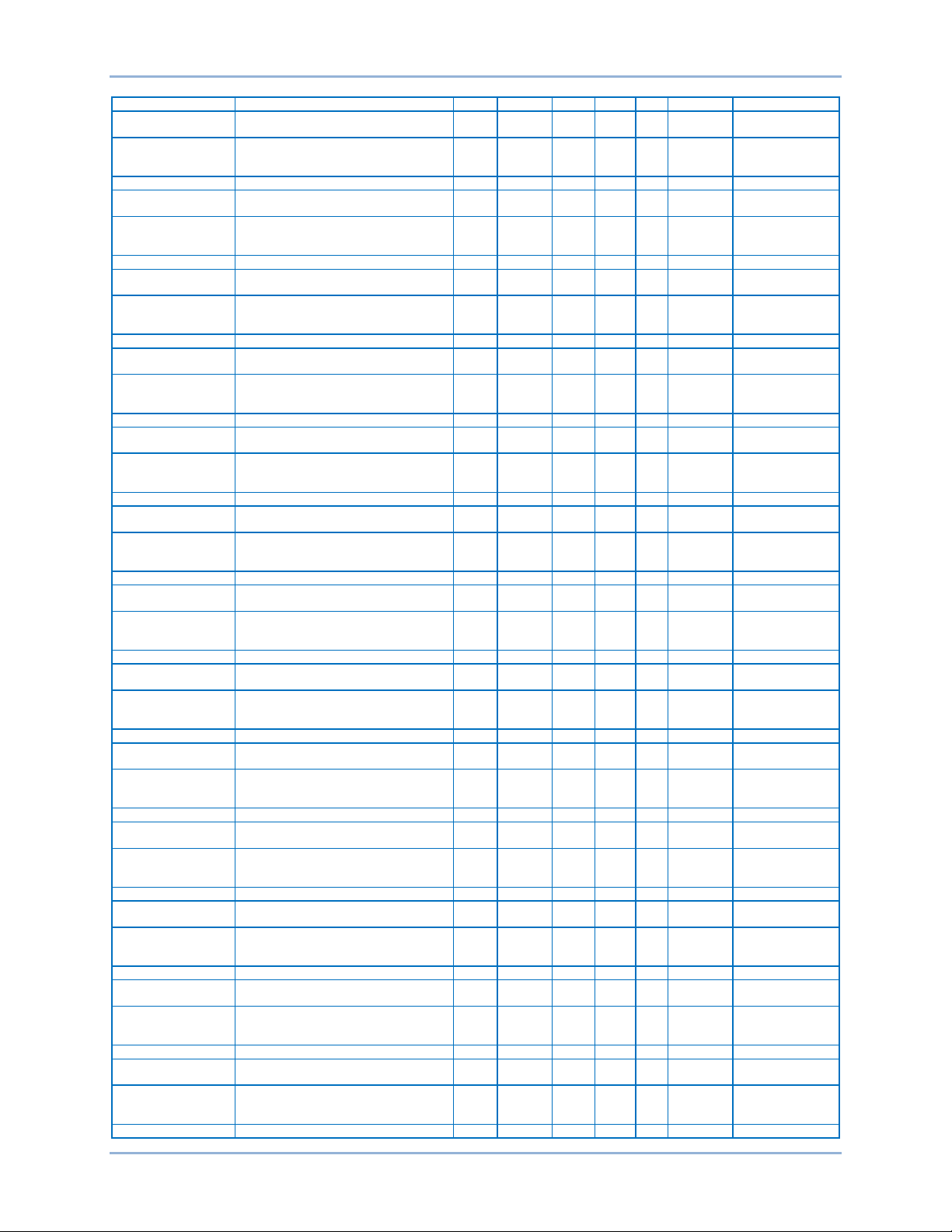
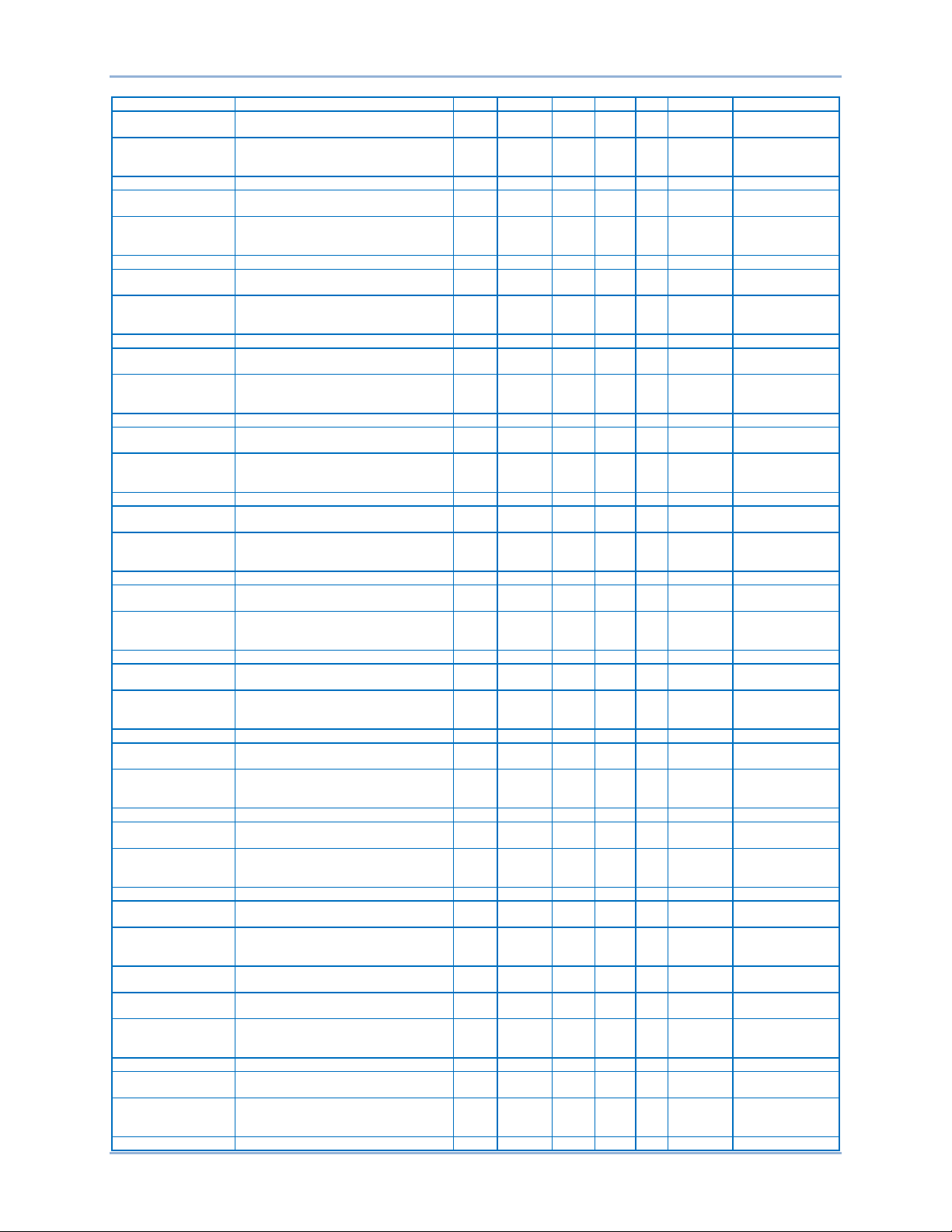
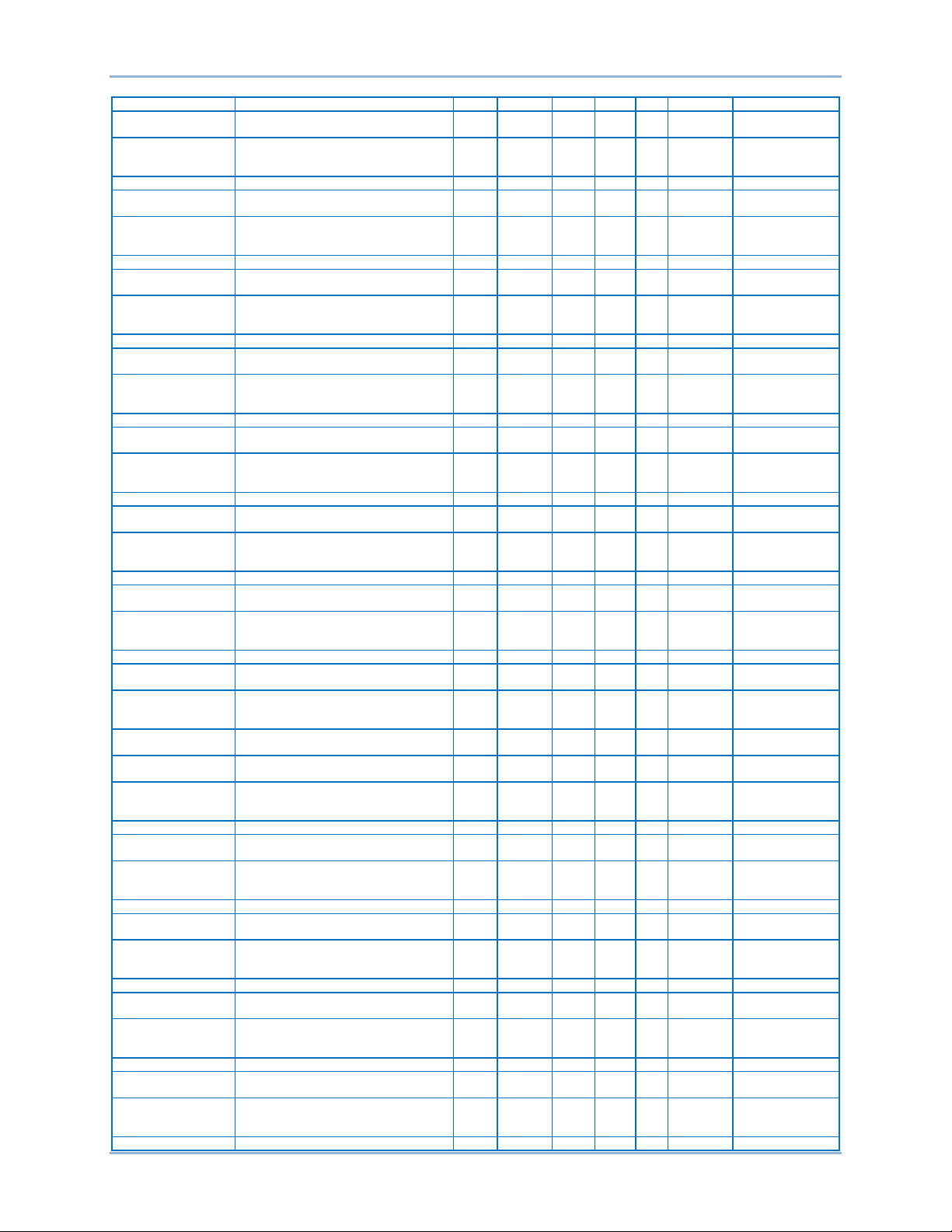
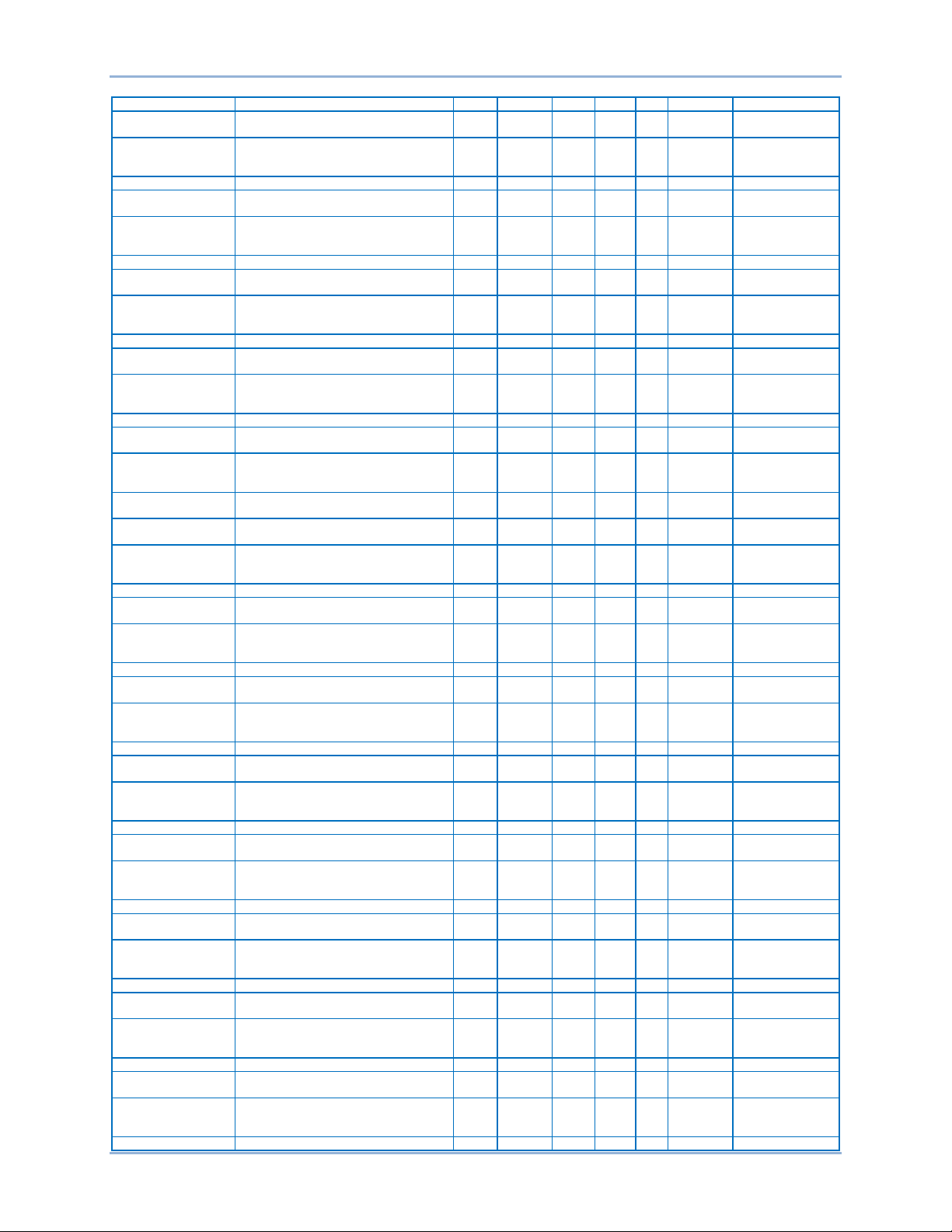
Default Register Table
The register table on the following pages contains the following groups:
General, Binary Points, Bias Control, Breaker Settings, Bus Condition, DGC Settings, Pulse Outputs,
Control Settings, Global Settings, Configuration, Remote Module Settings, Metering, and Protection
Settings.
General
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Reserved 0001-34
Land Line Modem Modem Answer Rings GG 0035 Uint8 1 R W n/a 1 - 9
Land Line Modem Modem Offline Delay GG 0036 Uint16 2 R W Minute 1 - 240
Land Line Modem Inter Dialout Activation Delay GG 0037 Uint8 1 R W n/a 15 SEC=15
Land Line Modem Pager Buffer Limit GG 0038 Uint8 1 R W n/a 80 CHARS=80
Land Line Modem Pager Comms Data Format GG 0039 Uint8 1 R W n/a 8 Bit No Parity=0
System Data Model Number GG 0040 String 64 R n/a 0 - 64
System Data Firmware Part Number GG 0072 String 64 R n/a 0 - 64
System Data
System Data
External Version GG 0104 String 32 R n/a 0 - 32
External Boot Version GG 0120 String 32 R n/a 0 - 32
30 SEC=30
60 SEC=60
120 SEC=120
120 CHARS=120
160 CHARS=160
200 CHARS=200
7 Bit Even Parity=1
Time Time GG 0144 String 16 R n/a 0 - 16
Time Year GG 0152 Uint32 4 R W n/a 2000 - 2099
Time Month GG 0154 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 12
Time Day GG 0156 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 31
Time Hour GG 0158 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 23
Time Minute GG 0160 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 59
Time Second GG 0162 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 59
Time Millisecond GG 0164 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 999
Time Time Zone Hour Offset GG 0166 Int32 4 R W n/a -24 - 24
Time Time Zone Minute Offset GG 0168 Int32 4 R W n/a -59 - 59
Time DST Config GG 0170 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Time DST UTC Respective GG 0172 Uint32 4 R W n/a No=0
Time DST Start Month GG 0174 Uint32 4 R W n/a January=0
Time DST Start Day GG 0176 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 31
Time DST Start Week Of Month GG 0178 Uint32 4 R W n/a First=0
Time DST Start Day Of Week GG 0180 Uint32 4 R W n/a Sunday=0
Time DST Start Hour GG 0182 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 23
Time DST Start Minute GG 0184 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 59
Floating=1
Fixed=2
Yes=1
February=1
March=2
April=3
May=4
June=5
July=6
August=7
September=8
October=9
November=10
December=11
Second=1
Third=2
Fourth=3
Last=4
Monday=1
Tuesday=2
Wednesday=3
Thursday=4
Friday=5
Saturday=6
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 18
12 9469300991 Rev A
Last=4
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Time DST End Month GG 0186 Uint32 4 R W n/a January=0
Time DST End Day GG 0188 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 31
Time DST End Week Of Month GG 0190 Uint32 4 R W n/a First=0
Time DST End Day Of Week GG 0192 Uint32 4 R W n/a Sunday=0
Time DST End Hour GG 0194 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 23
Time DST End Minute GG 0196 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 59
Time DST Bias Hours GG 0198 Int32 4 R W n/a -23 - 23
Time DST Bias Minutes GG 0200 Int32 4 R W n/a -59 - 59
Time Twelve-Hour Mode GG 0202 Uint32 4 R W n/a 12 Hour Mode=0
Time Date Format GG 0204 Uint32 4 R W n/a YYYY-MM-DD=0
Unit Information Style Number GG 0206 String 32 R W n/a 0 - 32
Unit Information Serial Number GG 0222 String 32 R W n/a 0 - 32
Load Detection EPS Threshold GG 0238 Uint32 4 R W Percent 3 - 10
Load Detection Low-Line Scale GG 0240 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Load Share Settings System Type GG 0242 Uint32 4 R W n/a Single Generator=0
Load Share Settings Enable Comms Fail Pre Alarm GG 0244 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Auto Restart Auto Restart Enable GG 0246 Uint32 4 R W n/a No=0
Auto Restart Auto Restart Timeout S ec GG 0248 Uint32 4 R W Second 30 - 1800
Auto Restart Auto Restart Attempts GG 0250 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 10
ECU Config CANBus Enabled By User GG 0252 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
ECU Config DTC Enable GG 0254 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
ECU Config J1939 Source Address GG 0256 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 253
ECU Config ECU Control Output GG 0258 Uint32 4 R W n/a FL CNTCT=0
ECU Config Pulsing Enable GG 0260 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
ECU Config ECU Settling Time GG 0262 Uint32 4 R W Millisecond 5500 - 30000
ECU Config ECU Pulse Cycle Time GG 0264 Uint32 4 R W Minute 1 - 60
ECU Config ECU Disconnect Time GG 0266 Uint32 4 R W Second 1 - 60
ECU Config ECU Connect Time GG 0268 Uint32 4 R W Second 1 - 60
ECU Config CAN Bus Eng Ctrl Param Transmit Enable GG 0270 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
ECU Config Requested MTU SMC Eng Operating
Mode
ECU Config SPN Conversion Method GG 0274 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 4
ECU Config Voltage Regulator CANbus type GG 0276 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
ECU Config Voltage Regulator Primary Voltage
Setpoint
ECU Config Voltage Regulator Alternate Voltage
Setpoint
ECU Config Voltage Regulator Voltage Adjust
Bandwidth
ECU Config Voltage Regulator Field Current GG 0284 Uint32 4 R W Milliamp 0 - 3000000
ECU Config Voltage Regulator Primary
Underfrequency Knee
GG 0272 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 2
GG 0278 Uint32 4 R W Decivolt 1000 - 6000
GG 0280 Uint32 4 R W Decivolt 1000 - 6000
GG 0282 Uint32 4 R W Centivolt 0 - 3000
GG 0286 Uint32 4 R W Decihertz 400 - 700
February=1
March=2
April=3
May=4
June=5
July=6
August=7
September=8
October=9
November=10
December=11
Second=1
Third=2
Fourth=3
Monday=1
Tuesday=2
Wednesday=3
Thursday=4
Friday=5
Saturday=6
24 Hour Mode=1
MM-DD-YYYY=1
DD-MM-YYYY=2
Multiple
Generator=1
Enabled=1
Yes=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
PS CNTCT=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Marathon=1
Basler=2
J1939=3
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 19
9469300991 Rev A 13
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
ECU Config Voltage Regulator Alternate
ECU Config Voltage Regulator Underfrequency Slope GG 0290 Uint32 4 R W n/a 100 - 500
ECU Config ECU Comms Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 0292 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
ECU Config Active DTC Pre-Alarm Enable Data GG 0294 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Auto Transfer Switch Contact Input GG 0296 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Auto Transfer Switch Contact Recognition GG 0298 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Auto Transfer Switch Alarm Configuration GG 0300 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Auto Transfer Switch Activation Delay GG 0302 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Grounded Delta
Override
Grounded Delta
Override
Grounded Delta
Override
Grounded Delta
Override
Battle Override Contact Input GG 0312 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Battle Override Contact Recognition GG 0314 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Battle Override Alarm Configuration GG 0316 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Battle Override Activation Delay GG 0318 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Underfrequency Knee
Contact Input GG 0304 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Contact Recognition GG 0306 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Alarm Configuration GG 0308 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Activation Delay GG 0310 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
GG 0288 Uint32 4 R W Centiunit 400 - 700
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 20

14 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Low-Line Override Contact Input GG 0320 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Low-Line Override Contact Recognition GG 0322 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Low-Line Override Alarm Configuration GG 0324 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Low-Line Override Activation Delay GG 0326 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Single-Phase AC
Override
Single-Phase AC
Override
Single-Phase AC
Override
Single-Phase AC
Override
Battery Charger Fail Contact Input GG 0336 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Battery Charger Fail Contact Recognition GG 0338 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Battery Charger Fail Alarm Configuration GG 0340 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Battery Charger Fail Activation Delay GG 0342 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input GG 0328 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Contact Recognition GG 0330 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Alarm Configuration GG 0332 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Activation Delay GG 0334 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 21
9469300991 Rev A 15
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Low Coolant Level Contact Input GG 0344 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Low Coolant Level Contact Recognition GG 0346 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Low Coolant Level Alarm Configuration GG 0348 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Low Coolant Level Activation Delay GG 0350 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Fuel Leak Detect Contact Input GG 0352 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Fuel Leak Detect Contact Recognition GG 0354 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Fuel Leak Detect Alarm Configuration GG 0356 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Fuel Leak Detect Activation Delay GG 0358 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Emergency Stop Contact Input GG 0360 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Emergency Stop Contact Recognition GG 0362 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Emergency Stop Alarm Configuration GG 0364 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Emergency Stop Activation Delay GG 0366 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 22
16 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Single-Phase Override Contact Input GG 0368 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Single-Phase Override Contact Recognition GG 0370 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Config Element 1 Contact Recognition GG 0372 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Config Element 1 Alarm Configuration GG 0374 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Config Element 1 Activation Delay GG 0376 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Config Element 2 Contact Recognition GG 0378 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Config Element 2 Alarm Configuration GG 0380 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Config Element 2 Activation Delay GG 0382 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Config Element 3 Contact Recognition GG 0384 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Config Element 3 Alarm Configuration GG 0386 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Config Element 3 Activation Delay GG 0388 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Config Element 4 Contact Recognition GG 0390 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Config Element 4 Alarm Configuration GG 0392 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Config Element 4 Activation Delay GG 0394 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Config Element 5 Contact Recognition GG 0396 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Config Element 5 Alarm Configuration GG 0398 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Config Element 5 Activation Delay GG 0400 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Config Element 6 Contact Recognition GG 0402 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Config Element 6 Alarm Configuration GG 0404 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Config Element 6 Activation Delay GG 0406 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Config Element 7 Contact Recognition GG 0408 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Config Element 7 Alarm Configuration GG 0410 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Config Element 7 Activation Delay GG 0412 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Config Element 8 Contact Recognition GG 0414 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Config Element 8 Alarm Configuration GG 0416 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Config Element 8 Activation Delay GG 0418 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 1 Contact Recognition GG 0420 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 1 Alarm Configuration GG 0422 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 1 Activation Delay GG 0424 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 2 Contact Recognition GG 0426 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 2 Alarm Configuration GG 0428 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 2 Activation Delay GG 0430 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Input 1=1
Input 2=2
Input 3=3
Input 4=4
Input 5=5
Input 6=6
Input 7=7
Input 8=8
Input 9=9
Input 10=10
Input 11=11
Input 12=12
Input 13=13
Input 14=14
Input 15=15
Input 16=16
Engine Running=1
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 23
9469300991 Rev A 17
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Contact Input 3 Contact Recognition GG 0432 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 3 Alarm Configuration GG 0434 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 3 Activation Delay GG 0436 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 4 Contact Recognition GG 0438 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 4 Alarm Configuration GG 0440 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 4 Activation Delay GG 0442 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 5 Contact Recognition GG 0444 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 5 Alarm Configuration GG 0446 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 5 Activation Delay GG 0448 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 6 Contact Recognition GG 0450 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 6 Alarm Configuration GG 0452 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 6 Activation Delay GG 0454 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 7 Contact Recognition GG 0456 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 7 Alarm Configuration GG 0458 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 7 Activation Delay GG 0460 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 8 Contact Recognition GG 0462 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 8 Alarm Configuration GG 0464 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 8 Activation Delay GG 0466 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 9 Contact Recognition GG 0468 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 9 Alarm Configuration GG 0470 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 9 Activation Delay GG 0472 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 10 Contact Recognition GG 0474 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 10 Alarm Configuration GG 0476 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 10 Activation Delay GG 0478 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 11 Contact Recognition GG 0480 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 11 Alarm Configuration GG 0482 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 11 Activation Delay GG 0484 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 12 Contact Recognition GG 0486 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 12 Alarm Configuration GG 0488 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 12 Activation Delay GG 0490 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 13 Contact Recognition GG 0492 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 13 Alarm Configuration GG 0494 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 13 Activation Delay GG 0496 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 14 Contact Recognition GG 0498 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 14 Alarm Configuration GG 0500 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 14 Activation Delay GG 0502 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Input 15 Contact Recognition GG 0504 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 15 Alarm Configuration GG 0506 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 15 Activation Delay GG 0508 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 24
18 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Contact Input 16 Contact Recognition GG 0510 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Contact Input 16 Alarm Configuration GG 0512 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Contact Input 16 Activation Delay GG 0514 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input 1 Contact Recognition GG 0516 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 1 Alarm Configuration GG 0518 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 1 Activation Delay GG 0520 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input 2 Contact Recognition GG 0522 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 2 Alarm Configuration GG 0524 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 2 Activation Delay GG 0526 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input 3 Contact Recognition GG 0528 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 3 Alarm Configuration GG 0530 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 3 Activation Delay GG 0532 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input 4 Contact Recognition GG 0534 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 4 Alarm Configuration GG 0536 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 4 Activation Delay GG 0538 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input 5 Contact Recognition GG 0540 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 5 Alarm Configuration GG 0542 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 5 Activation Delay GG 0544 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input 6 Contact Recognition GG 0546 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 6 Alarm Configuration GG 0548 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 6 Activation Delay GG 0550 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input 7 Contact Recognition GG 0552 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 7 Alarm Configuration GG 0554 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 7 Activation Delay GG 0556 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input 8 Contact Recognition GG 0558 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 8 Alarm Configuration GG 0560 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 8 Activation Delay GG 0562 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input 9 Contact Recognition GG 0564 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 9 Alarm Configuration GG 0566 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 1 Contact Input 9 Activation Delay GG 0568 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 1 Contact Input
10
CEM 1 Contact Input
10
CEM 1 Contact Input
10
CEM 2 Contact Input 1 Contact Recognition GG 0576 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 1 Alarm Configuration GG 0578 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 1 Activation Delay GG 0580 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 2 Contact Input 2 Contact Recognition GG 0582 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 2 Alarm Configuration GG 0584 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 2 Activation Delay GG 0586 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Recognition GG 0570 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Alarm Configuration GG 0572 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Activation Delay GG 0574 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 25
9469300991 Rev A 19
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
CEM 2 Contact Input 3 Contact Recognition GG 0588 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 3 Alarm Configuration GG 0590 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 3 Activation Delay GG 0592 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 2 Contact Input 4 Contact Recognition GG 0594 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 4 Alarm Configuration GG 0596 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 4 Activation Delay GG 0598 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 2 Contact Input 5 Contact Recognition GG 0600 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 5 Alarm Configuration GG 0602 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 5 Activation Delay GG 0604 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 2 Contact Input 6 Contact Recognition GG 0606 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 6 Alarm Configuration GG 0608 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 6 Activation Delay GG 0610 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 2 Contact Input 7 Contact Recognition GG 0612 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 7 Alarm Configuration GG 0614 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 7 Activation Delay GG 0616 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 2 Contact Input 8 Contact Recognition GG 0618 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 8 Alarm Configuration GG 0620 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 8 Activation Delay GG 0622 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 2 Contact Input 9 Contact Recognition GG 0624 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 9 Alarm Configuration GG 0626 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 2 Contact Input 9 Activation Delay GG 0628 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 2 Contact Input
10
CEM 2 Contact Input
10
CEM 2 Contact Input
10
CEM 3 Contact Input 1 Contact Recognition GG 0636 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 1 Alarm Configuration GG 0638 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 1 Activation Delay GG 0640 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 3 Contact Input 2 Contact Recognition GG 0642 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 2 Alarm Configuration GG 0644 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 2 Activation Delay GG 0646 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 3 Contact Input 3 Contact Recognition GG 0648 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 3 Alarm Configuration GG 0650 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 3 Activation Delay GG 0652 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 3 Contact Input 4 Contact Recognition GG 0654 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 4 Alarm Configuration GG 0656 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 4 Activation Delay GG 0658 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 3 Contact Input 5 Contact Recognition GG 0660 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 5 Alarm Configuration GG 0662 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 5 Activation Delay GG 0664 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Recognition GG 0630 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Alarm Configuration GG 0632 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Activation Delay GG 0634 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 26
20 9469300991 Rev A
Alarm=2
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
CEM 3 Contact Input 6 Contact Recognition GG 0666 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 6 Alarm Configuration GG 0668 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 6 Activation Delay GG 0670 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 3 Contact Input 7 Contact Recognition GG 0672 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 7 Alarm Configuration GG 0674 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 7 Activation Delay GG 0676 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 3 Contact Input 8 Contact Recognition GG 0678 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 8 Alarm Configuration GG 0680 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 8 Activation Delay GG 0682 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 3 Contact Input 9 Contact Recognition GG 0684 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 9 Alarm Configuration GG 0686 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 3 Contact Input 9 Activation Delay GG 0688 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 3 Contact Input
10
CEM 3 Contact Input
10
CEM 3 Contact Input
10
CEM 4 Contact Input 1 Contact Recognition GG 0696 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 1 Alarm Configuration GG 0698 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 1 Activation Delay GG 0700 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 4 Contact Input 2 Contact Recognition GG 0702 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 2 Alarm Configuration GG 0704 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 2 Activation Delay GG 0706 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 4 Contact Input 3 Contact Recognition GG 0708 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 3 Alarm Configuration GG 0710 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 3 Activation Delay GG 0712 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 4 Contact Input 4 Contact Recognition GG 0714 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 4 Alarm Configuration GG 0716 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 4 Activation Delay GG 0718 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 4 Contact Input 5 Contact Recognition GG 0720 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 5 Alarm Configuration GG 0722 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 5 Activation Delay GG 0724 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 4 Contact Input 6 Contact Recognition GG 0726 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 6 Alarm Configuration GG 0728 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 6 Activation Delay GG 0730 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 4 Contact Input 7 Contact Recognition GG 0732 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 7 Alarm Configuration GG 0734 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 7 Activation Delay GG 0736 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 4 Contact Input 8 Contact Recognition GG 0738 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 8 Alarm Configuration GG 0740 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 8 Activation Delay GG 0742 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Contact Recognition GG 0690 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Alarm Configuration GG 0692 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Activation Delay GG 0694 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 27
9469300991 Rev A 21
Alarms
NTP Sync Lost Alarm
1000
14
Uint16
2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms
Unsupported Number of CEMs
1002 1 Uint16
2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
CEM 4 Contact Input 9 Contact Recognition GG 0744 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 9 Alarm Configuration GG 0746 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
CEM 4 Contact Input 9 Activation Delay GG 0748 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
CEM 4 Contact Input
10
CEM 4 Contact Input
10
CEM 4 Contact Input
10
Auto Config Detect Enable GG 0756 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Auto Config Detect Single-Phase Detection Threshold GG 0758 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 480
Auto Config Detect Single-Phase Detection Gen Connection GG 0760 Uint32 4 R W n/a AB=0
Auto Config Detect Low-Line Detection Threshold GG 0762 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 480
Contact Recognition GG 0750 Uint32 4 R W n/a Always=0
Alarm Configuration GG 0752 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Activation Delay GG 0754 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Engine Running=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Enabled=1
AC=1
Binary Points
Scale Factor Override Alternate Frequency Override 1000 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Reserved 1000 1
System Data Logic 0 1000 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
System Data Logic 1 1000 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Real-Time Clock Alarm 1000 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Date/Time Set Alarm 1000 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Firmware Change Alarm 1000 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Frequency Out-of-Range Alarm 1000 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Ethernet Link 1 Lost Alarm 1000 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Ethernet Link 2 Lost Alarm 1000 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms USB COM Alarm 1000 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms IRIG Sync Lost Alarm 1000 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Logic = None Alarm 1000 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms No User Setting Alarm 1000 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms uP Reset Alarm 1000 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 1 1001 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 2 1001 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 3 1001 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 4 1001 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 5 1001 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 6 1001 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 7 1001 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 8 1001 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 9 1001 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 10 1001 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 11 1001 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 12 1001 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 13 1001 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 14 1001 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 15 1001 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Programmable Alarm 16 1001 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Unsupported Number of AEMs 1002 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Alarms Logic Alarm 1002 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Logic Pre-Alarm 1002 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Global Sender Fail Alarm 1002 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Clock Not Set Alarm 1002 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarms Clock Battery Low Alarm 1002 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Alarm Report Alarm Output 1002 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Pre-Alarm Report Alarm Output 1002 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 1 1002 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 2 1002 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 3 1002 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 4 1002 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 5 1002 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 6 1002 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 7 1002 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 8 1003 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 9 1003 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 10 1003 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 28
22 9469300991 Rev A
Contact Outputs Output 11 1003 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Output 12 1003 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Preheat Prelube Relay 1003 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Fuel Solenoid Relay 1003 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Outputs Master Start Relay 1003 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 1 1003 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 2 1003 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 3 1003 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 4 1003 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 5 1003 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 6 1003 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Buzzer Alarm Silence Active 1003 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Power Meter PF Lagging 1003 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Power Meter 2 PF Lagging 1004 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Power Meter 3 PF Lagging 1004 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-1 Block 1004 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-1 Pickup 1004 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-1 Trip 1004 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-1 Pre-Alarm 1004 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-1 Alarm 1004 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-2 Block 1004 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-2 Pickup 1004 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-2 Trip 1004 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-2 Pre-Alarm 1004 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-2 Alarm 1004 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-3 Block 1004 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-3 Pickup 1004 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-3 Trip 1004 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-3 Pre-Alarm 1004 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-3 Alarm 1005 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-4 Block 1005 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-4 Pickup 1005 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-4 Trip 1005 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-4 Pre-Alarm 1005 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-4 Alarm 1005 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-5 Block 1005 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-5 Pickup 1005 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-5 Trip 1005 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-5 Pre-Alarm 1005 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-5 Alarm 1005 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-6 Block 1005 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-6 Pickup 1005 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-6 Trip 1005 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-6 Pre-Alarm 1005 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
27P-6 Alarm 1005 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-1 Block 1006 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-1 Pickup 1006 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-1 Trip 1006 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-1 Pre-Alarm 1006 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-1 Alarm 1006 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-2 Block 1006 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-2 Pickup 1006 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-2 Trip 1006 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-2 Pre-Alarm 1006 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-2 Alarm 1006 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-3 Block 1006 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-3 Pickup 1006 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-3 Trip 1006 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-3 Pre-Alarm 1006 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-3 Alarm 1006 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-4 Block 1006 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-4 Pickup 1007 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-4 Trip 1007 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-4 Pre-Alarm 1007 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-4 Alarm 1007 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-5 Block 1007 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-5 Pickup 1007 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-5 Trip 1007 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-5 Pre-Alarm 1007 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-5 Alarm 1007 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-6 Block 1007 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-6 Pickup 1007 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-6 Trip 1007 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-6 Pre-Alarm 1007 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
59P-6 Alarm 1007 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 29
9469300991 Rev A 23
47-1 Block 1007 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-1 Pickup 1007 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-1 Trip 1008 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-1 Pre-Alarm 1008 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-1 Alarm 1008 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-2 Block 1008 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-2 Pickup 1008 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-2 Trip 1008 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-2 Pre-Alarm 1008 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-2 Alarm 1008 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-3 Block 1008 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-3 Pickup 1008 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-3 Trip 1008 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-3 Pre-Alarm 1008 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-3 Alarm 1008 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-4 Block 1008 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-4 Pickup 1008 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-4 Trip 1008 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-4 Pre-Alarm 1009 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-4 Alarm 1009 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-5 Block 1009 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-5 Pickup 1009 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-5 Trip 1009 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-5 Pre-Alarm 1009 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-5 Alarm 1009 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-6 Block 1009 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-6 Pickup 1009 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-6 Trip 1009 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-6 Pre-Alarm 1009 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
47-6 Alarm 1009 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-1 Block 1009 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-1 Pickup 1009 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-1 Trip 1009 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-1 Pre-Alarm 1009 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-1 Alarm 1010 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-2 Block 1010 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-2 Pickup 1010 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-2 Trip 1010 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-2 Pre-Alarm 1010 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-2 Alarm 1010 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-3 Block 1010 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-3 Pickup 1010 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-3 Trip 1010 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-3 Pre-Alarm 1010 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-3 Alarm 1010 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-4 Block 1010 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-4 Pickup 1010 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-4 Trip 1010 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-4 Pre-Alarm 1010 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-4 Alarm 1010 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-5 Block 1011 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-5 Pickup 1011 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-5 Trip 1011 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-5 Pre-Alarm 1011 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-5 Alarm 1011 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-6 Block 1011 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-6 Pickup 1011 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-6 Trip 1011 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-6 Pre-Alarm 1011 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-6 Alarm 1011 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-7 Block 1011 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-7 Pickup 1011 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-7 Trip 1011 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-7 Pre-Alarm 1011 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-7 Alarm 1011 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-8 Block 1011 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-8 Pickup 1012 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-8 Trip 1012 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-8 Pre-Alarm 1012 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
81-8 Alarm 1012 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
40Q-1 Block 1012 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
40Q-1 Pickup 1012 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
40Q-1 Trip 1012 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
40Q-1 Pre-Alarm 1012 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
40Q-1 Alarm 1012 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 30
24 9469300991 Rev A
40Q-2 Block 1012 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
40Q-2 Pickup 1012 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
40Q-2 Trip 1012 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
40Q-2 Pre-Alarm 1012 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
40Q-2 Alarm 1012 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-1 Block 1012 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-1 Pickup 1012 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-1 Trip 1013 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-1 Pre-Alarm 1013 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-1 Alarm 1013 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-2 Block 1013 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-2 Pickup 1013 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-2 Trip 1013 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-2 Pre-Alarm 1013 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-2 Alarm 1013 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-3 Block 1013 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-3 Pickup 1013 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-3 Trip 1013 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-3 Pre-Alarm 1013 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-3 Alarm 1013 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-4 Block 1013 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-4 Pickup 1013 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-4 Trip 1013 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-4 Pre-Alarm 1014 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-4 Alarm 1014 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-5 Block 1014 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-5 Pickup 1014 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-5 Trip 1014 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-5 Pre-Alarm 1014 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-5 Alarm 1014 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-6 Block 1014 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-6 Pickup 1014 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-6 Trip 1014 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-6 Pre-Alarm 1014 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
32-6 Alarm 1014 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-1 Block 1014 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-1 Pickup 1014 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-1 Trip 1014 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-1 Pre-Alarm 1014 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-1 Alarm 1015 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-2 Block 1015 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-2 Pickup 1015 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-2 Trip 1015 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-2 Pre-Alarm 1015 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-2 Alarm 1015 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-3 Block 1015 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-3 Pickup 1015 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-3 Trip 1015 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-3 Pre-Alarm 1015 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-3 Alarm 1015 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-4 Block 1015 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-4 Pickup 1015 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-4 Trip 1015 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-4 Pre-Alarm 1015 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-4 Alarm 1015 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-5 Block 1016 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-5 Pickup 1016 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-5 Trip 1016 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-5 Pre-Alarm 1016 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-5 Alarm 1016 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-6 Block 1016 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-6 Pickup 1016 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-6 Trip 1016 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-6 Pre-Alarm 1016 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
51-6 Alarm 1016 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-1 Block 1016 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-1 Pickup 1016 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-1 Trip 1016 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-1 Pre-Alarm 1016 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-1 Alarm 1016 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-2 Block 1016 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-2 Pickup 1017 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-2 Trip 1017 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-2 Pre-Alarm 1017 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
78-2 Alarm 1017 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 31

9469300991 Rev A 25
Battery Voltage Protection Weak Battery Pre-Alarm 1017 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Battery Voltage Protection Low Battery Voltage Pre-Alarm 1017 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Battery Voltage Protection Battery Over Voltage Pre-Alarm 1017 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Oil Pressure Protection Low Oil Pressure Alarm 1017 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Oil Pressure Protection Low Oil Pressure Pre-Alarm 1017 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coolant Temperature Protection High Coolant Temp Alarm 1017 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coolant Temperature Protection High Coolant Temp Pre-Alarm 1017 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coolant Temperature Protection Low Coolant Temp Pre-Alarm 1017 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Fuel Level Protection Low Fuel Alarm 1017 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Fuel Level Protection Low Fuel Pre-Alarm 1017 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Fuel Level Protection High Fuel Pre-Alarm 1017 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Over Speed Protection Over Speed Alarm 1017 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coolant Level Protection Low Coolant Level Alarm 1018 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coolant Level Protection Low Coolant Level Pre-Alarm 1018 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coolant Level Protection Coolant Level Sender Fail Alarm 1018 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Engine Source Speed Sender Fail Alarm 1018 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Engine Source Unexpected Shutdown Alarm 1018 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Engine Source MPU Fail Pre-Alarm 1018 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1018 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1018 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1018 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1018 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1018 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1018 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1018 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1018 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1018 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1018 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1019 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 1 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1019 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1019 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1019 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1019 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1019 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1019 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1019 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1019 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1019 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1019 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1019 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1019 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 2 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1019 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1019 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1019 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1020 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1020 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1020 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1020 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1020 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1020 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1020 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1020 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1020 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 3 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1020 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1020 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1020 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1020 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1020 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1020 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1020 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1021 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1021 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1021 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1021 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1021 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 4 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1021 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1021 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1021 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1021 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1021 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1021 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1021 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1021 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1021 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1021 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 32

26 9469300991 Rev A
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1021 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1022 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 5 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1022 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1022 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1022 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1022 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1022 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1022 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1022 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1022 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1022 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1022 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1022 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1022 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 6 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1022 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1022 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1022 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1023 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1023 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1023 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1023 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1023 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1023 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1023 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1023 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1023 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 7 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1023 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1023 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1023 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1023 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1023 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1023 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1023 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1024 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1024 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1024 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1024 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1024 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Protection 8 Configurable Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1024 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Connected 1024 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Comms Failure 1024 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Duplicate AEM 1024 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 1 Out-of-Range 1024 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1024 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1024 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 2 Out-of-Range 1024 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1024 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1024 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 3 Out-of-Range 1024 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1025 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1025 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 4 Out-of-Range 1025 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1025 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1025 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 5 Out-of-Range 1025 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 5 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1025 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 5 Out-of-Range Alarm 1025 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 6 Out-of-Range 1025 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 6 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1025 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 6 Out-of-Range Alarm 1025 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 7 Out-of-Range 1025 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 7 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1025 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 7 Out-of-Range Alarm 1025 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 8 Out-of-Range 1025 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 8 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1025 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Input 8 Out-of-Range Alarm 1026 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range 1026 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1026 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1026 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range 1026 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1026 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1026 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range 1026 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1026 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1026 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 33

9469300991 Rev A 27
AEM 1 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range 1026 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1026 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1026 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range 1026 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1026 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range Alarm 1026 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range 1027 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1027 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range Alarm 1027 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range 1027 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1027 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range Alarm 1027 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range 1027 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1027 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range Alarm 1027 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range 1027 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1027 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1027 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range 1027 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1027 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1027 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 1 Out-of-Range 1027 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1028 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1028 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 2 Out-of-Range 1028 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1028 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1028 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 3 Out-of-Range 1028 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1028 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1028 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 4 Out-of-Range 1028 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1028 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Output 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1028 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Not Configured 1028 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1028 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1028 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1028 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1028 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1029 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1029 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1029 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1029 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1029 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1029 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1029 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1029 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1029 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1029 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1029 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1029 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1029 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1029 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1029 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1029 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1030 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1030 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1030 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1030 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Trip 1030 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1030 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm 1030 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Trip 1030 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1030 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm 1030 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Trip 1030 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1030 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm 1030 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Trip 1030 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1030 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm 1030 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Trip 1031 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1031 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm 1031 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Trip 1031 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1031 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 34

28 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm 1031 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Trip 1031 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1031 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm 1031 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Trip 1031 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1031 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm 1031 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Trip 1031 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1031 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm 1031 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Trip 1031 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1032 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm 1032 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Trip 1032 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1032 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm 1032 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Trip 1032 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1032 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm 1032 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Trip 1032 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1032 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm 1032 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Trip 1032 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1032 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm 1032 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Trip 1032 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1032 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm 1033 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Trip 1033 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1033 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm 1033 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Trip 1033 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1033 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm 1033 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Trip 1033 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1033 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm 1033 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Trip 1033 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1033 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm 1033 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Trip 1033 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1033 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm 1033 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Trip 1034 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1034 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm 1034 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Trip 1034 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1034 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm 1034 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Trip 1034 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1034 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm 1034 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Trip 1034 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1034 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm 1034 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1034 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1034 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1034 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1034 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1035 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1035 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1035 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1035 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1035 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1035 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1035 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1035 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1035 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1035 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1035 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1035 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1035 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1035 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1035 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1035 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 35

9469300991 Rev A 29
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1036 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1036 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1036 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1036 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Trip 1036 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1036 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm 1036 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Trip 1036 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1036 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm 1036 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Trip 1036 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1036 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm 1036 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Trip 1036 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1036 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm 1036 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Trip 1037 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1037 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm 1037 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Trip 1037 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1037 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm 1037 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Trip 1037 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1037 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm 1037 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Trip 1037 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1037 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm 1037 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Trip 1037 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1037 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm 1037 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Trip 1037 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1038 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm 1038 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Trip 1038 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1038 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm 1038 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Trip 1038 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1038 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm 1038 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Trip 1038 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1038 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm 1038 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Trip 1038 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1038 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm 1038 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Trip 1038 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1038 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm 1039 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Trip 1039 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1039 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm 1039 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Trip 1039 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1039 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm 1039 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Trip 1039 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1039 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm 1039 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Trip 1039 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1039 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm 1039 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Trip 1039 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1039 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm 1039 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Trip 1040 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1040 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm 1040 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Trip 1040 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1040 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm 1040 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Trip 1040 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1040 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm 1040 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Trip 1040 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1040 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 36

30 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 1 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm 1040 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1040 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1040 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1040 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1040 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1041 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1041 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1041 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1041 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1041 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1041 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1041 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1041 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1041 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1041 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1041 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1041 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1041 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1041 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1041 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1041 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1042 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1042 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1042 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 1 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1042 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Connected 1042 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Comms Failure 1042 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Duplicate AEM 1042 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 1 Out-of-Range 1042 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1042 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1042 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 2 Out-of-Range 1042 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1042 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1042 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 3 Out-of-Range 1042 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1042 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1042 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 4 Out-of-Range 1043 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1043 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1043 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 5 Out-of-Range 1043 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 5 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1043 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 5 Out-of-Range Alarm 1043 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 6 Out-of-Range 1043 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 6 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1043 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 6 Out-of-Range Alarm 1043 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 7 Out-of-Range 1043 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 7 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1043 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 7 Out-of-Range Alarm 1043 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 8 Out-of-Range 1043 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 8 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1043 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Input 8 Out-of-Range Alarm 1043 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range 1043 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1044 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1044 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range 1044 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1044 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1044 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range 1044 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1044 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1044 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range 1044 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1044 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1044 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range 1044 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1044 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range Alarm 1044 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range 1044 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1044 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range Alarm 1045 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range 1045 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1045 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range Alarm 1045 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range 1045 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1045 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 37

9469300991 Rev A 31
AEM 2 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range Alarm 1045 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range 1045 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1045 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1045 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range 1045 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1045 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1045 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 1 Out-of-Range 1045 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1045 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1045 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 2 Out-of-Range 1046 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1046 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1046 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 3 Out-of-Range 1046 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1046 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1046 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 4 Out-of-Range 1046 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1046 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Output 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1046 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Not Configured 1046 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1046 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1046 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1046 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1046 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1046 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1046 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1047 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1047 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1047 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1047 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1047 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1047 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1047 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1047 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1047 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1047 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1047 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1047 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1047 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1047 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1047 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1047 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1048 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1048 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Trip 1048 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1048 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm 1048 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Trip 1048 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1048 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm 1048 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Trip 1048 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1048 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm 1048 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Trip 1048 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1048 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm 1048 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Trip 1048 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1048 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm 1049 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Trip 1049 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1049 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm 1049 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Trip 1049 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1049 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm 1049 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Trip 1049 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1049 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm 1049 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Trip 1049 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1049 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm 1049 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Trip 1049 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1049 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm 1049 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Trip 1050 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 38

32 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1050 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm 1050 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Trip 1050 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1050 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm 1050 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Trip 1050 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1050 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm 1050 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Trip 1050 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1050 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm 1050 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Trip 1050 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1050 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm 1050 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Trip 1050 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1051 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm 1051 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Trip 1051 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1051 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm 1051 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Trip 1051 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1051 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm 1051 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Trip 1051 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1051 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm 1051 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Trip 1051 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1051 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm 1051 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Trip 1051 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1051 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm 1052 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Trip 1052 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1052 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm 1052 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Trip 1052 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1052 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm 1052 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Trip 1052 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1052 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm 1052 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1052 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1052 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1052 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1052 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1052 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1052 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1053 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1053 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1053 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1053 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1053 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1053 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1053 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1053 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1053 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1053 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1053 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1053 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1053 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1053 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1053 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1053 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1054 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1054 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Trip 1054 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1054 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm 1054 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Trip 1054 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1054 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm 1054 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Trip 1054 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1054 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm 1054 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Trip 1054 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 39

9469300991 Rev A 33
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1054 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm 1054 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Trip 1054 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1054 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm 1055 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Trip 1055 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1055 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm 1055 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Trip 1055 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1055 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm 1055 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Trip 1055 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1055 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm 1055 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Trip 1055 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1055 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm 1055 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Trip 1055 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1055 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm 1055 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Trip 1056 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1056 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm 1056 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Trip 1056 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1056 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm 1056 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Trip 1056 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1056 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm 1056 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Trip 1056 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1056 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm 1056 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Trip 1056 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1056 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm 1056 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Trip 1056 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1057 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm 1057 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Trip 1057 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1057 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm 1057 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Trip 1057 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1057 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm 1057 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Trip 1057 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1057 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm 1057 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Trip 1057 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1057 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm 1057 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Trip 1057 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1057 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm 1058 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Trip 1058 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1058 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm 1058 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Trip 1058 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1058 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm 1058 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Trip 1058 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1058 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm 1058 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1058 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1058 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1058 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1058 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1058 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1058 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1059 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1059 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1059 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1059 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1059 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1059 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1059 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 40

34 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1059 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1059 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1059 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1059 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1059 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1059 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1059 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1059 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1059 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1060 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 2 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1060 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Connected 1060 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Comms Failure 1060 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Duplicate AEM 1060 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 1 Out-of-Range 1060 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1060 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1060 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 2 Out-of-Range 1060 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1060 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1060 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 3 Out-of-Range 1060 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1060 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1060 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 4 Out-of-Range 1060 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1060 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1061 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 5 Out-of-Range 1061 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 5 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1061 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 5 Out-of-Range Alarm 1061 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 6 Out-of-Range 1061 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 6 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1061 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 6 Out-of-Range Alarm 1061 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 7 Out-of-Range 1061 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 7 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1061 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 7 Out-of-Range Alarm 1061 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 8 Out-of-Range 1061 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 8 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1061 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Input 8 Out-of-Range Alarm 1061 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range 1061 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1061 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1061 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range 1062 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1062 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1062 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range 1062 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1062 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1062 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range 1062 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1062 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1062 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range 1062 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1062 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range Alarm 1062 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range 1062 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1062 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range Alarm 1062 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range 1062 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1063 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range Alarm 1063 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range 1063 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1063 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range Alarm 1063 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range 1063 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1063 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1063 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range 1063 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1063 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1063 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 1 Out-of-Range 1063 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1063 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1063 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 2 Out-of-Range 1063 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1063 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1064 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 3 Out-of-Range 1064 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 41

9469300991 Rev A 35
AEM 3 Output 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1064 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1064 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 4 Out-of-Range 1064 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1064 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Output 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1064 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Not Configured 1064 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1064 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1064 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1064 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1064 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1064 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1064 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1064 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1064 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1065 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1065 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1065 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1065 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1065 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1065 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1065 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1065 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1065 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1065 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1065 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1065 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1065 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1065 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1065 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1065 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Trip 1066 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1066 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm 1066 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Trip 1066 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1066 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm 1066 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Trip 1066 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1066 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm 1066 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Trip 1066 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1066 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm 1066 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Trip 1066 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1066 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm 1066 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Trip 1066 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1067 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm 1067 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Trip 1067 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1067 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm 1067 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Trip 1067 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1067 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm 1067 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Trip 1067 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1067 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm 1067 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Trip 1067 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1067 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm 1067 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Trip 1067 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1067 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm 1068 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Trip 1068 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1068 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm 1068 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Trip 1068 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1068 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm 1068 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Trip 1068 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1068 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm 1068 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Trip 1068 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1068 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm 1068 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 42

36 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Trip 1068 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1068 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm 1068 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Trip 1069 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1069 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm 1069 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Trip 1069 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1069 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm 1069 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Trip 1069 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1069 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm 1069 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Trip 1069 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1069 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm 1069 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Trip 1069 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1069 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm 1069 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Trip 1069 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1070 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm 1070 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Trip 1070 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1070 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm 1070 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Trip 1070 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1070 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm 1070 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1070 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1070 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1070 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1070 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1070 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1070 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1070 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1070 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1071 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1071 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1071 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1071 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1071 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1071 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1071 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1071 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1071 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1071 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1071 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1071 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1071 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1071 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1071 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1071 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Trip 1072 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1072 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm 1072 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Trip 1072 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1072 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm 1072 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Trip 1072 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1072 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm 1072 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Trip 1072 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1072 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm 1072 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Trip 1072 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1072 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm 1072 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Trip 1072 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1073 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm 1073 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Trip 1073 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1073 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm 1073 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Trip 1073 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1073 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm 1073 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 43

9469300991 Rev A 37
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Trip 1073 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1073 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm 1073 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Trip 1073 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1073 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm 1073 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Trip 1073 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1073 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm 1074 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Trip 1074 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1074 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm 1074 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Trip 1074 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1074 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm 1074 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Trip 1074 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1074 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm 1074 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Trip 1074 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1074 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm 1074 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Trip 1074 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1074 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm 1074 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Trip 1075 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1075 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm 1075 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Trip 1075 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1075 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm 1075 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Trip 1075 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1075 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm 1075 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Trip 1075 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1075 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm 1075 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Trip 1075 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1075 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm 1075 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Trip 1075 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1076 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm 1076 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Trip 1076 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1076 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm 1076 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Trip 1076 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1076 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm 1076 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1076 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1076 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1076 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1076 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1076 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1076 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1076 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1076 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1077 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1077 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1077 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1077 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1077 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1077 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1077 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1077 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1077 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1077 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1077 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1077 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1077 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1077 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1077 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 3 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1077 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Connected 1078 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Comms Failure 1078 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Duplicate AEM 1078 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 44
38 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 4 Input 1 Out-of-Range 1078 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1078 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1078 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 2 Out-of-Range 1078 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1078 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1078 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 3 Out-of-Range 1078 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1078 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1078 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 4 Out-of-Range 1078 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1078 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1078 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 5 Out-of-Range 1078 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 5 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1079 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 5 Out-of-Range Alarm 1079 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 6 Out-of-Range 1079 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 6 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1079 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 6 Out-of-Range Alarm 1079 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 7 Out-of-Range 1079 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 7 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1079 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 7 Out-of-Range Alarm 1079 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 8 Out-of-Range 1079 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 8 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1079 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Input 8 Out-of-Range Alarm 1079 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range 1079 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1079 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1079 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range 1079 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1079 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1080 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range 1080 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1080 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1080 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range 1080 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1080 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1080 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range 1080 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1080 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 5 Out-of-Range Alarm 1080 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range 1080 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1080 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 6 Out-of-Range Alarm 1080 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range 1080 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1080 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 7 Out-of-Range Alarm 1080 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range 1081 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1081 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Input 8 Out-of-Range Alarm 1081 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range 1081 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1081 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermalcouple 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1081 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range 1081 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1081 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermalcouple 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1081 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 1 Out-of-Range 1081 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 1 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1081 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 1 Out-of-Range Alarm 1081 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 2 Out-of-Range 1081 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 2 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1081 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 2 Out-of-Range Alarm 1081 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 3 Out-of-Range 1081 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 3 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1082 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 3 Out-of-Range Alarm 1082 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 4 Out-of-Range 1082 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 4 Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1082 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Output 4 Out-of-Range Alarm 1082 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Not Configured 1082 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1082 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1082 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1082 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1082 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1082 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1082 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1082 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1082 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 45
9469300991 Rev A 39
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1082 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1082 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1083 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1083 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1083 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1083 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1083 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1083 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1083 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1083 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1083 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1083 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1083 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1083 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1083 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1083 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Trip 1083 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1083 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm 1084 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Trip 1084 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1084 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm 1084 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Trip 1084 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1084 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm 1084 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Trip 1084 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1084 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm 1084 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Trip 1084 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1084 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm 1084 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Trip 1084 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1084 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm 1084 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Trip 1085 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1085 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm 1085 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Trip 1085 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1085 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm 1085 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Trip 1085 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1085 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm 1085 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Trip 1085 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1085 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm 1085 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Trip 1085 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1085 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm 1085 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Trip 1085 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1086 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm 1086 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Trip 1086 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1086 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm 1086 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Trip 1086 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1086 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm 1086 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Trip 1086 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1086 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm 1086 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Trip 1086 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1086 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm 1086 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Trip 1086 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1086 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm 1087 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Trip 1087 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1087 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm 1087 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Trip 1087 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1087 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm 1087 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Trip 1087 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1087 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 46

40 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 4 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm 1087 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Trip 1087 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1087 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm 1087 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Trip 1087 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1087 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm 1087 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Trip 1088 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1088 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm 1088 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Trip 1088 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1088 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm 1088 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1088 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1088 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1088 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1088 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1088 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1088 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1088 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1088 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1088 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1088 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1089 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1089 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1089 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1089 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1089 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1089 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1089 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1089 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1089 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1089 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1089 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1089 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1089 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1089 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Trip 1089 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1089 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm 1090 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Trip 1090 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1090 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm 1090 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Trip 1090 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1090 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm 1090 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Trip 1090 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1090 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm 1090 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Trip 1090 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1090 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm 1090 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Trip 1090 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1090 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm 1090 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Trip 1091 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1091 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm 1091 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Trip 1091 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1091 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm 1091 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Trip 1091 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1091 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm 1091 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Trip 1091 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1091 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm 1091 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Trip 1091 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1091 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm 1091 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Trip 1091 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1092 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm 1092 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Trip 1092 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1092 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 47

9469300991 Rev A 41
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm 1092 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Trip 1092 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1092 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm 1092 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Trip 1092 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1092 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm 1092 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Trip 1092 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1092 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm 1092 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Trip 1092 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1092 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm 1093 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Trip 1093 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1093 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm 1093 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Trip 1093 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1093 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm 1093 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Trip 1093 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1093 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm 1093 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Trip 1093 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1093 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm 1093 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Trip 1093 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1093 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm 1093 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Trip 1094 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1094 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm 1094 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Trip 1094 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1094 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 RTD Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm 1094 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Trip 1094 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1094 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm 1094 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Trip 1094 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1094 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm 1094 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Trip 1094 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1094 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm 1094 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Trip 1094 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1095 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm 1095 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Trip 1095 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1095 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm 1095 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Trip 1095 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1095 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm 1095 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Trip 1095 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1095 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm 1095 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Trip 1095 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1095 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AEM 4 Thermal Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm 1095 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Connected 1095 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Comms Failure 1095 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Duplicate CEM 1096 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 1 1096 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 2 1096 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 3 1096 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 4 1096 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 5 1096 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 6 1096 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 7 1096 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 8 1096 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 9 1096 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Input 10 1096 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 1 1096 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 2 1096 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 3 1096 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 4 1096 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 48

42 9469300991 Rev A
CEM 1 Output 5 1096 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 6 1097 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 7 1097 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 8 1097 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 9 1097 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 10 1097 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 11 1097 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 12 1097 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 13 1097 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 14 1097 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 15 1097 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 16 1097 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 17 1097 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 18 1097 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 19 1097 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 20 1097 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 21 1097 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 22 1098 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 23 1098 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Output 24 1098 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Hardware Mismatch 1098 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Not Configured 1098 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Connected 1098 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Comms Failure 1098 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Duplicate CEM 1098 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 1 1098 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 2 1098 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 3 1098 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 4 1098 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 5 1098 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 6 1098 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 7 1098 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 8 1098 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 9 1099 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Input 10 1099 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 1 1099 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 2 1099 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 3 1099 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 4 1099 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 5 1099 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 6 1099 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 7 1099 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 8 1099 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 9 1099 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 10 1099 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 11 1099 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 12 1099 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 13 1099 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 14 1099 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 15 1100 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 16 1100 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 17 1100 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 18 1100 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 19 1100 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 20 1100 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 21 1100 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 22 1100 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 23 1100 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Output 24 1100 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Hardware Mismatch 1100 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Not Configured 1100 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Connected 1100 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Comms Failure 1100 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Duplicate CEM 1100 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 1 1100 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 2 1101 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 3 1101 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 4 1101 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 5 1101 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 6 1101 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 7 1101 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 8 1101 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 9 1101 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Input 10 1101 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 1 1101 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 49

9469300991 Rev A 43
CEM 3 Output 2 1101 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 3 1101 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 4 1101 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 5 1101 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 6 1101 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 7 1101 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 8 1102 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 9 1102 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 10 1102 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 11 1102 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 12 1102 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 13 1102 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 14 1102 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 15 1102 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 16 1102 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 17 1102 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 18 1102 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 19 1102 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 20 1102 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 21 1102 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 22 1102 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 23 1102 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Output 24 1103 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Hardware Mismatch 1103 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Not Configured 1103 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Connected 1103 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Comms Failure 1103 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Duplicate CEM 1103 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 1 1103 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 2 1103 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 3 1103 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 4 1103 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 5 1103 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 6 1103 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 7 1103 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 8 1103 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 9 1103 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Input 10 1103 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 1 1104 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 2 1104 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 3 1104 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 4 1104 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 5 1104 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 6 1104 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 7 1104 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 8 1104 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 9 1104 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 10 1104 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 11 1104 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 12 1104 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 13 1104 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 14 1104 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 15 1104 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 16 1104 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 17 1105 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 18 1105 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 19 1105 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 20 1105 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 21 1105 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 22 1105 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 23 1105 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Output 24 1105 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Hardware Mismatch 1105 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Not Configured 1105 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Ready State 1105 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Cranking State 1105 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Resting State 1105 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Running State 1105 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Alarm State 1105 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Prestart State 1105 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Cooling State 1106 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Connecting State 1106 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Disconnect State 1106 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Pulsing State 1106 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller External Start Delay 1106 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 50

44 9469300991 Rev A
Genset Controller Start Delay Bypass 1106 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Overcrank Alarm 1106 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Off Mode Cooldown 1106 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Cooldown and Stop Request From Logic 1106 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Cooldown Request From Logic 1106 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller In Unloading State 1106 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Auto Mode Status 1106 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Off Mode Status 1106 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Run Mode Status 1106 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Paralleled to Mains 1106 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Emergency Stop Button 1106 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Cooldown Timer Active 1107 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Idle Request Active 1107 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Low Coolant Pre-Alarm Global 1107 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Low Coolant Alarm Global 1107 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Low Coolant Status Global 1107 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coms Control Group Reset Active 1107 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coms Control Group Lamp Test Active 1107 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Load Detection Supplying Load 1107 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Run Statistics Maintenance Due 1107 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Unit ID Table ID Missing Pre-Alarm 1107 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Unit ID Table ID Repeat Pre-Alarm 1107 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Load Share Settings Intergenset Comms Fail 1107 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Auto Restart Auto Restart Fail Alarm 1107 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Loss of ECU Comm Alarm 1107 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Loss of ECU Comm Pre-Aalarm 1107 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Diagnostic Trouble Code Pre-Alarm 1107 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Shutdown 1108 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DEF Empty 1108 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DEF Engine Derate 1108 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DEF Inducement Override 1108 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DEF Low 1108 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DEF Presevere Inducement 1108 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DEF Severe Inducement 1108 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DPF Regenerate Disabled 1108 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DPF Regenerate Required 1108 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DPF Soot Level High Least Severe 1108 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DPF Soot Level High Moderately Severe 1108 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config DPF Soot Level High Most Severe 1108 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Fuel Filter 1 Leak 1108 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Fuel Filter 2 Leak 1108 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config High Exhaust Temp 1108 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Low Coolant Level Alarm From DTC 1108 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU High Charge Air Temp Alarm 1109 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU High Oil Temp Alarm 1109 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU High Coolant Temp Alarm 1109 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Low Aftercooler Cool LVL Alarm 1109 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Low Fuel Delivery Pressure Alarm 1109 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Low Oil Pressure Alarm 1109 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Overspeed Alarm 1109 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Combined Red Alarm Status From ECU 1109 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU High ECU Temp Pre-Alarm 1109 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU High Oil Temp Pre-Alarm 1109 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU High Intercooler Temp Pre-Alarm 1109 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU High Charge Air Temp Pre-Alarm 1109 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU High Coolant Temp Pre-Alarm 1109 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Shutdown Override Pre-Alarm 1109 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU High Fuel Rail Pressure Pre-Alarm 1109 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Low Fuel Rail Pressure Pre-Alarm 1109 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Low Coolant Level Pre-Alarm 1110 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Low Charge Air Pressure Pre-Alarm 1110 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Low Fuel Delivery Pressure Pre-Alarm 1110 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Low Oil Pressure Pre-Alarm 1110 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Combined Yellow Pre-Alarm 1110 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Hi Fuel Filter Diff Pressure Pre-Alarm 1110 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config MTU Test Overspeed Active Pre-Alarm 1110 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config CAN Mode Feedback Status 1110 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Cylinder Cutout Status 1110 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config ECU Faulty Pre-Alarm 1110 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config ECU Override Feedback Status 1110 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Engine Running Status Bit 1110 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Engine Speed Too Low Pre-Alarm 1110 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config External Stop Active Status 1110 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Hi Day Tank Level Pre-Alarm 1110 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config High ECU Supply Voltage Alarm 1110 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 51

9469300991 Rev A 45
ECU Config High Exhaust Temp A Pre-Alarm 1111 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config High Exhaust Temp B Pre-Alarm 1111 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config High Fuel Temp Pre-Alarm 1111 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config High Storage Tank Level Pre-Alarm 1111 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config High Voltage Supply Pre-Alarm 1111 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Hi Pressure IN 1 Pre-Alarm 1111 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Hi Pressure IN 2 Pre-Alarm 1111 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Hi T Ambient Pre-Alarm 1111 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Hi TCOIL 1 Pre-Alarm 1111 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Hi TCOIL 2 Pre-Alarm 1111 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Hi TCOIL 3 Pre-Alarm 1111 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Idle Speed Low Pre-Alarm 1111 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Load Gen On Status 1111 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Low Charge Air Coolant Level Pre-Alarm 1111 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Low Day Tank Level Pre-Alarm 1111 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Low ECU Supply Voltage Pre-Alarm 1111 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Low Storage Tank Level Pre-Alarm 1112 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Low Voltage Supply Pre-Alarm 1112 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Preheat Temp Not Reached Status 1112 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Priming Fault Pre-Alarm 1112 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Priming Pump On Status 1112 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Run-up Speed Low Pre-Alarm 1112 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Speed DEC Feedback Status 1112 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Speed Demand Fail Mode Status 1112 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Speed Demand Fail Pre-Alarm 1112 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Speed INC Feedback Status 1112 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config Start Speed Low Pre-Alarm 1112 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
ECU Config T Alternator Wiring Pre-Alarm 1112 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Settings Group Use SG0 1112 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Settings Group Use SG1 1112 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Settings Group Use SG2 1112 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Settings Group Use SG3 1112 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Sync Active 1113 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Sync Breaker Close OK 1113 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Sync Volt OK 1113 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Sync Freq OK 1113 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Sync Phase OK 1113 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Sync Sync OK 1113 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Generator Breaker Breaker Status 1113 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Generator Breaker Sync Fail 1113 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Generator Breaker Fail to Close 1113 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Generator Breaker Fail to Open 1113 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Mains Breaker Breaker Status 1113 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Mains Breaker Sync Fail 1113 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Mains Breaker Fail to Close 1113 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Mains Breaker Fail to Open 1113 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Breaker Local Request Generation Mains Fail Transfer Inhibit From PLC 1113 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Breaker Local Request Generation Closed Transition Override From PLC 1113 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Breaker Local Request Generation Mains Fail Test Active 1114 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Breaker Local Request Generation Auto Breaker OP Inhibit 1114 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Breaker Local Request Generation Mains Fail Transfer Enabled 1114 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Breaker Local Request Generation Mains Fail Transfer Fail 1114 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Breaker Local Request Generation Mains Fail Transfer Complete 1114 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Breaker Local Request Generation Mains Zero Power Flow 1114 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Gen Reverse Rotation 1114 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Bus 1 ReverseRotation 1114 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Genset Controller Bus 2 ReverseRotation 1114 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Bias Control Take Over Load Active 1114 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Bias Control var Mode Active 1114 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Bias Control PF Mode Active 1114 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Gen Condition Dead 1114 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Gen Condition Failed 1114 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Gen Condition Stable 1114 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Bus 1 Condition Dead 1114 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Bus 1 Condition Failed 1115 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Bus 1 Condition Stable 1115 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Bus 2 Condition Dead 1115 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Bus 2 Condition Failed 1115 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Bus 2 Condition Stable 1115 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coolant Temp Sender Fail Alarm 1115 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Coolant Temp Sender Fail Pre-Alarm 1115 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Oil Pressure Sender Fail Alarm 1115 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Oil Pressure Sender Fail Pre-Alarm 1115 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Fuel Level Sender Fail Alarm 1115 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Fuel Level Sender Fail Pre-Alarm 1115 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 52

46 9469300991 Rev A
Voltage Sensing Sender Fail Alarm 1115 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Voltage Sensing Sender Fail Pre-Alarm 1115 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Auto Transfer Switch Status 1115 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Auto Transfer Switch Alarm 1115 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Auto Transfer Switch Pre-Alarm 1115 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Grounded Delta Override Status 1116 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Grounded Delta Override Alarm 1116 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Grounded Delta Override Pre-Alarm 1116 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Battle Override Status 1116 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Battle Override Alarm 1116 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Battle Override Pre-Alarm 1116 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Low-Line Override Status 1116 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Low-Line Override Alarm 1116 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Low-Line Override Pre-Alarm 1116 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Single-Phase AC Override Status 1116 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Single-Phase AC Override Alarm 1116 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Single-Phase AC Override Pre-Alarm 1116 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Battery Charger Fail Status 1116 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Battery Charger Fail Alarm 1116 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Battery Charger Fail Pre-Alarm 1116 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Low Coolant Level Status 1116 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Fuel Leak Detect Status 1117 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Fuel Leak Detect Alarm 1117 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Fuel Leak Detect Pre-Alarm 1117 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Emergency Stop Status 1117 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Emergency Stop Alarm 1117 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Emergency Stop Pre-Alarm 1117 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Single-Phase Override Status 1117 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 1 Output 1117 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 1 Alarm 1117 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 1 Pre-Alarm 1117 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 2 Output 1117 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 2 Alarm 1117 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 2 Pre-Alarm 1117 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 3 Output 1117 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 3 Alarm 1117 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 3 Pre-Alarm 1117 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 4 Output 1118 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 4 Alarm 1118 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 4 Pre-Alarm 1118 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 5 Output 1118 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 5 Alarm 1118 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 5 Pre-Alarm 1118 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 6 Output 1118 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 6 Alarm 1118 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 6 Pre-Alarm 1118 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 7 Output 1118 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 7 Alarm 1118 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 7 Pre-Alarm 1118 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 8 Output 1118 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 8 Alarm 1118 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Configurable Element 8 Pre-Alarm 1118 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 1 Alarm 1118 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 1 Pre-Alarm 1119 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 1 State 1119 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 2 Alarm 1119 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 2 Pre-Alarm 1119 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 2 State 1119 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 3 Alarm 1119 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 3 Pre-Alarm 1119 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 3 State 1119 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 4 Alarm 1119 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 4 Pre-Alarm 1119 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 4 State 1119 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 5 Alarm 1119 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 5 Pre-Alarm 1119 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 5 State 1119 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 6 Alarm 1119 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 6 Pre-Alarm 1119 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 6 State 1120 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 7 Alarm 1120 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 7 Pre-Alarm 1120 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 7 State 1120 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 8 Alarm 1120 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 8 Pre-Alarm 1120 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 53

9469300991 Rev A 47
Contact Input 8 State 1120 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 9 Alarm 1120 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 9 Pre-Alarm 1120 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 9 State 1120 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 10 Alarm 1120 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 10 Pre-Alarm 1120 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 10 State 1120 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 11 Alarm 1120 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 11 Pre-Alarm 1120 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 11 State 1120 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 12 Alarm 1121 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 12 Pre-Alarm 1121 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 12 State 1121 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 13 Alarm 1121 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 13 Pre-Alarm 1121 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 13 State 1121 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 14 Alarm 1121 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 14 Pre-Alarm 1121 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 14 State 1121 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 15 Alarm 1121 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 15 Pre-Alarm 1121 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 15 State 1121 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 16 Alarm 1121 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 16 Pre-Alarm 1121 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Contact Input 16 State 1121 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 1 Alarm 1121 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 1 Pre-Alarm 1122 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 1 State 1122 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 2 Alarm 1122 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 2 Pre-Alarm 1122 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 2 State 1122 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 3 Alarm 1122 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 3 Pre-Alarm 1122 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 3 State 1122 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 4 Alarm 1122 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 4 Pre-Alarm 1122 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 4 State 1122 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 5 Alarm 1122 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 5 Pre-Alarm 1122 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 5 State 1122 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 6 Alarm 1122 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 6 Pre-Alarm 1122 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 6 State 1123 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 7 Alarm 1123 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 7 Pre-Alarm 1123 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 7 State 1123 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 8 Alarm 1123 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 8 Pre-Alarm 1123 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 8 State 1123 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 9 Alarm 1123 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 9 Pre-Alarm 1123 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 9 State 1123 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 10 Alarm 1123 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 10 Pre-Alarm 1123 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 1 Contact Input 10 State 1123 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 1 Alarm 1123 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 1 Pre-Alarm 1123 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 1 State 1123 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 2 Alarm 1124 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 2 Pre-Alarm 1124 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 2 State 1124 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 3 Alarm 1124 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 3 Pre-Alarm 1124 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 3 State 1124 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 4 Alarm 1124 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 4 Pre-Alarm 1124 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 4 State 1124 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 5 Alarm 1124 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 5 Pre-Alarm 1124 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 5 State 1124 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 6 Alarm 1124 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 6 Pre-Alarm 1124 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 6 State 1124 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 7 Alarm 1124 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 7 Pre-Alarm 1125 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 54

48 9469300991 Rev A
CEM 2 Contact Input 7 State 1125 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 8 Alarm 1125 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 8 Pre-Alarm 1125 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 8 State 1125 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 9 Alarm 1125 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 9 Pre-Alarm 1125 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 9 State 1125 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 10 Alarm 1125 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 10 Pre-Alarm 1125 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 2 Contact Input 10 State 1125 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 1 Alarm 1125 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 1 Pre-Alarm 1125 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 1 State 1125 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 2 Alarm 1125 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 2 Pre-Alarm 1125 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 2 State 1126 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 3 Alarm 1126 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 3 Pre-Alarm 1126 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 3 State 1126 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 4 Alarm 1126 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 4 Pre-Alarm 1126 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 4 State 1126 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 5 Alarm 1126 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 5 Pre-Alarm 1126 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 5 State 1126 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 6 Alarm 1126 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 6 Pre-Alarm 1126 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 6 State 1126 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 7 Alarm 1126 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 7 Pre-Alarm 1126 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 7 State 1126 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 8 Alarm 1127 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 8 Pre-Alarm 1127 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 8 State 1127 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 9 Alarm 1127 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 9 Pre-Alarm 1127 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 9 State 1127 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 10 Alarm 1127 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 10 Pre-Alarm 1127 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 3 Contact Input 10 State 1127 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 1 Alarm 1127 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 1 Pre-Alarm 1127 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 1 State 1127 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 2 Alarm 1127 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 2 Pre-Alarm 1127 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 2 State 1127 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 3 Alarm 1127 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 3 Pre-Alarm 1128 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 3 State 1128 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 4 Alarm 1128 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 4 Pre-Alarm 1128 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 4 State 1128 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 5 Alarm 1128 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 5 Pre-Alarm 1128 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 5 State 1128 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 6 Alarm 1128 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 6 Pre-Alarm 1128 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 6 State 1128 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 7 Alarm 1128 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 7 Pre-Alarm 1128 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 7 State 1128 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 8 Alarm 1128 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 8 Pre-Alarm 1128 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 8 State 1129 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 9 Alarm 1129 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 9 Pre-Alarm 1129 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 9 State 1129 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 10 Alarm 1129 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 10 Pre-Alarm 1129 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
CEM 4 Contact Input 10 State 1129 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 1 1129 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 2 1129 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 3 1129 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 4 1129 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 5 1129 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 55

9469300991 Rev A 49
LCR Outputs Output 6 1129 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 7 1129 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 8 1129 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 9 1129 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 10 1130 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 11 1130 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 12 1130 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 13 1130 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 14 1130 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 15 1130 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LCR Outputs Output 16 1130 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range 1130 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1130 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range Alarm 1130 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1130 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1130 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1130 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1130 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1130 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1130 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1131 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1131 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1131 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1131 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1131 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 1 Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1131 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range 1131 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1131 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range Alarm 1131 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1131 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1131 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1131 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1131 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1131 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1131 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1131 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1132 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1132 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1132 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1132 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 2 Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1132 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range 1132 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1132 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range Alarm 1132 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1132 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1132 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1132 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1132 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1132 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1132 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1132 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1132 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1133 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1133 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1133 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 3 Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1133 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range 1133 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1133 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Configuration Analog Input Out-of-Range Alarm 1133 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 1 Trip 1133 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 1 Pre-Alarm 1133 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 1 Alarm 1133 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 2 Trip 1133 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 2 Pre-Alarm 1133 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 2 Alarm 1133 12 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 3 Trip 1133 13 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 3 Pre-Alarm 1133 14 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 3 Alarm 1133 15 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 4 Trip 1134 0 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 4 Pre-Alarm 1134 1 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Analog Input 4 Protection Threshold 4 Alarm 1134 2 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AVR Output Out-of-Range 1134 3 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AVR Output Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1134 4 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
AVR Output Out-of-Range Alarm 1134 5 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
GOV Output Out-of-Range 1134 6 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 56

50 9469300991 Rev A
Bias Control
AVR Output Upper Limit
GG
2016
Float 4 R W
n/a
0 - 1000
Bias Control
kvar Ki For Analog Bias Out
GG
2042
Float 4 R W
n/a
0 - 1000
Bias Control
kW Load Rate
GG
2084
Float 4 R W
Percent
0 - 100
GOV Output Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1134 7 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
GOV Output Out-of-Range Alarm 1134 8 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LS Output Out-of-Range 1134 9 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LS Output Out-of-Range Pre-Alarm 1134 10 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
LS Output Out-of-Range Alarm 1134 11 Uint16 2 R False=0 True=1
Name Description Register Bit Type Bytes R/W Range
Bias Control
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bias Control AVR Kp For Analog Bias Out GG 2000 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control AVR Ki For Analog Bias Out GG 2002 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control AVR Kd For Analog Bias Out GG 2004 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control AVR Td GG 2006 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1
Bias Control AVR Loop Gain For Analog Bias Out GG 2008 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control AVR Enable Windup Limit GG 2010 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Bias Control AVR Integrator Limit Plus GG 2012 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control AVR Integrator Limit Minus GG 2014 Float 4 R W n/a -1000 - 0
Bias Control AVR Output Lower Limit GG 2018 Float 4 R W n/a -1000 - 0
Bias Control GOV Kp For Analog Bias Out GG 2020 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control GOV Ki For Analog Bias Out GG 2022 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control GOV Kd For Analog Bias Out GG 2024 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control GOV Td GG 2026 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1
Bias Control GOV Loop Gain For Analog Bias Out GG 2028 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control GOV Enable Windup Limit GG 2030 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Bias Control GOV Integrator Limit Plus GG 2032 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control GOV Integrator Limit Minus GG 2034 Float 4 R W n/a -1000 - 0
Bias Control GOV Output Upper Limit GG 2036 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control GOV Output Lower Limit GG 2038 Float 4 R W n/a -1000 - 0
Bias Control kvar Kp For Analog Bias Out GG 2040 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Bias Control kvar Kd For Analog Bias Out GG 2044 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kvar Td GG 2046 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1
Bias Control kvar Loop Gain For Analog Bias Out GG 2048 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kvar Enable Windup Limit GG 2050 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Bias Control kvar Integrator Limit Plus GG 2052 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kvar Integrator Limit Minus GG 2054 Float 4 R W n/a -1000 - 0
Bias Control kvar Output Upper Limit GG 2056 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kvar Output Lower Limit GG 2058 Float 4 R W n/a -1000 - 0
Bias Control kW Kp For Analog Bias Out GG 2060 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kW Ki For Analog Bias Out GG 2062 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kW Kd For Analog Bias Out GG 2064 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kW Td GG 2066 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1
Bias Control kW Loop Gain For Analog Bias Out GG 2068 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kW Enable Windup Limit GG 2070 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Bias Control kW Integrator Limit Plus GG 2072 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kW Integrator Limit Minus GG 2074 Float 4 R W n/a -1000 - 0
Bias Control kW Output Upper Limit GG 2076 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control kW Output Lower Limit GG 2078 Float 4 R W n/a -1000 - 0
Bias Control kW Droop Percentage GG 2080 Float 4 R W Percent 0.5 - 10
Bias Control Load Control Enabled GG 2082 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Bias Control Breaker Open Setpoint GG 2086 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
Bias Control AVR Output Type GG 2088 Uint32 4 R W n/a Contact=0
Bias Control GOV Output Type GG 2090 Uint32 4 R W n/a Contact=0
Bias Control Governor Droop Gain GG 2092 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control AVR Droop Gain GG 2094 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
Bias Control Speed Trim Enabled GG 2096 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Bias Control Voltage Trim Enabled GG 2098 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Bias Control Ramped Watt Demand Per Unit GG 2100 Float 4 R W n/a n/a
Bias Control Watt Demand Per Unit GG 2102 Float 4 R W n/a n/a
Bias Control Ramped var Demand Per Unit GG 2104 Float 4 R W n/a n/a
Bias Control AVR Inner Controller Output GG 2106 Float 4 R W n/a n/a
Bias Control AVR Outer Controller Output GG 2108 Float 4 R W n/a n/a
Bias Control GOV Inner Controller Output GG 2110 Float 4 R W n/a n/a
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Analog=1
Analog=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 57

9469300991 Rev A 51
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bias Control GOV Outer Controller Output GG 2112 Float 4 R W n/a n/a
Bias Control GOV Inner Controller Error GG 2114 Float 4 R W n/a n/a
Bias Control GOV Outer Controller Error GG 2116 Float 4 R W n/a n/a
Bias Control Speed Trim Setpoint GG 2118 Float 4 R W Hertz 47 - 100
Bias Control var Control Enabled GG 2120 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Bias Control kvar Load Rate GG 2122 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
Bias Control kW Setpoint Source GG 2124 Uint32 4 R W n/a User Setting=0
Bias Control kvar Setpoint Source GG 2126 Uint32 4 R W n/a User Setting=0
Enabled=1
Local Analog Input 1=1
Local Analog Input 2=2
Local Analog Input 3=3
Local Analog Input 4=4
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=5
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=6
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=7
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=8
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=9
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=10
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=11
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=12
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=13
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=14
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=15
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=16
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=17
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=18
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=19
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=20
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=21
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=22
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=23
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=24
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=25
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=26
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=27
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=28
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=29
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=30
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=31
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=32
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=33
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=34
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=35
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=36
Local Analog Input 1=1
Local Analog Input 2=2
Local Analog Input 3=3
Local Analog Input 4=4
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=5
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=6
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=7
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=8
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=9
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=10
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=11
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=12
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=13
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=14
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=15
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=16
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=17
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=18
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=19
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=20
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=21
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=22
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=23
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=24
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=25
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=26
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=27
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=28
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=29
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=30
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=31
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=32
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=33
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=34
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=35
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=36
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 58

52 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bias Control PF Setpoint Source GG 2128 Uint32 4 R W n/a User Setting=0
Bias Control Base Load Analog Max GG 2130 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
Bias Control Base Load Analog Min GG 2132 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
Bias Control kvar Analog Max GG 2134 Float 4 R W Percent -100 - 100
Bias Control kvar Analog Min GG 2136 Float 4 R W Percent -100 - 100
Bias Control PF Analog Max GG 2138 Uint32 4 R W n/a 160 - 240
Bias Control PF Analog Min GG 2140 Uint32 4 R W n/a 160 - 240
Bias Control var Droop Percentage GG 2142 Float 4 R W Percent 0.5 - 10
Bias Control Base Load Level GG 2144 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
Bias Control kvar Setpoint GG 2146 Float 4 R W Percent -100 - 100
Bias Control PF Setpoint GG 2148 Uint32 4 R W n/a 160 - 240
Bias Control var Control Mode GG 2150 Uint32 4 R W n/a var Control=0
Bias Control Load Share Interface GG 2152 Uint32 4 R W n/a Load Share Line=0
Local Analog Input 1=1
Local Analog Input 2=2
Local Analog Input 3=3
Local Analog Input 4=4
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=5
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=6
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=7
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=8
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=9
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=10
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=11
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=12
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=13
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=14
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=15
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=16
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=17
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=18
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=19
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=20
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=21
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=22
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=23
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=24
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=25
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=26
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=27
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=28
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=29
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=30
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=31
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=32
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=33
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=34
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=35
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=36
PF Control=1
Ethernet Comms=1
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 59

9469300991 Rev A 53
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bias Control Remote Speed Bias Source GG 2154 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
Bias Control Remote Speed Bias Setpoint GG 2156 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 5
BiasControl KwRampStatus GG 2158 Uint32 4 R n/a Up=0
BiasControl KvarRampStatus GG 2160 Uint32 4 R n/a Up=0
Bias Control Speed Bias Output GG 2162 Float 4 R n/a n/a
Bias Control Voltage Bias Output GG 2164 Float 4 R n/a n/a
Bias Control Generated kW GG 2166 Float 4 R kilowatt n/a
Bias Control Generated kvar GG 2168 Float 4 R kilovar n/a
Local Analog Input 1=1
Local Analog Input 2=2
Local Analog Input 3=3
Local Analog Input 4=4
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=5
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=6
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=7
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=8
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=9
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=10
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=11
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=12
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=13
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=14
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=15
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=16
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=17
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=18
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=19
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=20
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=21
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=22
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=23
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=24
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=25
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=26
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=27
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=28
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=29
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=30
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=31
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=32
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=33
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=34
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=35
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=36
Down=1
None=2
Down=1
None=2
Breaker Settings
81-1 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2500 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-1 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2502 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-1 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2504 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-1 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2506 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-2 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2508 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-2 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2510 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-2 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2512 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-2 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2514 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-3 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2516 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-3 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2518 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-3 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2520 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-3 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2522 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-4 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2524 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Page 60

54 9469300991 Rev A
Breaker Management
Breaker Close Wait Time
GG
2586
Uint32
4
R W
Millisecond
100 - 600000
81-4 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2526 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-4 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2528 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-4 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2530 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-5 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2532 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-5 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2534 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-5 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2536 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-5 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2538 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-6 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2540 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-6 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2542 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-6 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2544 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-6 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2546 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-7 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2548 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-7 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2550 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-7 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2552 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-7 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2554 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-8 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2556 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-8 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2558 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-8 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2560 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
81-8 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2562 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
78-1 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2564 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
78-1 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2566 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
78-1 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2568 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
78-1 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2570 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
78-2 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG0 2572 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
78-2 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG1 2574 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
78-2 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG2 2576 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
78-2 Open Mains Breaker On Trip SG3 2578 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Breaker Management Dead Bus Close Enable GG 2580 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Breaker Management Dead Gen Close Enable GG 2582 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Breaker Management In Phase Monitor Enable GG 2584 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Breaker Management Close Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 2588 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enabled=1
Breaker Management Open Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 2590 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enabled=1
Breaker Management Close Fail Pre-Alarm Monitor GG 2592 Uint32 4 R W n/a Transition Only=0
Always=1
Breaker Management Open Fail Pre-Alarm Monitor GG 2594 Uint32 4 R W n/a Transition Only=0
Always=1
Breaker Management Bus Live Close Enable GG 2596 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enabled=1
Breaker Management Breaker System Config GG 2598 Uint32 4 R W n/a None=0
GB=1
GB-MB=2
GB-MB with Load
Sesing=3
Sync Sync Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 2600 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enabled=1
Page 61

9469300991 Rev A 55
Generator Breaker
Breaker Close Time
GG
2634
Uint32
4
R W
Millisecond
0 - 1000
Sync Source Volt Greater Than
Sync Voltage Difference GG 2604 Float 4 R W Percent 2 - 15
Sync Synchronizer Type GG 2606 Uint32 4 R W n/a Anticipatory=0
Sync Volt Error Gain GG 2608 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 1000
Sync Speed Error Gain GG 2610 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 1000
Sync Max Slip Control Limit GG 2612 Float 4 R W Hertz 0 - 2
Sync Min Slip Control Limit GG 2614 Float 4 R W Hertz 0 - 2
Sync Slip Frequency GG 2616 Float 4 R W Hertz 0.01 - 0.5
Sync Source Freq Greater Than
Sync Closing Angle GG 2620 Float 4 R W Degree 3 - 20
Sync Sync Fail Activation Delay GG 2622 Uint32 4 R W Millisecond 100 - 600000
Sync Activation Delay GG 2624 Uint32 4 R W Millisecond 100 - 800
Sync Sync Mode GG 2626 Uint32 4 R W n/a Sync Run=0
Generator Breaker Continuous Output GG 2628 Uint32 4 R W n/a Pulse=0
Generator Breaker Open Pulse Time GG 2630 Uint32 4 R W Millisecond 10 - 10000
Generator Breaker Close Pulse Time GG 2632 Uint32 4 R W Millisecond 10 - 10000
Generator Breaker Configured GG 2636 Uint32 4 R W n/a Not Configured=0
Generator Breaker Source Bus GG 2638 Uint32 4 R W n/a Gen=0
Generator Breaker Destination Bus GG 2640 Uint32 4 R W n/a Gen=0
Generator Breaker Transition Delay GG 2642 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 10
Generator Breaker External Status Change Action GG 2644 Uint32 4 R W n/a Ignore=0
Generator Breaker Open Attempts GG 2646 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 20
Generator Breaker Close Attempts GG 2648 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 20
Generator Breaker Retry Delay GG 2650 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 1200
Generator Breaker Fail Output Config GG 2652 Uint32 4 R W n/a Retain=0
Mains Breaker Continuous Output GG 2654 Uint32 4 R W n/a Pulse=0
Mains Breaker Open Pulse Time GG 2656 Uint32 4 R W Millisecond 10 - 10000
Mains Breaker Close Pulse Time GG 2658 Uint32 4 R W Millisecond 10 - 10000
Mains Breaker Breaker Close Time GG 2660 Uint32 4 R W Millisecond 0 - 1000
Mains Breaker Configured GG 2662 Uint32 4 R W n/a Not Configured=0
Mains Breaker Source Bus GG 2664 Uint32 4 R W n/a Gen=0
Mains Breaker Destination Bus GG 2666 Uint32 4 R W n/a Gen=0
Mains Breaker Transition Delay GG 2668 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 10
Mains Breaker External Status Change Action GG 2670 Uint32 4 R W n/a Ignore=0
Mains Breaker Open Attempts GG 2672 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 20
Mains Breaker Close Attempts GG 2674 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 20
Mains Breaker Retry Delay GG 2676 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 1200
Mains Breaker Fail Output Config GG 2678 Uint32 4 R W n/a Retain=0
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Destination Volt
Destination Freq
Transfer Enabled GG 2680 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Closed Transfer Enabled GG 2682 Uint32 4 R W n/a Open=0
Reverse Rotation Mains Fail
Transfer Inhibit
Return Delay GG 2686 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 1800
Transfer Delay GG 2688 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Max Transfer Time GG 2690 Uint32 4 R W Second 10 - 120
Max Parallel Time GG 2692 Uint32 4 R W Decisecond 1 - 100000
Alarm State Transfer To Mains GG 2694 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
GG 2602 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enabled=1
Phase Lock Loop=1
GG 2618 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enabled=1
Sync Check=1
Sync Only=2
Continuous=1
Configured=1
Bus 1=1
Bus 2=2
Bus 1=1
Bus 2=2
Follow Always=1
Follow In Auto=2
Remove=1
Continuous=1
Configured=1
Bus 1=1
Bus 2=2
Bus 1=1
Bus 2=2
Follow Always=1
Follow In Auto=2
Remove=1
Enabled=1
Closed=1
GG 2684 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 62

56 9469300991 Rev A
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Breaker Local Request
Generation
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Mains Breaker Open Config GG 2696 Uint32 4 R W n/a Generator Start=0
Generator Stable=1
Mains Zero Power Flow Level GG 2698 Uint32 4 R W Percent 1 - 100
Open Transition Delay GG 2700 Uint32 4 R W Decisecond 0 - 100,000
Bus Condition
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Gen Condition Dead Pickup SG0 1P 3000 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Gen Condition Dead Time Delay SG0 1P 3002 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG0 1P 3004 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG0 1P 3006 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG0 1P 3008 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG0 1P 3010 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG0 1P 3012 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG0 1P 3014 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG0 1P 3016 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG0 1P 3018 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Time Delay SG0 1P 3020 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Fail Time Delay SG0 1P 3022 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Low-Line Scale SG0 1P 3024 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Gen Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG0 1P 3026 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Gen Condition Dead Pickup SG0 3P 3028 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Gen Condition Dead Time Delay SG0 3P 3030 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG0 3P 3032 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG0 3P 3034 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG0 3P 3036 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG0 3P 3038 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG0 3P 3040 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG0 3P 3042 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG0 3P 3044 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG0 3P 3046 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Time Delay SG0 3P 3048 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Fail Time Delay SG0 3P 3050 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Low-Line Scale SG0 3P 3052 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Gen Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG0 3P 3054 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Gen Condition Dead Pickup SG1 1P 3056 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Gen Condition Dead Time Delay SG1 1P 3058 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG1 1P 3060 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG1 1P 3062 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG1 1P 3064 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG1 1P 3066 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG1 1P 3068 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG1 1P 3070 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG1 1P 3072 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG1 1P 3074 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Time Delay SG1 1P 3076 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Fail Time Delay SG1 1P 3078 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Low-Line Scale SG1 1P 3080 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Gen Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG1 1P 3082 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Gen Condition Dead Pickup SG1 3P 3084 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Gen Condition Dead Time Delay SG1 3P 3086 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG1 3P 3088 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG1 3P 3090 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG1 3P 3092 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG1 3P 3094 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG1 3P 3096 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG1 3P 3098 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG1 3P 3100 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG1 3P 3102 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Time Delay SG1 3P 3104 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Fail Time Delay SG1 3P 3106 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Low-Line Scale SG1 3P 3108 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Gen Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG1 3P 3110 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Gen Condition Dead Pickup SG2 1P 3112 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Gen Condition Dead Time Delay SG2 1P 3114 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG2 1P 3116 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG2 1P 3118 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG2 1P 3120 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG2 1P 3122 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG2 1P 3124 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG2 1P 3126 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 63

9469300991 Rev A 57
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG2 1P 3128 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG2 1P 3130 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Time Delay SG2 1P 3132 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Fail Time Delay SG2 1P 3134 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Low-Line Scale SG2 1P 3136 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Gen Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG2 1P 3138 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Gen Condition Dead Pickup SG2 3P 3140 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Gen Condition Dead Time Delay SG2 3P 3142 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG2 3P 3144 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG2 3P 3146 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG2 3P 3148 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG2 3P 3150 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG2 3P 3152 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG2 3P 3154 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG2 3P 3156 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG2 3P 3158 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Time Delay SG2 3P 3160 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Fail Time Delay SG2 3P 3162 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Low-Line Scale SG2 3P 3164 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Gen Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG2 3P 3166 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Gen Condition Dead Pickup SG3 1P 3168 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Gen Condition Dead Time Delay SG3 1P 3170 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG3 1P 3172 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG3 1P 3174 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG3 1P 3176 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG3 1P 3178 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG3 1P 3180 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG3 1P 3182 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG3 1P 3184 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG3 1P 3186 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Time Delay SG3 1P 3188 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Fail Time Delay SG3 1P 3190 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Low-Line Scale SG3 1P 3192 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Gen Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG3 1P 3194 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Gen Condition Dead Pickup SG3 3P 3196 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Gen Condition Dead Time Delay SG3 3P 3198 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG3 3P 3200 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG3 3P 3202 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG3 3P 3204 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG3 3P 3206 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG3 3P 3208 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG3 3P 3210 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG3 3P 3212 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG3 3P 3214 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Gen Condition Stable Time Delay SG3 3P 3216 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Fail Time Delay SG3 3P 3218 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Gen Condition Low-Line Scale SG3 3P 3220 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Gen Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG3 3P 3222 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus1 Condition Dead Pickup SG0 1P 3224 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus1 Condition Dead Time Delay SG0 1P 3226 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG0 1P 3228 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG0 1P 3230 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG0 1P 3232 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG0 1P 3234 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG0 1P 3236 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG0 1P 3238 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG0 1P 3240 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG0 1P 3242 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Time Delay SG0 1P 3244 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Fail Time Delay SG0 1P 3246 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Low-Line Scale SG0 1P 3248 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus1 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG0 1P 3250 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus1 Condition Dead Pickup SG0 3P 3252 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus1 Condition Dead Time Delay SG0 3P 3254 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG0 3P 3256 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG0 3P 3258 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG0 3P 3260 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG0 3P 3262 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG0 3P 3264 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG0 3P 3266 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG0 3P 3268 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG0 3P 3270 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Time Delay SG0 3P 3272 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Fail Time Delay SG0 3P 3274 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Low-Line Scale SG0 3P 3276 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 64

58 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus1 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG0 3P 3278 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus1 Condition Dead Pickup SG1 1P 3280 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus1 Condition Dead Time Delay SG1 1P 3282 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG1 1P 3284 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG1 1P 3286 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG1 1P 3288 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG1 1P 3290 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG1 1P 3292 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG1 1P 3294 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG1 1P 3296 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG1 1P 3298 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Time Delay SG1 1P 3300 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Fail Time Delay SG1 1P 3302 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Low-Line Scale SG1 1P 3304 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus1 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG1 1P 3306 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus1 Condition Dead Pickup SG1 3P 3308 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus1 Condition Dead Time Delay SG1 3P 3310 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG1 3P 3312 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG1 3P 3314 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG1 3P 3316 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG1 3P 3318 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG1 3P 3320 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG1 3P 3322 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG1 3P 3324 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG1 3P 3326 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Time Delay SG1 3P 3328 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Fail Time Delay SG1 3P 3330 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Low-Line Scale SG1 3P 3332 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus1 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG1 3P 3334 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus1 Condition Dead Pickup SG2 1P 3336 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus1 Condition Dead Time Delay SG2 1P 3338 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG2 1P 3340 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG2 1P 3342 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG2 1P 3344 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG2 1P 3346 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG2 1P 3348 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG2 1P 3350 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG2 1P 3352 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG2 1P 3354 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Time Delay SG2 1P 3356 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Fail Time Delay SG2 1P 3358 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Low-Line Scale SG2 1P 3360 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus1 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG2 1P 3362 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus1 Condition Dead Pickup SG2 3P 3364 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus1 Condition Dead Time Delay SG2 3P 3366 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG2 3P 3368 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG2 3P 3370 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG2 3P 3372 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG2 3P 3374 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG2 3P 3376 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG2 3P 3378 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG2 3P 3380 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG2 3P 3382 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Time Delay SG2 3P 3384 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Fail Time Delay SG2 3P 3386 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Low-Line Scale SG2 3P 3388 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus1 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG2 3P 3390 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus1 Condition Dead Pickup SG3 1P 3392 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus1 Condition Dead Time Delay SG3 1P 3394 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG3 1P 3396 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG3 1P 3398 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG3 1P 3400 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG3 1P 3402 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG3 1P 3404 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG3 1P 3406 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG3 1P 3408 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG3 1P 3410 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Time Delay SG3 1P 3412 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Fail Time Delay SG3 1P 3414 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Low-Line Scale SG3 1P 3416 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus1 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG3 1P 3418 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus1 Condition Dead Pickup SG3 3P 3420 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus1 Condition Dead Time Delay SG3 3P 3422 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG3 3P 3424 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG3 3P 3426 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 65

9469300991 Rev A 59
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG3 3P 3428 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG3 3P 3430 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG3 3P 3432 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG3 3P 3434 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG3 3P 3436 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG3 3P 3438 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus1 Condition Stable Time Delay SG3 3P 3440 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Fail Time Delay SG3 3P 3442 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus1 Condition Low-Line Scale SG3 3P 3444 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus1 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG3 3P 3446 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus2 Condition Dead Pickup SG0 1P 3448 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus2 Condition Dead Time Delay SG0 1P 3450 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG0 1P 3452 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG0 1P 3454 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG0 1P 3456 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG0 1P 3458 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG0 1P 3460 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG0 1P 3462 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG0 1P 3464 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG0 1P 3466 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Time Delay SG0 1P 3468 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Fail Time Delay SG0 1P 3470 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Low-Line Scale SG0 1P 3472 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus2 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG0 1P 3474 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus2 Condition Dead Pickup SG0 3P 3476 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus2 Condition Dead Time Delay SG0 3P 3478 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG0 3P 3480 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG0 3P 3482 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG0 3P 3484 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG0 3P 3486 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG0 3P 3488 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG0 3P 3490 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG0 3P 3492 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG0 3P 3494 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Time Delay SG0 3P 3496 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Fail Time Delay SG0 3P 3498 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Low-Line Scale SG0 3P 3500 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus2 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG0 3P 3502 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus2 Condition Dead Pickup SG1 1P 3504 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus2 Condition Dead Time Delay SG1 1P 3506 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG1 1P 3508 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG1 1P 3510 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG1 1P 3512 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG1 1P 3514 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG1 1P 3516 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG1 1P 3518 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG1 1P 3520 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG1 1P 3522 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Time Delay SG1 1P 3524 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Fail Time Delay SG1 1P 3526 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Low-Line Scale SG1 1P 3528 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus2 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG1 1P 3530 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus2 Condition Dead Pickup SG1 3P 3532 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus2 Condition Dead Time Delay SG1 3P 3534 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG1 3P 3536 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG1 3P 3538 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG1 3P 3540 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG1 3P 3542 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG1 3P 3544 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG1 3P 3546 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG1 3P 3548 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG1 3P 3550 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Time Delay SG1 3P 3552 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Fail Time Delay SG1 3P 3554 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Low-Line Scale SG1 3P 3556 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus2 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG1 3P 3558 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus2 Condition Dead Pickup SG2 1P 3560 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus2 Condition Dead Time Delay SG2 1P 3562 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG2 1P 3564 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG2 1P 3566 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG2 1P 3568 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG2 1P 3570 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG2 1P 3572 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG2 1P 3574 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG2 1P 3576 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 66

60 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG2 1P 3578 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Time Delay SG2 1P 3580 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Fail Time Delay SG2 1P 3582 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Low-Line Scale SG2 1P 3584 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus2 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG2 1P 3586 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus2 Condition Dead Pickup SG2 3P 3588 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus2 Condition Dead Time Delay SG2 3P 3590 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG2 3P 3592 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG2 3P 3594 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG2 3P 3596 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG2 3P 3598 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG2 3P 3600 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG2 3P 3602 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG2 3P 3604 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG2 3P 3606 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Time Delay SG2 3P 3608 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Fail Time Delay SG2 3P 3610 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Low-Line Scale SG2 3P 3612 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus2 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG2 3P 3614 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus2 Condition Dead Pickup SG3 1P 3616 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus2 Condition Dead Time Delay SG3 1P 3618 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG3 1P 3620 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG3 1P 3622 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG3 1P 3624 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG3 1P 3626 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG3 1P 3628 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG3 1P 3630 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG3 1P 3632 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG3 1P 3634 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Time Delay SG3 1P 3636 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Fail Time Delay SG3 1P 3638 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Low-Line Scale SG3 1P 3640 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus2 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG3 1P 3642 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
Bus2 Condition Dead Pickup SG3 3P 3644 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 4800
Bus2 Condition Dead Time Delay SG3 3P 3646 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Pickup SG3 3P 3648 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Undervoltage Dropout SG3 3P 3650 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Pickup SG3 3P 3652 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Overvoltage Dropout SG3 3P 3654 Float 4 R W Volt 10 - 99999
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Pickup SG3 3P 3656 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Underfrequency Dropout SG3 3P 3658 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Pickup SG3 3P 3660 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Overfrequency Dropout SG3 3P 3662 Float 4 R W Hertz 46 - 64
Bus2 Condition Stable Time Delay SG3 3P 3664 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Fail Time Delay SG3 3P 3666 Float 4 R W Second 0.1 - 600
Bus2 Condition Low-Line Scale SG3 3P 3668 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
Bus2 Condition Alternate Frequency Scale SG3 3P 3670 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 100
DGC Settings
CAN Bus J1939 Address GG 4000 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 253
CAN Bus Baud Rate GG 4002 Uint32 4 R W n/a 125 kbps=0
Reserved 4004-5
LCD Settings LCD Backlight Timeout GG 4006 Uint8 1 R W Minute 1 - 120
LCD Settings LCD Contrast GG 4007 Uint8 1 R W Percent 0 - 100
LCD Settings LCD Sleep Mode GG 4008 Uint8 1 R W n/a Disabled=0
Real Time Clock Alert RTC Alert Enable GG 4009 Uint32 4 R W n/a No=0
Buzzer Buzzer Enabled GG 4011 Uint8 1 R W n/a Disabled=0
Buzzer Not In Auto Buzzer Enabled GG 4012 Uint8 1 R W n/a Disabled=0
AEM1 Enable GG 4013 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
AEM2 Enable GG 4015 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
AEM3 Enable GG 4017 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
AEM4 Enable GG 4019 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
250 kbps=1
Enabled=1
Yes=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Page 67

9469300991 Rev A 61
Enabled=1
CEM 1 Enable GG 4021 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
CEM 1 CEM Output Configuration GG 4023 Uint32 4 R W n/a 18 Outputs=0
CEM 2 Enable GG 4025 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
CEM 2 CEM Output Configuration GG 4027 Uint32 4 R W n/a 18 Outputs=0
CEM 3 Enable GG 4029 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
CEM 3 CEM Output Configuration GG 4031 Uint32 4 R W n/a 18 Outputs=0
CEM 4 Enable GG 4033 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
CEM 4 CEM Output Configuration GG 4035 Uint32 4 R W n/a 18 Outputs=0
Genset Controller Restart Delay GG 4037 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 120
Genset Controller Cool Down Time GG 4039 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 60
Genset Controller Prestart Contact Configuration GG 4041 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller Prestart Rest Configuration GG 4043 Uint32 4 R W n/a Off during crank=0
Genset Controller Cranking Style GG 4045 Uint32 4 R W n/a Continuous=0
Genset Controller Number of Crank Cycles GG 4047 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 7
Genset Controller Cycle Crank Time GG 4049 Uint32 4 R W Second 5 - 15
Genset Controller Continuous Crank Time GG 4051 Uint32 4 R W Second 5 - 60
Genset Controller Crank Disconnect Limit GG 4053 Uint32 4 R W Second 10 - 100
Genset Controller Pre Crank Delay GG 4055 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 30
Genset Controller Oil Pressure Crank Disconnect GG 4057 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller Crank Disconnect Pressure PSI GG 4059 Float 4 R W PSI 2.9 - 150
Genset Controller Crank Disconnect Pressure kPa GG 4061 Float 4 R W kPa 20 - 1034.5
Genset Controller Crank Disconnect Pressure bar GG 4063 Float 4 R W bar 2 - 10.3
Genset Controller Power Up Delay GG 4065 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 60
Genset Controller Off Mode Cool Down Enabled GG 4067 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller Remaining Cooldown Time Minutes GG 4069 Uint32 4 R Minute 0 - 59
Genset Controller Remaining Cooldown Time Seconds GG 4071 Uint32 4 R Second 0 - 59
Genset Controller Pending NFPA Level GG 4073 Uint32 4 R W n/a Zero=0
Pre-Alarm Enable Ethernet 1 Link Lost GG 4075 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Pre-Alarm Enable Ethernet 2 Link Lost GG 4077 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller Gen Reverse Rotation Pre-Alarm
Genset Controller Bus 1 Reverse Rotation Pre-Alarm
Genset Controller Bus 2 Reverse Rotation Pre-Alarm
Genset Controller AEM 1 Comm Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 4085 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller AEM 2 Comm Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 4087 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller AEM 3 Comm Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 4089 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller AEM 4 Comm Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 4091 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller CEM 1 Comm Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 4093 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller CEM 2 Comm Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 4095 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller CEM 3 Comm Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 4097 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Genset Controller CEM 4 Comm Fail Pre-Alarm Enable GG 4099 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Coolant Temp Sender Fail Alarm Configuration GG 4101 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Coolant Temp Sender Fail Coolant Activation Delay GG 4103 Uint32 4 R W Second 300 - 1800
Oil Pressure Sender Fail Alarm Configuration GG 4105 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Oil Pressure Sender Fail Activation Delay GG 4107 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Enabled=1
24 Outputs=1
Enabled=1
24 Outputs=1
Enabled=1
24 Outputs=1
Enabled=1
24 Outputs=1
Enabled=1
On during rest=1
Preheat before
crank=2
Cycle=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
One=1
Two=2
Enabled=1
Enable
GG 4079 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
GG 4081 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enable
GG 4083 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enable
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 68

62 9469300991 Rev A
Proportional=1
Fuel Level Sender Fail Alarm Configuration GG 4109 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Fuel Level Sender Fail Activation Delay GG 4111 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Voltage Sensing Sender
Fail
Voltage Sensing Sender
Fail
Single Ph Override Single-Phase Sense GG 4117 Uint32 4 R W n/a AB=0
AVR Output Out-of-Range Activation Delay GG 4119 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AVR Output Alarm Configuration GG 4121 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
GOV Output Out-of-Range Activation Delay GG 4123 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
GOV Output Alarm Configuration GG 4125 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
LS Output Out of Range Activation Delay GG 4127 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
LS Output Alarm Configuration GG 4129 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Alarm Configuration GG 4113 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Activation Delay GG 4115 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AC=1
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pulse Outputs
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
AVR Pulse Output Mode GG 5000 Uint32 4 R W n/a Continuous=0
AVR Pulse Output Correction Pulse Width GG 5002 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 99.9
AVR Pulse Output Correction Pulse Interval GG 5004 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 99.9
GOV Pulse Output Mode GG 5006 Uint32 4 R W n/a Continuous=0
GOV Pulse Output Correction Pulse Width GG 5008 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 99.9
GOV Pulse Output Correction Pulse Interval GG 5010 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 99.9
Proportional=1
Control Settings
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 1 State GG 5500 Uint32 4 R W n/a Open=0
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 2 State GG 5502 Uint32 4 R W n/a Open=0
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 3 State GG 5504 Uint32 4 R W n/a Open=0
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 4 State GG 5506 Uint32 4 R W n/a Open=0
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 5 State GG 5508 Uint32 4 R W n/a Open=0
Virtual Switch Virtual Switch 6 State GG 5510 Uint32 4 R W n/a Open=0
Coms Control Group Emergency Stop: Writing a 1 will toggle
Coms Control Group Remote Start GG 5514 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Remote Stop GG 5516 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Run Mode GG 5518 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Off Mode GG 5520 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Auto Mode GG 5522 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Gen Breaker Open Request GG 5524 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Gen Breaker Close Request GG 5526 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Mains Breaker Open Request GG 5528 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Mains Breaker Close Request GG 5530 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Emergency Stop GG 5532 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Run Request GG 5534 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Coms Alarm Reset GG 5536 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Reset Generator Maximum ROCOF GG 5538 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Reset Bus 1 Maximum ROCOF GG 5540 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Reset Bus 2 Maximum ROCOF GG 5542 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Reset Generator Maximum Vector Shift GG 5544 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Reset Bus 1 Maximum Vector Shift GG 5546 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Coms Control Group Reset Bus 2 Maximum Vector Shift GG 5548 Uint32 4 R W n/a Trigger=1
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Closed=1
Closed=1
Closed=1
Closed=1
Closed=1
Closed=1
GG 5512 Uint32 4 R W n/a Toggle On/Off=1
emergency stop from off to on. Writing a 1
again will toggle emergency stop from on to
off. When read, Off state =0 and On state =1.
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 69

9469300991 Rev A 63
PLC Timed Element Settings
Timer 12 Timeout Seconds
GG
6070
Uint32
4
R W
Second
0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings
Counter 7 Timeout
GG
6108
Float 4 R W
n/a
0 - 1800
Coms Control Group Bus 1 Protection Reset GG 5550 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Coms Control Group Bus 2 Protection Reset GG 5552 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Coms Control Group Bus 1 Bus 2 Protection Reset GG 5554 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
High Current Contacts Fuel Solenoid Logic Control GG 5556 Uint32 4 R W n/a Predefined=0
High Current Contacts Engine Start Delay Logic Control GG 5558 Uint32 4 R W n/a Predefined=0
High Current Contacts Master Start Output Logic Control GG 5560 Uint32 4 R W n/a Predefined=0
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Programmable=1
Programmable=1
Programmable=1
Global Settings
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 1 Timeout Hours GG 6000 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 1 Timeout Minutes GG 6002 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 1 Timeout Seconds GG 6004 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 2 Timeout Hours GG 6006 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 2 Timeout Minutes GG 6008 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 2 Timeout Seconds GG 6010 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 3 Timeout Hours GG 6012 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 3 Timeout Minutes GG 6014 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 3 Timeout Seconds GG 6016 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 4 Timeout Hours GG 6018 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 4 Timeout Minutes GG 6020 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 4 Timeout Seconds GG 6022 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 5 Timeout Hours GG 6024 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 5 Timeout Minutes GG 6026 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 5 Timeout Seconds GG 6028 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 6 Timeout Hours GG 6030 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 6 Timeout Minutes GG 6032 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 6 Timeout Seconds GG 6034 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 7 Timeout Hours GG 6036 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 7 Timeout Minutes GG 6038 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 7 Timeout Seconds GG 6040 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 8 Timeout Hours GG 6042 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 8 Timeout Minutes GG 6044 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 8 Timeout Seconds GG 6046 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 9 Timeout Hours GG 6048 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 9 Timeout Minutes GG 6050 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 9 Timeout Seconds GG 6052 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 10 Timeout Hours GG 6054 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 10 Timeout Minutes GG 6056 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 10 Timeout Seconds GG 6058 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 11 Timeout Hours GG 6060 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 11 Timeout Minutes GG 6062 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 11 Timeout Seconds GG 6064 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 12 Timeout Hours GG 6066 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 12 Timeout Minutes GG 6068 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 13 Timeout Hours GG 6072 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 13 Timeout Minutes GG 6074 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 13 Timeout Seconds GG 6076 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 14 Timeout Hours GG 6078 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 14 Timeout Minutes GG 6080 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 14 Timeout S econds GG 6082 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 15 Timeout Hours GG 6084 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 15 Timeout Minutes GG 6086 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 15 Timeout Seconds GG 6088 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 16 Timeout Hours GG 6090 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 250
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 16 Timeout Minutes GG 6092 Uint32 4 R W Minute 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Timer 16 Timeout Seconds GG 6094 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 59
PLC Timed Element Settings Counter 1 Timeout GG 6096 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1800
PLC Timed Element Settings Counter 2 Timeout GG 6098 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1800
PLC Timed Element Settings Counter 3 Timeout GG 6100 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1800
PLC Timed Element Settings Counter 4 Timeout GG 6102 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1800
PLC Timed Element Settings Counter 5 Timeout GG 6104 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1800
PLC Timed Element Settings Counter 6 Timeout GG 6106 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1800
PLC Timed Element Settings Counter 8 Timeout GG 6110 Float 4 R W n/a 0 - 1800
Unit ID Table ID Missing Pre Alarm Enable GG 6112 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Enabled=1
Page 70

64 9469300991 Rev A
Grounded Delta=9
Unit ID Table ID Repeat Pre Alarm Enable GG 6114 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Remote Display Panel Enable Programmable Alarm 1 GG 6116 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Remote Display Panel Enable Programmable Alarm 2 GG 6118 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Remote Display Panel Enable Programmable Pre-Alarm 1 GG 6120 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Remote Display Panel Enable Programmable Pre-Alarm 2 GG 6122 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Enabled=1
Configuration
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
System Configuration Nominal Frequency GG 6500 Uint32 4 R W n/a 50 Hz=50
System Configuration Metric English GG 6502 Uint32 4 R W n/a English=0
System Configuration Metric Units GG 6504 Uint32 4 R W n/a bar=0
System Configuration Alternate Frequency GG 6506 Float 4 R W Hertz 10 - 90
System Configuration Aux CT 1 GG 6508 Uint32 4 R W n/a CT Not Connected=7
System Configuration Aux CT 2 GG 6510 Uint32 4 R W n/a CT Not Connected=7
System Configuration Aux CT 3 GG 6512 Uint32 4 R W n/a CT Not Connected=7
System Configuration Aux CT 4 GG 6514 Uint32 4 R W n/a CT Not Connected=7
System Configuration Engine Rated RPM GG 6516 Uint32 4 R W n/a 750 - 3600
System Configuration RPM Adjustment Bandwidth GG 6518 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 1000
System Configuration 24V Battery GG 6520 Uint32 4 R W n/a 12V=0
System Configuration Gen CT Low-Line Scale Factor GG 6522 Float 4 R W n/a 0.001 - 3
System Configuration Redundant Ethernet GG 6524 Uint32 4 R W n/a No=0
Gen Volt
Configuration
Gen Volt
Configuration
Gen Volt
Configuration
Gen Volt
Configuration
Bus 1 Volt Config Connection GG 6534 Int32 4 R W n/a Delta=7
Bus 1 Volt Config Ratio Primary GG 6536 Float 4 R W n/a 1 - 500000
Connection GG 6526 Int32 4 R W n/a Delta=7
Ratio Primary GG 6528 Float 4 R W n/a 1 - 500000
Ratio Secondary GG 6530 Float 4 R W n/a 1 - 600
Rated Primary LL GG 6532 Float 4 R W Volt 1 - 500000
60 Hz=60
Metric=1
kPa/MPA=1
Bus 1 Phase A=0
Bus 1 Phase B=1
Bus 1 Phase C=2
Bus 2 Phase A=3
Bus 2 Phase B=4
Bus 2 Phase C=5
Ground Current=6
Bus 1 Phase A=0
Bus 1 Phase B=1
Bus 1 Phase C=2
Bus 2 Phase A=3
Bus 2 Phase B=4
Bus 2 Phase C=5
Ground Current=6
Bus 1 Phase A=0
Bus 1 Phase B=1
Bus 1 Phase C=2
Bus 2 Phase A=3
Bus 2 Phase B=4
Bus 2 Phase C=5
Ground Current=6
Bus 1 Phase A=0
Bus 1 Phase B=1
Bus 1 Phase C=2
Bus 2 Phase A=3
Bus 2 Phase B=4
Bus 2 Phase C=5
Ground Current=6
24V=1
Yes=1
Wye=8
1 Phase AB=0
1 Phase AC=2
Grounded Delta=9
Wye=8
1 Phase AB=0
1 Phase AC=2
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 71

9469300991 Rev A 65
Bus 2 Current Config
Ratio Primary
GG
6568
Float 4 R W
n/a
1 - 9999
Factor
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus 1 Volt Config Ratio Secondary GG 6538 Float 4 R W n/a 1 - 600
Bus 1 Volt Config Rated Primary LL GG 6540 Float 4 R W Volt 1 - 500000
Bus 2 Volt Config Connection GG 6542 Int32 4 R W n/a Delta=7
Bus 2 Volt Config Ratio Primary GG 6544 Float 4 R W n/a 1 - 500000
Bus 2 Volt Config Ratio Secondary GG 6546 Float 4 R W n/a 1 - 600
Bus 2 Volt Config Rated Primary LL GG 6548 Float 4 R W Volt 1 - 500000
Gen Current
Configuration
Gen Current
Configuration
Gen Current
Configuration
Gen Current
Configuration
Bus 1 Current Config Connection GG 6558 Int32 4 R W n/a CT A=0
Bus 1 Current Config Ratio Primary GG 6560 Float 4 R W n/a 1 - 9999
Bus 1 Current Config Ratio Secondary GG 6562 Int32 4 R W n/a 1=1
Bus 1 Current Config Rated Primary GG 6564 Float 4 R Amp 0 - 180000
Bus 2 Current Config Connection GG 6566 Int32 4 R W n/a CT A=0
Connection GG 6550 Int32 4 R W n/a CT A=0
Ratio Primary GG 6552 Float 4 R W n/a 1 - 9999
Ratio Secondary GG 6554 Int32 4 R W n/a 1=1
Rated Primary GG 6556 Float 4 R Amp 0 - 180000
Wye=8
1 Phase AB=0
1 Phase AC=2
Grounded Delta=9
CT B=1
CT C=2
CT AB=3
CT BC=4
CT CA=5
CT ABC=6
5=5
CT B=1
CT C=2
CT AB=3
CT BC=4
CT CA=5
CT ABC=6
5=5
CT B=1
CT C=2
CT AB=3
CT BC=4
CT CA=5
CT ABC=6
Bus 2 Current Config Ratio Secondary GG 6570 Int32 4 R W n/a 1=1
Bus 2 Current Config Rated Primary GG 6572 Float 4 R Amp 0 - 180000
Gen Config Rated PF GG 6574 Float 4 R W Power
Factor
Gen Config Rated kW GG 6576 Float 4 R W kilowatt 0 - 1000000
Gen Config Rotation GG 6578 Int32 4 R W n/a ABC=0
Bus 1 Config Rated PF GG 6580-81 Float 4 R W Power
Factor
Bus 1 Config Rated kW GG 6582 Float 4 R W kilowatt 0 - 1000000
Reserved 6584
Bus 2 Config Rated PF GG 6586-87 Float 4 R W Power
Bus 2 Config Rated kW GG 6588 Float 4 R W kilowatt 0 - 1000000
Reserved 6590
RS232 Settings Baud Rate GG 6592 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1200 Baud=1200
RS232 Settings Parity GG 6594 Uint32 4 R W n/a Even Parity=0
RS232 Settings Bits Per Character GG 6596 Uint32 4 R W n/a 8-Bits=8
RS232 Settings Stop Bits GG 6598 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 Stop Bit=1
5=5
-2 - 2
ACB=1
-2 - 2
-2 - 2
2400 Baud=2400
4800 Baud=4800
9600 Baud=9600
19200 Baud=19200
38400 Baud=38400
57600 Baud=57600
115200 Baud=115200
Odd Parity=1
No Parity=2
7-Bits=7
2 Stop Bits=2
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 72
66 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
RS485 Settings Baud Rate GG 6600 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1200 Baud=1200
RS485 Settings Parity GG 6602 Uint32 4 R W n/a Even Parity=0
RS485 Settings Bits Per Character GG 6604 Uint32 4 R W n/a 8-Bits=8
RS485 Settings Stop Bits GG 6606 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 Stop Bit=1
Ethernet 0 Settings Subnet Mask GG 6608 IP
Address
Ethernet 0 Settings Gateway Address GG 6610 IP
Address
Ethernet 0 Settings Use DHCP GG 6612 Uint32 4 R W n/a Off=0
Ethernet 0 Settings Active IP GG 6614 IP
Address
Ethernet 0 Settings Active Gateway GG 6616 IP
Address
Ethernet 0 Settings Active Subnet GG 6618 IP
Address
Ethernet 1 Settings Subnet Mask GG 6620 IP
Address
Ethernet 1 Settings Gateway Address GG 6622 IP
Address
Ethernet 1 Settings Use DHCP GG 6624 Uint32 4 R W n/a Off=0
Ethernet 1 Settings Active IP GG 6626 IP
Address
Ethernet 1 Settings Active Gateway GG 6628 IP
Address
Ethernet 1 Settings Active Subnet GG 6630 IP
Address
Modbus Modbus Ethernet Unit ID GG 6632 Uint16 2 R W n/a 1 - 247
Modbus Modbus Serial Unit ID GG 6633 Uint16 2 R W n/a 1 - 247
Reserved 6634-39
Engine Source Speed Mode GG 6640 Uint32 4 R W n/a Magnetic Pickup=1
Engine Source Flywheel Teeth GG 6642 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 500
Engine Source Speed Sender Fail Time Delay GG 6644 Uint32 4 R W Second 0 - 300
4 R W n/a n/a
4 R W n/a n/a
4 R n/a n/a
4 R n/a n/a
4 R n/a n/a
4 R W n/a n/a
4 R W n/a n/a
4 R n/a n/a
4 R n/a n/a
4 R n/a n/a
2400 Baud=2400
4800 Baud=4800
9600 Baud=9600
19200 Baud=19200
38400 Baud=38400
57600 Baud=57600
115200 Baud=115200
Odd Parity=1
No Parity=2
7-Bits=7
2 Stop Bits=2
On=1
On=1
Gen Freq=2
MPU/Gen Freq=3
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 73

9469300991 Rev A 67
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Engine Source Fuel Level Source GG 6646 Uint32 4 R W n/a Resistive Sender=0
Engine Source Fuel Level Function GG 6648 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disable=0
Engine Source Coolant Temp Source GG 6650 Uint32 4 R W n/a Resistive Sender=0
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=1
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=2
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=3
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=4
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=5
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=6
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=7
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=8
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=9
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=10
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=11
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=12
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=13
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=14
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=15
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=16
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=17
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=18
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=19
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=20
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=21
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=22
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=23
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=24
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=25
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=26
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=27
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=28
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=29
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=30
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=31
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=32
Analog Input 1=33
Analog Input 2=34
Analog Input 3=35
Analog Input 4=36
Fuel Level=1
Natural Gas=2
Liquid Propane=3
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=1
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=2
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=3
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=4
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=5
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=6
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=7
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=8
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=9
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=10
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=11
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=12
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=13
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=14
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=15
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=16
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=17
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=18
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=19
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=20
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=21
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=22
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=23
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=24
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=25
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=26
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=27
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=28
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=29
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=30
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=31
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=32
Analog Input 1=33
Analog Input 2=34
Analog Input 3=35
Analog Input 4=36
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 74

68 9469300991 Rev A
Display
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Engine Source Oil Pressure Source GG 6652 Uint32 4 R W n/a
Resistive Sender=0
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=1
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=2
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=3
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=4
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=5
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=6
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=7
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=8
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=9
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=10
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=11
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=12
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=13
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=14
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=15
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=16
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=17
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=18
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=19
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=20
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=21
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=22
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=23
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=24
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=25
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=26
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=27
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=28
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=29
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=30
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=31
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=32
Analog Input 1=33
Analog Input 2=34
Analog Input 3=35
Analog Input 4=36
Gen Exerciser Start Day of Month GG 6654 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 31
Gen Exerciser Start Day of Week GG 6656 Uint32 4 R W n/a Sunday=0
Monday=1
Tuesday=2
Wednesday=3
Thursday=4
Friday=5
Saturday=6
Gen Exerciser Start Hour GG 6658 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 23
Gen Exerciser Start Minute GG 6660 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 59
Gen Exerciser Period Hours GG 6662 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 23
Gen Exerciser Period Minutes GG 6664 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 59
Gen Exerciser Run with Load GG 6666 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enabled=1
Gen Exerciser Exerciser Mode GG 6668 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Daily=1
Weekly=2
Monthly=3
Run Statistics Commission Date Day GG 6670 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 31
Run Statistics Commission Date Month GG 6672 Uint32 4 R W n/a 1 - 12
Run Statistics Commission Date Year GG 6674 Uint32 4 R W n/a 2000 - 2099
Run Statistics Maintenance Interval Enable GG 6676 Uint32 4 R W n/a Disabled=0
Enabled=1
Run Statistics Maintenance Interval GG 6678 Uint32 4 R W Hour 0 - 5000
Run Statistics Hours Until Maintenance GG 6680 Int32 4 R W Hour 0 - 5000
Run Statistics Cumulative Starts GG 6682 Uint32 4 R W n/a 0 - 32767
Run Statistics Session Number Starts GG 6684 Uint32 4 R n/a n/a
Run Statistics Session Total kWh GG 6686 Uint32 4 R kWh 0 - 999999999
Run Statistics Session Peak kW GG 6688 Float 4 R Watt 0 - 3.00E+14
Run Statistics Cumulative Total Run Hours For
Run Statistics Cumulative Total Run Minutes For
GG 6690 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 999999
GG 6692 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 59
Display
Run Statistics Cumulative Loaded Run Hours For
GG 6694 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 999999
Display
Run Statistics Cumulative Loaded Run Minutes
GG 6696 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 59
For Display
Run Statistics Cumulative Unloaded Run Hours
GG 6698 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 999999
For Display
Run Statistics Cumulative Unloaded Run Minutes
GG 6700 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 59
For Display
Run Statistics Session Total Run Hours For
GG 6702 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 999999
Display
Run Statistics Session Total Run Minutes For
GG 6704 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 59
Display
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 75

9469300991 Rev A 69
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Run Statistics Session Loaded Run Hours For
Display
Run Statistics Session Loaded Run Minutes For
Display
Run Statistics Session Unloaded Run Hours For
Display
Run Statistics Session Unloaded Run Minutes For
Display
GG 6706 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 999999
GG 6708 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 59
GG 6710 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 999999
GG 6712 Uint32 4 R n/a 0 - 59
Remote Module Settings
AEM 1 Input Config. 1 Param Min GG 7000 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 1 Param Max GG 7002 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 1 Current Min GG 7004 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 1 Current Max GG 7006 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 1 Voltage Min GG 7008 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 1 Voltage Max GG 7010 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 1 Alarm Configuration GG 7012 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 1 Input Config. 2 Param Min GG 7014 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 2 Param Max GG 7016 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 2 Current Min GG 7018 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 2 Current Max GG 7020 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 2 Voltage Min GG 7022 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 2 Voltage Max GG 7024 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 2 Alarm Configuration GG 7026 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 1 Input Config. 3 Param Min GG 7028 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 3 Param Max GG 7030 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 3 Current Min GG 7032 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 3 Current Max GG 7034 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 3 Voltage Min GG 7036 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 3 Voltage Max GG 7038 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 3 Alarm Configuration GG 7040 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 1 Input Config. 4 Param Min GG 7042 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 4 Param Max GG 7044 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 4 Current Min GG 7046 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 4 Current Max GG 7048 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 4 Voltage Min GG 7050 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 4 Voltage Max GG 7052 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 4 Alarm Configuration GG 7054 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 1 Input Config. 5 Param Min GG 7056 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 5 Param Max GG 7058 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 5 Current Min GG 7060 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 5 Current Max GG 7062 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 5 Voltage Min GG 7064 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 5 Voltage Max GG 7066 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 5 Alarm Configuration GG 7068 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 1 Input Config. 6 Param Min GG 7070 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 6 Param Max GG 7072 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 6 Current Min GG 7074 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 6 Current Max GG 7076 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 6 Voltage Min GG 7078 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 6 Voltage Max GG 7080 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 6 Alarm Configuration GG 7082 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 1 Input Config. 7 Param Min GG 7084 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 7 Param Max GG 7086 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 7 Current Min GG 7088 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 7 Current Max GG 7090 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 7 Voltage Min GG 7092 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 7 Voltage Max GG 7094 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 7 Alarm Configuration GG 7096 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 76
70 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 1 Protection 1
Threshold 3 Activation Delay
GG
7130
Float 4 R W
Second
0 - 300
AEM 1 Input Config. 8 Param Min GG 7098 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 8 Param Max GG 7100 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Input Config. 8 Current Min GG 7102 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 8 Current Max GG 7104 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 1 Input Config. 8 Voltage Min GG 7106 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 8 Voltage Max GG 7108 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 1 Input Config. 8 Alarm Configuration GG 7110 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 1 Protection 1 Hysteresis GG 7112 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 1 Protection 1 Arming Delay GG 7114 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7116 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7118 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7122 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7124 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7128 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7134 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7136 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 2 Hysteresis GG 7140 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 1 Protection 2 Arming Delay GG 7142 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7144 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7146 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7150 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7152 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Pickup GG 7156 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7158 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7162 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7164 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 3 Hysteresis GG 7168 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 1 Protection 3 Arming Delay GG 7170 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7172 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7174 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7178 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7180 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Pickup GG 7184 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7186 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7190 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7192 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 4 Hysteresis GG 7196 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 1 Protection 4 Arming Delay GG 7198 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
GG 7120 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7126 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7132 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7138 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7148 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7154 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7160 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7166 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7176 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7182 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7188 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7194 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 77

9469300991 Rev A 71
AEM 1 Protection 6
Threshold 4 Activation Delay
GG
7276
Float 4 R W
Second
0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7200 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7202 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7206 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7208 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Pickup GG 7212 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7214 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7218 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7220 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 5 Hysteresis GG 7224 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 1 Protection 5 Arming Delay GG 7226 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7228 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7230 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7234 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7236 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7240 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7242 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7246 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7248 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 6 Hysteresis GG 7252 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 1 Protection 6 Arming Delay GG 7254 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7256 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7258 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7262 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7264 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7268 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7270 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7274 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
GG 7204 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7210 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7216 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7222 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7232 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7238 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7244 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7250 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7260 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7266 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7272 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
AEM 1 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 7 Hysteresis GG 7280 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 1 Protection 7 Arming Delay GG 7282 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7284 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7286 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7290 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7292 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7296 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7298 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
GG 7278 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7288 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7294 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Page 78

72 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7302 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7304 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 8 Hysteresis GG 7308 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 1 Protection 8 Arming Delay GG 7310 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7312 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7314 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7318 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7320 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7324 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7326 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7330 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7332 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 1 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 1
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Parameter Selection GG 7336 Int32 4 R W n/a No Parameter=0
GG 7300 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7306 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7316 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7322 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7328 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7334 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Oil Pressure=1
Coolant Temp=2
Battery Volts=3
RPM=4
Fuel Level=5
Gen Hz=6
Gen VAB=7
Gen VBC=8
Gen VCA=9
Gen Vavg LL=10
Gen VAN=11
Gen VBN=12
Gen VCN=13
Gen Vavg LN=14
Bus 1 Hz=15
Bus 1 VAB=16
Bus 1 VBC=17
Bus 1 VCA=18
Bus 1 Vavg LL=19
Bus 1 VA=20
Bus 1 VB=21
Bus 1 VC=22
Bus 1 Vavg LN=23
Bus 2 Hz=24
Bus 2 VAB=25
Bus 2 VBC=26
Bus 2 VCA=27
Bus 2 Vavg LL=28
Bus 2 VAN=29
Bus 2 VBN=30
Bus 2 VCN=31
Bus 2 Vavg LN=32
Gen PF=33
Bus 1 PF=34
Bus 2 PF=35
Gen Pos kWh=36
Gen Neg kWh=37
Bus 1 Pos kWh=38
Bus 1 Neg kWh=39
Bus 2 Pos kWh=40
Bus 2 Neg kWh=41
Gen IA=42
Gen IB=43
Gen IC=44
Gen I Avg=45
Bus 1 IA=46
Bus 1 IB=47
Bus 1 IC=48
Bus 1 Iavg=49
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 79

9469300991 Rev A 73
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus 2 IAN=50
Bus 2 IBN=51
Bus 2 ICN=52
Bus 2 Iavg=53
IG=54
I Aux=55
Gen kW A=56
Gen kW B=57
Gen kW C=58
Gen kW Total=59
Bus 1 kW A=60
Bus 1 kW B=61
Bus 1 kW C=62
Bus 1 kW Total=63
Bus 2 kW A=64
Bus 2 kW B=65
Bus 2 kW C=66
Bus 2 kW Total=67
Gen kVA A=68
Gen kVA B=69
Gen kVA C=70
Gen kVA Total=71
Bus 1 kVA A=72
Bus 1 kVA B=73
Bus 1 kVA C=74
Bus 1 kVA Total=75
Bus 2 kVA A=76
Bus 2 kVA B=77
Bus 2 kVA C=78
Bus 2 kVA Total=79
Gen kvar A=80
Gen kvar B=81
Gen kvar C=82
Gen kvar Total=83
Bus 1 kvar A=84
Bus 1 kvar B=85
Bus 1 kvar C=86
Bus 1 kvar Total=87
Bus 2 kvar A=88
Bus 2 kvar B=89
Bus 2 kvar C=90
Bus 2 kvar Total=91
Fuel Pressure=92
Injector metering rail
pressure=93
Total Fuel Used=94
Fuel temperature=95
Engine oil temperature=96
Engine intercooler
temperature=97
Coolant pressure=98
Fuel Rate=99
Boost pressure=100
Intake manifold
temperature=101
Charge air temperature=102
Engine Percent Load=103
Analog Input 1=104
Analog Input 2=105
Analog Input 3=106
Analog Input 4=107
kW Load Percent=108
Number of Units Online=109
System kW Capacity=110
System Total Gen kW=111
System Total Gen kvar=112
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=300
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=301
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=302
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=303
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=304
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=305
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=306
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=307
AEM 1 RTD Input 1=308
AEM 1 RTD Input 2=309
AEM 1 RTD Input 3=310
AEM 1 RTD Input 4=311
AEM 1 RTD Input 5=312
AEM 1 RTD Input 6=313
AEM 1 RTD Input 7=314
AEM 1 RTD Input 8=315
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 80

74 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 1 TC Input 1=316
AEM 1 TC Input 2=317
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=318
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=319
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=320
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=321
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=322
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=323
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=324
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=325
AEM 2 RTD Input 1=326
AEM 2 RTD Input 2=327
AEM 2 RTD Input 3=328
AEM 2 RTD Input 4=329
AEM 2 RTD Input 5=330
AEM 2 RTD Input 6=331
AEM 2 RTD Input 7=332
AEM 2 RTD Input 8=333
AEM 2 TC Input 1=334
AEM 2 TC Input 2=335
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=336
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=337
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=338
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=339
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=340
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=341
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=342
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=343
AEM 3 RTD Input 1=344
AEM 3 RTD Input 2=345
AEM 3 RTD Input 3=346
AEM 3 RTD Input 4=347
AEM 3 RTD Input 5=348
AEM 3 RTD Input 6=349
AEM 3 RTD Input 7=350
AEM 3 RTD Input 8=351
AEM 3 TC Input 1=352
AEM 3 TC Input 2=353
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=354
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=355
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=356
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=357
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=358
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=359
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=360
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=361
AEM 4 RTD Input 1=362
AEM 4 RTD Input 2=363
AEM 4 RTD Input 3=364
AEM 4 RTD Input 4=365
AEM 4 RTD Input 5=366
AEM 4 RTD Input 6=367
AEM 4 RTD Input 7=368
AEM 4 RTD Input 8=369
AEM 4 TC Input 1=370
AEM 4 TC Input 2=371
AVR Output=372
GOV Output=373
Out-of-Range Activation
Delay
Param Minimum GG 7340 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Param Maximum GG 7342 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Current Minimum GG 7344 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Current Maximum GG 7346 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Voltage Minimum GG 7348 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Voltage Maximum GG 7350 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Alarm Configuration GG 7352 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Parameter Selection GG 7354 Int32 4 R W n/a No Parameter=0
GG 7338 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
LS Output=374
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Oil Pressure=1
Coolant Temp=2
Battery Volts=3
RPM=4
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 81

9469300991 Rev A 75
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Fuel Level=5
Gen Hz=6
Gen VAB=7
Gen VBC=8
Gen VCA=9
Gen Vavg LL=10
Gen VAN=11
Gen VBN=12
Gen VCN=13
Gen Vavg LN=14
Bus 1 Hz=15
Bus 1 VAB=16
Bus 1 VBC=17
Bus 1 VCA=18
Bus 1 Vavg LL=19
Bus 1 VA=20
Bus 1 VB=21
Bus 1 VC=22
Bus 1 Vavg LN=23
Bus 2 Hz=24
Bus 2 VAB=25
Bus 2 VBC=26
Bus 2 VCA=27
Bus 2 Vavg LL=28
Bus 2 VAN=29
Bus 2 VBN=30
Bus 2 VCN=31
Bus 2 Vavg LN=32
Gen PF=33
Bus 1 PF=34
Bus 2 PF=35
Gen Pos kWh=36
Gen Neg kWh=37
Bus 1 Pos kWh=38
Bus 1 Neg kWh=39
Bus 2 Pos kWh=40
Bus 2 Neg kWh=41
Gen IA=42
Gen IB=43
Gen IC=44
Gen I Avg=45
Bus 1 IA=46
Bus 1 IB=47
Bus 1 IC=48
Bus 1 Iavg=49
Bus 2 IAN=50
Bus 2 IBN=51
Bus 2 ICN=52
Bus 2 Iavg=53
IG=54
I Aux=55
Gen kW A=56
Gen kW B=57
Gen kW C=58
Gen kW Total=59
Bus 1 kW A=60
Bus 1 kW B=61
Bus 1 kW C=62
Bus 1 kW Total=63
Bus 2 kW A=64
Bus 2 kW B=65
Bus 2 kW C=66
Bus 2 kW Total=67
Gen kVA A=68
Gen kVA B=69
Gen kVA C=70
Gen kVA Total=71
Bus 1 kVA A=72
Bus 1 kVA B=73
Bus 1 kVA C=74
Bus 1 kVA Total=75
Bus 2 kVA A=76
Bus 2 kVA B=77
Bus 2 kVA C=78
Bus 2 kVA Total=79
Gen kvar A=80
Gen kvar B=81
Gen kvar C=82
Gen kvar Total=83
Bus 1 kvar A=84
Bus 1 kvar B=85
Bus 1 kvar C=86
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 82

76 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus 1 kvar Total=87
Bus 2 kvar A=88
Bus 2 kvar B=89
Bus 2 kvar C=90
Bus 2 kvar Total=91
Fuel Pressure=92
Injector metering rail
pressure=93
Total Fuel Used=94
Fuel temperature=95
Engine oil temperature=96
Engine intercooler
temperature=97
Coolant pressure=98
Fuel Rate=99
Boost pressure=100
Intake manifold
temperature=101
Charge air temperature=102
Engine Percent Load=103
Analog Input 1=104
Analog Input 2=105
Analog Input 3=106
Analog Input 4=107
kW Load Percent=108
Number of Units Online=109
System kW Capacity=110
System Total Gen kW=111
System Total Gen kvar=112
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=300
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=301
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=302
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=303
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=304
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=305
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=306
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=307
AEM 1 RTD Input 1=308
AEM 1 RTD Input 2=309
AEM 1 RTD Input 3=310
AEM 1 RTD Input 4=311
AEM 1 RTD Input 5=312
AEM 1 RTD Input 6=313
AEM 1 RTD Input 7=314
AEM 1 RTD Input 8=315
AEM 1 TC Input 1=316
AEM 1 TC Input 2=317
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=318
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=319
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=320
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=321
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=322
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=323
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=324
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=325
AEM 2 RTD Input 1=326
AEM 2 RTD Input 2=327
AEM 2 RTD Input 3=328
AEM 2 RTD Input 4=329
AEM 2 RTD Input 5=330
AEM 2 RTD Input 6=331
AEM 2 RTD Input 7=332
AEM 2 RTD Input 8=333
AEM 2 TC Input 1=334
AEM 2 TC Input 2=335
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=336
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=337
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=338
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=339
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=340
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=341
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=342
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=343
AEM 3 RTD Input 1=344
AEM 3 RTD Input 2=345
AEM 3 RTD Input 3=346
AEM 3 RTD Input 4=347
AEM 3 RTD Input 5=348
AEM 3 RTD Input 6=349
AEM 3 RTD Input 7=350
AEM 3 RTD Input 8=351
AEM 3 TC Input 1=352
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 83
9469300991 Rev A 77
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 3 TC Input 2=353
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=354
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=355
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=356
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=357
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=358
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=359
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=360
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=361
AEM 4 RTD Input 1=362
AEM 4 RTD Input 2=363
AEM 4 RTD Input 3=364
AEM 4 RTD Input 4=365
AEM 4 RTD Input 5=366
AEM 4 RTD Input 6=367
AEM 4 RTD Input 7=368
AEM 4 RTD Input 8=369
AEM 4 TC Input 1=370
AEM 4 TC Input 2=371
AVR Output=372
GOV Output=373
Out-of-Range Activation
Delay
Param Minimum GG 7358 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Param Maximum GG 7360 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Current Minimum GG 7362 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Current Maximum GG 7364 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Voltage Minimum GG 7366 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Voltage Maximum GG 7368 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Alarm Configuration GG 7370 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Parameter Selection GG 7372 Int32 4 R W n/a No Parameter=0
GG 7356 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
LS Output=374
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Oil Pressure=1
Coolant Temp=2
Battery Volts=3
RPM=4
Fuel Level=5
Gen Hz=6
Gen VAB=7
Gen VBC=8
Gen VCA=9
Gen Vavg LL=10
Gen VAN=11
Gen VBN=12
Gen VCN=13
Gen Vavg LN=14
Bus 1 Hz=15
Bus 1 VAB=16
Bus 1 VBC=17
Bus 1 VCA=18
Bus 1 Vavg LL=19
Bus 1 VA=20
Bus 1 VB=21
Bus 1 VC=22
Bus 1 Vavg LN=23
Bus 2 Hz=24
Bus 2 VAB=25
Bus 2 VBC=26
Bus 2 VCA=27
Bus 2 Vavg LL=28
Bus 2 VAN=29
Bus 2 VBN=30
Bus 2 VCN=31
Bus 2 Vavg LN=32
Gen PF=33
Bus 1 PF=34
Bus 2 PF=35
Gen Pos kWh=36
Gen Neg kWh=37
Bus 1 Pos kWh=38
Bus 1 Neg kWh=39
Bus 2 Pos kWh=40
Bus 2 Neg kWh=41
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 84

78 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Gen IA=42
Gen IB=43
Gen IC=44
Gen I Avg=45
Bus 1 IA=46
Bus 1 IB=47
Bus 1 IC=48
Bus 1 Iavg=49
Bus 2 IAN=50
Bus 2 IBN=51
Bus 2 ICN=52
Bus 2 Iavg=53
IG=54
I Aux=55
Gen kW A=56
Gen kW B=57
Gen kW C=58
Gen kW Total=59
Bus 1 kW A=60
Bus 1 kW B=61
Bus 1 kW C=62
Bus 1 kW Total=63
Bus 2 kW A=64
Bus 2 kW B=65
Bus 2 kW C=66
Bus 2 kW Total=67
Gen kVA A=68
Gen kVA B=69
Gen kVA C=70
Gen kVA Total=71
Bus 1 kVA A=72
Bus 1 kVA B=73
Bus 1 kVA C=74
Bus 1 kVA Total=75
Bus 2 kVA A=76
Bus 2 kVA B=77
Bus 2 kVA C=78
Bus 2 kVA Total=79
Gen kvar A=80
Gen kvar B=81
Gen kvar C=82
Gen kvar Total=83
Bus 1 kvar A=84
Bus 1 kvar B=85
Bus 1 kvar C=86
Bus 1 kvar Total=87
Bus 2 kvar A=88
Bus 2 kvar B=89
Bus 2 kvar C=90
Bus 2 kvar Total=91
Fuel Pressure=92
Injector metering rail
pressure=93
Total Fuel Used=94
Fuel temperature=95
Engine oil temperature=96
Engine intercooler
temperature=97
Coolant pressure=98
Fuel Rate=99
Boost pressure=100
Intake manifold
temperature=101
Charge air temperature=102
Engine Percent Load=103
Analog Input 1=104
Analog Input 2=105
Analog Input 3=106
Analog Input 4=107
kW Load Percent=108
Number of Units Online=109
System kW Capacity=110
System Total Gen kW=111
System Total Gen kvar=112
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=300
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=301
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=302
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=303
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=304
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=305
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=306
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=307
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 85

9469300991 Rev A 79
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 1 RTD Input 1=308
AEM 1 RTD Input 2=309
AEM 1 RTD Input 3=310
AEM 1 RTD Input 4=311
AEM 1 RTD Input 5=312
AEM 1 RTD Input 6=313
AEM 1 RTD Input 7=314
AEM 1 RTD Input 8=315
AEM 1 TC Input 1=316
AEM 1 TC Input 2=317
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=318
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=319
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=320
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=321
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=322
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=323
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=324
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=325
AEM 2 RTD Input 1=326
AEM 2 RTD Input 2=327
AEM 2 RTD Input 3=328
AEM 2 RTD Input 4=329
AEM 2 RTD Input 5=330
AEM 2 RTD Input 6=331
AEM 2 RTD Input 7=332
AEM 2 RTD Input 8=333
AEM 2 TC Input 1=334
AEM 2 TC Input 2=335
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=336
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=337
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=338
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=339
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=340
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=341
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=342
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=343
AEM 3 RTD Input 1=344
AEM 3 RTD Input 2=345
AEM 3 RTD Input 3=346
AEM 3 RTD Input 4=347
AEM 3 RTD Input 5=348
AEM 3 RTD Input 6=349
AEM 3 RTD Input 7=350
AEM 3 RTD Input 8=351
AEM 3 TC Input 1=352
AEM 3 TC Input 2=353
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=354
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=355
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=356
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=357
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=358
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=359
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=360
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=361
AEM 4 RTD Input 1=362
AEM 4 RTD Input 2=363
AEM 4 RTD Input 3=364
AEM 4 RTD Input 4=365
AEM 4 RTD Input 5=366
AEM 4 RTD Input 6=367
AEM 4 RTD Input 7=368
AEM 4 RTD Input 8=369
AEM 4 TC Input 1=370
AEM 4 TC Input 2=371
AVR Output=372
GOV Output=373
Out-of-Range Activation
Delay
Parameter Minimum GG 7376 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Parameter Maximum GG 7378 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Current Minimum GG 7380 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Current Maximum GG 7382 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Voltage Minimum GG 7384 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Voltage Maximum GG 7386 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
GG 7374 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
LS Output=374
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 86

80 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Output 3
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 4
Alarm Configuration GG 7388 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Parameter Selection GG 7390 Int32 4 R W n/a No Parameter=0
Oil Pressure=1
Coolant Temp=2
Battery Volts=3
RPM=4
Fuel Level=5
Gen Hz=6
Gen VAB=7
Gen VBC=8
Gen VCA=9
Gen Vavg LL=10
Gen VAN=11
Gen VBN=12
Gen VCN=13
Gen Vavg LN=14
Bus 1 Hz=15
Bus 1 VAB=16
Bus 1 VBC=17
Bus 1 VCA=18
Bus 1 Vavg LL=19
Bus 1 VA=20
Bus 1 VB=21
Bus 1 VC=22
Bus 1 Vavg LN=23
Bus 2 Hz=24
Bus 2 VAB=25
Bus 2 VBC=26
Bus 2 VCA=27
Bus 2 Vavg LL=28
Bus 2 VAN=29
Bus 2 VBN=30
Bus 2 VCN=31
Bus 2 Vavg LN=32
Gen PF=33
Bus 1 PF=34
Bus 2 PF=35
Gen Pos kWh=36
Gen Neg kWh=37
Bus 1 Pos kWh=38
Bus 1 Neg kWh=39
Bus 2 Pos kWh=40
Bus 2 Neg kWh=41
Gen IA=42
Gen IB=43
Gen IC=44
Gen I Avg=45
Bus 1 IA=46
Bus 1 IB=47
Bus 1 IC=48
Bus 1 Iavg=49
Bus 2 IAN=50
Bus 2 IBN=51
Bus 2 ICN=52
Bus 2 Iavg=53
IG=54
I Aux=55
Gen kW A=56
Gen kW B=57
Gen kW C=58
Gen kW Total=59
Bus 1 kW A=60
Bus 1 kW B=61
Bus 1 kW C=62
Bus 1 kW Total=63
Bus 2 kW A=64
Bus 2 kW B=65
Bus 2 kW C=66
Bus 2 kW Total=67
Gen kVA A=68
Gen kVA B=69
Gen kVA C=70
Gen kVA Total=71
Bus 1 kVA A=72
Bus 1 kVA B=73
Bus 1 kVA C=74
Bus 1 kVA Total=75
Bus 2 kVA A=76
Bus 2 kVA B=77
Bus 2 kVA C=78
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 87

9469300991 Rev A 81
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus 2 kVA Total=79
Gen kvar A=80
Gen kvar B=81
Gen kvar C=82
Gen kvar Total=83
Bus 1 kvar A=84
Bus 1 kvar B=85
Bus 1 kvar C=86
Bus 1 kvar Total=87
Bus 2 kvar A=88
Bus 2 kvar B=89
Bus 2 kvar C=90
Bus 2 kvar Total=91
Fuel Pressure=92
Injector metering rail
pressure=93
Total Fuel Used=94
Fuel temperature=95
Engine oil temperature=96
Engine intercooler
temperature=97
Coolant pressure=98
Fuel Rate=99
Boost pressure=100
Intake manifold
temperature=101
Charge air temperature=102
Engine Percent Load=103
Analog Input 1=104
Analog Input 2=105
Analog Input 3=106
Analog Input 4=107
kW Load Percent=108
Number of Units Online=109
System kW Capacity=110
System Total Gen kW=111
System Total Gen kvar=112
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=300
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=301
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=302
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=303
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=304
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=305
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=306
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=307
AEM 1 RTD Input 1=308
AEM 1 RTD Input 2=309
AEM 1 RTD Input 3=310
AEM 1 RTD Input 4=311
AEM 1 RTD Input 5=312
AEM 1 RTD Input 6=313
AEM 1 RTD Input 7=314
AEM 1 RTD Input 8=315
AEM 1 TC Input 1=316
AEM 1 TC Input 2=317
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=318
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=319
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=320
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=321
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=322
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=323
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=324
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=325
AEM 2 RTD Input 1=326
AEM 2 RTD Input 2=327
AEM 2 RTD Input 3=328
AEM 2 RTD Input 4=329
AEM 2 RTD Input 5=330
AEM 2 RTD Input 6=331
AEM 2 RTD Input 7=332
AEM 2 RTD Input 8=333
AEM 2 TC Input 1=334
AEM 2 TC Input 2=335
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=336
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=337
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=338
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=339
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=340
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=341
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=342
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=343
AEM 3 RTD Input 1=344
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 88

82 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 4
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 4
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 4
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 4
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 4
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 4
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 4
AEM 1 Remote Analog
Output 4
AEM 2 Input Config. 1 Parameter Minimum GG 7408 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 1 Parameter Maximum GG 7410 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 1 Current Minimum GG 7412 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 1 Current Maximum GG 7414 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 1 Voltage Minimum GG 7416 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 1 Voltage Maximum GG 7418 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 1 Alarm Configuration GG 7420 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 2 Input Config. 2 Parameter Minimum GG 7422 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 2 Parameter Maximum GG 7424 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 2 Current Minimum GG 7426 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 2 Current Maximum GG 7428 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 2 Voltage Minimum GG 7430 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 2 Voltage Maximum GG 7432 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 2 Alarm Configuration GG 7434 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 2 Input Config. 3 Parameter Minimum GG 7436 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 3 Parameter Maximum GG 7438 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 3 Current Minimum GG 7440 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 3 Current Maximum GG 7442 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 3 Voltage Minimum GG 7444 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 3 Voltage Maximum GG 7446 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 3 Alarm Configuration GG 7448 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 2 Input Config. 4 Parameter Minimum GG 7450 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 4 Parameter Maximum GG 7452 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 4 Current Minimum GG 7454 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 4 Current Maximum GG 7456 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 4 Voltage Minimum GG 7458 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Out-of-Range Activation
Delay
Parameter Minimum GG 7394 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Parameter Maximum GG 7396 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Current Minimum GG 7398 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Current Maximum GG 7400 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Voltage Minimum GG 7402 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Voltage Maximum GG 7404 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Alarm Configuration GG 7406 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
GG 7392 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 3 RTD Input 2=345
AEM 3 RTD Input 3=346
AEM 3 RTD Input 4=347
AEM 3 RTD Input 5=348
AEM 3 RTD Input 6=349
AEM 3 RTD Input 7=350
AEM 3 RTD Input 8=351
AEM 3 TC Input 1=352
AEM 3 TC Input 2=353
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=354
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=355
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=356
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=357
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=358
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=359
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=360
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=361
AEM 4 RTD Input 1=362
AEM 4 RTD Input 2=363
AEM 4 RTD Input 3=364
AEM 4 RTD Input 4=365
AEM 4 RTD Input 5=366
AEM 4 RTD Input 6=367
AEM 4 RTD Input 7=368
AEM 4 RTD Input 8=369
AEM 4 TC Input 1=370
AEM 4 TC Input 2=371
AVR Output=372
GOV Output=373
LS Output=374
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 89

9469300991 Rev A 83
AEM 2 Input Config. 7
Parameter Minimum
GG
7492
Float 4 R W
n/a
-999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 1
Arming Delay
GG
7522
Float 4 R W
Second
0 - 300
AEM 2 Input Config. 4 Voltage Maximum GG 7460 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 4 Alarm Configuration GG 7462 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 2 Input Config. 5 Parameter Minimum GG 7464 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 5 Parameter Maximum GG 7466 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 5 Current Minimum GG 7468 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 5 Current Maximum GG 7470 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 5 Voltage Minimum GG 7472 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 5 Voltage Maximum GG 7474 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 5 Alarm Configuration GG 7476 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 2 Input Config. 6 Parameter Minimum GG 7478 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 6 Parameter Maximum GG 7480 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 6 Current Minimum GG 7482 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 6 Current Maximum GG 7484 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 6 Voltage Minimum GG 7486 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 6 Voltage Maximum GG 7488 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 6 Alarm Configuration GG 7490 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 2 Input Config. 7 Parameter Maximum GG 7494 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 7 Current Minimum GG 7496 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 7 Current Maximum GG 7498 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 7 Voltage Minimum GG 7500 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 7 Voltage Maximum GG 7502 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 7 Alarm Configuration GG 7504 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 2 Input Config. 8 Parameter Minimum GG 7506 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 8 Parameter Maximum GG 7508 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Input Config. 8 Current Minimum GG 7510 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 8 Current Maximum GG 7512 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
AEM 2 Input Config. 8 Voltage Minimum GG 7514 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 8 Voltage Maximum GG 7516 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
AEM 2 Input Config. 8 Alarm Configuration GG 7518 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
AEM 2 Protection 1 Hysteresis GG 7520 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7524 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7526 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 1 Alarm
Configuration
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7530 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7532 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 2 Alarm
Configuration
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7536 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7538 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 3 Alarm
Configuration
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7542 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7544 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 1 Threshold 4 Alarm
Configuration
AEM 2 Protection 2 Hysteresis GG 7548 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 2 Protection 2 Arming Delay GG 7550 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7552 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7554 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 1 Alarm
Configuration
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7558 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7560 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 2 Alarm
Configuration
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7564 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7566 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
GG 7528 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7534 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7540 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7546 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7556 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7562 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 90

84 9469300991 Rev A
AEM 2 Protection 5
Threshold 2 Activation Delay
GG
7644
Float 4 R W
Second
0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7570 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7572 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 2 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 3 Hysteresis GG 7576 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 2 Protection 3 Arming Delay GG 7578 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7580 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7582 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7586 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7588 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7592 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7594 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7598 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7600 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 3 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 4 Hysteresis GG 7604 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 2 Protection 4 Arming Delay GG 7606 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7608 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7610 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7614 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7616 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7620 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7622 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7626 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7628 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 4 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 5 Hysteresis GG 7632 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 2 Protection 5 Arming Delay GG 7634 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7636 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7638 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7642 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
GG 7568 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7574 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7584 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7590 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7596 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7602 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7612 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7618 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7624 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7630 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7640 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7648 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7650 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7654 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7656 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 5 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 6 Hysteresis GG 7660 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 2 Protection 6 Arming Delay GG 7662 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7664 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7666 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
GG 7646 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7652 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7658 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Page 91

9469300991 Rev A 85
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7670 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7672 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7676 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7678 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7682 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7684 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 6 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 7 Hysteresis GG 7688 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 2 Protection 7 Arming Delay GG 7690 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7692 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7694 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7698 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7700 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7704 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7706 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7710 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7712 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 7 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 8 Hysteresis GG 7716 Float 4 R W Percent 0 - 100
AEM 2 Protection 8 Arming Delay GG 7718 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Pickup GG 7720 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Activation Delay GG 7722 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 1 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Pickup GG 7726 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Activation Delay GG 7728 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 2 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 3P ickup GG 7732 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Activation Delay GG 7734 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 3 Alarm
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Pickup GG 7738 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Activation Delay GG 7740 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
AEM 2 Protection 8 Threshold 4 Alarm
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 1
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Parameter Selection GG 7744 Int32 4 R W n/a No Parameter=0
GG 7668 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7674 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7680 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7686 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7696 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7702 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7708 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7714 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7724 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7730 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7736 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
GG 7742 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Oil Pressure=1
Coolant Temp=2
Battery Volts=3
RPM=4
Fuel Level=5
Gen Hz=6
Gen VAB=7
Gen VBC=8
Gen VCA=9
Gen Vavg LL=10
Gen VAN=11
Gen VBN=12
Gen VCN=13
Gen Vavg LN=14
Bus 1 Hz=15
Bus 1 VAB=16
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 92

86 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus 1 VBC=17
Bus 1 VCA=18
Bus 1 Vavg LL=19
Bus 1 VA=20
Bus 1 VB=21
Bus 1 VC=22
Bus 1 Vavg LN=23
Bus 2 Hz=24
Bus 2 VAB=25
Bus 2 VBC=26
Bus 2 VCA=27
Bus 2 Vavg LL=28
Bus 2 VAN=29
Bus 2 VBN=30
Bus 2 VCN=31
Bus 2 Vavg LN=32
Gen PF=33
Bus 1 PF=34
Bus 2 PF=35
Gen Pos kWh=36
Gen Neg kWh=37
Bus 1 Pos kWh=38
Bus 1 Neg kWh=39
Bus 2 Pos kWh=40
Bus 2 Neg kWh=41
Gen IA=42
Gen IB=43
Gen IC=44
Gen I Avg=45
Bus 1 IA=46
Bus 1 IB=47
Bus 1 IC=48
Bus 1 Iavg=49
Bus 2 IAN=50
Bus 2 IBN=51
Bus 2 ICN=52
Bus 2 Iavg=53
IG=54
I Aux=55
Gen kW A=56
Gen kW B=57
Gen kW C=58
Gen kW Total=59
Bus 1 kW A=60
Bus 1 kW B=61
Bus 1 kW C=62
Bus 1 kW Total=63
Bus 2 kW A=64
Bus 2 kW B=65
Bus 2 kW C=66
Bus 2 kW Total=67
Gen kVA A=68
Gen kVA B=69
Gen kVA C=70
Gen kVA Total=71
Bus 1 kVA A=72
Bus 1 kVA B=73
Bus 1 kVA C=74
Bus 1 kVA Total=75
Bus 2 kVA A=76
Bus 2 kVA B=77
Bus 2 kVA C=78
Bus 2 kVA Total=79
Gen kvar A=80
Gen kvar B=81
Gen kvar C=82
Gen kvar Total=83
Bus 1 kvar A=84
Bus 1 kvar B=85
Bus 1 kvar C=86
Bus 1 kvar Total=87
Bus 2 kvar A=88
Bus 2 kvar B=89
Bus 2 kvar C=90
Bus 2 kvar Total=91
Fuel Pressure=92
Injector metering rail
pressure=93
Total Fuel Used=94
Fuel temperature=95
Engine oil temperature=96
Engine intercooler
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 93

9469300991 Rev A 87
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
temperature=97
Coolant pressure=98
Fuel Rate=99
Boost pressure=100
Intake manifold
temperature=101
Charge air temperature=102
Engine Percent Load=103
Analog Input 1=104
Analog Input 2=105
Analog Input 3=106
Analog Input 4=107
kW Load Percent=108
Number of Units Online=109
System kW Capacity=110
System Total Gen kW=111
System Total Gen kvar=112
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=300
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=301
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=302
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=303
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=304
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=305
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=306
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=307
AEM 1 RTD Input 1=308
AEM 1 RTD Input 2=309
AEM 1 RTD Input 3=310
AEM 1 RTD Input 4=311
AEM 1 RTD Input 5=312
AEM 1 RTD Input 6=313
AEM 1 RTD Input 7=314
AEM 1 RTD Input 8=315
AEM 1 TC Input 1=316
AEM 1 TC Input 2=317
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=318
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=319
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=320
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=321
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=322
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=323
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=324
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=325
AEM 2 RTD Input 1=326
AEM 2 RTD Input 2=327
AEM 2 RTD Input 3=328
AEM 2 RTD Input 4=329
AEM 2 RTD Input 5=330
AEM 2 RTD Input 6=331
AEM 2 RTD Input 7=332
AEM 2 RTD Input 8=333
AEM 2 TC Input 1=334
AEM 2 TC Input 2=335
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=336
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=337
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=338
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=339
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=340
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=341
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=342
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=343
AEM 3 RTD Input 1=344
AEM 3 RTD Input 2=345
AEM 3 RTD Input 3=346
AEM 3 RTD Input 4=347
AEM 3 RTD Input 5=348
AEM 3 RTD Input 6=349
AEM 3 RTD Input 7=350
AEM 3 RTD Input 8=351
AEM 3 TC Input 1=352
AEM 3 TC Input 2=353
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=354
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=355
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=356
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=357
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=358
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=359
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=360
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=361
AEM 4 RTD Input 1=362
AEM 4 RTD Input 2=363
AEM 4 RTD Input 3=364
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 94

88 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 1
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 4 RTD Input 4=365
AEM 4 RTD Input 5=366
AEM 4 RTD Input 6=367
AEM 4 RTD Input 7=368
AEM 4 RTD Input 8=369
AEM 4 TC Input 1=370
AEM 4 TC Input 2=371
AVR Output=372
GOV Output=373
Out-of-Range Activation
Delay
Parameter Minimum GG 7748 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Parameter Maximum GG 7750 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Current Minimum GG 7752 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Current Maximum GG 7754 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Voltage Minimum GG 7756 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Voltage Maximum GG 7758 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Alarm Configuration GG 7760 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Parameter Selection GG 7762 Int32 4 R W n/a No Parameter=0
GG 7746 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
LS Output=374
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Oil Pressure=1
Coolant Temp=2
Battery Volts=3
RPM=4
Fuel Level=5
Gen Hz=6
Gen VAB=7
Gen VBC=8
Gen VCA=9
Gen Vavg LL=10
Gen VAN=11
Gen VBN=12
Gen VCN=13
Gen Vavg LN=14
Bus 1 Hz=15
Bus 1 VAB=16
Bus 1 VBC=17
Bus 1 VCA=18
Bus 1 Vavg LL=19
Bus 1 VA=20
Bus 1 VB=21
Bus 1 VC=22
Bus 1 Vavg LN=23
Bus 2 Hz=24
Bus 2 VAB=25
Bus 2 VBC=26
Bus 2 VCA=27
Bus 2 Vavg LL=28
Bus 2 VAN=29
Bus 2 VBN=30
Bus 2 VCN=31
Bus 2 Vavg LN=32
Gen PF=33
Bus 1 PF=34
Bus 2 PF=35
Gen Pos kWh=36
Gen Neg kWh=37
Bus 1 Pos kWh=38
Bus 1 Neg kWh=39
Bus 2 Pos kWh=40
Bus 2 Neg kWh=41
Gen IA=42
Gen IB=43
Gen IC=44
Gen I Avg=45
Bus 1 IA=46
Bus 1 IB=47
Bus 1 IC=48
Bus 1 Iavg=49
Bus 2 IAN=50
Bus 2 IBN=51
Bus 2 ICN=52
Bus 2 Iavg=53
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 95

9469300991 Rev A 89
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
IG=54
I Aux=55
Gen kW A=56
Gen kW B=57
Gen kW C=58
Gen kW Total=59
Bus 1 kW A=60
Bus 1 kW B=61
Bus 1 kW C=62
Bus 1 kW Total=63
Bus 2 kW A=64
Bus 2 kW B=65
Bus 2 kW C=66
Bus 2 kW Total=67
Gen kVA A=68
Gen kVA B=69
Gen kVA C=70
Gen kVA Total=71
Bus 1 kVA A=72
Bus 1 kVA B=73
Bus 1 kVA C=74
Bus 1 kVA Total=75
Bus 2 kVA A=76
Bus 2 kVA B=77
Bus 2 kVA C=78
Bus 2 kVA Total=79
Gen kvar A=80
Gen kvar B=81
Gen kvar C=82
Gen kvar Total=83
Bus 1 kvar A=84
Bus 1 kvar B=85
Bus 1 kvar C=86
Bus 1 kvar Total=87
Bus 2 kvar A=88
Bus 2 kvar B=89
Bus 2 kvar C=90
Bus 2 kvar Total=91
Fuel Pressure=92
Injector metering rail
pressure=93
Total Fuel Used=94
Fuel temperature=95
Engine oil temperature=96
Engine intercooler
temperature=97
Coolant pressure=98
Fuel Rate=99
Boost pressure=100
Intake manifold
temperature=101
Charge air temperature=102
Engine Percent Load=103
Analog Input 1=104
Analog Input 2=105
Analog Input 3=106
Analog Input 4=107
kW Load Percent=108
Number of Units Online=109
System kW Capacity=110
System Total Gen kW=111
System Total Gen kvar=112
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=300
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=301
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=302
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=303
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=304
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=305
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=306
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=307
AEM 1 RTD Input 1=308
AEM 1 RTD Input 2=309
AEM 1 RTD Input 3=310
AEM 1 RTD Input 4=311
AEM 1 RTD Input 5=312
AEM 1 RTD Input 6=313
AEM 1 RTD Input 7=314
AEM 1 RTD Input 8=315
AEM 1 TC Input 1=316
AEM 1 TC Input 2=317
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=318
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=319
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 96

90 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 2
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=320
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=321
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=322
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=323
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=324
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=325
AEM 2 RTD Input 1=326
AEM 2 RTD Input 2=327
AEM 2 RTD Input 3=328
AEM 2 RTD Input 4=329
AEM 2 RTD Input 5=330
AEM 2 RTD Input 6=331
AEM 2 RTD Input 7=332
AEM 2 RTD Input 8=333
AEM 2 TC Input 1=334
AEM 2 TC Input 2=335
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=336
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=337
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=338
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=339
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=340
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=341
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=342
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=343
AEM 3 RTD Input 1=344
AEM 3 RTD Input 2=345
AEM 3 RTD Input 3=346
AEM 3 RTD Input 4=347
AEM 3 RTD Input 5=348
AEM 3 RTD Input 6=349
AEM 3 RTD Input 7=350
AEM 3 RTD Input 8=351
AEM 3 TC Input 1=352
AEM 3 TC Input 2=353
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=354
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=355
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=356
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=357
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=358
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=359
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=360
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=361
AEM 4 RTD Input 1=362
AEM 4 RTD Input 2=363
AEM 4 RTD Input 3=364
AEM 4 RTD Input 4=365
AEM 4 RTD Input 5=366
AEM 4 RTD Input 6=367
AEM 4 RTD Input 7=368
AEM 4 RTD Input 8=369
AEM 4 TC Input 1=370
AEM 4 TC Input 2=371
AVR Output=372
GOV Output=373
Out-of-Range Activation
Delay
Parameter Minimum GG 7766 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Parameter Maximum GG 7768 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Current Minimum GG 7770 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Current Maximum GG 7772 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Voltage Minimum GG 7774 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Voltage Maximum GG 7776 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Alarm Configuration GG 7778 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Parameter Selection GG 7780 Int32 4 R W n/a No Parameter=0
GG 7764 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
LS Output=374
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Oil Pressure=1
Coolant Temp=2
Battery Volts=3
RPM=4
Fuel Level=5
Gen Hz=6
Gen VAB=7
Gen VBC=8
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 97

9469300991 Rev A 91
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Gen VCA=9
Gen Vavg LL=10
Gen VAN=11
Gen VBN=12
Gen VCN=13
Gen Vavg LN=14
Bus 1 Hz=15
Bus 1 VAB=16
Bus 1 VBC=17
Bus 1 VCA=18
Bus 1 Vavg LL=19
Bus 1 VA=20
Bus 1 VB=21
Bus 1 VC=22
Bus 1 Vavg LN=23
Bus 2 Hz=24
Bus 2 VAB=25
Bus 2 VBC=26
Bus 2 VCA=27
Bus 2 Vavg LL=28
Bus 2 VAN=29
Bus 2 VBN=30
Bus 2 VCN=31
Bus 2 Vavg LN=32
Gen PF=33
Bus 1 PF=34
Bus 2 PF=35
Gen Pos kWh=36
Gen Neg kWh=37
Bus 1 Pos kWh=38
Bus 1 Neg kWh=39
Bus 2 Pos kWh=40
Bus 2 Neg kWh=41
Gen IA=42
Gen IB=43
Gen IC=44
Gen I Avg=45
Bus 1 IA=46
Bus 1 IB=47
Bus 1 IC=48
Bus 1 Iavg=49
Bus 2 IAN=50
Bus 2 IBN=51
Bus 2 ICN=52
Bus 2 Iavg=53
IG=54
I Aux=55
Gen kW A=56
Gen kW B=57
Gen kW C=58
Gen kW Total=59
Bus 1 kW A=60
Bus 1 kW B=61
Bus 1 kW C=62
Bus 1 kW Total=63
Bus 2 kW A=64
Bus 2 kW B=65
Bus 2 kW C=66
Bus 2 kW Total=67
Gen kVA A=68
Gen kVA B=69
Gen kVA C=70
Gen kVA Total=71
Bus 1 kVA A=72
Bus 1 kVA B=73
Bus 1 kVA C=74
Bus 1 kVA Total=75
Bus 2 kVA A=76
Bus 2 kVA B=77
Bus 2 kVA C=78
Bus 2 kVA Total=79
Gen kvar A=80
Gen kvar B=81
Gen kvar C=82
Gen kvar Total=83
Bus 1 kvar A=84
Bus 1 kvar B=85
Bus 1 kvar C=86
Bus 1 kvar Total=87
Bus 2 kvar A=88
Bus 2 kvar B=89
Bus 2 kvar C=90
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 98

92 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus 2 kvar Total=91
Fuel Pressure=92
Injector metering rail
pressure=93
Total Fuel Used=94
Fuel temperature=95
Engine oil temperature=96
Engine intercooler
temperature=97
Coolant pressure=98
Fuel Rate=99
Boost pressure=100
Intake manifold
temperature=101
Charge air temperature=102
Engine Percent Load=103
Analog Input 1=104
Analog Input 2=105
Analog Input 3=106
Analog Input 4=107
kW Load Percent=108
Number of Units Online=109
System kW Capacity=110
System Total Gen kW=111
System Total Gen kvar=112
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=300
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=301
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=302
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=303
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=304
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=305
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=306
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=307
AEM 1 RTD Input 1=308
AEM 1 RTD Input 2=309
AEM 1 RTD Input 3=310
AEM 1 RTD Input 4=311
AEM 1 RTD Input 5=312
AEM 1 RTD Input 6=313
AEM 1 RTD Input 7=314
AEM 1 RTD Input 8=315
AEM 1 TC Input 1=316
AEM 1 TC Input 2=317
AEM 2 Analog Input 1=318
AEM 2 Analog Input 2=319
AEM 2 Analog Input 3=320
AEM 2 Analog Input 4=321
AEM 2 Analog Input 5=322
AEM 2 Analog Input 6=323
AEM 2 Analog Input 7=324
AEM 2 Analog Input 8=325
AEM 2 RTD Input 1=326
AEM 2 RTD Input 2=327
AEM 2 RTD Input 3=328
AEM 2 RTD Input 4=329
AEM 2 RTD Input 5=330
AEM 2 RTD Input 6=331
AEM 2 RTD Input 7=332
AEM 2 RTD Input 8=333
AEM 2 TC Input 1=334
AEM 2 TC Input 2=335
AEM 3 Analog Input 1=336
AEM 3 Analog Input 2=337
AEM 3 Analog Input 3=338
AEM 3 Analog Input 4=339
AEM 3 Analog Input 5=340
AEM 3 Analog Input 6=341
AEM 3 Analog Input 7=342
AEM 3 Analog Input 8=343
AEM 3 RTD Input 1=344
AEM 3 RTD Input 2=345
AEM 3 RTD Input 3=346
AEM 3 RTD Input 4=347
AEM 3 RTD Input 5=348
AEM 3 RTD Input 6=349
AEM 3 RTD Input 7=350
AEM 3 RTD Input 8=351
AEM 3 TC Input 1=352
AEM 3 TC Input 2=353
AEM 4 Analog Input 1=354
AEM 4 Analog Input 2=355
AEM 4 Analog Input 3=356
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
Page 99

9469300991 Rev A 93
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 3
AEM 2 Remote Analog
Output 4
AEM 4 Analog Input 4=357
AEM 4 Analog Input 5=358
AEM 4 Analog Input 6=359
AEM 4 Analog Input 7=360
AEM 4 Analog Input 8=361
AEM 4 RTD Input 1=362
AEM 4 RTD Input 2=363
AEM 4 RTD Input 3=364
AEM 4 RTD Input 4=365
AEM 4 RTD Input 5=366
AEM 4 RTD Input 6=367
AEM 4 RTD Input 7=368
AEM 4 RTD Input 8=369
AEM 4 TC Input 1=370
AEM 4 TC Input 2=371
AVR Output=372
GOV Output=373
Out-of-Range Activation
Delay
Parameter Minimum GG 7784 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Parameter Maximum GG 7786 Float 4 R W n/a -999999 - 999999
Current Minimum GG 7788 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Current Maximum GG 7790 Float 4 R W Milliamp 4 - 20
Voltage Minimum GG 7792 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Voltage Maximum GG 7794 Float 4 R W Volt 0 - 10
Alarm Configuration GG 7796 Uint32 4 R W n/a Status Only=0
Parameter Selection GG 7798 Int32 4 R W n/a No Parameter=0
GG 7782 Float 4 R W Second 0 - 300
LS Output=374
Pre-Alarm=1
Alarm=2
Oil Pressure=1
Coolant Temp=2
Battery Volts=3
RPM=4
Fuel Level=5
Gen Hz=6
Gen VAB=7
Gen VBC=8
Gen VCA=9
Gen Vavg LL=10
Gen VAN=11
Gen VBN=12
Gen VCN=13
Gen Vavg LN=14
Bus 1 Hz=15
Bus 1 VAB=16
Bus 1 VBC=17
Bus 1 VCA=18
Bus 1 Vavg LL=19
Bus 1 VA=20
Bus 1 VB=21
Bus 1 VC=22
Bus 1 Vavg LN=23
Bus 2 Hz=24
Bus 2 VAB=25
Bus 2 VBC=26
Bus 2 VCA=27
Bus 2 Vavg LL=28
Bus 2 VAN=29
Bus 2 VBN=30
Bus 2 VCN=31
Bus 2 Vavg LN=32
Gen PF=33
Bus 1 PF=34
Bus 2 PF=35
Gen Pos kWh=36
Gen Neg kWh=37
Bus 1 Pos kWh=38
Bus 1 Neg kWh=39
Bus 2 Pos kWh=40
Bus 2 Neg kWh=41
Gen IA=42
Gen IB=43
Gen IC=44
Gen I Avg=45
DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol Default Register Table
Page 100

94 9469300991 Rev A
Name Description Group Register Type Bytes R/W Unit Range
Bus 1 IA=46
Bus 1 IB=47
Bus 1 IC=48
Bus 1 Iavg=49
Bus 2 IAN=50
Bus 2 IBN=51
Bus 2 ICN=52
Bus 2 Iavg=53
IG=54
I Aux=55
Gen kW A=56
Gen kW B=57
Gen kW C=58
Gen kW Total=59
Bus 1 kW A=60
Bus 1 kW B=61
Bus 1 kW C=62
Bus 1 kW Total=63
Bus 2 kW A=64
Bus 2 kW B=65
Bus 2 kW C=66
Bus 2 kW Total=67
Gen kVA A=68
Gen kVA B=69
Gen kVA C=70
Gen kVA Total=71
Bus 1 kVA A=72
Bus 1 kVA B=73
Bus 1 kVA C=74
Bus 1 kVA Total=75
Bus 2 kVA A=76
Bus 2 kVA B=77
Bus 2 kVA C=78
Bus 2 kVA Total=79
Gen kvar A=80
Gen kvar B=81
Gen kvar C=82
Gen kvar Total=83
Bus 1 kvar A=84
Bus 1 kvar B=85
Bus 1 kvar C=86
Bus 1 kvar Total=87
Bus 2 kvar A=88
Bus 2 kvar B=89
Bus 2 kvar C=90
Bus 2 kvar Total=91
Fuel Pressure=92
Injector metering rail
pressure=93
Total Fuel Used=94
Fuel temperature=95
Engine oil temperature=96
Engine intercooler
temperature=97
Coolant pressure=98
Fuel Rate=99
Boost pressure=100
Intake manifold
temperature=101
Charge air temperature=102
Engine Percent Load=103
Analog Input 1=104
Analog Input 2=105
Analog Input 3=106
Analog Input 4=107
kW Load Percent=108
Number of Units Online=109
System kW Capacity=110
System Total Gen kW=111
System Total Gen kvar=112
AEM 1 Analog Input 1=300
AEM 1 Analog Input 2=301
AEM 1 Analog Input 3=302
AEM 1 Analog Input 4=303
AEM 1 Analog Input 5=304
AEM 1 Analog Input 6=305
AEM 1 Analog Input 7=306
AEM 1 Analog Input 8=307
AEM 1 RTD Input 1=308
AEM 1 RTD Input 2=309
AEM 1 RTD Input 3=310
AEM 1 RTD Input 4=311
Default Register Table DGC-2020HD Modbus™ Protocol
 Loading...
Loading...