Page 1

HomePlug AV 200Mbps 4-Port Wireless-N Router
Page 2

User Manual
2008 Copyright. All rights reserved. Version 1.0
No part of this document may be reproduced, republished, or retransmitted in any form or by any means
whatsoever, whether electronically or mechanically, including, but not limited to, by way of photocopying,
recording, information recording, or through retrieval systems without the express written permission. We
reserve the right to revise this document at any time without the obligation to notify any person and/or
entity. All other company or product names mentioned are used for identification purposes only and may
be trademarks of their respective owners.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY AND DAMAGES
THE PRODUCT AND THE SOFTWARES WITHIN ARE PROVIDED "AS IS," BASIS. THE MANUFACTURER AND
MANUFACTURER’S RESELLERS (COLLECTIVELY REFERRED TO AS “THE SELLERS”) DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES,
EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR ANY WARRANTIES ARISING
FROM COURSE OF DEALING, COURSE OF PERFORMANCE, OR USAGE OF TRADE. IN NO EVENT WILL THE SELLERS
BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES OR LOSS, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL WILLFUL,
PUNITIVE, INCIDENTAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL, DAMAGES, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS
PROFITS, OR DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS OF ANY CUSTOMER OR ANY THIRD PARTY ARISING OUT OF THE
USE OR THE INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCT OR THE SOFTWARES, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THOSE
RESULTING FROM DEFECTS IN THE PRODUCT OR SOFTWARE OR DOCUMENTATION, OR LOSS OR INACCURACY OF
DATA OF ANY KIND, WHETHER BASED ON CONTRACT, TORT OR ANY OTHER LEGAL THEORY, EVEN IF THE PARTIES
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE RESULTS AND
PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT OR ITS SOFTWARE IS ASSUMED BY CUSTOMER. BECAUSE SOME STATES DO NOT
ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY
TO THE PARTIES. IN NO EVENT WILL THE SELLERS’ TOTAL CUMULATIVE LIABILITY OF EACH AND EVERY KIND IN
RELATION TO THE PRODUCT OR ITS SOFTWARE EXCEED THE AMOUNT PAID BY CUSTOMER FOR THE PRODUCT.
Page 2 of 73
Page 3

Contents
About the Product
About the Product................................
About the ProductAbout the Product
................................................................
................................................................
Requirements.............................................................................................. 6
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
User Manual
............................................
................................................................
............5555
........................
Package Contents ........................................................................................ 6
Device Design .............................................................................................. 7
Getting Started
Getting Started ................................
Getting StartedGetting Started
................................................................
................................................................
Planning Your Network ............................................................................. 11
Remove or Disable Conflicts ...................................................................... 12
Internet Sharing, Proxy, and Security Applications ................................................12
Configuring TCP/IP Settings.......................................................................................13
Configuring Internet Properties.................................................................................13
Removing Temporary Internet Files .........................................................................14
Setup the Device .......................................................................................15
Connecting to the Internet ........................................................................ 16
Connecting Wireless Devices ..................................................................... 18
Manual Setup ..............................................................................................................18
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) .....................................................................................19
WCN (Windows Connect Now)..................................................................................20
Creating a HomePlug AV Network............................................................. 21
Using Simple Connect Button....................................................................................21
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
..............................................
................................................................
..............10
............................
10
1010
Using HomePlug AV Utility ........................................................................................22
Abo
About the Web Manager
ut the Web Manager ................................
AboAbo
ut the Web Managerut the Web Manager
................................................................
................................................................
Menus........................................................................................................26
Basic Menu ..................................................................................................................26
Advanced Menu ..........................................................................................................26
Maintenance................................................................................................................26
Basic Menu
Basic Menu ................................
Basic MenuBasic Menu
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
Quick Start ................................................................................................. 27
Product Info...............................................................................................29
Advanced Menu
Advanced Menu ................................
Advanced MenuAdvanced Menu
................................................................
................................................................
QoS ............................................................................................................32
StreamEngine ..............................................................................................................32
WISH .............................................................................................................................35
NAT (Network Address Translation) ..........................................................38
Port Forwarding ..........................................................................................................38
Port Trigger..................................................................................................................40
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
...............................................................
................................................................
....................................................
................................................................
...............................25
..............................................................
....................27
........................................
.............................................
................................................................
.............31
..........................
25
2525
27
2727
31
3131
Page 3 of 73
Page 4

User Manual
Virtual Server...............................................................................................................41
DMZ...............................................................................................................................43
Routing...................................................................................................... 44
Static Routing ..............................................................................................................44
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) ..........................................................................46
Security......................................................................................................47
Access Control .............................................................................................................47
Firewall Settings .........................................................................................................48
Inbound Filter ..............................................................................................................52
Inbound Filter Rules List.............................................................................................53
MAC Address Filter (Network Filter).........................................................................53
Website Filter ..............................................................................................................54
Applications............................................................................................... 55
DDNS (Dynamic DNS) .................................................................................................55
Schedules.....................................................................................................................56
Syslog ...........................................................................................................................57
Time..............................................................................................................................58
UPnP .............................................................................................................................59
Wireless.....................................................................................................60
Status ........................................................................................................ 63
Internet Sessions.........................................................................................................63
Logs ..............................................................................................................................64
Routing.........................................................................................................................65
Traffic Status................................................................................................................66
Wireless Clients ...........................................................................................................67
WISH Sessions..............................................................................................................67
Maintenance.............................................................................................. 69
System .........................................................................................................................69
System Settings ..........................................................................................................70
Firmware Upgrade......................................................................................................71
Reboot..........................................................................................................................71
Regulatory Compliance Notices
Regulatory Compliance Notices ................................
Regulatory Compliance NoticesRegulatory Compliance Notices
................................................................
................................................................
FCC Statement ...........................................................................................72
................................................................
................................................................
.....................................................
................................................................
.....................72
..........................................
72
7272
Page 4 of 73
Page 5

User Manual
About the Product
The HomePlug AV 200Mbps 4-port Wireless-N Router offers an All-in-one In-house Networking Device. The
HomePlug wireless router offers high capacity for HD and SD multimedia distribution, while carrying other
Internet services, is easy to use, simple to install and requires no new wires. It instantly converts existing
power lines installations into high-speed virtual Ethernet networks.
The HomePlug Wireless Router combines the benefits of HomePlug AV and 802.11n Wireless-N features,
provides dedicated powerline date rate up to 200Mbps - perfect for streaming HD IPTV and VoD (Video-on-
Demand) while offering full in-house wireless coverage at a speed up to 300Mbps*. On top of that, the
HomePlug wireless router has built-in QoS (Quality-of-Service) engine for enhanced Internet experience.
For powerline security, HomePlugAV 4-port wireless 802.11n Router supports 128-bit Advanced Encryption
Standard (AES) to ensure maximum security. Coupled with "Simple Connect" button to enable the security
and pairing up of HomePlug Adapters at a simple touch of a button. For maximum wireless security, the
HomePlug wireless router supports WEP, WPA and WPA2 with WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) feature.
Applications: High Definition (HD) and Standard Definition (SD) video distribution, TV over IP (IPTV), Higher
data rate broadband sharing, Shared broadband internet access, Audio and video streaming and transfer,
Expanding the coverage of wireless LANs, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), PC files and applications
sharing, Printer and peripheral sharing, Network and online gaming, Security camera.
Page 5 of 73
Page 6

User Manual
Requirements
Your computer must meet the following minimum requirements.
Any operating system can be used
Internet Explorer 4.0 or Netscape Navigator 3.02
233MHz processor
CD-ROM Drive
Ethernet network adapter
Package Contents
Package contents are listed below. For any missing items, please contact your dealer immediately. Product
contents vary for different models.
Router
Ethernet cable
+12VDC, 1.67A Power Adapter
Easy Start Guide
Resource CD
Page 6 of 73
Page 7

Device Design
Front Panel
Front Panel
Front PanelFront Panel
User Manual
HHHH
GGGG
FFFF
EEEE
DDDD
CCCC
AAAA
BBBB
Page 7 of 73
Page 8
User Manual
Label
AAAA Simple Connect
CCCC Powerline
DDDD USB
EEEE WLAN
Label Action
LabelLabel
Simple Connect
Simple ConnectSimple Connect
Button
Button
Button Button
Power
PowerPower
Powerline
Powerline Powerline
Activity
Activity
Activity Activity
USB Blinking light Will blink 3 times indicating Windows Connect Now (WCN)
USBUSB
WLAN
WLANWLAN
Action Description
ActionAction
Press for 2 seconds to create or join a HomePlug AV
network.
Press for 10 seconds to reset the Private Network Name to
a random key.
Off No power is supplied to the device BBBB Power
Steady light Connected to an AC power supply
Off No Homeplug connection
Steady light Homeplug connection established
The LED colors represents the connection rate within the
HomePlug AV network whether it is good (red), better
(amber), or best (green).
Blinking light Transmitting/Receiving data
Process
Off Wireless Disabled
Description
DescriptionDescription
FFFF WAN
WAN
WANWAN
GGGG Ethernet 1
Ethernet 1----4
Ethernet 1Ethernet 1
HHHH WPS
WPS
WPSWPS
(Wi
(Wi----Fi Protected
Fi Protected
(Wi(Wi
Fi Protected Fi Protected
Setup)
Setup)
Setup)Setup)
4
4 4
Steady Light Wireless Enabled
Blinking light Transmitting/Receiving data wirelessly
Off No modem connection
Steady light Connected to an active modem
Blinking light Transmitting/Receiving data
Off No Ethernet connection
Steady light Connected to an active Ethernet device
Blinking light Transmitting/Receiving data
Press for two seconds (or until the LED blinks) to start WPS
pairing.
Wireless client must be WPS-enabled and must be pressed
within 3 minutes.
Page 8 of 73
Page 9

Back Panel
Back Panel
Back PanelBack Panel
User Manual
Label
1111 Power
2222 USB
3333 Reset
4444 WAN
5555 Ethernet 1
6666 Antenna 1
Label Used for…
LabelLabel
Power Connecting the +12VDC, 1.67A DC power adapter
PowerPower
USB Windows Connect Now (WCN)
USBUSB
Reset Press for 10 seconds to reset the router
ResetReset
WAN Connecting with a modem using an Ethernet cable
WANWAN
Ethernet 1----4444 Connecting with computers/devices using an Ethernet cable
Ethernet 1Ethernet 1
Antenna 1----3333 Sending/receiving wireless signals
Antenna 1Antenna 1
Used for…
Used for…Used for…
Page 9 of 73
Page 10
User Manual
setting or disable some application
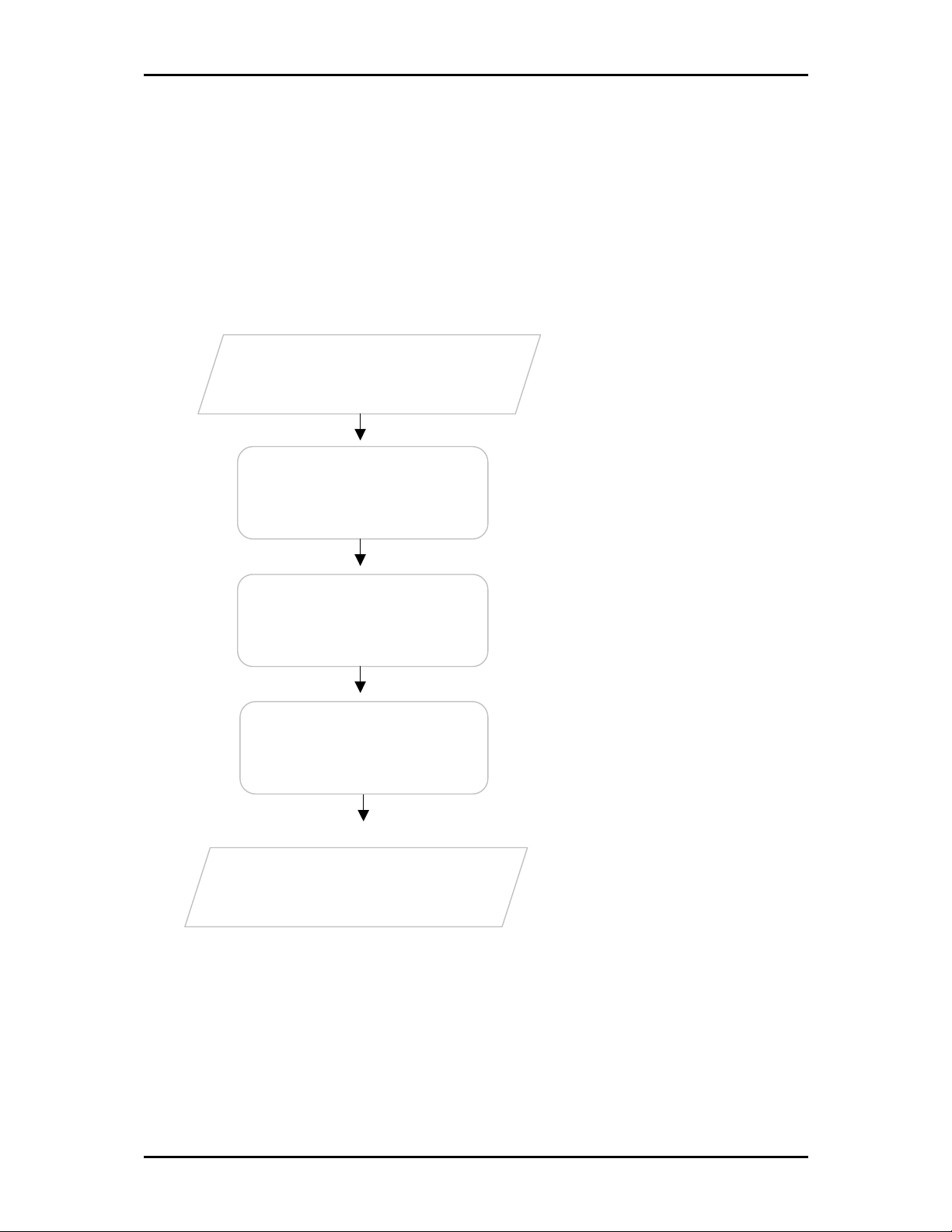
Getting Started
Setting up the device is easy. The flowchart below provides an outline of the steps needed to complete the
installation. Brief descriptions appear beside each step. Detailed instructions are provided in the
subsequent pages.
Plan your Network
Remove/Disable
Conflicts
Setup the Router
Connect to the
Internet
Ready to Use
You may need to check some
before installation.
Connect the modem, computer, and
power adaptor to the router.
Open a browser to access the Web
Manager and then use Setup Wizard
to connect to the Internet.
Page 10 of 73
Page 11
User Manual
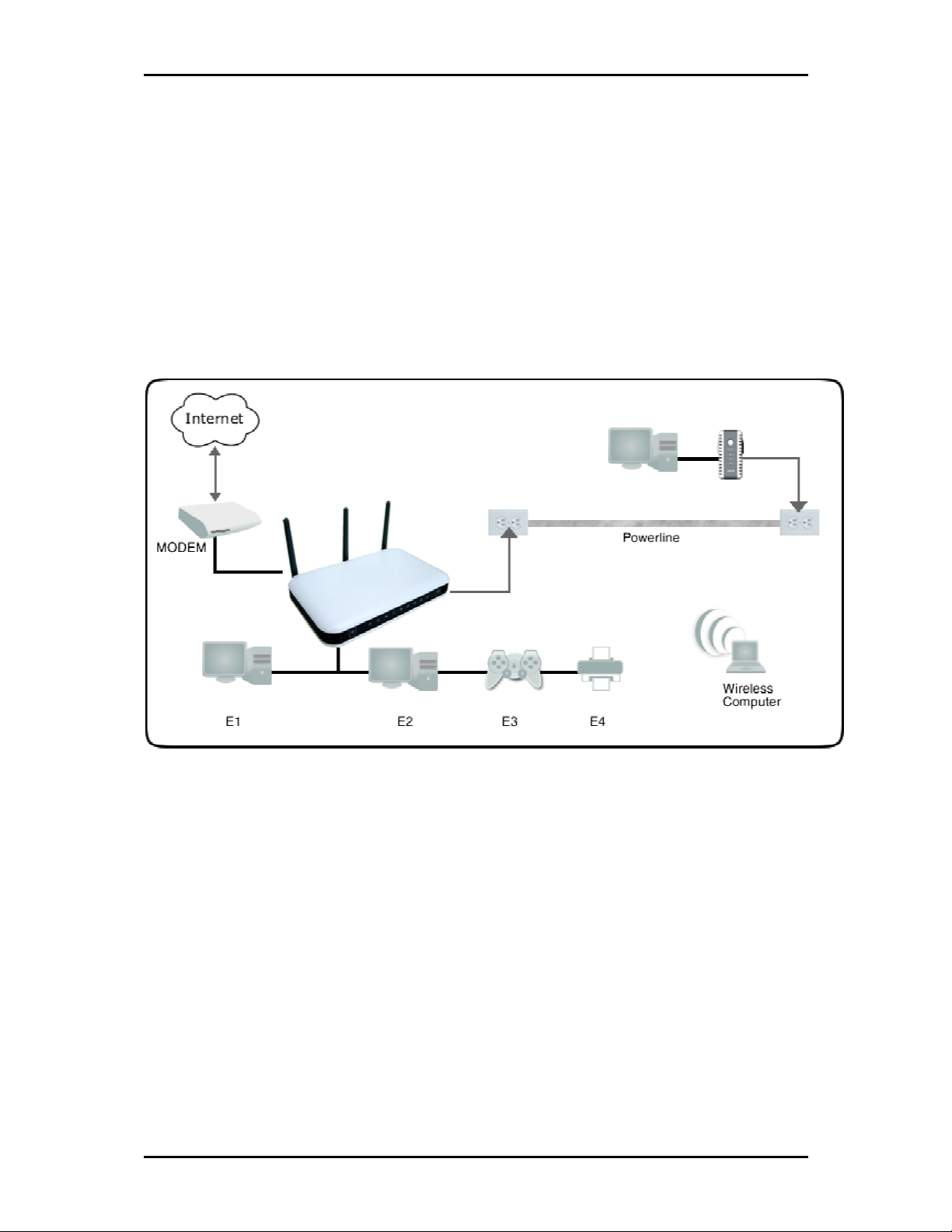
Planning Your Network
Before moving ahead to setup your network, it is a good idea to draw out a network diagram to help
identify your network devices and plan out how to connect these devices. The illustration below is an
example of a network diagram.
To create a network diagram:
For wireless devices, identify the wireless devices you want to include in the network
For wired devices, identify which router port you want to use for each device.
For HomePlug devices, identify the HomePlug devices you want to include in the network.
Page 11 of 73
Page 12

User Manual
Remove or Disable Conflicts
To make sure the router installation moves on smoothly, you need to remove or disable conflicts that may
interfere the installation. Probable conflicts may include:
Internet sharing applications
Proxy software
Security software
TCP/IP settings
Internet properties
Temporary Internet files
Internet Sharing, Proxy, and Security Applications
Internet sharing, proxy software, and firewall applications may interfere with the router installation. These
should be removed or disabled before start the installation.
If you have any of the following or similar applications installed on your computer, remove or disable them
according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Internet Sharing Applications
Internet Sharing Applications Proxy Software
Internet Sharing ApplicationsInternet Sharing Applications
Microsoft Internet Sharing WinGate Symantec
WinProxy Zone Alarm
Proxy Software Security Software
Proxy SoftwareProxy Software
Security Software
Security SoftwareSecurity Software
Page 12 of 73
Page 13

Configuring TCP/IP Settings
Check if your computer uses the default TCP/IP settings.
To check the TCP/IP properties:
1. Click the Start button, and then click Run. This opens the Run dialog box.
2. Type control ncpa.cpl, and then click OK. This opens the Network Connections in your computer.
3. Right-click LAN, and then select Properties. This opens the Local Area Connection Properties dialog
box.
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties. This opens the Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) dialog box.
5. Check Obtain an IP address automatically.
6. To close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) dialog box, click OK.
User Manual
7. To close the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, click OK.
Configuring Internet Properties
To set the Internet Properties:
1. Click the Start button, and then click Run. This opens the Run dialog box.
2. Type control inetcpl.cpl, and then click OK. This opens Internet Properties.
3. Click Connections tab.
4. In Dial-up and Virtual Private Network settings, check Never dial a connection.
5. To close Internet Properties, click OK.
Page 13 of 73
Page 14

User Manual
Removing Temporary Internet Files
Temporary Internet files are files from Web sites that are stored in your computer. Delete these files to
clean the cache and remove footprints left by the Web pages you visited.
To remove temporary Internet files:
1. Click the Start button, and then click Run. This opens the Run dialog box.
2. Type control, and then click OK. This opens Control Panel.
3. Double-click Internet Options. This opens Internet Options.
4. In the Temporary Internet Files pane, click Delete Cookies.
5. Click Delete Files.
6. To close Internet Properties, click OK.
Page 14 of 73
Page 15
User Manual
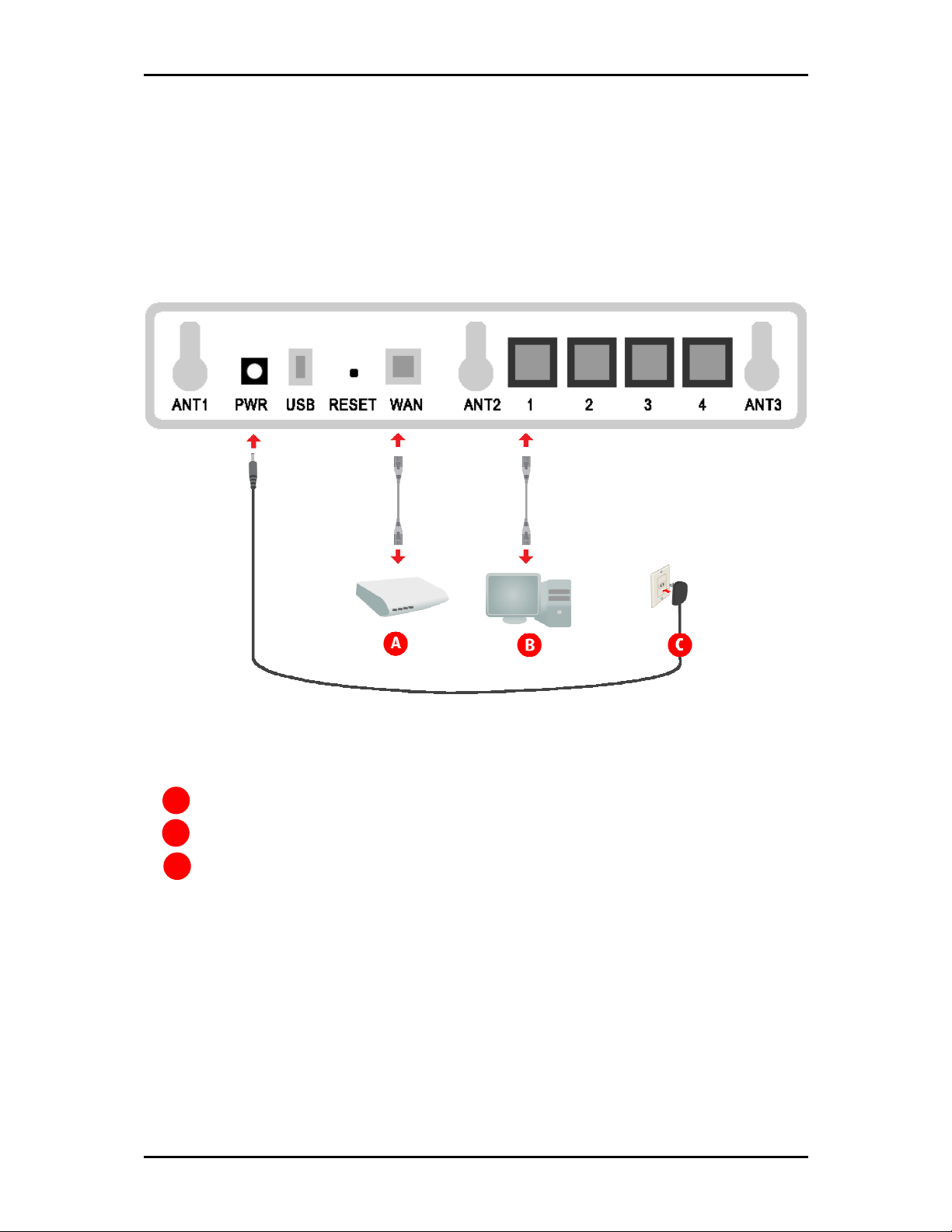
Setup the Device
When installing the router, find an area where there are enough electrical outlets for the router, the main
computer, and your other computer devices.
To setup the router:
AAAA Use an Ethernet cable to connect a modem to the WAN port.
BBBB Use an Ethernet cable to connect a computer to any of the available Ethernet ports from 1-4.
CCCC Connect the power adapter and then plug it to an electrical source.
Page 15 of 73
Page 16
User Manual
Connecting to the Internet
To connect to the Internet, use the Web Manager’s Setup Wizard.
Note:
Note: To connect to the Internet, make sure that your router is connected to a modem and you have an
Note:Note:
active Internet service account.
To connect to the Internet via the Web Interface:
1. Open your browser.
2. Type 192.168.1.1 in the address field and then press Enter. This opens the Log In Authentication
page.
3. Type your Username and Password. The default username is admin, with blank password.
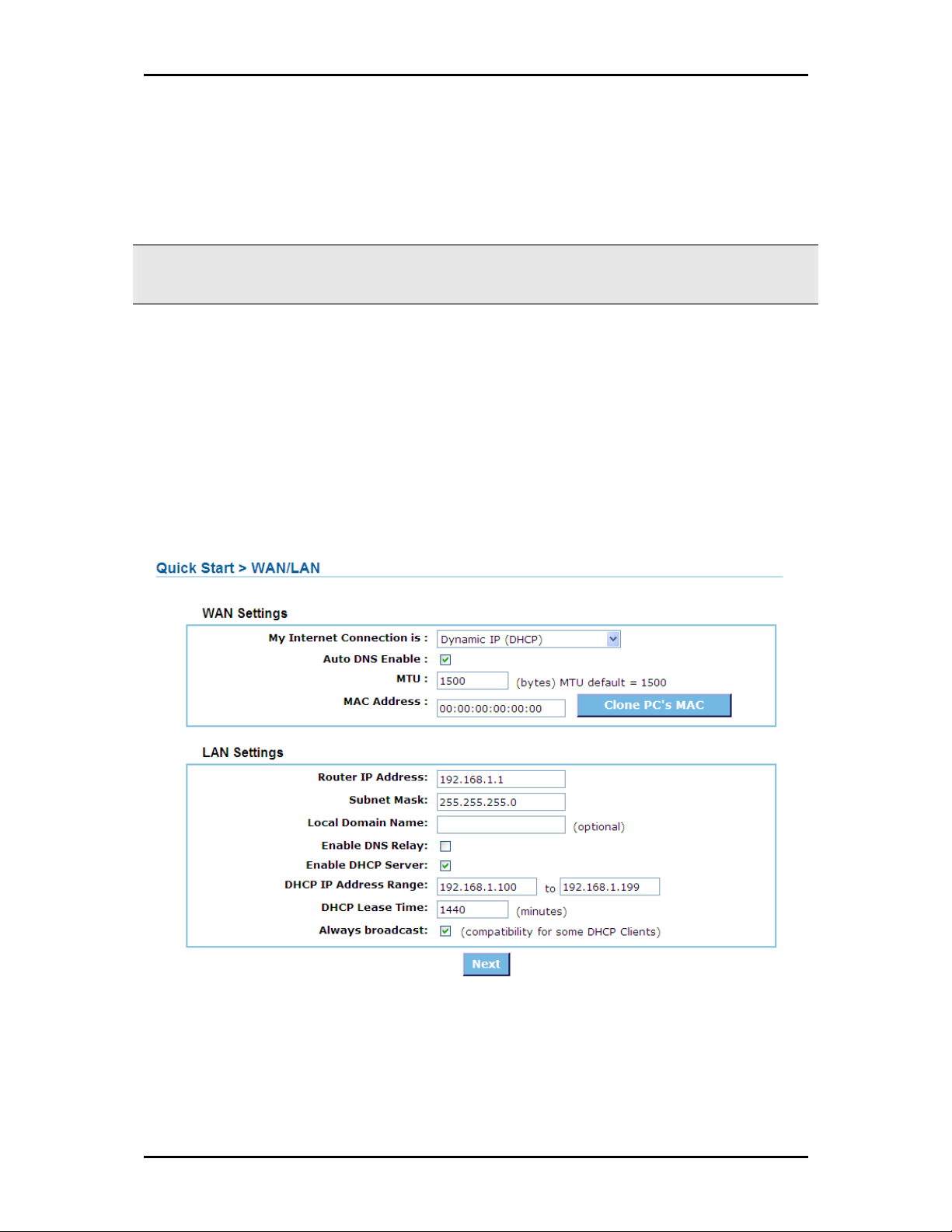
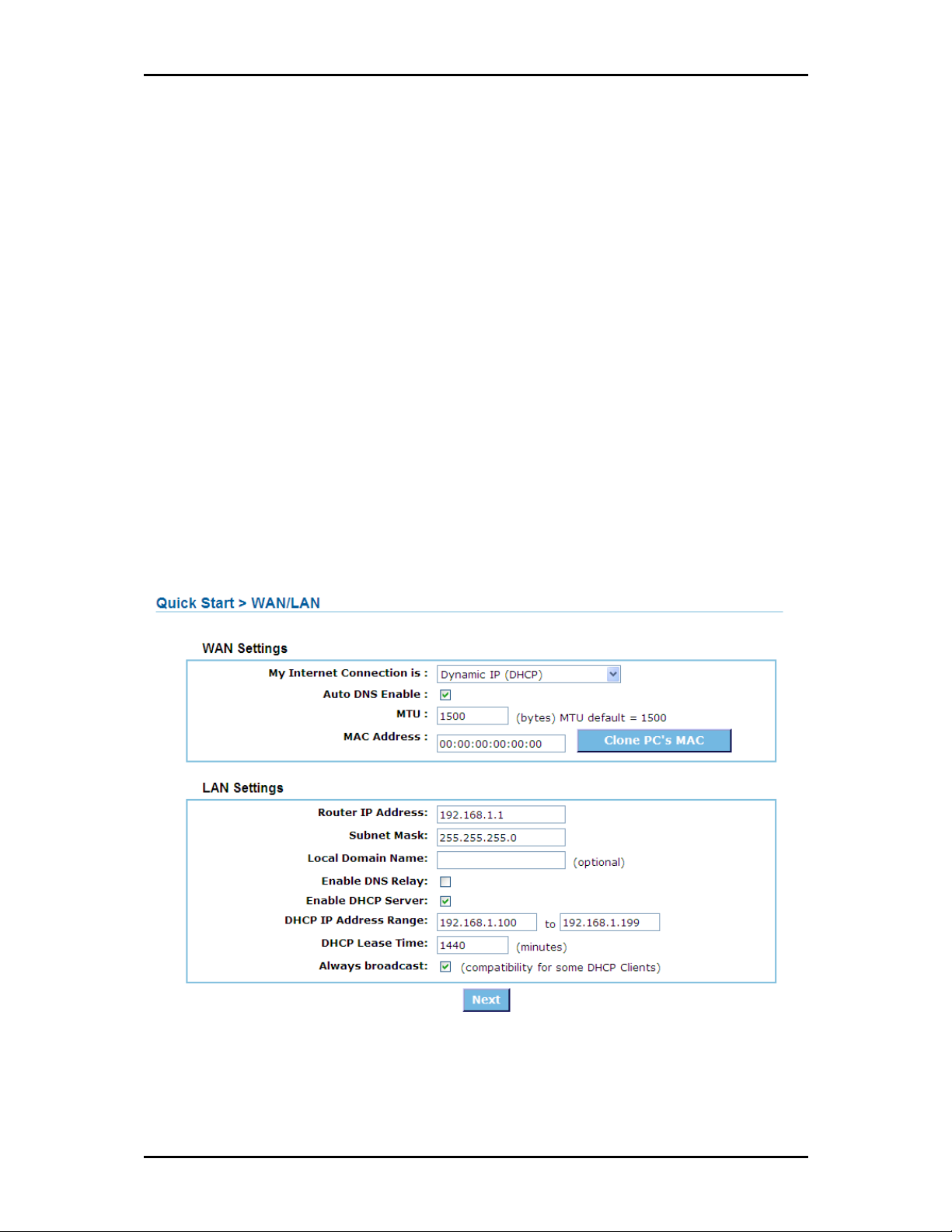
4. Quick Start Setup opens. You will be asked to provide the WAN and LAN Settings.
5. Configure the WAN and LAN settings, and click Next.
Page 16 of 73
Page 17
User Manual
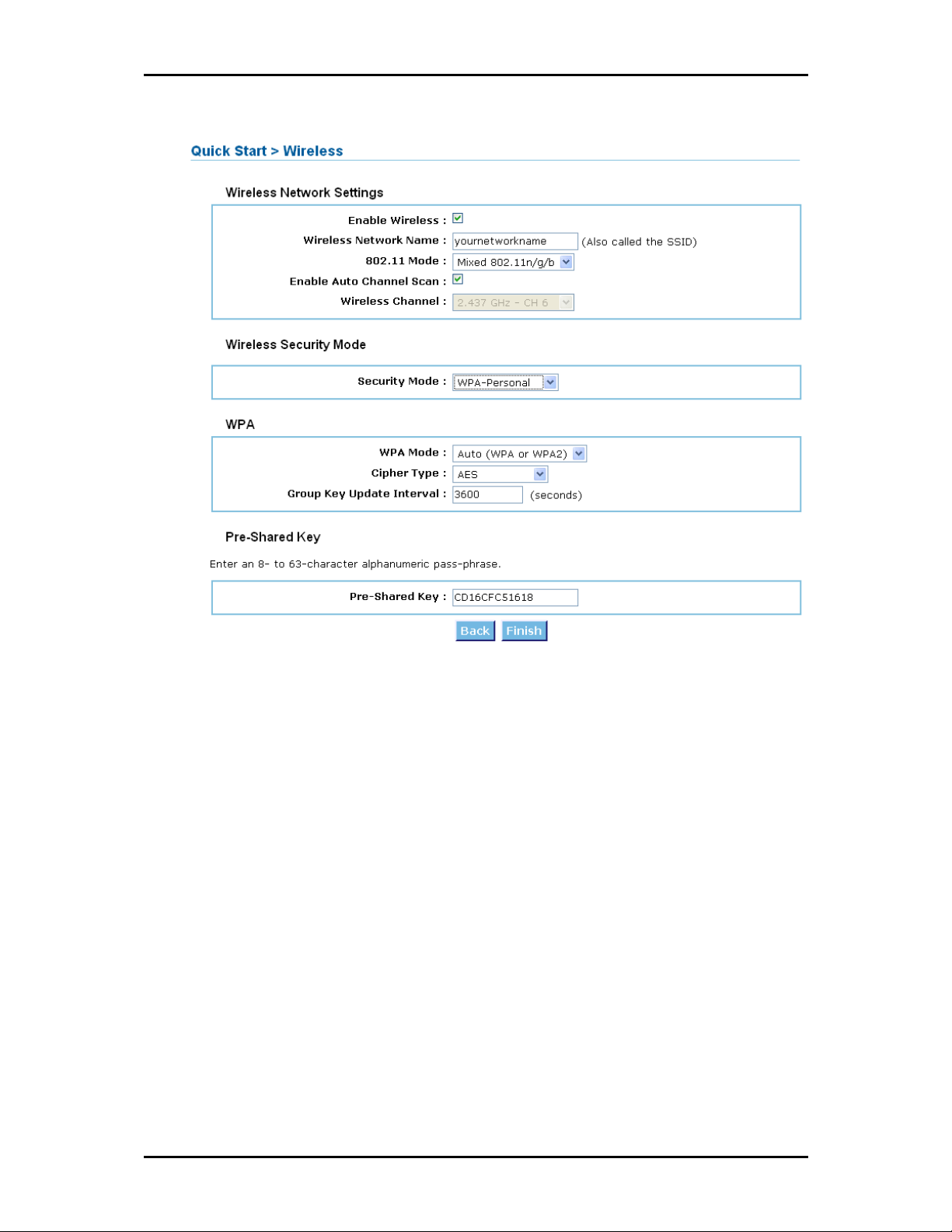
6. Configure the Wireless Network Settings including the Wireless Security Mode and click Finish.
7. After you click Finish, the router will save the new settings and then try to establish a connection
with your Internet service provider.
To verify if your connection has been successful, click Product Info under the Basic Menu. A WAN IP
address will appear under the WAN Connection Information pane.
Page 17 of 73
Page 18

User Manual
Connecting Wireless Devices
Manual Setup
Using WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
Using WCN (Windows Connect Now)
Manual Setup
After you setup the Router settings through the main computer, you can connect other devices with
wireless capabilities. Wireless devices relieve you from the task of laying out cables and allow you to use
the Internet connection from your router.
To connect with wireless devices:
1. Turn on your wireless device.
2. Open the software you use to detect a wireless connection. This opens a window to ask for the
connection settings.
3. Enter the connection settings for the wireless network. These settings are defined in your router
during setup.
Page 18 of 73
Page 19

User Manual
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
WPS button allows you to enable Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS). When enabled, Wi-Fi Protected Setup
automatically detects and connects wireless clients into the wireless network by broadcasting the wireless
network settings from your Access Point to you wireless device/s.
To setup WPS:
1. Press the WPS button on the router for two seconds, or until the LED blinks
2. Within 3 minutes, press the WPS button on the Wireless Client.
Note:
Note: WPS can only be used with wireless client devices that have a compatible WPS component.
Note:Note:
Page 19 of 73
Page 20

User Manual
WCN (Windows Connect Now)
WCN (Windows Connect Now) technology allows users to easily create a wireless network and add
additional wireless devices using a USB flash drive.
With Windows Connect Now, users running Windows XP Service Pack 2 and later Windows OS version can
create wireless network configuration settings and transmit them to the access point and other wireless
devices.
To setup WCN (Windows Connect Now):
1. Click Start and then click Control Panel.
2. For Control Panel Category View: click Network and Internet Connections, and then click Wireless
Network Setup Wizard.
For Control Panel Classic View: click Wireless Network Setup Wizard.
3. Follow the instructions on your screen.
4. Choose "Use a USB flash drive"
5. Insert the USB Flash drive into your computer. Wireless network configuration settings will be
saved to the flash drive.
6. Plug the flash drive into your Access Point, wireless client or Windows Connect Now compatible
device that you want to add to the wireless network.
Note:
Note: Windows Connect Now can only be used with WCN compatible devices.
Note:Note:
Page 20 of 73
Page 21
User Manual
Creating a HomePlug AV Network
HomePlug AV utilizes the existing electrical wiring in the house as a path to create a secured network of
computers and Ethernet devices. With a maximum data rate of up to 200 Mbps, HomePlug AV can reliably
handle high requirement applications like broadband Internet, high definition video streaming, and Voice
over IP. HomePlug AV converts digital signals to a complex analog signal that traverses along the electrical
wires. When receiving the analog signal, HomePlug AV converts the analog signal back to digital. To make
the signal secured, a 128-bit AES encryption is applied.
To create a HomePlug AV network, you need at least two HomePlug AV devices using random Private
Network Names. When you press Simple Connect on both devices, a common Private Network Name
will be automatically generated to enable them to communicate with each other.
When a HomePlug AV communicates with another device, the Powerline Activity LED color will give you
an idea about the connection rate: red means below 40 Mbps; amber means 40 to 105 Mbps; and green
means more than 105 Mbps.
Using Simple Connect Button
Simple Connect provides a more convenient way of creating your HomePlug AV network without the
need to open the HomePlug AV Utility software from a computer.
To create a HomePlug AV network using Simple Connect:
Plug your HomePlug AV adaptor near your Router where you can easily observe the LED behavior.
1. Upon connection, the LEDs will blink simultaneously and then the Power LED lights on steadily.
2. Press Simple Connect for two seconds on your Router. After you release the button, the Simple
Connect will blink. If the Simple Connect did not blink, press the button again for two
seconds.
Note:
Note: Do not press Simple Connect for more than 2 seconds.
Note:Note:
3. Press Simple Connect for two seconds on your HomePlug AV adaptor. After you release the button,
the Simple Connect will blink. If the Simple Connect did not blink, press button again for
two seconds.
Page 21 of 73
Page 22

User Manual
4. Make sure to press Simple Connect on your HomePlug AV adaptor within two minutes after you
press Simple Connect on your Router. The LEDs on both devices will switch off and on twice to
signify that they are searching for another device to pair with.
5. To confirm if the connection was established, check the LEDs. The Power LEDs and the Powerline
Activity LEDs on your Router and HomePlug Adaptor are on. When the Powerline Activity LED on
either Router or HomePlug Adaptor is off, this means the pairing is not successful. In this case,
press the Simple Connect button for 10 seconds (or until all the LEDs turns Off and On) to reset to a
random Private Network Name, and redo the Pairing process.
6. Unplug the HomePlug AV adaptor and then connect it to your Ethernet-enabled device using an
Ethernet cable. After connecting the Ethernet cable, plug the HomePlug adaptor directly to a wall
outlet.
Note:
Note: HomePlug AVs work best when connected directly to a wall socket. Avoid plugging it to a power strip
Note:Note:
or power extension. Other electrical devices in the power strip produce electrical noise that may affect the
performance of the HomePlug.
Using HomePlug AV Utility
HomePlug AV Utility is a software application that allows you to configure HomePlug AV. To create a
HomePlug AV network using HomePlug AV Utility:
1. Install HomePlug AV Utility to your computer. Utility installer can be found in the Resource CD
included with your Router.
2. After installation, click the Start button, click Programs, click HomePlug AV, click HomePlug AV
Ethernet Adapter, and then click HomePlug AV Utility.
Page 22 of 73
Page 23

3. Select Private Network Name Tab.
User Manual
4. Type the new Private Network Name. This field is case sensitive. It accepts 8 to 64 alphanumeric
characters including punctuation marks but no spaces.
5. Click Apply. When the process is complete, the message Settings Applied appears.
To setup the Private Network Name of a remote HomePlug AV Adaptor:
1. Select Change Private Network Name of remote device.
2. Type the Device ID of the remote device. The Device ID can be found on the label pasted on the
device.
Page 23 of 73
Page 24

User Manual
3. Click Apply. When the process is complete, the message Settings Applied appears.
Page 24 of 73
Page 25

User Manual
About the Web Manager
The Web User Interface gives you the capability to configure the router settings. It is divided into the
following sections:
Basic Menu
Advanced Menu
Maintenance Menu
To access the Web User Interface:
Open a browser after setting up the device.
Enter 192.168.1.1.
Enter the User Name and Password. The default User Name is
admin,
and the Password is
blank.
Page 25 of 73
Page 26

User Manual
Menus
The web interface includes the following menus:
Basic Menu
Provides the Setup Wizard link and Product Information.
Advanced Menu
The Advanced Menu provides advanced router configuration settings.
Maintenance
The Maintenance Menu provides System Settings and Firmware Upgrade feature.
Page 26 of 73
Page 27
User Manual
Basic Menu
The options for the Basic Menu include:
Quick Start
Product Info
WPS
Quick Start
Setup Wizard gives you the ability to instantly connect to the Internet and configure the Web Manager
settings.
Page 27 of 73
Page 28

User Manual
To use Quick Start:
Under Basic Menu, click Quick Setup. This opens the Setup Wizard.
Configure the WAN and LAN Settings, and click Next.
Configure the Wireless Network Settings including the Wireless Security Mode and click Finish.
After you click Finish, the router will save the new settings and then try to establish a connection with your
Internet service provider.
To verify if your connection has been successful, click Product Info under the Basic Menu. A WAN IP address
will appear under the WAN Connection Information pane.
Page 28 of 73
Page 29
User Manual
Product Info
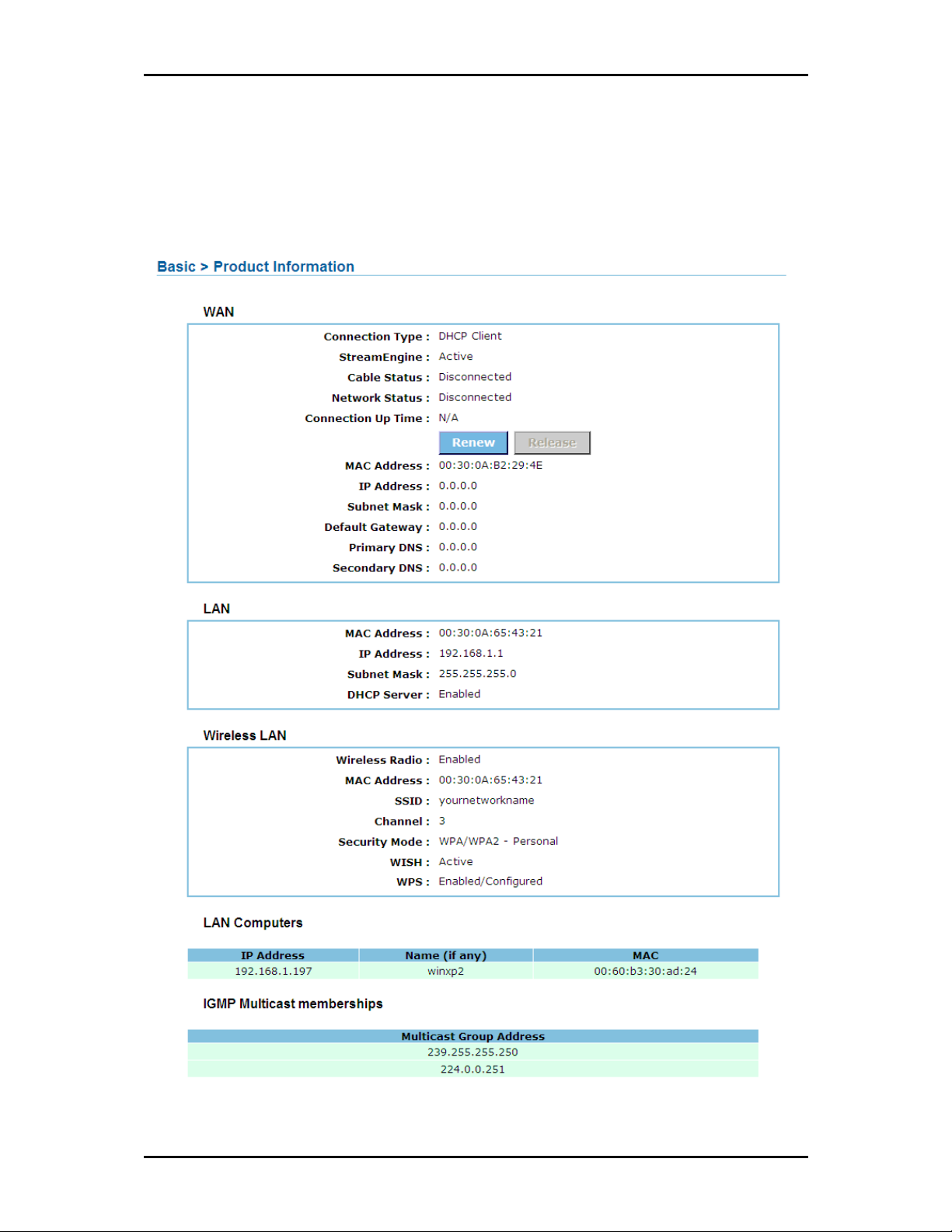
The Product Info page provides a one-page summary about the Connection Information, Router
Information, Local Network Information, and Wireless Network settings.
Page 29 of 73
Page 30

User Manual
WAN Information
The Connection Information pane gives you an idea about the status of your Internet connection. This pane
includes a Renew/Release button or Connect/Disconnect button (depending on your WAN Connection
Type. When clicked, the router makes an attempt to connect to the Internet using the parameters saved in
the router.
LAN Information
This pane provides all the necessary information to determine the firmware version, LAN MAC Address, LAN
IP Address, and DHCP Server status.
Wireless LAN Information
This pane displays the current wireless configuration settings for the router’s access point.
LAN Computers
Displays the MAC Address, Computer Name, and IP Address of Computers connected to the Router.
IGMP Multicast memberships
If IGMP is enabled, this area of the screen shows all multicast groups of which any LAN devices are
members.
Page 30 of 73
Page 31

Advanced Menu
The options for the Advanced Menu include:
QoS
NAT
Routing
Security
Wireless
Applications
Status
User Manual
Page 31 of 73
Page 32

User Manual
QoS
QoS options include:
StreamEngine
WISH
StreamEngine
The StreamEngine feature helps improve your network performance by prioritizing applications.
Page 32 of 73
Page 33

User Manual
WAN Traffic Shaping
Enab
Enable Traffic Shaping
le Traffic Shaping When this option is enabled, the router restricts the flow of outbound traffic so as
EnabEnab
le Traffic Shaping le Traffic Shaping
not to exceed the WAN uplink bandwidth.
Automatic Uplink Speed
Automatic Uplink Speed When enabled, this option causes the router to automatically measure the useful
Automatic Uplink SpeedAutomatic Uplink Speed
uplink bandwidth each time the WAN interface is re-established (after a reboot, for example).
Measured Uplink Speed
Measured Uplink Speed This is the uplink speed measured when the WAN interface was last re-established.
Measured Uplink SpeedMeasured Uplink Speed
The value may be lower than that reported by your ISP as it does not include all of the network protocol
overheads associated with your ISP's network. Typically, this figure will be between 87% and 91% of the
stated uplink speed for xDSL connections and around 5 kbps lower for cable network connections.
Manual Uplink S
Manual Uplink Speed
Manual Uplink SManual Uplink S
manually. Uplink speed is the speed at which data can be transferred from the router to your ISP. This is
determined by your ISP. ISPs often specify speed as a downlink/uplink pair; for example,
1.5Mbps/284kbps. For this example, you would enter "284".
peed If Automatic Uplink Speed is disabled, this options allows you to set the uplink speed
peedpeed
Connection Type
Connection Type By default, the router automatically determines whether the underlying connection is an
Connection TypeConnection Type
xDSL/Frame-relay network or some other connection type (such as cable modem or Ethernet), and it
displays the result as Detected xDSL or Frame Relay Network. If you have an unusual network connection in
which you are actually connected via xDSL but for which you configure either "Static" or "DHCP" in the WAN
settings, setting this option to xDSL or Other Frame Relay Network ensures that the router will recognize
that it needs to shape traffic slightly differently in order to give the best performance. Choosing xDSL or
Other Frame Relay Network causes the measured uplink speed to be reported slightly lower than before on
such connections, but gives much better results.
Detected xDSL or Frame Relay Network
Detected xDSL or Frame Relay Network When Connection Type is set to Auto-detect, the automatically
Detected xDSL or Frame Relay Network Detected xDSL or Frame Relay Network
detected connection type is displayed here.
StreamEngine Setup
Enable StreamEngine
Enable StreamEngine Enable this option for better performance and experience with online games and
Enable StreamEngineEnable StreamEngine
other interactive applications, such as VoIP.
Automatic Classification
Automatic Classification This option is enabled by default so that your router will automatically determine
Automatic ClassificationAutomatic Classification
which programs should have network priority. For best performance, use the Automatic Classification
option to automatically set the priority for your applications.
Dynamic Fragmentation
Dynamic Fragmentation This option should be enabled when you have a slow Internet uplink. It helps to
Dynamic FragmentationDynamic Fragmentation
reduce the impact that large low priority network packets can have on more urgent ones by breaking the
large packets into several smaller packets.
Page 33 of 73
Page 34

User Manual
Add/Edit StreamEngine Rules
A StreamEngine Rule identifies a specific message flow and assigns a priority to that flow. For most
applications, automatic classification will be adequate, and specific StreamEngine Rules will not be
required.
StreamEngine supports overlaps between rules, where more than one rule can match for a specific
message flow. If more than one rule is found to match the rule with the highest priority will be used.
Enable
Enable Specifies whether the entry will be active or inactive.
EnableEnable
Name
Name Create a name for the rule that is meaningful to you.
NameName
Priority
Priority The priority of the message flow is entered here -- 0 receives the highest priority (most urgent)
PriorityPriority
and 255 receives the lowest priority (least urgent).
Protocol
Protocol The protocol used by the messages.
ProtocolProtocol
Local IP Range
Local IP Range The rule applies to a flow of messages whose LAN-side IP address falls within the range set
Local IP RangeLocal IP Range
here.
Local Port Range
Local Port Range The rule applies to a flow of messages whose LAN-side port number is within the range
Local Port RangeLocal Port Range
set here.
Remote IP Range
Remote IP Range The rule applies to a flow of messages whose WAN-side IP address falls within the range
Remote IP RangeRemote IP Range
set here.
Remote Port Range
Remote Port Range The rule applies to a flow of messages whose WAN-side port number is within the
Remote Port RangeRemote Port Range
range set here.
Save/Update
Save/Update Record the changes you have made into the following list.
Save/UpdateSave/Update
Clear
Clear Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
ClearClear
StreamEngine Rules
This section lists all the defined StreamEngine Rules. Click the Enable checkbox at the left to directly
activate or de-activate the entry. An entry can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or can be deleted by
clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit StreamEngine
Rule" section is activated for editing.
Page 34 of 73
Page 35

User Manual
WISH
WISH is short for Wireless Intelligent Stream Handling, a technology developed to enhance your experience
of using a wireless network by prioritizing the traffic of different applications.
WISH
Enable WISH
Enable WISH Enable this option if you want to allow WISH to prioritize your traffic.
Enable WISHEnable WISH
Priority Classifiers
HTTP
HTTP Allows the router to recognize HTTP transfers for many common audio and video streams and
HTTPHTTP
prioritize them above other traffic. Such streams are frequently used by digital media players.
Page 35 of 73
Page 36

User Manual
Windows Media Center
Windows Media Center Enables the router to recognize certain audio and video streams generated by a
Windows Media CenterWindows Media Center
Windows Media Center PC and to prioritize these above other traffic. Such streams are used by systems
known as Windows Media Extenders, such as the Xbox 360.
Automatic
Automatic When enabled, this option causes the router to automatically attempt to prioritize traffic streams
AutomaticAutomatic
that it doesn't otherwise recognize, based on the behaviour that the streams exhibit. This acts to
deprioritize streams that exhibit bulk transfer characteristics, such as file transfers, while leaving interactive
traffic, such as gaming or VoIP, running at a normal priority.
Add/Edit WISH Rule
A WISH Rule identifies a specific message flow and assigns a priority to that flow. For most applications, the
priority classifiers ensure the right priorities and specific WISH Rules are not required.
WISH supports overlaps between rules. If more than one rule matches for a specific message flow, the rule
with the highest priority will be used.
Enable
Enable Specifies whether the entry will be active or inactive.
EnableEnable
Name
Name Create a name for the rule that is meaningful to you.
NameName
Priority
Priority The priority of the message flow is entered here. Four priorities are defined:
PriorityPriority
BK: Background (least urgent).
BE: Best Effort.
VI: Video.
VO: Voice (most urgent).
Protocol
Protocol The protocol used by the messages.
ProtocolProtocol
Host 1 IP Range
Host 1 IP Range The rule applies to a flow of messages for which one computer's IP address falls within the
Host 1 IP RangeHost 1 IP Range
range set here.
Host 1 Port Range
Host 1 Port Range The rule applies to a flow of messages for which host 1's port number is within the
Host 1 Port RangeHost 1 Port Range
range set here.
Host 2 IP Range
Host 2 IP Range The rule applies to a flow of messages for which the other computer's IP address falls
Host 2 IP RangeHost 2 IP Range
within the range set here.
Host 2 Port Range
Host 2 Port Range The rule applies to a flow of messages for which host 2's port number is within the
Host 2 Port RangeHost 2 Port Range
range set here.
Save/Update
Save/Update Record the changes you have made into the following list.
Save/UpdateSave/Update
Clear
Clear Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
ClearClear
Page 36 of 73
Page 37

User Manual
WISH Rules
This section lists the defined WISH Rules. Click the Enable checkbox at the left to directly activate or de-
activate the entry. An entry can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or can be deleted by clicking the
Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit WISH Rule" section is
activated for editing.
Page 37 of 73
Page 38

User Manual
NAT (Network Address Translation)
NAT options include:
Port Forwarding
Port Trigger
Virtual Server
DMZ
Port Forwarding
Multiple connections are required by some applications, such as internet games, video conferencing,
Internet telephony, and others. These applications have difficulties working through NAT (Network Address
Translation). This section is used to open multiple ports or a range of ports in your router and redirect data
through those ports to a single PC on your network. You can enter ports in various formats:
Range(50-100)
Individual(80,68,888)
Mixed (1020-5000, 689)
Page 38 of 73
Page 39

User Manual
Add/Edit Port Forwarding Rule
Use this section to add a Port Forwarding Rule to the following list or to edit a rule already in the list.
Enable
Enable Specifies whether the entry will be active or inactive.
EnableEnable
Name
Name Give the rule a name that is meaningful to you, for example Game Server. You can also select from a
NameName
list of popular games, and many of the remaining configuration values will be filled in accordingly.
However, you should check whether the port values have changed since this list was created, and you
must fill in the IP address field.
IP Address
IP Address Enter the local network IP address of the system hosting the server, for example 192.168.0.50.
IP AddressIP Address
You can select a computer from the list of DHCP clients in the "Computer Name" drop-down menu, or you
can manually enter the IP address of the server computer.
TCP
TCP Ports
Ports Enter the TCP ports to open (for example 6159-6180, 99).
TCPTCP
Ports Ports
UDP
UDP Ports
Ports Enter the UDP ports to open (for example 6159-6180, 99).
UDPUDP
PortsPorts
Schedule
Schedule Select a schedule for the times when this rule is in effect. If you do not see the schedule you
ScheduleSchedule
need in the list of schedules, go to the Advanced>Applications>Schedule screen and create a new schedule.
Inbound Filter
Inbound Filter Select a filter that controls access as needed for this rule. If you do not see the filter you
Inbound FilterInbound Filter
need in the list of filters, go to the Advanced>Security>Inbound Filter screen and create a new filter.
Save/Update
Save/Update Record the changes you have made into the following list.
Save/UpdateSave/Update
Clear
Clear Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
ClearClear
Note that different LAN computers cannot be associated with Port Forwarding rules that contain any ports
in common; such rules would contradict each other.
Port Forwarding Rules
This is a list of the defined Port Forwarding Rules. Click the Enable checkbox at the left to directly activate
or de-activate the entry. An entry can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or can be deleted by clicking the
Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit Port Forwarding Rule"
section is activated for editing.
Page 39 of 73
Page 40

User Manual
Port Trigger
Port Trigger rule is used to open single or multiple ports on your router when the router senses data sent to
the Internet on a "trigger" port or port range. An application rule applies to all computers on your internal
network.
Enable
Enable Specifies whether the entry will be active or inactive.
EnableEnable
Name
Name Enter a name for the Special Application Rule, for example Game App, which will help you identify
NameName
the rule in the future. Alternatively, you can select from the Application list of common applications.
Application
Application Instead of entering a name for the Special Application rule, you can select from this list of
ApplicationApplication
common applications, and the remaining configuration values will be filled in accordingly.
Trigger Port
Trigger Port Enter the outgoing port range used by your application (for example 6500-6700).
Trigger PortTrigger Port
Trigger Traffic Type
Trigger Traffic Type Select the outbound protocol used by your application (for example Both).
Trigger Traffic TypeTrigger Traffic Type
Firewall Port
Firewall Port Enter the port range that you want to open up to Internet traffic (for example 6000-6200).
Firewall PortFirewall Port
Firewall Traffic Type
Firewall Traffic Type Select the protocol used by the Internet traffic coming back into the router through the
Firewall Traffic TypeFirewall Traffic Type
opened port range (for example Both).
Schedule
Schedule Select a schedule for when this rule is in effect. If you do not see the schedule you need in the
ScheduleSchedule
list of schedules, go to the Advanced>Applications>Schedule screen and create a new schedule.
Save/Update
Save/Update Record the changes you have made into the following list.
Save/UpdateSave/Update
Clear
Clear Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
ClearClear
Page 40 of 73
Page 41
User Manual
Application Rules
This is a list of the defined application rules. Click the Enable checkbox at the left to directly activate or de-
activate the entry. An entry can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or can be deleted by clicking the
Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit Application Rule" section is
activated for editing.
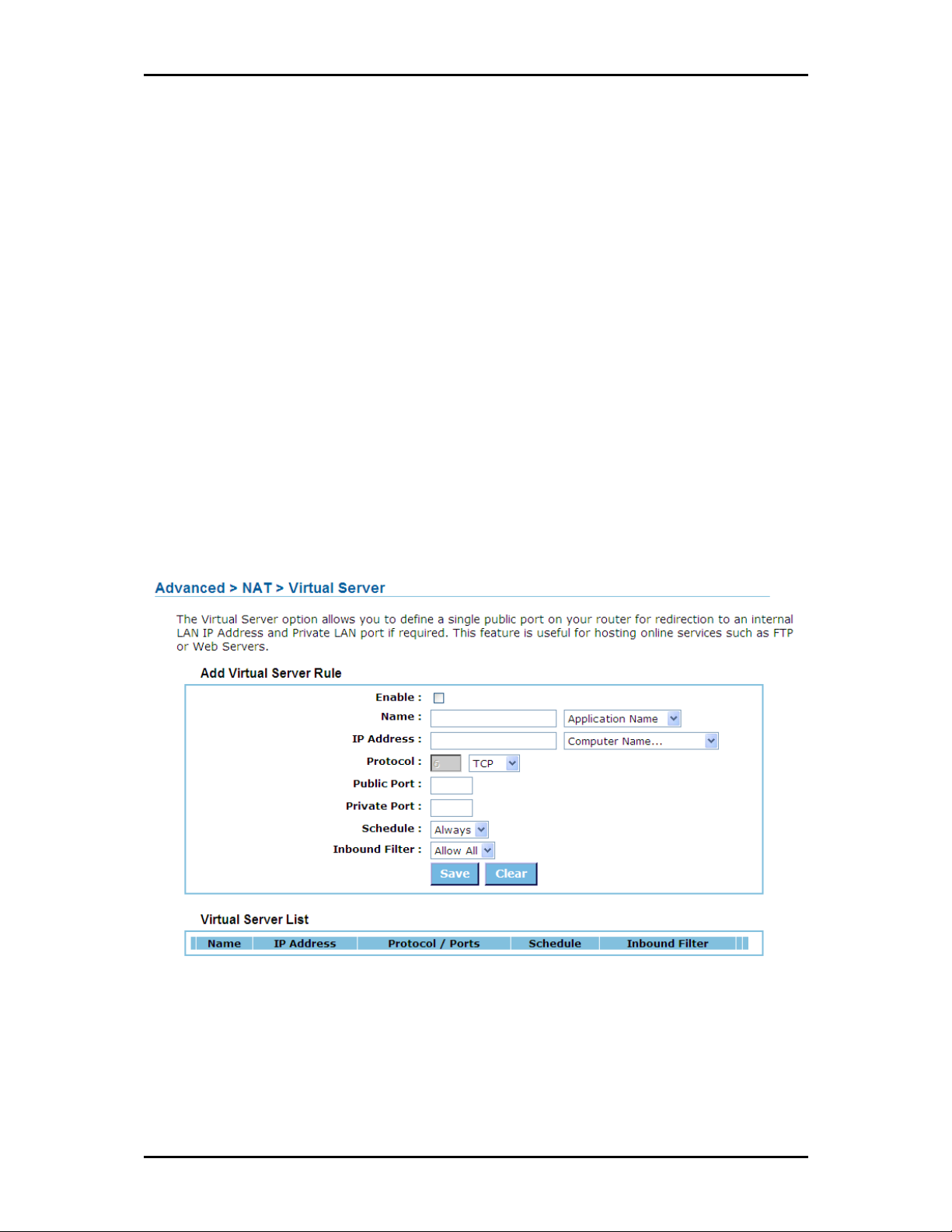
Virtual Server
The Virtual Server option gives Internet users access to services on your LAN. This feature is useful for
hosting online services such as FTP, Web, or game servers. For each Virtual Server, you define a public port
on your router for redirection to an internal LAN IP Address and LAN port.
Page 41 of 73
Page 42

User Manual
Add/Edit Virtual Server
Enable
Enable Specifies whether the entry will be active or inactive.
EnableEnable
Name
Name Assign a meaningful name to the virtual server, for example Web Server. Several well-known types
NameName
of virtual server are available from the "Application Name" drop-down list. Selecting one of these entries
fills some of the remaining parameters with standard values for that type of server.
IP Address
IP Address The IP address of the system on your internal network that will provide the virtual service, for
IP AddressIP Address
example 192.168.0.50. You can select a computer from the list of DHCP clients in the "Computer Name"
drop-down menu, or you can manually enter the IP address of the server computer.
Protocol
Protocol Select the protocol used by the service. The common choices -- UDP, TCP, and both UDP and TCP --
ProtocolProtocol
can be selected from the drop-down menu. To specify any other protocol, select "Other" from the list, then
enter the corresponding protocol number (as assigned by the IANA) in the Protocol box.
Priva
Private Port
te Port The port that will be used on your internal network. Public Port The port that will be accessed
PrivaPriva
te Portte Port
from the Internet.
Schedule
Schedule Select a schedule for when the service will be enabled. If you do not see the schedule you need
ScheduleSchedule
in the list of schedules, go to the Advanced>Applications>Schedule screen and create a new schedule.
Inbound Filter
Inbound Filter Select a filter that controls access as needed for this virtual server. If you do not see the filter
Inbound FilterInbound Filter
you need in the list of filters, go to the Advanced>Security>Inbound Filter screen and create a new filter.
Save/Update
Save/Update Record the changes you have made into the following list.
Save/UpdateSave/Update
Clear
Clear Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
ClearClear
Virtual Server List
This is a list of the defined Virtual Servers. Click the Enable checkbox at the left to directly activate or de-
activate the entry. An entry can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or can be deleted by clicking the
Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit Virtual Servers" section is
activated for editing.
Page 42 of 73
Page 43
User Manual
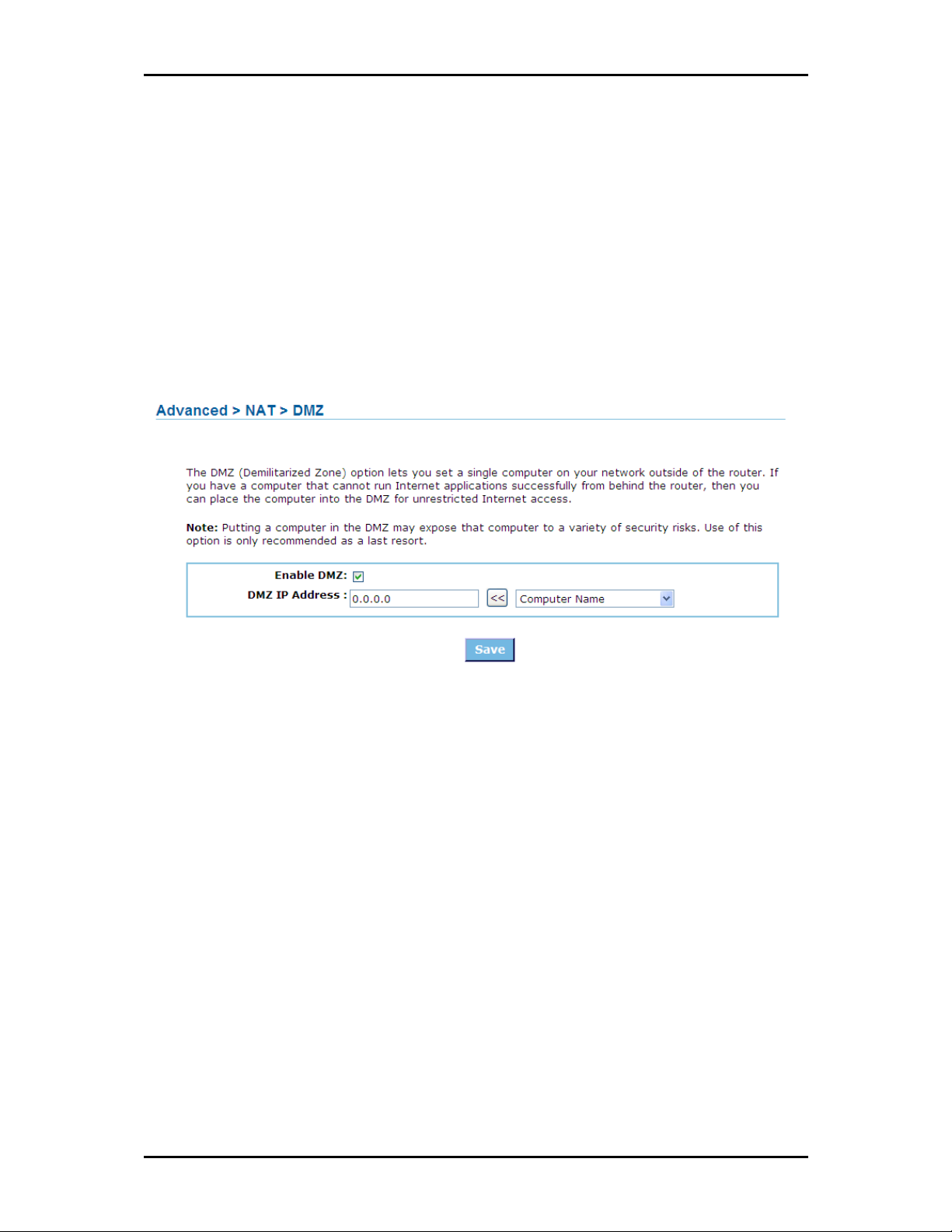
DMZ
DMZ means "Demilitarized Zone." If an application has trouble working from behind the router, you can
expose one computer to the Internet and run the application on that computer.
When a LAN host is configured as a DMZ host, it becomes the destination for all incoming packets that do
not match some other incoming session or rule. If any other ingress rule is in place, that will be used
instead of sending packets to the DMZ host; so, an active session, virtual server, active port trigger, or port
forwarding rule will take priority over sending a packet to the DMZ host. (The DMZ policy resembles a
default port forwarding rule that forwards every port that is not specifically sent anywhere else.)
Enable DMZ
Enable DMZ Checked by default.
Enable DMZEnable DMZ
DMZ IP Address
DMZ IP Address Specify the LAN IP address of the LAN computer that you want to have unrestricted
DMZ IP AddressDMZ IP Address
Internet communication. It is advisable for the computer to have a Static IP Address so that the IP address
of the DMZ computer does not change.
Page 43 of 73
Page 44

User Manual
Routing
Routing options include:
Static
RIP
Static Routing
If the router is connected to more than one network, you may need to set up a static route between them.
A static route is a pre-defined pathway that network information must travel to reach a specific host or
network. You can use static routing to allow different IP domain users to access the Internet through the
router.
The Destination IP is the address of the remote LAN network or host to which you want to assign a static
route. Enter the IP address of the host for which you wish to create a static route here. For a standard Class
C IP domain, the network address is the first three fields of the New Destination IP, while the last field
should be 0.
The Subnet Mask identifies which portion of an IP address is the network portion, and which portion is the
host portion. For a full Class C Subnet, the Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0. The Gateway IP address should be
the IP address of the gateway device that allows for contact between the Gateway and the remote
network or host.
Page 44 of 73
Page 45

User Manual
Add/Edit Route
Adds a new route to the IP routing table or edits an existing route.
Enable
Enable Specifies whether the entry will be enabled or disabled.
EnableEnable
Destination IP
Destination IP The IP address of packets that will take this route.
Destination IPDestination IP
Netmask
Netmask One bits in the mask specify which bits of the IP address must match.
NetmaskNetmask
Gateway
Gateway Specifies the next hop to be taken if this route is used. A gateway of 0.0.0.0 implies there is no
GatewayGateway
next hop, and the IP address matched is directly connected to the router on the interface specified: LAN or
WAN.
Metric
Metric The route metric is a value from 1 to 16 that indicates the cost of using this route. A value of 1 is the
MetricMetric
lowest cost, and 15 is the highest cost. A value of 16 indicates that the route is not reachable from this
router. When trying to reach a particular destination, computers on your network will select the best route,
ignoring unreachable routes.
Interface
Interface Specifies the interface -- LAN or WAN -- that the IP packet must use to transit out of the router,
InterfaceInterface
when this route is used.
Save/Update
Save/Update Record the changes you have made into the following list.
Save/UpdateSave/Update
Clear
Clear Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
ClearClear
Routes List
The section shows the current routing table entries. Certain required routes are predefined and cannot be
changed. Routes that you add can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or can be deleted by clicking the
Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit Route" section is activated
for editing. Click the Enable checkbox at the left to directly activate or de-activate the entry.
Page 45 of 73
Page 46

User Manual
RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
Use this section to configure the internal network settings of your router and also to configure the built-in
DHCP Server to assign IP addresses to the computers on your network. The IP Address that is configured
here is the IP Address that you use to access the Web-based management interface. If you change the IP
Address here, you may need to adjust your PC's network settings to access the network again.
Page 46 of 73
Page 47
User Manual
Security
Security options include:
Access Control
Firewall Settings
Inbound Filter
MAC Address filter
Web Filter
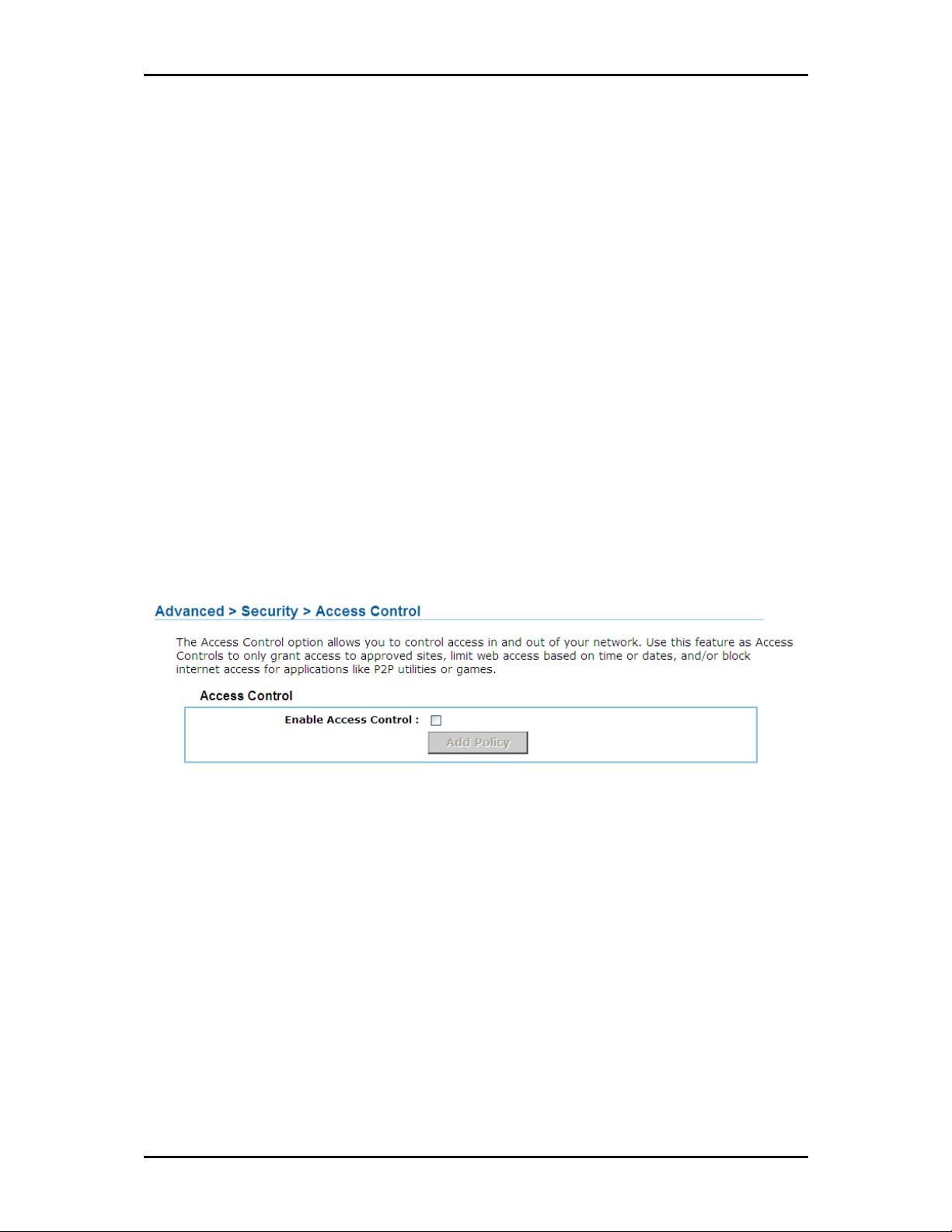
Access Control
The Access Control section allows you to control access in and out of devices on your network. Use this
feature as Parental Controls to only grant access to approved sites, limit web access based on time or
dates, and/or block access from applications such as peer-to-peer utilities or games.
EEEEnable
nable By default, the Access Control feature is disabled. If you need Access Control, check this option.
nablenable
Note:
Note: When Access Control is disabled, every device on the LAN has unrestricted access to the Internet.
Note: Note:
However, if you enable Access Control, Internet access is restricted for those devices that have an Access
Control Policy configured for them. All other devices have unrestricted access to the Internet.
Policy Wizard
Policy Wizard The Policy Wizard guides you through the steps of defining each access control policy. A
Policy Wizard Policy Wizard
policy is the "Who, What, When, and How" of access control -- whose computer will be affected by the
control, what internet addresses are controlled, when will the control be in effect, and how is the control
implemented. You can define multiple policies. The Policy Wizard starts when you click the button below
and also when you edit an existing policy.
Add Policy
Add Policy Click this button to start creating a new access control policy.
Add Policy Add Policy
Page 47 of 73
Page 48

User Manual
Policy Table
Policy Table This section shows the currently defined access control policies. A policy can be changed by
Policy Table Policy Table
clicking the Edit icon, or deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the Policy Wizard
starts and guides you through the process of changing a policy. You can enable or disable specific policies
in the list by clicking the "Enable" checkbox.
Firewall Settings
The router provides a tight firewall by virtue of the way NAT works. Unless you configure the router to the
contrary, the NAT does not respond to unsolicited incoming requests on any port, thereby making your LAN
invisible to Internet cyberattackers. However, some network applications cannot run with a tight firewall.
Those applications need to selectively open ports in the firewall to function correctly. The options on this
page control several ways of opening the firewall to address the needs of specific types of applications.
Page 48 of 73
Page 49

User Manual
Firewall Settings
Enable SPI
Enable SPI SPI ("stateful packet inspection" also known as "dynamic packet filtering") helps to prevent
Enable SPI Enable SPI
cyberattacks by tracking more state per session. It validates that the traffic passing through that session
conforms to the protocol. When the protocol is TCP, SPI checks that packet sequence numbers are within
the valid range for the session, discarding those packets that do not have valid sequence numbers.
Whether SPI is enabled or not, the router always tracks TCP connection states and ensures that each TCP
packet's flags are valid for the current state.
NAT Endpoint Filtering
The NAT Endpoint Filtering options control how the router's NAT manages incoming connection requests to
ports that are already being used.
Endpoint Independent
Endpoint Independent Once a LAN-side application has created a connection through a specific port, the
Endpoint Independent Endpoint Independent
NAT will forward any incoming connection requests with the same port to the LAN-side application
regardless of their origin. This is the least restrictive option, giving the best connectivity and allowing some
applications (P2P applications in particular) to behave almost as if they are directly connected to the
Internet.
Address Rest
Address Restricted
Address RestAddress Rest
come from the same IP address with which a connection was established. This allows the remote
application to send data back through a port different from the one used when the outgoing session was
created.
Port And Address Restricted
Port And Address Restricted The NAT does not forward any incoming connection requests with the same
Port And Address Restricted Port And Address Restricted
port address as an already establish connection.
Note that some of these options can interact with other port restrictions. Endpoint Independent Filtering
takes priority over inbound filters or schedules, so it is possible for an incoming session request related to
an outgoing session to enter through a port in spite of an active inbound filter on that port. However,
packets will be rejected as expected when sent to blocked ports (whether blocked by schedule or by
inbound filter) for which there are no active sessions. Port and Address Restricted Filtering ensures that
inbound filters and schedules work precisely, but prevents some level of connectivity, and therefore might
require the use of port triggers, virtual servers, or port forwarding to open the ports needed by the
application. Address Restricted Filtering gives a compromise position, which avoids problems when
communicating with certain other types of NAT router (symmetric NATs in particular) but leaves inbound
filters and scheduled access working as expected.
UDP Endpoint Filtering
UDP Endpoint Filtering Controls endpoint filtering for packets of the UDP protocol.
UDP Endpoint Filtering UDP Endpoint Filtering
ricted The NAT forwards incoming connection requests to a LAN-side host only when they
ricted ricted
TCP Endpoint Filter
TCP Endpoint Filtering
TCP Endpoint FilterTCP Endpoint Filter
ing Controls endpoint filtering for packets of the TCP protocol.
ing ing
Page 49 of 73
Page 50

User Manual
NAT Port Preservation
NAT Port preservation (on by default) tries to ensure that, when a LAN host makes an Internet connection,
the same LAN port is also used as the Internet visible port. This ensures best compatibility for internet
communications.
Under some circumstances it may be desirable to turn off this feature.
Anti-Spoof checking
Enabling this option can provide protection from certain kinds of "spoofing" attacks.
Non-UDP/TCP/ICMP LAN Sessions
When a LAN application that uses a protocol other than UDP, TCP, or ICMP initiates a session to the Internet,
the router's NAT can track such a session, even though it does not recognize the protocol. This feature is
useful because it enables certain applications (most importantly a single VPN connection to a remote host)
without the need for an ALG.
Note that this feature does not apply to the DMZ host (if one is enabled). The DMZ host always handles
these kinds of sessions.
Application Level Gateway (ALG) Configuration
Here you can enable or disable ALGs. Some protocols and applications require special handling of the IP
payload to make them work with network address translation (NAT). Each ALG provides special handling
for a specific protocol or application. A number of ALGs for common applications are enabled by default.
PPTP
PPTP
PPTP PPTP
Allows multiple machines on the LAN to connect to their corporate networks using PPTP protocol. When the
PPTP ALG is enabled, LAN computers can establish PPTP VPN connections either with the same or with
different VPN servers. When the PPTP ALG is disabled, the router allows VPN operation in a restricted way -
- LAN computers are typically able to establish VPN tunnels to different VPN Internet servers but not to the
same server. The advantage of disabling the PPTP ALG is to increase VPN performance.
IPSec (VPN)
IPSec (VPN)
IPSec (VPN) IPSec (VPN)
Allows multiple VPN clients to connect to their corporate networks using IPSec. Some VPN clients support
traversal of IPSec through NAT. This option may interfere with the operation of such VPN clients. If you are
having trouble connecting with your corporate network, try disabling this option.
Check with the system adminstrator of your corporate network whether your VPN client supports NAT
traversal.
Page 50 of 73
Page 51

User Manual
Note that L2TP VPN connections typically use IPSec to secure the connection. To achieve multiple VPN pass-
through in this case, the IPSec ALG must be enabled.
RTSP
RTSP
RTSP RTSP
Allows applications that use Real Time Streaming Protocol to receive streaming media from the internet.
QuickTime and Real Player are some of the common applications using this protocol.
Windows/MSN Messenger
Windows/MSN Messenger
Windows/MSN Messenger Windows/MSN Messenger
Supports use on LAN computers of Microsoft Windows Messenger (the Internet messaging client that ships
with Microsoft Windows) and MSN Messenger. The SIP ALG must also be enabled when the Windows
Messenger ALG is enabled.
FTP
FTP
FTP FTP
Allows FTP clients and servers to transfer data across NAT. Refer to the Virtual Server page if you want to
host an FTP server.
H.323 (Netmeeting)
H.323 (Netmeeting)
H.323 (Netmeeting) H.323 (Netmeeting)
Allows H.323 (specifically Microsoft Netmeeting) clients to communicate across NAT. Note that if you want
your buddies to call you, you should also set up a virtual server for NetMeeting.
SIP
SIP
SIP SIP
Allows devices and applications using VoIP (Voice over IP) to communicate across NAT. Some VoIP
applications and devices have the ability to discover NAT devices and work around them. This ALG may
interfere with the operation of such devices. If you are having trouble making VoIP calls, try turning this
ALG off.
Wake
Wake----On
On----LAN
OnOn
LAN
LAN LAN
WakeWake
This feature enables forwarding of "magic packets" (that is, specially formatted wake-up packets) from the
WAN to a LAN computer or other device that is "Wake on LAN" (WOL) capable. The WOL device must be
defined as such on the Virtual Server Settings page. The LAN IP address for the virtual server is typically set
to the broadcast address 192.168.0.255. The computer on the LAN whose MAC address is contained in the
magic packet will be awakened.
MMS
MMS
MMS MMS
Allows Windows Media Player, using MMS protocol, to receive streaming media from the internet.
Page 51 of 73
Page 52

User Manual
Inbound Filter
When you use the Virtual Server, Port Forwarding, or Remote Administration features to open specific ports
to traffic from the Internet, you could be increasing the exposure of your LAN to cyberattacks from the
Internet. In these cases, you can use Inbound Filters to limit that exposure by specifying the IP addresses of
internet hosts that you trust to access your LAN through the ports that you have opened. You might, for
example, only allow access to a game server on your home LAN from the computers of friends whom you
have invited to play the games on that server.
Add/Edit Inbound Filter Rule
Here you can add entries to the Inbound Filter Rules List below, or edit existing entries.
Name
Name Enter a name for the rule that is meaningful to you.
Name Name
Action
Action The rule can either Allow or Deny messages.
Action Action
Remote IP Range
Remote IP Range Define the ranges of Internet addresses this rule applies to. For a single IP address, enter
Remote IP Range Remote IP Range
the same address in both the Start and End boxes. Up to eight ranges can be entered. The Enable checkbox
allows you to turn on or off specific entries in the list of ranges.
Sa
Save/Update
ve/Update Record the changes you have made into the following list.
SaSa
ve/Update ve/Update
Clear
Clear Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
Clear Clear
Page 52 of 73
Page 53

User Manual
Inbound Filter Rules List
The section lists the current Inbound Filter Rules. An entry can be changed by clicking the Edit icon or can
be deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and the "Edit
Inbound Filter Rule" section is activated for editing.
In addition to the filters listed here, two predefined filters are available wherever inbound filters can be
applied:
Allow All
Allow All Permit any WAN user to access the related capability.
Allow All Allow All
Deny All
Deny All Prevent all WAN users from accessing the related capability. (LAN users are not affected by
Deny All Deny All
Inbound Filter Rules.)
MAC Address Filter (Network Filter)
The MAC address filter section can be used to filter network access by machines based on the unique MAC
addresses of their network adapter(s). It is most useful to prevent unauthorized wireless devices from
connecting to your network. A MAC address is a unique ID assigned by the manufacturer of the network
adapter.
MAC Filtering Setup
Choose the type of MAC filtering needed.
Turn MAC Filtering OFF
Turn MAC Filtering OFF: When "OFF" is selected, MAC addresses are not used to control network access.
Turn MAC Filtering OFFTurn MAC Filtering OFF
Turn MAC Filtering ON and ALLOW computers listed to access the network
Turn MAC Filtering ON and ALLOW computers listed to access the network: When "ALLOW" is selected, only
Turn MAC Filtering ON and ALLOW computers listed to access the networkTurn MAC Filtering ON and ALLOW computers listed to access the network
computers with MAC addresses listed in the MAC Filtering Rules list are granted network access.
Turn MAC Filtering ON and DENY computers listed t
Turn MAC Filtering ON and DENY computers listed to access the network
Turn MAC Filtering ON and DENY computers listed tTurn MAC Filtering ON and DENY computers listed t
computer with a MAC address listed in the MAC Filtering Rules list is refused access to the network.
o access the network: When "DENY" is selected, any
o access the networko access the network
Page 53 of 73
Page 54

User Manual
Add MAC Filtering Rule
Use this section to add MAC addresses to the list below.
MAC Address
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of a computer that you want to control with MAC filtering. Computers
MAC Address MAC Address
that have obtained an IP address from the router's DHCP server will be in the DHCP Client List. Select a
device from the drop down menu.
Save
Save Record the changes you have made into the following list.
Save Save
MAC Filtering Rules
MAC Filtering Rules This section lists the network devices that are under control of MAC filtering.
MAC Filtering Rules MAC Filtering Rules
Website Filter
The Web sites listed here are used when the Web Filter option is enabled in Access Control Page.
Add Web Filtering Rule
This section is where you add the Web sites to be used for Access Control.
Website URL/Domain
Website URL/Domain Enter the URL (address) of the Web Site that you want to allow; for example:
Website URL/Domain Website URL/Domain
google.com. Do not enter the http:// preceding the URL. Enter the most inclusive domain; for example,
enter google.com and access will be permitted to both www.google.com and support.google.com.
Save
Save Record the changes you have made into the following list.
Save Save
Note: Many web sites construct pages with images and content from other web sites. Access will be
forbidden if you do not enable all the web sites used to construct a page. For example, to access
my.yahoo.com, you need to enable access to yahoo.com, yimg.com, and doubleclick.net.
Website Filtering Rules
The section lists the currently allowed web sites.
Page 54 of 73
Page 55
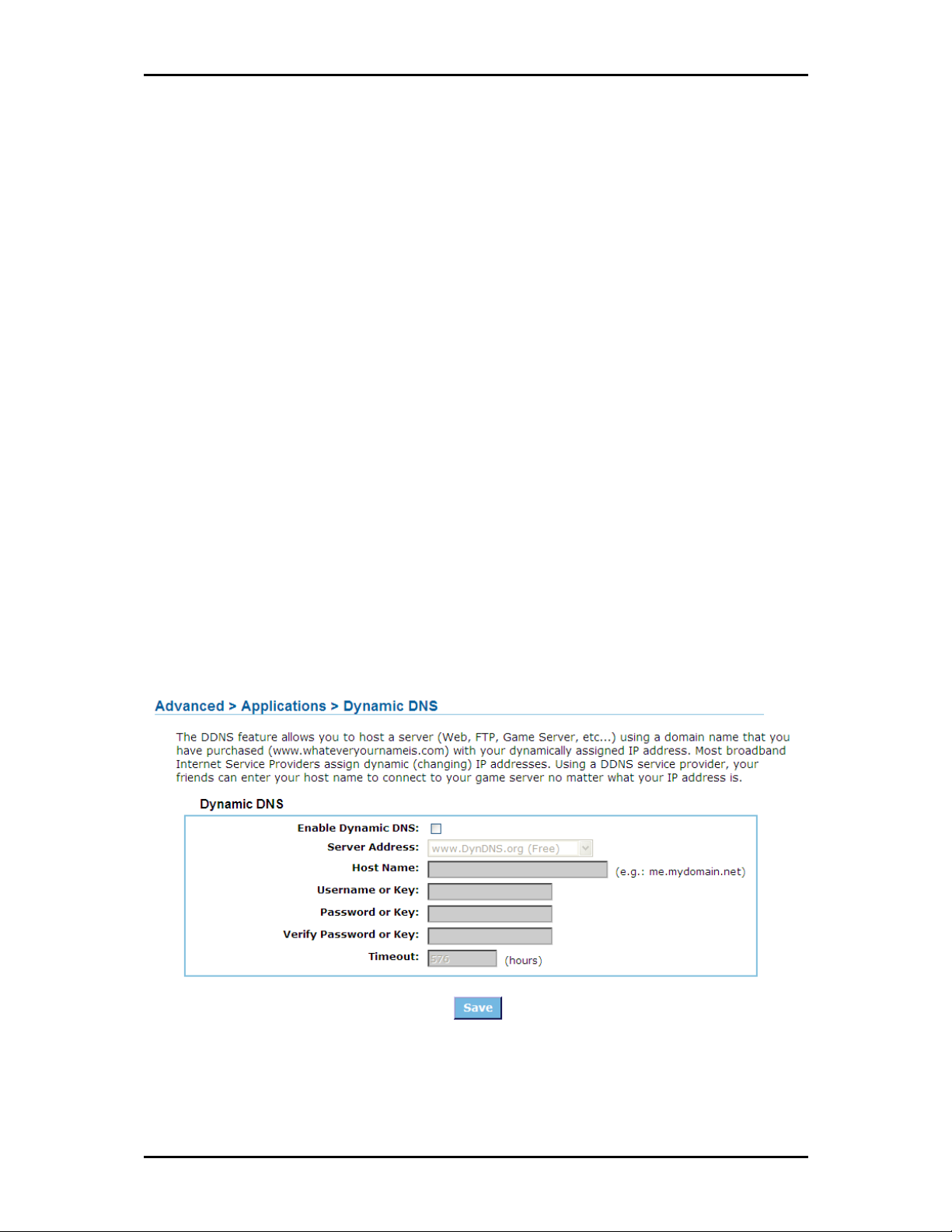
Applications
Applications options include:
DDNS
Schedules
Syslogs
Time
UPnP
DDNS (Dynamic DNS)
User Manual
The Dynamic DNS feature allows you to host a server (Web, FTP, Game Server, etc.) using a domain name
that you have purchased (www.whateveryournameis.com) with your dynamically assigned IP address.
Most broadband Internet Service Providers assign dynamic (changing) IP addresses. When you use a
Dynamic DNS service provider, your friends can enter your host name to connect to your server, no matter
what your IP address is.
Page 55 of 73
Page 56

User Manual
Enable Dynamic DNS
Enable Dynamic DNS Enable this option only if you have purchased your own domain name and registered
Enable Dynamic DNS Enable Dynamic DNS
with a dynamic DNS service provider. The following paramters are displayed when the option is enabled.
Server Address
Server Address Select a dynamic DNS service provider from the pull-down list.
Server Address Server Address
Host Name
Host Name Enter your host name, fully qualified; for example: myhost.mydomain.net.
Host Name Host Name
Username or Key
Username or Key Enter the username or key provided by your service provider. If the Dynamic DNS
Username or Key Username or Key
provider supplies only a key, enter that key in all three fields.
Password or Key
Password or Key Enter the password or key provided by your service provider. If the Dynamic DNS provider
Password or Key Password or Key
supplies only a key, enter that key in all three fields.
Verify Password or K
Verify Password or Key
Verify Password or KVerify Password or K
provider supplies only a key, enter that key in all three fields.
Timeout
Timeout The time between periodic updates to the Dynamic DNS, if your dynamic IP address has not
Timeout Timeout
changed. The timeout period is entered in hours.
Note: If a dynamic DNS update fails for any reason (for example, when incorrect parameters are entered),
the router automatically disables the Dynamic DNS feature and records the failure in the log.
ey Re-type the password or key provided by your service provider. If the Dynamic DNS
ey ey
Schedules
Schedules can be created for use with enforcing rules. For example, if you want to restrict web access to
Mon-Fri from 3pm to 8pm, you could create a schedule selecting Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, and Fri and enter a
Start Time of 3pm and End Time of 8pm.
Page 56 of 73
Page 57

User Manual
Add/Edit Schedule Rule
In this section you can add entries to the Schedule Rules List below or edit existing entries.
Name
Name Give the schedule a name that is meaningful to you, such as "Weekday rule".
Name Name
Day(s)
Day(s) Place a checkmark in the boxes for the desired days or select the All Week radio button to select all seven
Day(s) Day(s)
days of the week.
All Day
All Day ---- 24 hrs
All Day All Day
Start Time
Start Time If you don't use the All Day option, then you enter the time here. The start time is entered in two
Start Time Start Time
fields. The first box is for the hour and the second box is for the minute. Email events are normally triggered only
by the start time.
End Time
End Time The end time is entered in the same format as the start time. The hour in the first box and the minutes
End Time End Time
in the second box. The end time is used for most other rules, but is not normally used for email events.
Save/Update
Save/Update Record the changes you have made into the following list.
Save/Update Save/Update
Clear
Clear Re-initialize this area of the screen, discarding any changes you have made.
Clear Clear
24 hrs Select this option if you want this schedule in effect all day for the selected day(s).
24 hrs 24 hrs
Schedule Rules List
This section shows the currently defined Schedule Rules. An entry can be changed by clicking the Edit icon
or can be deleted by clicking the Delete icon. When you click the Edit icon, the item is highlighted, and the
"Edit Schedule Rule" section is activated for editing.
Syslog
This section allows you to archive your log files to a Syslog Server.
Enable Logging to Syslog Server
Enable Logging to Syslog Server Enable this option if you have a syslog server currently running on the LAN
Enable Logging to Syslog Server Enable Logging to Syslog Server
and wish to send log messages to it.
Syslog Server IP Address
Syslog Server IP Address Enter the LAN IP address of the Syslog Server.
Syslog Server IP Address Syslog Server IP Address
Page 57 of 73
Page 58
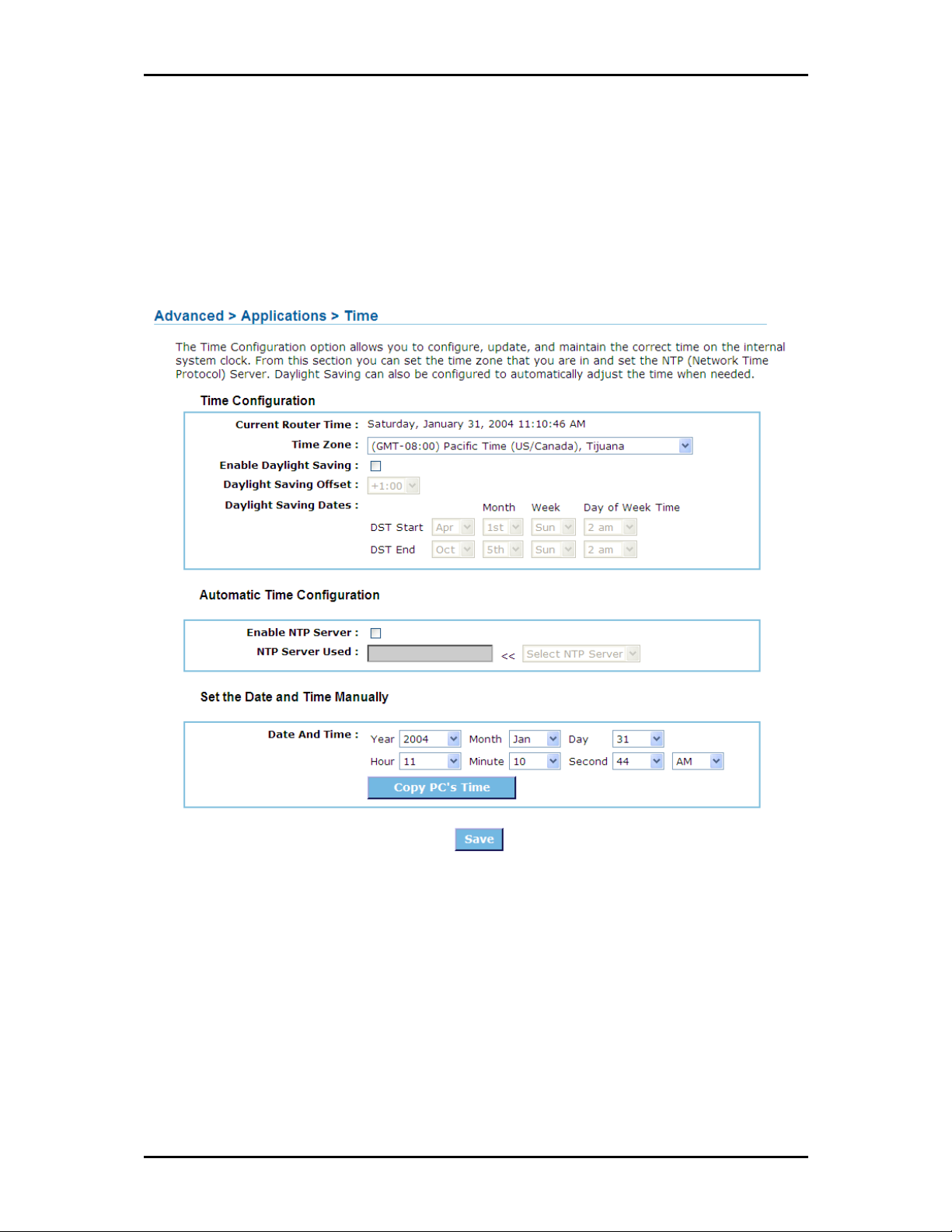
User Manual
Time
The Time Configuration option allows you to configure, update, and maintain the correct time on the
router's internal system clock. From this section you can set the time zone that you are in and set the Time
Server. Daylight saving can also be configured to automatically adjust the time when needed.
Time Configuration
Current Router Time
Current Router Time Displays the time currently maintained by the router. If this is not correct, use the
Current Router Time Current Router Time
following options to configure the time correctly.
Time Zone
Time Zone Select your local time zone from pull down menu.
Time Zone Time Zone
Enable Daylight Saving
Enable Daylight Saving Check this option if your location observes daylight saving time.
Enable Daylight Saving Enable Daylight Saving
Daylight Sa
Daylight Saving Offset
Daylight SaDaylight Sa
Page 58 of 73
ving Offset Select the time offset, if your location observes daylight saving time.
ving Offset ving Offset
Page 59
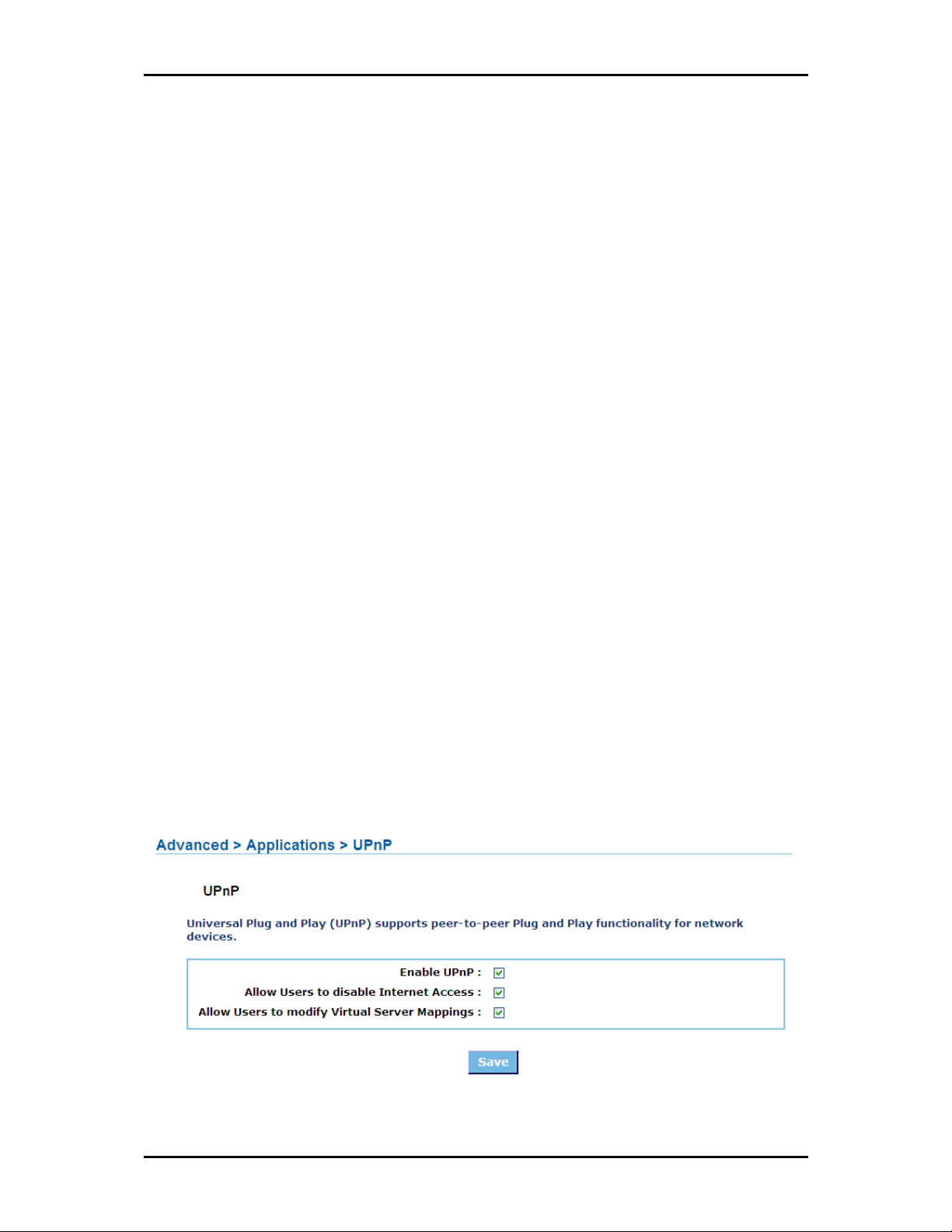
User Manual
DST Start and DST End
DST Start and DST End Select the starting and ending times for the change to and from daylight saving
DST Start and DST End DST Start and DST End
time. For example, suppose for DST Start you select Month="Oct", Week="3rd", Day="Sun" and Time="2am".
This is the same as saying: "Daylight saving starts on the third Sunday of October at 2:00 AM."
Automatic Time Configuration
Enable NTP Server
Enable NTP Server Select this option if you want to synchronize the router's clock to a Network Time Server
Enable NTP Server Enable NTP Server
over the Internet. If you are using schedules or logs, this is the best way to ensure that the schedules and
logs are kept accurate.
Note that, even when NTP Server is enabled, you must still choose a time zone and set the daylight saving
parameters.
NTP Server Used
NTP Server Used Select a Network Time Server for synchronization. You can type in the address of a time
NTP Server Used NTP Server Used
server or select one from the list. If you have trouble using one server, select another.
Set the Date and Time Manually
If you do not have the NTP Server option in effect, you can either manually set the time for your router
here, or you can click the Copy PC’s Time
sure that computer's time is set correctly.)
Note:
Note: If the router loses power for any reason, it cannot keep its clock running, and will not have the
Note: Note:
correct time when it is started again. To maintain correct time for schedules and logs, either you must
enter the correct time after you restart the router, or you must enable the NTP Server option.
Copy PC’s Time button to copy the time from the computer you are using. (Make
Copy PC’s TimeCopy PC’s Time
UPnP
Universal Plug and Play, supports peer-to-peer Plug and Play functionality for network devices.
Page 59 of 73
Page 60
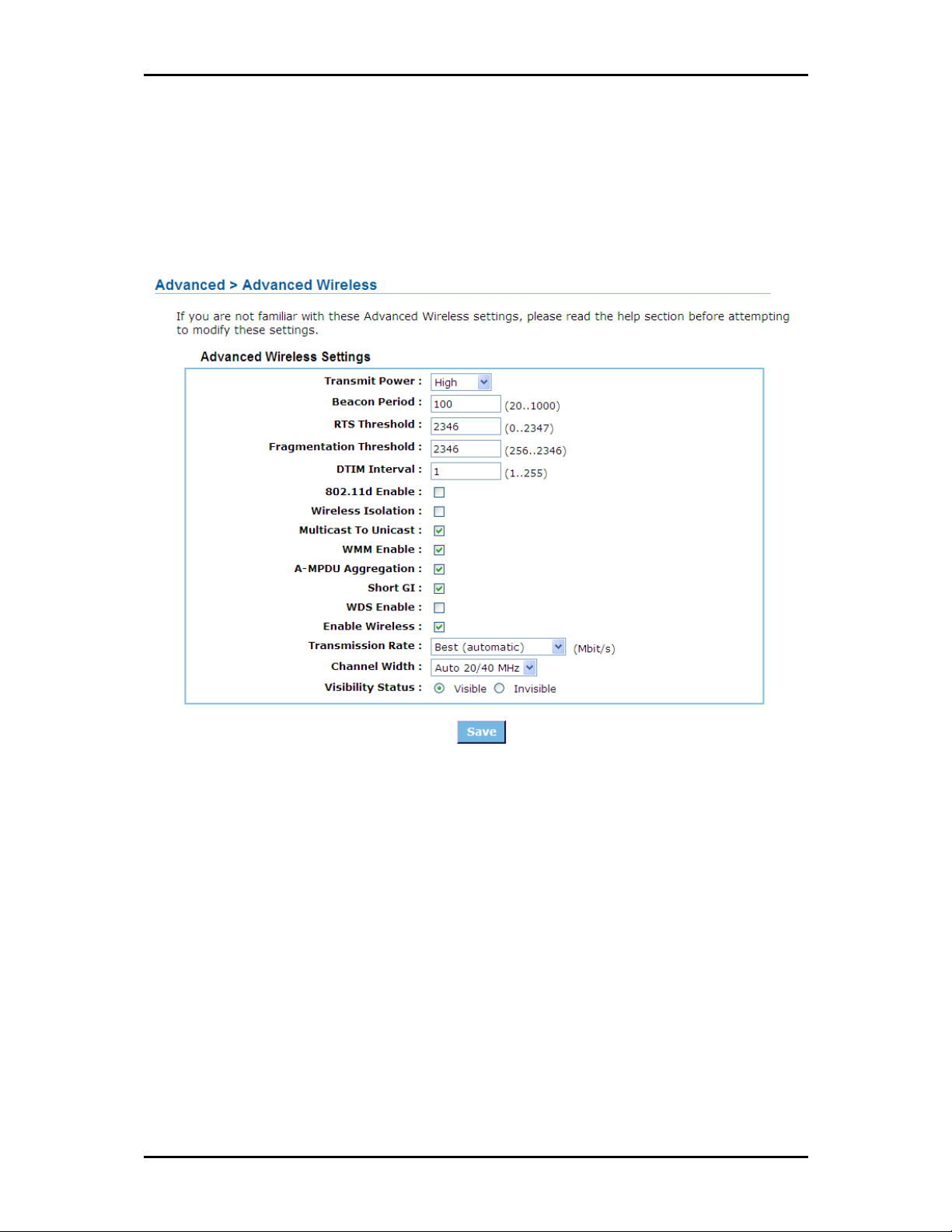
User Manual
Wireless
The wireless section is used to configure the advanced wireless settings for your router. Note that changes
made in this section may also need to be duplicated on wireless clients that you want to connect to your
wireless network.
Transmit Power
Transmit Power Normally the wireless transmitter operates at 100% power. In some circumstances,
Transmit Power Transmit Power
however, there might be a need to isolate specific frequencies to a smaller area. By reducing the power of
the radio, you can prevent transmissions from reaching beyond your corporate/home office or designated
wireless area.
Beacon Period
Beacon Period Beacons are packets sent by a wireless router to synchronize wireless devices. Specify a
Beacon PeriodBeacon Period
Beacon Period value between 20 and 1000. The default value is set to 100 milliseconds.
RTS Threshold
RTS Threshold When an excessive number of wireless packet collisions are occurring, wireless performance
RTS Threshold RTS Threshold
can be improved by using the RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send) handshake protocol. The wireless
transmitter will begin to send RTS frames (and wait for CTS) when data frame size in bytes is greater than
the RTS Threshold. This setting should remain at its default value of 2346 bytes.
Fragmentation Threshold
Fragmentation Threshold Wireless frames can be divided into smaller units (fragments) to improve
Fragmentation Threshold Fragmentation Threshold
performance in the presence of RF interference and at the limits of RF coverage. Fragmentation will occur
Page 60 of 73
Page 61

User Manual
when frame size in bytes is greater than the Fragmentation Threshold. This setting should remain at its
default value of 2346 bytes. Setting the Fragmentation value too low may result in poor performance.
DTIM Interval
DTIM Interval A DTIM is a countdown informing clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and
DTIM Interval DTIM Interval
multicast messages. When the wireless router has buffered broadcast or multicast messages for associated
clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value. Wireless clients detect the beacons and awaken
to receive the broadcast and multicast messages. The default value is 1. Valid settings are between 1 and
255.
802.11d Enable
802.11d Enable Enables 802.11d operation. 802.11d is a wireless specification for operation in additional
802.11d Enable 802.11d Enable
regulatory domains. This supplement to the 802.11 specifications defines the physical layer requirements
(channelization, hopping patterns, new values for current MIB attributes, and other requirements to extend
the operation of 802.11 WLANs to new regulatory domains (countries). The current 802.11 standard defines
operation in only a few regulatory domains (countries). This supplement adds the requirements and
definitions necessary to allow 802.11 WLAN equipment to operate in markets not served by the current
standard. Enable this option if you are operating in one of these "additional regulatory domains".
Wireless Isolation
Wireless Isolation Enabling Wireless Isolation prevents associated wireless clients from communicating with
Wireless Isolation Wireless Isolation
each other.
WMM Enable
WMM Enable Enabling WMM can help control latency and jitter when transmitting multimedia content over
WMM Enable WMM Enable
a wireless connection.
AAAA----MPDU Aggregation
MPDU Aggregation Aggregation of wireless packets based on MAC protocol data units is a technique for
MPDU Aggregation MPDU Aggregation
maximizing performance. This option should normally be left enabled.
Short GI
Short GI Using a short (400ns) guard interval can increase throughput. However, it can also increase error
Short GI Short GI
rate in some installations, due to increased sensitivity to radio-frequency reflections. Select the option that
works best for your installation.
WDS Enable
WDS Enable When WDS is enabled, this access point functions as a wireless repeater and is able to
WDS Enable WDS Enable
wirelessly communicate with other APs via WDS links. Note that WDS is incompatible with WPA -- both
features cannot be used at the same time. A WDS link is bidirectional; so this AP must know the MAC
Address (creates the WDS link) of the other AP, and the other AP must have a WDS link back to this AP.
Make sure the APs are configured with same channel number.
WDS AP MAC Address
WDS AP MAC Address Specifies one-half of the WDS link. The other AP must also have the MAC address of
WDS AP MAC Address WDS AP MAC Address
this AP to create the WDS link back to this AP. Enter a MAC address for each of the other APs that you want
to connect with WDS.
Enable Wireless
Enable Wireless This option turns off and on the wireless connection feature of the router. When you set
Enable Wireless Enable Wireless
this option, the following parameters are in effect.
Channel Width
Channel Width The "Auto 20/40 MHz" option is usually best. The other options are available for special
Channel Width Channel Width
circumstances.
Page 61 of 73
Page 62

User Manual
Transmission Rate
Transmission Rate By default the fastest possible transmission rate will be selected. You have the option of
Transmission Rate Transmission Rate
selecting the speed if necessary.
Visibility Status
Visibility Status The Invisible option allows you to hide your wireless network. When this option is set to
Visibility Status Visibility Status
Visible, your wireless network name is broadcast to anyone within the range of your signal. If you're not
using encryption then they could connect to your network. When Invisible mode is enabled, you must enter
the Wireless Network Name (SSID) on the client manually to connect to the network.
Page 62 of 73
Page 63

Status
Status options includes:
Internet Sessions
Logs
Routing
Traffic Status
Wireless Clients
WISH Sessions
Internet Sessions
User Manual
The Internet Sessions page displays full details of active Internet sessions through your router. An Internet
session is a conversation between a program or application on a LAN-side computer and a program or
application on a WAN-side computer.
Local
Local The IP address and, where appropriate, port number of the local application.
Local Local
NAT
NAT The port number of the LAN-side application as viewed by the WAN-side application.
NAT NAT
Internet
Internet The IP address and, where appropriate, port number of the application on the Internet.
Internet Internet
Protocol
Protocol The communications protocol used for the conversation.
Protocol Protocol
State
State State for sessions that use the TCP protocol.
State State
NO: None -- This entry is used as a placeholder for a future connection that may occur.
SS: SYN Sent -- One of the systems is attempting to start a connection.
EST: Established -- the connection is passing data.
FW: FIN Wait -- The client system has requested that the connection be stopped.
CW: Close Wait -- the server system has requested that the connection be stopped.
TW: Time Wait -- Waiting for a short time while a connection that was in FIN Wait is fully closed.
LA: Last ACK -- Waiting for a short time while a connection that was in Close Wait is fully closed.
Page 63 of 73
Page 64
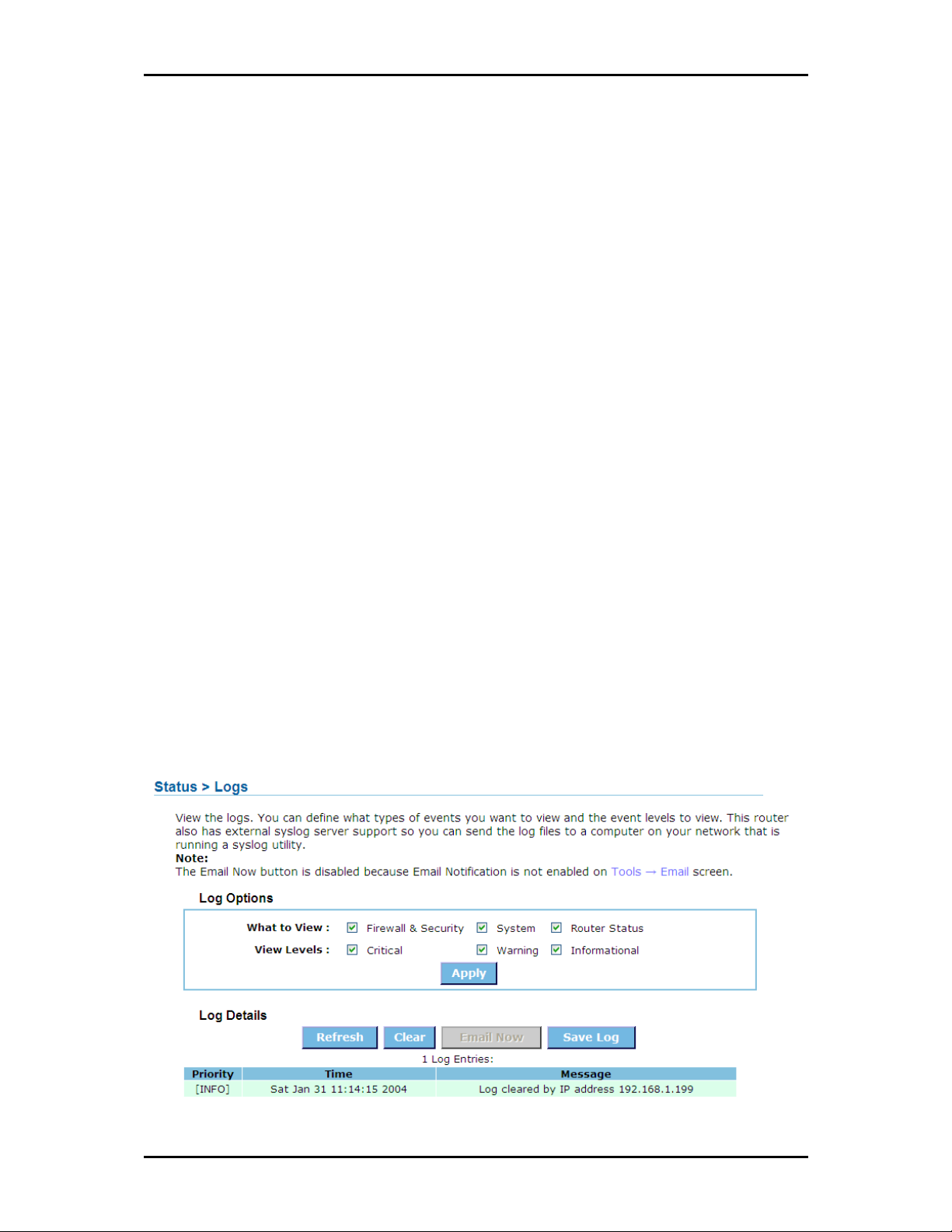
User Manual
CL: Closed -- The connection is no longer active but the session is being tracked in case there are
any retransmitted packets still pending.
Dir
Dir The direction of initiation of the conversation:
Dir Dir
Out
Out Initiated from LAN to WAN.
Out Out
In
In Initiated from WAN to LAN.
In In
Priority
Priority The preference given to outbound packets of this conversation by the QoS Engine logic. Smaller
Priority Priority
numbers represent higher priority.
Time Out
Time Out The number of seconds of idle time until the router considers the session terminated. The initial
Time Out Time Out
value of Time Out depends on the type and state of the connection.
300 seconds
300 seconds UDP connections.
300 seconds 300 seconds
240 seconds
240 seconds Reset or closed TCP connections. The connection does not close instantly so that
240 seconds 240 seconds
lingering packets can pass or the connection can be re-established.
7800 seconds
7800 seconds Established or closing TCP connections.
7800 seconds 7800 seconds
Logs
The router automatically logs (records) events of possible interest in its internal memory. If there is not
enough internal memory for all events, logs of older events are deleted, but logs of the latest events are
retained. The Logs option allows you to view the router logs. You can define what types of events you
want to view and the level of events to view. This router also has external Syslog Server support so you
can send the log files to a computer on your network that is running a Syslog utility.
Page 64 of 73
Page 65

What to View
Select the kinds of events that you want to view.
Firewall and Security
System
Router Status
View Levels
Select the level of events that you want to view.
Critical
Warning
Informational
User Manual
Apply Log Settings Now
Apply Log Settings Now Click this button after changing Log Options to make them effective and
Apply Log Settings Now Apply Log Settings Now
permanent.
Refresh
Refresh Clicking this button refreshes the display of log entries. There may be new events since the last
Refresh Refresh
time you accessed the log.
Clear
Clear Clicking this button erases all log entries.
Clear Clear
Email Now S
Email Now Sends the router log to the configured email address.
Email Now SEmail Now S
Save Log
Save Log Select this option to save the router log to a file on your computer.
Save Log Save Log
Routing
Displays the Routing details configured for the Router.
Page 65 of 73
Page 66

User Manual
Traffic Status
Displays traffic Statistics, receive and transmit packets passing through the router.
Page 66 of 73
Page 67

User Manual
Wireless Clients
Allows you to view the wireless clients that are connected to your wireless router.
MAC Address
MAC Address The Ethernet ID (MAC address) of the wireless client.
MAC Address MAC Address
IP Address
IP Address The LAN-side IP address of the client.
IP Address IP Address
Mode
Mode The transmission standard being used by the client. Values are 11a, 11b, 11g, or 11n for 802.11a,
Mode Mode
802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11n respectively.
Rate
Rate The actual transmission rate of the client in megabits per second.
Rate Rate
Signal
Signal This is a relative measure of signal quality. The value is expressed as a percentage of theoretical
Signal Signal
best quality. Signal quality can be reduced by distance, by interference from other radio-frequency sources
(such as cordless telephones or neighboring wireless networks), and by obstacles between the router and
the wireless device.
WISH Sessions
Displays full details of active local wireless sessions through your router when WISH has been enabled. A
WISH session is a conversation between a program or application on a wirelessly connected LAN-side
computer and another computer, however connected.
Page 67 of 73
Page 68

User Manual
Originator
Originator The IP address and, where appropriate, port number of the computer that originated a network
Originator Originator
connection.
Target
Target The IP address and, where appropriate, port number of the computer to which a network connection
Target Target
has been made.
Protocol
Protocol The communications protocol used for the conversation.
Protocol Protocol
State
State State for sessions that use the TCP protocol.
State State
NO: None -- This entry is used as a placeholder for a future connection that may occur.
SS: SYN Sent -- One of the systems is attempting to start a connection.
EST: Established -- the connection is passing data.
FW: FIN Wait -- The client system has requested that the connection be stopped.
CW: Close Wait -- the server system has requested that the connection be stopped.
TW: Time Wait -- Waiting for a short time while a connection that was in FIN Wait is fully closed.
LA: Last ACK -- Waiting for a short time while a connection that was in Close Wait is fully closed.
CL: Closed -- The connection is no longer active but the session is being tracked in case there are
any retransmitted packets still pending.
Priority
Priority The priority given to packets sent wirelessly over this conversation by the WISH logic. The priorities
Priority Priority
are:
BK: Background (least urgent).
BE: Best Effort.
VI: Video.
VO: Voice (most urgent).
Time Out
Time Out The number of seconds of idle time until the router considers the session terminated. The initial
Time Out Time Out
value of Time Out depends on the type and state of the connection.
300 seconds
300 seconds UDP connections.
300 seconds 300 seconds
240 seconds
240 seconds Reset or closed TCP connections. The connection does not close instantly so that
240 seconds 240 seconds
lingering packets can pass or the connection can be re-established.
7800 seconds
7800 seconds Established or closing TCP connections.
7800 seconds 7800 seconds
Page 68 of 73
Page 69

Maintenance
Maintenance Menu includes:
System
Firmware Upgrade
Reboot
System
User Manual
Page 69 of 73
Page 70

User Manual
The Administrator Settings section is used to set-up secure access to the Web-based management. By
default no password is configured. It is highly recommended that you create a password to keep your new
router secure.
Admin Password
Admin Password Enter a password for the user "admin", who will have full access to the Web-based
Admin Password Admin Password
management interface.
User Password
User Password Enter a password for the user "user", who will have read-only access to the Web-based
User PasswordUser Password
management interface.
Gateway Name
Gateway Name The name of the router can be changed here.
Gateway NameGateway Name
Inactivity Time Out
Inactivity Time Out If the router does not detect any administrative activity (from WAN or LAN) during this
Inactivity Time OutInactivity Time Out
number of minutes, it logs the adminstrator off.
Enable HTTPS Server
Enable HTTPS Server Enabling this option makes it possible to perform remote management with the
Enable HTTPS ServerEnable HTTPS Server
Secure HTTP (HTTPS) protocol.
Enable Remote Management
Enable Remote Management Enabling Remote Management allows you to manage the router from
Enable Remote ManagementEnable Remote Management
anywhere on the Internet. Disabling Remote Management allows you to manage the router only from
computers on your LAN.
Remote Admin Port
Remote Admin Port The port that you will use to address the management interface from the Internet. For
Remote Admin PortRemote Admin Port
example, if you specify port 1080 here, then, to access the router from the Internet, you would use a URL
of the form: http://my.domain.com:1080/.
Use HTTPS
Use HTTPS Setting this option requires all remote administration to use the Secure HTTP (HTTPS) protocol.
Use HTTPS Use HTTPS
For example, if you specify port 1080 above, then, to access the router from the Internet, you would use a
URL of the form: https://my.domain.com:1080/.
Remote Admin Inbound Filter
Remote Admin Inbound Filter Select a filter that controls access as needed for this admin port. If you do not
Remote Admin Inbound Filter Remote Admin Inbound Filter
see the filter you need in the list of filters, go to the Inbound Filter Section screen and create a new filter.
System Settings
Restore to Factory Default
Allows you to reset the device to its factory settings.
Restore Defaults
Restore Defaults The Restore Defaults button will clear all user-entered modification and will reset the
Restore Defaults Restore Defaults
device settings back to its factory default values.
• LAN IP address: 192.168.1.1
Username: admin Password: blank
•
Page 70 of 73
Page 71

User Manual
Firmware Upgrade
The Upgrade Firmware page displays the Upgrade Firmware window so that you could update the latest
firmware. Please make sure that you have downloaded the latest and correct firmware from the product
support website and store it in local drive.
To upgrade the latest firmware, click Browse to locate the firmware upgrade file, and then click Upload.
Please wait for 70 seconds.
Warning!
Warning! Do not power off the unit when it is being upgraded.
Warning! Warning!
Upload.
Upload.Upload.
Reboot
Click Reboot to reboot the device.
Page 71 of 73
Page 72

User Manual
Regulatory Compliance Notices
FCC Statement
This equipment has been tested and complies with the specifications for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used according to the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which is found by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
Increase the separation between the equipment or devices
Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver’s
Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
Page 72 of 73
Page 73

Safety Warnings
For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
Do not open the device. Opening or removing the device cover can expose you to dangerous high
voltage points or other risks. Only qualified service personnel can service the device. Please
contact your vendor for further information.
Do not use your device during a thunderstorm. There may be a risk of electric shock brought about
by lightning.
Do not expose your device to dust or corrosive liquids.
Do not use this product near water sources.
Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
Do not obstruct the ventilation slots on the device.
User Manual
Page 73 of 73
 Loading...
Loading...