Page 1
Table of
Contents
585-229-107
Issue 2
April, 1996
OneVision DEFINITY G3
Proxy Agen t Installation and
Connectivity
Graphics © AT&T 1988
Page 2
Contents
About Th is Book xiii
Book Overview xiii
Intended Audiences xiv
Typographical Conventions xvi
■ Keyboard conventions xvii
Your Proxy Ag ent Package xix
Trademarks xxi
Related Resources xxii
Reader Comments xxiv
1 Before You Begin 1-1
Chapter Overview 1-1
■ About the Proxy Agent 1-2
Section Overview 1-2
Stages of Translating PBX Data 1-3
Supported PBXs 1-4
■ Requirements 1-5
Section Overview 1-5
PC Requirements 1-6
To Check Disk Space 1-7
Recom mended Hardwar e 1-9
Recommended Software 1-10
■ About Installations 1-11
Section Overview 1-11
Issue 2 April 1996 iii
Page 3
Contents
UnixWare Method ology 1-12
Installation and Setup Task List 1-13
2 PC Hardware Installation 2-1
Chapter Overview 2-1
PC Setup Checklist 2-2
3 UnixWare Installation 3-1
Chapter Overview 3-1
■ Installation Procedures 3-2
Section Overview 3-2
New Installations 3-3
UnixWare 2.01 Upgrades 3-6
To S et System and Node Names 3-9
■ TCP/IP Administration 3-11
Section Overview 3-11
To Configure the Ethernet Interface 3-12
To Set the Hosts File 3-14
To Test the TCP/IP Connection 3-16
To Tr oubleshoot the TCP/IP Connection 3-17
iv Issue 2 April 1996
Page 4
Contents
4 Uni xWare Administrati on 4-1
Chapter Overview 4-1
■ Login Administration 4-2
Section Overview 4-2
About Logins 4-3
To Add New Logins: UNIX Shell 4-4
To Add New Logins: OA&M 4-6
To Add New Login s: Desktop 4-9
To Verify Group Assignments 4-11
■ Maintenance Administration 4-13
Section Overview 4-13
About Port Monitors 4-14
To Assign Devices to Ports 4-15
To Back Up and Restore 4-17
5 Planning Connectivity 6-1
Chapter Overview 6-1
■ About Connectivity 6-2
Section Overview 6-2
Proxy Agent Connectivity 6-3
Communications Hardware 6-5
■ Data Commu nications Hardware 6-6
Section Overview 6-6
To Choose the Hardware 6-8
Proxy Age nt an d Mod e m Connections 6-9
Proxy Age nt a n d Data Module Connections 6-10
Issue 2 Ap ril 1996 v
Page 5

Contents
■ PC Hardware Connections 6-23
■ Alarm Stream 6-31
Proxy Agent and ADU Connections 6-11
To Choose Circuit Packs 6-12
PBX and Modem Connections 6-13
PBX and Data Module Connections 6-14
PBX and ADU Connections 6-15
Cables for Modems 6-16
Cables for Data Modules 6-19
Cables for ADUs 6-21
Section Overview 6-23
PC Hardware Connections 6-24
Cables and Connectors 6-25
To Validate D ial Strings 6-27
To Set the Dip Switch 6-28
Section Overview 6-31
To Connect the Modem to the PC 6-32
Alarm Path 6-33
6 Connectiv ity 7-1
Chapter Overview 7-1
■ Dial-Up Connections 7-2
Section Overview 7-2
Port Terminations 7-3
Analog Connections 7-4
Digital Connections 7-7
vi Issue 2 April 1996
Page 6
Contents
To Program P BX Ports 7-9
Site-Specific Connections 7-13
Multiple Connections 7-14
■ Direct Connection s 7-15
Section Overview 7-15
Requirements 7-16
Proced ural Overview 7-18
To Install the Hardware 7-18
To Configure Data Modules 7-19
To Set Data Mod ule Extensions 7-22
To Update the Abbreviat e d Dial ing List 7-24
To Edit the Devices File 7-26
To Set Up a Hotline Connection 7-27
To Administer the Proxy Agent 7-28
7 Serial I/O Cards 8-1
Chapter Overview 8-1
■ Installation Procedures 8-2
Section Overview 8-2
DigiBoard Xem 8-3
Equinox SST 8-6
Equinox XP 8-7
Specialix XIO 8-10
■ Administration Procedures 8-11
Section Overview 8-11
To Assign Devices to the Proxy Agent 8-12
Issue 2 April 1996 vii
Page 7
Contents
To Verify Device Types 8-14
To Verify Dial Strings 8-15
To Create Port Monitor Entries 8-17
8 Proxy Agen t Installat ion 9-1
Chapter Overview 9-1
About the Proxy Agent 9-2
Making Preparations 9-3
To Verify Hardware Co nnect ions 9-4
To Verify Installed Software 9-5
Proxy Agent Installation 9-6
9 Proxy Agent Admini st ration 10-1
Chapter Overview 10-1
■ Maintenance 10-2
Section Overview 10-2
UNIX Permissions 10-3
Printers 10-4
Back Up Your System 10-5
Remove the Software 10-6
■ Proxy Agent Configuration 10-7
Section Overview 10-7
To Verify the Installation 10-8
viii Issue 2 Apr i l 199 6
Page 8

Contents
To Change Hardware Configuration 10-10
To Change the User Interface 10-13
■ Pr oxy Agent Connectivity 10-17
Section Overview 10-17
To Define External Systems 10-18
To Connect to a PBX 10-20
To Dis connect from a PBX 10-22
■ Proxy Agent Customization 10-23
Section Overview 10-23
To Start the Proxy Agent 10-24
The Online Guide 10-25
To Check the Proxy Agent Status 10-26
To Change Clients 10-27
To Change Managers 10-28
10 Alarms 11-1
Chapter Overview 11-1
■ Alarm Reception 11-2
Section Overview 11-2
Program the Alarm Receiver Port 11-3
Set Mo d em Options for Alarm Reception 11-9
■ Alarm Forwarding 11-12
Section Overview 11-12
Program the Alarm Sender Port 11-13
Edit the Dialers File 11-14
Set the Mode m Op t ions fo r Alarm Forwarding 11-15
Issue 2 April 1996 ix
Page 9
Contents
■ Program the Proxy Agent 11-16
Section Overview 11-16
Change Alarm Forwarding 11-17
11 Post-Installati on Te sts 12-1
Chapter Overview 12-1
Technician Checklist 12-2
Customer Checklist 12-3
A PA001 Form A-1
Appendix Overview A-1
PA001 Administration Request Form A-2
B Design Configuration B-1
Appendix Overview B-1
■ Proxy Agent Network B-2
Digital Switch On-Network B-2
Analog On-Network B-4
“Other” On-Network B-6
Customer-Provided Multiplexor Data Networks B-8
x Issue 2 April 1996
Page 10
Contents
■ Proxy Agent Connectivity B-11
Local Connection: 200 0’ or Less
Sys75 R1V3; G1; G3i V1, V2, V3; G3 vsV1, V2, V3 B-12
Local Connection: 200 0’ or Less
G3rV1, V2, V3 B-13
Local Connection: 200 0’ or Less
Sys75 R1V3; G1; G3i V1, V2, V3; G3 vsV1, V2, V3 B-14
Local Connection: 500 0’ or Less
G3rV1, V2, V3 B-15
Remo te Connection:
Sys75 R1V3; G1; G3i V1, V2, V3; G3 vsV1, V2, V3 B-16
Remo te Connection:
G3rV1, V2, V3 B-17
C Basic vi C-1
Appendix Overview C-1
vi Edito r C-2
D Proxy Agent Quick Reference D-1
Appendix Overview D-1
Hotkeys D-2
Commands D-3
Issue 2 April 1996 xi
Page 11

Contents
GL Glossary GL-1
IN Index IN-1
xii Issue 2 April 1996
Page 12

About This Book
Book Overview
In this
preface
This preface explains how to use this book and includes the
following topics.
For this in formation … See page …
Intended Audiences xiv
Typographical Conventions xvi
Your Proxy Agent Package xix
Trademarks xxi
Re lated Resources xxii
Reader Comments xxiv
Issue 2 Apr il 1996 xiii
Page 13

About This Book
Intende d Au diences
Intended Audiences
Introduction This book is intended fo r AT& T customers who use OneVision
Network Management Solutions DEFINITY
G3 applications to
manage their PBXs on a network management system (NMS). In
particular, this book is intended for:
■ Network managers who use a SNMP-b ased network
management system as a management tool
■ System a d minist rators who se t up t he OneVision Net work
Management Solutions DEFIN ITY G3 Proxy Agent and
ensure that it performs correctly
■ AT&T support personnel who are responsible for setting up
and insta lling the Proxy Agent
What you
should know
Before you use this book to help you install the Proxy Agent, you
should already understand how to:
■ Install the require d hardw a re
■ Use UnixWare
■ Execute the UNIX
Release 2.01 for system ad minist ra tio n
commands necessary to move around
in the d irectories and fil es
■ Verify that the o p erati n g s ystem is running a n d in g ood
healt h
■ Use one of the UNIX Ed itors (v i o r ed) to customize Proxy
Agent to meet site requirements
Earlier
versions of
UNIX
Because administration tools vary across different versions
of UNIX, knowledge of an earlier version of UNIX may be
insufficient.
xiv Issue 2 Ap ril 1996
Page 14

About This Book
Intended Audiences
How to use
this book
This book is d e si gned to help you get the infor m ati on you ne e d
quickly. Mos t likely, you will not need to use the enti re book, but
will need particular information in it to meet your requirement s.
Issue 2 April 1996 xv
Page 15

About This Book
Typographical Conventions
Typographical
Conv entions
Introduction Before you start installin g the Proxy Age n t, it is im p or tant to
understand the typographical conventions used in this document.
Formatting
conventions
The following kinds of formatting in the text identify sp ecial
informati o n.
Format of text Typ e of inform ation
constant width
■ Words or characters that you type.
Examp le: Ente r Proxy Agent.
■ Text that displays on your screen.
Example: Please remove the
installation diskette and
continue when ready.
italic
type Specialized terms.
Titles of other books in the OneVision
docume nt set.
[Bracketed text] Placeholders for informat ion t hat you
supply.
Example: Ent er public!g3mgt!
[client string] means that you
type public!g3mgt! exactly as shown,
but de t ermi ne the value of the cl i ent
string.
End In a table, signifies the end of a
xvi Issue 2 Ap ril 1996
procedure.
Page 16
About This Book
Typographical Conventions
Keyboard conventions
This book uses the following keyboard conventions.
Keys Comments
Key names All keys are shown in small type.
Example: Press
Enter.
The keys on your keyboard may not
be labeled exactly a s they are i n this
book.
Combination keys You will frequently hold down one
key while you press another key.
These combination keys are
sep arate d by a h y p hen.
Example: Press
Ctrl-Y.
Sequential keys You press sequential key
co mbinations in the o rd er shown.
Example : Press
Esc Esc means to
press the Escape key twice.
Sometimes a co m bination key is
immediately followed by another
key.
Example : Press
hold down
release both keys and press
Ctrl-G G means to
Ctrl while pressing G, then
G
again.
Enter and Return These keys generally perform the
same function. This bo ok uses
Enter.
If your keyboard does not have an
Enter key, you can substitute the
Return ke y.
Issue 2 April 1996 xvii
Page 17
About This Book
Typographical Conventions
Syntax
conventions
Window
conventions
Some conventions i n syntax are:
Syntax Comments
Enter The word "enter" means to type the word
shown in constant width type, then press
Enter key.
the
Examp le: Ente r installpkg means type
installpkg and then press the
Enter key.
Procedures for window-style screens use the following
co nventi ons.
Format Comments
à
Shows menu selections.
Examp le: Sel ect O p tions
à
Print, means to
select Options, then select Print from the
pull-down menu.
Bold In dicates buttons on the window that you
click.
xviii Issue 2 April 1996
Example : Click on Apply.
Page 18

About This Book
Your Proxy Agent Package
Your Proxy Agent
Package
What’s in
your
package
Online
documents
How to
access online
documents
Your Proxy Agent p ackage includes the following resources:
■ This book,
and Connectivity
■ Proxy Age nt softwa re an d online d ocuments
■ Novell's UnixWare Release 2.01 o perating system software
OneVision DEFINITY G3 Proxy Agent Installation
and documentation
In addition to this book, your Proxy Agent p ackage includes the
following online documents:
■ Comman d-line help provides a list of commands.
■ Field help briefly exp lai ns the fie l d s on a Proxy Age n t form.
■ T he Proxy Agent online guide has an overview of Proxy
Agent applications and fea tur es, tells you about menus and
forms, and provides information about each application
and how to use it. It also contai ns a table of contents, an
index, and a glossary.
You can access the online docume nts anyti me you are using the
Proxy Agent.
If you want to access
this type of help … Then press these keys …
Field help
Online g uide
Ctrl-Y
Ctrl-G G
Issue 2 April 1996 xix
Page 19

About This Book
Your Proxy Agent Package
Closing the
online guide
You can exit the Proxy Agent online guide at any time by pressing
Ctrl-X.
xx Issue 2 April 1996
Page 20

About This Book
Trademarks
Trademarks
AT&T
trademarks
Third-party
trademarks
■ DEFINITY is a registered trademark.
■ OneVision is a trademark.
All other brand and product names are the trademarks of their
respective holders.
Issue 2 April 1996 xxi
Page 21

About This Book
Related Resources
Related Resources
Ty pes of
documents
Fault Management
documents
Other d o c uments that are related to the Proxy Agent, b ut not
included with your Proxy Agent package are:
■
AT&T OneVision Definity Enterprise Management Project
Provisioning Packag e
■ Fault Management do c u m ents
■ DEFINITY
G3 docume nts
The Fault Management do c u m ents are:
■
OneVision Network Management Solutions DEFINITY G3
F ault Management Installation and Integration
—
for HP Open View on a HP9000
—
for HP OpenView on a Sun Sparc OS
—
for Cabletron SPECTRU M o n a S un Sparc OS
, 585-229-104
, 585-229-105
,
585-229-110
for IBM NetView
—
■
OneVision Network Management Solutions DEFINITY G3
, 585-229-114
F ault Management Online User Guide
DEFINI TY
documents
Some useful DEFINITY docu m ents are:
■ Str ea mlined Implemen ta tion Librar y
■
DEFINITY Communications System Generic 3 Feature
Description
■
DEFINITY Communications System Generic 3 Capabilities
555-230-499
xxii Issue 2 A pril 1996
, 555-230-204
,
Page 22

About This Book
Related Resources
■
DEFINITY Communications System Generic 1 and Generic
3 System M anagement
■
DEFINITY Communications System Generic 3r
Implementation
■
DEFINITY Communications System Generic 3i
Implementation
, 555-230-651
, 555-230-650
, 555-230-500
Ordering
information
Third-party
documents
For more informat ion about t hese books an d other AT&T
pu bl ications, see the
Publications Catalog
Glo bal Business Comm unications Sy s te ms
, 555-000-010.
You may find it helpful to refer to the installat ion do c ume nts tha t
come with your hardware and software.
Issue 2 April 1996 xxiii
Page 23

About This Book
Reader Comments
Reader Comments
Comment
card
Where to
find the card
If the card is
missing
We are interested in your suggestions for documentation
imp rovem ents a n d u rg e you to fill out the co mm ent c ard a n d
return it to us.
The reader comment card is behind the title page.
If the comment card is missing, please send your comments to the
following add ress:
AT&T
Product Documentation Development
Room 22-2C11
11900 North Pecos Street
Denver, Colorado 80234
Fax: (303) 538-1741
Remember to write down the document name and number on
your com me nt sheet.
Example Proxy Agent Installation and Connectivity guide, 585-229-107.
xxiv Issue 2 A p r i l 1996
Page 24

Before You Begin
Chapter Overview
1
In this
chapter
This chapter c overs infor mat ion you need to know before you
be g in installing and setting up the Proxy Agent.
For this in formation … See page …
About the Proxy Agent 1-2
Requirements 1-5
Abo ut Installations 1-12
Issue 2 April 1996 1-1
Page 25

Before You Begin
Section Overview
About the Proxy Agent
Section Overview
In this
section
This section contains the following information.
For this in formation … See page …
Stages o f Translating PBX Data 1-3
Supported PBXs 1-4
1-2 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 26
Before You Begin
Stages of Translating PBX Data
Stages of Translating
PBX Data
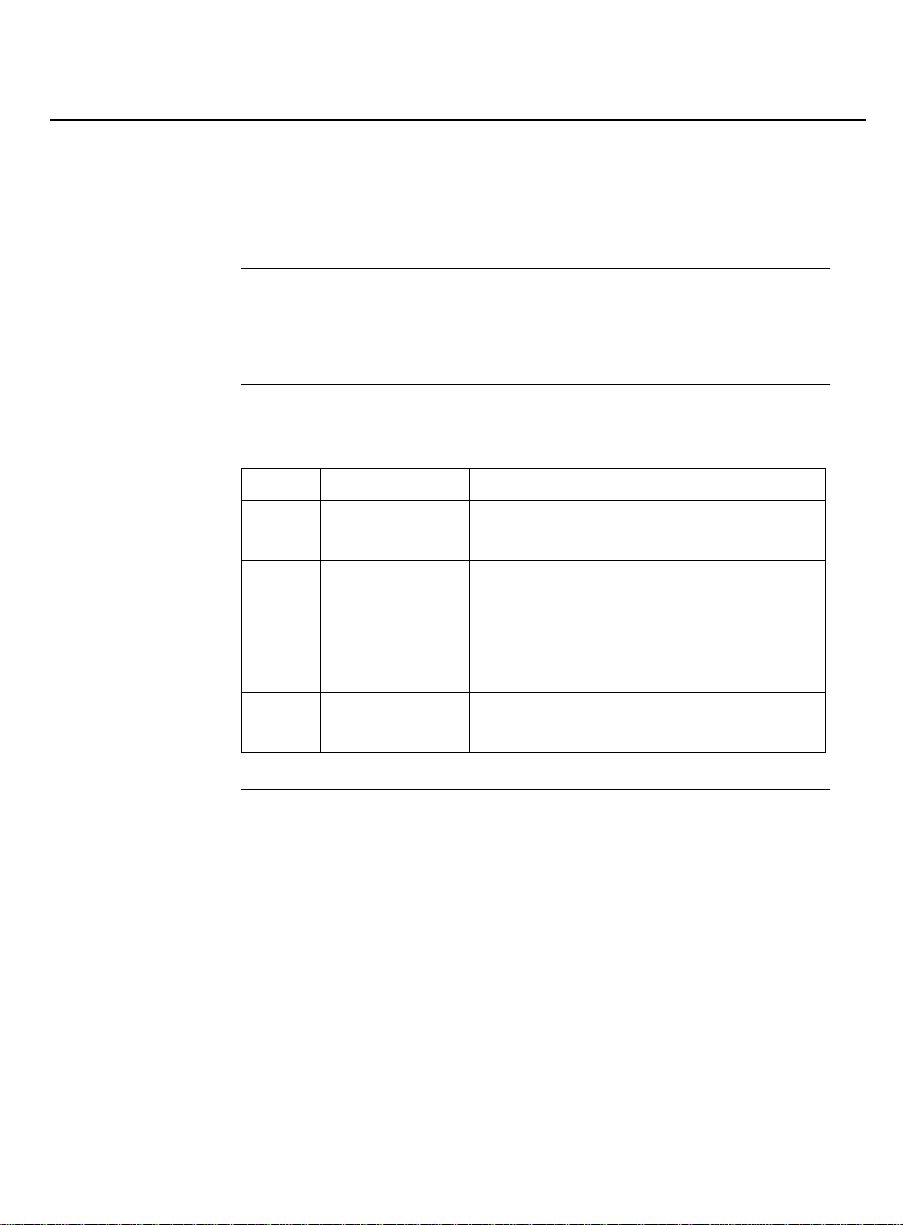
Description The Proxy Age nt tran slates data from a DEFIN ITY G3 PBX i nto a
format that yo ur ne twork man agement system can understand.
Process The following table shows the p rocess for translati n g PBX data.
Step What does it Description
Other
functions
1 DEFINITY G3
PBX
2 Proxy Agent Translates the data from the
3 Proxy Agent Forwards the P BX management data
The Proxy Agent also provides administrative access to th e switch
to accommodate those functions not p rovided by SNMP.
Sends PBX management d a ta to the
Proxy Agent.
D EFINITY OSSI (Operating Support
Sys te m Interface) and alarm format
to the SNMP (Simple Network
Managemen t Protocol) format.
to the network mana g e m ent system.
Issue 2 April 1996 1-3
Page 27
Before You Begin
Supported PBXs
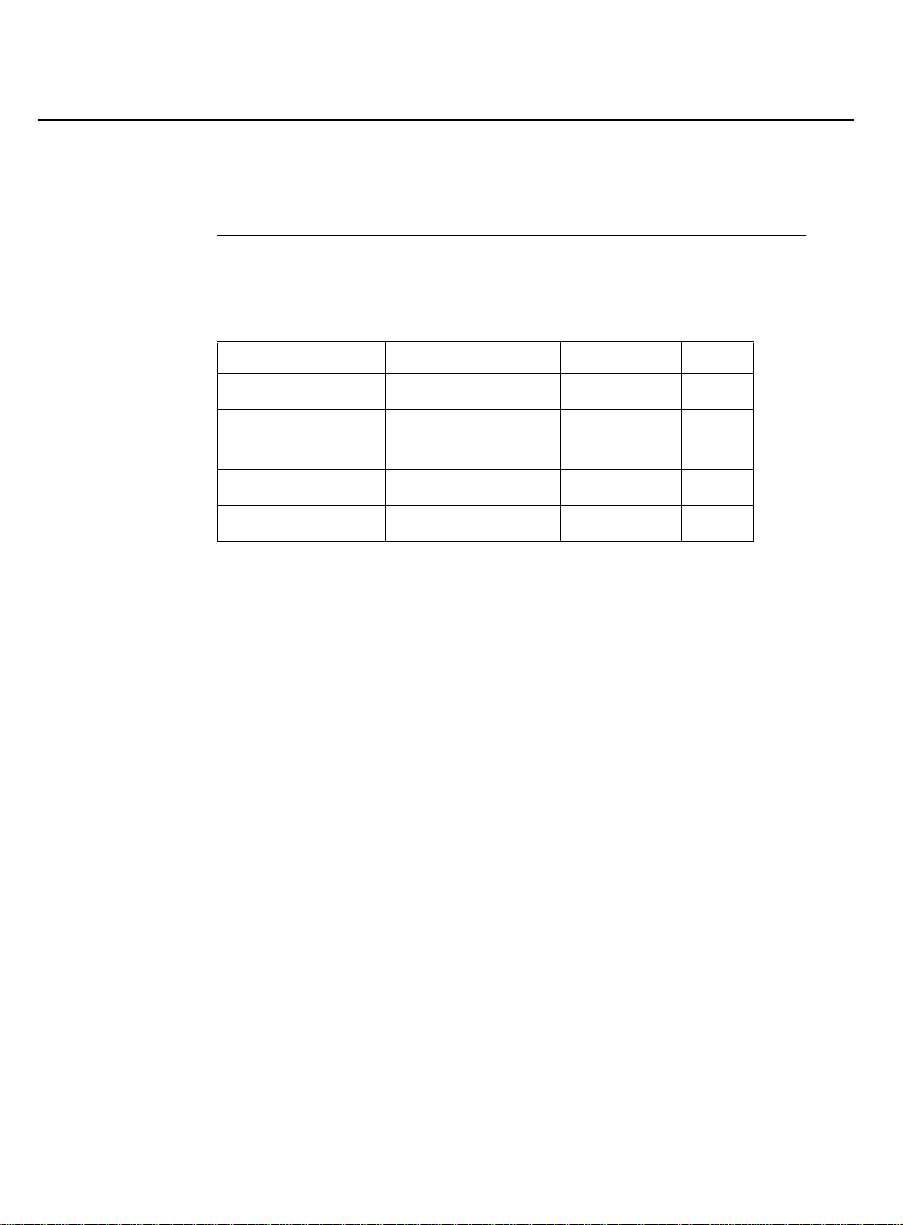
Supported PBXs
Ty pes of
PBXs
The Proxy Agent supports the following DEFINITY G3 PBXs.
G3vs G3s G3i G3r
V1.1 - ABP/PBP V1.1 - ABP/PBP V1.1 - 286 V1.1
V2 - ABP/PBP V2 - ABP/PBP V2 - 386
V2 - 286
V3 - ABP/PBP V3 - ABP/PBP V3 - 386 V3
V4 - ABP/PBP V4 - ABP/PBP V4 - 386 V4
V2
1-4 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 28

Before You Begin
Section Overview
Requirements
Section Overview
In this
section
This section contains the following information.
For this in formation … See page …
PC Requirements 1-6
T o Check Disk Spac e 1-7
Recommended Hardware 1-10
Recommended Software 1-11
Issue 2 April 1996 1-5
Page 29
Before You Begin
PC Requirements
PC Requirements
Type of PC The Proxy Ag e nt req uires an industry standard Intel 486 (or later)
processor-based personal comp uter with ISA BUS slots.
Required
configuration
Required
disk spac e
For the Proxy Agent to run properly, your PC must have:
■ A 3.5-inch, 1.44-MB diskette drive
■ 16 MB of random access memory
■ A h ard disk of at least 500 MB
■ A CD-ROM drive , 2x or gre ater
■ A Serial I/O ports board
■ Uni xWare Release 2.01 com p at ible, 10 Mbit network
interface card
See Recomm ended Hard wa re on page 1-10 for more inform at ion.
Estimates of the disk space that the Proxy Agent requires during
installation are in the following table. Disk space on UnixWare is in
512-byte blocks.
Directory Blocks
/tmp 2,000
/usr 2,000
Remember, space re quirements expand as you generate d at a
files.
1-6 Issue 2 April 1996
Total 4,000
Page 30

Before You Begin
To Check Disk Space
To Check Disk Space
When to use Check the amount of unused disk space before you install the
Proxy Agent to ensure that there is enough room.
Ty pes of
directories
The install script for th e Proxy Agent uses the following directories.
Issue 2 April 1996 1-7
Page 31

Before You Begin
To Check Disk Space
Directory Description
/tmp Stores the temporary files that the install script
creates when you install Proxy Agent applications.
This directory uses disk space as the install script
installs each a pplication file on the hard disk.
After the install script c o pies the files to th e Proxy
Agent’s home direct ory, it deletes the space from
the /tmp directory.
If there is insufficient disk space in the Proxy
Agent’s home directory to create these files, the
install sc rip t a b orts.
/usr By def ault , the insta ll script loads the Proxy Agent
into the /usr directory. This directory stores all of
the user files and subd i rectories.
The total space required by the /usr directory must
be e q u al to or g reat er than th e sum of:
■ The amount of s p a c e that is req ui red for all
Proxy Agent applications, and
■ The space needed for the customer data that
the Proxy Agent generates.
This sp ace requi reme nt may g row if the Proxy
Agent supports more than two large PBXs.
Procedure Use the following steps to check for sufficient unused disk space.
1-8 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 32

Before You Begin
To Check Disk Space
Step Action
1 At the UNIX prompt, enter the following command:
df /tmp
2 Does the /tmp directory have at least 2,000 blocks of
unused disk space?
■ If yes, go to step 3.
■ If no, allocate more space to /tmp.
3 Enter the following comman d:
df /usr
4 Does the /usr directory have at least 2,000 blo cks of
unused disk space?
■ If yes, your PC has enough unused disk space to
install the Proxy Agent.
■ If no, allocate more space to /usr.
End
Issue 2 April 1996 1-9
Page 33

Before You Begin
Recommended Hardware
Recommended
Hardware
Hardware
certification
TSO sup port T he Technical Support Organization ( TSO) will make its best effort
See also Your project provisionin g package also contains some design
Novell, Inc. p u b l ishes a list of PC hardware that is certified for
use with UnixWare 2.01. (Your project provisioning package has a
toll-free number that you can call to order this list.)
AT&T certifies communications hardware.
We reco m men d that yo u only op erat e the Proxy Agent using
certified hardware.
to support the Proxy Agent on non-certified hardware in other
configurations. If you use hardwa re that is not certified, the TSO
will bill you for any support on a time-and-materials basis.
configurations and ord ering information for hardware. For your
co nvenience, this part of the provisioning pac kage is reprod uced
in B.
1-10 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 34

Before You Begin
Recommended Software
Recommended Software
TSO sup port T he Technical Service Organization (TSO) in the U.S.A. supports
the Proxy Agent if you install only certified software on your Proxy
Ag ent PC.
See also Your project provisionin g package lists the cert if ied software.
Ordering
information
AT&T includes UnixWare in the software package that you receive
when you ord er the Proxy Agent.
Issue 2 April 1996 1-11
Page 35

Before You Begin
Section Overview
About Installations
Section Overview
In this
section
This section contains the following information.
For this in formation … See page …
UnixWare Methodology 1-13
Installation and Setup Task List 1-14
1-12 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 36

Before You Begin
UnixWare Methodology
UnixWare Methodology
Introduction UnixWare is an operating system that allows you to use either of
the following meth ods to co m p lete most tasks:
■ Desktop
■ Shell co m m a n d-line inter face
Desktop The desktop is a graphical user interface (GUI) that uses
windows, icons, and the mouse.
If you are a begi nning UnixWare user, we suggest you use the
desk t op becau se it is more i n t u i tive and does more error checking
than the shell com man d-line interface.
Shell The shell command-line interface requires you to type commands
to work with UnixWare.
If you are knowledgeable about the UNIX operat ing system, you
ca n use either the shell or the d esktop to do your work.
Procedures
in this book
The UnixWare procedures in this book focus on how to use the
shell. To use the desktop, click on the ap propriate icons to open
the file you want to change, then use the procedure described in
this book.
See also See your
Uni xWare Syst em O w ner Handb o o k
for instructions on
using the d eskto p .
Issue 2 April 1996 1-13
Page 37

Before You Begin
Installa ti on a n d Set u p Tas k List
Inst alla tion and Setup
Task List
Introduction The task list in this section is designed to help you organize your
installation and setup activities.
Customize
the task list
You may want to customize this list by a ddi n g the fo llowin g items:
■ The people or organizations who are responsible for each
task
■ The d ate e ac h task needs to be comp leted
Task list We recommend that you c o mplete the fo llowi n g steps
se quent iall y.
Step Action C hapter
1 Work with your AT&T representa tives to
complete the OneVision DEF INITY Enterprise
Management Project Provisioning Package .
Mail or FAX the PA001 form to the TSO (in
the U.S.A.)
2 Ensure that all hardware is certified. 1
3 Configure your Proxy Agent PC. 2
A
1-14 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 38

Before You Begin
Installation and Setup Task List
Step Action Chapter
4 Is UnixWare 2.01 installed on your Proxy
3
Agent PC?
■ If yes, go to step 5.
■ If no, install (or up grade to) UnixWare
2.01.
5 Administer the TCP/IP connection. 3
6 Admi nister UnixW are. 4
7 Connect the Proxy Agent an d the PBX. 6 , 8
8 Install the serial I/O card. 7
9 Install the Proxy A gent software. 8
10 Confi g ure the Proxy Agent. 9
11 Customize the Proxy Agent for your
9
business.
12 Set alarm reception an d forwarding . 10
13 Test the installation. 11
End
Issue 2 April 1996 1-15
Page 39

PC Hardware Installation
Chapter Overview
2
In this
chapter
This chapter co ntai ns a list of the PC hardware that you need for
the Proxy Agent PC.
For this in formation … See page …
PC Se tup Checklist 2-2
Issue 2 April 1996 2-1
Page 40

PC Hardware Installat ion
PC Setup Checklist
PC Setup Checklist
Introduction The first step in installing the Proxy Agent is to ensure that your
Novell-ce r tified hardw a re is set up and runnin g pro p erly.
Materials
needed
Checklist Use the following checklist when you set u p your Proxy Agent PC:
You need the hardware (and its documentation) listed in the
project provisioning package.
❏ Assemble th e PC ’s keyboard, monitor , and mouse.
❏ Install the network interface card.
❏ Install the SCSI Host Bus ad a p t e r.
❏ Install the Serial I/O ports card.
2-2 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 41

UnixW are Installatio n
3
Chapter Overview
Introduction This chap t er ex p lains how to install UnixWare onto your Proxy
Ag ent PC.
Who inst alls
UnixWare
When to use Use the p rocedures in this chapter after you have installed all of
In this
chapter
This chapter is written for field technicians who are trained in
UNIX.
the PC hardwa re.
This chap t e r co ntai ns the followin g sect i ons.
Issue 2 April 1996 3-1
Page 42

UnixWare Installation
Chapter Overview
For this in formation … See page …
Installation Proce dures 3-3
TCP/IP Administration 3-12
3-2 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 43

UnixWare Installation
Section Overview
Installation Procedures
Section Overview
Introduction This section explains how to start the installation software that
comes with UnixWare 2.01. It also provides guidelines to help you
throu g h the inst alla tio n.
Once you have the installation sof tware runn ing, refer to the
UnixWare installation han dbook to compl ete the s creens and
fields.
In this
section
This section contains the following installation p rocedures.
For this in formation … See page …
New Installations 3-4
UnixWare 2.01 Upgrades 3-7
To Set Syst em and Node N a m e s 3-10
Issue 2 April 1996 3-3
Page 44

UnixWare Installation
New Installations
New Installations
When to use Use the following procedure only if you are installing UnixWare for
the first time. If your Proxy Agent PC already has UnixWare
software installed, see UnixWare 2.01 Upgrades.
Materials
needed
■ Y our Proxy Agent PC hardware set up and ready to load the
software
■ The installation diskette with the following label:
UnixWare
Application Server 2.0
Install Disk 1 of 1
■ The UnixWare CD with the following l a b el:
Novell
UnixWare 2
Version 2.01
■ The UnixWare installation handbook for release 2.01
If you have not yet loaded the software, you may also need the
installation diskettes for the following cards:
■ Ethernet card
■ Host bus ada p ter ca rd
Time needed Installation takes about 2 hours, and depends on the speed of the
processor in your Proxy Agent PC.
3-4 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 45

UnixWare Installation
New Installatio ns
Installation
guidelines
Before you begin the installation, review the following guidelines:
■ We recom men d that you co mplete the installa tion
ch ecklist s in your UnixWare installation handbook before
you be gin the installation.
■ Use the installation default s as much as possible.
Procedure To start the installati on proc e ss:
Step Action
1 Insert the installation diskette and the CD for UnixWare.
2 Reboot your computer.
Result: First the startup screen displays. Then the
welcome screen displ ays.
3 Follow the screen prompts.
Hint: If you need help, see the UnixWare installation
handbook for release 2.01 .
End
Installation
prompts
During the install ation, your s c reen promp ts you for inform ation
about your system’s co nfiguration. In gen eral, use the UnixWare
d efaults. However, some of the prompts require information
specific to the Proxy Agent.
The following table provides this information:
Issue 2 April 1996 3-5
Page 46

UnixWare Installation
New Installations
Screen or field What you enter
Owner Login ID root2
Destructive Installation ENTIRE DISK
System Node Name The name of your Proxy Agent as per
Package Selectio n On this screen:
your PA001 form a n d uname
command.
1. S elect ALL . (Press
F5.)
2. Deselect A ddi tional Platform
Utilities.
3. Accept all settin g s .
3-6 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 47

UnixWare Installation
UnixWare 2.01 Upgrades
UnixWare 2.01 Upgrades
When to use Use the following procedure only if your P r oxy Agent PC is loaded
with UnixWare softw a re that is older than release 2.01. If you are
installi n g UnixWare for the first time, see New Installations.
Materials
needed
■ Y our Proxy Agent PC hardware set up and ready to load the
software
■ The ad minist ra tio n manu al for you r cu rrent operatin g
system (for b acku p instructions)
■ The installation diskette with the following label:
UnixWare
Application Server 2.0
Install Disk 1 of 1
■ The UnixWare CD with the following l a b el:
Novell
UnixWare 2
Version 2.01
■ The UnixWare installation handbook for release 2.01
If you have not yet loaded the software, you may also need the
installation diskettes for the following cards:
■ Ethernet card
■ Host bus ada p ter ca rd
Time needed Installation takes about 2 hours, and depends on the speed of the
processor in your Proxy Agent PC and the number of files in your
release 1.2 Proxy Agen t.
Issue 2 April 1996 3-7
Page 48

UnixWare Installation
UnixWare 2.01 Upgrades
Installation
guidelines
Before you begin the installation, review the following guidelines:
■ We recommend that you complete the installation
ch ecklist s in your UnixWare installation handbook before
you be gin the installation.
■ Use the installation default s as much as possible.
■ When the Selecting an Owner screen displays, change the
Owner Login ID field to root2.
!
Be sure to perform a nondestructive installation. This type of
installation replaces the operating system but does not
replace your data files.
Procedure To upgrade UnixWare:
Step Action
1 Back up any existing data, including user files,
password files , and administrative files.
Hint: If you need help, see the administrati on man ual
for your current operating system.
CAUTION:
2 Enter the following comman d at the root p rompt:
3-8 Issue 2 April 1996
cd /: shutdown -i0 -g0 -y
Result: Shutd own me ssages display.
Page 49

UnixWare Installation
UnixWare 2.01 Upgrades
Step Action
3 Insert the installation diskette and the CD for UnixWare.
4 Reboot your computer.
5 Follow the screen prompts.
Result: First the startup screen displays. Then the
welcome screen d ispla ys.
Hint: If you need help, see the UnixWare installation
handbook for release 2.01.
End
Issue 2 April 1996 3-9
Page 50

UnixWare Installation
To Set System and Node Names
To Set System and Node
Names
Introduction Before the Proxy Ag e nt can interact with your network properly:
■ The system and n od e nam es must m a t c h.
■ T he system name that is on the P A001 form must match the
system name that is on your network.
Definitions
■ The
■ The
system name
node name
is the name of your Proxy Agent PC as it is
is the name of your Proxy Agent.
known to the TCP/IP network.
When to use You set your syste m an d nod e nam es after you have installed
UnixWare.
Materials
needed
UNIX
options
To set the system and node names, you need the name of your
system as it is printed on the PA001 form.
The following table desc ribes the UNIX options that are used with
the uname co m man d to compare system names.
Option Description
-n Node name
-s System name
3-10 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 51

UnixWare Installation
To Set Sy stem and Node Names
The node name and the system nam e are the same for a Proxy
Ag e nt installa tion .
Procedure Use th e following steps to set the system an d node nam es.
Step Action
1 Enter the following comman d at the UNIX prompt:
uname -sn
Result: The syst e m displays the system and node
names.
Example: agent2 agent2
2 Do the names on you r sc re e n matc h b o t h each other
and the sy stem name on the PA001 form?
■ If yes, you have completed this procedure.
■ If no, go to step 3.
3 Enter the following comman d at the UNIX prompt.
Make sure that the system name an d the node name
mat c h the system name on t he PA001 form exactly.
setuname -s [system name] -n [node name]
Example: setuname -s agent2 -n agent2
Issue 2 April 1996 3-11
End
Page 52

UnixWare Installation
Section Overview
TCP/IP Administration
Section Overview
Introduction After you esta b lish the hardware connections be t ween the Proxy
Ag e nt PC and the network, you must a d m inist er the TCP/IP
cap ability on the Proxy Agent.
In this
section
This section contains the following procedures for admin isterin g
T CP/IP. For the best results, complete these procedures in the
order shown.
For this in formation … See page …
To Configure the Ethernet Interfa ce 3-13
To Set the Hosts File 3-15
To Test the TCP/IP Connection 3-17
To Troubleshoot the TCP/IP Connection 3-18
3-12 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 53
UnixWare Installation
To Configure the Ethernet Inte rf ace
To Configure the
Ethernet Interface
Introduction You configure the Ethernet interface for the Proxy Agent when you
set the ifconfig options in the UNIX system.
When to use Configure the Ethernet interface after you set the system name for
the Proxy Agent PC.
Materials
needed
UNIX
commands
You need the following informat ion to c o n fi g ure the Ethernet
interface:
■ The IP ad d ress for the Proxy Agen t PC.
■ The system name as it appears on the PA001 form.
■ Your network’s configuration, including the net mask for your
local network. (See your network adm in istrat or if you need
help.)
Use the following steps to configure the Ether net interface.
Command Description
ifconfig Assigns an address to a netwo rk interfac e a n d
configures the interface’s parameters.
netmask Determines which part of your network address
is used as a network ID and which pa rt is used
as the Proxy Ag ent I D.
Issue 2 April 1996 3-13
Page 54

UnixWare Installation
To Configure the Ethernet Interface
Procedure Use th e following steps to set the ifc o nfi g opt ions.
Step Action
1 Enter the following c o m mand at the UNIX pr om pt:
/etc/confnet.d/configure -i
2 Follo w t h e pro mp ts to set t he appropriate
configurations.
End
UnixWare
bug
During the installati on, UnixWare disp lays the defaul t for the IP
hostna me . This nam e contains an extra numb e r, 2, at the end of
the n a m e . For exam ple:
If your IP hostname is … Then UnixWare displays this …
agent5 agent52
To c orre c t this b ug, enter the correct IP hostname manually.
3-14 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 55

UnixWare Installation
To Set the Hosts File
To Set the Hosts File
When to use Set the hosts file after you configure the Ethernet card.
Inputs To set the hosts file, you nee d a val i d IP address for the NMS. If
necessary, ask your network administrat or to assig n one.
Example IP
address
Procedure Use th e following steps to set the hosts file.
An example of an IP address in the hosts file is:
123.45.67. 8 nm s
The IP address
for the NMS
Step Action
1 Use a UNIX edi tor to o p en the following file:
/etc/hosts
Hint: You can use the UNIX editor of you r c ho ice.
(Appendix C lists basic vi operations.)
2 Page down to the end of the file.
The node name
on the NMS
Issue 2 April 1996 3-15
Page 56

UnixWare Installation
To Set the Hosts File
Step Action
3 Enter the IP address of the net work management
4 Save and c l ose the file.
5 Enter the following c o m mand to reboot the system:
station.
Example: 123.45.67.8 nms
cd /;shutdown -i6 -g0 -y
End
3-16 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 57

UnixWare Installation
To Test the TCP/IP Connection
To Test the TCP/IP
Connection
Introduction To make sure that the Proxy Age nt is connected to the network
and to the Fault Manager, you must test the connection.
When to use Test th e network connection after you set the hosts file.
Procedure Use th e following steps to test the network connection.
Step Action
1 Enter the following c o m mand at the UNIX pr om pt:
/usr/sbin/ping [NMS name]
2 Does the UNIX system display the following message?
[nms] is alive
■ If yes, you have completed this procedure.
■ If no, troubleshoot the connection as described in
the next section.
Issue 2 April 1996 3-17
End
Page 58

UnixWare Installation
To Troubleshoo t the TCP/IP Connect ion
To Troubleshoot the
TCP/IP Connection
When to use Use the troub leshoot i n g g u i d elin es in this section if your network
is not functioning properly after you administer the TCP/IP.
Check
hardware
Definitions
Check the
hosts file
■ Is the network management station functional on the
network?
■ Is the ethernet cabling installed?
■ A
host
is the com puter in charge of a telecommunications
or a local area network session.
■ The
local host
is the name that network software uses to
identify each PC on the network.
■ A
proxy agent
is the name of the Proxy Agent PC.
Open the /etc/hosts file. If the answer to any of the following
questions is “no,” make the appropriate corrections.
■ D oe s the fil e co ntai n lines of text simi lar to the foll owing ?
127.0.0.1 [localhost]
123.45.67.9 [proxyagent]
■ Do the values of [localhost] and [proxyagent]
match those in the report that displays when you run the
netstat -i command? (See Example status data, later in this
section.)
3-18 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 59

UnixWare Installation
To Troubleshoot the TCP/IP Connection
■ Does the file show the IP address and the name of the
network management station correctly?
Check
network
status
Use the following steps to check the status of the network.
Step Action
1 Enter the following command at the UNIX prompt:
netstat -i
Result: The UNIX system displays the network’s status.
S ee Exampl e S ta tu s Data for sample data.
2 Does the Add ress column c o ntai n the names of the
NMS and the Proxy Age nt?
■ If yes, go to step 3.
■ If no, verify the ifconfig options. (See Configure the
Ethernet Card for more information.)
3 Do these names match the ones in the hosts file
exactly? (See Check the Hosts File.)
■ If yes, go to step 4.
■ If no, verify the ifconfig options.
4 Are the [localhost] and [proxyagent] names in
the hosts file correct?
■ If yes, the network status an d the hosts file are OK.
If no, make the a p prop riat e changes.
Issue 2 April 1996 3-19
End
Page 60

UnixWare Installation
To Troubleshoo t the TCP/IP Connect ion
Example
status data
Name Mtu Network Address Ipkts Ierrs Opkts Oerrs Collis
lo0 8256 Loopback localhost 1764 0 1764 0 0
ee160 1500 123.45.6 proxya 179747 0 226385 1 13986
An example of the data that displays after you run the netstat -i
command follows.
The data may a p p e a r differently in your install ati on. However, the
Address column must list the name of your local host and the
name of your Proxy Agent.
In this example, the name of the Proxy Ag ent is proxya.
3-20 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 61

UnixW are Administrat ion
Chapter Overview
Introduction This chap t er ex p lains how to:
■ Ad d log i ns for new user of the Proxy Agent
■ Verify group assignments
■ Assign termi nals and mo d e m to ports
■ Back up and re store the Proxy Agent
4
In this
chapter
This chap t e r co ntai ns the followin g sections.
For this in formation … See page …
Login Administration 4-2
Maintenance Administration 4-13
Issue 2 April 1996 4-1
Page 62

UnixWare Administration
Section Overview
Login Administration
Section Overview
Introduction Login administration invol ves the foll owing:
■ A dd lo g i ns for new users of the Proxy Ag ent
■ Verify group assignments
Methods Use any of the following methods to add a new user to the Proxy
Agent.
■ UNIX shell comm a n d s
■ UnixWare OA&M Ad m in istrat ive Int e r f a c e util ity
■ UnixWare desktop
In this
This section contains the following information.
section
For this in formation … See page …
Ab out Lo g i ns 4-3
To Add New Logins: UNIX Shell 4-4
To Add New Logins: OA&M 4-6
To Add New Logins: Desktop 4-9
To Verify Group Assignment s 4-11
4-2 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 63

UnixWare Administration
About Logins
About Logins
Introduction You a dd a new user to the Proxy Agent by assign ing the user a
login and p assword.
Who assigns
logins
Where to
assign
logins
Materials
needed
Your UNIX syste m a d m ini strator is res p onsible for as s igning
unique logins to new Proxy Agen t users.
These logins must be assigned under the g3ma group ID number ,
and must include the following:
■ Gr oup ID
■ Login ID
■ Password
To assign a login successfully, you need the following items:
■ Enough disk space to assign a home directory to each user
■ The ID number for the g 3ma g roup
■ A unique login ID and password for each new user
Issue 2 April 1996 4-3
Page 64

UnixWare Administration
To Add New Logins: UNIX Shell
To Add New Lo gins:
UNIX Shell
Introduction You can use the UNIX shell commands to add Proxy Agent logins,
or you can choose another metho d .
When to use Add a new Proxy Agen t user to your system after you have
install e d UnixWare and tested the network connections.
Procedure Use th e following steps to add a new login.
Step Action
1 Log in as root.
2 Enter the following comman d on a single command
3 Enter the following comman d to assign a password for
4 Enter the ap propriate p assword o ptions.
4-4 Issue 2 April 1996
line. All arguments are optional except login_ID.
usradd -u usr_number -g primary_group_
ID\-G supplementary_group_ID -c
comment\-d home-_directory -s program -m
login_ID
your new user:
passwd options login_ID
Hint : The fol lowing table describes some of thes e
options.
End
Page 65

UnixWare Administration
To Add New Logins: UNIX Shell
UNIX
options
The syntax for the passwor d options in ste p 4 are:
Option Des cription
-n days Se ts th e m in i mu m number of days before a us er can
change the password.
-x Sets the maximum number of days that the
password is active.
-f Forces the user to change the password at the next
login session.
Issue 2 April 1996 4-5
Page 66

UnixWare Administration
To Add New Logins: OA&M
To Add New Lo gins:
OA&M
Introduction You can use the OA&M Adm ini strat ive Inter f a c e to a dd Proxy
Ag e nt logins, or you can choose another method.
When to use Add a new Proxy Agen t user to your system after you have
install e d UnixWare and tested the network connections.
Definition The
See also If you need help using the OA&M Administrative Interface, see
Procedure To ad d a new log in:
OA&M Administrative Interface
allows you to administer logins for Proxy Ag en t users. This utility is
located in the sysadm file.
The OA&M Administrative Interface displays a series of screens
that step you through the process of administering logins.
your UnixWare documentation.
is a UnixWare utility that
4-6 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 67

UnixWare Administration
To Add New Logins: OA&M
Step Action
1 Enter the following comman d at the UNIX prompt:
2 Follow the instructions in your OA&M Administrative
/usr/sbin/sysadm
Result: The Op erations, Administration and
Maintenanc e menu displays.
Interface manual for addin g a new user ID.
Hint: See the following table for the settings r e quired
for ad ding a new Proxy Age n t user.
End
Required
settings
Example
data
The following table lists the settings that are required for adding a
new Proxy Agent user .
OA&M screen Field What you enter
Add a User Login A unique login
name
User ID A unique user
ID
Primary group The g 3m a
group ID
Define User
Password Information
Password
status
The password
An example of the user’s password data, as displayed on the
Define User Password Informat ion screen follows.
gah PS 07/24/95 7 60 10
Issue 2 April 1996 4-7
Page 68

UnixWare Administration
To Add New Logins: OA&M
UNIX syntax The fo l lowing table uses the password data shown in the previous
example to describe the options for the user’s login and
password.
Syntax Description
gah Login ID
PS Password stat us
07/24/95 Date the p a s sword was ente red
60 Number of days the user password is valid
10 Number of days the password warning
message is displayed before the password will
be disabled
See also For more inform at ion about UN I X System Ad m inist rati on, see
Uni xWare Syst em Admini st r ation Intro d u c t ion to System
Adm i nistrat ion.
4-8 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 69

UnixWare Administration
To Add New Logins: Desktop
To Add New Lo gins:
Desktop
Introduction You can use the UnixWare desktop to add Proxy Agent logins, or
you can choose another tool.
When to use Add a new Proxy Agen t user to your system after you have
install e d UnixWare and tested the network connections.
Definition UnixWare
tools and services handy while you are using your co m puter. You
ca n a c cess these tools and services while you are in another
application.
Procedure Use the following steps to add a new login.
desktop
is a program that keeps often-needed business
Issue 2 April 1996 4-9
Page 70

UnixWare Administration
To Add New Logins: Desktop
Step Action
1 At the login prompt, enter:
2 O p en the User Setup : A d d New User Account screen.
3 Select both of the following items:
4 Clic k Add.
root2
Result: The UnixWare desktop opens.
Hint: To navigate through the deskt o p , click on the
Admin_Tools and User_Setup icons. Then, from the
User Setup: User Accounts menu, select Account
New.
■ Type: either desktop or nondesktop. (We
recommend desktop.)
■ Groups: g3ma.
à
5 Clic k Yes.
4-10 Issue 2 April 1996
End
Page 71

UnixWare Administration
To Verify Group Assignments
To Verify Group
Assignments
Definition The
grou p assig nment
is the g3ma group number.
When to use Imm e d iately after you assign the login and password, verify that
each n ew use r has been assigned the correct g 3ma g roup
number.
UNIX group assignment verification can also b e done through the
UnixWare desktop .
Guidelines
for using
UNIX editor
Procedural
overview
To verify g rou p assig n m ent s, you must use a UNIX editor such as
vi to read the appropriate files. Appendix C describes some basic
vi ope ratio ns.
To verify g rou p assig n m ent s, c o m p l e te the following procedures:
■ Procedure 1: Check the Group File
■ Procedure 2: Check the Passwd File
You can complete these procedures in any order.
Procedure 1:
check the
group file
Use the following steps to check the group file.
Issue 2 April 1996 4-11
Page 72

UnixWare Administration
To Verify Group Assignments
Step Action
1 Use any UNIX editor to open the /etc/group file.
2 Note the grou p ID num ber for G3-MA.
3 Locate the g3ma line.
4 Is th e Proxy Agent user’s name listed?
5 Repeat step 4 for each user.
6 Writ e an d qu i t the fi le to save th e changes.
■ If yes, go to step 5.
■ If no, add the name to the g3ma line
End
Procedure 2:
Use the following steps to check the passwd file.
check the
passwd file
Step Action
1 Use any UNIX editor to open the /etc/passwd file.
2 Lo c ate t he entry for th e new user’s group ID.
3 Is the group ID for that entry the same as the G3-MA
4 Write and quit the file to save the changes.
4-12 Issue 2 April 1996
group ID number?
■ If yes, go to step 4.
■ If no, change the entry to the g3ma group ID
numb er
End
Page 73

UnixWare Administration
Section Overview
Maintenance Administration
Section Overview
Introduction You can use either of the following to p erf or m m aint enance
administration in UnixWare:
■ UnixWare desktop
■ OA&M Administrative Interface
This book discusses procedures for using the OA&M
Adm in istrat ive Int er f a c e.
In this
section
This section contains the following information.
For this in formation … See page …
Abo ut Port Monitors 4-14
To Assign Devices to Ports 4-15
To Back Up and Restore 4-17
Issue 2 April 1996 4-13
Page 74

UnixWare Administration
About Port Monitors
About Port Monitors
Introduction Your system uses a po rt monitor to do the following:
■ Set terminal mod es, baud rates, and line disciplines
■ Identify authorized u ser s
T ypes of port
monitors
Your system uses a STREAMS-based TTY port monitor, ttymon.
Port administration includes assigning terminals an d modems to
the por ts on your system.
4-14 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 75

UnixWare Administration
To Assign Devices to Ports
To Assign Devices to
Ports
Introduction You need to assign devices (terminals and modems) to the ports
on your system so that the p ort monito rs can recognize them.
When to use Assign devices to ports after you have installed UnixWare.
Procedure Use t he following steps to assign a terminal or a modem to a port:
Step Action
1 Enter the following c o m mand at the UNIX pr om pt:
/usr/sbin/sysadm
Result: The OA& M Op erati ons, A dministrat ion and
Maintenance menu displays.
2 Op en the Qui ck Terminal Setup screen.
Hint: Select the following options to navigate through the
OA&M screens:
At this screen . . . Se l ect this option . . .
OA&M Op erat ions,
Administration and
Maintenance
Service Access Management quick-terminal
Quick Terminal Setup add
ports
Issue 2 April 1996 4-15
Page 76

UnixWare Administration
To Assign Devices to Ports
Step Action
3 Exit OA&M.
4 At the UNIX prompt, enter the information for the type of
5 Modify the user’s .profile for the terminal type.
terminal that you are adding.
For example, to assign your terminal to the first serial
port, enter:
/dev/term/00s
For example, add the following line for a PC running a
terminal emulator application like ctrm:
TERM=ctrm; export TERM
End
4-16 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 77

UnixWare Administration
To Back Up and Restore
To Back Up and Restore
When to use We recommend that you back up the Proxy Agent as follows:
■ If you have a tape d rive, p erform a full system backup and
a shutdown of the UNIX system twice a month.
■ I f you do not have a tape drive, back up the /usr/g3-ma
directory twice a month using floppy diskettes.
Procedure Use the following procedure to backup or restore the Proxy Agent.
Step Action
1 Log in as root.
2 Enter the following comman d at the UNIX prompt:
/usr/sbin/sysadm
Result: The OA&M O perations, Administration and
Maintenanc e menu displays.
3 Select one of the following options:
■ backup_service
■ restore_service
4 Follow the system prompts.
Issue 2 April 1996 4-17
End
Page 78

UnixWare Administration
To Back Up and Restore
4-18 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 79

Planning Connectivity
Chapter Overview
Introduction This chapter ex p lains how to c o n nect the Proxy Agent to:
■ A PB X and to the NMS via a LAN
■ The appropriate data communications hard w are
You can use this information to establish the correct connections.
5
In this
chapter
This chapter includes the following se ct i ons.
For this in formation … See page …
Abo ut Connectivity 5-2
Data Communications Hardware 5-6
PC Hardware Connections 5-24
Alarm Stream 5-33
Issue 2 April 1996 5-1
Page 80

Planning Connectivity
Section Overview
About Connectivity
Section Overview
Introduction This section helps yo u p lan for th e c o rre c t c o n nectivit y.
In this
section
This section includes the following information.
For this in formation … See page …
Proxy Agent Connectivity 5-3
Communications Hardware 5-5
5-2 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 81

Planning Connectivity
Proxy Agent Connectivity
Proxy Agent
Connectivity
Introduction Proxy Agent connectivity can be divided into the following
ca t eg ories:
■ Emulation and management data
■ Alarm stream
■
Definitions
Emulation da t a
that simulates the function of anothe r hard w are or softwa re
product.
■
Management data
needed t o plan, organize, and c o ntrol operations.
is data that is generated from a program
is data that provides the information
Required
connections
Connectivity
overview
■ An
alarm stream
is UNIX system architecture that provides
a flexible communication path for alarms traveling between
the Proxy Agent and device drivers.
The connections required for the Proxy Agent to work properly
are:
■ From the Proxy Agent PC to the dat a c ommunications
hardware (modem, data module, or ADU)
■ From the d a t a co mmuni cations hardware to the PBX
The following diagram is a high-level overview of Proxy Agent
connectivit y to a PBX. Notice the dial-up connections to the
switch .
Issue 2 April 1996 5-3
Page 82

Planning Connectivity
Proxy Agent Connectivity
2
1
3
Legend
1. PBX
2. Alarm stream
3. Dial-up switc h connection
4. Proxy Agent PC
4
5-4 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 83

Planning Connectivity
Communications Hardware
Communicat ions
Hardware
Introduction The connections between the Proxy Agent an d the PBX and LAN
can involve a number of different pieces of hardware, including
the following :
■ Modems o r d at a modules
■ House wiring and cables
It is essenti al that AT&T ce r t ifies this h ardware and that you
c o nfi gure it c o r rectly.
Gender
changers
The connections described in this book may require gen der
ch angers. You may wish to have several gender changers on
hand when you establish the hardware connections.
Certification The configurations described in this chapter are the certified
Proxy Agent confi gurations supported b y AT&T.
NOTE:
Other c o nfigurat ions can also work. However, if you use
configurations other than the ones described in this book,
and if you req uire assistance from the Technical Service
Organization (TSO) to make them work, the TSO will make a
"best effort" to assist you. You will be billed for that effort on a
time and materials basis.
Issue 2 April 1996 5-5
Page 84

Planning Connectivity
Section Overview
Data Communications Hardware
Section Overview
Introduction Your da t a c o m mun ications hardware can be any of the following:
■ Modem
■ 7 400B data modu le
■ Asynchronous data unit (ADU)
In this
section
This section includes the following information.
For this in formation … See page …
To Choose the Hardware 5-8
Proxy Agent and Modem Connections 5-9
Proxy Agent and Data Module
5-11
Connections
Proxy Agent and ADU Connections 5-12
To Choose Circuit Packs 5-13
PBX and Modem Connections 5-14
PBX and Data Module Connections 5-15
PBX and ADU Connections 5-16
Ca b les for Modems 5-17
Cab les for Dat a Modules 5-20
Ca b les for ADUs 5-22
5-6 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 85

Planning Connectivity
Section Overview
See also Refer to the DEFINITY G3 documentation for more detail. For a
complete list of DEFINITY G3 product documentation, see Related
Resources in the About This Book.
Issue 2 April 1996 5-7
Page 86

Planning Connectivity
To Choose the Hardwar e
To Choose the Hardware
Introduction Before you choose your data communication hardware, consider
these site-specific issues:
■ Whether or not you want to make connections through the
public network
■ Distance requirements
■ Cost factors
Type of
hardware
The following table lists the types of data c ommunications
hardware that you need for connecting to a network. It also lists
d istance and eq uipment requirements.
Network Hardware
Public Any
supported
modem
Private 7400B d ata
mo dule
Distance
from PBX
unlimited Modem pooling on
Within
5000 feet
Hardware
requiremen ts
the DEFINITY G3
PBX
A port on a digital
board (TN754 in the
U.S.A.)
ADU Within
2000 feet
A port on a dataline
board (TN726 E in
the U.S.A.)
(An ADU is less
exp ensive th an the
7400 B da ta
mo d ule.)
5-8 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 87

Planning Connectivity
Proxy Agent and Modem Connections
Proxy Agent and Modem
Connections
Introduction The following diagram shows the connection between the Proxy
Agent PC and a modem.
1
2
3
Legend
1. PBX
2. Site-specific network connections
3. Modem
For a list of certified modems, conta ct your design
speciali st.
4. Proxy Agent PC
5. Serial I/O mod u lar adap ter
6. Serial I/O cable
3
5
4
6
7
4
Issue 2 April 1996 5-9
Page 88

Planning Connectivity
Proxy Agent and Modem Connections
7. Serial I/O p ort s c a rd
5-10 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 89

Planning Connectivity
Proxy Agent and Data Module Connections
Proxy Agent and Data
Modu le C onnec ti ons
Introduction The following diagram shows the connection between the Proxy
Agent PC an d a 7400B data module.
1
2
3
Legend
1. PBX
2. Site-specific network connections
3. 74 00B d ata mod ule
4. Proxy Agent PC
5. Serial I/O mod u lar adap ter
6. Serial I/O cable
7. Serial I/O p ort s c a rd
3
5
4
6
4
7
Issue 2 April 1996 5-11
Page 90

Planning Connectivity
Proxy Agent an d ADU Connections
Proxy Agent and ADU
Connections
Introduction The following diagram shows the connection between the Proxy
Agent PC and an ADU.
1
2
3
5
Legend
1. PBX
2. Site-specific network connections
3. ADU
4. Proxy Agent PC
5. Moss adapter
6. Serial I/O mod u lar adap ter
7. Serial I/O cable
3
6
4
7
8
4
8. Serial I/O p ort s c a rd
5-12 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 91

Planning Connectivity
To Choose Circuit Packs
To Choose Circ uit Packs
Introduction Before you can connect your communications hardwar e to the
PBX, you must choose the appropriate ci rcui t pack.
Line type The line type of the circuit pack depends on whether you use a
modem, a data module, or an ADU.
The following table matches the data c o m munication hardware
and the li ne type.
Hardware Line type Circuit pack *
Any sup porte d mo d em analog TN746
TN742
7400B d ata mod ule d igital TN754
ADU data TN726B
* The TN num bers for circuit packs are for use in the United
States. International users must check the DEFINITY G3
Appl ication No tes for t h e c or rect ci rcuit pack.
Issue 2 April 1996 5-13
Page 92

Planning Connectivity
PBX and Modem Connections
PBX and Modem
Connections
Introduction The following diagram shows the dial-up connection between the
PBX and a modem.
1
5
6
2
Legend
1. PBX
2. Site-specific network connections
3. Modem
For a list of certified modems, c onta c t your AT&T d e sign
speciali st.
4. Proxy Agent PC
5. M odem pool
6. Analog circuit pack on PBX
3
2
4
3
5-14 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 93

Planning Connectivity
PBX and Data Module Connections
PBX and Data Module
Connections
Introduction The following d iagram shows the di al-up connection between the
PBX and a d ata mo dule.
1
5
2
2
Legend
1. PBX
2. Site-specific network connections
3. 74 00B d ata mod ule
4. Proxy Agent PC
5. Di g i t al-li n e c irc u i t pack on PBX
3
4
3
Issue 2 April 1996 5-15
Page 94

Planning Connectivity
PBX and ADU Connecti ons
PBX and ADU
Connections
Dial-up
connection
The following diagram shows the dial-up connection between the
PBX an d an AD U.
1
5
2
2
3
3
4
6
Legend
1. PBX
2. Site-specific network connections
3. ADU
4. Proxy Agent PC
5. Di g i t al-li n e c irc u i t pack on PBX
6. Moss adapter
5-16 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 95

Planning Connectivity
Cables for Modems
Cables for Modems
Introduction The diagrams in this section show the pos sible confi gurations for
mo d em cab les.
Diagram 1 M odem ca b les, c o n f ig uration A:
1
2
3 8
4
5
6
7
9
Legend
1. PBX
2. Analog-line circuit pack on PBX
3. B25A cable
4. Cross connection at main distribution frame (MDF)
5. 10 3A or wall j a c k
6. RJ11 cable
7. M odem
8. Cable (See your PC documentat ion .)
9. Proxy Agent PC
Issue 2 April 1996 5-17
Page 96

Planning Connectivity
Cables for Modems
Diagram 2 M odem ca b les, c o n f ig uration B:
1
2
3
5
4
Legend
1. 10 3A or wall j a c k
2. RJ11 cable
3. M odem
4. Proxy Agent PC
5. Analog p u b lic or private network
Type of PBX The type of PBX you have does not affect the cab ling.
tty port UnixWare selects a tty port based on the baud rate specified for
the connection by the system administrator.
See also If you need help choosing the correct cables to connect your PC
to a mod em, refer to your PC documentation.
5-18 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 97

Planning Connectivity
Cables for Modems
If you have a S erial I /O p ort s ca rd inst alled in your UnixWare PC,
refer to Chapter 7, "Serial I/ O C a rds" an d t o the documentation
furnished with the ports card for information needed to install
hardware and software.
Issue 2 April 1996 5-19
Page 98

Planning Connectivity
Cables for Data Modules
Cables for Data Modules
Type of PBX The type of PBX you have does not affect the cab ling.
Data module
cables
1
2
The following diagram shows the ca bling for a configuration tha t
includes a 7400B data module.
10
4
3
5
6
7
11
8
9
Legend
1. PBX
2. Di g i t al-li n e c irc u i t pack on PBX
3. B25A cable
4. Cross connection at main distribution frame
5. 10 3A or wall j a c k
6. D8W-87 cable
7. 74 00B d ata mod ule
8. M25A cable
9. Proxy Agent PC
10. 5000 feet maximum between the PBX and data module
5-20 Issue 2 April 1996
Page 99

Planning Connectivity
Cables for Data Modules
11. 5 0 feet maximum b etwe en the d a ta module and Proxy
Agent
tty port UnixWare selects a tty port based on the baud rate specified for
the connection by the system administrator.
See also If you need help choosing the correct cables to connect your PC
to a data mod u le, refer to your PC documentation.
If you have a S erial I /O p ort s ca rd inst alled in your UnixWare PC,
refer to Chapter 7, "Serial I/ O C a rds" an d t o the documentation
furnished with the ports card for information needed to install
hardware and software.
Issue 2 April 1996 5-21
Page 100

Planning Connectivity
Cables for ADUs
Cables for ADUs
Type of PBX The type of PBX you have does not affect the cab ling.
ADU cables The following d iagram shows the ca bling for a configuration tha t
includes an ADU.
11 12
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Legend
1. PBX
2. Di g i t al-li n e c irc u i t pack on PBX
3. B25A cable
4. Cross connection at main distribution frame
5. 10 3A or wall j a c k
6. D8W-87 cable
7. ADU
8. Moss adapter
9. Z3A4 cable
10. Proxy Agent PC
11. 2000 feet maximum between the PBX and data module
5-22 Issue 2 April 1996
 Loading...
Loading...