Page 1

R
P/I P65UP5
Baseboard for CPU Cards
USER’S MANUAL
Page 2

USER'S NOTICE
No part of this manual, including the products and softwares described in it, may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language
in any form or by any means, except documentation kept by the purchaser for backup purposes, without the express written permission of ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (“ASUS”).
ASUS PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED
W ARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL ASUS, ITS DIRECTORS, OFFICERS,
EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF
PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF USE OR DAT A, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS AND THE LIKE), EVEN IF ASUS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGES ARISING FROM ANY DEFECT OR ERROR IN THIS MANUAL
OR PRODUCT.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for identification or
explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
• Intel, LANDesk, and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
• IBM and OS/2 are registered trademarks of International Business Machines.
• Symbios is a registered trademark of Symbios Logic Corporation.
• Windows and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
• Sound Blaster AWE32 and SB16 are trademarks of Creative Technology Ltd.
• Adobe and Acrobat are registered trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
The product name and revision number are both printed on the board itself. Manual revisions
are released for each board design represented by the digit before and after the period of the
manual revision number. Manual updates are represented by the third digit in the manual
revision number.
For previous or updated manuals, BIOS, drivers, or product release information, contact ASUS
at http://www.asus.com.tw or through any of the means indicated on the following page.
SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL ARE FURNISHED FOR INFORMATIONAL USE ONLY, AND ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE AT
ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE, AND SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS A COMMITMENT BY ASUS. ASUS ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBLITY OR LIABILITY FOR
ANY ERRORS OR INACCURACIES THAT MA Y APPEAR IN THIS MANUAL, INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS AND SOFTWARES DESCRIBED IN IT.
Copyright © 1997 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved.
Product Name: P/I-P65UP5
Manual Revision: 2.04
Release Date: July 1997
2
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 3

ASUS CONTACT INFORMATION
ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC.
Marketing Info
Address: 150 Li-Te Road, Peitou, Taipei, Taiwan 112, ROC
Telephone: +886-2-894-3447
Fax: +886-2-894-3449
Email: info@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
Fax: +886-2-895-9254
BBS: +886-2-896-4667
Email: tsd@asus.com.tw
WWW: www.asus.com.tw
Gopher: gopher.asus.com.tw
FTP: ftp.asus.com.tw/pub/ASUS
ASUS COMPUTER INTERNATIONAL
Marketing Info
Address: 721 Charcot Avenue, San Jose, CA 95131, USA
Telephone: +1-408-474-0567
Fax: +1-408-474-0568
Email: info-usa@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
BBS: +1-408-474-0569
Email: tsd-usa@asus.com.tw
WWW: www.asus.com
ASUS COMPUTER GmbH
Marketing Info
Address: Harkort Str. 25, 40880 Ratingen, BRD, Germany
Telephone: 49-2102-445011
Fax: 49-2102-442066
Email: info-ger@asus.com.tw
Technical Support
BBS: 49-2102-448690
Email: tsd-ger@asus.com.tw
Hotline: 49-2102-499712
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 3
Page 4

CONTENTS
I. INTRODUCTION.........................................................7
How this Manual is Organized ........................................................7
Item Checklist ..................................................................................7
Features of the ASUS P/I-P65UP5 Baseboard ................................8
II. FEATURES ..................................................................8
Parts of the ASUS Baseboard ..........................................................9
III. INSTALLATION .....................................................10
ASUS Baseboard Layout ...............................................................10
Installation Steps............................................................................12
1. Jumpers ......................................................................................12
Jumper Settings ..................................................................13
2. System Memory (DRAM/SDRAM & SRAM) ........................16
DRAM Memory Installation Procedures............................17
3. Central Processing Unit ............................................................18
System Case........................................................................18
4. Expansion Cards .......................................................................20
Expansion Card Installation Procedure ..............................20
Assigning IRQs for Expansion Cards.................................20
Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards...........................21
5. External Connectors..................................................................22
IV. ASUS PCI SCSI Cards ............................................28
Symbios SCSI BIOS and Drivers ..................................................28
ASUS PCI-SC200 & PCI-SC860 SCSI Cards ..............................28
Setting Up the ASUS PCI-SC200 & PCI-SC860 .....................29
Setting the INT Assignment for the ASUS PCI-SC200 ...........29
Terminator Requirements for SCSI Devices ............................29
Terminator Settings for the ASUS PCI-SC860 ........................30
Terminator Settings for the ASUS PCI-SC200 ........................30
SCSI ID Numbers for SCSI Devices .......................................31
SCSI ID Priority .......................................................................31
V. ASUS I-A16C Audio Card........................................32
ASUS I-A16C Audio Features .................................................32
Layout and Connectors ............................................................32
Connectors ..........................................................................32
CD-Audio Connector Pin Definitions ......................................32
4
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 5

(This page was intentionally left blank.)
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 5
Page 6
FCC & DOC COMPLIANCE
Federal Communications Commission Statement
This device complies with FCC Rules Part 15. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference, and
• This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with manufacturer's instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Re-orient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
WARNING! The use of shielded cables for connection of the monitor to the
graphics card is required to assure compliance with FCC regulations. Changes
or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
Canadian Department of Communications Statement
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions
from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
6
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 7

I. INTRODUCTION
How this Manual is Organized
This manual is divided into the following sections:
I. Introduction: Manual information and checklist
II. Features: Information and specifications concerning this product
III.Installation: Instructions on setting up the baseboard
IV. SCSI Cards: Installation of ASUS SCSI cards (optional)
Item Checklist
Please check that your package is complete. If you discover damaged or missing
items, please contact your retailer.
þ ASUS P/I-P65UP5 baseboard
þ C-P6ND, C-P55T2D, or C-PKND CPU card
þ 2 serial port ribbon cables attached to a mounting bracket
I. INTRODUCTION
(Manual / Checklist)
þ 1 parallel ribbon cable with mounting bracket
þ 1 IDE ribbon cable
þ 1 floppy ribbon cable
þ This user’s manual
¨ Infrared module (optional)
¨ USB cable with mounting bracket set (optional)
¨ ASUS PCI-SC200 Fast SCSI or PCI-SC860 Ultra-Fast SCSI card (optional)
¨ ASUS I-A16C audio card and manual* (optional)
*
Online help is provided with the Creative 16X audio drivers. A separate manual is
provided for the Creative 16C Series audio drivers.
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 7
Page 8

II. FEATURES
Features of the ASUS P/I-P65UP5 Baseboard
The P/I-P65UP5 is carefully designed for the demanding PC user who wants great
versatility in a computer system. This baseboard:
• Easy Installation: Is equipped with BIOS that supports autodetection of hard
drives and Plug and Play to make setup of hard drives and expansion cards
virtually automatic.
II. FEATURES
(Features)
• Desktop Management Interface (DMI): Supports DMI through BIOS, which
allows hardware to communicate within a standard protocol creating a higher
level of compatibility. (Requires DMI-enabled components.)
• Versatile Processor Support: Supports dual 75–233MHz Pentium, 150–
200MHz Pentium Pro, 233–333MHz Pentium II processors.
• Versatile DRAM Memory Support: Supports eight 72-pin SIMMs of 4MB,
8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB to form a memory size between 8MB to 512MB.
Supports both Fast Page Mode (FPM), and Extended Data Output (EDO) SIMMs.
Burst Extended Data Output (BEDO) supported with the C-P6ND CPU card.
• ISA and PCI Expansion Slots: Provides three 16-bit ISA slots, four 32-bit PCI slots, and
one PCI/MediaBus shared slot for either a standard PCI card or ASUS MediaBus Card.
• ASUS MediaBus: Features an expansion slot extension shared with PCI Slot 5
for an optional high-performance expansion card, which includes two functions
in one easy-to-install card.
• Super Multi-I/O: Provides two high-speed UART-compatible serial ports and
one parallel port with EPP and ECP capabilities. Supports two of either 5.25- or
3.5-inch disk drives (1.44MB or 2.88MB) without an external card.
• PCI Bus Master IDE Controller: Comes with an onboard PCI Bus Master
IDE controller with two connectors that supports four IDE devices in two channels, supports PIO Modes 3 and 4 and Bus Master IDE DMA Mode 2, and
supports Enhanced IDE devices such as Tape Backup and CD-ROM drives.
Supports Japanese standard “Floppy 3 mode” (3.5-inch disk drive: 1.2MB)
and LS-120 floppy disk drives (3.5-inch disk drive: 120 MB, 1.44MB, 720K).
BIOS supports IDE CD-ROM or SCSI device boot-up.
• Optional IrDA Module: Supports an optional infrared port module for wireless
file transfers and communication.
• SCSI BIOS: Supports optional ASUS SCSI controller cards through onboard firmware.
• Intelligence: Supports Fan Status Monitoring and Alarm, Temperature Moni-
toring and Alert, Voltage Monitoring and Alert, System Resources Alert, and
Virus Write Protection through the optional onboard LM78 Hardware Monitor
and Intel
8 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
®
LANDesk Client Manager (LDCM) software.
Page 9
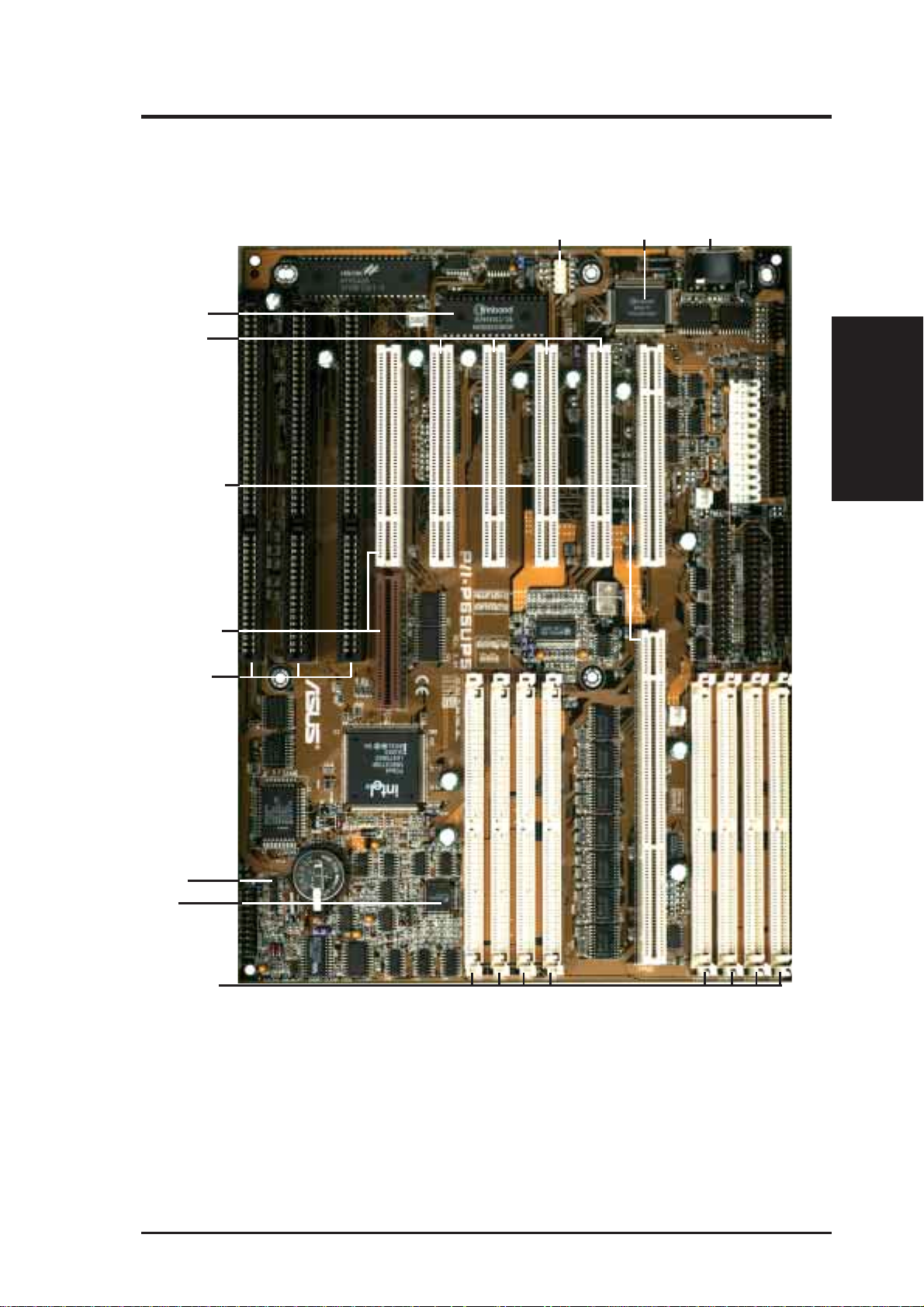
II. FEATURES
Parts of the ASUS Baseboard
Programmable
Flash ROM
4 PCI Slots
CPU Card Slot
PCI 5 or ASUS
MediaBus
Universal
Serial Bus
Super
Multi-I/O
Keyboard
II. FEATURES
(Parts of Board)
3 ISA Slots
Infrared Module
Support
LM78
Hardware Monitor
(Optional)
(8) 72-pin
SIMM Sockets
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 9
Page 10
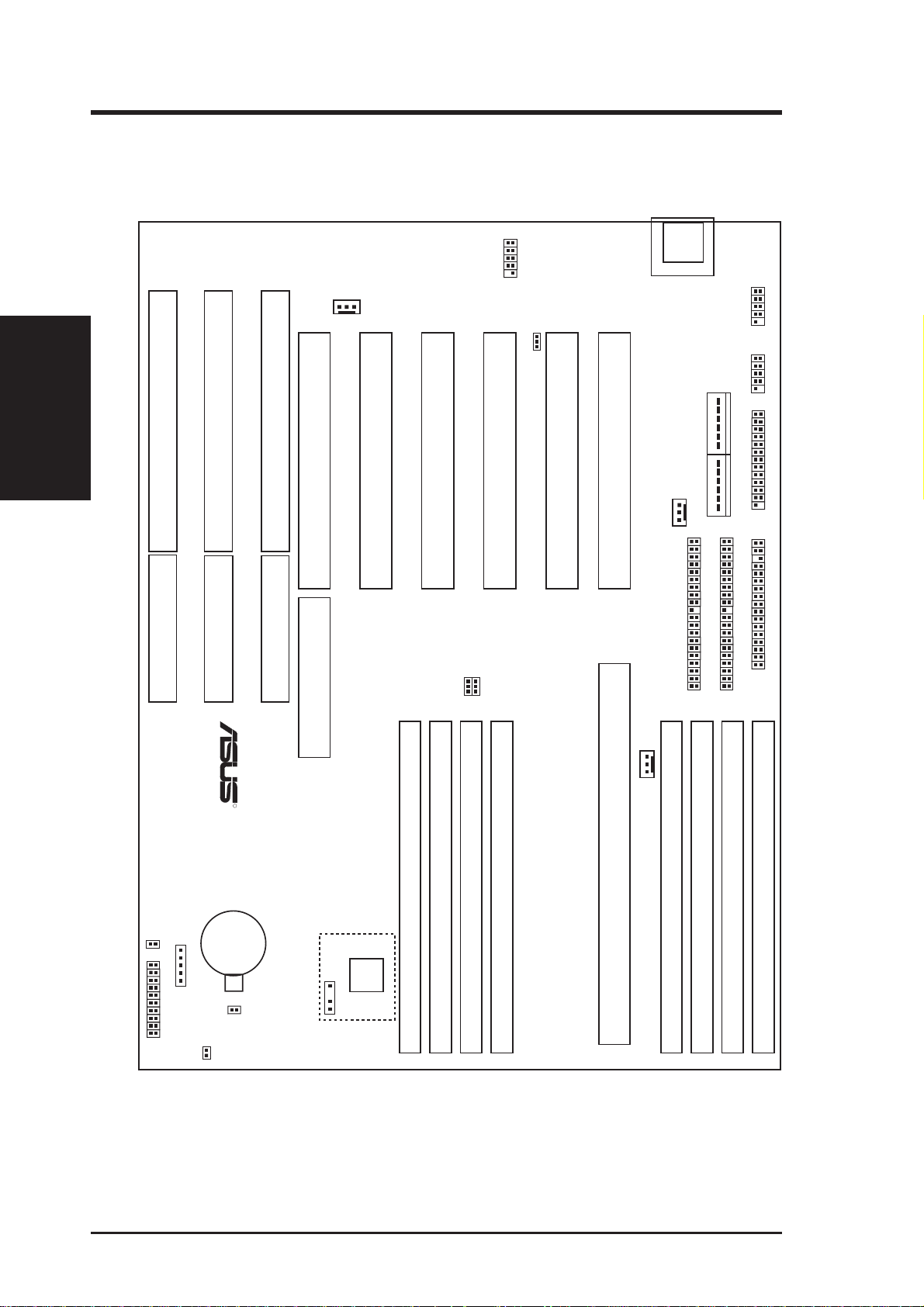
III. INSTALLATION
ASUS Baseboard Layout
Keyboard
III. INSTALLATION
(Board Layout)
ISA Slot 3
ISA Slot 2
ISA Slot 1
FANPWR3
PCI Slot 5 / MediaBus
PCI Slot 4
Universal Serial Bus
PCI Slot 3
JP2
JP3
BUS Freq.
JP1
PCI Slot 2
Multi-i/O Enable/Disable
PCI Slot 1
CPU Card Slot
FANPWR1
CPU Card Slot
COM 1
COM 2
Board Power Input
P9 P8
Secondary IDE
Primary IDE
Serial Ports
Parallel Port
Floppy Drives
SIMM Socket 2 (Bank 0)
SIMM Socket 4 (Bank 1)
SIMM Socket 6 (Bank 2)
IDE LED
Case Connector
CR2032 3Volts
Lithium Cell
Infrared Con
BIOS Power
JP9
Battery Test
JP7
RTC RAM
Operation/Clear CMOS
SIMM Socket 8 (Bank 3)
R
Hardware
Monitor
LM78
Chassis Conn.
SIMM Socket 1 (Bank 0)
SIMM Socket 3 (Bank 1)
SIMM Socket 5 (Bank 2)
FANPWR2
SIMM Socket 7 (Bank 3)
The items in outline are only available on the baseboard with onboard LM78 Hardware Monitor.
10 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 11

III. INSTALLATION
Jumpers
1) JP1 p. 13 Mlti-I/O Selection (Enable/Disable)
2) JP4 p. 13 Flash ROM Boot Block Programming (Protect/Prog)
3) JP2, JP3 p. 14 CPU External Frequency (BUS) Selection
4) JP7, JP9 p. 15 Real Time Clock RAM (Operation/Clear CMOS)
Expansion Slots
1) System Memory p. 16 System Memory (DRAM/SDRAM & SRAM)
2) SIMM1–SIMM8 p. 17 72-Pin SIMM Sockets
3) CPU1 p. 18 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Card Slot
4) PCI5/MEDIA p. 20 32-bit PCI Bus Slot and Media Bus Extension
5) PCI1, PCI2, PCI3, PCI4 p. 20 32-bit PCI Bus Expansion Slots
6) SLOT1, SLOT2, SLOT3 p. 21 16-bit ISA Bus Expansion Slots
Connectors
1) KB p. 22 Keyboard Connector (5-pin female)
2) FLOPPY p. 22 Floppy Disk Drive Connector (34-pin block)
3) PRINTER p. 23 Parallel Port Connector (26-pin block)
4) COM1, COM2 p. 23 Serial Port Connectors (10-pin blocks)
5) PRIMARY IDE, SECONDAR Y IDE p. 24 Primary/Secondary IDE Connectors (40-pin blocks)
6) PWRCON p. 24 AT Power Supply Connector (12-pin block)
7) IDE LED p. 25 IDE Activity LED
8) IR p. 25 Second Infrared Port Module Connector (5-pin block)
9) TB LED (CON1) p. 26 Turbo LED Lead (2 pins)
10) SMI (CON1) p. 26 SMI Suspend Switch Lead (2 pins)
1 1) RESET (CON1) p. 26 Reset Switch Lead (2 pins)
12)
PWR LED (
13)
KEYLOCK (
14) SPEAKER (CON1) p. 26 Speaker Output Connector (4 pins)
CON1
CON1
)
)
p. 26 System Power LED Lead (3 pins)
p. 26 Keyboard Lock Switch Lead (2 pins)
(Board Layout)
III. INSTALLATION
15) F ANPWR1, FANPWR2, F ANPWR3 p. 27 Power Supply, CPU Fan Power Connectors
16) USB p. 27 USB Module Connector (18-pin block)
17) CHASSIS (optional) p. 27 Chassis Open Alarm Connector (3-pin block)
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 11
Page 12

III. INSTALLATION
III. INSTALLATION
Installation Steps
Before using your computer, you must complete the following steps:
1. Set Jumpers on the Baseboard
2. Install DRAM Memory Modules
3. Install the Central Processing Unit (CPU) Card
4. Install Expansion Cards
5. Connect Ribbon Cables, Cabinet Wires, and Power Supply
6. Setup the BIOS Software (see the CPU Card BIOS section)
1. Jumpers
Several hardware settings are made through the use of jumper caps to connect jumper
pins (JP) on the baseboard. See “Baseboard Layout” on page 10 for locations of
jumpers. The jumper settings will be described numerically such as [----], [1-2],
(Jumpers)
[2-3] for no connection, connect pins 1&2, and connect pins 2&3 respectively. Pin
1 for our baseboards is always on top
baseboard with the keyboard connector away from yourself. A “1” is written be-
sides pin 1 on jumpers with three pins. The jumpers will also be shown graphically
such as
two pins will be shown as for short (On) and for open (Off). For manufacturing simplicity, the jumpers may be sharing pins from other groups. Use the
diagrams in this manual instead of following the pin layout on the board. Settings
with two jumper numbers require that both jumpers be moved together . To connect
the pins, simply place a plastic jumper cap over the two pins as diagramed.
WARNING! Computer motherboards, baseboards and components, such as SCSI
cards, contain very delicate Integrated Circuit (IC) chips. To protect them against
damage from static electricity , you should follow some precautions whenever you
work on your computer.
to connect pins 1&2 and to connect pins 2&3. Jumpers with
Pin 1
or on the left
Pin 1
when holding the
1. Unplug your computer when working on the inside.
2. Use a grounded wrist strap before handling computer components. If you do
not have one, touch both of your hands to a safely grounded object or to a
metal object, such as the power supply case.
3. Hold components by the edges and try not to touch the IC chips, leads or
connectors, or other components.
4. Place components on a grounded antistatic pad or on the bag that came with
the component whenever the components are separated from the system.
12 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 13

III. INSTALLATION
Jumper Settings
1. On-Board Multi-I/O Selection (JP1)
You can disable the onboard Multi-I/O (floppy, serial, parallel, and IrDA) individually through BIOS or entirely with the following jumper to use your own
multi-I/O card.
Multi-I/O JP1
Enable [1-2] (Default)
Disable [2-3]
JP1
1
2
3
Enable (Default) Disable
R
JP1
1
2
3
Multi I/O Setting
2. Flash ROM Boot Block Programming (JP4)
This sets the operation mode of the boot block area of the BIOS Flash ROM to
allow programming in the Prog (Program or enabled) position.
Programming JP4
Protect (Disabled) [1-2] (Default)
Prog (Enabled) [2-3]
(Jumpers)
III. INSTALLATION
R
Boot Block Programming
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 13
JP4
1
2
3
Protect (Default)
JP4
1
2
3
Prog
Page 14

III. INSTALLATION
3. CPU External (BUS) Frequency Selection (JP2, JP3)
These jumpers tells the clock generator what frequency to send to the CPU.
These allow the selection of the CPU’ s External frequency (or BUS Clock). The
BUS Clock multiplied by the BUS Ratio equals the CPU’s Internal frequency
(the advertised CPU speed).
BUS Freq. JP3 JP2
66MHz [1-2] [2-3]
60MHz [2-3] [1-2]
50MHz [1-2] [1-2]
JP2
JP3
JP3
JP2
JP3
JP2
III. INSTALLATION
(Jumpers)
1
2
R
3
66MHz
1
2
3
60MHz
1
2
3
50MHz
CPU External Clock (BUS) Frequency Selection
Intel Pentium Pro (P6) Processor: (Chipset Freq (CPU Ext. Freq
CPU BUS (CPU Card BUS Ratio) on CPU Card) Ext. on Baseboard)
Internal Ratio JP13 JP14 JP15 JP16 JP6 JP7 Freq. JP3 JP2
200MHz 3.0x [ON] [ON] [OFF] [ON] [ON] [OFF] 66MHz [1-2] [2-3]
180MHz 3.0x [ON] [ON] [OFF] [ON] [OFF] [ON] 60MHz [2-3] [1-2]
166MHz 2.5x [ON] [OFF] [ON] [ON] [ON] [OFF] 66MHz [1-2] [2-3]
150MHz 2.5x [ON] [OFF] [ON] [ON] [OFF] [ON] 60MHz [2-3] [1-2]
Intel Pentium (P5) Processor: (CPU Ext. Freq
CPU BUS (CPU Card BUS Ratio) Ext. on Baseboard)
Internal Ratio JP15 JP16 Freq. JP3 JP2
200MHz 3.0x [ON] [OFF] 66MHz [1-2] [2-3]
166MHz 2.5x [ON] [ON] 66MHz [1-2] [2-3]
150MHz 2.5x [ON] [ON] 60MHz [2-3] [1-2]
133MHz 2.0x [OFF] [ON] 66MHz [1-2] [2-3]
120MHz 2.0x [OFF] [ON] 60MHz [2-3] [1-2]
100MHz 1.5x [OFF] [OFF] 66MHz [1-2] [2-3]
90MHz 1.5x [OFF] [OFF] 60MHz [2-3] [1-2]
75MHz 1.5x [OFF] [OFF] 50MHz [1-2] [1-2]
14 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 15

III. INSTALLATION
Intel Pentium II Processor:
(CPU Ext. Freq
CPU BUS (CPU Card BUS Ratio) Ext. on Baseboard)
Internal Ratio JP1 JP2 JP3 JP4 Freq. JP3 JP2
266MHz 4.0x [short] [short [open] [short] 66MHz [1-2] [2-3]
233MHz 35x [open] [open] [short] [short] 66MHz [1-2] [2-3]
4. Real Time Clock (RTC) RAM (JP7)
This clears the user-entered information stored in the CMOS RAM of the Real
Time Clock such as hard disk information and passwords. To clear the RTC
data: (1) T urn off your computer and unplug the AC power, (2) Move this jumper
to Clear CMOS, (3) Power on the computer, (4) Turn off the PC, (5) Remove
this jumper, (6) Power on the computer , (7) Hold down <Delete> during bootup
and enter BIOS setup to re-enter user preferences.
WARNING! You must unplug the power cord to your power supply to ensure
that there is no power to your baseboard. The CMOS RAM containing the BIOS
setup information may be cleared by this action. You must enter BIOS to “Load
Setup Defaults” and re-enter any user information after removing and reapplying this jumper.
Selections JP7
Operation [open] (Default)
Clear CMOS [short] (momentarily)
JP9
Battery Test
R
RTC RAM
JP7
Operation
Open (Default)
JP7
Clear CMOS
Short
(Jumpers)
III. INSTALLATION
Battery Test Jumper (JP9)
You can test the battery’s current by removing the jumper and attaching a current meter to pins 1 and 2.
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 15
Page 16

III. INSTALLATION
III. INSTALLATION
2. System Memory (DRAM/SDRAM & SRAM)
This baseboard supports eight 72-pin SIMMs (Single Inline Memory Modules) of
4MB, 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB to form a memory size between 8MB to 512MB.
The DRAM can be either 60ns or 70ns Fast Page Mode (Asymmetric or Symmetric), Extended Data Output (EDO), or Burst Extended Data Output (BEDO) (with
C-P6ND only). SIMMs must be installed in pairs so that each bank contains two of
the same size memory modules. To support ECC, you must use true (opposed to
phantom parity generated by TTL chips) 36-bit parity-type SIMM (e.g. 8 chips + 4
parity chips) in pairs for all modules. Mixing 32-bit non-parity SIMM (e.g. 8 chips)
and 36-bit SIMM (e.g. 12 chips) will work minus the ECC feature.
IMPORTANT: Memory setup is required in “Auto Configuration” in the
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP of Section IV BIOS software. Each bank must
have the same size memory installed in pairs.
(Memory)
Install memory in any or all of the banks in any combination as follows:
Bank Memory Module Total Memory
Bank 0 4MB, 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB x2
SIMM Slots 1&2 72-pin FPM, EDO, BEDO SIMM
Bank 1 4MB, 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB x2
SIMM Slots 3&4 72-pin FPM, EDO, BEDO SIMM
Bank 2 4MB, 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB x2
SIMM Slots 5&6 72-pin FPM, EDO, BEDO SIMM
Bank 3 4MB, 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB x2
SIMM Slots 7&8 72-pin FPM, EDO, BEDO SIMM
Total System Memory =
NOTE: Memory on socket 1 has a clearance of 5.0 cm when the C-PKND and
C-P6ND CPU cards are installed and 5.5 cm when the C-P55T2D CPU card is installed.
NOTE: SIMM numbers are not in sequence, (2, 4, 6, 8, 1, 3, 5, 7 from left to right.)
IMPORTANT: Each bank must have the same size memory installed in pairs. Do
not use memory modules with more than 24 chips per module. Modules with more
than 24 chips exceed the design specifications of the memory subsystem and will be
unstable.
16 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 17

III. INSTALLATION
DRAM Memory Installation Procedures
IMPORTANT: Install memory modules in symmetric pairs.
1. The SIMM memory modules will only fit in one orientation as shown because
of a “Plastic Safety Tab” on one end of the SIMM slots which requires the
“Notched End” of the SIMM memory modules.
2468 1357
R
Notched End
B0 B1 B2 B3
72-Pin SIMM Sockets
B0 B1 B2 B3
B=Bank
2. Press the memory module firmly into place starting from a 45 degree angle
making sure that all the contacts are aligned with the slot.
3. With your finger tips, rock the memory module into a vertical position so that
it clicks into place.
Support Clip
Safety Tab (This Side Only)
72 Pin DRAM in SIMM Socket
Mounting Hole
4. The plastic guides should go through the two mounting holes on the sides and
the clips should snap on the other side.
(DRAM Memory)
III. INSTALLATION
5. T o release the memory module, squeeze both clips outward and rock the module out of the clips.
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 17
Page 18

III. INSTALLATION
3. Central Processing Unit
The P/I-P65UP5 baseboard provides a CPU card slot that can be used with any ASUS
CPU cards, which are available separately. You must purchase any one of these CPU
cards (see next page for a brief description) to complete the system’ s board.
System Case
The system case must be either a mid- to full-size tower or desktop (for C-P6ND
and C-P55T2D CPU cards) or server (C-PKND) case to give a clearance as follows:
Expansion Cards
CPU + Fan
PS/2
Mouse
III. INSTALLATION
(CPU Card)
PS/2
Keyboard
ISA 3 Long Expansion Card
PCI 1 Long Expansion Card
PCI 2 Short Expansion Card
CPU Card
9.00” (22.5 cm)
System Cabinet Clearance Area Requirement for the C-P6ND/C-P55T2D CPU Cards
Pentium II Processor
PS/2
Mouse
Heatsink
PS/2
Keyboard
PCI 1 Long Expansion Card
C-PKND CPU Card
9.25” (23.5 cm)
System Cabinet Clearance Area Requirement for the C-PKND CPU Card
Expansion Cards
PCI 2 Short Expansion Card
PCI 4 Long Expansion Card
PCI 3 Short Expansion Card
Baseboard
PCI 4 Long Expansion Card
PCI 3 Short Expansion Card
Baseboard
ISA 2 Long Expansion Card
ISA 1/PCI 5/MediaBus Long Card
ISA 3 Long Expansion Card
ISA 2 Long Expansion Card
ISA 1/PCI 5/MediaBus Long Card
5” (12.7 cm)
5” (12.7 cm)
The P/I-P65UP5 baseboard is a standard 3/4 baby AT size 11 x 8.75” and will fit
almost all system cases, but the CPU card will require that the floppy disk and CDROM drives not be hanging over the baseboard. Depending on the height of the SIMM
memory modules and the CPU fan and/or heatsink, the area above the SIMM memory
modules may not be available. For both the C-P6ND and C-P55T2D CPU cards, be
sure that your case has a minimum area clearance of 11 x 9.25 x 5” (28.5 x 23.5 x 12.7
cm), and for the C-PKND CPU card, 13.5 x 9.25 x 5” (34.3 x 23.5 x 12.7 cm).
18 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 19

III. INSTALLATION
One end of the CPU card has a bracket, which should slide into the system case front
panel. Be sure that the system case can support a long PCI card on the first slot and
that a groove is available for the bracket. Refer to your respective CPU card’ s documentation for details.
General Installation Procedures for the ASUS CPU Card:
1. Remove the CPU card from its packaging without touching the integrated circuit
(IC) chips, connectors, and other components. Place it onto the antistatic bag.
2. Follow instructions in the CPU card manual on installing the processor/s, support bracket, and setting jumpers.
3. Remove the expansion slot cover for the first slot.
4. Carefully align the CPU card over the CPU Card Slot (CPU SLOT A and CPU
SLOT B).
5. Be sure that the card is perpendicular to the baseboard. Firmly press one end of
the card halfway in, the other end halfway in, then the first end completely in,
and finally, the second end completely in. Be sure that all the connectors are
evenly inserted into the slots.
6. Screw in the metal bracket to the system case.
WARNING! Move the system carefully and only with the power off because
the CPU card is heavy as well as delicate.
R
C-P55T2D C-P6ND C-PKND
CPU Card Slot
NOTE: The BIOS on the CPU cards are different. When adding a CPU card, find
the BIOS chip that came with the CPU card and replace it with the one on the baseboard, if one is present.
(CPU Card)
III. INSTALLATION
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 19
Page 20

4. Expansion Cards
First read your expansion card documentation on any hardware and software settings that may be required to set up your specific card.
NOTE: PCI Slot 5 has a MediaBus extension, which allows the installation of either
a PCI card or a MediaBus card (optional multifunctional card).
WARNING! Unplug your power supply when adding or removing expansion
cards or other system components. Failure to do so may cause severe damage to
both your baseboard and expansion cards.
Expansion Card Installation Procedure
1. Read the documentation for your expansion card.
III. INSTALLATION
(Expansion Cards)
2. Set any necessary jumpers on your expansion card.
3. Remove your computer system’s cover.
4. Remove the bracket on the slot you intend to use. Keep the bracket for possible
5. Carefully align the card’s connectors and press firmly.
6. Secure the card on the slot with the screw you removed in step 4.
7. Replace the computer system’s cover.
8. Set up the BIOS if necessary (such as IRQ xx Used By ISA: Yes in PNP AND
9. Install the necessary software drivers for your expansion card.
III. INSTALLATION
future use.
PCI SETUP)
Assigning IRQs for Expansion Cards
IMPORTANT: PCI Slots 4 & 5 share the same IRQ. If using PCI cards on both
slots 4 & 5, make sure that the drivers support “Share IRQ” or that one card does not
need an IRQ assignment. Conflicts will arise on PCI Slots 4 & 5 that will make the
system unstable.
Some expansion cards need to use an IRQ to operate. Generally an IRQ must be
exclusively assigned to one use. In a standard design there are 16 IRQs available but
most of them are already in use, leaving 6 IRQs free for expansion cards.
Both ISA and PCI expansion cards may require to use IRQs. System IRQs are available to cards installed in the ISA expansion bus first, then any remaining IRQs are
available to PCI cards. Currently , there are two types of ISA cards. The original ISA
expansion card design, now referred to as legacy ISA cards, requires that you configure the card’ s jumpers manually and then install it in any available slot on the ISA
20 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 21

III. INSTALLATION
bus. You may use Microsoft Diagnostics (MSD.EXE) utility located in the Windows directory to see a map of your used and free IRQs. If you use W indows 95, the
Resources tab under Device Manager displays the resource settings being used by
a particular device (to gain access, double-click the System icon under the Control
Panel program). Ensure that no two devices share the same IRQs or your computer
will experience problems when those two devices are in use at the same time.
T o simplify this process, the baseboard complies with the Plug and Play (PnP) specification, which was developed to allow automatic system configuration whenever a
PnP-compliant card is added to the system. For PnP cards, IRQs are assigned automatically from those available.
If the system has both legacy and PnP ISA cards installed, IRQs are assigned to PnP
cards from those not used by legacy cards. The PCI and PNP configuration section
of the BIOS setup utility can be used to assign which IRQs are being used by legacy
cards. For older legacy cards that do not work with the BIOS, you may contact your
vendor for an ISA Configuration Utility.
An IRQ number is automatically assigned to PCI expansion cards after those used
by legacy and PnP ISA cards. In the PCI bus design, the BIOS automatically assigns
an IRQ to a PCI slot that contains a card requiring an IRQ. T o install a PCI card, you
need to set the INT (interrupt) assignment. Since all the PCI slots on this baseboard
use an INTA #, set the jumpers on your PCI cards to INT A.
Assigning DMA Channels for ISA Cards
Some ISA cards, both legacy and PnP, may also need to use a DMA (Direct Memory
Access) channel. DMA assignments for this baseboard are handled the same way as
the IRQ assignment process described earlier . Y ou can select a DMA channel in the
PCI and PnP configuration section of the BIOS Setup utility.
IMPORTANT: To avoid conflicts, reserve the necessary IRQs and DMAs for legacy
ISA cards (under PNP AND PCI SETUP of the BIOS SOFTWARE, choose Yes in
IRQ xx Used By ISA and DMA x Used By ISA for those IRQs and DMAs you want to
reserve).
(DMA Channels)
III. INSTALLATION
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 21
Page 22

III. INSTALLATION
(Connectors)
III. INSTALLATION
5. External Connectors
WARNING! Some pins are used for connectors or power sources. These are
clearly differentiated from jumpers as shown in the baseboard layout on page
10. Placing jumper caps over these pins will cause damage to your baseboard.
IMPORTANT: Connect ribbon cables such that the red stripe is on the pin 1 side of
the connector . The four corners of the connectors are labeled on the baseboard. Pin
1 is the side closest to the power connector on hard and floppy disk drives. IDE
ribbon cable must be less than 18in. (46cm), with the second drive connector no
more than 6in. (15cm) from the first connector.
1. Keyboard Connector (5-pin female)
This connector is for either a standard IBM-compatible, 101/102-key, or 104key (Windows 95-compatible) keyboard. Use either the A T keyboard connector
on the baseboard or PS/2 keyboard connector on the CPU card.
Keyboard Connector
(5-pin female)
R
Connector Plug
from Keyboard
PS/2 Keyboard
Port (CPU Card)
2. Floppy Disk Drive Connector (34-pin block)
This connector supports the provided floppy drive ribbon cable. After connecting the single end to the board, connect the two plugs on the other end to the
floppy drives. (Pin 5 is removed to prevent inserting in the wrong orienta-
tion when using ribbon cables with pin 5 plugged).
Pin 1
Orient the red stripe on the
floppy ribbon cable to Pin 1
R
Floppy Drive Connector
22 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 23

III. INSTALLATION
3. Parallel Printer Connector (26-Pin Block)
This connector supports the included parallel port ribbon cable with mounting
bracket. Connect the ribbon cable to this connector and mount the bracket to the
case on an open slot. You can make available the parallel port and choose the
IRQ Onboard Parallel Port in Chipset Features of the BIOS SOFTWARE.
(Pin 26 is removed to prevent inserting in the wr ong orientation when using
ribbon cables with pin 26 plugged)
Pin 1 Orient the red stripe on the
R
parallel ribbon cable to Pin 1
For the parallel port connector to be available,
connect the included parallel (25-pin female)
cable set to a free expansion port.
TIP: You may also remove the bracket
connectors and mount them directly to
the case to save expansion slot space.
4. Serial Port COM1 and COM2 Connectors (Two 10-pin blocks)
These connectors support the provided serial port ribbon cables with mounting
bracket. Connect the ribbon cables to these connectors and mount the bracket to
the case on an open slot. You can make available the serial port and choose the
IRQ Onboard Serial Port in Chipset Features of the BIOS SOFTWARE. (Pin
10 is removed to prevent inserting in the wrong orientation when using
ribbon cables with pin 10 plugged)
Pin 1
Orient the red stripe on the
serial ribbon cable to Pin 1
(Connectors)
III. INSTALLATION
R
Serial Port Connectors
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 23
Pin 1
COM 1
COM 2
For the serial port connectors to be available,
connect the included serial cable set from
COM1 (using 9-pin male) and COM2 (using
25-pin male) to a free expansion port.
TIP: You may also remove the bracket
connectors and mount them directly to
the case to save expansion slot space.
Page 24

III. INSTALLATION
5. Primary/Secondary IDE Connectors (Two 40-pin Block)
These connectors support the provided IDE hard disk ribbon cable.
After connecting the single end to the board, connect the two plugs at the other
end to your hard disk(s). If you install two hard disks on one connector (channel), then you must configure a second drive as Slave mode by setting its jumper
according to your hard disk jumper diagram. You may also configure two hard
disks to be both Masters using one ribbon cable on the primary IDE connector
and another on the secondary IDE connector . A new BIOS feature allows SCSI
hard drive bootup (see “HDD Sequence SCSI/IDE First” in the BIOS FEATURES SETUP of the BIOS software). (Pin 20 is r emoved to pr event insert-
ing in the wrong orientation when using ribbon cables with pin 20 plugged).
III. INSTALLATION
(Connectors)
Pin 1
R
Orient the red stripe on the
IDE ribbon cable to Pin 1
Secondary IDE Connector
Primary IDE Connector
IDE (Hard Disk Drive) Connectors
6. Power Connector (12-pin block)
This connector connects to a standard 5 Volt power supply . To connect the leads
from the power supply, ensure first that the power supply is not plugged. Most
power supplies provide two plugs (P8 and P9), each containing six wires, two of
which are black. Orient the connectors so that the black wires are located in the
middle.
+5V
-5V
GND
R
+12V
PG
-12V
+5V
RED
RED
RED
WHT
BLK
BLK
BLK
BLK
BLU
YLW
RED
ORG
P9
P8
Power Connector
on Motherboard
Power Plugs from
Power Supply
AT Power Connector
Using a slight angle, align the plastic guide pins on the lead to their receptacles
on the connector . Once aligned, press the lead onto the connector until the lead
locks into place.
24 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 25

III. INSTALLATION
7. IDE Activity LED (IDE LED)
This connector connects to the hard disk activity indicator light on the system
cabinet. Read and write activity by devices connected to the Primary or Secondary IDE connectors will cause the LED to light up.
TIP: If the case-mounted LED
does not light, try reversing
the 2-pin plug.
R
IDE LED
+
IDE Activity LED Lead
8. IrDA-compliant Infrared Module Connector (IR)
This connector supports the optional wireless transmitting and receiving infrared module. This module mounts to a small opening on system cases that support this feature. You must also configure the setting through BIOS setup in
Chipset Features to select whether UART2 is directed for use with COM2 or
IrDA. Use the five pins (as defined by Intel) as shown below (Back View) and
connect a ribbon cable from the module to the baseboard according to the pin
definitions. The ribbon cable that may be supplied may either have five or ten
pins (for other standards). If using a ten-pin ribbon cable, use only the top five
row of the ribbon cable plug.
For the infrared feature to be available, connect an
infrared module (optional) to the baseboard.
Back ViewFront View
IRTX
GND
+5V
NC
IRRX
NC
GND
R
Infrared Module Connector
+5V
IRRX
IRTX
(Connectors)
III. INSTALLATION
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 25
Page 26

III. INSTALLATION
(Connectors)
III. INSTALLATION
9. Turbo LED Switch (TB LED)
The baseboard’s turbo function is always on. The turbo LED connection is labeled here but the LED will remain constantly lit while the system power is on.
You may wish to connect the Power LED from the system case to this lead.
10.SMI Suspend Switch Lead (SMI)
This allows the user to manually place the system into a suspend mode or “Green”
mode where system activity will be instantly decreased to save electricity and expand the life of certain components when the system is not in use. This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted suspend switch. If the switch is not available,
you can use the turbo switch. SMI is activated when it detects a short to open moment; leaving it shorted, therefore, will not cause any problems. This may require
one or two presses depending on the switch’s position. Wake-up can be controlled
through the BIOS but the keyboard will always wake up (the SMI lead cannot wake
up) the system. If you want to use this connector , the “Suspend Mode” under Power
Management Setup of the BIOS SOFTWARE must be set to Enable.
11. Reset Switch Lead (RESET)
This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted reset switch to allow the
restarting of your computer without having to turn off it off. This is a preferred
method of restarting to prolong the life of the system’s power supply.
12. System Power LED (KEYLOCK)
This 3-pin connector connects the system power LED, which lights when the
system is powered on and blinks when it is in sleep mode.
13.Keyboard Lock Switch Lead (KEYLOCK)
This 2-pin connector connects to the case-mounted key switch to allow keyboard locking.
14.Speaker Connector (SPEAKER)
This 4-pin connector connects to the case-mounted speaker.
Turbo or
Power LED
SMI Lead
R
Reset SW
+5V
GND
GND
GND
+5V
NC
Power LED
GND
LOCK
Keyboard Lock
GND
+5V
Speaker
GND
GND
Connector
SPKR
System Panel Connectors
26 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 27

III. INSTALLATION
15.Power Supply, CPU Fan Connectors (FANPWR1, FANPWR2, FANPWR3)
This connector supports a 3-pin CPU cooling fan of 500Amp (6watts) or less with a
minimum of 3,500RPM. Depending on the fan manufacturer, the wiring and plug
may be different. The red wire should be positive and the black wire should be gr ound.
Power Supply Fan
Ground
(NC)
+12 Volts
R
CPU Fan Power (2)
(NC)
+12 Volts
Ground
Power Supply, CPU Fan Power
16.USB Module Connector (USB)
If you want to use the universal serial bus (USB), you need to purchase an external connector set. The external connector connects to the 9-pin block.
1
2
910
1: USB +5Volt
3: USB Port 1 –
5: USB Port 1 +
7: Ground
R
9: (no connection)
USB Module Connector
2: USB +5Volt
4: USB Port 0 –
6: USB Port 0 +
8: Ground
10: (no connection)
(Connectors)
III. INSTALLATION
17. Chassis Open Alarm Connector (CHASSIS) (with optional LM78)
This lead is for an open chassis monitor . A high level signal to the chassis signal
lead will indicate to the system that the chassis has been opened.
For the chassis open alarm feature to work, you must have
the LM78 hardware monitor (optional) onboard and connect
a sensor or switch to the connector.
The +5V power comes from the power supply, when the A/C
is connected. With the A/C power disconnected, the +3V power
comes from the onboard button cell battery.
R
Power (+3V/+5V)
Chassis Signal
Ground
Chassis Connector (optional)
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 27
Page 28

IV. ASUS PCI SCSI Cards
Symbios SCSI BIOS and Drivers
Aside from the system BIOS, the Flash memory chip on the baseboard also contains
the Symbios SCSI BIOS. This Symbios SCSI BIOS works in conjunction with the
optional ASUS PCI-SC200 controller card to provide Fast SCSI-2 interface when
using compatible SCSI devices or the ASUS PCI-SC860 SCSI controller cards to
provide Ultra-Fast SCSI-2 interface when using Ultra-Fast SCSI-2 devices.
All SCSI devices you install on your system require driver software to function.
The Symbios SCSI BIOS directly supports SCSI hard disks under the DOS, Windows and OS/2 environments. It also uses device drivers from the DOS floppy disk
included in the ASUS PCI-SC200 and ASUS PCI-SC860 controller card packages
to support hard disks and other SCSI devices working under DOS, Microsoft Windows, Microsoft Windows NT, Novell NetWare and IBM OS/2. These drivers provide higher performance than the direct BIOS support. To use these drivers, you
must install them into your system and add them to your system configuration files.
Driver support for SCSI devices used with SCO UNIX is also provided. These drivers are included in the second SCO UNIX floppy disk. W indows 95 support is also
available using the device drivers included within the W indows software. The ASUS
PCI-SC200 and ASUS PCI-SC860 are Plug and Play adapters that are autodetected
by BIOS and current operating systems that support Plug and Play features.
IV. ASUS SCSI Cards
(SCSI BIOS)
For information about these drivers and their usage, view the Readme files included
in the driver packages.
ASUS PCI-SC200 & PCI-SC860 SCSI Cards
The ASUS PCI-SC200 or the ASUS PCI-SC860 may be bundled with your baseboard or purchased separately . Both cards provide the option of connecting internal
or external SCSI devices for a total of 7 devices on each SCSI card.
28 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 29

Setting Up the ASUS PCI-SC200 & PCI-SC860
There are two jumper settings you may need to make on the ASUS PCI-SC200 to set
it up. One setting assigns the PCI INT interrupt, the other sets the card’ s termination.
The ASUS PCI-SC860 has no jumper settings (see Terminator Requirements”).
Setting the INT Assignment for the ASUS PCI-SC200
You must use PCI INT A setting to properly assign the ASUS PCI-SC200’s interrupt. On the ASUS PCI-SC200, you assign the INT by setting jumper JP1 or JP2.
The default setting for the card already is INT A, so you do not need to change the
setting to use the ASUS PCI-SC200 with this baseboard.
JP 1JP
2
INT A (Def)
Interrupt Settings (A, B, C, or D)
JP 1JP
2
1
2
3
INT B
JP 1JP
2
1
2
3
INT C
JP 1JP
1
2
3
2
1
2
3
INT D
Terminator Requirements for SCSI Devices
SCSI devices are connected together in a “chain” by cables. Internal devices connect to the ASUS PCI-SC200 or ASUS PCI-SC860 with a fifty-pin flat ribbon cable.
External devices connect to the external port with a SCSI-2 cable. If there are more
than one internal or external devices, additional devices are connected with cables
to form a “daisy chain.” T erminating the devices on the ends of the SCSI Bus “chain”
is necessary for SCSI devices to work properly . Termination of the devices between
the ends must be Disabled.
(Setup)
IV. ASUS SCSI Cards
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 29
Page 30

IV. ASUS PCI SCSI Cards
Terminator Settings for the ASUS PCI-SC860
Many SCSI devices including the ASUS PCI-SC860 use a set of onboard active
resistors to terminate the devices at the ends automatically. Automatic termination
requires that the SCSI devices be connected in a straight linear connection or “chain.”
Connect SCSI devices to one or two of the SCSI connectors in a linear “chain” for
auto termination of the ASUS PCI-SC860 to be effective. Other formations will
cause your SCSI devices to not mount properly . You must use the end of the ribbon
cable when using the internal connector(s) to keep a linear path.
Additional Note: The Symbios Logic SCSI Configuration Utility is a powerful
tool. If, while using it, you somehow disable all your controllers or cannot enter
the configuration utility, pressing “Ctrl-A” after memory count during reboot
allows you to recover and reconfigure.
Terminator Settings for the ASUS PCI-SC200
The ASUS PCI-SC200, on the other hand, has “active” termination that you must
set using jumper JP5. There are two settings, “terminated” and “not terminated,” as
shown below.
IV. ASUS SCSI Cards
(Jumpers)
Decide whether or not you need to terminate the ASUS PCI-SC200 based on its
position in the SCSI chain. Only the devices at each end of the chain need to be
terminated. If you have only internal or only external devices connected to the
ASUS PCI-SC200, then you must terminate the ASUS PCI-SC200. If you have
both internal and external devices connected, you must not terminate the card. See
the following example, which illustrates this concept.
JP
5
Terminated (Default) Not Terminated
Terminator Setting (Terminated / Not Terminated)
JP
5
30 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
Page 31

IV. ASUS PCI SCSI Cards
Termination Required
(JP5 Open)
No Termination Required
(JP5 Short)
SCSI Device 1
SCSI Device 3
SCSI Device 2
SCSI Device 2
Termination Required
(End Device)
SCSI Device 4
Termination Required
(End Device)
Termination Required
(End Device)
SCSI Device 1
SCSI ID Numbers for SCSI Devices
All SCSI devices, including the ASUS PCI-SC200 and ASUS PCI-SC860 interface
card must have a SCSI identification number that is not in use by any other SCSI
device. There are eight possible ID numbers, 0 through 7. The ASUS PCI-SC200 and
ASUS PCI-SC860 cards have fixed SCSI IDs of 7. The SCSI ID serves two purposes:
• It uniquely defines each SCSI device on the bus.
• It determines which device controls the bus when two or more devices try to use
it at the same time.
SCSI IDs on one channel do not interfere with the IDs on another channel. This applies to two SCSI host adapters that implement different buses as well as dual channels
on a single host adapter. You can connect up to seven SCSI devices to the interface
card. You must set a SCSI ID number (ID 0 to ID 6) for each device. SCSI devices
vary in how they set the ID number. Some use jumpers, others have some kind of
selector switch. Refer to the manual for any device you install for details on how to set
its ID number .
SCSI ID Priority
The ASUS PCI-SC200 and ASUS PCI-SC860 are 8bit single-channel SCSI cards.
SCSI ID 7 has the highest priority, and SCSI ID 0 has the lowest priority.
(SCSI ID Numbers)
IV. ASUS SCSI Cards
ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual 31
Page 32

V. ASUS I-A16C Audio Card
NOTE: The ASUS I-A16C 16-bit ISA audio card comes with certain motherboard
or baseboard packages and is not sold separately.
ASUS I-A16C Audio Features
• Creative Labs V iBRA 16C PnP Audio Chip • Software Includes:
• Full Duplex Support DOS/Window 3.1/W indows 95 Drivers
• 16/8 bit PCM 5KHz to 44.1KHz Wave Editor, Wave OLE, Quick CD
• Wave Table Upgradeable Mixer Control, Quick Player
WARNING! Be cautious when unpacking and handling the audio card. Refer
to page 12 for some precautionary measures.
Layout and Connectors
Connectors
The audio input connectors are used when you wish to control software mixer settings (for example, bass, treble, volume) for audio CDs that are played with your
CD-ROM. If the “Audio Out” from the CD-ROM is not connected to the “Audio
In” on the card, you can only use the direct output located in the front panel of the
CD-ROM and adjust volume level by the knob.
(Features/Precautions)
V. ASUS I-A16C
CD-Audio Connector Pin Definitions
Sony Audio In Mitsumi Audio In Panasonic Audio In
Pin Definition Pin Definition Pin Definition
l Right Signal 1 Ground 1 Left Signal
2 Ground 2 Left Signal 2 Ground
3 Ground 3 Ground 3 Right Signal
4 Left Signal 4 Right Signal -- ----
Mitsumi Audio In
Sony Audio In
Panasonic Audio In
PC Speaker In
Volume Control
Wave Table Upgrade
PC Speaker Out
Speaker Out
Line Out
Line In
Microphone
MIDI/Game
PC Speaker In PC Speaker Out Volume Control
Pin Definition Pin Definition Pin Definition
1 Mono Signal 1 Right Signal 1 Ground
2 Ground 2 Ground 2 Volume Up
-- ---- 3 Left Signal 3 Ground
-- ---- 4 Ground 4 Volume Down
-- ---- -- ---- 5 Ground
32 ASUS P/I-P65UP5 User’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...