Page 1

890GX Extreme4
User Manual
Version 1.0
Published July 2010
Copyright©2010 ASRock INC. All rights reserved.
11
1
11
Page 2
Copyright Notice:Copyright Notice:
Copyright Notice:
Copyright Notice:Copyright Notice:
No part of this manual may be reproduced, transcribed, transmitted, or translated in
any language, in any form or by any means, except duplication of documentation by
the purchaser for backup purpose, without written consent of ASRock Inc.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be regis-
tered trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for
identification or explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
Disclaimer:Disclaimer:
Disclaimer:
Disclaimer:Disclaimer:
Specifications and information contained in this manual are furnished for informa-
tional use only and subject to change without notice, and should not be constructed
as a commitment by ASRock. ASRock assumes no responsibility for any errors or
omissions that may appear in this manual.
With respect to the contents of this manual, ASRock does not provide warranty of
any kind, either expressed or implied, including but not limited to the implied warran-
ties or conditions of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
In no event shall ASRock, its directors, officers, employees, or agents be liable for
any indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages (including damages for
loss of profits, loss of business, loss of data, interruption of business and the like),
even if ASRock has been advised of the possibility of such damages arising from any
defect or error in the manual or product.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
(1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
CALIFORNIA, USA ONLY
The Lithium battery adopted on this motherboard contains Perchlorate, a toxic
substance controlled in Perchlorate Best Management Practices (BMP) regulations
passed by the California Legislature. When you discard the Lithium battery in
California, USA, please follow the related regulations in advance.
“Perchlorate Material-special handling may apply, see
www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/perchlorate”
ASRock Website: http://www.asrock.com
22
2
22
Page 3

ContentsContents
Contents
ContentsContents
1.1.
IntroductionIntroduction
1.
Introduction
1.1.
IntroductionIntroduction
1.1 Package Contents ..................................................................... 5
1.2 Specifications ............................................................................ 6
1.3 Motherboard Layout ................................................................. 12
1.4 I/O Panel .................................................................................... 13
2.2.
InstallationInstallation
2.
Installation
2.2.
InstallationInstallation
Pre-installation Precautions ............................................................... 15
2.1 CPU Installation ......................................................................... 16
2.2 Installation of CPU Fan and Heatsink ....................................... 16
2.3 Installation of Memory Modules (DIMM) .................................... 17
2.4 Expansion Slots (PCI and PCI Express Slots) .......................... 19
2.5 Dual Monitor and Surround Display Features .......................... 20
2.6 CrossFireXTM, 3-Way CrossFireXTM and Quad CrossFireX
Operation Guide ........................................................................ 23
2.7 ATITM Hybrid CrossFireXTM Operation Guide............................. 29
2.8 Jumpers Setup .......................................................................... 31
2.9 Onboard Headers and Connectors.......................................... 32
2.10 Smart Switches ........................................................................ 37
2.11 Dr. Debug .................................................................................. 38
2.12 Serial ATA3 (SATA3) Hard Disks Installation ............................ 41
2.13 Hot Plug and Hot Swap Functions for SATA3 HDDs ............... 41
2.14 SATA3 HDD Hot Plug Feature and Operation Guide ................. 42
2.15 Driver Installation Guide ............................................................ 44
2.16 Installing Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / Vista
XP 64-bit With RAID Functions ................................................. 44
2.16.1 Installing Windows® XP / XP 64-bit With RAID
2.16.2 Installing Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / Vista
2.17 Installing Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / Vista
XP 64-bit Without RAID Functions ............................................ 46
2.17.1 Installing Windows® XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID
2.17.2 Installing Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / Vista
2.18 Untied Overclocking Technology .............................................. 47
........................................................................................................................
............................................................
........................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
..............................................................
............................................................................................................................
TM
64-bit / XP /
Functions .................................................................... 44
With RAID Functions ..................................................... 45
Functions ...................................................................... 46
Without RAID Functions ................................................ 47
TM
64-bit / XP /
TM
TM
TM
64-bit
64-bit
5 5
5
5 5
15 15
15
15 15
33
3
33
Page 4

3.3.
BIOS SBIOS S
3.
BIOS S
3.3.
BIOS SBIOS S
3.1 Introduction ............................................................................... 48
3.2 Main Screen .............................................................................. 49
3.3 OC Tweaker Screen ................................................................. 50
3.4 Advanced Screen .................................................................... 58
3.5 Hardware Health Event Monitoring Screen ............................. 68
3.6 Boot Screen .............................................................................. 69
3.7 Security Screen ........................................................................ 70
3.8 Exit Screen ............................................................................... 71
4.4.
Software SupportSoftware Support
4.
Software Support
4.4.
Software SupportSoftware Support
4.1 Install Operating System ........................................................... 72
4.2 Support CD Information ............................................................. 72
ETUP UTILITYETUP UTILITY
ETUP UTILITY
ETUP UTILITYETUP UTILITY
3.1.1 BIOS Menu Bar ............................................................... 48
3.1.2 Navigation Keys ............................................................. 49
3.4.1 CPU Configuration .......................................................... 59
3.4.2 Chipset Configuration ..................................................... 60
3.4.3 ACPI Configuration ......................................................... 62
3.4.4 Storage Configuration .................................................... 63
3.4.5 PCIPnP Configuration ...................................................... 65
3.4.6 Super IO Configuration ................................................... 66
3.4.7 USB Configuration .......................................................... 67
3.6.1 Boot Settings Configuration ........................................... 69
4.2.1 Running Support CD ....................................................... 72
4.2.2 Drivers Menu .................................................................. 72
4.2.3 Utilities Menu ................................................................... 72
4.2.4 Contact Information ........................................................ 72
......................................................................................................
...................................................
......................................................................................................
......................................................................................................
...................................................
......................................................................................................
48 48
48
48 48
72 72
72
72 72
44
4
44
Page 5
1.1.
IntroductionIntroduction
1.
Introduction
1.1.
IntroductionIntroduction
Thank you for purchasing ASRock 890GX Extreme4 motherboard, a reliable
motherboard produced under ASRock’s consistently stringent quality control. It de-
livers excellent performance with robust design conforming to ASRock’s commit-
ment to quality and endurance.
In this manual, chapter 1 and 2 contain introduction of the motherboard and step-by-step
guide to the hardware installation. Chapter 3 and 4 contain the configuration guide to
BIOS setup and information of the Support CD.
Because the motherboard specifications and the BIOS software might be
updated, the content of this manual will be subject to change without
notice. In case any modifications of this manual occur, the updated
version will be available on ASRock website without further notice. You
may find the latest VGA cards and CPU support lists on ASRock website
as well. ASRock website
If you require technical support related to this motherboard, please visit
our website for specific information about the model you are using.
www.asrock.com/support/index.asp
1.11.1
PP
ackack
1.1
1.11.1
ASRock 890GX Extreme4 Motherboard
(ATX Form Factor: 12.0-in x 9.6-in, 30.5 cm x 24.4 cm)
ASRock 890GX Extreme4 Quick Installation Guide
ASRock 890GX Extreme4 Support CD
4 x Serial ATA (SATA) Data Cables (Optional)
2 x Serial ATA (SATA) HDD Power Cables (Optional)
1 x I/O Panel Shield
1 x Front USB 3.0 Panel
6 x Screws
age Contentsage Contents
P
ack
age Contents
PP
ackack
age Contentsage Contents
http://www.asrock.com
55
5
55
Page 6
1.21.2
SpecificationsSpecifications
1.2
Specifications
1.21.2
SpecificationsSpecifications
Platform - ATX Form Factor: 12.0-in x 9.6-in, 30.5 cm x 24.4 cm
- All Solid Capacitor design (100% Japan-made high-quality
Conductive Polymer Capacitors)
CPU - Support for Socket AM3 processors: AMD Phenom
X4 / X3 / X2 (except 920 / 940) / Athlon II X4 / X3 / X2 /
Sempron processors
- Six-Core CPU Ready
- Supports UCC feature (Unlock CPU Core) (see CAUTION 1)
- Advanced V8 + 2 Power Phase Design
- Supports CPU up to 140W
- Supports AMD’s Cool ‘n’ QuietTM Technology
- FSB 2600 MHz (5.2 GT/s)
- Supports Untied Overclocking Technology (see CAUTION 2)
- Supports Hyper-Transport 3.0 (HT 3.0) Technology
Chipset - Northbridge: AMD 890GX
- Southbridge: AMD SB850
Memory - Dual Channel DDR3 Memory Technology (see CAUTION 3)
- 4 x DDR3 DIMM slots
- Support DDR3 1866(OC)/1800(OC)/1600(OC)/1333/1066/800
non-ECC, un-buffered memory (see CAUTION 4)
- Max. capacity of system memory: 16GB (see CAUTION 5)
Expansion Slot - 3 x PCI Express 2.0 x16 slot (PCIE2/PCIE3: single at x16 or
dual at x8/x8 mode; PCIE4: x4 mode)
- 1 x PCI Express 2.0 x1 slot
- 3 x PCI slots
- Supports ATITM Quad CrossFireXTM, 3-Way CrossFireXTM,
CrossFireXTM and Hybrid CrossFireX
Graphics - Integrated AMD Radeon HD 4290 graphics
- DX10.1 class iGPU, Shader Model 4.1
- Max. shared memory 512MB (see CAUTION 6)
- Built-in 128MB DDR3 1333/1200MHz SidePort Memory
- Three VGA Output options: D-Sub, DVI-D and HDMI
- Supports HDMI Technology with max. resolution up to
1920x1200 (1080P)
- Supports Dual-link DVI with max. resolution up to 2560x1600
@ 75Hz
- Supports D-Sub with max. resolution up to 2048x1536
@ 85Hz
- Supports HDCP function with DVI and HDMI ports
TM
TM
II X6 /
66
6
66
Page 7
- Supports Full HD 1080p Blu-ray (BD) / HD-DVD playback
with DVI and HDMI ports
Audio - 7.1 CH HD Audio with Content Protection
(Realtek ALC892 Audio Codec)
- Premium Blu-ray audio support
- Supports THX TruStudio Pro
TM
LAN - PCIE x1 Gigabit LAN 10/100/1000 Mb/s
- Realtek RTL8111E
- Supports Wake-On-LAN
- Supports LAN Cable Detection
- Supports Energy Efficient Ethernet 802.3az
Rear Panel I/O I/O Panel
- 1 x PS/2 Keyboard Port
- 1 x VGA/D-Sub Port
- 1 x VGA/DVI-D Port
- 1 x HDMI Port
- 1 x Optical SPDIF Out Port
- 4 x Ready-to-Use USB 2.0 Ports
- 1 x eSATA3 Connector
- 2 x Ready-to-Use USB 3.0 Ports
- 1 x RJ-45 LAN Port with LED (ACT/LINK LED and SPEED LED)
- 1 x IEEE 1394 Port
- 1 x Clear CMOS Switch with LED
- HD Audio Jack: Rear Speaker/Central/Bass/Line in/
Front Speaker/Microphone (see CAUTION 7)
SATA3 - 5 x SATA3 6.0 Gb/s connectors, support RAID (RAID 0,
RAID 1, RAID 0+1 and RAID 5), NCQ, AHCI and "Hot Plug"
functions
USB 3.0 - 2 x Rear USB 3.0 ports by NEC UPD720200, support
USB 1.0/2.0/3.0 up to 5Gb/s
- 1 x Front USB 3.0 header (supports 2 USB 3.0 ports) by NEC
UPD720200, supports USB 1.0/2.0/3.0 up to 5Gb/s
Connector - 5 x SATA3 6.0Gb/s connectors
- 1 x IR header
- 1 x COM port header
- 1 x IEEE 1394 header
- 1 x HDMI_SPDIF header
- 1 x Power LED header
- CPU/Chassis/Power FAN connector
- 24 pin ATX power connector
- 8 pin 12V power connector
- Front panel audio connector
77
7
77
Page 8
- 3 x USB 2.0 headers (support 6 USB 2.0 ports)
- 1 x USB 3.0 header (supports 2 USB 3.0 ports)
- 1 x Dr. Debug (7-Segment Debug LED)
Smart Switch - 1 x Clear CMOS Switch with LED
- 1 x Power Switch with LED
- 1 x Reset Switch with LED
BIOS Feature - 8Mb AMI BIOS
- AMI Legal BIOS
- Supports “Plug and Play”
- ACPI 1.1 Compliance Wake Up Events
- Supports jumperfree
- SMBIOS 2.3.1 Support
- CPU, VCCM, NB, SB Voltage Multi-adjustment
Support CD - Drivers, Utilities, AntiVirus Software (Trial Version), AMD
OverDriveTM Utility, AMD Live! Explorer, AMD Fusion, ASRock
Software Suite (CyberLink DVD Suite - OEM and Trial)
Unique Feature - ASRock OC Tuner (see CAUTION 8)
- Intelligent Energy Saver (see CAUTION 9)
- Instant Boot
- ASRock Instant Flash (see CAUTION 10)
- ASRock OC DNA (see CAUTION 11)
- ASRock AIWI (see CAUTION 12)
- ASRock APP Charger (see CAUTION 13)
- Hybrid Booster:
- CPU Frequency Stepless Control (see CAUTION 14)
- ASRock U-COP (see CAUTION 15)
- Boot Failure Guard (B.F.G.)
- Turbo 25 / Turbo 30 GPU Overclocking
Hardware - CPU Temperature Sensing
Monitor - Chassis Temperature Sensing
- CPU/Chassis/Power Fan Tachometer
- CPU Quiet Fan
- CPU/Chassis Fan Multi-Speed Control
- Voltage Monitoring: +12V, +5V, +3.3V, Vcore
OS - Microsoft
®
Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
TM
/ VistaTM 64-bit
/ XP / XP 64-bit compliant
Certifications - FCC, CE, WHQL
- ErP/EuP Ready (ErP/EuP ready power supply is required)
(see CAUTION 16)
* For detailed product information, please visit our website: http://www.asrock.com
88
8
88
Page 9
WARNING
Please realize that there is a certain risk involved with overclocking, including adjusting
the setting in the BIOS, applying Untied Overclocking Technology, or using the third-
party overclocking tools. Overclocking may affect your system stability, or even
cause damage to the components and devices of your system. It should be done at
your own risk and expense. We are not responsible for possible damage caused by
overclocking.
CAUTION!
1. ASRock UCC (Unlock CPU Core) feature simplifies AMD CPU activation. As
long as a simple switch of the BIOS option “ASRock UCC”, you can unlock the
extra CPU core to enjoy an instant performance boost. When UCC feature is
enabled, the dual-core or triple-core CPU will boost to the quad-core CPU, and
some CPU, including quad-core CPU, can also increase L3 cache size up to
6MB, which means you can enjoy the upgrade CPU performance with a better
price. Please be noted that UCC feature is supported with AM3 CPU only, and
in addition, not every AM3 CPU can support this function because some
CPU’s hidden core may be malfunctioned.
2. This motherboard supports Untied Overclocking Technology. Please read “Un-
tied Overclocking Technology” on page 47 for details.
3. This motherboard supports Dual Channel Memory Technology. Before you
implement Dual Channel Memory Technology, make sure to read the
installation guide of memory modules on page 17 for proper installation.
4. Whether 1866/1800/1600MHz memory speed is supported depends on the
AM3 CPU you adopt. If you want to adopt DDR3 1866/1800/1600 memory
module on this motherboard, please refer to the memory support list on our
website for the compatible memory modules.
ASRock website http://www.asrock.com
5. Due to the operating system limitation, the actual memory size may be
less than 4GB for the reservation for system usage under Windows® 7 /
TM
/ XP. For Windows® OS with 64-bit CPU, there is no such limitation.
Vista
6. The maximum shared memory size is defined by the chipset vendor and
is subject to change. Please check AMD website for the latest information.
7. For microphone input, this motherboard supports both stereo and mono modes.
For audio output, this motherboard supports 2-channel, 4-channel, 6-channel,
and 8-channel modes. Please check the table on page 13 for proper connection.
8. It is a user-friendly ASRock overclocking tool which allows you to surveil
your system by hardware monitor function and overclock your hardware
devices to get the best system performance under Windows
environment. Please visit our website for the operation procedures of
ASRock OC Tuner. ASRock website:
http://www.asrock.com
®
99
9
99
Page 10
9. Featuring an advanced proprietary hardware and software design,
Intelligent Energy Saver is a revolutionary technology that delivers
unparalleled power savings. The voltage regulator can reduce the
number of output phases to improve efficiency when the CPU cores are
idle. In other words, it is able to provide exceptional power saving and
improve power efficiency without sacrificing computing performance.
To use Intelligent Energy Saver function, please enable Cool ‘n’ Quiet
option in the BIOS setup in advance. Please visit our website for the
operation procedures of Intelligent Energy Saver.
ASRock website:
10. ASRock Instant Flash is a BIOS flash utility embedded in Flash ROM.
This convenient BIOS update tool allows you to update system BIOS
without entering operating systems first like MS-DOS or Windows
this utility, you can press <F6> key during the POST or press <F2> key to
BIOS setup menu to access ASRock Instant Flash. Just launch this tool
and save the new BIOS file to your USB flash drive, floppy disk or hard
drive, then you can update your BIOS only in a few clicks without prepar-
ing an additional floppy diskette or other complicated flash utility. Please
be noted that the USB flash drive or hard drive must use FAT32/16/12 file
system.
11. The software name itself – OC DNA literally tells you what it is capable of.
OC DNA, an exclusive utility developed by ASRock, provides a conve-
nient way for the user to record the OC settings and share with others. It
helps you to save your overclocking record under the operating system
and simplifies the complicated recording process of overclocking settings.
With OC DNA, you can save your OC settings as a profile and share with
your friends! Your friends then can load the OC profile to their own system
to get the same OC settings as yours! Please be noticed that the OC
profile can only be shared and worked on the same motherboard.
12. To experience intuitive motion controlled games is no longer only available
at Wii. ASRock AIWI utility introduces a new way of PC gaming operation.
ASRock AIWI is the world's first utility to turn your iPhone/iPod touch as
a game joystick to control your PC games. All you have to do is just to
install the ASRock AIWI utility either from ASRock official website or
ASRock software support CD to your motherboard, and also download the
free AIWI Lite from App store to your iPhone/iPod touch. Connecting your
PC and apple devices via Bluetooth or WiFi networks, then you can start
experiencing the exciting motion controlled games. Also, please do not
forget to pay attention to ASRock official website regularly, we will
continuously provide you the most up-do-date supported games!
ASRock website: http://www.asrock.com/Feature/Aiwi/index.asp
http://www.asrock.com
®
. With
1010
10
1010
Page 11

13. If you desire a faster, less restricted way of charging your Apple devices,
such as iPhone/iPod/iPad Touch, ASRock has prepared a wonderful
solution for you - ASRock APP Charger. Simply installing the APP Charger
driver, it makes your iPhone charged much quickly from your computer
and up to 40% faster than before. ASRock APP Charger allows you to
quickly charge many Apple devices simultaneously and even supports
continuous charging when your PC enters into Standby mode (S1), Sus-
pend to RAM (S3), hibernation mode (S4) or power off (S5). With APP
Charger driver installed, you can easily enjoy the marvelous charging
experience than ever.
ASRock website: http://www.asrock.com/Feature/AppCharger/index.asp
14. Although this motherboard offers stepless control, it is not recommended
to perform over-clocking. Frequencies other than the recommended CPU
bus frequencies may cause the instability of the system or damage the
CPU.
15. While CPU overheat is detected, the system will automatically shutdown.
Before you resume the system, please check if the CPU fan on the
motherboard functions properly and unplug the power cord, then plug it
back again. To improve heat dissipation, remember to spray thermal
grease between the CPU and the heatsink when you install the PC system.
16. EuP, stands for Energy Using Product, was a provision regulated by
European Union to define the power consumption for the completed system.
According to EuP, the total AC power of the completed system shall be
under 1.00W in off mode condition. To meet EuP standard, an EuP ready
motherboard and an EuP ready power supply are required. According to
Intel’s suggestion, the EuP ready power supply must meet the standard of
5v standby power efficiency is higher than 50% under 100 mA current
consumption. For EuP ready power supply selection, we recommend you
checking with the power supply manufacturer for more details.
1111
11
1111
Page 12
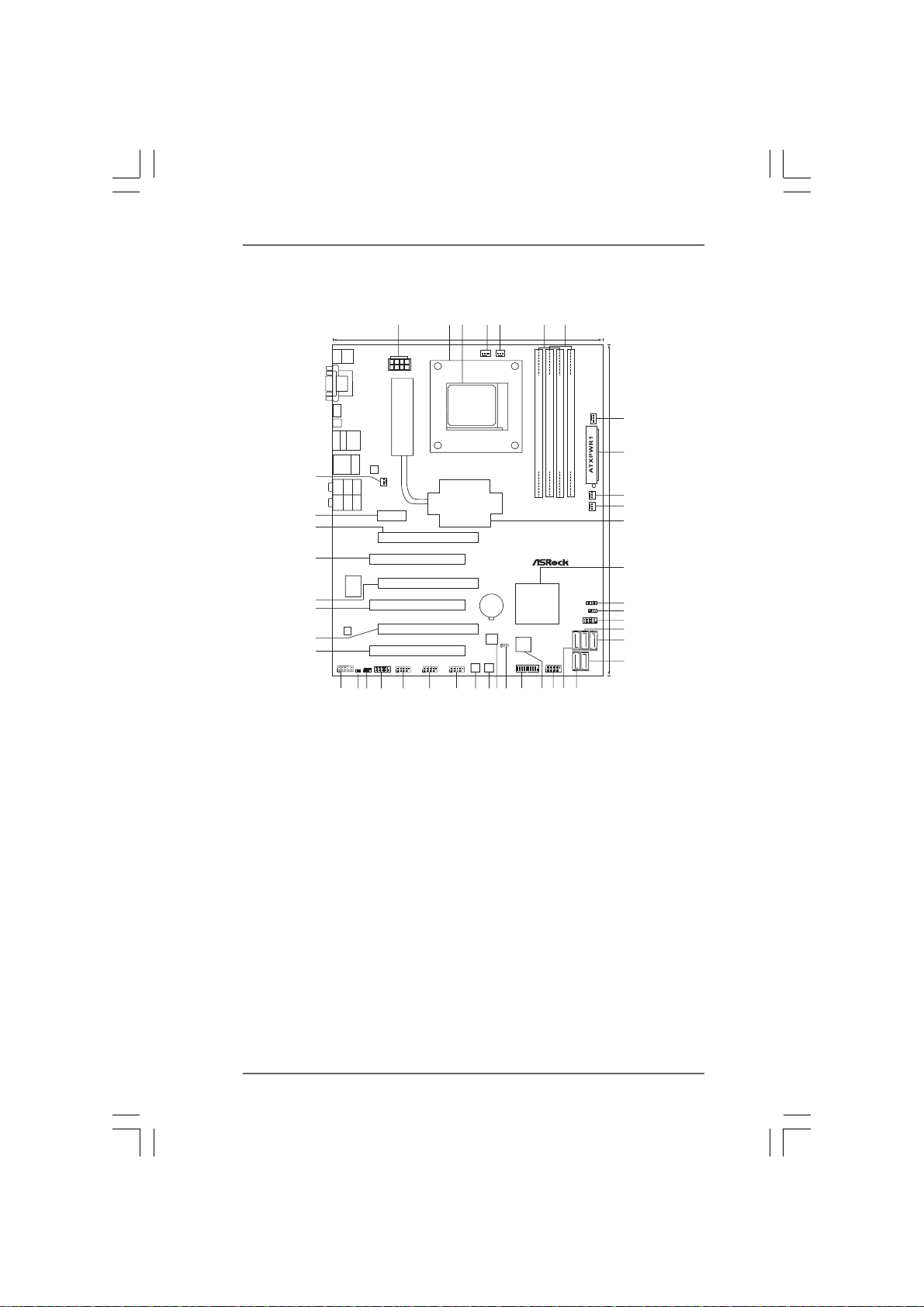
1.3 Motherboard Layout1.3 Motherboard Layout
1.3 Motherboard Layout
1.3 Motherboard Layout1.3 Motherboard Layout
3
5
6
Dual Channel HT3.0 AM3 FSB2.6GHz
DDR3 1866 Phenom II 140W CPU
SATA36Gb/s
AMD
SB850
Chipset
Dr.
USB3_2_3
FSB800
DDR3_A1(64 bit, 240-pinmodule)
FRONT_1394
11
DDR3_A2(64 bit, 240-pinmodule)
222324
7
FSB800
DDR3_B1(64 bit, 240-pinmodule)
SATA3(PORT2)
SATA4(PORT3)
SATA1(PORT0)
21
DDR3_B2(64 bit, 240-pinmodule)
SATA5(PORT4)
SATA2(PORT1)
20
1394a
8
CHA_FAN1
9
10
CHA_FAN2
11
CHA_FAN3
12
30.5cm (12.0-in)
13
SPEAKER1
1
14
PLED1
1
15
PANEL1
PLEDPWRBTN
1
16
HDLED RESET
17
18
19
1
Keyboard
PS2
USB2.0
T:US B4
B:USB5
VGA1
HDMI1
Clr
CMOS
IEEE1394
eSATA3
USB3.0
T:U SB 0
B:USB1
43
REAR SPK
Bottom:
Optical
SPDIF
Bottom:
MIC IN
FRONT
42
DVI_CON1
USB2.0
T:U SB 2
B:USB3
RJ-45LAN
Top:
CTR BASS
Center:
Top:
LINE IN
Center:
ATX12V1
LAN
PHY
PWR_FAN1
PCIE1
41
COM1
IR1
1
1
1
HDMI_SPDIF1
32
34
33
PCI Express2.0
890GX Extreme4
ErP/EuP Ready
Designed inTaipei
USB6_7
1
31
40
39
38
37
36
RoHS
Super
I/O
AUDIO
CODEC
HD_AUDIO1
1
35
24
24.4cm (9.6-in)
DX10.1
AMD
890GX
Chipset
Sideport memory128MB
PCIE2
PCI1
Support 6-CoreCPU
NEC USB3.0
PCIE3
PCI2
PCIE4
PCI3
USB8_91USB10_11
1
30
CPU_FAN2
CPU_FAN1
SOCKET AM3
CMOS
BATTERY
Front USB3.0
8Mb
BIOS
CLRCMOS1
1
Debug
RSTBTN
PWRBTN
27
2526
28
29
1 ATX 12V Power Connector (ATX12V1) 22 Front Panel IEEE 1394 Header
2 CPU Heatsink Retention Module (FRONT_1394, White)
3 AM3 CPU Socket 23 Dr. Debug (LED)
4 CPU Fan Connector (CPU_FAN1) 24 USB 3.0 Header (USB3_2_3, Light Blue)
5 CPU Fan Connector (CPU_FAN2) 25 Clear CMOS Jumper (CLRCMOS1)
6 2 x 240-pin DDR3 DIMM Slots 26 SPI Flash Memory (8Mb)
(Dual Channel A: DDR3_A1, DDR3_B1; Blue) 27 Reset Switch (RSTBTN)
7 2 x 240-pin DDR3 DIMM Slots 2 8 Power Switch (PWRBT N)
(Dual Channel B: DDR3_A2, DDR3_B2; White) 29 USB 2.0 Header (USB10_11, Blue)
8 Chassis Fan Connector (CHA_FAN1) 3 0 USB 2.0 Header (USB8_9, Blue)
9 ATX Power Connector (A TXPW R1) 31 USB 2.0 Header (USB6_7, Blue)
10 Chassis Fan Connector (CHA_FAN2) 32 Serial Port Connector (COM1)
11 Chassis Fan Connector (CHA_FAN3) 33 Infrared Module Header (IR1)
12 Northbridge Controller 34 HDMI_SPDIF Header (HDMI_SPDIF1, White)
13 Southbridge Controller 35 Front Panel Audio Header
14 Chassis Speaker Header (SPEAKER 1, White) (HD_AUDIO1, White)
15 Power LED Header (PLED1) 36 PCI Slot (PCI3)
16 System Panel Hea der (P ANEL1, White) 37 PCI Express 2.0 x16 Slot (PCIE4; Blue)
17 SA TA3 Connector (SATA4 (PORT 3), White) 38 PCI Slot (PCI2)
18 SA TA3 Connector (SATA5 (PORT 4), White) 39 PCI Express 2.0 x16 Slot (PCIE3; Blue)
19 SA TA3 Connector (SATA2 (PORT 1), White) 40 PCI Slot (PCI1)
20 SA TA3 Connector (SATA1 (PORT 0), White) 41 PCI Express 2.0 x16 Slot (PCIE2; Blue)
21 SA TA3 Connector (SATA3 (PORT 2), White) 42 PCI Express 2.0 x1 Slot (PCIE1; White)
43 Power Fan Connector (PWR_FAN1)
1212
12
1212
Page 13
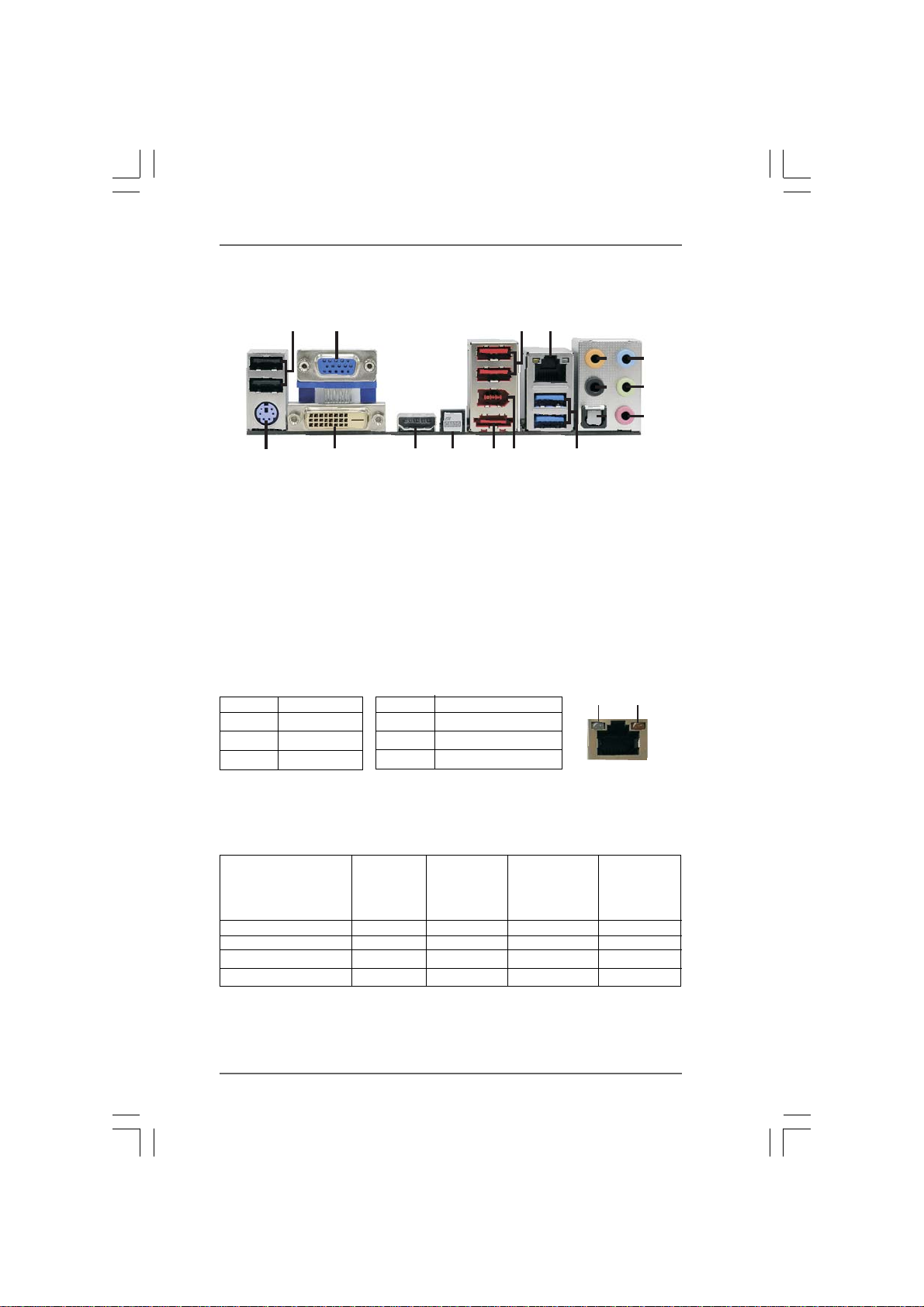
1.41.4
1.4
1.41.4
I/O PI/O P
I/O P
I/O PI/O P
anelanel
anel
anelanel
2
1
17
1 USB 2.0 Ports (USB45) 10 Microphone (Pink)
2 VGA/D-Sub Port 11 USB 3.0 Port (USB01)
3 USB 2.0 Ports (USB23) 12 IEEE 1394 Port (IEEE 1394)
* 4 LAN RJ-45 Port *** 13 eSATA3 Connector
5 Central / Bass (Orange) 14 Clear CMOS Switch (CLRCBTN)
6 Rear Speaker (Black) 15 V GA/HDMI Port
7 Optical SPDIF Out Port 16 V GA/DVI-D Port
8 Line In (Light Blue) 17 PS/2 Keyboard Port (Purple)
** 9 Front Speaker (Lime)
* There are two LED next to the LAN port. Please refer to the table below for the LAN port LED
indications.
Activity/Link LED SPEED LED
Status Description Status Description
Off No Link Off 10Mbps connection
Blinking Data Activity Orange 100Mbps connection
On Link Green 1Gbps connection
16
LAN Port LED Indications
15
14
13
12
3
4
8
5
6
9
7
10
11
ACT/LINK
LED
SPEED
LED
LAN Port
** If you use 2-channel speaker, please connect the speaker’s plug into “Front Speaker Jack”.
See the table below for connection details in accordance with the type of speaker you use.
TABLE for Audio Output Connection
Audio Output Channels Front Speaker Rear Speaker Central / Bass Line In
(No. 9) (No. 6) (No. 5) or
Side Speaker
(No. 8)
2 V -- -- -4VV---6VVV-8VVVV
1313
13
1313
Page 14
To enable Multi-Streaming function, you need to connect a front panel audio cable to the front
panel audio header. After restarting your computer, you will find “Mixer” tool on your system.
Please select “Mixer ToolBox” , click “Enable playback multi-streaming”, and click
“ok”. Choose “2CH”, “4CH”, “6CH”, or “8CH” and then you are allowed to select “Realtek HDA
Primary output” to use Rear Speaker, Central/Bass, and Front Speaker, or select “Realtek
HDA Audio 2nd output” to use front panel audio.
*** eSATA3 connector supports SATA Gen3 in cable 1M.
1414
14
1414
Page 15

2.2.
InstallationInstallation
2.
Installation
2.2.
InstallationInstallation
This is an ATX form factor (12.0-in x 9.6-in, 30.5 cm x 24.4 cm) motherboard.
Before you install the motherboard, study the configuration of your chassis to en-
sure that the motherboard fits into it.
Pre-installation PrecautionsPre-installation Precautions
Pre-installation Precautions
Pre-installation PrecautionsPre-installation Precautions
Take note of the following precautions before you install motherboard
components or change any motherboard settings.
Before you install or remove any component, ensure that the
power is switched off or the power cord is detached from the
power supply. Failure to do so may cause severe damage to the
motherboard, peripherals, and/or components.
1. Unplug the power cord from the wall socket before touching any
component.
2. To avoid damaging the motherboard components due to static
electricity, NEVER place your motherboard directly on the carpet or
the like. Also remember to use a grounded wrist strap or touch a
safety grounded object before you handle components.
3. Hold components by the edges and do not touch the ICs.
4. Whenever you uninstall any component, place it on a grounded anti-
static pad or in the bag that comes with the component.
5. When placing screws into the screw holes to secure the motherboard
to the chassis, please do not over-tighten the screws! Doing so may
damage the motherboard.
1515
15
1515
Page 16

2.12.1
CPU InstallationCPU Installation
2.1
CPU Installation
2.12.1
CPU InstallationCPU Installation
Step 1. Unlock the socket by lifting the lever up to a 90
o
angle.
Step 2. Position the CPU directly above the socket such that the CPU corner with
the golden triangle matches the socket corner with a small triangle.
Step 3. Carefully insert the CPU into the socket until it fits in place.
The CPU fits only in one correct orientation. DO NOT force the CPU
into the socket to avoid bending of the pins.
Step 4. When the CPU is in place, press it firmly on the socket while you push
down the socket lever to secure the CPU. The lever clicks on the side tab
to indicate that it is locked.
Lever 90° Up
CPU Golden Triangle
Socker Corner Small Triangle
STEP 1:
Lift Up The Socket Lever
2.22.2
Installation of CPU Fan and HeatsinkInstallation of CPU Fan and Heatsink
2.2
Installation of CPU Fan and Heatsink
2.22.2
Installation of CPU Fan and HeatsinkInstallation of CPU Fan and Heatsink
STEP 2 / STEP 3:
Match The CPU Golden Triangle
To The Socket Corner Small
Triangle
STEP 4:
Push Down And Lock
The Socket Lever
After you install the CPU into this motherboard, it is necessary to install a
larger heatsink and cooling fan to dissipate heat. You also need to spray
thermal grease between the CPU and the heatsink to improve heat
dissipation. Make sure that the CPU and the heatsink are securely fas-
tened and in good contact with each other. Then connect the CPU fan to
the CPU FAN connector (CPU_FAN1, see Page 12, No. 4 or CPU_FAN2,
see Page 12, No. 5). For proper installation, please kindly refer to the
instruction manuals of the CPU fan and the heatsink.
1616
16
1616
Page 17
2.3 Installation of Memory Modules (DIMM)2.3 Installation of Memory Modules (DIMM)
2.3 Installation of Memory Modules (DIMM)
2.3 Installation of Memory Modules (DIMM)2.3 Installation of Memory Modules (DIMM)
This motherboard provides four 240-pin DDR3 (Double Data Rate 3) DIMM slots,
and supports Dual Channel Memory Technology. For dual channel configuration,
you always need to install identical (the same brand, speed, size and chip-
type) DDR3 DIMM pair in the slots of the same color. In other words, you have to
install identical DDR3 DIMM pair in Dual Channel A (DDR3_A1 and DDR3_B1;
Blue slots; see p.12 No.6) or identical DDR3 DIMM pair in Dual Channel B
(DDR3_A2 and DDR3_B2; White slots; see p.12 No.7), so that Dual Channel
Memory Technology can be activated. This motherboard also allows you to
install four DDR3 DIMMs for dual channel configuration, and please install iden-
tical DDR3 DIMMs in all four slots. You may refer to the Dual Channel Memory
Configuration Table below.
Dual Channel Memory Configurations
DDR3_A1 DDR3_A2 DDR3_B1 DDR3_B2
(Blue Slot) (White Slot) (Blue Slot) (White Slot)
(1) Populated - Populated -
(2) - Populated - Populated
(3)* Populated Populated Populated Populated
* For the configuration (3), please install identical DDR3 DIMMs in all four
slots.
1. If you want to install two memory modules, for optimal compatibility
and reliability, it is recommended to install them in the slots of the
same color. In other words, install them either in the set of blue slots
(DDR3_A1 and DDR3_B1), or in the set of white slots (DDR3_A2
and DDR3_B2).
2. If only one memory module or three memory modules are installed
in the DDR3 DIMM slots on this motherboard, it is unable to activate
the Dual Channel Memory Technology.
3. If a pair of memory modules is NOT installed in the same Dual
Channel, for example, installing a pair of memory modules in
DDR3_A1 and DDR3_A2, it is unable to activate the Dual Channel
Memory Technology .
4. It is not allowed to install a DDR or DDR2 memory module into
DDR3 slot; otherwise, this motherboard and DIMM may be damaged.
5. If you adopt DDR3 1866/1800/1600 memory modules on this
motherboard, it is recommended to install them on DDR3_A2 and
DDR3_B2 slots.
1717
17
1717
Page 18
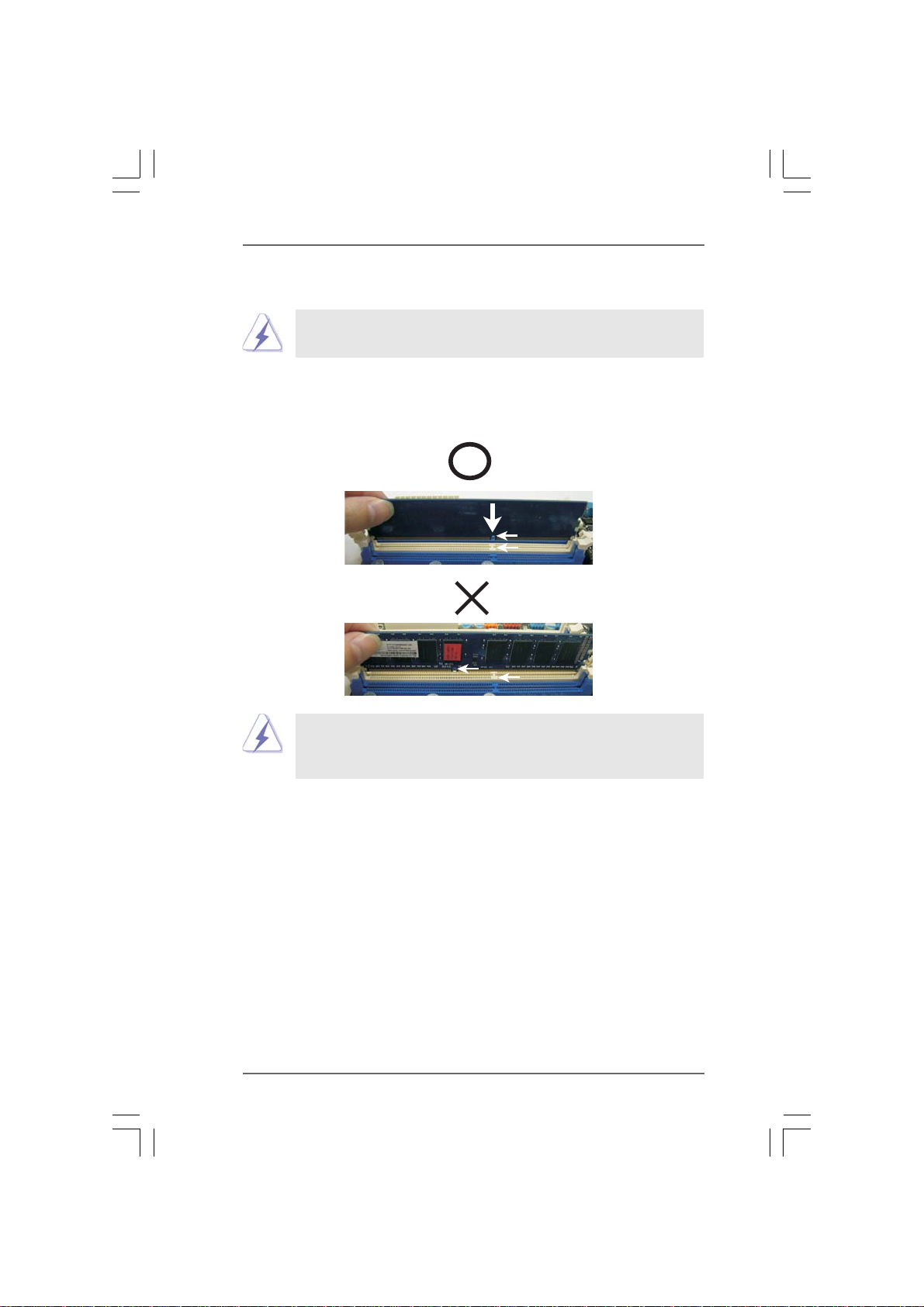
Installing a DIMMInstalling a DIMM
Installing a DIMM
Installing a DIMMInstalling a DIMM
Please make sure to disconnect power supply before adding or
removing DIMMs or the system components.
Step 1. Unlock a DIMM slot by pressing the retaining clips outward.
Step 2. Align a DIMM on the slot such that the notch on the DIMM matches the break
on the slot.
notch
break
notch
break
The DIMM only fits in one correct orientation. It will cause permanent
damage to the motherboard and the DIMM if you force the DIMM into the slot
at incorrect orientation.
Step 3. Firmly insert the DIMM into the slot until the retaining clips at both ends fully
snap back in place and the DIMM is properly seated.
1818
18
1818
Page 19
2.4 Expansion Slots (PCI and PCI Express Slots)2.4 Expansion Slots (PCI and PCI Express Slots)
2.4 Expansion Slots (PCI and PCI Express Slots)
2.4 Expansion Slots (PCI and PCI Express Slots)2.4 Expansion Slots (PCI and PCI Express Slots)
There are 3 PCI slots and 4 PCI Express slots on this motherboard.
PCI Slots: PCI slots are used to install expansion cards that have the 32-bit PCI
interface.
PCIE Slots:
PCIE1 (PCIE x1 slot; White) is used for PCI Express cards with x1 lane
width cards, such as Gigabit LAN card and SATA2 card.
PCIE2 / PCIE3 (PCIE x16 slot; Blue) is used for PCI Express x16 lane
width graphics cards, or used to install PCI Express graphics cards to
support CrossFireXTM function.
PCIE4 (PCIE x16 slot; Blue) is used for PCI Express x4 lane width
cards, or used to install PCI Express graphics cards to support 3-Way
CrossFireXTM function.
1. In single VGA card mode, it is recommended to install a PCI Express
x16 graphics card on PCIE2 slot.
2. In CrossFireXTM mode, please install PCI Express x16 graphics cards
on PCIE2 and PCIE3 slots. Therefore, both these two slots will work at
x8 bandwidth.
3. In 3-Way CrossFireX
cards on PCIE2, PCIE3 and PCIE4 slots. Therefore, PCIE2 and PCIE3
slots will work at x8 bandwidth while PCIE4 slot will work at x4 bandwidth.
4. Please connect a chassis fan to motherboard chassis fan connector
(CHA_FAN1, CHA_FAN2 or CHA_FAN3) when using multiple
graphics cards for better thermal environment.
5. PCIE1 slot is shared with PCIE4 slot. If you use PCIE1 slot, PCIE4
slot will work at x1 bandwidth. If you use PCIE4 slot, PCIE1 slot will be
disabled.
TM
mode, please install PCI Express x16 graphics
Installing an expansion cardInstalling an expansion card
Installing an expansion card
Installing an expansion cardInstalling an expansion card
Step 1. Before installing the expansion card, please make sure that the power
supply is switched off or the power cord is unplugged. Please read the
documentation of the expansion card a nd ma ke necessary hardware
settings for the card before you start the installation.
Step 2. Remove the system unit cover (if your motherboard is already installed in a
chassis).
Step 3. Remove the bracket fa cing the slot that you intend to use. Keep the screws
for later use.
Step 4. Align the card connector with the slot and press firmly until the card is
completely seated on the slot.
Step 5. Fasten the card to the chassis with screws.
Step 6. Replace the system cover .
1919
19
1919
Page 20

2.5 Dual Monitor and Surround Display Features2.5 Dual Monitor and Surround Display Features
2.5 Dual Monitor and Surround Display Features
2.5 Dual Monitor and Surround Display Features2.5 Dual Monitor and Surround Display Features
Dual Monitor Feature
This motherboard supports dual monitor feature. With the internal VGA output
support (DVI-D, D-Sub and HDMI), you can easily enjoy the benefits of dual monitor
feature without installing any add-on VGA card to this motherboard. This
motherboard also provides independent display controllers for DVI-D, D-Sub and
HDMI to support dual VGA output so that DVI-D, D-sub and HDMI can drive same or
different display contents.
To enable dual monitor feature, please follow the below steps:
1. Connect DVI-D monitor cable to VGA/DVI-D port on the I/O panel, connect D-Sub
monitor cable to VGA/D-Sub port on the I/O panel, or connect HDMI monitor
cable to HDMI port on the I/O panel.
VGA/D-Sub port
VGA/DVI-D port
2. If you have installed onboard VGA driver from our support CD to your system
already, you can freely enjoy the benefits of dual monitor function after your
system boots. If you haven’t installed onboard VGA driver yet, please install
onboard VGA driver from our support CD to your system and restart your
computer. Then you can start to use dual monitor function on this motherboard.
1. DVI-D and HDMI ports cannot function at the same time. When one of
them is enabled, the other one will be disabled.
2. When you playback HDCP-protected video from Blu-ray (BD) or
HD-DVD disc, the content will be displayed only in one of the two
monitors instead of both monitors.
HDMI port
2020
20
2020
Page 21

Surround Display Feature
This motherboard supports surround display upgrade. With the internal VGA
output support (DVI-D, D-Sub and HDMI) and external add-on PCI Express VGA
cards, you can easily enjoy the benefits of surround display feature.
Please refer to the following steps to set up a surround display environment:
1. Install the ATITM PCI Express VGA cards on PCIE2, PCIE3 and PCIE4 slots. Please
refer to page 19 for proper expansion card installation procedures for details.
2. Connect DVI-D monitor cable to VGA/DVI-D port on the I/O panel, connect D-Sub
monitor cable to VGA/D-Sub port on the I/O panel, or connect HDMI monitor
cable to HDMI port on the I/O panel. Then connect other monitor cables to the
corresponding connectors of the add-on PCI Express VGA cards on PCIE2,
PCIE3 and PCIE4 slots.
3. Boot your system. Press <F2> to enter BIOS setup. Enter “UMA Frame Buffer
Size” option to adjust the memory capability to [32MB], [64MB], [128MB] [256MB]
or [512MB] to enable the function of VGA/D-sub. Please make sure that the
value you select is less than the total capability of the system memory. If you do
not adjust the BIOS setup, the default value of “Share Memory”, [Auto], will
disable VGA/D-Sub function when the add-on VGA card is inserted to this
motherboard.
4. Install the onboard VGA driver and the add-on PCI Express VGA card driver to
your system. If you have installed the drivers already, there is no need to install
them again.
5. Set up a multi-monitor display.
For Windows® XP / XP 64-bit OS:
Right click the desktop, choose “Properties”, and select the “Settings” tab
so that you can adjust the parameters of the multi-monitor according to the
steps below.
A. Click the “Identify” button to display a large number on each monitor.
B. Right-click the display icon in the Display Properties dialog that you wish
to be your primary monitor, and then select “Primary”. When you use
multiple monitors with your card, one monitor will always be Primary,
and all additional monitors will be designated as Secondary.
C. Select the display icon identified by the number 2.
D. Click “Extend my Windows desktop onto this monitor”.
E. Right-click the display icon and select “Attached”, if necessary.
F. Set the “Screen Resolution” and “Color Quality” as appropriate for the
second monitor. Click “Apply” or “OK” to apply these new values.
G. Repeat steps C through E for the diaplay icon identified by the number
one, two, three, four, five, six, seven and eight.
2121
21
2121
Page 22
For Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit OS:
Right click the desktop, choose “Personalize”, and select the “Display
Settings” tab so that you can adjust the parameters of the multi-monitor
according to the steps below.
A. Click the number ”2” icon.
B. Click the items “This is my main monitor” and “Extend the desktop onto
this monitor”.
C. Click “OK” to save your change.
D. Repeat steps A through C for the display icon identified by the number
three, four, five, six, seven and eight.
6. Use Surround Display. Click and drag the display icons to positions representing
the physical setup of your monitors that you would like to use. The placement
of display icons determines how you move items from one monitor to another.
HDCP Function
HDCP function is supported on this motherboard. To use HDCP
function with this motherboard, you need to adopt the monitor that
supports HDCP function as well. Therefore, you can enjoy the
superior display quality with high-definition HDCP encryption
contents. Please refer to below instruction for more details about
HDCP function.
What is HDCP?
HDCP stands for High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection, a
specification developed by Intel® for protecting digital entertainment
content that uses the DVI interface. HDCP is a copy protection
scheme to eliminate the possibility of intercepting digital data
midstream between the video source, or transmitter - such as a
computer, DVD player or set-top box - and the digital display, or
receiver - such as a monitor, television or projector. In other words,
HDCP specification is designed to protect the integrity of content as it
is being transmitted.
Products compatible with the HDCP scheme such as DVD players,
satellite and cable HDTV set-top-boxes, as well as few entertain-
ment PCs requires a secure connection to a compliant display. Due
to the increase in manufacturers employing HDCP in their equipment,
it is highly recommended that the HDTV or LCD monitor you purchase
is compatible.
2222
22
2222
Page 23

TMTM
TM
2.62.6
CrossFCrossF
2.6
CrossF
2.62.6
CrossFCrossF
CrossFireXCrossFireX
CrossFireX
CrossFireXCrossFireX
This motherboard supports CrossFireXTM, 3-way CrossFireX
CrossFireXTM feature. CrossFireXTM technology offers the most advantageous means
available of combining multiple high performance Graphics Processing Units (GPU) in
a single PC. Combining a range of different operating modes with intelligent software
design and an innovative interconnect mechanism, CrossFireXTM enables the highest
possible level of performance and image quality in any 3D application. Currently
CrossFireXTM feature is supported with Windows® XP with Service Pack 2 / Vista
/ 7 OS. 3-way CrossFireXTM and Quad CrossFireX
Windows® VistaTM / 7 OS only. Please check AMD website for ATITM CrossFireX
driver updates.
TMTM
ireXireX
, 3-, 3-
WW
ireX
ireXireX
TMTM
TM
TMTM
ay CrossFay CrossF
, 3-
W
ay CrossF
, 3-, 3-
WW
ay CrossFay CrossF
Operation Guide Operation Guide
Operation Guide
Operation Guide Operation Guide
ireXireX
ireX
ireXireX
TMTM
TM
TMTM
and Quad and Quad
and Quad
and Quad and Quad
TM
and Quad
TM
feature are supported with
TM
TM
1. If a customer incorrectly configures their system they will not see the
performance benefits of CrossFireX
CrossFireX
CrossFireX
benefit from the CrossFireX
2. If you pair a 12-pipe CrossFireX
will operate as 12-pipe cards while in CrossFireX
2.6.1 Graphics Card Setup2.6.1 Graphics Card Setup
2.6.1 Graphics Card Setup
2.6.1 Graphics Card Setup2.6.1 Graphics Card Setup
2.6.1.1 Installing T2.6.1.1 Installing T
2.6.1.1 Installing T
2.6.1.1 Installing T2.6.1.1 Installing T
Cards Cards
Cards
Cards Cards
Different CrossFireXTM cards may require different methods to enable CrossFireX
feature. In below procedures, we use Radeon HD 3870 as the example graphics card.
For other CrossFireX
refer to ATI
Step 1. Insert one Radeon graphics card into PCIE2 slot and the other Radeon
graphics card to PCIE3 slot. Make sure that the cards are properly seated
on the slots.
TM
Ready graphics card, a CrossFireXTM Ready motherboard and a
TM
Edition co-processor graphics card, must be installed correctly to
wo CrossFwo CrossF
wo CrossF
wo CrossFwo CrossF
TM
TM
cards that ATITM has released or will release in the future, please
graphics card manuals for detailed installation guide.
TM
. All three CrossFireXTM components, a
TM
multi-GPU platform.
TM
Edition card with a 16-pipe card, both cards
ireXireX
ireX
ireXireX
TM
mode.
TMTM
TM
TMTM
-R-R
eady Graphicseady Graphics
-R
eady Graphics
-R-R
eady Graphicseady Graphics
TM
2323
23
2323
Page 24

Step 2. Connect two Radeon graphics cards by installing CrossFire Bridge on
CrossFire Bridge Interconnects on the top of Radeon graphics cards.
(CrossFire Bridge is provided with the graphics card you purchase, not
bundled with this motherboard. Please refer to your graphics card vendor
for details.)
CrossFire Bridge
or
Step 3. Connect the DVI monitor cable to the DVI connector on the Radeon graphics
card on PCIE2 slot. (You may use the DVI to D-Sub adapter to convert the
DVI connector to D-Sub interface, and then connect the D-Sub monitor
cable to the DVI to D-Sub adapter.)
2424
24
2424
Page 25

TMTM
TM
2.6.1.2 Installing Three CrossFireX2.6.1.2 Installing Three CrossFireX
2.6.1.2 Installing Three CrossFireX
2.6.1.2 Installing Three CrossFireX2.6.1.2 Installing Three CrossFireX
Cards Cards
Cards
Cards Cards
Step 1. Install one Radeon graphics card to PCIE2 slot. For the proper installation
procedures, please refer to section “Expansion Slots”.
Step 2. Install one Radeon graphics card to PCIE3 slot. For the proper installation
procedures, please refer to section “Expansion Slots”.
Step 3. Install one Radeon graphics card to PCIE4 slot. For the proper installation
procedures, please refer to section “Expansion Slots”.
TMTM
-Ready Graphics-Ready Graphics
-Ready Graphics
-Ready Graphics-Ready Graphics
Step 4. Use one CrossFireTM Bridge to connect Radeon graphics cards on PCIE2
and PCIE3 slots, and use the other CrossFireTM Bridge to connect Radeon
graphics cards on PCIE3 and PCIE4 slots. (CrossFireTM Bridge is provided
with the graphics card you purchase, not bundled with this motherboard.
Please refer to your graphics card vendor for details.)
2525
25
2525
Page 26

CrossFireTM Bridge
Step 5. Connect the DVI monitor cable to the DVI connector on the Radeon graphics
card on PCIE2 slot. (You may use the DVI to D-Sub adapter to convert the
DVI connector to D-Sub interface, and then connect the D-Sub monitor
cable to the DVI to D-Sub adapter.)
2626
26
2626
Page 27

2.6.2 Driver Installation and Setup2.6.2 Driver Installation and Setup
2.6.2 Driver Installation and Setup
2.6.2 Driver Installation and Setup2.6.2 Driver Installation and Setup
Step 1. Power on your computer and boot into OS.
Step 2. Remove the ATI
The Catalyst Uninstaller is an optional download. We recommend using this
utility to uninstall any previously installed Catalyst drivers prior to installation.
Please check AMD website for ATITM driver updates.
Step 3. Install the required drivers to your system.
For Windows® XP OS:
A. ATITM recommends Windows® XP Service Pack 2 or higher to be
installed (If you have Windows® XP Service Pack 2 or higher installed
in your system, there is no need to download it again):
http://www.microsoft.com/windowsxp/sp2/default.mspx
B. You must have Microsoft .NET Framework installed prior to
downloading and installing the CATALYST Control Center. Please
check Microsoft website for details.
For Windows® 7 / VistaTM OS:
Install the CATALYST Control Center. Please check AMD website for details.
Step 4. Restart your computer.
Step 5. Install the VGA card drivers to your system, and restart your computer.
Then you will find “ATI Catalyst Control Center” on your Windows® taskbar.
TM
driver if you have any VGA driver installed in your system.
ATI Catalyst Control Center
Step 6. Double-click “ATI Catalyst Control Center”. Click “View”, select
“CrossFireXTM”, and then check the item “Enable CrossFireXTM”. Select “2
GPUs” and click “Apply” (if you install two Radeon graphics cards). Select
“3 GPUs” and click “OK” (if you install three Radeon graphics cards).
2727
27
2727
Page 28

Although you have selected the option “Enable CrossFireTM”, the CrossFireX
function may not work actually. Your computer will automatically reboot. After
restarting your computer, please confirm whether the option “Enable
CrossFireTM” in “ATI Catalyst Control Center” is selected or not; if not, please
select it again, and then you are able to enjoy the benefit of CrossFireX
feature.
TM
Step 7. You can freely enjoy the benefit of CrossFireXTM, 3-Way CrossFireXTM or
Quad CrossFireXTM feature.
* CrossFireXTM appearing here is a registered trademark of ATITM Technologies Inc., and is
used only for identification or explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
* For further information of ATITM CrossFireXTM technology, please check AMD website for
updates and details.
TM
2828
28
2828
Page 29

TMTM
TM
2.72.7
2.7
2.72.7
This motherboard supports ATITM Hybrid CrossFireXTM feature. ATITM Hybrid
CrossFireXTM brings multi-GPU performance capabilities by enabling an AMD
890GX integrated graphics processor and a discrete graphics processor to
operate simultaneously with combined output to a single display for blisteringly-
fast frame rates. Currently, ATITM Hybrid CrossFireXTM Technology is only
supported with Windows® Vista
OS. In the future, ATITM Hybrid CrossFireXTM may be supported with Windows® XP
OS. Please visit our website for updated information.
TMTM
AA
TITI
Hybrid CrossF Hybrid CrossF
A
TI
Hybrid CrossF
AA
TITI
Hybrid CrossF Hybrid CrossF
TM
What does an ATITM Hybrid CrossFireXTM system include?
An ATITM Hybrid CrossFireXTM system includes an ATITM RadeonTM 2400, 3450 or 5450
series graphics processor and a motherboard based on an AMD 890GX integrated
chipset, all operating in a Windows® VistaTM / 7 environment. Please refer to below
PCI Express graphics card support list for ATI
update of more compatible PCI Express graphics cards, please visit our website for
further information.
Vendor Chipset Model Driver
ATI RADEON HD2400XT POWERCOLOR HD2400 XT Support CD 8.70
RADEON HD3450 POWERCOLOR AX3450 Support CD 8.70
RADEON HD5450 ATI RADEON HD5450 1GB Support CD 8.70
TMTM
TM
TMTM
ireXireX
Operation Guide Operation Guide
ireX
Operation Guide
ireXireX
Operation Guide Operation Guide
/ 7 OS, and is not available with Windows® XP
TM
Hybrid CrossFireXTM. For the future
256MB DDR3
256MD2-S
TMTM
TM
Enjoy the benefit of AEnjoy the benefit of A
Enjoy the benefit of A
Enjoy the benefit of AEnjoy the benefit of A
Step 1. Install one compatible PCI Express graphics card to PCIE2 slot (blue). For
the proper installation procedures, please refer to section “Expansion Slots”.
Step 2. Connect the monitor cable to the correspondent connector on the PCI
Express graphics card on PCIE2 slot.
Step 3. Boot your system. Press <F2> to enter BIOS setup. Enter “Advanced”
screen, and enter “Chipset Settings”. Then set the option “Surround View”
to [Enabled].
Step 4. Boot into OS. Please remove the ATITM driver if you have any VGA driver
installed in your system.
Step 5. Install the onboard VGA driver from our support CD to your system for both
the onboard VGA and the discrete graphics card.
Step 6. Restart your computer. Then you will find “ATI Catalyst Control Center” on
your Windows® taskbar.
ATI Catalyst Control Center
TMTM
TITI
Hybrid CrossF Hybrid CrossF
TI
Hybrid CrossF
TITI
Hybrid CrossF Hybrid CrossF
2929
29
2929
ireXireX
ireX
ireXireX
TMTM
TM
TMTM
Page 30

Step 7. Double-click “ATI Catalyst Control Center”. Click “View”, click “CrossFireTM”,
and then select the option “Enable CrossFireTM”.
View
CrossFire
TM
Step 8. Click “Yes” to continue.
Step 9. Click “OK” to save your change.
Enable CrossFire
TM
Step 10. Reboot your system. Then you can freely enjoy the benefit of Hybrid
TM
CrossFireXTM feature.
* Hybrid CrossFireXTM appearing here is a registered trademark of ATITM Technologies Inc.,
and is used only for identification or explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to
infringe.
* For further information of ATI
for up dates and details.
TM
Hybrid CrossFireXTM technology, please check AMD website
3030
30
3030
Page 31

2.82.8
Jumpers SetupJumpers Setup
2.8
Jumpers Setup
2.82.8
Jumpers SetupJumpers Setup
The illustration shows how jumpers are
setup. When the jumper cap is placed on
pins, the jumper is “Short”. If no jumper cap
is placed on pins, the jumper is “Open”. The
illustration shows a 3-pin jumper whose pin1
and pin2 are “Short” when jumper cap is
placed on these 2 pins.
Jumper Setting
Clear CMOS Jumper
(CLRCMOS1)
(see p.12, No. 25)
Note: CLRCMOS1 allows you to clear the data in CMOS. The data in CMOS includes
system setup information such as system password, date, time, and system
setup parameters. To clear and reset the system parameters to default setup,
please turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power
supply. After waiting for 15 seconds, use a jumper cap to short pin2 and pin3
on CLRCMOS1 for 5 seconds. However, please do not clear the CMOS right
after you update the BIOS. If you need to clear the CMOS when you just finish
updating the BIOS, you must boot up the system first, and then shut it down
before you do the clear-CMOS action.
1_2
Default
2_3
Clear CMOS
3131
31
3131
Page 32

2.9 Onboard Headers and Connectors2.9 Onboard Headers and Connectors
2.9 Onboard Headers and Connectors
2.9 Onboard Headers and Connectors2.9 Onboard Headers and Connectors
Onboard headers and connectors are NOT jumpers. Do NOT place
jumper caps over these headers and connectors. Placing jumper caps
over the headers and connectors will cause permanent damage of the
motherboard!
Serial ATA3 Connectors These five Serial ATA3
(SATA1 (PORT 0): see p.12, No. 20) (SATA3) connectors support
(SATA2 (PORT 1): see p.12, No. 19) SATA data cables for internal
(SATA3 (PORT 2): see p.12, No. 21) storage devices. The current
(SATA4 (PORT 3): see p.12, No. 17) SATA3 interface allows up to
(SATA5 (PORT 4): see p.12, No. 18) 6.0 Gb/s data transfer rate.
SATA1 (PORT 0)
SATA2 (PORT 1)
SATA3 (PORT 2)
SATA4 (PORT 3)
SATA5 (PORT 4)
Serial ATA (SATA) Either end of the SATA data cable
Data Cable can be connected to the SATA3
(Optional) hard disk or the SATA3
connector on this motherboard.
Serial ATA (SATA) Please connect the black end of
Power Cable SATA power cable to the power
(Optional) connector on each drive. Then
connect to the SATA HDD
power connector
connect to the
power supply
connect the white end of SATA
power cable to the power
connector of the power supply.
1
1
1
USB_PW R
P-7
P-6
USB_PW R
USB_PWR
P-9
P-8
USB_PWR
USB_PW R
P-11
P-10
USB_PW R
P+7
P+6
P+9
P+8
P+11
P+10
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
3232
32
3232
motherboard. Each USB 2.0
header can support two USB
2.0 ports.
USB 2.0 Headers Besides four default USB 2.0
(9-pin USB6_7) ports on the I/O panel, there are
(see p.12 No. 31) three USB 2.0 headers on this
(9-pin USB8_9)
(see p.12 No. 30)
(9-pin USB10_11)
(see p.12 No. 29)
Page 33

USB 3.0 Header Besides two default USB 3.0
(19-pin USB3_2_3) ports on the I/O panel, there is
(see p.12 No. 24) one USB 3.0 header on this
IntA_P2_D+
IntA_P2_D-
GND
IntA_P2_SSTX+
IntA_P2_SSTX-
GND
IntA_P2_SSRX+
IntA_P2_SSRX-
Vbus
motherboard. This USB 3.0
header can support two USB
1
ID
IntA_P1_D-
IntA_P1_D+
IntA_P1_SSTX-
IntA_P1_SSTX+
GND
IntA_P1_SSRX-
IntA_P1_SSRX+
GND
Vbus
3.0 ports.
Infrared Module Header This header supports an
(5-pin IR1) optional wireless transmitting
(see p.12 No. 33) and receiving infrared module.
Front Panel Audio Header This is an interface for the front
(9-pin HD_AUDIO1) panel audio cable that allows
IRTX
1
IRRX
GND
PRESENCE#
+5V
DUMMY
GND
MIC_RET
OUT_RET
(see p.12, No. 35) convenient connection and
1
MIC2_R
MIC2_L
J_SENSE
OUT2_R
OUT2_L
control of audio devices.
1. High Definition Audio supports Jack Sensing, but the panel wire on
the chassis must support HDA to function correctly. Please follow the
instruction in our manual and chassis manual to install your system.
2. If you use AC’97 audio panel, please install it to the front panel audio
header as below:
A. Connect Mic_IN (MIC) to MIC2_L.
B. Connect Audio_R (RIN) to OUT2_R and Audio_L (LIN) to OUT2_L.
C. Connect Ground (GND) to Ground (GND).
D. MIC_RET and OUT_RET are for HD audio panel only. You don’t
need to connect them for AC’97 audio panel.
E. To activate the front mic.
For Windows
®
XP / XP 64-bit OS:
Select “Mixer”. Select “Recorder”. Then click “FrontMic”.
For Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit OS:
Go to the "FrontMic" Tab in the Realtek Control panel. Adjust
“Recording Volume”.
1
PLED+
PLED-
HDLED-
HDLED+
PWRBTN#
GND
DUMMY
RESET#
GND
3333
33
3333
System Panel Header This header accommodates
(9-pin PANEL1) several system front panel
(see p.12 No. 16) functions.
Page 34

Connect the power switch, reset switch and system status indicator on
the chassis to this header according to the pin assignments below. Note
the positive and negative pins before connecting the cables.
PWRBTN (Power Switch):
Connect to the power switch on the chassis front panel. You may
configure the way to turn off your system using the power switch.
RESET (Reset Switch):
Connect to the reset switch on the chassis front panel. Press the reset
switch to restart the computer if the computer freezes and fails to
perform a normal restart.
PLED (System Power LED):
Connect to the power status indicator on the chassis front panel. The LED
is on when the system is operating. The LED keeps blinking when the
sys-tem is in S1 sleep state. The LED is off when the system is in S3/S4
sleep state or powered off (S5).
HDLED (Hard Drive Activity LED):
Connect to the hard drive activity LED on the chassis front panel. The
LED is on when the hard drive is reading or writing data.
The front panel design may differ by chassis. A front panel module
mainly consists of power switch, reset switch, power LED, hard drive
activity LED, speaker and etc. When connecting your chassis front panel
module to this header, make sure the wire assignments and the pin
assign-ments are matched correctly.
Power LED Header Please connect the chassis
(3-pin PLED1) power LED to this header to
(see p.12 No. 15) indicate system power status.
1
PLED+
PLED+
PLED-
The LED is on when the system
is operating. The LED keeps
blinking in S1 state. The LED is
off in S3/S4 state or S5 state
(power off).
Chassis Speaker Header Please connect the chassis
(4-pin SPEAKER 1) speaker to this header.
(see p.12 No. 14)
1
SPEAKER
DUMMY
DUMMY
+5V
3434
34
3434
Page 35

Chassis and Power Fan Connectors Please connect the fan cables
(4-pin CHA_FAN1) to the fan connectors and
(see p.12 No. 8) match the black wire to the
(3-pin CHA_FAN2) speed can be controlled through
(see p.12 No. 10) BIOS or OC Tuner utility.
(3-pin CHA_FAN3)
(see p.12 No. 11)
(3-pin PWR_FAN1)
(see p.12 No. 43)
GND
+12V
CHA_FAN_SPEED
FAN_SPEED_CONTROL
GND
+12V
CHA_FAN_SPEED
GND
+12V
CHA_FAN_SPEED
ground pin. CHA_FAN1/2/3 fan
CPU Fan Connectors Please connect the CPU fan
(4-pin CPU_FAN1) cable to this connector and
(see p.12 No. 4) match the black wire to the
1 2 3 4
Though this motherboard provides 4-Pin CPU fan (Quiet Fan) support, the 3-Pin
CPU fan still can work successfully even without the fan speed control function.
If you plan to connect the 3-Pin CPU fan to the CPU fan connector on this
motherboard, please connect it to Pin 1-3.
(3-pin CPU_FAN2)
(see p.12 No. 5)
ground pin.
Pin 1-3 Connected
3-Pin Fan Installation
ATX Power Connector Please connect an ATX power
(24-pin ATXPWR1) supply to this connector.
(see p.12 No. 9)
Though this motherboard provides 24-pin ATX power connector,
it can still work if you adopt a traditional 20-pin ATX power supply.
12 124
13
12
To use the 20-pin ATX power supply, please plug your power
supply along with Pin 1 and Pin 13.
20-Pin ATX Power Supply Installation
3535
35
3535
1
24
13
Page 36

ATX 12V Power Connector Please connect an ATX 12V
(8-pin ATX12V1) power supply to this connector.
(see p.12 No. 1)
8 5
4 1
Though this motherboard provides 8-pin ATX 12V power connector, it can still work
if you adopt a traditional 4-pin ATX 12V power supply. To use the 4-pin ATX power
supply, please plug your power supply along with Pin 1 and Pin 5.
8 5
4-Pin ATX 12V Power Supply Installation
IEEE 1394 Header Besides one default IEEE 1394
(9-pin FRONT_1394) port on the I/O panel, there is one
(see p.12 No. 22) IEEE 1394 header
RXTPAM_0
1
RXTPAP_0
GND
RXTPBM_0
RXTPBP_0
GND
+12V
+12V
GND
(FRONT_1394) on this
motherboard. This IEEE 1394
header can support one IEEE
4 1
1394 port.
Serial port Header This COM1 header supports a
(9-pin COM1) serial port module.
(see p.12 No.32)
1
RRXD1
DDTR#1
TTXD1
DDCD#1
DDSR#1
CCTS#1
RRTS#1
GND
RRI#1
HDMI_SPDIF Header HDMI_SPDIF header, providing
(2-pin HDMI_SPDIF1) SPDIF audio output to HDMI VGA
(see p.12 No. 34) card, allows the system to
1
GND
SPDIFOUT
connect HDMI Digital TV/
projector/LCD devices. Please
connect the HDMI_SPDIF
connector of HDMI VGA card to
this header.
Front USB 3.0 Panel This front USB 3.0 panel can
support 2 additional USB 3.0
ports besides the I/O panel.
Please connect the light blue
connector on the cable of this
front USB 3.0 panel to the USB
3.0 header (USB3_2_3) and
fasten the front USB 3.0 panel to
the chassis with the bundled
six screws.
3636
36
3636
Page 37

2.10 Smart Switches2.10 Smart Switches
2.10 Smart Switches
2.10 Smart Switches2.10 Smart Switches
This motherboard has three smart switches: power switch, reset switch and
clear CMOS switch, allowing users to quickly turn on/off or reset the system or
clear the CMOS values.
Power Switch Power Switch is a smart switch,
(PWRBTN) allowing users to quickly turn
(see p.12 No. 28) on/off the system.
Reset Switch Reset Switch is a smart switch,
(RSTBTN) allowing users to quickly reset
(see p.12 No. 27) the system.
RESET
Clear CMOS Switch Clear CMOS Switch is a smart
(CLRCBTN) switch, allowing users to quickly
(see p.13 No. 14) clear the CMOS values
You are not allowed to use Clear CMOS switch function if you set up the system
password. If you want to clear the CMOS values, please clean your system
password in advance or refer to page 31 “Clear CMOS jumper” description
instead.
clr
CMOS
3737
37
3737
Page 38

2.11 Dr. Debug2.11 Dr. Debug
2.11 Dr. Debug
2.11 Dr. Debug2.11 Dr. Debug
Dr. Debug is used to provide code information, which makes troubleshooting even
easier. Please see the diagrams below for reading the Dr. Debug codes.
The Bootblock initialization code sets up the chipset, memory and other
components before system memory is available. The following table describes the
type of checkpoints that may occur during the bootblock initialization portion of the
BIOS:
Checkpoint Description
Before D1 Early chipset initialization is done. Early super I/O initialization is done
including RTC and keyboard controller. NMI is disabled.
D1 Perform keyboard controller BAT test. Check if waking up from power
management suspend state. Save power-on CPUID value in scratch
CMOS.
D0 Go to flat mode with 4GB limit and GA20 enabled. Verify the bootblock
checksum.
D2 Disable CACHE before memory detection. Execute full memory sizing
module. Verify that flat mode is enabled.
D3 If memory sizing module not executed, start memory refresh and do
memory sizing in Bootblock code. Do additional chipset initialization.
Re-enable CACHE. Verify that flat mode is enabled.
D4 Test base 512KB memory. Adjust policies and cache first 8MB. Set stack.
D5 Bootblock code is copied from ROM to lower system memory and control
is given to it. BIOS now executes out of RAM.
D6 Both key sequence and OEM specific method is checked to determine if
BIOS recovery is forced. Main BIOS checksum is tested. If BIOS recovery
is necessary, control flows to checkpoint E0.
D7 Restore CPUID value back into register. The Bootblock-Runtime interface
module is moved to system memory and control is given to it. Determine
whether to execute serial flash.
D8 The Runtime module is uncompressed into memory. CPUID information is
stored in memory.
D9 Store the Uncompressed pointer for future use in PMM. Copying Main BIOS
into memory. Leaves all RAM below 1MB Read-Write including E000 and
F000 shadow areas but closing SMRAM.
DA Restore CPUID value back into register. Give control to BIOS POST
(ExecutePOSTKernel).
3838
38
3838
Page 39

The POST code checkpoints are the largest set of checkpoints during the BIOS
pre-boot process. The following table describes the type of checkpoints that may
occur during the POST portion of the BIOS:
Checkpoint Description
03 Disable NMI, Parity, video for EGA, and DMA controllers. Initialize BIOS,
POST, Runtime data area. Also initialize BIOS modules on POST entry and
GPNV area. Initialized CMOS as mentioned in the Kernel Variable
“wCMOSFlags.”
04 Check CMOS diagnostic byte to determine if battery power is OK and
CMOS checksum is OK. Verify CMOS checksum manually by reading
storage area. If the CMOS checksum is bad, update CMOS with power-on
default values and clear passwords. Initialize status register A.
Initializes data variables that are based on CMOS setup questions.
Initializes both the 8259 compatible PICs in the system
05 Initializes the interrupt controlling hardware (generally PIC) and interrupt
vector table.
06 Do R/W test to CH-2 count reg. Initialize CH-0 as system timer. Install the
POSTINT1Ch handler. Enable IRQ-0 in PIC for system timer interrupt.
Traps INT1Ch vector to “POSTINT1ChHandlerBlock.”
08 Initializes the CPU. The BAT test is being done on KBC. Program the
keyboard controller command byte is being done after Auto detection of
KB/MS using AMI KB-5.
C0 Early CPU Init Start — Disable Cache - Init Local APIC
C1 Set up boot strap proccessor Information
C2 Set up boot strap proccessor for POST
C5 Enumerate and set up application proccessors
C6 Re-enable cache for boot strap proccessor
C7 Early CPU Init Exit
0A Initializes the 8042 compatible Key Board Controller.
0B Detects the presence of PS/2 mouse.
0C Detects the presence of Keyboard in KBC port.
0E Testing and initialization of different Input Devices. Also, update the Kernel
Variables. Traps the INT09h vector, so that the POST INT09h handler gets
control for IRQ1. Uncompress all available language, BIOS logo, and Silent
logo modules.
13 Early POST initialization of chipset registers.
24 Uncompress and initialize any platform specific BIOS modules.
30 Initialize System Management Interrupt.
2A Initializes different devices through DIM.
See DIM Code Checkpoints section of document for more information.
2C Initializes different devices. Detects and initializes the video adapter
installed in the system that have optional ROMs.
2E Initializes all the output devices.
31 Allocate memory for ADM module and uncompress it. Give control to ADM
module for initialization. Initialize language and font modules for ADM.
Activate ADM module.
3939
39
3939
Page 40

33 Initializes the silent boot module. Set the window for displaying text
information.
37 Displaying sign-on message, CPU information, setup key message, and
any OEM specific information.
38 Initializes different devices through DIM.
39 Initializes DMAC-1 & DMAC-2.
3A Initialize RTC date/time.
3B Test for total memory installed in the system. Also, Check for DEL or ESC
keys to limit memory test. Display total memory in the system.
3C Mid POST initialization of chipset registers.
40 Detect different devices (Parallel ports, serial ports, and coprocessor in
CPU, etc.) successfully installed in the system and update the BDA,
EBDA, etc.
50 Programming the memory hole or any kind of implementation that needs an
adjustment in system RAM size if needed.
52 Updates CMOS memory size from memory found in memory test.
Allocates memory for Extended BIOS Data Area from base memory.
60 Initializes NUM-LOCK status and programs the KBD typematic rate.
75 Initialize Int-13 and prepare for IPL detection.
78 Initializes IPL devices controlled by BIOS and option ROMs.
7A Initializes remaining option ROMs.
7C Generate and write contents of ESCD in NVRam.
84 Log errors encountered during POST.
85 Display errors to the user and gets the user response for error.
87 Execute BIOS setup if needed / requested.
8C Late POST initialization of chipset registers.
8D Build ACPI tables (if ACPI is supported)
8E Program the peripheral parameters. Enable/Disable NMI as selected
90 Late POST initialization of system management interrupt.
A0 Check boot password if installed.
A1 Clean-up work needed before booting to OS.
A2 Takes care of runtime image preparation for different BIOS modules. Fill
the free area in F000h segment with 0FFh. Initializes the Microsoft IRQ
Routing Table. Prepares the runtime language module. Disables the system
configuration display if needed.
A4 Initialize runtime language module.
A7 Displays the system configuration screen if enabled. Initialize the CPU’s
before boot, which includes the programming of the MTRR’s.
A8 Prepare CPU for OS boot including final MTRR values.
A9 Wait for user input at config display if needed.
AA Uninstall POST INT1Ch vector and INT09h vector. Deinitializes the ADM
module.
AB Prepare BBS for Int 19 boot.
AC End of POST initialization of chipset registers.
B1 Save system context for ACPI.
00 Passes control to OS Loader (typically INT19h).
4040
40
4040
Page 41

2.122.12
Serial ASerial A
2.12
Serial A
2.122.12
Serial ASerial A
This motherboard adopts AMD SB850 chipset that supports Serial ATA3 (SATA3)
hard disks and RAID functions. You may install SATA3 hard disks on this
motherboard for internal storage devices. This section will guide you to install the
SATA3 hard disks.
STEP 1: Install the SATA3 hard disks into the drive bays of your chassis.
STEP 2: Connect the SATA power cable to the SATA3 hard disk.
STEP 3: Connect one end of the SATA data cable to the motherboard’s SATA3
connector.
STEP 4: Connect the other end of the SATA data cable to the SATA3 hard disk.
TT
A3 (SAA3 (SA
T
A3 (SA
TT
A3 (SAA3 (SA
TT
A3) Hard Disks InstallationA3) Hard Disks Installation
T
A3) Hard Disks Installation
TT
A3) Hard Disks InstallationA3) Hard Disks Installation
2.13 Hot Plug and Hot Swap F2.13 Hot Plug and Hot Swap F
2.13 Hot Plug and Hot Swap F
2.13 Hot Plug and Hot Swap F2.13 Hot Plug and Hot Swap F
This motherboard supports Hot Plug and Hot Swap functions for SATA3 in RAID/
AHCI mode. AMD SB850 chipset provides hardware support for Advanced Host
controller Interface (AHCI), a new programming interface for SATA host controllers
developed thru a joint industry effort.
NOTE
What is Hot Plug Function?
If the SATA3 HDDs are NOT set for RAID configuration, it is called “Hot
Plug” for the action to insert and remove the SATA3 HDDs while the
system is still power-on and in working condition.
However, please note that it cannot perform Hot Plug if the OS has been
installed into the SATA3 HDD.
What is Hot Swap Function?
If SATA3 HDDs are built as RAID 1 or RAID 5 then it is called “Hot Swap”
for the action to insert and remove the SATA3 HDDs while the system is
still power-on and in working condition.
unctions for SAunctions for SA
unctions for SA
unctions for SAunctions for SA
TT
A3 HDDsA3 HDDs
T
A3 HDDs
TT
A3 HDDsA3 HDDs
4141
41
4141
Page 42

2.14 SA2.14 SA
2.14 SA
2.14 SA2.14 SA
This motherboard supports Hot Plug feature for SATA3 HDD in RAID / AHCI mode.
Please read below operation guide of Hot Plug feature carefully. Before you process
the SATA3 HDD Hot Plug, please check below cable accessories from the motherboard
gift box pack.
A. 7-pin SATA data cable
B. SATA power cable with SATA 15-pin power connector interface
TT
A3 HDD Hot Plug FA3 HDD Hot Plug F
T
A3 HDD Hot Plug F
TT
A3 HDD Hot Plug FA3 HDD Hot Plug F
A. SATA data cable (Red) B. SATA power cable
eature and Operation Guideeature and Operation Guide
eature and Operation Guide
eature and Operation Guideeature and Operation Guide
SATA 7-pin
connector
The SATA 15-pin power
connector (Black) connect
to SATA3 HDD
1x4-pin conventional
power connector (White)
connect to power supply
Caution
1. Without SATA 15-pin power connector interface, the SATA3 Hot Plug cannot be
processed.
2. Even some SATA3 HDDs provide both SATA 15-pin power connector and IDE
1x4-pin conventional power connector interfaces, the IDE 1x4-pin conventional
power connector interface is definitely not able to support Hot Plug and will
cause the HDD damage and data loss.
Points of attention, before you process the Hot Plug:
1. Below operation procedure is designed only for our motherboard, which
supports SATA3 HDD Hot Plug.
* The SATA3 Hot Plug feature might not be supported by the chipset because of
its limitation, the SATA3 Hot Plug support information of our motherboard is
indicated in the product spec on our website: www.asrock.com
2. Make sure your SATA3 HDD can support Hot Plug function from your dealer or
HDD user manual. The SATA3 HDD, which cannot support Hot Plug function, will
be damaged under the Hot Plug operation.
3. Please make sure the SATA3 driver is installed into system properly. The latest
SATA3 driver is available on our support website: www.asrock.com
4. Make sure to use the SATA power cable & data cable, which are from our
motherboard package.
5. Please follow below instructions step by step to reduce the risk of HDD crash
or data loss.
4242
42
4242
Page 43

How to Hot Plug a SA TA3 HDD:
Points of attention, before you process the Hot Plug:
Please do follow below instruction sequence to process the Hot Plug, improper
procedure will cause the SATA3 HDD damage and data loss.
Step 1
Please connect SATA power cable 1x4-pin end
(White) to the power supply 1x4-pin cable.
SATA power cable 1x4-pin
power connector (White)
Step 3
Connect SATA 15-pin power cable connector
(Black) end to SATA3 HDD.
Step 2
Connect SATA data cable to
the motherboard’s SATA3 connector.
Step 4
Connect SATA data cable to
the SATA3 HDD.
How to Hot Unplug a SATA3 HDD:
Points of attention, before you process the Hot Unplug:
Please do follow below instruction sequence to process the Hot Unplug, improper
procedure will cause the SATA3 HDD damage and data loss.
Step 1
Unplug SATA data cable from SATA3 HDD side.
Unplug SATA 15-pin power cable connector (Black) from SATA3 HDD side.
Step 2
4343
43
4343
Page 44

2.152.15
Driver Installation GuideDriver Installation Guide
2.15
Driver Installation Guide
2.152.15
Driver Installation GuideDriver Installation Guide
To install the drivers to your system, please insert the support CD to your optical
drive first. Then, the drivers compatible to your system can be auto-detected and
listed on the support CD driver page. Please follow the order from up to bottom
side to install those required drivers. Therefore, the drivers you install can work
properly.
®®
®
2.162.16
Installing WindowsInstalling Windows
2.16
Installing Windows
2.162.16
Installing WindowsInstalling Windows
TMTM
TM
TMTM
VistaVista
Vista
VistaVista
If you want to install Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit on
a RAID disk composed of 2 or more SATA3 HDDs with RAID functions, please follow
below procedures according to the OS you install.
2.16.1 Installing Windows2.16.1 Installing Windows
2.16.1 Installing Windows
2.16.1 Installing Windows2.16.1 Installing Windows
F F
F
F F
If you want to install Windows® XP / XP 64-bit on a RAID disk composed of 2 or more
SATA3 HDDs with RAID functions, please follow below steps.
STEP 1: Set up BIOS.
A. Enter BIOS SETUP UTILITY Advanced screen Storage
Configuration.
B. Set the “SATA Operation Mode” option to [RAID].
STEP 2: Make a SATA3 Driver Diskette. (Please use USB floppy or floppy
disk.)
A. Insert the ASRock Support CD into your optical drive to boot your system.
B. During POST at the beginning of system boot-up, press <F11> key, and
C. When you see the message on the screen, “Generate Serial ATA driver
D. Then you will see these messages,
E. The system will start to format the floppy diskette and copy SATA3
64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit With RAID Functions 64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit With RAID Functions
64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit With RAID Functions
64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit With RAID Functions 64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit With RAID Functions
unctionsunctions
unctions
unctionsunctions
then a window for boot devices selection appears. Please select CD-
ROM as the boot device.
diskette [YN]?”, press <Y>.
All data in the disk will be destroyed,
proceed? [Y/N]
Please insert a floppy diskette into the floppy drive, and press any key.
drivers into the floppy diskette.
®®
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista 7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista 7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
®®
®
®®
XP / XP 64-bit With RAID XP / XP 64-bit With RAID
XP / XP 64-bit With RAID
XP / XP 64-bit With RAID XP / XP 64-bit With RAID
TMTM
TM
TMTM
/ /
/
/ /
4444
44
4444
Page 45

STEP 3: Use “RAID Installation Guide” to set RAID configuration.
Before you start to configure RAID function, you need to check the RAID installation
guide in the Support CD for proper configuration. Please refer to the BIOS RAID installation
guide part of the document in the following path in the Support CD:
.. \ RAID Installation Guide
STEP 4: Install Windows® XP / XP 64-bit OS on your system.
After step 1, 2, 3, you can start to install Windows® XP / XP 64-bit OS on your system.
At the beginning of Windows® setup, press F6 to install a third-party RAID driver.
When prompted, insert the SATA3 driver diskette containing the AMD RAID driver.
After reading the floppy disk, the driver will be presented. Select the driver to install
according to the OS you install.
®®
®
2.16.2 Installing Windows2.16.2 Installing Windows
2.16.2 Installing Windows
2.16.2 Installing Windows2.16.2 Installing Windows
TMTM
TM
Vista Vista
Vista
Vista Vista
If you want to install Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit on a RAID disk
composed of 2 or more SATA3 HDDs with RAID functions, please follow below
steps.
STEP 1: Set up BIOS.
A. Enter BIOS SETUP UTILITY Advanced screen Storage
Configuration.
B. Set the “SATA Operation Mode” option to [RAID].
STEP 2: Use “RAID Installation Guide” to set RAID configuration.
Before you start to configure RAID function, you need to check the RAID installation
guide in the Support CD for proper configuration. Please refer to the BIOS RAID installation
guide part of the document in the following path in the Support CD:
.. \ RAID Installation Guide
STEP 3: Make a SATA3 Driver Diskette.
Make a SATA3 driver diskette by following section 2.16.1 step 2 on page 44.
STEP 4: Install Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit OS on your
system.
TMTM
64-bit With RAID Functions 64-bit With RAID Functions
64-bit With RAID Functions
64-bit With RAID Functions 64-bit With RAID Functions
®®
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista 7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista 7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
TMTM
TM
TMTM
/ /
/
/ /
4545
45
4545
Page 46

®®
®
2.172.17
Installing WindowsInstalling Windows
2.17
Installing Windows
2.172.17
Installing WindowsInstalling Windows
TMTM
TM
TMTM
VistaVista
Vista
VistaVista
If you want to install Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit OS
on your SATA3 HDDs without RAID functions, please follow below procedures
according to the OS you install.
2.17.1 Installing Windows2.17.1 Installing Windows
2.17.1 Installing Windows
2.17.1 Installing Windows2.17.1 Installing Windows
Functions Functions
Functions
Functions Functions
If you want to install Windows® XP / XP 64-bit on your SATA3 HDDs without RAID
functions, please follow below steps.
Using SATA3 HDDs with NCQ and Hot Plug functions (AHCI mode)
STEP 1: Set Up BIOS.
A. Enter BIOS SETUP UTILITY Advanced screen Storage
Configuration.
B. Set the “SATA Operation Mode” option to [AHCI].
STEP 2: Make a SATA3 Driver Diskette.
Make a SATA3 driver diskette by following section 2.16.1 step 2 on page 44.
STEP 3: Install Windows® XP / XP 64-bit OS on your system.
You can start to install Windows® XP / XP 64-bit OS on your system. At the beginning
of Windows® setup, press F6 to install a third-party AHCI driver. When prompted,
insert the SATA3 driver diskette containing the AMD AHCI driver. After reading the
floppy disk, the driver will be presented. Select the driver to install according to the
OS you install.
64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID Functions 64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID Functions
64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID Functions
64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID Functions 64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID Functions
®®
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista 7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista 7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
®®
®
®®
XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID
XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID
XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID XP / XP 64-bit Without RAID
TMTM
TM
TMTM
/ /
/
/ /
Using SATA3 HDDs without NCQ and Hot Plug functions (IDE mode)
STEP 1: Set up BIOS.
A. Enter BIOS SETUP UTILITY Advanced screen Storage
Configuration.
B. Set the “SATA Operation Mode” option to [IDE].
STEP 2: Install Windows® XP / XP 64-bit OS on your system.
4646
46
4646
Page 47

®®
®
2.17.2 Installing Windows2.17.2 Installing Windows
2.17.2 Installing Windows
2.17.2 Installing Windows2.17.2 Installing Windows
TMTM
TM
Vista Vista
Vista
Vista Vista
If you want to install Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit on your SATA3
HDDs without RAID functions, please follow below steps.
Using SATA3 HDDs with NCQ and Hot Plug functions (AHCI mode)
STEP 1: Set Up BIOS.
A. Enter BIOS SETUP UTILITY Advanced screen Storage
Configuration.
B. Set the “SATA Operation Mode” option to [AHCI].
STEP 2: Install Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit OS on your
system.
Using SATA3 HDDs without NCQ and Hot Plug functions (IDE mode)
STEP 1: Set up BIOS.
A. Enter BIOS SETUP UTILITY Advanced screen Storage
Configuration.
B. Set the “SATA Operation Mode” option to [IDE].
STEP 2: Install Windows® 7 / 7 64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit OS on your
system.
TMTM
64-bit Without RAID Functions 64-bit Without RAID Functions
64-bit Without RAID Functions
64-bit Without RAID Functions 64-bit Without RAID Functions
®®
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista 7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
7 / 7 64-bit / Vista 7 / 7 64-bit / Vista
TMTM
TM
TMTM
/ /
/
/ /
2.182.18
Untied Overclocking TUntied Overclocking T
2.18
Untied Overclocking T
2.182.18
Untied Overclocking TUntied Overclocking T
This motherboard supports Untied Overclocking Technology, which means during
overclocking, FSB enjoys better margin due to fixed PCI / PCIE buses. Before you
enable Untied Overclocking function, please enter “Overclock Mode” option of BIOS
setup to set the selection from [Auto] to [Manual]. Therefore, CPU FSB is untied
during overclocking, but PCI / PCIE buses are in the fixed mode so that FSB can
operate under a more stable overclocking environment.
Please refer to the warning on page 9 for the possible overclocking risk
before you apply Untied Overclocking Technology.
echnologyechnology
echnology
echnologyechnology
4747
47
4747
Page 48

3.3.
BIOS SETUP UTILITYBIOS SETUP UTILITY
3.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
3.3.
BIOS SETUP UTILITYBIOS SETUP UTILITY
3.1 Introduction3.1 Introduction
3.1 Introduction
3.1 Introduction3.1 Introduction
This section explains how to use the BIOS SETUP UTILITY to configure your system.
The SPI Memory on the motherboard stores the BIOS SETUP UTILITY. You may run the
BIOS SETUP UTILITY when you start up the computer. Please press <F2> or <Del>
during the Power-On-Self-Test (POST) to enter the BIOS SETUP UTILITY, otherwise,
POST will continue with its test routines.
If you wish to enter the BIOS SETUP UTILITY after POST, restart the system by
pressing <Ctl> + <Alt> + <Delete>, or by pressing the reset button on the system
chassis. You may also restart by turning the system off and then back on.
Because the BIOS software is constantly being updated, the following
BIOS setup screens and descriptions are for reference purpose only,
and they may not exactly match what you see on your screen.
3.1.13.1.1
BIOS Menu BarBIOS Menu Bar
3.1.1
BIOS Menu Bar
3.1.13.1.1
BIOS Menu BarBIOS Menu Bar
The top of the screen has a menu bar with the following selections:
Main To set up the system time/date information
OC Tweaker To set up overclocking features
Advanced To set up the advanced BIOS features
H/W Monitor To display current hardware status
Boot To set up the default system device to locate and load the
Operating System
Security To set up the security features
Exit To exit the current screen or the BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Use < > key or < > key to choose among the selections on the menu bar,
and then press <Enter> to get into the sub screen.
4848
48
4848
Page 49

3.1.23.1.2
Navigation KeysNavigation Keys
3.1.2
Navigation Keys
3.1.23.1.2
Navigation KeysNavigation Keys
Please check the following table for the function description of each navigation
key.
Navigation Key(s) Function Description
/ Moves cursor left or right to select Screens
/ Moves cursor up or down to select items
+ / - To change option for the selected items
<Enter> To bring up the selected screen
<F1> To display the General Help Screen
<F9> To load optimal default values for all the settings
<F10> To save changes and exit the BIOS SETUP UTILITY
<ESC> To jump to the Exit Screen or exit the current screen
3.23.2
Main ScreenMain Screen
3.2
Main Screen
3.23.2
Main ScreenMain Screen
When you enter the BIOS SETUP UTILITY, the Main screen will appear and display
the system overview.
OC Tweaker H/W Monitor Boot Security ExitAdvanced
Main
System Overview
System Time
System Date
BIOS Version
Processor Type
Processor Speed
Microcode Update
L1 Cache Size
L2 Cache Size
L3 Cache Size
Total Memory
DDR3_A1
DDR3_B1
DDR3_A2
DDR3_B2
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2005, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[ :00:09]
17
: 890GX Extreme4 P1.00
: AMD Phenom(tm) II X2 555
Processor (64bit)
: 3200MHz
: 100F43/10000B6
: 256KB
: 2048KB
: 6144KB
: 1024MB with 128MB shared memory
Single-Channel Memory Mode
: 1024MB/667MHz DDR3_1333
: None
: None
: None
[Thu 07/15/2010]
System Time [Hour:Minute:Second]
Use this item to specify the system time.
System Date [Day Month/Date/Year]
Use this item to specify the system date.
4949
49
4949
Use [Enter], [TAB]
or [SHIFT-TAB] to
select a field.
Use [+] or [-] to
configure system Time.
Select Screen
Select Item
+- Change Field
Tab Select Field
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Page 50

3.33.3
OC TOC T
weakweak
3.3
3.33.3
OC T
OC TOC T
weak
weakweak
er Screener Screen
er Screen
er Screener Screen
In the OC Tweaker screen, you can set up overclocking features.
Main
OC Tweaker
EZ Overclocking
Turbo 30 [Press Enter]
Load Optimized CPU OC Setting
Load Optimized mGPU OC Setting
CPU Configuration
Overclock Mode
CPU Frequency (MHZ)
PCIE Frequency (MHz)
Spread Spectrum
Boot Failure Guard
Boot Failure Guard Count
ASRock UCC
CPU Active Core Control
Processor Maximum Frequency
North Bridge Maximum Frequency
Processor Maximum Voltage
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2005, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Advanced H/W Monitor Boot Security Exit
Overclocking may cause
[Press Enter]
[Press Enter]
[Auto]
[200]
[100]
[Auto]
[Enabled]
[3]
[Disabled]
[All Cores]
x10.5 2100 MHZ
x9.0 1800 MHZ
1.2500 V
damage to your CPU and
motherboard.
It should be done at
your own risk and
expense.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Go to Sub Screen
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
EZ Overclocking
Turbo 30
You can use this option to increase your system performance. Configura-
tion options: [Press Enter], [OFF], [System Performance Increases 25%]
and [System Performance Increases 30%].
Load Optimized CPU OC Setting
You can use this option to load the optiomized CPU overclocking setting.
Configuration options: [Press Enter], [Default], [5% (3570MHz)] to [50%
(5100MHz)]. Please note that overclocking may cause damage to your
CPU and motherboard. It should be done at your own risk and expense.
Load Optimized mGPU OC Setting
You can use this option to load the optiomized mGPU overclocking setting.
Configuration options: [Press Enter], [Default], [750MHz] to [1000MHz].
Please note that overclocking may cause damage to your mGPU and
motherboard. It should be done at your own risk and expense.
CPU Configuration
Overclock Mode
Use this to select Overclock Mode. The default value is [Auto]. Configura-
tion options: [Auto] and [Manual].
CPU Frequency (MHz)
Use this option to adjust CPU frequency.
PCIE Frequency (MHz)
Use this option to adjust PCIE frequency.
5050
50
5050
Page 51

Spread Spectrum
This item should always be [Auto] for better system stability.
Boot Failure Guard
Enable or disable the feature of Boot Failure Guard.
Boot Failure Guard Count
Enable or disable the feature of Boot Failure Guard Count.
ASRock UCC
ASRock UCC (Unlock CPU Core) feature simplifies AMD CPU activation. As
long as a simple switch of the BIOS option “ASRock UCC”, you can unlock
the extra CPU core to enjoy an instant performance boost. When UCC
feature is enabled, the dual-core or triple-core CPU will boost to the quad-
core CPU, and some CPU, including quad-core CPU, can also increase L3
cache size up to 6MB, which means you can enjoy the upgrade CPU
performance with a better price. Please be noted that UCC feature is sup-
ported with AM3 CPU only, and in addition, not every AM3 CPU can support
this function because some CPU’s hidden core may be malfunctioned.
CPU Active Core Control
This allows you to adjust CPU Active Core Control feature. The configura-
tion options depend on the CPU core you adopt. The default value is [All
Cores].
Processor Maximum Frequency
It will display Processor Maximum Frequency for reference.
North Bridge Maximum Frequency
It will display North Bridge Maximum Frequency for reference.
Processor Maximum Voltage
It will display Processor Maximum Voltage for reference.
Multiplier/Voltage Change
This item is set to [Auto] by default. If it is set to [Manual], you may adjust the
value of Processor Frequency and Processor Voltage. However, it is
recommended to keep the default value for system stability.
Main
OC Tweaker
Load Optimized CPU OC Setting
Load Optimized mGPU OC Setting
CPU Configuration
Overclock Mode
CPU Frequency (MHZ)
PCIE Frequency (MHz)
Spread Spectrum
Boot Failure Guard
Boot Failure Guard Count
ASRock UCC
CPU Active Core Control
Processor Maximum Frequency
North Bridge Maximum Frequency
Processor Maximum Voltage
Multiplier/Voltage Change
HT Bus Speed
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2005, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Advanced H/W Monitor Boot Security Exit
[Press Enter]
[Press Enter]
[Auto]
[200]
[100]
[Auto]
[Enabled]
[3]
[Disabled]
[All Cores]
x10.5 2100 MHZ
x9.0 1800 MHZ
1.2500 V
[Manual]
[Auto]
If Manual, multiplier
and voltage will be
set based on user
selection. Final
result is depending
on CPU’s capability.
And Cool ‘n’ Quiet
will be disabled.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Go to Sub Screen
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
5151
51
5151
Page 52

CPU Frequency Multiplier
For safety and system stability, it is not recommended to adjust the value of
this item.
CPU Voltage
It allows you to adjust the value of CPU voltage. However, for safety and
system stability, it is not recommended to adjust the value of this item.
NB Frequency Multiplier
For safety and system stability, it is not recommended to adjust the value of
this item.
NB Voltage
It allows you to adjust the value of NB voltage. However, for safety and
system stability, it is not recommended to adjust the value of this item.
HT Bus Speed
This feature allows you selecting Hyper-Transport bus speed. Configura-
tion options: [Auto], [x1 200MHz] to [x10 2000MHz].
HT Bus Width
This feature allows you selecting Hyper-Transport bus width. Configura-
tion options: [Auto], [8 Bit] and [16 Bit].
Memory Configuration
Memory Clock
This item can be set by the code using [Auto]. You can set one of the
standard values as listed: [400MHz DDR3_800], [533MHz DDR3_1066],
[667MHz DDR3_1333] and [800MHz DDR3_1600].
DRAM Voltage
Use this to select DRAM voltage. Configuration options: [Auto], [1.250V] to
[2.065V]. The default value is [Auto].
5252
52
5252
Page 53

Memory Timing
OC Tweaker
Memory Timing
Memory Controller Mode
Power Down Enable
Bank Interleaving
Channel Interleaving
CAS Latency (CL)
TRCD
TRP
TRAS
TRTP
TRRD
TWTR
TWR
TRC
TRWTWB
TRWTTO
TWRRD
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[Unganged]
[Disabled]
[Auto]
[HASH 2]
[Auto]
9
[Auto]
12
[Auto]
12
[Auto]
30
[Auto]
5
[Auto]
4
[Auto]
5
[Auto]
10
[Auto]
33
[Auto]
8
[Auto]
7
[Auto]
2
Select Screen
Select Screen
Select Item
Select Item
+- Change Option
+- Change Option
F1 General Help
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
ESC Exit
Memory Controller Mode
It allows you to adjust the memory controller mode. Configuration options:
[Unganged] and [Ganged]. The default value is [Unganged].
Power Down Enable
Use this item to enable or disable DDR power down mode.
Bank Interleaving
Interleaving allows memory accesses to be spread out over banks on the
same node, or accross nodes, decreasing access contention.
Channel Interleaving
It allows you to enable Channel Memory Interleaving. Configuration options:
[Disabled], [Address bits 6], [Address bits 12], [HASH 1] and [HASH 2]. The
default value is [HASH 2].
CAS Latency (CL)
Use this item to adjust the means of memory accessing. Configuration
options: [Auto], [4CLK] to [12CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TRCD
Use this to adjust TRCD values. Configuration options: [Auto], [5CLK] to
[12CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TRP
Use this to adjust TRP values. Configuration options: [Auto], [5CLK] to
[12CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TRAS
Use this to adjust TRAS values. Configuration options: [Auto], [15CLK] to
[30CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TRTP
Use this to adjust TRTP values. Configuration options: [Auto], [4CLK] to
[7CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
5353
53
5353
Page 54

TRRD
Use this to adjust TRRD values. Configuration options: [Auto], [4CLK] to
[7CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TWTR
Use this to adjust TWTR values. Configuration options: [Auto], [4CLK] to
[7CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TWR
Use this to adjust TWR values. Configuration options: [Auto], [5CLK] to
[12CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TRC
Use this to adjust TRC values. Configuration options: [Auto], [11CLK] to
[42CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TRWTWB
Use this to adjust TRWTWB values. Configuration options: [Auto], [3CLK] to
[18CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TRWTTO
Use this to adjust TRWTTD values. Configuration options: [Auto], [3CLK] to
[17CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TWRRD
Use this to adjust TWRRD values. Configuration options: [Auto], [2CLK] to
[10CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TWRWR
Use this to adjust TWRWR values. Configuration options: [Auto], [2CLK] to
[10CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TRDRD
Use this to adjust TRWTTD values. Configuration options: [Auto], [3CLK] to
[10CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
TRFC0
Use this to adjust TRFC0 values. Configuration options: [Auto], [90ns],
[110ns], [160ns], [300ns] and [350ns]. The default value is [Auto].
TRFC1
Use this to adjust TRFC1 values. Configuration options: [Auto], [90ns],
[110ns], [160ns], [300ns] and [350ns]. The default value is [Auto].
MA Timing
Use this to adjust values for MA timing. Configuration options: [Auto], [2T],
[1T]. The default value is [Auto].
CHA ADDR/CMD Delay
Use this to adjust values for CHA ADDR/CMD Delay feature. Configuration
options: [Auto], [No Delay], [1/64CLK] to [31/64CLK]. The default value is
[Auto].
5454
54
5454
Page 55

CHA ADDR/CMD Setup
Use this to adjust values for CHA ADDR/CMD Setup feature. Configuration
options: [Auto], [1/2CLK] and [1CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
CHA CS/ODT Delay
Use this to adjust values for CHA CS/ODT Delay feature. Configuration
options: [Auto], [No Delay], [1/64CLK] to [31/64CLK]. The default value is
[Auto].
CHA CS/ODT Setup
Use this to adjust values for CHA CS/ODT Setup feature. Configuration
options: [Auto], [1/2CLK] and [1CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
CHB ADDR/CMD Delay
Use this to adjust values for CHB ADDR/CMD Delay feature. Configuration
options: [Auto], [No Delay], [1/64CLK] to [31/64CLK]. The default value is
[Auto].
CHB ADDR/CMD Setup
Use this to adjust values for CHB ADDR/CMD Setup feature. Configuration
options: [Auto], [1/2CLK] and [1CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
CHB CS/ODT Delay
Use this to adjust values for CHB CS/ODT Delay feature. Configuration
options: [Auto], [No Delay], [1/64CLK] to [31/64CLK]. The default value is
[Auto].
CHB CS/ODT Setup
Use this to adjust values for CHB CS/ODT Setup feature. Configuration
options: [Auto], [1/2CLK] and [1CLK]. The default value is [Auto].
CHA CKE Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHA CKE Drive. Configuration options: [Auto],
[1.00x], [1.25x], [1.50x] and [2.00x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHA CS/ODT Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHA CS/ODT Drive. Configuration options:
[Auto], [1.00x], [1.25x], [1.50x] and [2.00x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHA ADDR/CMD Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHA ADDR/CMD Drive. Configuration options:
[Auto], [1.00x], [1.25x], [1.50x] and [2.00x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHA CLK Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHA CLK Drive. Configuration options: [Auto],
[0.75x], [1.00x], [1.25x] and [1.50x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHA DATA Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHA DATA Drive. Configuration options: [Auto],
[0.75x], [1.00x], [1.25x] and [1.50x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHA DQS Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHA DQS Drive. Configuration options: [Auto],
[0.75x], [1.00x], [1.25x] and [1.50x]. The default value is [Auto].
5555
55
5555
Page 56

CHA Processor ODT
Use this to adjust values for CHA Processor ODT. Configuration options:
[Auto], [240 ohms], [120 ohms] and [60 ohms]. The default value is [Auto].
CHB CKE Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHB CKE Drive. Configuration options: [Auto],
[1.00x], [1.25x], [1.50x] and [2.00x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHB CS/ODT Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHB CS/ODT Drive. Configuration options:
[Auto], [1.00x], [1.25x], [1.50x] and [2.00x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHB ADDR/CMD Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHB ADDR/CMD Drive. Configuration options:
[Auto], [1.00x], [1.25x], [1.50x] and [2.00x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHB CLK Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHB CLK Drive. Configuration options: [Auto],
[0.75x], [1.00x], [1.25x] and [1.50x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHB DATA Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHB DATA Drive. Configuration options: [Auto],
[0.75x], [1.00x], [1.25x] and [1.50x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHB DQS Drive
Use this to adjust values for CHB DQS Drive. Configuration options: [Auto],
[0.75x], [1.00x], [1.25x] and [1.50x]. The default value is [Auto].
CHB Processor ODT
Use this to adjust values for CHB Processor ODT. Configuration options:
[Auto], [240 ohms], [120 ohms] and [60 ohms]. The default value is [Auto].
5656
56
5656
Page 57

Chipset Settings
SidePort Clock Speed
This allows you to select sideport clock speed. The default value is [Auto].
Configuration options: [Auto], [533MHz] to [1700MHz].
Onboard GPU Clock Override
This allows you to enable or disable the Onboard GPU Clock Override
feature.
Onboard GPU Clock
This option only appears when you enable “Onboard GPU Clock
Override”. The default value is [700].
HT Voltage
Use this to select Hyper-Transport voltage. Configuration options: [Auto],
[1.106V] to [1.820V]. The default value is [Auto].
NB Voltage
Use this to select NB voltage. Configuration options: [Auto], [1.108V] to
[1.794V]. The default value is [Auto].
SB Voltage
Use this to select SB voltage. Configuration options: [Auto], [1.10V] to
[1.40V]. The default value is [Auto].
SidePort Voltage
Use this to select SidePort voltage. Configuration options: [Auto], [1.50V]
and [1.80V]. The default value is [Auto].
CPU VDDA Voltage
Use this to select CPU VDDA voltage. Configuration options: [Auto], [2.56V]
and [2.70V]. The default value is [Auto].
PCIE VDDA Voltage
Use this to select PCIE VDDA voltage. Configuration options: [Auto], [1.81V]
and [1.92V]. The default value is [Auto].
Would you like to save current setting user defaults?
In this option, you are allowed to load and save three user defaults
according to your own requirements.
5757
57
5757
Page 58

3.43.4
Advanced ScreenAdvanced Screen
3.4
Advanced Screen
3.43.4
Advanced ScreenAdvanced Screen
In this section, you may set the configurations for the following items: CPU
Configuration, Chipset Configuration, ACPI Configuration, Storage Configuration, PCIPnP
Configuration, SuperIO Configuration, and USB Configuration.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Main OC Tweaker
Advanced Settings
WARNING: Setting wrong values in below sections
BIOS Update Utility
ASRock Instant Flash
may cause system to malfunction.
CPU Configuration
Chipset Configuration
ACPI Configuration
Storage Configuration
PCIPnP Configuration
SuperIO Configuration
USB Configuration
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2005, American Megatrends, Inc.
H/W Monitor Boot Security Exit
Advanced
Options for CPU
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Go to Sub Screen
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Setting wrong values in this section may cause
the system to malfunction.
ASRock Instant Flash
ASRock Instant Flash is a BIOS flash utility embedded in Flash ROM. This
convenient BIOS update tool allows you to update system BIOS without
entering operating systems first like MS-DOS or Windows®. Just launch
this tool and save the new BIOS file to your USB flash drive, floppy disk or
hard drive, then you can update your BIOS only in a few clicks without
preparing an additional floppy diskette or other complicated flash utility.
Please be noted that the USB flash drive or hard drive must use FAT32/16/
12 file system. If you execute ASRock Instant Flash utility, the utility will
show the BIOS files and their respective information. Select the proper
BIOS file to update your BIOS, and reboot your system after BIOS update
process completes.
5858
58
5858
Page 59

3.4.13.4.1
CPU ConfigurationCPU Configuration
3.4.1
CPU Configuration
3.4.13.4.1
CPU ConfigurationCPU Configuration
Advanced
CPU Configuration
Cool ‘n’ Quiet
Secure Virtual Machine
Enhanced Halt State
L3 Cache Allocation
CPU Thermal Throttle
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[Auto]
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
[Auto]
[Auto]
Enabling this function
may reduce CPU voltage
andmemoryfreq.,and
lead to system
stability or
compatibility issue
with some memory
modules or power
supplies. Please set
this item to [Disabled]
if above issue occurs.
Select Screen
Select Screen
Select Item
Select Item
+- Change Option
+- Change Option
F1 General Help
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
ESC Exit
Cool ‘n’ Quiet
Use this item to enable or disable AMD’s Cool ‘n’ QuietTM technology. The
default value is [Enabled]. Configuration options: [Auto], [Enabled] and
[Disabled]. If you install Windows® 7 / VistaTM and want to enable this
function, please set this item to [Enabled]. Please note that enabling this
function may reduce CPU voltage and memory frequency, and lead to
system stability or compatibility issue with some memory modules or power
supplies. Please set this item to [Disable] if above issue occurs.
Secure Virtual Machine
When this option is set to [Enabled], a VMM (Virtual Machine Architecture)
can utilize the additional hardware capabilities provided by AMD-V. The
default value is [Enabled]. Configuration options: [Enabled] and [Disabled].
Enhance Halt State
All processors support the Halt State (C1). The C1 state is supported
through the native processor instructions HLT and MWAIT and requires no
hardware support from the chipset. In the C1 power state, the processor
maintains the context of the system caches.
L3 Cache Allocation
The default value is [Auto]. Configuration options: [Auto], [BSP Only] and
[All Cores].
CPU Thermal Throttle
Use this item to enable CPU internal thermal control mechanism to keep the
CPU from overheated. Configuration options: [Disabled], [Auto], [12.5%],
[25%], [37.5%], [50%], [62.5%], [75%] and [87.5%]. The default value is
[Auto].
5959
59
5959
Page 60

3.4.23.4.2
3.4.2
3.4.23.4.2
Chipset ConfigurationChipset Configuration
Chipset Configuration
Chipset ConfigurationChipset Configuration
Advanced
Chipset Settings
Onboard 80 Port LED
Onboard HD Audio
Front Panel
Onboard Lan
Energy Efficient Ethernet
Dr. LAN
Link speed : 10Mbps
Onboard IEEE 1394
Primary Graphics Adapter
Internal Graphics Mode
Share Memory
Onboard HDMI HD Audio
Surround View
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[Auto]
[Auto]
[Auto]
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
[Enabled]
[PCI]
[UMA+SIDEPORT]
[Auto]
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
Options
Disabled
Enabled
Select Screen
Select Item
+ - Change Option
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Onboard 80 Port LED
This allows you to enable or disable the onboard 80 port LED.
Onboard HD Audio
Select [Auto], [Enabled] or [Disabled] for the onboard HD Audio feature. If
you select [Auto], the onboard HD Audio will be disabled when PCI Sound
Card is plugged.
Front Panel
Select [Auto] or [Disabled] for the onboard HD Audio Front Panel.
Onboard Lan
This allows you to enable or disable the onboard Lan feature.
Energy Efficient Ethernet
This allows you to enable or disable Energy Efficient Ethernet. The default
value is [Disabled].
Dr. LAN
This allows you to select “LAN Cable Detection” function.
Onboard IEEE 1394
This allows you to enable or disable the “Onboard IEEE 1394” feature.
Primary Graphics Adapter
This item will switch the PCI Bus scanning order while searching for video
card. It allows you to select the type of Primary VGA in case of multiple
video controllers. The default value of this feature is [PCI]. Configuration
options: [Onboard], [PCI] and [PCI Express].
Internal Graphics Mode
This allows you to adjust internal graphics mode. The default value is
[UMA+SIDEPORT]. Configuration options: [UMA], [SIDEPORT] and
[UMA+SIDEPORT].
6060
60
6060
Page 61

Share Memory
This allows you to set share memory feature. The default value is [Auto].
Configuration options: [Auto], [32MB], [64MB], [128MB], [256MB] and
[512MB].
Onboard HDMI HD Audio
This allows you to enable or disable the onboard HDMI HD Audio in AMD
890GX. If you use Dual-link DVI monitor, please set this item to [Disabled].
Surround View
This allows you to enable or disable the Surround View feature or Hybrid
CrossFireXTM feature.
6161
61
6161
Page 62

3.4.33.4.3
3.4.3
3.4.33.4.3
ACPI ConfigurationACPI Configuration
ACPI Configuration
ACPI ConfigurationACPI Configuration
Advanced
ACPI Settings
Suspend To RAM
Check Ready Bit
Away Mode Support
Restore on AC / Power Loss
Ring-In Power On
PCI Devices Power On
PS /2 Keyboard Power On
RTC Alarm Power On
ACPI HPET Table
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[Auto]
[Auto]
[Disabled]
[Power Off]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
Select auto-detect or
disable the STR
feature.
Select Screen
Select Item
+- Change Option
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Suspend to RAM
Use this item to select whether to auto-detect or disable the Suspend-to-
RAM feature. Select [Auto] will enable this feature if the OS supports it.
Check Ready Bit
Use this item to enable or disable the feature Check Ready Bit.
Away Mode Support
Use this item to enable or disable Away Mode support under Windows® XP
Media Center OS. The default value is [Disabled].
Restore on AC/Power Loss
This allows you to set the power state after an unexpected AC/power
loss. If [Power Off] is selected, the AC/power remains off when the
power recovers. If [Power On] is selected, the AC/power resumes
and the system starts to boot up when the power recovers.
Ring-In Power On
Use this item to enable or disable Ring-In signals to turn on the system from
the power-soft-off mode.
PCI Devices Power On
Use this item to enable or disable PCI devices to turn on the system from the
power-soft-off mode.
PS/2 Keyboard Power On
Use this item to enable or disable PS/2 keyboard to turn on the system from
the power-soft-off mode.
RTC Alarm Power On
Use this item to enable or disable RTC (Real Time Clock) to power on the
system.
ACPI HPET Table
Use this item to enable or disable ACPI HPET Table. The default value is
[Disabled]. Please set this option to [Enabled] if you plan to use this
motherboard to submit Windows® VistaTM certification.
6262
62
6262
Page 63

3.4.43.4.4
Storage ConfigurationStorage Configuration
3.4.4
Storage Configuration
3.4.43.4.4
Storage ConfigurationStorage Configuration
Advanced
Storage Configuration
Onboard SATA Controller
SATA Operation Mode
SATA IDE Combined Mode
SATA3_6 Mode
SATA3_1
SATA3_2
SATA3_3
SATA3_4
SATA3_5
SATA3_6
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[Enabled]
[IDE]
[Enabled]
[Gen2]
[Hard Disk]
[Not Detected]
[Not Detected]
[Not Detected]
[Not Detected]
[Not Detected]
Configure onboard
serial ATA
controller.
Select Screen
Select Screen
Select Item
Select Item
+- Change Option
+- Change Option
F1 General Help
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
ESC Exit
Onboard SATA Controller
Use this item to enable or disable the “Onboard SATA Controller” feature.
SATA Operation Mode
Use this item to adjust SATA Operation Mode. The default value of this
option is [IDE]. Configuration options: [AHCI], [RAID] and [IDE].
If you set this item to RAID mode, it is suggested to install
SATA ODD driver on SATA5 port.
AMD AHCI BIOS ROM
Use this item to enable or disable AMD AHCI BIOS ROM. This option appears
only when you set “SATA Operation Mode” to [AHCI]. The default value is
[Disabled].
SATA IDE Combined Mode
This item is for SATA5 and SATA6/eSATA ports only. Use this item to enable
or disable SATA IDE combined mode. The default value is [Enabled].
If you want to build RAID on SATA5 and SATA6/eSATA ports,
please disable this item.
SATA3_6 Mode
Use this item to select SATA6 mode. Configuration mode: [Auto] and [Gen2].
The default value is [Gen2]. If SATA6 port is used internally, not eSATA,
please set [Auto] for SATA3 support.
6363
63
6363
Page 64

Advanced
SATA3_1 Master
:Hard Disk
Device
:MAXTOR 6L080J4
Vendor
:80.0 GB
Size
:Supported
LBA Mode
:16Sectors
Block Mode
:4
PIO Mode
:MultiWord DMA-2
Async DMA
:Ultra DMA-6
Ultra DMA
:Supported
S.M.A.R.T.
Type
LBA/Large Mode
Block (Multi-Sector Transfer)
PIO Mode
DMA Mode
S.M.A.R.T.
32Bit Data Transfer
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[Auto]
[Auto]
[Auto]
[Auto]
[Auto]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
Select the type
of device connected
to the system.
Select Screen
Select Item
+- Change Option
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
TYPE
Use this item to configure the type of the IDE device that you specify.
Configuration options: [Not Installed], [Auto], [CD/DVD], and [ARMD].
[Not Installed]: Select [Not Installed] to disable the use of IDE device.
[Auto]: Select [Auto] to automatically detect the hard disk drive.
After selecting the hard disk information into BIOS, use a disk
utility, such as FDISK, to partition and format the new IDE hard
disk drives. This is necessary so that you can write or read data
from the hard disk. Make sure to set the partition of the Primary
IDE hard disk drives to active.
[CD/DVD]:This is used for IDE CD/DVD drives.
[ARMD]: This is used for IDE ARMD (ATAPI Removable Media Device),
such as MO.
LBA/Large Mode
Use this item to select the LBA/Large mode for a hard disk > 512 MB under
DOS and Windows; for Netware and UNIX user, select [Disabled] to
disable the LBA/Large mode.
Block (Multi-Sector Transfer)
The default value of this item is [Auto]. If this feature is enabled, it will
enhance hard disk performance by reading or writing more data during
each transfer.
PIO Mode
Use this item to set the PIO mode to enhance hard disk performance by
optimizing the hard disk timing.
DMA Mode
DMA capability allows the improved transfer-speed and data-integrity for
compatible IDE devices.
6464
64
6464
Page 65

S.M.A.R.T.
Use this item to enable or disable the S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis,
and Reporting Technology) feature. Configuration options: [Disabled], [Auto],
[Enabled].
32Bit Data Transfer
Use this item to enable 32-bit access to maximize the IDE hard disk data
transfer rate.
3.4.53.4.5
PCIPnP ConfigurationPCIPnP Configuration
3.4.5
PCIPnP Configuration
3.4.53.4.5
PCIPnP ConfigurationPCIPnP Configuration
Advanced
Advanced PCI / PnP Settings
PCI Latency Timer
PCI IDE BusMaster
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[32]
[Enabled]
Value in units of PCI
clocks for PCI device
latency timer
register.
Select Screen
Select Item
+- Change Option
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Setting wrong values in this section may cause
the system to malfunction.
PCI Latency Timer
The default value is 32. It is recommended to keep the default value unless
the installed PCI expansion cards’ specifications require other settings.
PCI IDE BusMaster
Use this item to enable or disable the PCI IDE BusMaster feature.
6565
65
6565
Page 66

3.4.63.4.6
Super IO ConfigurationSuper IO Configuration
3.4.6
Super IO Configuration
3.4.63.4.6
Super IO ConfigurationSuper IO Configuration
Advanced
Configure Super IO Chipset
Serial Port Address
Infrared Port Address
PS/2 Port Type
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[3F8 /IRQ4]
[Disabled]
[Auto]
Allow BIOS to Select
SerialPortBase
Addresses.
Select Screen
Select Item
+- Change Option
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Serial Port Address
Use this item to set the address for the onboard serial port or disable it.
Configuration options: [Disabled], [3F8 / IRQ4], [2F8 / IRQ3], [3E8 / IRQ4],
[2E8 / IRQ3].
Infrared Port Address
Use this item to set the address for the onboard infrared port or disable it.
Configuration options: [Disabled], [3F8 / IRQ4], [2F8 / IRQ3], [3E8 / IRQ4] and
[2E8 / IRQ3].
PS/2 Port Type
Use this item to set the PS/2 port type.
6666
66
6666
Page 67

3.4.73.4.7
USB ConfigurationUSB Configuration
3.4.7
USB Configuration
3.4.73.4.7
USB ConfigurationUSB Configuration
Advanced
USB Configuration
USB Controller
Legacy USB Support
USB 3.0 Controller
USB Keyboard/Remote Power On
USB Mouse Power On
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
[Disabled]
To enable or disable
the onboard USB
controllers.
Select Screen
Select Item
+- Change Option
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
USB Controller
Use this item to enable or disable the use of USB controller.
Legacy USB Support
Use this option to select legacy support for USB devices. There are four
configuration options: [Enabled], [Auto], [Disabled] and [BIOS Setup
Only]. The default value is [Enabled]. Please refer to below descriptions
for the details of these four options:
[Enabled] - Enables support for legacy USB.
[Auto] - Enables legacy support if USB devices are connected.
[Disabled] - USB devices are not allowed to use under legacy OS and
BIOS setup when [Disabled] is selected. If you have USB compatibility
issue, it is recommended to select [Disabled] to enter OS.
[BIOS Setup Only] - USB devices are allowed to use only under BIOS
setup and Windows / Linux OS.
USB 3.0 Controller
Use this item to enable or disable the use of USB 3.0 controller.
USB Keyboard/Remote Power On
Use this item to enable or disable USB Keyboard/Remote Power On on the
system.
USB Mouse Power On
Use this item to enable or disable USB Mouse Power On on the system.
6767
67
6767
Page 68

3.53.5
Hardware Health Event Monitoring ScreenHardware Health Event Monitoring Screen
3.5
Hardware Health Event Monitoring Screen
3.53.5
Hardware Health Event Monitoring ScreenHardware Health Event Monitoring Screen
In this section, it allows you to monitor the status of the hardware on your system,
including the parameters of the CPU temperature, motherboard temperature, CPU fan
speed, chassis fan speed, and the critical voltage.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Main OC Tweaker Advanced
Hardware Health Event Monitoring
CPU Temperature
M /B Temperature
CPU Fan 1 Speed
CPU Fan 2 Speed
ChassisFan1Speed
ChassisFan2Speed
ChassisFan3Speed
Power Fan Speed
Vcore
+ 3.30V
+ 5.00V
+ 12.00V
CPU Fan Setting
Chassis Fan Setting
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
H/W Monitor
: 37C/98F
: 27C/80F
: 4722 RPM
: 4722 RPM
:N/A
:N/A
:N/A
:N/A
: 1.216V
: 3.248V
: 5.136V
: 12.091V
Boot Security Exit
Enable/Disable
CPU Quiet Fan
Function.
Select Screen
Select Item
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
CPU Fan 1 & 2 Setting
This allows you to set the CPU fan 1 & 2 speed. Configuration options: [Full
On] and [Automatic mode]. The default is value [Full On].
Chassis Fan 1 Setting
This allows you to set the chassis fan 1 speed. Configuration options:
[Full On], [Automatic mode] and [Manual Mode]. The default is value [Full
On].
Chassis Fan 2 Setting
This allows you to set the chassis fan 2 speed. Configuration options:
[Full On] and [Manual Mode]. The default is value [Full On].
Chassis Fan 3 Setting
This allows you to set the chassis fan 3 speed. Configuration options:
[Full On] and [Manual Mode]. The default is value [Full On].
6868
68
6868
Page 69

3.63.6
Boot ScreenBoot Screen
3.6
Boot Screen
3.63.6
Boot ScreenBoot Screen
In this section, it will display the available devices on your system for you to config-
ure the boot settings and the boot priority.
Main OC Tweaker Advanced H/W Monitor
Boot Settings
Boot Settings Configuration
1st Boot Device
2nd Boot Device
3rd Boot Device
4th Boot Device
Hard Disk Drives
Removable Drives
CD/DVD Drives
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2005, American Megatrends, Inc.
3.6.13.6.1
3.6.1
3.6.13.6.1
Boot Settings ConfigurationBoot Settings Configuration
Boot Settings Configuration
Boot Settings ConfigurationBoot Settings Configuration
Boot Settings Configuration
Full Screen Logo
AddOn ROM Display
Boot From Onboard LAN
Bootup Num-Lock
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[1st Floppy Device]
[HDD: PM -HDS722580VL]
[CD/DVD: 3S-CD-ROM C]
[USB]
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
[Enabled]
[Enabled]
[Disabled]
[On]
Boot
Security Exit
Configure Settings
during System Boot.
Enter Go to Sub Screen
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Boot
Disabled: Displays
normal POST messages.
Enabled: Displays OEM
Logo instead of POST
messages.
+ - Change Option
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
Select Screen
Select Item
Select Screen
Select Item
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2003, American Megatrends, Inc.
Full Screen Logo
Use this item to enable or disable OEM Logo. The default value is [Enabled].
AddOn ROM Display
Use this option to adjust AddOn ROM Display. If you enable the option
“Full Screen Logo” but you want to see the AddOn ROM information when
the system boots, please select [Enabled]. Configuration options: [Enabled]
and [Disabled]. The default value is [Enabled].
6969
69
6969
Page 70

Boot From Onboard LAN
Use this item to enable or disable the Boot From Onboard LAN feature.
Boot Up Num-Lock
If this item is set to [On], it will automatically activate the Numeric Lock
function after boot-up.
3.73.7
Security ScreenSecurity Screen
3.7
Security Screen
3.73.7
Security ScreenSecurity Screen
In this section, you may set or change the supervisor/user password for the system.
For the user password, you may also clear it.
Main OC Tweaker Advanced H/W Monitor Boot
Security Settings
Supervisor Password : Not Installed
User Password : Not Installed
Change Supervisor Password
Change User Password
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2005, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Security
Exit
Install or Change the
password.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Change
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
7070
70
7070
Page 71

3.83.8
Exit ScreenExit Screen
3.8
Exit Screen
3.83.8
Exit ScreenExit Screen
Main OC Tweaker Advanced H/W Monitor Boot Security
Exit Options
Save Changes and Exit
Discard Changes and Exit
Discard Changes
Load BIOS Defaults
Load Performance Setup Default
Load Power Saving Setup Default
v02.54 (C)Copyright 1985-2005, American Megatrends, Inc.
BIOS SETUP UTILITY
Save Changes and Exit
When you select this option, it will pop-out the following message, “Save
configuration changes and exit setup?” Select [OK] to save the changes
and exit the BIOS SETUP UTILITY.
Discard Changes and Exit
When you select this option, it will pop-out the following message, “Dis-
card changes and exit setup?” Select [OK] to exit the BIOS SETUP UTILITY
without saving any changes.
Discard Changes
When you select this option, it will pop-out the following message, “Dis-
card changes?” Select [OK] to discard all changes.
Load BIOS Defaults
Load BIOS default values for all the setup questions. F9 key can be used
for this operation.
Load Performance Setup Default
This performance setup default may not be compatible with all system
configurations. If system boot failure occurs after loading, please resume
optimal default settings. F5 key can be used for this operation.
Load Power Saving Setup Default
Load power saving setup default. F6 key can be used for this operation.
Exit
Exit system setup
after saving the
changes.
F10 key can be used
for this operation.
Select Screen
Select Item
Enter Go to Sub Screen
F1 General Help
F9 Load Defaults
F10 Save and Exit
ESC Exit
7171
71
7171
Page 72

4.4.
SofSof
4.
4.4.
4.1 Install Operating System4.1 Install Operating System
4.1 Install Operating System
4.1 Install Operating System4.1 Install Operating System
This motherboard supports various Microsoft® Windows® operating systems: 7 / 7
64-bit / VistaTM / VistaTM 64-bit / XP / XP 64-bit. Because motherboard settings and
hardware options vary, use the setup procedures in this chapter for general refer-
ence only. Refer to your OS documentation for more information.
4.2 Support CD Information4.2 Support CD Information
4.2 Support CD Information
4.2 Support CD Information4.2 Support CD Information
The Support CD that came with the motherboard contains necessary drivers and
useful utilities that enhance the motherboard features.
4.2.1 Running The Support CD4.2.1 Running The Support CD
4.2.1 Running The Support CD
4.2.1 Running The Support CD4.2.1 Running The Support CD
To begin using the support CD, insert the CD into your CD-ROM drive. The CD
automatically displays the Main Menu if “AUTORUN” is enabled in your computer.
If the Main Menu did not appear automatically, locate and double click on the file
“ASSETUP.EXE” from the BIN folder in the Support CD to display the menus.
4.2.2 Drivers Menu4.2.2 Drivers Menu
4.2.2 Drivers Menu
4.2.2 Drivers Menu4.2.2 Drivers Menu
The Drivers Menu shows the available devices drivers if the system detects the
installed devices. Please install the necessary drivers to activate the devices.
4.2.3 Utilities Menu4.2.3 Utilities Menu
4.2.3 Utilities Menu
4.2.3 Utilities Menu4.2.3 Utilities Menu
The Utilities Menu shows the applications software that the motherboard supports.
Click on a specific item then follow the installation wizard to install it.
tware Supportware Suppor
Sof
tware Suppor
SofSof
tware Supportware Suppor
tt
t
tt
4.2.44.2.4
4.2.4
4.2.44.2.4
If you need to contact ASRock or want to know more about ASRock, welcome
to visit ASRock’s website at http://www.asrock.com; or you may contact your
dealer for further information.
Contact InformationContact Information
Contact Information
Contact InformationContact Information
7272
72
7272
 Loading...
Loading...