Page 1

Pages ’08
User’s Guide
Page 2

K
Apple Inc.
© 2008 Apple Inc. All rights reserved.
Under the copyright laws, this manual may not be
copied, in whole or in part, without the written consent
of Apple. Your rights to the software are governed by
the accompanying software license agreement.
The Apple logo is a trademark of Apple Inc., registered
in the U.S. and other countries. Use of the “keyboard”
Apple logo (Option-Shift-K) for commercial purposes
without the prior written consent of Apple may
constitute trademark infringement and unfair
competition in violation of federal and state laws.
Every effort has been made to ensure that the
information in this manual is accurate. Apple is not
responsible for printing or clerical errors.
Apple
1 Infinite Loop
Cupertino, CA 95014-2084
408-996-1010
www.apple.com
Apple, the Apple logo, AppleWorks, ColorSync, iMovie,
iPhoto, iTunes, Mac, Mac OS, Numbers, Pages, Quartz,
and QuickTime are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered
in the U.S. and other countries.
Finder, iWeb, iWork, Safari, and Spotlight are trademarks
of Apple Inc.
AppleCare is a service mark of Apple Inc., registered in
the U.S. and other countries.
Adobe and Acrobat are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the U.S.
and/or other countries.
Other company and product names mentioned herein
are trademarks of their respective companies. Mention
of third-party products is for informational purposes
only and constitutes neither an endorsement nor a
recommendation. Apple assumes no responsibility with
regard to the performance or use of these products.
019-1278 06/2008
Page 3

Contents
1
Preface 14 Welcome to the
Pages User’s Guide
Chapter 1 16 Pages Tools and Techniques
16
Pages Templates
18
Document Viewing Aids
18
19
19
21
22
23
23
24
25
25
25
26
27
28
28
29
Zoom Levels
Document Page Views
Layout View
Formatting Characters (Invisibles)
The Toolbar
The Format Bar
The Inspector Window
The Media Browser
The Font Panel
The Colors Window
Rulers and Alignment Guides
The Styles Drawer
Scroll Bars, Scroll Arrows, and Thumbnails
The Warnings Window
Research and Reference Tools
Keyboard Shortcuts and Shortcut Menus
Chapter 2 30 Working with a Pages Document
30
Working with Word Processing and Page Layout Templates
30
31
31
31
33
33
34
34
Word Processing Templates
Page Layout Templates
Creating, Opening, and Importing a Pages Document
Creating a New Document
Importing a Document
Opening an Existing Pages Document
Saving Your Document
Saving a Document
3
Page 4

35
35
35
36
36
36
37
37
38
38
Undoing Changes
Saving a Document as a Template
Saving a Copy of a Document
Automatically Saving a Backup Version of a Document
Closing a Document Without Quitting Pages
Storing Information About a Document
Designing Documents
Document Layout and Style
Appearance of Text
Graphics and Other Objects
Chapter 3 39 Working with Document Parts
41
Setting Page Orientation and Size
42
Setting Document Margins
42
Using Page and Line Breaks
42
43
43
43
44
44
44
44
45
46
47
47
47
48
48
49
49
49
49
50
50
51
51
51
51
52
Inserting a Page Break
Starting Paragraphs on a New Page
Keeping Paragraphs Together on a Page
Keeping an Entire Paragraph on the Same Page
Inserting a Manual Line Break
Preventing Widow and Orphan Lines
Using Layouts
Defining Columns
Defining Column Breaks
Defining Layout Breaks
Defining Layout Margins
Using Left- and Right-Facing Pages
Defining Margins for Facing Pages
Defining Headers and Footers for Facing Pages
Viewing Facing Pages
Using Headers and Footers
Using Footnotes and Endnotes
Adding and Editing Footnotes and Endnotes
Adding a Footnote
Adding an Endnote at the End of a Document
Adding an Endnote at the End of a Section
Deleting Footnotes and Endnotes
Converting Footnotes to Endnotes and Vice Versa
Formatting Footnotes and Endnotes
Jumping Between a Mark and Its Related Footnote or Endnote
Numbering Footnotes and Endnotes
4
Contents
Page 5

52
52
53
53
53
54
54
54
55
55
55
56
56
56
56
56
57
58
58
59
Defining Marks for Numbering Footnotes and Endnotes
Changing Marks for Numbering Footnotes and Endnotes
Restarting Footnote and Section Endnote Numbering
Using Sections
Creating Sections
Managing Sections with the Thumbnail View
Viewing Thumbnails
Adding and Deleting Sections
Reorganizing Sections
Defining Section Attributes
Changing Headers and Footers in a Section
Restarting Page Numbering in a Section
Setting Up a Unique Format for a Section’s First Page
Formatting Facing Pages in a Section
Setting Section Margins
Reusing Sections
Using Master Objects (Repeated Background Images)
Using a Table of Contents
Creating and Updating a Table of Contents
Styling a Table of Contents
Chapter 4 61 Reviewing and Revising Documents
62
Using Change Tracking
63
65
66
67
68
68
A Tour of Change Tracking
Starting, Pausing, and Stopping Change Tracking
Controlling Change Tracking Information
Accepting and Rejecting Edits
Saving with Change Tracking Off
Using Comments
Chapter 5 70 Working with Text
70
Adding Text
70
71
71
72
72
72
73
74
74
75
Using Placeholder Text
Placeholders in Main Text Areas
Placeholders in Text Boxes
Placeholders in Tables
Placeholders in Columns
Adding New Template Pages
Deleting Pages
Deleting, Copying, and Pasting Text
Selecting Text
Formatting Text Size and Appearance
Contents
5
Page 6

75
75
75
76
76
76
77
77
77
Using the Format Bar to Format Text
Using the Format Menu to Format Text
Making Text Bold or Italic Using the Menus
Creating Outlined Text Using the Menus
Underlining Text Using the Menus
Changing Text Size Using the Menus
Making Text Subscript or Superscript Using the Menus
Changing Text Capitalization Using the Menus
Using the Font Panel to Format Text
79 Making the Font Panel Easy to Use
79 Changing Fonts Using the Font Panel
79 Changing Underlining Using the Font Panel
80 Adding a Strikethrough to Text Using the Font Panel
80 Changing Text Color Using the Font Panel
80 Changing the Paragraph Background Color Using the Font Panel
81 Creating Shadows on Text Using the Font Panel
81 Adding Accents and Special Characters
81 Adding Accent Marks
82 Viewing Keyboard Layouts for Other Languages
82 Typing Special Characters and Symbols
83 Using Smart Quotes
83 Using Advanced Typography Features
84 Adjusting Font Smoothing
84 Setting Text Alignment, Spacing, and Color
85 Aligning Text Horizontally
86 Aligning Text Vertically
87 Adjusting the Spacing Between Lines of Text
88 Adjusting the Spacing Before or After a Paragraph
88 Adjusting the Spacing Between Characters
89 Changing Text Color
89 Setting Tab Stops to Align Text
90 Setting Tab Stops Using the Horizontal Ruler
90 Setting a New Tab Stop Using the Horizontal Ruler
91 Changing a Tab Stop Using the Horizontal Ruler
91 Deleting a Tab Stop Using the Horizontal Ruler
91 Setting Tab Stops Using the Text Inspector
92 Setting the Default Distance Between Tabs
92 Setting a New Tab Stop Using the Text Inspector
93 Changing a Tab Stop Using the Text Inspector
93 Deleting a Tab Stop Using the Text Inspector
6
Contents
Page 7

94 Setting Indents
94 Setting Indents for Paragraphs Using the Text Inspector
94 Setting Indents for Paragraphs Using the Horizontal Ruler
95 Changing the Inset Margin of Text in Objects
95 Setting Indents for Lists
95 Using Bulleted, Numbered, and Ordered Lists (Outlines)
95 Generating Lists Automatically
96 Using Bulleted Lists
98 Using Numbered Lists
99 Using Ordered Lists (Outlines)
10 0 Using Text Boxes, Shapes, and Other Effects to Highlight Text
10 0 Adding Text Boxes
10 0 Adding a Floating Text Box
101 Adding an Inline Text Box
10 2 Linking Floating Text Boxes
10 4 Setting Character and Paragraph Fill Colors
10 4 Adding Borders and Rules
10 5 Presenting Text in Columns
10 6 Putting Text Inside a Shape
10 6 Formatting a Text Box or Shape
10 7 Using Hyperlinks and Bookmarks
10 7 Linking to a Webpage
10 8 Linking to a Preaddressed Email Message
10 9 Linking to Pages in a Document
11 0 Editing Hyperlink Text
11 0 Wrapping Text Around an Object
11 0 Wrapping Text Around a Floating Object
111 Wrapping Text Around an Inline Object
111 Adjusting Text Around an Inline or Floating Object
112 Inserting Page Numbers and Other Changeable Values
113 Using Automatic Hyphenation
113 Automatically Substituting Text
11 4 Inserting a Nonbreaking Space
11 4 Checking for Spelling and Proofreading Documents
11 4 Finding Misspelled Words
11 4 Working with Spelling Suggestions
11 5 Proofreading Documents
11 6 Finding and Replacing Text
117 Searching for All Occurrences of Words and Phrases
Contents 7
Page 8

Chapter 6 118 Working with Styles
11 9 About Styles
12 0 Applying Styles
121 Importing Styles From Another Document
12 2 Changing the Style of Text
12 2 Finding and Replacing a Style
12 3 Copying and Pasting Character and Paragraph Styles
12 3 Modifying and Creating New Paragraph Styles
12 3 Modifying Paragraph Styles
12 6 Creating New Paragraph Styles
12 7 Modifying and Creating New Character Styles
12 7 Modifying Character Styles
12 8 Creating New Character Styles
12 9 Modifying and Creating New List Styles
12 9 Modifying Bulleted or Numbered List Styles
13 2 Modifying a Tiered List Style for Ordered Lists
13 3 Creating New List Styles
13 3 Renaming a Style
13 3 Deleting a Style
Chapter 7 134 Working with Shapes, Graphics, and Other Objects
13 4 Using Floating and Inline Objects
13 5 Selecting Objects
13 6 Copying or Duplicating Objects
13 6 Deleting Objects
13 7 Moving Objects
13 7 Moving an Object Forward or Backward
13 8 Moving an Object to the Background
13 8 Aligning Objects
13 9 Spacing Objects Evenly on a Page
13 9 Using Alignment Guides
13 9 Changing How Alignment Guides Appear
14 0 Creating New Alignment Guides
14 0 Setting Precise Positions of Floating Objects
141 Modifying Objects
141 Resizing Objects
14 2 Flipping and Rotating Objects
14 2 Changing the Style of Borders
14 3 Framing Objects
14 4 Adding Shadows
14 5 Adding a Reflection
8 Contents
Page 9

14 6 Adjusting Opacity
14 7 Grouping and Locking Objects
14 7 Grouping and Ungrouping Objects
14 7 Locking and Unlocking Objects
14 7 Filling Objects
14 7 Filling an Object with Color
14 8 Using the Colors Window
14 9 Filling an Object with an Image
151 Using Shapes
151 Adding a Predrawn Shape
151 Adding a Custom Shape
15 2 Making Shapes Editable
15 3 Manipulating Points of a Shape
15 4 Reshaping a Curve
15 4 Reshaping a Straight Segment
15 5 Transforming Corner Points into Curved Points and Vice Versa
15 5 Editing Specific Predrawn Shapes
15 5 Editing a Rounded Rectangle
15 5 Editing Single and Double Arrows
15 6 Editing a Star
15 6 Editing a Polygon
157 Using Media Placeholders
15 8 Working with Images
15 8 Adding Images
15 8 Importing an Image as a Floating Object
15 8 Importing an Image as an Inline Object
15 9 Masking (Cropping) Images
15 9 Cropping an Image Using the Default (Rectangular) Mask
160 Masking an Image with a Shape
161 Unmasking an Image
161 Removing the Background or Unwanted Elements from an Image
162 Changing an Image’s Brightness, Contrast, and Other Settings
163 Using PDF Files as Graphics
164 Using Sound and Movies
164 Adding a Sound File
165 Adding a Movie File
165 Adjusting Media Playback Settings
Chapter 8 167 Using Tables
167 About Tables
168 Working with Tables
168 Adding a Table
Contents 9
Page 10

168 Using Table Tools
17 0 Resizing a Table
171 Moving Tables
171 Copying Tables Among iWork Applications
17 2 Converting Text to a Table
17 2 Selecting Tables and Their Components
17 2 Selecting a Table
17 2 Selecting a Table Cell
17 3 Selecting a Group of Table Cells
174 Selecting a Row or Column
174 Selecting Table Cell Borders
17 5 Working with Content in Table Cells
17 5 Adding and Editing Cell Values
17 5 Working with Text in Cells
17 6 Working with Numbers in Cells
17 7 Working with Dates in Cells
17 7 Displaying Content Too Large for Its Cell
17 8 Formatting Cell Values
17 8 Using the Number Format
17 9 Using the Currency Format
17 9 Using the Percentage Format
18 0 Using the Date and Time Format
18 0 Using the Fraction Format
18 0 Using the Scientific Format
18 0 Using the Text Format
181 Monitoring Cell Values
18 2 Adding Images or Color to Cells
18 2 Autofilling Table Cells
183 Working with Rows and Columns
183 Adding Rows
183 Adding Columns
18 4 Deleting Table Rows and Columns
18 4 Using a Table Header Row or Column
185 Using a Footer Row
185 Resizing Table Rows and Columns
185 Alternating Row Colors
18 6 Working with Table Cells
18 6 Merging Table Cells
18 6 Splitting Table Cells
10 Contents
Page 11

187 Formatting Table Cell Borders
187 Copying and Moving Cells
18 8 Sorting Table Cells
Chapter 9 189 Using Formulas and Functions in Tables
18 9 Using Formulas
19 0 A Tour of Using Formulas
19 2 Adding a Quick Formula
19 3 Performing a Basic Calculation Using Column Values
19 3 Performing a Basic Calculation Using Row Values
19 4 Removing a Formula
19 4 Using the Formula Editor
19 4 Adding a New Formula with the Formula Editor
19 5 Editing a Formula with the Formula Editor
19 5 Using Cell References
19 6 Adding Cell References to a Formula
19 6 Copying or Moving Formulas with Cell References
19 7 Applying a Formula Once to Cells in a Column or Row
19 7 Handling Errors and Warnings
19 7 Using Operators
19 8 Performing Arithmetic Operations
19 8 Understanding the Arithmetic Operators
19 9 Understanding the Comparison Operators
200 Using Functions
Chapter 10 201 Using Charts
201 About Charts
204 Adding a Chart
204 Selecting a Chart Type
204 Picking an Initial Chart Type
205 Changing a Chart from One Type to Another
206 Editing Chart Data
207 Copying Data into the Chart Data Editor
207 Working with Rows and Columns in the Chart Data Editor
207 Formatting General Chart Attributes
207 Using a Legend
208 Using a Chart Title
208 Resizing a Chart
209 Rotating Charts
209 Adding Labels and Axis Markings
209 Showing Axes and Borders
210 Using Axis Titles
Contents 11
Page 12

210 Showing Data Point Labels
211 Formatting the Value Axis
212 Placing Labels, Gridlines, and Tick Marks
213 Formatting the Elements in a Data Series
213 Formatting Titles, Labels, and Legends
214 Adding Descriptive Text to a Chart
214 Formatting Specific Types of Charts
214 Pie Charts
214 Selecting Individual Pie Wedges
214 Showing Series Names in a Pie Chart
215 Separating Individual Pie Wedges
215 Adding Shadows to Pie Charts and Wedges
216 Adjusting the Opacity of Pie Charts
216 Rotating 2D Pie Charts
216 Bar and Column Charts
216 Adjusting Spacing of Bar and Column Charts
217 Adding Shadows to Bar and Column Charts
217 Adjusting the Opacity of Bar and Column Charts
217 Area Charts and Line Charts
218 Scatter Charts
219 3D Charts
Chapter 11 220 Personalizing Documents with Address Book Data
220 Using Address Book Fields
221 Using Address Book Fields
221 Inserting Sender Data
221 Inserting Recipient Data for One Contact
222 Inserting Recipient Data for Address Book Groups
222 Inserting Recipient Data for Contacts in Multiple Cards
222 Using Contact Data Not in Address Book or a vCard
223 Defining Your Own Address Book Fields
223 Creating an Address Book Field
224 Changing an Address Book Field
224 Changing an Address Book Field Label
Chapter 12 225 Printing and Exporting Your Document to Other Formats
225 Printing Your Document
225 Setting the Paper Size and Orientation
226 Previewing a Document Before Printing It
227 Printing Comments
227 Printing All or Part of Your Document
12 Contents
Page 13

228 Setting a Print Layout and Other Options
229 Adjusting the Document Color with ColorSync
230 Exporting to Other Document Formats
230 Exporting a Document for Use in Another Application
231 Saving a Document as a Previous iWork Version
232 Sending a Pages Document to iWeb
Chapter 13 233 Designing Your Own Document Templates
233 Designing a Template
234 Step 1: Set Up the Document
234 Step 2: Define Default Attributes
235 Defining Default Styles
235 Defining Default Table of Contents Attributes
235 Defining Default Attributes for Text Boxes and Shapes
236 Defining Default Attributes for Tables
236 Defining Default Attributes for Charts
237 Defining Default Attributes for Imported Images
238 Step 3: Create Placeholder Text and Media Placeholders
238 Creating Placeholder Text
238 Creating Media Placeholders
239 Step 4: Add Sections to Your Template
240 Step 5: Save a Custom Template
Index 241
Contents 13
Page 14

Welcome to the Pages User’s Guide
This full-color PDF document provides extensive instructions
for using Pages.
Before using this document, you may want to look at the Pages tutorial in iWork ’08
Getting Started. It’s a quick way to prepare yourself to be a self-sufficient Pages user.
iWork ’08 Getting Started also provides additional resources for getting acquainted with
Pages, such as a tour of its features and how-to videos.
When you need detailed instructions to help you accomplish specific tasks, you’ll find
them in this user’s guide. Most of the tasks in this guide are also available in online
help.
Preface
14
Page 15

The following table tells you where to find information in this guide. In Help, you can
find information by browsing or searching.
For information about See
Using Pages windows and tools
to create and format documents
Creating, saving, and managing
a Pages document
Creating, organizing, and
formatting document parts
Tracking edits in a Pages
document
Formatting text in a Pages
document
Changing the appearance of
text with paragraph, character,
and list styles
Using graphics, shapes, sound,
and more to enhance a
document
Creating, organizing, and
formatting tables and the table
values in them
Automating calculations by
using formulas and functions
Creating charts to graphically
display data
Displaying Address Book data in
a Pages document
Sharing a Pages document Chapter 12, “Printing and Exporting Your Document to Other
Modifying an existing Pages
template
Chapter 1, “Pages Tools and Techniques,” on page 16
Chapter 2, “Working with a Pages Document,” on page 30
Chapter 3, “Working with Document Parts,” on page 39
Chapter 4, “Reviewing and Revising Documents,” on page 61
Chapter 5, “Working with Text,” on page 70
Chapter 6, “Working with Styles,” on page 118
Chapter 7, “Working with Shapes, Graphics, and Other Objects,” on
page 134
Chapter 8, “Using Tables,” on page 167
Chapter 9, “Using Formulas and Functions in Tables,” on page 189
Chapter 10, “Using Charts,” on page 201
Chapter 11, “Personalizing Documents with Address Book Data,” on
page 220
Formats,” on page 225
Chapter 13, “Designing Your Own Document Templates,” on
page 233
Preface Welcome to the Pages User’s Guide 15
Page 16
1 Pages Tools and Techniques
1
This chapter introduces you to the windows and tools you’ll
use in Pages.
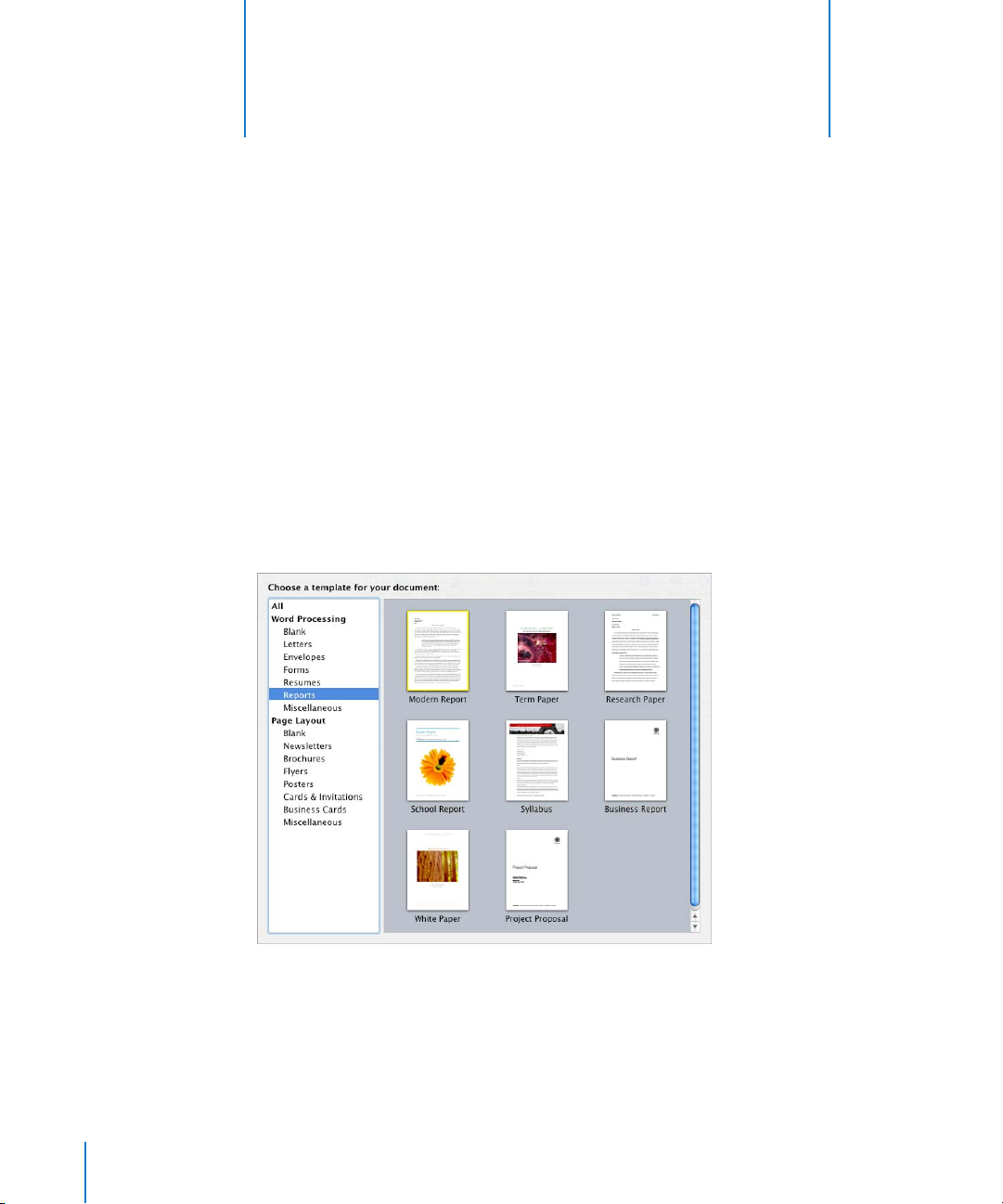
When you create a Pages document, you first select a template to start from.
Pages Templates
When you first open the Pages application (by clicking its icon in the Dock or by
double-clicking its icon in the Finder), the Template Chooser window presents a variety
of document types from which to choose.
16
Page 17

Pick the type that best fits your purpose and design goals. Use Word Processing
templates to write documents such as letters, reports, and resumes. Use Page Layout
templates to arrange elements in documents, such as invitations, posters, and flyers.
After selecting a template, click Choose to work with a new document based on the
selected template.
The new document contains placeholder text, placeholder images, and other items,
which represent elements of the finished document:
Address Book fields let you
personalize documents with
Address Book data.
Media placeholders
indicate the size and
placement of graphics
in a document template.
Placeholder text indicates
where you can type new
text and how your text will
look on the page.
The Page View control lets you
zoom in or out so you can see
your document larger or
smaller on the screen.
Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques 17
Page 18

 Placeholder text shows you how your text will look on the page. If you click
placeholder text, the entire text area is selected. When you begin typing, the
placeholder text disappears and is replaced by what you type. To learn more, see
“Using Placeholder Text” on page 70.
 Media placeholders can hold images, audio files, and movies. Drag your own images,
audio files, or movies to the placeholder. Media placeholders automatically size and
position the image or movie. You can drag media files anywhere in a document (not
only to a media placeholder). To learn more, see “Using Media Placeholders” on
page 157.
 Many templates also contain Address Book fields. Address Book fields let you easily
insert names, phone numbers, addresses (any data you’ve defined for contacts in
Address Book) into Pages documents. This capability lets you reuse a document, such
as a letter or contract, for multiple people by inserting person-specific data into
Address Book fields in the document. To learn more, see “Using Address Book Fields”
on page 221.
 Sometimes graphics, such as watermarks or logos, appear on pages. These objects
are called master objects. If you cannot select an object in a template, it’s probably a
master object. To learn more, see “Using Master Objects (Repeated Background
Images)” on page 57.
You can drag or place objects on a page, including imported graphics, movies, and
sound, or objects that you create within Pages, including text boxes, charts, tables, and
shapes.
You can also insert pages that have been preformatted for the template you’re using.
Click Pages or Sections in the toolbar and choose a template page. The new page is
added immediately after the page where you placed the insertion point.
Document Viewing Aids
As you work on your document, you may want to zoom in or out to get a better view
of what you are doing, or use other techniques for viewing the document.
Zoom Levels
You can enlarge (zoom in) or reduce (zoom out) your view of a document. It’s often
useful to reduce your view of a document so that you can see several pages at once.
Here are ways to zoom in or out of the document:
m Choose View > Zoom > zoom level.
18 Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques
Page 19
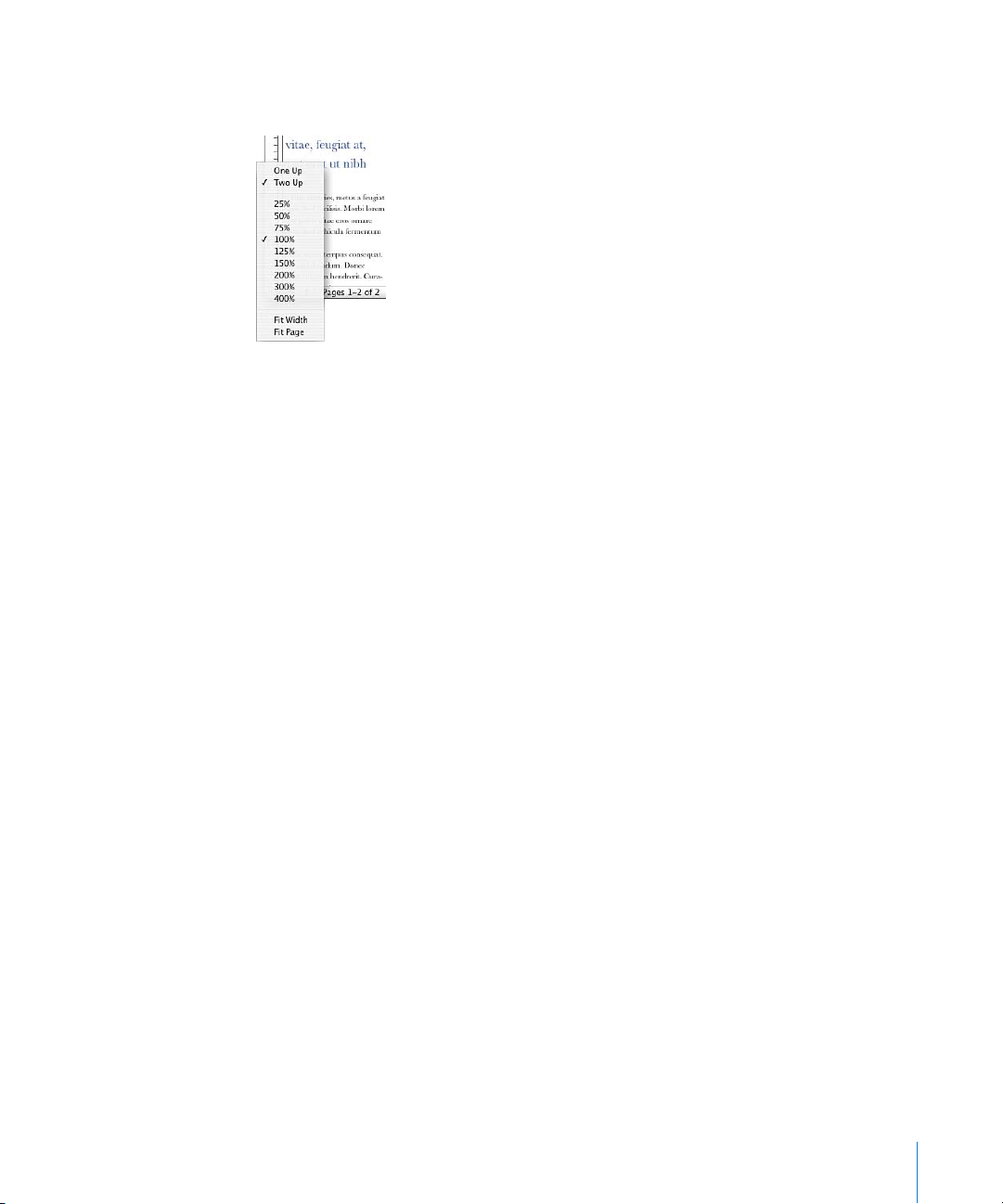
m Choose a magnification level from the View pop-up menu at the bottom left of the
window.
To use a certain zoom level every time you open a document, choose Pages >
Preferences, click General, and then choose a zoom level from the Default Zoom popup menu.
Document Page Views
You can arrange the way pages are displayed in the Pages window.
To choose a way to view document pages in the Pages window:
1 Click the View pop-up menu in the bottom-left corner of the window.
2 Choose one of the page view options.
One Up presents the pages above and below each other.
Two Up presents two pages side-by-side on the screen.
Fit Width scales the document to the width of the window. You can stretch the Pages
window to fill your screen, or make it short or narrow. Choose Fit Width to view all the
content on side-by-side (Two Up) pages.
Fit Page causes a single document page to fill the window.
Layout View
In layout view you can see the outlines of the different text areas of your document,
including headers, footers, columns, text boxes, and the document body (the main area
of text in the document).
In layout view document rulers and alignment guides become visible. Pages also
displays the document ruler, which contains controls for formatting text, when you
show a document’s layout.
Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques 19
Page 20

To show or hide a document’s layout:
m Click View in the toolbar and then choose Show Layout or Hide Layout.
In the following example, you can see the page layout includes two columns at the top,
two layout breaks, and then three columns, a floating image, and the footer area.
Two columns
Layout break
A floating image
Three columns
Layout break
Footer
A layout is part of a document in which you have defined layout margins and columns.
As the example above illustrates, you can have multiple layouts on a single page. A
layout break ends one layout and starts a new one with a different number of columns.
See “Using Layouts” on page 44 for details.
The example above shows a floating image. A floating image stays where you place it
on a page, unless you drag it to a new position. Text flows around a floating image as
you type. There’s a second kind of image: an inline image. An inline image is an image
placed so that it’s anchored to text. An inline image moves with the text around it. To
learn how to place images so that they’re floating or inline, see “Adding Images” on
page 158.
20 Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques
Page 21

Formatting Characters (Invisibles)
Each time you press the Space bar, the Tab key, or the Return key, or add a column,
layout, page break, or section break, Pages inserts a formatting character in the
document. These formatting marks are called invisibles because, by default, you can’t
see them.
Making formatting characters visible is often useful, especially when you’re formatting
a more complex document. For example, you can change your document format by
selecting an invisible and then pressing the Delete key to remove formatting.
To see invisibles:
1 Click View in the toolbar and choose Show Invisibles.
2 To make invisibles stand out better, you can change their color. Choose Pages >
Preferences, click General, click the Invisibles color well, and then select a color.
The table below shows what each formatting character represents.
Invisible character Represents
Space
Nonbreaking space (Option-Space bar)
Tab
Line break (Shift-Return)
Paragraph break (Return)
Page break
Column break (page 46)
Layout break (page 46)
Section break (page 53)
Anchor point (for inline objects with text wrapping)
Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques 21
Page 22

Show thumbnails,
comments, the
Styles drawer, rulers,
invisibles, and more.
The Toolbar
The Pages toolbar gives you one-click access to many of the actions you’ll use when
working with documents. As you work in Pages and get to know which actions you
perform most often, you can add, remove, and rearrange toolbar buttons to suit your
working style.
To see a description of what a button does, hold the pointer over the button.
The default set of toolbar buttons for a word processing document is shown below.
Add a comment for
selected text or object.
Add preformatted pages
to your document.
Add text boxes, shapes,
tables, and charts.
To customize the toolbar:
1 Choose View > Customize Toolbar or Control-click on the toolbar, and then choose
Customize Toolbar. The Customize Toolbar sheet appears.
2 Make changes to the toolbar as desired.
To add an item to the toolbar, drag its icon to the toolbar at the top.
To remove an item from the toolbar, drag it out of the toolbar.
To restore the default set of toolbar buttons, drag the default set to the toolbar.
To make the toolbar icons smaller, select Use Small Size.
To display only icons or only text, choose an option from the Show pop-up menu.
To rearrange items in the toolbar, drag them.
3 Click Done when you have finished.
Track edits in your
document.
Open the Inspector window,
Media Browser, Colors
window, and Font panel.
You can perform several toolbar customization activities without using the Customize
Toolbar sheet:
 To remove an item from the toolbar, press the Command key while dragging the item
out of the toolbar.
You can also press the Control key while you click the item, and then choose Remove
Item from the shortcut menu.
22 Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques
Page 23
 To move an item, press the Command key while dragging the item around in the
toolbar.
To show or hide the toolbar, choose View > Show Toolbar or View > Hide Toolbar.
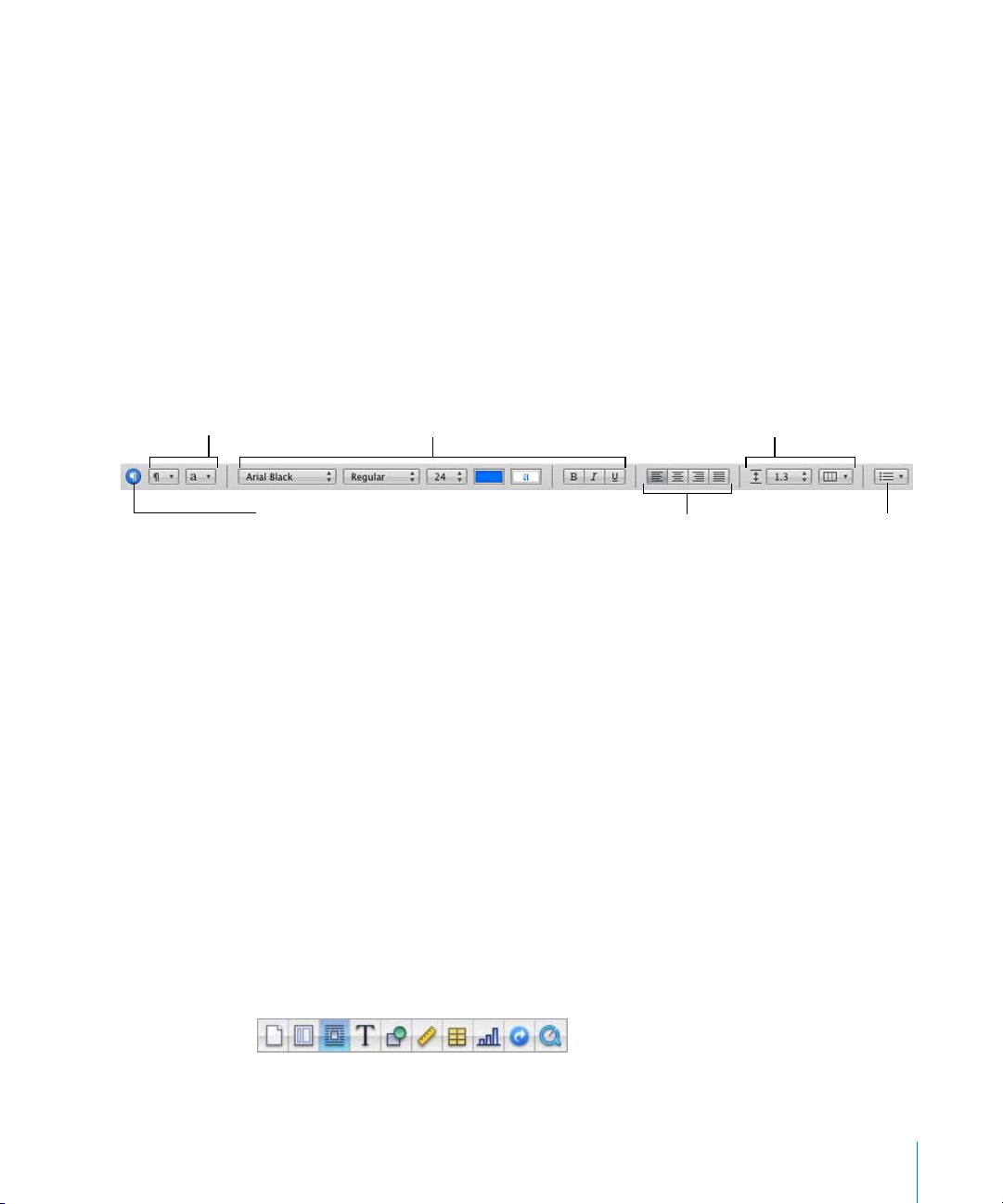
The Format Bar
Use the Format Bar, displayed beneath the toolbar, to quickly change the appearance
of text, styles, fonts, and other elements in your document.
The controls in the Format Bar vary with the object selected. To see a description of
what a Format Bar control does, hold the pointer over it.
Here’s what the Format Bar looks like when text is selected.
Choose a paragraph
or character style.
Choose the line
spacing and the
number of columns.
Choose a list style.
Click to open the
Styles drawer.
Change the font, font style,
font size, and color.
Align selected text.
To show or hide the Format Bar:
m Choose View > Show Format Bar or View > Hide Format Bar.
The Inspector Window
You can format most elements of your document using the panes of the Inspector
window, including text appearance, size and positioning of graphics, and much more.
Open multiple Inspector windows to make working with your document easier. For
example, if you have a Graphic Inspector and a Text Inspector open, you have all the
text and image formatting options at your fingertips as you work.
Hold the pointer over buttons and other controls in the Inspector panes to see a
description of what the controls do.
Here are ways to open an Inspector window:
m Click Inspector in the toolbar.
m Choose View > Show Inspector.
The buttons at the top of the Inspector
window open the ten Inspectors:
Document, Layout, Wrap, Text, Graphic,
Metrics, Table, Chart, Link, and QuickTime.
Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques 23
Page 24
Click one of the buttons at the top of the Inspector window to display a particular
Inspector. Hover the pointer over a button to display its name. Clicking the fourth
button from the left, for example, displays the Text Inspector.
m To open another Inspector window, press the Option key while clicking an Inspector
window button.
When the Inspector window opens, click one of the buttons at the top to display a
different inspector. Clicking the second button from the left, for example, displays the
Layout Inspector.
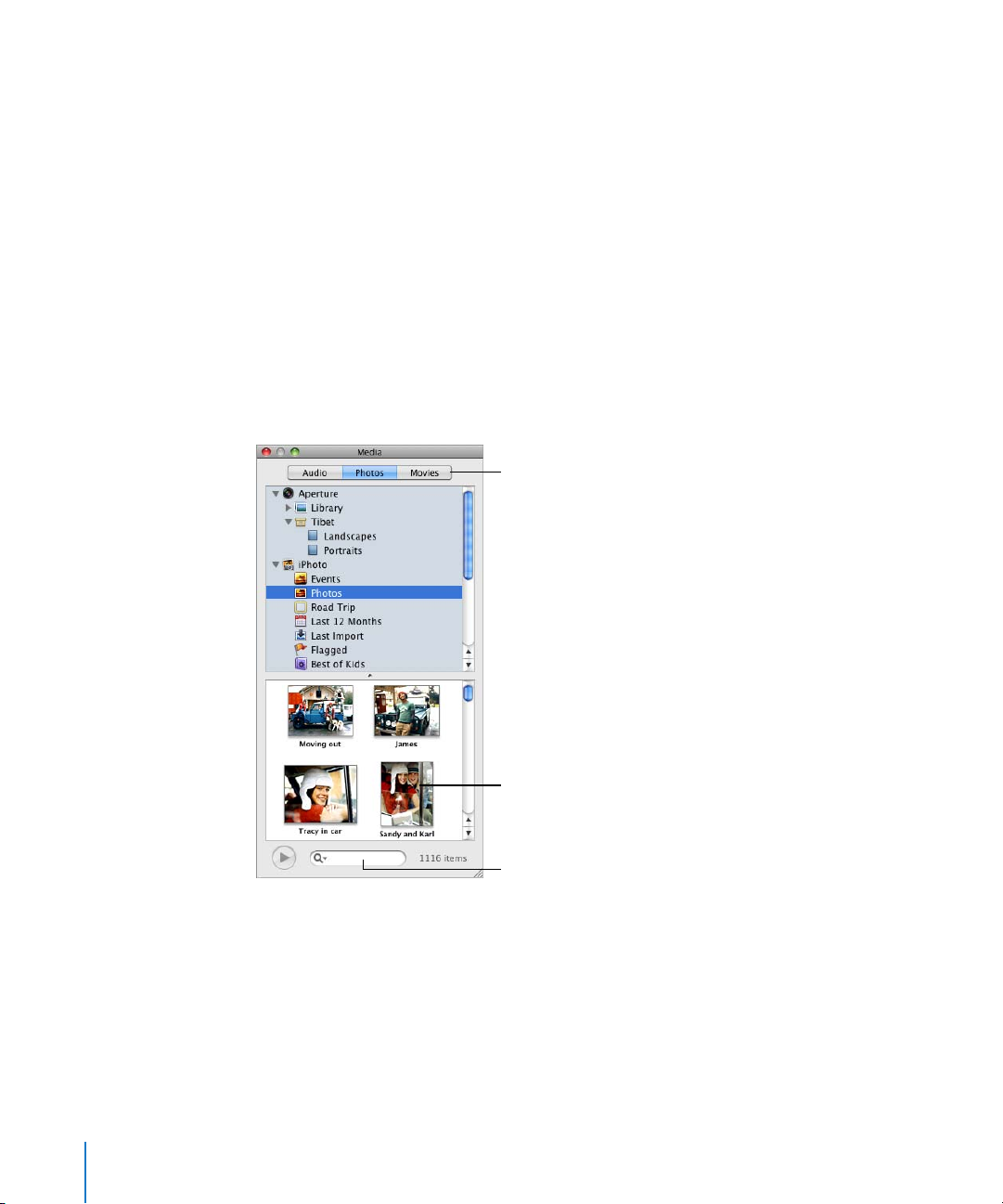
The Media Browser
The Media Browser provides access to all the media files in your iPhoto library, your
iTunes library, and your Movies folder. You can drag an item from the Media Browser to
a page or to an image well in an inspector.
Click a button to view the files in
your iTunes library, your iPhoto
library, your Aperture library, or
your Movies folder.
Drag a file to your
document.
Search for a file.
Here are ways to open the Media Browser:
m Click Media in the toolbar.
m Choose View > Show Media Browser.
24 Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques
Page 25

The Font Panel
Using the Mac OS X Font panel—accessible from any application—you can change a
font’s typeface, size, and other options.
To open the Font panel:
m Click Fonts in the toolbar.
Use the Font panel to select fonts, font sizes, and other font formatting features,
including text shadows and strikethrough. For more detailed information about using
the Font panel and changing the look of text, see “Using the Font Panel to Format Text”
on page 77.
The Colors Window
You use the Mac OS X Colors window to choose colors for text, objects, and lines.
Here are ways to open the Colors window:
m Click the color well in the Format Bar and choose “Show Colors”.
m Click Colors in the toolbar.
For more information, see “Using the Colors Window” on page 148.
Rulers and Alignment Guides
As you move objects around in a document, alignment guides automatically appear to
help you position objects on the page. See “Aligning Objects” on page 138 for details
about using the alignment guides.
Rulers help you set
margins and tabs where
you want them.
You can use the horizontal ruler to set tab stops, page margins, and column widths. For
more information, see “Setting Tab Stops Using the Horizontal Ruler” on page 90,
“Setting Indents for Paragraphs Using the Horizontal Ruler” on page 94, and “Defining
Columns” on page 44.
Blue icons on the top ruler indicate
text indents and tab settings. Drag
them to reset the position of text.
Gray rectangles inside
the rulers indicate column
margins. Drag the
rectangles to change the
column gutter widths.
Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques 25
Page 26
You can also display the vertical ruler in a Word Processing template. See “Setting Tab
Stops Using the Horizontal Ruler” on page 90 for more information.
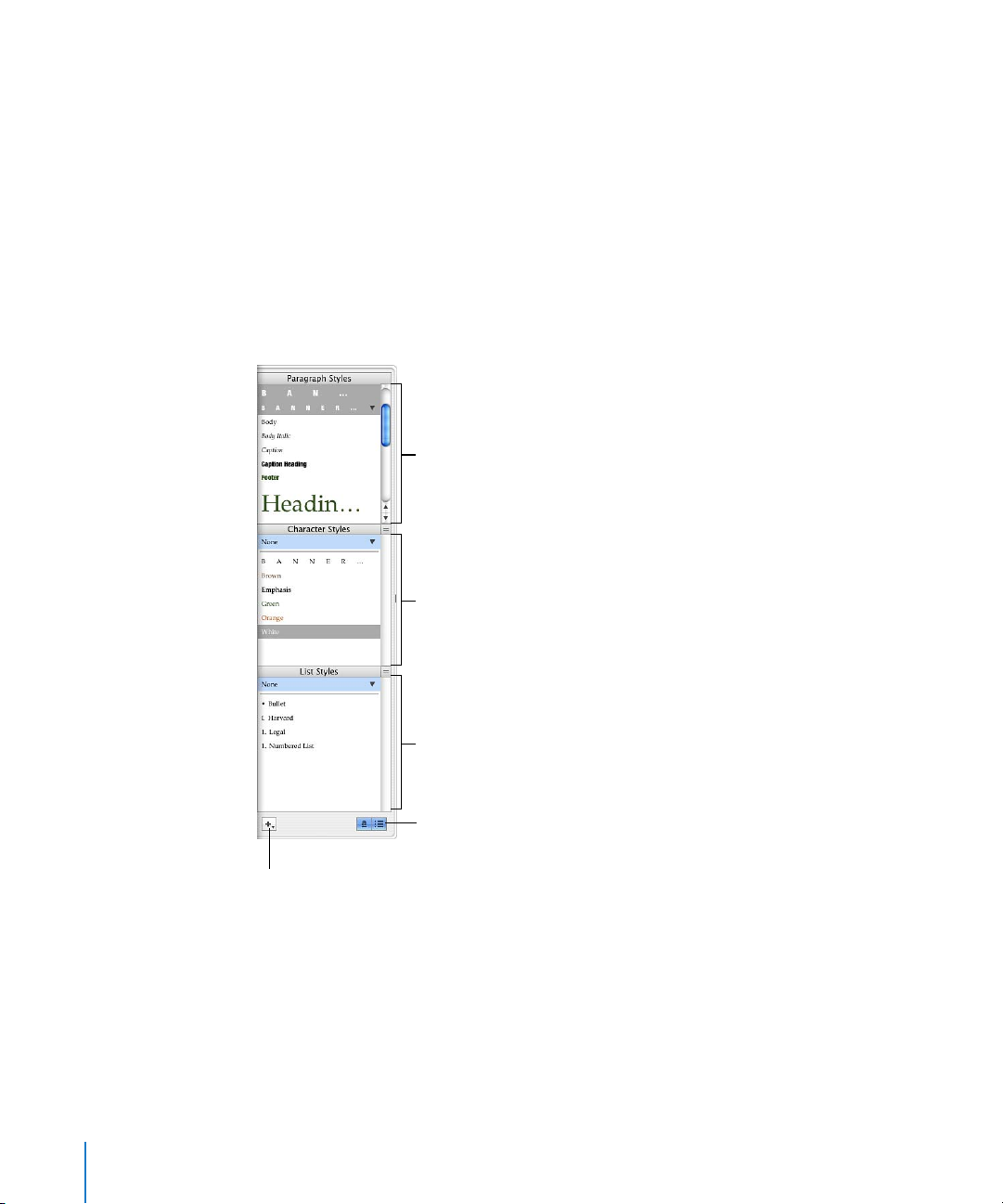
The Styles Drawer
As you create a document, you may want to use a certain text style for every chapter
title, heading, bulleted list, and body text paragraph. Each template comes with a set of
preset styles that you can choose from. “About Styles” on page 119 provides more
details about styles.
The Styles drawer lists and provides a preview of all the text styles in the template you
are using, so you can create, customize, and manage styles easily.
Select a paragraph style to
apply it to selected paragraphs
or the paragraph that contains
the insertion point.
Select a character style to
apply it to selected text or the
word that contains the
insertion point.
Select a list style to apply it to
selected paragraph text or the
paragraph that contains the
insertion point.
Click to show and hide list and
character styles in the drawer.
Press and hold, and then
choose an option to create
a new style.
Here are ways to open the Styles drawer:
m Click View in the toolbar and choose Show Styles Drawer.
m Click the Styles Drawer button in the Format Bar.
See “Applying Styles” on page 120 to learn how to use the Styles drawer.
26 Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques
Page 27
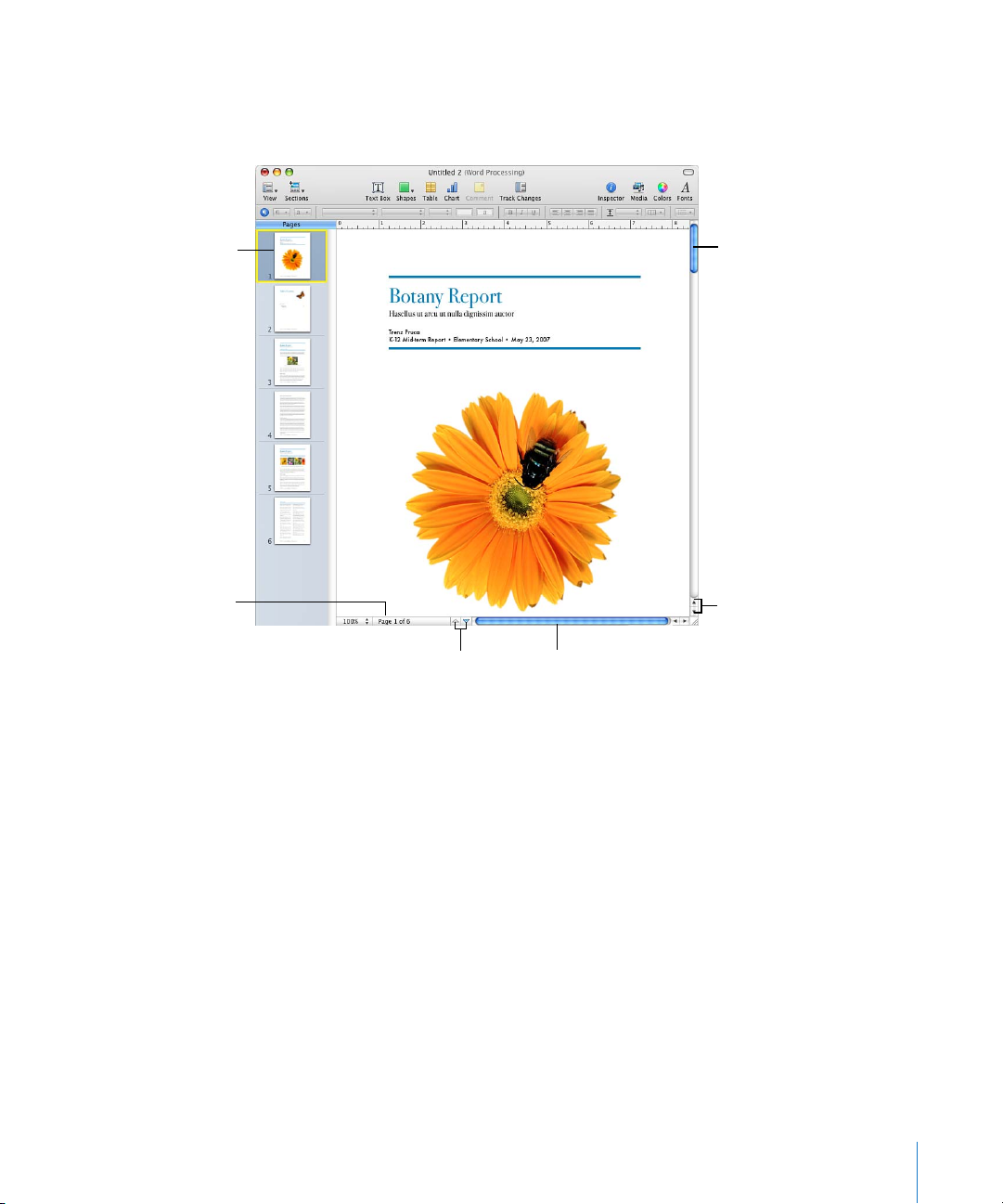
Scroll Bars, Scroll Arrows, and Thumbnails
You can use the scroll bars, Previous Page and Next Page arrows, page thumbnails, and
the Go to Page button to move around a document.
Click a thumbnail to
display a particular page.
Click the Page button
to toggle to the Go to
Page button.
Drag the vertical
scroller to quickly
scroll up and down.
Click the scroll arrows to
move forward or backward
in small increments.
Click the Previous Page or Next
Page arrows to move forward or
back a page at a time.
Drag the horizontal
scroller to scroll left
and right.
Here are ways to navigate through a document:
m To move forward or backward in small increments, click the scroll arrows.
m To scroll quickly, drag the vertical scroller up or down, or drag the horizontal scroller
from left to right.
m To move forward or backward one page at a time, click the Previous Page button (looks
like an up arrow) or the Next Page button (looks like a down arrow) at the bottom of
the document window.
m To go to a specific page in a document, click View in the toolbar and choose Show
Page Thumbnails. Then click in the thumbnail view to go to a particular page. You can
also navigate to a page in a document by clicking the Page button in the lower left of
the document window, typing the specific page number in the Go to Page field, and
then pressing Return.
Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques 27
Page 28

m To show facing pages in the thumbnail view, select Facing Pages in the Document
Inspector’s Document pane. To open the Inspector window, click Inspector in the
toolbar, then click the Document Inspector button.
See “Managing Sections with the Thumbnail View” on page 54 for more information
about using thumbnails.
If your keyboard has them, you can also use the Page Up, Page Down, Home, End, and
arrow keys to move around.
The Warnings Window
When you import a document into a Pages document, some elements might not
transfer as expected. The Warnings window lists any problems encountered. You might
get warnings in other situations, such as saving a document in an earlier version of the
application.
If problems are encountered, you’ll see a message enabling you to review the warnings.
If you choose not to review them, you can see the Document Warnings window at any
time by choosing View > Show Document Warnings.
If you see a warning about a missing font, you can select the warning and click Replace
Font to choose a replacement font.
You can copy one or more warnings by selecting them in the Document Warnings
window and choosing Edit > Copy. You can then paste the copied text into an email
message, text file, or some other document.
Research and Reference Tools
Use the research and reference tools to look for files on your hard drive, review
document information, and find word definitions or facts on selected text.
Here are ways to access research and reference tools:
m To locate files on your hard drive, select the text related to the files you wish to find and
choose Edit > Writing Tools > Search in Spotlight.
m To view document information, choose Edit > Writing Tools > Show Statistics.
m To look up word definitions quickly, select the word you wish to reference and choose
Edit > Writing Tools > Look Up in Dictionary and Thesaurus.
m To research information on the Internet, select the text you wish to investigate and
choose Edit > Writing Tools > Search in Google or Edit > Writing Tools > Search in
Wikipedia.
You can also Control-click to quickly access the research and reference tools.
28 Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques
Page 29

Keyboard Shortcuts and Shortcut Menus
You can use the keyboard to perform many of the Pages menu commands and tasks.
To see a comprehensive list of keyboard shortcuts, open Pages and choose Help >
Keyboard Shortcuts.
Many commands are available in shortcut menus that you can access directly from the
object you are working with. Shortcut menus are especially useful for working with
tables and charts.
To open a shortcut menu:
m Press the Control key while you click text or an object.
Chapter 1 Pages Tools and Techniques 29
Page 30

2 Working with a Pages Document
2
This chapter describes how to create, open, import, and save
Pages documents. It also tells you how to design and lay out
a Pages document.
Working with Word Processing and Page Layout Templates
Word Processing and Page Layout templates have styles and formatting features
tailored to their use:
 Word Processing templates are best suited for text-intensive documents, such as
letters and reports.
 Page Layout templates are most useful for documents that are more layout intensive,
such as invitations and flyers.
30
Word Processing Templates
Use Word Processing templates to create linear, text-intensive documents.
Here are the distinguishing features of a Word Processing template:
 You can add and edit a table of contents in your document. See “Using a Table of
Contents” on page 58 for more information.
 Text flows from one page to another. See “Adding Text” on page 70 for more
information.
 Page thumbnails are hidden by default. See “Using Sections” on page 53 for more
information.
 Only a horizontal ruler is available by default. See “Rulers and Alignment Guides” on
page 25 for more information.
You can also display the vertical ruler in a Word Processing template. See “Setting Tab
Stops Using the Horizontal Ruler” on page 90 for more information.
Page 31

 Word Processing templates contain floating and inline objects. For more information
about working with floating and inline objects, see “Using Floating and Inline
Objects” on page 134.
Page Layout Templates
Use Page Layout templates to arrange images and other elements in your document.
Here are the distinguishing features of a Page Layout template:
 Page Layout templates contain floating objects such as images and text boxes that
can be easily moved anywhere on the page. For more information about working
with floating objects, see “Using Floating and Inline Objects” on page 134.
 Text in a Page Layout template must either replace placeholder text in a template
text box or a text box must be added to the page. See “Adding Text” on page 70 for
more information.
 Text can flow between text boxes. See “Linking Floating Text Boxes” on page 102 for
more information.
 Vertical and horizontal rulers are displayed by default. See “Rulers and Alignment
Guides” on page 25 for more information.
 Page thumbnails are displayed by default. See “Layout View” on page 19 and
“Managing Sections with the Thumbnail View” on page 54 for more information.
Creating, Opening, and Importing a Pages Document
When you create a new Pages document, you pick a template to provide its initial
formatting. You expand your new document by adding text, images, and other objects
to it. You can also create a new Pages document by importing a document created in
another application, such as Microsoft Word or AppleWorks.
Creating a New Document
To create a new Pages document, you pick the Word Processing or Page Layout
template that provides appropriate formatting and layout characteristics.
Chapter 2 Working with a Pages Document 31
Page 32

To create a new Pages document:
1 Open Pages by clicking its icon in the Dock or by double-clicking its icon in the Finder.
2 In the Template Chooser window, select a template category in the left column to
display related Word Processing or Page Layout templates, and then select the
template that best matches the document you want to create.
If you want to begin in a document without any text or media placeholders, select
Blank under Word Processing or Page Layout.
In a Blank page layout document, text is added by inserting a text box and then typing
in the text box. To add text to a Blank word processing document, begin typing.
3 Click Choose. A new document opens on your screen.
If you don’t see the Template Chooser when you first open Pages, you can make it
appear by setting a preference in Pages preferences. Choose Pages > Preferences, click
General, and then select “For New Documents: Show Template Chooser.”
Alternatively, you can set Pages to automatically open a Blank document or the
document template of your choice every time you open it. Choose Pages > Preferences,
click General, select “For New Documents: Use template: template name,” and then
click Choose. Select a template name, and then click Choose.
32 Chapter 2 Working with a Pages Document
Page 33

Importing a Document
You can create a new Pages document by importing a document created in another
application, such as Microsoft Office 2007 or AppleWorks. Pages can import the
following file formats: plain text (.txt), Rich Text Format (.rtf and .rtfd), AppleWorks 6
word processing (.cwk), and Microsoft Word (.doc).
As much as possible, Pages preserves the original document’s text, colors, layout, and
other formatting options.
From Microsoft Word, you can import styles, tables, inline and floating objects, charts,
footnotes and endnotes, bookmarks, hyperlinks, lists, sections, change tracking, and
more.
From AppleWorks, you can only import word processing documents.
Here are ways to import a document:
m Drag the document to the Pages application icon. A new Pages document opens, and
the contents of the imported document are displayed.
m Choose File > Open, select the document, and then click Open.
If you can’t import a document, try opening the document in another application and
saving it in a format Pages can read, or copy and paste the contents into an existing
Pages document.
You can also export Pages documents to Microsoft Word, PDF, Rich Text Format (RTF),
and Plain Text. See “Exporting a Document for Use in Another Application” on page 230
for details.
Opening an Existing Pages Document
There are several ways to open a document that was created using Pages.
Here are ways to open a Pages document:
m To open a document when you’re working in Pages, choose File > Open, select the
document, and then click Open.
m To open a document you’ve worked with recently, choose File > Open Recent and
choose the document from the submenu.
m To open a Pages document from the Finder, double-click the document icon or drag it
to the Pages application icon.
Chapter 2 Working with a Pages Document 33
Page 34

You can open a Pages document created using an older version of Pages (from
iWork ’05 or iWork ’06). To take advantage of new features, save the document in
iWork ’08 format. To preserve the document for use with iWork ’05 or iWork ’06, save it
in the same format. See “Saving a Document as a Previous iWork Version” on page 231.
If you see a message that a font or file is missing, you can still use the document. Pages
substitutes fonts for missing fonts. To use missing fonts, quit Pages and add the fonts to
your Fonts folder (for more information, see Mac Help). To make missing movies or
sound files appear, add them to the document again.
Saving Your Document
When you create a Pages document, all of the graphics and any chart data are
contained within that document, which can be moved from one computer to another.
However, fonts are not included as part of the document. If you transfer a Pages
document to another computer, make sure the fonts used in the document have been
installed in the Fonts folder of that computer.
Saving a Document
It’s a good idea to save your document often as you work. After you’ve saved it for the
first time, you can press Command-S to resave it using the same settings.
To save a document for the first time:
1 Choose File > Save, or press Command-S.
2 In the Save As field, type a name for the document.
3 If your file directory isn’t visible in the Where pop-up menu, click the disclosure triangle
to the right of the Save As field.
4 Choose where you want to save the document.
5 If you want the document to be opened using Pages in iWork ’05 or iWork ’06, select
“Save a copy as,” and then choose iWork ’05 or iWork ’06 from the pop-up menu.
6 If you or someone else will open the document on another computer, click Advanced
Options and consider the following:
Copy audio and movies into document: Selecting this checkbox saves audio and video
files with the document, so the files play if the document is opened on another
computer. You might want to deselect this checkbox so that the file size is smaller, but
media files won’t play on another computer unless you transfer them as well.
Copy template images into document: If you don’t select this option and you open the
document on a computer that doesn’t have the same template installed (if you created
your own template, for example), the document might look different.
34 Chapter 2 Working with a Pages Document
Page 35

7 Click Save.
You can generally save Pages documents only to computers and servers that use
Mac OS X. Pages is not compatible with Mac OS 9 computers and Windows servers
running Services for Macintosh. If you must use a Windows computer, try using AFP
server software available for Windows to do so.
If you plan to share the document with others who don’t have Pages installed on their
computers, you can export the document for use in another application. To learn about
exporting your document in other file formats (including Microsoft Word, rich text
format, plain text, and PDF), see “Exporting a Document for Use in Another Application”
on page 230.
You can also send a document to iWeb. For more information, see “Sending a Pages
Document to iWeb” on page 232.
Undoing Changes
If you don’t want to save changes you made to your document since opening it or last
saving it, you can undo them.
Here are ways to undo changes:
m To undo your most recent change, choose Edit > Undo.
m To undo multiple changes, choose Edit > Undo multiple times. You can undo any
changes you made since opening the document or reverting to the last saved version.
m To undo one or more Edit > Undo operations, choose Edit > Redo one or more times.
m To undo all changes you made since the last time you saved your document, choose
File > “Revert to Saved” and then click Revert.
Saving a Document as a Template
When you save a document as a template, it appears in the Template Chooser.
To save a document as a template:
m Choose File > Save as Template.
Saving a Copy of a Document
If you want to make a copy of your document—to create a backup copy or multiple
versions, for example—you can save it using a different name or location. (You can also
automate saving a backup version, as “Automatically Saving a Backup Version of a
Document” describes.)
Chapter 2 Working with a Pages Document 35
Page 36

To save a copy of a document:
m Choose File > Save As and specify a name and location.
The document with the new name remains open. To work with the previous version,
choose File > Open Recent and choose the previous version from the submenu.
Automatically Saving a Backup Version of a Document
Each time you save a document, you can save a copy without the changes you made
since last saving it. That way, if you change your mind about edits you have made, you
can go back to (revert to) the backup version of the document.
Here are ways to create and use a backup version:
m To automatically save a backup version of a document, choose Pages > Preferences,
click General, and then select “Back up previous version when saving.”
The next time you save your document, a backup version is created in the same
location, with “Backup of” preceding the filename. Only one version—the last saved
version—is backed up. Every time you save the document, the old backup file is
replaced with the new backup file.
m To revert to the last saved version after making unsaved changes, choose File > Revert
to Saved. The changes in your open document are undone.
Closing a Document Without Quitting Pages
When you have finished working with a document, you can close it without quitting
Pages.
Here are ways to close documents and keep the application open:
m To close the active document, choose File > Close or click the close button in the
upper-left corner of the document window.
m To close all open Pages documents, press the Option key and choose File > Close All or
click the active document’s close button.
If you’ve made changes since you last saved the document, Pages prompts you to save.
Storing Information About a Document
You can store such information as author name and keywords and later display that
information as well as statistics created automatically (number of words, creation date,
and so forth).
Here are ways to work with information about a document:
m To add or change descriptive information about a document (author, title, comments,
and keywords), click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Document Inspector button, and
then click Info. Enter or change information in the fields in the pane.
This information is searchable using Spotlight on computers with Mac OS X version
10.4 and later.
36 Chapter 2 Working with a Pages Document
Page 37

m To display document statistics, such as number of words, pages, lines, paragraphs,
sections, graphics, and characters in the document, click Inspector in the toolbar, click
the Document Inspector button, and then click Info.
If a range of text is selected, you can specify the extent of the displayed statistics by
choosing Selection or Document from the Range pop-up menu in the Document
Inspector.
m To display a document’s file information, including its size, its location, and the dates it
was created and last modified, click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Document
Inspector button, click Info, and then click the Show File Info button.
Designing Documents
Document layout and style, the appearance of text, and the use of graphics and other
media all play a role in a document’s effectiveness.
Document Layout and Style
Think about how you want the document to appear as a whole, including how it’s laid
out and how it uses space.
 What type of document are you creating and which template most closely matches
the layout you need?
 Does the document need a landscape or portrait page orientation? Make sure to set
this option in the Page Setup dialog before you begin. See “Setting the Paper Size
and Orientation” on page 225.
 If you are designing a unique page layout, are the document margins set the way
you need? See “Setting Document Margins” on page 42.
 Will the document be divided into sections with different page numbering, headers
and footers, or design elements? See “Using Headers and Footers” on page 49 and
“Using Sections” on page 53.
 Will the document be bound? If so, be aware of how the page numbers, margins,
and section breaks will fall on the right- and left-facing pages of your document. See
“Using Left- and Right-Facing Pages” on page 47.
 Does the document layout require columns? See “Using Layouts” on page 44.
 Will the document require a table of contents? If so, make sure to use consistent
heading styles throughout the document. See “Using a Table of Contents” on
page 58.
Chapter 2 Working with a Pages Document 37
Page 38

Appearance of Text
Consider how you might use text in your document to emphasize the organization of
content and to create a compelling design.
 Which fonts will you use in the document? See “Formatting Text Size and
Appearance” on page 75.
 Are there heading styles or fonts that you would like to use consistently throughout
the document? See “About Styles” on page 119.
 What shape or image would you like to use for bullets? What number styles for
outlines? See “Using Bulleted, Numbered, and Ordered Lists (Outlines)” on page 95.
 Will you make use of callouts, sidebars, or other highlighted text in your document?
See “Using Text Boxes, Shapes, and Other Effects to Highlight Text” on page 100.
Graphics and Other Objects
Think about how you will use graphical elements in your document, where they will
appear in the document flow, and what kinds of graphics you might use.
 Do you want objects to remain with text as the text changes (inline objects), or do
you want objects to stay in a particular location (floating objects)? See “Using
Floating and Inline Objects” on page 134 for more information about these two
options.
 How will images be used in your document? See “Working with Images” on
page 158.
 Can you use tables to clearly present information? See “About Tables” on page 167.
 Can you use charts to effectively display data? See “About Charts” on page 201.
 What will be the final format for your document (printed page, and so on)? See
“Printing Your Document” on page 225 and “Exporting to Other Document Formats”
on page 230.
 Will you make use of sound or movies in your document? See “Using Sound and
Movies” on page 164.
38 Chapter 2 Working with a Pages Document
Page 39

3 Working with Document Parts
3
This chapter describes how to set up overall document
characteristics, including margins, facing pages, text columns,
and sections, and how to create a table of contents,
footnotes, and endnotes.
Before adding content to your document, it’s a good idea to set up such document
settings as page orientation and size, page margins, master objects (background
graphics, such as watermarks), and facing-page differences. You change most of these
settings in the Document Inspector and the Layout Inspector.
39
Page 40

To open the Document Inspector:
m Click Inspector in the toolbar, and then click the Document Inspector button.
Use the TOC pane to set up a table
of contents for the document.
The Document
Inspector button
Select to add headers
and footers to a
document.
Use automatic
hyphenation throughout
the document.
Use the Info pane to see document
statistics, such as word count, date,
and keywords.
Use the Page Setup dialog to specify
paper size and orientation.
Set up margins for the left, right, top,
and bottom edges of the page.
Select the kind of note to create.
Choose a footnote or endnote style.
Adjust the space between notes.
Use any available font ligatures
throughout the document.
Formatting set in the Document Inspector applies to the entire document.
40 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 41

To open the Layout Inspector:
m Click Inspector in the toolbar, and then click the Layout Inspector button.
The Layout Inspector button
Use the Section pane to set up
page number, facing-page, and
other section attributes.
Set the number
of columns.
Select to start the
current layout at the
top of a page.
Set the space between
the current layout and
the preceding and
following layouts.
Deselect to set unequal
column widths.
Select a column or
gutter width and type
a new value.
Set the margins for the
current layout.
You use the Layout Inspector to set up text column layouts. It also lets you control
formatting options for document sections, such as chapters; for example, you can
create a different first page, left page, and right page layout for each section.
Setting Page Orientation and Size
By default, most Pages templates are created for standard paper sizes, with the text
printed in portrait (vertical) orientation. If your document will require a different paper
size or you want to print it in landscape (horizontal) orientation, you should set the
paper size and orientation at the start. This way, as you work in your document, you will
have a clearer idea of what it’s going to look like.
If you start with a Blank (word processing) or Blank Canvas (page layout) document, it is
in portrait orientation by default. “Setting the Paper Size and Orientation” on page 225
provides instructions for changing the page orientation and setting up paper size.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 41
Page 42

Setting Document Margins
Every document has margins (blank space between the document’s content and the
edges of the paper). These margins are indicated onscreen by light gray lines when
you’re using layout view. To show layout view, click View in the toolbar and then
choose Show Layout.
The default margins for most of the Pages templates, including Blank, are set to one
inch from the left and right sides of the page, and one inch from the top and bottom.
This means that the body text of the document will not expand outside these margins.
To change the page margins:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Document Inspector button, and then click
Document.
2 Enter values in the Left, Right, Top, and Bottom fields.
If you want to set different margins in different sections of your document, you must
use the Layout Inspector. To learn about setting layout margins, see “Defining Layout
Margins” on page 47.
If you are creating a document that will be bound, you may want your document
margins to take into account which side of the page will go into the binding (the inside
margin) and which will be the loose edge of each page (the outside margin). To do this,
you must create a document with left- and right-facing pages. To read about this, see
“Using Left- and Right-Facing Pages” on page 47.
Using Page and Line Breaks
You can insert page breaks, make a particular paragraph always start on a new page,
make sure certain paragraphs always remain on the same page, and more.
When you insert breaks, Pages inserts a special formatting character called an invisible.
See “Formatting Characters (Invisibles)” on page 21 for more information about
invisibles.
Inserting a Page Break
In a word processing document, you can force the page to break at a particular place
by inserting a page break. This creates a new page within the current section and is
ready for typing text. In a page layout document, you can create a new page by adding
a new page to your document. This creates a new page in a new section, and is ready
to have a text box added for typing text.
42 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 43

Here are ways to insert a page break:
m In a word processing document, click where you want the break to occur, and then
choose Insert > Page Break.
To remove a page break, click at the beginning of the line that follows the break and
press the Delete key.
m In a page layout document, to insert a new page in your document, choose Insert >
Pages > template page.
Starting Paragraphs on a New Page
You can make a paragraph always start on a new page, regardless of what precedes it
in a document.
To start a paragraph on a new page:
1 Select the paragraph you want to start on a new page.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click More.
3 Select “Paragraph starts on a new page.”
In a Blank Canvas (Page Layout) template, once a new page has been added, it's ready
to have a text box added for typing text.
Keeping Paragraphs Together on a Page
You can make two or more paragraphs always appear on the same page unless you
insert a page break between them.
To keep paragraphs together on a page:
1 Click the paragraph that you always want to appear with the paragraph following it.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click More.
3 Select “Keep with following paragraph.”
Keeping an Entire Paragraph on the Same Page
You can make all the lines in a paragraph always appear on the same page.
To avoid breaking a paragraph across pages:
1 Click the paragraph whose lines you want to remain together.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click More.
3 Select “Keep lines together.”
In a page layout document, text is contained in text boxes. For more information about
linking text boxes, see “Linking Floating Text Boxes” on page 102.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 43
Page 44

Inserting a Manual Line Break
You can use a manual line break, also called a soft return, if you want to start a new line
without starting a new paragraph.
To insert a manual line break:
1 Click where you want the break to occur.
2 Press Return while holding down the Shift key.
Preventing Widow and Orphan Lines
You can prevent the first line of a paragraph from appearing alone at the bottom of a
page (called a widow line) or the last line of a paragraph from appearing alone at the
top of a page (called an orphan line).
To prevent widow and orphan lines in a paragraph:
1 Click the paragraph in which you want to prevent a widow or orphan.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click More.
3 Select “Prevent widow & orphan lines.”
Using Layouts
In Pages, you can vary the design of pages in a page layout document by creating
columns in text boxes, and in a word processing document through layouts separated
by layout breaks.
For more information about working with text boxes in page layout documents, “Using
Text Boxes, Shapes, and Other Effects to Highlight Text” on page 100.
In a word processing document, layouts are separated by layout breaks. A layout is part
of a document in which you’ve defined specific column attributes and space around
the columns, called the layout margin.
You can have multiple layouts in a section of your document, or even on a single page.
Defining Columns
Depending on the page size and column width you specify for a document, you can
create as many as ten text columns (for example, in a standard letter size with
landscape orientation).
When you type in a column and reach the end of the column, text automatically flows
to the next column as you type. To change where a column breaks, follow the
instructions in “Defining Column Breaks” on page 45.
When you want to vary the number or appearance of columns at some point in a
document, create a new layout. See “Defining Layout Breaks” on page 46 for
instructions.
44 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 45

To format a document into multiple columns:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Layout Inspector button, click Layout, and then
specify the number of columns you want in the Columns field. To type a number in the
Columns field, place the insertion point inside a text area in your document, type the
number in the Columns field, and then press Return.
2 To make all columns the same width, select “Equal column width.”
To adjust the width of all columns, double-click any value in the column list and type a
new number. To adjust the space between each column, double-click any value in the
Gutter list and type a new number.
3 To specify different widths for the columns, deselect “Equal column width.”
To adjust the width of a specific column, double-click its value in the Column list and
type a new number. To adjust the space between adjacent columns, double-click a
value in the Gutter list and type a new number.
4 In a word processing document, to adjust the space around the outside margins of
columns, specify new values in the Left, Right, Before, and After fields.
Layout margins are not adjustable in a page layout document.
5 In a word processing document, to move columns to the top of the next page, select
“Layout starts on a new page.”
“Layout starts on a new page” is not selectable in a page layout document.
6 To quickly create as many as four columns, click the Columns pop-up menu in the
Format Bar and choose the number of columns you want to use from the pop-up
menu.
7 To quickly modify column width and spacing, use the document ruler. Click View in the
toolbar, and then choose Show Rulers. Drag the left or right edges of the gray gutter
areas in the horizontal ruler.
The white areas in the
ruler denote the text area
within columns.
The gray areas denote the
column gutters.
Defining Column Breaks
In a word processing document, a column break ends the text flow in one column
(leaving the rest of the column blank) and continues it in the next.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 45
Page 46

To create a column break:
1 Click after the word where you want to end the text flow.
2 Choose Insert > Column Break.
The text breaks where the insertion point was placed and continues in the next text
column. If you insert a column break in a single-column layout, the text continues at
the top of the next page.
When you show invisibles in your document (click View in the toolbar and choose
Show Invisibles), a column break symbol marks the location of the column break.
To delete a column break, click at the beginning of the line that follows the break and
press the Delete key.
Defining Layout Breaks
In a word processing document, a layout break ends one layout and starts a new one in
which you can define different column characteristics and different layout margins.
Using layout breaks doesn’t affect the headers, footers, page numbering, or other
formatting specific to the document or section.
To insert a layout break in a word processing document:
1 Place the insertion point after the word where you want to end the current layout and
change to a new layout.
2 Choose Insert > Layout Break.
A layout break is inserted and the insertion point is moved to the top of the next
layout.
3 The layout following the break has the same formatting and number of text columns as
the previous layout until you change it. To change the layout attributes, click Inspector
in the toolbar and click the Layout Inspector button. In the Layout pane, set the
number of columns, and then format them.
4 To move the new layout to the top of a page, select “Layout starts on new page.”
When you show invisibles in your document (click View in the toolbar and then choose
Show Invisibles), a layout break symbol marks the location of the layout break.
To delete a layout break, click at the beginning of the line that follows the break and
press the Delete key.
46 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 47

Defining Layout Margins
In a word processing document, a layout margin is the space around columns in a
layout.
To change the layout margin in a word processing document:
1 Click in a column.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Layout Inspector button, and then click Layout.
3 To change the outside margins of the column(s), enter values in the Left and Right
fields under Layout Margins.
4 To specify the amount of space above and below the column(s), enter values in the
Before and After fields under Layout Margins.
The new margins can’t extend outside the page margins set for the document in the
Document Inspector.
Using Left- and Right-Facing Pages
If you intend to print a document double-sided and bind it, the document will have
left- and right-facing pages.
The left and right pages of these documents usually have different inside and outside
margins. For example, you may want the inside margins of a document that will be
bound to be wider than the outside margins.
Select to set the margins
for left- and right-facing
pages independently.
If your document contains sections, such as chapters, you can use different headers or
footers for left and right pages when you want to place page numbers on the outer
corners of each page.
Defining Margins for Facing Pages
Use the Document Inspector to set up different margins for left and right pages.
To create different margins for left- and right-facing pages:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Document Inspector button, and then click
Document.
2 Select Facing Pages.
Specify a value for the
margin on the outside
edges of the pages.
Specify a value for the
margin that will go into
the binding.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 47
Page 48

3 Set inside and outside margins. The inside margin is the side of left or right pages that
goes into the binding. The outside margin is the side that is on the outside edge of left
or right pages.
Defining Headers and Footers for Facing Pages
In word processing documents, if your document uses sections, you can set up
different headers and footers for left and right pages, such as when you want the page
number to appear on the outer edge of the footers. See “Using Sections” on page 53
for information about defining sections.
To set up headers and footers for facing pages in a section:
1 Click inside the section.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Layout Inspector, and then click Section.
3 Select “Left and right pages are different.”
4 Deselect “Use previous headers & footers.”
5 On a left page in the section, define the header and footer you want to use for all left
pages in the section. See “Using Headers and Footers” on page 49 for instructions.
6 On a right page in the section, define the header and footer you want to use for all
right pages in the section.
7 If you want the first page of the section to have a unique header or footer, select “First
page is different” and define the header and footer on the first page of the section.
Viewing Facing Pages
When your document has facing pages, there are several ways to view them in Pages.
Here are ways to view facing pages:
m Click View in the toolbar and choose Show Page Thumbnails to view facing pages in
the thumbnail view.
m Click the Page View control in the bottom-left corner of the window, and then choose
Two Up from the pop-up menu to view facing pages side by side in the main
document window.
48 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 49

Using Headers and Footers
You can have the same text or graphic appear on multiple pages in a document.
Recurring information that appears at the top of the page is called a header; at the
bottom it’s called a footer.
You can put your own text or graphics in a header or footer, and you can use formatted
text fields. Formatted text fields allow you to insert text that is automatically updated.
For example, inserting the date field shows the current date whenever you open the
document. Similarly, page number fields keep track of page numbers as you add or
delete pages.
To define the contents of a header or footer:
1 Click View in the toolbar and choose Show Layout. You can see the header and footer
areas at the top and bottom of the page.
2 To add text or graphics to a header or footer, place the insertion point in the header or
footer and type or paste text or graphics.
3 To add page numbers or other changeable values, see the instructions in “Inserting
Page Numbers and Other Changeable Values” on page 112.
Whatever you type in a header or footer is repeated on every page. If you want to
change the header and footer text in different sections of your document, see
“Changing Headers and Footers in a Section” on page 55.
Using Footnotes and Endnotes
In a word processing document, you can add special marks (numbers or symbols) in a
document that link to notes at the bottom of a page (footnotes) or at the end of a
document or section (endnotes).
You can’t mix footnotes and endnotes in a document, but you can convert notes from
one type to the other.
Adding and Editing Footnotes and Endnotes
In a word processing document, footnotes and endnotes can contain text as well as
inline objects.
Adding a Footnote
In a word processing document, you can add special marks in a document that link to
notes at the bottom of the page. These notes are called footnotes.
To add a footnote:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Document Inspector button, and then click
Document.
2 Choose Use Footnotes from the Footnotes & Endnotes pop-up menu.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 49
Page 50

3 Choose a numbering format.
4 Place the insertion point in the main text flow (not in a text box, table, or other object)
where you want the footnote mark to appear.
5 Choose Insert > Footnote.
A footnote mark appears and the insertion point moves to the corresponding footnote
field at the bottom of the page.
6 Type the footnote information. In addition to text, you can use inline shapes, graphics,
and other objects; see “Using Floating and Inline Objects” on page 134 for instructions.
Adding an Endnote at the End of a Document
In a word processing document, you can add special marks in a document that link to
notes at the end of the document. These notes are called document endnotes.
To add an endnote at the end of a document:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Document Inspector button, and then click
Document.
2 Choose Use Document Endnotes from the Footnotes & Endnotes pop-up menu.
3 Choose a numbering format.
4 Place the insertion point in the main text flow (not in a text box, table, or other object)
where you want the endnote mark to appear.
5 Choose Insert > Endnote.
An endnote mark appears and the insertion point moves to the corresponding
endnote field, at the end of the document following a section break. If you don’t want
the endnotes on a new page, delete the section break.
6 Type the endnote information.
In addition to text, you can use inline shapes, graphics, and other objects; see “Using
Floating and Inline Objects” on page 134 for instructions.
Adding an Endnote at the End of a Section
In a word processing document, you can add special marks in a document that link to
notes at the end of each section. These notes are called section endnotes.
To add an endnote at the end of a section:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Document Inspector button, and then click
Document.
2 Choose Use Section Endnotes from the Footnotes & Endnotes pop-up menu.
3 Choose a numbering format.
4 Place the insertion point in the main text flow (not in a text box, table, or other object)
where you want the endnote mark to appear.
50 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 51

5 Choose Insert > Section Endnote.
An endnote mark appears and the insertion point moves to the corresponding
endnote field, at the end of the section in which the mark appears. A line separates the
endnotes from other information in the section.
6 Type the endnote information.
In addition to text, you can use inline shapes, graphics, and other objects; see “Using
Floating and Inline Objects” on page 134 for instructions.
Deleting Footnotes and Endnotes
In a word processing document, deleting footnotes and endnotes is easy.
To delete a footnote or endnote:
m Delete the mark within your document that refers to the note.
Converting Footnotes to Endnotes and Vice Versa
In a word processing document, you can change all the footnotes in a document into
endnotes, or all the endnotes into footnotes. You can also convert all document
endnotes to section endnotes and vice versa. However, you can’t mix endnotes and
footnotes in the same document.
To convert footnotes to endnotes and vice versa:
m In the Document pane of the Document Inspector, change the setting in the
Footnotes & Endnotes pop-up menu.
Formatting Footnotes and Endnotes
In a word processing document, you can format footnotes, endnotes, and marks to
change their appearance or control the amount of space between notes.
Here are ways to format notes:
m To change the appearance of notes and marks, select the note text and/or mark and
format it as you would any text using the Font panel, the Text Inspector, and the Styles
drawer.
m To adjust the space between notes, in the Document pane of the Document Inspector,
increase or decrease the number in the Space Between Notes field.
Jumping Between a Mark and Its Related Footnote or Endnote
In a word processing document, you can jump to a note from its mark or to the mark
from a note.
Here are ways to jump between marks and notes:
m In the note, double-click the mark to jump to the location in the document where the
mark appears.
m In the document body, double-click the mark to jump to its note.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 51
Page 52

Numbering Footnotes and Endnotes
In a word processing document, you can use one of the predefined autonumbering
styles for the mark that refers to the note. Predefined numbering styles are Arabic
numbers (1, 2, 3), Roman numerals (i, ii, iii), and symbols (*, †, ‡). Numbering can be
continuous through the document, or restarted for each document section or page.
Instead of or in addition to using autonumbering, you can use custom marks, which
you define yourself. There’s no autonumbering for custom marks; if you use custom
marks, you need to specify the mark you want to use every time you create a footnote
or endnote.
Defining Marks for Numbering Footnotes and Endnotes
In a word processing document, you can use a predefined number or symbol format or
define your own marks.
Here are ways to define marks:
m To use a predefined number or symbol format, in the Document pane of the Document
Inspector, choose a numbering style from the Format pop-up menu. The numbering
style you choose will be the same throughout the document.
m To insert a custom mark, place the insertion point at the location in the document
where you want the mark to appear.
Click the Insert menu, then press the Option key. Choose Custom Endnote, Custom
Section Endnote, or Custom Footnote. What appears in the menu depends on the
setting in the Footnotes & Endnotes pop-up menu.
In the dialog that appears, type or select a custom mark, and then click OK.
The mark appears and the insertion point moves to the appropriate location in the
document for you to type the note.
Changing Marks for Numbering Footnotes and Endnotes
In a word processing document, you can switch from custom mark numbering to
predefined number formatting and vice versa.
Here are ways to change mark numbering styles:
m To change the numbering format from predefined to custom, Control-click an endnote
or footnote mark, and then choose Use Custom Mark from the shortcut menu.
In the dialog that appears, type or choose a custom mark, and then click OK. The
custom mark replaces the predefined mark.
m To change custom numbering to predefined numbering, Control-click a custom mark,
and then choose Use Automatic Numbering from the shortcut menu.
The mark that replaces the custom mark reflects the number format settings in the
Document pane of the Document Inspector.
52 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 53

Restarting Footnote and Section Endnote Numbering
If you don’t want mark numbers to be continuous, you can restart numbering on each
page or for each section in a word processing document.
To restart mark numbering:
m Choose Restarts on Each Page or Restarts for Each Section from the Numbering pop-
up menu in the Document pane of the Document Inspector.
Using Sections
Use sections to separate your document into distinct parts that use different layouts,
numbering, or other document formatting. You can use sections to make the following
formatting elements different from one part of your document to the next: headers,
footers, page numbering, margins, column layout, and master objects (repeated
background images).
Creating Sections
In a word processing document, a section consists of one or more pages.
Each Pages template consists of one or more predefined sections. Every time you add
pages to the document by using the Sections (word processing) or Pages (page layout)
button in the toolbar, you add a new section.
In a page layout document, each page is one section. You can use the predefined
sections as they are, or you can modify or remove them one page at a time.
In a word processing document, you can use the predefined sections as they are, or
you can create or remove section breaks to define your own sections. To add a page to
a section, add more content and pages will be automatically added, or insert a page
break.
Here are ways to work with section breaks in word processing documents:
m To insert a section break, place the pointer where you want the break to occur, and
then choose Insert > Section Break or click Sections in the toolbar and choose an item
from the list.
When you show invisibles in your document (click View in the toolbar and then choose
Show Invisibles), a section break symbol marks the location of the section break.
The new section has the same formatting as the previous section until you change it.
Changes you make to master objects, headers, footers, or page numbering will apply
only to the section in which you make the changes. See “Using Master Objects
(Repeated Background Images)” on page 57 for information about master objects.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 53
Page 54

m To remove a section break, click at the beginning of the line that follows the break and
press the Delete key.
Managing Sections with the Thumbnail View
You can view miniature versions (thumbnails) of all the pages in a document.
Displaying page thumbnails makes it easy to see all your document’s pages at once,
quickly duplicate or go to a specific page, or change the order of sections in a
document.
Viewing Thumbnails
Use thumbnails to view your Pages document.
Here are ways to view thumbnails:
m To show the thumbnail view in a word processing document, click View in the toolbar
and choose Show Page Thumbnails. In a page layout document, thumbnails are
displayed by default.
To hide the thumbnail view, click View in the toolbar and choose Hide Page
Thumbnails.
m To show facing pages in the thumbnail view, select Facing Pages in the Document
Inspector’s Document pane.
m To go to a specific page, click its thumbnail or click on the page in the document. The
page appears in the main viewing area and the page’s thumbnail is highlighted to
indicate your place in the document.
You can also navigate to a page in a document by clicking the Page button in the lower
left of the document window, typing the specific page number in the Go to Page field,
and then pressing Return.
Adding and Deleting Sections
You can quickly add and delete sections in your Pages document using thumbnails.
Here are ways to add and delete sections:
m To delete a section and its contents, select the section in the thumbnail view, press the
Delete key.
m To copy (or cut) and paste one or more sections, in the thumbnail view select the
sections you want to copy or cut and choose Edit > Copy or Edit > Cut.
Select the section after which you want to paste the sections, and then choose Edit >
Paste.
You can also copy and paste one or more sections by Option-dragging selected
sections to a new destination in the thumbnail view. As you drag, sections shift to
make room for what you’re pasting.
m To paste a copy of selected sections immediately following them, select the sections
and then choose Edit > Duplicate.
54 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 55

Reorganizing Sections
Reorganize your Pages document effectively using thumbnails.
Here are ways to reorganize sections:
m To select one or more sections in the thumbnail view, click a page. A yellow box
surrounds all the page thumbnails that are in the same section as the selected page.
To select multiple adjacent sections, hold down the Shift key, and then select the first
and last section you want.
You can also select multiple sections by dragging. Click to the left or right of a page
thumbnail, and then drag up or down to select adjacent sections.
m To move sections, select the sections, click a page thumbnail in one of the selected
sections, and then drag the sections to a new location in the thumbnail view. Sections
shift to make room for your insertion as you drag.
Defining Section Attributes
When you insert a section break, the new document section inherits all of the
formatting and layout attributes of the previous section. You can change settings such
as page numbering, headers and footers, margins, and master objects for each section.
Many section attributes are set in the Section pane of the Layout Inspector.
Make page numbering
continuous with the previous
section or enter a number to
start renumbering pages.
Make headers and footers and
master objects different on the
first page or alternate pages, or
continue from the previous section.
Make the new section begin
on a left- or right-facing page.
Changing Headers and Footers in a Section
You can change headers and footers to be unique to a section. You can also change
headers and footers within a section.
To change headers and footers:
1 Place the insertion point in the section.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Layout Inspector button, and then click Section.
3 Deselect “Use previous headers and footers.”
4 Type the new header or footer in the header or footer area of your document.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 55
Page 56

Restarting Page Numbering in a Section
You can start a new page-numbering scheme for a section.
To restart page numbering in a document section:
m Click in the section, select “Start at” in the Section pane of the Layout Inspector, and
then specify the number of the first page of the section.
Setting Up a Unique Format for a Section’s First Page
You can make the header, footer, and master objects different for the first page of a
section.
Here are ways to make the first page of a section unique:
m To make the headers and footers on the first page unique, click in the section, select
“First page is different” in the Section pane of the layout inspector, and then change
the header and footer as “Using Headers and Footers” on page 49 describes.
m To place a master object on the first page, follow the instructions in “Using Master
Objects (Repeated Background Images)” on page 57.
Formatting Facing Pages in a Section
You can make headers, footers, and master objects different on facing pages in a
section.
Click in the section to select it, and then format its facing pages.
Here are ways to format facing pages in a selected section:
m To put different headers and footers on alternate pages, select “Left and right pages are
different” in the Section pane of the Layout Inspector.
m To make the first page of the section always start on the left- or right-facing page,
choose Left Page or Right Page from the “Section starts on” pop-up menu. Otherwise,
choose Any Page.
m To place a master object on left or right pages, follow the instructions in “Using Master
Objects (Repeated Background Images)” on page 57.
For more information about facing pages, see “Using Left- and Right-Facing Pages” on
page 47.
Setting Section Margins
If you want to set different margins in different sections of your document, you must
use the Layout Inspector and change the layout margins. To learn about setting layout
margins, see “Defining Layout Margins” on page 47.
Reusing Sections
You can make a section in a document reusable by adding it to the pop-up menu that
appears when you click Pages in the toolbar.
56 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 57

To reuse some or all the pages in a section:
1 Select the section in the thumbnail view.
2 Choose Format > Advanced > Capture Pages.
3 In the dialog that appears, type a name for the page or pages, use the Include pop-up
menu to indicate which pages you want to reuse, and then click OK.
The page or pages are available in the pop-up menu that appears when you click the
Pages button in the toolbar.
Using Master Objects (Repeated Background Images)
You may want to add watermarks, logos, or other background images that appear in
the same spot on every page of your word processing and page layout documents.
These repeated graphics are called master objects.
If your document is divided into sections, you can put different master objects in each
section. Within a section, you can put a different master object on the first page of the
section and on right and left pages in the section. See “Setting Up a Unique Format for
a Section’s First Page” on page 56 and “Formatting Facing Pages in a Section” on
page 56 for more information.
To add a master object:
1 Add an object.
See “Using Floating and Inline Objects” on page 134 for information about floating
objects.
2 Position the object wherever you want it on the page.
3 Choose Format > Advanced > Move Object to Section Master, and make sure that
Format> Advanced > Make Master Objects Selectable does not have a checkmark next
to it.
The selection handles disappear from the object, so you can no longer select it.
To edit or move a master object, you must first make master objects selectable for the
entire document by choosing Format > Advanced > Make Master Objects Selectable if
it has no checkmark in front of it. Selectable master objects look different from other
objects because they have blue selection handles.
Master objects have
blue selection handles.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 57
Page 58

Using a Table of Contents
Using a Word Processing template, Pages can automatically generate a table of
contents for your document. Many Word Processing templates come with a
preformatted table of contents that you can add to your document.
In order to create a table of contents in a word processing document, you need to
consistently use paragraph styles for headings in your document. To learn about styles,
see “About Styles” on page 119 and “Applying Styles” on page 120.
After you create a table of contents, you can format it to change its appearance.
Creating and Updating a Table of Contents
Each table of contents you create using a Word Processing template lists only the
content that follows it, up until the next table of contents. If you want a master table of
contents for the entire document, it must be the only table of contents, and it must be
at the beginning of the document.
To create a table of contents:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Document Inspector button, and then click TOC.
2 Select the checkboxes next to the paragraph styles whose text you want to appear in
the table of contents. For example, if you want all the first-level headings and
subheadings to appear in the table of contents, select the paragraph style that you
used for first-level headings and subheadings.
Select the checkbox in
Select the paragraph
styles whose text you
want to appear in the
table of contents.
58 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
the #’s column if you want
page numbers to appear
with each entry.
Click to update the table
of contents after making
changes to your document.
Page 59

If the styles you select are not used anywhere in the document, you will see a message
that your table of contents is empty when you create the table of contents. If you select
styles that are used very frequently in the document, your table of contents might be
longer than you want.
3 In the #’s column, select the checkboxes of those styles whose entries you want to
include a page number.
4 Place the insertion point at the beginning of the line where you want the table of
contents to appear, and then choose Insert > Table of Contents.
If the Word Processing template you’re working with has a table of contents predefined
for it, click in the page preceding where you want to insert the table of contents, click
Sections in the toolbar, and then choose Table of Contents.
To update the TOC after editing a document, click any entry in the table of contents, or
click Update Now in the TOC pane of the Document Inspector. If you don’t update the
table of contents after changing a document, it updates automatically when you close
the document.
Styling a Table of Contents
You can change the look of text in the table of contents as you would any other text in
a word processing document. You can also add a leader line between an entry and its
associated page number, and you can create new TOC styles.
To change the look of a table of contents entry:
1 In the table of contents, select the entry type that you want to format, such as a first-
level heading. All entries of the same type are automatically selected. They cannot be
individually selected.
2 To open the Styles drawer, click the Styles drawer button in the Format Bar. Notice that
the Styles drawer now displays a list of table of contents styles. The TOC style that
corresponds to the selected entry is also selected.
When a table of contents
entry is selected, the Styles
drawer displays table of
contents styles.
Click the arrow and choose
whether to redefine the
selected style, create a new
style, or just rename it.
Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts 59
Page 60

3 To change the font attributes of the TOC heading, use the Format Bar controls. Other
ways to change font attributes are the Font panel, the Text Inspector, and the Colors
window.
4 To create leader lines from an entry to its associated page number, select the TOC entry,
click the tab in the Tab Stops column in the Tabs pane of the Text Inspector, and then
choose a line style from the Leader pop-up menu.
5 To change the style in the Styles drawer to match the entry, click the arrow to the right
of the style name and choose Redefine Style From Selection.
To create a new TOC style instead, click the arrow to the right of the style name and
choose Create New TOC Style From Selection, and then type a name for the new style.
You can also add a new style by clicking the Add (+) button at the bottom-left corner
of the Styles drawer. In either case, type a name for the new style, and then select
“Apply this new style on creation” if you want it to be applied immediately to the
selected text.
6 To rename the style in the Styles drawer, click the arrow next to the style name and
choose Rename Style. Type a new name for the style.
60 Chapter 3 Working with Document Parts
Page 61

4 Reviewing and Revising
Documents
4
In this chapter, learn how to use change tracking, comments,
and other Pages features that are useful when you review
and revise documents.
Pages includes several features that are especially useful when you’re revising a
document:
 Change tracking: Track changes within a document until you decide which edits you
want to accept or reject.
 Comments: Like margin notes, they allow you to annotate a paragraph without
changing it.
 Color and font changes: Draw attention to particular parts of a document by
modifying color and font style. For example, color the background of several
paragraphs orange, and then use a comment at the beginning of the document to
ask reviewers to help complete the orange paragraphs.
This chapter focuses on change tracking and comments. To learn about emphasizing
text using color and font changes, see “Formatting Text Size and Appearance” on
page 75 and “Adding Accents and Special Characters” on page 81. Instructions for using
color appear in “Setting Character and Paragraph Fill Colors” on page 104.
61
Page 62

Tracked changes made
to your document are
highlighted in the page
thumbnails.
Using Change Tracking
With change tracking you can monitor changes that you or others make to text,
character format, or paragraph style.
Click to start and stop
change tracking.
Use the Change Tracking
control bar to manage and
navigate changes to your
document.
Change bubbles flag edits
made to your document.
When change tracking is on, you can see:
 Text that has been added, deleted, edited, or replaced in the document body, header,
footer, shapes, and text boxes
 Tables, charts, and shapes that have been added or deleted inline
 Paragraph additions, deletions, or replacements
 Text with style changes
 Character and paragraph formatting changes
 New or deleted hyperlinks, Address Book fields, placeholders, or bookmarks
 A new or deleted table of contents
 Edits displayed in thumbnail view
62 Chapter 4 Reviewing and Revising Documents
Page 63

A Tour of Change Tracking
The following scenario illustrates how to use change tracking to consolidate and
respond to changes that two reviewers, Anne and Tom, make to text in a document.
1 With a document open, Tom turns on change tracking by clicking the Track Changes
button in the toolbar.
Click to start and stop
change tracking.
Click Track Changes in
the toolbar and the
Change Tracking control
bar is displayed.
The Comments pane
opens when you use
change tracking.
When change tracking is on, the Change Tracking control bar is visible below the
Format Bar.
Click arrow buttons to navigate
between change bubbles.
Click to pause
change tracking.
Click to accept or reject
selected changes.
Click to open Markup
View pop-up menu.
Click to open the
Action menu.
These controls help manage and navigate changes to your document. For more
information about the Change Tracking control bar see, “Starting, Pausing, and
Stopping Change Tracking” on page 65.
Chapter 4 Reviewing and Revising Documents 63
Page 64

2 Tom saves the document without making changes, closes it, and emails it to Anne. This
version of the document is the original version.
3 Anne opens the document and decides to change some text.
A change bubble flags her changes.
4 Anne saves the document, closes it, and emails it back to Tom.
5 Tom opens the document and reads Anne’s edited version of the text.
In the following examples, you can see Tom’s original document and the edited version
using change tracking.
The document now displays the original text in black, and Anne’s changes in colored
text.
6 When Tom opens the document, both the original text and the colored, edited text are
visible.
Original text is
displayed in black.
The change bubble displays
author name, date and time,
and type of edit.
64 Chapter 4 Reviewing and Revising Documents
Edited text is
displayed in color.
Page 65

7 Tom decides he likes Anne’s revisions and clicks the checkmark in Anne’s change
bubbles.
Click to accept changes.
Click to reject changes.
The change bubbles disappear. The text is no longer tracked as changed and the text is
black.
See “Accepting and Rejecting Edits” on page 67, to learn other ways to accept and
reject changes.
Starting, Pausing, and Stopping Change Tracking
After you start change tracking for a document, changes are tracked until you pause or
stop change tracking.
Here are ways to control change tracking:
m To start change tracking, click the Track Changes button in the toolbar or choose Edit >
Track Text Changes.
When change tracking is turned on, the Comments pane opens and the Change
Tracking control bar is displayed.
m To pause change tracking, click Paused on the Change Tracking control bar. To resume
tracking, click Tracking: On.
Pausing retains all previous changes, but suspends change tracking until you resume it.
Pause change tracking when you want to make changes but don’t want to track them.
For example, you may decide to change the color of all the text in a document or apply
a new text margin to all the text in a section.
m To stop change tracking, click Stop Tracking in the toolbar or choose Edit > Turn Off
Tracking.
You can also choose Turn Off Tracking from the Action menu on the Change Tracking
control bar.
Select to stop
tracking changes.
Chapter 4 Reviewing and Revising Documents 65
Page 66

If your document has changes you haven’t yet accepted or rejected, a dialog asks you
to cancel the operation or accept or reject the edits before continuing.
Controlling Change Tracking Information
Select your change bubble color, review your document using thumbnails, and more
with change tracking.
Choose how edited text is
displayed, author color, and set
change tracking preferences.
Here are ways to control change tracking information:
m To hide text markup, choose Hide Text Markup from the Markup View pop-up menu.
Edits in your document are displayed without author color or markup preferences. To
show text markup, choose Show Text Markup from the Markup View pop-up menu.
m To hide deleted text, choose Hide Deleted Text from the Markup View pop-up menu.
The text previously displayed with a strikethrough is hidden from view. To display
deleted text, choose Show Deleted Text from the Markup View pop-up menu.
Deleted text can be displayed in different text styles. To change how deleted text is
displayed, choose Preferences from the Markup View pop-up menu, and then choose a
text style from the Deleted Text Style pop-up menu.
m To hide change bubbles, choose Hide Change Bubbles from the Markup View pop-up
menu. The Comments pane closes and change bars appear next to edited portions of
your document. To show change bubbles, choose Show Change Bubbles from the
Markup View pop-up menu.
m To select your author color, choose Select Author Color from the Markup View pop-up
menu on the Change Tracking control bar, and then choose your author color.
m To change your author name, markup text style, and deleted text style, choose
Preferences from the Markup View pop-up menu.
m To view your document using thumbnails, click the View button on the toolbar, and
then choose Show Page Thumbnails.
Tracked changes made to your document are highlighted in the page thumbnails.
66 Chapter 4 Reviewing and Revising Documents
Page 67

Accepting and Rejecting Edits
Change tracking allows you to accept or reject edits made to text in your Pages
document.
Here are ways of accepting or rejecting edits:
m To accept an edit, select the edited text and click the Accept Change button in the
change bubble or click the Accept button on the Change Tracking control bar.
m To reject an edit, select the edited text and click the Reject Change button in the
change bubble or click the Reject button on the Change Tracking control bar.
m To accept selected edits, select the text with the editing changes you want to keep,
and then choose Accept Selected Changes from the Action menu in the Change
Tracking control bar.
m To review edits for selection, click a change bubble in the Comments pane or click
anywhere in the document body, and then click the up or down arrow buttons in the
Change Tracking control bar.
Click arrow buttons to navigate
between change bubbles.
Select change bubbles to review
edits made to your document.
m To reject selected edits, select the text with the editing changes you don’t want, and
then choose Reject Selected Changes from the Action menu.
m To accept all edits, choose Accept all Changes from the Action menu.
m To reject all edits, choose Reject all Changes from the Action menu.
Chapter 4 Reviewing and Revising Documents 67
Page 68

Saving with Change Tracking Off
Save a “clean” copy of your document with change tracking turned off and comments
deleted.
Saving a copy of your document with change tracking turned off is useful when you
want a version with all the changes accepted.
Select to save a “clean”
copy of your document.
To save a document with change tracking off:
m With change tracking on, choose Save a Copy as Final from the Action menu in the
Change Tracking control bar. All editing changes made to your document are accepted.
Using Comments
With comments you can annotate a document or parts of it without changing the
document. Comments are useful for making notes to yourself, asking questions of
reviewers, conveying editorial suggestions, and so on.
Comments are
displayed in the
Comments pane and
are anchored to part
of the document.
Identify the part of the document a comment applies to by placing an insertion point
or by selecting words or objects. The part of the document associated with a comment
is called the comment anchor.
Click Comment to add
a comment to your
document.
68 Chapter 4 Reviewing and Revising Documents
Page 69

Here are ways to manage comments:
m To add comments to your document, click Comment in the toolbar or choose Insert >
Comment.
In the comment bubble that appears, type your comment. The size of the comment
bubble grows and shrinks to accommodate your text.
m To change a comment, click in the comment bubble and edit it just as you would text
and objects elsewhere in your document.
You can use character and paragraph styles to modify the appearance of text.
m To delete a comment, click the Delete button in the right corner of the comment
bubble.
Click to delete
the comment.
m To view comments, click the View button, and then choose Show Comments.
If change tracking is on, all comments and change bubbles associated with the current
version are visible in the Comments pane.
If comments are not visible, inserting one displays all comments.
m To hide comments, click the View button and then choose Hide Comments.
m To print comments, choose File > Print. Printed pages are adjusted to make room for
the comments.
Chapter 4 Reviewing and Revising Documents 69
Page 70

5 Working with Text
5
This chapter describes how to add and modify the
appearance of text, including lists, in text boxes, table cells,
and shapes.
Adding Text
Add text by typing in a blank word processing document, replacing placeholder text,
using text boxes and lists, placing text in shapes, and more.
 To learn about working with placeholder text in templates and Address Book fields,
see “Using Placeholder Text” on page 70 and “Using Address Book Fields” on
page 220.
 To add different text styles, or create your own, see “About Styles” on page 119.
 To learn how to add new template pages, see “Adding New Template Pages” on
page 72.
 To delete pages from your document, see “Deleting Pages” on page 73.
 To learn how to delete, copy, and paste text, see “Deleting, Copying, and Pasting
Text” on page 74.
 To add text to a text box or shape, see “Using Text Boxes, Shapes, and Other Effects
to Highlight Text” on page 100.
 To add text that’s formatted as a list, see “Using Bulleted, Numbered, and Ordered
Lists (Outlines)” on page 95.
 To learn how to add text to table cells, see “Working with Text in Cells” on page 175
or “Working with Content in Table Cells” on page 175.
70
Using Placeholder Text
Templates contain placeholder text, which shows you what text will look like and where
it will be placed in the finished document. Most placeholder text appears in Latin (for
example, lorem ipsum) in the document body, text boxes, headers, and elsewhere.
Other predefined text, such as the title of a newsletter, appears in the language you’re
using.
Page 71

You select the placeholder text, and then type your own text to replace it. The text you
type keeps the same style and formatting as the placeholder text. If you don’t want to
use the style and size of fonts the placeholder text uses, you can change the selected
text by clicking the font family and font size controls in the Format Bar.
Placeholders in Main Text Areas
When you click placeholder text in a document template, the entire text area is
highlighted.
Placeholder text
The entire text area is
selected when you click.
When you type, the placeholder text disappears and is replaced by whatever text you
are typing. The text you type behaves like regular text.
Placeholders in Text Boxes
Some placeholder text is contained in text boxes to preserve formatting. When you
click placeholder text that’s in a text box, a rectangular, gray border appears around it
when layout view is turned on. To turn layout view on, Click View in the toolbar and
choose Show Layout.
To select the placeholder text inside a text box:
m Click once to select the text box, and then click to select the text inside the box.
Text box placeholder text is part of the template’s default design. To preserve the
design, be careful not to press Delete after you select the text box or you’ll remove the
text box from the page. If you accidentally delete a text box, press Command-Z (the
shortcut for undo).
Chapter 5 Working with Text 71
Page 72

Placeholders in Tables
Some tables contain placeholder text. When you select text that’s inside a table cell, a
highlighted rectangle appears around it.
Individual table cell
selected for editing.
To select the placeholder text inside a table:
m Click once to select the table, and then double-click to select an individual cell and its
placeholder text.
The text inside the cell is selected for editing when you select the individual cell. You
can tell it’s placeholder text if it is highlighted; otherwise, it’s regular text.
Table placeholder text is part of the template’s default design. To preserve the design,
be careful not to press Delete after you select the table or you’ll remove it from the
page. If you accidentally delete a table, press Command-Z.
You can also add text to table cells that don’t contain placeholder text. See “Working
with Content in Table Cells” on page 175 for instructions.
Placeholders in Columns
Occasionally, templates may contain placeholder text formatted in columns. It may be
easier to work with text columns if the document layout is visible. To show the
document layout, click View in the toolbar and choose Show Layout.
To select the placeholder text inside a column:
m Click the placeholder text in the column.
Adding New Template Pages
Each page of a Pages template has a unique design. You can choose to use the page
designs shown when the document first opens. Or, if the page designs don’t meet your
needs, you can choose from additional pages designed to fit the template.
Adding new template pages lets you quickly add pages that already contain text,
images, tables, charts, or other formatting options you want to use.
To add a new template page:
1 Click in the section you want the new page to follow. A section is a group of one or
more pages that have the same layout, numbering, and other document attributes. A
chapter is an example of a section.
72 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 73

Choose additional pages
from the Sections or
Pages pop-up menu.
2 Click the Sections (Word Processing template) or Pages (Page Layout template) button
in the toolbar, and choose a page type to add to your document.
See “Using Sections” on page 53 for more information about working with sections.
Deleting Pages
There are several techniques for deleting entire pages.
Here are ways to delete a page:
m To remove a page without deleting other pages in its section, delete all the text and
objects on the page or select a thumbnail and press Delete.
m To delete a section and all the pages in it, click View in the toolbar and then choose
Show Page Thumbnails. Select the section in the thumbnail view and press the Delete
key. Pages confirms which pages will be deleted. Click Delete.
m You can also delete a section by clicking in a paragraph in the section and choosing
Edit > Delete Pages. Pages confirms which pages will be deleted. Click Delete.
For more information about sections, see “Using Sections” on page 53.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 73
Page 74

Deleting, Copying, and Pasting Text
The Edit menu contains commands that help you perform text editing operations.
Here are ways to edit text:
m To copy (or cut) and paste text, select the text and choose Edit > Copy or Edit > Cut.
Click where you want to paste the text.
To have the copied text retain its style formatting, choose Edit > Paste.
To have the copied text take on the style formatting of the text around it, choose Edit >
Paste and Match Style.
m To delete text, select the text and choose Edit > Delete or press the Delete key.
If you accidentally delete text, choose Edit > Undo to restore it.
When you use the Copy or Cut command, the selected text is placed in a holding area
called the Clipboard, where it remains until you choose Copy or Cut again or you turn
off your computer. The Clipboard holds the contents of only one copy or cut operation
at a time.
To avoid unintentionally changing a document’s format by removing formatting
characters in addition to text, it’s a good idea to display formatting characters
(invisibles) before cutting or deleting text. To show invisibles, click View in the toolbar
and then click Show Invisibles.
Selecting Text
Before you format or perform other operations on text, you need to select the text you
want to work with.
Here are ways to select text:
m To select one or more characters, click in front of the first character and drag across the
characters you want to select.
m To select a word, double-click the word.
m To select a paragraph, click three times in the paragraph.
m To select all text in a document, choose Edit > Select All.
m To select blocks of text, click the start of a text block, and then click the end of another
text block while holding down the Shift key.
m To select from the insertion point to the beginning of the paragraph, press the Up
Arrow key while holding down the Shift and Option keys.
m To select from the insertion point to the end of the paragraph, press the Down Arrow
key while holding down the Shift and Option keys.
m To extend the selection one character at a time, press the Left Arrow or Right Arrow key
while holding down the Shift key.
74 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 75

m To extend the selection one line at a time, press the Up Arrow or Down Arrow key
while holding down the Shift key.
m To select multiple words or blocks of text that are not next to each other, select the first
amount of text you want, and then select additional text while holding down the
Command key.
Formatting Text Size and Appearance
You can do text formatting using the Format Bar, the Pages menus, the Text Inspector,
and the Font panel.
You can do basic text formatting using the Format Bar and the Format menu. If you
want to apply advanced formatting to text, use the Font panel and Text Inspector.
Using the Format Bar to Format Text
The Format Bar makes changing the size and appearance of text in a text box, shape, or
comment quick and easy. When text in a text box, shape, or comment is selected, you
can change the font style and size, adjust the color of the text and its background,
make text bold or italics or underlined, align text, and set line spacing.
Here’s what the Format Bar looks like when text is selected. The first four controls are
also available in the Format Bar when text in a table is selected.
Set color of text.
Change font typeface,
style, and size.
Set text background color.
Make text bold, italics,
or underlined.
Using the Format Menu to Format Text
The items in the Font submenu of the Format menu give you basic control over the size
and appearance of text.
Making Text Bold or Italic Using the Menus
You can make characters bold or italic.
To make text bold or italic:
1 Select the text you want to make bold or italic, or click where you want to type new
text.
2 Choose Format > Font > Bold. Or choose Format > Font > Italic.
Some fonts contain several bold and italic typefaces. To choose from a variety of bold
and italic typefaces, use the Font panel. See “Using the Font Panel to Format Text” on
page 77.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 75
Page 76

Creating Outlined Text Using the Menus
You can change text to appear as a stenciled outline.
To create outlined text:
1 Select the text you want to make outlined, or click where you want to type new text.
2 Choose Format > Font > Outline.
Outlined text you create in Pages may look different if the document is opened in
another application. If you plan to share a document that contains outlined text with
people who don’t have Pages installed on their computers, export the document as a
PDF file and then share this file with others.
Underlining Text Using the Menus
You can underline text and then format the underline to change the underline style or
color.
To underline text:
1 Select the text you want to underline, or click where you want to type new text.
2 Choose Format > Font > Underline.
To modify the underline style or color, click Fonts in the toolbar and use the Text
Underline button in the Font panel. See “Using the Font Panel to Format Text” on
page 77.
Many templates include an underline character style. To display the character styles
defined for your document, click the Character Styles button in the Format Bar. Select
the text you want to underline, and then choose the underline character style from the
character styles displayed.
Changing Text Size Using the Menus
You can change the point size of text to make the text larger or smaller.
To change the size of selected text:
1 Select the text you want to resize.
2 To change the text size in 1-point increments, choose Format > Font > Bigger. Or
choose Format > Font > Smaller.
You can also add Bigger and Smaller icons to the toolbar. Choose View > Customize
Toolbar, drag the icons to the toolbar, and then click Done.
To specify a precise size for selected text, click Fonts in the toolbar and use the Size
controls in the Font panel. See “Using the Font Panel to Format Text” on page 77.
76 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 77

Making Text Subscript or Superscript Using the Menus
You can raise or lower text from its baseline.
To make text subscript or superscript:
1 Select the text you want to raise or lower, or click where you want to type new text.
2 To create a subscript or superscript that has a smaller font size than the text it
accompanies, choose Format > Font > Baseline > Subscript. Or choose Format > Font >
Baseline > Superscript.
3 To raise or lower text without reducing its font size, choose Raise or Lower from the
Baseline submenu.
4 To restore text to the same baseline as the body text, choose Use Default from the
Baseline submenu.
You can add Subscript and Superscript icons to the toolbar. Choose View > Customize
Toolbar, drag the icons to the toolbar, and then click Done.
To specify a precise amount to raise or lower text, use the Text Inspector. Click Inspector
in the toolbar, click Text, click More, and then use the Baseline Shift controls.
Changing Text Capitalization Using the Menus
You can quickly make blocks of text all uppercase or lowercase, or format text as a title.
To change text capitalization:
1 Select the text you want to change, or click where you want to type new text.
2 Choose Format > Font > Capitalization and choose an option from the submenu.
Choose All Caps to change the text to capitals.
Choose Small Caps to change the text to smaller capitals with larger capitals for
uppercase letters.
Choose Title to change the text to a title format, which capitalizes the first letter of each
word.
Choose None to change text from all capitals to initial caps. Uppercase characters, such
as the first word of each sentence, are capitals but the rest are lowercase.
Using the Font Panel to Format Text
The Mac OS X Font panel gives you access to all the fonts installed on your computer. It
provides a preview of the available typefaces (such as bold and italic) and sizes for each
font. The buttons in the Font panel let you add underlines, strikethrough lines, color,
and shadow to text. You can even change the background page color in the Font
panel.
For information on installing fonts, creating and managing font collections, or
troubleshooting font-related issues, see Mac Help.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 77
Page 78

Create interesting
text effects using
these buttons.
The Action menu
To open the Font panel:
m Click Fonts in the toolbar.
Preview the selected typeface (you
might need to choose Show Preview
from the Action menu).
Apply a shadow to
selected text. Modify
the shadow using the
opacity, blur, offset, and
angle controls.
Select a font size to apply
to selected text in your
document.
Find fonts by typing
a font name in the
search field.
Select a typeface to
apply to selected text
in your document.
You can change the appearance of any text in your document by selecting it and then
selecting options in the Font panel. When you make formatting changes in the Font
panel, the selected text changes right away, so you can try different formatting options
and quickly see what looks best.
Here is a summary of what the text effects buttons do, from left to right:
 The Text Underline pop-up menu lets you choose an underline style (such as single
or double).
 The Text Strikethrough pop-up menu lets you choose a strikethrough style (such as
single or double).
 The Text Color pop-up menu lets you apply a color to text.
 The Document Color pop-up menu lets you apply a color behind a paragraph.
 The Text Shadow button applies a shadow to selected text.
 The Shadow Opacity, Shadow Blur, Shadow Offset, and Shadow Angle controls
control the appearance of the shadow.
If you don’t see the text effects buttons, choose Show Effects from the Action pop-up
menu in the lower-left corner of the Font panel.
78 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 79

Making the Font Panel Easy to Use
If you frequently use the Font panel, there are several techniques for saving time.
Here are tips for using the Font panel:
m To quickly locate fonts you frequently use, organize them into font collections. Click the
Add (+) button to create a font collection, and then drag a typeface into the new
collection.
m To make it easy to change fonts often, leave the Font panel open. If it takes up too
much space on your screen, you can shrink it by dragging its resize control (the
bottom-right corner of the panel), so that only the font families and typefaces in your
selected font collection are visible. To close the panel, click the Fonts button again or
the Close button in the upper-left corner.
Changing Fonts Using the Font Panel
The Font panel gives you extensive control over fonts. Use size controls and
typography settings to customize the appearance of your text.
To modify the font of selected text:
1 Click Fonts in the toolbar.
2 In the Font panel, select a font style in the Family column and then select the typeface
in the Typeface column.
If you don't see all the font families you know are installed on your computer, select All
Fonts in the Collections column or type the name of the font you are looking for in the
search field at the bottom of the Font panel.
A preview of the selected font appears in the preview pane at the top of the Font
panel. If you don't see a preview pane, choose Show Preview from the Action pop-up
menu in the lower-left corner of the Font panel.
3 Adjust the font size using the size slider or other size controls.
4 Adjust the typography settings of the selected font by choosing Typography from the
Action pop-up menu. In the Typography window, click the disclosure triangles to see
and select the different typography effects that are available for the selected font.
Different fonts have different typography effects available. See “Using Advanced
Typography Features” on page 83 for more information.
Changing Underlining Using the Font Panel
You can use the Font panel to change the appearance of underlines.
To modify underlining of text:
1 Click Fonts in the toolbar.
2 Click the Text Underline button in the Font panel (the first button on the left), and
choose None, Single, or Double from the pop-up menu.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 79
Page 80

3 To change the underline color, choose Color from the Text Underline pop-up menu,
and then select a color in the Colors window.
Adding a Strikethrough to Text Using the Font Panel
You can mark text with a strikethrough line, and make the line’s color different from the
text color.
To add a strikethrough to selected text:
1 Click Fonts in the toolbar.
2 Click the Text Strikethrough button (the second button from the left), and choose
None, Single, or Double from the pop-up menu. A single or double strikethrough
appears through the selected text in the same color as the text.
3 To change the strikethrough color, choose Color from the Text Strikethrough pop-up
menu, and then select a color in the Colors window. The strikethrough takes on the
color you select in the Colors window, but the text remains its original color.
Many templates include a strikethrough character style. To display the character styles
defined for your document, click the Character Styles button in the Format Bar. Select
the text you want to strike through, and then choose the strikethrough character style
in the Styles drawer.
Changing Text Color Using the Font Panel
Changes made to text color in the Font panel will override text color changes made in
the Text Inspector, and vice versa. (To read about changing color using the Text
Inspector, see “Changing Text Color” on page 89.)
To modify the color of selected text:
1 Click Fonts in the toolbar.
2 Click the Text Color button menu in the Font panel (the third button from the left), and
then select a color in the Colors window. See “Using the Colors Window” on page 148
for instructions.
Changing the Paragraph Background Color Using the Font Panel
You can use the Font panel to add a color behind a paragraph.
To modify the background color of a selected paragraph:
1 Click Fonts in the toolbar.
2 Click the Document Color button in the Font panel (the fourth button from the left),
and then select a color in the Colors window. See “Using the Colors Window” on
page 148 for instructions.
You can also modify paragraph background color in the Text Inspector, as described in
“Setting Character and Paragraph Fill Colors” on page 104.
80 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 81

Creating Shadows on Text Using the Font Panel
You can use the Font panel to create and format shadows on text.
To define shadows on selected text:
1 Click Fonts in the toolbar.
2 Click the Text Shadow button in the Font panel (the fifth button from the left).
3 Drag the shadow opacity slider (the first slider on the left) to the right to make the
shadow darker.
4 Drag the shadow blur slider (the middle slider) to the right to make the shadow more
diffuse.
5 Drag the shadow offset slider (the third slider) to the right to separate the shadow from
the text.
6 Rotate the Shadow Angle wheel to set the direction of the shadow.
You can also set text shadows in the Graphic Inspector, as described in “Adding
Shadows” on page 144.
Adding Accents and Special Characters
If you need to type characters with accent marks (such as ü), mathematical symbols,
arrows, or other special characters, you can use the International preferences pane or
the Character Palette. You can also see where characters are located on keyboards used
for other languages by using the Keyboard Viewer (for example, you can see how the
keys on an Italian keyboard are laid out). All of these are built-in tools of Mac OS X.
Adding Accent Marks
You can use the Keyboard Viewer available in System Preferences to add accent marks
to characters.
To add accent marks:
1 Choose Apple > System Preferences and click International.
2 Click Input Menu, then select the checkbox next to Keyboard Viewer.
3 Choose Show Keyboard Viewer from the Input menu on the right side of the menu bar
(the one that looks like a flag or alphabetical symbol).
The Keyboard Viewer shows the characters for your keyboard. (If you've selected a
different keyboard layout or input method in the Input menu, it shows the characters
for the selected keyboard layout.) For example, if U.S. is chosen in the Input menu, you
see the characters that appear on a U.S. keyboard in the Keyboard Viewer.
4 To see the different accent marks that you can type highlighted in the Keyboard
Viewer, press Option, or the Option and Shift keys.
The accent mark keys appear with white outlines. Depending on your keyboard, you
may not need to press any of the modifier keys to see the accent keys.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 81
Page 82

5 Place the insertion point in your document where you want to type.
6 Press the modifier key you pressed in step 4 (Shift, Option, Option-Shift, or none) and
press the key on your keyboard that is in the same place as the accent you see in the
Keyboard Viewer. Then release the modifier key and press the key for the character you
want to accent.
The accent key modifies the key you type next. For example, on a U.S. keyboard, to
make the é appear, press Option and E (the accent key), then press E (the letter on
which you want that accent to appear).
Viewing Keyboard Layouts for Other Languages
You can use the Keyboard Viewer available in System Preferences to see where
characters are located on keyboards used for other languages.
You must have fonts installed for the language you want to see in the Keyboard Viewer.
To see keyboard layouts for different languages:
1 Choose Apple > System Preferences and click International.
2 Click Input Menu, then select the checkbox next to Keyboard Viewer.
3 To see the character layout on keyboards used in different countries, select the On
checkbox next to the country's keyboard layout or input method.
4 Choose Show Keyboard Viewer from the Input menu on the right side of the menu bar
(the one that looks like a flag or alphabetical character).
The Keyboard Viewer shows the characters for the keyboard layout or input method
selected in the Input menu. For example, if U.S. is chosen in the Input menu, you see
the characters that appear on a U.S. keyboard in the Keyboard Viewer.
5 To see the keyboard layout for a different country, choose its keyboard layout from the
Input menu.
Typing Special Characters and Symbols
Using the Mac OS X Character Palette, you can insert special characters, such as
mathematical symbols, letters with accent marks, arrows and other “dingbats,” and
more. You can also use this palette to enter Japanese, Traditional Chinese, Simplified
Chinese, and Korean characters, as well as characters from other languages.
To insert special characters or symbols:
1 Place the insertion point where you want the special character or symbol to appear.
2 Choose Edit > Special Characters to open the Character Palette (or choose Characters
from the Action pop-up menu in the lower-left corner of the Font panel).
3 Choose the type of characters you want to see from the View pop-up menu at the top
of the Character Palette. If you don't see the View menu, click the button in the upperright corner of the window to show the top portion of the window. Click this button
again to hide the top portion of the window.
82 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 83

4 Click an item in the list on the left to see the characters that are available in each
category.
5 Double-click the character or symbol on the right that you want to insert into your
document, or select the character and click Insert.
If the character or symbol has variations, they appear at the bottom of the window
when you click the Character Info triangle or Font Variation triangle at the bottom of
the palette. Double-click one to insert it in your document.
If the character doesn’t appear in your document, Pages may not support that
character.
Using Smart Quotes
Smart quotes are opening and closing quotation marks that are curly; the opening
quotation marks are different from the closing marks. When you don’t use smart
quotes, the marks are straight and the opening and closing marks don’t differ.
Smart quotes
Straight quotes
To use smart quotes:
m Choose Pages > Preferences, click Auto-Correction, and then select “Use smart quotes.”
Using Advanced Typography Features
Some fonts, such as Zapfino and Hoefler, have advanced typography features, which let
you create different effects. If you are using a font in a text box that has different
typography effects available, you can change many of the effects in the Font submenu
of the Format menu. For example, you may be able to adjust the following:
 Tracking: Place characters closer together or farther apart.
 Ligature: Use or leave out stylish flourishes between letters or at the end or
beginning of lines that combine two or more text characters into one glyph.
Ligature not used
Ligature used
In the Ligature submenu, choose Use Default to use ligature settings specified in the
Typography window for the font you’re using, choose Use None to turn off ligatures
for selected text, or choose Use All to turn on additional ligatures for the selected
text.
 Baseline: Move text higher or lower than the text around it.
 Capitalization: Convert characters to all capital letters, small capital letters, or initial
capital letters (title style).
Chapter 5 Working with Text 83
Page 84

Advanced typography features are available in the Typography window.
To open the Typography window:
1 Click Fonts in the toolbar.
2 In the Font panel, choose Typography from the Action pop-up menu (in the lower-left
corner).
To enable ligatures for an entire document, Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the
Document Inspector button, click Document, and then select “Use ligatures.” To turn off
ligatures for a specific paragraph, click in the paragraph, open the Text Inspector, click
More, and then select “Remove ligatures.”
Adjusting Font Smoothing
If the fonts on your screen look fuzzy, blurry, or jagged, you may want to adjust the font
smoothing style or change the text size at which Mac OS X starts to smooth fonts.
To smooth the fonts on your screen:
1 Open System Preferences and click Appearance.
2 Choose a font smoothing style from the pop-up menu at the bottom. Depending on
the type of display you have, you may notice only small or no differences between
smoothing styles.
3 If you plan to use small font sizes in your document, choose a point size from the “Turn
off text smoothing for font sizes” pop-up menu. When text smoothing (or “antialiasing”)
is on, smaller fonts can be harder to read.
Setting Text Alignment, Spacing, and Color
The primary tools for adjusting text attributes are the Format Bar and the Text
Inspector. You can make some horizontal alignment adjustments (such as centering
text or aligning it on the left) by using the Format menu.
Color and alignment controls are also available on the Format Bar when text is selected.
When text in a text box, comment, or shape is selected, you can set the color of text
and its background, align text, and set line spacing.
Set color of text and
its background.
84 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Align text horizontally.
Set line spacing.
Page 85

The Text Inspector
When you’re working with text in a table cell, you can use the Format Bar to align text
both horizontally and vertically in the cell.
Align text horizontally.
Align text vertically.
The Text pane of the Text Inspector gives you access to more alignment and line
spacing settings.
Horizontal alignment buttons:
Click to align selected text left, right,
center, or to the left and right, or
special table cell alignment.
button.
Click to change the
color of selected text.
Character and
line spacing:
Adjust character, line,
and paragraph spacing
for selected text.
Vertical alignment buttons:
Click to align text to the top,
center, or bottom of a text box,
shape, or table cell.
Drag to adjust the amount of space
between text and the inside borders
of text boxes, table cells, and shapes.
To open the Text pane of the Text Inspector:
m Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Text.
Aligning Text Horizontally
You can change the alignment of paragraphs in a page, column, table cell, text box, or
shape so that text is aligned to the left or right border, centered, or aligned on both left
and right (justified).
Use the Alignment buttons in the Format Bar to quickly change the alignment of text
in your document. To change the alignment of text, select the text, and then click the
Alignment buttons in the Format Bar.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 85
Page 86

To align text left, center, right, or justified using the Text Inspector:
1 Select the text you want to change.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Text.
3 Click one of the five horizontal alignment buttons, located to the right of the color well.
From left to right, these buttons have the following effects.
The Align Left button places each line of text against the left margin of the object.
The Center button sets the center of each line of text at the center of the object.
The Align Right button sets each line of text against the right margin of the object.
The Justify button spaces characters in each line so that the lines reach both the left
and right margins of the object.
The Auto Align Table Cell button left justifies text and right justifies numbers in a table
cell.
The first four alignment buttons are available on the Format Bar when text is selected.
Five horizontal alignment buttons are also available on the Format Bar when a table
cell is selected.
You can also align text horizontally by choosing Format > Text > Align Left, Center, Align
Right, Justify.
If you want to indent the first line of text in a paragraph, or learn how to undo
paragraph indenting, see “Setting Indents” on page 94.
Aligning Text Vertically
You can change the alignment of paragraphs in a table cell, text box, or shape so that
text is aligned to the top or bottom border or centered between them.
To align text to the top, center, or bottom of a text box, table cell, or shape:
1 Select the text box, table cell, or shape whose alignment you want to change.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Text.
3 Click one of the three vertical alignment buttons, located below Color & Alignment, to
align text to the top, middle, or bottom of the table cell, text box, or shape.
The vertical alignment buttons are also available on the Format Bar when you’re
working with a table cell.
86 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 87

Adjusting the Spacing Between Lines of Text
You can increase or decrease the distance between lines of text.
Use the Line Spacing control in the Format Bar to quickly change the distance between
lines of text. To adjust line spacing, select the text, and then click the Line Spacing
control in the Format Bar.
To adjust spacing using the Text Inspector:
1 Select the text you want to change.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Text.
3 Move the Line slider left to decrease spacing or right to increase it.
To specify a precise line spacing value, type a point value in the Line field, or click the
Up Arrow or Down Arrow next to the field.
4 Choose a line spacing option from the Line spacing pop-up menu that appears when
you click the text below the line field.
Line field:
Type a value (or click the
arrows) to specify the space
between lines of text in a
paragraph.
Line spacing pop-up menu:
Click the text below the Line
field and choose a line
spacing option.
Standard line spacing (Single, Double, Multiple): The space between lines is proportional
to font size. Use this when the relative distance between ascenders (parts of letters that
extend to the top of the line) and descenders (parts of letters that extend below the
line) should remain fixed. Single sets line spacing to single-spaced, and Double sets it
to double-spaced. Multiple lets you set line spacing values between single and double,
or greater than double.
At Least: The distance from one line to the next will never be less than the value you
set, but it may be larger for larger fonts in order to prevent overlapping text lines. Use
this when the distance between lines should remain fixed, but overlap is not desired if
the text gets large.
Exactly: The distance between the baselines.
Between: The value you set increases the space between the lines, instead of increasing
the height of the lines. By contrast, double-spacing doubles the height of each line.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 87
Page 88

Line spacing can also be controlled by using the Line Spacing pop-up menu on the
Format Bar when text is selected.
Click to change the amount of
space between lines of text.
Adjusting the Spacing Before or After a Paragraph
You can increase or decrease the spacing before or after paragraphs.
Use the Line Spacing control in the Format Bar to quickly change the distance before or
after paragraphs. To adjust spacing before or after paragraphs, select the text, and then
click the Line Spacing control in the Format Bar.
To adjust the amount of space before or after a paragraph:
1 Select the paragraphs you want to change.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Text.
3 Drag the Before Paragraph or After Paragraph slider. You can also specify a precise value
(5 pt, for example) in the text boxes.
If the Before Paragraph or After Paragraph values for adjacent paragraphs aren’t equal,
the higher spacing value will be used. For example, if the current paragraph’s Before
Paragraph value is 12 points and the paragraph preceding it has an After Paragraph
value of 14 points, the spacing between paragraphs will be 14 points.
Spacing before a paragraph does not appear if the paragraph is the paragraph in a text
box, shape, or table cell.
To set spacing around text in boxes, shapes, and table cells, use the Inset Margin
control, described in “Changing the Inset Margin of Text in Objects” on page 95.
Adjusting the Spacing Between Characters
You can increase or decrease the amount of space between characters.
To adjust the amount of space between characters:
1 Select the text you want to change, or click where you want to type new text.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Text.
3 Drag the Character slider or specify a new percentage in the Character field.
You can also adjust the space between selected characters by choosing Format >
Font > Tracking and choosing an option from the submenu.
88 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 89

Changing Text Color
You can change text color by using the Format Bar, the Text Inspector, and the Font
panel. Changes you make with any of these tools overrides color changes already made
with the other tools.
Here are ways to change text color:
m Click the Text Color or Text Background color well in the Format Bar. In the color matrix
that appears, select a color by clicking it or click Show Colors to open the Colors
window for additional color options.
m Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, click Text, and then click
the color well. The Colors window opens.
“Using the Colors Window” on page 148 provides instructions for using the Colors
window.
Setting Tab Stops to Align Text
You can align text at specific points by setting tab stops in a document, text box, table
cell, or shape. When you press the Tab key (or Option-Tab when you’re working in a
table cell), the insertion point (and any text to the right of it) moves to the next tab
stop, and text you type starts at that point.
You can work with tab stop settings by manipulating the tab symbols on the horizontal
rulers. You can see symbols for existing tab stops on the horizontal ruler when you click
View in the toolbar, choose Show Rulers, and then select some text on a page.
Note: Don’t use these instructions to set tab stops in lists. See “Using Bulleted,
Numbered, and Ordered Lists (Outlines)” on page 95 for information about indenting
items in lists.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 89
Page 90

Setting Tab Stops Using the Horizontal Ruler
You can work with tab stop settings by manipulating the tab symbols on the horizontal
rulers. You can see symbols for existing tab stops on the horizontal ruler when you click
View in the toolbar, choose Show Rulers, and then select some text on a page.
Left tab
Center tab
Right tab
Blue tab symbols appear on
the horizontal ruler when
you select tabbed text.
Decimal tab
To set tab stops in lists, see “Using Bulleted, Numbered, and Ordered Lists (Outlines)” on
page 95 for information about indenting items in lists.
Here are ways to work with rulers:
m To show or hide rulers, click View in the toolbar and choose Show Rulers or Hide Rulers.
m To change the units of measure in the rulers, choose Pages > Preferences, click General,
and choose an item from the Ruler Units pop-up menu.
m To display measurements as a percentage of the distance across the page, choose
Pages > Preferences, click General, and then select “Display ruler units as percentage.”
m To place the ruler’s horizontal origin point at the center of the page, choose Pages >
Preferences, click General, and then select “Place origin at center of ruler.”
m To display the vertical ruler in a word processing document, choose Pages >
Preferences, and then select “Enable vertical ruler in word processing documents.”
When you change ruler settings in Pages preferences, the new settings apply to all
documents viewed in Pages until you change the settings again.
Setting a New Tab Stop Using the Horizontal Ruler
You use the horizontal ruler to add a new tab stop.
To create a new tab stop:
1 Click View in the toolbar and choose Show Rulers.
2 Click the horizontal ruler to place a tab symbol where you want to set the tab stop.
3 Control-click the tab symbol and choose an option from the shortcut menu.
Choose from among
these tab types.
Left Tab: Aligns the left side of text with the tab stop.
Center Tab: Places the center of text at the tab stop.
90 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 91

Right Tab: Aligns the right side of text with the tab stop.
Decimal Tab: For numbers, aligns the decimal character (such as a period or comma)
with the tab stop. (You can specify the character to serve as the decimal tab character;
see “Setting a New Tab Stop Using the Text Inspector” on page 92.)
You can also double-click the tab symbol repeatedly until the type of tab you want
appears.
Changing a Tab Stop Using the Horizontal Ruler
You can change the location and type of tab stops using the horizontal ruler.
To change tab stops:
1 Click View in the toolbar and choose Show Rulers.
2 To move a tab stop, drag its blue tab symbol in the horizontal ruler.
3 To change the tab to a different type, Control-click the tab symbol and choose an
option from the shortcut menu. Or double-click the tab symbol in the ruler repeatedly
until the type of tab you want appears.
Deleting a Tab Stop Using the Horizontal Ruler
You can quickly remove a tab stop using the horizontal ruler.
To delete a tab stop:
1 Click View in the toolbar and choose Show Rulers.
2 Drag the tab off the horizontal ruler.
Setting Tab Stops Using the Text Inspector
Every document has built-in tab stops, usually spaced half an inch apart across the
page.
In the Tabs pane of the Text Inspector, you can change the default tab spacing or the
decimal tab character for the entire document. You can also set additional tab stops in
any paragraph, or add a leader line, so that when you press the Tab key, a dashed or
dotted line extends across the tabbed distance. This is useful, for example, for inserting
dashed lines between a chapter title and its page number in a table of contents.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 91
Page 92

To open the Tabs pane of the Text Inspector:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar.
2 Click the Text Inspector button, and then click Tabs.
Set how far you want
the first line of each
paragraph to indent.
Type a new character
to change the character
used for decimal tabs.
If you want to indent a paragraph
relative to the page margins,
specify how far to indent it.
Set the default distance
between tabs.
For a tab stop selected in the
Tab Stops column, select how
you want the text to align.
Choose a leader line for any
tab stop selected in the Tab
Stops column.
Add or remove tab stops
from the column.
Setting the Default Distance Between Tabs
Although the default distance between tab stops is usually a half inch, you can change
the distance using the Text Inspector.
To change how far apart tabs are by default:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Tabs.
2 Use the Default Tabs field to set the default distance between tabs.
Setting a New Tab Stop Using the Text Inspector
You can use the Tab pane of the Text Inspector to add a new tab stop.
To create a new tab stop:
1 In the document, click where you want to create a new tab stop.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Tabs.
3 Click the Add (+) button in the bottom-left corner of the Tabs pane of the Text
Inspector. The new tab stop appears in the Tab Stops column.
4 To change the tab stop location, double-click the tab stop in the Tab Stops column and
type a new value.
92 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 93

5 With the tab stop selected, select an Alignment option to indicate how you want text
to align at the tab stop.
Left: Aligns the left side of text with the tab stop.
Center: Places the center of text at the tab stop.
Right: Aligns the right side of text with the tab stop.
Decimal: For numbers, aligns the decimal character (such as a period or comma) with
the tab stop.
6 To specify a decimal tab character for the document, type a new character in the
Decimal Tab Character field.
7 If you want to add a dashed or dotted line to the tab, choose a line style from the
Leader pop-up menu. Otherwise, choose None.
Changing a Tab Stop Using the Text Inspector
You can change the location and type of tab stops and the decimal tab character for
the document using the Text Inspector.
To change tab stops:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Tabs.
2 To change the tab stop location, double-click the tab stop in the Tab Stops column and
type a new value.
3 To change the tab to a different type, select an Alignment option.
4 To change the decimal tab character for the document, type a new character in the
Decimal Tab Character field.
5 To change the leader line setting, choose an option from the Leader pop-up menu.
6 To change the default spacing between tabs, use the Default Tabs field.
Deleting a Tab Stop Using the Text Inspector
You can quickly remove a tab stop using the Text Inspector.
To delete a tab stop:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Tabs.
2 Select the tab stop you want to delete in the Tab Stops column, and then click the
Delete (–) button.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 93
Page 94

Setting Indents
You can modify the amount of space between the edge of a paragraph and the
document margins. You can also adjust the amount of space between text and the
inside border of a text box, shape, or table cell.
Setting Indents for Paragraphs Using the Text Inspector
You can use the Text Inspector to set indents for paragraphs.
To set indents using the Text Inspector:
1 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Tabs.
2 Select the paragraph or paragraphs you want to change.
3 To set the first line indent (or overhang), specify values in the First Line and Left fields
under Paragraph Indents. If you want the first line to be indented relative to the second
line of text, the First Line value should be higher than the value in the Left field. If you
want the first line to overhang the left side of the paragraph margin, the value in the
First Line field should be lower than the value in the Left field.
4 To set off a paragraph using indentation (as when you want to include a long quote in
your text), enter a value in the Left field and the Right field under Paragraph Indents.
You can also drag the margin symbols in the document ruler to change the margins for
selected paragraphs.
Setting Indents for Paragraphs Using the Horizontal Ruler
You can change indentation by dragging the indentation controls on the text ruler.
To set indents using the rulers:
1 Click View in the toolbar, and then choose Show Rulers.
2 To change the right indent, drag the right indent symbol (downward blue triangle on
the right side of the horizontal ruler) to the position where you want the right edge of
the paragraph to end.
Left indent
First line indent
3 To change the left indent, drag the left indent symbol (downward blue triangle on the
left side of the ruler) to where you want the left edge of the paragraph to begin.
To change the left margin independently from the left indent, hold down the Option
key as you drag.
Right indent
94 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 95

4 To change the first line indent, drag the first line indent (blue rectangle) to where you
want the first line to start.
If you want the first line to remain flush with the left margin, make sure the rectangle
aligns with the left indent symbol.
If you want to create a hanging indent, drag the rectangle to the left of the left indent
symbol.
Changing the Inset Margin of Text in Objects
You can change the amount of space between text and the inside border of a text box,
shape, or table cell. This measurement is called the inset margin. The amount of space
you specify is applied equally around the text on all sides.
To set the spacing between text and the inside border of its object:
1 If there’s no insertion point in the object, select the object. (If the insertion point is
inside the object, press Command-Return to get out of text editing mode and select
the object.)
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click Text.
3 Drag the Inset Margin slider to the right to increase the space between text and the
inside border of the object, or type a number in the Inset Margin box and press Return.
You can also click the arrows to increase and decrease space.
Specify how much space you
want around text inside a text
box, shape, or table. cell.
Setting Indents for Lists
To manage the indentation of bullets, numbers, and text that accompanies them in
bulleted lists, numbered lists, and ordered lists, you use the Text Inspector. See “Using
Bulleted, Numbered, and Ordered Lists (Outlines)” for details.
Using Bulleted, Numbered, and Ordered Lists (Outlines)
Pages provides pre-formatted bullet and numbering styles for creating simple or
ordered lists (outlines). Bulleted and numbered lists are simple lists without the nested
hierarchies of information like those you would see in an outline.
Generating Lists Automatically
When you use automatic list generation, Pages automatically formats a list for you
based on what you type. To use this feature, first choose Pages > Preferences, click
Auto-Correction, and make sure that “Automatically detect lists” is selected.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 95
Page 96

Here are ways to automatically generate lists:
m To create a bulleted list, press Option-8 to type a bullet (•) or a hyphen (-), a space,
some text, and then press Return.
m To create a list with labels that are asterisks (*) or hyphens (-), type an asterisk or a
hyphen, a space, some text, and then press Return.
m To create a list with labels that are numbers, letters, or Roman numerals, type the
number, letter, or Roman numeral; a period; a space; and some text. Then press Return.
You can use any of the character formats on the numbering style pop-up menu in the
Text Inspector. To access this menu, in the Text Inspector click Bullets and choose
Numbers from the Bullets & Numbering pop-up menu.
m To enter a new list topic at the next lower indent level, press Tab. To enter a new list
topic at the next higher level, press Shift-Tab.
m To end your list, press Return twice.
Note: If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in
the Table Inspector, press Option-Return instead of Return.
Using Bulleted Lists
Although you can use automatic list generation to create a simple bulleted list, using
the Text Inspector gives you many options for formatting bulleted lists. See “Generating
Lists Automatically” on page 95 for information about automatic list generation.
You can also add a bulleted list style by using the List button in the Format Bar. Place
the insertion point where you want the list to begin, click the List button in the Format
Bar, and then select Bullet.
To add and format a bulleted list using the Text Inspector:
1 Place the insertion point where you want the list to begin.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click List.
3 Choose a bullet style from the Bullets & Numbering pop-up menu.
To use a typed character as a bullet, choose Text Bullets and choose a character from
the list or type a new character in the field.
96 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Select a list style to apply it
to selected text.
Click to make list styles
appear in the Styles drawer.
Page 97

To use one of the image bullets that comes with Pages, choose Image Bullets and
choose an image from the scrolling list.
To use your own image as a bullet, choose Custom Image and choose an image in the
Open dialog that appears.
4 To change the size of an image bullet, specify a percentage of the original image size in
the Size field. Or, select the “Scale with text” checkbox and specify a percentage of the
text size; this option maintains the image-to-text size ratio of the bullets even if you
later change the font size of text.
5 To adjust the space between bullets and the left margin, use the Bullet Indent field. To
adjust the space between bullets and text, use the Text Indent field.
6 To position bullets higher or lower relative to text, use the Align field.
Use these techniques to add and indent bulleted items in your list:
 To add a new topic at the current indent level, press Return. If you’re working in a
table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in the Table Inspector, press
Option-Return instead.
 To create an unbulleted paragraph within a topic, press Return while holding down
the Shift key. If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is
selected in the Table Inspector, press Control-Return instead.
 To enter a new topic at the next lower indent level, press Tab. To enter a new topic at
the next higher level, press Shift-Tab. You can also click and hold a bullet, and then
drag to the right, to the left, down and to the right, or down and to the left.
If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in the
Table Inspector, use the Indent Level controls in the List pane of the Text Inspector to
increase or decrease the indentation of list entries.
 To return to regular text at the end of your list, press Return and choose No Bullets
from the Bullets & Numbering pop-up menu. You may also need to adjust the indent
level.
If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in the
Table Inspector, press Option-Return instead of Return.
To learn about modifying list styles or creating your own list style, see “Modifying and
Creating New List Styles” on page 129.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 97
Page 98

Using Numbered Lists
Although you can use automatic list generation to create a simple numbered list, using
the Text Inspector gives you many options for formatting numbered lists. See
“Generating Lists Automatically” on page 95 for information about automatic list
generation.
You can also choose a numbered list style in the Styles drawer. Click the Styles Drawer
button in the Format Bar, and then select the list style. If you don’t see list styles in the
Styles drawer, click the button in the lower-right corner of the drawer to make the
styles appear.
Here are ways to add and format a numbered list:
m Place the insertion point where you want the list to begin, click the List button in the
Format Bar, and then choose Numbered List.
m Place the insertion point where you want the list to begin, click Inspector in the toolbar,
click the Text Inspector button, and then click List. Choose Numbers from the Bullets &
Numbering pop-up menu, and then choose a numbering style from the pop-up menu
directly below it.
To adjust the space between numbers and the left margin, use the Number Indent
field. To adjust the space between numbers and text, use the Text Indent field.
Use these techniques to add and indent items in your list:
 To add a new topic at the current indent level, press Return. If you’re working in a
table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in the Table Inspector, press
Option-Return instead.
 To create an unnumbered paragraph within a topic, press Return while holding
down the Shift key. If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next
cell” is selected in the Table Inspector, press Control-Return instead.
 To enter a new topic at the next lower indent level, press Tab. To enter a new topic at
the next higher level, press Shift-Tab. You can also click and hold a number, and then
drag to the right, to the left, down and to the right, or down and to the left.
If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in the
Table Inspector, use the Indent Level controls in the List pane of the Text Inspector to
increase or decrease the indentation of list entries.
 To return to regular text at the end of your list, press Return and choose No Bullets
from the Bullets & Numbering pop-up menu. You may also need to adjust the indent
level.
If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in the
Table Inspector, press Option-Return instead of Return.
 To add an existing paragraph to a numbered list, click the paragraph, choose a
numbering style, and click “Continue from previous.”
98 Chapter 5 Working with Text
Page 99

 To start a new numbered sequence in a list, click “Start at” and specify the number
you want the sequence to begin with.
If you want items in your list to have labeled subtopics (like in an outline), use an
ordered list instead of a numbered list.
To learn about modifying list styles or creating your own list style, see “Modifying and
Creating New List Styles” on page 129.
Using Ordered Lists (Outlines)
Ordered lists (or outlines) provide different numbering styles for each indent level in a
list, allowing you to create a hierarchy of information. For example:
 You can create an outline using numbering sequence such as the following as you
proceed from the highest level to lower levels: I, A, 1, a), (1), (a), i), (1), and (a).
 You can create a legal style outline, which appends an additional number or letter at
each lower level: 1, 1.1, 1.1.1 , and so on.
You can also choose an ordered list style in the Styles drawer. Click the Styles Drawer
button in the Format Bar, and then select the list style. If you don’t see list styles in the
Styles drawer, click the List Styles button in the lower-right corner of the drawer to
make the styles appear.
You can add and format ordered lists using the Text Inspector.
To add and format an ordered list:
1 Place the insertion point where you want the list to begin.
2 Click Inspector in the toolbar, click the Text Inspector button, and then click List.
3 To create a legal style list, choose Tiered Numbers from the Bullets & Numbering pop-
up menu. Otherwise, choose Numbers instead.
4 Choose a numbering style from the pop-up menu directly below it.
5 To adjust the space between numbers and the left margin, use the Number Indent
field. To adjust the space between numbers and text, use the Text Indent field.
Use these techniques to add and indent items in your list:
 To add a new topic at the current indent level, press Return. If you’re working in a
table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in the Table Inspector, press
Option-Return instead.
 To create an unnumbered paragraph within a topic, press Return while holding
down the Shift key. If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next
cell” is selected in the Table Inspector, press Control-Return instead.
Chapter 5 Working with Text 99
Page 100

 To enter a new topic at the next lower indent level, press Tab. To enter a new topic at
the next higher level, press Shift-Tab. To move among levels you can also click and
hold a number, and then drag to the right, to the left, down and to the right, or
down and to the left.
If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in the
Table Inspector, use the Indent Level controls in the List pane of the Text Inspector to
increase or decrease the indentation of list entries.
 To return to regular text at the end of your list, press Return and choose No Bullets
from the Bullets & Numbering pop-up menu. You may also need to adjust the indent
level.
If you’re working in a table cell and “Return key moves to next cell” is selected in the
Table Inspector, press Option-Return instead of Return.
 To add an existing paragraph to a numbered list, click the paragraph, choose a
numbering style, and then click “Continue from previous.”
 To start a new numbered sequence in a list, click “Start at” and specify the number
you want the sequence to begin with.
To learn about modifying list styles or creating your own list style, see “Modifying and
Creating New List Styles” on page 129.
Using Text Boxes, Shapes, and Other Effects to Highlight Text
Callouts and sidebars are used to make text stand out from the main body of text in a
document. Pages offers many ways to emphasize text:
 Adding text to text boxes
 Adding a background (or fill color) to paragraphs
 Adding borders and rules to text
 Typing text in shapes
You can also use table cells to hold callouts. To read about working with tables, see
“Working with Tables” on page 168
Adding Text Boxes
You can add text boxes to create rectangular blocks of text anywhere on your page.
You can format text inside a text box as you would any other text, changing colors,
adding shadows, applying styles, and so on.
Adding a Floating Text Box
When you add a text box as a floating text box, it’s anchored to a position on the page
so that body text on the page flows around it. You can move the floating text box by
selecting it and dragging it.
100 Chapter 5 Working with Text
 Loading...
Loading...