Page 1
K
Service Source
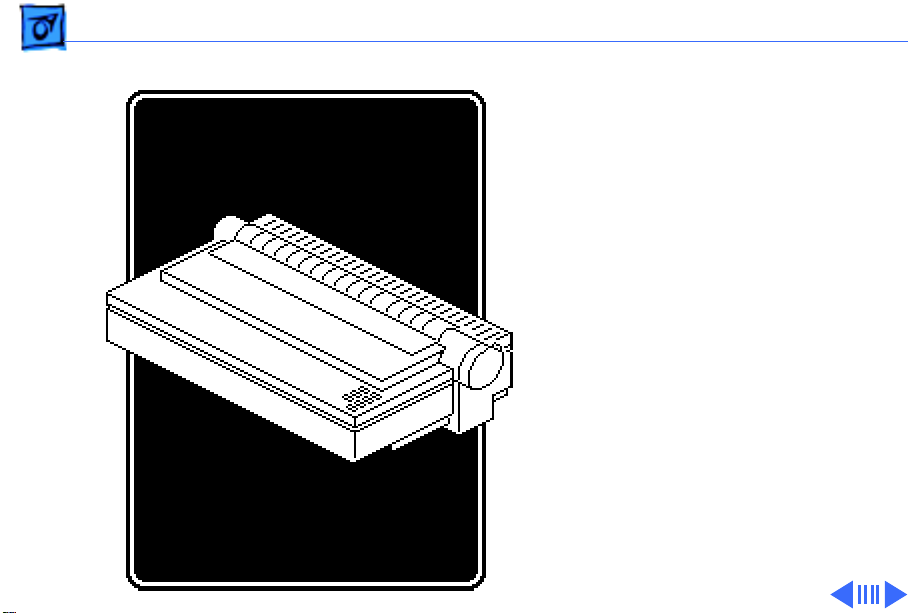
ImageWriter II/L
Page 2
Basics Introduction - 1
Introduction
The electrical operation of
the printer consists of five
printed circuit boards,
three motors, and several
switches.
The boards are the power
supply board, main board,
sub PCB board, print head
board, and the operation
panel board.
Page 3
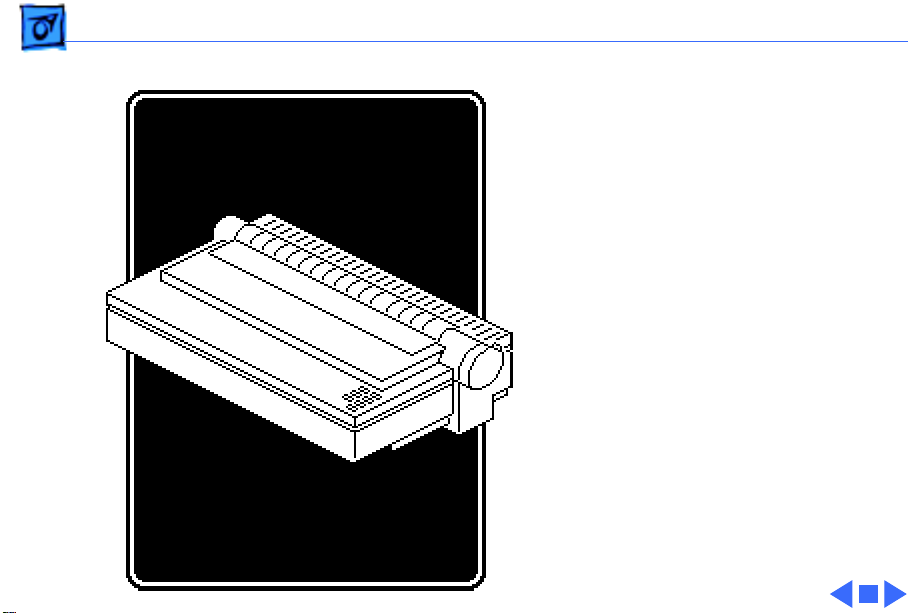
Basics Introduction - 2
The three motors are the
carrier motor, line feed
motor, and the ribbon
position motor.
Switches are the home
position switch, paper-out
sensor switch, and the
ribbon switch.
Page 4
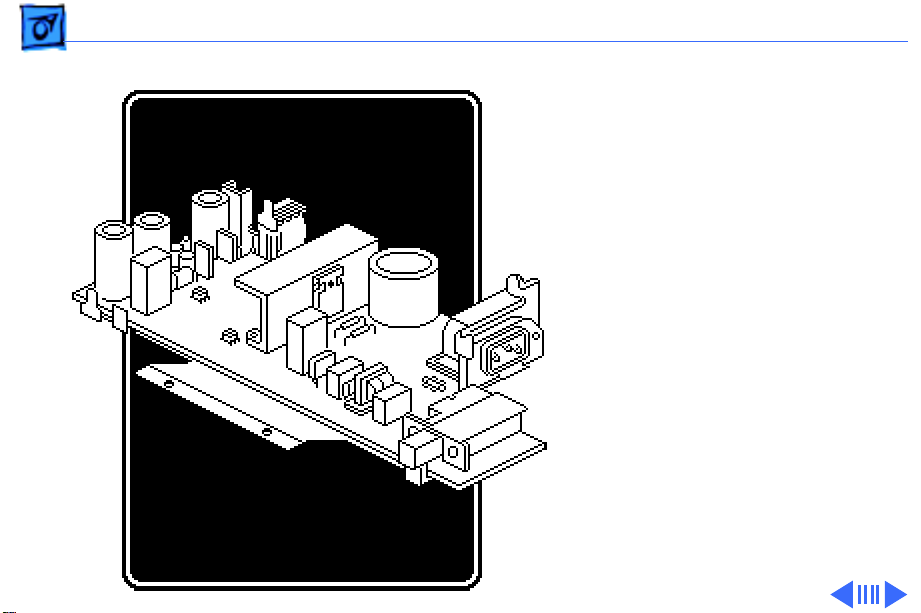
Basics Power Supply - 3
Power Supply
The ImageWriter II/L has a
switching type power supply
that eliminates the need for
a bulky transformer. When
the input AC current is
applied to this board, the
power supply reduces and
rectifies the voltage to the
following DC voltages:
• + 5 V DC
• – 5 V DC
• + 26 V DC
Page 5
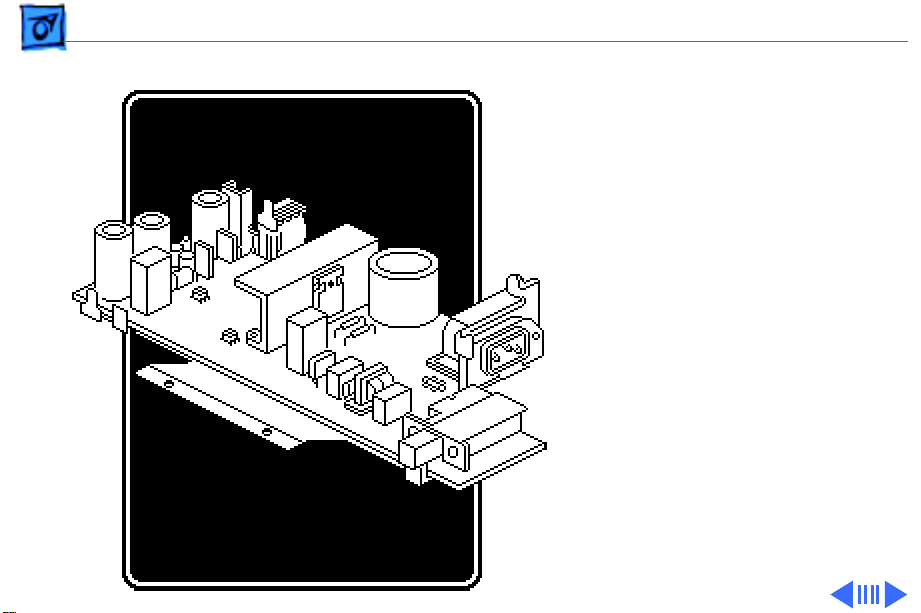
Basics Power Supply - 4
The + 5 and –5 V DC voltages
are for logic; the + 26 V DC
is for motor drive. All the
voltages are fed from
connector CN5 on the power
supply board to connector
CN3 on the main board.
From the main board the
voltages are distributed to
the other boards and motors.
Page 6
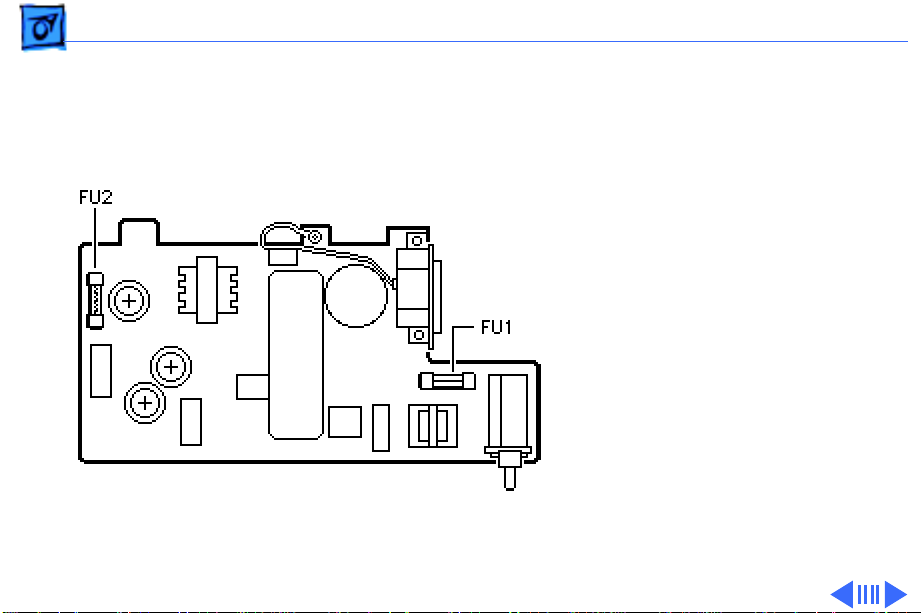
Basics Power Supply - 5
The power supply has two
fuses to help protect the
electronics—FU1 is a 120 V
2-amp fuse and FU2 is a
125 V 4–amp fuse.
Note:
Although not on the
power supply board, there
is another fuse, FU1, located
on the main board that
protects the + 26 motor
voltage.
Page 7
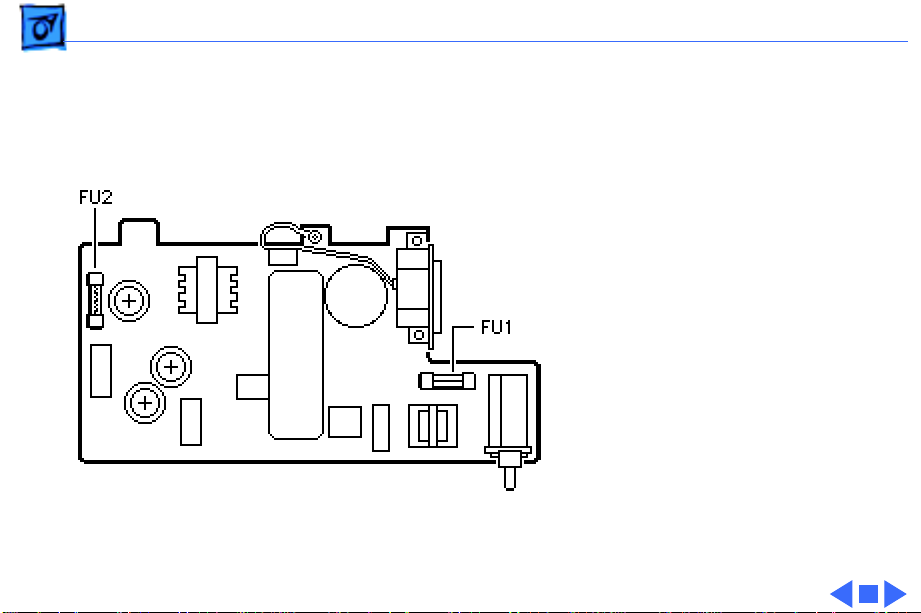
Basics Power Supply - 6
The on/off power switch is
connected to the power
supply board and disconnects
or connects the main AC
current to the board. The
switch is comprised of a
cable type plunger that is
attached to the power
supply board.
Caution:
is not compatible with the
older ImageWriter II. Do
not attempt to switch the
power supplies between
models.
This power supply
Page 8
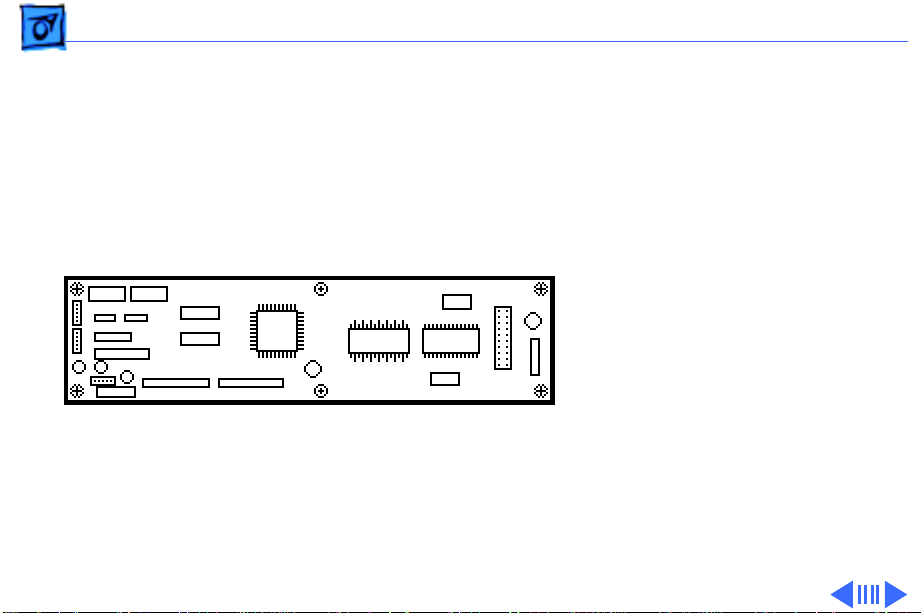
Basics Main Board - 7
Main Board
The main board is the heart
of the printer. Besides
handling the distribution of
the voltages, it also handles
all the logic that controls the
printer. It is also the source
of the drive signals for the
print head. All sensor
signals that affect the
operation of the printer are
fed to this board.
Page 9

ImageWriter II/L Basics - 8
ROM
The ROM (IC10) chip has the start-up
routines and several features such as
character sets and self-test routines built
in.
RAM
The RAM (IC9) is used in the transfer of
data and acts as a buffer. When printing
starts, the data to be printed is transferred
from the host CPU to the RAM on the
printer. From the RAM the data is passed
through the logic and sent to the print head
to print. Turning off the printer clears the
RAM.
Interface Circuits
The interface circuits (IC2 and IC3) on the
main board handle the data transferred
from the host CPU via the sub PCB board.
These circuits also handle the status and
control lines from the printer to the host
CPU.
Print Head Drivers
The print head drivers (IC5 and IC6)
process the print head drive signals from
the CPU and gate array. The signals are sent
to the print head board through CN5.
Page 10

ImageWriter II/L Basics - 9
CPU and Gate Array
The CPU (IC8) along with the gate array
(IC4), handles the logic and decisionmaking of the printer. They combine to
evaluate the status of the printer and issue
commands concerning when to transfer
data, when to start printing, when to run
the motors, and what actually prints. All
the functions of the printer are controlled
by these two devices. The rest of the
circuits are supporting circuits.
Carrier Motor Drivers
The carrier motor circuit is made up of
transistors Q1, Q2, Q12, Q13 and IC1. The
transistors make up a circuit that is used as
common returns from the motor. The
transistors also supply the higher voltage
and current needed to drive the motor. IC1
is a transistor pack that completes the
drive signals circuit when turned on. Each
of the four signals drives a phase of the
motor. These drive signals go to the carrier
motor on the printer through CN2.
Page 11

ImageWriter II/L Basics - 10
Line Feed
The drive circuit is made up of transistors
Q8, Q9, Q10, and Q11. Four drive signals
from the gate array are processed in this
circuit. Higher voltage and current are
added to the phase control signals to turn on
the line feed motor. The signals are sent to
the line feed motor and the ribbon motor
through CN1.
Ribbon Motor Drivers
This circuit is made up of transistors Q3,
Q4, Q5, Q6 and Q7. When turned on, the line
feed motor signals from the gate array are
supplied with more current in the drive
circuit and sent out to the motor. The
common return line is on Q7, which is
turned on for each phase signal sent to the
motor. These signals are sent through CN5.
Page 12

ImageWriter II/L Basics - 11
Reset Circuit
This circuit is used when the printer is
turned on to keep the logic in a reset state
until the voltages are up to correct values.
Once the voltages are at the correct level,
reset is released and the logic is allowed to
start functioning from a known state.
Connector CN6
This connector is a LocalTalk option card
connector. This card allows the printer to
communicate on the LocalTalk network so
that multiple users can use the printer.
Clock Crystals
There are two clock crystals on the main
board. The clock X1 for the gate array IC4
runs at 17.2 MHz. The clock X2 for the CPU
runs at 12 MHz.
DIP Switches
The configuration DIP switches are mounted
on the main board and can be changed to
make the printer perform in different
modes, or control printer protocols. The
switch settings affect both the CPU and the
gate array logic.
Page 13
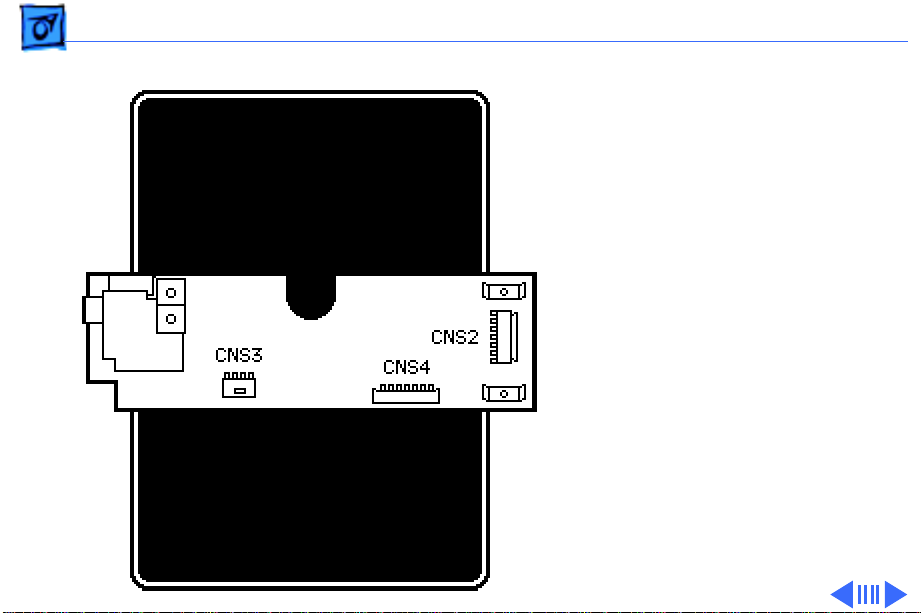
Basics Sub PCB Board - 12
Sub PCB Board
The sub PCB board acts as an
interface board. The
interface cable from the host
CPU is plugged into the
connector CNS1 on this
board. The signals from the
host CPU pass through the
sub PCB board on their way
to the main board. If a cutsheet feeder is attached to
the printer, the signals
pass through the sub PCB
board through CNS2, which
controls the actions of the
feeder.
Page 14
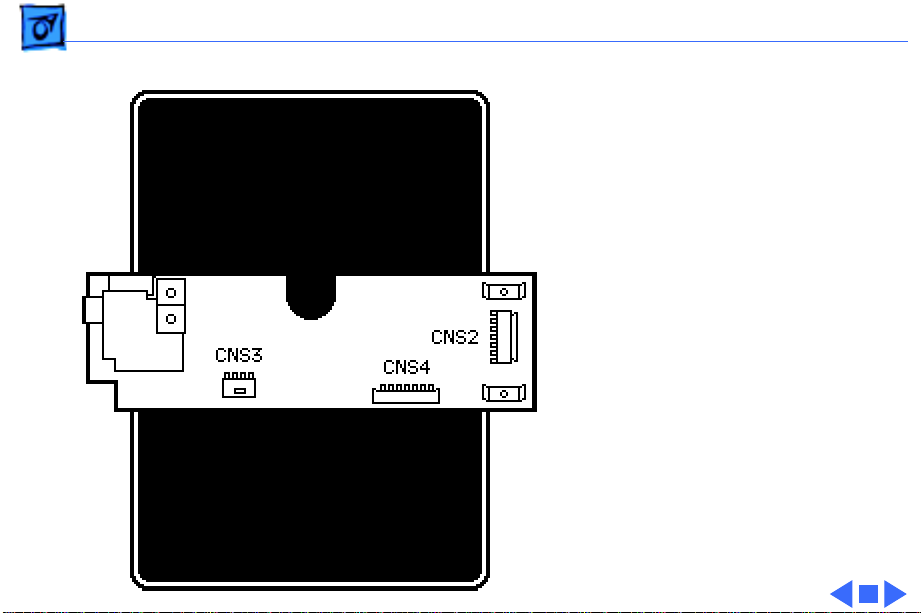
Basics Sub PCB Board - 13
The paper-out sensor wires
go to this board through
CNS3 and are passed along to
the main board.
All the signals coming or
going to the sub PCB board
are sent through CNS4 and
the ribbon cable to the main
board at connector CN4.
Page 15
Basics Print Head Board - 14
Print Head Board
The print head board
receives the print head
drive signals from the main
board through CNH1. The
signals are then sent out on
connector CNH2 to the print
head. This board also handles
the ribbon motor drive
signals and the ribbon
switch signals. If the switch
is activated, a color ribbon
is detected.
Page 16
Basics Print Head Board - 15
This information is sent to
the main board, which in
turn sends controlling
signals to the ribbon motor
to control the position of the
ribbon to allow color
printing.
The home position switch
alerts the CPU that the
carriage is at the far left
side of the printer, which is
home position.
Page 17
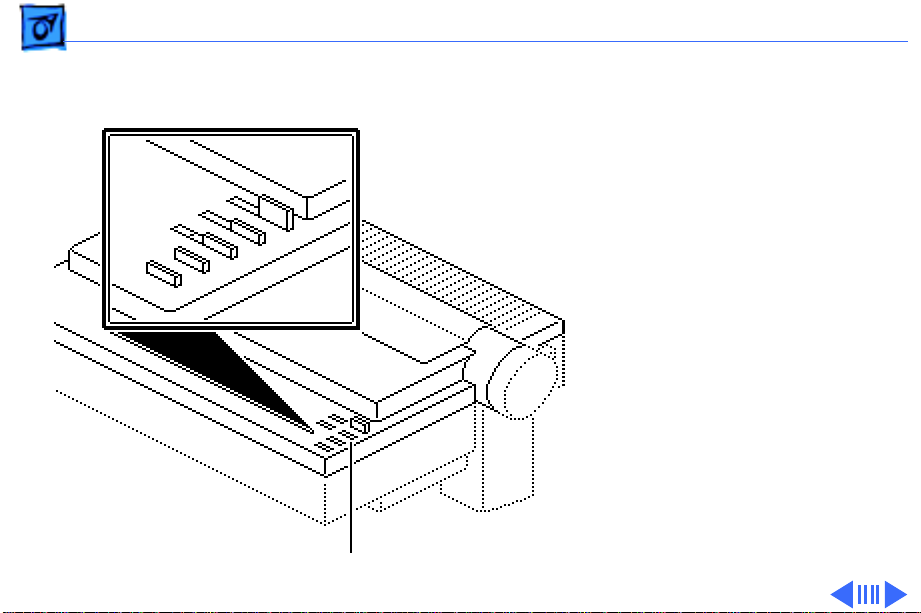
Basics Operation Panel Board - 16
Operation Panel Board
The operation panel board
has the switches (select,
print quality, line feed, and
form feed) and indicators
(error, power, print
quality, and select) mounted
on it. It interfaces with the
CPU through CN7 on the
main board. While the power
switch button is located on
the operation panel, it is not
connected to the operation
panel board.
Operation Panel
Page 18
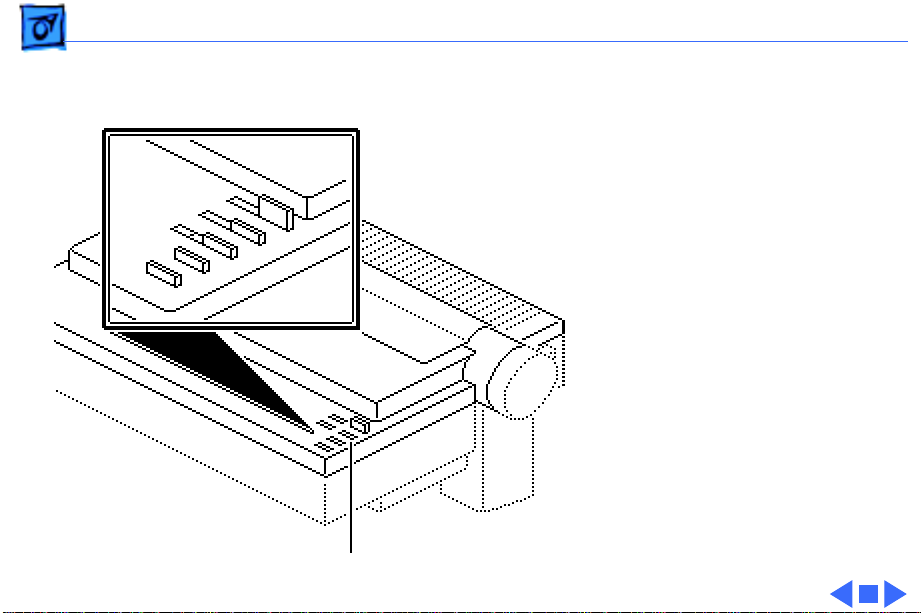
Basics Operation Panel Board - 17
The switch button just
passes through to the switch
mounted on the main frame
underneath the operation
panel.
Operation Panel
Page 19
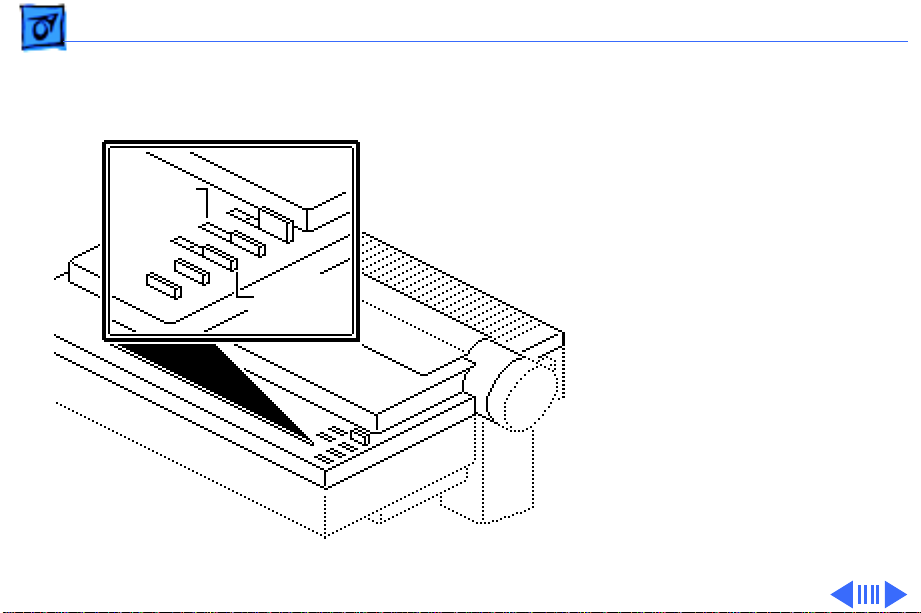
Basics Operation Panel - 18
Operation Panel
The operation panel consists
Indicator
Lights
Operating
Switches
of operating switches and
indicator lights.
The operating switches are
the buttons with which you
control the printer, and the
indicator lights let you know
what state the printer is in.
Page 20
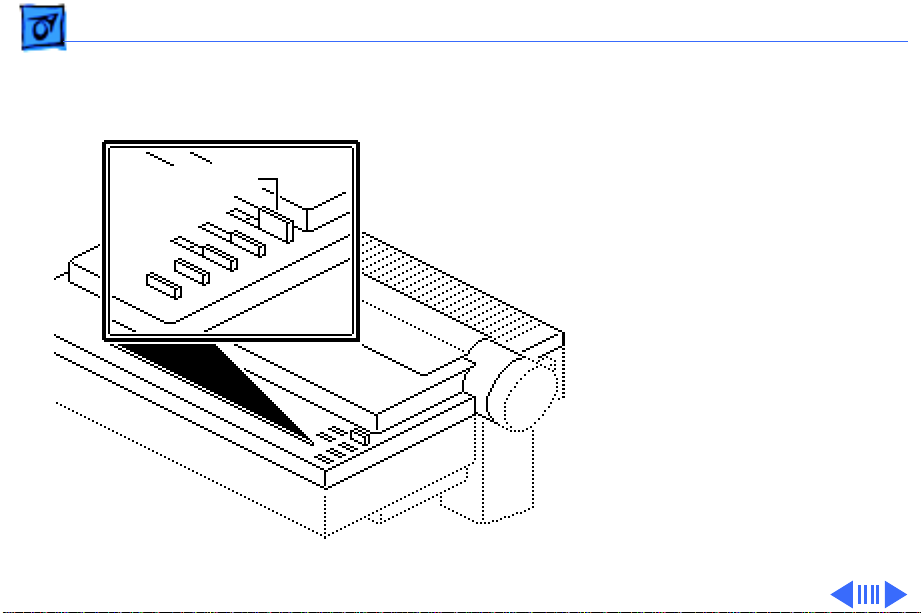
Basics Operation Panel - 19
Operating Switches
Power Switch
Power Switch
switch turns the printer on
and off.
- The power
Page 21
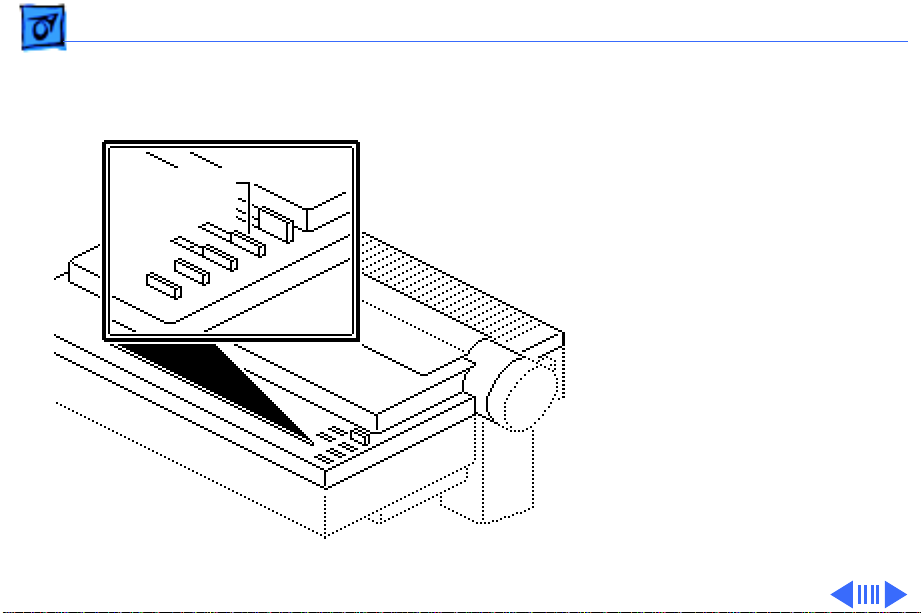
Basics Operation Panel - 20
Select
Switch
Select Switch
- The select
switch toggles the printer
between a selected (online)
and a deselected (off-line)
state. If printing is in
progress when the select
switch is pressed, the
printer finishes printing
the current line and a
maximum of two additional
lines, and stops printing.
Page 22
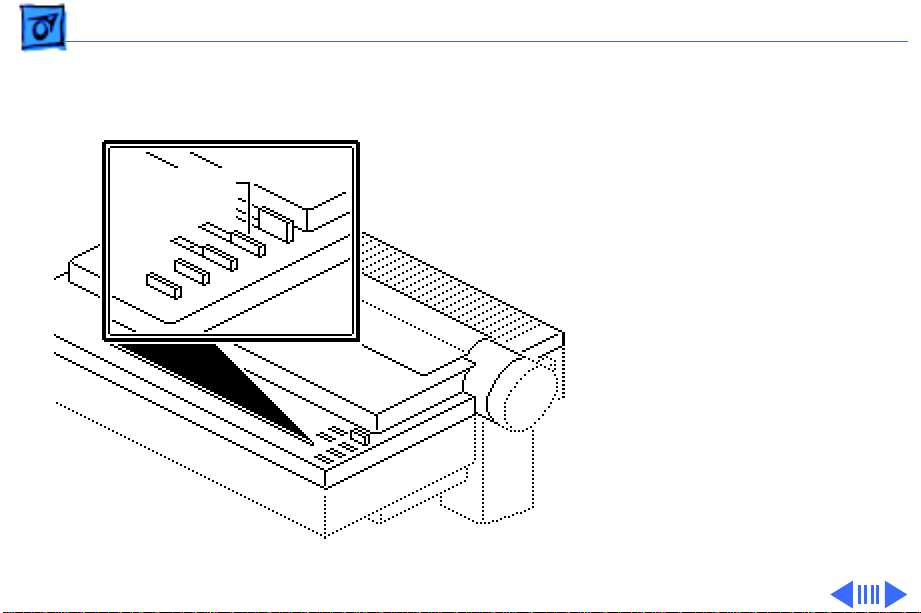
Basics Operation Panel - 21
If you want to clear the
buffer, you must turn off
the printer. Pressing the
select switch also clears a
Select
Switch
corrected error condition.
If an out-of-paper
condition exists, pressing
the select switch
temporarily overrides the
error to allow the print of
one line. This process is
repeatable as long as there
is printable data in the
printer buffer.
Page 23
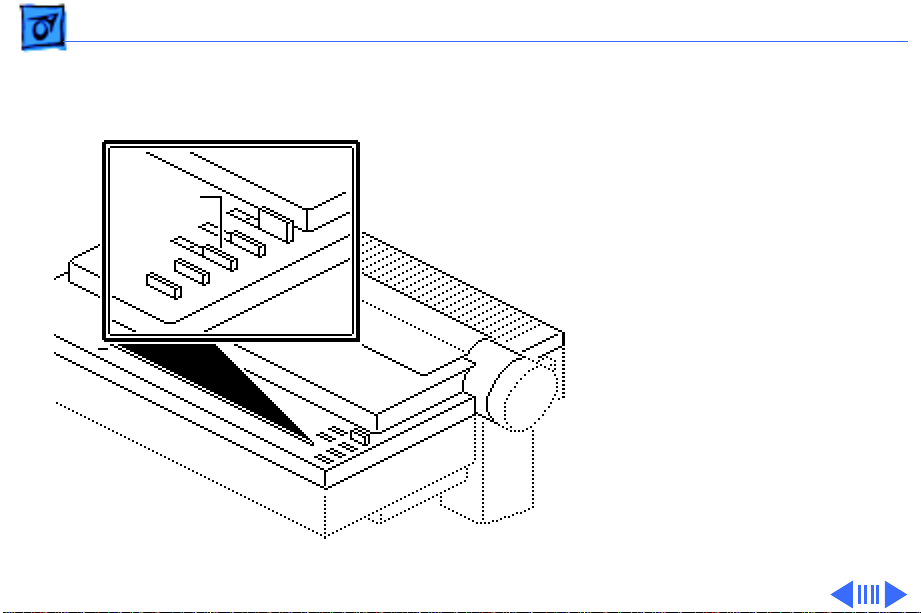
Basics Operation Panel - 22
Print
Quality
Print Quality Switch
- The
print quality switch allows
the user to choose one of
three printing modes.
Pressing the print quality
switch repeatedly changes
the mode from the standard
print mode, to the NLQ print
mode, to the draft print
mode, back to the standard
print mode again. The print
quality switch does not
function unless the printer
is in an off-line
(deselected) state.Ê
Page 24
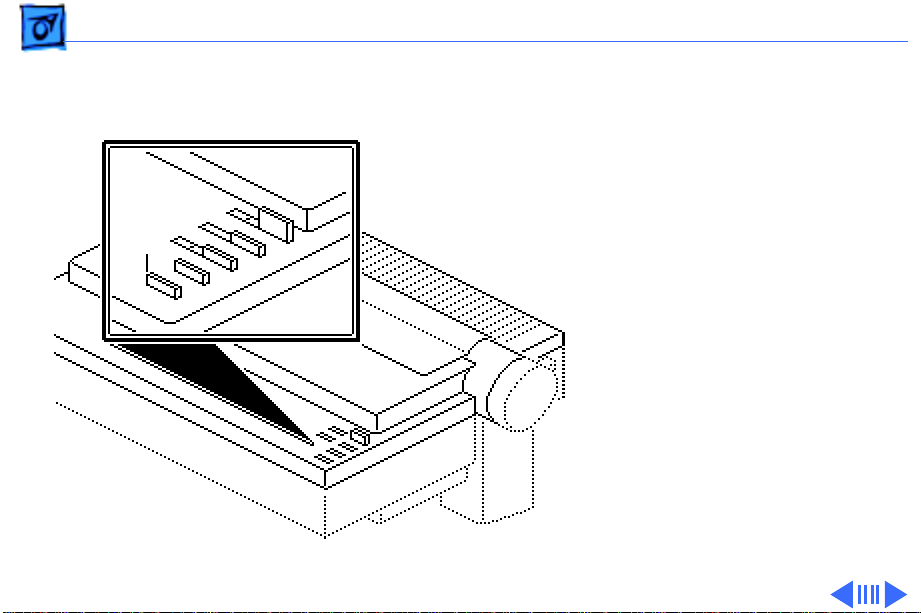
Basics Operation Panel - 23
Form
Feed
Form Feed
- The form feed
switch does not function
unless the printer is in an
off-line (deselected) state.
When the form feed switch
is pressed, the printer
feeds paper until the next
top of form is reached.
Page 25
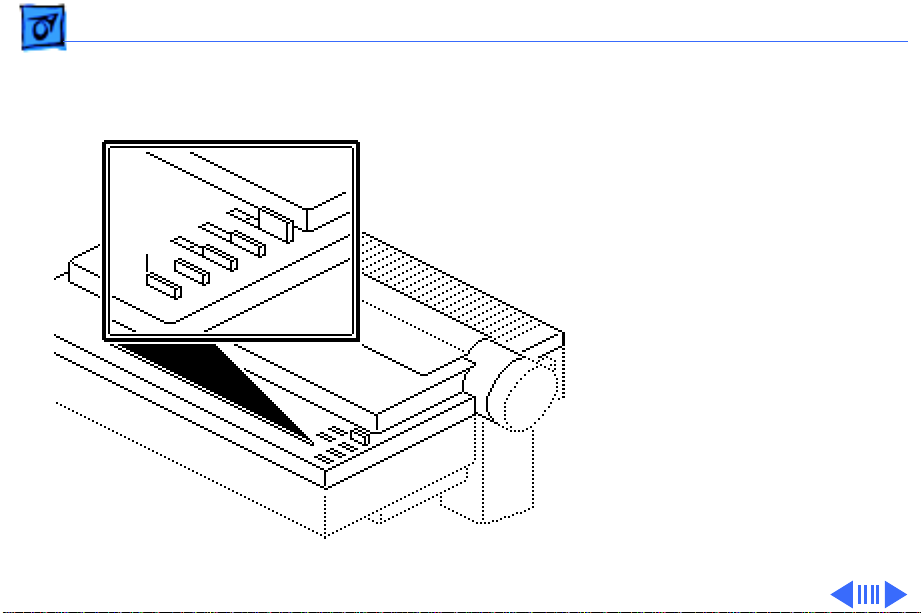
Basics Operation Panel - 24
If the switch is pressed and
no paper is present, the
printer assumes a single
sheet is being loaded. The
printer feeds the single
Form
Feed
sheet up to the top of form
position. If the switch is
pressed and paper is
present, the printer
monitors the paper-off
switch while feeding paper.
If the printer detects an
out-of-paper condition
before the top of form is
reached, the printer
assumes that single sheets
are being fed.
Page 26
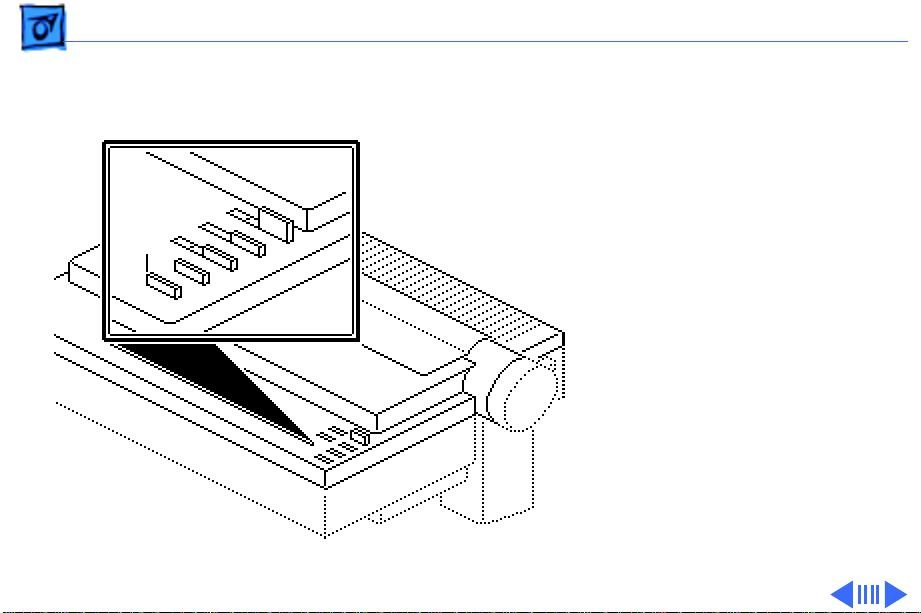
Basics Operation Panel - 25
For the single sheet case,
four inches of paper motion
is added to the form feed to
ensure that the page is
properly ejected.
Form
Feed
Page 27
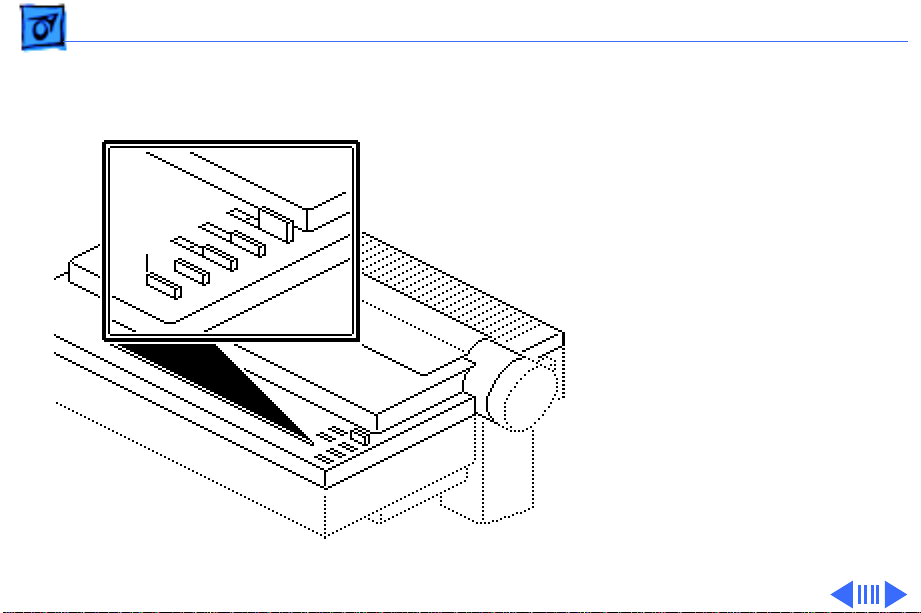
Basics Operation Panel - 26
When an automatic cutsheet feeder is present, the
paper-loading sequence is
slightly different. When the
form feed is pressed with no
Form
Feed
paper present, the printer
first rolls the platen to
check if a single sheet had
been inserted. If no paper is
found, the printer loads a
sheet from the automatic
sheet feeder and positions it
at the top-of-form position.
Page 28
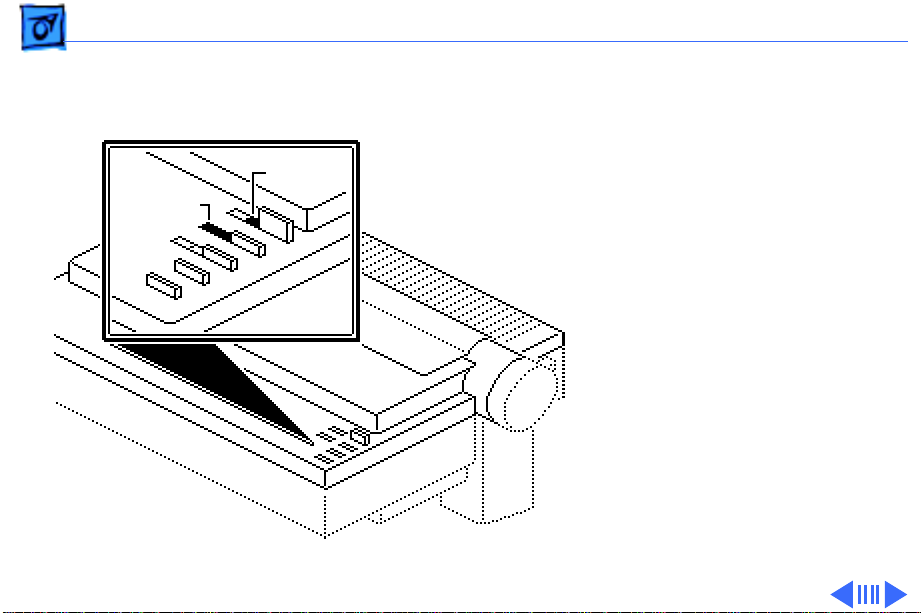
Basics Operation Panel - 27
Indicators
Select
Power
Power
light indicates that power is
on.
Select
indicator is lit, the printer
is online, in a ready state so
that a transmission can take
place.
- When lit, the power
- When the select
Page 29
Basics Operation Panel - 28
Print
Quality
Print Quality
- The print
quality light indicates three
modes of operation:
• NLQ–When both the
left and right
indicators are lit, the
printer is in the Near
Letter Quality print
mode.
• Draft–When just the
left indicator is lit,
the printer is in the
Draft print mode.
Page 30
Basics Operation Panel - 29
• Standard–If the right
indicator is lit, the
printer is in the
Standard print mode.
Print
Quality
This is the default
mode when the
printer is turned on.
Page 31

Basics Operation Panel - 30
Error
- The error light has
three ways of indicating an
error condition in the
printer:
Error
• If the error light comes
on steady and stays on
(and the select light goes
off), the printer is out of
paper.
• If the light blinks in a
steady fashion (evenly
spaced blinks), a cover
is open or a left-margin
error has occurred.
Page 32

Basics Operation Panel - 31
• If the light blinks in a
repeating sequence of
one short blink and a
long blink, an
Error
interface
communication or a
RAM check error has
occurred.
Page 33

K
Service Source
Specifications
ImageWriter II/L
Page 34

Specifications Characteristics - 1
Characteristics
Print Methods
Throughput
Print Head
Response Time
Draft Mode: 250 characters per second (cps); 25 in. per second
(ips) at 10 characters per in. (cpi)
Standard Mode: 180 cps; 18 ips at 10 cpi
NLQ Mode: 25 cps
100 in. per minute (ipm) at 80 dpi
9 wires
.0139 in. (.353 mm) nominal
Standard:.0118 in. (.300 mm) nominal
Japan:.0098 in. (.250 mm) nominal
1440 Hz
Page 35

Specifications Characteristics - 2
Life
Graphics Duty Cycle
Character Sets
Ribbon
Standard: 4 by 108 strokes/wire
Japan: 2 by 108 strokes/wire
25% minimum
ASCII (96 characters)
Six European sets
MouseText (32 characters)
Fabric ribbon
Black or four-color (cannot use color with Kanji print head)
Page 36

Specifications I/O Interfaces - 3
I/O Interfaces
Interface
LocalTalk
Operation
Connectors
Data Format
Standard asynchronous
With option board
Asynchronous, switch selectable; Data ready/busy (hardware
handshake), or Xon/Xoff serial protocols
Mini DIN-8
26-pin male (optional)
Asynchronous serial/no parity bit shall be sent
Page 37

Specifications I/O Interfaces - 4
Transmission Speed
Input Buffer
Switch selectable (300, 1200, 2400, and 9600 baud)
254K
Page 38

Specifications Paper Feed - 5
Paper Feed
Method
Accessories
Direction
Type
Thickness
Friction feed, adjustable tractors, and automatic single-sheet
loader
Automatic, cut-sheet feeder
Bidirectional (friction feed or tractor feed)
Single sheets, sprocket feed, multicopy (original + three copies),
single-width labels
.002–.011 in. (.05–.28 mm) equivalent to 15–25 lb. bond
3.5 in. minimum to “n” in. maximum (“n” is typically 11 or 14
for cut sheets)
Page 39

Specifications Electrical - 6
Electrical
Line V oltage
USA/Japan: 85–132 VAC; 48–62 Hz
Europe/Australia: 185–265 VAC; 48–62 Hz
Stand-by:20 W maximum
Operation: 180 W maximum
Page 40

Specifications Physical - 7
Physical
Dimensions
Weight
Height: 5 in.
Width: 17 in.
Depth: 12 in.
25 lb. maximum
Page 41

Specifications Environmental - 8
Environmental
Temperature
Relative Humidity
Operation:10–40°C
Storage: (one year) –40 to 47°C
Transit: (72 hours) –40 to 65°C
Storage: (six months) 10–95%
Page 42

K
Service Source
Troubleshooting
ImageWriter II/L
Page 43

Troubleshooting General/ - 1
General
The Symptom Charts included in this chapter will help you
diagnose specific symptoms related to your product. Because cures
are listed on the charts in the order of most likely solution, try
the first cure first. Verify whether or not the product continues to
exhibit the symptom. If the symptom persists, try the next cure.
(Note: If you have replaced a module, reinstall the original module
before you proceed to the next cure.)
If you are not sure what the problem is, or if the Symptom Charts
do not resolve the problem, refer to the Flowchart for the product
family.
For additional assistance, contact Apple Technical Support.
Page 44

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts /Preliminary Check - 2
Symptom Charts
Preliminary Check
Error light blinks 1 Verify that paper cover is secure.
2 Verify that paper cover magnet is in place.
3 Try known-good software.
4 Verify that option card dip switch SW2-4 is open/off with
no card installed.
Select light off, error light on
Select light does come on1 Verify that paper cover is secure.
1 Add paper or reset paper feed tray.
2 Verify that paper-out sensor works correctly (see Take
Apart).
2 Verify that paper cover magnet is in place.
3 Verify that operation cable under top cover is secure.
Page 45

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts /Preliminary Check - 3
No printing or garbled printing
Software-specific problem
Prints OK for a while; then prints garbage
Overprinting Verify that program is set for correct line spacing and line length.
Light printing 1 Change ribbon cartridge.
1 Check interface cable connection between printer and
computer.
2 Verify that DIP switches (2-1 through 2-4) are set
correctly.
Try known-good software.
Set DIP switch SW2-3 to correct serial protocol.
2 Adjust impression lever (see Adjustments).
3 Check for excessive play in carrier assembly. Make sure
assembly is seated correctly (see Take Apart).
Page 46

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Preliminary Check - 4
Erratic carrier motion, loud hum
Printing has
squashed lines;
misregistration
problems with pin
feed paper
Remove black tube-shaped shipping protection from carrier
shaft.
1 For best print quality, instruct customer to place stack of
paper behind printer and no more than three feet below
printer. The paper should have a clear, unobstructed entry
and exit path.
2 Verify that power cord or printer cable does not obstruct
paper path.
3 Avoid printing in top and bottom one inch of paper (the areas
where squashed line and misregistration problems will be
most apparent).
4 Use 20-pound paper.
Page 47

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts /Print Quality - 5
Print Quality
Compressed first or second line
Print is darker or lighter on one side
Top row of dots missing on printout
Power light on, no printing
1 Check position of paper behind printer to ensure there isn’t
anything blocking paper entry or exit.
2 Replace main board.
Remove or install shims. See the Shims topic in the Additional
Procedures chapter.
Perform “Ribbon Adjustment” (refer to Adjustments).
1 Verify that ribbon frame assembly rides on the spiral ridge
on color ribbon cam (see Adjustments).
2 Remove dot head and verify that pins in the connector on dot
head board are not bent.
3 Go to “Indicator Lights” (see Flowcharts).
Page 48

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Print Quality - 6
Missing dots 1 Check flexible cable connection.
2 Remove dot head and verify that pins in connector on dot head
board are not bent.
3 Go to “Printing” (see Flowcharts).
Color self-test does not work
When printing from a
Macintosh, characters
sometimes appear
smudged, or top of
form gradually creeps
down page in one-line
increments
1 Verify that color ribbon detect switch operates and wires are
unbroken. If defective, replace switch.
2 Top plate of carrier assembly (under ribbon cartridge) is
not properly engaged with color ribbon cam (see Take Apart
or Adjustments).
Verify that ImageWriter II/L driver software is the most current
version.
Page 49

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts /Carriage Movement - 7
Carriage Movement
Carriage doesn’t move; LEDs are not lit
Carriage doesn’t move; LEDs are lit
Carriage assembly
moves to the left and
does not return to
center
1 Replace main board.
2 Replace power supply board.
1 Replace main board.
2 Replace power supply board.
1 Verify operation of switch on print head board. If switch is
frozen or defective, replace print head board.
2 Verify that metal tab actuating left-side home position
switch is bent correctly. Use a feeler gauge and bend tab 1
mm toward right side.
3 Replace main board.
4 Replace power supply board.
5 Replace flexible ribbon cable.
Page 50

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Carriage Movement - 8
Carriage moves to the left and hums very loudly
Carriage assembly grinds or is difficult to move
Carrier binds on left side
Carrier
intermittently locks
up and gives light or
dark print
1 Verify that flexible ribbon cable is properly connected to
main board and to its connector under carriage assembly on
print head board.
2 Replace flexible ribbon cable.
3 Replace power supply board.
1 Replace fuse on main board.
2 Replace power supply board.
Paper guide is too close to platen. Readjust paper guide.
Verify that rear of carrier assembly does not lift. If it does, it is
not seated correctly in the guide rail. Gently push down on rear of
carrier assembly until it snaps into place.
Page 51

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Carriage Movement - 9
Self-test produces no
carrier movement
(LEDs are lit)
1 Remove mechanical assembly to ensure that wires to carrier
motor are not pinched. If wires to carrier motor are worn,
replace them.
2 Replace fuse on main board.
3 Replace main board.
Page 52

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Paper Feed - 10
Paper Feed
Grinding during paper feed
Paper adjustment lever does not move
1 Remove platen knob to verify that there are no obstructions
in the gears beneath knob.
2 Adjust paper guide (refer to Adjustments).
3 Replace line feed motor.
4 Replace main board.
Verify that power on/off cable is not pinched between lever and
metal frame or plastic case.
Page 53

Troubleshooting Symptom Charts/Miscellaneous - 11
Miscellaneous
Hexadecimal data prints
Power supply goes bad repeatedly
Ribbon jams or does not advance
Power printer off and then on.
Verify that power supply and motor wires are not pinched. If
wires are pinched, lift mechanical assembly and reposition wires.
1 Check gear box on carrier assembly. Verify that gear with
cross (+) sticks through carrier assembly top plate and
engages ribbon cartridge.
2 Verify that ribbon wire is properly installed in gear box
3 Verify that print head wires are not striking platen too hard.
If they are, replace main board. If replacement of main board
does not correct problem, reinstall original main board and
replace print head.
Page 54

K
Service Source
T ak e Apart
ImageWriter II/L
Page 55

Take Apart Covers - 1
Covers
Top Cover
Ribbon Cartridge
Ribbon Cover
Paper Cover
Tractor Cover
No preliminary steps are
required before you begin
this procedure.
Caution:
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
Note:
the removal of the top cover,
tractor cover, ribbon cover,
and ribbon cartridge.
Note:
easier, label all cables and
connectors during the takeapart procedure.
Review the ESD
This procedure covers
To make reassembly
Page 56

Take Apart Covers - 2
Paper Cover
Ribbon Cover
Note:
The paper cover
Paper Cover
assembly must be in place
for the printer to work.
Gently pull the paper cover
up and forward and remove
the cover.
Replacement Note:
the paper cover from the
ribbon cover only if the
paper cover is broken and
needs replacement. Push in
the two tabs and separate the
paper cover from the ribbon
cover.
Remove
Page 57

Take Apart Covers - 3
Ribbon Cartridge
Gently pull the tabs apart
Tab
Tab
Ribbon Cartridge
and lift the cartridge out.
Page 58

Take Apart Covers - 4
Top Cover
Captive
Screw
Platen
Knob
Captive
Screw
1 Push the carrier
assembly to the far left.
2 Pull off the platen knob.
3 Loosen the two captive
screws.
Page 59

Take Apart Covers - 5
4 Grasp the top cover on
the left at the part that
goes over the leg.
Latch
5 Release the latch and lift
the cover one inch.
Top Cover
Page 60

Take Apart Covers - 6
6 Gently rotate the cover
toward the front and
turn the cover over.
7 Using your thumb and
forefinger, unlock
connector CN7 and
remove the ribbon cable.
8 Lift off the top cover.
Replacement Note:
Perform the self-test.
Connector CN7
Page 61

Take Apart Covers - 7
Tractor Cover
Tractor Cover
Gently pull the tractor cover
up and forward until the
cover snaps free.
Page 62

Take Apart Operation Panel - 8
Operation Panel
Before you begin, remove
the covers.
Operation Panel
Caution:
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
Review the ESD
Page 63

Take Apart Operation Panel - 9
Cable
Top Cover
Right-
1 Remove the three screws
and lift the operation
panel board from the top
cover.
2 Disconnect the cable
from the operation
panel board.
Operation
Panel
Board
-Left
Page 64

Take Apart Operation Panel - 10
3
Note
: To make
reinstallation easier,
observe the position of
the power switch
Power
Switch
Plunger
plunger and spring.
Remove the spring and
power switch plunger
from the top cover.
Replacement Note:
Perform the self-test.
See the Additional
Procedures chapter.
Top Cover
Page 65

Take Apart Main Board - 11
Main Board
Before you begin, remove
the following:
• Covers
• Option board
Main Board
Caution:
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
Review the ESD
Page 66

Take Apart Main Board - 12
1 Disconnect the three
cable connectors from
the left side of the main
board:
• CN1
• CN2
• CN3
Right-
Main Board
Page 67

Take Apart Main Board - 13
2 Remove the six screws.
3 Tilt the front half of the
board up and gently lift
the board partially out.
Ground Clip
Main Board
Replacement Note:
Make
sure to replace the
ground clip on the screw
at the lower left of the
board.
Page 68

Take Apart Main Board - 14
4
Caution:
release both sides of the
connector before you
pull out the ribbon
cable.
Using a small
screwdriver, unlock
each side of connectors
CN4 and CN5 and
remove the two ribbon
cables.
Make sure you
Replacement Note:
Perform the self-test.
Page 69

Take Apart Print Head and Paper Guide - 15
Print Head and Paper Guide
Before you begin, remove
the covers.
Caution
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
Note
have to be removed in order
to remove the paper guide.
: Review the ESD
: The print head does not
Page 70

Take Apart Print Head and Paper Guide - 16
Print Head
1 Lift the paper bail to its
highest position.
2 Set the paper thickness
lever to its widest
setting.
Page 71

Take Apart Print Head and Paper Guide - 17
3 Gently push and hold
aside the white print
head clamp release
lever and slowly lift the
print head straight out of
the connector.
Replacement Note:
Perform the self-test.
Page 72

Take Apart Print Head and Paper Guide - 18
Paper Guide
Remove the two screws and
lift out the paper guide.
Replacement Note:
the paper guide. See the
Adjustments chapter.
Adjust
Page 73

Take Apart Ribbon Cam Assembly - 19
Ribbon Cam Assembly
Before you begin, remove
the covers.
Caution
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
Note
of the ribbon cam assembly.
One has a plastic cap and the
other has a hex nut, without
the cap.
: Review the ESD
: There are two versions
Page 74

Take Apart Ribbon Cam Assembly - 20
1 Unscrew the plastic cap
Plastic Cap
from the ribbon cam.
2 Remove the red
Adjustment Ring
adjustment ring and the
spring.
Spring
Plastic Collar
3 Remove the plastic
collar.
Page 75

Take Apart Ribbon Cam Assembly - 21
4
Note
: For versions with
the hex nut, remove the
nut and proceed with the
rest of the procedure.
Using small needlenose
pliers, remove the
retaining clip and two
washers.
5 Remove the vertical
knurled nut.
Page 76

Take Apart Ribbon Cam Assembly - 22
6 Turn and lift off the
ribbon cam.
7 Remove the spring.
Page 77

Take Apart Ribbon Cam Assembly - 23
Replacement Note:
you replace the cam, set the
cam at its lowest setting.
Verify that the two tabs of
the ribbon plate are riding
on the cam ridge. Improper
positioning of the cam can
cause poor-quality prints or
no prints.
Replacement Note
the ribbon cam (see
“Ribbon Cam” in the
Adjustments chapter).
When
: Adjust
Page 78

Take Apart Carrier Assembly Top Plate - 24
Carrier Assembly Top Plate
Before you begin, remove
the covers.
Caution
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
: Review the ESD
Page 79

Take Apart Carrier Assembly Top Plate - 25
1
Caution
when you remove the
black plastic arms. You
will break them.
Using a small flat-blade
screwdriver, push out
the black bearing arm.
2 With another small
screwdriver, gently pry
the arm upward at a
slight angle.
3 Move the small arm to
the top.
: Do not use force
Page 80

Take Apart Carrier Assembly Top Plate - 26
4 Gently pull the plastic
bearing straight out and
remove the small
washer.
5 Repeat for the right side.
Replacement Note
bearings are not
interchangeable.
: The
Page 81

Take Apart Carrier Assembly Top Plate - 27
6 Gently pry the top of the
wire clamp from the
carrier assembly and
remove the color ribbon
detect switch wires from
the clamp.
Page 82

Take Apart Carrier Assembly Top Plate - 28
7 Using a jeweler’s
screwdriver, push the
gear assembly tabs
toward the center of the
ribbon plate and lift off
the top plate. Leave the
gear assembly in the
carrier housing.
Page 83

Take Apart Carrier Assembly Top Plate - 29
Color Ribbon Detect Switch
1
Note:
Do not bend the
plastic tabs that hold the
wires.
Carefully pry the wires
out of the embedded track
of the top plate.
Page 84

Take Apart Carrier Assembly Top Plate - 30
2 Turn over the top plate.
Using a small
screwdriver, gently pry
the four latches and at
the same time push
down on the bottom of the
switch so the switch
comes out from the top of
the plate.
Page 85

Take Apart Ribbon Wire and Gears - 31
Ribbon Wire and Gears
Before you begin, remove
the following:
• Covers
• Carrier assembly top
plate
Caution
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
: Review the ESD
Page 86

Take Apart Ribbon Wire and Gears - 32
1 Unhook the ribbon wire
from the right side of the
frame, and then from the
left side of the frame.
Remove the ribbon wire.
Page 87

Take Apart Ribbon Wire and Gears - 33
2 Lift the gear assembly
from the carrier
housing.
Replacement Note:
Perform the self-test.
Replacement Note:
sure the wire is
rewrapped with the wire
crossing in front of the
gear. Then secure the
wire on the right side.
Be
Page 88

Take Apart Drive Belt/Carrier Motor - 34
Drive Belt/Carrier Motor
Before you begin, remove
the covers.
Caution
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
: Review the ESD
Page 89

Take Apart Drive Belt/Carrier Motor - 35
Drive Belt
1 Loosen the screw on the
pulley tension plate. Do
not remove the screw.
2 Using a large
screwdriver, push
toward the right side
and remove the drive
belt from the right-side
pulley.
Adjustment
Screw
Right Side
Pulley
Carrier
Pulley Arm
Page 90

Take Apart Drive Belt/Carrier Motor - 36
3 Remove the drive belt
from the left-side
pulley.
Page 91

Take Apart Drive Belt/Carrier Motor - 37
4 Remove the screw from
the retaining clip.
5 Using a small flat-blade
screwdriver, pry up the
retaining clip from the
housing and remove the
belt.
Replacement Note:
retaining clip is glued to
the drive belt.
The
Page 92

Take Apart Drive Belt/Carrier Motor - 38
Carrier Motor
Remove the three screws
that secure the carrier
motor and remove the
carrier motor.
Replacement Note:
the self-adhesive damping
pad between the motor and
the frame. Replace the pad if
necessary.
Inspect
Page 93

Take Apart Mechanical Assembly - 39
Mechanical Assembly
Before you begin, remove
the covers.
Caution: Review the ESD
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
Page 94

Take Apart Mechanical Assembly - 40
1 Remove the six screws
that hold the mechanical
assembly to the bottom
case.
Note: Do not remove
screw A at the back of the
assembly nearest the left
side. This screw holds
the sub board in place.
Page 95

Take Apart Mechanical Assembly - 41
Replacement Note: Two
screws make the ground
connection between the
power supply plate and the
rest of the mechanical
assembly. If you do not
replace both screws, the
ground is not complete and
logic errors or hazards can
result.
Page 96

Take Apart Mechanical Assembly - 42
2 Remove the two screws
that hold the power
switch cable in place.
3 If the main board is in
the printer, disconnect
the connector at CN3 on
the main board.
Page 97

Take Apart Mechanical Assembly - 43
4 Grasp the middle of the
back tractor bar. With
the other hand hold the
middle of the support
wall and lift the entire
mechanical assembly
from the case.
Page 98

Take Apart Mechanical Assembly - 44
Replacement Note: As you
lower the assembly into
place, make sure to route
the power supply cable
correctly and to align the
power switch cable
correctly. Correct
placement will ensure that
the cables do not pinch when
you lower the assembly into
place.
Page 99

Take Apart Flexible Ribbon Cable - 45
Flexible Ribbon Cable
Before you begin, remove
the following:
• Covers
• Mechanical assembly
• Carrier assembly top
plate
Caution: Review the ESD
Flexible Ribbon Cable
precautions in Bulletins/
Safety.
Page 100

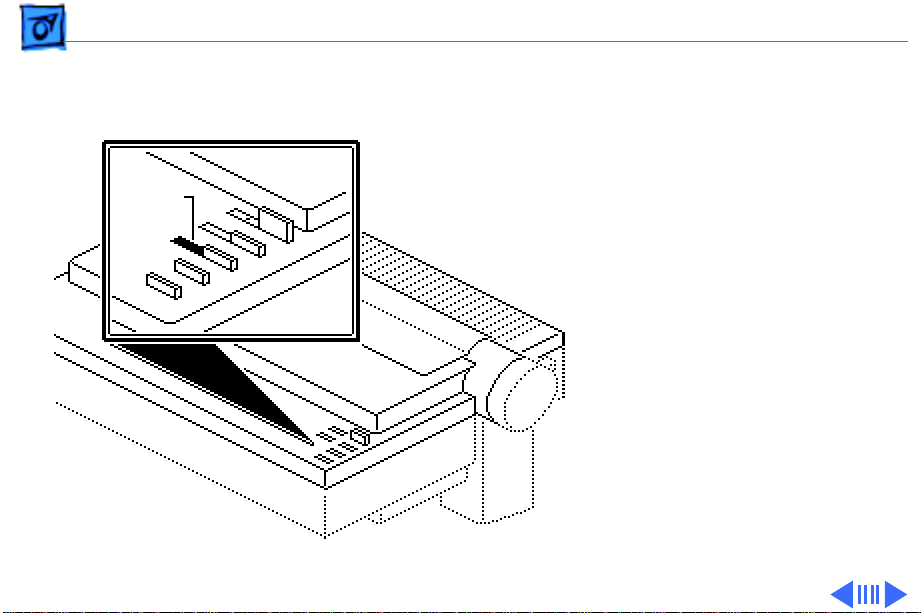
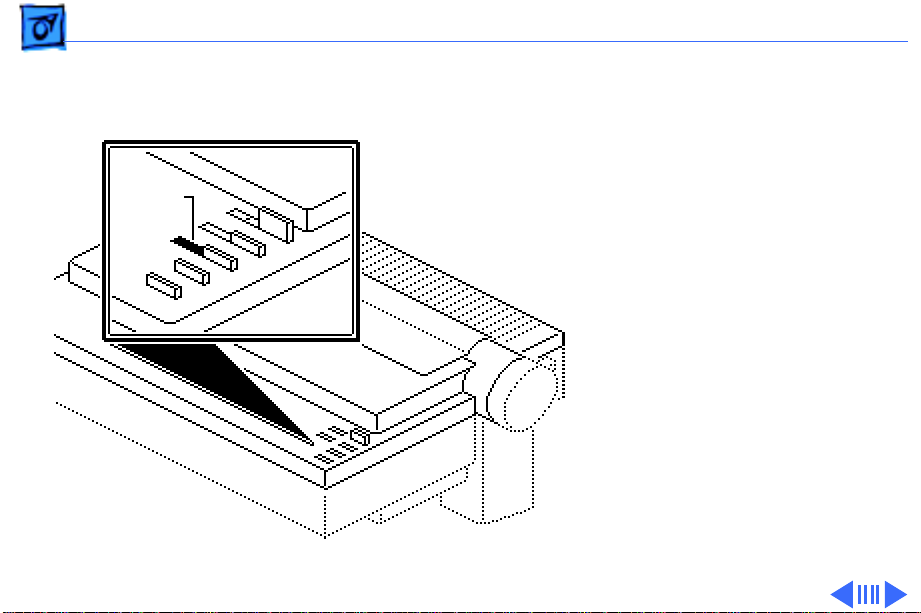
Take Apart Flexible Ribbon Cable - 46
1 Remove the ribbon cable
from connector CN5 on
the main board.
2 Move the carrier
assembly toward the
right side of the carrier
until the assembly is
lined up with the right
edge of the board.
 Loading...
Loading...