Evaluation Board User Guide
One Technology Way • P. O . Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. • Tel : 781.329.4700 • Fax : 781.461.3113 • www.analog.com
UG-192
Evaluation Board for SSM2317 Filterless Class-D Audio Amplifier
PACKAGE CONTENTS
SSM2317-EVALZ
OTHER SUPPORTING DOCUMENTATION
SSM2317 data sheet
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SSM2317 is a fully integrated, single-chip, mono Class-D audio
amplifier that is designed to maximize performance for mobile phone
applications. The application circuit requires a minimum of external components and operates from a single 2.5 V to 5.5 V supply. It
is capable of delivering 3 W of continuous output power with less
than 1% THD + N driving a 3 load from a single 5.0 V supply.
The SSM2317 is equipped with a differential mode input port and a
high efficiency, full H-bridge at the output that enables direct coupling
of the audio power signal to the loudspeaker. The differential mode
input stage allows for cancelling of common-mode noise.
Automatic level control (ALC) can be activated to suppress
clipping and improve dynamic range. This feature only requires
one external resistor tied to GND via the VTH pin and an
activation voltage on the ALC_EN pin. For setup configuration
and sync operation, see the SSM2317 data sheet.
The part also features a high efficiency, low noise output modulation
scheme that does not require external LC output filters when
attached to an inductive load. The modulation provides high
efficiency even at low output power. Filterless operation also helps
to decrease distortion due to the nonlinearities of output LC filters.
This user guide describes how to configure and use the SSM2317
evaluation board to evaluate the SSM2317. It is recommended
that this data sheet be read in conjunction with the SSM2317
data sheet, which provides more detailed information about the
specifications, internal block diagrams, and application guidance
for the amplifier IC.
EVALUATION BOARD OVERVIEW
The SSM2317 evaluation board carries a complete application
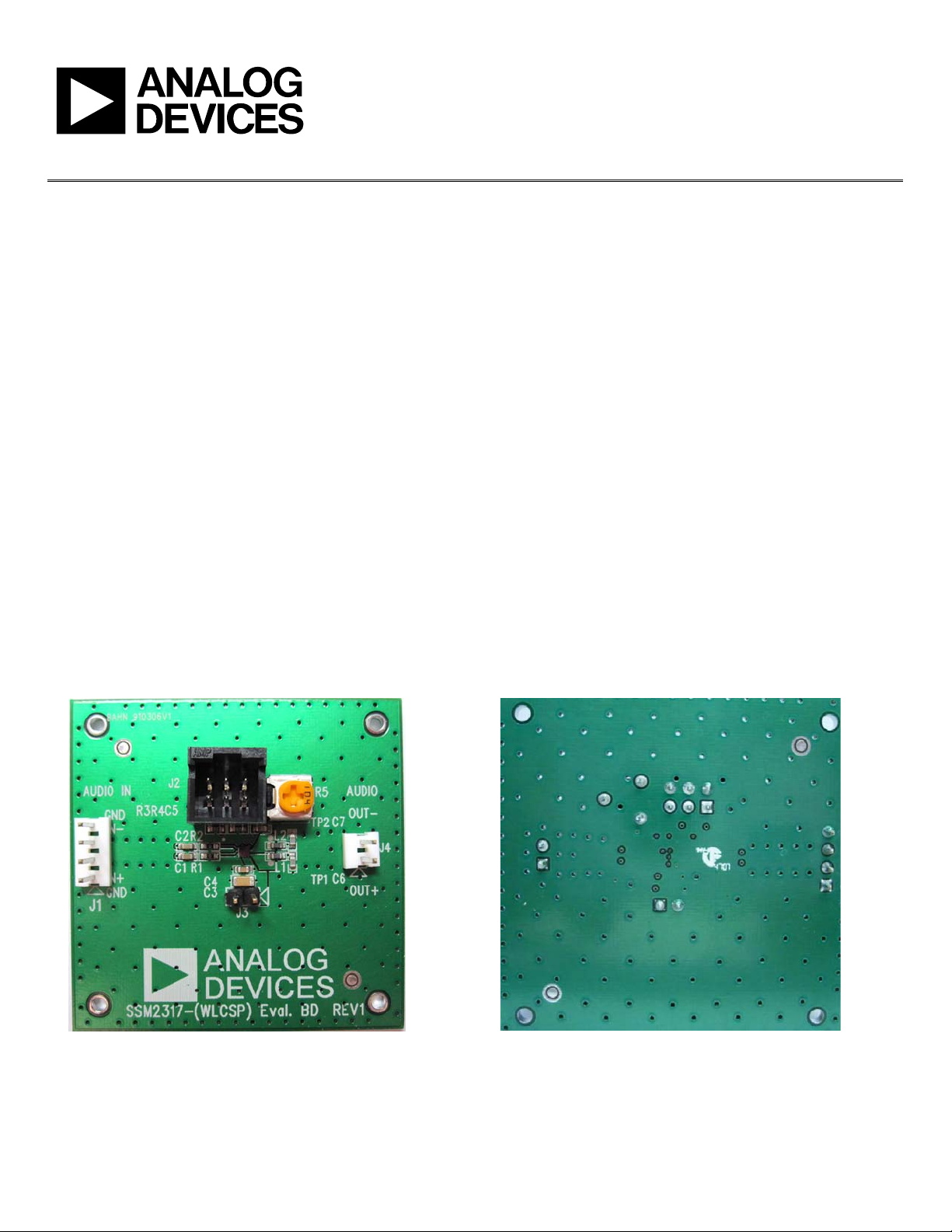
circuit for driving a loudspeaker. Figure 1 shows the top view of
the evaluation board, and Figure 2 shows the bottom view.
Figure 1. SSM2317 Evaluation Board Top View
PLEASE SEE THE LAST PAGE FOR AN IMPORTANT
WARNING AND LEGAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS.
09354-001
Rev. 0 | Page 1 of 8
Figure 2. SSM2317 Evaluation Board Bottom View
09354-002

UG-192 Evaluation Board User Guide
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Package Contents.............................................................................. 1
Other Supporting Documentation................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Evaluation Board Overview ............................................................1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Setting Up the Evaluation Board .................................................... 3
Input Configuration..................................................................... 3
Operation Mode Configuration ................................................. 3
REVISION HISTORY
10/10—Revision 0: Initial Version
Output Configuration...................................................................3
Power Supply Configuration .......................................................3
Component Selection ...................................................................3
Getting Started...............................................................................4
What to Test...................................................................................4
Evaluation Board Schematic and Artwork.....................................5
Ordering Information.......................................................................8
Bill of Materials..............................................................................8
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 8

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-192
+
SETTING UP THE EVALUATION BOARD
INPUT CONFIGURATION
A 4-pin header (J1) on the middle left side of the board feeds the
audio signal into the board (see Figure 1). If the input audio signal
is differential (IN+ and IN−), three pins of J1 are used for IN+,
IN−, and signal ground. For a single-ended audio input, only two
pins of J1 are used. One is for the signal ground and the other is
for either IN+ or IN−. If IN+ is used, place a jumper between
Pin 3 and Pin 4 of J1, shorting IN− to ground. If IN− is used,
place the jumper between Pin 1 and Pin 2 of J1, connecting IN+
to ground.
OPERATION MODE CONFIGURATION
The 6-pin header, J2, is used to turn on/off the SSM2317 amplifier and configure the ALC operation modes. Placing a jumper
across Pin 1 and Pin 2 of J2 shuts down the SSM2317 so that only
a minimum current (about 20 nA) is drawn from the power supply
(when R3 is shorted). Removing the jumper puts the SSM2317 in
normal operation. Placing a jumper across Pin 3 and Pin 4 of J2
disables ALC mode, while removing the jumper activates ALC
mode. When ALC is disabled, the SSM2317 behaves like a traditional amplifier with a fixed 18 dB. Placing a jumper across Pin 5
and Pin 6 of J2 shorts across the ALC threshold resistor (on
board) and sets a maximum limiter level of 90% of V
(when
DD
ALC is activated).
OUTPUT CONFIGURATION
The output connector, J4, is located on the right side of the board
(see Figure 1). J4 drives a loudspeaker whose impedance should
be no less than 3 .
Although the SSM2317 does not require any external LC output
filters due to a low noise modulation scheme, if the speaker length
is >10 cm, it is recommended to put a ferrite bead (L1 and L2) near
each output pin of the SSM2317 to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), as shown in the schematic in Figure 3. Some users may
want to replace the ferrite beads with these inductors to evaluate
applications with specific EMI vs. audio performance constraints. As
an aid, a properly tuned ferrite bead-based EMI filter is assembled at
the output terminals of the device.
For optimal performance, as specified in the SSM2317 data sheet
(in particular, for THD and SNR), remove the entire EMI filter,
short across the ferrite bead terminals, and open the capacitor
terminals.
POWER SUPPLY CONFIGURATION
The evaluation board schematic is shown in Figure 3. The 2-pin
header, J3, must be used to power the board. Care must be taken
to connect the dc power with correct polarity and voltage. The
positive voltage terminal of J3 (VDD) is indicated with an arrow
in Figure 1.
Polarity and Voltage
The wrong power supply polarity or an overvoltage may damage
the board permanently. The maximum peak current is approximately 0.33 A when driving an 8 Ω load and when the input
voltage is 5 V.
COMPONENT SELECTION
Selecting the proper components is the key to achieving the
performance required at the cost budgeted.
ALC Threshold Setting Resistor—R5
When ALC mode is active, the maximum output amplitude
threshold (V
from 90% to 45% of V
between the VTH pin and GND. Shorting the VTH pin to GND
sets V
TH
V
to 45% of VDD. The relation of RTH to VTH is shown by the
TH
following equation:
V ×
TH
Maximum output power is derived from V
equation:
P
OUT
R
where
To tune a variety of V
the evaluation board. To measure the potentiometer resistance setting, insert an ohmmeter across Pin 5 and Pin 6 of J2.
Note that measuring the resistance across the potentiometer is not
adequate to determine the actual R
internal input resistance of 50 k at the VTH pin. The user must
take into account the internal resistance while evaluating actual
R
. For example, after tuning R5 to a desirable level, the user
TH
measures the resistance from Pin 5 and Pin 6 of J2. Then, to infer
the actual R
where:
R
Threshold
to GND.
R
Measured
) during the limiting operation can be adjusted
TH
by inserting an external resistor, RTH,
DD
to 90% of VDD. Leaving the VTH pin unconnected sets
R
k50
TH
×=
9.0
V
⎛
TH
⎜
2
⎝
=
R
SP
is the speaker impedance.
SP
, use this simple calculation:
TH
RR
2k50
2
⎞
⎟
⎠
levels, a potentiometer, R5, is mounted on
TH
−=
MeasuredThreshold
V
DD
R
×+
TH
by the following
TH
value. This is due to the
TH
111
k50
is the desired external resistor value from the VTH pin
is the measured resistance from the VTH pin to GND.
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 8

UG-192 Evaluation Board User Guide
Input Coupling Capacitor Selection—C1 and C2
The input coupling capacitors, C1 and C2, should be large enough
to couple the low frequency signal components in the incoming
signal but small enough to filter out unnecessary low frequency
signals. For music signals, the cutoff frequency chosen is, typically,
between 20 Hz and 30 Hz. The value of the input capacitor is
calculated by
πRf
C = 1/(2
)
c
where:
R = 40 kΩ + Rext (the external resistor used to fine-tune the
desired gain; on the schematics (see Figure 3), this is the 0
resistor at the input pins).
is the cutoff frequency.
f
c
Output Ferrite Beads—L1 and L2
The output beads, L1 and L2, are necessary components for
filtering out the EMI caused at the switching output nodes when
the length of the speaker wire is greater than 10 cm. The penalty
for using ferrite beads for EMI filtering is slightly worse noise and
distortion performance at the system level due to the nonlinearity
of the beads.
Ensure that these beads have enough current-conducting capability
while providing sufficient EMI attenuation. The current rating
needed for an 8 Ω load is approximately 420 mA, and impedance
at 100 MHz should be ≥120 . In addition, the lower the dc
resistance (DCR) of these beads is, the better for minimizing their
power consumption. Tab le 1 describes the recommended beads.
Output Shunting Capacitors
There are two output shunting capacitors, C6 and C7, that work
with the ferrite beads, L1 and L2. Use small size (0603 or 0402),
multilayer ceramic capacitors that are made of X7R or COG (NPO)
materials. Note that the capacitors can be used in pairs: a capacitor
with small capacitance (up to 100 pF) plus a capacitor with a
bigger capacitance (less than 1 nF). This configuration provides
thorough EMI reduction for the entire frequency spectrum. For
BOM cost reduction and capable performance, a single capacitor
of approximately 470 pF can be used.
Output Inductors
If using inductors for the purpose of EMI filtering at the output
nodes, choose inductance that is <2.2 µH for these inductors. The
higher the inductance is, the lower the EMI becomes at the output.
However, the cost and power consumption by the inductors are
higher. Using 0.47 µH to 2.2 µH inductors is recommended, and
the current rating needs >600 mA (saturation current) for an 8 Ω
load. Tabl e 2 shows the recommended inductors. Note that these
inductors are not populated on the evaluation board.
GETTING STARTED
To ensure proper operation, carefully follow Step 1 through Step 7.
If a jumper is across Pin 1 and Pin 2 of J2, remove the jumper
1.
to enable the amplifier.
2.
Remove the jumper across Pin 3 and Pin 4 of J2 to ensure that
the device is in ALC mode. To put in standard 12 dB
configuration and disable ALC, insert a jumper across Pin 3
and Pin 4.
For most audio quality testing, the EMI filtering (L1/L2 and
3.
C6/C7) must be removed. Short across the L1 and L2
terminals to make a direct connection from the device output
to the J4 speaker header.
Connect the load to the audio output connector, J4.
4.
Connect the audio input to the board in either differential
5.
mode or single-ended mode, depending on the application.
6.
Connect the power supply with the proper polarity and
voltage.
Turn R5 potentiometer to the desired V
7.
setting.
TH
WHAT TO TEST
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI)—connect wires for the
speakers, making sure that they are the same length as the
wires required for the actual application environment; then
complete the EMI test.
• Signal-to-noise ratio.
• Output noise—make sure to use an A-weighted filter to filter
the output before reading the measurement meter.
• Maximum output power.
• Distortion.
• Efficiency.
Table 1. Recommended Output Beads
Part No. Manufacturer Z (Ω) I
BLM18PG121SN1D Murata 120 2000 0.05 1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
MPZ1608S101A TDK 100 3000 0.03 1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
MPZ1608S221A TDK 220 2000 0.05 1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
BLM18EG221SN1D Murata 220 2000 0.05 1.6 × 0.8 × 0.8
(mA) DCR (Ω) Size (mm)
MAX
Table 2. Recommended Output Inductors
Part No. Manufacturer L (μH) I
LQM31PNR47M00 Murata 0.47 1400 0.07 3.2 × 1.6 × 0.85
LQM31PN1R0M00 Murata 1.0 1200 0.12 3.2 × 1.6 × 0.85
LQM21PNR47MC0 Murata 0.47 1100 0.12 2.0 × 1.25 × 0.5
LQM21PN1R0MC0 Murata 1.0 800 0.19 2.0 × 1.25 × 0.5
LQH32CN2R2M53
Murata 2.2 790 0.1 3.2 × 2.5 × 1.55
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 8
(mA) DCR (Ω) Size (mm)
MAX

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-192
V
EVALUATION BOARD SCHEMATIC AND ARTWORK
DD
J3
HDR1X2
C3
10µF
C4
J1J1
CON4
0.1µF
1C
C1
0.1µF
1
2
3
4
IN+
IN-
C2
0.1µF
VDD
R1
0Ω
R2
0Ω
100kΩ
SSM2317/BGA
R3
U1
1B
IN+
1A
IN–
GND
OUT+
OUT–
ALC_EN
SD2AVTH
2B
2C
VDD
3C
3B
3A
L1
B0603
TP1
TP2
L2
B0603
C6
1nF
C7
1nF
OUT+
OUT–
J4
HDR1X2
R4
100kΩ
123456
CON6A
J2
R5
100kΩ
C5
0.1µF
9354-003
Figure 3. Schematic of the SSM2317 Evaluation Board
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 8

UG-192 Evaluation Board User Guide
09354-004
Figure 4. Top Layer with Top Silkscreen
Figure 6. Top Layer
09354-006
Figure 5. Top Silkscreen
09354-005
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 8
Figure 7. Layer 2 (Ground Plane)
09354-006

Evaluation Board User Guide UG-192
Figure 8. Layer 3 (Power Plane)
09354-008
Figure 9. Bottom Layer
09354-009
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 8

UG-192 Evaluation Board User Guide
ORDERING INFORMATION
BILL OF MATERIALS
Table 3.
Qty Reference Designator Description Supplier/Part No.
3 C1, C2, C4 Ceramic capacitor, 0.1 F Panasonic, ECJ-ZEB1A104M
1 C3 Ceramic capacitor, 10 F, 10 V Murata, GRM31MF51A106ZA01L
2 C6, C7 Ceramic capacitor, 1 nF, 10%, 50 V Kemet, C0603C102J5GACTU
1 J1 CON4, header connector Tyco, 640452-4
1 J2 CON6A, six-position header connector Tyco, 3-87589-6
2 J3, J4 HDR1X2 header connector Tyco, 640452-2
2 L1, L2 Ferrite chip, B0603, 220 Ω TDK, MPZ1608S221A
2 R1, R2 Resistor, 0 Ω Panasonic, ERJ-3GEY0R00V
2 R3, R4 Resistor, 100 kΩ Yageo, RT0603FRE07100KL
2 TP1, TP2 Test pad N/A
1 U1 SSM2317/BGA Analog Devices, SSM2317
1 C5 Ceramic capacitor, 0.1 µF Panasonic, ECJ-ZEB1A104M
1 R5 Potentiometer, 100 kΩ to 0 Ω Panasonic, EVN-D8AA03B15
ESD Caution
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Charged devices and circuit boards can discharge without detection. Although this product features patented or proprietary protection
circuitry, damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy ESD. Therefore, proper ESD precautions should be taken to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
Legal Terms and Conditions
By using the evaluation board discussed herein (together with any tools, components documentation or support materials, the “Evaluation Board”), you are agreeing to be bound by the terms and conditions
set forth below (“Agreement”) unless you have purchased the Evaluation Board, in which case the Analog Devices Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale shall govern. Do not use the Evaluation Board until you
have read and agreed to the Agreement. Your use of the Evaluation Board shall signify your acceptance of the Agreement. This Agreement is made by and between you (“Customer”) and Analog Devices, Inc.
(“ADI”), with its principal place of business at One Technology Way, Norwood, MA 02062, USA. Subject to the terms and conditions of the Agreement, ADI hereby grants to Customer a free, limited, personal,
temporary, non-exclusive, non-sublicensable, non-transferable license to use the Evaluation Board FOR EVALUATION PURPOSES ONLY. Customer understands and agrees that the Evaluation Board is provided
for the sole and exclusive purpose referenced above, and agrees not to use the Evaluation Board for any other purpose. Furthermore, the license granted is expressly made subject to the following additional
limitations: Customer shall not (i) rent, lease, display, sell, transfer, assign, sublicense, or distribute the Evaluation Board; and (ii) permit any Third Party to access the Evaluation Board. As used herein, the term
“Third Party” includes any entity other than ADI, Customer, their employees, affiliates and in-house consultants. The Evaluation Board is NOT sold to Customer; all rights not expressly granted herein, including
ownership of the Evaluation Board, are reserved by ADI. CONFIDENTIALITY. This Agreement and the Evaluation Board shall all be considered the confidential and proprietary information of ADI. Customer may
not disclose or transfer any portion of the Evaluation Board to any other party for any reason. Upon discontinuation of use of the Evaluation Board or termination of this Agreement, Customer agrees to
promptly return the Evaluation Board to ADI. ADDITIONAL RESTRICTIONS. Customer may not disassemble, decompile or reverse engineer chips on the Evaluation Board. Customer shall inform ADI of any
occurred damages or any modifications or alterations it makes to the Evaluation Board, including but not limited to soldering or any other activity that affects the material content of the Evaluation Board.
Modifications to the Evaluation Board must comply with applicable law, including but not limited to the RoHS Directive. TERMINATION. ADI may terminate this Agreement at any time upon giving written notice
to Customer. Customer agrees to return to ADI the Evaluation Board at that time. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. THE EVALUATION BOARD PROVIDED HEREUNDER IS PROVIDED “AS IS” AND ADI MAKES NO
WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS OF ANY KIND WITH RESPECT TO IT. ADI SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY REPRESENTATIONS, ENDORSEMENTS, GUARANTEES, OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, RELATED
TO THE EVALUATION BOARD INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, TITLE, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NONINFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL
PROPERTY RIGHTS. IN NO EVENT WILL ADI AND ITS LICENSORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM CUSTOMER’S POSSESSION OR USE OF
THE EVALUATION BOARD, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOST PROFITS, DELAY COSTS, LABOR COSTS OR LOSS OF GOODWILL. ADI’S TOTAL LIABILITY FROM ANY AND ALL CAUSES SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE
AMOUNT OF ONE HUNDRED US DOLLARS ($100.00). EXPORT. Customer agrees that it will not directly or indirectly export the Evaluation Board to another country, and that it will comply with all applicable
United States federal laws and regulations relating to exports. GOVERNING LAW. This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the substantive laws of the Commonwealth of
Massachusetts (excluding conflict of law rules). Any legal action regarding this Agreement will be heard in the state or federal courts having jurisdiction in Suffolk County, Massachusetts, and Customer hereby
submits to the pers onal jurisdiction and venu e of such courts. The United Nations Conventi on on Contracts for the Internation al Sale of Goods shall not apply to this Agreement and is expressly disclaimed.
©2010 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
UG09354-0-10/10(0)
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 8
 Loading...
Loading...