Hardware User Guide
UG-180
One Technology Way • P. O . Box 9106 • Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A. • Tel : 781.329.4700 • Fax : 781.461.3113 • www.analog.com
Advantiv ADV7611 HDMI Receiver Functionality and Features
SCOPE
This user guide provides a detailed description of the Advantiv™ ADV7611 HDMI® receiver functionality and features.
DISCLAIMER
Information furnished by Analog Devices, Inc., is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog
Devices for its use, nor any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications are subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of
Analog Devices. Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
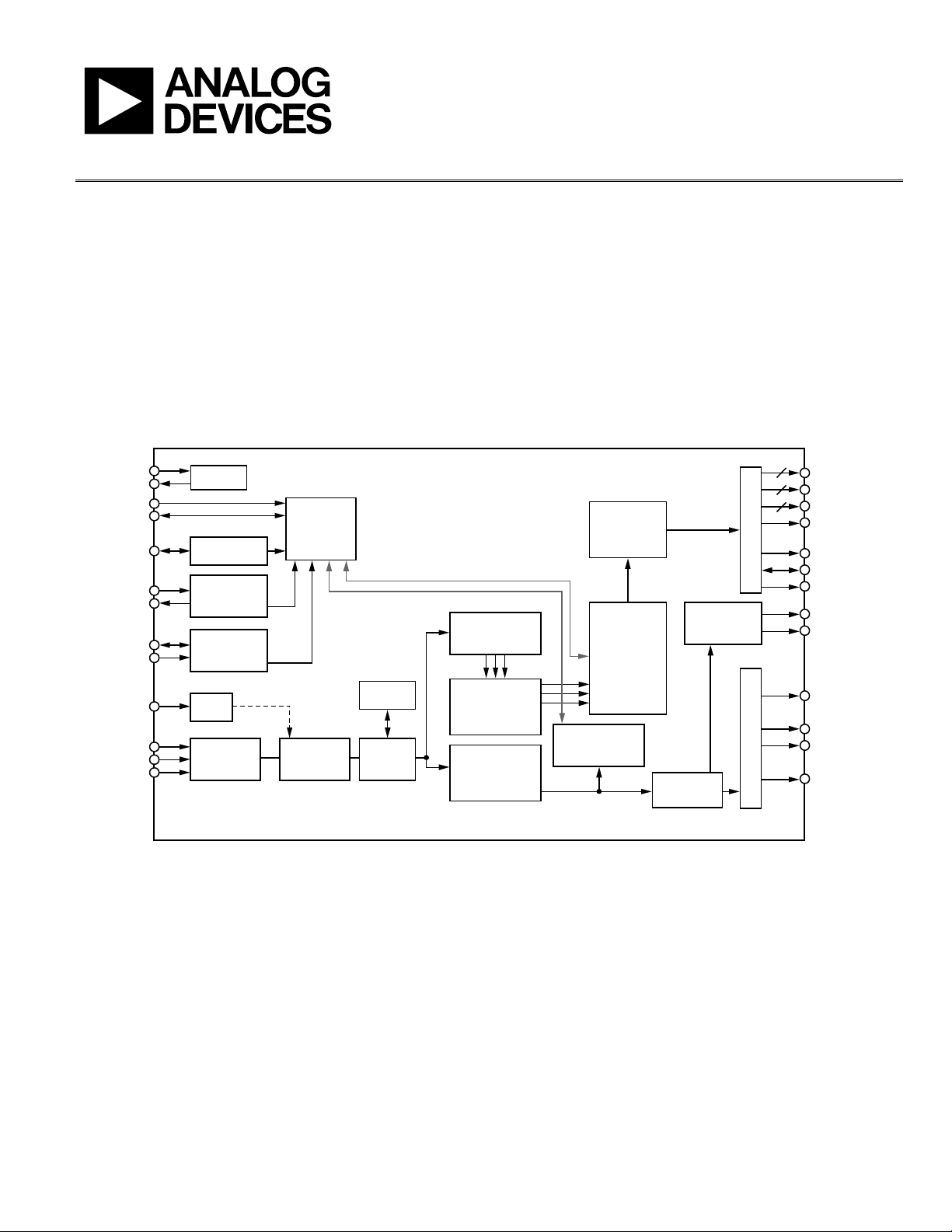
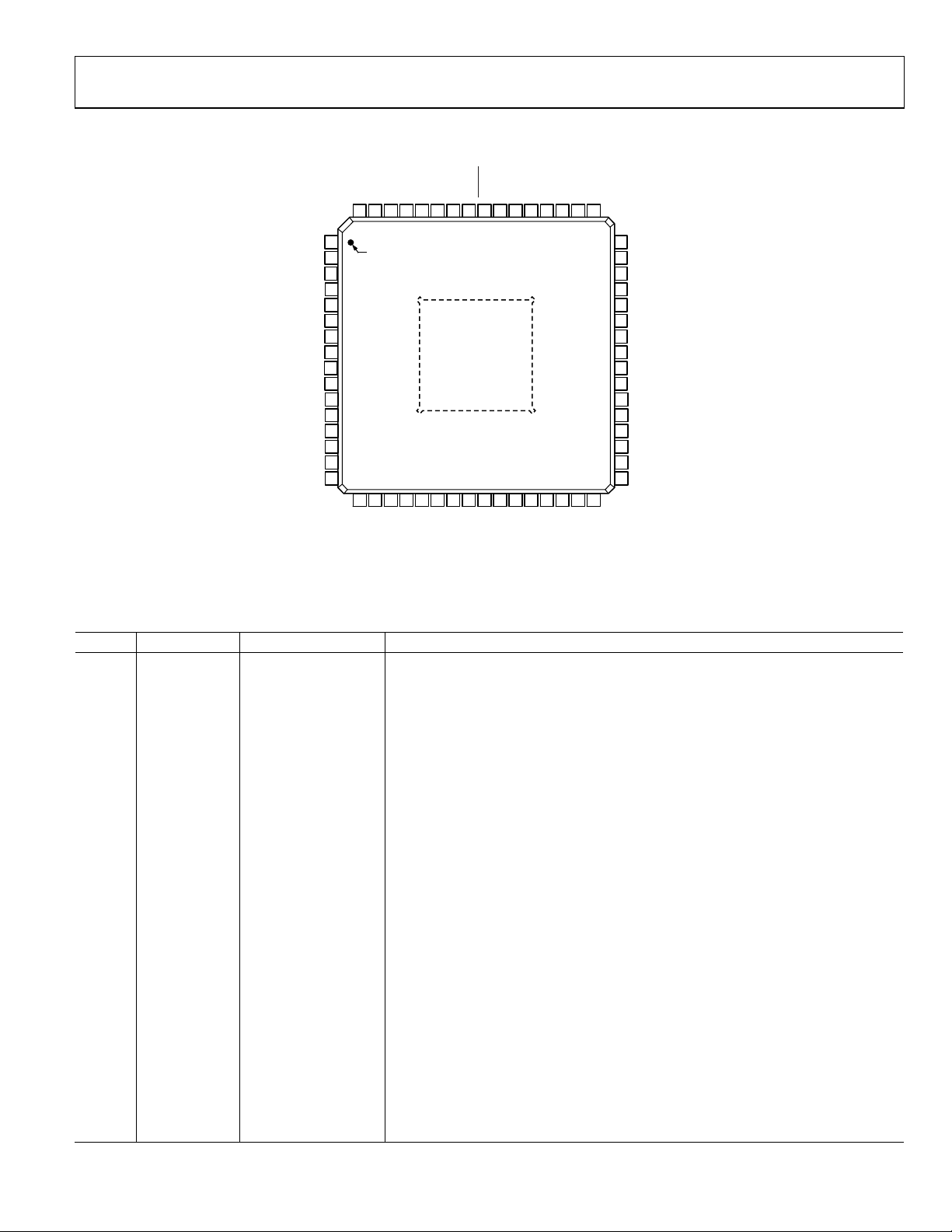
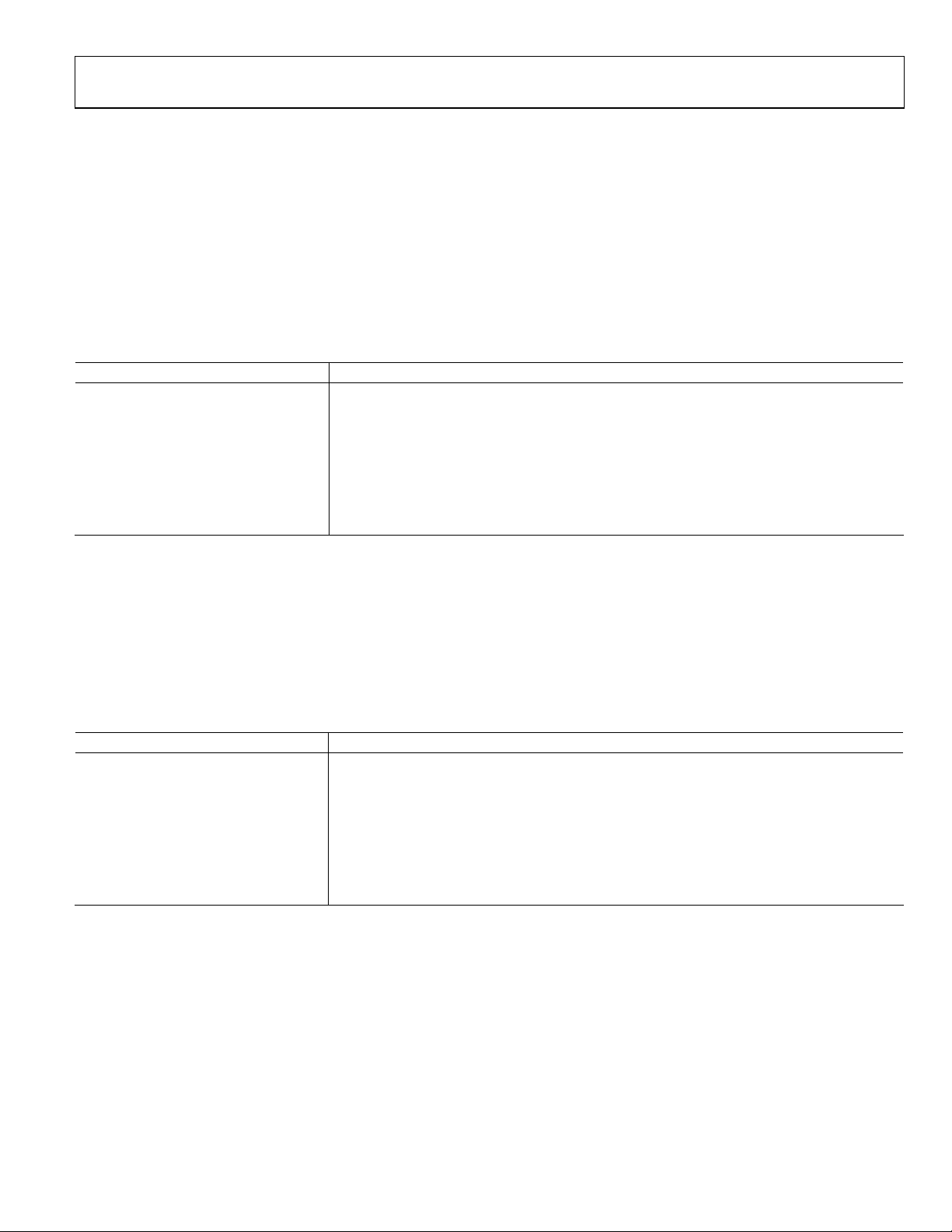
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
XTALP
XTALN
SCL
SDA
CEC
RXA_5V
HPA_A/INT2*
DDCA_SDA
DDCA_SCL
RXA_C±
RXA_0±
RXA_1±
RXA_2±
DPLL
CONTROL
INTERFACE
2
I
CEC
CONTRO LLER
5V DETECT
AND HPD
CONTRO LLER
EDID
REPEATER
CONTRO LLER
PLL
EQUALIZER EQUALIZE R
C
CONTROL
AND DATA
HDCP
EEPROM
HDCP
ENGINE
HDMI
PROCESSOR
DATA
PREPROCESSOR
AND COLOR
SPACE
CONVERSION
PACKET
PROCESSOR
BACKEND
COLOR SPACE
CONVERSION
COMPONENT
PROCESSOR
A
B
C
PACKET/
INFOFRAME
MEMORY
INTERRUPT
CONTRO LLER
(INT1, INT2)
MUTE
AUDIO
PROCESSOR
ADV7611
12
12
12
AUDIO OUTPUT FORMATTER OUTPUT FORMATTER
P0 TO P7
P8 TO P15
P16 TO P23
LLC
HS
VS/FIELD/ALSB
DE
INT1
INT2*
AP
LRCLK
SCLK/INT2*
MCLK/INT2*
*INT2 CAN BE ONLY OUTPUT ON ONE OF THE PINS: SCLK/INT2, MCLK/INT2, OR HPA_A/INT2.
Figure 1.
PLEASE SEE THE LAST PAGE FOR AN IMPORTANT
WARNING AND LEGAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS.
Rev. A | Page 1 of 184
09238-001

UG-180 Hardware User Guide
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Scope .................................................................................................. 1
Disclaimer.......................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 5
Using the ADV7611 Hardware User Guide .................................. 6
Number Notations........................................................................ 6
Register Access Conventions ...................................................... 6
Acronyms and Abbreviations ..................................................... 6
Field Function Descriptions........................................................ 8
Example Field Function Description..................................... 8
References...................................................................................... 8
Introduction to the ADV7611 ........................................................ 9
HDMI Receiver............................................................................. 9
Component Processor ................................................................. 9
Main Features of ADV7611 ........................................................ 9
HDMI Receiver......................................................................... 9
Component Video Processing ................................................ 9
Video Output Formats........................................................... 10
Additional Features ................................................................ 10
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions....................... 11
Global Control Registers ............................................................... 13
ADV7611 Revision Identification ............................................ 13
Power-Down Controls............................................................... 13
Primary Power-Down Controls ........................................... 13
Secondary Power-Down Controls ....................................... 13
Power-Down Modes .............................................................. 14
Global Pin Control..................................................................... 15
Reset Pin .................................................................................. 15
Reset Controls......................................................................... 15
Tristate Output Drivers ......................................................... 15
Tristate LLC Driver ................................................................16
Tristate Synchronization Output Drivers............................16
Tristate Audio Output Drivers..............................................16
Drive Strength Selection........................................................ 17
Output Synchronization Selection ....................................... 17
Output Synchronization Signals Polarity............................18
Digital Synthesizer Controls.................................................19
Crystal Frequency Selection ................................................. 19
Primary Mode and Video Standard............................................. 20
Primary Mode and Video Standard Controls......................... 20
V_FREQ .................................................................................. 22
HDMI Decimation Modes........................................................ 22
Primary Mode and Video Standard Configuration for
HDMI Free Run.......................................................................... 22
Recommended Settings for HDMI Inputs.............................. 23
Pixel Port Configuration ............................................................... 25
Pixel Port Output Modes........................................................... 25
Bus Rotation and Reordering Controls............................... 25
Pixel Data and Synchronization Signals Control............... 25
LLC Controls............................................................................... 26
DLL on LLC Clock Path............................................................ 26
Adjusting DLL Phase in All Modes ..................................... 26
DLL Settings for 656, 8-/10-/12-Bit Modes........................ 27
HDMI Receiver............................................................................... 28
+5 V Cable Detect ...................................................................... 28
Hot Plug Assert........................................................................... 29
E-EDID/Repeater Controller.................................................... 31
E-EDID Data Configuration..................................................... 31
Notes........................................................................................ 32
E-EDID Support for Power-Down Modes ......................... 32
Transitioning of Power Modes ................................................. 32
Structure of Internal E-EDID................................................... 32
Notes........................................................................................ 33
TMDS Equalization ................................................................... 33
Port Selection.............................................................................. 33
TMDS Clock Activity Detection .............................................. 33
Important ................................................................................ 34
Clock and Data Termination Control ................................. 34
HDMI/DVI Status Bits .............................................................. 34
Video 3D Detection ................................................................... 34
TMDS Measurement.................................................................. 35
TMDS Measurement after TMDS PLL ............................... 35
Deep Color Mode Support........................................................ 36
Notes........................................................................................ 36
Video FIFO.................................................................................. 36
Pixel Repetition .......................................................................... 38
HDCP Support ........................................................................... 39
HDCP Decryption Engine.................................................... 39
Internal HDCP Key OTP ROM........................................... 40
HDCP Keys Access Flags...................................................... 40
Rev. A | Page 2 of 184

Hardware User Guide UG-180
HDCP Ri Expired ...................................................................42
HDMI Synchronization Parameters.........................................43
Notes.........................................................................................43
Horizontal Filter and Measurements ...................................43
Primary Port Horizontal Filter Measurements...................43
Horizontal Filter Locking Mechanism.................................45
Vertical Filters and Measurements .......................................45
Primary Port Vertical Filter Measurements ........................45
Vertical Filter Locking Mechanism ......................................48
Important.................................................................................48
Audio DPLL.............................................................................49
Locking Mechanism ...............................................................49
ACR Parameters Loading Method .......................................49
Audio DPLL Coast Feature....................................................49
Audio FIFO..................................................................................49
Audio Packet Type Flags ............................................................51
Notes.........................................................................................52
Audio Output Interface ..............................................................53
I2S/SPDIF Audio Interface and Output Controls...............54
Notes.........................................................................................55
MCLKOUT Setting.....................................................................57
Audio Channel Mode.................................................................58
Audio Muting ..............................................................................58
Delay Line Control .................................................................58
Audio Mute Configuration....................................................59
Internal Mute Status ...............................................................61
AV Mute Status........................................................................61
Audio Mute Signal ..................................................................61
Audio Stream with Incorrect Parity Error...........................62
Audio Clock Regeneration Parameters ....................................62
ACR Parameters Readbacks ..................................................62
Monitoring ACR Parameters.................................................62
Channel Status.............................................................................63
Validity Status Flag..................................................................63
General Control and Mode Information .............................64
Category Code.........................................................................65
Source Number and Channel Number ................................65
Sampling and Frequency Accuracy ......................................66
Word Length............................................................................66
Channel Status Copyright Value Assertion .........................67
Monitoring Change of Audio Sampling Frequency ...........67
Packets and InfoFrames Registers ............................................67
InfoFrames Registers..............................................................67
InfoFrame Collection Mode..................................................68
InfoFrame Checksum Error Flags........................................68
AVI InfoFrame Registers .......................................................69
Audio InfoFrame Registers....................................................70
SPD InfoFrame Registers.......................................................71
MPEG Source InfoFrame Registers......................................72
Vendor Specific InfoFrame Registers...................................73
Packet Registers...........................................................................74
ACP Packet Registers .............................................................74
ISRC Packet Registers.............................................................75
Gamut Metadata Packets .......................................................77
Customizing Packet/InfoFrame Storage Registers .................78
Repeater Support.........................................................................79
Repeater Routines Performed by the EDID/Repeater
Controller.................................................................................79
Repeater Actions Required by External Controller ...........80
HDCP Registers Available in Repeater Map.......................81
Interface to DPP Section............................................................86
Notes.........................................................................................87
Pass Through Mode....................................................................87
4:2:2 Pass Through..................................................................87
4:4:4 Pass Through..................................................................87
Color Space Information Sent to the DPP and
CP Sections ..................................................................................88
Status Registers............................................................................88
HDMI Section Reset Strategy ...................................................91
HDMI Packet Detection Flag Reset .........................................91
Data Preprocessor and Color Space Conversion and Color
Controls............................................................................................92
Color Space Conversion Matrix................................................92
CP CSC Selection....................................................................92
Selecting Auto or Manual CP CSC Conversion Mode......93
Auto Color Space Conversion Matrix..................................93
HDMI Automatic CSC Operation........................................95
Manual Color Space Conversion Matrix .............................97
CSC in Pass-Through Mode................................................101
Color Controls...........................................................................101
Component Processor..................................................................103
Introduction to the Component Processor ...........................103
Clamp Operation ......................................................................103
Rev. A | Page 3 of 184

UG-180 Hardware User Guide
CP Gain Operation................................................................... 105
Features of Manual Gain Control ...................................... 105
Features of Automatic Gain Control .................................105
Manual Gain and Automatic Gain Control Selection.....105
Manual Gain Control...........................................................106
Manual Gain Filter Mode....................................................108
Other Gain Controls............................................................108
CP Offset Block......................................................................... 109
Notes ......................................................................................109
AV Code Block.......................................................................... 110
CP Data Path for HDMI Modes ............................................. 112
Pregain Block ........................................................................ 112
Sync Processed by CP Section ................................................115
Sync Routing from HDMI Section .................................... 115
Standard Detection and Identification.............................. 115
Detailed Mechanism of STDI Block Horizontal/Vertical
Lock Mechanism ..................................................................118
CP Output Synchronization Signal Positioning................... 122
CP Synchronization Signals ................................................ 124
HSync Timing Controls ...................................................... 124
VSync Timing Controls.......................................................126
DE Timing Controls ............................................................ 128
FIELD Timing Controls......................................................129
HCOUNT Timing Control................................................. 133
CP HDMI Controls.................................................................. 134
Free Run Mode .........................................................................134
Free Run Mode Thresholds.................................................134
Free Run Feature in HDMI Mode...................................... 136
Free Run Default Color Output.......................................... 137
CP Status.................................................................................... 138
CP_REG_FF.......................................................................... 138
CP Core Bypassing.................................................................... 138
Consumer Electronics Control................................................... 139
Main Controls........................................................................... 139
CEC Transmit Section ............................................................. 140
CEC Receive Section................................................................ 142
Logical Address Configuration ..........................................142
Receive Buffers...................................................................... 143
CEC Message Reception Overview.................................... 146
Antiglitch Filter Module .......................................................... 147
Typical Operation Flow ...........................................................148
Initializing CEC Module..................................................... 148
Using CEC Module as Initiator.......................................... 149
Using CEC Module as Follower .........................................150
Low Power CEC Message Monitoring................................... 151
Interrupts....................................................................................... 153
Interrupt Architecture Overview........................................... 153
Interrupt Pins............................................................................ 156
Notes...................................................................................... 156
Interrupt Duration............................................................... 157
Interrupt Drive Level........................................................... 157
Interrupt Manual Assertion................................................ 157
Multiple Interrupt Events.................................................... 158
Description of Interrupt Bits .................................................. 159
General Operation ...............................................................159
HDMI Video Mode.............................................................. 159
CEC........................................................................................ 159
HDMI Only Mode ...............................................................159
Additional Explanations.......................................................... 160
STDI_DATA_VALID_RAW............................................... 160
CP_LOCK, CP_UNLOCK ................................................. 161
HDMI Interrupts Validity Checking Process ................... 161
Storing Masked Interrupts .................................................. 163
Register Access and Serial Ports Description ........................... 174
Main I2C Port............................................................................ 174
Register Access .....................................................................174
IO I2C Map Address............................................................. 174
Addresses of Other Maps.................................................... 175
Protocol for Main I2C Port.................................................. 176
DDC Ports................................................................................. 177
I2C Protocols for Access to the Internal EDID................. 177
I2C Protocols for Access to HDCP Registers.................... 177
DDC Port A .......................................................................... 177
Appendix A ................................................................................... 178
PCB Layout Recommendations .............................................178
Power Supply Bypassing.......................................................... 178
Example of a Current Loop................................................. 178
Digital Outputs (Data and Clocks)........................................ 178
Digital Inputs ............................................................................ 179
XTAL and Load Cap Value Selection .................................... 179
Example................................................................................. 179
Rev. A | Page 4 of 184

Hardware User Guide UG-180
Appendix B .................................................................................... 180
Recommended Unused Pin Configurations ........................ 180
REVISION HISTORY
12/11—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Change to Video Output Formats Section ................................... 10
Changes to RD_INFO[15:0] Table in ADV7611 Revision
Identification Section ...................................................................... 13
Change to XTAL_FREQ_SEL[1:0] Table in Crystal
Frequency Selection Section .......................................................... 19
Changes to Table 7 .......................................................................... 23
Added Endnote to OP_FORMAT_SEL[7:0] Table in Pixel
Port Output Modes Section ........................................................... 25
Added LLC_DLL_DOUBLE to DLL on LLC C
ction .............................................................................................. 26
Se
lock Path
Appendix C .................................................................................... 182
Pixel Output Formats ............................................................... 182
Added DLL Settings for 656, 8-/10-/12-Bit Modes Section ...... 27
Changes to Audio Mute Signal Section ........................................ 61
Added 1001 to CS_DATA[27:24] Table in Sampling and
Frequency Accuracy Section ......................................................... 66
Changes to Check the Value of Each Coefficient Section ....... 100
Changes to CP_HUE[7:0], Addr 44 (CP), Address 0x3D[7:0]
in Color Controls Section; Changes to CP_HUE[7:0] Table ..... 102
Changes to INT2_POL Table in Interrupt Drive Level Section ... 157
Added Endnote to Table 71 ......................................................... 182
10/10—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. A | Page 5 of 184
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
USING THE ADV7611 HARDWARE USER GUIDE
NUMBER NOTATIONS
Table 1.
Notation Description
Bit N Bits are numbered in little endian format, that is, the least significant bit of a number is referred to as Bit 0.
V[X:Y] Bit field representation covering Bit X to Bit Y of a value or a field (V).
0xNN Hexadecimal (base-16) numbers are preceded by the prefix ‘0x’.
0bNN Binary (base-2) numbers are preceded by the prefix ‘0b’.
NN Decimal (base-10) are represented using no additional prefixes or suffixes.
REGISTER ACCESS CONVENTIONS
Table 2.
Mode Description
R/W Memory location has read and write access.
R Memory location is read access only. A read always returns 0 unless otherwise specified.
W Memory location is write access only.
ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
Table 3.
Acronym/Abbreviation Description
ACP Audio content protection.
AGC Automatic gain control.
Ainfo HDCP register. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References section.
AKSV
An 64-bit pseudo-random value generated by HDCP cipher function of Device A.
AP Audio output pin.
AVI Auxiliary video information.
BCAPS HDCP register. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References section.
BKSV HDCP receiver key selection vector. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References section.
CP Component processor.
CSC Color space converter/conversion.
DDR Double data rate.
DE Data enable.
DLL Delay locked loop.
DPP Data preprocessor.
DVI Digital visual interface.
EAV End of active video.
EMC Electromagnetic compatibility.
EQ Equalizer.
HD High definition.
HDCP High bandwidth digital content protection.
HDMI High bandwidth multimedia interface.
HDTV High definition television.
HPA Hot plug assert.
HPD Hot plug detect.
HSync Horizontal synchronization.
IC Integrated circuit.
ISRC International standard recording code.
I2S Inter IC sound.
HDCP transmitter key selection vector. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References
section.
Rev. A | Page 6 of 184
Hardware User Guide UG-180
Acronym/Abbreviation Description
I2C Inter integrated circuit.
KSV Key selection vector.
LLC Line locked clock.
LSB Least significant bit.
L-PCM Linear pulse coded modulated.
Mbps Megabit per second.
MPEG Moving picture expert group.
ms Millisecond.
MSB Most significant bit.
NC No connect.
OTP One-time programmable.
Pj’
Ri’ HDCP link verification response. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References section.
Rx Receiver.
SAV Start of active video.
SDR Single data rate.
SHA-1 Refer to HDCP documentation.
SMPTE Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers.
SOG Sync on green.
SOY Sync on Y.
SPA Source physical address.
SPD Source production descriptor.
STDI Standard detection and identification.
TDM Time division multiplexed.
TMDS Transition minimized differential signaling.
Tx Transmitter.
VBI Video blanking interval.
VSync Vertical synchronization.
XTAL Crystal oscillator.
HDCP enhanced link verification response. Refer to digital content protection documentation in the References
section.
Rev. A | Page 7 of 184
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
FIELD FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Throughout this user guide, a series of function tables are provided. The function of a field is described in a table preceded by the bit
name, a short function description, the I
The detailed description consists of:
• For a readable field, the values the field can take
• For a writable field, the values the field can be set to
Example Field Function Description
This section provides an example of a field function table followed by a description of each part of the table.
PRIM_MODE[3:0], IO Map, Address 0x01[3:0].
A control to select the primary mode of operation of the decoder.
Function
PRIM_MODE[3:0] Description
0000 Reserved
0001 Reserved
0010 Reserved
0011 Reserved
0100 Reserved
0101 HDMI-Comp
0110 (default) HDMI-GR
0111 to 1111 Reserved
In this example
• The name of the field is PRIM_MODE and it is four bit long.
2
• Address 0x01 is the I
C location of the field in big endian format (MSB first, LSB last).
• The address is followed by a detailed description of the field.
2
C map, the register location within the I2C map, and a detailed description of the field.
• The first column of the table lists values the field can take or can be set to. These values are in binary format if not preceded by 0x or
in hexadecimal format if preceded by 0x.
• The second column describes the function of each field for each value the field can take or can be set to. Values are in binary format.
REFERENCES
CEA, CEA-861-D, A DTV Profile for Uncompressed High Speed Digital Interfaces, Revision D, July 18, 2006.
Digital Content Protection (DCP) LLC, High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection System, Revision 1.4, July 8, 2009.
HDMI Licensing and LLC, High-Definition Multimedia Interface, Revision 1.4a, March 4, 2010.
ITU, ITU-R BT.656-4, Interface for Digital Component Video Signals in 525-Line and 625-Line Television Systems Operating
at the 4:2:2 Level of Recommendation ITU-R BT.601, February 1998.
Rev. A | Page 8 of 184

Hardware User Guide UG-180
INTRODUCTION TO THE ADV7611
The ADV7611 is a high quality, single input, high definition multimedia interface (HDMI®) receiver. It incorporates an HDMI receiver
that supports all mandatory HDMI 1.4a 3D TV formats up to 1080 p60@8-bit. It integrates a CEC controller that supports the capability
discovery and control (CDC) feature.
The ADV7611 has an audio output port for the audio data extracted from the HDMI stream. The receiver has an advanced mute
controller that prevents audible extraneous noise in the audio output. Additionally, the ADV7611 can be set to output TDM I
allows four multiplexed I
2
S channels to be sent.
Fabricated in an advanced CMOS process, the ADV7611 is provided in a 10 mm × 10 mm, 64-pin surface-mount LQFP_EP, RoHScompliant package and is specified over the −40°C to +85°C temperature range.
HDMI RECEIVER
The ADV7611 HDMI receiver incorporates equalization of the HDMI data signals to compensate for the losses inherent in HDMI and
DVI cabling, especially at longer lengths and higher frequencies. The equalizer is highly effective and is capable of equalizing for long
cables to achieve robust receiver performance.
With the inclusion of high-bandwidth digital content protection (HDCP), displays can receive encrypted video content. The HDMI
interface of the ADV7611 allows a video receiver to authenticate, decrypt encoded data and renew that authentication during
transmission, as specified by the HDCP v1.4 protocol.
The ADV7611 offers an audio output port for audio data extraction from the HDMI stream. The receiver has an advanced mute
controller that prevents audible extraneous noise in the audio output. Additionally, the ADV7611 can be set to output time division
multiplexed (TDM) I
2
S, which allows four multiplexed I2S channels to be sent.
2
S, which
COMPONENT PROCESSOR
The component processor (CP) is located behind the HDMI receiver. It processes the video data received from the HDMI receiver. The
CP section provides color adjustment features, such as brightness, saturation, and hue. The color space conversion (CSC) matrix allows
the color space to be changed as required. The standard detection and identification (STDI) block allows the detection of video timings.
MAIN FEATURES OF ADV7611
HDMI Receiver
• HDMI 1.4a features supported
• 3D HDMI 1.4a video format support
• Full colorimetry, including sYCC601, Adobe RGB, Adobe YCC601, and xvYCC extended gamut color
• CEC 1.4-compatible
• HDCP v1.4-compliant receiver
• Supports all display resolutions up to UXGA 60 Hz 8-bit
• Supports stereo audio formats with a sampling frequency up to 192 kHz
• Supports multichannel audio with sampling frequency up to 48 kHz in TDM I
• Programmable front-end equalization for long cable lengths
• Audio mute for removing extraneous noise
• Programmable interrupt generator to detect HDMI packets
• Internal EDID support
• Repeater support
Component Video Processing
• An any-to-any 3 × 3 CSC matrix support YCrCb to RGB and RGB to YCrCb
• Provides color controls, such as saturation, brightness, hue, and contrast
• STDI block that enables format detection
• Free run output mode provides stable timing when no video input is present
2
S mode
Rev. A | Page 9 of 184

UG-180 Hardware User Guide
Video Output Formats
• Double data rate (DDR) 8-/12-bit 4:2:2 YCrCb.
• DDR supported only up to 50 MHz (an equivalent to ata rate clocked with 100 MHz clock in SDR mode)
• Pseudo DDR (CCIR-656 type stream) 8-/12-bit 4:2:2 YCrCb for 525i, 625i, 525P, and 625P
• SDR 16-/24-bit 4:2:2 YCrCb for all standards
• SDR 24-bit 4:4:4 YCrCb/RGB for all HDMI standards
• DDR 24-bit 4:4:4 RGB
Additional Features
• HS, VS, FIELD, and DE output signals with programmable position, polarity, and width
• Numerous interrupt sources available for the INT1 and INT2 interrupt request output pins, available via one of the selected pins, that
is, SCLK/INT2, MCLK/INT2, or HPA_A/INT2
• Temperature range of −40°C to +85°C
• 10 mm × 10 mm, 64-pin LQFP_EP package
Rev. A | Page 10 of 184
Hardware User Guide UG-180
A
A
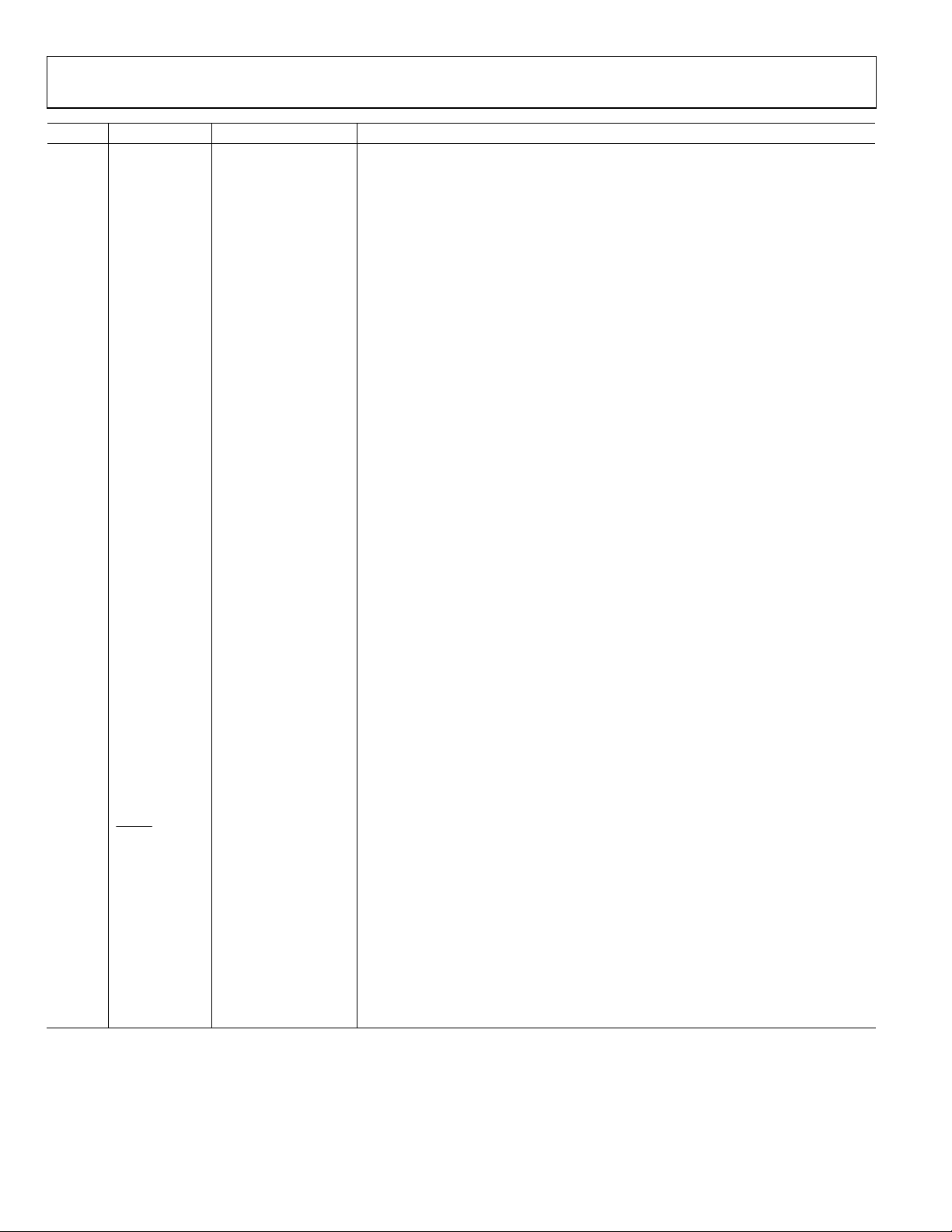
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
RXA_5V63DDCA_SD
DDCA_SD
64
CEC60DVDD59XTALN58XTALP57PVDD56RESET55INT154SDA53SCL52DVDD51MCLK/INT250LRCLK49SCLK/INT2
62
61
CVDD
TVDD
RXA_0–
RXA_0+
TVDD
RXA_1–
RXA_1+
TVDD
RXA_2–
RXA_2+
CVDD
P23
P22
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
PIN 1
P2118P2019P1920P1821P1722P16
ADV7611
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
23
24
25
LLC
DVDD
DVDDIO
26
P1527P1428P1329P12
HPA_A/INT2
RXA_C–
RXA_C+
NOTES
1. CONNECT EXP OSED PAD–PIN0 TO GROUND (BOTTOM) .
30
P11
48
AP
47
VS/FIELD/ALSB
46
HS
45
DE
44
DVDDIO
43
P0
42
P1
41
P2
40
DVDD
39
P3
38
P4
37
P5
36
P6
35
P7
34
DVDDIO
33
P8
31
32
P9
P10
09238-003
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
Table 4. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
0 GND Ground Ground.
1 HPA_A/INT2 Miscellaneous digital
A dual function pin that can be configured to output Hot Plug Assert signal (for HDMI
Port A) or an Interrupt2 signal.
2 CVDD Power HDMI Analog Block Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
3 RXA_C− HDMI input Digital Input Clock Complement of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
4 RXA_C+ HDMI input Digital Input Clock True of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
5 TVDD Power Terminator Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
6 RXA_0− HDMI input Digital Input Channel 0 Complement of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
7 RXA_0+ HDMI input Digital Input Channel 0 True of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
8 TVDD Power Terminator Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
9 RXA_1− HDMI input Digital Input Channel 1 Complement of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
10 RXA_1+ HDMI input Digital Input Channel 1 True of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
11 TVDD Power Terminator Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
12 RXA_2− HDMI input Digital Input Channel 2 Complement of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
13 RXA_2+ HDMI input Digital Input Channel 2 True of Port A in the HDMI Interface.
14 CVDD Power HDMI Analog Block Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
15 P23 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
16 P22 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
17 P21 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
18 P20 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
19 P19 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
20 P18 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
21 P17 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
22 P16 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
23 DVDDIO Power Digital I/O Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
24 DVDD Power Digital Core Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
Rev. A | Page 11 of 184
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
Pin No. Mnemonic Type Description
25 LLC Digital video output Line Locked Output Clock for the Pixel Data (Range is 13.5 MHz to 162.5 MHz).
26 P15 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
27 P14 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
28 P13 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
29 P12 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
30 P11 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
31 P10 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
32 P9 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
33 P8 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
34 DVDDIO Power Digital I/O Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
35 P7 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
36 P6 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
37 P5 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
38 P4 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
39 P3 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
40 DVDD Power Digital Core Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
41 P2 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
42 P1 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
43 P0 Digital video output Video Pixel Output Port.
44 DVDDIO Power Digital I/O Supply Voltage (3.3 V).
45 DE Miscellaneous digital DE (data enable) is a signal that indicates active pixel data.
46 HS Digital video output HS is a horizontal synchronization output signal.
47 VS/FIELD/ALSB Digital input/output
48 AP Miscellaneous
49 SCLK/INT2 Miscellaneous digital
50 LRCLK Miscellaneous Audio Left/Right Clock.
51 MCLK/INT2 Miscellaneous
52 DVDD Power Digital Core Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
53 SCL Miscellaneous digital I2C Port Serial Clock Input. SCL is the clock line for the control port.
54 SDA Miscellaneous digital I2C Port Serial Data Input/Output Pin. SDA is the data line for the control port.
55 INT1 Miscellaneous digital
56
RESET
Miscellaneous digital
57 PVDD Power PLL Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
58 XTALP Miscellaneous analog
59 XTALN Miscellaneous analog Crystal Input. Input pin for 28.63636 MHz crystal.
60 DVDD Power Digital Core Supply Voltage (1.8 V).
61 CEC Digital input/output Consumer Electronic Control Channel.
62 DDCA_SCL HDMI input HDCP Slave Serial Clock Port A. DDCA_SCL is a 3.3 V input that is 5 V tolerant.
63 DDCA_SDA HDMI input HDCP Slave Serial Data Port A. DDCA_SDA is a 3.3 V input that is 5 V tolerant.
64 RXA_5V HDMI input 5 V Detect Pin for Port A in the HDMI Interface.
VS is a vertical synchronization output signal. FIELD is a field synchronization output
signal in all interlaced video modes. VS or FIELD can be configured for this pin. The
ALSB allows selection of the I
Audio Output Pin. Pin can be configured to output SPDIF Digital Audio Output (SPDIF)
or Time-Division-Multiplexed I
2
C address.
2
S.
A dual function pin that can be configured to output Audio Serial Clock or an
Interrupt2 signal.
A dual fuction pin that can be configured to output Audio Master Clock or an
Interrupt2 signal.
Interrupt. This pin can be active low or active high. When status bits change, this pin is
triggered. The events that trigger an interrupt are under user configuration.
System Reset Input. Active low. A minimum low reset pulse width of 5 ms is required
to reset the ADV7611 circuitry.
Input Pin for 28.63636 MHz Crystal or an External 1.8 V, 28.63636 MHz Clock Oscillator
Source to Clock the ADV7611.
Rev. A | Page 12 of 184

Hardware User Guide UG-180
GLOBAL CONTROL REGISTERS
The register control bits described in this section deal with the general control of the chip, and the CP and the HDMI receiver sections of
the ADV7611.
ADV7611 REVISION IDENTIFICATION
RD_INFO[15:0], IO, Address 0xEA[7:0]; Address 0xEB[7:0] (Read Only)
Chip revision code.
Function
RD_INFO[15:0] Description
0x2041 = Final Silicon ADV7612 ADV7612
0x2051 = Final Silicon ADV7611 ADV7611
POWER-DOWN CONTROLS
Primary Power-Down Controls
POWER_DOWN is the main power-down control. It is the main control for power-down Mode 0 and Mode 1. See the Power-Down
Modes section for more details.
POWER_DOWN, IO, Address 0x0C[5]
A control to enable power-down mode. This is the main I
Function
POWER_DOWN Description
0 Chip operational
1 (default) Enables chip power down
Secondary Power-Down Controls
The following controls allow various sections of the ADV7611 to be powered down.
It is possible to stop the clock to the CP to reduce power for a power-sensitive application. The CP_PWRDN bit enables this power-save
mode. The HDMI block is not affected by this power-save mode. This allows the use of limited HDMI, STDI monitoring features while
reducing the power consumption. For full processing of the HDMI input, the CP core needs to be powered up.
CP_PWRDN, IO, Address 0x0C[2]
A power-down control for the CP core.
Function
CP_PWRDN Description
0 (default) Powers up clock to CP core.
1 Powers down clock to CP core. HDMI block not affected by this bit.
XTAL_PDN
XTAL_PDN allows the user to power down the XTAL clock in the following sections:
2
C power-down control.
• STDI blocks
• Free run synchronization generation block
2
C sequencer block, which is used for the configuration of the gain, clamp, and offset
• I
• CP and HDMI section
The XTAL clock is also provided to the HDCP engine, EDID, and the repeater controller within the HDMI receiver. The XTAL clock
within these sections is not affected by XTAL_PDN.
XTAL_PDN, IO, Address 0x0B[0]
A power-down control for the XTAL in the digital blocks.
Function
XTAL_PDN Description
0 (default) Powers up XTAL buffer to digital core
1 Powers down XTAL buffer to digital core
Rev. A | Page 13 of 184
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
CORE_PDN
CORE_PDN allows the user to power down clocks, with the exception of the XTAL clock, in the following sections:
• CP block
• Digital section of the HDMI block
CORE_PDN, IO, Address 0x0B[1]
A power-down control for the DPP, CP core, and digital sections of the HDMI core.
Function
CORE_PDN Description
0 (default) Powers up CP and digital sections of HDMI block
1 Powers down CP and digital section of HDMI block
Power-Down Modes
The ADV7611 supports the following power-down modes:
• Power-Down Mode 0
• Power-Down Mode 1
Tabl e 5 shows the power-down and normal modes of ADV7611.
Table 5. Power-Down Modes
POWER_DOWN Bit CEC_POWER_UP Bit CEC EDID Power-Down Mode
0 0 Disabled Enabled Power-Down Mode 0
0 1 Enabled Enabled Power-Down Mode 1
1 0 Disabled Enabled1 Normal mode
1 1 Enabled Enabled1 Normal mode
1
Dependent on the values of EDID_X_ENABLE_CPU and EDID_X_ENABLE for the HDMI port (where X is A).
Power-Down Mode 0
In Power-Down Mode 0, selected sections and pads are kept active to provide EDID and +5 V antiglitch filter functionality.
In Power-Down Mode 0, the sections of the ADV7611 are disabled except for the following blocks:
• I2C slave section
• EDID/repeater controller
• EDID ring oscillator
The ring oscillator provides a clock to the EDID/repeater controller (refer to the E-EDID/Repeater Controller section) and the +5 V
power supply antiglitch filter. The clock output from the ring oscillator runs at approximately 50 MHz.
The following pads only are enabled in Power-Down Mode 0:
2
• I
C pads
• SDA
• SCL
• +5 V pads
• RXA_5V
• HPA_A
• DDC pads
• DDCA_SCL
• DDCA_SDA
• Reset pad
Power-Down Mode 0 is initiated through a software (I
RESET
2
C register) configuration.
Rev. A | Page 14 of 184

Hardware User Guide UG-180
Entering Power-Down Mode 0 via Software
The ADV7611 can be put into Power-Down Mode 0 by setting POWER_DOWN to 1 (default value) and CEC_POWER_UP to 0. This
method allows an external processor to put the system in which the ADV7611 is integrated into standby mode. In this case, the CP and
HDMI cores of the ADV7611 are kept powered up from the main power (for example, ac power) and set in or out of power-down Mode 0
through the POWER_DOWN bit.
Power-Down Mode 1
Power-Down Mode 1 is enabled when the following conditions are met:
• POWER_DOWN bit is set to 1
• CEC section is enabled by setting CEC_POWER_UP to 1
Power-Down Mode 1 provides the same functionality as Power-Down Mode 0, with the addition of the following sections:
• XTAL clock
• CEC section
• Interrupt controller section
The following pads are enabled in Power-Down Mode 1:
• Same pads as enabled in Power-Down Mode 0
• CEC pad
• INT1 and INT2 interrupt pads
The internal EDID is also accessible through the DDC bus for Port A in Power-Down Mode 0 and Power-Down Mode 1.
GLOBAL PIN CONTROL
Reset Pin
The ADV7611 can be reset by a low reset pulse on the reset pin with a minimum width of 5 ms. It is recommended to wait 5 ms after the
low pulse before an I
Reset Controls
MAIN_RESET, IO, Address 0xFF[7] (Self-Clearing)
Main reset where I
Function
MAIN_RESET Description
0 (default) Normal operation
1 Applies main I2C reset
Tristate Output Drivers
PA D S _ P DN , IO, Address 0x0C[0]
A power-down control for pads of the digital output s. When enabled, the pads are tristated and the input path is disabled. This control
applies to the DE, HS, VS/FIELD/ALSB, INT1, and LLC pads and to the P0 to P23 pixel pads.
Function
PADS_PDN Description
0 (default) Powers up pads of digital output pins
1 Powers down pads of digital output pins
DDC_PWRDN[7:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x73[7:0]
A power-down control for DDC pads.
Function
DDC_PWRDN[7:0] Description
0 (default) Powers up DDC pads
1 Powers down DDC pads
2
C write is performed to the ADV7611.
2
C registers are reset to their default values.
Rev. A | Page 15 of 184
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
TRI_PIX
This bit allows the user to tristate the output driver of pixel outputs. Upon setting TRI_PIX, the pixel output P[23:0] is tristated.
TRI_PIX, IO, Address 0x15[1]
A control to tristate the pixel data on the pixel pins, P[23:0].
Function
TRI_PIX Description
0 Pixel bus active
1 (default) Tristates pixel bus
Tristate LLC Driver
TRI_LLC, IO, Address 0x15[2]
A control to tristate the output pixel clock on the LLC pin.
Function
TRI_LLC Description
0 LLC pin active
1 (default) Tristates LLC pin
Tristate Synchronization Output Drivers
The following output synchronization signals are tristated when TRI_SYNCS is set:
• VS/FIELD/ALSB
• HS
• DE
The drive strength controls for these signals are provided via the DR_STR_SYNC bits. The ADV7611 does not support tristating via a
dedicated pin.
TRI_SYNCS, IO, Address 0x15[3]
Synchronization output pins tristate control. The synchronization pins under this control are HS, VS/FIELD/ALSB, and DE.
Function
TRI_SYNCS Description
0 Sync output pins active
1 (default) Tristates sync output pins
Tristate Audio Output Drivers
TRI_AUDIO, IO Map, Address 0x15[4]
TRI_AUDIO allows the user to tristate the drivers of the following audio output signals:
• AP
• SCLK/INT2
• LRCLK
• MCLK/INT2
The drive strength for the output pins can be controlled by the DR_STR[1:0] bits. The ADV7611 does not support tristating via a
dedicated pin.
TRI_AUDIO, IO, Address 0x15[4]
A control to tristate the audio output interface pins (AP).
Function
TRI_AUDIO Description
0 Audio output pins active
1 (default) Tristates audio output pins
Rev. A | Page 16 of 184
Hardware User Guide UG-180
Drive Strength Selection
DR_STR
It may be desirable to strengthen or weaken the drive strength of the output drivers for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
and crosstalk reasons. This section describes the controls to adjust the output drivers used by the CP and HDMI modes.
The drive strenth DR_STR_SYNC[1:0] bits allow the user to select the strength of the following synchronization signals:
• DE
• HS
• VS/FIELD
The DR_STR[1:0] drive strength bits affect output drivers for the following output pins:
• P[23:0]
• AP
• SCLK
• SDA
• SCL
The drive strength DR_STR_CLK[1:0] bits affect output driver for LLC line.
DR_STR[1:0], IO, Address 0x14[5:4]
A control to set the drive strength of the data output drivers.
Function
DR_STR[1:0] Description
00 Reserved
01 Medium low (2×)
10 (default) Medium high (3×)
11 High (4×)
DR_STR_CLK[1:0], IO, Address 0x14[3:2]
A control to set the drive strength control for the output pixel clock out signal on the LLC pin.
Function
DR_STR_CLK[1:0] Description
00 Reserved
01 Medium low (2×) for LLC up to 60 MHz
10 (default) Medium high (3×) for LLC from 44 MHz to 105 MHz
11 High (4×) for LLC greater than 100 MHz
DR_STR_SYNC[1:0], IO, Address 0x14[1:0]
A control to set the drive strength of the synchronization pins, HS, VS/FIELD/ALSB, and DE.
Function
DR_STR_SYNC[1:0] Description
00 Reserved
01 Medium low (2×)
10 (default) Medium high (3×)
11 High (4×)
Output Synchronization Selection
VS_OUT_SEL, IO, Address 0x06[7]
A control to select the VSync or FIELD signal to be output on the VS/FIELD/ALSB pin.
Function
VS_OUT_SEL Description
0 Selects FIELD output on VS/FIELD/ALSB pin
1 (default) Selects VSync output on VS/FIELD/ALSB pin
Rev. A | Page 17 of 184
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
F_OUT_SEL, IO, Address 0x05[4]
A control to select the DE or FIELD signal to be output on the DE pin.
Function
F_OUT_SEL Description
0 (default) Selects DE output on DE pin
1 Selects FIELD output on DE pin
Output Synchronization Signals Polarity
INV_LLC_POL, IO Map, Address 0x06, [0]
The polarity of the pixel clock provided by the ADV7611 via the LLC pin can be inverted using the INV_LLC_POL bit. Note that this
inversion affects only the LLC output pin. The other output pins are not affected by INV_LLC_POL.
Changing the polarity of the LLC clock output may be necessary in order to meet the setup and hold time expectations of the downstream
devices processing the output data of the ADV7611. It is expected that these parameters must be matched regardless of the type of video
data that is transmitted. Therefore, INV_LLC_POL is designed to be mode independent.
INV_LLC_POL, IO, Address 0x06[0]
A control to select the polarity of the LLC.
Function
INV_LLC_POL Description
0 (default) Does not invert LLC
1 Inverts LLC
The output synchronization signals HS, VS/FIELD/ALSB, and DE can be inverted using the following control bits:
• INV_HS_POL
• INV_VS_POL
• INV_F_POL
INV_HS_POL, IO, Address 0x06[1]
A control to select the polarity of the HS signal.
Function
INV_HS_POL Description
0 (default) Negative polarity HS
1 Positive polarity HS
INV_VS_POL, IO, Address 0x06[2]
A control to select the polarity of the VS/FIELD/ALSB signal.
Function
INV_VS_POL Description
0 (default) Negative polarity VS/FIELD/ALSB
1 Positive polarity VS/FIELD/ALSB
INV_F_POL, IO, Address 0x06[3]
A control to select the polarity of the DE signal.
Function
INV_F_POL Description
0 (default) Negative FIELD/DE polarity
1 Positive FIELD/DE polarity
Rev. A | Page 18 of 184
Hardware User Guide UG-180
Digital Synthesizer Controls
The ADV7611 features two digital encoder synthesizers that generate the following clocks:
• Video DPLL: this clock synthesizer generates the pixel clock. It undoes the effect of deep color and pixel repetition that are inherent
to HDMI streams. The output of the LLC pin is either this pixel clock or a divided down version, depending on the datapath
configuration. It takes less than one video frame for this synthesizer to lock.
• Audio DPLL: this clock synthesizer generates the audio clock. As per HDMI specifications, the incoming HDMI clock is divided
down by CTS and then multiplied up by N. This audio clock is used as the main clock in the audio stream section. The output of
MCLK represents this clock. It takes less than 5 ms after a valid ACR packet for this synthesizer to lock.
Crystal Frequency Selection
The ADV7611 supports 27.0, 28.63636, 24.576, and 24.0 MHz frequency crystals. The control described here allows selection of crystal
frequency.
XTAL_FREQ_SEL[1:0], IO, Address 0x04[2:1]
A control to set the XTAL frequency.
Function
XTAL_FREQ_SEL[1:0] Description
00 27 MHz
01 (default) 28.63636 MHz
10 24.576 MHz
11 24.0 MHz
Rev. A | Page 19 of 184
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
PRIMARY MODE AND VIDEO STANDARD
Setting the primary mode and choosing a video standard are the most fundamental settings when configuring the ADV7611. There
are two primary modes for the ADV7611: HDMI-component and HDMI-graphic modes. The appropriate mode should be set with
PRIM_MODE[3:0].
In HDMI modes, the ADV7611 can receive and decode HDMI or DVI data throughout the DVI/HDMI receiver front end. Video data
from the HDMI receiver is routed to the CP block while audio data is available on the audio interface. One of these modes is enabled by
selecting either the HDMI-component or the HDMI-graphics primary mode.
Note: The HDMI receiver decodes and processes any applied HDMI stream irrespective of the video resolution. However, many primary
mode and video standard combinations can be used to define how the decoded video data routed to the DPP and CP blocks is processed.
This allows for free run features and data decimation modes that some systems may require.
If free run and decimation are not required, it is recommended to set the following configuration for HDMI mode:
• PRIM_MODE[3:0]: 0x06
• VID_STD[5:0]: 0x02
PRIMARY MODE AND VIDEO STANDARD CONTROLS
PRIM_MODE[3:0], IO, Address 0x01[3:0]
A control to select the primary mode of operation of the decoder. Setting the appropriate HDMI mode is important for free run mode to
work properly. This control is used with VID_STD[5:0].
Function
PRIM_MODE[3:0] Description
0000 Reserved
0001 Reserved
0010 Reserved
0011 Reserved
0100 Reserved
0101 HDMI component
0110 (default) HDMI graphics
0111 to 1111 Reserved
VID_STD[5:0], IO, Address 0x00[5:0]
Sets the input video standard mode. Configuration is dependent on PRIM_MODE[3:0]. Setting the appropriate mode is important for
free run mode to work properly.
Function
VID_STD[5:0] Description
000010 Default value
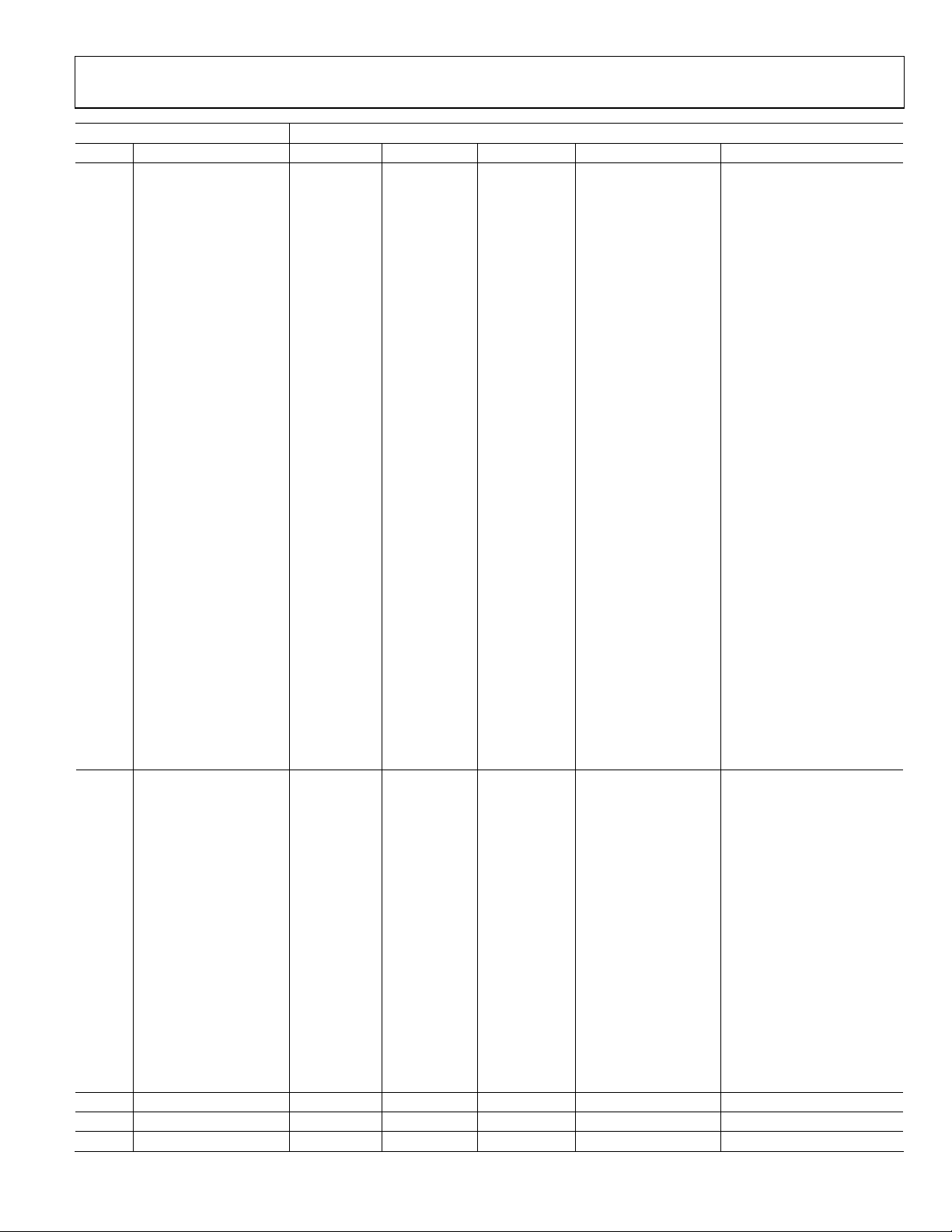
PRIM_MODE[3:0] should be used with VID_STD[5:0] to select the required video mode. These controls are set according to Tabl e 6.
Table 6. Primary Mode and Video Standard Selection
PRIM_MODE[3:0] VID_STD[5:0]
Code Description Processor Code Input Video Output Resolution Comment
0000 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
0001 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
0010 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
0100 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
0011 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
Rev. A | Page 20 of 184
Hardware User Guide UG-180
PRIM_MODE[3:0] VID_STD[5:0]
Code Description Processor Code Input Video Output Resolution Comment
0101 HDMI-COMP
(Component video)
0110 HDMI-GR
(Graphics)
0111 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1000 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1001 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
CP 000000 SD 1×1 525i 720 × 480
CP 000001 SD 1×1 625i 720 × 576
CP 000010 SD 2×1 525i 720 × 480
CP 000011 SD 2×1 625i 720 × 576
000100 Reserved Reserved
000101 Reserved Reserved
000110 Reserved Reserved
000111 Reserved Reserved
001000 Reserved Reserved
001001 Reserved Reserved
CP 001010 PR 1×1 525p 720 × 480
CP 001011 PR 1×1 625p 720 × 576
CP 001100 PR 2×1 525p 720 × 480
CP 001101 PR 2×1 625p 720 × 576
001110 Reserved Reserved
001111 Reserved Reserved
010000 Reserved Reserved
010001 Reserved Reserved
010010 Reserved Reserved
CP 010011 HD 1×1 1280 × 720
CP 010100 HD 1×1 1920 × 1080
CP 010101 HD 1×1 1920 × 1035
CP 010110 HD 1×1 1920 × 1080
CP 010111 HD 1×1 1920 × 1152
011000 Reserved Reserved
CP 011001 HD 2×1 720p 1280 × 720
CP 011010 HD 2×1 1125 1920 × 1080
CP 011011 HD 2×1 1125 1920 × 1035
CP 011100 HD 2×1 1250 1920 × 1080
CP 011101 HD 2×1 1250 1920 × 1152
CP 011110 HD 1×1 1920 × 1080
CP 011111 HD 1×1 1920 × 1080
CP 000000 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 56
CP 000001 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 60
CP 000010 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 72
CP 000011 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 75
CP 000100 SVGA 800 × 600 @ 85
CP 000101 SXGA 1280 × 1024 @ 60
CP 000110 SXGA 1280 × 1024 @ 75
000111 Reserved Reserved
CP 001000 VGA 640 × 480 @ 60
CP 001001 VGA 640 × 480 @ 72
CP 001010 VGA 640 × 480 @ 75
CP 001011 VGA 640 × 480 @ 85
CP 001100 XGA 1024 × 768 @ 60
CP 001101 XGA 1024 × 768 @ 70
CP 001110 XGA 1024 × 768 @ 75
CP 001111 XGA 1024 × 768 @ 85
01xxxx Reserved
HDMI receiver support
HDMI receiver support
Rev. A | Page 21 of 184
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
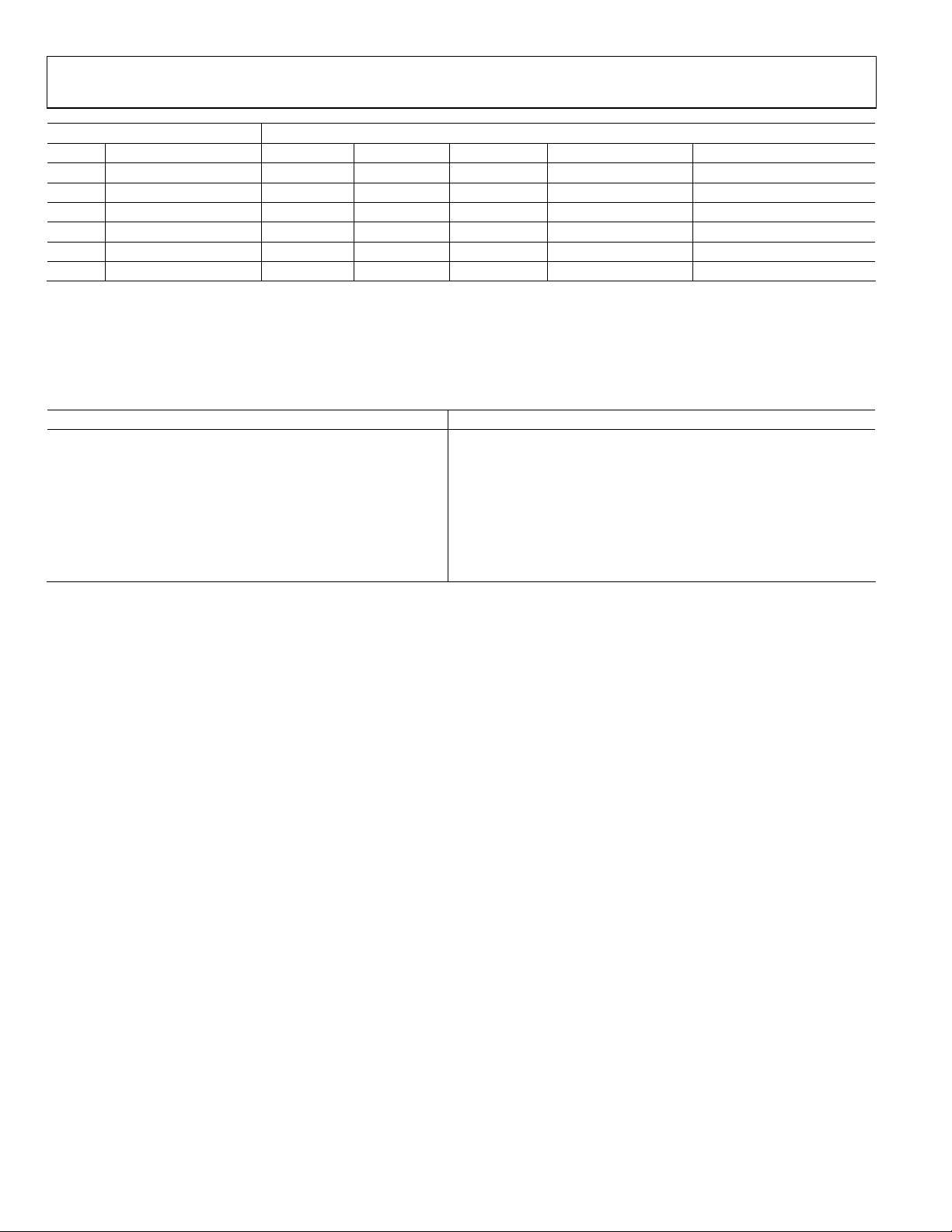
PRIM_MODE[3:0] VID_STD[5:0]
Code Description Processor Code Input Video Output Resolution Comment
1010 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1011 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1100 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1101 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1110 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
1111 Reserved xxxxxx Reserved Reserved
V_FREQ
This control is set to allow free run to work correctly (refer to Tabl e 7).
V_FREQ[2:0], IO, Address 0x01[6:4]
A control to set vertical frequency.
Function
V_FREQ[2:0] Description
000 (default) 60 Hz
001 50 Hz
010 30 Hz
011 25 Hz
100 24 Hz
101 Reserved
110 Reserved
111 Reserved
HDMI DECIMATION MODES
Some of the modes defined by VID_STD have an inherent 2×1 decimation. For these modes, the main clock generator and the decimation filters in the DPP block are configured automatically. This ensures the correct data rate at the input to the CP block. Refer to the
Data Preprocessor and Color Space Conversion and Color Controls section for more information on the automatic configuration of the
DPP block.
The ADV7611 correctly decodes and processes any incoming HDMI stream with the required decimation, irrespective of its video
resolution:
• In 1×1 mode (that is, without decimation), as long the PRIM_MODE and VID_STD registers are programmed for any HDMI mode
without decimation.
For example:
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x5 and VID_STD to 0x00
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x5 and VID_STD to 0x13
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x6 and VID_STD to 0x02
• In 2×1 decimation mode, as long the PRIM_MODE and VID_STD registers are programmed for any HDMI mode with 2×1
decimation. For example:
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x5 and VID_STD to 0x0C
• Set PRIM_MODE to 0x5 and VID_STD to 0x19
Note: Decimating the video data from an HDMI stream is optional and should be performed only if it is required by the downstream
devices connected to the ADV7611.
PRIMARY MODE AND VIDEO STANDARD CONFIGURATION FOR HDMI FREE RUN
If free run is enabled in HDMI mode, PRIM_MODE[3:0] and VID_STD[5:0] specify the input resolution expected by the ADV7611 (for
free run Mode 1) and/or the output resolution to which the ADV7611 free runs (for free run Mode 0 and Mode 1). Refer to the Free Run
Mode section for additional details on the free run feature for HDMI inputs and to HDMI_FRUN_MODE.
Rev. A | Page 22 of 184
Hardware User Guide UG-180
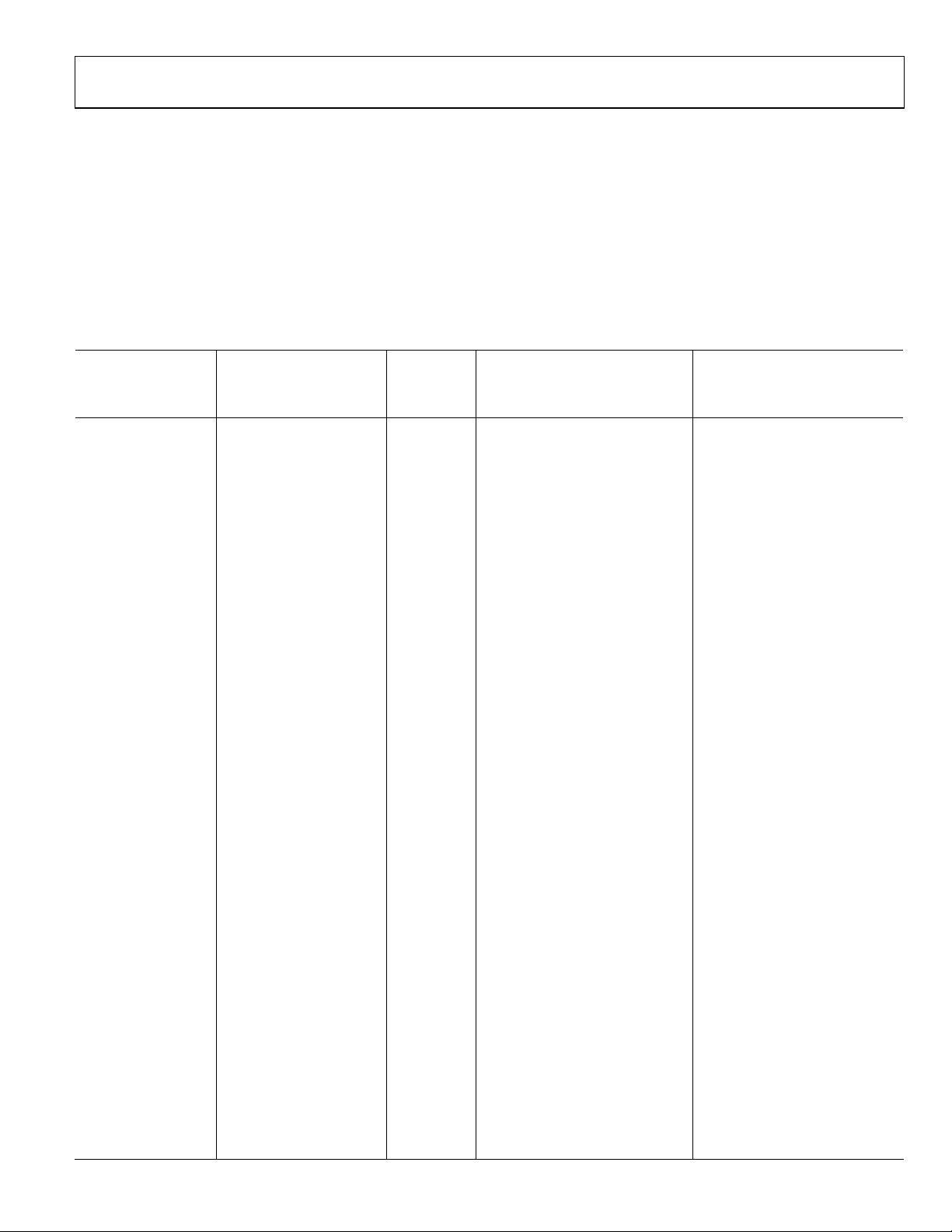
RECOMMENDED SETTINGS FOR HDMI INPUTS
This section provides the recommended settings for an HDMI input encapsulating a video resolution corresponding to a selection Video
ID Code described in the 861 specification.
Tabl e 7 provides the recommended settings for the following registers:
• PRIM_MODE
• VID_STD
• V_FREQ (V_FREQ should be set to 0x0 if not specified in Ta ble 7 .)
• INV_HS_POL = 1 (INV_HS_POL should be set to 1 if not specified in Ta ble 7 .)
• INV_VS_POL = 1 (INV_VS_POL should be set to 1 if not specified in Ta ble 7 .)
Table 7. Recommended Settings for HDMI Inputs
Recommended Settings
Recommended Settings
Video ID Codes
(861 Specification) Formats
2, 3 720 × 480p @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
4 1280 × 720p @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
5 1920 × 1080i @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
6, 7 720 (1440) × 480i @ 60 Hz 1 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
10, 11 2880 × 480i @ 60 Hz 3 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
14, 15 1440 × 480p @ 60 Hz 1 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
16 1920 × 1080p @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
17, 18 720 × 576p @ 60 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
19 1280 × 720p @ 50 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
20 1920 × 1080i @ 50 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
21, 22 720 (1440) ×576i @ 60 Hz 1 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
25, 26 2880 × 480i @ 60 Hz 3 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
29, 30 144 0× 576p @ 60 Hz 1 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
31 1920 × 1080p @ 50 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
32 1920 × 1080p @ 24 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
33 1920 × 1080p @ 25 Hz 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
35, 36 2880 × 480p @ 60 Hz 3 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
37, 38 2880 × 576p @ 60 Hz 3 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
Pixel
Repetition
Rev. A | Page 23 of 184
if Free Run Used and
DIS_AUTO_PARAM_BUFF = 0
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
VID_STD = 0x2
if Free Run Not Used
or Free Run Used and
DIS_AUTO_PARAM_BUFF = 1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x13
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x14
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x0
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x0
PRIM_MODE=0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x1E
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xB
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA3
V_FREQ = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x14
V_FREQ = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x1
PRIM_MODE=0x5
VID_STD = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x1E
V_FREQ = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x1E
V_FREQ = 0x4
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0x1E
V_FREQ = 0x3
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
PRIM_MODE = 0x5
VID_STD = 0xA
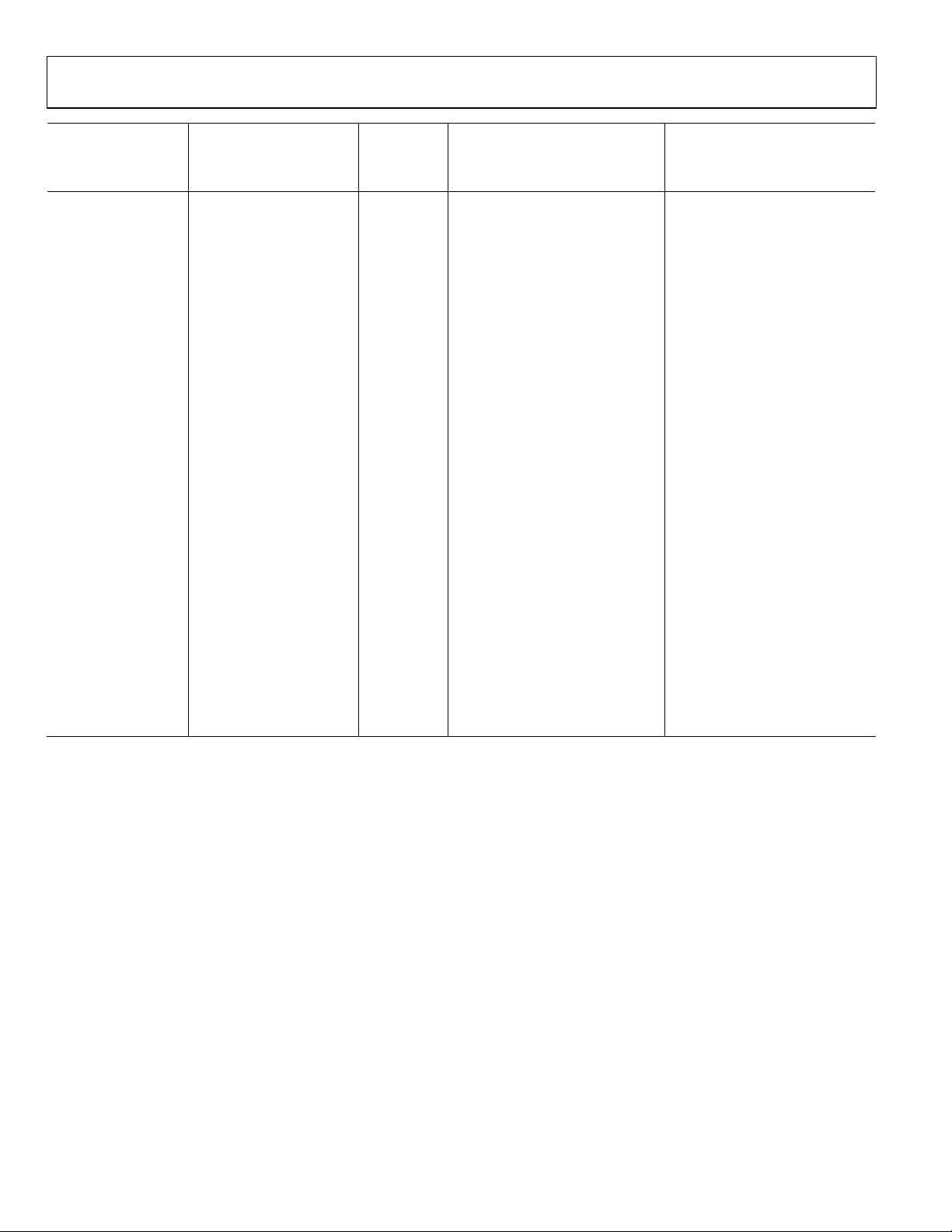
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
Recommended Settings
Recommended Settings
Video ID Codes
(861 Specification) Formats
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 56 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 60 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 72 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 75 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A SVGA 800 × 600p @ 85 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A SXGA 1280 × 1024p @ 60 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A SXGA 1280 × 1024p @ 75 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A VGA 640 × 480p @ 60 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A VGA 640 × 480p @ 72 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A VGA 640 × 480p @ 75 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A VGA 640 × 480p @ 85 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A VGA 1024 × 768p @ 60 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A VGA 1024 × 768p @ 70 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A VGA 1024 × 768p @ 75 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
N/A VGA 1024 × 768p @ 85 0 PRIM_MODE = 0x6
Pixel
Repetition
if Free Run Used and
DIS_AUTO_PARAM_BUFF = 0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
VID_STD = 0x0
if Free Run Not Used
or Free Run Used and
DIS_AUTO_PARAM_BUFF = 1
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x1
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x2
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x3
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x04
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x05
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x06
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x08
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x09
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0A
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0B
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0C
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0D
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0E
PRIM_MODE = 0x6
VID_STD = 0x0F
Rev. A | Page 24 of 184
Hardware User Guide UG-180
PIXEL PORT CONFIGURATION
The ADV7611 has a very flexible pixel port, which can be configured in a variety of formats to accommodate downstream ICs. The
ADV7611 can provide output modes up to 24 bits.
This section details the controls required to configure the ADV7611 pixel port. Appendix C contains tables describing pixel port
configurations.
PIXEL PORT OUTPUT MODES
OP_FORMAT_SEL[7:0], IO, Address 0x03[7:0]
A control to select the data format and pixel bus configuration. Refer to the pixel port configuration for full information on pixel port
modes and configuration settings.
Function
OP_FORMAT_SEL[7:0] Description
0x00 (default)1 8-bit SDR ITU-656 mode
0x0A1 12-bit SDR ITU Mode 2
0x20 8-bit 4:2:2 DDR mode
0x2A 12-bit DDR 4:2:2 Mode 2
0x40 24-bit 4:4:4 SDR mode
0x60 24-bit 4:4:4 DDR mode
0x80 16-bit ITU-656 SDR mode
0x8A 24-bit ITU-656 SDR Mode 2
1
Refer to the DLL settings for 656, 8-/10-/12-bit modes in the DLL on LLC Clock Path section.
Bus Rotation and Reordering Controls
Bus reordering controls are available for ADV7611. OP_CH_SEL[2:0] allows the three output buses to be rearranged, thus providing six
different output possibilities.
OP_CH_SEL[2:0], IO, Address 0x04[7:5]
A control to select the configuration of the pixel data bus on the pixel pins. Refer to the pixel port configuration for full information on
pixel port modes and configuration settings.
Function
OP_CH_SEL[2:0] Description
000 P[23:16] Y/G, P[15:8] U/CrCb/B, P[7:0] V/R
001 P[23:16] Y/G, P[15:8] V/R, P[7:0] U/CrCb/B
010 P[23:16] U/CrCb/B, P[15:8] Y/G, P[7:0] V/R
011 (default) P[23:16] V/R, P[15:8] Y/G, P[7:0] U/CrCb/B
100 P[23:16] U/CrCb/B, P[15:8] V/R, P[7:0]Y/G
101 P[23:16] V/R, P[15:8] U/CrCb/B, P[7:0] Y/G
110 Reserved
111 Reserved
Pixel Data and Synchronization Signals Control
The polarity of the LLC and synchronization signals can be inverted, and the LLC, the synchronization signals, and the pixel data output
can be tristated. Refer to the information on the following controls:
• INV_F_POL
• INV_VS_POL
• INV_HS_POL
• TRI_PIX
• TRI_LLC
• TRI_SYNCS
Rev. A | Page 25 of 184

UG-180 Hardware User Guide
OP_SWAP_CB_CR, IO, Address 0x05[0]
A control for the swapping of Cr and Cb data on the pixel buses.
Function
OP_SWAP_CB_CR Description
0 (default) Outputs Cr and Cb as per OP_FORMAT_SEL
1 Inverts the order of Cb and Cr in the interleaved data stream
OP_SWAP_CB_CR swaps the order in which Cb and Cr are interleaved in the output data stream. It caters for cases in which the data on
Channels B and C are swapped. It is effective only if OP_FORMAT_SEL[7:0] is set to a 4:2:2 compatible output mode.
Note: It has no effect for 24-bit SDR modes and DDR modes.
LLC CONTROLS
The ADV7611 has a limited number of adjustment features available for the line locked clock (LLC) output. The polarity of the LLC can
be inverted and the LLC of the output driver can be tristated. Controls also exist to skew the LLC versus the output data to achieve
suitable setup and hold times for any back end device.
The LLC controls are as follows:
• INV_LLC_POL
• TRI_LLC
• LLC_DLL_EN
• LLC_DLL_MUX
• LLC_DLL_PHASE[4:0]
DLL ON LLC CLOCK PATH
A delay locked loop (DLL) block is implemented on the LLC clock path. This DLL allows the changing of the phase of the output pixel
clock on the LLC pin.
LLC_DLL_DOUBLE, IO, Address 0x19[6]
A control to double LLC frequency.
Function
LLC_DLL_DOUBLE Description
0 (default) Normal LLC frequency
1 Double LLC frequency
Adjusting DLL Phase in All Modes
LLC_DLL_EN, IO, Address 0x19[7]
A control to enable the DLL for the output pixel clock.
Function
LLC_DLL_EN Description
1 Enables LLC DLL
0 (default) Disables LLC DLL
LLC_DLL_MUX, IO, Address 0x33[6]
A control to apply the pixel clock DLL to the pixel clock output on the LLC pin.
Function
LLC_DLL_MUX Description
0 (default) Bypasses the DLL
1 Muxes the DLL output on LLC output
Rev. A | Page 26 of 184

Hardware User Guide UG-180
LLC_DLL_PHASE[4:0], IO, Address 0x19[4:0]
A control to adjust LLC DLL phase in increments of 1/32 of a clock period.
Function
LLC_DLL_PHASE[4:0] Description
00000 (default) Default
xxxxx Sets one of 32 phases of DLL to vary LLC CLK
DLL Settings for 656, 8-/10-/12-Bit Modes
The following table shows the settings that must be used to enable 8-/10-/12-bit, 656 output.
Address Setting Description
IO Map Address 0x19[7] 1 Enables LLC DLL
IO Map Address 0x33[6] 1 Muxes the DLL output on LLC output
IO Map Address 0x19[6] 1 Doubles the clock
Rev. A | Page 27 of 184
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
HDMI RECEIVER
HPA_A/INT2
RXA_5V
CEC
DDCA_SDA/DDCA_SC L
RXA_C±
RXA_0±
RXA_1±
RXA_2±
5V DETECT
AND HPA
CONTROLLER
CEC
CONTROLLER
EDID/
REPEATER
CONTROLLER
PLL
HDCP
EEPROM
HDCP
BLOCK
SAMPLEREQUALIZER
TO INTERRUPT
CONTROL LER
DEEP COLOR
CONVERSION
DATA
4:2:2 TO 4:4:4
CONVERSION
FILTER
PACKET/
INFOF RAME
MEMORY
PACKET
HDMI DECODE + PORT MEASUREMENT
PROCESSOR
HS
VS
DE
AUDIO
PROCESSOR
AUDIO OUT POUT FORMATTER
TO DPP
TO DPP
TO DPP
TO DPP
AP
SCLK/INT2
MCLK/INT2
09238-004
Figure 3. Functional Block Diagram of HDMI Core
+5 V CABLE DETECT
The HDMI receiver in the ADV7611 can monitor the level on the +5 V power signal pin of the HDMI port. The results of this detection
can be read back from the following I
CABLE_DET_A_RAW, IO, Address 0x6F[0] (Read Only)
Raw status of Port A +5 V cable detection signal.
Function
CABLE_DET_A_RAW Description
0 (default) No cable detected on Port A
1 Cable detected on Port A (high level on RXA_5V)
The ADV7611 provides a digital glitch filter on the +5 V power signals from the HDMI port. The output of this filter is used to reset the
HDMI block (refer to the HDMI Section Reset Strategy section).
The +5 V power signal must be constantly high for the duration of the timer (controlled by FILT_5V_DET_TIMER[6:0]), otherwise the
output of the filter is low. The output of the filter returns low as soon as any change in the +5 V power signal is detected.
FILT_5V_DET_DIS, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x56[7]
This control is used to disable the digital glitch filter on the HDMI 5 V detect signals. The filtered signals are used as interrupt flags and
used to reset the HDMI section. The filter works from an internal ring oscillator clock and, therefore, is available in power-down mode.
The clock frequency of the ring oscillator is 42 MHz ± 10%.
Function
FILT_5V_DET_DIS Description
0 (default) Enabled
1 Disabled
Note: If the +5 V pins are not used and are left unconnected, the +5 V detect circuitry must be disconnected from the HDMI reset signal
by setting DIS_CABLE_DET_RST to 1. This avoids holding the HDMI section in reset.
2
C registers. These readbacks are valid even when the part is not configured for HDMI mode.
Rev. A | Page 28 of 184

Hardware User Guide UG-180
FILT_5V_DET_TIMER[6:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x56[6:0]
This control is used to set the timer for the digital glitch filter on the HDMI +5 V detect inputs. The unit of this parameter is two clock
cycles of the ring oscillator (~ 47 ns). The input must be constantly high for the duration of the timer; otherwise, the filter output remains
low. The output of the filter returns low as soon as any change in the +5 V power signal is detected.
Function
FILT_5V_DET_TIMER[6:0] Description
1011000 (default) Approximately 4.2 μs
xxxxxxx Time duration of +5 V deglitch filter. Unit of this parameter is 2 clock cycles of the ring oscillator (~47 ns).
DIS_CABLE_DET_RST, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x48[6]
This control disables the reset effects of cable detection. DIS_CABLE_DET_RST must be set to 1 if the +5 V pins are unused and left
unconnected.
Function
DIS_CABLE_DET_RST Description
0 (default)
1 Does not use 5 V input pins as reset signal for HDMI section
HOT PLUG ASSERT
The ADV7611 features hot plug assert (HPA) control for its HDMI port. The purpose of the control and its corresponding output pin is
to communicate to an HDMI transmitter that it is possible to access the enhanced-extended display identification (E-EDID) connected to
the DDC bus.
HPA_MANUAL, Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6C[0]
Manual control enable for the HPA output pins. Automatic control of these pins is disabled by setting this bit. Manual control is
determined by the HPA_MAN_VALUE_X (where X = A).
Function
HPA_MANUAL Description
0 (default) HPA takes its value based on HPA_AUTO_INT_EDID
1 HPA takes its value from HPA_MAN_VALUE_X
HPA_MAN_VALUE_A, IO, Address 0x20[7]
A manual control for the value of HPA on Port A. Valid only if HPA_MANUAL is set to 1.
Function
HPA_MAN_VALUE_A Description
0 0 V applied to HPA_A pin
1 (default) High level applied to HPA_A pin
Note: The HPA_A pin is open drain. An external pull-up resistor is required to pull it high.
Resets HDMI section if 5 V input pin corresponding to selected HDMI port (for example, RXA_5V for Port A)
is inactive
Rev. A | Page 29 of 184
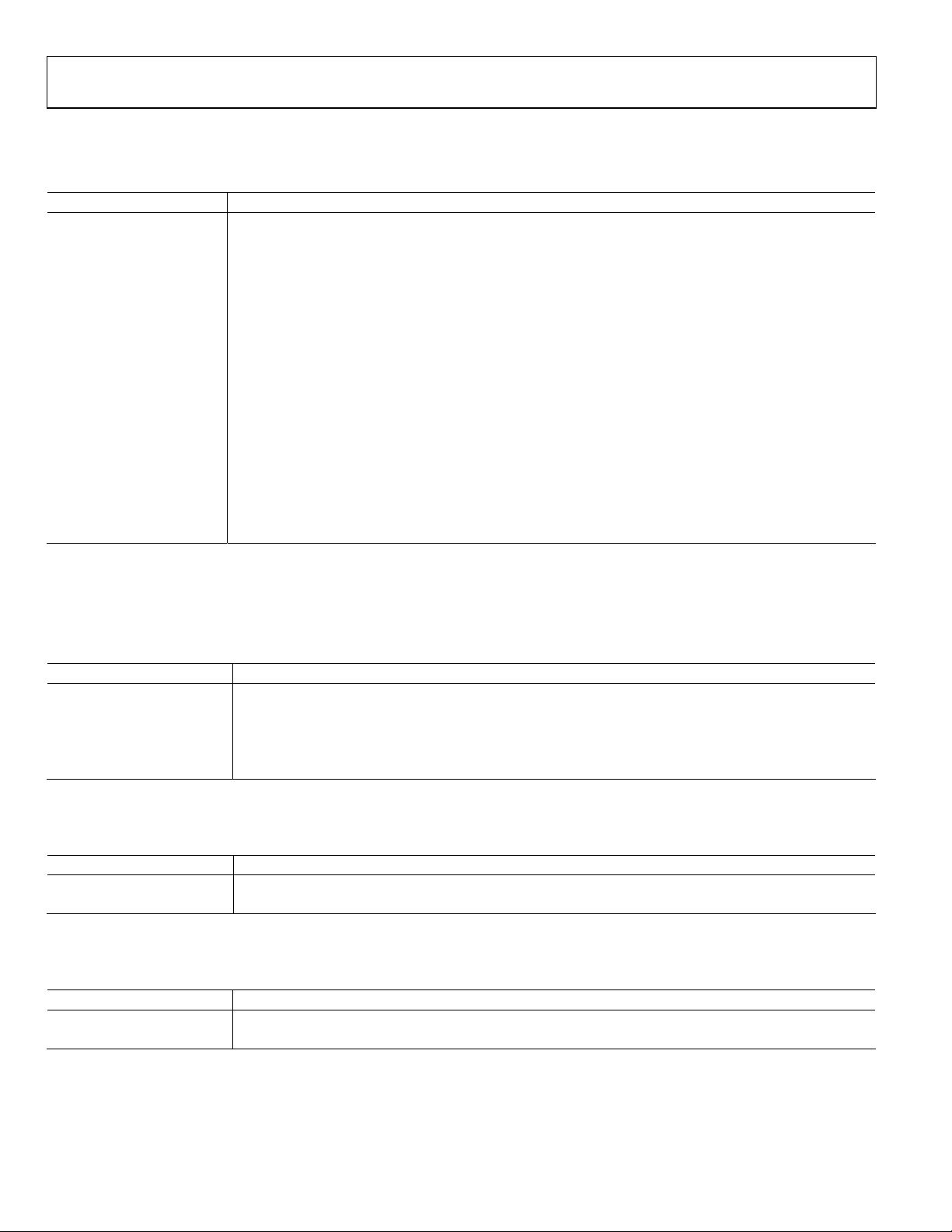
UG-180 Hardware User Guide
HPA_AUTO_INT_EDID[1:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6C[2:1]
This control selects the type of automatic control on the HPA output pins. This bit has no effect when HPA_MANUAL is set to 1.
Function
HPA_AUTO_INT_EDID[1:0] Description
00
01 (default)
10 HPA of an HDMI port asserted high after two conditions met.
11 HPA of an HDMI port is asserted high after three conditions met:
Note: The delay is programmable via HPA_DELAY_SEL[3:0]. Refer to EDID_ENABLE for details on enabling the internal E-EDID for an
HDMI port. In HPA_MAN_VALUE_X and CABLE_DET_X_RAW, X refers to A.
HPA_DELAY_SEL[3:0], Addr 68 (HDMI), Address 0x6C[7:4]
Sets a delay between +5 V detection and hot plug assertion on the HPA output pins, in increments of 100 ms per bit.
Function
HPA_DELAY_SEL[3:0] Description
0000 No delay
0001 100 ms delay
0010 200 ms delay
1010 (default) 1 sec delay
1111 1.5 sec delay
HPA_TRISTATE_A, IO, Address 0x20[3]
Tristates HPA output pin for Port A.
Function
HPA_TRISTATE_A Description
0 (default) HPA_A pin active
1 Tristates HPA_A pin
HPA_STATUS_PORT_A, IO, Address 0x21[3] (Read Only)
Readback of HPA status for Port A.
Function
HPA_STATUS_PORT_A Description
0 (default) +5 V not applied to HPA_A pin by chip
1 +5 V applied to HPA_A pin by chip
HPA of an HDMI port asserted high immediately after internal EDID activated for that port. HPA of a specific
HDMI port deasserted low immediately after internal E-EDID is de-activated for that port.
HPA of an HDMI port asserted high following a programmable delay after part detects an HDMI cable plug
on that port. HPA of an HDMI port immediately deasserted after part detects a cable disconnect on that
HDMI port.
1. Internal EDID is active for that port.
2. Delayed version of cable detect signal CABLE_DET_X_RAW for that port is high.
HPA of an HDMI port immediately deasserted after either of these two conditions are met:
1. Internal EDID is de-activated for that port.
2. Cable detect signal CABLE_DET_X_RAW for that port is low.
1. Internal EDID is active for that port.
2. Delayed version of cable detect signal CABLE_DET_X_RAW for that port is high.
3. User has set manual HPA control for that port to 1 via HPA_MAN_VALUE_X controls.
HPA of an HDMI port immediately deasserted after any of these three conditions met:
1. Internal EDID de-activated for that port.
2. Cable detect signal CABLE_DET_X_RAW for that port is low.
3. User sets the manual HPD control for that port to 0 via HPA_MAN_VALUE_X controls
Rev. A | Page 30 of 184
 Loading...
Loading...