Dual/Quad Rail-to-Rail
Operational Amplifiers
OP295/OP495
FEATURES
Rail-to-Rail Output Swing
Single-Supply Operation: 3 V to 36 V
Low Offset Voltage: 300 mV
Gain Bandwidth Product: 75 kHz
High Open-Loop Gain: 1,000 V/mV
Unity-Gain Stable
Low Supply Current/Per Amplifier: 150 A max
APPLICATIONS
Battery-Operated Instrumentation
Servo Amplifiers
Actuator Drives
Sensor Conditioners
Power Supply Control
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Rail-to-rail output swing combined with dc accuracy are the
key features of the OP495 quad and OP295 dual CBCMOS
operational amplifiers. By using a bipolar front end, lower
noise and higher accuracy than that of CMOS designs has
been achieved. Both input and output ranges include the
negative supply, providing the user zero-in/zero-out capability. For users of 3.3 V systems such as lithium batteries, the
OP295/OP495 is specified for 3 V operation.
Maximum offset voltage is specified at 300 µV for 5 V operation,
and the open-loop gain is a minimum of 1000 V/mV. This yields
performance that can be used to implement high accuracy systems,
even in single-supply designs.
The ability to swing rail-to-rail and supply 15 mA to the load
makes the OP295/OP495 an ideal driver for power transistors
and “H” bridges. This allows designs to achieve higher efficiencies and to transfer more power to the load than previously
possible without the use of discrete components. For applications such as transformers that require driving inductive loads,
PIN CONNECTIONS
8-Lead Narrow-Body SOIC
(S Suffix)
OUT A
–IN A
+IN A
1
2
OP295
3
V–
4
8
7
6
5
V+
OUT B
–IN B
+IN B
14-Lead PDIP
(P Suffix)
1
OUT A
–IN A
+IN A
+IN B
–IN B
OUT B
2
3
4
V+
OP495
5
6
7
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
OUT D
–IN D
+IN D
V–
+IN C
–IN C
OUT C
8-Lead Narrow-Body SOIC
(S Suffix)
OUT A
–IN A
+IN A
1
OP295
2
3
V–
4
8
7
6
5
V+
OUT B
–IN B
+IN B
14-Lead PDIP
(P Suffix)
OUT D
1
OUT A
–IN A
2
3
+IN A
4
V+
5
+IN B
6
–IN B
7
OUT B
8
NC
NC = NO CONNECT
OP495
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
–IN D
+IN D
V–
+IN C
–IN C
OUT C
NC
increases in efficiency are also possible. Stability while driving
capacitive loads is another benefit of this design over CMOS
rail-to-rail amplifiers. This is useful for driving coax cable or
large FET transistors. The OP295/OP495 is stable with loads in
excess of 300 pF.
The OP295 and OP495 are specified over the extended industrial
(–40°C to +125°C) temperature range. OP295s are available
in 8-lead plastic DIP plus SOIC-8 surface-mount packages.
OP495s are available in 14-lead plastic and SOIC-16 surfacemount packages.
REV. D
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
OP295/OP495–SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(@ VS = 5.0 V, VCM = 2.5 V, TA = 25ⴗC, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage V
Input Bias Current I
Input Offset Current I
Input Voltage Range V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ 4.0 V, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C90110 dB
Large Signal Voltage Gain A
OS
B
OS
CM
VO
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C 800 µV
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C30nA
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C ±5nA
0 4.0 V
RL = 10 kΩ, 0.005 ≤ V
RL = 10 kΩ, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C 500 V/mV
≤ 4.0 V 1,000 10,000 V/mV
OUT
30 300 µV
820 nA
±1 ±3nA
Offset Voltage Drift ∆VOS/∆T 15 µV/°C
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing High V
Output Voltage Swing Low V
Output Current I
OH
OL
OUT
RL = 100 kΩ to GND 4.98 5.0 V
RL = 10 kΩ to GND 4.90 4.94 V
I
= 1 mA, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C 4.7 V
OUT
RL = 100 kΩ to GND 0.7 2 mV
RL = 10 kΩ to GND 0.7 2 mV
I
= 1 mA, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C90mV
OUT
±11 ±18 mA
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR ± 1.5 V ≤ VS ≤ ± 15 V 90 110 dB
±1.5 V ≤ VS ≤ ± 15 V,
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C85dB
Supply Current Per Amplifier I
SY
V
= 2.5 V, RL = ∞, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C 150 µA
OUT
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Skew Rate SR RL = 10 kΩ 0.03 V/µs
Gain Bandwidth Product GBP 75 kHz
Phase Margin θ
O
86 Degrees
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Voltage Noise en p-p 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 1.5 µV p-p
Voltage Noise Density e
Current Noise Density i
Specifications subject to change without notice.
n
n
f = 1 kHz 51 nV/√Hz
f = 1 kHz <0.1 pA/√Hz
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(@ VS = 3.0 V, VCM = 1.5 V, TA = 25ⴗC, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage V
Input Bias Current I
Input Offset Current I
Input Voltage Range V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR 0 V ≤ VCM ≤ 2.0 V, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C90110 dB
Large Voltage Gain A
Offset Voltage Drift ∆VOS/∆T 1 µV/°C
OS
B
OS
CM
VO
RL = 10 kΩ 750 V/mV
0 2.0 V
100 500 µV
820 nA
±1 ±3nA
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing High V
Output Voltage Swing Low V
OH
OL
RL = 10 kΩ to GND 2.9 V
RL = 10 kΩ to GND 0.7 2 mV
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR ± 1.5 V ≤ VS ≤ ± 15 V 90 110 dB
±1.5 V ≤ VS ≤ ± 15 V,
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C85dB
Supply Current Per Amplifier I
SY
V
= 1.5 V, RL = ∞, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C 150 µA
OUT
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Slew Rate SR RL = 10 kΩ 0.03 V/µs
Gain Bandwidth Product GBP 75 kHz
Phase Margin θ
O
85 Degrees
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Voltage Noise en p-p 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 1.6 µV p-p
Voltage Noise Density e
Current Noise Density i
Specifications subject to change without notice.
n
n
f = 1 kHz 53 nV/√Hz
f = 1 kHz <0.1 pA/√Hz
REV. D–2–
OP295/OP495
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(@ VS = ±15.0 V, TA = 25ⴗC, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage V
Input Bias Current I
OS
–40°C ≤ T
B
VCM = 0 V 7 20 nA
≤ +125°C 800 µV
A
300 500 µV
VCM = 0 V, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C30nA
Input Offset Current I
Input Voltage Range V
OS
CM
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR –15.0 V ≤ V
Large Signal Voltage Gain A
VO
VCM = 0 V ±1 ±3nA
V
= 0 V, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C ±5nA
CM
–15 13.5 V
≤ +13.5 V, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C90 110 dB
CM
RL = 10 kΩ 1,000 4,000 V/mV
Offset Voltage Drift ∆VOS/∆T 1 µV/°C
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing High V
OH
RL = 100 kΩ to GND 14.95 V
RL = 10 kΩ to GND 14.80 V
Output Voltage Swing Low V
Output Current I
OL
OUT
RL = 100 kΩ to GND –14.95 V
R
= 10 kΩ to GND –14.85 V
L
±15 ±25 mA
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR VS = ± 1.5 V to ± 15 V 90 110 dB
VS = ±1.5 V to ±15 V, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C85 dB
Supply Current I
SY
VO = 0 V, RL = ∞, VS = ±18 V,
–40°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C 175 µA
Supply Voltage Range V
S
3 (±1.5) 36 (±18) V
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Slew Rate SR RL = 10 kΩ 0.03 V/µs
Gain Bandwidth Product GBP 85 kHz
Phase Margin θ
O
83 Degrees
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Voltage Noise en p-p 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 1.25 µV p-p
Voltage Noise Density e
Current Noise Density i
Specifications subject to change without notice.
n
n
f =1 kHz 45 nV/√Hz
f = 1 kHz <0.1 pA/√Hz
REV. D
–3–
OP295/OP495
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V
Input Voltage
Differential Input Voltage
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± 18 V
3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36 V
1, 2
Output Short-Circuit Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indefinite
Storage Temperature Range
P, S Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Operating Temperature Range
OP295G, OP495G . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–40°C to +125°C
Junction Temperature Range
P, S Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering, 60 sec) . . . . . . . . 300°C
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Range Description Option
OP295GP –40°C to +125°C 8-Lead Plastic DIP P-8 (N-8)
OP295GS –40°C to +125°C 8-Lead SOIC S-8 (R-8)
OP295GS-REEL –40°C to +125°C 8-Lead SOIC S-8 (R-8)
OP295GS-REEL7 –40°C to +125°C 8-Lead SOIC S-8 (R-8)
OP495GP –40°C to +125°C 14-Lead Plastic DIP P-14 (N-14)
OP495GS –40°C to +125°C 16-Lead SOIC S-16 (RW-16)
OP495GS-REEL –40°C to +125°C 16-Lead SOIC S-16 (RW-16)
OP495GSZ* –40°C to +125°C 16-Lead SOIC S-16 (RW-16)
OP495GSZ-REEL7* –40°C to +125°C 16-Lead SOIC S-16 (RW-16)
*Z = Pb-free part.
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; and functional operation
of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Absolute maximum ratings apply to packaged parts, unless otherwise noted.
3
For supply voltages less than ± 18 V, the absolute maximum input voltage is equal
to the supply voltage.
Package Type JA*
JC
Unit
8-Lead Plastic DIP (P) 103 43 °C/W
8-Lead SOIC (S) 158 43 °C/W
14-Lead Plastic DIP (P) 83 39 °C/W
16-Lead SOIC (S) 98 30 °C/W
*JA is specified for worst case mounting conditions, i.e., JA is specified for device
in socket for CERDIP, PDIP, and LCC packages; JA is specified for device
soldered to printed circuit board for SOIC package.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the
OP295/OP495 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
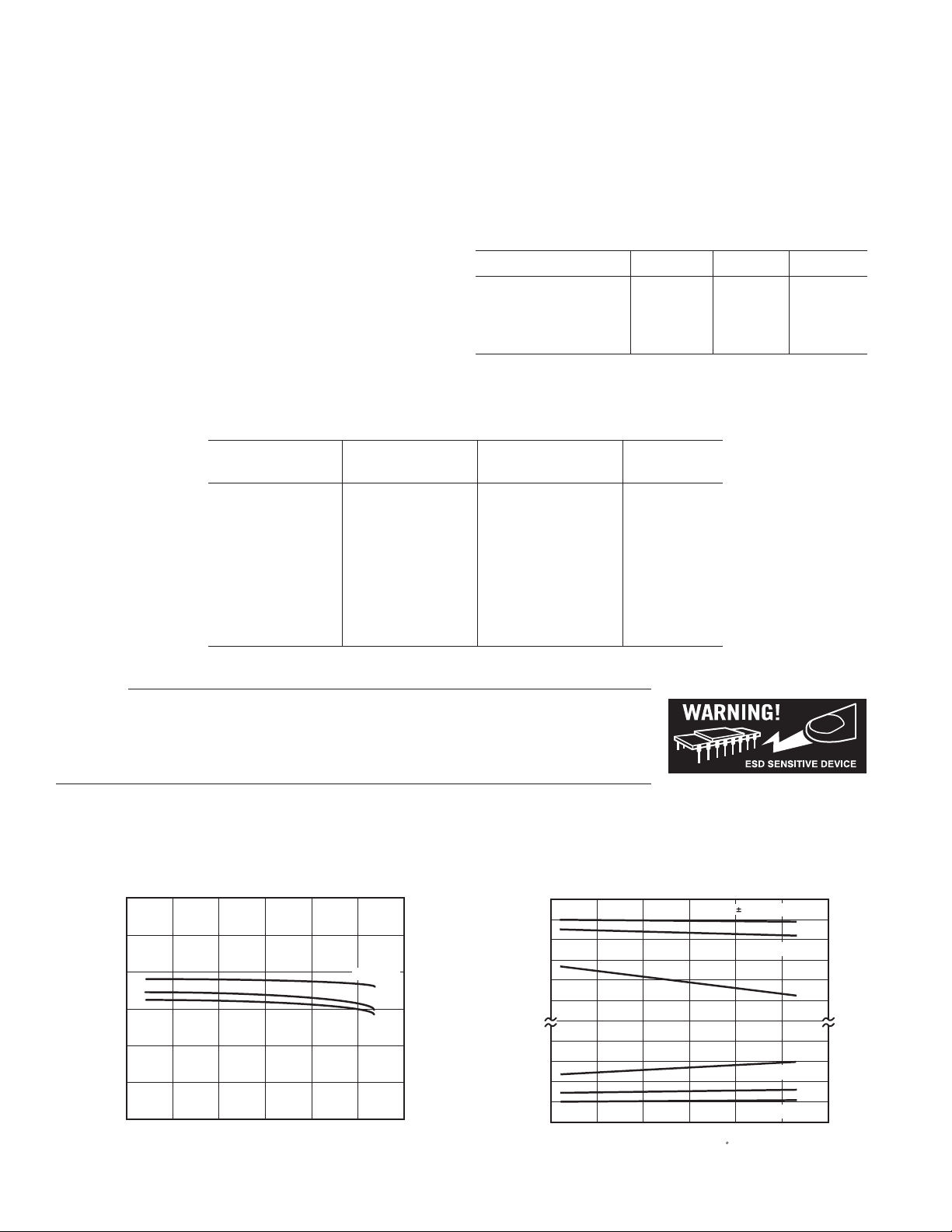
Typical Performance Characteristics
140
120
100
80
60
SUPPLY CURRENT – A
40
20
–50
–25
TEMPERATURE – ⴗC
VS = 36V
VS = 5V
V
= 3V
S
7550250
100
TPC 1. Supply Current Per Amplifier vs. Temperature
15.2
15.0
14.8
14.6
14.4
14.2
–14.4
–14.6
–14.8
–15.0
–15.2
– OUTPUT SWING – V + OUTPUT SWING – V
–50
–25
TEMPERATURE –
TPC 2. Output Voltage Swing vs. Temperature
VS = 15V
C
R
= 100k⍀
L
RL = 10k⍀
= 2k⍀
R
L
RL = 2k⍀
RL = 10k⍀
RL = 100k⍀
7550250
100
REV. D–4–
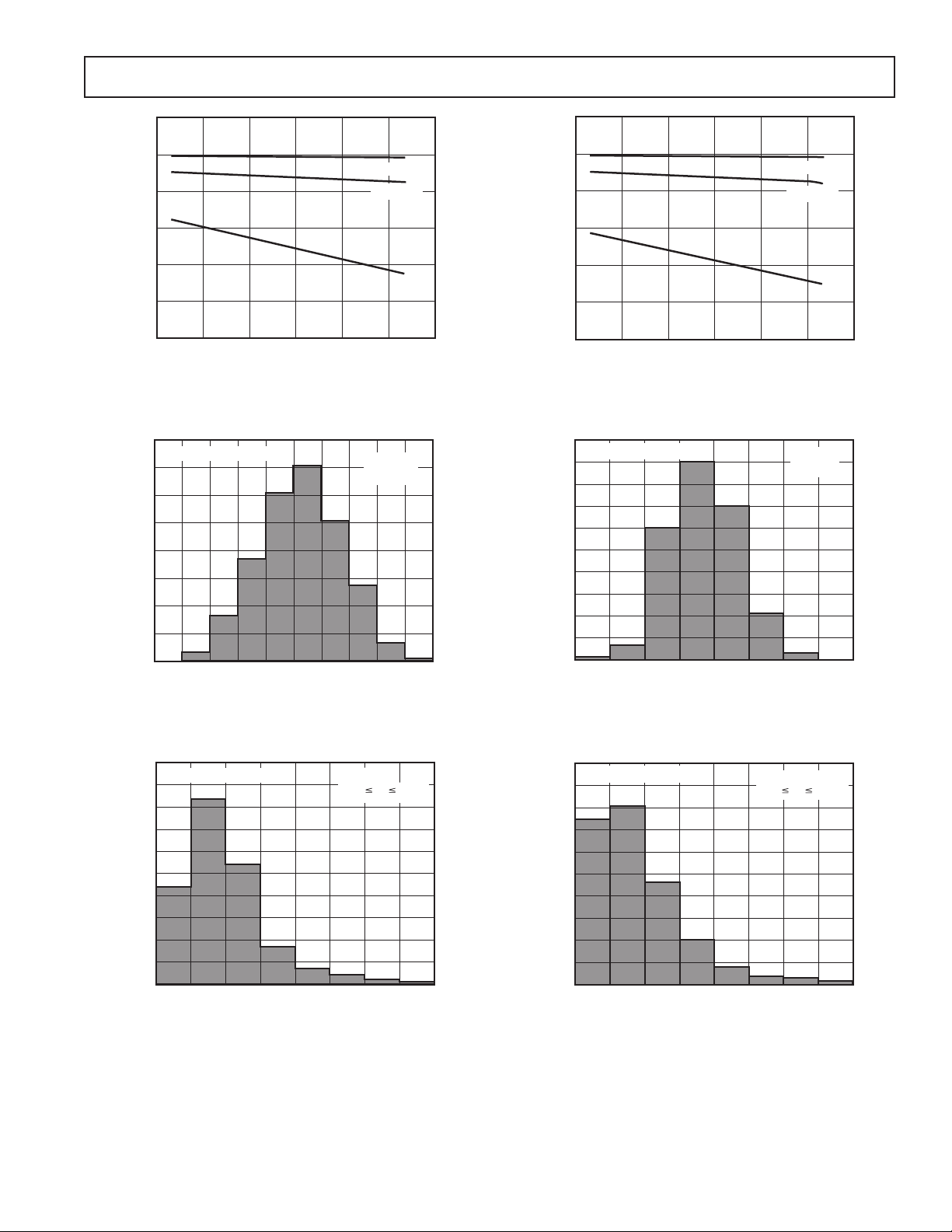
OP295/OP495
500
0
300
150
50
–50
100
–100
300
200
250
350
400
450
250200150100500
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE – V
UNITS
VS = 5V
T
A
= 25ⴗC
BASED ON 1200 OP AMPS
500
0
3.2
150
50
0.4
100
0
300
200
250
350
400
450
2.82.42.01.61.20.8
T
C
– VOS – V/ⴗC
UNITS
VS = 5V
–40ⴗ
TA +85ⴗC
BASED ON 1200 OP AMPS
3.10
VS = 3V
3.00
2.90
2.80
2.70
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V
2.60
2.50
–50
–25
TEMPERATURE – ⴗC
RL = 100k⍀
RL = 10k⍀
RL = 2k⍀
7550250
100
TPC 3. Output Voltage Swing vs. Temperature
200
BASED ON 600 OP AMPS
175
150
125
100
UNITS
75
VS = 5V
T
= 25ⴗC
A
5.10
VS = 5V
5.00
4.90
4.80
4.70
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V
4.60
4.50
–50
–25
TEMPERATURE – ⴗC
RL = 100k⍀
RL = 10k⍀
RL = 2k⍀
7550250
100
TPC 6. Output Voltage Swing vs. Temperature
50
25
0
–200–250
TPC 4. OP295 Input Offset (VOS) Distribution
250
BASED ON 600 OP AMPS
225
200
175
150
125
UNITS
100
75
50
25
0
0
TPC 5. OP295 TC–VOS Distribution
REV. D
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE – V
0.4
T
– VOS – V/ⴗC
C
VS = 5V
–40ⴗ
200150100500–50–100–150
TA +85ⴗC
2.82.42.01.61.20.8
250
TPC 7. OP495 Input Offset (VOS) Distribution
3.2
TPC 8. OP495 TC–VOS Distribution
–5–
 Loading...
Loading...