Analog Devices AD1868 Datasheet
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
13
14
15
11
16
18-BIT
DAC
18-BIT
SERIAL
REGISTER
18-BIT
SERIAL
REGISTER
AD1868
LL
DL
CK
DR
LR
DGND
NRL
AGND
NRR
V
L
VBR
V
B
L
V
S
VOL
V
O
R
V
S
18-BIT
DAC
–
+
–
+
V
REF
V
REF
Single Supply
a
Dual 18-Bit Audio DAC
AD1868*
FEATURES
Dual Serial Input, Voltage Output DACs
Single +5 V Supply
0.004% THD+N (typ)
Low Power: 50 mW (typ)
108 dB Channel Separation (min)
Operates at 83 Oversampling
16-Pin Plastic DIP or SOIC Package
APPLICATIONS
Portable Compact Disc Players
Portable DAT Players and Recorders
Automotive Compact Disc Players
Automotive DAT Players
Multimedia Workstations
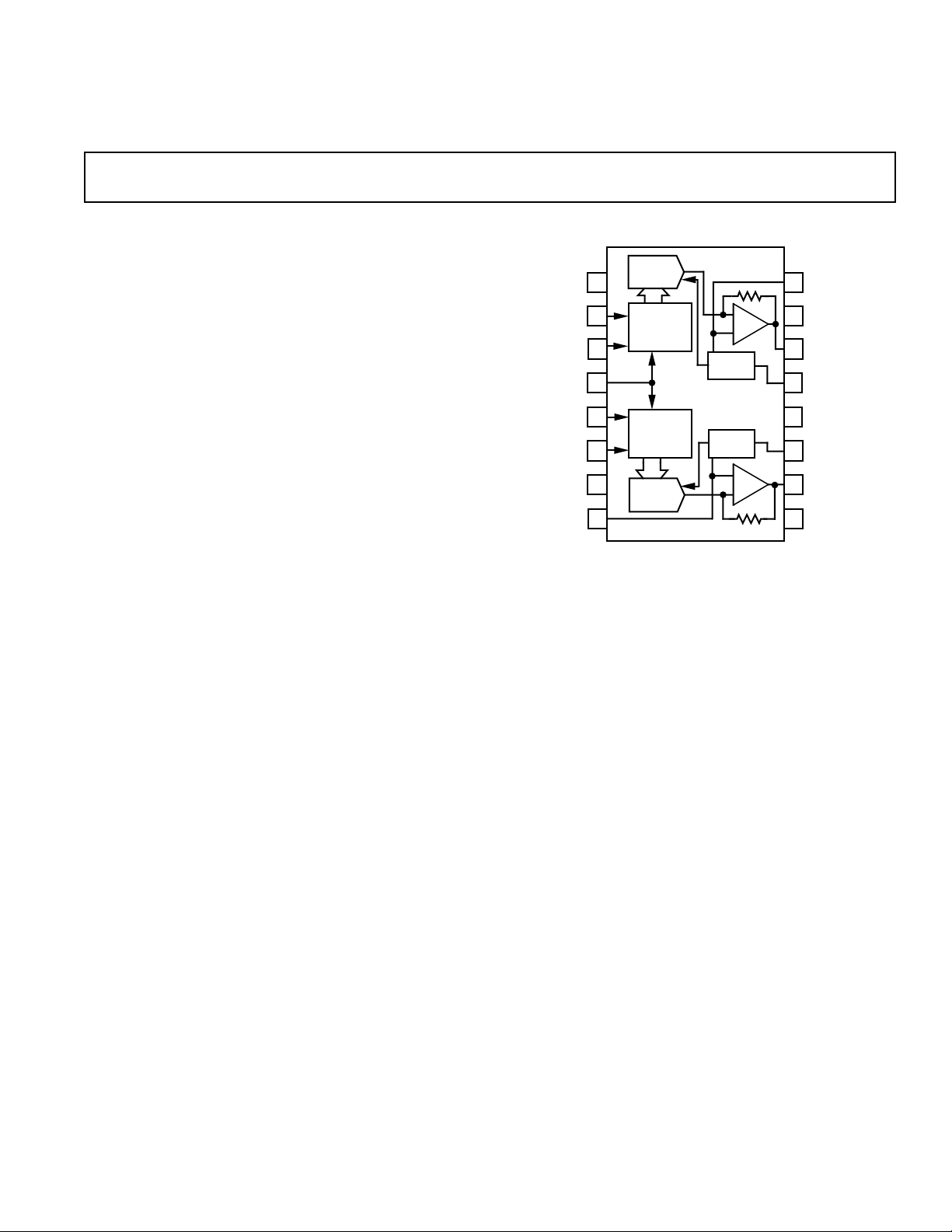
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD1868 is a complete dual 18-bit DAC offering excellent
performance while requiring a single +5 V power supply. It is
fabricated on Analog Devices’ ABCMOS wafer fabrication process. The monolithic chip includes CMOS logic elements, bipolar and MOS linear elements, and laser-trimmed thin-film
resistor elements. Careful design and layout techniques have resulted in low distortion, low noise, high channel separation, and
low power dissipation.
The DACs on the AD1868 chip employ a partially segmented
architecture. The first three MSBs of each DAC are segmented
into seven elements. The 15 LSBs are produced using standard
R-2R techniques. The segments and R-2R resistors are laser
trimmed to provide extremely low total harmonic distortion.
The AD1868 requires no deglitcher or trimming circuitry. Low
noise is achieved through the use of two noise-reduction capacitors.
Each DAC is equipped with a high performance output amplifier. These amplifiers achieve fast settling and high slew rate,
producing ± 1 V signals at load currents up to ±1 mA. The
buffered output signal range is 1.5 V to 3.5 V. Reference voltages of 2.5 V are provided, eliminating the need for “False
Ground” networks.
A versatile digital interface allows the AD1868 to be directly
connected to all digital filter chips. Fast CMOS logic elements
allow for an input clock rate of up to 13.5 MHz. This allows for
operation at 2×, 4×, 8×, or 16× the sampling frequency for each
channel. The digital input pins of the AD1868 are TTL and
+5 V CMOS compatible.
*Protected by U.S. Patent Numbers: 3,961,326; 4,141,004; 4,349,811;
4,857,862; and patents pending.
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
The AD1868 operates on +5 V power supplies. The digital supply, V
duced digital feedthrough. Separate analog and digital ground
pins are also provided. In systems employing a single +5 volt
power supply, V
tery operated systems, operation will continue even with reduced
supply voltage. Typically, the AD1868 dissipates 50 mW.
The AD1868 is packaged in either a 16-pin plastic DIP or a 16pin plastic SOIC package. Operation is guaranteed over the temperature range of –35°C to +85°C and over the voltage supply
range of 4.75 V to 5.25 V.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Single-supply operation @ +5 V.
2. 50 mW power dissipation (typical).
3. THD+N is 0.004% (typical).
4. Signal-to-Noise Ratio is 97.5 dB (typical).
5. 108 dB channel separation (minimum).
6. Compatible with all digital filter chips.
7. 16-pin DIP and 16-pin SOIC packages.
8. No deglitcher required.
9. No external adjustments required.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 617/329-4700 Fax: 617/326-8703
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
, can be separated from the analog supply, VS, for re-
L
and VS should be connected together. In bat-
L
AD1868–SPECIFICA TIONS
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
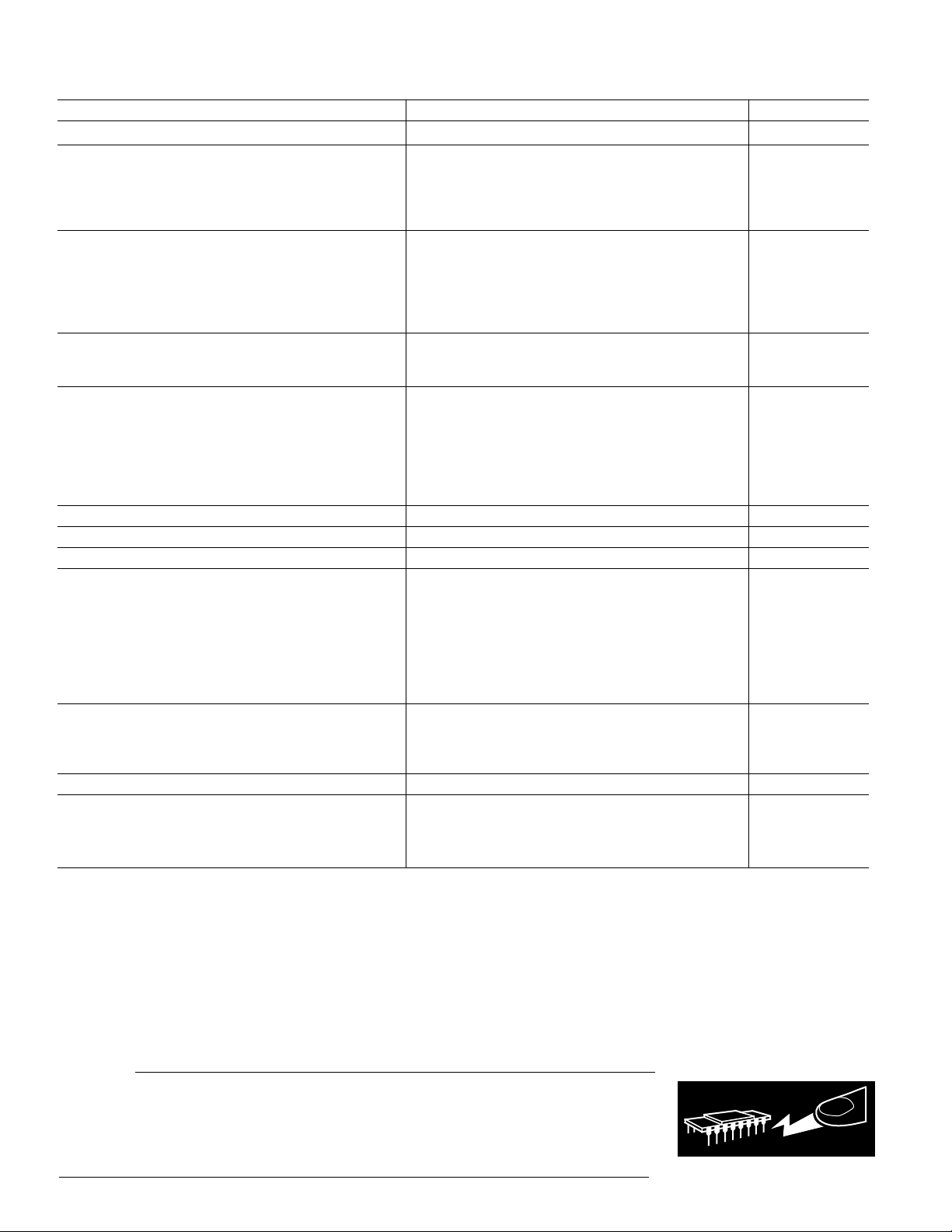
(typical at TA = +258C and +5 V supplies unless otherwise noted)
Min Typ Max Units
RESOLUTION 18 Bit
DIGITAL INPUTS V
IH
V
IL
, VIH = V
I
IH
, VIL = DGND 1.0 µA
I
IL
L
2.4 V
0.8 V
1.0 µA
Maximum Clock Input Frequency 13.5 MHz
ACCURACY
Gain Error ±1 % of FSR
Gain Matching ±1 % of FSR
Midscale Error ±15 mV
Midscale Error Matching ±10 mV
Gain Linearity Error ±3dB
DRIFT (0°C to +70°C)
Gain Drift ±100 ppm/°C
Midscale Drift ±100 µV/°C
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
0 dB, 990.5 Hz AD1868N 0.004 0.008 %
AD1868N-J 0.004 0.006 %
–20 dB, 990.5 Hz AD1868N 0.020 0.08 %
AD1868N-J 0.020 0.08 %
–60 dB, 990.5 Hz AD1868N 2.0 5.0 %
AD1868N-J 2.0 5.0 %
CHANNEL SEPARATION 1 kHz, 0 dB 108 NIL* dB
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO (with A-Weight Filter) 95 97.5 dB
D-RANGE (with A-Weight Filter) 86 92 dB
OUTPUT
Voltage Output Pins (V
L, VOR)
O
Output Range (±3%) ±1V
Output Impedance 0.1 Ω
Load Current ±1mA
Bias Voltage Pins (V
L, VBR)
B
Output Voltage +2.5 V
Output Impedance 350 Ω
POWER SUPPLY
Specification, V
Operation, V
and V
L
and V
L
S
S
4.75 5 5.25 V
3.5 5.25 V
+I, VL and VS = 5 V 10 14 mA
POWER DISSIPATION 50 70 mW
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Specification 0 25 70 °C
Operation –35 85 °C
Storage –60 100 °C
*Above 115 dB.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
VL to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0 V to 6 V
V
to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0 V to 6 V
S
AGND to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±0.3 V
Digital Inputs to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–0.3 to V
*Stresses greater than those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
L
Soldering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+300°C, 10 sec
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD1868 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–2–
REV. A
Typical Per formance of the AD1868
150
140
130
120
110
100
FREQUENCY – Hz
CHANNEL SEPARATION – dB
10
3
10
4
–30
AD1868
–40
–50
–60
–70
THD +N – dB
–80
–90
–100
0.5 2.5 4.5
6.5 8.5 10.5 12.5 14.5
FREQUENCY – kHz
–60dB
–20dB
0dB
16.5 18.5 20.5
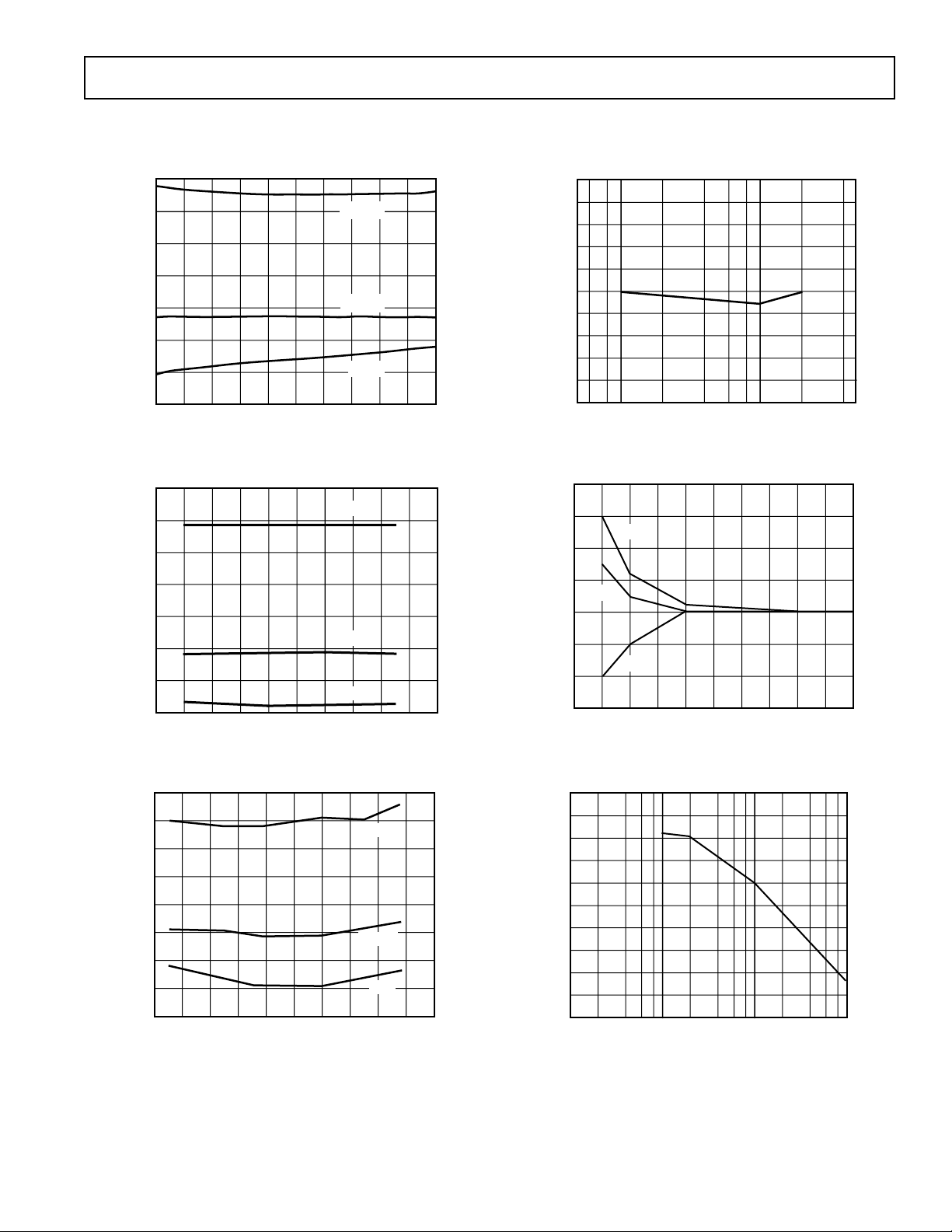
Figure 1. THD+N vs. Frequency
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
THD +N – dB
–70
–80
–90
4.4 4.6 4.8 5.0 5.2 5.4
VOLTAGE SUPPLY
–60dB
–20dB
0dB
Figure 2. Channel Separation vs. Frequency
8
6
0°C
4
2
25°C
0
–2
GAIN LINEARITY ERROR – dB
–4
–6
–100 –80 –60
70°C
INPUT AMPLITUDE – dB
–40
–20
–10
0
THD +N – dB
–100
REV. A
Figure 3. THD+N vs. Supply Voltage
–20
–
60dB
–40
–60
–
20dB
–80
0dB
–50 –30 –10 10 30 50 70 90 110 130
TEMPERATURE – °C
Figure 5. THD+N vs. Temperature
140
Figure 4. Gain Linearity Error vs. Input Amplitude
90
80
70
PSRR – dB
60
50
40
2
10
SUPPLY MODULATION FREQUENCY – Hz
3
10
4
10
Figure 6. Power Supply Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency
–3–
5
10
AD1868
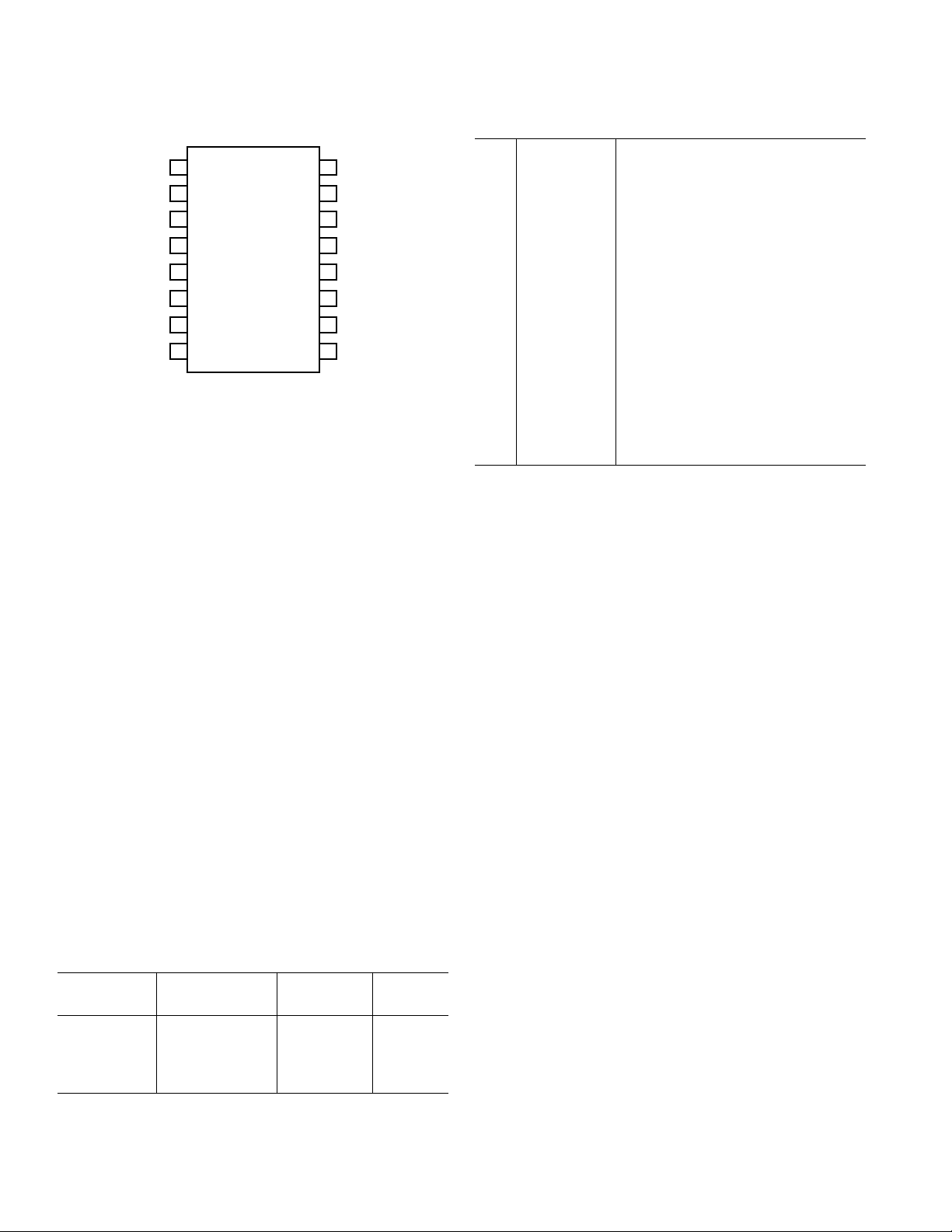
PIN CONFIGURATION
V
1
L
2
LL
3
DL
VBL
16
V
15
S
VOL
14
AD1868
CK
DR
LR
DGND
VBR
4
5
6
7
8
TOP VIEW
(Not To Scale)
13
NRL
AGND
12
11
NRR
VOR
10
V
S
9
DEFINITION OF SPECIFICATIONS
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
Total harmonic distortion plus noise (THD+N) is defined as
the ratio of the square root of the sum of the squares of the amplitudes of the harmonics and noise to the amplitude of the fundamental input frequency. It is usually expressed in percent (%)
or decibels (dB).
D-Range Distortion
D-range distortion is the ratio of the amplitude of the signal at
an amplitude of –60 dB to the amplitude of the distortion plus
noise. In this case, an A-weight filter is used. The value specified for D-range performance is the ratio measured plus 60 dB.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
The signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the amplitude
of the output when a full-scale output is present to the amplitude of the output with no signal present. It is expressed in
decibels (dB) and measured using an A-weight filter.
Gain Linearity
Gain linearity is a measure of the deviation of the actual output
amplitude from the ideal output amplitude. It is determined by
measuring the amplitude of the output signal as the amplitude
of that output signal is digitally reduced to a lower level. A perfect D/A converter exhibits no difference between the ideal and
actual amplitudes. Gain linearity is expressed in decibels (dB).
Midscale Error
Midscale error is the difference between the analog output and
the bias when the twos complement input code representing
midscale is loaded in the input register. Midscale error is expressed in mV.
PIN DESIGNATIONS
11V
L
Digital Supply (+5 Volts)
12 LL Left Channel Latch Enable
13 DL Left Channel Data Input
14 CK Clock Input
15 DR Right Channel Data Input
16 LR Right Channel Latch Enable
17 DGND Digital Common
18V
19V
10 V
R Right Channel Bias
B
S
R Right Channel Output
O
Analog Supply (+5 Volts)
11 NRR Right Channel Noise Reduction
12 AGND Analog Common
13 NRL Left Channel Noise Reduction
14 V
15 V
L Left Channel Output
O
S
Analog Supply (+5 Volts)
16 VBL Left Channel Bias
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The AD1868 is a complete, voltage output dual 18-bit digital
audio DAC which operates with a single +5 volt supply. As
shown in the block diagram, each channel contains a voltage
reference, an 18-bit DAC, an output amplifier, an 18-bit input
latch, and an 18-bit serial-to-parallel input register.
The voltage reference section provides a reference voltage and a
false ground voltage for each channel. The low noise bandgap
circuits produce reference voltages that are unaffected by
changes in temperature, time, and power supply.
The output amplifier uses both MOS and bipolar devices and
incorporates an NPN class-A output stage. It is designed to produce high slew rate, low noise, low distortion, and optimal frequency response.
Each 18-bit DAC uses a combination of segmented decoder
and R-2R architecture to achieve good integral and differential
linearity. The resistors which form the ladder structure are fabricated with silicon-chromium thin film. Laser trimming of
these resistors further reduces linearity error, resulting in low
output distortion.
The input registers are fabricated with CMOS logic gates.
These gates allow fast switching speeds and low power consumption, contributing to the fast digital timing, low glitch, and
low power dissipation of the AD1868.
ORDERING GUIDE
THD + N Package
Model @ F
S
SNR Option*
AD1868N 0.008% 95 dB N-16
AD1868R 0.008% 95 dB R-16
AD1868N-J 0.006% 95 dB N-16
AD1868R-J 0.006% 95 dB R-16
*N = Plastic DIP; R = SOIC.
–4–
REV. A
 Loading...
Loading...