Page 1

User Guide
English ( 3 – 9 )
Guía del usuario
Español ( 10 – 16 )
Guide d'utilisation
Français ( 17 – 23 )
Guida per l'uso
Italiano ( 24 – 30 )
Benutzerhandbuch
Deutsch ( 31 – 37 )
Gebruikershandleiding
Nederlands ( 38 – 44 )
Appendix
English ( 45 )
Page 2

Page 3

User Guide (English)
Introduction
Box Contents
Live 2404
Power Cable
User Guide
Safety & Warranty Manual
Support
For the latest information about this product (system requirements, compatibility information,
etc.) and product registration, visit altoprofessional.com/live2404.
For additional product support, visit altoprofessional.com/support.
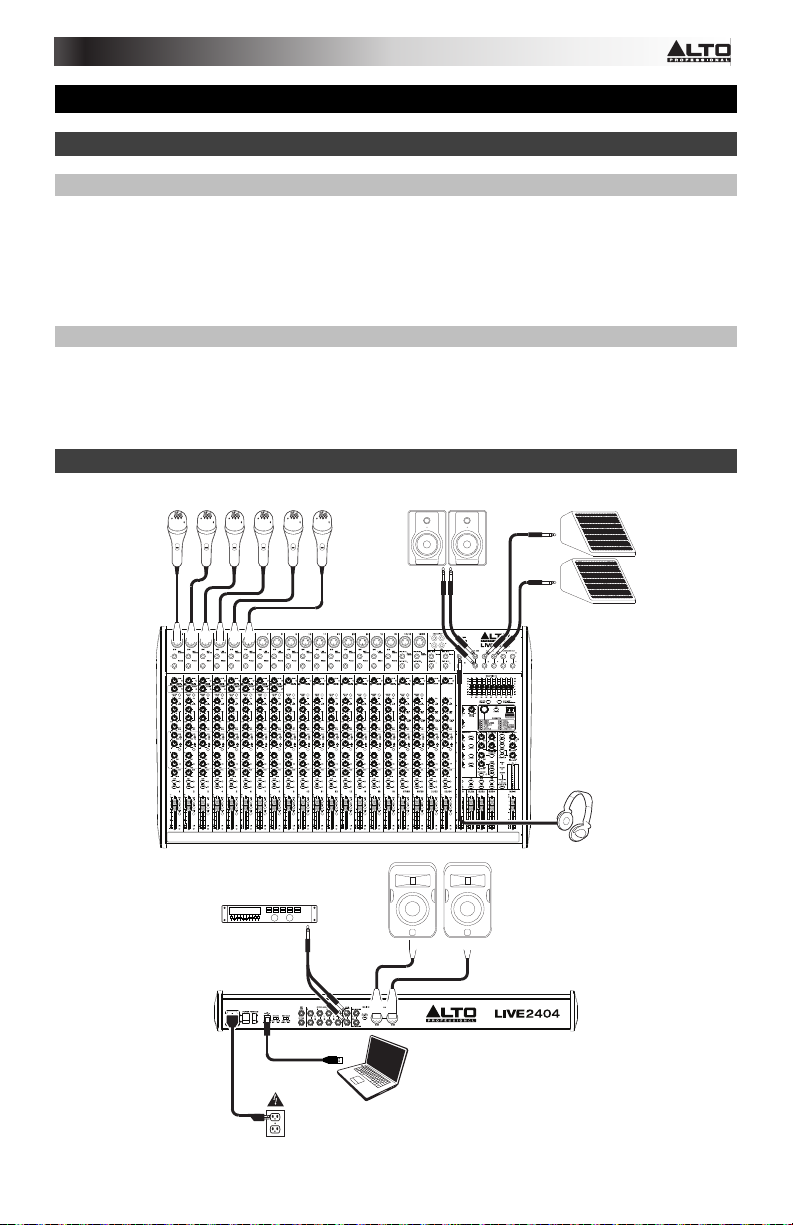
Quick Start / Connection Diagram
Microphones
Booth/Cue Monitors
Stage
Monitors
Top Panel
View
Headphones
External Effects
Processor
Rear Panel
View
Computer
Power
3
House
Loudspeakers
Items not listed in Box Contents
are not included.
Page 4

Features
Top Panel
Note: The channels have essentially
the same controls with some minor
variations between Channels 1-8, 9-16,
17-20, and 21-24. The five different
channel types are shown here.
1. Mic Input: Connect a microphone
or line-level device to these inputs
with an XLR cable.
2. Line Input: Connect line-level
devices to these inputs with 1/4"
cables.
3. Insert: Use a standard 1/4" TRS
cable to connect an external
processor (such as a compressor,
limiter, external EQ unit, etc.) to
this jack. The signal will be taken
after the channel's gain control
and returned before the channel's
EQ controls. The tip of the TRS
connection is the send, and the
ring is the return.
4. Gain: Adjusts the channel audio
level (pre-fader and pre-EQ gain).
Adjust this so that the Signal LED
lights up.
5. Peak LED: The LED will flash if
the signal is clipping. If this
happens, decrease the setting of
the Gain knob.
6. Compressor: Adjusts the amount
of compression on the channel,
applied by the mixer's built-in
compressor. The LED next to the
knob will light up when the
compressor is on.
7. Low Cut Filter: When this button
is depressed, that channel's
audio will be sent through a 75 Hz
low-frequency filter with a slope
of 18 dB per octave. This is useful
for reducing low-frequency noise
when using microphones.
8. Hi EQ: Adjusts the high (treble) frequencies of the channel.
9. Mid EQ: Adjusts the mid-range frequencies of the channel.
10. Mid Freq: Adjusts the mid-range frequency band (100 Hz – 8 kHz) affected by the Mid
EQ knob.
11. Hi-Mid EQ: Adjusts the high-mid-range frequency (3 KHz) of the channel.
19
20
4
6
8
9
10
13
14
14
16
17
18
21
4
1
2
3
7
15
22
22
22
23
1
2
3
5
4
7
8
9
10
13
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
22
21
22
22
23
1
2
2
5
4
8
11
12
13 13
14
14
16
17
18
19
20
21
7
15
22
22
22
23
2
2
5
5
4
8
11
12
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
19
20
22
21
22
22
23
Page 5

12. Low-Mid EQ: Adjusts the low-mid-range frequency (500 Hz) of the channel.
13. Low EQ: Adjusts the low (bass) frequencies of the channel.
14. Aux 1/2 Knobs: Adjusts the level of the signal sent from that channel to the
corresponding Aux bus. Use the Aux Post/Pre button to set whether the level is sent
pre-fader or post-fader.
15. Aux Post/Pre: When raised, the Aux 1/2 knobs control the post-fader level of the signal
sent from that channel to the corresponding Aux bus. When depressed the signal is prefader.
16. Aux 3 Knob: Adjusts the post-fader level of the signal sent from that channel to the Aux 3
bus.
17. Aux 4 / DFX Knob: Adjusts the post-fader level of the signal sent to the mixer's effects
processor, whose level is controlled by the DFX Return Fader (DFX Rtn). If an external
effects processor is connected to Aux Send 4, then the signal will be sent there instead
of to the mixer's effects processor.
18. Channel Pan / Balance: If this knob is labeled Pan, it adjusts the (mono) channel's
position in the stereo field. If the knob is labeled Bal, it adjusts the balance between the
left and right channels of that stereo signal.
19. Channel Mute: Press this button to mute/unmute the channel. The LED next to the
button will light up when the channel is muted.
20. Channel Solo: Press this button to solo/unsolo the channel. The LED next to the button
and the Solo Active LED will light up when the channel is soloed. Use this to view its level
in the LED Meters and to audition its audio alone in the Control Room Mix.
21. Channel Fader: Adjusts the audio level on the channel.
22. Output Buttons: Depress any combination of these buttons to send the channel's postfader signal to the corresponding outputs: Sub 1-2 (Subgroups 1 and 2), Sub 3-4
(Subgroups 3 and 4), and/or Main L/R (Main Outputs).
23. Signal LED (Sig): Indicates that the channel's incoming audio signal is within an optimal
range.
5
Page 6

24. Control Room Outputs
(Ctrl Out): Use standard
1/4" TRS cables to
connect these outputs to
your control room
(booth) monitors or
amplifier system.
25. Subgroups Outputs: Use standard 1/4"
TRS cables to connect these outputs to
your monitoring amplifier system, and
control their levels with the Subgroup
Faders. You can use these outputs for
group processing or for sending certain
channels to a destination other than the
Main Mix.
26. 2-Track Inputs (2 Track In): Connect
these inputs to the outputs of an external
sound source using a standard stereo
RCA cable (sold separately). Use the 2
Track In Source button to send this
signal either to the Main Mix Outputs or
to the Control Room Outputs (Ctrl Out).
27. 2-Track Outputs (2 Track Out): Connect
these outputs to the inputs of an external
recording device using a standard stereo
RCA cable (sold separately).
28. Aux Send: Use 1/4" TRS cables to
connect these outputs to the inputs of an
external amplifier or active monitor. Use
the Aux Send knobs on each channel to
control the level of the signal sent to these
outputs. This is useful for creating a
custom monitor mix for onstage
musicians.
29. Aux Sends Knobs: Use these knobs to
control the overall level of the signal sent
to the Aux Sends. (Use the Aux 1-4
Knobs on each channel to control the
signal sent here from each channel.)
30. Aux Sends Solo: Depress these buttons
to solo that channel in the Phones
Outputs.
31. Aux Return Knob (Aux Rtn): Controls the
audio level sent into the Aux Return (Aux
Rtn) inputs. The first and second knobs
control the Aux Return levels sent to the
Main Mix.
32. Aux Returns to Aux Sends: Use these knobs to control the level of the signal sent from
the corresponding Aux Return to the Aux Send bus with the same number. This is helpful
when using cascading mixers (e.g., sending the submixer's Aux Sends to this mixer's Aux
Returns, allowing the submixer's Control Room Mix to be sent to this mixer's subgroups
and then into its Control Room Mix).
26 27
59
2444
28
28
25 25
36
37 38
42 43
39
41
40
42
30
29
29
29
29
31 32 46
30
30
31
30
31
35
51 51 51 51
3231
33
34
34
45
45
48
47
49
53
58
50 50 50 50 52
54
55
56
57
6
Page 7

33. Aux Return 3 Routing: When this button is depressed, the signal sent into Aux Return 3
will be routed to the Control Room Mix. When this button is raised, the signal is sent to
the Main Mix.
34. Aux Return 4 Routing: Depress any combination of these buttons to send the signal
sent into Aux Return 4 to the corresponding outputs: Sub 1/2 (Subgroups 1 and 2), Sub
3/4 (Subgroups 3 and 4), and/or the Main Mix (Main Outputs).
35. Aux Return Solo: Depress this button to solo Aux Returns 1-4 in the Control Room Mix.
36. Graphic Equalizer: When the EQ On/Off switch is on (depressed), you can use these
controls to adjust the equalization of the main mix.
37. EQ On/Off: Enables or disables the Graphic Equalizer.
38. Main Out / Monitor Out: When this button is raised, the Graphic Equalizer will affect the
signal sent to the Main Mix Outputs. When this button is depressed, the Graphic
Equalizer will affect the signal sent to the Aux 1/2 (Mon) Output.
39. Effect Selector: This knob determines what effect the mixer's internal effects processor
will apply to the various channels. Turn the knob to change the effect number, and push
the knob to select it. The display next to the DFX Mute button will show the preset
number. Each channel can send different levels of audio to the processor by adjusting its
DFX Knob. See the Effects section for an explanation of the available effects.
40. DFX Mute: Press this button to mute/unmute the effects.
41. DFX Peak LED: The LED will flash if the signal is clipping. If this happens, decrease the
setting of your source channels' DFX Knobs. When the effects processor is muted, the
LED will be solidly lit.
42. DFX Out to Aux 1/2: These knobs control the level of the signal sent from the effects
processor to Aux Sends 1 and 2.
43. DFX Out to Main: This knob controls the level of the signal sent from the effects
processor to the Main Outputs.
44. Phones Output: Connect 1/4" stereo headphones to these outputs. The Phones
knob controls the volume.
45. Control Room Source: When any combination of these buttons is depressed, the
signals from those sources will be heard in the Control Room Mix: Main Mix, Sub 1/2
(Subgroups 1 and 2), and/or Sub 3/4 (Subgroups 3 and 4).
Note: If any Solo button is depressed, the soloed audio will replace the signal heard in
the Control Room Mix, regardless of the positions of these buttons.
46. Phones Volume: Adjusts the volume of Phones Output.
47. Control Room Volume: Adjusts the volume of Control Room Outputs (Ctrl Out).
48. 2 Track In Source: Depress the 2Tk In button to include the 2 Track In signal with the
Control Room Mix. Depress the 2Tk to Main button to include the 2 Track In signal with
the Main Mix.
49. 2 Track Level: Adjusts the level of the 2 Track In signal.
50. Subgroup Fader: Adjusts the level of the corresponding Subgroup.
51. Subgroup Assignments: Depress any combination of these buttons to assign their
corresponding Subgroups (beneath them) to that channel (Left or Right) of the Main Mix,
52. Main Fader: Adjusts the level of the Main Mix Outputs.
53. LED Meters: Shows the audio level of the Main Mix Outputs or the Control Room
Outputs (Ctrl Out), depending on the position of the Control Room Source buttons. The
Clip LED can light up occasionally, but if it happens too often, reduce the volume of the
mix and/or individual channels.
7
Volume
Page 8

r
A
54. Power LED: Illuminates when the mixer is on.
55. Phantom Power LED: Illuminates when the Phantom Power switch is on.
56. Level Set: Illuminates when the LED Meters are showing the pre-fader audio level of any
actively soloed channels rather than those of the Main Mix or Control Room Mix. The
Solo Mode button must be in the raised position (PFL) (changes to fader levels will not
affect the LED meters and the level heard).
57. Solo Active: Illuminates when the LED Meters are showing the after-level audio level of
any actively soloed channels rather than those of the Main Mix or Control Room Mix. The
Solo Mode button must be in the depressed position (AFL) (changes to fader levels will
affect the LED meters and the level heard).
58. Solo Mode: When raised, the audio from a channel whose Solo button is depressed will
be heard pre-fader (PFL). When depressed, the audio will be heard post-fader (afterfader or AFL).
59. USB Power Connection: You can use this USB port to connect and power (or charge) a
device that requires power from a 5V USB bus.
Effects
To apply effects, turn the Effects Preset Knob and press it to select one of the available
presets. To send a channel's signal to the effects processor, turn up that channel's DFX Knob
(Aux 4).
Each effect has 10 variations. Select one that suits the environment and your preferences.
Numbers Effect Description
00-09 Delay Reproduces the signal after a small period of time.
10-19 Delay+Verb Delay effect with room reverb.
20-29 Tremolo Rapidly increases and decreases the signal volume at a regula
30-39 Plate Simulates bright plate reverb.
40-49 Chorus Simulates the full, complex, watery sound of several instruments
50-59 Vocal Reverb, simulating a room with a small delay time.
60-69 Rotary Simulates the classic Doppler effect of the spinning horn inside
70-79 Small Room Reverb simulating a bright studio space.
80-89 Flange+Verb
90-99 Large Hall Reverb simulating a large acoustic space.
rate.
playing the same thing.
an organ speaker.
pplies room reverb plus a classic stereo flanging effect.
8
Page 9

Rear Panel
11
1
234
1. Power In: Use the included power cable to connect the mixer to a power outlet. While
the power is switched off, connect the power cable into the mixer first, then connect the
power cable to a power outlet.
2. Fuse Cover: If the fuse is broken, use a screwdriver or other tool to lift this tab, and
replace the fuse with a fuse with the same rating (printed just above the Power In). Using
a fuse with an incorrect rating can damage the unit and/or fuse.
3. Power Switch: Powers the mixer on and off. Turn on the mixer only after connecting all
of your input devices but before turning on your amplifiers. Turn off amplifiers before you
turn off the mixer.
4. Phantom Power: Activates/deactivates phantom power. When activated, phantom
power supplies +48V to the XLR mic inputs. Please note that most dynamic microphones
do not require phantom power, while most condenser microphones do. Consult your
microphone's documentation to find out whether it needs phantom power.
5. Main Mix Outputs: Use standard XLR or 1/4" TRS cables to connect either pair of these
outputs to your loudspeakers or amplifier system. Use the Main Fader to control the level
of these outputs.
6. Main Mix Pad: When this button is depressed, the signal sent to the Main Mix Outputs is
reduced by 10 dB. When raised, the signal is increased by 4 dB. Set this switch
depending on the nominal operating level of your equipment; professional-grade
equipment works at a nominal +4 dBu while consumer-grade equipment works at a
nominal -10 dBV.
7. Main Mix Insert: Use a standard 1/4" TRS Y-cable to connect an external processor
(such as a compressor, limiter, external EQ unit, etc.) to this jack. The signal will be taken
after the Graphic Equalizer and returned before the Main Fader. The tip of the TRS
connection is the send, and the ring zis the return.
8. USB Port: Use a standard USB cable to connect this USB port to a computer. The mixer
can send or receive audio to or from your computer through this connection.
• When sending audio, the Main Mix or Subgroups 1 and 2 will be sent from the mixer
to your computer, depending on the position of the Record switch.
• When receiving audio, it will be sent from your computer to Channels 23/24 or Main
Mix, depending on the position of the Play Back switch.
9. Record: This switch determines what audio is sent to the computer from the mixer's USB
Port: Subgroups 1 and 2 (
10. Play Back: This switch determines where the audio sent from the computer (to the
mixer's USB Port) will be routed when it returns to the mixer: Channels 23/24 (Ch 23/24)
or the Main Mix.
11. DFX Out: Use a standard 1/4" TRS cable to connect this output to an amplifier system.
The signal from the mixer's effects processor will be sent to this output.
12. Bypass: Connect an optional standard 1/4" TS footswitch (sold separately) to this input.
You can use the footswitch to activate or deactivate the mixer's effects processor.
13. Stereo Aux Return: Connect the outputs of an external device to these inputs with 1/4"
mono cables. If your source is mono, plug it into the left jack and it will be heard on both
the left and right sides.
9
8
10
9
Sub 1/2) or the Main Mix.
12 13 13 13 13
6
575
5
Page 10

Guía del usuario (Español)
Introducción
Contenido de la caja
Live 2404
Cable de alimentación
Guía del usuario
Manual sobre la seguridad y garantía
Soporte
Para obtener la información más reciente acerca de este producto (requisitos de sistema,
información de compatibilidad, etc.) y registrar el producto, visite
altoprofessional.com/live2404.
Para soporte adicional del producto, visite altoprofessional.com/support.
Diagrama de inicio y conexión rápida
Micrófonos
Monitores de cue/cabina
Monitores de
escenario
Vista del
panel
superior
efectos externo
Vista del
trasero
Procesador de
panel
Suministro eléctrico
10
Altavoces
del salón
Computadora
Los elementos que no se enumeran en
Contenido de la caja no están incluidos.
Auriculares
Page 11

Características
Panel superior
Nota: Los canales tienen esencialmente
los mismos controles con algunas
variaciones menores entre los canales 18, 9-16, 17-20 y 21-24. Se muestran aquí
los cinco tipos de canales diferentes.
1. Entrada de micrófono: Conecte un
micrófono o dispositivo de nivel de
línea a estas entradas con un cable
XLR.
2. Entrada de línea: Conecte
dispositivos de nivel de línea a
estas entradas con cables de 1/4
pulg.
3. Inserción: Use un cable TRS de 1/4
pulg. estándar para conectar a este
conector un procesador externo
(como un compresor, limitador,
ecualizador externo, etc.). La señal
se toma después del control de
ganancia del canal y retorna antes
de los controles del ecualizador del
canal. La señal se envía por la
punta de la conexión TRS y retorna
por la nuca.
4. Ganancia: Ajusta el nivel de audio
del canal (ganancia pre-fader y preecualización). Ajuste esto para que
el LED de señal se encienda.
5. LED de pico: El LED destella si la
señal se está recortando. Si esto
sucede, disminuya el ajuste de la
perilla Gain (Ganancia).
6. Compresor: Ajusta la cantidad de
compresión en el canal, aplicada
por el compresor incorporado del
mezclador. El LED junto a la perilla
se encenderá cuando el compresor
esté activado.
7. Filtro pasabajos: Cuando se pulsa
este botón, el audio de ese canal se
envía a través de un filtro de baja
frecuencia de 75 Hz con una pendiente de 18 dB por octava. Esto resulta útil para reducir
el ruido de baja frecuencia cuando se usan micrófonos.
8. Ecualización de agudos: Ajusta las altas frecuencias (agudos) del canal.
9. Ecualización de medios: Ajusta las frecuencias medias del canal.
10. Frecuencias medias: Ajusta la banda de frecuencias medias (100 Hz – 8 kHz) afectada
por la perilla Mid EQ.
19
20
4
6
8
9
10
13
14
14
16
17
18
21
1
2
3
15
22
22
22
23
1
2
3
5
4
7
8
9
10
13
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
22
21
22
22
23
1
2
2
5
4
7
8
11
12
13 13
14
14
16
17
18
19
20
21
7
15
22
22
22
23
2
2
5
5
4
8
11
12
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
19
20
20
22
21
22
22
23
11
Page 12

11. Ecualización de medios-altos: Ajusta las frecuencias de gama media-alta (3 KHz) del
canal.
12. Ecualización de bajos-medios: Ajusta las frecuencias de gama baja-media (500 Hz) del
canal.
13. Ecualización de graves: Ajusta las bajas frecuencias (graves) del canal.
14. Perillas auxiliares 1/2: Ajusta el nivel de la señal enviada desde ese canal hacia el bus
auxiliar correspondiente. Utilice el botón Aux Post/Pre para establecer si el nivel se envía
al pre o al post fader.
15. Post/Pre Aux: En la posición levantada, las perillas Aux 1/2 controlan el nivel de postfader de la señal enviada desde ese canal hacia el bus auxiliar correspondiente. Cuando
se pulsa, la señal es de pre-fader.
16. Perilla Aux 3: Ajusta el nivel de post-fader de la señal enviada desde ese canal hacia el
bus auxiliar 3.
17. Perilla Aux 4 / DFX: Ajusta el nivel de post-fader de la señal enviada hacia el procesador
de efectos del mezclador, cuyo nivel se controla con el fader de retorno de DFX (DFX
Rtn). Si se conecta un procesador de efectos externo a la salida Aux Send 4, la señal se
enviará allí en lugar del procesador de efectos del mezclador.
18. Pan / balance del canal: Si esta perilla indica Pan, ajusta la posición del canal (mono) en
el campo estéreo. Si la perilla indica Bal, ajusta el balance entre los canales izquierdo y
derecho de esa señal estéreo.
19. Silenciamiento de canal: Pulse este botón para silenciar/anular el silenciamiento del
canal. El LED junto al botón se encenderá cuando el canal esté silenciado.
20. Solo de canal: Pulse este botón para realizar/anular el solo del canal. El LED junto al
botón y el LED de activación de solo se iluminarán cuando se realice un solo del canal.
Utilice esto para ver su nivel en los medidores de LED y escuchar solamente su audio
en la mezcla de la sala de control.
21. Fader de canal: Ajusta el nivel de audio del canal.
22. Botones de salida: Pulse cualquier combinación de estos botones para enviar la señal
de post-fader del canal hacia las salidas correspondientes: Sub 1-2 (subgrupos 1 y 2),
Sub 3-4 (subgrupos 3 y 4) y/o Main L/R (Salidas principales).
23. LED de señal (Sig): Indica que la señal entrante de audio del canal está dentro de un
rango óptimo.
12
Page 13

24. Salidas de la cabina de
control (Ctrl Out): Use
cables TRS de 1/4 pulg.
estándar para conectar
estas salidas al sistema
de amplificador o
monitores de su cabina de control.
25. Salidas de subgrupos: Utilice cables TRS
de 1/4 pulg. estándar para conectar estas
salidas a su sistema amplificado de
monitorización y controle sus niveles con
los faders de subgrupo. Puede utilizar
estas salidas para procesamiento en grupo
o para enviar ciertos canales a un destino
que no sea la mezcla principal
26. Entradas de 2 pistas (2 Track In): Conecte
estas entradas a las salidas de una fuente
de sonido externa mediante un cable RCA
estéreo estándar (que se vende por
separado). Use el botón 2 Track In Source
(Fuente de entrada de 2 pistas) para enviar
esta señal a las salidas Main Mix Output o
hacia las salidas de la cabina de control
(Ctrl Out).
27. Salidas de 2 pistas (2 Track Out): Conecte
estas salidas a las entradas de un
dispositivo de grabación externo mediante
un cable RCA estéreo estándar (que se
vende por separado).
28. Envío auxiliar: Use cables TRS de 1/4 pulg.
para conectar estas salidas a las entradas
de un amplificador o monitor activo externo.
Utilice las perillas Aux Send (Envío auxiliar)
en cada canal para controlar el nivel de la
señal enviada a estas salidas. Esto es útil
para crear una mezcla de monitor
personalizada para los músicos en el
escenario.
29. Perillas de envío auxiliar: Utilice estas
perillas para controlar en nivel general de la
señal enviada a las salidas auxiliares.
(Utilice las perillas Aux 1 a 4 en cada canal
para controla la señal enviada aquí desde
cada canal).
30. Solo de envíos auxiliares: Pulse estos
botones para realizar un solo en ese canal
en las salidas para auriculares.
31. Perilla de retorno de auxiliares (Aux Rtn):
Controla el nivel de audio enviado a las
entradas Aux Return (Aux Rtn) (Retorno de auxiliares). La primera y segunda perilla controlan
los niveles de retorno de auxiliares enviados a la mezcla principal.
32. Retornos de auxiliares a envíos auxiliares: Utilice estas perillas para controlar el nivel de la
señal enviada desde el retorno de auxiliar correspondiente hacia el bus de envío de auxiliar con
el mismo número. Esto es útil cuando se utilizan mezcladores en cascada (por ejemplo, cuando
se mandan los envíos de auxiliares del submezclador a los retornos de auxiliares de este
mezclador, permitiendo que la mezcla de la cabina de control del submezclador se envíe a los
subgrupos de este mezclador y después a su mezcla de la cabina de control.
13
26 27
59
28
2444
28
25 25
36
37 38
42 43
39
41
40
42
30
29
29
29
29
31 32 46
30
30
31
30
31
35
51 51 51 51
3231
33
34
34
45
45
48
47
49
53
58
50 50 50 50 52
54
55
56
57
Page 14

33. Encaminamiento del retorno de auxiliar 3: Cuando se pulsa este botón, la señal enviada al
retorno de auxiliar 3 será encaminada a la mezcla de la cabina de control. Cuando de levanta
este botón, la señal se envía a la mezcla principal.
34. Encaminamiento del retorno de auxiliar 4: Pulse cualquier combinación de estos botones
para enviar la señal enviada al retorno de auxiliar 4 hacia las salidas correspondientes: Sub 1/2
(subgrupos 1 y 2), Sub 3/4 (subgrupos 3 y 4) y/o Main Mix (Salidas de la mezcla principal).
35. Solo de retorno de auxiliar: Pulse este botón para hacer un solo de los retornos de auxiliar
1-4 en la mezcla de la cabina de control.
36. Ecualizador gráfico: Cuando el interruptor EQ On/Off (Ecualizador encendido/apagado) está
conectado (pulsado), estos controles se pueden usar para ajustar la ecualización de la mezcla
principal.
37. Ecualizador encendido/apagado: Activa o desactiva el ecualizador gráfico.
38. Salida principal / Salida de Monitor: Cuando este botón está levantado, el ecualizador gráfico
afecta la señal enviada a salidas Main Mix Output (Mezcla principal). Cuando este botón está
pulsado, el ecualizador gráfico afecta la señal enviada a Aux 1/2 (Mon) Output (Salida Aux 1
[Mon]).
39. Selector de efectos: Esta perilla selecciona el efecto que el procesador de efectos interno del
mezclador aplica a los diversos canales. Gire la perilla para modificar el número de efecto y
púlsela para seleccionarlo. La pantalla al costado del botón DFX Mute (Silenciamiento de DFX)
muestra el número de preset. Cada canal puede enviar al procesador niveles diferentes de
audio ajustando su perilla de DFX. Consulte la sección Efectos una explicación de los efectos
disponibles.
40. Silenciamiento de DFX: Pulse este botón para silenciar/anular los efectos.
41. LED de pico de DFX: El LED destella si la señal se está recortando. Si esto sucede, disminuya
el ajuste de las perillas de DFX de sus canales fuente. Cuando el procesador de efectos está
silenciado, el LED está encendido permanentemente.
42. Salida de DFX a Aux 1/2: Estas perillas controlan el nivel de la señal enviada desde el
procesador de efectos al envío de auxiliar 1 y 2.
43. Salida de DFX a principal: Esta perilla controla el nivel de la señal enviada desde el
procesador de efectos a las salidas principales.
44. Salida para auriculares: Conecte a estas salidas auriculares estéreo de 1/4 pulg. El volumen
se controla con la perilla Phones Volume (Volumen de auriculares).
45. Fuente de cabina de control: Cuando se pulse cualquier combinación de estos botones, las
señales de estas fuentes se escucharán en la mezcla de la cabina de control: Mezcla
principal, Sub 1/2 (subgrupos 1 y 2), y/o Sub 3/4 (subgrupos 3 y 4).
Nota: Si solamente se pulsa el botón Solo el audio al que le aplicó el solo reemplazará la señal
que se escucha en la mezcla de la cabina de control sin importar las posiciones de estos
botones.
46. Volumen de auriculares: Ajusta el volumen de la salida Phones.
47. Volumen de cabina de control: Ajusta el volumen de las salidas de la cabina de control (Ctrl
Out).
48. Fuente de entrada de 2 pistas: Pulse el botón 2Tk In para incluir la señal 2 Track In en la
mezcla de la cabina de control. Pulse el botón 2Tk to Main para incluir la señal 2 Track In en
la mezcla principal.
49. Nivel de 2 pistas: Ajusta el nivel de la señal 2 Track In.
50. Fader de subgrupo: Ajusta el nivel del subgrupo correspondiente.
51. Asignaciones de subgrupos: Pulse cualquier combinación de estos botones para asignar sus
subgrupos correspondientes (debajo de ellos) a ese canal (izquierdo o derecho) de la mezcla
principal,
52. Fader principal: Ajusta el nivel de las salidas Main Mix Outputs.
14
Page 15

A
V
A
53. Medidores LED: Muestra el nivel de audio de las salidas Main Mix Outputs o las salidas de la
cabina de control (Ctrl Out), según la posición de los botones Control Room Source (Fuente
de la cabina de control). Puede encenderse ocasionalmente el LED de recorte, pero si sucede
con demasiada frecuencia, reduzca el volumen de la mezcla y/o los canales individuales.
54. LED de encendido: Se ilumina cuando el mezclador está prendido.
55. LED de potencia fantasma: Se ilumina cuando el interruptor de potencia fantasma está
encendido.
56. Nivel establecido: Se ilumina cuando los medidores LED están mostrando el nivel de audio
pre-fader de cualquier canal al que se le haya realizado un solo activo, en lugar de los de la
mezcla principal o los de la mezcla de la cabina de control. El botón Solo Mode (Modo Solo)
debe estar en posición levantada (PFL) (los cambios en los niveles de los faders no afectarán a
los medidores LED y al nivel que se escucha).
57. Solo Activo: Se ilumina cuando los medidores LED están mostrando el nivel de audio prefader de cualquier canal al que se le haya realizado un solo activo, en lugar de los de la mezcla
principal o los de la mezcla de la cabina de control. El botón Solo Mode (Modo Solo) debe
estar en posición hacia abajo (AFL) (los cambios en los niveles de los faders no afectarán a los
medidores LED y al nivel que se escucha).
58. Modo solo: Al estar levantado, el audio desde un canal que tenga pulsado el botón Solo se
escuchará previo al fader (PFL). Al estar pulsado, el audio se escuchará post-fader (después
del fader o AFL).
59. Conexión de alimentación USB: Puede utilizar este puerto USB para conectar y alimentar (o
cargar) un dispositivo que requiera alimentación USB de 5 V.
Efectos
Para aplicar efectos, gire la perilla de presets de efectos y púlsela para seleccionar uno de los
presets disponibles. Para enviar la señal de un canal al procesador de efectos, aumente el ajuste de
la perilla de DFX (Aux 4).
Cada efecto tiene 10 variaciones. Seleccione una que se adapte al ambiente y a sus preferencias.
Números Efecto Descripción
00-09 Delay (Retardo) Reproduce la señal después de un breve período de tiempo.
10-19 Delay+Verb
20-29 Tremolo
30-39 Plate (Placa) Simula la reverberación de una placa brillante
40-49 Chorus (Coro) Simula el sonido pleno, complejo y acuoso de varios
50-59
60-69 Rotary (Giratorio) Simula el clásico efecto Doppler de la bocina giratoria adentro
70-79 Small Room
80-89 Flange+Verb
90-99 Large Hall (Sala de
(Retardo+reverberación)
ocal Reverberación, que simula una sala con pequeño tiempo de
(Sala pequeña)
(Flange+reverberación)
concierto grande)
Efecto de retardo con reverberación de sala.
umenta y disminuye rápidamente el volumen de la señal a
un ritmo constante.
instrumentos que tocan lo mismo.
retardo
de un altavoz de órgano.
Reverberación que simula una sala de estudio brillante.
plica reverberación de sala más un efecto de flange estéreo
clásico.
Reverberación que simula un espacio acústico grande.
15
Page 16

Panel trasero
11
1
234
1. Entrada de alimentación: Use el cable de alimentación incluido para conectar el mezclador a
un tomacorriente alimentado. Con la alimentación eléctrica desconectada, enchufe el cable de
alimentación al mezclador primero y luego al tomacorriente.
2. Tapa de fusibles: Si se quemó el fusible, use un destornillador u otra herramienta para levantar
esta lengüeta a fin de reemplazar el fusible con otro de la misma especificación (impresa justo
sobre la entrada de alimentación). Si utiliza un fusible de especificación incorrecta, puede
dañarse la unidad y/o el fusible.
3. Interruptor de encendido: Enciende y apaga la unidad. Encienda la mezcladora luego de
conectar todos sus dispositivos de entrada pero antes de encender sus amplificadores.
Apague los amplificadores antes de apagar el mezclador.
4. Potencia fantasma: Activa/desactiva la alimentación fantasma. Cuando se activa, la
alimentación fantasma suministra +48 V a las entradas de micrófono XLR. Tenga en cuenta que
la mayoría de los micrófonos dinámicos no requieren alimentación fantasma, mientras que la
mayoría de los micrófonos de condensador la requieren. Consulte la documentación de su
micrófono para averiguar si necesita alimentación fantasma.
5. Salidas de la mezcla principal: Use un cable XLR o TRS de 1/4 pulg. estándar para conectar
cualquier par de estas salidas a sus altavoces o sistema de amplificador. Use el fader Main
(Principal) para controlar el nivel de estas salidas.
6. Nivel de funcionamiento de la mezcla principal: Cuando se pulsa este botón, la señal
enviada a las salidas de la mezcla principal se reduce en 10 dB. Cuando se lo deja levantado,
la señal se incrementa en 4 dB. Ajuste este interruptor según el nivel de funcionamiento
nominal de su equipo; los equipos de grado profesional funcionan con +4 dBu mientras que
los equipos de grado de consumidor funcionan a -10 dBV nominales.
7. Inserción en mezcla principal: Utilice un cable TRS en “Y” de 1/4 pulg. estándar para
conectar a este conector un procesador externo (como un compresor, limitador, ecualizador
externo, etc.). La señal se llevará después del ecualizador gráfico y se devolverá antes del
fader principal. La señal se envía por la punta de la conexión TRS y retorna por la nuca.
8. Puerto USB: Utilice un cable USB estándar para conectar este puerto USB a su ordenador. El
mezclador puede enviar o recibir audio desde o hacia su ordenador a través de esta conexión.
• Al enviar audio, se enviará la mezcla principal o los subgrupos 1 y 2 desde el mezclador
hacia su ordenador, según la posición del interruptor Record (Grabar).
• Al recibir audio, se enviará desde su ordenador hacia los canales 23/24 o mezcla
principal, según la posición del interruptor Play Back.
9. Grabar: Este interruptor determina qué audio se envía al ordenador desde el puerto USB del
mezclador: Los subgrupos 1 y 2 (Sub 1/2) o la mezcla principal.
10. Reproducción: Este interruptor determina adónde se encaminará el audio enviado desde el
ordenador (hacia el puerto USB del mezclador) cuando vuelva del mezclador: Los canales
23/24 (Ch 23/24) o la mezcla principal.
11. Salida de DFX: Utilice un cable TRS estándar de 1/4 pulg. para conectar esta salida un
sistema de amplificación. La señal proveniente del procesador de efectos del mezclador se
enviará hacia esta salida.
12. Puenteo: Conecte un interruptor de pedal TS de 1/4 pulg. estándar opcional (que se vende por
separado) a esta entrada. Puede utilizar el interruptor de pedal para activar o desactivar el
procesador de efectos del mezclador.
13. Retorno de auxiliar estéreo: Conecte a estas entradas las salidas de un dispositivo externo
con cables mono de 1/4 pulg. Si su fuente es mono, enchúfela en el conector izquierdo y se
escuchará en ambos lados, izquierdo y derecho.
8
9
10
12 13 13 13 13
16
6
575
5
Page 17
Guide d'utilisation (Français)
Présentation
Contenu de la boîte
Live 2404
Câble d'alimentation
Guide d'utilisation
Consignes de sécurité et informations concernant la garantie
Assistance technique
Pour les toutes dernières informations concernant ce produit (configuration système,
compatibilité, etc.) et l’enregistrement, veuillez visiter le site altoprofessional.com/live2404.
Pour de l’assistance supplémentaire, veuillez visiter le site altoprofessional.com/support.
Démarrage rapide/Schéma de connexion
Microphones
Moniteurs cabine/pré-écoute
Moniteurs
de scène
Panneau
supérieur
Casque d’écoute
Processeur
d’effets externe
Panneau
arrière
Ordinateur
Alimentation
17
Haut-parleurs
maison
Les articles qui ne sont pas énumérés
dans le Contenu de la boîte de ce
guide ne sont pas inclus.
Page 18

Caractéristiques
Panneau supérieur
Remarque : Les canaux ont essentiellement
les mêmes commandes, mais avec certaines
différences entre les canaux 1 à 8, 9 à 16, 17
à 20, 21 à 24. Les cinq types de canaux sont
indiqués ci-dessous.
1. Entrée micro : Ces entrées
permettent de brancher un
microphone ou un appareil à niveau
ligne avec un câble XLR.
2. Entrée ligne : Ces entrées
permettent de brancher des appareils
à niveau ligne à l’aide d’un câble
6,35 mm (¼ po).
3. Connecteurs TRS : Utilisez des
câbles TRS 6,35 mm (¼ po) afin de
brancher des processeurs externes
tels que des compresseurs, limiteurs,
égaliseurs, etc., à ces prises. Le
signal est acheminé après
l’atténuation, puis retourné avant
l’égalisation. La pointe de la fiche
TRS est le départ, et la bague est le
retour.
4. Gain : Ces potentiomètres permettent
de régler le niveau du signal audio
pré-atténuation et pré-égalisation du
canal correspondant. Réglez le niveau
afin que la DEL Signal s'allume.
5. Témoin d’écrêtage : En présence
d'écrêtage, le voyant DEL clignote.
Pour remédier à l’écrêtage, diminuez
le réglage du potentiomètre Gain du
canal correspondant.
6. Compresseur : Ces potentiomètres
permettent de régler le niveau de
compression sur le canal, appliquée
par compresseur intégré de la
console de mixage. La DEL à côté du
potentiomètre s’allume lorsque le
compresseur est activé.
7. Filtre passe-bas : Lorsque cette touche est enfoncée, le signal de ce canal est acheminé
par un filtre passe-bas de 75 Hz avec une courbe d’intensité de 18 dB par octave. Ceci
peut être utile pour réduire le ronflement et filtrer les bruits à basse fréquence indésirés
lors de l’utilisation de microphones.
8. Égalisation hautes fréquences : Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler le niveau des
hautes fréquences du canal correspondant.
9. Égalisation moyennes fréquences : Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler le niveau
des moyennes fréquences du canal correspondant.
19
20
18
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
5
4
1
2
2
5
4
2
2
5
5
4
6
7
8
9
10
13
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
22
21
22
22
23
8
9
10
13
14
14
16
17
18
21
7
11
12
13 13
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
22
21
22
22
23
7
8
8
11
12
14
14
15
15
16
17
18
19
19
20
20
22
22
22
23
21
22
22
22
23
Page 19

10. Bande des fréquences médianes : Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler la bande
des fréquences médianes affectée par la touche MID EQ.
11. Bande des hautes fréquences médianes : Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler le
niveau des hautes fréquences médianes (3 kHz) du canal correspondant.
12. Bande des basses fréquences médianes : Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler le
niveau des basses fréquences médianes (500 Hz) du signal audio du canal
correspondant.
13. Égalisation des basses fréquences : Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler le niveau
des basses fréquences du canal correspondant.
14. Aux 1/2 : Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler les niveaux du signal transmis aux
bus auxiliaires correspondants. Utilisez la touche Aux Post/Pre afin de définir si le niveau
est transmis pré-atténuation ou post-atténuation.
15. Aux Post/Pre : Lorsque désactivés, les potentiomètres Aux 1/2 permettent de régler les
niveaux post-atténuation du signal transmis par ce canal aux bus auxiliaires
correspondants. Lorsqu'enfoncée, le signal est transmis pré-atténuation.
16. Aux 3 : Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler les niveaux post-atténuation du signal
transmis par ce canal aux bus auxiliaires 3.
17. Aux 4/DFX : Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler les niveaux post-atténuation du
signal transmis au processeur d'effet de la console de mixage, dont le niveau est contrôlé
par le curseur DFX Rtn. Si un processeur d'effets externe est branché à la sortie Aux
Send 4, le signal sera transmis à celui-ci là plutôt qu’au processeur d'effet de la console
de mixage.
18. Panoramique/Balance : Le potentiomètre Pan permet d'ajuster la position du canal
(mono) dans le champ stéréo. Le potentiomètre Bal permet d’ajuster l’équilibre entre les
canaux gauche et droit pour ce signal stéréo.
19. Mise en sourdine du canal : Cette touche permet de mettre en sourdine ou de réactiver
le canal. La DEL à côté de la touche s’allume lorsque le canal est mis en sourdine.
20. Mise en solo du canal : Cette touche permet d’activer et de désactiver la mise en solo
du canal. La DEL à côté de la touche s’allume lorsque le canal est mis en sourdine.
Utilisez cette option pour afficher ses niveaux sur les vumètres DEL et pour écouter le
signal isolé dans le mix de pré-écoute (Control Room Mix).
21. Curseur de canal : Ces curseurs permettent de régler le niveau du signal audio du canal
correspondant.
22. Sélecteur de sortie : Appuyez sur n'importe quelle combinaison de ces touches afin de
transmettre le signal post-atténuation du canal aux sorties correspondantes : Sub 1-2
(sous-groupes 1 et 2), Sub 3-4
gauches/droites).
23. DEL du signal : Ces voyants DEL indiquent que le signal audio entrant est dans une
plage optimale.
(sous-groupes 3 et 4), et/ou Main L/R (sorties principales
19
Page 20

24. Sorties de pré-écoute
(Ctrl Out) : Utilisez des
câbles TRS 6,35 mm (¼ po)
standards afin de brancher
ces sorties à des enceintes
moniteur (pré-écoute) ou à
un système de sonorisation.
25. Sorties sous-groupes : Utilisez des câbles
TRS 6,35 mm (¼ po) standard pour relier ces
sorties à vos enceintes moniteur (pré-écoute)
ou à un système de sonorisation. Leurs
niveaux sont contrôlés par les curseurs de
sous-groupes. Vous pouvez utiliser ces
sorties pour le traitement de plusieurs sorties
à la fois ou pour transmettre les signaux de
certains canaux vers d’autres sorties autres
que les sorties mix principales.
26. Entrées 2-Track : Ces entrées permettent de
brancher une source audio externe à l’aide
d’un câble RCA standard (vendu
séparément). Utilisez la touche 2 Track In
Source afin de transmettre ce signal aux
sorties mix principales (Main Mix Output) ou
aux sorties de pré-écoute (Ctrl Out).
27. Sorties 2-Track : Ces sorties permettent de
brancher un appareil d’enregistrement
externe à l’aide d’un câble RCA standard
(vendu séparément).
28. Sorties auxiliaires : Ces sorties permettent
de brancher un amplificateur externe ou un
moniteur actif à l’aide de câbles TRS
6,35 mm (¼ po). Utilisez les potentiomètres
Aux Send de chaque canal afin de régler le
niveau du signal transmis à ces sorties. Ceci
peut être utile pour créer un mix de préécoute pour les musiciens sur scène.
29. Potentiomètres des sorties auxiliaires : Ces
potentiomètres permettent de régler le niveau
du signal global transmis aux sorties
auxiliaires. (Utilisez les potentiomètres Aux
Send 1 à 4 de chaque canal afin de régler le
niveau du signal transmis de chaque canal.
30. Mise en solo des sorties auxiliaires :
Enfoncez ces touches afin d’isoler le signal
de ce canal dans les sorties casque.
31. Potentiomètres des entrées auxiliaires :
Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler le
niveau transmis aux entrées auxiliaires. Les deux premièrs potentiomètres Aux Returns
commandes le niveau des entrées auxiliaires transmis aux sorties mix principales (Main Mix).
32. Entrées auxiliaires aux sorties auxiliaires :
du signal transmis par l’entrée auxiliaire au bus de la sortie auxiliaire correspondante. Ceci est
utile lorsque vous utilisez des consoles de mixage reliées en parallèle (c.-à-d., transmettre le
signal des sorties auxiliaires (mix de pré-écoute) d’une première console aux sous-groupes
d’une deuxième console, afin de les transmettre à son mix de pré-écoute).
26 27
59
2444
28
28
25 25
36
37 38
42 43
39
41
40
42
29
29
29
29
30
31 32 46
30
30
31
30
31
35
3231
45
45
48
33
34
34
51 51 51 51
58
50 50 50 50 52
Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler le niveau
47
49
53
54
55
56
57
20
Page 21

33. Routage de l'entrée auxiliaire 3 : Lorsque cette est enfoncée, le signal transmis à l’entrée
auxiliaire 3 est acheminé vers le mix de pré-écoute (Control Room Mix). Lorsque la touche est
relâchée, le signal est acheminé vers le mix principal (Main Mix Out).
34. Routage de l'entrée auxiliaire 4 : Appuyez sur n'importe quelle combinaison de ces touches
afin de transmettre le signal transmis à l’entrée auxiliaire 4 aux sorties correspondantes : Sub
1/2 (sous-groupes 1 et 2), Sub 3/4 (sous-groupes 3 et 4), et/ou Main Mix (sorties principales).
35. Mise en solo des entrées auxiliaires : Cette touche permet d’isoler les entrées auxiliaires 1
à 4 dans le mix de pré-écoute (Control Room Mix).
36. Égalisateur graphique : Lorsque la touche EQ On/Off est enfoncée, vous pouvez utiliser ces
commandes afin de régler l’égalisation du mix principal.
37. EQ On/Off : Cette touche permet d’activer/désactiver l'égaliseur graphique.
38. Main Out/Monitor Out : Lorsque la touche est relâchée, l’égaliseur graphique modifie le signal
acheminé vers les sorties mix principales (Main Mix Out). Lorsque la touche est enfoncée,
l’égaliseur graphique modifie le signal acheminé vers les sorties auxiliaires 1 et 2 (pré-écoute).
39. Sélecteur d’effet : Ce bouton permet de sélectionner l'effet que le processeur d’effet interne
ajoutera aux différents canaux. Tournez le bouton pour modifier le numéro d’effet, puis
appuyez dessus afin de sélectionner l’effet. L'écran à proximité de la touche DFX Mute affiche
le numéro du préréglage. Chaque canal peut envoyer différents niveaux d’audio au processeur
en réglant le potentiomètre DFX correspondant. Veuillez consulter la section Effets pour une
explication des différents effets disponibles.
40. DFX Mute : Cette touche permet de mettre en sourdine et de réactiver les effets.
41. DEL d’écrêtage des effets : En présence d'écrêtage, le voyant DEL clignote. Pour remédier à
l’écrêtage, diminuez le réglage des potentiomètres DFX des canaux de la source. Lorsque le
processeur d’effets est mis en sourdine, la DEL s’allume.
42. DFX Out to Aux 1/2 – Ces potentiomètres permettent de régler le niveau du signal du
processeur d’effet acheminé aux sorties auxiliaires 1 et 2.
43. DFX Out to Main : Ce potentiomètre permet de régler le niveau du signal du processeur d’effet
acheminé aux sorties principales (MAIN).
44. Sortie casque : Cette sortie permet de brancher un casque d’écoute stéréo doté d’une fiche
de 6,35 mm (¼ po). Les niveaux de ces sorties sont commandés par le potentiomètre Volume
casque.
45. Source pré-écoute : Appuyez sur n'importe quelle combinaison de ces touches afin de
transmettre les signaux provenant de ces sources au mix de pré-écoute : Main Mix (mix
principal), Sub 1/2 (sous-groupes 1 et 2) et/ou Sub 3/4 (sous-groupes 3 et 4).
Remarque : Si une des touches Solo est enfoncée, le signal isolé remplacera le signal entendu
dans le mix de pré-écoute, quelle que soit la position de ces touches.
46. Volume casque : Permet d'ajuster le niveau du volume de la sortie casque.
47. Volume pré-écoute : Ce potentiomètre permet de régler les niveaux des sorties de pré-
écoute (Ctrl Out).
48. 2 Track In Source : Enfoncer la touche 2Tk In permet d’ajouter le signal de l’entrée 2 Track In
au mix de pré-écoute (Control Room Mix). Enfoncer la touche 2Tk to Main permet d’ajouter le
signal de l’entrée 2 Track In au mix principale (Main Mix).
49. 2 Track Level : Ce potentiomètre permet de régler les niveaux du signal de l’entrée 2 Track In.
50. Curseurs des sous-groupes : Ces curseurs permettent de régler les niveaux du sous-groupe
correspondant.
51. Affectation des sous-groupes : Appuyez sur n'importe quelle combinaison de ces touches
afin d’attribuer les sous-groupes (dessous) aux canaux correspondants (
mix principal (Main Mix).
52. Curseur principal : Ce curseur permet de régler les niveaux des sorties principales (Main Mix
Output).
gauche ou droit) du
21
Page 22

V
53. Vumètres : Ces vumètres indiquent les niveaux des sorties mix principales (Main Mix
Output) ou des sorties du mix de pré-écoute (Ctrl Out), selon la position des touches de la
section Control Room Source. La DEL d’écrêtage peut s’allumer occasionnellement, mais si
cela arrive trop souvent, réduisez les niveaux du mix ou de chacun des canaux.
54. Témoin DEL d'alimentation : Cette DEL s’allume lorsque la console de mixage est sous
tension.
55. Témoin DEL d'alimentation fantôme : Cette DEL s’allume lorsque l’alimentation fantôme est
activée.
56. Level Set : Cette DEL s'allume lorsque les vumètres indiquent les niveaux pré-atténuation d’un
des canaux mis en solo plutôt que ceux du mix principal ou du mix de pré-écoute. La touche
Solo Mode ne doit pas être enfoncée (PFL) (les modifications apportées aux niveaux des
curseurs n’affecteront pas les vumètres et les niveaux entendus).
57. Solo Active : Cette DEL s'allume lorsque les vumètres indiquent les niveaux post-atténuation
d’un des canaux mis en solo plutôt que ceux du mix principal ou du mix de pré-écoute. La
touche Solo Mode doit être enfoncée (AFL) (les modifications apportées aux niveaux des
curseurs n’affecteront pas les vumètres et les niveaux entendus).
58. Solo Mode : Lorsque relâchée, le signal d’un canal dont la touche Solo est enfoncée sera
entendu pré-atténuation (PFL). Lorsqu’enfoncée, le signal sera entendu post-atténuation (AFL).
59. Alimentation USB : Ce port USB permet de connecter et d’alimenter (ou recharger) un appareil
qui nécessite une alimentation par bus USB de 5 V.
Effets
Pour ajouter des effets, tournez le sélecteur d'effet jusqu’à ce que l’effet souhaité s’affiche et
appuyez sur le bouton afin de sélectionner l'une des préconfigurations disponibles. Pour transmettre
le signal d'un canal au processeur d'effets, tournez le potentiomètre DFX (Aux 4) pour ce canal.
Chaque effet dispose de 10 variantes. Sélectionnez celui qui convient à l'environnement et à vos
préférences.
Numéros Effet Description
00-09 Delay Réinjection du signal mono après un court délai.
10-19 Delay+Verb Simulation d’un écho avec la réverbération d’une salle.
20-29 Tremolo Augmente et diminue rapidement le volume du signal à un rythme
30-39 Plate Simulation d’un son clair classique.
40-49 Chorus Simulation du son riche et dense donnant l’impression d’entendre
50-59
60-69 Rotary Simulation de l'effet Doppler classique de la corne de la filature à
70-79 Small Room Réverbération, simulation d’une salle de studio « claire ».
80-89 Flange+Verb Ajoute une réverbération Room et un effet flanger classique stéréo.
90-99 Large Hall Réverbération, simulation de l’acoustique d’une grande salle
ocal Simulation d’une salle avec un temps de réverbération court.
régulier.
plusieurs instruments jouant simultanément la même partie.
l'intérieur d'une enceinte d'orgue.
acoustique.
22
Page 23

Panneau arrière
11
1
234
1. Entrée d’alimentation : Utilisez le câble d’alimentation inclus pour brancher la console de mixage
dans une prise secteur. Avec la console de mixage hors tension, branchez d’abord le câble
d'alimentation à la console, puis dans la prise secteur.
2. Couvercle de fusible : Si le fusible de l’appareil est endommagé, utiliser un tournevis ou autre outil
pour soulever le couvercle afin de remplacer le fusible par un nouveau de même calibre (calibre
indiqué au-dessus de l’entrée d’alimentation). L’utilisation d’un fusible de calibre inapproprié pourrait
endommager l’appareil et/ou le fusible.
3. Interrupteur d'alimentation : Interrupteur de mise sous et hors tension de la console de mixage.
Veuillez mettre la console de mixage sous tension seulement après avoir effectué le raccordement de
tous les appareils d'entrée, et avant d'allumer vos amplificateurs. Veuillez mettre les amplificateurs
hors tension avant de mettre la console de mixage hors tension.
4. Alimentation fantôme : Cet interrupteur permet d’activer et de désactiver l’alimentation fantôme.
Lorsqu'elle est activée, l’alimentation fantôme fournit +48 V aux entrées micro XLR. Veuillez noter que
la plupart des microphones électrodynamiques ne nécessitent pas d’alimentation fantôme, alors que
les microphones à condensateur en ont besoin. Veuillez consulter la documentation fournie avec votre
microphone pour savoir si vous devez utiliser l'alimentation fantôme.
5. Sorties mix principales : Utilisez des câbles XLR ou 6,35 mm (¼ po) standards afin de brancher ces
sorties à des enceintes ou à un système de sonorisation. Les niveaux de ces sorties sont commandés
par le curseur principal.
6. Niveau de fonctionnement nominal : Lorsque cette touche est enfoncée, le signal transmis aux
sorties mix principales est réduit de 10 dB. Lorsque relâchée, le signal est augmenté de 4 dB. Réglez
cette touche en fonction du niveau de fonctionnement nominal de votre équipement ; l'équipement de
qualité professionnelle fonctionne à un niveau nominal de +4 dBu, alors que l’équipement grand
public fonctionne à un niveau nominal -10 dBV.
7. Connecteurs TRS : Utilisez des câbles TRS 6,35 mm (¼ po) afin de brancher des processeurs
externes tels que des compresseurs, limiteurs, égaliseurs, etc., à cette prise. Le signal est acheminé
après l’égalisation, puis retourné avant l’atténuation. La pointe de la fiche TRS est le départ, et la
bague est le retour.
8. Port USB : Utilisez un câble USB standard afin de brancher ce port USB au port USB d’un ordinateur.
La console de mixage peut transmettre ou recevoir des signaux audio de votre ordinateur grâce à
cette connexion.
• Lors de la transmission du signal, le mix principal ou les sous-groupes 1 et 2 seront transmis à
votre ordinateur, selon la position du commutateur Record.
• Lors de la réception audio, le signal sera transmis par l’ordinateur aux canaux 23 et 24 ou sorties
mix principales, selon la position de la touche Play Back.
9. Record : Ce commutateur détermine quel signal est transmis à l'ordinateur par le port USB de la
console de mixage : Sous-groupes 1 et 2 (Sub 1/2) ou sorties mix principales (Main Mix)
10. Play Back : Ce commutateur détermine par quelle entrée sera transmis le signal de l'ordinateur au
port USB de la console de mixage : Canaux 23 et 24 (Ch 23/24) ou sorties mix principales (Main Mix).
11. Sortie des effets : Utilisez un câble TRS 6,35 mm (¼ po) standard afin de brancher cette sortie à un
système de sonorisation. Le signal du processeur d’effets de la console sera transmis par cette sortie.
12. Dérivation des effets : Cette entrée permet de brancher une commande au pied standard de type à
bascule de 6,35 mm (vendue séparément), afin de contourner le processeur d’effets intégré de la
console de mixage.
13. Entrées auxiliaires stéréo : Vous pouvez brancher les sorties d’un appareil externe à ces entrées à
l’aide de câbles mono 6,35 mm (¼ po). Si votre source est mono, branchez-la dans l’entrée gauche
afin qu’elle soit entendue des deux côtés.
8
9
10
12 13 13 13 13
23
6
575
5
.
Page 24

Guida per l'uso (Italiano)
Introduzione
Contenuti della confezione
Live 2404
Cavo di alimentazione
Guida per l'uso
Istruzioni di sicurezza e garanzia
Assistenza
Per le ultime informazioni in merito a questo prodotto (requisiti di sistema, informazioni sulla
compatibilità, ecc.) e per effettuarne la registrazione, recarsi alla pagina
altoprofessional.com/live2404.
Per ulteriore assistenza sul prodotto, recarsi alla pagina altoprofessional.com/support.
Guida rapida / Schema dei collegamenti
Microfoni
Monitor booth/cue
Monitor da
palcoscenico
Vista
pannello
superior
Processore effetti
Vista
pannello
posteriore
esterno
Alimentazione
Computer
24
Cuffie
Altoparlanti
Gli elementi che non sono elencati
nei Contenuti della confezione
non sono inclusi.
Page 25

Caratteristiche
Pannello superiore
Nota bene: i canali hanno
essenzialmente gli stessi comandi con
alcune varianti minori tra i canali 1-8, 916, 17-20 e 21-24. I cinque diversi tipi di
canale sono illustrati qui.
1. Ingresso mic: collegare un
microfono o un dispositivo a livello
di linea a questi ingressi
servendosi di un cavo XLR.
2. Ingresso di linea: collegare
dispositivi a livello di linea a questi
ingressi servendosi di cavi da 1/4”.
3. Insert: servirsi di un cavo standard
TRS da 1/4" per collegare un
processore esterno (quale un
compressore, limitatore, unità di
EQ esterna, ecc.) a questo jack. Il
segnale sarà preso dopo il
controllo di guadagno del canale e
inviato prima dei comandi EQ del
canale. La punta del collegamento
TRS è il send, l'anello è il return.
4. Gain (guadagno): regola il livello
audio del canale (guadagno prefader e pre EQ). Configurarlo in
modo che il LED segnale si
accenda.
5. LED di picco: il LED lampeggia se
il segnale salta. Se ciò dovesse
accadere, diminuire l’impostazione
della manopola Gain (guadagno).
6. Compressore: regola la quantità
di compressione sul canale,
applicata dal compressore
incorporato del mixer. Quando il
compressore è attivato, il LED di
fianco alla manopola si accende.
7. Filtro passa basso: quando
questo pulsante è premuto, l'audio
di quel canale sarà inviato tramite
un filtro a bassa frequenza da 75
Hz con un picco di 18 dB per
ottava. Ciò è utile per ridurre il ronzio e altri rumori dovuti alla bassa frequenza quando si
utilizzano i microfoni.
8. Hi EQ: regola le frequenze alte (treble) del canale.
9. Mid EQ: regola le frequenze medie del canale.
19
20
4
6
8
9
10
13
14
14
16
17
18
21
1
2
3
15
22
22
22
23
1
2
3
5
4
7
8
9
10
13
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
22
21
22
22
23
1
2
2
5
4
7
8
11
12
13 13
14
14
16
17
18
19
20
21
5
7
15
19
20
22
22
22
23
4
8
11
12
14
14
16
17
18
21
2
2
5
15
19
20
22
22
22
23
25
Page 26

10. Mid Freq (freq. medie): regola la banda delle frequenze medie (100 Hz – 8 kHz) di
competenza della manopola Mid EQ.
11. Hi-Mid EQ: regola la gamma di frequenze medio-alte (3 KHz) del canale.
12. Low-Mid EQ: regola la gamma di frequenze medio-basse (500 Hz) del canale.
13. Low EQ: regola le frequenze basse (bass) del canale.
14. Manopole Aux 1/2: regolano il livello del segnale inviato da quel segnale alla bus Aux
corrispondente. Servirsi del tasto Aux Post/Pre per stabilire se inviare il livello pre o post
fader.
15. Aux Post/Pre: quando sollevate, le manopole Aux 1/2 controllano il livello post-fader del
segnale inviato da quel canale alle bus Aux corrispondente. Se premute, il segnale è prefader.
16. Manopola Aux 3: regola il livello post fader del segnale inviato da quel canale alla bus
Aux 3.
17. Manopola Aux 4/DFX: regola il livello post-fader del segnale inviato al processore di
effetti del mixer, il cui livello è controllato dal fader DFX Return (DFX Rtn). Se il
processore di effetti esterno è collegato a Aux Send 4, il segnale sarà inviato lì anziché al
processore di effetti del mixer.
18. Pan / Balance di canale: se sulla manopola compare "Pan", regola la posizione (mono)
del canale nel campo stereo. Se compare "Bal", regola l'equilibrio tra i canali sinistro e
destro di quel segnale stereo.
19. Mute di canale: premere questo tasto per silenziare o riattivare il canale. Quando il
canale è silenziato, il LED di fianco al pulsante si accende.
20. Channel Solo (assolo di canale): premere questo tasto per attivare o disattivare l'assolo
del canale. Il LED di fianco al pulsante e il LED Solo Active si accende quando il canale è
in assolo. Servirsene per visualizzare il relativo livello nei Misuratori LED e per avere
un'anteprima del suo audio nel mix sala di controllo.
21. Fader canale: regola il livello audio sul canale.
22. Tasti uscita: premere qualsiasi combinazione di questi tasti per inviare il segnale postfader alle uscite corrispondenti: Sub 1-2 (sottogruppi 1 e 2), Sub 3-4 (sottogruppi 3 e 4),
e/o Main L/R (uscite Main).
23. LED segnale (Sig): indica che il segnale audio in ingresso del canale è compreso in una
gamma ottimale.
26
Page 27

24. Uscite Control Room
(Ctrl Out): servirsi di
cavi standard TRS da
1/4" per collegare
queste uscite ai monitor
della sala di controllo
(booth) o all'impianto di amplificazione.
25. Uscite sottogruppi: servirsi di cavi
standard TRS da 1/4" per collegare
queste uscite al sistema di amplificazione
e controllarne i livelli con i fader
sottogruppo. Si possono utilizzare
queste uscite per l'elaborazione di gruppo
o per inviare determinati canali a una
destinazione diversa dal mix principale
(Main).
26. Ingressi 2-Track (2 Track In): collegare
questi ingressi alle uscite di una fonte
audio esterna servendosi di un cavo RCA
stereo standard (venduto separatamente).
Servirsi del tasto 2 Track In Source per
inviare questo segnale alle uscite Main
Mix o alle uscite Control Room (Ctrl
Out).
27. Uscite 2-Track (2 Track Out): collegare
queste uscite agli ingressi di un
dispositivo di registrazione esterno
servendosi di un cavo RCA stereo
standard (venduto separatamente).
28. Aux Send: servirsi di cavi TRS da 1/4"
per collegare queste uscite agli ingressi di
un amplificatore esterno o di un monitor
attivo. Servirsi delle manopole Aux Send
su ciascun canale per controllare il livello
di segnale inviato a queste uscite. Ciò è
utile per creare un mix monitor
personalizzato per musicisti sul palco.
29. Manopole Aux Send: servirsi di queste
manopole per controllare il livello
complessivo del segnale inviato ad Aux
Send. (Servirsi delle manopole Aux 1-4
su ciascun canale per controllare il
segnale inviato qui da ciascun canale.)
30. Assolo Aux Send: premere questi tasti
per effettuare l'assolo di quel canale nelle
uscite cuffie.
31. Manopola Aux Return (Aux Rtn): controlla il livello audio inviato agli ingressi Aux Return
(Aux Rtn). La prima e la seconda manopola controllano i livelli Aux Return inviati al mix
principale (Main).
26 27
59
2444
28
28
25 25
36
37 38
42 43
39
41
40
42
30
29
29
29
29
31 32 46
30
30
31
30
31
35
51 51 51 51
3231
33
34
34
45
45
48
47
49
53
58
50 50 50 50 52
54
55
56
57
27
Page 28

32. Da Aux return a Aux Send: servirsi di queste manopole per controllare il livello del
segnale inviato dall'Aux Return corrispondente alla bus Aux Send avente lo stesso
numero. Ciò è utile quando si utilizzano mixer a cascata (ad es. inviando gli Aux Send del
sottomixer alle Aux Return di questo mixer, consentendo al mix sala di controllo del
sottomixer di essere inviato ai sottogruppi di questo mixer e quindi al relativo mix sala di
controllo).
33. Convogliamento Aux Return 3: quando questo tasto è premuto, il segnale inviato
all'Aux Return 3 sarà convogliato al mix sala di controllo. Quando è sollevato, il segnale
viene inviato al mix principale (Main).
34. Convogliamento Aux Return 4: premere qualsiasi combinazione di questi tasti per
inviare il segnale inviato ad Aux Return 4 alle uscite corrispondenti: Sub 1/2 (sottogruppi
1 e 2), Sub 3/4 (sottogruppi 3 e 4), e/o Main Mix (uscite Main).
35. Assolo Aux Return: premere questo tasto per effettuare l'assolo delle Aux Return 1-4
nel mix sala di controllo.
36. Equalizzatore grafico: quando l'interruttore EQ On/Off è acceso (premuto), si possono
utilizzare questi comandi per regolare l'equalizzazione del mix principale.
37. EQ On/Off: attiva o disattiva l'Equalizzatore grafico.
38. Uscita Main / Uscita Monitor: quando questo tasto è sollevato, l'equalizzatore grafico
influirà sul segnale inviato alle uscite main mix. Quando questo tasto è premuto,
l'equalizzatore grafico influirà sul segnale inviato all'uscita Aux 1/2 (Mon).
39. Selettore effetti: questa manopola determina quale effetto sarà applicato dal processore
di effetti interno del mixer ai vari canali. Girare la manopola per cambiare il numero di
effetto, e premerla per selezionarlo. Il display accanto al tasto DFX Mute mostrerà il
numero di preset. Ciascun canale può inviare diversi livelli di audio al processore
regolando la manopola DFX. Si veda la sezione Effetti per una spiegazione in merito agli
effetti disponibili.
40. DFX Mute: premere questo tasto per silenziare o riattivare gli effetti.
41. LED di picco DFX: il LED lampeggia se il segnale salta. Se ciò dovesse accadere,
diminuire l’impostazione delle manopole DFX del canale sorgente. Quando il processore
di effetti è silenziato, il LED sarà acceso in maniera fissa.
42. Uscita DFX ad Aux 1/2: queste manopole controllano il livello del segnale inviato dal
processore di effetti ad Aux Sends 1 e 2.
43.
Uscita DFX a Main: questa manopola controlla il livello del segnale inviato dal
processore di effetti alle uscite Main.
44. Uscita cuffie: collegare cuffie stereo da 1/4" a queste uscite. La manopola Phones
Volume regola il volume.
45. Fonte sala di controllo: quando viene premuta qualsiasi combinazione di questi tasti, i
segnali provenienti da queste fonti si sentiranno nel mix sala di controllo: Main Mix, Sub
1/2 (sottogruppi 1 e 2), e/o Sub 3/4 (sottogruppi 3 e 4).
Nota bene: se viene premuto qualsiasi tasto Solo, l'audio riprodotto in assolo prenderà il
posto del segnale udito nel mix sala di controllo, indipendentemente dalle posizioni di
questi tasti.
46. Volume cuffie: regola il volume dell’uscita cuffie (phones).
47. Volume sala di controllo: regola il volume delle uscite sala di controllo (Ctrl Out).
48. 2 Track In Source: premere il tasto 2Tk In per includere il segnale 2 Track In nel mix
sala di controllo. Premere il tasto 2Tk to Main per includere il segnale 2 Track In nel mix
principale (Main).
49. 2 Track Level: regola il livello del segnale 2 Track In.
50. Fader sottogruppo: regola il livello del sottogruppo corrispondente.
28
Page 29

A
A
51. Assegnazioni sottogruppo: premere qualsiasi combinazione di tasti per assegnare i loro
corrispondenti sottogruppi a tale canale (sinistro o destro) del mix principale (Main).
52. Main Fader: regola il livello delle uscite Main Mix.
53. Misuratori LED: mostrano il livello audio delle uscite Main Mix o delle uscite Control
Room (Ctrl Out), a seconda della posizione dei tasti Control Room Source. Il LED Clip
si può accendere di tanto in tanto, ma se ciò avviene troppo spesso, ridurre il volume del
mix e/o di singoli canali.
54. LED di alimentazione: si illumina quando il mixer è acceso.
55. LED di alimentazione phantom: si illumina quando l'interruttore alimentazione
Phantom è acceso.
56. Level Set: si illumina quando i misuratori a LED mostrano il livello di audio pre-fader di
qualsiasi canale dall'assolo attivo piuttosto che quelli del mix principale (Main) o del mix
sala di controllo. Il tasto Solo Mode (modalità assolo) deve essere in posizione sollevata
(PFL) (modifiche ai livelli dei fader non influiranno sui misuratori a LED e sul livello udito).
57. Solo Active (assolo attivo): si illumina quando i misuratori a LED mostrano il livello di
audio after-level di qualsiasi canale dall'assolo attivo piuttosto che quelli del mix
principale (Main) o del mix sala di controllo. Il tasto Solo Mode (modalità assolo) deve
essere in posizione premuta (AFL) (modifiche ai livelli dei fader non influiranno sui
misuratori a LED e sul livello udito).
58. Modalità Solo (assolo): quando sollevato, l'audio di un canale il cui tasto Solo è premuto
si sentirà pre-fader (PFL). Quando premuto, l'audio si sentirà post-fader (after-fader o
AFL).
59. Connettore di alimentazione USB: servirsi di questa porta USB per collegare e
alimentare (o caricare) un dispositivo che richiede alimentazione da un bus USB a 5V.
Effetti
Per applicare gli effetti, girare la manopola Effects Preset e premerla per selezionare uno dei
preset disponibili. Per inviare il segnale di un canale al processore di effetti, alzare la
manopola DFX (Aux 4) di quel canale.
Ciascun effetto ha 10 varianti. Selezionarne una adatta all'ambiente e alle proprie preferenze.
Numeri Effetto Descrizione
00-09 Delay Riproduce il segnale dopo un breve periodo di tempo.
10-19 Delay+Verb Effetto delay con riverbero room
20-29 Tremolo
30-39 Plate Simula il riverbero di un piatto limpido.
40-49 Chorus Simula il suono intero, complesso e acquoso di numerosi strumenti
50-59 Voce Riverbero, che simula una sala con un piccolo tempo di delay.
60-69 Rotary Simula il classico effetto Doppler del corno rotante all'interno di un
70-79 Small Room Riverbero, che simula uno studio limpido.
80-89 Flange+Verb
90-99 Large Hall Riverbero, che simula un grande spazio acustico.
29
umenta e diminuisce rapidamente il volume del segnale con
cadenza regolare.
che suonano la stessa cosa.
altoparlante di un organo.
pplica un riverbero alla sala, oltre a un classico effetto di flanging
stereo.
Page 30

Pannello posteriore
11
1
234
1. Ingresso di alimentazione: servirsi del cavo di alimentazione in dotazione per collegare il
mixer ad una presa di alimentazione. Ad alimentazione spenta, collegare il cavo di
alimentazione elettrica innanzitutto nel mixer, quindi ad una presa elettrica.
2. Coperchio dei fusibili: se il fusibile è rotto, servirsi di un cacciavite o di un altro attrezzo per
sollevare questa linguetta e sostituire il fusibile con un fusibile dallo stesso valore di tensione
nominale (stampato subito sopra l'ingresso di alimentazione Power In). L'utilizzo di un fusibile
dalla tensione nominale errata può danneggiare l'apparecchio e/o il fusibile.
3. Interruttore di alimentazione: accende e spegne il mixer. Accendere il mixer solo dopo aver
collegato tutti i dispositivi di ingresso, ma prima di accendere gli amplificatori. Spegnere gli
amplificatori prima di spegnere il mixer.
4. Alimentazione Phantom: attiva/disattiva l'alimentazione phantom. Quando attivata,
l’alimentazione phantom fornisce +48V a entrambi gli ingressi mic XLR. Va notato che la
maggior parte dei microfoni dinamici non richiede alimentazione phantom, mentre la maggior
parte dei microfoni a condensatore sì. Consultare la documentazione del microfono per
scoprire se necessita di alimentazione phantom o meno.
5. Uscite Main Mix: servirsi di cavi XLR o TRS da 1/4" standard per collegare una coppia di
queste uscite agli altoparlanti o all'impianto di amplificazione. Servirsi del Fader Main per
controllare il livello di queste uscite.
6. Pad Main Mix: quando questo tasto è premuto, il segnale inviato alle uscite Main Mix è ridotto
di 10 dB. Quando è sollevato, il segnale è aumentato di 4 dB. Impostare questo interruttore a
seconda del livello operativo nominale dell'apparecchio; un'attrezzatura di livello professionale
funzionano a +4 dBu nominali mentre attrezzature di uso comune funzionano a -10 dBV
nominali.
7. Inserimento Main Mix: servirsi di un cavo a Y standard TRS da 1/4" per collegare un
processore esterno (quale un compressore, limitatore, unità di EQ esterna, ecc.) a questo jack.
Il segnale sarà preso dopo l'Equalizzatore Grafico e inviato prima del Fader Main. La punta
del collegamento TRS è il send, l'anello è il return.
8. Porta USB: servirsi di un cavo USB standard per collegare questa porta USB al computer. Il
mixer può inviare o ricevere audio da e verso il computer tramite questo collegamento.
• Al momento di inviare audio, il mix principale (Main) o i Sottogruppi 1 e 2 saranno inviati
dal mixer al computer, a seconda della posizione dell'interruttore Record.
• Al momento di ricevere audio, questo sarà inviato dal computer ai canali 23/24 o al mix
principale (Main), a seconda della posizione dell'interruttore Play Back.
9. Record (registra): questo interruttore determina quale audio viene inviato al computer dalla
porta USB del mixer: Sottogruppi 1 e 2 (Sub 1/2) o il Main Mix.
10. Play Back (riproduzione): questo interruttore determina dove verrà convogliato l'audio inviato
dal computer (alla porta USB del mixer) quando torna al mixer: canali 23 e 24 (Ch 23/24) o il
Main Mix.
11. Uscita DFX: servirsi di un cavo TRS standard da 1/4" per collegare questa uscita a un sistema
di amplificazione. Il segnale dal processore di effetti del mixer sarà inviato a questa uscita.
12. Bypass: collegare un interruttore a pedale standard TS da 1/4" opzionale (venduto
separatamente) a questo ingresso. Si può utilizzare l'interruttore a pedali per attivare o
disattivare il processore di effetti del mixer.
13. Ritorno Aux Stereo: è possibile collegare le uscite di un dispositivo esterno a questi ingressi
servendosi di cavi mono da 1/4". Se la fonte è mono, collegarla al jack sinistro, e si sentirà su
entrambi i lati, sinistro e destro.
8
9
10
12 13 13 13 13
30
6
575
5
Page 31

Benutzerhandbuch (Deutsch)
Einführung
Lieferumfang
Live 2404
Stromkabel
Benutzerhandbuch
Sicherheitshinweise und Garantieinformationen
Kundendienst
Für die neuesten Informationen zu diesem Produkt (Systemanforderungen, Informationen zur
Kompatibilität etc.) und zur Produktregistrierung besuchen Sie
altoprofessional.com/live2404.
Für weitere Unterstützung besuchen Sie altoprofessional.com/support.
Schnellstart / Anschlussdiagramm
Mikrofone
Booth-/Cue-Monitore
Bühnenmonitore
Ansicht
Oberseite
Kopfhörer
Externer
Effektprozessor
Ansicht
Rückseite
Computer
Stromversorgung
31
Heimlautsprecher
Teile, die nicht im Lieferumfang
angegeben sind, sind separat erhältlich.
Page 32
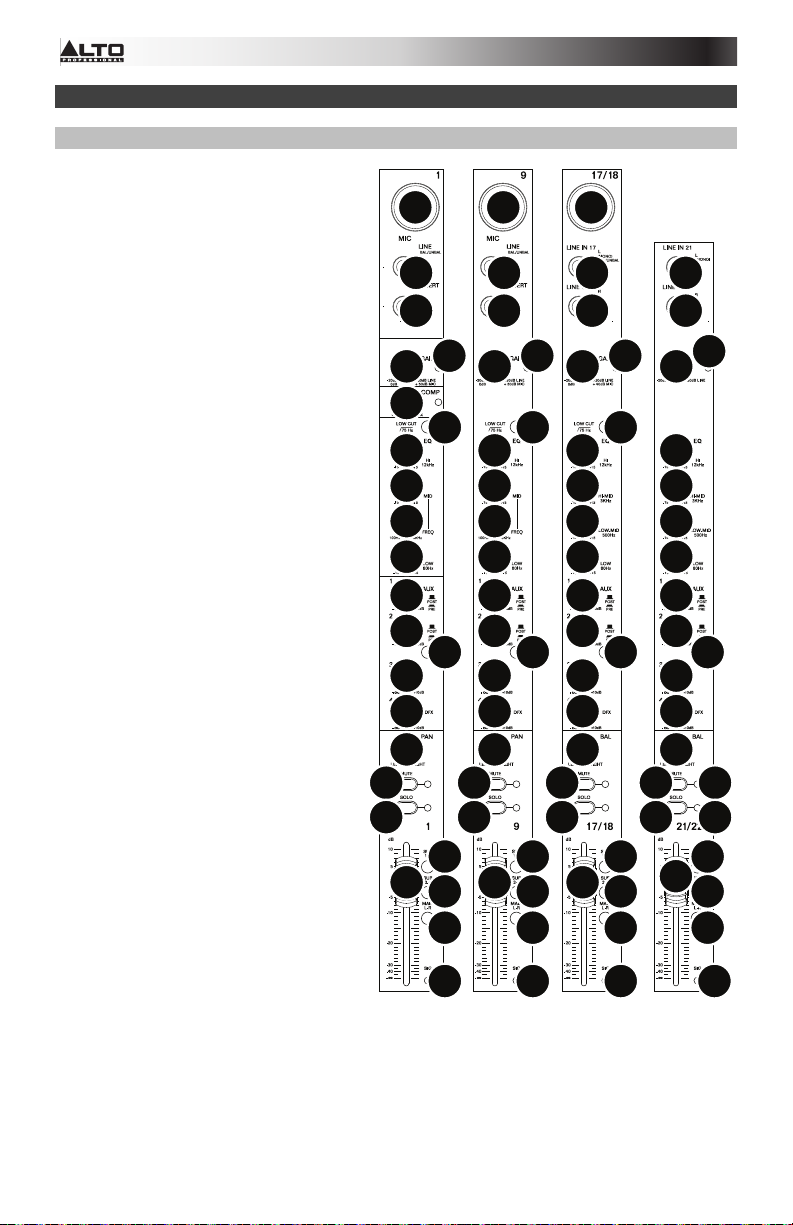
Funktionen
Oberseite
Hinweis: Die Kanäle haben im
Wesentlichen die gleichen Regler mit
einigen geringfügigen Abweichungen
zwischen den Kanälen 1-8, 9-16, 17-20
und 21-24. Die fünf verschiedenen
Kanaltypen werden hier gezeigt.
1. Mic-Eingang: Schließen Sie ein
Mikrofon oder ein Line-Gerät mit
einem XLR-Kabel an diese
Eingänge an.
2. Line-Eingang: Schließen Sie hier
Line-Geräte über ein 1/4"-Kabel an.
3. Insert: Verwenden Sie ein
handelsübliches 1/4" TRS-Kabel,
um diese Buchse an externe
Prozessoren anzuschließen (wie
z.B. Kompressoren, Limiter,
externe EQs etc.) Es wird das
Signal nach dem Gain des
Kanalreglers und vor den EQReglern des Kanals ausgegeben.
Die Spitze des TRS-Anschlusses ist
mit "Send" belegt, der Ring mit
"Return".
4. Gain: Regelt die Lautstärke des
Kanals (Pre-Fader und Pre-EQGain). Stellen Sie diese so ein, dass
die Signal-LED leuchtet.
5. Peak-LED: Sobald das Signal
übersteuert, blinkt die LED. Wenn
dies geschieht, verringern Sie den
Wert des Gain-Reglers.
6. Kompressor: Regelt die Stärke der
Kompression am Kanal, die vom im
Mischpult eingebauten Kompressor
angewendet wird. Die LED neben
dem Drehregler leuchtet auf, wenn
der Kompressor eingeschaltet ist.
7. Low Cut Filter: Wenn diese Taste
gedrückt ist, wird das Audiosignal
dieses Kanals durch einen 75 HzNiederfrequenzfilter mit einer Flanke von 18 dB pro Oktave gesendet. Dies dient der
Reduzierung von tieffrequenten Geräuschen bei der Verwendung von Mikrofonen.
8. Hi-EQ: Passt die hohen Frequenzen (Höhen) des Kanals an.
9. Mid-EQ: Passt die mittleren Frequenzen des Kanals an.
10. Mid Freq: Passt das mittlere Frequenzband (100 Hz - 8 kHz) an, das vom Mid EQ-Regler
beeinflusst wird.
19
20
4
6
8
9
10
13
14
14
16
17
18
21
1
2
3
15
22
22
22
23
1
2
3
5
4
7
8
9
10
13
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
22
21
22
22
23
1
2
2
5
4
7
8
11
12
13 13
14
14
16
17
18
19
20
21
7
15
22
22
22
23
2
2
5
5
4
8
11
12
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
19
20
22
21
22
22
23
32
Page 33

11. Hi-Mid EQ: Stellt die hohen, mittleren Frequenzen (3 kHz) des Kanals ein.
12. Low-Mid-EQ: Stellt die tieferen, mittleren Frequenzen (500 Hz) des Kanals ein.
13. Low EQ: Passt die tieferen Frequenzen (Bass) des Kanals an.
14. Aux 1/2-Regler: Passt den Pegel des von diesem Kanal gesendeten Signals an den
entsprechenden Aux-Bus an. Verwenden Sie die Aux Post/Pre-Taste, um festzulegen,
ob der Pegel Pre-Fader oder Post-Fader gesendet wird.
15. Aux Post/Pre: In der angehobenen Position steuern die Aux 1/2-Regler die Post-FaderPegel des von diesem Kanal an den entsprechenden Aux-Bus gesendeten Signals. In der
heruntergedrückten Position ist das Signal Pre-Fader.
16. Aux 3-Regler: Stellt die Post-Fader-Pegel des von diesem Kanal an den Aux 3 Bus
gesendeten Signals ein.
17. Aux 4 / DFX-Regler: Regelt den Post-Fader-Pegel des Signals, das zum Effektprozessor
des Mixers gesendet wird. Der Pegel des Effektprozessors wird mit dem DFX Return
Fader (DFX Rtn) geregelt. Wenn ein externer Effektprozessor mit Aux Send 4 verbunden
ist, dann wird das Signal dorthin gesendet - und nicht an den Effektprozessor des Mixers.
18. Pan/Balance des Kanals: Wenn dieser Regler die Bezeichnung Pan aufweist, passt er
die (Mono-) Kanalposition im Stereo-Feld an. Wenn der Regler die Bezeichnung Bal
aufweist, passt er die Balance zwischen linkem und rechtem Kanal des Stereosignals an.
19. Kanal Stummschalten: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um den Kanal stumm zu schalten. Die
LED neben der Taste leuchtet auf, wenn der Kanal stummgeschaltet ist.
20. Kanal-Solo: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um den Kanal solo/nicht solo zu schalten. Die LED
neben der Taste und die Solo-Aktiv-LED leuchten auf, wenn der Kanal auf Solo
geschaltet ist. Verwenden Sie dies, um seinen Pegel über die LED-Anzeige anzuzeigen
und sein Audiosignal allein im Control Room Mix abzuhören.
21. Kanal-Fader: Passt die Audiopegel am Kanal an.
22. Ausgangstasten: Drücken Sie eine beliebige Kombination dieser Tasten, um das PostFader-Signal des Kanals an die entsprechenden Ausgänge zu senden: Sub 1-2
(Untergruppen 1 und 2), Sub 3-4 (Untergruppen 3 und 4) und/oder Main L/R
(Hauptausgänge).
23. Signal-LED (Sig): Zeigt an, dass das eingehende Audiosignal dieses Kanals im optimalen
Bereich liegt.
33
Page 34

24. Control Room-Ausgänge
(Ctrl Out): Verwenden Sie
handelsübliche 1/4" TRSKabel, um diese Ausgänge
an Ihre Control RoomMonitore (Booth) oder Ihr
Verstärkersystem anzuschließen.
25. Untergruppenausgänge: Verwenden Sie
handelsübliche 1/4" TRS-Kabel, um diese
Ausgänge mit Ihrem MonitoringVerstärkersystem zu verbinden und ihre
Pegel mit den Untergruppen-Fadern zu
steuern. Sie können diese Ausgänge zur
Gruppenverarbeitung oder zum Senden
von bestimmten Kanälen an andere Ziele
als den Main Mix verwenden.
26. 2-Track Eingänge (2 Track In): Sie
können diese Eingänge mit den Ausgängen
einer externen Tonquelle verbinden, indem
Sie handelsübliche Stereo-Cinch-Kabel
(separat erhältlich) verwenden. Verwenden
Sie die Taste 2 Track In-Quelle, um dieses
Signal entweder an die Main Mix-
Ausgänge oder die Control RoomAusgänge (Ctrl Out) zu senden.
27. 2-Track Ausgänge (2 Track Out): Sie
können diese Ausgänge mit den Eingängen
eines externen Aufnahmegeräts verbinden,
indem Sie ein handelsübliches StereoCinch-Kabel (separat erhältlich) verwenden.
28. Aux-Send: Verwenden Sie 1/4"-TRSKabel, um diese Ausgänge an die Eingänge
eines externen Verstärkers oder aktiven
Monitors anzuschließen. Verwenden Sie die
Aux Send-Regler auf jedem Kanal, um den
Pegel des Signals zu steuern, der an diese
Ausgänge gesendet wurde. Dies ist
nützlich für das Erstellen eines
benutzerdefinierten Monitor-Mix für die
Musiker auf der Bühne.
29. Aus Sends-Regler: Mit diesen Reglern
können Sie den Gesamtpegel des Signals
steuern, das an die Aux Sends geschickt
wurde. (Mit den Aux 1-4 Reglern auf
jedem Kanal können Sie das Signal
steuern, das von jedem Kanal hierher gesendet wird.)
30. Aux Sends Solo: Drücken Sie diese Tasten, um den Kanal in den Kopfhörerausgängen
solo zu schalten.
31. Aux Return-Regler (Aux Rtn): Regelt den Pegel, der an die Aux Return (Aux Rtn)Eingänge gesendet wird. Die ersten und zweiten Drehregler steuern die Aux ReturnPegel, die zum Main Mix geschickt werden.
26 27
59
2444
28
28
25 25
36
37 38
42 43
39
41
40
42
30
29
29
29
29
31 32 46
30
30
31
30
31
35
51 51 51 51
3231
33
34
34
45
45
48
47
49
53
58
50 50 50 50 52
54
55
56
57
34
Page 35

32. Aux Returns an Aux Sends: Benutzen Sie diese Regler, um den Pegel des Signals
einzustellen, das vom entsprechenden Aux Return an den Aux Send-Bus mit der gleichen
Nummer gesendet wird. Dies ist hilfreich, wenn Sie kaskadierende Mixer verwenden
(wenn Sie z. B. die Aux Sends des Submixers an die Aux Returns dieses Mixers senden,
damit der Control Room Mix des Submixers an die Untergruppen dieses Mixers und dann
an seinen Control Room Mix geschickt werden kann).
33. Aux Return 3 Routing: Wenn diese Taste heruntergedrückt ist, wird das an Aux Return 3
gesendete Signal zum Control Room Mix geroutet. Wenn diese Taste erhoben ist, wird
das Signal zum Main Mix geschickt.
34. Aux Return 4 Routing: Drücken Sie eine beliebige Kombination dieser Tasten, um das
an Aux Return 4 gesendete Signal an die entsprechenden Ausgänge zu senden: Sub 1/2
(Untergruppen 1 und 2), Sub 3/4 (Untergruppen 3 und 4) und/oder Main Mix
(Hauptausgänge).
35. Aux Return Solo: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Aux Returns 1-4 im Control Room
Mix solo zu schalten.
36. Grafischer Equalizer: Wenn der EQ Ein/Aus-Schalter aktiviert (gedrückt) ist, können Sie
diese Steuerelemente verwenden, um den Equalizer im Main Mix einzustellen.
37. EQ Ein/Aus: Aktiviert oder deaktiviert den Grafischen Equalizer.
38. Hauptausgang/Monitorausgang: Wenn diese Taste angehoben ist, wird der grafische
Equalizer das Signal beeinflussen, das zu den Main Mix-Ausgängen gesendet wurde.
Wenn diese Taste gedrückt ist, wird der grafische Equalizer jenes Signal beeinflussen,
das zum Aux 1/2 (Mon) Ausgang gesendet wurde.
39. Effektwahlschalter: Dieser Regler bestimmt, welchen Effekt der interne Effektprozessor
des Mixers auf die verschiedenen Kanäle anwenden wird. Drehen Sie den Regler, um die
Effektnummer zu ändern und drücken Sie den Regler, um den Effekt auszuwählen. Die
Anzeige neben der Taste DFX Stummschalten wird die Preset-Nummer anzeigen. Jeder
Kanal kann unterschiedliche Anteile an den Prozessor senden, indem der entsprechende
DFX-Regler angepasst wird. Eine Beschreibung der verfügbaren Effekte finden Sie im
Abschnitt Effekte.
40. DFX Stummschalten: Drücken Sie diese Taste, um die Effekte stumm zu schalten bzw.
um die Stummschaltung aufzuheben.
41. DFX Peak-LED: Sobald das Signal übersteuert, blinkt die LED. Wenn dies passiert,
verringern Sie die Einstellung der DFX-Regler an Ihren Quellkanälen. Wenn der
Effektprozessor stumm geschaltet ist, leuchtet die LED konstant auf.
42. DFX Out an Aux 1/2: Diese Regler steuern den Pegel des Signals, das vom
Effektprozessor an Aux Sends 1 und 2 gesendet wird.
43. DFX Out an Main: Dieser Regler steuert den Pegel des Signals, das vom Effektprozessor
an die Hauptausgänge gesendet wird.
44. Kopfhörerausgang: Schließen Sie 1/4" Stereo-Kopfhörer an diese Ausgänge an. Die
Lautstärke regeln Sie über den Kopfhörer-Lautstärkeregler.
45. Control Room-Quelle: Wenn eine Kombination dieser Tasten heruntergedrückt ist,
werden die Signale aus diesen Quellen im Control Room Mix zu hören sein: Main Mix,
Sub 1/2 (Untergruppen 1 und 2) und/oder Sub 3/4 (Untergruppen 3 und 4).
Hinweis: Falls irgendeine Solo-Taste heruntergedrückt ist, wird das solo-geschaltete
Audiosignal das Signal ersetzen, das im Control Room Mix zu hören ist und zwar
unabhängig von den Positionen dieser Tasten.
46. Kopfhörerlautstärke: Regelt die Lautstärke des Kopfhörerausgangs.
47. Control Room-Lautstärke: Regelt die Lautstärke der Control Room-Ausgänge (Strg
Out).
48. 2 Track In Quelle: Drücken Sie die Taste 2Tk In herunter, um das 2 Track In-Signal zum
Control Room Mix zu addieren. Drücken Sie die Taste 2Tk to Main, um das 2 Track InSignal im Main Mix zu hören.
35
Page 36

49. 2 Track-Pegel: Stellt den Pegel des 2 Track In-Signals ein.
50. Untergruppen-Fader: Stellt den Pegel der entsprechenden Untergruppe ein.
51. Zuweisungen der Untergruppe: Drücken Sie eine beliebige Kombination dieser Tasten,
um ihre entsprechenden Untergruppen (darunter) diesem Main Mix-Kanal zuzuweisen
(Links oder Rechts).
52. Haupt-Fader: Stellt den Pegel der Main Mix-Ausgänge ein.
53. LED-Anzeigen: Zeigt den Audiopegel der Main Mix-Ausgänge oder der Control Room-
Ausgänge (Ctrl Out) an, und zwar je nach Position der Control Room-Quellentasten.
Die Clip-LED kann gelegentlich aufleuchten - wenn dies jedoch zu oft geschieht, sollten
Sie die Lautstärke des Mix und/oder der einzelnen Kanäle reduzieren.
54. Power-LED: Leuchtet, wenn der Mixer eingeschaltet ist.
55. Phantomspeisungs-LED: Leuchtet, wenn die Phantomspeisung eingeschaltet ist
56. Pegel-Set: Leuchtet, wenn die LED-Anzeige die Pre-Fader-Audiopegel aller Kanäle
zeigt, die aktiv solo geschaltet sind und nicht die Pegel des Main Mix oder des Control
Room-Mix. Die Taste Solo-Modus muss in der erhobenen Position (PFL) sein
(Änderungen an den Fader-Pegeln wirken sich nicht auf die LED-Anzeige und den
gehörten Pegel aus).
57. Solo Aktiv: Leuchtet, wenn die LED-Anzeigen den After-Fader Audiopegel aller aktiv
solo geschalteter Kanäle zeigen und nicht die Pegel des Main Mix oder des Control
Room-Mix. Die Taste Solo-Modus muss in der heruntergedrückten Position (AFL) sein
(Änderungen an den Fader-Pegeln beeinflussen die LED-Anzeige und den gehörten
Pegel).
58. Solo-Modus: Ist der Schalter in der erhobenen Position, ist das Signal eines Kanals,
dessen Solo-Taste heruntergedrückt ist, als Pre-Fader-Signal zu hören (PFL). Ist der
Schalter heruntergedrückt, wird das Signal als Post-Fader-Signal zu hören sein (AfterFader oder AFL).
59. Stromversorgung über USB: Sie können diesen USB-Port dazu verwenden, um ein
Gerät, das Strom von einem 5V USB-Bus benötigt, mit Strom zu versorgen (oder
aufzuladen).
Effekte
Um Effekte anzuwenden, drehen Sie den Regler für Effekt-Presets und drücken ihn, um
eines der verfügbaren Presets auszuwählen. Um ein Kanalsignal an den Effektprozessor zu
senden, drehen Sie den DFX-Regler (Aux 4) dieses Kanals.
Jeder Effekt verfügt über 10 Variationen. Wählen Sie eine, die der Umgebung und Ihren
Vorlieben entspricht.
Nummer Effekt Beschreibung
00-09 Delay Reproduziert das Signal nach kurzer Zeit.
10-19 Delay + Reverb Delay-Effekt mit Room-Reverb.
20-29 Tremolo Erhöht und senkt den Signalpegel rasch und gleichmäßig.
30-39 Platte Simuliert einen hellen Plate-Reverb.
40-49 Chorus Simuliert den komplexen, vollen Klang mehrerer Instrumente, die
50-59 Gesangsstimme Reverb, der einen Raum mit einer kurzen Verzögerungszeit simuliert.
60-69 Rotary Simuliert den klassischen Doppler-Effekt eines rotierenden Orgelhorns.
70-79 Kleiner Raum Reverb, der einen hellen Studioraum simuliert.
80-89 Flanger+Reverb Wendet Room-Reverb und einen klassischen Stereo-Flanger-Effekt an.
90-99 Große Halle Reverb, der einen großen akustischen Raum simuliert.
denselben Ton spielen.
36
Page 37

Rückseite
11
1
234
1. Netzeingang: Verwenden Sie das mitgelieferte Netzkabel, um den Mixer mit einer Steckdose zu
verbinden. Stellen Sie sicher, dass das Gerät ausgeschaltet ist. Verbinden Sie zuerst das Stromkabel
mit dem Mixer und stecken das Netzteil dann in eine Steckdose.
2. Sicherungsabdeckung: Wenn die Sicherung defekt ist, heben Sie diese Platte mit einem
Schraubendreher oder einem anderen Werkzeug an, um die Sicherung mit einer neuen Sicherung mit
demselben Sicherungswert zu ersetzen (Sicherungswert ist direkt oberhalb des Netzeingangs
angegeben). Die Verwendung einer Sicherung mit falschem Sicherungswert kann das Gerät und/oder
Sicherung beschädigen.
3. Netzschalter: Schaltet den Mixer an und aus. Schalten Sie den Mixer erst ein, nachdem Sie all Ihre
Eingabegeräte verbunden haben, aber bevor Sie Ihre Verstärker einschalten. Schalten Sie die
Verstärker aus, bevor Sie den Mixer ausschalten.
4. Phantomspeisung: Aktiviert/deaktiviert die Phantomspeisung. Wenn diese Funktion aktiviert ist,
versorgt die Phantomspeisung die XLR-Mikrofoneingänge mit +48 V. Bitte beachten Sie, dass die
meisten dynamischen Mikrofone keine Phantomspeisung benötigen. Die meisten
Kondensatormikrofone tun dies jedoch. Schlagen Sie im Handbuch Ihres Mikrofons nach, um
herauszufinden, ob es eine Phantomspeisung benötigt.
5. Main Mix-Ausgänge: Verwenden Sie handelsübliche XLR- oder 1/4" TRS-Kabel, um eines dieser
Ausgangspaare mit Ihren Lautsprechern oder Ihrem Verstärkersystem zu verbinden. Verwenden Sie
den Haupt-Fader, um den Pegel dieser Ausgänge zu regeln.
6. Main Mix Pad: Wenn diese Taste heruntergedrückt ist, wird das an die Main Mix-Ausgänge
gesendete Signal um 10 dB reduziert. Wenn die Taste in erhobener Position ist, wird das Signal um 4
dB erhöht. Stellen Sie diesen Schalter je nach Arbeitspegel Ihrer Anlage ein; Profi-Geräte arbeiteten
mit einem Nominalwert von +4 dBu, während Verbrauchergeräte mit einem Nominalwert von -10 dBV
arbeiten.
7. Main Mix Insert: Verwenden Sie ein handelsübliches 1/4" TRS-Y-Kabel, um diese Buchse an externe
Prozessoren anzuschließen (wie z.B. Kompressoren, Limiter, externe EQs etc.) Das Signal wird nach
dem Grafischen Equalizer verarbeitet und vor dem Haupt-Fader zurückgeleitet. Die Spitze des TRSAnschlusses ist mit "Send" belegt, der Ring mit "Return".
8. USB-Port: Verwenden Sie ein Standard-USB-Kabel, um diesen USB-Port mit Ihrem Computer zu
verbinden. Der Mixer kann über die Verbindung Audiosignale an den Computer senden bzw. vom
Computer empfangen.
• Beim Senden von Audiosignalen wird der Main Mix oder die Untergruppen 1 und 2 vom Mixer an
Ihren Computer gesendet - je nach Position des Aufnahme-Schalters.
• Beim Empfangen von Audiosignalen werden sie von Ihrem Computer auf die Kanäle 23/24 oder
den Main Mix gesendet, je nach Position des Play Back-Schalters.
9. Aufnehmen: Dieser Schalter legt fest, welche Audiosignale an den Computer vom USB-Anschluss
des Mixers gesendet werden: Untergruppen 1 und 2 (Sub 1/2) oder der Main Mix.
10. Play Back: Dieser Schalter legt fest, wo das vom Computer (an den USB-Anschluss des Mixers)
gesendete Audiosignal hingeleitet wird, wenn es an den Mixer zurückgeleitet wird: Kanäle 23/24 (Ch
23/24) oder Main Mix.
11. DFX Out: Verwenden Sie ein handelsübliches 1/4" TRS-Kabel, um diesen Ausgang mit einem
Verstärkersystem zu verbinden. Das Signal vom Effektprozessor des Mixers wird an diesen Ausgang
gesendet.
12. Bypass: Schließen Sie einen optionalen, handelsüblichen 1/4" TS-Fußschalter (separat erhältlich) an
diesen Eingang an. Sie können den Fußschalter verwenden, um den Effektprozessor des Mixers zu
aktivieren oder zu deaktivieren.
13. Stereo Aux Return: Sie können die Ausgänge eines externen Gerätes mit 1/4" Mono-Kabeln mit
diesen Eingängen verbinden. Wenn Sie über eine Mono-Tonquelle verfügen, so schließen Sie diese an
die linke Buchse an. Die Tonquelle wird dann sowohl links als auch rechts zu hören sein.
8
9
10
12 13 13 13 13
37
6
575
5
Page 38

Gebruikershandleiding (Nederlands)
Inleiding
Inhoud van de doos
Live 2404
Stroomkabel
Gebruikershandleiding
Veiligheidsvoorschriften en handleiding
Ondersteuning
Voor de laatste informatie over dit product (systeemvereisten, informatie over compatibiliteit,
enz.) en productregistratie, ga naar: altoprofessional.com/live2404.
Surf voor aanvullende productondersteuning naar altoprofessional.com/support.
Snelstartgids / Aansluitschema
Microfoons
Cabine-/cue-monitoren
Podiummonitoren
Aanzicht
bovenpaneel
effectprocessor
Aanzicht
achterpaneel
Externe
Voeding
Computer
38
Koptelefoon
Luidsprekers
Artikelen die niet vermeld zijn in
Inhoud van de doos zijn niet
meegeleverd.
Page 39
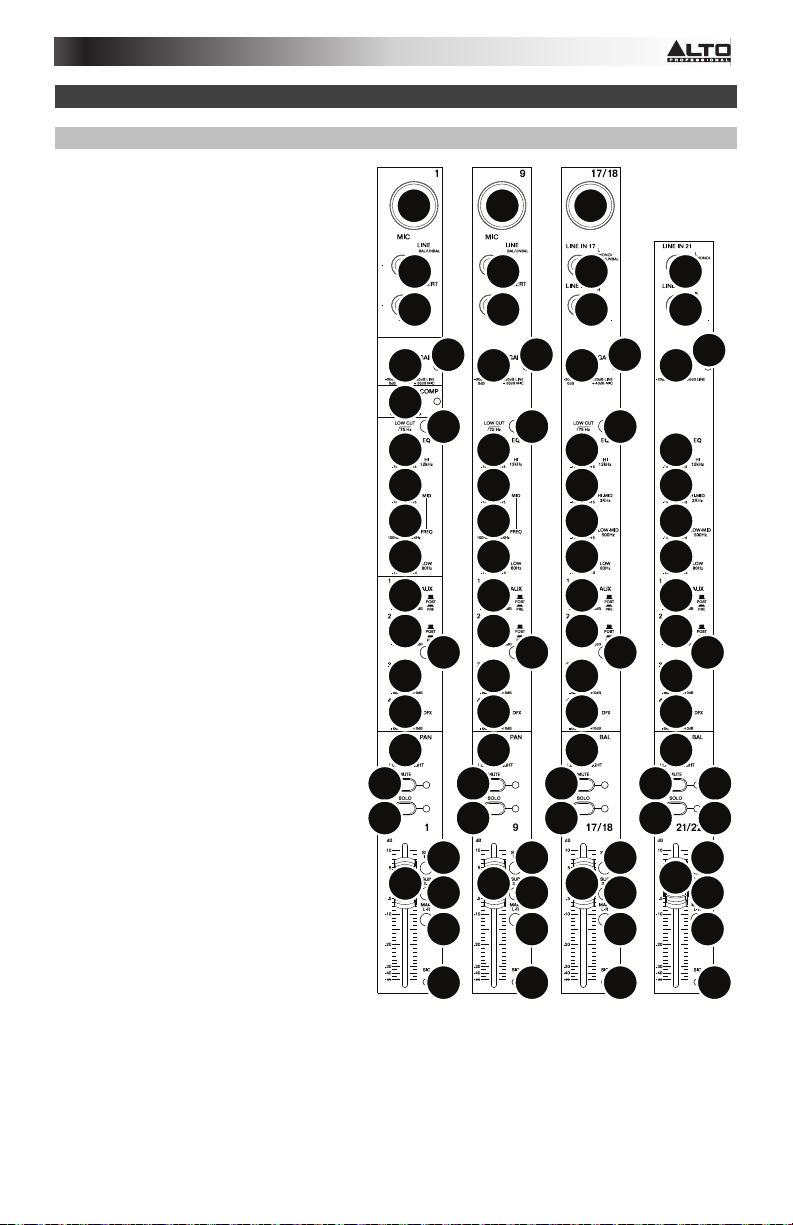
Kenmerken
Bovenpaneel
Opmerking: De kanalen hebben
grotendeels dezelfde bedieningsknoppen,
met enkele kleine verschillen tussen
kanalen 1-8, 9-16, 17-20 en 21-24. De vijf
verschillende kanaaltypes worden hier
getoond.
1. Mic-ingang: Sluit met behulp van
een XLR-kabel op deze ingangen
een microfoon of apparaat op
lijnniveau aan.
2. Lijningang: Gebruik 1/4”-kabels
om op deze ingangen apparaten
op lijnniveau aan te sluiten.
3. Insert: Gebruik een standaard 1/4"
TRS-kabel om een externe
processor op deze uitgang aan te
sluiten (zoals een compressor,
limiter, externe equalizer, enz.). Het
geluidssignaal wordt afgenomen na
de gain-regeling van het kanaal en
wordt geretourneerd voor het naar
de EQ van het kanaal gaat. De top
van de TRS-jack is het sendsignaal; de ring is het returnsignaal.
4. Gain: Regelt het geluidsniveau van
het kanaal (pre-fader en pre-EQ
gain). Regel dit bij tot de signaalLED gaat branden.
5. Piek-LED: De LED gaat knipperen
wanneer het signaal overstuurd
wordt. Als dat gebeurt, verlaag dan
de instelling van de Gain-knop.
6. Compressor: Regelt de
hoeveelheid compressie die de
ingebouwde compressor van het
mengpaneel op het kanaal toepast.
De LED naast de knop gaat
branden wanneer de compressor
aanstaat.
7. Low Cut Filter: Wanneer deze
knop wordt ingedrukt, wordt het
geluidssignaal van dat kanaal door een 75 Hz laagfrequentiefilter gestuurd met een
hellingsgraad van 18 dB per octaaf. Dit is handig voor het verminderen laagfrequent
lawaai bij het gebruik van microfoons.
8. Hi EQ: Regelt de hoge frequenties van het kanaal.
9. Mid EQ: Regelt de middenfrequenties van het kanaal.
19
20
4
6
8
9
10
13
14
14
16
17
18
21
1
2
3
15
22
22
22
23
1
2
3
5
4
7
7
8
9
10
13
14
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
22
21
22
22
23
1
2
2
5
4
8
11
12
13 13
14
14
16
17
18
19
20
21
5
7
15
19
20
22
22
22
23
4
8
11
12
14
14
16
17
18
21
2
2
5
15
19
20
22
22
22
23
39
Page 40

10. Mid Freq: Past de frequentieband (100 Hz - 8 kHz) aan die door de Mid EQ-knop wordt
beïnvloed.
11. Hi-Mid EQ: Regelt de hoge middenfrequenties (3 kHz) van het kanaal.
12. Low-Mid EQ: Regelt de lage middenfrequenties (500 Hz) van het kanaal.
13. Low EQ: Regelt de lage frequenties (bassen) van het kanaal.
14. Aux 1/2-knoppen: Regelt het volume van het signaal dat van dat kanaal naar de
overeenkomstige Aux-bus wordt gestuurd. Gebruik de knop Aux Post/Pre om in te
stellen of het niveau pre-fader of post-fader wordt verstuurd.
15. Aux Post/Pre: Wanneer niet ingedrukt, bedienen de Aux 1/2-knoppen het postfadervolume van het signaal dat van dat kanaal naar de overeenkomstige Aux-bus wordt
gestuurd. Wanneer ingedrukt, wordt het signaal aan pre-fadervolume verstuurd.
16. Aux 3-knop: Regelt het post-fadervolume van het signaal dat van dat kanaal naar de Aux
3-bus wordt gestuurd.
17. Aux 4-/DFX-knop: Regelt het volume van het signaal dat naar de effectenprocessor van
het mengpaneel wordt gestuurd. Het volume van de effectenprocessor wordt geregeld
door de DFX Return Fader (DFX Rtn). Als een externe effectenprocessor met Aux Send
4 is verbonden, dan wordt het signaal naar deze processor gestuurd in plaats van naar de
effectenprocessor van het mengpaneel.
18. Channel Pan / Balance: Als deze knop Pan is gelabeld, dan past hij de positie aan van
het (mono)kanaal in het stereoveld. Als de knop Bal is gelabeld, past hij de balans aan
tussen de twee monokanalen van dit stereosignaal.
19. Kanaal dempen: Druk op deze knop om het kanaal te dempen of terug aan te zetten.
Wanneer het kanaal is gedempt, gaat de LED naast de knop branden.
20. Kanaal in solo: Druk op deze knop om het kanaal solo/niet solo af te spelen. De LED
naast de knop en de LED Solo Actief gaan branden wanneer het kanaal solo wordt
afgespeeld. Gebruik dit om het kanaalniveau op de LED-meters weer te geven en om de
audio afzonderlijk in de controlekamermix te beluisteren.
21. Kanaalfader: Past het geluidsniveau van het kanaal aan.
22. Uitgangsknoppen: Druk eender welke combinatie in van deze knoppen om het postfadersignaal van het kanaal naar de overeenkomstige uitgangen te versturen: Sub 1-2
(subgroepen 1 en 2), Sub 3-4 (subgroepen 3 en 4), en/of Main L/R (Hoofduitgangen).
23. Signaal-LED (Sig): Geeft aan dat het binnenkomende audiosignaal van het kanaal zich
binnen een optimaal bereik bevindt.
40
Page 41

24. Control Room-uitgangen
(Ctrl Out): Gebruik
standaard 1/4"-kabels om
deze uitgangen aan te
sluiten op de monitors of
aan uw versterkersysteem
in uw controlekamer (cabine).
25. Uitgangen van de subgroepen: Gebruik
standaard 1/4"-kabels om deze uitgangen
aan te sluiten op het versterkersysteem in
uw controlekamer en regel hun volume met
de Subgroepfaders. U kunt deze
uitgangen gebruiken voor
groepbewerkingen of om bepaalde kanalen
naar een andere bestemming dan de
Hoofdmix te sturen.
26. 2-Track-ingangen (2 Track In): U kunt
deze ingangen verbinden met de uitgangen
van een externe geluidsbron met behulp
van een standaard stereo RCA-kabel
(afzonderlijk verkrijgbaar). Gebruik de 2
Track In Source-knop om dit signaal ofwel
naar de Main Mix-uitgangen ofwel naar de
Control Room-uitgangen (Ctrl Out) te
sturen.
27. 2-Track-uitgangen (2 Track Out): Sluit
deze uitgangen aan op de ingangen van
een extern opnameapparaat met behulp
van een standaard stereo RCA-kabel
(afzonderlijk verkrijgbaar).
28. Aux Send: Gebruik 1/4" TRS-kabels om
deze uitgangen aan te sluiten op de
ingangen van een externe versterker of
actieve monitor. Gebruik Aux Send-
knoppen op elk kanaal om het volume te
regelen van het signaal dat naar deze
uitgangen wordt verstuurd. Dit is handig
om voor muzikanten op het podium een
aangepaste monitormix te maken.
29. Aux Send-knoppen: Gebruik deze
knoppen om het algemene volume te
regelen van het signaal dat naar de Aux
Send-uitgangen wordt gestuurd. (Gebruik
de Aux 1-4-knoppen op elk kanaal om het
signaal te regelen dat van elk kanaal hier
naartoe wordt gestuurd.)
30. Aux Sends Solo: Druk deze knoppen in om dat kanaal solo af te spelen in de
Koptelefoonuitgangen.
31. Aux Return-knop (Aux Rtn): Regelt het geluidsniveau dat verstuurd wordt naar de Aux
Return (Aux Rtn)-ingangen. De eerste en tweede knoppen regelen de Aux Returnvolumes die naar de Hoofdmix worden gestuurd.
26 27
59
2444
28
28
25 25
36
37 38
42 43
39
41
40
42
30
29
29
29
29
31 32 46
30
30
31
30
31
35
51 51 51 51
3231
33
34
34
45
45
48
47
49
53
58
50 50 50 50 52
54
55
56
57
41
Page 42

32. Aux Returns naar Aux Sends: Gebruik deze knoppen om het niveau te regelen van het
signaal dat wordt gestuurd van de overeenkomstige Aux Return naar de Aux Send-bus
met hetzelfde nummer. Dit is behulpzaam bij het gebruik van mengpanelen in cascadeopstelling (bv. bij het versturen van Aux Sends van de submixer naar de Aux Returns van
dit mengpaneel, waardoor de controlekamermix van de submixer naar de subgroepen
van deze mixer kunnen worden gestuurd en vervolgens naar de controlekamermix).
33. Routering van Aux Return 3: Wanneer deze knop wordt ingedrukt, zal het signaal dat
naar Aux Return 3 wordt gestuurd naar de controlekamermix worden gerouteerd.
Wanneer deze knop niet is ingedrukt, wordt het signaal naar de Hoofdmix gestuurd.
34. Routering van Aux Return 4: Druk een willekeurige combinatie van deze knoppen in om
het naar Aux Return 4 verstuurde signaal naar de overeenkomstige uitgangen te sturen:
Sub 1/2 (subgroepen 1 en 2), Sub 3/4 (subgroepen 3 en 4), en/of de Hoofdmix (Mainuitgangen).
35. Aux Return Solo: Druk deze knop in om de Aux Returns 1-4 solo af te spelen in de
controlekamermix.
36. Grafische equalizer: Wanneer de schakelaar EQ Aan/Uit is ingeschakeld (ingeduwd),
kunt u deze knoppen gebruiken om de toon van de hoofdmix te regelen.
37. EQ Aan/Uit: Schakelt de Grafische equalizer aan of uit.
38. Main Out / Monitor Out: Wanneer deze knop niet is ingedrukt, beïnvloedt de Grafische
equalizer het signaal dat naar de uitgangen van de Hoofdmix wordt gestuurd. Wanneer
deze knop is ingedrukt, beïnvloedt de Grafische equalizer het signaal dat naar de Aux 1/2
(Mon)-uitgang wordt gestuurd.
39. Effectkeuzeschakelaar: Deze knop selecteert het effect dat de interne
effectenprocessor van het mengpaneel op de verschillende kanalen toepast. Draai aan de
knop het nummer van het effect te veranderen en druk op de knop om het te selecteren.
Het scherm naast de DFX Mute-toets toont het programmanummer. Elk kanaal kan
verschillende geluidsniveaus naar de processor sturen, door de DFX-knop bij te regelen.
Zie de sectie Effecten voor uitleg over de beschikbare effecten.
40. DFX Mute: Druk op deze knop om de effecten te dempen of terug aan te zetten.
41. Piek-LED van DFX: De LED gaat knipperen wanneer het signaal overstuurd wordt. Als
dat gebeurt, verlaag dan de instelling van de DFX-knoppen van uw bronkanaal. Wanneer
de effectenprocessor gedempt is, blijft de LED branden.
42. DFX Out naar Aux 1/2: Deze knoppen regelen het volume van het signaal dat van de
effectenprocessor naar Aux Send 1 en 2 wordt gestuurd.
43. DFX Out naar Main: Deze knop regelt het volume van het signaal dat van de
effectenprocessor naar de Main-uitgangen wordt gestuurd.
44. Koptelefoonuitgang: Sluit op deze uitgangen een 1/4" stereo koptelefoon aan. De
Phones Volume-knop regelt het volume.
45. Controlekamerbron: Wanneer een willekeurige combinatie van deze knoppen is
ingedrukt, zullen de signalen van deze bronnen hoorbaar zijn in de controlekamermix:
Main Mix, Sub 1/2 (subtgroepen 1 en 2), en/of Sub 3/4 (subgroepen 3 en 4).
Opmerking: Als een Solo-knop is ingedrukt, dan zal het gesoleerde audiosignaal het
signaal vervangen dat wordt afgespeeld in de controlekamermix, ongeacht de stand van
deze knoppen.
46. Koptelefoonvolume: Past het volume aan van de Koptelefoonuitgang.
47. Controlekamervolume: Regelt het volume van de controlekameruitgangen (Ctrl Out).
48. 2 Track In Source: Druk de knop 2Tk In in om het 2 Track In-signaal aan de
controlekamermix toe te voegen. Druk de knop 2Tk naar Main in om het 2 Track Insignaal toe te voegen aan de Hoofdmix.
49. 2 Track-volume: Regelt het volume van het 2 Track In-signaal.
42
Page 43

V
50. Subgroepfader: Regelt het volume van de overeenkomstige subgroep.
51. Subgroeptoewijzingen: Druk een willekeurige combinatie van deze knoppen in om hun
overeenkomstige Subgroepen (eronder) aan dat kanaal (Links of Rechts) van de
Hoofdmix toe te wijzen.
52. Main-fader: Past het geluidsniveau aan van de Main Mix-uitgangen.
53. LED-meters: Geeft het geluidsniveau weer van de Main Mix-uitgangen of de Control
Room-uitgangen (Ctrl Out), naargelang de stand van de Control Room Sourceknoppen. De Clip-LED mag af en toe branden. Als dit echter te vaak gebeurt, verlaagt u
het beste het volume van de mix en/of de afzonderlijke kanalen.
54. Stroom-LED: Gaat branden wanneer het mengpaneel aanstaat.
55. Fantoomvoeding-LED: Brandt wanneer de fantoomvoedingschakelaar is
ingeschakeld.
56. Ingesteld niveau: Gaat branden wanneer de LED-meters het pre-fader audioniveau
weergeven van een actief gesoleerd kanaal en niet het niveau van de hoofdmix of de
controlekamermix. De knop Solo-modus mag niet ingedrukt zijn (PFL) (wijzigingen van
de faderniveaus hebben geen invloed op de LED-meters en het gehoorde niveau).
57. Solo actief: Gaat branden wanneer de LED-meters het post-fader audioniveau
weergeven van de actieve gesoleerde kanalen in plaats van de kanalen van de hoofdmix
of controlekamermix. De knop Soleermodus moet ingedrukt zijn (AFL) (veranderingen in
de faderniveaus beïnvloeden de LED-meters en het gehoorde volume).
58. Soleermodus: Indien niet-ingedrukt, wordt de audio van een kanaal met ingedrukte
Solo-knop pre-fader afgespeeld (PFL). Wanneer ingedrukt, wordt de audio post-fader
afgespeeld (na de fader of AFL).
59. USB-stroomaansluiting: Via deze USB-poort kunt u een apparaat dat stroom gebruikt
en beschikt over een 5 V USB-poort voorzien van stroom (of opladen).
Effecten
Om effecten toe te passen, draait u aan de Knop met effectprogramma's en drukt u erop om
een van de beschikbare programma's te selecteren. Om het signaal van een kanaal naar de
effectenprocessor te sturen, zet u de DFX-knop (Aux 4) van het kanaal luider.
Elk effect heeft 10 variaties. Selecteer een effect dat past bij de omgeving en bij uw
voorkeuren.
Nummers Effect Beschrijving
00-09 Delay Reproduceert het signaal na een korte vertragingstijd.
10-19 Delay+Galm Delay-effect met ruimtegalm.
20-29 Tremolo
30-39 Plaat Bootst een heldere plaatgalm na.
40-49 Chorus Simuleert het volle, complexe en vloeiende geluid van
50-59 Zang Galm die een kamer nabootst, met een korte vervaltijd.
60-69 Rotary Simuleert het klassieke dopplereffect van de draaiende hoorn in
70-79 Kleine ruimte Galm die een heldere studioruimte nabootst.
80-89 Flanger+Galm Past kamergalm toe plus een klassiek stereo flanger-effect.
90-99 Grote zaal Galm die een grote akoestische ruimte nabootst.
43
erhoogt en verlaagt snel het signaalvolume aan een regelmatige
snelheid.
verschillende instrumenten die hetzelfde spelen.
de luidspreker van een orgel.
Page 44
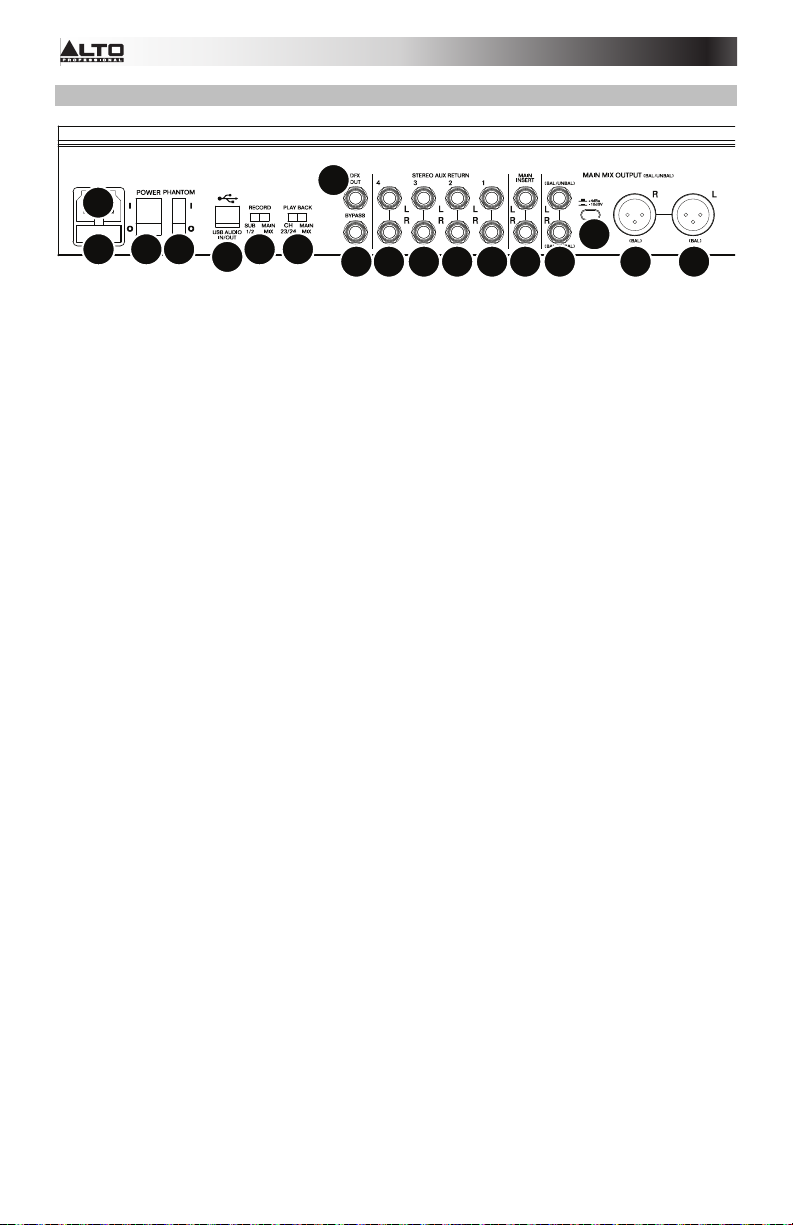
Achterpaneel
11
1
234
1. Stroomingang: Gebruik de meegeleverde IEC-stroomkabel om het mengpaneel aan te sluiten op een
stopcontact. Sluit terwijl de voeding uit staat de stroomkabel aan op het mengpaneel en verbindt deze
vervolgens met het stopcontact.
2. Afsluitklep zekering: Als de zekering van het apparaat kapot is, gebruik dan een schroevendraaier of
ander gereedschap om dit klepje op te tillen en de zekering te vervangen door een zekering met
dezelfde waarde (afgedrukt boven de Stroomingang). Een zekering met onjuiste waarde kan het
apparaat en/of de zekering beschadigen.
3. Aan/uit-schakelaar: Zet het mengpaneel aan en uit. Zet het mengpaneel alleen aan nadat u al uw
invoerapparaten hebt aangesloten, maar voor u uw versterkers aanzet. Schakel de versterkers uit
voordat u de mixer uitzet.
4. Fantoomvoeding Activeert/deactiveert fantoomvoeding. Wanneer geactiveerd, leveren de
fantoomvoedingen +48V aan de XLR-microfooningangen. Houd er rekening mee dat de meeste
dynamische microfoons geen fantoomvoeding vereisen, terwijl de meeste condensatormicrofoons dit
wel nodig hebben. Raadpleeg de documentatie van uw microfoon om te controleren of
fantoomvoeding nodig is.
5. Main Mix-uitgangen: Gebruik standaard XLR- of 1/4” TRS-kabels om een paar van deze uitgangen
aan te sluiten op uw luidsprekers of versterkersysteem. Gebruik de Main Fader om het geluidsniveau
van deze uitgangen te regelen.
6. Hoofdmix dempen Wanneer deze knop is ingedrukt, wordt het signaal dat naar de uitgangen van de
Hoofdmix wordt gestuurd met 10 dB verlaagd. Wanneer niet ingedrukt, wordt het signaal met 4 dB
verhoogd. Zet deze schakelaar op een stand die overeenkomt met het nominale werkingsniveau van
uw apparatuur; apparatuur voor professioneel gebruik werkt aan een nominaal niveau van +4dBu,
terwijl consumentenapparatuur werkt aan een nominaal niveau van -10 dBV.
7. Insert van de Hoofdmix: Gebruik een standaard 1/4" TRS Y-kabel om een externe processor op deze
uitgang aan te sluiten (zoals een compressor, limiter, externe equalizer, enz.). Het geluidssignaal wordt
afgenomen na de Grafische equalizer en wordt geretourneerd voor de Hoofdfader. De top van de
TRS-jack is het send-signaal; de ring is het return-signaal.
8. USB-poort: Gebruik een standaard USB-kabel om deze USB-poort te verbinden met een computer.
Via deze verbinding kan het mengpaneel audio van en naar uw computer verzenden of ontvangen.
• Bij het verzenden van audio worden de Hoofdmix of Subgroepen 1 en 2 van het mengpaneel
naar uw computer gestuurd, afhankelijk van de stand van de Opnameschakelaar.
• Bij het
afhankelijk van de stand van de Afspeelschakelaar.
9. Opnemen: Deze schakelaar bepaalt welk audiosignaal vanaf de USB-poort van het mengpaneel naar
de computer wordt gestuurd: Subgroepen 1 en 2 (Sub 1/2) of de Hoofdmix.
10. Afspelen: Deze schakelaar bepaalt hoe de audio, verstuurd van de computer (naar de USB-poort van
het mengpaneel) bij terugkeer naar het mengpaneel zal worden gerouteerd: Kanalen 23/24 (Ch 23/24)
of Hoofdmix.
11. DFX Out: Gebruik een standaard 1/4” TRS-kabel om deze uitgang met een versterkersysteem te
verbinden. Het signaal van de effectenprocessor van het mengpaneel zal naar deze uitgang worden
gezonden.
12. Bypass: Sluit een optionele standaard 1/4” TS-voetschakelaar (afzonderlijk verkrijgbaar) aan op deze
ingang. U kunt de voetschakelaar gebruiken om de effectenprocessor van het mengpaneel te
activeren of uit te schakelen.
13. Stereo Aux Return: Gebruik 1/4" monokabels om de uitgangen van een extern apparaat met deze
ingangen te verbinden. Als uw bron mono is, sluit de kabel dan aan op de linkse aansluiting. Dat
maakt het signaal hoorbaar in zowel het linker- als rechterkanaal.
8
ontvangen van audio wordt het signaal gestuurd naar kanalen 23/24 of de Hoofdmix,
9
10
12 13 13 13 13
44
6
575
5
Page 45

Appendix (English)
Technical Specifications
Mono Input
Channels
Line Inputs
Impedances
Equalization Mono Channels
DSP Section (DFX) A/D & D/A converters: 24-bit
Main Mix Noise (bus noise):
Power Supply Main voltage:
Dimensions
(width x depth x height)
Weight
Trademarks and Licenses
Alto Professional is a trademark of inMusic Brands, Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
All other product or company names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
45
Microphone inputs: Electronically balanced, discrete input configuration
Frequency response: 20 Hz to 20 kHz, +0.5 dB
THD+N: <0.005% at 0 dBu, 1 kHz
Gain range: 0 dB to 50 dB (Mic)
SNR: 90 dB
Electronically balanced
Frequency response: 20 Hz to 20 kHz, +0.5 dB
THD+N: <0.03% at 0 dBu, 1 kHz
Sensitivity range: -15 dBu to 30 dBu
Microphone inputs: 51.1 KΩ
Channel insert return: 200 KΩ
All other inputs: >100 KΩ
2-Track outputs: 10 KΩ
All other outputs: 20 KΩ
High-shelving: ±15 dB @ 12 kHz
Mid-bell (mono): ±15 dB sweep able from 100 Hz --- 8 KHz
Low-shelving: ±15 dB @ 80 Hz
Stereo Channels
High-shelving: ±15 dB @ 12 kHz
High-Mid-bell (mono): ±15 dB @ 3 KHz
Low-Mid-bell (mono): ±15 dB @ 500 Hz
Low-shelving: ±15 dB @ 80 Hz
Main EQ: 9 EQ bands (63 Hz, 125 Hz, 250 Hz, 500 Hz, 1 kHz, 2 kHz, 4 kHz, 8 kHz,
16 kHz), ±15 dB
DSP Resolution: 24-bit
Effects: 10 DSP effects families with 10 variations available per family
Presets: 100 total
Controls: Rotary encoder to select preset, DSP mute switch, peak LED indicator
Fader 0 dB, channels muted: -84 dBr (ref: +4 dBu)
Fader 0 dB, all input channels assigned & set to unity gain: -73 dBr (ref: +4 dBu)
Phantom Power: Mic Pin2/Pin3 and Pin1 48±2V
USA/Canada: 100-120 VAC ~60 Hz
UK/Australia: 240 VAC ~50 Hz
Europe: 210-240 VAC ~50 Hz
Power consumption: 50 W
Fuse: 1.25 A
Main connection: Standard IEC receptacle
28.1" x 16.4" x 3.1"
71.4 cm x 41.7 cm x 7.9 cm
18.3 lbs.
8.3 kg
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Page 46

Page 47

Page 48

altoprofessional.com
Manual Version 1.1
 Loading...
Loading...