Page 1
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board Reference Manual
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
101 Innovation Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
www.altera.com
MNL-01075-1.1
Feedback Subscribe
Page 2

© 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos
are trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance of its
semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and
services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service
described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying
on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 3
Contents
Chapter 1. Overview
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Board Component Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Development Board Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–4
Handling the Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–4
Chapter 2. Board Components
Board Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Featured Device: Cyclone V E FPGA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–4
I/O Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–5
MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–5
FPGA Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–10
FPGA Programming over Embedded USB-Blaster II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–10
FPGA Programming from Flash Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–13
FPGA Programming over External USB-Blaster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–14
FPGA Programming using EPCQ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–15
Status Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–15
Setup Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–16
Board Settings DIP Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–17
JTAG Chain Control DIP Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–17
CPU Reset Push Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–17
MAX V Reset Push Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–18
Program Configuration Push Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–18
Program Select Push Button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–18
Clock Circuitry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–18
On-Board Oscillators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–18
Off-Board Clock Input/Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–20
General User Input/Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–20
User-Defined Push Buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–20
User-Defined DIP Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–21
User-Defined LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–21
General LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–21
HSMC LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–22
Character LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–22
Debug Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–23
Components and Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–24
10/100/1000 Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–24
HSMC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–27
RS-232 Serial UART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–30
USB-UART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–31
Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–32
DDR3 SDRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–32
LPDDR2 SDRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–35
EEPROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–37
Synchronous SRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–38
Flash . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–39
Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–41
Power Distribution System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–42
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 4

iv ContentsContents
Power Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–43
Chapter 3. Board Components Reference
Board Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
Statement of China-RoHS Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–2
CE EMI Conformity Caution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–2
Additional Information
Board Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
Document Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
How to Contact Altera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
Typographic Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–2
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 5
This document describes the hardware features of the Cyclone® V E FPGA
development board, including the detailed pin-out and component reference
information required to create custom FPGA designs that interface with all
components of the board.
General Description
The Cyclone V E FPGA development board provides a hardware platform for
developing and prototyping low-power, high-performance, and logic-intensive
designs using Altera’s Cyclone V E FPGA. The board provides a wide range of
peripherals and memory interfaces to facilitate the development of Cyclone V E
FPGA designs.
1. Overview
One high-speed mezzanine card (HSMC) connector is available to add additional
functionality via a variety of HSMCs available from Altera
f To see a list of the latest HSMCs available or to download a copy of the HSMC
specification, refer to the Development Board Daughtercards page of the Altera
website.
Design advancements and innovations, such as partial reconfiguration, ensure that
designs implemented in the Cyclone V E FPGAs operate faster, with lower power,
and have a faster time to market than previous FPGA families.
f For more information on the following topics, refer to the respective documents:
■ Cyclone V device family, refer to the Cyclone V Device Handbook.
■ HSMC Specification, refer to the High Speed Mezzanine Card (HSMC) Specification.
®
and various partners.
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 6

1–2 Chapter 1: Overview
Board Component Blocks
Board Component Blocks
The development board features the following major component blocks:
■ One Cyclone V E FPGA (5CEFA7F31I7N) in a 896-pin FineLine BGA (FBGA)
package
■ 149,500 LEs
■ 56,480 adaptive logic modules (ALMs)
■ 6,860 Kbit (Kb) M10K and 836 Kb MLAB memory
■ Seven fractional phase locked loops (PLLs)
■ 312 18x18-bit multipliers
■ 480 general purpose input/output (GPIO)
■ 1.1-V core voltage
■ FPGA configuration circuitry
■ Active Serial (AS) x1 or AS x4 configuration (EPCQ256SI16N)
■ MAX
®
V CPLD (5M2210ZF256I5N) in a 256-pin FBGA package as the System
Controller
■ Flash fast passive parallel (FPP) configuration
■ MAX II CPLD (EPM240M100I5N) in a 100-pin FBGA package as part of the
embedded USB-Blaster
■ Clocking circuitry
■ Programmable clock generator for the FPGA reference clock input
■ 50-MHz single-ended oscillator for the FPGA and MAX V CPLD clock input
■ 100-MHz single-ended oscillator for the MAX V CPLD configuration clock
TM
II for use with the Quartus® II Programmer
input
■ SMA input (LVDS)
■ Memory
■ Two 256-Mbyte (MB) DDR3 SDRAM devices with a 16-bit data bus
■ One 18-Mbit (Mb) SSRAM
■ One 512-Mb synchronous flash
■ One 512-MB LPDDR2 SDRAM with a 32-bit data bus (only 16-bit data bus is
used on this board)
■ One 64-Kb I
2
C serial electrically erasable PROM (EEPROM)
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 7

Chapter 1: Overview 1–3
Board Component Blocks
■ General user input/output
■ LEDs and displays
■ Four user LEDs
■ One configuration load LED
■ One configuration done LED
■ One error LED
■ Three configuration select LEDs
■ Four embedded USB-Blaster II status LEDs
■ Three HSMC interface LEDs
■ Ten Ethernet LEDs
■ Two UART data transmit and receive LEDs
■ Two USB-UART interface TX / RX LEDs
■ One power on LED
■ One two-line character LCD display
■ Push buttons
■ One CPU reset push button
■ One MAX V reset push button
■ One program select push button
■ One program configuration push button
■ Four general user push buttons
■ DIP switches
■ Four MAX V CPLD System Controller control switches
■ Two JTAG chain control DIP switches
■ One fan control DIP switch
■ Four general user DIP switches
■ Power supply
■ 14–20-V (laptop) DC input
■ Mechanical
■ 6.5" x 4.5" size board
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 8
1–4 Chapter 1: Overview
5CEFA7F31I7N
N
Data x 16
Addr x 25
Control x 23
2.5V
JTAG Chain
LEDs
Clock In
125 M, 50 M
Clock In
100 M, 50 M
Debug
Header
DSUB 9-pin
Connector
x5
x1
x2
EPCQ
5M2210ZF256I5N
CLKIN x3
CLKOUT x3
LVDS/Single-Ended
Type-A USB
Connector
x80
2.5 V
x31
2.5 V
x6
2.5 V
x4
2.5 Vx42.5 V
x16 2.5 V
x16 1.5 V
x16 HSUL 1.2
x22
RGMII
2.5 V
x19 USB
Interface 2.5 V
x32
SSTL - 15
x11
2.5 V
x4
3.3 V
x2
3.3 V
USB-to-
UART
LCD
Character
32 Kb
UART
32 Kb
EEPROM
SMA
Clock Out
18 Mb
SSRAM
512 Mb
Flash
Clock Enable
Fan
Connector
AS x1,x4
FPP x16
Configuration
Buttons &
Switches
2 x 256 MB
DDR3
EPM570GM100I5N
Embedded
USB-Blaster II
2 x RJ-45
LAN
Connector
USB CLK to
Cyclone V
and MAX V
Cypress
USB 2.0
Controller
Type-B
USB
Connector
512 MB
LPDDR2
2x Gigabit
Ethernet PHY
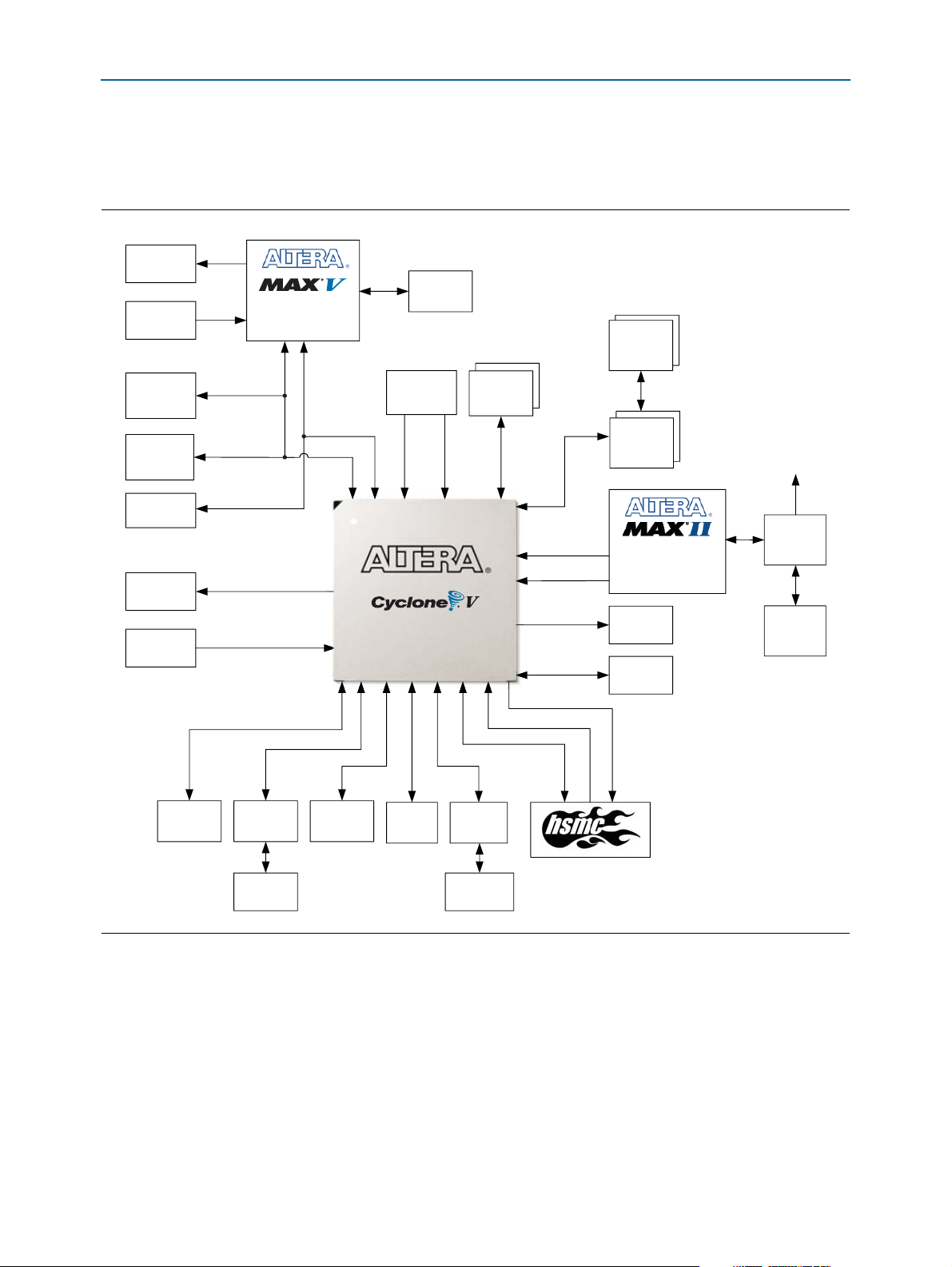
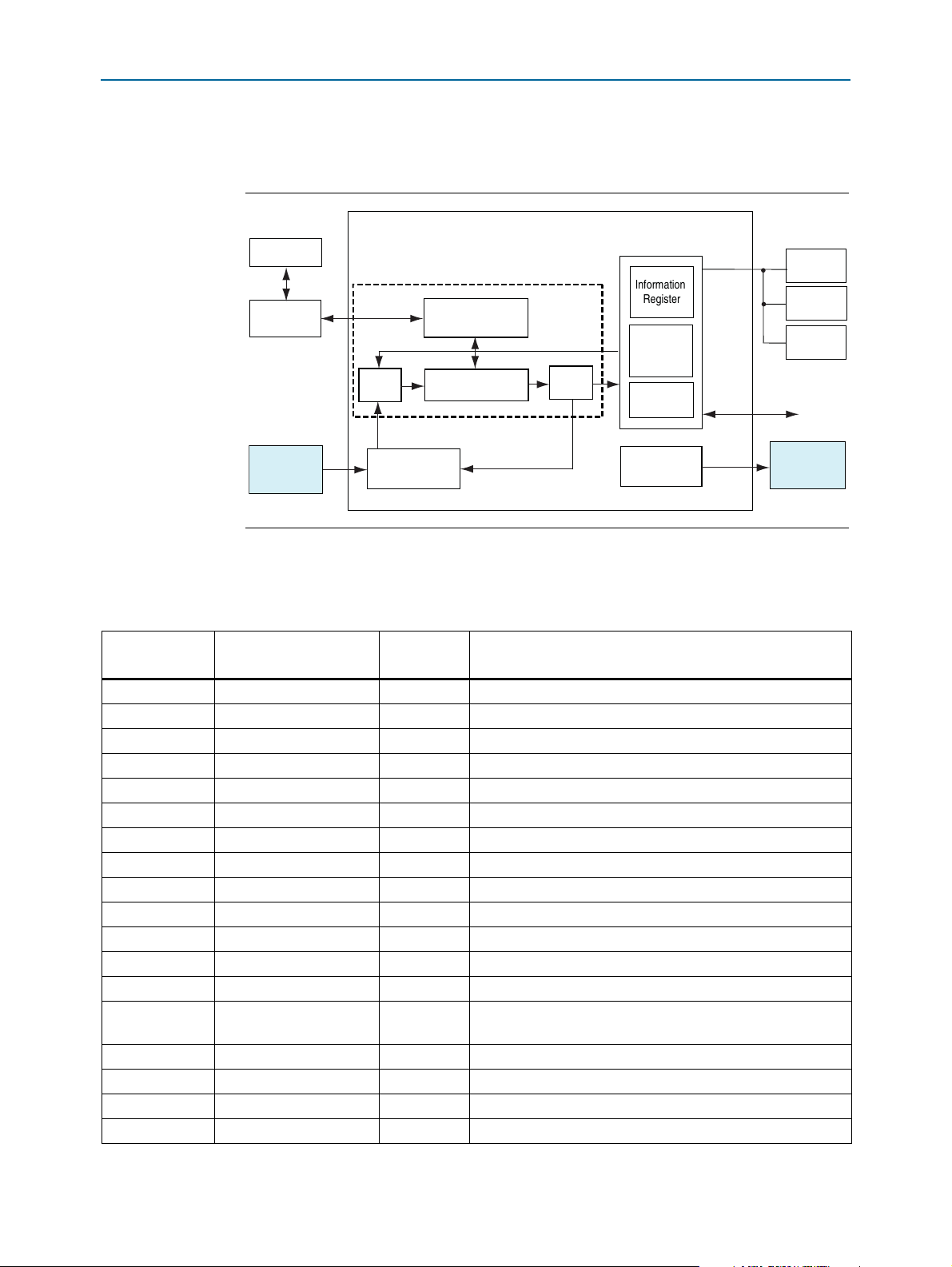
Development Board Block Diagram
Development Board Block Diagram
Figure 1–1 shows a block diagram of the Cyclone V E FPGA development board.
Figure 1–1. Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board Block Diagram
Handling the Board
When handling the board, it is important to observe the following static discharge
precaution:
c Without proper anti-static handling, the board can be damaged. Therefore, use
anti-static handling precautions when touching the board.
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 9
2. Board Components
This chapter introduces the major components on the Cyclone V E FPGA
development board. Figure 2–1 illustrates the component locations and Ta bl e 2– 1
provides a brief description of all component features of the board.
1 A complete set of schematics, a physical layout database, and GERBER files for the
development board reside in the Cyclone V E FPGA development kit documents
directory.
f For information about powering up the board and installing the demonstration
software, refer to the Cyclone V E FPGA Development Kit User Guide.
This chapter consists of the following sections:
■ “Board Overview”
■ “Featured Device: Cyclone V E FPGA” on page 2–4
■ “MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller” on page 2–5
■ “FPGA Configuration” on page 2–10
■ “Clock Circuitry” on page 2–18
■ “General User Input/Output” on page 2–20
■ “Components and Interfaces” on page 2–24
■ “Memory” on page 2–32
■ “Power Supply” on page 2–41
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 10
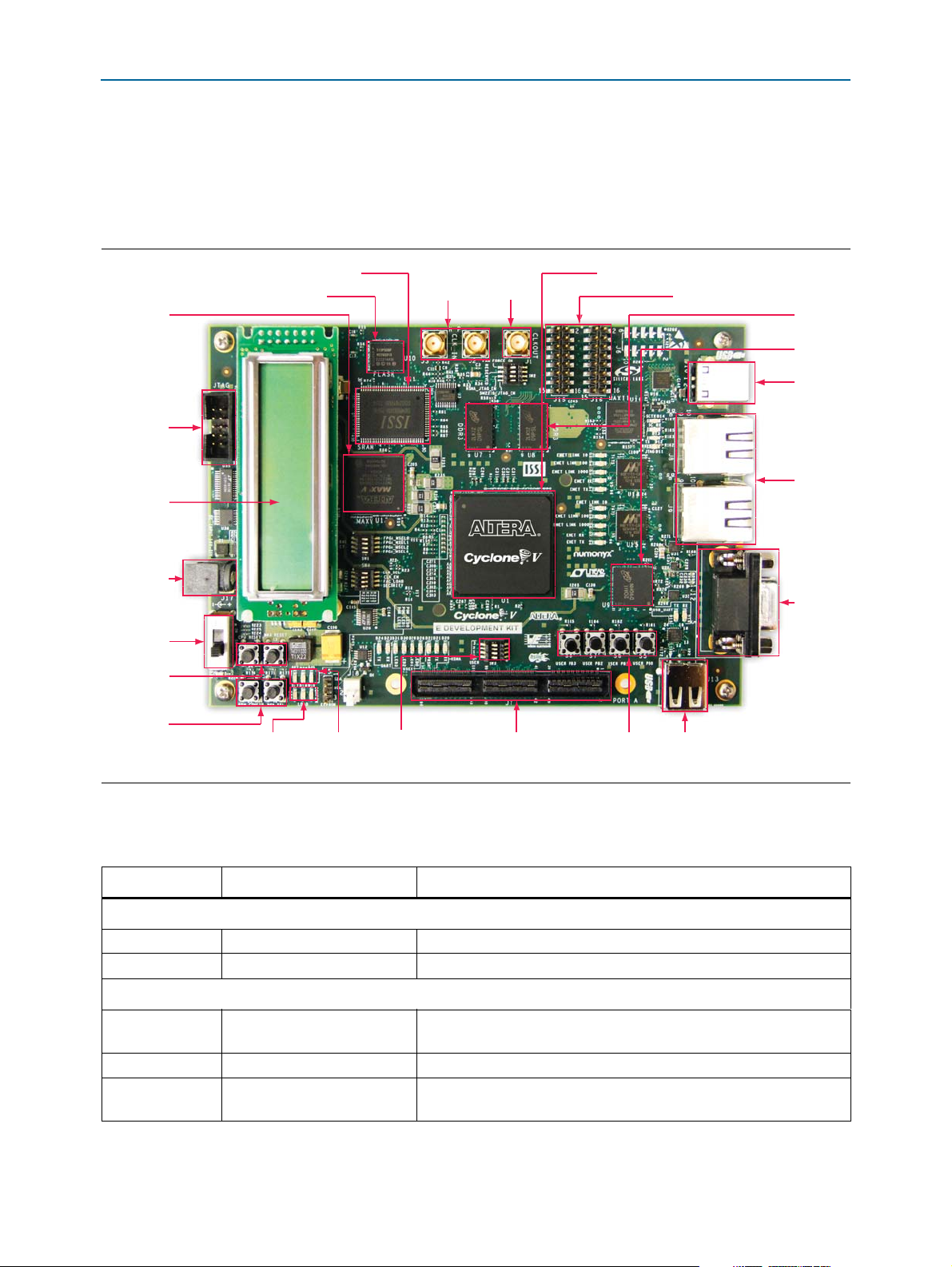
2–2 Chapter 2: Board Components
Clock Input SMA
Connectors
(J2, J3)
General User
Push Buttons
(S5-S8)
Flash x16 Memory (U10)
LPDDR2 x16
Memory (U9)
Serial UART
Connector
(J12)
DDR3 x32
Memory
(U7, U8)
DC Input
Jack (J17)
Character
LCD (J14)
CPU Reset,
MAX V Reset
Push Buttons
(S3, S4)
Power Switch
(SW5)
User
DIP Switch
(SW3)
MAX V CPLD
EPM2210 System
Controller (U13)
Clock Output
SMA Connector
(J4)
HSMC Port
(J1)
Configuration Done,
Load, and Error
LEDs (D17-D19)
Program Config,
Program Select
Push Buttons
(S1, S2)
Program Select
LEDs (D25-D27)
USB Type-B
Connector
(J10)
USB-UART
Connector (J13)
SSRAM x16 Memory (U11)
Debug Headers (J15, J16)
Gigabit
Ethernet
Port (J11)
JTAG Chain
Header
(J4)
Cyclone V E FPGA (U1)
Board Overview
Board Overview
This section provides an overview of the Cyclone V E FPGA development board,
including an annotated board image and component descriptions. Figure 2–1 shows
an overview of the board features.
Figure 2–1. Overview of the Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board Features
Tab le 2– 1 describes the components and lists their corresponding board references.
Table 2–1. Board Components (Part 1 of 3)
Board Reference Type Description
Featured Devices
U1 FPGA Cyclone V E FPGA, 5CEFA7F31I7N, 896-pin FBGA.
U13 CPLD MAX V CPLD, 5M2210ZF256I5N, 256-pin FBGA.
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
J4 JTAG chain header
Provides access to the JTAG chain and disables the embedded
USB-Blaster II when using an external USB-Blaster cable.
SW2 JTAG chain control DIP switch Remove or include devices in the active JTAG chain.
J10 USB type-B connector
USB interface for FPGA programming and debugging through the
embedded USB-Blaster II JTAG via a type-B USB cable.
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 11
Chapter 2: Board Components 2–3
Board Overview
Table 2–1. Board Components (Part 2 of 3)
Board Reference Type Description
Controls the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller functions such
SW3 Board settings DIP switch
as clock enable, SMA clock input control, and which image to load
from flash memory at power-up.
SW1 MSEL DIP switch
S2 Program select push button
S1
Program configuration push
button
Controls the configuration scheme on the board. MSEL pins 0, 1, 2 and
4 connects to the DIP switch while MSEL pin 3 connects to ground.
Toggles the program select LEDs, which selects the program image
that loads from flash memory to the FPGA.
Load image from flash memory to the FGPA based on the settings of
the program select LEDs.
D19 Configuration done LED Illuminates when the FPGA is configured.
D18 Load LED
Illuminates when the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller is
actively configuring the FPGA.
D17 Error LED Illuminates when the FPGA configuration from flash memory fails.
D35 Power LED Illuminates when 5.0-V power is present.
Illuminates to show the LED sequence that determines which flash
D25~D27 Program select LEDs
memory image loads to the FPGA when you press the program select
push button. Refer to Tab le 2–6 for the LED settings.
D1~D10 Ethernet LEDs
Illuminates to show the connection speed as well as transmit or
receive activity.
D20, D21 HSMC port LEDs You can configure these LEDs to indicate transmit or receive activity.
D22 HSMC port present LED Illuminates when a daughter card is plugged into the HSMC port.
D15, D16 USB-UART LEDs Illuminates when the USB-UART transmitter and receiver are in use.
D23, D24 Serial UART LEDs Illuminates when UART transmitter and receiver are in use.
Clock Circuitry
Programmable oscillator with default frequencies of 125 MHz. The
X1 Programmable oscillator
frequency is programmable using the clock control GUI running on the
MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller.
U4 50-MHz oscillator 50.000-MHz crystal oscillator for general purpose logic.
X3 100-MHz oscillator
100.000-MHz crystal oscillator for the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System
Controller.
J2, J3 Clock input SMA connectors Drive LVDS-compatible clock inputs into the clock multiplexer buffer.
J4 Clock output SMA connector Drive out 2.5-V CMOS clock output from the FPGA.
General User Input/Output
D28~D31 User LEDs Four user LEDs. Illuminates when driven low.
SW3 User DIP switch Quad user DIP switches. When the switch is ON, a logic 0 is selected.
S4 CPU reset push button Reset the FPGA logic.
S3 MAX V reset push button Reset the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller.
S5~S8 General user push buttons Four user push buttons. Driven low when pressed.
Memory Devices
U7, U8 DDR3 x32 memory Two 256-MB DDR3 SDRAM with a 16-bit data bus.
U9 LPDDR2 x 16 memory
512-MB LPDDR 2 SDRAM with 32-bit bus, only 16-bit bus is used on
this board.
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 12
2–4 Chapter 2: Board Components
Featured Device: Cyclone V E FPGA
Table 2–1. Board Components (Part 3 of 3)
Board Reference Type Description
U10 Flash x16 memory
U11 SSRAM x16 memory
U12 EEPROM 64-Mb I
Communication Ports
J1 HSMC port Provides 84 CMOS or 17 LVDS channels per HSMC specification.
J11 Gigabit Ethernet port
J12 Serial UART port
J13 USB-UART port USB connector with USB-to-UART bridge for serial UART interface.
J15, J16 Debug headers Two 2×8 headers for debug purposes.
Video and Display Ports
J14 Character LCD
512-Mb synchronous flash devices with a 16-bit data bus for
non-volatile memory.
18-Mb standard synchronous RAM with a 12-bit data bus and 4-bit
parity.
2
C serial EEPROM.
RJ-45 connector which provides a 10/100/1000 Ethernet connection
via a Marvell 88E1111 PHY and the FPGA-based Altera Triple Speed
Ethernet MegaCore function in RGMII mode.
DSUB 9-pin connector with RS-232 transceiver to implement RS-232
serial UART channel.
Connector that interfaces to a provided 16 character × 2 line LCD
module along with two standoffs.
Power Supply
J17 DC input jack Accepts a 14–20-V DC power supply.
SW5 Power switch
Switch to power on or off the board when power is supplied from the
DC input jack.
Featured Device: Cyclone V E FPGA
The Cyclone V E FPGA development board features a Cyclone V E FPGA
5CEFA7F31I7N device (U1) in a 896-pin FBGA package.
f For more information about Cyclone V device family, refer to the Cyclone V Device
Handbook.
Tab le 2– 2 describes the features of the Cyclone V E FPGA 5CEFA7F31I7N device.
Table 2–2. Cyclone V E FPGA Features
ALMs Equivalent LEs M10K RAM Blocks
56,480 149,500 6,860 836 312 7 896-pin FBGA
Total RAM
(Kbits)
18-bit × 18-bit
Multipliers
PLLs Package Type
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 13
Chapter 2: Board Components 2–5
MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller
I/O Resources
The Cyclone V E FPGA 5CEFA7F31I7N device has total of 480 user I/Os. Table 2–3
lists the Cyclone V E FPGA I/O pin count and usage by function on the board.
Table 2–3. Cyclone V E FPGA I/O Pin Count
Function I/O Standard I/O Count Special Pins
DDR3 1.5-V SSTL 71 One differential x4 DQS pin
LPDDR2 1.2-V HSUL 37 One differential x2 DQS pin
Flash, SSRAM, EEPROM, and MAX V
FSM bus
HSMC port 2.5-V CMOS + LVDS 79 17 LVDS, I
Gigabit Ethernet port 2.5-V CMOS 42 —
Embedded USB-Blaster II 2.5-V CMOS 20 —
Debug Header 1.5-V, 2.5-V 20 —
UART 3.3-V LVTTL 4 —
USB-UART 2.5-V CMOS 12 —
Push buttons 2.5-V CMOS 5 One
DIP switches 2.5-V CMOS 4 —
Character LCD 2.5-V CMOS 11 —
LEDs 2.5-V CMOS 9 —
Clock or Oscillators 2.5-V CMOS + LVDS 12 One clock out pin
Total I/O Used: 395
2.5-V CMOS, 3.3-V LVCMOS 69 —
2
C
DEV_CLRn
pin
MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller
The board utilizes the 5M2210 System Controller, an Altera MAX V CPLD, for the
following purposes:
■ FPGA configuration from flash
■ Power measurement
■ Control and status registers for remote system update
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 14
2–6 Chapter 2: Board Components
MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller
Figure 2–2 illustrates the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller's functionality and
external circuit connections as a block diagram.
Figure 2–2. MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller Block Diagram
MAX V CPLD System Controller
PC
Embedded
USB-Blaster II
Encoder
JTAG Control
SLD-HUB
Virtual-JTAG
Information
Register
Control
Register
Decoder
PFL
FSM Bus
FPGA
Flash
SSRAM
GPIO
Power
Measurement
Results
LTC2418
Controller
Tab le 2– 4 lists the I/O signals present on the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System
Controller. The signal names and functions are relative to the MAX V device.
Table 2–4. MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller Device Pin-Out (Part 1 of 5)
Board
Reference (U13)
N4
E9
H12
A15
A13
J12
D9
C9
D10
P12
T13
T15
A2
R14
N12
C8
N7
R5
Schematic Signal Name I/O Standard Description
5M2210_JTAG_TMS
CLK50_EN
CLK_CONFIG
CLK_ENABLE
CLK_SEL
CLKIN_50_MAXV
CLOCK_SCL
CLOCK_SDA
CPU_RESETN
EXTRA_SIG0
EXTRA_SIG1
EXTRA_SIG2
FACTORY_LOAD
FACTORY_REQUEST
FACTORY_STATUS
FAN_FORCE_ON
FLASH_ADVN
FLASH_CEN
3.3-V MAX V JTAG TMS
2.5-V 50 MHz oscillator enable
2.5-V 100 MHz configuration clock input
2.5-V DIP switch for clock oscillator enable
2.5-V DIP switch for clock select—SMA or oscillator
2.5-V 50 MHz clock input
2.5-V Programmable oscillator I2C clock
2.5-V Programmable oscillator I2C data
2.5-V FPGA reset push button
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V DIP switch to load factory or user design at power-up
2.5-V
Embedded USB-Blaster II request to send FACTORY
command
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II FACTORY command status
2.5-V DIP switch to on or off the fan
2.5-V FSM bus flash memory address valid
2.5-V FSM bus flash memory chip enable
Si570
Controller
Si570
Programmable
Oscillator
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 15
Chapter 2: Board Components 2–7
MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller
Table 2–4. MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller Device Pin-Out (Part 2 of 5)
Board
Reference (U13)
R6
M6
T5
P7
N6
K1
D3
C2
C3
E3
D2
E4
D1
E5
F3
E1
F4
F2
F1
F6
G2
G3
K4
J3
N1
J4
H1
P2
E2
F5
L5
E14
C14
C15
E13
E12
D15
F14
D16
Schematic Signal Name I/O Standard Description
FLASH_CLK
FLASH_OEN
FLASH_RDYBSYN
FLASH_RESETN
FLASH_WEN
FPGA_CONF_DONE
FPGA_CONFIG_D0
FPGA_CONFIG_D1
FPGA_CONFIG_D2
FPGA_CONFIG_D3
FPGA_CONFIG_D4
FPGA_CONFIG_D5
FPGA_CONFIG_D6
FPGA_CONFIG_D7
FPGA_CONFIG_D8
FPGA_CONFIG_D9
FPGA_CONFIG_D10
FPGA_CONFIG_D11
FPGA_CONFIG_D12
FPGA_CONFIG_D13
FPGA_CONFIG_D14
FPGA_CONFIG_D15
FPGA_MAX_DCLK
FPGA_DCLK
FPGA_NCONFIG
FPGA_NSTATUS
FPGA_PR_DONE
FPGA_PR_ERROR
FPGA_PR_READY
FPGA_PR_REQUEST
FPGA_MAX_NCS
FSM_A1
FSM_A2
FSM_A3
FSM_A4
FSM_A5
FSM_A6
FSM_A7
FSM_A8
2.5-V FSM bus flash memory clock
2.5-V FSM bus flash memory output enable
2.5-V FSM bus flash memory ready
2.5-V FSM bus flash memory reset
2.5-V FSM bus flash memory write enable
3.3-V FPGA configuration done LED
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration data
3.3-V FPGA configuration clock
3.3-V FPGA configuration clock
3.3-V FPGA configuration active
3.3-V FPGA configuration ready
3.3-V FPGA partial reconfiguration done
3.3-V FPGA partial reconfiguration error
3.3-V FPGA partial reconfiguration ready
3.3-V FPGA partial reconfiguration request
3.3-V FPGA configuration chip select
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 16
2–8 Chapter 2: Board Components
MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller
Table 2–4. MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller Device Pin-Out (Part 3 of 5)
Board
Reference (U13)
F13
E15
E16
F15
G14
F16
G13
G15
G12
G16
H14
H20
H13
H16
J13
J16
T2
P5
J14
J15
K16
K13
K15
K14
L16
L11
L15
L12
M16
L13
M15
L14
N16
M13
B8
L6
M5
P3
Schematic Signal Name I/O Standard Description
FSM_A9
FSM_A10
FSM_A11
FSM_A12
FSM_A13
FSM_A14
FSM_A15
FSM_A16
FSM_A17
FSM_A18
FSM_A19
FSM_A20
FSM_A21
FSM_A22
FSM_A23
FSM_A24
FSM_A25
FSM_A26
FSM_D0
FSM_D1
FSM_D2
FSM_D3
FSM_D4
FSM_D5
FSM_D6
FSM_D7
FSM_D8
FSM_D9
FSM_D10
FSM_D11
FSM_D12
FSM_D13
FSM_D14
FSM_D15
HSMA_PRSNTN
JTAG_5M2210_TDI
JTAG_5M2210_TDO
JTAG_TCK
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM address bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V FSM data bus
2.5-V HSMC port present
3.3-V MAX V CPLD JTAG chain data in
3.3-V MAX V CPLD JTAG chain data out
3.3-V JTAG chain clock
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 17
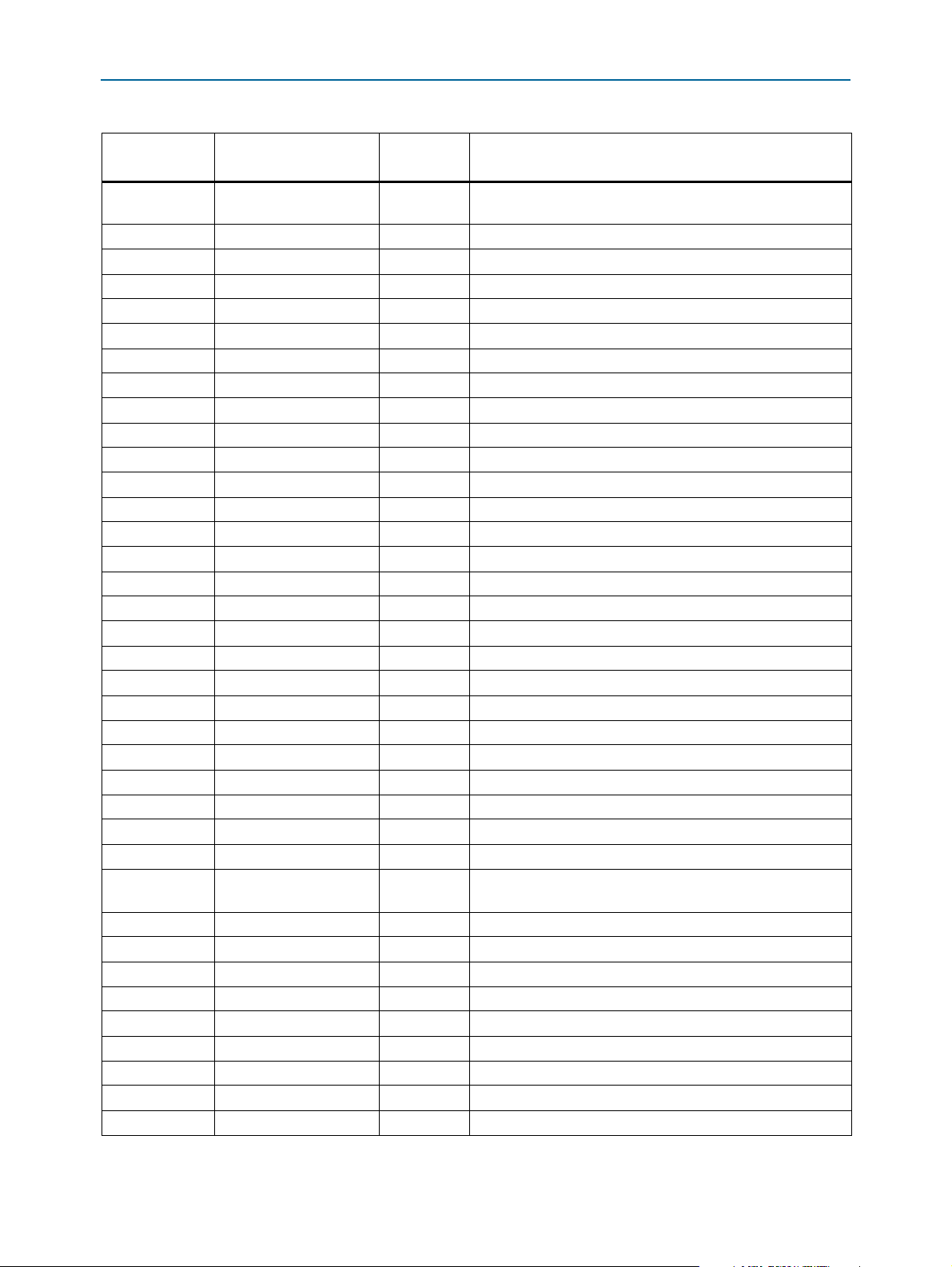
Chapter 2: Board Components 2–9
MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller
Table 2–4. MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller Device Pin-Out (Part 4 of 5)
Board
Reference (U13)
P11
M1
P10
R11
T12
N11
T11
R10
M10
N10
E11
A4
A6
M9
B7
D12
B14
C13
B16
B13
H4
G1
G4
H2
G5
H3
J1
R12
E7
A5
D7
B6
A9
R4
T4
P8
T7
Schematic Signal Name I/O Standard Description
M570_CLOCK
M570_JTAG_EN
MAX5_BEN0
MAX5_BEN1
MAX5_BEN2
MAX5_BEN3
MAX5_CLK
MAX5_CSN
MAX5_OEN
MAX5_WEN
MAX_CONF_DONEN
MAX_ERROR
MAX_LOAD
MAX_RESETN
OVERTEMP
PGM_CONFIG
PGM_LED0
PGM_LED1
PGM_LED2
PGM_SEL
PSAS_CSn
PSAS_DCLK
PSAS_CONF_DONE
PSAS_CONFIGn
PSAS_DATA1
PSAS_DATA0_ASD0
PSAS_CEn
SECURITY_MODE
SENSE_CS0N
SENSE_SCK
SENSE_SDI
SENSE_SDO
SI570_EN
USB_CFG0
USB_CFG1
USB_CFG2
USB_CFG3
2.5-V
3.3-V Low signal to disable the embedded USB-Blaster II
2.5-V FSM bus MAX V byte enable 0
2.5-V FSM bus MAX V byte enable 1
2.5-V FSM bus MAX V byte enable 2
2.5-V FSM bus MAX V byte enable 3
2.5-V FSM bus MAX V clock
2.5-V FSM bus MAX V chip select
2.5-V FSM bus MAX V output enable
2.5-V FSM bus MAX V write enable
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II configuration done LED
2.5-V FPGA configuration error LED
2.5-V FPGA configuration active LED
2.5-V MAX V reset push button
2.5-V Temperature monitor fan enable
2.5-V Load the flash memory image identified by the PGM LEDs
2.5-V Flash memory PGM select indicator 0
2.5-V Flash memory PGM select indicator 1
2.5-V Flash memory PGM select indicator 2
2.5-V Toggles the
3.3-V AS configuration chip select
3.3-V AS configuration clock
3.3-V AS configuration done
3.3-V AS configuration active
3.3-V AS configuration data
3.3-V AS configuration data
3.3-V AS configuration chip enable
2.5-V
2.5-V Power monitor chip select
2.5-V Power monitor SPI clock
2.5-V Power monitor SPI data in
2.5-V Power monitor SPI data out
2.5-V Si570 programmable XO enable
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
25-MHz clock to embedded USB-Blaster II for sending
FACTORY command
PGM_LED[2:0]
LED sequence
DIP switch for the embedded USB-Blaster II to send FACTORY
command at power up
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 18
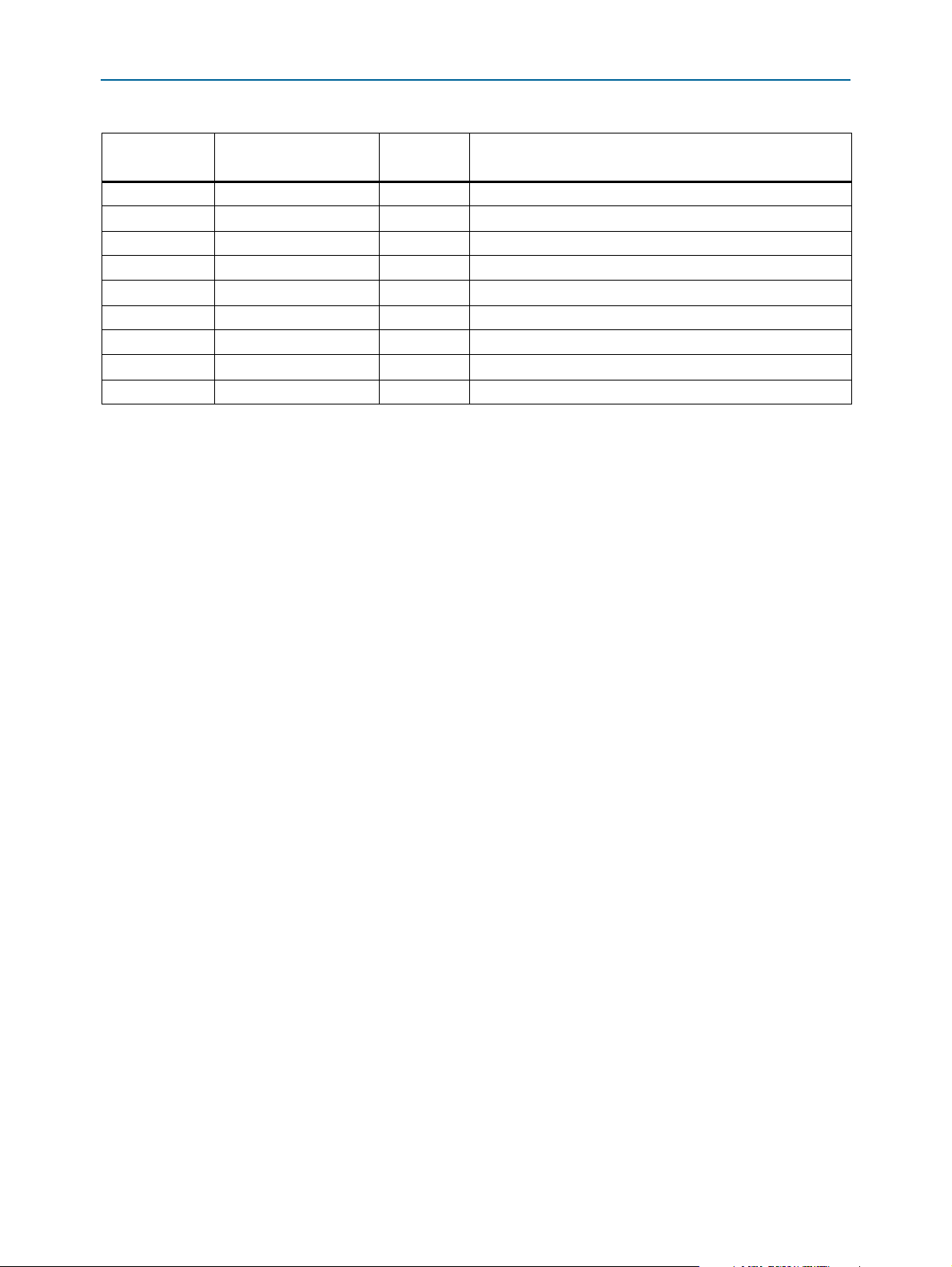
2–10 Chapter 2: Board Components
FPGA Configuration
Table 2–4. MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller Device Pin-Out (Part 5 of 5)
Board
Reference (U13)
N8
R8
T8
T9
R9
P9
M8
T10
H5
Schematic Signal Name I/O Standard Description
USB_CFG4
USB_CFG5
USB_CFG6
USB_CFG7
USB_CFG8
USB_CFG9
USB_CFG10
USB_CFG11
USB_CLK
FPGA Configuration
This section describes the FPGA, flash memory, and MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System
Controller device programming methods supported by the Cyclone V E FPGA
development board.
The Cyclone V E FPGA development board supports the following configuration
methods:
■ Embedded USB-Blaster II is the default method for configuring the FPGA using
the Quartus II Programmer in JTAG mode with the supplied USB cable.
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
2.5-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface. Reserved for future use
3.3-V Embedded USB-Blaster II interface clock
■ Flash memory download for configuring the FPGA using stored images from the
flash memory on either power-up or pressing the program configuration
push button (S1).
■ External USB-Blaster for configuring the FPGA using an external USB-Blaster that
connects to the JTAG chain header (J4).
■ EPCQ device for serial or quad-serial FPGA configuration that supports AS x1 or
AS x4 configuration schemes.
FPGA Programming over Embedded USB-Blaster II
This configuration method implements a USB type-B connector (J10), a USB 2.0 PHY
device (U18), and an Altera MAX II CPLD EPM570GF100I5N (U16) to allow FPGA
configuration using a USB cable. This USB cable connects directly between the USB
type-B connector on the board and a USB port of a PC running the Quartus II
software.
The embedded USB-Blaster II in the MAX II CPLD EPM570GF100I5N normally
masters the JTAG chain.
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 19

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–11
Embedded
USB-Blaster II
GPIO
TCK
Cyclone V E
FPGA
Analog
Switch
MAX V CPLD
5M2210
System
Controller
HSMC
Port
GPIO
TMS
GPIO
TDO
GPIO
GPIO
TDI
JTAG Master
GPIO
Disable
Enable
Enable
JTAG Slave
HSMC
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
TCK
2.5 V
TMS
TDI
TDO
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
JTAG Slave
JTAG Slave
Analog
Switch
Always
Enabled
(in JTAG chain)
DIP Switch
DIP Switch
10-pin
JTAG Header
Flash
Memory
2.5 V
FPGA Configuration
Figure 2–3 illustrates the JTAG chain.
Figure 2–3. JTAG Chain
The JTAG chain control DIP switch (SW2) controls the jumpers shown in Figure 2–3.
To connect a device or interface in the chain, their corresponding switch must be in
the OFF position. Slide all the switches to the ON position to only have the FPGA in
the chain.
1 The MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller must be in the JTAG chain to use some
Table 2–5. USB 2.0 PHY Schematic Signal Names and Functions (Part 1 of 2)
Board Reference
(U18)
C1
C2
E1
E2
H7
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
of the GUI interfaces.
Tab le 2– 5 lists the USB 2.0 PHY schematic signal names and their corresponding
Cyclone V E FPGA pin numbers.
Schematic
Signal Name
24M_XTALIN
24M_XTALOUT
FX2_D_N
FX2_D_P
FX2_FLAGA
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin Number
— 3.3-V Crystal oscillator input
— 3.3-V Crystal oscillator output
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY data
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY data
— 3.3-V Slave FIFO output status
I/O Standard Description
Reference Manual
Page 20

2–12 Chapter 2: Board Components
FPGA Configuration
Table 2–5. USB 2.0 PHY Schematic Signal Names and Functions (Part 2 of 2)
Board Reference
(U18)
G7
H8
G6
F8
F7
F6
C8
C7
C6
H3
F4
H4
G4
H5
G5
F5
H6
A8
A7
B6
A6
B3
A3
C3
A2
B8
F3
G3
A1
B1
B7
G2
Schematic
Signal Name
FX2_FLAGB
FX2_FLAGC
FX2_PA1
FX2_PA2
FX2_PA3
FX2_PA4
FX2_PA5
FX2_PA6
FX2_PA7
FX2_PB0
FX2_PB1
FX2_PB2
FX2_PB3
FX2_PB4
FX2_PB5
FX2_PB6
FX2_PB7
FX2_PD0
FX2_PD1
FX2_PD2
FX2_PD3
FX2_PD4
FX2_PD5
FX2_PD6
FX2_PD7
FX2_RESETN
FX2_SCL
FX2_SDA
FX2_SLRDN
FX2_SLWRN
FX2_WAKEUP
USB_CLK
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
— 3.3-V Slave FIFO output status
— 3.3-V Slave FIFO output status
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port A interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port A interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port A interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port A interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port A interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port A interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port A interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port B interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port B interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port B interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port B interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port B interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port B interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port B interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port B interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port D interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port D interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port D interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port D interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port D interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port D interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port D interface
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY port D interface
V21 3.3-V Embedded USB-Blaster hard reset
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY serial clock
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY serial data
— 3.3-V Read strobe for slave FIFO
— 3.3-V Write strobe for slave FIFO
— 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY wake signal
AA23 3.3-V USB 2.0 PHY 48-MHz interface clock
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 21

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–13
FPGA Configuration
FPGA Programming from Flash Memory
Flash memory programming is possible through a variety of methods. The default
method is to use the factory design—Board Update Portal. This design is an
embedded webserver, which serves the Board Update Portal web page. The web page
allows you to select new FPGA designs including hardware, software, or both in an
industry-standard S-Record File (.flash) and write the design to the user hardware
page (page 1) of the flash memory over the network.
The secondary method is to use the pre-built parallel flash loader (PFL) design
included in the development kit. The development board implements the Altera PFL
megafunction for flash memory programming. The PFL megafunction is a block of
logic that is programmed into an Altera programmable logic device (FPGA or CPLD).
The PFL functions as a utility for writing to a compatible flash memory device. This
pre-built design contains the PFL megafunction that allows you to write either page 0,
page 1, or other areas of flash memory over the USB interface using the Quartus II
software. This method is used to restore the development board to its factory default
settings.
Other methods to program the flash memory can be used as well, including the
®
Nios
II processor.
f For more information on the Nios II processor, refer to the Nios II Processor page of
the Altera website.
On either power-up or by pressing the program configuration push button,
PGM_CONFIG
(S1), the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller's PFL configures the
FPGA from the flash memory. The PFL megafunction reads 16-bit data from the flash
memory and converts it to fast passive parallel (FPP) format. This 16-bit data is then
written to the dedicated configuration pins in the FPGA during configuration.
Pressing the
based on which
that loads when you press the
Table 2–6. PGM_LED Settings
PGM_LED0 (D25) PGM_LED1 (D26) PGM_LED2 (D27) Design
Note to Tab le 2– 6:
(1) ON indicates a setting of ’0’ while OFF indicates a setting of ’1’.
PGM_CONFIG
PGM_LED[2:0]
ON OFF OFF Factory hardware
OFF ON OFF User hardware 1
OFF OFF ON User hardware 2
push button (S1) loads the FPGA with a hardware page
(D25, D26, D27) illuminates. Table 2–6 lists the design
PGM_CONFIG
(1)
push button.
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 22

2–14 Chapter 2: Board Components
MAX V CPLD
5M2210 System Controller
FPGA_DATA [0]
FPGA_DCLK
FLASH_A [25:1]
FLASH_D [15:0]
DATA [0]
DCLK
nSTATUS
nCONFIG
CONF_DONE
CONF_DONE
MSEL[4:0]
2.5 V
10 kΩ
nCE
CFI Flash
FLASH_CEn
FLASH_OEn
FLASH_WEn
FLASH_A [25:0]
FLASH_D [15:0]
FLASH_CEn
FLASH_OEn
FLASH_WEn
FLASH_WPn
FLASH_ADVn
FPGA_nCONFIG
FPGA_CONF_DONE
FLASH_RYBSYn
FLASH_RYBSYn
FPGA_nSTATUS
2.5 V
10 kΩ
FLASH_ADVn
CONF_DONE_LED
2.5 V
FLASH_CLK
FLASH_CLK
FLASH_RSTn
FLASH_RESETn
PS PORT
Flash Interface
56.2 Ω
100 Ω56.2 Ω
56.2 Ω
50 MHz
100 MHz
INIT_DONE
FPGA_INIT_DONE
2.5 V
2.5 V 2.5 V
ERROR
LOAD
MAX_CONF_DONE1
SEC_MODE
FACT_LOAD
CLK_EN
CLK_SEL
MAX_RESETn
PGM_CONFIG
PGM_SEL
PGM_LED0
PGM_LED1
PGM_LED2
DIP Switch
10 kΩ
Cyclone V FPGA
DIP Switch
FPGA Configuration
Figure 2–4 shows the PFL configuration.
Figure 2–4. PFL Configuration
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
f For more information on the following topics, refer to the respective documents:
■ Board Update Portal, PFL design, and flash memory map storage, refer to the
■ PFL megafunction, refer to Parallel Flash Loader Megafunction User Guide.
FPGA Programming over External USB-Blaster
The JTAG chain header provides another method for configuring the FPGA using an
external USB-Blaster device with the Quartus II Programmer running on a PC. To
prevent contention between the JTAG masters, the embedded USB-Blaster is
automatically disabled when you connect an external USB-Blaster to the JTAG chain
through the JTAG chain header.
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Kit User Guide.
Page 23

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–15
EPCQ Device
EPCQ Device
V
CCPGM
10 kΩ
DATA0
DATA1
DATA2
DATA3
DCLK
nCS
AS_DATA0/ASDO
AS_DATA1
AS_DATA2
AS_DATA3
DCLK
nSTATUS
CONF_DONE
nCONFIG
nCE
nCSO
nCEO
NC
MSEL[4:0]
CLKUSR
Status Elements
FPGA Programming using EPCQ
The low-cost ECPQ device with non-volatile memory features a simple six-pin
interface and a small form factor. The ECPQ supports AS x1 and x4 modes.
By default, this board has a FPP configuration scheme setting. In order to set the
configuration scheme to AS mode, resistor rework needs to be done. Configure the
MSEL setting using the MSEL DIP switch (SW1) to change the configuration scheme.
Figure 2–5 shows the connection between the EPCQ and the Cyclone V E FPGA.
Figure 2–5. EPCQ Configuration
Status Elements
The development board includes status LEDs. This section describes the status
elements.
Tab le 2– 7 lists the LED board references, names, and functional descriptions.
Table 2–7. Board-Specific LEDs (Part 1 of 2)
Board
Reference
D35
D19
D17
D18
D25
D26
D27
Schematic Signal Name
Power
MAX_CONF_DONEn
MAX_ERROR
MAX_LOAD
PGM_LED[0]
PGM_LED[1]
PGM_LED[2]
Standard
I/O
Description
5.0-V Blue LED. Illuminates when 5.0 V power is active.
2.5-V
Green LED. Illuminates when the FPGA is successfully configured.
Driven by the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller.
Red LED. Illuminates when the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System
2.5-V
Controller fails to configure the FPGA. Driven by the MAX V CPLD
5M2210 System Controller.
Green LED. Illuminates when the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System
2.5-V
Controller is actively configuring the FPGA. Driven by the MAX V
CPLD 5M2210 System Controller.
2.5-V
Green LEDs. Illuminates to indicate which hardware page loads
from flash memory when you press the
PGM_SEL
push button.
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 24

2–16 Chapter 2: Board Components
Setup Elements
Table 2–7. Board-Specific LEDs (Part 2 of 2)
Board
Reference
D11, D12
D13, D14
D1
D2
D5
D4
D3
D19
D22
D24
D20
D21
D15, D16
D23, D24
D3
Schematic Signal Name
JTAG_RX, JTAG_TX
SC_RX, SC_TX
ENETA_LED_TX
ENETA_LED_RX
ENETA_LED_LINK10
ENETA_LED_LINK100
ENETA_LED_LINK1000
ENETB_LED_TX
ENETB_LED_RX
ENETB_LED_LINK10
ENETB_LED_LINK100
ENETB_LED_LINK1000
USB_UART_TX_TOGGLE,
USB_UART_RX_TOGGLE
UART_RXD_LED,
UART_TXD_LED
HSMA_PRSNTn
I/O
Standard
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
2.5-V
3.3-V
Description
Green LEDs. Illuminates to indicate USB-Blaster II receive and
transmit activities.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet PHY transmit activity.
Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet PHY receive activity.
Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet linked at 10 Mbps
connection speed. Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet linked at 100 Mbps
connection speed. Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet linked at 1000 Mbps
connection speed. Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet PHY B transmit activity.
Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet PHY B receive activity.
Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet B linked at 10 Mbps
connection speed. Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet B linked at 100 Mbps
connection speed. Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet B linked at 1000 Mbps
connection speed. Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate USB_UART receive and transmit
activities.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate UART receive and transmit
activities.
Green LED. Illuminates when HSMC port has a board or cable
plugged-in such that pin 160 becomes grounded. Driven by the
add-in card.
Setup Elements
The development board includes several different kinds of setup elements. This
section describes the following setup elements:
■ Board settings DIP switch
■ JTAG settings DIP switch
■ CPU reset push button
■ MAX V reset push button
■ Program configuration push button
■ Program select push button
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 25

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–17
Setup Elements
f For more information about the default settings of the DIP switches, refer to the
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Kit User Guide.
Board Settings DIP Switch
The board settings DIP switch (SW4) controls various features specific to the board
and the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller logic design. Tab le 2 –8 lists the
switch controls and descriptions.
Table 2–8. Board Settings DIP Switch Controls
Switch Schematic Signal Name Description
CLK_SEL
1
2
CLK_ENABLE
3
FACTORY_LOAD
SECURITY_MODE
4
ON : Select programmable oscillator clock
OFF : Select SMA input clock
ON : Disable on-board oscillator
OFF : Enable on-board oscillator
ON : Load the user design from flash at power up
OFF : Load the factory design from flash at power up
ON : Embedded USB-Blaster II sends FACTORY command at
power up.
OFF : Embedded USB-Blaster II does not send FACTORY
command at power up.
JTAG Chain Control DIP Switch
The JTAG chain control DIP switch (SW2) either removes or includes devices in the
active JTAG chain. The Cyclone V E FPGA is always in the JTAG chain. Ta bl e 2– 9 lists
the switch controls and its descriptions.
Table 2–9. JTAG Chain Control DIP Switch
Switch Schematic Signal Name Description
5M2210_JTAG_EN
1
2
HSMC_JTAG_EN
3
FAN_FORCE_ON
4
RESERVED
CPU Reset Push Button
The CPU reset push button,
DEV_CLRn
This push button is the default reset for both the FPGA and CPLD logic. The MAX V
CPLD 5M2210 System Controller also drives this push button during power-on-reset
(POR).
pin and is an open-drain I/O from the MAX V CPLD System Controller.
ON : Bypass MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller
OFF : MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller in-chain
ON : Bypass HSMC port
OFF : HSMC port in-chain
ON : Enable fan
OFF : Disable fan
Reserved
CPU_RESETn
(S4), is an input to the Cyclone V E FPGA
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 26

2–18 Chapter 2: Board Components
Clock Circuitry
MAX V Reset Push Button
The MAX V reset push button,
5M2210 System Controller. This push button is the default reset for the CPLD logic.
Program Configuration Push Button
The program configuration push button,
CPLD 5M2210 System Controller. This input forces a FPGA reconfiguration from the
flash memory. The location in the flash memory is based on the settings of
PGM_LED[2:0]
settings include
reserved for FPGA designs.
Program Select Push Button
The program select push button,
5M2210 System Controller. This push button toggles the
selects which location in the flash memory is used to configure the FPGA. Refer to
Tab le 2– 6 for the
Clock Circuitry
This section describes the board's clock inputs and outputs.
MAX_RESETn
, which is controlled by the program select push button,
PGM_LED0, PGM_LED1
PGM_SEL
PGM_LED[2:0]
sequence definitions.
(S3), is an input to the MAX V CPLD
PGM_CONFIG
, or
PGM_LED2
(S2), is an input to the MAX V CPLD
(S1), is an input to the MAX V
on the three pages in flash memory
PGM_LED[2:0]
PGM_SEL
sequence that
. Valid
On-Board Oscillators
The development board include oscillators with a frequency of 50-MHz, 100-MHz,
and a programmable oscillator.
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 27

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–19
FA-128
24.0000 MB-W
24 MHz
Crystal
Cypress
CY7C68013A
USB Microcontroller
MAX II
Embedded
USB-Blaster
Si510
SE 50 MHz
Fixed Oscillator
SL18860DC
Clock Fanout
X4 SE 50 MHz
Ch3
Ch2
Ch1
CLK_USB
48 MHz
SG-310DF
25.0000M-B3
25 MHz
Fixed Oscillator
10/100/1000
Base-T
Ethernet PHY
88E1111
Bank 8A Bank 7A
Bank 3A
Bank 3B Bank 4A
Bank 5A Bank 5B Bank 6A
Transceiver Block
SMA Clock Out
Two Channels
Unused
Top Bank
Bottom Bank
SMA LVDS
Clock Input
Si570 LVDS
Clock Output
125 MHz
Programmable
LV D S
HSMC
Differential
Clock In x 2
HSMC SE
Clock In
MAX V CPLD 5M2210
System Controller
SI510 SE 100 MHz
Fixed Oscillator
ICS8543
Clock
Fanout
Clock Circuitry
Figure 2–6 shows the default frequencies of all external clocks going to the
Cyclone V E FPGA development board.
Figure 2–6. Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board Clocks
development board.
Tab le 2– 10 lists the oscillators, its I/O standard, and voltages required for the
Table 2–10. On-Board Oscillators
Source Schematic Signal Name Frequency I/O Standard
U4
X3
X1 and U3
(buffer)
CLKIN_50_FPGA_TOP
CLKIN_50_FPGA_RIGHT
CLK_CONFIG
DIFF_CLKIN_TOP_125_P
DIFF_CLKIN_TOP_125_N
DIFF_CLKIN_BOT_125_P
50.000 MHz Single-Ended
100.000 MHz 2.5V CMOS — Fast FPGA configuration
125.000 MHz LVDS
DIFF_CLKIN_BOT_125_N
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin Number
L14
P22
L15
K15
AB17
AB18
Application
Top and right edge
Top and bottom edge
Reference Manual
Page 28

2–20 Chapter 2: Board Components
General User Input/Output
Off-Board Clock Input/Output
The development board has input and output clocks which can be driven onto the
board. The output clocks can be programmed to different levels and I/O standards
according to the FPGA device’s specification.
Tab le 2– 11 lists the clock inputs for the development board.
Table 2–11. Off-Board Clock Inputs
Source
SMA
Samtec HSMC
Samtec HSMC
Samtec HSMC
Schematic Signal
Name
CLKIN_SMA_P
CLKIN_SMA_N
HSMA_CLK_IN0
HSMA_CLK_IN_P1
HSMA_CLK_IN_N1
HSMA_CLK_IN_P2
HSMA_CLK_IN_N2
Tab le 2– 12 lists the clock outputs for the development board.
Table 2–12. Off-Board Clock Outputs
Source
Samtec HSMC
Samtec HSMC
Samtec HSMC
SMA
Schematic Signal
Name
HSMA_CLK_OUT0
HSMA_CLK_OUT_P1
HSMA_CLK_OUT_N1
HSMA_CLK_OUT_P2
HSMA_CLK_OUT_N2
CLKOUT_SMA
Cyclone V E
I/O Standard
LVDS —
LVDS —
2.5-V AB16
LVDS/2.5-V AB14
LVDS/LVTTL AC14
LVDS/LVTTL Y15
LVDS/LVTTL AA15
I/O Standard
2.5V CMOS AJ14 FPGA CMOS output (or GPIO)
LVDS/2.5V CMOS AE22
LVDS/2.5V CMOS AF23
LVDS/2.5V CMOS AG23
LVDS/2.5V CMOS AH22
2.5V CMOS F9 FPGA CMOS output (or GPIO)
FPGA Pin
Number
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin
Number
Description
Input to LVDS fan-out buffer.
Single-ended input from the installed HSMC cable
or board.
LVDS input from the installed HSMC cable or
board. Can also support 2x LVTTL inputs.
LVDS input from the installed HSMC cable or
board. Can also support 2x LVTTL inputs.
Description
LVDS output. Can also support 2x CMOS
outputs.
LVDS output. Can also support 2x CMOS
outputs.
General User Input/Output
This section describes the user I/O interface to the FPGA, including the push buttons,
DIP switches, LEDs, and character LCD.
User-Defined Push Buttons
The development board includes three user-defined push buttons. For information on
the system and safe reset push buttons, refer to “Setup Elements” on page 2–16.
Board references S5, S6, S7, and S8 are push buttons for controlling the FPGA designs
that loads into the Cyclone V E FPGA device. When you press and hold down the
switch, the device pin is set to logic 0; when you release the switch, the device pin is
set to logic 1. There are no board-specific functions for these general user push
buttons.
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 29

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–21
General User Input/Output
Tab le 2– 13 lists the user-defined push button schematic signal names and their
corresponding Cyclone V E FPGA pin numbers.
Table 2–13. User-Defined Push Button Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board Reference Schematic Signal Name
S5
S6
S7
S8
USER_PB0
USER_PB1
USER_PB2
USER_PB3
User-Defined DIP Switch
Board reference SW3 is a four-pin DIP switch. This switch is user-defined and
provides additional FPGA input control. When the switch is in the OFF position, a
logic 1 is selected. When the switch is in the ON position, a logic 0 is selected. There
are no board-specific functions for this switch.
Tab le 2– 14 lists the user-defined DIP switch schematic signal names and their
corresponding Cyclone V E FPGA pin numbers.
Table 2–14. User-Defined DIP Switch Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board Reference Schematic Signal Name
1
2
3
4
USER_DIPSW0
USER_DIPSW1
USER_DIPSW2
USER_DIPSW3
Cyclone V E FPGA Pin
Number
AB12 2.5-V
AB13 2.5-V
AF13 2.5-V
AG12 2.5-V
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
Y12 2.5-V
AA13 2.5-V
AF11 2.5-V
AG11 2.5-V
I/O Standard
I/O Standard
User-Defined LEDs
The development board includes general and HSMC user-defined LEDs. This section
describes all user-defined LEDs. For information on board specific or status LEDs,
refer to “Status Elements” on page 2–15.
General LEDs
Board references D28 through D31 are four user-defined LEDs. The status and
debugging signals are driven to the LEDs from the designs loaded into the
Cyclone V E FPGA. Driving a logic 0 on the I/O port turns the LED on while driving a
logic 1 turns the LED off. There are no board-specific functions for these LEDs.
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 30

2–22 Chapter 2: Board Components
General User Input/Output
Tab le 2– 15 lists the general LED schematic signal names and their corresponding
Cyclone V E FPGA pin numbers.
Table 2–15. General LED Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board Reference Schematic Signal Name
D28
D29
D30
D31
USER_LED0
USER_LED1
USER_LED2
USER_LED3
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
AK3 2.5-V
AJ4 2.5-V
AJ5 2.5-V
AK6 2.5-V
I/O Standard
HSMC LEDs
Board references D20 and D21 are LEDs for the HSMC port. There are no boardspecific functions for the HSMC LEDs. The LEDs are labeled TX and RX, and are
intended to display data flow to and from the connected daughtercards. The LEDs are
driven by the Cyclone V E FPGA device.
Tab le 2– 16 lists the HSMC LED schematic signal names and their corresponding
Cyclone V E FPGA pin numbers.
Table 2–16. HSMC LED Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board Reference Schematic Signal Name
D1
D2
HSMC_RX_LED
HSMC_TX_LED
Cyclone V E FPGA Pin
Number
AH12 2.5-V
AH11 2.5-V
I/O Standard
Character LCD
The development board includes a single 14-pin 0.1" pitch dual-row header that
interfaces to a 2 line × 16 character Lumex character LCD. The character LCD has a
14-pin receptacle that mounts directly to the board's 14-pin header, so it can be easily
removed for access to components under the display. You can also use the header for
debugging or other purposes.
Tab le 2– 17 summarizes the character LCD pin assignments. The signal names and
directions are relative to the Cyclone V E FPGA device.
Table 2–17. Character LCD Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions
Board
Reference (J14)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Schematic Signal Name
LCD_DATA0
LCD_DATA1
LCD_DATA2
LCD_DATA3
LCD_DATA4
LCD_DATA5
LCD_DATA6
LCD_DATA7
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
AJ7 2.5-V LCD data bus
AK7 2.5-V LCD data bus
AJ8 2.5-V LCD data bus
AK8 2.5-V LCD data bus
AF9 2.5-V LCD data bus
AG9 2.5-V LCD data bus
AH9 2.5-V LCD data bus
AJ9 2.5-V LCD data bus
I/O Standard Description
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 31

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–23
General User Input/Output
Table 2–17. Character LCD Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions
Board
Reference (J14)
4
5
6
Schematic Signal Name
LCD_D_Cn
LCD_WEn
LCD_CSn
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
AK11 2.5-V LCD data or command select
AK10 2.5-V LCD write enable
AJ12 2.5-V LCD chip select
Tab le 2– 18 lists the LCD pin definitions, and is an excerpt from Lumex data sheet.
Table 2–18. LCD Pin Definitions and Functions
Pin
Number
1V
2V
3V
Symbol Level Function
DD
SS
0
—
—GND (0 V)
Power supply
— For LCD drive
5 V
Register select signal
4RS H/L
H: Data input
L: Instruction input
5R/W H/L
H: Data read (module to MPU)
L: Data write (MPU to module)
6 E H, H to L Enable
7–14 DB0–DB7 H/L Data bus—software selectable 4-bit or 8-bit mode
f For more information such as timing, character maps, interface guidelines, and other
related documentation, visit www.lumex.com.
Debug Header
This development board includes two 2×8 debug headers for debug purposes. The
FPGA I/Os route directly to the header for design testing, debugging, or quick
verification.
Tab le 2– 19 summarizes the debug header pin assignments, signal names, and
functions.
Table 2–19. Debug Header Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 1 of 2)
Board
Reference
Debug Header (J15)
1
5
9
13
4
8
12
Schematic Signal
Name
HEADER_D0
HEADER_D1
HEADER_D2
HEADER_D3
HEADER_D4
HEADER_D5
HEADER_D6
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
I/O
Standard
Description
H21 1.5-V Single-ended signal for debug purposes only
G21 1.5-V Single-ended signal for debug purposes only
G22 1.5-V Single-ended signal for debug purposes only
E26 1.5-V Single-ended signal for debug purposes only
E25 1.5-V Single-ended signal for debug purposes only
C27 1.5-V Single-ended signal for debug purposes only
C26 1.5-V Single-ended signal for debug purposes only
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 32

2–24 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Interfaces
Table 2–19. Debug Header Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 2 of 2)
Board
Reference
16
Debug Header (J16)
1 and 2
3 and 4
7 and 8
9 and 10
13 and 14
15 and 16
Schematic Signal
Name
HEADER_D7
HEADER_P0 and
HEADER_N0
HEADER_P1 and
HEADER_N1
HEADER_P2 and
HEADER_N2
HEADER_P3 and
HEADER_N3
HEADER_P4 and
HEADER_N4
HEADER_P5 and
HEADER_N5
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
B27 1.5-V Single-ended signal for debug purposes only
H25 and H26 2.5-V Pseudo-differential signals for debug purposes only
P20 and N20 2.5-V Pseudo-differential signals for debug purposes only
J22 and J23 2.5-V Pseudo-differential signals for debug purposes only
D28 and D29 2.5-V Pseudo-differential signals for debug purposes only
E27 and D27 2.5-V Pseudo-differential signals for debug purposes only
H24 and J25 2.5-V Pseudo-differential signals for debug purposes only
Components and Interfaces
This section describes the development board's communication ports and interface
cards relative to the Cyclone V E FPGA device. The development board supports the
following communication ports:
I/O
Standard
Description
■ RS-232 Serial UART
■ 10/100/1000 Ethernet
■ HSMC
■ USB UART
10/100/1000 Ethernet
The development board supports two 10/100/1000 base-T Ethernet using two
external Marvell 88E1111 PHY and Altera Triple-Speed Ethernet MegaCore MAC
function. The PHY-to-MAC interfaces employ RGMII interface. The MAC function
must be provided in the FPGA for typical networking applications.
The Marvell 88E1111 PHY uses 2.5-V and 1.0-V power rails and requires a 25-MHz
reference clock driven from a dedicated oscillator. The PHY interfaces to a RJ45 model
with internal magnetics that can be used for driving copper lines with Ethernet traffic.
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 33

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–25
10/100/1000 Mbps
Ethernet MAC
Marvell 88E1111
PHY
Device
Transformer
RJ45
RGMII Interface
TXD[3:0]
RXD[3:0]
CAT 5 UTP:
- 10BASE-T
- 100BASE-TX
- 1000BASE-T
Components and Interfaces
Figure 2–7 shows the RGMII interface between the FPGA (MAC) and Marvell 88E1111
PHY.
Figure 2–7. RGMII Interface between FPGA (MAC) and Marvell 88E1111 PHY
Tab le 2– 20 lists the Ethernet PHY interface pin assignments.
Table 2–20. Ethernet PHY Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions (Part 1 of 3)
Board
Reference
Schematic Signal Name
Ethernet PHY A (U14)
8
23
60
70
76
74
73
58
69
68
25
24
28
2
95
92
93
91
94
11
12
14
16
9
55
29
31
ENETA_GTX_CLK
ENETA_INTN
ENETA_LED_DUPLEX
ENETA_LED_DUPLEX
ENETA_LED_LINK10
ENETA_LED_LINK100
ENETA_LED_LINK1000
ENETA_LED_RX
ENETA_LED_RX
ENETA_LED_TX
ENETA_MDC
ENETA_MDIO
ENETA_RESETN
ENETA_RX_CLK
ENETA_RX_D0
ENETA_RX_D1
ENETA_RX_D2
ENETA_RX_D3
ENETA_RX_DV
ENETA_TX_D0
ENETA_TX_D1
ENETA_TX_D2
ENETA_TX_D3
ENETA_TX_EN
ENETA_XTAL_25MHZ
ENETA_MDI_P0
ENETA_MDI_N0
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
H27 2.5-V CMOS 125-MHz RGMII transmit clock
J27 2.5-V CMOS Management bus interrupt
— 2.5-V CMOS Duplex or collision LED. Not used
— 2.5-V CMOS Duplex or collision LED. Not used
— 2.5-V CMOS 10-Mb link LED
— 2.5-V CMOS 100-Mb link LED
— 2.5-V CMOS 1000-Mb link LED
— 2.5-V CMOS RX data active LED
— 2.5-V CMOS RX data active LED
— 2.5-V CMOS TX data active LED
G29 2.5-V CMOS Management bus data clock
L25 2.5-V CMOS Management bus data
N22 2.5-V CMOS Device reset
T23 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive clock
N26 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data bus
N27 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data bus
N24 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data bus
N25 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data bus
L25 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data valid
J28 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit data bus
J29 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit data bus
H29 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit data bus
H30 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit data bus
F30 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit enable
— 2.5-V CMOS 25-MHz RGMII transmit clock
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 34

2–26 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Interfaces
Table 2–20. Ethernet PHY Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions (Part 2 of 3)
Board
Reference
33
34
39
41
42
43
Schematic Signal Name
ENETA_MDI_P1
ENETA_MDI_N1
ENETA_MDI_P2
ENETA_MDI_N2
ENETA_MDI_P3
ENETA_MDI_N3
Ethernet PHY B (U11)
8
23
60
70
76
74
73
58
69
68
25
24
28
2
95
92
93
91
94
11
12
14
16
9
55
29
31
33
34
39
41
ENETB_GTX_CLK
ENETB_INTN
ENETB_LED_DUPLEX
ENETB_LED_DUPLEX
ENETB_LED_LINK10
ENETB_LED_LINK100
ENETB_LED_LINK1000
ENETB_LED_RX
ENETB_LED_RX
ENETB_LED_TX
ENETB_MDC
ENETB_MDIO
ENETB_RESETN
ENETB_RX_CLK
ENETB_RX_D0
ENETB_RX_D1
ENETB_RX_D2
ENETB_RX_D3
ENETB_RX_DV
ENETB_TX_D0
ENETB_TX_D1
ENETB_TX_D2
ENETB_TX_D3
ENETB_TX_EN
ENETB_XTAL_25MHZ
ENETB_MDI_P0
ENETB_MDI_N0
ENETB_MDI_P1
ENETB_MDI_N1
ENETB_MDI_P2
ENETB_MDI_N2
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
E28 2.5-V CMOS 125-MHz RGMII transmit clock
K22 2.5-V CMOS Management bus interrupt
— 2.5-V CMOS Duplex or collision LED. Not used
— 2.5-V CMOS Duplex or collision LED. Not used
— 2.5-V CMOS 10-Mb link LED
— 2.5-V CMOS 100-Mb link LED
— 2.5-V CMOS 1000-Mb link LED
— 2.5-V CMOS RX data active LED
— 2.5-V CMOS RX data active LED
— 2.5-V CMOS TX data active LED
A29 2.5-V CMOS Management bus data clock
L23 2.5-V CMOS Management bus data
M21 2.5-V CMOS Device reset
R23 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive clock
F25 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data bus
F26 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data bus
R20 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data bus
T21 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data bus
L24 2.5-V CMOS RGMII receive data valid
F29 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit data bus
D30 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit data bus
C30 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit data bus
F28 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit data bus
B29 2.5-V CMOS RGMII transmit enable
— 2.5-V CMOS 25-MHz RGMII transmit clock
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 35

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–27
Bank 3
Powe r
D(79.40)
-or-
LVDS
CLKIN2, CLKOUT2
Bank 2
Powe r
D(39:0)
-or-
D[3:0] + LVDS
CLKIN1, CLKOUT1
Bank 1
8 TX Channels CDR
8 RX Channels CDR
JTAG
SMB
CLKIN0, CLKOUT0
Components and Interfaces
Table 2–20. Ethernet PHY Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions (Part 3 of 3)
Board
Reference
42
43
HSMC
Schematic Signal Name
ENETB_MDI_P3
ENETB_MDI_N3
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
— 2.5-V CMOS Media dependent interface
The development board supports a HSMC interface. The HSMC interface supports a
full SPI4.2 interface (17 LVDS channels), three input and output clocks, as well as
JTAG and SMB signals. The LVDS channels can be used for CMOS signaling or LVDS.
1 The HSMC is an Altera-developed open specification, which allows you to expand
the functionality of the development board through the addition of daughtercards
(HSMCs).
f For more information about the HSMC specification such as signaling standards,
signal integrity, compatible connectors, and mechanical information, refer to the High
Speed Mezzanine Card (HSMC) Specification manual.
The HSMC connector has a total of 172 pins, including 120 signal pins, 39 power pins,
and 13 ground pins. The ground pins are located between the two rows of signal and
power pins, acting both as a shield and a reference. The HSMC host connector is
based on the 0.5 mm-pitch QSH/QTH family of high-speed, board-to-board
connectors from Samtec. There are three banks in this connector. Bank 1 has every
third pin removed as done in the QSH-DP/QTH-DP series. Bank 2 and bank 3 have
all the pins populated as done in the QSH/QTH series. Since the Cyclone V E FPGA
development board is not a transceiver board, the transceiver pins of the HSMC is not
connected to the Cyclone V E FPGA device.
Figure 2–8 shows the bank arrangement of signals with respect to the Samtec
connector's three banks.
Figure 2–8. HSMC Signal and Bank Diagram
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 36

2–28 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Interfaces
The HSMC interface has programmable bi-directional I/O pins that can be used as
2.5-V LVCMOS, which is 3.3-V LVTTL-compatible. These pins can also be used as
various differential I/O standards including, but not limited to, LVDS, mini-LVDS,
and RSDS with up to 17 full-duplex channels.
1 As noted in the High Speed Mezzanine Card (HSMC) Specification manual, LVDS and
single-ended I/O standards are only guaranteed to function when mixed according to
either the generic single-ended pin-out or generic differential pin-out.
Tab le 2– 21 lists the HSMC interface pin assignments, signal names, and functions.
Table 2–21. HSMC Interface Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 1 of 3)
Board
Reference (J7)
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
47
48
49
50
53
54
55
56
59
60
61
62
65
66
67
68
71
Schematic Signal Name
HSMC_SDA
HSMC_SCL
JTAG_TCK
HSMC_JTAG_TMS
HSMC_JTAG_TDO
JTAC_FPGA_TDO_RETIMER
HSMC_CLK_OUT0
HSMC_CLK_IN0
HSMC_D0
HSMC_D1
HSMC_D2
HSMC_D3
HSMC_TX_D_P0
HSMC_RX_D_P0
HSMC_TX_D_N0
HSMC_RX_D_N0
HSMC_TX_D_P1
HSMC_RX_D_P1
HSMC_TX_D_N1
HSMC_RX_D_N1
HSMC_TX_D_P2
HSMC_RX_D_P2
HSMC_TX_D_N2
HSMC_RX_D_N2
HSMC_TX_D_P3
HSMC_RX_D_P3
HSMC_TX_D_N3
HSMC_RX_D_N3
HSMC_TX_D_P4
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin
I/O Standard Description
Number
AB22 2.5-V CMOS Management serial data
AC22 2.5-V CMOS Management serial clock
AC7 2.5-V CMOS JTAG clock signal
— 2.5-V CMOS JTAG mode select signal
— 2.5-V CMOS JTAG data output
— 2.5-V CMOS JTAG data input
AJ14 2.5-V CMOS Dedicated CMOS clock out
AB16 2.5-V CMOS Dedicated CMOS clock in
AH10 2.5-V CMOS Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 0
AJ10 2.5-V CMOS Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 1
Y13 2.5-V CMOS Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 2
AA14 2.5-V CMOS Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 3
AK27 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 0 or CMOS bit 4
Y16 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 0 or CMOS bit 5
AK28 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 0n or CMOS bit 6
AA26 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 0n or CMOS bit 7
AJ27 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 1 or CMOS bit 8
Y17 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 1 or CMOS bit 9
AK26 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 1n or CMOS bit 10
Y18 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 1n or CMOS bit 11
AG26 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 2 or CMOS bit 12
AA18 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 2 or CMOS bit 13
AH26 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 2n or CMOS bit 14
AA19 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 2n or CMOS bit 15
AJ25 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 3 or CMOS bit 16
Y20 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 3 or CMOS bit 17
AK25 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 3n or CMOS bit 18
AA20 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 3n or CMOS bit 19
AH24 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 4 or CMOS bit 20
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 37

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–29
Components and Interfaces
Table 2–21. HSMC Interface Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 2 of 3)
Board
Reference (J7)
72
73
74
77
78
79
80
83
84
85
86
89
90
91
92
95
96
97
98
101
102
103
104
107
108
109
110
113
114
115
116
119
120
121
122
125
126
127
Schematic Signal Name
HSMC_RX_D_P4
HSMC_TX_D_N4
HSMC_RX_D_N4
HSMC_TX_D_P5
HSMC_RX_D_P5
HSMC_TX_D_N5
HSMC_RX_D_N5
HSMC_TX_D_P6
HSMC_RX_D_P6
HSMC_TX_D_N6
HSMC_RX_D_N6
HSMC_TX_D_P7
HSMC_RX_D_P7
HSMC_TX_D_N7
HSMC_RX_D_N7
HSMC_CLK_OUT_P1
HSMC_CLK_IN_P1
HSMC_CLK_OUT_N1
HSMC_CLK_IN_N1
HSMC_TX_D_P8
HSMC_RX_D_P8
HSMC_TX_D_N8
HSMC_RX_D_N8
HSMC_TX_D_P9
HSMC_RX_D_P9
HSMC_TX_D_N9
HSMC_RX_D_N9
HSMC_TX_D_P10
HSMC_RX_D_P10
HSMC_TX_D_N10
HSMC_RX_D_N10
HSMC_TX_D_P11
HSMC_RX_D_P11
HSMC_TX_D_N11
HSMC_RX_D_N11
HSMC_TX_D_P12
HSMC_RX_D_P12
HSMC_TX_D_N12
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin
I/O Standard Description
Number
AA21 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 4 or CMOS bit 21
AJ24 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 4n or CMOS bit 22
AB21 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 4n or CMOS bit 23
AH21 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 5 or CMOS bit 24
AB19 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 5 or CMOS bit 25
AJ22 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 5n or CMOS bit 26
AC19 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 5n or CMOS bit 27
AJ23 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 6 or CMOS bit 28
AC21 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 6 or CMOS bit 29
AK23 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 6n or CMOS bit 30
AD20 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 6n or CMOS bit 31
AK21 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 7 or CMOS bit 32
AD19 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 7 or CMOS bit 33
AK22 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 7n or CMOS bit 34
AE20 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 7n or CMOS bit 35
AE22 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS or CMOS clock out 1 or CMOS bit 36
AB14 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS or CMOS clock in 1 or CMOS bit 37
AF23 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS or CMOS clock out 1 or CMOS bit 38
AC14 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS or CMOS clock in 1 or CMOS bit 39
AJ20 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 8 or CMOS bit 40
AF21 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 8 or CMOS bit 41
AK20 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 8n or CMOS bit 42
AG22 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 8n or CMOS bit 43
AJ19 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 9 or CMOS bit 44
AF20 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 9 or CMOS bit 45
AK18 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 9n or CMOS bit 46
AG21 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 9n or CMOS bit 47
AJ17 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 10 or CMOS bit 48
AF18 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 10 or CMOS bit 49
AJ18 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 10n or CMOS bit 50
AF19 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 10n or CMOS bit 51
AK25 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 11 or CMOS bit 52
AG18 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 11 or CMOS bit 53
AG24 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 11n or CMOS bit 54
AG19 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 11n or CMOS bit 55
AH19 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 12 or CMOS bit 56
AK16 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 12 or CMOS bit 57
AH20 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 12n or CMOS bit 58
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 38

2–30 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Interfaces
Table 2–21. HSMC Interface Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 3 of 3)
Board
Reference (J7)
128
131
132
133
134
137
138
139
140
143
144
145
146
149
150
151
152
155
156
157
158
160
Schematic Signal Name
HSMC_RX_D_N12
HSMC_TX_D_P13
HSMC_RX_D_P13
HSMC_TX_D_N13
HSMC_RX_D_N13
HSMC_TX_D_P14
HSMC_RX_D_P14
HSMC_TX_D_N14
HSMC_RX_D_N14
HSMC_TX_D_P15
HSMC_RX_D_P15
HSMC_TX_D_N15
HSMC_RX_D_N15
HSMC_TX_D_P16
HSMC_RX_D_P16
HSMC_TX_D_N16
HSMC_RX_D_N16
HSMC_CLK_OUT_P2
HSMC_CLK_IN_P2
HSMC_CLK_OUT_N2
HSMC_CLK_IN_N2
HSMC_PRSNTn
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin
Number
AK17 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 12n or CMOS bit 59
AG17 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 13 or CMOS bit 60
AF16 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 13 or CMOS bit 61
AH17 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 13n or CMOS bit 62
AG16 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 13n or CMOS bit 63
AJ15 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 14 or CMOS bit 64
AE16 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 14 or CMOS bit 65
AK15 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 14n or CMOS bit 66
AF15 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 14n or CMOS bit 67
AH14 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 15 or CMOS bit 68
AD17 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 15 or CMOS bit 69
AH15 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 15n or CMOS bit 70
AE17 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 15n or CMOS bit 71
AE15 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 16 or CMOS bit 72
AD18 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 16 or CMOS bit 73
AF14 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS TX bit 16n or CMOS bit 74
AE18 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS RX bit 16n or CMOS bit 75
AG23 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS or CMOS clock out 2 or CMOS bit 76
Y15 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS or CMOS clock in 2 or CMOS bit 77
AH22 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS or CMOS clock out 2 or CMOS bit 78
AA15 LVDS or 2.5-V LVDS or CMOS clock in 2 or CMOS bit 79
AK5 2.5-V CMOS HSMC port presence detect
I/O Standard Description
RS-232 Serial UART
A female angled DSUB 9-pin connector along with a supporting RS-232 transceiver
provides support for implementing a standard RS-232 serial UART channel on this
board. The connector has the same pinouts as a data terminal device and requires only
a standard cable (no null modem required for PC interface). A dedicated level-shifting
buffer is used to translate between LVTTL and RS-232 levels. Board references D23
and D24 are serial UART LEDs that illuminate to indicate RX and TX activity.
Tab le 2– 24 lists the RS-232 serial UART pin assignments, signal names, and functions.
The signal names and types are relative to the Cyclone V E FPGA in terms of I/O
setting and direction.
Table 2–22. RS-232 Serial UART Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board
Reference (U20)
14
15
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Schematic
Signal Name
UART_TXD
UART_RTS
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
AB9 3.3-V Transmit data
AH6 3.3-V Request to send
I/O Standard Description
Page 39

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–31
Components and Interfaces
Table 2–22. RS-232 Serial UART Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board
Reference (U20)
16
13
Schematic
Signal Name
UART_RXD
UART_CTS
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
AG6 3.3-V Receive data
AF8 3.3-V Clear to send
USB-UART
The development board supports UART interface through a USB connector using
Silicon Labs CP2104 USB-to-UART bridge. To facilitate host communication with
CP2104, you are required to use the USB-to-UART bridge Virtual COM Port (VCP)
drivers.
f The VCP drivers are available at:
www.silabs.com/products/mcu/Pages/USBtoUARTBridgeVCPDrivers.aspx
Tab le 2– 23 lists the USB-UART pin assignments, signal names, and functions. The
signal names and types are relative to the Cyclone V E FPGA in terms of I/O setting
and direction.
Table 2–23. USB-UART Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board
Reference (U20)
1
24
22
21
19
12
23
20
18
15
17
9
Schematic
Signal Name
USB_UART_RI
USB_UART_DCD
USB_UART_DSR
USB_UART_RXD
USB_UART_RTS
USB_UART_GPIO2
USB_UART_DTR
USB_UART_TXD
USB_UART_CTS
USB_UART_SUSPENDn
USB_UART_SUSPEND
USB_UART_RSTn
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
AD12 2.5-V Ring indicator control input (active low)
AD13 2.5-V
V12 2.5-V Data set ready control input (active low)
AF10 2.5-V Asynchronous data input (UART receive)
AE12 2.5-V Ready to send control output (active low)
AE13 2.5-V User-configurable input or output.
AE10 2.5-V
W12 2.5-V Asynchronous data output (UART transmit)
AJ1 2.5-V Clear to send control input (active low)
—2.5-V
—2.5-V
— 2.5-V Device reset
I/O Standard Description
I/O Standard Description
Data carrier detect control input (active
low)
Data terminal ready control output (active
low)
Pin is logic low when the CP2104 is in the
USB suspend state.
Pin is logic high when the CP2104 is in the
USB suspend state.
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 40

2–32 Chapter 2: Board Components
Memory
Memory
This section describes the development board’s memory interface support and also
their signal names, types, and connectivity relative to the Cyclone V E FPGA. The
development board has the following memory interfaces:
■ DDR3 SDRAM
■ LPDDR2 SDRAM
■ EEPROM
■ Synchronous SRAM
■ Synchronous flash
f For more information about the memory interfaces, refer to the following documents:
■ Timing Analysis section in the External Memory Interface Handbook.
■ DDR, DDR2, and DDR3 SDRAM Design Tutorials section in the External Memory
Interface Handbook.
DDR3 SDRAM
The development board supports two 16Mx16x8 and two 16Mx8x8 DDR3 SDRAM
interfaces for very high-speed sequential memory access.
The 32-bit data bus comprises of two x16 devices using soft memory controller (SMC)
interface. With SMC, this memory interface runs at a target frequency of 300 MHz for
a maximum theoretical bandwidth of over 9.6 Gbps. The maximum frequency for this
DDR3 device is 800 MHz with a CAS latency of 11.
Tab le 2– 24 lists the DDR3 pin assignments, signal names, and functions. The signal
names and types are relative to the Cyclone V E FPGA in terms of I/O setting and
direction.
Table 2–24. DDR3 Device Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 1 of 4)
Board
Reference
DDR3 x16 (U8)
N3
P7
P3
N2
P8
P2
R8
R2
T8
R3
L7
Schematic
Signal Name
DDR3_A0
DDR3_A1
DDR3_A2
DDR3_A3
DDR3_A4
DDR3_A5
DDR3_A6
DDR3_A7
DDR3_A8
DDR3_A9
DDR3_A10
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
A16 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
G23 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
E21 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
E22 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
A20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
A26 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
A15 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
B26 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
H17 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
D14 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
E23 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 41

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–33
Memory
Table 2–24. DDR3 Device Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 2 of 4)
Board
Reference
R7
N7
T3
M2
N8
M3
K3
K9
J7
K7
L2
E7
D3
E3
H8
F7
H7
F2
G2
F8
H3
A7
C3
A3
D7
A2
C2
B8
C8
F3
G3
C7
B7
K1
Schematic
Signal Name
DDR3_A11
DDR3_A12
DDR3_A13
DDR3_BA0
DDR3_BA1
DDR3_BA2
DDR3_CASN
DDR3_CKE
DDR3_CLK_P
DDR3_CLK_N
DDR3_CSN
DDR3_DM0
DDR3_DM1
DDR3_DQ0
DDR3_DQ1
DDR3_DQ2
DDR3_DQ3
DDR3_DQ4
DDR3_DQ5
DDR3_DQ6
DDR3_DQ7
DDR3_DQ8
DDR3_DQ9
DDR3_DQ10
DDR3_DQ11
DDR3_DQ12
DDR3_DQ13
DDR3_DQ14
DDR3_DQ15
DDR3_DQS_P0
DDR3_DQS_N0
DDR3_DQS_P1
DDR3_DQS_N1
DDR3_ODT
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
E20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
C25 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
B13 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
J18 1.5-V SSTL Class I Bank address bus
F20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Bank address bus
D19 1.5-V SSTL Class I Bank address bus
L20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Row address select
C11 1.5-V SSTL Class I Column address select
J20
H20
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Differential output clock
Differential output clock
G17 1.5-V SSTL Class I Chip select
D23 1.5-V SSTL Class I Write mask byte lane
D18 1.5-V SSTL Class I Write mask byte lane
A25 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 0
D22 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 0
C21 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 0
C19 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 0
C20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 0
C22 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 0
D25 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 0
D20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 0
B24 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 1
A21 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 1
B21 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 1
F19 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 1
C24 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 1
B23 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 1
E18 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 1
A23 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 1
K20
J19
L18
K18
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Data strobe P byte lane 0
Data strobe N byte lane 0
Data strobe P byte lane 1
Data strobe N byte lane 1
H19 1.5-V SSTL Class I On-die termination enable
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 42

2–34 Chapter 2: Board Components
Memory
Table 2–24. DDR3 Device Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 3 of 4)
Board
Reference
J3
T2
L3
L8
DDR3 x16 (U7)
N3
P7
P3
N2
P8
P2
R8
R2
T8
R3
L7
R7
N7
T3
M2
N8
M3
K3
K9
K7
J7
L2
E7
D3
F2
F8
E3
F7
H3
G2
H7
H8
A2
Schematic
Signal Name
DDR3_RASN
DDR3_RESETN
DDR3_WEN
DDR3_ZQ01
DDR3_A0
DDR3_A1
DDR3_A2
DDR3_A3
DDR3_A4
DDR3_A5
DDR3_A6
DDR3_A7
DDR3_A8
DDR3_A9
DDR3_A10
DDR3_A11
DDR3_A12
DDR3_A13
DDR3_BA0
DDR3_BA1
DDR3_BA2
DDR3_CASN
DDR3_CKE
DDR3_CLK_P
DDR3_CLK_N
DDR3_CSN
DDR3_DM2
DDR3_DM3
DDR3_DQ16
DDR3_DQ17
DDR3_DQ18
DDR3_DQ19
DDR3_DQ20
DDR3_DQ21
DDR3_DQ22
DDR3_DQ23
DDR3_DQ24
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
A24 1.5-V SSTL Class I Row address select
L19 1.5-V SSTL Class I Reset
B22 1.5-V SSTL Class I Write enable
— 1.5-V SSTL Class I ZQ impedance calibration
A16 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
G23 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
E21 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
E22 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
A20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
A26 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
A15 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
B26 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
H17 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
D14 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
E23 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
E20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
C25 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
B13 1.5-V SSTL Class I Address bus
J18 1.5-V SSTL Class I Bank address bus
F20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Bank address bus
D19 1.5-V SSTL Class I Bank address bus
L20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Row address select
AK18 1.5-V SSTL Class I Column address select
J20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Differential output clock
H20 1.5-V SSTL Class I Differential output clock
G17 1.5-V SSTL Class I Chip select
A19 1.5-V SSTL Class I Write mask byte lane
B14 1.5-V SSTL Class I Write mask byte lane
G18 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 2
B18 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 2
A18 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 2
F18 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 2
C14 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 2
C17 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 2
B17 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 2
B19 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 2
C15 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 3
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 43

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–35
Memory
Table 2–24. DDR3 Device Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 4 of 4)
Board
Reference
C2
D7
A7
A3
C3
B8
C8
F3
G3
C7
B7
K1
J3
T2
L3
L8
Schematic
Signal Name
DDR3_DQ25
DDR3_DQ26
DDR3_DQ27
DDR3_DQ28
DDR3_DQ29
DDR3_DQ30
DDR3_DQ31
DDR3_DQS_P2
DDR3_DQS_N2
DDR3_DQS_P3
DDR3_DQS_N3
DDR3_ODT
DDR3_RASN
DDR3_RESETN
DDR3_WEN
DDR3_ZQ2
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
D17 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 3
C12 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 3
E17 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 3
C16 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 3
A14 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 3
D12 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 3
A13 1.5-V SSTL Class I Data bus byte lane 3
K16
L16
K17
J17
H19 1.5-V SSTL Class I On-die termination enable
A24 1.5-V SSTL Class I Row address select
L19 1.5-V SSTL Class I Reset
B22 1.5-V SSTL Class I Write enable
— 1.5-V SSTL Class I ZQ impedance calibration
I/O Standard Description
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Differential 1.5-V
SSTL Class I
Data strobe P byte lane 2
Data strobe N byte lane 2
Data strobe P byte lane 3
Data strobe N byte lane 3
LPDDR2 SDRAM
The LPDDR2 is a mobile low-power DDR2 SDRAM device that operates at 1.2 V. This
interface connects to the horizontal I/O banks on the top edge of the FPGA device.
The device speed is 300 MHz. Only x16 configuration is used although the LPDDR2
SDRAM on the board is a x32 device.
Tab le 2– 25 lists the LPDDR2 SDRAM pin assignments, signal names, and functions.
The signal names and types are relative to the Cyclone V E FPGA in terms of I/O
setting and direction.
Table 2–25. LPDDR2 SDRAM Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board
Reference (U9)
AC6
AB6
AC7
AB8
AB9
W1
V2
U1
Schematic
Signal Name
LPDDR2_CA0
LPDDR2_CA1
LPDDR2_CA2
LPDDR2_CA3
LPDDR2_CA4
LPDDR2_CA5
LPDDR2_CA6
LPDDR2_CA7
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin Number
Y30 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
T30 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
W29 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
AB29 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
W30 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
U29 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
AC30 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
R30 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
I/O Standard Description
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 44

2–36 Chapter 2: Board Components
Memory
Table 2–25. LPDDR2 SDRAM Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board
Reference (U9)
T2
T1
Y2
Y1
AC3
AB3
N23
L23
AB20
B20
AA23
Y22
W22
W23
V23
U22
T22
T23
H22
H23
G23
F22
E22
E23
D23
C22
AB12
AC13
AB14
AC14
AB15
AC16
AB17
AC17
B17
A17
A16
B15
B14
Schematic
Signal Name
LPDDR2_CA8
LPDDR2_CA9
LPDDR2_CK
LPDDR2_CKN
LPDDR2_CKE
LPDDR2_CSN
LPDDR2_DM0
LPDDR2_DM1
LPDDR2_DM2
LPDDR2_DM3
LPDDR2_DQ0
LPDDR2_DQ1
LPDDR2_DQ2
LPDDR2_DQ3
LPDDR2_DQ4
LPDDR2_DQ5
LPDDR2_DQ6
LPDDR2_DQ7
LPDDR2_DQ8
LPDDR2_DQ9
LPDDR2_DQ10
LPDDR2_DQ11
LPDDR2_DQ12
LPDDR2_DQ13
LPDDR2_DQ14
LPDDR2_DQ15
LPDDR2_DQ16
LPDDR2_DQ17
LPDDR2_DQ18
LPDDR2_DQ19
LPDDR2_DQ20
LPDDR2_DQ21
LPDDR2_DQ22
LPDDR2_DQ23
LPDDR2_DQ24
LPDDR2_DQ25
LPDDR2_DQ26
LPDDR2_DQ27
LPDDR2_DQ28
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
T28 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
T25 1.2-V HSUL Address bus
V21 Differential 1.2-V HSUL Differential output clock P
V22 Differential 1.2-V HSUL Differential output clock N
T29 1.2-V HSUL Clock enable
R26 1.2-V HSUL Chip select
AG29 1.2-V HSUL Data mask
AB27 1.2-V HSUL Data mask
— 1.2-V HSUL Data mask
— 1.2-V HSUL Data mask
AG28 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 0
AH30 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 0
AA28 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 0
AH29 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 0
Y28 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 0
AE30 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 0
AJ28 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 0
AD30 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 0
AC29 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 1
AF30 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 1
AA30 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 1
AE28 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 1
AF29 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 1
AD28 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 1
V27 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 1
W28 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 1
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 2
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 2
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 2
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 2
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 2
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 2
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 2
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 2
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 3
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 3
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 3
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 3
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 3
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 45

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–37
Memory
Table 2–25. LPDDR2 SDRAM Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board
Reference (U9)
A14
A13
B12
R23
P22
J22
K23
AB18
AC19
B18
A19
P1
EEPROM
Schematic
Signal Name
LPDDR2_DQ29
LPDDR2_DQ30
LPDDR2_DQ31
LPDDR2_DQS0
LPDDR2_DQSN0
LPDDR2_DQS1
LPDDR2_DQSN1
LPDDR2_DQS2
LPDDR2_DQSN2
LPDDR2_DQS3
LPDDR2_DQSN4
LPDDR2_ZQ
Cyclone V E
FPGA Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 3
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 3
— 1.2-V HSUL Data bus byte lane 3
V26 Differential 1.2-V HSUL Data strobe P byte lane 0
U26 Differential 1.2-V HSUL Data strobe N byte lane 0
U27 Differential 1.2-V HSUL Data strobe P byte lane 1
U28 Differential 1.2-V HSUL Data strobe N byte lane 1
— Differential 1.2-V HSUL Data strobe P byte lane 2
— Differential 1.2-V HSUL Data strobe N byte lane 2
— Differential 1.2-V HSUL Data strobe P byte lane 3
— Differential 1.2-V HSUL Data strobe N byte lane 3
— 1.2-V ZQ impedance calibration
This board includes a 64-Kb EEPROM device. This device has a 2-wire serial interface
2
bus I
C.
Tab le 2– 26 lists the EEPROM pin assignments, signal names, and functions. The signal
names and types are relative to the Cyclone V E FPGA in terms of I/O setting and
direction.
Table 2–26. EEPROM Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board
Reference (U12)
1
2
3
5
6
7
Schematic
Signal Name
EEPROM_A0
EEPROM_A1
EEPROM_A2
EEPROM_SDA
EEPROM_SCL
EEPROM_WP
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
— 3.3-V Chip address
— 3.3-V Chip address
— 3.3-V Chip address
AH7 3.3-V Serial address or data
AG7 3.3-V Serial clock
— 3.3-V Write protect input
I/O Standard Description
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 46

2–38 Chapter 2: Board Components
Memory
Synchronous SRAM
The development board supports a 18-Mb standard synchronous SRAM for
instruction and data storage with low-latency random access capability. The device
has a 1024K x 18-bits interface. This device is part of the shared FSM bus that connects
to the flash memory, SRAM, and MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller.
The device speed is 250 MHz single-data-rate. There is no minimum speed for this
device. The theoretical bandwidth of this interface is 4 Gbps for continuous bursts.
The read latency for any address is two clocks while the write latency is one clock.
Tab le 2– 27 lists the SSRAM pin assignments, signal names, and functions.
Table 2–27. SSRAM Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 1 of 2)
Board
Reference (U11)
86
87
37
36
44
42
34
47
43
46
45
35
32
33
50
48
100
99
82
80
49
81
39
58
59
62
63
68
69
Schematic
Signal Name
SRAM_OEN
SRAM_WEN
FSM_A1
FSM_A2
FSM_A3
FSM_A4
FSM_A5
FSM_A6
FSM_A7
FSM_A8
FSM_A9
FSM_A10
FSM_A11
FSM_A12
FSM_A13
FSM_A14
FSM_A15
FSM_A16
FSM_A17
FSM_A18
FSM_A19
FSM_A20
FSM_A21
FSM_D0
FSM_D1
FSM_D2
FSM_D3
FSM_D4
FSM_D5
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
E7 2.5-V Output enable
D6 2.5-V Write enable
B11 2.5-V Address bus
A11 2.5-V Address bus
D9 2.5-V Address bus
C10 2.5-V Address bus
A10 2.5-V Address bus
A9 2.5-V Address bus
C9 2.5-V Address bus
B8 2.5-V Address bus
B7 2.5-V Address bus
A8 2.5-V Address bus
B6 2.5-V Address bus
A6 2.5-V Address bus
C7 2.5-V Address bus
C6 2.5-V Address bus
F13 2.5-V Address bus
E13 2.5-V Address bus
A5 2.5-V Address bus
A4 2.5-V Address bus
J7 2.5-V Address bus
H7 2.5-V Address bus
J9 2.5-V Address bus
F16 2.5-V Data bus
E16 2.5-V Data bus
M9 2.5-V Data bus
M8 2.5-V Data bus
F15 2.5-V Data bus
E15 2.5-V Data bus
I/O Standard Description
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 47

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–39
Memory
Table 2–27. SSRAM Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 2 of 2)
Board
Reference (U11)
72
73
23
22
19
18
12
13
8
9
85
84
83
93
94
97
92
98
89
88
31
64
Schematic
Signal Name
FSM_D6
FSM_D7
FSM_D8
FSM_D9
FSM_D10
FSM_D11
FSM_D12
FSM_D13
FSM_D14
FSM_D15
SRAM_ADSCN
SRAM_ADSPN
SRAM_ADVN
SRAM_BWAN
SRAM_BWBN
SRAM_CE2
SRAM_CE3N
SRAM_CEN
SRAM_CLK
SRAM_GWN
SRAM_MODE
SRAM_ZZ
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
E12 2.5-V Data bus
D13 2.5-V Data bus
J15 2.5-V Data bus
H15 2.5-V Data bus
E11 2.5-V Data bus
D10 2.5-V Data bus
L10 2.5-V Data bus
L9 2.5-V Data bus
G14 2.5-V Data bus
F14 2.5-V Data bus
E6 2.5-V Address status controller
J10 2.5-V Address status processor
G6 2.5-V Address valid
A3 2.5-V Byte write select
A2 2.5-V Byte write select
— 2.5-V Chip enable 2
— 2.5-V Chip enable 3
D7 2.5-V Chip enable 1
K10 2.5-V Clock
— 2.5-V Global write enable
— 2.5-V Burst sequence selection
— 2.5-V Power sleep mode
I/O Standard Description
Flash
The development board supports a 512-Mb CFI-compatible synchronous flash device
for non-volatile storage of FPGA configuration data, board information, test
application data, and user code space. This device is part of the shared FSM bus that
connects to the flash memory, SSRAM, and MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller.
This 16-bit data memory interface can sustain burst read operations at up to 52 MHz
for a throughput of 832 Mbps per device. The write performance is 270 µs for a single
word buffer while the erase time is 800 ms for a 128 K array block.
Tab le 2– 28 lists the flash pin assignments, signal names, and functions. The signal
names and types are relative to the Cyclone V E FPGA in terms of I/O setting and
direction.
Table 2–28. Flash Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 1 of 3)
Board
Reference (U10)
F6
B4
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Schematic Signal Name
FLASH_ADVN
FLASH_CEN
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
H12 2.5-V Address valid
H14 2.5-V Chip enable
I/O Standard Description
Reference Manual
Page 48

2–40 Chapter 2: Board Components
Memory
Table 2–28. Flash Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 2 of 3)
Board
Reference (U10)
E6
F8
F7
D4
G8
C6
A1
B1
C1
D1
D2
A2
C2
A3
B3
C3
D3
C4
A5
B5
C5
D7
D8
A7
B7
C7
C8
A8
G1
H8
B6
B8
F2
E2
G3
E4
E5
G5
G6
Schematic Signal Name
FLASH_CLK
FLASH_OEN
FLASH_RDYBSYN
FLASH_RESETN
FLASH_WEN
FLASH_WPN
FSM_A1
FSM_A2
FSM_A3
FSM_A4
FSM_A5
FSM_A6
FSM_A7
FSM_A8
FSM_A9
FSM_A10
FSM_A11
FSM_A12
FSM_A13
FSM_A14
FSM_A15
FSM_A16
FSM_A17
FSM_A18
FSM_A19
FSM_A20
FSM_A21
FSM_A22
FSM_A23
FSM_A24
FSM_A25
FSM_A26
FSM_D0
FSM_D1
FSM_D2
FSM_D3
FSM_D4
FSM_D5
FSM_D6
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
I/O Standard Description
N12 2.5-V Clock
L11 2.5-V Output enable
J12 2.5-V Ready
K11 2.5-V Reset
P12 2.5-V Write enable
— 2.5-V Write protect
B11 2.5-V Address bus
A11 2.5-V Address bus
D9 2.5-V Address bus
C10 2.5-V Address bus
A10 2.5-V Address bus
A9 2.5-V Address bus
C9 2.5-V Address bus
B8 2.5-V Address bus
B7 2.5-V Address bus
A8 2.5-V Address bus
B6 2.5-V Address bus
A6 2.5-V Address bus
C7 2.5-V Address bus
C6 2.5-V Address bus
F13 2.5-V Address bus
E13 2.5-V Address bus
A5 2.5-V Address bus
A4 2.5-V Address bus
J7 2.5-V Address bus
H7 2.5-V Address bus
J9 2.5-V Address bus
H9 2.5-V Address bus
G9 2.5-V Address bus
F8 2.5-V Address bus
E8 2.5-V Address bus
D8 2.5-V Address bus
F16 2.5-V Data bus
E16 2.5-V Data bus
M9 2.5-V Data bus
M8 2.5-V Data bus
F15 2.5-V Data bus
E15 2.5-V Data bus
E12 2.5-V Data bus
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 49

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–41
Power Supply
Table 2–28. Flash Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 3 of 3)
Board
Reference (U10)
H7
E1
E3
F3
F4
F5
H5
G7
E7
FSM_D7
FSM_D8
FSM_D9
FSM_D10
FSM_D11
FSM_D12
FSM_D13
FSM_D14
FSM_D15
Power Supply
Schematic Signal Name
Cyclone V E FPGA
Pin Number
D13 2.5-V Data bus
J15 2.5-V Data bus
H15 2.5-V Data bus
E11 2.5-V Data bus
D10 2.5-V Data bus
L10 2.5-V Data bus
L9 2.5-V Data bus
G14 2.5-V Data bus
F14 2.5-V Data bus
I/O Standard Description
You can power up the development board from a laptop-style DC power input. The
input voltage must be in the range of 14 V to 20 V, current of 4.3 A, and a maximum
wattage of 65 W. The DC voltage is then stepped down to various power rails used by
the board components and installed into the HSMC connectors. An on-board
multi-channel analog-to-digital converter (ADC) measures the current for several
specific board rails.
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 50

1.2 V LDO
1.5 A, +/- 5%
LTC3026
HSMC, Fan
EEPROM
HSMC
MAX II VCCIO
MAX V VCCIO
USB-Blaster II PHY VCC
Clock Buffer
EPCQ
USB PHY
Battery
3 V
5.37 V LDO
20 mA, +/- 5%
LT3009
5.37 V at 0.3 mA
Powe r
Monitor
1.0 V LDO
1.5 A, +/- 5%
LTC3026
1.0 V at
500 mA
1.8 V LDO
500 mA, +/- 5%
LTC3025-1
1.8 V at
200 mA
Enet PHY
Flash
LPDDR2
MAX II VCCINT
MAX V VCCINT
Enet PHY
SSRAM
Flash
Max V VCCIO
MAX II VCCIO
Oscillators, Clock
Generators, and Buffers
USB PHY
RS-232
Filter
VCC Core
VCCIO
LPDDR2
3.3 V at 3.1 A
12 V at 4.25 A
DC Input
14 - 20 V
FPGA Power Rails
Board Main Power Rails
1.2 V at 650 mA
1.1 V Low Noise
Switcher
8A, +/- 30 mV
LTC3608
1.1 V at 4.1 A
1.5 V Switcher
1.5 A, +/- 5%
LTC3600
1.5 V at
1.2 A
2.5 V Switcher
8 A, +/- 5%
LTC3608
2.5 V at 3.2 A
3.3 V Switcher
300 mA, +/- 5%
LTC3103
2.5 V at 3 A
3.3 V at 200 mA
VCCIO
VCCPD
VCCPGM
LCD Level Shifter
0.75 VTT LDO
5V at 8.8 mA
12 V (7A) and 3.3 V (5A)
Switcher +/- 5%
LTC3855 Dual Switcher
5 V LDO
20 mA, +/- 5%
LT3009
FPGA
VCCBAT
VCCIO
VCCPD
VCCAUX
VCCA_FPLL
VCCBAT
0.75 V LDO
3 A, +/- 5%
TPS51100DGQ
0.75 V at
350 mA
DDR3 VTT
VCCIO
DDR3
2–42 Chapter 2: Board Components
Power Supply
Power Distribution System
Figure 2–9 shows the power distribution system on the development board. Regulator
inefficiencies and sharing are reflected in the currents shown, which are conservative
absolute maximum levels.
Figure 2–9. Power Distribution System
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 51

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–43
SCK
SPI Bus
DSI
DSO
CSn
8 Ch.
Power Supply Load #0-7
R
SENSE
MAX V CPLD
5M2210
System
Controller
Cyclone V E
FPGA
To User PC
JTAG Chain
Feedback
14-pin
2x16
Character
LCD
E
RW
RS
D(0:7)
Supply
#0-7
EPM570
USB
PHY
Embedded
USB-Blaster II
Power Supply
Power Measurement
There are eight power supply rails that have on-board current sense capabilities using
24-bit differential ADC devices. Precision sense resistors split the ADC devices and
rails from the primary supply plane for the ADC to measure current. A SPI bus
connects these ADC devices to the MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System Controller.
Figure 2–10 shows the block diagram for the power measurement circuitry.
Figure 2–10. Power Measurement Circuit
Tab le 2– 29 lists the targeted rails. The schematic signal name column specifies the
name of the rail being measured while the device pin column specifies the devices
attached to the rail.
Table 2–29. Power Measurement Rails
Channel Schematic Signal Name Voltage (V) Device Pin Description
1 VCC 1.1 VCC FPGA core power
2 VCCAUX 2.5 VCC_AUX Auxiliary
3 VCCA_FPLL 2.5 VCCA_FPLL PLL analog power
VCCPD3B4A,
5 VCCIO_VCCPD_2.5V 2.5
VCCPD5A,
VCCPD5B,
VCCPD6A,
VCCPD7A8A
I/O pre-drivers banks 3B, 4A, 5A, 5B, 6A,
7A, and 8A
VCCIO3B,
VCCIO6A,
7 VCCIO_1.2V 1.2
8 VCCIO_1.5V 1.5 VCCIO_4A VCC I/O bank 4A (DDR3)
VCCIO7A,
VCCIO8A
VCCIO5A,
VCCIO5B,
VCC I/O banks 3B, 6A, 7A, and 8A
VCC I/O banks 5A and 5B (LPDDR2)
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 52

2–44 Chapter 2: Board Components
Power Supply
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 53

3. Board Components Reference
This chapter describes the Cyclone V E FPGA development board components, the
manufacturing information, and the board compliance statements.
Board Components
Table lists the component reference and manufacturing information of all the
components on the development board.
Table 3–1. Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board
Reference
U1
U13
U18 High-Speed USB peripheral controller Cypress CY7C68013A www.cypress.com
D1-D16,
D18-D31,
D17 Red LED Lumex Inc. SML-LXT0805IW-TR www.lumex.com
D35 Blue LED Lumex Inc. SML-LX0805USBC-TR www.lumex.com
SW1–SW4 Four-position DIP switches
S1-S8 Push buttons Panasonic EVQPAC07K www.panasonic.com
S5 Slide switch E-switch EG2201A www.e-switch.com
X1
X3
X2
J12
U21 USB-to-UART bridge Silicon Labs CP2104 www.silabs.com
J14
U14, U15 Ethernet PHY BASE-T devices
J8, J9
J7
U20 RS-232 dual transceiver Linear Technology LTC2803-1 www.linear.com
FPGA, Cyclone V E F896, 149,500
LEs, leadfree
MAX V CPLD 5M2210 System
Controller
Green LEDs Lumex Inc. SML-LXT0805GW-TR www.lumex.com
Programmable LVDS clock 125M
defaults
100 MHz crystal oscillator, ±50 ppm,
CMOS, 2.5 V
50 MHz crystal oscillator, ±50 ppm,
CMOS, 2.5 V
Female angled PCB WR-DSUB 9-pin
connector
2×7 pin LCD socket strip Samtec TSM-107-07-G-D www.samtec.com
2×16 character LCD, 5×8 dot matrix Lumex Inc. LCM-S01602DSR/C www.lumex.com
RJ-45 connectors,
10/100/1000 Mbps
HSMC, custom version of QSH-DP
family high-speed socket.
Component Manufacturer
Corporation 5CEFA7F31I7N www.altera.com
Altera
Altera
Corporation 5M2210ZF256I5N www.altera.com
C&K Components/
ITT Industries
Silicon Labs 570FAB000973DG www.silabs.com
Silicon Labs 510GBA100M000BAGx www.silabs.com
Silicon Labs 510GBA50M0000BAGx www.silabs.com
Wurth Elektronik 618009231121 www.we-online.com
Marvell
Semiconductor
Wurth Elektronik 7499111001A www.we-online.com
Samtec ASP-122953-01 www.samtec.com
Manufacturing
Part Number
TDA04H0SB1 www.ittcannon.com
88E1111-B2-
CAA1C000
Manufacturer
Website
www.marvell.com
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 54

3–2 Chapter 3: Board Components Reference
Statement of China-RoHS Compliance
Table 3–1. Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board
Reference
U12 64-Kb EEPROM Microchip 24AA64 www.microchip.com
J15, J16 2 x 8 debug headers Samtec TSM-108-01-L-DV www.samtec.com
U7, U8 16M × 16 × 8, 256-MB DDR3 SDRAM Micron MT41J128M16 www.micron.com
U9
U11
U10 512-Mb synchronous flash Numonyx PC28F512P30BF www.numonyx.com
U35 16-channel differential 24-bit ADC Linear Technology LTC2418CGN#PBF www.linear.com
16M × 32 × 8, 512-MB LPDDR2
SDRAM
1024K × 18 bit 18-Mb synchronous
SRAM
Component Manufacturer
Micron MT42L128M32 www.micron.com
Integrated Silicon
Solution, Inc.
Manufacturing
Part Number
IS61VPS102418A-
250TQL
Manufacturer
Website
www.issi.com
Statement of China-RoHS Compliance
Tab le 3– 2 lists hazardous substances included with the kit.
(Hg)
(1), (2)
Polybrominated
biphenyls (PBB)
Polybrominated
diphenyl Ethers
(PBDE)
Table 3–2. Table of Hazardous Substances’ Name and Concentration Notes
Part Name
Cyclone V E development board X* 0 0 0 0 0
15 V power supply 0 0 0 0 0 0
Type A-B USB cable 0 0 0 0 0 0
User guide 0 0 0 0 0 0
Notes to Table 3–2:
(1) 0 indicates that the concentration of the hazardous substance in all homogeneous materials in the parts is below the relevant threshold of the
SJ/T11363-2006 standard.
(2) X* indicates that the concentration of the hazardous substance of at least one of all homogeneous materials in the parts is above the relevant
threshold of the SJ/T11363-2006 standard, but it is exempted by EU RoHS.
Lead
(Pb)
Cadmium
(Cd)
Hexavalent
Chromium
(Cr6+)
Mercury
CE EMI Conformity Caution
This development kit is delivered conforming to relevant standards mandated by
Directive 2004/108/EC. Because of the nature of programmable logic devices, it is
possible for the user to modify the kit in such a way as to generate electromagnetic
interference (EMI) that exceeds the limits established for this equipment. Any EMI
caused as the result of modifications to the delivered material is the responsibility of
the user.
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 55

This chapter provides additional information about the document and Altera.
Board Revision History
The following table lists the versions of all releases of the Cyclone V E FPGA
Development Board.
Release Date Version Description
March 2013 Production silicon
November 2012 Engineering silicon Initial release.
■ New board revision. New device part number—5CEFA7F31I7N.
■ Board passed CE compliance testing.
Document Revision History
Additional Information
The following table lists the revision history for this document.
Date Version Changes
March 2013 1.1
November 2012 1.0 Initial release.
■ Revised the FPGA device part number for production silicon release.
■ Added a section about “CE EMI Conformity Caution” on page 3–2.
How to Contact Altera
To locate the most up-to-date information about Altera products, refer to the
following table.
Contact
Technical support Website www.altera.com/support
Technical training
Product literature Website www.altera.com/literature
Nontechnical support (general) Email nacomp@altera.com
Note to Table:
(1) You can also contact your local Altera sales office or sales representative.
(1)
(software licensing) Email authorization@altera.com
Contact Method Address
Website www.altera.com/training
Email custrain@altera.com
March 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 56

Info–2 Additional InformationAdditional Information
Typographic Conventions
Typographic Conventions
The following table shows the typographic conventions this document uses.
Visual Cue Meaning
Bold Type with Initial Capital
Letters
bold type
Italic Type with Initial Capital Letters Indicate document titles. For example, Stratix IV Design Guidelines.
italic type
Initial Capital Letters
“Subheading Title”
Courier type
r An angled arrow instructs you to press the Enter key.
1., 2., 3., and
a., b., c., and so on
■ ■ ■ Bullets indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is not important.
1 The hand points to information that requires special attention.
h The question mark directs you to a software help system with related information.
f The feet direct you to another document or website with related information.
m The multimedia icon directs you to a related multimedia presentation.
c
w
Indicate command names, dialog box titles, dialog box options, and other GUI
labels. For example, Save As dialog box. For GUI elements, capitalization matches
the GUI.
Indicates directory names, project names, disk drive names, file names, file name
extensions, software utility names, and GUI labels. For example, \qdesigns
directory, D: drive, and chiptrip.gdf file.
Indicates variables. For example, n + 1.
Variable names are enclosed in angle brackets (< >). For example, <file name> and
<project name>.pof file.
Indicate keyboard keys and menu names. For example, the Delete key and the
Options menu.
Quotation marks indicate references to sections in a document and titles of
Quartus II Help topics. For example, “Typographic Conventions.”
Indicates signal, port, register, bit, block, and primitive names. For example,
tdi
, and
input
. The suffix n denotes an active-low signal. For example,
data1
resetn
.
Indicates command line commands and anything that must be typed exactly as it
appears. For example,
c:\qdesigns\tutorial\chiptrip.gdf
.
Also indicates sections of an actual file, such as a Report File, references to parts of
files (for example, the AHDL keyword
TRI
example,
).
SUBDESIGN
), and logic function names (for
Numbered steps indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is important,
such as the steps listed in a procedure.
A caution calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can damage or
destroy the product or your work.
A warning calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can cause you
injury.
The envelope links to the Email Subscription Management Center page of the Altera
website, where you can sign up to receive update notifications for Altera documents.
The feedback icon allows you to submit feedback to Altera about the document.
Methods for collecting feedback vary as appropriate for each document.
,
Cyclone V E FPGA Development Board March 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
 Loading...
Loading...