Page 1
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
101 Innovation Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
www.altera.com
MNL-01058-1.1
Feedback Subscribe
Page 2

© 2013 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos
are trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance of its
semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and
services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service
described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying
on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 3
Contents
Chapter 1. Overview
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Board Component Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Development Board Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
Handling the Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–4
Chapter 2. Board Components
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Board Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Featured Device: Cyclone IV GX Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–5
I/O Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–6
MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–12
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–12
FPGA Configuration over Embedded USB-Blaster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–12
FPGA Configuration from Flash Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–14
FPGA Configuration using External USB-Blaster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–15
FPGA Configuration using EPCS Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–15
Status Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–16
Setup Elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–17
Board Settings DIP Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–17
JTAG Chain Select DIP Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–18
PCIe Control DIP Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–19
Configuration Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–19
Configuration Push Buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–20
Clock Circuitry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–20
General User Input/Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–21
User-Defined Push Buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–21
User-Defined LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–22
General User-Defined LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–22
HSMC User-Defined LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–22
User-Defined DIP Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–23
LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–24
Components and Transceiver Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–26
PCIe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–26
10/100/1000 Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–28
Transceiver Connector (Optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–29
High-Speed Mezzanine Cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–29
Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–38
DDR2 SDRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–38
DDR2 SDRAM Top Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–39
DDR2 SDRAM Bottom Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–41
SSRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–43
Flash . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–45
Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–46
Power Distribution System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–47
Power Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–48
Statement of China-RoHS Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–49
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 4

iv Contents
Additional Information
Document Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
How to Contact Altera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
Typographic Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 5
This document describes the hardware features of the Cyclone® IV GX FPGA
development board, including the detailed pin-out and component reference
information required to create custom FPGA designs that interface with all
components of the board.
General Description
The Cyclone IV GX FPGA development board provides a hardware platform for
developing and prototyping low-power, high-volume, feature-rich designs as well as
to demonstrate the Cyclone IV GX device's on-chip memory, embedded multipliers,
and the Nios
memory interfaces to facilitate the development of the Cyclone IV GX FPGA designs.
f For more information on the Cyclone IV device family, refer to the Cyclone IV Device
Handbook.
1. Overview
®
II embedded soft processor. The board provides peripherals and
Board Component Blocks
The board features the following major component blocks:
■ Cyclone IV GX EP4CGX150DF31 FPGA in the 896-pin FineLine BGA (FBGA)
package
■ 1.2-V core power
■ MAX
■ FPGA configuration circuitry
■ On-Board ports
■ Communication ports
®
II EPM2210GF256 CPLD in the 256-pin FBGA package
■ 1.8-V core power
■ MAX
II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller and flash fast passive parallel (FPP)
configuration
■ Active serial configuration
■ On-board USB-Blaster
■ JTAG header for external USB-Blaster with the Quartus II Programmer
■ Embedded USB-Blaster
■ One gigabit Ethernet port
TM
for use with the Quartus® II Programmer
■ PCI Express (PCIe) edge connector
■ 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet PHY with RJ-45 connector
■ Two High-Speed Mezzanine Card (HSMC) interfaces
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 6

1–2 Chapter 1: Overview
Board Component Blocks
■ On-Board memory
■ 4-MB (x16) Synchronous Static Random Access Memory (SSRAM)
■ Two 32-MB (x32) DDR2 SDRAM
■ 64-MB flash
■ On-Board clocking circuitry
■ 50.000-MHz oscillator
■ 125.000-MHz oscillator
■ SMA clock input
■ SMA clock output
■ Programmable oscillator (default: 100.000-MHz)
■ General user I/O
■ LEDs and display
■ Eight FPGA user LEDs
■ One configuration done LED
■ One error LED
■ Five Ethernet status LEDs
■ One USB status LED
■ One power status LED
■ Five configuration LEDs
■ A two-line 16-character LCD display
■ Push buttons
■ One CPU reset push button
■ One MAX II configuration reset push button
■ One program-load push button—configure the FPGA from flash memory
■ One program-select push button—select image to load from flash memory
or serial configuration (EPCS) device
■ Four general user push buttons
■ DIP switches
■ Board settings DIP switch
■ JTAG chain select DIP switch
■ PCIe control DIP switch
■ Configuration settings DIP switch
■ User DIP switch
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 7
Chapter 1: Overview 1–3
EP4CGX150DF31
XCVR x4
10/100/1000
Ethernet RGMII
Translator
User LEDs
Push-Button,
Switches
14-pin LCD
Header
CPLD
(x18)
64 MB Flash
(x16)
4 MB SSRAM
(x18)
RJ45
Jack
Power
Measure
1.8 V
CMOS
1.8 V
CMOS
LVDS
1.8 V
2.5 V
Port B
USB
Blaster
100 MHz XTAL
SMA Input
125 MHz XTAL
32 MB DDR2
(x32)
SMA Output
1.8 V
HSTL
32 MB DDR2
(x32)
Translator
Port A
Translator
For TX/RX
[8:16]
1.8 V
XCVR x4
2.5 V
1.8 V
2.5 V
1.8 V
x4 Edge
XCVR x4
2.5 V (For TX/RX [0:7])
Development Board Block Diagram
■ Power supply
■ 16-V DC input
■ 2.5-mm barrel jack for DC power input
■ On/Off slide power switch
■ On-Board power measurement circuitry
■ 20-W per HSMC interface
■ Mechanical
■ PCIe small form factor board
■ Bench-top operation
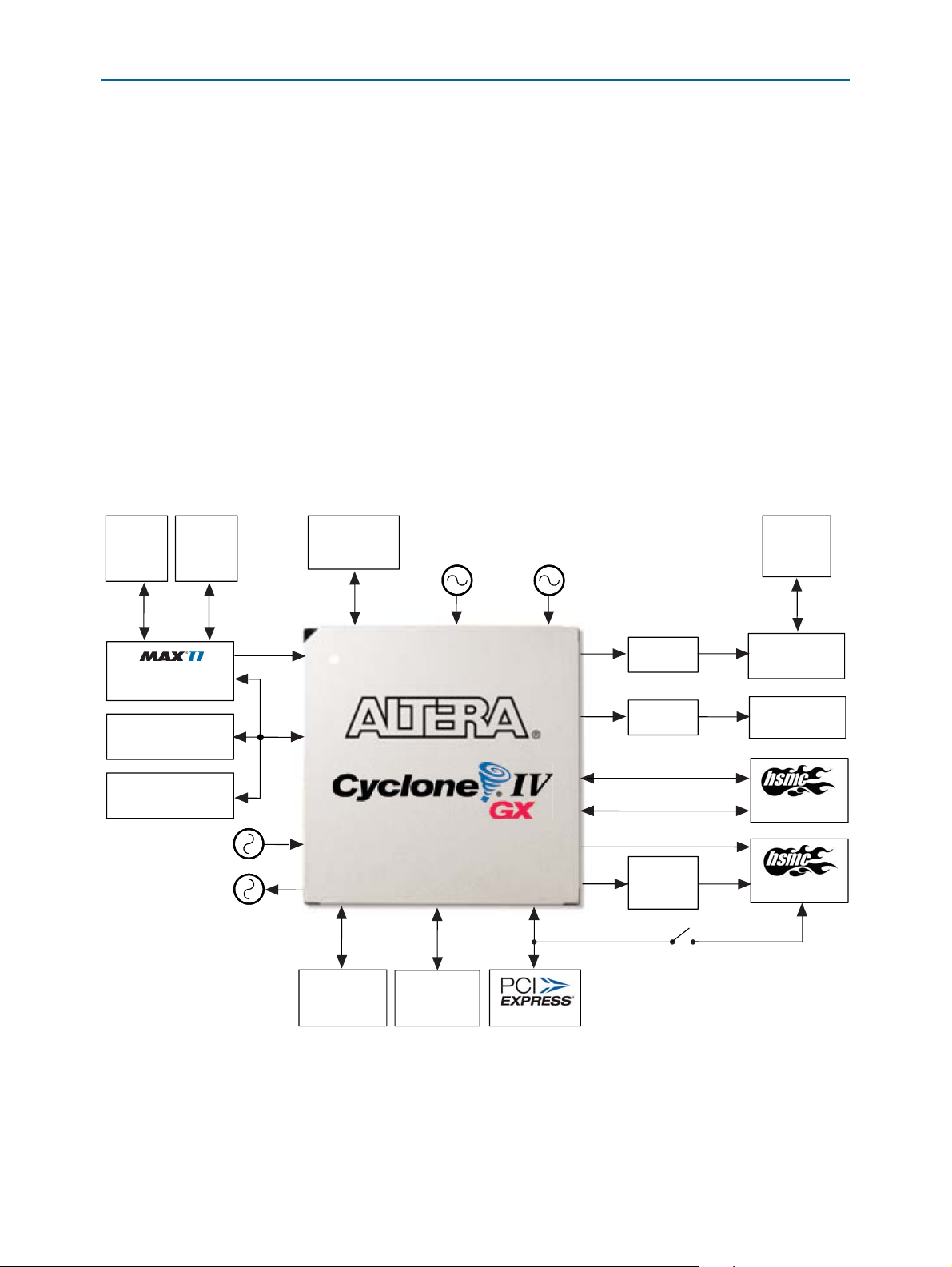
Development Board Block Diagram
Figure 1–1 shows the block diagram of the Cyclone IV GX FPGA development board.
Figure 1–1. Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board Block Diagram
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 8

1–4 Chapter 1: Overview
Handling the Board
Handling the Board
When handling the board, it is important to observe the following static discharge
precaution:
c Without proper anti-static handling, the board can be damaged. Therefore, use
anti-static handling precautions when touching the board.
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 9
Introduction
1 A complete set of schematics, a physical layout database, and GERBER files for the
f For information about powering up the board and installing the demonstration
2. Board Components
This chapter introduces the major components on the Cyclone IV GX FPGA
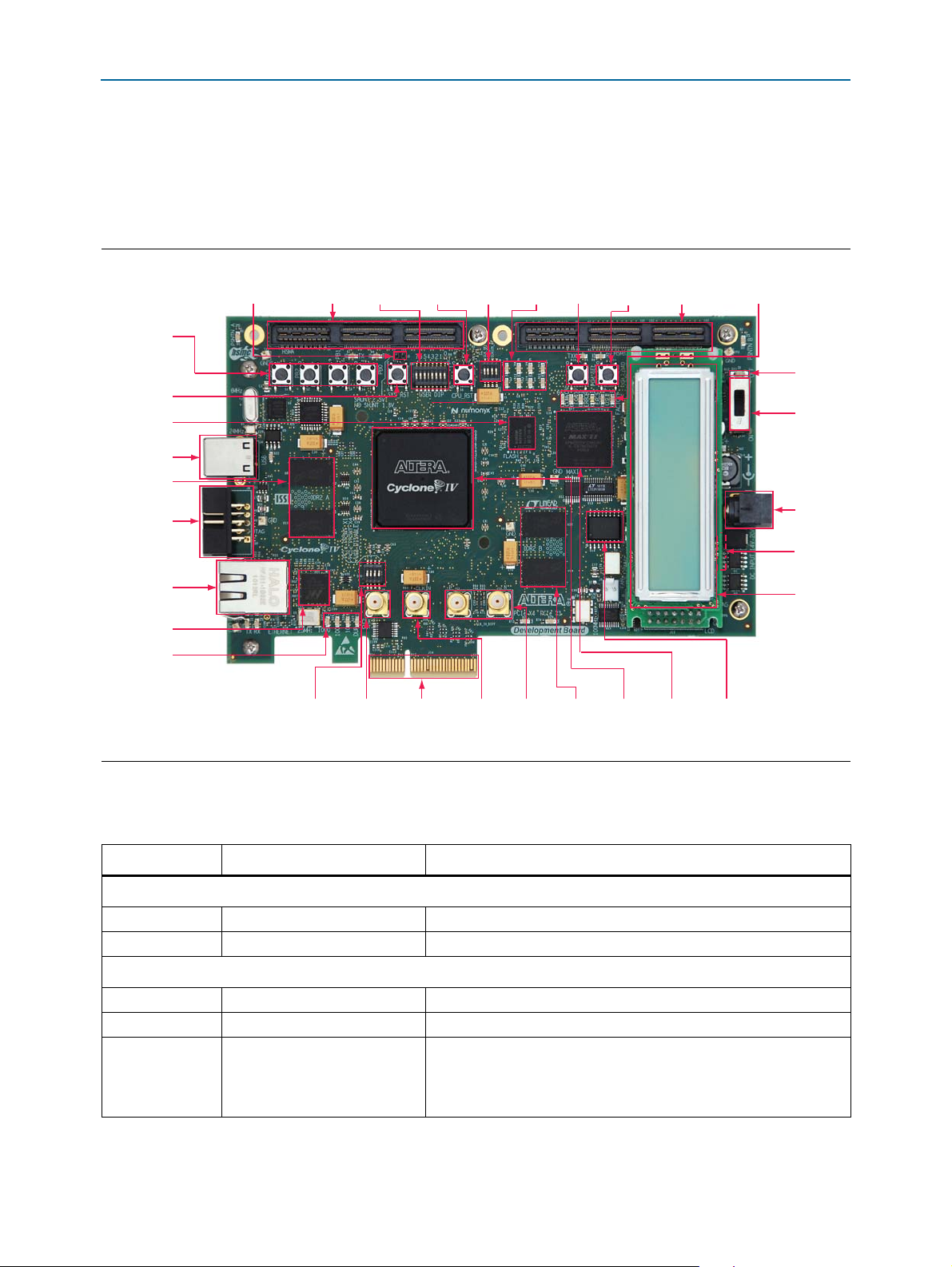
development board. Figure 2–1 illustrates major component locations and Ta bl e 2– 1
provides a brief description of all component features of the board.
development board reside in the Cyclone IV GX FPGA development kit documents
directory.
software, refer to the Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Kit User Guide.
This chapter consists of the following sections:
■ “Board Overview”
■ “Featured Device: Cyclone IV GX Device” on page 2–5
■ “MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller” on page 2–7
■ “Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements” on page 2–12
■ “Clock Circuitry” on page 2–20
■ “General User Input/Output” on page 2–21
■ “Components and Transceiver Interfaces” on page 2–26
■ “Memory” on page 2–38
■ “Power Supply” on page 2–46
■ “Statement of China-RoHS Compliance” on page 2–49
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 10
2–2 Chapter 2: Board Components
Clock Input
Differential
SMAs
Connectors
(J11, J12)
System Reset
Push-Button
Switch (S5)
Select
Push-Button
Switch (S7)
DC Input
Jack (J5)
Cyclone
IV GX
FPGA
(U10)
Character
LCD
(J13)
CPU Reset
Push-Button
Switch (S6)
Powe r
Switch
(SW3)
Clock Input
SMA
Connector
(J10)
Ethernet LEDs
(D24-D27)
MAX II CPLD
EPM2210
System Controller
(U7)
User LEDs
(D7-D10,
D12-D15)
Flash x16
Memory (U6)
PCI Express
Edge Connector
(J14)
USB Type-B
Connector (J4)
RJ-45 Connector
(J7)
JTAG
Connector
(J6)
Configuration Done, Load,
Error, EPCS, User,
and Factory LEDs (D16-D21)
Load
Push-Button
Switch (S8)
Power LED
(D11)
HSMC Port A
(J1)
User Push-Button
Switches (S1-S4)
User DIP
Switch
(SW2)
Clock output
SMA
Connector
(J9)
HSMC Port B
(J2)
Gigabit Ethernet
(U21)
HSMC Bank Selection
Jumper (J3)
Board Settings
DIP Switch
(SW1)
DDR2A x32
(U8, U15)
EPCS
Device
(U18)
PCI Express
Control
DIP Switch
(SW4)
DDR2B x32
(U17, U19)
JTAG Chain
Select DIP
Switch (SW5)
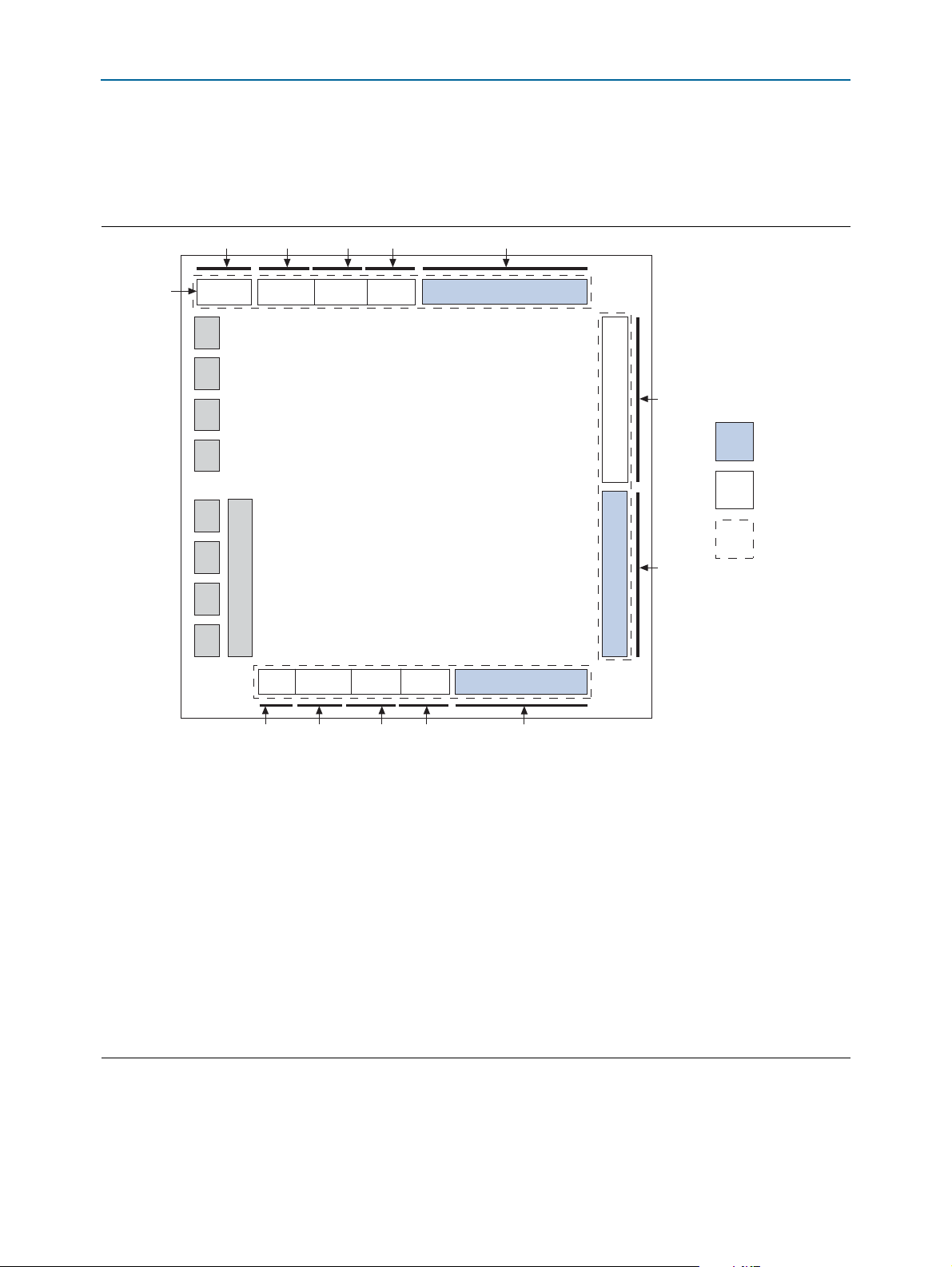
Board Overview
Board Overview
This section provides an overview of the Cyclone IV GX FPGA development board,
including an annotated board image and component descriptions. Figure 2–1
provides an overview of the development board features.
Figure 2–1. Overview of the Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board Features
Tab le 2 –1 describes the components and lists their corresponding board references.
Table 2–1. Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board Components (Part 1 of 3)
Board Reference Type Description
Featured Devices
U10 FPGA EP4CGX150DF31, 896-pin FBGA.
U7 CPLD EPM2210GF256, 256-pin FBGA.
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
J4 USB Type-B connector Connects to the computer to enable embedded USB-Blaster JTAG.
J6 JTAG connector Disables embedded blaster (for use with external USB-Blasters).
Flash memory device with a serial interface which stores
U18
EPCS128 serial configuration
device
configuration data for FPGA device that supports active serial
configuration and reloads the data to the FPGA upon power-up or
reconfiguration.
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 11
Chapter 2: Board Components 2–3
Board Overview
Table 2–1. Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board Components (Part 2 of 3)
Board Reference Type Description
D17 Load LED
Illuminates when the MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller is
actively configuring the FPGA.
D18 Error LED Illuminates when the FPGA configuration from flash memory fails.
D24–D27, D30,
D31
Ethernet LEDs Shows the connection speed as well as transmit or receive activity.
D11 Power LED Illuminates when 14-V – 20-V DC power is present.
D28 PCIe x4 LED You can configure this LED to illuminate when PCIe is in x4 mode.
D29 PCIe x1 LED You can configure these LEDs to illuminate when PCIe is in x1 mode.
SW4 PCIe DIP switch
SW5 JTAG chain select DIP switch
Controls the PCIe lane width (connecting
PCIe edge connector) or disables the embedded USB-Blaster.
Enables and disables devices in the JTAG chain. The switch is located
under the character LCD.
prsnt
pins together on the
Controls the Max II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller functions
SW1 Board settings DIP switch
such as enabling the 125-MHz clock or programmable clock, as well
as selection between the SMA clock input or the programmable clock
for buffer multiplexer.
S5 System reset push button Press to reset the MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller.
S6 CPU reset push button Press to reset the FPGA logic.
Toggles the LEDs which selects the program image that loads either
S7 Program select push button
from the flash memory (FPP mode) or the EPCS device (active serial
mode) to the FPGA.
S8 Program load push button
Configure the FGPA from flash memory based on the program select
LEDs setting.
Clock Circuitry
X2 125-MHz oscillator 125-MHz crystal oscillator for general use such as memories.
X3 50-MHz oscillator
X5 25-MHz oscillator
Y2 6-MHz oscillator
X1 24-MHz oscillator
50-MHz crystal oscillator for configuration purpose. This oscillator is
located at the bottom of the board.
25-MHz crystal oscillator for 10 Gigabit Ethernet. This oscillator is
located at the bottom of the board.
6-MHz crystal oscillator for USB PHY. This oscillator is located at the
bottom of the board.
24-MHz crystal oscillator for USB PHY. This oscillator is located at
the bottom of the board.
Programmable oscillator for PCIe or general use such as memories.
X4 Programmable oscillator
Multiplexed with
CLKIN_SMA_P/N
signals based on
CLK_SEL
value.
J11, J12 Clock input SMA
Drive LVPECL-compatible clock input into the clock multiplexer
buffer.
J10 Single-ended clock input 1.8-V single-ended clock input.
J9 Clock output SMA Drives out 2.5-V CMOS clock output from the FPGA.
switch
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 12
2–4 Chapter 2: Board Components
Board Overview
Table 2–1. Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board Components (Part 3 of 3)
Board Reference Type Description
General User Input/Output
D7–D10,
D12–D15
User LEDs Eight user LEDs. Illuminates when driven low.
S1–S4 User push buttons Four user push buttons. Driven low when pressed.
J13 Character LCD
Connector which interfaces to the provided 16 character × 2 line LCD
module.
Memory Devices
U44 SSRAM x18 memory
U6 Flash x64 memory
Standard synchronous RAM which provides a 72-Mbit (Mb) SSRAM
port. This SSRAM is located at the bottom of the board.
Synchronous burst mode flash device which provides a 256-Mb
non-volatile memory port.
U8, U15 DDR2 x32 SDRAM A Two 16-bit memory device.
U17, U19 DDR2 x32 SDRAM B Two 16-bit memory device.
Components Interfaces
Provides 10/100/1000 BASE-T Ethernet connection via a Marvell
J7 RJ-45 connector
88E1111 PHY and the FPGA-based Altera Triple Speed Ethernet
MegaCore function in RGMII mode.
A Marvell 88E1111 PHY device for 10/100/1000 BASE-T Ethernet
U21 Gigabit Ethernet
connection. The device is an auto-negotiating Ethernet PHY with an
RGMII interface to the FPGA.
Interfaces to a PCIe root port such as an appropriate PC
J14 PCIe edge connector
motherboard. Made of gold-plated edge fingers for up to ×4 signaling
in Gen1 mode.
J1 HSMC port A
J2 HSMC port B
Provides eight transceiver channels and 84 CMOS or 17 LVDS
channels per the HSMC specification.
Provides eight transceiver channels and 84 CMOS channels per the
HSMC specification.
Power Supply
J5 DC input jack
SW3 Power switch
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Accepts a 16-V DC power supply. Do not use this input jack while the
board is plugged into a PCIe slot.
Switch to power on or off the board when power is supplied from the
DC input jack.
Page 13

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–5
Featured Device: Cyclone IV GX Device
Featured Device: Cyclone IV GX Device
The Cyclone IV GX FPGA development board features the Cyclone IV GX
EP4CGX150DF31 device (U10) in a 896-pin FBGA package.
f For more information about Cyclone IV device family, refer to the Cyclone IV Device
Handbook.
Tab le 2 –2 describes the features of the Cyclone IV GX EP4CGX150DF31 device.
Table 2–2. Cyclone IV GX EP4CGX150DF31 Device Features
Equivalent LEs
149,760 6,480 360 8 8 475 896-pin FBGA
Embedded
Memory (Kbits)
18-bit × 18-bit
Multipliers
Transceivers PLLs User I/O Package Type
Tab le 2 –3 lists the Cyclone IV GX device component reference and manufacturing
information.
Table 2–3. Cyclone IV GX Device Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
U10
FPGA, Cyclone IV GX, 896-pin
FBGA package, lead-free.
Altera
Corporation EP4CGX150DF31 www.altera.com
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 14
2–6 Chapter 2: Board Components
Right, Top, and Bottom Banks Support:
3.3-V LVTTL/LVCMOS
3.0-V LVTTL/LVCMOS
2.5-V LVTTL/LVCMOS
1.8-V LVTTL/LVCMOS
1.5-V LVCMOS
1.2-V LVCMOS
PPDS
LVDS
RSDS
mini-LVDS
Bus LVDS (7)
LVPECL (3)
SSTL-2 class I and II
SSTL-18 CLass I and II
HSTL-18 Class I and II
HSTL-15 Class I and II
HSTL-12 Class I and II (4)
Differential SSTL-2 (5)
Differential SSTL-18 (5)
Differential HSTL-18 (5)
Differential HSTL-15 (5)
Differential HSTL-12 (6)
3.0-V PCI/PCI-X (8)
VCCIO9
Configuration
pins
Config
pins
VCCIO8 VCC_CLKIN8A
VCC_CLKIN3A
VCCIO7
VCCIO6
VCCIO5
VCCIO4VCCIO3
I/O Bank 9 I/O Bank 7
I/O Bank 4
I/O Bank 5
PCIe hard IP x1, x2, and x4
I/O Bank 6
VCC_CLKIN8B
VCCIO3 VCC_CLKIN3B
Ch0 Ch1 Ch2
GXBL0
Ch3 Ch0 Ch1 Ch2
GXBL1
Ch3
I/O bank with
calibration block
I/O bank without
calibration block
Calibration block
coverage
I/O Bank 8
I/O Bank
8A (10)
I/O Bank 8B
(10), (11)
I/O Bank 3
I/O Bank
3A (10)
I/O Bank 3B
(10), (11)
Featured Device: Cyclone IV GX Device
I/O Resources
Figure 2–2 illustrates the bank organization and I/O count for the EP4CGX150DF31
device in the 896-pin FBGA package.
Figure 2–2. EP4CGX150DF31 Device I/O Bank Diagram
(1)
Notes to Figure 2–2:
(1) This is a top view of the silicon die. For exact pin locations, refer to the pin list and the Quartus II software.
(2) True differential (PPDS, LVDS, mini-LVDS, and RSDS I/O standards) outputs are supported in row I/O banks 5 and 6 only. External resistors are
needed for the differential outputs in column I/O banks.
(3) The LVPECL I/O standard is only supported on clock input pins. This I/O standard is not supported on output pins.
(4) The HSTL-12 Class II is supported in column I/O banks 4, 7, and 8.
(5) The differential SSTL-18 and SSTL-2, differential HSTL-18, and HSTL-15 I/O standards are supported only on clock input pins and phase-locked
loops (PLLs) output clock pins. PLL output clock pins do not support Class II interface type of differential SSTL-18, HSTL-18, HSTL-15, and
HSTL-12 I/O standards.
(6) The differential HSTL-12 I/O standard is only supported on clock input pins and PLL output clock pins. Differential HSTL-12 Class II is supported
only in column I/O banks 4, 7, and 8.
(7) BLVDS output uses two single-ended outputs with the second output programmed as inverted. BLVDS input uses the LVDS input buffer.
(8) The PCI-X I/O standard does not meet the IV curve requirement at the linear region.
(9) The OCT block is located in the shaded banks 4, 5, and 7.
(10) The dedicated clock input I/O banks 3A, 3B, 8A, and 8B can be used either for HSSI input reference clock pins or clock input pins.
(11) Single-ended clock input support is available for dedicated clock input I/O banks 3B and 8B.
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 15
Chapter 2: Board Components 2–7
MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller
Tab le 2 –4 lists the Cyclone IV GX device pin count and usage by function on the
development board.
Table 2–4. Cyclone IV GX Device I/O Pin Count and Usage
Function I/O Standard I/O Count Special Pins
Clocks or Oscillators 1.8-V CMOS 9 3 clock inputs, 1 clock input
DDR2A x32 (Top) 1.8-V SSTL 63 —
DDR2B x32 (Bottom) 1.8-V SSTL 63 —
Flash, SSRAM, MAX 1.8-V CMOS 55 —
Gigabit Ethernet 2.5-V CMOS
(1)
16 —
User I/O (LEDs, Push buttons) 1.8-V 25 —
14-pin LCD 2.5-V CMOS
(1)
11 —
HSMC Port A 2.5-V/1.8-V CMOS 103 —
HSMC Port B 2.5-V CMOS
(1)
87 —
PCIe x4 2.5-V CMOS 7 —
PCIe (for HSMC port B transceiver multiplexer) XCVR 16 —
Passive serial and active serial configuration 2.5-V CMOS 21 —
Device I/O Total:
Note to Table 2–4:
(1) Translated from 1.8-V to 2.5-V using a bidirectional voltage translator.
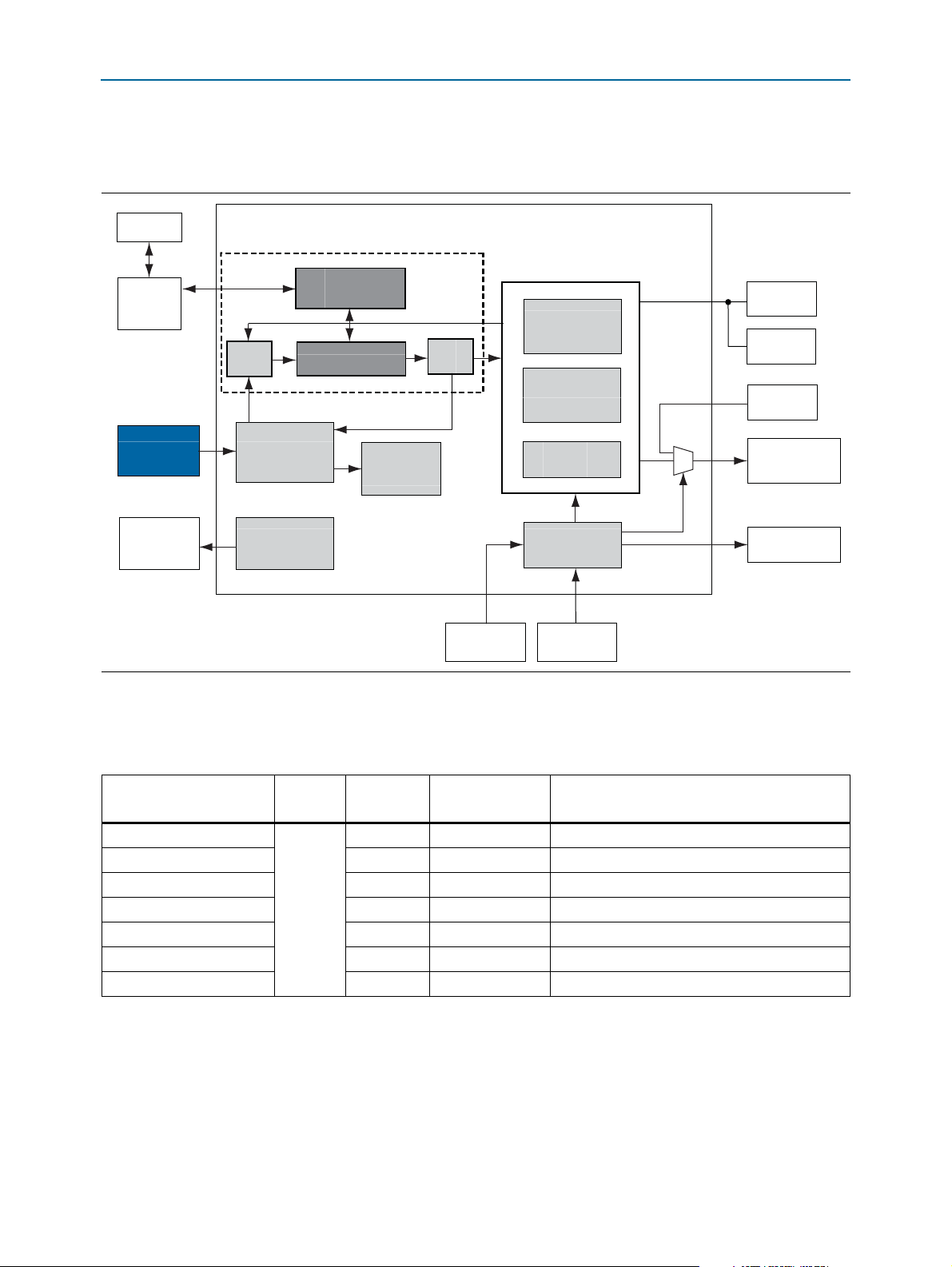
MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller
The board utilizes the EPM2210 System Controller, an Altera MAX II CPLD, for the
following purposes:
■ FPGA configuration from flash memory
■ Power consumption monitoring
■ Virtual JTAG interface for PC-based GUI
■ Control registers for clocks
■ Control registers for remote system update
476
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 16
2–8 Chapter 2: Board Components
Information
Register
MAX II
Embedded
USB-Blaster
MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller
Power
Calculations
SLD-HUB
PFL
Power
Measurement
Results
Virtual-JTAG
PC
EP4CGX150
EPCS
LTC2418
Controller
FLASH
Decoder
Encoder
JTAG Control
Control
Register
Clock
Controller
Programmable
Clock
Configuration State
Machine
User/Factory
DIP Switch
Configuration
Push Buttons
Configuration
Signals (GPIO on
MAX Device)
Configuration
Status LEDs
MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller
Figure 2–3 illustrates the MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller's functionality
and external circuit connections as a block diagram.
Figure 2–3. MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller Block Diagram
Tab le 2 –5 lists the I/O signals present on the MAX
Controller. The signal names and functions are relative to the MAX
II CPLD EPM2210 System
II device (U7).
Table 2–5. MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller Device Pin-Out (Part 1 of 4)
Schematic Signal Name
CLKA_EN
CLKA_SDA
CLKA_SCL
CLK125_EN
CLKIN_50
CLKIN_MAX_100
FAN_CNTL
I/O
Standard
2.5-V
EPM2210
Pin Number
H3 — 125-MHz oscillator enable
EP4CGX15BF14
Pin Number
Description
J1 — 125-MHz programming data
H4 — 125-MHz programming clock
J2 — 125-MHz oscillator enable
H5 — 50-MHz oscillator
J5 — MAX II clock input
P2 — Fan control
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 17
Chapter 2: Board Components 2–9
MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller
Table 2–5. MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller Device Pin-Out (Part 2 of 4)
Schematic Signal Name
FACTORY_CONFIGn
FLASH_ADVn
FLASH_RESETn
FLASH_WEn
FLASH_OEn
FLASH_RDYBSYn
FLASH_CLK
FLASH_CEn
FPGA_DATA0
FPGA_DATA1
FPGA_DATA2
FPGA_DATA3
FPGA_DATA4
FPGA_DATA5
FPGA_DATA6
FPGA_DATA7
FPGA_DCLK
FPGA_CONF_DONE
FPGA_STATUSn
FPGA_CONFIGn
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TMS
JTAG_FPGA_TDO
JTAG_EPM2210_TDO
I/O
Standard
1.8-V
2.5-V
EPM2210
Pin Number
EP4CGX15BF14
Pin Number
Description
G12 — Factory configuration enable
L13 F24 FSM bus flash memory address valid
M15 A28 FSM bus flash memory reset
L12 C13 FSM bus flash memory write enable
M16 F7 FSM bus flash memory output enable
L11 B7 FSM bus flash memory ready
L15 Y21 FSM bus flash memory clock
K14 E25 FSM bus flash memory chip enable
D3 A3 FPGA data
L1 G9 FPGA data
J16 H9 FPGA data
J13 D1 FPGA data
H16 C2 FPGA data
H13 AE4 FPGA data
H15 AE5 FPGA data
H14 AE10 FPGA data
C2 B3 FPGA configuration clock
E3 B1 FPGA configuration done
C3 AJ1 FPGA configuration ready
E4 AB9 FPGA configuration active
P3 F2 FPGA JTAG TCK
N4 E1 FPGA JTAG TMS
L6 F1 FPGA JTAG TDO
M5 E2 MAX II JTAG TDO
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 18

2–10 Chapter 2: Board Components
MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller
Table 2–5. MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller Device Pin-Out (Part 3 of 4)
Schematic Signal Name
FSM_A1
FSM_A2
FSM_A3
FSM_A4
FSM_A5
FSM_A6
FSM_A7
FSM_A8
FSM_A9
FSM_A10
FSM_A11
FSM_A12
FSM_A13
FSM_A14
FSM_A15
FSM_A16
FSM_A17
FSM_A18
FSM_A19
FSM_A20
FSM_A21
FSM_A22
FSM_A23
I/O
Standard
1.8-V
EPM2210
Pin Number
EP4CGX15BF14
Pin Number
P7 AD6 FSM bus address
R6 AK29 FSM bus address
R5 AA21 FSM bus address
R4 AG25 FSM bus address
R3 AH5 FSM bus address
M8 AH27 FSM bus address
P6 AJ12 FSM bus address
P8 AF16 FSM bus address
R7 AH20 FSM bus address
N6 AK23 FSM bus address
P4 AH17 FSM bus address
P5 AB21 FSM bus address
N8 AF19 FSM bus address
T6 AF12 FSM bus address
N5 AG27 FSM bus address
M6 AK26 FSM bus address
N7 AH4 FSM bus address
T5 AK3 FSM bus address
R1 AH9 FSM bus address
M7 AG6 FSM bus address
T2 AK25 FSM bus address
T7 AE21 FSM bus address
T4 AA18 FSM bus address
Description
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 19

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–11
MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller
Table 2–5. MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller Device Pin-Out (Part 4 of 4)
Schematic Signal Name
FSM_A24
FSM_A25
FSM_D0
FSM_D1
FSM_D2
FSM_D3
FSM_D4
FSM_D5
FSM_D6
FSM_D7
FSM_D8
FSM_D9
FSM_D10
FSM_D11
FSM_D12
FSM_D13
FSM_D14
FSM_D15
HSMA_PSNTn
HSMB_PSNTn
MAX_EPCS
MAX_ERROR
MAX_FACTORY
MAX_USER
MAX_FAN
MAX_CSn
MAX_OEn
MAX_WEn
MSEL0
MSEL2
MSEL3
RESET_CONFIGn
SENSE_CSn
SENSE_SCK
SENSE_SDI
SENSE_SDO
SYS_RESETn
USER_FACTORY
I/O
Standard
EPM2210
Pin Number
EP4CGX15BF14
Pin Number
Description
R8 AK27 FSM bus address
M9 AF21 FSM bus address
E9 AK14 FSM bus data
A9 AE6 FSM bus data
E7 AG21 FSM bus data
B7 AE9 FSM bus data
A6 AK28 FSM bus data
A8 AD23 FSM bus data
1.8-V
C7 AG24 FSM bus data
B6 AB22 FSM bus data
E8 AE22 FSM bus data
B8 AJ24 FSM bus data
D8 Y19 FSM bus data
D7 AH23 FSM bus data
A7 AK22 FSM bus data
C8 AH24 FSM bus data
B5 Y18 FSM bus data
A5 AJ13 FSM bus data
G5 A25 HSMC port A present LED
H2 C26 HSMC port B present LED
2.5-V
G3 — MAX II EPCS memory chip enable
G2 — FPGA configuration error LED
G4 — FPGA factory configuration LED
G1 — FPGA user configuration LED
B1 — FPGA fan LED
1.8-V
L16 B12 MAX II chip select
K13 G8 MAX II output enable
K15 A9 MAX II write enable
L2 AD7 FPGA MSEL0 configuration mode select
2.5-V
M1 AC7 FPGA MSEL2 configuration mode select
M2 AC8 FPGA MSEL3 configuration mode select
1.8-V G16 AF27 Force FPGA configuration push button
F5 — Power monitor chip select
Power monitor serial peripheral interface (SPI)
clock
2.5-V
E1 —
F4 — Power monitor SPI data in
E2 — Power monitor SPI data out
1.8-V J15 AF27 System reset push button
2.5-V N1 — User reset push button
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 20

2–12 Chapter 2: Board Components
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
Tab le 2 –6 lists the MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller component reference
and manufacturing information.
Table 2–6. MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
U7
IC - MAX II CPLD EPM2210G
256FBGA -3 LF 1.8V VCCINT
Corporation EPM2210GF256C3N www.altera.com
Altera
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
This section describes the board's configuration, status, and setup elements.
Configuration
This section describes the FPGA, flash memory, and MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System
Controller device configuration methods supported by the Cyclone IV GX FPGA
development board. The Cyclone IV GX FPGA development board supports the
following configuration methods:
■ Embedded USB-Blaster is the default method for configuring the FPGA at any
time using the Quartus II Programmer in JTAG mode with the supplied USB cable.
■ Flash memory download is used for storing FPGA images which the MAX
CPLD EPM2210 System Controller uses to configure the Cyclone IV GX device
either on board power-up or after the program load push-button switch (S8) is
pressed.
■ External USB-Blaster for configuring the FPGA using an external USB-Blaster.
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
II
■ Serial configuration (EPCS) device (U18) is used to store configuration data for
FPGA device that supports active serial (AS) configuration and reloads the data to
the FPGA upon reconfiguration. Use the program select push-button switch (S7) to
select the configuration files to be loaded from either page 0 (factory location),
page 1 (user location), or from the EPCS device.
FPGA Configuration over Embedded USB-Blaster
The USB-Blaster is implemented using a USB Type-B connector (J4), a FTDI USB 2.0
PHY device (U4), and an Altera MAX II CPLD (U7). This allows the configuration of
the FPGA using a USB cable directly connected between the USB port on the board
(J4) and a USB port of a PC running the Quartus II software. The JTAG chain is
normally mastered by the embedded USB-Blaster found in the MAX
EPM2210 System Controller.
II CPLD
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 21

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–13
Embedded
Blaster
GPIO
TCK
EP4CGX150
FPGA
Analog
Switch
EPM2210
System
Controller
HSMC
Port A
HSMC
Port B
GPIO
TMS
GPIO
TDO
GPIO
TDI
JTAG Master
GPIO
DISABLED
JTAG Master/Slave
JTAG Master/Slave
Installed
HSMC
Card
Installed
HSMC
Card
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
JTAG Slave
JTAG Slave
Analog
Switch
Analog
Switch
EPM2210_JTAG_EN
HSMA_JTAG_EN
HSMB_JTAG_EN
ALWAYS
ENABLED
(in chain)
SW5.1
SW5.2
SW5.3
SW5
10-pin
JTAG Header
Flash
Memory
(on install)
PCI Express
Edge
Connector
JTAG Master/Slave
PCI Express
Motherboard
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
Analog
Switch
PCIE_JTAG_EN
SW5.4
Embedded
Blaster
Connection
USB
PHY
J4
J6
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
The embedded USB-Blaster is automatically disabled when an external USB-Blaster is
connected to the JTAG chain. Figure 2–4 illustrates the JTAG chain.
Figure 2–4. JTAG Chain
The Cyclone IV GX FPGA is configured via JTAG using the MAX II configuration
controller design (embedded blaster) as the primary configuration mode. The board
includes a MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller which interfaces directly to the
Cyclone IV GX FPGA for configuration, LCD control, power monitor control, and
other purposes. The MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller contains the required
state machine and control logic to determine the configuration source for the Cyclone
IV GX FPGA.
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 22

2–14 Chapter 2: Board Components
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
Flash Memory Programming
Flash memory programming is possible through a variety of methods using the
Cyclone IV GX device.
The default method is to use the factory design called the Board Update Portal. This
design is an embedded web server, which serves the Board Update Portal web page.
The web page allows you to select new FPGA designs including hardware, software,
or both in an industry-standard S-Record File (.flash) and write the design to the user
hardware page (page 1) of the flash memory over the network.
The secondary method is to use the pre-built parallel flash loader (PFL) design
included in the development kit. The development board implements the Altera PFL
megafunction for flash memory programming. The PFL megafunction is a block of
logic that is programmed into an Altera programmable logic device (FPGA or CPLD).
The PFL functions as a utility for writing to a compatible flash memory device. This
prebuilt design contains the PFL megafunction that allows you to write either page 0,
page 1, or other areas of flash memory over the USB interface using the Quartus II
software. This method is used to restore the development board to its factory default
settings.
Other methods to program the flash memory can be used as well, including the
®
Nios
II processor.
f For more information on the Nios II processor, refer to the Nios II Processor page of
the Altera website.
FPGA Configuration from Flash Memory
On either power-up or by pressing the program load push-button switch (S8), the
MAX
II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller's PFL configures the FPGA from the flash
memory hardware page 0 or 1 based on whether
The PFL megafunction reads the data from the flash memory and loads to the FPGA
using the FPP interface.
There are two pages reserved for the FPGA configuration data. The factory hardware
(page 0) is loaded upon power-up if the board settings DIP switch (SW1) is set to '0'.
Otherwise, the user hardware (page 1) is loaded. Pressing the program load
push-button switch (S8) loads the FPGA with a hardware page based on the LED
settings. Ta bl e 2– 7 defines the hardware page that loads when the program load
push-button switch (S8) is pressed.
Table 2–7. Program Load Push Button (S8) LED Settings
USER LED FACTORY LED Design
OFF ON Factory hardware
ON OFF User hardware
Note to Tab le 2–7:
(1) ON indicates that the LED is illuminated while OFF indicates that the LED is not illuminated.
USER
(1)
or
FACTORY
LED is illuminated.
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 23

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–15
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
FPGA Configuration using External USB-Blaster
The JTAG programming header provides another method for configuring the FPGA
using an external USB-Blaster device with the Quartus II Programmer running on a
PC. The external USB-Blaster is connected to the board through the JTAG connector
(J6). Figure 2–4 on page 2–13 illustrates the JTAG chain.
By default, the FPGA is the first device in the JTAG chain. To add the MAX II CPLD
EPM2210 System Controller into the JTAG chain, set the JTAG chain select DIP switch
(SW5) to '0'. Table 2–10 on page 2–17 summarizes the board settings DIP switch
controls.
FPGA Configuration using EPCS Device
Active serial configuration can be performed using an Altera® EPCS device. During
configuration, the FPGA is the master and the EPCS128 device is the slave. The
configuration data is transferred to the FPGA on the
clock cycle. This configuration data is synchronized to the
1 Before you program the EPCS device, press the program select push button (S7) to
select the AS configuration scheme. After programming the EPCS device, press the
program load push button (S8) load the design from the EPCS device to the FPGA
when you power up the board.
DATA0
pin at a rate of one bit per
DCLK
input.
EPCS Programming
EPCS programming is possible through a variety of methods. One method to program
the EPCS device is to use the Serial FlashLoader (SFL), a JTAG-based in-system
programming solution for Altera serial configuration devices. The SFL is a bridge
design for the FPGA that uses the JTAG connector (J6) to access the JTAG Indirect
Configuration Device Programming File (.jic) and then uses the AS interface to
program the EPCS device. Both the JTAG and AS interfaces are bridged together
inside the SFL design.
Another method to program the EPCS device is to perform in-system programming
through the AS programming header (J16).
Other methods to program the EPCS can be used as well, including the Nios II
processor.
f For more information on the following topics, refer to the respective documents:
Topic Reference
Board Update Portal Cyclone IV GX Development Kit User Guide
PFL Design Cyclone IV GX Development Kit User Guide
PFL Megafunction AN 386: Using the Parallel Flash Loader with the Quartus II Software
SFL Megafunction AN 370: Using the Serial FlashLoader with the Quartus II Software
Managing and programming
EPCS memory contents
Nios II Flash Programmer User Guide
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 24

2–16 Chapter 2: Board Components
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
Status Elements
The development board includes status LEDs. This section describes the status
elements.
Tab le 2 –8 lists the LED board references, names, and functional descriptions.
Table 2–8. Board-Specific LEDs
Board Reference LED Name Description
Green LED. Illuminates when the HSMC port A has a board or cable
D1 PSNTN A
D2 PSNTN B
D11 POWER Blue LED. Illuminates when 3.3-V power is active.
D16 FPGA_CONF_DONE
D17 FAN
D18 MAX_ERROR
PROGRAM
D19,
D20,
D21
MAX_EPCS
MAX_USER
MAX_FACTORY
D22 USB
D24 1000
D25 100
D26 10
D27 DUP
D28 PCIE_LED_X1
D29 PCIE_LED_X4
D30 ENET TX
D31 ENET RX
plugged-in such that pin 160 becomes grounded. Driven by the add-in
card.
Green LED. Illuminates when the HSMC port B has a board or cable
plugged-in such that pin 160 becomes grounded. Driven by the add-in
card.
Green LED. Illuminates when the FPGA is successfully configured. Driven
by the MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller.
Red LED. Illuminates when the FPGA needs to use the fan and heatsink.
Driven by the MAX II CPLD.
Red LED. Illuminates when the MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller
fails to configure the FPGA. Driven by the MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System
Controller.
Green LEDs. Illuminates to show the LED sequence that determines
which flash memory image is loaded to the FPGA. The image to be loaded
depends on the selection of the three LEDs. Driven by the MAX II CPLD
EPM2210 System Controller.
Green LED. Illuminates when the embedded USB-Blaster is in use to
program the FPGA. Driven by the MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System
Controller.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet linked at 1000 Mbps
connection speed. Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet linked at 100 Mbps
connection speed. Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet linked at 10 Mbps connection
speed. Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet in full-duplex operation.
Driven by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate PCIe connection with channel width of
×1. Driven by the FPGA.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate PCIe connection with channel width of
×4. Driven by the FPGA.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet PHY transmit activity. Driven
by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Green LED. Illuminates to indicate Ethernet PHY receive activity. Driven
by the Marvell 88E1111 PHY.
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 25

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–17
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
Tab le 2 –9 lists the board-specific LEDs component references and manufacturing
information.
Table 2–9. Board-Specific LEDs Component References and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Description Manufacturer Manufacturer Part Number Manufacturer Website
D17, D18 Red LED Lumex, Inc. SML-LXT0805IW-TR www.lumex.com
D1, D2, D11, D16,
D19–D22, D24–D27,
Green LEDs Lumex, Inc. SML-LXT0805GW-TR www.lumex.com
D30, D31
D11 Blue LED Lumex, Inc. SML-LX1206USBC-TR www.lumex.com
Setup Elements
The development board includes several different kinds of setup elements. This
section describes the following setup elements:
■ Board settings DIP switch
■ JTAG chain select DIP switch
■ PCIe control DIP switch
■ Configuration push buttons
■ System reset push button
Board Settings DIP Switch
The board settings DIP switch (S1) controls various features specific to the board and
the MAX
switch controls and descriptions.
Table 2–10. Board Settings DIP Switch Controls
Board
Reference
SW1.1
SW1.2
SW1.3
SW1.4
Note to Table 2–10:
(1) ON indicates a setting of ’0’ while OFF indicates a setting of ’1’.
Schematic Signal Name Description Default
USER_FACTORY
CLK125_EN
CLKA_EN
CLKA_SEL
II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller logic design. Table 2–10 shows the
ON : Factory image
OFF : User image
ON : 125-MHz clock enabled
OFF : 125-MHz clock disabled
ON : On-Board oscillator enabled
OFF : On-Board oscillator disabled
ON : 100-MHz oscillator input select
OFF : SMA input select
(1)
ON
ON
ON
ON
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 26

2–18 Chapter 2: Board Components
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
Tab le 2 –11 lists the board settings DIP switch component reference and
manufacturing information.
Table 2–11. Board Settings DIP Switch Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board
Reference
Description Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Part Number
Manufacturer Website
SW1 Four-position slide DIP switch C & K Components TDA04H0SB1 www.ck-components.com
JTAG Chain Select DIP Switch
The JTAG chain select DIP switch (SW5) controls the selection of devices in the JTAG
chain. Table 2–10 shows the switch controls and descriptions.
Table 2–12. JTAG Chain Select DIP Switch Controls
Board
Reference
SW5.1 EPM2210_JTAG_EN
SW5.2 HSMA_JTAG_EN
SW5.3 HSMB_JTAG_EN
SW5.4 PCIE_JTAG_EN
Notes to Table 2–12:
(1) ON indicates a setting of ’0’ while OFF indicates a setting of ’1’.
(2) You are required to install the biderectional voltage translator analog device (part number ADG3304BRUZ) to chain the PCIe to the JTAG chain.
Schematic Signal Name Description Default
ON : Bypass Max II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller
OFF : Max II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller in-chain
ON : Bypass HSMC port A
OFF : HSMC port A in-chain
ON : Bypass HSMC port B
OFF : HSMC port B in-chain
(2)
ON : Bypass PCIe
OFF : PCIe in-chain
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
(1)
Tab le 2 –11 lists the JTAG chain select DIP switch component reference and
manufacturing information.
Table 2–13. JTAG Chain Select DIP Switch Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board
Reference
Description Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Part Number
Manufacturer Website
SW5 Four-position slide DIP switch C & K Components TDA04H0SB1 www.ck-components.com
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 27

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–19
Configuration, Status, and Setup Elements
PCIe Control DIP Switch
The PCIe control DIP switch (SW4) is provided to enable or disable the different
configurations. Table 2–10 shows the switch controls and descriptions.
Table 2–14. PCIe Control DIP Switch Controls
Board
Reference
SW4.1
SW4.2
SW4.4
Note to Table 2–14:
(1) ON indicates a setting of ’0’ while OFF indicates a setting of ’1’.
Schematic Signal Name Description Default
PCIE_PRSNT2n_x1
PCIE_PRSNT2n_x4
USB_DISABLE
ON : Enable x1 presence detect
OFF : Disable x1 presence detect
ON : Enable x4 presence detect
OFF : Disable x4 presence detect
ON : Embedded USB-Blaster disabled
OFF : Embedded USB-Blaster enabled
Tab le 2 –11 lists the PCIe control DIP switch component reference and manufacturing
information.
Table 2–15. PCIe Control DIP Switch Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board
Reference
Description Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Part Number
Manufacturer Website
SW4 Four-position slide DIP switch C & K Components TDA04H0SB1 www.ck-components.com
Configuration Settings
The MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller controls the configuration settings. A
configuration scheme is selected by driving the MSEL pins either high or low, as
shown in Ta bl e 2– 16 .
(1)
ON
ON
OFF
Table 2–16. Configuration Settings
Configuration Scheme
(1)
Setting
MSEL3 MSEL2 MSEL1 MSEL0
POR
Delay
Active Serial—Enables active serial
configuration with fast or standard
1 1 0 1 Standard
power-on-reset delay.
Fast Passive Parallel—Enables FPP
configuration with fast or standard
0 0 0 1 Standard
power-on-reset delay.
JTAG—JTAG-based configuration X
Notes to Table 2–16:
(1) ON indicates a setting of ’0’ while OFF indicates a setting of ’1’.
(2) X indicates does not care. The JTAG-based configuration takes precedence over other configuration schemes and therefore, the
settings are ignored.
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
(2)
Reference Manual
MSEL[]
—
pin
Page 28

2–20 Chapter 2: Board Components
CLKIN SMA (J10)
ICS8543
CLKBUF
(U25)
FPGA
(U10)
CLKOUT SMA (J9)
PCI Express Reference Clock
125-MHz Oscillator (X2)
50-MHz Oscillator (X3)
LVPECL Input Clock (J11, J12)
100-MHz Oscillator (X4)
CLKA_SEL
CLK125_EN
CLKA_EN
Bank 8
Bank 4
Bank 8A
Bank 3A
Bank 8B
Bank 3B Bank 4
Clock Circuitry
Configuration Push Buttons
The program load push button (S8), is an input to the MAX II CPLD EPM2210 System
Controller. The push button forces a reconfiguration of the FPGA from flash memory.
The location in the flash memory is based on the
position. Valid settings include
FACTORY
or
The program select push button (S7), toggles the program LEDs (D3, D4) sequence.
Refer to Table 2–8 on page 2–16 for the LED sequence definitions.
Tab le 2 –1 7 lists the configuration push buttons component reference and
manufacturing information.
Table 2–17. Configuration Push Buttons Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
board settings
USER
.
DIP switch’s
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Part Number
Manufacturer Website
S7, S8 Push buttons Panasonic EVQPAC07K www.panasonic.com/industrial/
Clock Circuitry
The dedicated clock inputs are located on the top bank 8B and bottom bank 3B of the
Cyclone IV GX device. An on-board programmable oscillator or a bench supply clock
can be distributed to these dedicated clock inputs. The clock going to bank 3B is a
dedicated clock input for 3G applications.
The non-dedicated clocks are located on banks 3A and 8A of the Cyclone IV GX
device. The PCIe reference clock is on bank 3A while the 125-MHz clock is on bank
8A.
Figure 2–5 shows the Cyclone IV GX FPGA development board’s transceiver clock
structure.
Figure 2–5. Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board Transceiver Clock Structure
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 29

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–21
General User Input/Output
General User Input/Output
The development board includes several user I/O interfaces to the FPGA. This section
describes the following I/O interfaces:
■ User-defined push buttons
■ User-defined LEDs
■ User DIP switch
■ Character LCD
User-Defined Push Buttons
The development board includes four user-defined push buttons, a CPU reset push
button, and a system reset push button.
Board references S1, S2, S3, and S4 are push buttons that allow you to interact with the
Cyclone IV GX device. When you press and hold the switch, the device pin is set to
logic 0; when you release the switch, the device pin is set to logic 1. There is no boardspecific function for these general user push buttons.
The system reset push button,
SYS_RESETn
(S5), resets the MAX II CPLD EPM2210
System Controller.
The CPU reset push button,
CPU_RESETn
(S6), resets the FPGA design loaded into the
Cyclone IV GX device. This switch also acts as a regular I/O pin.
Tab le 2 –1 8 lists the user-defined push button schematic signal names and their
corresponding Cyclone IV GX device pin numbers.
Table 2–18. User-Defined Push Button Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board Reference Description
S4
S3
S2
S1
S5
S6
User-defined push button. When the
switch is pressed, a logic 0 is
selected. When the switch is released,
a logic 1 is selected.
Schematic Signal
Name
USER_PB0
USER_PB1
USER_PB2
USER_PB3
SYS_RESETn
CPU_RESETn
I/O Standard
1.8-V
Tab le 2 –1 9 lists the user-defined push button component reference and the
manufacturing information.
Table 2–19. User-Defined Push Button Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Cyclone IV GX
Device Pin Number
C12
D11
F4
D8
AF27
G20
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
S1–S6 Push button Panasonic EVQPAC07K www.panasonic.com/industrial/
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Manufacturer
Part Number
Manufacturer Website
Reference Manual
Page 30

2–22 Chapter 2: Board Components
General User Input/Output
User-Defined LEDs
The development board includes general user-defined LEDs and HSMC user-defined
LEDs. This section describes all user-defined LEDs. For information on board-specific
or status LEDs, refer to “Status Elements” on page 2–16.
General User-Defined LEDs
Board references D7–D10 and D12–D15 are eight user-defined LEDs which allow
status and debugging signals to be driven to the LEDs from the FPGA designs loaded
into the Cyclone IV GX device. The LEDs illuminate when a logic 0 is driven, and
turns off when a logic 1 is driven. There is no board-specific function for these LEDs.
Tab le 2 –2 0 lists the user-defined LED schematic signal names and their corresponding
Cyclone IV GX pin numbers.
Table 2–20. User-Defined LED Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board Reference Description
D15
D14
D13
D12
D10
D9
D8
D7
User-defined LEDs.
Driving a logic 0 on the I/O port turns
the LED ON. Driving a logic 1 on the
I/O port turns the LED OFF.
Schematic
Signal Name
USER_LED0
USER_LED1
USER_LED2
USER_LED3
USER_LED4
USER_LED5
USER_LED6
USER_LED7
I/O Standard
2.5-V
Cyclone IV GX Device
Pin Number
E4
C7
A4
F6
D4
J9
D12
B6
Tab le 2 –2 1 lists the user-defined LED component reference and the manufacturing
information.
Table 2–21. User-Defined LED Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Device Description Manufacturer Manufacturer Part Number Manufacturer Website
D7–D10, D12–D15 Green LEDs Lumex, Inc. SML-LXT0805GW-TR www.lumex.com
HSMC User-Defined LEDs
The HSMC port A and B have two LEDs located nearby. There are no board-specific
functions for the HSMC LEDs. However, the LEDs are labeled TX and RX, and are
intended to display data flow to and from the connected HSMC cards. The LEDs are
driven by the Cyclone IV GX device.
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 31

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–23
General User Input/Output
Tab le 2 –2 2 lists the HSMC user-defined LED schematic signal names and their
corresponding Cyclone IV GX pin numbers.
Table 2–22. HSMC User-Defined LED Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board Reference Description
D4
D3
D6
D5
User-Defined LEDs.
Labeled RX for HSMC Port A.
User-Defined LEDs.
Labeled TX for HSMC Port A.
User-Defined LEDs.
Labeled RX for HSMC Port B.
User-Defined LEDs.
Labeled TX for HSMC Port B.
Schematic
Signal Name
HSMA_RX_LED
HSMA_TX_LED
HSMB_RX_LED
HSMB_TX_LED
I/O Standard
2.5-V
Cyclone IV GX Device
Pin Number
C24
B25
C10
D25
Tab le 2 –2 3 lists the HSMC user-defined LED component reference and the
manufacturing information.
Table 2–23. HSMC User-Defined LED Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Device Description Manufacturer Manufacturer Part Number Manufacturer Website
D3–D6 Green LEDs Lumex, Inc. SML-LXT0805GW-TR www.lumex.com
User-Defined DIP Switch
Board reference SW2 is an 8-pin DIP switch. The switch is user-defined, and is
provided for additional FPGA input control. There is no board-specific function for
this switch.
Tab le 2 –2 4 lists the user-defined DIP switch schematic signal names and their
corresponding Cyclone IV GX pin numbers.
Table 2–24. User-Defined DIP Switch Schematic Signal Names and Functions
Board Reference Description
SW2.1
SW2.2
SW2.3
SW2.4
SW2.5
SW2.6
SW2.7
SW2.8
User-defined DIP switch connected to
FPGA device. When the switch is in
the OPEN or OFF position, a logic 1 is
selected. When the switch is in the
CLOSED or ON position, a logic 0 is
selected.
Schematic
Signal Name
USER_DIPSW0
USER_DIPSW1
USER_DIPSW2
USER_DIPSW3
USER_DIPSW4
USER_DIPSW5
USER_DIPSW6
USER_DIPSW7
I/O Standard
2.5-V
Cyclone IV GX Device
Pin Number
A5
G15
E9
C8
C4
F14
G12
E7
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 32

2–24 Chapter 2: Board Components
General User Input/Output
Tab le 2 –2 1 lists the user-defined LED component reference and the manufacturing
information.
Table 2–25. User-Defined DIP Switch Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Device Description Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Part Number
Manufacturer Website
SW2 Eight-Position DIP switch C & K Components TDA08H0SB1 www.ck-components.com
LCD
The development board contains a single 14-pin 0.1" pitch dual-row header that
interfaces to a 16 character × 2 line Lumex LCD display. The LCD has a 14-pin
receptacle that mounts directly to the board's 14-pin header, so it can be easily
removed for access to components under the display. You can also use the header for
debugging or other purposes.
Tab le 2 –2 6 summarizes the LCD pin assignments. The signal names and directions are
relative to the Cyclone IV GX FPGA.
Table 2–26. LCD Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions
Board Reference Description
J13.4 LCD data or command select
J13.5 LCD write enable
J13.6 LCD chip select
J13.7 LCD data bus
J13.8 LCD data bus
J13.9 LCD data bus
J13.10 LCD data bus
J13.11 LCD data bus
J13.12 LCD data bus
J13.13 LCD data bus
J13.14 LCD data bus
Note to Table 2–26:
(1) All signals are translated from 1.8-V to 2.5-V using a dual/quad low-voltage level translators except for
the
PLL4_CLKOUTn
pin of the Cyclone IV GX FPGA.
Schematic Signal
Name
LCD_D_Cn
LCD_WEn
LCD_CSn
LCD_DATA0
LCD_DATA1
LCD_DATA2
LCD_DATA3
LCD_DATA4
LCD_DATA5
LCD_DATA6
LCD_DATA7
I/O Standard
2.5-V CMOS
LCD_DATA4
Device Pin Number
(1)
, which connects directly to
Cyclone IV GX
D5
E6
C3
C15
F9
D7
E21
C27
G13
E10
F16
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 33

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–25
General User Input/Output
Tab le 2 –2 7 shows the LCD pin definitions, and is an excerpt from the Lumex data
sheet.
f For more information such as timing, character maps, interface guidelines, and other
related documentation, visit www.lumex.com.
Table 2–27. LCD Pin Definitions and Functions
Pin
Number
1V
2V
3V
Symbol
DD
SS
0
Level
—
—GND (0 V)
Power supply
— For LCD drive
Register select signal
4RS H/L
H: Data input
L: Instruction input
5R/W H/L
H: Data read (module to MPU)
L: Data write (MPU to module)
6 E H, H to L Enable
7–14 DB0–DB7 H/L Data bus, software selectable 4-bit or 8-bit mode
1 The particular model used does not have a backlight and the LCD drive pin is not
connected to the power pin for maximum pixel drive.
Tab le 2 –2 8 lists the LCD component references and the manufacturing information.
Table 2–28. LCD Component References and Manufacturing Information
Board
Reference
J13
2×7 pin, 100 mil, vertical header Samtec TSM-107-07-G-D www.samtec.com
2×16 character display, 5×8 dot matrix Lumex Inc. LCM-S01602DSR/C www.lumex.com
Description Manufacturer
Function
Manufacturer
Part Number
5 V
Manufacturer
Website
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 34

2–26 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
This section describes the development board's communication ports and interface
cards relative to the Cyclone IV GX device. The development board supports the
following communication ports:
■ PCIe
■ 10/100/1000 Ethernet
■ HSMC
PCIe
The Cyclone IV GX FPGA development board fits entirely into a PC motherboard
with a ×4 PCIe slot which can accommodate a short-form PCIe add-in card. The
development board comes with a full height I/O bracket for its low profile form factor
card. This interface uses the Cyclone IV GX device's PCIe hard IP block in ×4 lane
configuration, saving logic resources for the user logic application.
f For more information on using the PCIe hard IP block, refer to the PCI Express
Compiler User Guide.
The PCIe interface supports a channel width of ×4 as well as the connection speed of
Gen1 at 2.5 Gbps/lane.
The board’s power can be sourced entirely from the PCIe edge connector when
installed into a PC motherboard. Turn the power switch (SW3) to the
ON
position
when you install the board into a PC motherboard. Although the board can also be
powered by a laptop power supply for use on a lab bench, it is not recommended to
use from both supplies at the same time. Ideal diode power sharing devices have been
designed into this board to prevent damages or back-current from one supply to the
other.
The
PCIE_REFCLK_P
and
PCIE_REFCLK_N
signals are a 100-MHz differential input that
is driven from the PC motherboard onto this board through the PCIe edge connector.
This signal connects directly to a Cyclone IV GX
REFCLK
input pin pair. This clock is
terminated on the motherboard and therefore, no on-board termination is required.
This clock can have spread-spectrum properties that change its period between
9.847 ps to 10.203 ps. The I/O standard is High-Speed Current Steering Logic (HCSL).
1 PCIe signals and HSMC Port B XCVR signals are muxed via resistors and capacitors.
By default, the
PCIE_RX_P
connected to the
and
XCVR_RX_P
PCIE_RX_N
PCIE_TX_P
and
XCVR_RX_N
signals, while the
and
PCIE_TX_N
channels of the FPGA are connected to the
XCVR_TX_P
and
XCVR_TX_N
channels are
signals.
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 35

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–27
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Tab le 2 –2 9 summarizes the PCIe pin assignments. The signal names and directions are
relative to the Cyclone IV GX FPGA.
Table 2–29. PCIe Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions
Cyclone IV GX
Board Reference Description
J14.A16 Add-in card transmit bus
J14.A17 Add-in card transmit bus
J14.A21 Add-in card transmit bus
J14.A22 Add-in card transmit bus
J14.A25 Add-in card transmit bus
J14.A26 Add-in card transmit bus
J14.A29 Add-in card transmit bus
J14.A30 Add-in card transmit bus
J14.B14 Add-in card receive bus
J14.B15 Add-in card receive bus
J14.B19 Add-in card receive bus
J14.B20 Add-in card receive bus
J14.B23 Add-in card receive bus
J14.B24 Add-in card receive bus
J14.B27 Add-in card receive bus
J14.B28 Add-in card receive bus
J14.A13 Motherboard reference clock
J14.A14 Motherboard reference clock
J14.A11 Reset
J14.B5 SMB clock
J14.B6 SMB data
J14.B11 Wake signal
J14.B17 x1 Present
J14.B31 x4 Present
J14.A5 Motherboard TCK
J14.A6 Motherboard TDI
J14.A7 Motherboard TDO
J14.A8 Motherboard TMS
Notes to Table 2–29:
(1) This signal is multiplexed with the signal on HSMC port B interface.
(2) The Quartus II version 10.1sp1 and newer only support an I/O standard of 1.5-V PCML for the PCI Express transmitter as stated in Altera’s
knowledge base webpage—solution ID rd12272010_575.
Schematic Signal Name
PCIE_TX_P0
PCIE_TX_N0
PCIE_TX_P1
PCIE_TX_N1
PCIE_TX_P2
PCIE_TX_N2
PCIE_TX_P3
PCIE_TX_N3
PCIE_RX_P0
PCIE_RX_N0
PCIE_RX_P1
PCIE_RX_N1
PCIE_RX_P2
PCIE_RX_N2
PCIE_RX_P3
PCIE_RX_N3
PCIE_REFCLK_P
PCIE_REFCLK_N
PCIE_T_PERSTn
PCIE_T_SMBCLK
PCIE_T_SMBDAT
PCIE_WAKEn_R
PCIE_PRSNT2n_x1
PCIE_PRSNT2n_x4
PCIE_JTAG_TCK
PCIE_JTAG_TDI
PCIE_JTAG_TDO
PCIE_JTAG_TMS
I/O Standard
Device
Pin Number
(1)
AB4
(1)
AB3
(1)
Y4
(1)
Y3
(1)
V4
(1)
V3
(1)
T4
(1)
1.5-V PCML
HCSL
(2)
T3
AC2
AC1
AA2
AA1
W2
W1
U2
U1
V15
W15
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
A7
LVT TL
F15
E12
—
——
——
—
3.3-V
—
—
—
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 36

2–28 Chapter 2: Board Components
10/100/1000 Mbps
Ethernet MAC
Marvell 88E1111
PHY
Device
RJ45
RGMII Interface
Translator
(1.8 V to 2.5 V)
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
10/100/1000 Ethernet
A Marvell 88E1111 PHY device is used for 10/100/1000 BASE-T Ethernet connection.
The device is an auto-negotiating Ethernet PHY with an RGMII interface to the FPGA.
The MAC function must be provided in the FPGA for typical networking applications
such the Altera Triple Speed Ethernet MegaCore design. The Marvell 88E1111 PHY
uses 2.5-V and 1.1-V power rails and requires a 25-MHz reference clock driven from a
dedicated oscillator. The device interfaces to a Halo Electronics HFJ11-1G02E model
RJ45 with internal magnetics that can be used for driving copper lines with Ethernet
traffic.
Figure 2–6 shows the RGMII interface between the FPGA (MAC) and Marvell 88E1111
PHY.
Figure 2–6. SGMII Interface between FPGA (MAC) and Marvell 88E1111 PHY
Tab le 2 –3 0 lists the Ethernet PHY interface pin assignments.
Table 2–30. Ethernet PHY Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Board Reference Description
U21.11 RGMII TX data
U21.12 RGMII TX data
U21.13 RGMII TX data
U21.14 RGMII TX data
U21.8 RGMII TX clock
U21.9 RGMII TX control
U21.95 RGMII RX data
U21.92 RGMII RX data
U21.93 RGMII RX data
U21.91 RGMII RX data
U21.2 RGMII RX clock
U21.94 RGMII RX data valid
U21.25 Management bus control
U21.24 Management bus data
U21.23 Management bus interrupt
U21.28 Device reset
U21.68 RX data active LED
U21.69 TX data active LED
U21.76 10 Mbps connection speed LED
Schematic Signal Name
ENET_T_TX_D0
ENET_T_TX_D1
ENET_T_TX_D2
ENET_T_TX_D3
ENET_T_GTX_CLK
ENET_T_TX_EN
ENET_T_RX_D0
ENET_T_RX_D1
ENET_T_RX_D2
ENET_T_RX_D3
ENET_T_RX_CLK
ENET_T_RX_DV
ENET_T_MDC
ENET_T_MDIO
ENET_T_INTN
ENET_T_RESETn
ENET_LED_TX
ENET_LED_RX
ENET_LED_LINK10
I/O Standard
1.8-V CMOS
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
G10
E3
D10
B10
D9
A27
F5
B9
G14
E13
B15
E15
K21
G7
A11
D6
—
—
—
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 37

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–29
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Table 2–30. Ethernet PHY Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions
Cyclone IV GX
Board Reference Description
U21.74 100 Mbps connection speed LED
U21.73 1000 Mbps connection speed LED
U21.70 Duplex or collision LED
Schematic Signal Name
ENET_LED_LINK100
ENET_LED_LINK1000
ENET_LED_DUPLEX
I/O Standard
1.8-V CMOS
Device
Pin Number
—
—
—
Tab le 2 –3 1 lists the Ethernet PHY interface component reference and manufacturing
information.
Table 2–31. Ethernet PHY Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board
Reference
U21 Ethernet PHY BASE-T device Marvell Semiconductor 88E1111-B2-CAAIC000 www.marvell.com
Description Manufacturer
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
Transceiver Connector (Optional)
The HSMC port B interface (J2) uses the same transceivers as the PCIe interface. A
capacitor or resistor stuffing option is used to select the transceivers for either the
PCIe or the HSMC port B interface. The default stuffing option is the PCIe interface.
Tab le 2 –3 2 lists the capacitor or resistor stuffing option to enable either the PCIe
interface or the HSMC port B interface. The multiplexer capacitors are 0.1 μF and the
multiplexer resistors are 0 Ω.
Table 2–32. Multiplexer Location for PCIe Interface and HSMC Port B Interface
Selection Multiplexer Location
PCIe interface
HSMC port B interface
Populate C324, C326, C328, C330, C341, C343, C345, C347, R80,
R81, R84, R86, R88, R89, R92, R96
Populate C323, C325, C327, C329, C340, C342, C344, C346, R82,
R83, R85, R87, R90, R91, R93, R97
High-Speed Mezzanine Cards
The development board contains two HSMC interfaces—port A and port B. The
HSMC port A interface supports both single-ended and differential signaling while
the HSMC port B interface only supports single-ended signaling. The HSMC interface
also allows JTAG, SMB, clock outputs and inputs, as well as power for compatible
HSMC cards. The HSMC is an Altera-developed open specification, which allows you
to expand the functionality of the development board through the addition of
daughtercards.
f For more information about the HSMC specification such as signaling standards,
signal integrity, compatible connectors, and mechanical information, refer to the High
Speed Mezzanine Card (HSMC) Specification manual.
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 38

2–30 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
The HSMC connector has a total of 172 pins, including 120 signal pins, 39 power pins,
and 13 ground pins. The ground pins are located between the two rows of signal and
power pins, acting both as a shield and a reference. The HSMC host connector is
based on the 0.5 mm-pitch QSH/QTH family of high-speed, board-to-board
connectors from Samtec. There are three banks in this connector. Bank 1 has every
third pin removed as done in the QSH-DP/QTH-DP series. Bank 2 and bank 3 have
all the pins populated as done in the QSH/QTH series.
The HSMC port A interface has programmable bi-directional I/O pins that can be
used as 2.5-V LVCMOS, which is 3.3-V LVTTL-compatible. These pins can also be
used as various differential I/O standards including, but not limited to, LVDS,
mini-LVDS, and RSDS with up to 17 full-duplex channels. The HSMC port B interface
is translated from 1.8 V (on the FPGA) to 2.5 V (on the HSMC connector) using a
bidirectional voltage translator.
1 As noted in the High Speed Mezzanine Card (HSMC) Specification manual, LVDS and
single-ended I/O standards are only guaranteed to function when mixed according to
either the generic single-ended pin-out or generic differential pin-out.
Tab le 2 –3 3 lists the HSMC port A interface pin assignments, signal names, and
functions.
Table 2–33. HSMC Port A Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 1 of 4)
Board
Reference
J1.17 Transceiver TX bit 3
J1.19 Transceiver TX bit 3n
J1.18 Transceiver RX bit 3
J1.20 Transceiver RX bit 3n
J1.21 Transceiver TX bit 2
J1.23 Transceiver TX bit 2n
J1.22 Transceiver RX bit 2
J1.24 Transceiver RX bit 2n
J1.25 Transceiver TX bit 1
J1.27 Transceiver TX bit 1n
J1.26 Transceiver RX bit 1
J1.28 Transceiver RX bit 1n
J1.29 Transceiver TX bit 0
J1.31 Transceiver TX bit 0n
J1.30 Transceiver RX bit 0
J1.32 Transceiver RX bit 0n
J1.33 Management serial data
J1.34 Management serial clock
J1.35 JTAG clock signal
J1.36 JTAG mode select signal
J1.37 JTAG data output
Description
Schematic Signal
Name
HSMA_TX_P3
HSMA_TX_N3
HSMA_RX_P3
HSMA_RX_N3
HSMA_TX_P2
HSMA_TX_N2
HSMA_RX_P2
HSMA_RX_N2
HSMA_TX_P1
HSMA_TX_N1
HSMA_RX_P1
HSMA_RX_N1
HSMA_TX_P0
HSMA_TX_N0
HSMA_RX_P0
HSMA_RX_N0
HSMA_T_SDA
HSMA_T_SCL
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TMS
HSMA_JTAG_TDO
I/O Standard
1.5 V
2.5-V
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
H4
H3
J2
J1
K4
K3
L2
L1
M4
M3
N2
N1
P4
P3
R2
R1
C25
B24
F2
E1
—
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 39

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–31
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Table 2–33. HSMC Port A Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 2 of 4)
Board
Reference
Description
J1.38 JTAG data input
J1.39 Dedicated CMOS clock out
J1.40 Dedicated CMOS clock in
J1.41 Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 0
J1.42 Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 1
J1.43 Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 2
J1.44 Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 3
J1.47 LVDS TX bit 0 or CMOS bit 4
J1.48 LVDS RX bit 0 or CMOS bit 5
J1.49 LVDS TX bit 0n or CMOS bit 6
J1.50 LVDS RX bit 0n or CMOS bit 7
J1.53 LVDS TX bit 1 or CMOS bit 8
J1.54 LVDS RX bit 1 or CMOS bit 9
J1.55 LVDS TX bit 1n or CMOS bit 10
J1.56 LVDS RX bit 1n or CMOS bit 11
J1.59 LVDS TX bit 2 or CMOS bit 12
J1.60 LVDS RX bit 2 or CMOS bit 13
J1.61 LVDS TX bit 2n or CMOS bit 14
J1.62 LVDS RX bit 2n or CMOS bit 15
J1.65 LVDS TX bit 3 or CMOS bit 16
J1.66 LVDS RX bit 3 or CMOS bit 17
J1.67 LVDS TX bit 3n or CMOS bit 18
J1.68 LVDS RX bit 3n or CMOS bit 19
J1.71 LVDS TX bit 4 or CMOS bit 20
J1.72 LVDS RX bit 4 or CMOS bit 21
J1.73 LVDS TX bit 4n or CMOS bit 22
J1.74 LVDS RX bit 4n or CMOS bit 23
J1.77 LVDS TX bit 5 or CMOS bit 24
J1.78 LVDS RX bit 5 or CMOS bit 25
J1.79 LVDS TX bit 5n or CMOS bit 26
J1.80 LVDS RX bit 5n or CMOS bit 27
J1.83 LVDS TX bit 6 or CMOS bit 28
J1.84 LVDS RX bit 6 or CMOS bit 29
J1.85 LVDS TX bit 6n or CMOS bit 30
J1.86 LVDS RX bit 6n or CMOS bit 31
J1.89 LVDS TX bit 7 or CMOS bit 32
J1.90 LVDS RX bit 7 or CMOS bit 33
J1.91 LVDS TX bit 7n or CMOS bit 34
Schematic Signal
Name
HSMA_JTAG_TDI
HSMA_CLK_OUT0
HSMA_CLK_IN0
HSMA_D0
HSMA_D1
HSMA_D2
HSMA_D3
HSMA_TX_D_P0
HSMA_RX_D_P0
HSMA_TX_D_N0
HSMA_RX_D_N0
HSMA_TX_D_P1
HSMA_RX_D_P1
HSMA_TX_D_N1
HSMA_RX_D_N1
HSMA_TX_D_P2
HSMA_RX_D_P2
HSMA_TX_D_N2
HSMA_RX_D_N2
HSMA_TX_D_P3
HSMA_RX_D_P3
HSMA_TX_D_N3
HSMA_RX_D_N3
HSMA_TX_D_P4
HSMA_RX_D_P4
HSMA_TX_D_N4
HSMA_RX_D_N4
HSMA_TX_D_P5
HSMA_RX_D_P5
HSMA_TX_D_N5
HSMA_RX_D_N5
HSMA_TX_D_P6
HSMA_RX_D_P6
HSMA_TX_D_N6
HSMA_RX_D_N6
HSMA_TX_D_P7
HSMA_RX_D_P7
HSMA_TX_D_N7
I/O Standard
2.5-V
LVDS or 2.5-V or
1.8-V
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
—
—
—
AC27
Y27
AF30
AD27
C29
D29
C30
D30
E27
G26
E28
G27
F26
N24
F27
M25
F30
N25
E30
M26
F28
R24
F29
P25
H30
N27
G30
N28
G28
M29
G29
M30
J29
N29
J30
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 40

2–32 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Table 2–33. HSMC Port A Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 3 of 4)
Board
Reference
Description
J1.92 LVDS RX bit 7n or CMOS bit 35
J1.95 LVDS or CMOS clock out 1 or CMOS bit 36
J1.96 LVDS or CMOS clock in 1 or CMOS bit 37
J1.97 LVDS or CMOS clock out 1 or CMOS bit 38
J1.98 LVDS or CMOS clock in 1 or CMOS bit 39
J1.101 LVDS TX bit 8 or CMOS bit 40
J1.102 LVDS RX bit 8 or CMOS bit 41
J1.103 LVDS TX bit 8n or CMOS bit 42
J1.104 LVDS RX bit 8n or CMOS bit 43
J1.107 LVDS TX bit 9 or CMOS bit 44
J1.108 LVDS RX bit 9 or CMOS bit 45
J1.109 LVDS TX bit 9n or CMOS bit 46
J1.110 LVDS RX bit 9n or CMOS bit 47
J1.113 LVDS TX bit 10 or CMOS bit 48
J1.114 LVDS RX bit 10 or CMOS bit 49
J1.115 LVDS TX bit 10n or CMOS bit 50
J1.116 LVDS RX bit 10n or CMOS bit 51
J1.119 LVDS TX bit 11 or CMOS bit 52
J1.120 LVDS RX bit 11 or CMOS bit 53
J1.121 LVDS TX bit 11n or CMOS bit 54
J1.122 LVDS RX bit 11n or CMOS bit 55
J1.125 LVDS TX bit 12 or CMOS bit 56
J1.126 LVDS RX bit 12 or CMOS bit 57
J1.127 LVDS TX bit 12n or CMOS bit 58
J1.128 LVDS RX bit 12n or CMOS bit 59
J1.131 LVDS TX bit 13 or CMOS bit 60
J1.132 LVDS RX bit 13 or CMOS bit 61
J1.133 LVDS TX bit 13n or CMOS bit 62
J1.134 LVDS RX bit 13n or CMOS bit 63
J1.137 LVDS TX bit 14 or CMOS bit 64
J1.138 LVDS RX bit 14 or CMOS bit 65
J1.139 LVDS TX bit 14n or CMOS bit 66
J1.140 LVDS RX bit 14n or CMOS bit 67
J1.143 LVDS TX bit 15 or CMOS bit 68
J1.144 LVDS RX bit 15 or CMOS bit 69
J1.145 LVDS TX bit 15n or CMOS bit 70
J1.146 LVDS RX bit 15n or CMOS bit 71
J1.149 LVDS TX bit 16 or CMOS bit 72
Schematic Signal
Name
HSMA_RX_D_N7
HSMA_CLK_OUT_P1
HSMA_CLK_IN_P1
HSMA_CLK_OUT_N1
HSMA_CLK_IN_N1
HSMA_TX_D_P8
HSMA_RX_D_P8
HSMA_TX_D_N8
HSMA_RX_D_N8
HSMA_TX_D_P9
HSMA_RX_D_P9
HSMA_TX_D_N9
HSMA_RX_D_N9
HSMA_TX_D_P10
HSMA_RX_D_P10
HSMA_TX_D_N10
HSMA_RX_D_N10
HSMA_TX_D_P11
HSMA_RX_D_P11
HSMA_TX_D_N11
HSMA_RX_D_N11
HSMA_TX_D_P12
HSMA_RX_D_P12
HSMA_TX_D_N12
HSMA_RX_D_N12
HSMA_TX_D_P13
HSMA_RX_D_P13
HSMA_TX_D_N13
HSMA_RX_D_N13
HSMA_TX_D_P14
HSMA_RX_D_P14
HSMA_TX_D_N14
HSMA_RX_D_N14
HSMA_TX_D_P15
HSMA_RX_D_P15
HSMA_TX_D_N15
HSMA_RX_D_N15
HSMA_TX_D_P16
I/O Standard
LVDS or 2.5-V or
1.8-V
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
N30
P21
T29
N21
T30
L30
P27
K30
P28
J28
R30
H28
P30
J27
R27
H27
R28
L27
T28
L28
R29
M27
R25
M28
R26
K26
T26
K27
T27
K25
U25
J26
T25
J25
T23
H25
T24
M21
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 41

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–33
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Table 2–33. HSMC Port A Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 4 of 4)
Board
Reference
Description
J1.150 LVDS RX bit 16 or CMOS bit 73
J1.151 LVDS TX bit 16n or CMOS bit 74
J1.152 LVDS RX bit 16n or CMOS bit 75
J1.155 LVDS or CMOS clock out 2 or CMOS bit 76
J1.156 LVDS or CMOS clock in 2 or CMOS bit 77
J1.157 LVDS or CMOS clock out 2 or CMOS bit 78
J1.158 LVDS or CMOS clock in 2 or CMOS bit 79
J1.160 HSMC Port A presence detect
D4
D3
User LED to show RX data activity on
HSMC Port A
User LED to show TX data activity on
HSMC Port A
Schematic Signal
Name
HSMA_RX_D_P16
HSMA_TX_D_N16
HSMA_RX_D_N16
HSMA_CLK_OUT_P2
HSMA_CLK_IN_P2
HSMA_CLK_OUT_N2
HSMA_CLK_IN_N2
HSMA_PSNTn
HSMA_RX_LED
HSMA_TX_LED
I/O Standard
LVDS or 2.5-V or
1.8-V
2.5-V
Tab le 2 –3 4 lists the HSMC port B interface pin assignments, signal names, and
functions.
Table 2–34. HSMC Port B Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 1 of 5)
.
Board
Reference
Description Schematic Signal
J2.17 Transceiver TX bit 3
J2.18 Transceiver RX bit 3
J2.19 Transceiver TX bit 3n
J2.20 Transceiver RX bit 3n
J2.21 Transceiver TX bit 2
J2.22 Transceiver RX bit 2
J2.23 Transceiver TX bit 2n
J2.24 Transceiver RX bit 2n
J2.25 Transceiver TX bit 1
J2.26 Transceiver RX bit 1
J2.27 Transceiver TX bit 1n
J2.28 Transceiver RX bit 1n
J2.29 Transceiver TX bit 0
J2.30 Transceiver RX bit 0
J2.31 Transceiver TX bit 0n
J2.32 Transceiver RX bit 0n
J2.33 Management serial data
J2.34 Management serial clock
J2.37 JTAG data output
J2.38 JTAG data input
Name
HSMB_TX_P3
HSMB_RX_P3
HSMB_TX_N3
HSMB_RX_N3
HSMB_TX_P2
HSMB_RX_P2
HSMB_TX_N2
HSMB_RX_N2
HSMB_TX_P1
HSMB_RX_P1
HSMB_TX_N1
HSMB_RX_N1
HSMB_TX_P0
HSMB_RX_P0
HSMB_TX_N0
HSMB_RX_N0
HSMB_T_SDA
HSMB_T_SCL
HSMB_JTAG_TDO
HSMB_JTAG_TDI
I/O Standard
1.5-V
2.5-V
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
— C329.1
—R97.2
— C346.1
— R101.2
— C327.1
—R94.2
— C344.1
—R95.2
— C325.1
—R89.2
— C342.1
—R91.2
— C323.1
—R86.2
— C340.1
—R87.2
—U39.1
—U39.8
— U2.5
— U1.9; U2.2
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
U21
M22
T21
K28
V29
K29
V30
A25
C24
D25
Other
Connections
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 42

2–34 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Table 2–34. HSMC Port B Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 2 of 5)
Board
Reference
Description Schematic Signal
J2.39 Dedicated CMOS clock out
J2.40 Dedicated CMOS clock in
J2.41 Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 0
J2.42 Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 1
J2.43 Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 2
J2.44 Dedicated CMOS I/O bit 3
J2.47 CMOS bit 4
J2.48 CMOS bit 5
J2.49 CMOS bit 6
J2.50 CMOS bit 7
J2.53 CMOS bit 8
J2.54 CMOS bit 9
J2.55 CMOS bit 10
J2.56 CMOS bit 11
J2.59 CMOS bit 12
J2.60 CMOS bit 13
J2.61 CMOS bit 14
J2.62 CMOS bit 15
J2.65 CMOS bit 16
J2.66 CMOS bit 17
J2.67 CMOS bit 18
J2.68 CMOS bit 19
J2.71 CMOS bit 20
J2.72 CMOS bit 21
J2.73 CMOS bit 22
J2.74 CMOS bit 23
J2.77 CMOS bit 24
J2.78 CMOS bit 25
J2.79 CMOS bit 26
J2.80 CMOS bit 27
J2.83 CMOS bit 28
J2.84 CMOS bit 29
J2.85 CMOS bit 30
J2.86 CMOS bit 31
J2.89 CMOS bit 32
J2.90 CMOS bit 33
J2.91 CMOS bit 34
J2.92 CMOS bit 35
Name
HSMB_CLK_OUT0
HSMB_CLK_IN0
HSMB_D0
HSMB_D1
HSMB_D2
HSMB_D3
HSMB_TX_D_P0
HSMB_RX_D_P0
HSMB_TX_D_N0
HSMB_RX_D_N0
HSMB_TX_D_P1
HSMB_RX_D_P1
HSMB_TX_D_N1
HSMB_RX_D_N1
HSMB_TX_D_P2
HSMB_RX_D_P2
HSMB_TX_D_N2
HSMB_RX_D_N2
HSMB_TX_D_P3
HSMB_RX_D_P3
HSMB_TX_D_N3
HSMB_RX_D_N3
HSMB_TX_D_P4
HSMB_RX_D_P4
HSMB_TX_D_N4
HSMB_RX_D_N4
HSMB_TX_D_P5
HSMB_RX_D_P5
HSMB_TX_D_N5
HSMB_RX_D_N5
HSMB_T_TX_D_P6
HSMB_T_RX_D_P6
HSMB_T_TX_D_N6
HSMB_T_RX_D_N6
HSMB_T_TX_D_P7
HSMB_T_RX_D_P7
HSMB_T_TX_D_N7
HSMB_T_RX_D_N7
I/O Standard
2.5-V
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
Other
Connections
AA22 —
—U30.4
AH29 —
AE30 —
AD29 —
AG29 —
AB28 —
AB30 —
AC30 —
AA28 —
Y28 —
AA27 —
AA26 —
AD30 —
AC28 —
AB27 —
AB26 —
AB25 —
AG30 —
AE28 —
V21 —
AD26 —
AF28 —
AC25 —
AE27 —
AD25 —
AE26 —
AJ30 —
AE25 —
Y22 —
— U36.12
— U38.17
— U36.13
— U38.16
— U36.14
— U38.15
— U36.15
— U38.12
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 43

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–35
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Table 2–34. HSMC Port B Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 3 of 5)
Board
Reference
Description Schematic Signal
J2.95 CMOS clock out 1 or CMOS bit 36
J2.96 CMOS clock in 1 or CMOS bit 37
J2.97 CMOS clock out 1 or CMOS bit 38
J2.98 CMOS clock in 1 or CMOS bit 39
J2.101 CMOS bit 40
J2.102 CMOS bit 41
J2.103 CMOS bit 42
J2.104 CMOS bit 43
J2.107 CMOS bit 44
J2.108 CMOS bit 45
J2.109 CMOS bit 46
J2.110 CMOS bit 47
J2.113 CMOS bit 48
J2.114 CMOS bit 49
J2.115 CMOS bit 50
J2.116 CMOS bit 51
J2.119 CMOS bit 52
J2.120 CMOS bit 53
J2.121 CMOS bit 54
J2.122 CMOS bit 55
J2.125 CMOS bit 56
J2.126 CMOS bit 57
J2.127 CMOS bit 58
J2.128 CMOS bit 59
J2.131 CMOS bit 60
J2.132 CMOS bit 61
J2.133 CMOS bit 62
J2.134 CMOS bit 63
J2.137 CMOS bit 64
J2.138 CMOS bit 65
J2.139 CMOS bit 66
J2.140 CMOS bit 67
J2.143 CMOS bit 68
J2.144 CMOS bit 69
J2.145 CMOS bit 70
J2.146 CMOS bit 71
J2.149 CMOS bit 72
J2.150 CMOS bit 73
Name
HSMB_CLK_OUT_P1
HSMB_CLK_IN_P1
HSMB_CLK_OUT_N1
HSMB_CLK_IN_N1
HSMB_T_TX_D_P8
HSMB_T_RX_D_P8
HSMB_T_TX_D_N8
HSMB_T_RX_D_N8
HSMB_T_TX_D_P9
HSMB_T_RX_D_P9
HSMB_TX_D_N9
HSMB_T_RX_D_N9
HSMB_T_TX_D_P10
HSMB_T_RX_D_P10
HSMB_T_TX_D_N10
HSMB_T_RX_D_N10
HSMB_T_TX_D_P11
HSMB_T_RX_D_P11
HSMB_T_TX_D_N11
HSMB_T_RX_D_N11
HSMB_T_TX_D_P12
HSMB_T_RX_D_P12
HSMB_T_TX_D_N12
HSMB_T_RX_D_N12
HSMB_T_TX_D_P13
HSMB_T_RX_D_P13
HSMB_T_TX_D_N13
HSMB_T_RX_D_N13
HSMB_T_TX_D_P14
HSMB_T_RX_D_P14
HSMB_T_TX_D_N14
HSMB_T_RX_D_N14
HSMB_T_TX_D_P15
HSMB_T_RX_D_P15
HSMB_T_TX_D_N15
HSMB_T_RX_D_N15
HSMB_T_TX_D_P16
HSMB_T_RX_D_P16
I/O Standard
2.5-V
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
AA25 —
W30 R167.1
AH30 —
W29 R167.2
— U36.16
— U37.15
— U35.17
— U37.16
AD28 —
— U36.17
— U38.14
— U29.13
— U37.19
— U29.14
— U37.14
— U36.19
— U37.13
— U29.15
— U38.18
— U29.16
— U29.12
— U35.19
— U29.17
— U35.13
— U28.15
— U35.16
AF18 U38.19
— U35.15
— U28.16
— U28.19
— U28.17
— U35.12
— U28.18
Other
Connections
U35.14
U38.13
U37.17
U37.18
U35.18
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 44

2–36 Chapter 2: Board Components
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Table 2–34. HSMC Port B Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 4 of 5)
Board
Reference
Description Schematic Signal
J2.151 CMOS bit 74
J2.152 CMOS bit 75
J2.155 CMOS bit 76
J2.156 CMOS bit 77
J2.157 CMOS bit 78
J2.158 CMOS clock in 2 or CMOS bit 79
J2.160 HSMC Port B presence detect
D6
D5
User LED to show RX data activity
on HSMC Port B
User LED to show TX data activity
on HSMC Port B
——
— Dedicated CMOS clock in
— Dedicated CMOS clock out
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
— Management serial data
— Management serial clock
Name
HSMB_T_TX_D_N16
HSMB_T_RX_D_N16
HSMB_T_CLK_OUT_P2
HSMBT_CLK_IN_P2
HSMB_CLK_OUT_N2
HSMB_CLK_IN_N2
HSMB_PSNTn
HSMB_RX_LED
HSMB_TX_LED
HSMAT_CLK_IN0
HSMB_CLK_IN_P2
HSMB_CLK_OUT_P2
HSMB_RX_D_N6
HSMB_RX_D_N7
HSMB_RX_D_N8
HSMB_RX_D_N9
HSMB_RX_D_N10
HSMB_RX_D_N11
HSMB_RX_D_N12
HSMB_RX_D_N13
HSMB_RX_D_N14
HSMB_RX_D_N15
HSMB_RX_D_N16
HSMB_RX_D_P6
HSMB_RX_D_P7
HSMB_RX_D_P8
HSMB_RX_D_P9
HSMB_RX_D_P10
HSMB_RX_D_P11
HSMB_RX_D_P12
HSMB_RX_D_P13
HSMB_RX_D_P14
HSMB_RX_D_P15
HSMB_SCL
HSMB_SDA
I/O Standard
2.5-V
1.8-V
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
Other
Connections
— U36.18
— U37.12
—U34.3
—U33.4
Y25 —
V28 —
C26 U7.H2;R2.1
C10 D6.2
D25 D5.2
A15 U32.3
AG22 U33.3
AG19 U34.4
AE19 U38.5
AJ25 U38.9
Y20 U38.8
AE17 U37.4
AA20 U38.7
AK19 U37.7
AG20 U38.3
AD10 U29.4
AF18 U38.2
AG3 U28.4
AD16 U37.9
AE20 U38.4
AG23 U38.6
AK20 U37.6
AJ19 U37.5
AE16 U37.3
AG17 U37.2
AG18 U37.8
AG16 U29.9
AH3 U28.6
AK13 U28.5
K22 U39.5
F10 U39.4
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 45

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–37
Components and Transceiver Interfaces
Table 2–34. HSMC Port B Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 5 of 5)
Board
Reference
Description Schematic Signal
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
——
Name
HSMB_RX_D_P16
HSMB_TX_D_N6
HSMB_TX_D_N7
HSMB_TX_D_N8
HSMB_TX_D_N10
HSMB_TX_D_N11
HSMB_TX_D_N12
HSMB_TX_D_N13
HSMB_TX_D_N14
HSMB_TX_D_N15
HSMB_TX_D_N16
HSMB_TX_D_P6
HSMB_TX_D_P7
HSMB_TX_D_P8
HSMB_TX_D_P9
HSMB_TX_D_P10
HSMB_TX_D_P11
HSMB_TX_D_P12
HSMB_TX_D_P13
HSMB_TX_D_P14
HSMB_TX_D_P15
HSMB_TX_D_P16
HSMBT_CLK_IN0
I/O Standard
1.8-V
Cyclone IV GX
Device
Pin Number
D3 U28.3
AH28 U36.8
AJ27 U36.6
AH22 U35.7
AH21 U35.3
AF7 U29.7
AF9 U29.6
AJ21 U35.2
AF22 U35.5
AK6 U28.2
AH25 U36.3
AG28 U36.9
AJ28 U36.7
AG26 U36.5
AJ22 U35.4
AH26 U36.4
AK21 U29.8
AE23 U36.2
AF10 U29.5
AK24 U35.8
AD22 U35.6
AF25 U35.9
AJ16 U30.3
Other
Connections
Tab le 2 –3 5 lists the signals that multiplex between the PCIe and the HSMB
transceivers.
Table 2–35. HSMC Port B Transceiver and PCIe Signals (Part 1 of 2)
HSMC Port B Transceiver
Signal
PCIe Signal
HSMB_RX_N0 XCVR_RX_N0
HSMB_RX_N1 XCVR_RX_N1
HSMB_RX_N2 XCVR_RX_N2
HSMB_RX_N3 XCVR_RX_N3
HSMB_RX_P0 XCVR_RX_P0
HSMB_RX_P1 XCVR_RX_P1
HSMB_RX_P2 XCVR_RX_P2
HSMB_RX_P3 XCVR_RX_P3
HSMB_TX_N0 XCVR_TX_N0
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Cyclone IV GX Device Pin
Number
AC1
AA1
W1
U1
AC2
AA2
W2
U2
AB3
Reference Manual
Page 46

2–38 Chapter 2: Board Components
Memory
Table 2–35. HSMC Port B Transceiver and PCIe Signals (Part 2 of 2)
HSMC Port B Transceiver
Signal
HSMB_TX_N1 XCVR_TX_N1
HSMB_TX_N2 XCVR_TX_N2
HSMB_TX_N3 XCVR_TX_N3
HSMB_TX_P0 XCVR_TX_P0
HSMB_TX_P1 XCVR_TX_P1
HSMB_TX_P2 XCVR_TX_P2
HSMB_TX_P3 XCVR_TX_P3
PCIe Signal
Tab le 2 –3 6 lists the HSMC connector component reference and manufacturing
information.
Table 2–36. HSMC Connector Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
J1 and J2
HSMC, custom version of QSH-DP
family high-speed socket.
Samtec ASP-122953-01 www.samtec.com
Manufacturing
Part Number
Memory
Cyclone IV GX Device Pin
Number
Y3
V3
T3
AB4
Y4
V4
T4
Manufacturer
Website
This section describes the board's memory interface support and also their signal
names, types, and connectivity relative to the Cyclone IV GX device. The board has
the following memory interfaces:
■ DDR2 SDRAM
■ SSRAM
■ Flash
DDR2 SDRAM
There are four DDR2 devices, providing 256 MB of memory for each on-board DDR2
SDRAM device. Each device interface has a 16-bit data bus, which can be configured
to run individually or together as a 32-bit data bus.
Two DDR2 devices are pinned out to FPGA bank 3 and 4 (bottom port) while another
two are pinned out to FPGA bank 7 and 8 (top port). These memory interfaces are
designed to run at a maximum frequency of 167 MHz for a maximum theoretical
bandwidth of over 10.6 Gbps. The internal bus in the FPGA is typically 2 or 4 times
the width at full rate or half rate respectively. For example, a 167 MHz 16-bit interface
becomes a 83.5 MHz 64-bit bus.
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 47

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–39
Memory
DDR2 SDRAM Top Port
The DDR2 SDRAM top port consists of two DDR2 devices (U8 and U15). Table 2–37
lists the DDR2 top port pin assignments, signal names, and its functions. The signal
names and types are relative to the Cyclone IV GX device in terms of I/O setting and
direction.
Table 2–37. DDR2 SDRAM Top Port Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions (Part 1 of 2)
Cyclone IV GX
Board Reference Description Schematic Signal
Name
U8.R2, U15.R2 Address bus
U8.P7, U15.P7 Address bus
U8.M2, U15.M2 Address bus
U8.P3, U15.P3 Address bus
U8.P8, U15.P8 Address bus
U8.P2, U15.P2 Address bus
U8.N7, U15.N7 Address bus
U8.N3, U15.N3 Address bus
U8.N8, U15.N8 Address bus
U8.N2, U15.N2 Address bus
U8.M7, U15.M7 Address bus
U8.M3, U15.M3 Address bus
U8.M8, U15.M8 Address bus
U8.L3, U15.L3 Bank address bus
U8.L2, U15.L2 Bank address bus
U8.K7, U15.K7 Row address select
U8.L7, U15.L7 Column address select
U8.L8, U15.L8 Chip select
U8.K3, U15.K3 Write enable
U8.K9, U15.K9 Termination enable
U8.K2, U15.K2 Clock enable
U8.J8, U15.J8 Clock P
U8.K8, U15.K8 Clock N
U8.G8, Data bus byte lane 0
U8.G2 Data bus byte lane 0
U8.H7 Data bus byte lane 0
U8.H3 Data bus byte lane 0
U8.H1 Data bus byte lane 0
U8.H9 Data bus byte lane 0
U8.F1 Data bus byte lane 0
U8.F9 Data bus byte lane 0
U8.F3 Write mask byte lane 0
U8.F7 Data strobe byte lane 0
DDR2A_A12
DDR2A_A11
DDR2A_A10
DDR2A_A9
DDR2A_A8
DDR2A_A7
DDR2A_A6
DDR2A_A5
DDR2A_A4
DDR2A_A3
DDR2A_A2
DDR2A_A1
DDR2A_A0
DDR2A_BA1
DDR2A_BA0
DDR2A_RASn
DDR2A_CASn
DDR2A_CSn
DDR2A_WEn
DDR2A_ODT
DDR2A_CKE
DDR2A_CLK_P
DDR2A_CLK_N
DDR2A_DQ0
DDR2A_DQ1
DDR2A_DQ2
DDR2A_DQ3
DDR2A_DQ4
DDR2A_DQ5
DDR2A_DQ6
DDR2A_DQ7
DDR2A_DM0
DDR2A_DQS0
I/O Standard
1.8-V SSTL Class I
Device
Pin Number
F21
G18
C20
F20
K17
B22
F17
B21
F18
A21
D17
C19
D18
B19
A20
B18
A16
D20
A18
C17
A19
D23
C23
G23
D28
G24
C28
H24
F23
B30
F22
G22
A29
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 48

2–40 Chapter 2: Board Components
Memory
Table 2–37. DDR2 SDRAM Top Port Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions (Part 2 of 2)
Cyclone IV GX
Board Reference Description Schematic Signal
Name
U8.C8 Data bus byte lane 1
U8.C2 Data bus byte lane 1
U8.D7 Data bus byte lane 1
U8.D3 Data bus byte lane 1
U8.D1 Data bus byte lane 1
U8.D9 Data bus byte lane 1
U8.B1 Data bus byte lane 1
U8.B9 Data bus byte lane 1
U8.B3 Write mask byte lane 1
U8.B7 Data strobe byte lane 1
U15.G8 Data bus byte lane 2
U15.G2 Data bus byte lane 2
U15.H7 Data bus byte lane 2
U15.H3 Data bus byte lane 2
U15.H1 Data bus byte lane 2
U15.H9 Data bus byte lane 2
U15.F1 Data bus byte lane 2
U15.F9 Data bus byte lane 2
U15.F3 Write mask byte lane 2
U15.F7 Data strobe byte lane 2
U15.C8 Data bus byte lane 3
U15.C2 Data bus byte lane 3
U15.D7 Data bus byte lane 3
U15.D3 Data bus byte lane 3
U15.D1 Data bus byte lane 3
U15.D9 Data bus byte lane 3
U15.B1 Data bus byte lane 3
U15.B9 Data bus byte lane 3
U15.B3 Write mask byte lane 3
U15.B7 Data strobe byte lane 3
DDR2A_DQ8
DDR2A_DQ9
DDR2A_DQ10
DDR2A_DQ11
DDR2A_DQ12
DDR2A_DQ13
DDR2A_DQ14
DDR2A_DQ15
DDR2A_DM1
DDR2A_DQS1
DDR2A_DQ16
DDR2A_DQ17
DDR2A_DQ18
DDR2A_DQ19
DDR2A_DQ20
DDR2A_DQ21
DDR2A_DQ22
DDR2A_DQ23
DDR2A_DM2
DDR2A_DQS2
DDR2A_DQ24
DDR2A_DQ25
DDR2A_DQ26
DDR2A_DQ27
DDR2A_DQ28
DDR2A_DQ29
DDR2A_DQ30
DDR2A_DQ31
DDR2A_DM3
DDR2A_DQS3
I/O Standard
1.8-V SSTL Class I
Device
Pin Number
D22
A26
E24
D26
B28
D21
B27
F19
A24
G17
E19
D19
C18
A17
A23
E18
C22
K18
B16
K19
A13
C14
A12
A14
D16
F13
D15
F12
A8
C16
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 49

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–41
Memory
DDR2 SDRAM Bottom Port
The DDR2 SDRAM bottom port consists of two DDR2 devices (U17 and U19).
Tab le 2 –3 8 lists the DDR2 bottom port pin assignments, signal names, and its
functions. The signal names and types are relative to the Cyclone IV GX device in
terms of I/O setting and direction.
Table 2–38. DDR2 SDRAM Bottom Port Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions (Part 1 of 2)
Cyclone IV GX
Board Reference Description Schematic Signal
Name
U17.R2, U19.R2 Address bus
U17.P7, U19.P7 Address bus
U17.M2, U19.M2 Address bus
U17.P3, U19.P3 Address bus
U17.P8, U19.P8 Address bus
U17.P2, U19.P2 Address bus
U17.N7, U19.N7 Address bus
U17.N3, U19.N3 Address bus
U17.N8, U19.N8 Address bus
U17.N2, U19.N2 Address bus
U17.M7, U19.M7 Address bus
U17.M3, U19.M3 Address bus
U17.M8, U19.M8 Address bus
U17.L3, U19.L3 Bank address bus
U17.L2, U19.L2 Bank address bus
U17.K7, U19.K7 Row address select
U17.L7, U19.L7 Column address select
U17.L8, U19.L8 Chip select
U17.K3, U19.K3 Write enable
U17.K9, U19.K9 Termination enable
U17.K2, U19.K2 Clock enable
U17.J8, U19.J8 Clock P
U17.K8, U19.K8 Clock N
U19.G8, Data bus byte lane 0
U19.G2 Data bus byte lane 0
U19.H7 Data bus byte lane 0
U19.H3 Data bus byte lane 0
U19.H1 Data bus byte lane 0
U19.H9 Data bus byte lane 0
U19.F1 Data bus byte lane 0
U19.F9 Data bus byte lane 0
U19.F3 Write mask byte lane 0
U19.F7 Data strobe byte lane 0
DDR2B_A12
DDR2B_A11
DDR2B_A10
DDR2B_A9
DDR2B_A8
DDR2B_A7
DDR2B_A6
DDR2B_A5
DDR2B_A4
DDR2B_A3
DDR2B_A2
DDR2B_A1
DDR2B_A0
DDR2B_BA1
DDR2B_BA0
DDR2B_RASn
DDR2B_CASn
DDR2B_CSn
DDR2B_WEn
DDR2B_ODT
DDR2B_CKE
DDR2B_CLK_P
DDR2B_CLK_N
DDR2B_DQ0
DDR2B_DQ1
DDR2B_DQ2
DDR2B_DQ3
DDR2B_DQ4
DDR2B_DQ5
DDR2B_DQ6
DDR2B_DQ7
DDR2B_DM0
DDR2B_DQS0
I/O Standard
1.8-V SSTL Class I
Device
Pin Number
AB11
AE15
AH8
AG7
AA16
AG8
AH14
AK7
AG15
AH7
AB14
AK9
AG14
AJ9
AA12
AG12
AK10
AK12
AH10
AF13
AA13
AF4
AG4
AG5
AJ3
AK4
AJ4
AH2
AH6
AF3
AK5
AE3
AD9
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 50

2–42 Chapter 2: Board Components
Memory
Table 2–38. DDR2 SDRAM Bottom Port Pin Assignments, Signal Names and Functions (Part 2 of 2)
Cyclone IV GX
Board Reference Description Schematic Signal
Name
U19.C8 Data bus byte lane 1
U19.C2 Data bus byte lane 1
U19.D7 Data bus byte lane 1
U19.D3 Data bus byte lane 1
U19.D1 Data bus byte lane 1
U19.D9 Data bus byte lane 1
U19.B1 Data bus byte lane 1
U19.B9 Data bus byte lane 1
U19.B3 Write mask byte lane 1
U19.B7 Data strobe byte lane 1
U17.G8 Data bus byte lane 2
U17.G2 Data bus byte lane 2
U17.H7 Data bus byte lane 2
U17.H3 Data bus byte lane 2
U17.H1 Data bus byte lane 2
U17.H9 Data bus byte lane 2
U17.F1 Data bus byte lane 2
U17.F9 Data bus byte lane 2
U17.F3 Write mask byte lane 2
U17.F7 Data strobe byte lane 2
U17.C8 Data bus byte lane 3
U17.C2 Data bus byte lane 3
U17.D7 Data bus byte lane 3
U17.D3 Data bus byte lane 3
U17.D1 Data bus byte lane 3
U17.D9 Data bus byte lane 3
U17.B1 Data bus byte lane 3
U17.B9 Data bus byte lane 3
U17.B3 Write mask byte lane 3
U17.B7 Data strobe P byte lane 3
DDR2B_DQ8
DDR2B_DQ9
DDR2B_DQ10
DDR2B_DQ11
DDR2B_DQ12
DDR2B_DQ13
DDR2B_DQ14
DDR2B_DQ15
DDR2B_DM1
DDR2B_DQS1
DDR2B_DQ16
DDR2B_DQ17
DDR2B_DQ18
DDR2B_DQ19
DDR2B_DQ20
DDR2B_DQ21
DDR2B_DQ22
DDR2B_DQ23
DDR2B_DM2
DDR2B_DQS2
DDR2B_DQ24
DDR2B_DQ25
DDR2B_DQ26
DDR2B_DQ27
DDR2B_DQ28
DDR2B_DQ29
DDR2B_DQ30
DDR2B_DQ31
DDR2B_DM3
DDR2B_DQS3
I/O Standard
1.8-V SSTL Class I
Device
Pin Number
AJ10
AG9
AG13
AH11
AG10
AH12
AE12
AE13
AJ6
AH13
AA15
AK11
AH15
AE14
AK8
AH16
AJ7
AB16
AH18
AF15
AH18
AK17
AJ18
AK18
AK15
AE18
AJ15
AH19
Y17
AA17
Tab le 2 –3 9 lists the DDR2 component reference and manufacturing information.
Table 2–39. DDR2 Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
U8, U15, U17, U19
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
16 M × 16-bit × 4 banks, 533Mbps,
CL4
Micron MT47H16M16BG-37E:B www.micron.com
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
Page 51

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–43
Memory
SSRAM
The SSRAM consists of a single standard synchronous SRAM device with a 100-TQFP
package footprint. This device has 4 MB of memory with a 18-bit data bus but is
implemented for non-linear burst mode using only a 16-bit data bus. The device
speed is 200 MHz single-data-rate. There is no minimum speed for this device.
This device is part of the shared FSM bus which connects to the flash memory, SRAM,
and MAX
II CPLD EPM2210 System Controller.
Tab le 2 –4 0 lists the SSRAM pin assignments, signal names, and functions. The signal
names and types are relative to the Cyclone IV GX device in terms of I/O setting and
direction.
Table 2–40. SSRAM Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 1 of 2)
Board Reference Description
U44.46 Address bus
U44.44 Address bus
U44.42 Address bus
U44.37 Address bus
U44.36 Address bus
U44.48 Address bus
U44.43 Address bus
U44.49 Address bus
U44.47 Address bus
U44.39 Address bus
U44.35 Address bus
U44.34 Address bus
U44.50 Address bus
U44.45 Address bus
U44.33 Address bus
U44.32 Address bus
U44.100 Address bus
U44.80 Address bus
U44.81 Address bus
U44.99 Address bus
U44.82 Address bus
U44.23 Data bus
U44.59 Data bus
U44.22 Data bus
U44.63 Data bus
U44.68 Data bus
U44.72 Data bus
U44.12 Data bus
Schematic Signal Name
FSM_A1
FSM_A2
FSM_A3
FSM_A4
FSM_A5
FSM_A6
FSM_A7
FSM_A8
FSM_A9
FSM_A10
FSM_A11
FSM_A12
FSM_A13
FSM_A14
FSM_A15
FSM_A16
FSM_A17
FSM_A18
FSM_A19
FSM_A20
FSM_A21
FSM_D0
FSM_D1
FSM_D2
FSM_D3
FSM_D4
FSM_D5
FSM_D6
I/O Standard
1.8-V
Cyclone IV GX Device
Pin Number
AD6
AK29
AA21
AG25
AH5
AH27
AJ12
AF16
AH20
AK23
AH17
AB21
AF19
AF12
AG27
AK26
AH4
AK3
AH9
AG6
AK25
AK14
AE6
AG21
AE9
AK28
AD23
AG24
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 52

2–44 Chapter 2: Board Components
Memory
Table 2–40. SSRAM Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 2 of 2)
Board Reference Description
U44.9 Data bus
U44.58 Data bus
U44.62 Data bus
U44.19 Data bus
U44.18 Data bus
U44.69 Data bus
U44.13 Data bus
U44.8 Data bus
U44.73 Data bus
U44.14
U44.31
U44.74
U44.24
U44.83
U44.84
U44.85
Flow Through or Pipeline mode;
active low
Linear Burst Order mode; active
low
Ninth unused data bit for lower
byte lane
Ninth unused data bit for upper
byte lane
ADVn burst address counter
advance enable; active low
Address strobe (Processor,
Cache Controller); active low
Address strobe (Processor,
Cache Controller); active low
U44.86 Output enable; active low
U44.87 Byte lane write enable
U44.89 Clock
U44.98 Chip enable 1
U44.97 Chip enable 2
U44.92 Chip enable 3
U44.93
U44.94
Byte write enable for DQA Data
I/Os; active low
Byte write enable for DQB Data
I/Os; active low
U44.64 Sleep enable
Schematic Signal Name
FSM_D7
FSM_D8
FSM_D9
FSM_D10
FSM_D11
FSM_D12
FSM_D13
FSM_D14
FSM_D15
SSRAM_FTn
SSRAM_LBOn
SSRAM_DQP0
SSRAM_DQP1
SSRAM_ADVn
SSRAM_ADSPn
SSRAM_ADSCn
SSRAM_Gn
SSRAM_BWn
SSRAM_CLK
SSRAM_E1n
SSRAM_E2
SSRAM_E3n
SSRAM_BAn
SSRAM_BBn
SSRAM_ZZ
I/O Standard
1.8-V
Cyclone IV GX Device
Pin Number
AB22
AE22
AJ24
Y19
AH23
AK22
AH24
Y18
AJ13
Pulled low
Pulled low
Pulled low
Pulled low
Pulled high
Pulled high
Pulled low
G6
F8
F11
C6
Pulled high
Pulled low
D13
D27
Pulled low
Tab le 2 –4 1 lists the SSRAM component reference and manufacturing information.
Table 2–41. SSRAM Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board
Reference
U44
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Standard Synchronous Pipelined
SCD, 2 M × 18, 200 MHz
Description Manufacturer
GSI GS832018GT-200V www.gsitechnology.com
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer Website
Page 53

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–45
Memory
Flash
The flash interface consists of a single synchronous flash memory device, providing
64 MB of memory with a 16-bit data bus. This device is part of the shared FSM bus
which connects to the flash memory, SRAM, LCD, and MAX II CPLD EPM2210
System Controller.
This 16-bit data memory interface can sustain burst read operations at up to 52 MHz
for a throughput of 832 Mbps. The write performance is 125 μs for a single word and
440 μs for a 32-word buffer. The erase time is 400 ms for a 32 K parameter block and
1200 ms for a 128 K main block.
f For more information about the flash memory map storage, refer to the Cyclone IV GX
Development Kit User Guide.
Tab le 2 –4 2 lists the flash pin assignments, signal names, and functions. The signal
names and types are relative to the Cyclone IV GX device in terms of I/O setting and
direction.
Table 2–42. Flash Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 1 of 2)
Cyclone IV GX
Board Reference Description
U6.F6 Address valid
U6.B4 Chip enable
U6.E6 Clock
U6.F8 Output enable
U6.F7 Ready
U6.D4 Reset
U6.G8 Write enable
U6.C6 Write protect
U6.A1 Address bus
U6.B1 Address bus
U6.C1 Address bus
U6.D1 Address bus
U6.D2 Address bus
U6.A2 Address bus
U6.C2 Address bus
U6.A3 Address bus
U6.B3 Address bus
U6.C3 Address bus
U6.D3 Address bus
U6.C4 Address bus
U6.A5 Address bus
U6.B5 Address bus
U6.C5 Address bus
Schematic Signal Name
FLASH_ADVn
FLASH_CEn
FLASH_CLK
FSM_OEn
FLASH_RDYBSYn
FLASH_RESETn
FSM_WEn
FLASH_WPn
FSM_A1
FSM_A2
FSM_A3
FSM_A4
FSM_A5
FSM_A6
FSM_A7
FSM_A8
FSM_A9
FSM_A10
FSM_A11
FSM_A12
FSM_A13
FSM_A14
FSM_A15
I/O Standard
1.8-V
Device
Pin Number
F24
E25
Y21
F7
B7
A28
C13
Pulled high
AD6
AK29
AA21
AG25
AH5
AH27
AJ12
AF16
AH20
AK23
AH17
AB21
AF19
AF12
AG27
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 54

2–46 Chapter 2: Board Components
Power Supply
Table 2–42. Flash Pin Assignments, Schematic Signal Names, and Functions (Part 2 of 2)
Cyclone IV GX
Board Reference Description
U6.D7 Address bus
U6.D8 Address bus
U6.A7 Address bus
U6.B7 Address bus
U6.C7 Address bus
U6.C8 Address bus
U6.A8 Address bus
U6.G1 Address bus
U6.H8 Address bus
U6.B6 Address bus
U6.F2 Data bus
U6.E2 Data bus
U6.G3 Data bus
U6.E4 Data bus
U6.E5 Data bus
U6.G5 Data bus
U6.G6 Data bus
U6.H7 Data bus
U6.E1 Data bus
U6.E3 Data bus
U6.F3 Data bus
U6.F4 Data bus
U6.F5 Data bus
U6.H5 Data bus
U6.G7 Data bus
U6.E7 Data bus
Schematic Signal Name
FSM_A16
FSM_A17
FSM_A18
FSM_A19
FSM_A20
FSM_A21
FSM_A22
FSM_A23
FSM_A24
FSM_A25
FSM_D0
FSM_D1
FSM_D2
FSM_D3
FSM_D4
FSM_D5
FSM_D6
FSM_D7
FSM_D8
FSM_D9
FSM_D10
FSM_D11
FSM_D12
FSM_D13
FSM_D14
FSM_D15
I/O Standard
1.8-V
Device
Pin Number
AK26
AH4
AK3
AH9
AG6
AK25
AE21
AA18
AK27
AF21
AK14
AE6
AG21
AE9
AK28
AD23
AG24
AB22
AE22
AJ24
Y19
AH23
AK22
AH24
Y18
AJ13
Tab le 2 –4 3 lists the flash component reference and manufacturing information.
Table 2–43. Flash Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
U6 512-Mb synchronous flash Numonyx PC28F512P30BF www.numonyx.com
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
Power Supply
The development board's power is provided through a laptop-style DC power input.
The input voltage must be 16 V. The DC voltage is then stepped down to various
power rails used by the components on the board.
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 55

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–47
1.2V_VCCL_GXB
VCCP_PCC, VCC
16 V
DC INPUT
ideal
diode mux
12 V - PCI Express Motherboard
5.5 A Maximum
VCCA
2.5V_VCCA_VCCH_GXB
Linear
Regulator
(LTC3853)
Linear
Regulator
(LTC3850)
Linear
Regulator
(LTC3027)
12V_HSMC
1.8V
3.3V
5V
2.5V_USB
U43
U50
U41
Shunt installed = 2.5 V
Shunt not installed = 1.8 V
Linear
Regulator
(LTC3026)
2.5V_B5_B6
1.1V
U42
Linear
Regulator
(LTC3026)
U53
0.066 A
5V_USB
3.3 V
Linear
Regulator
(LTC3026)
1.8V_B3_B4
U40
2.5 V
1.8V_B7_B8
TPS51100DGQ
VTT_B3_B4
U45
1.8V_B3_B4
VREF_B3_B4
TPS51100DGQ
VTT_B7_B8
U47
1.8V_B7_B8
VREF_B7_B8
2.5 V
1.2 V
12 V
Power Supply
An on-board multi-channel analog-to-digital converter (ADC) measures both the
voltage and current for several specific board rails. The power utilization is displayed
using a GUI that can graph power consumption versus time.
Power Distribution System
Figure 2–7 shows the power distribution system on the development board. The
currents shown are conservative absolute maximum levels and reflects the regulator
inefficiencies and sharing.
Figure 2–7. Power Distribution System
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 56

2–48 Chapter 2: Board Components
SCK
DSI
DSO
CSn
8 Ch.
To Plane
Supply
R
SENSE
EPM2210
EP4CGX150
LTC2418
EPM
240
USB
PHY
To User PC
Power GUI
JTAG Chain
SPI Bus
Embedded
USB-Blaster
U36
Power Supply
Tab le 2 –4 4 lists the power supply component reference and manufacturing
information.
Table 2–44. Power Supply Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
— 16-V power supply EDAC Power Electronics EA1060A www.edac.com.tw
Power Measurement
There are eight power supply rails which have on-board voltage and current sense
capabilities. The power supply rails are split from the primary supply plane by a
low-value sense resistor for the 8-channel differential input 24-bit ADC device to
measure voltage and current. A SPI bus connects the ADC device to the MAX II CPLD
EPM2210 System Controller.
Figure 2–8 shows the block diagram for the power measurement circuitry.
Figure 2–8. Power Measurement Circuit
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
Tab le 2 –4 5 lists the targeted rails. The schematic signal name column specifies the
name of the rail being measured and the device pin column specifies the devices
attached to the rail. If no subnet is named, the power is the total output power for that
voltage.
Table 2–45. Power Rails Measurement Based on the Rail Selected in the Power GUI (Part 1 of 2)
Rail Schematic Signal Name Voltage (V) Device Pin Description
1
2
1.8V_B3_B4
1.8V_B7_B8
1.8 VCCIO 1.8-V power to banks 3 and 4
1.8 VCCIO 1.8-V power to banks 7and 8
1.8-V or 2.5-V power to banks 5 and 6.
3
2.5V_B5_B6
2.5 or 1.8 VCCIO
Voltage selected by jumper J3. When J3 is
shunted the voltage is 2.5 V and not shunted it
is 1.8 V
4
5
2.5V_VCCA_VCCH_GXB
6
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
VCCA
1.2V_VCCL_GXB
2.5
2.5
1.2 VCCL_GXB PMA auxiliary power
VCC_CLKIN
VCCA_GXB,
VCCH_GXB
VCCA,
PLL analog power
Transceiver buffer power
Page 57

Chapter 2: Board Components 2–49
Statement of China-RoHS Compliance
Table 2–45. Power Rails Measurement Based on the Rail Selected in the Power GUI (Part 2 of 2)
Rail Schematic Signal Name Voltage (V) Device Pin Description
7
8
VCCD_PLL
VCC
1.2 VCCD PLL digital power
1,2 VCC CORE
Tab le 2 –4 6 lists the power measurement ADC component reference and
manufacturing information.
Table 2–46. Power Measurement ADC Component Reference and Manufacturing Information
Board Reference Description Manufacturer
Manufacturing
Part Number
Manufacturer
Website
U13 8-channel differential input 24-bit ADC Linear Technology LTC2418 www.linear.com
Statement of China-RoHS Compliance
Tab le 2 –4 7 lists hazardous substances included with the kit.
(Hg)
(1), (2)
Polybrominated
biphenyls (PBB)
Polybrominated
diphenyl Ethers
(PBDE)
Table 2–47. Table of Hazardous Substances’ Name and Concentration Notes
Hexavalent
Chromium
(Cr6+)
Mercury
Part Name
Cyclone IV GX FPGA
development board
Lead
(Pb)
Cadmium
(Cd)
X* 0 0 0 0 0
16-V power supply 0 0 0 0 0 0
Type A-B USB cable 0 0 0 0 0 0
User guide 0 0 0 0 0 0
Notes to Table 2–47:
(1) 0 indicates that the concentration of the hazardous substance in all homogeneous materials in the parts is below the relevant threshold of the
SJ/T11363-2006 standard.
(2) X* indicates that the concentration of the hazardous substance of at least one of all homogeneous materials in the parts is above the relevant
threshold of the SJ/T11363-2006 standard, but it is exempted by EU RoHS.
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 58

2–50 Chapter 2: Board Components
Statement of China-RoHS Compliance
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
Page 59

This chapter provides additional information about the document and Altera.
Document Revision History
The following table shows the revision history for this document.
Date Version Changes
■ Updated Table 2–18—The I/O standard for user push buttons is 1.8-V.
■ Updated the note in Table 2–26—All signals are translated from 1.8-V to 2.5-V using a
dual/quad low-voltage level translators except for
May 2013 1.1
December 2010 1.0 Initial release.
■ Updated Table 2–29—The I/O standard for PCI Express transmit and receive bus is
1.5-V PCML.
■ Updated Table 2–33—HSMA pin J1.44 connects to FPGA pin AD27.
■ Updated the document template.
Additional Information
LCD_DATA4
.
How to Contact Altera
To locate the most up-to-date information about Altera products, refer to the
following table.
Contact
Technical support Website www.altera.com/support
Technical training
Product literature Website www.altera.com/literature
Nontechnical support (general) Email nacomp@altera.com
(software licensing) Email authorization@altera.com
Note to Table:
(1) You can also contact your local Altera sales office or sales representative.
(1)
Contact Method Address
Website www.altera.com/training
Email custrain@altera.com
May 2013 Altera Corporation Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board
Reference Manual
Page 60

Info–2 Additional Information
Typographic Conventions
Typographic Conventions
The following table shows the typographic conventions this document uses.
Visual Cue Meaning
Bold Type with Initial Capital
Letters
bold type
Italic Type with Initial Capital Letters Indicate document titles. For example, Stratix IV Design Guidelines.
italic type
Initial Capital Letters
“Subheading Title”
Courier type
r An angled arrow instructs you to press the Enter key.
1., 2., 3., and
a., b., c., and so on
■ ■ ■ Bullets indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is not important.
1 The hand points to information that requires special attention.
h The question mark directs you to a software help system with related information.
f The feet direct you to another document or website with related information.
m The multimedia icon directs you to a related multimedia presentation.
c
w
Indicate command names, dialog box titles, dialog box options, and other GUI
labels. For example, Save As dialog box. For GUI elements, capitalization matches
the GUI.
Indicates directory names, project names, disk drive names, file names, file name
extensions, software utility names, and GUI labels. For example, \qdesigns
directory, D: drive, and chiptrip.gdf file.
Indicates variables. For example, n + 1.
Variable names are enclosed in angle brackets (< >). For example, <file name> and
<project name>.pof file.
Indicate keyboard keys and menu names. For example, the Delete key and the
Options menu.
Quotation marks indicate references to sections in a document and titles of
Quartus II Help topics. For example, “Typographic Conventions.”
Indicates signal, port, register, bit, block, and primitive names. For example,
tdi
, and
input
. The suffix n denotes an active-low signal. For example,
data1
resetn
.
Indicates command line commands and anything that must be typed exactly as it
appears. For example,
c:\qdesigns\tutorial\chiptrip.gdf
.
Also indicates sections of an actual file, such as a Report File, references to parts of
files (for example, the AHDL keyword
TRI
example,
).
SUBDESIGN
), and logic function names (for
Numbered steps indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is important,
such as the steps listed in a procedure.
A caution calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can damage or
destroy the product or your work.
A warning calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can cause you
injury.
The envelope links to the Email Subscription Management Center page of the Altera
website, where you can sign up to receive update notifications for Altera documents.
The feedback icon allows you to submit feedback to Altera about the document.
Methods for collecting feedback vary as appropriate for each document.
,
Cyclone IV GX FPGA Development Board May 2013 Altera Corporation
Reference Manual
 Loading...
Loading...