
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors
Instruction Manual
Catalog #212205, #212206, #212207 and #212208
Revision B
Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
212205-12
LIMITED PRODUCT WARRANTY
This warranty limits our liability to replacement of this product. No other warranties of any kind, express
or implied, including without limitation, implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
purpose, are provided by Agilent. Agilent shall have no liability for any direct, indirect, consequential, or
incidental damages arising out of the use, the results of use, or the inability to use this product.
ORDERING INFORMATION AND TECHNICAL SERVICES
Email
techservices@agilent.com
World Wide Web
www.genomics.agilent.com
Telephone
Location Telephone
United States and Canada 800 227 9770
Austria 01 25125 6800
Benelux 02 404 92 22
Denmark 45 70 13 00 30
Finland 010 802 220
France 0810 446 446
Germany 0800 603 1000
Italy 800 012575
Netherlands 020 547 2600
Spain 901 11 68 90
Sweden 08 506 4 8960
Switzerland 0848 8035 60
UK/Ireland 0845 712 5292
All Other Countries Please visit www.genomics.agilent.com and click Contact Us

pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors
CONTENTS
Materials Provided .............................................................................................................................. 1
Storage Conditions .............................................................................................................................. 1
Introduction ......................................................................................................................................... 2
pBluescript II SK (+/–) Phagemids ....................................................................................... 3
pBluescript II KS (+/–) Phagemids ....................................................................................... 4
Ligation into pBluescript II Phagemids ............................................................................................ 5
Transformation with pBluescript II Phagemids .............................................................................. 6
Suggested Host Strain and Genotype .................................................................................... 6
Streaking Cells from a –80°C Bacterial Glycerol Stock ....................................................... 7
Preparation of a –80°C Bacterial Glycerol Stock .................................................................. 7
Blue-White Color Selection .................................................................................................. 7
Background White Colonies .................................................................................................. 8
Screening Colonies .............................................................................................................................. 8
Fixing Replica Sets of Colonies to Nitrocellulose Filters ..................................................... 9
Prehybridization .................................................................................................................. 10
Hybridization ....................................................................................................................... 11
Hybridization Solution ........................................................................................................ 11
Washes ................................................................................................................................. 12
Exposure to Film ................................................................................................................. 13
T3 and T7 RNA Transcription ......................................................................................................... 13
Handling RNA ..................................................................................................................... 13
Nonspecific Initiation with T7 and T3 RNA Polymerases .................................................. 14
Nonradioactive Transcripts ................................................................................................. 15
DNase Treatment after Transcription .................................................................................. 15
High-Specific-Activity RNA Probes ................................................................................... 15
Transcription Reaction ........................................................................................................ 16
Hybridization Conditions for RNA Probes in Southern Blots ...................................................... 17
Prehybridization .................................................................................................................. 17
Hybridization ....................................................................................................................... 17
Washes ................................................................................................................................. 17

Hybridization Conditions for RNA Probes in Northern Blots ...................................................... 17
Prehybridization .................................................................................................................. 17
Hybridization ....................................................................................................................... 17
Washes ................................................................................................................................. 17
Recovery of Single-Stranded DNA from Cells Containing pBluescript II Phagemids ............... 18
Single-Stranded Rescue Protocol ........................................................................................ 19
Site-Directed Mutagenesis ................................................................................................................ 20
Plasmid Boiling Miniprep Protocol ................................................................................................. 21
Troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................ 22
Preparation of Media and Reagents ................................................................................................ 22
References .......................................................................................................................................... 23
Endnotes ............................................................................................................................................. 23
MSDS Information ............................................................................................................................ 23
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors
ATERIALS PROVIDED
M
Material Provided
pBluescript II SK(+) phagemid, 1 μg/μl 20 μg — — —
pBluescript II SK(–) phagemid, 1 μg/μl — 20 μg — —
pBluescript II KS(+) phagemid, 1 μg/μl — — 20 μg —
pBluescript II KS(–) phagemid, 1 μg/μl — — — 20 μg
XL1-Blue MRF´ host strain, glycerol stock, Catalog #200301 1 tube 1 tube 1 tube 1 tube
#212205 #212206 #212207 #212208
Catalog Number
STORAGE CONDITIONS
Phagemids: –20°C
Bacterial Strains: –80°C
Revision B © Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2010.
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 1
INTRODUCTION
The pBluescript II phagemids (plasmids with a phage origin) are cloning
vectors designed to simplify commonly used cloning and sequencing
procedures, including the construction of nested deletions for DNA
sequencing, generation of RNA transcripts in vitro and site-specific
mutagenesis and gene mapping. The pBluescript II phagemids have an
extensive polylinker with 21 unique restriction enzyme recognition sites.
Flanking the polylinker are T7 and T3 RNA polymerase promoters that can
be used to synthesize RNA in vitro.
1, 2
The choice of promoter used to
initiate transcription determines which strand of the insert cloned into the
polylinker will be transcribed.
Circular maps and lists of features for the pBluescript II phagemids are
shown in figures 1 and 2. The polylinker and T7 and T3 RNA polymerase
promoter sequences are present in the N-terminal portion of a lacZ gene
fragment. A total of 131 amino acids of β-galactosidase coding sequence is
present in the pBluescript II phagemid, but the coding sequence is
interrupted by the large polylinker. (There are 36 amino acids from the
initiator Met sequence to the EcoR I site.) pBluescript II phagemids having
no inserts in the polylinker will produce blue colonies in the appropriate
strains of bacteria (i.e., strains containing lacZΔM15 on an F´ episome, such
as XL1-Blue MRF´, among others). pBluescript II phagemids that have
inserts will produce white colonies using the same strain, because the inserts
disrupt the coding region of the lacZ gene fragment.
pBluescript II (+) and (–) are available with two polylinker orientations
designated as either KS or SK using the following convention: (1) in the KS
orientation, the Kpn I restriction site is nearest the lacZ promoter and the
Sac I restriction site is farthest from the lacZ promoter; and (2) in the SK
orientation, the Sac I site is the closest restriction site to the lacZ promoter
and the Kpn I site is the farthest.
Flanking the T3 and T7 promoters are BssH II sites. This rare six-base cutter
will allow the insert plus the T phage RNA promoters to be excised and
used for gene mapping.
pBluescript II phagemids can be rescued as single-stranded (ss) DNA.
pBluescript II phagemids contain a 454-bp filamentous f1 phage intergenic
region (M13 related), which includes the 307-bp origin of replication. The
(+) and (–) orientations of the f1 intergenic region allow the rescue of sense
or antisense ssDNA by a helper phage. This ssDNA can be used for
dideoxynucleotide sequencing (Sanger method) or site-specific mutagenesis.
Note We have observed that using excess amounts of EcoR I to digest
pBluescript II results in EcoR I prime activity. This appears as
cleavage at a non-EcoR I site at the 3´ end of the f1 intergenic
region, causing confusion when interpreting results from an
agarose gel. If a restriction pattern appears incorrect, check
whether reducing the units of EcoR I restores a normal restriction
pattern.
2 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors
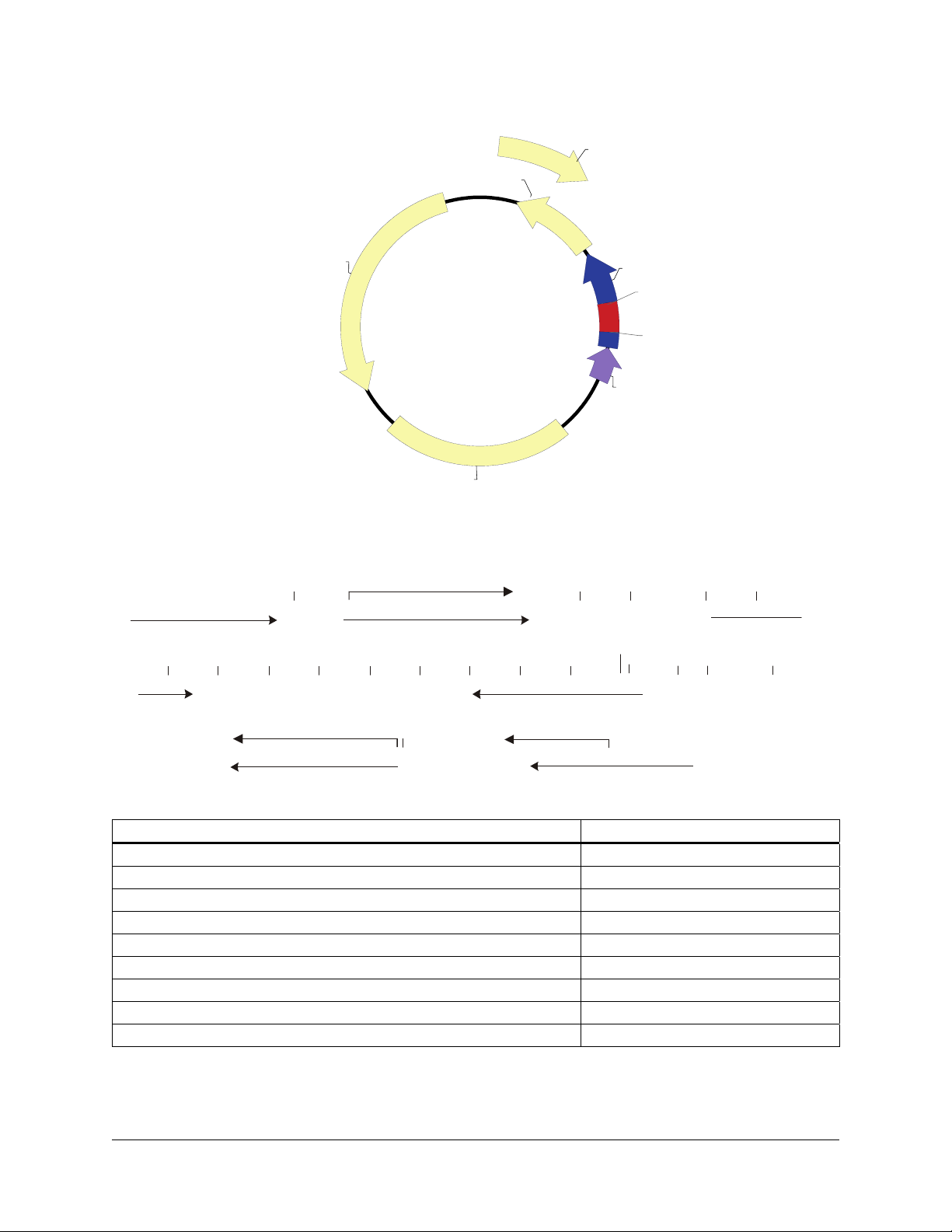
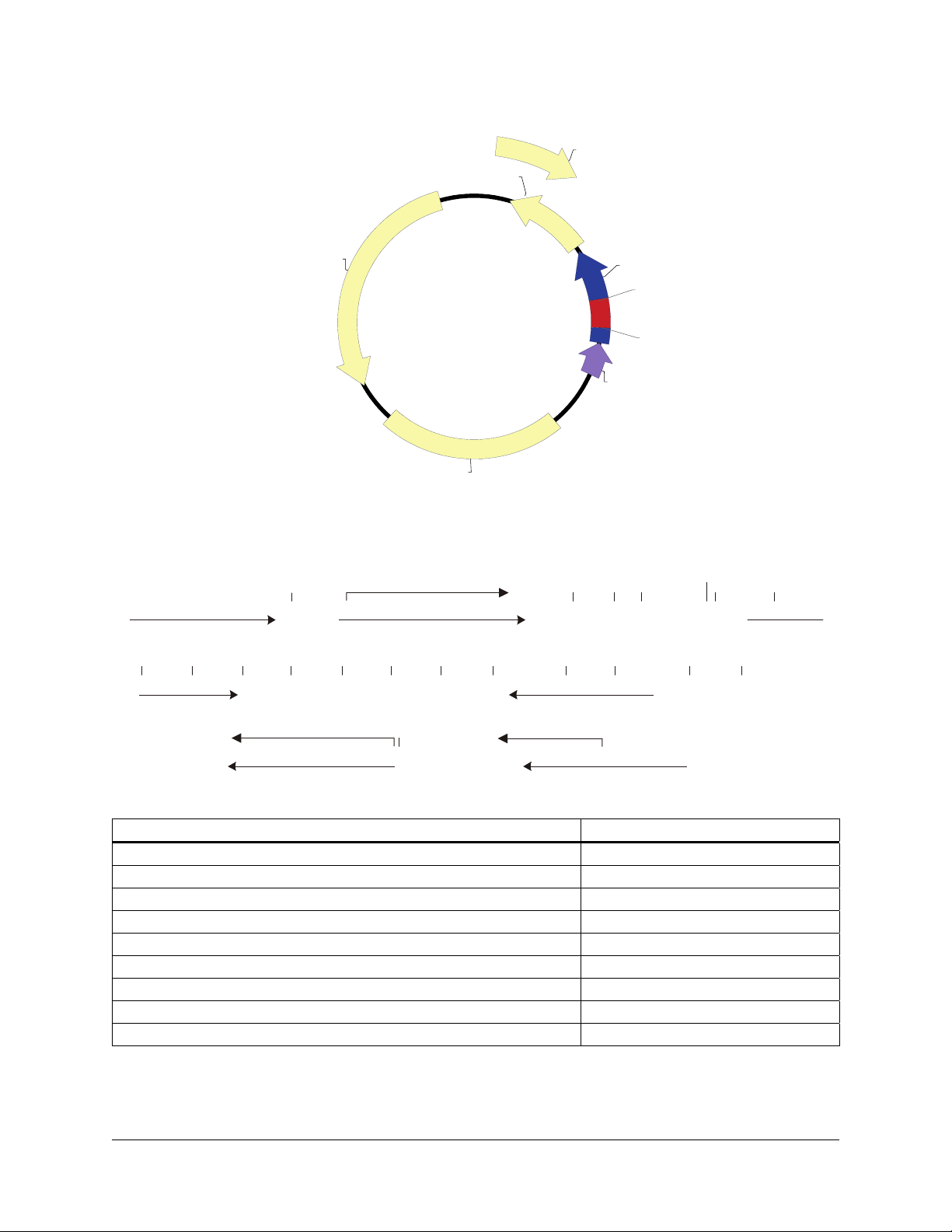
pBluescript II SK (+/–) Phagemids
n
f1 (+) ori
ampicillin
pBluescript II SK (+/-)
3.0 kb
pUC ori
pBluescript II SK (+/–) Multiple Cloning Site Regio
(sequence shown 598–826)
BssH II
TTGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTGAGCGCGCGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCGAATTGGGTACCGGGCCCCCCCTCGAGGTCGAC...
M13 –20 primer binding site
...GGTATCGATAAGCTTGATATCGAATTCCTGCAGCCCGGGGGATCCACTAGTTCTAGAGCGGCCGCCACCGCGGTGGAGCTC...
Bsp106 I
Cla I BamH I
EcoR IEcoR V
T7 Promoter
T7 primer binding site
Spe ISma I Xba IPst IHind III
SK primer binding site...KS primer binding site
f1 (-) ori
Kpn I
lacZ'
Kpn I
MCS
Sac I
P lac
Apa I
EcoO109 I
Dra II
Not I
Eag I
Xho I
KS primer binding site...
Sac II
BstX I
Hinc II
Acc I
Sal I
Sac I
T3 Promoter
...CAGCTTTTGTTCCCTTTAGTGAGGGTTAATTGCGCGCTTGGCGTAATCATGGTCATAGCTGTTTCC
T3 primer binding site
BssH II
βα
-gal -fragment
M13 Reverse primer binding site
Feature Nucleotide Position
f1 (+) origin of ss-DNA replication [pBluescript SK (+) only] 135–441
f1 (–) origin of ss-DNA replication [pBluescript SK (–) only] 21–327
β-galactosidase α-fragment coding sequence (lacZ’) 460–816
multiple cloning site 653–760
T7 promoter transcription initiation site 643
T3 promoter transcription initiation site 774
lac promoter 817–938
pUC origin of replication 1158–1825
ampicillin resistance (bla) ORF 1976–2833
FIGURE 1 The pBluescript II SK (+/–) phagemid vectors. The complete sequence and list of restriction sites are available at
www.genomics.agilent.com.
Genbank
®
#X52328 [SK(+)] and #X52330 [SK(–)].
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 3
pBluescript II KS (+/–) Phagemids
f1 (+) ori
ampicillin
pBluescript II KS (+/-)
3.0 kb
pUC ori
pBluescript II KS (+/–) Multiple Cloning Site Region
(sequence shown 598–826)
BssH II
TTGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTGAGCGCGCGTAAT ACGACTCACTA TAGGGCGAAT ...
M13 –20 primer binding site T7 primer binding site
Spe I Sma I
...ACTAGTGGATCCCCCGGGCTGCAGGAATT CGATATCAAGC TTATCGATACCG TCGACCTCGAG GGGGGGCCCGG TACC...
...SK primer binding site
Pst I
EcoR I EcoR V
T7 Promoter
Hind III
Bsp106 I
Cla IBamH I
f1 (-) ori
lacZ'
Sac I
MCS
Kpn I
P lac
Sac I
TGGAGCTCCACCGC GGTGGCGGCCGCTCTAGA
Hinc II
Acc I
Sal I
KS primer binding site
BstX I
Sac II
Not I
Eag I
SK primer binding site...
Apa I
EcoO109 I
Dra II
Kpn IXho I
Xba I
T3 Promoter
...CAGCTTTTGTTCCCTTTAGTGAGGGTTAA TTGCGCGCTTG GCGTAATCATGG TCATAGCTGTT TCC
T3 primer binding site
BssH II
βα
-gal -fragment
M13 Reverse primer binding site
Feature Nucleotide Position
f1 (+) origin of ss-DNA replication [pBluescript KS (+) only] 135–441
f1 (–) origin of ss-DNA replication [pBluescript KS (–) only] 21–327
β-galactosidase α-fragment coding sequence (lacZ’) 460–816
multiple cloning site 653–760
T7 promoter transcription initiation site 643
T3 promoter transcription initiation site 774
lac promoter 817–938
pUC origin of replication 1158–1825
ampicillin resistance (bla) ORF 1976–2833
FIGURE 2 The pBluescript II KS (+/–) phagemid vectors. The complete sequence and list of restriction sites are available at
www.genomics.agilent.com. Genbank
®
#X52327 [KS(+)] and #X52329 [KS(–)].
4 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors

LIGATION INTO PBLUESCRIPT II PHAGEMIDS
Dephosphorylate the digested pBluescript II phagemid with calf intestinal
alkaline phosphatase (CIAP) prior to ligation with the insert DNA. If more
than one restriction enzyme is used, the background can be reduced further
by electrophoresing the digested vector DNA on an agarose gel and
recovering the desired vector band through electroelution, leaving behind
the small fragment that appears between the two restriction enzyme sites.
After gel purification and ethanol precipitation of the DNA, resuspend in a
volume of TE buffer [5 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 0.1 mM EDTA] that will allow
the concentration of the vector DNA to be the same as the concentration of
the insert DNA (~0.1 μg/μl).
For ligation, the ideal ratio of insert to vector DNA is variable; however, a
reasonable starting point is 2:1 (insert:vector), measured in available
picomole ends. This is calculated as:
picomole ends/micrograms of DNA = (2 × 106) ÷ (number of base pairs × 660)
We suggest the following protocol, which includes three controls:
Component 1 2 3 4 5
Prepared vector (0.1 μg/μl) 1 μl 1 μl 1 μl 1 μl 0 μl
Prepared insert (0.1 μg/μl) X μl X μl 0 μl 0 μl 1 μl
10 mM rATP (pH 7.0) 1 μl 1 μl 1 μl 1 μl 1 μl
10× Ligase buffer 1 μl 1 μl 1 μl 1 μl 1 μl
T4 DNA ligase (4 U/μl) 0.5 μl 0.5 μl 0.5 μl 0 μl 0.5 μl
ddH2O (to 10 μl) X μl X μl X μl X μl X μl
1. Ligate for 2 hours at room temperature (22°C) or overnight at 4°C.
When ligating blunt ends, incubate the ligation overnight at 12–14°C.
2. Transform 1–2 μl of the ligation mix into the appropriate competent
bacteria. (See Transformation with pBluescript II Phagemids.) Plate on
selective media.
3. Interpretation of test results:
Reactions 1 and 2 vary the insert:vector ratio.
Control 3 tests for the effectiveness of the CIAP treatment.
Control 4 indicates if the vector was cleaved completely or if
residual uncut vector remains.
Control 5 verifies that the insert alone is not contaminated with
any vector DNA.
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 5

4. Expected plating results:
Plates 1 and 2 should have mostly white colonies, representing
recombinants.
Plate 3 should have low numbers of blue colonies if the CIAP
treatment was effective.
Plate 4 should have no colonies if the digest was complete.
Plate 5 should have no colonies if the insert was pure.
TRANSFORMATION WITH PBLUESCRIPT II PHAGEMIDS
Note pBluescript II phagemids will replicate autonomously as plasmids.
Therefore, colonies—not plaques—are obtained following
transformation.
Suggested Host Strain and Genotype
The XL1-Blue MRF´ host strain is recommended for propagation of
pBluescript II phagemids and for transformation of recombinant phagemids.
XL1-Blue MRF´ allows blue-white color selection and single-stranded DNA
rescue, and is restriction-deficient aiding in the construction of libraries
made from methylated DNA.
XL1-Blue MRF´ Genotype: Δ(mcrA)183 Δ(mcrCB-hsdSMR-mrr)173
endA1 supE44 thi-1 recA1 gyrA96 relA1 lac [F´ proAB lacI
r
)]
(Tet
3
q
ZΔM15 Tn10
Note The XL1-Blue MRF´ is provided as a glycerol stock. Additional
tubes of glycerol stock are available for purchase (Catalog
#200301). Alternatively, high-efficiency XL1-Blue MRF´ frozen
competent cells are also available (>1 × 10
9
colonies/μg of pUC
18, Catalog #200230).
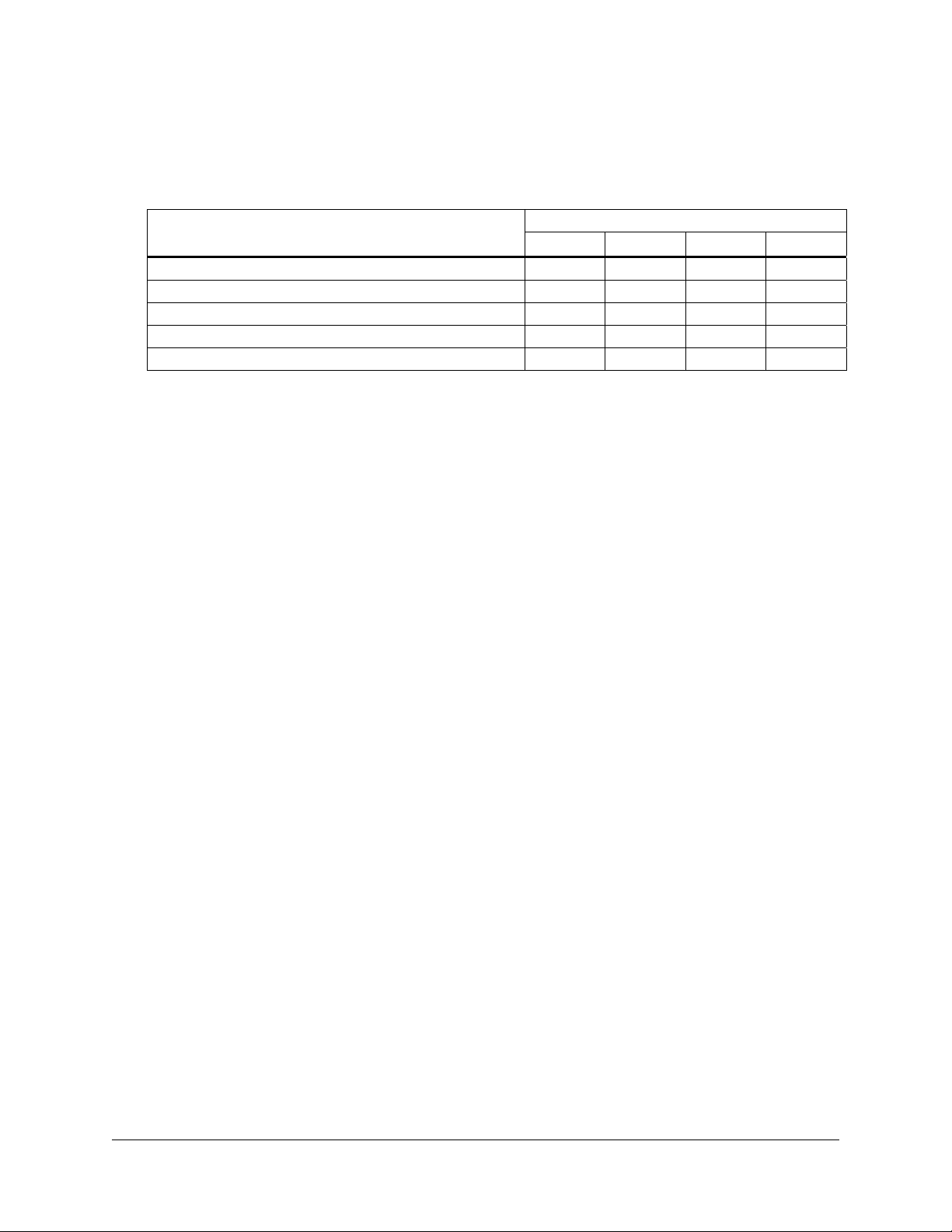
For the appropriate media and plates for growth of XL1-Blue MRF´, please
refer to the following table:
Bacterial strain
XL1-Blue MRF´ LB–tetracycline agara LB–tetracyclinea
a
12.5 μg/ml tetracycline.
Plates for bacterial
streak
Media for glycerol
stock
6 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors

Streaking Cells from a –80°C Bacterial Glycerol Stock
Prepare the following from a frozen glycerol stock:
Note Do not allow the contents of the vial to thaw. The vials can be
stored at –20° or –80°C, but most strains remain viable longer if
stored at –80°C.
1. Revive the stored cells by scraping off splinters of solid ice with a
sterile wire loop.
2. Streak the splinters onto an LB plate containing the appropriate
antibiotic.
Restreak the cells fresh each week.
Preparation of a –80°C Bacterial Glycerol Stock
1. In a sterile 50-ml conical tube, inoculate 10 ml of the appropriate liquid
media with one or two colonies from a plate of freshly-streaked cells.
Grow the cells to late log phase.
2. Add 4.5 ml of a sterile glycerol–liquid media solution (prepared by
combining 5 ml of glycerol + 5 ml of liquid media) to the bacterial
culture from step 1. Mix well.
3. Aliquot into sterile centrifuge tubes (1 ml/ tube). This preparation may
be stored at –20°C for 1–2 years or at –80°C for more than 2 years.
Blue-White Color Selection
The XL1-Blue MRF´ strain allows blue–white color selection for
pBluescript II phagemids because of lacZΔM15 complementation on the
F´ episome. The color selection may be seen when plating on LB plates
containing 100 μg/ml of ampicillin, 80 μg/ml of fresh X-gal, and 20 mM
IPTG. Alternatively, plates for color selection can be prepared by spreading
100 μl of 40 mM IPTG and 100 μl of 2% X-gal on LB–ampicillin plates
30 minutes prior to plating your transformants. X-gal should be prepared in
dimethyl formamide and IPTG in sterile, distilled H
at –20°C until use). Colonies containing phagemids without inserts will be
blue after incubation for 12–18 hours at 37°C. Colonies with phagemids
containing inserts will remain white. Further enhancement of the blue color
may be obtained by placing plates at 4°C for 2 hours following overnight
growth at 37°C.
Occasionally, β-galactosidase fusion proteins are toxic to the host bacteria.
If there is any suspicion that an insert might be toxic, the X-gal and IPTG
may be left out of the ampicillin plates. Under these conditions there will be
no color selection, but recombinants will express lower levels of the
potentially toxic proteins.
O (store stock solutions
2
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 7

Background White Colonies
Since the ΔM15 lac gene carried on the F´ episome is needed for the blue–
white color assay, host bacteria that have lost the F´ episome will remain as
white colonies on an X-gal/IPTG agar plate even if the pBluescript II
phagemid does not contain an insert. XL1-Blue MRF´ is a lac
derivative with Tn10, lacI
containing the F´ in this strain is accomplished by plating on 12.5 μg/ml
tetracycline instead of minimal media plates. XL1-Blue MRF´ transformants
containing pBluescript II phagemids can be plated on tetracycline–
ampicillin plates to select for colonies that contain both the F´ and the
pBluescript II phagemid. This advantage further reduces the background of
false positives.
For bacteria containing an F´ without a Tn10 gene, growth on a minimal
medium plate supplemented with 1 mM thiamine-HCl will maintain
selection for the F´; however, colonies will grow more slowly. If there is
any doubt about whether a white colony represents a pBluescript II
recombinant or a colony lacking the F´, streak it onto a minimal medium
plate.
carries the proAB genes on the F´ episome.
SCREENING COLONIES
–
AG1
q
, and lacZΔM15 on the F´. Selection for bacteria
4
A cell lacking an F´ will not grow; an F+ will grow slowly since it
Colonies containing pBluescript II phagemids may be screened for
recombinants by double-stranded DNA, RNA, or oligonucleotide
hybridization.
sequencing miniprep plasmid DNA. Antibodies may be used to screen
colonies
5
Colonies may also be screened by restriction mapping or by
6
since cDNA cloned into the appropriate reading frame of the lacZ
gene will be expressed as fusion proteins.
When screening with antibodies, the bacteria produce fusion proteins
containing several amino acids from the amino-terminus of the
β-galactosidase protein (3.5 kDa to the EcoR I site). Some fusion proteins
are toxic to E. coli. Therefore, it is best to initially plate transformants on
nitrocellulose filters on top of ampicillin plates lacking IPTG. After
8–10 hours (when the colonies are 1 mm in diameter), transfer the filters to
plates containing 5 mM IPTG for several hours. This will induce synthesis
of the fusion proteins. When screening with antibodies, the Agilent picoBlue
immunoscreening kit is recommended. To synthesize large amounts of the
fusion proteins in liquid culture, grow the cells to an OD
= 0.7 in the
600
absence of IPTG. Add IPTG to 5 mM and grow for another 2–3 hours. The
β-galactosidase portion of the fusion protein is ~3.5 kDa from the Met
amino acid to the EcoR I site in the polylinker.
Identification of recombinant clones within pBluescript II can be performed
by colony hybridization. The following protocol minimizes problems
associated with colony screening procedures. For the following protocol to
be effective, the screening should be performed on duplicate sets of filters.
8 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors

Fixing Replica Sets of Colonies to Nitrocellulose Filters
Use the following protocol to make multiple replica plates of transformants.
Keep the original or master filter to pick colonies identified by the screening
of the replica filters.
1. Place 100–mm Duralon–UV or nitrocellulose filters on 150–mm LB–
ampicillin plates.
6
2. Spread ~1.0 × 10
3. Incubate the plates at 37°C overnight or until colonies are 1.0 mm in
diameter (~7–10 hours).
4. Make a replica of the library growing on the nitrocellulose filter:
cfu on the filters.
a. Place a piece of sterile Whatman
®
3MM paper on a glass surface.
b. Remove the filter from the agar and place it colony side up on the
Whatman 3
MM paper.
c. Align a fresh filter, prewetted on an LB plate, over the master
filter and cover with another piece of Whatman 3
MM paper. Press
in place with a glass plate.
d. Mark the filters with a small needle to aid in realignment after
hybridization.
e. Separate the master and replica filters and place face up on LB
agar plates containing ampicillin.
f. Incubate both the master and replica filters for at least 4 hours
at 37°C.
®
g. Seal the master plate with Parafilm
and store at 4°C.
5. The replica filter is then prepared for hybridization:
a. Place the replica filter colony side up for 30 seconds on the surface
of Whatman 3
MM paper prewetted with 0.5 M NaOH.
b. Remove filter and place on another sheet of Whatman 3
MM paper
prewetted with 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) for 30 seconds.
c. Remove the filter and place on a third piece of Whatman 3
MM
paper prewetted with 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) and 1.5 M NaCl for
30 seconds.
d. Immerse the filter in 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) and 1.5 M NaCl and
remove bacterial debris by rubbing the filter gently with a gloved
hand.
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 9

Prehybridization
e. Rinse the filter in 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.6) and 1.5 M NaCl. Blot
dry on paper towels.
f. Crosslink the DNA to the filters using the autocrosslink setting on
the Stratalinker UV crosslinker (120,000 μJ of UV energy).
Alternatively, oven-bake at 80°C for ~1.5–2 hours.
Prehybridization Solution for Oligonucleotide Probe
6× SSC
20 mM NaH
2PO4
0.4% sodium dodecyl sulfate* (SDS)
5× Denhardt's
Denatured, sonicated salmon sperm DNA (500 μg/ml)
OR
Prehybridization Solution for Double-Stranded Probe
2× Pipes buffer
50% Deionized formamide
0.5% SDS*
Denatured, sonicated salmon sperm DNA (100 μg/ml)
The amount of prehybridization solution to make is dependent on the
number of filters used (generally 2–3 ml/membrane).
1. Preheat the prehybridization solution to ~50°C without the salmon
sperm DNA. Preboil the salmon sperm DNA for ~10 minutes and add it
to the warm prehybridization solution.
2. Wet each filter (quickly) in the prehybridization buffer in a tray,
placing each filter on top of the next, until each is wet through. Add
more prehybridization solution as necessary. (This helps wet the filters
completely to allow more even hybridization later.)
3. Put the wet prehybridization filter "stack" in a heat-seal bag, add the
remaining prehybridization buffer and heat seal.
4. Calculate the hybridization temperature (generally 42°C) and
prehybridize for a minimum of 1 hour.
5. Prehybridize and hybridize a blank filter ("background") along with the
rest and wash it to determine when and at what temperature the
background counts disappear.
* For Stratagene Duralon-UV™ membranes, increase the SDS concentration to 1% (w/v).
10 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors

Hybridization
Labeling Oligonucleotide Probes
Label oligonucleotides with fresh [γ-32P]ATP. High-specific-activity
γ-label yields the best results.
a. Perform a polynucleotide kinase (PNK) labeling in 1× ligase buffer for
30 minutes at 37°C.
b. Incubate for 15 minutes at 65°C to inactivate the kinase.
c. Run the solution over a G-50 column to get rid of the unincorporated
counts.
Labeling Double-Stranded Probes
When using double-stranded probes, nick translate with fresh [α-32P]dATP.
Alternatively, we offer the Prime-It II random primer labeling kit. designed
to produce high-specific-activity DNA probes in 2 minutes.
It is best to use ~1 × 10
the concentration of counts high and use ~1 × 10
6
–5 × 106 counts/ml of hybridization solution. Keep
7
counts/filter.
Hybridization Solution
Hybridization Solution for Oligonucleotide Probes
6× SSC
20 mM NaH
0.4% SDS*
Denatured, sonicated salmon sperm DNA (500 μg/ml)
1. Make the hybridization solution.
2. Boil the salmon sperm DNA and then add it to the prewarmed
hybridization solution.
3. Pour out the prehybridization buffer from the filter bag. Add the
hybridization solution and then the appropriate amount of labeled
oligonucleotide.
* For Stratagene Duralon-UV™ membranes, increase the SDS concentration to 1% (w/v).
2PO4
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 11

4. Heat seal and hybridize at 5–10°C below Tm. Calculate Tm using the
following formula:
Note The first method below overestimates the T
of hybrids involving
m
longer nucleotides.
O
LIGONUCLEOTIDES SHORTER THAN 18 BASES
= 2°C(A + T) + 4°C(G + C)
T
m
LIGONUCLEOTIDES 14 BASES AND LONGER (UP TO 60–70 NUCLEOTIDES)
O
= 81.5 – 16.6 (log10[Na+]) + 0.41(%G + C) – (600/N), where N = chain length
T
m
Hybridization Solution for Double-Stranded Probes
2× Pipes buffer
50% Deionized formamide
0.5% SDS*
Denatured, sonicated salmon sperm DNA (100 μg/ml)
1. Prepare the hybridization solution.
2. Warm the solution, boil the appropriate amount of salmon sperm DNA
with the probe for 4 minutes and then add it to the hybridization buffer.
3. Decant the prehybridization buffer and replace it with the hybridization
solution and probe. Hybridize overnight at 42°C.
Washes
Oligonucleotide Probes
Use 6× SSC buffer and 0.1% (w/v) SDS. Wash the filters three times for
5 minutes each at room temperature. The final washing temperature depends
on the GC ratio of the probe. It is best to stay several degrees below the
melting temperature. A rough estimate of the melting temperature of an
oligonucleotide probe can be determined by the following formula:
= 4(G + C) + 2(T + A)
T
m
If the probe sequence is unknown, start with a room temperature wash and
gradually increase the temperature until the background diminishes. DO
NOT allow the membranes to completely dry out or the probe may be
irreversibly bound.
Double-Stranded Probes
Use 0.1× SSC buffer and 0.1% (w/v) SDS. Wash the filters at 50–65°C with
agitation.
* For Stratagene Duralon-UV™ membranes, increase the SDS concentration to 1% (w/v).
12 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors

Exposure to Film
After washing, remove the excess liquid by blotting on Whatman 3MM
paper and place the filters between two sheets of plastic wrap in cassettes
with intensifying screens. Leave overnight at –80°C. (By keeping the filters
slightly moist between plastic wrap, you can wash again if the background
is high.)
T3 AND T7 RNA TRANSCRIPTION
The RNA transcripts synthesized from inserts cloned into vectors containing
either T3 or T7 polymerase promoters can be used for many purposes.
Transcripts can be used for both Southern and Northern hybridization
experiments and for either S1 or RNase A analysis. In addition, RNA
transcripts can be used to produce protein by translation in vitro or
translation in vivo after microinjection into Xenopus oocytes or tissue
culture cells.
The pBluescript II vectors have a BssH II site outside each RNA promoter.
This feature allows the excising of the insert with the promoters and
subsequent mapping using phosphorylated T3 and/or T7 primers.
Handling RNA
Note Wear gloves at all times to prevent RNase contamination.
When working with RNA, caution must be used to eliminate RNase
contamination from any source. The following general principles will help
in the production of full-length transcripts:
1. Make all buffers, DTT, and rNTPs in highly pure water treated with
diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) as follows:
Add DEPC to water to a final concentration of 0.1%, heat to 37°C for
8 hours and autoclave. If DEPC scent remains after autoclaving, place
the water in a 90°C water bath for at least 1 hour or until the
scent is gone.
Note Do not treat Tris solutions with DEPC!! Instead, use water that
has been treated with DEPC to make up all Tris solutions.
The Agilent RNAMaxx high-yield transcription kit (Catalog #200339)
may be used for transcription reactions performed with T7 RNA
polymerase.
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 13

2. All tubes and pipet tips should be autoclaved and baked for several
hours at 80°C. A common source of RNase contamination on gel
electrophoresis equipment comes from DNA minipreps which have
been treated with RNase A. Thoroughly clean all gel tanks, gel combs,
gel spacers and glassware, using soap and water followed with an
ethanol rinse. Next, soak the equipment in 3% hydrogen peroxide for
10 minutes at room temperature and rinse with DEPC-treated water.
Keep cleaned items covered and away from bare hands. Autoclave all
glass plates and other appropriate materials on dry cycle prior to use.
3. Phagemid templates for transcription must be RNase-free. Cesium
chloride preps are advisable, but minipreps may be used if care is taken
to remove contaminating RNases. Generally the plasmid template is
linearized with an enzyme that cleaves "downstream" of the RNA
polymerase promoter and the insert in the multiple cloning site. It is
strongly advised to purify the post-restriction digest DNA by adding
50 μg/ml proteinase K to the restriction buffer at 37°C for 30 minutes,
followed by two phenol–chloroform [1:1 (v/v)] extractions and ethanol
precipitation prior to the transcription reaction. Resuspend digested,
proteinase K treated DNA at 1 mg/ml in a 10 mM Tris (pH 7.4) and
0.1 mM EDTA solution made with DEPC-treated water.
4. Working with RNA is simplified by using a ribonuclease inhibitor in
transcription reactions. The Agilent RNase Block Ribonuclease
Inhibitor has been tested and adjusted to work optimally with Agilent’s
transcription kits.
Nonspecific Initiation with T7 and T3 RNA Polymerases
T7 and T3 RNA polymerases are highly specific for their respective
promoters,
the ends of the DNA template. This is most prevalent with a 3´-protruding
terminus. Nonspecific initiation may be reduced by increasing the NaCl
concentration in the transcription buffers to 100 mM, although this will
result in a decrease of the total transcription efficiency by ~50%. When
possible, use restriction enzymes that leave blunt or 5´-protruding ends.
When the T7 or T3 polymerase enzymes are used in molar excess of the
DNA template, there is a risk of polymerization from the wrong promoter.
T7 polymerase can synthesize RNA inefficiently from a plasmid containing
only a T3 promoter. Conversely, T3 polymerase can synthesize RNA
inefficiently from a plasmid containing only a T7 promoter. Synthesis is
extremely promoter specific when both promoters are present, provided that
the enzyme is not in molar excess of the specific promoter. Do not use
excessive amounts of the polymerases if promoter specificity is important to
your experiment. Best results are obtained when the ratios stated in this
manual are followed.
1
however, nonspecific initiation of RNA transcripts may occur at
14 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors

Nonradioactive Transcripts
Nonradioactive transcripts can be used for nucleotide sequencing, in vitro
translation and injection into cells for in vivo translation. Set up the
transcription reaction as described, but add 1 μl of 10 mM rUTP instead of
radioactive rUTP. For larger amounts of RNA, scale up the reaction
appropriately. Each molecule of DNA template yields 10–20 nonradioactive
RNA molecules if the ribonucleotides are not a limiting factor.
DNase Treatment after Transcription
The DNA template will be present after the transcription reaction and can be
removed with RNase-free DNase. After the transcription reaction, add 10 U
of RNase-free DNase/μg of DNA template and incubate at 37°C for
15 minutes. Extract with phenol–chloroform [1:1 (v/v)], add 1/10 volume of
3 M sodium acetate at pH 5.2 and precipitate RNA with 2.5 volumes of
100% (v/v) ethanol.
High-Specific-Activity RNA Probes
Any vector containing T3 and T7 RNA promoters can be used to synthesize
high specific activity, strand-specific RNA probes. The choice between T3
and T7 RNA polymerase will determine which strand will be used as the
template. This is important because probes used for Northern or S1 analysis
must complement the RNA targeted for detection.
The initiation of RNA transcription requires rGTP; the reaction has a K
~180 μM. The elongation reaction has a K
ribonucleotide. Therefore, radioactive rGTP should not be used to generate
high specific-activity probes unless the concentration of rGTP exceeds
180 μM. This usually means supplementing the radioactive rGTP with cold
rGTP. Adding 50 μCi of 500 Ci/mmol [
produces an rXTP concentration of 4 μM. To generate high specific-activity
probes, we suggest using radioactive rATP, rCTP, or rUTP as the labeled
nucleotide. However, any triphosphate present at just 4 μM will not produce
many transcripts per template molecule because the reaction simply runs out
of radioactive rXTP. To make large amounts of long, radioactive transcripts,
the reactions must be supplemented with cold rXTP. It is therefore
necessary to choose between full length, quantity and high-specific-activity
when producing probes.
m
of 40 μM for each
m
32
P]rXTP to a 25-μl reaction only
of
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 15

Transcription Reaction
Note The RNAMaxx high-yield transcription kit (Catalog #200339) may
1. In the order given, add
5 μl of 5× transcription buffer
1 μg of restricted, proteinase K-treated DNA template
1 μl of 10 mM rATP
1 μl of 10 mM rCTP
1 μl of 10 mM rGTP
[1 μl of 1 mM rUTP is optional (see above)]
1 μl of 0.75 M dithiothreitol (DTT)
1 μl of RNase Block Ribonuclease Inhibitor (optional)
5 μl of 400–800 Ci/mmol, 10 μCi/μl [α-
10 U of T3 or T7 RNA polymerase*
DEPC-treated water to a final volume of 25 μl
2. Incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes.
3. RNA transcripts may be purified away from the unincorporated
nucleotides using an RNase-free G-50 column.Take care to prevent the
presence ribonucleases in the column that could degrade the probe.
be used for transcription reactions performed with T7 RNA
polymerase.
§
32
P]rUTP
Note Do not use large excesses of T3 polymerase (10 U of polymerase
per pmol of promoter is sufficient). T3 RNA polymerase may
utilize the T7 promoter 1 in 20 times when the T3 enzyme
concentration exceeds the T3 promoter concentration by 10-fold.
However, T3 polymerase in the recommended concentrations will
not make T7 transcripts in the presence of a T3 promoter. If any
T7 hybridization should result from a T3 transcription, decrease
the amount of T3 polymerase by a factor of 5 or 10.
§
See Preparation of Media and Reagents.
* Use supplied RNA polymerase dilution buffer to dilute enzymes just before use.
16 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors

HYBRIDIZATION CONDITIONS FOR RNA PROBES IN SOUTHERN BLOTS
Prehybridization
Prehybridize the membrane with 0.1–0.5 ml/cm2 of the following solution
for 2 hours at 42°C with constant agitation in a heat-sealable bag:
6× SSC
5× Denhardt’s (see Preparation of Media and Reagents)
20 mM NaH
500 μg/ml of denatured, sonicated salmon sperm DNA
Hybridization
Pour off the prehybridization solution and add the probe to the bag with the
minimum volume of the following hybridization solution:
6× SSC
20 mM NaH
0.4% SDS*
500 μg/ml denatured sonicated salmon sperm DNA
Incubate overnight at 42°C with constant agitation.
Washes
Wash in 2× SSC buffer and 0.1% (w/v) SDS twice for 15 minutes each at
55°C and twice in 0.1× SSC buffer and 0.1% (w/v) SDS for 15 minutes each
at 55°C.
2PO4
2PO4
HYBRIDIZATION CONDITIONS FOR RNA PROBES IN NORTHERN BLOTS
Prehybridization
Prehybridize the membrane with 0.1–0.5 ml/cm2 of the following solution
for ~1 hour at 42°C with constant agitation in a heat-sealable bag:
50% deionized formamide
10% dextran sulfate
1% SDS*
1 M NaCl
100 μg/ml of denatured sonicated salmon sperm DNA
Hybridization
Hybridize overnight with the riboprobe at the same temperature and in the
prehybridization solution.
Washes
Wash in 2× SSC buffer and 0.1% (w/v) SDS twice for 15 minutes each at
42°C and twice in 0.1× SSC buffer and 0.1% (w/v) SDS for 15 minutes each
at 42°C. If a high background is observed, the temperature may be increased
or the NaCl concentration may be decreased for greater stringency.
* For Stratagene Duralon-UV and Illuminator membranes, increase the SDS concentration
to 1% (w/v).
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 17

RECOVERY OF SINGLE-STRANDED DNA FROM CELLS CONTAINING
BLUESCRIPT II PHAGEMIDS
P
pBluescript II is a phagemid that can be secreted as single-stranded DNA in
the presence of M13 helper phage. These phagemids contain the intergenic
(IG) region of a filamentous f1 phage. This region encodes all of the
cis-acting functions of the phage required for packaging and replication. In
E. coli with the F
phagemids will be secreted as single-stranded f1 "packaged" phage when the
bacteria has been infected by a helper phage. Since these filamentous helper
phages (M13, fI) will not infect E. coli without an F´ episome coding for
pili, it is essential to use XL1-Blue MRF´ or a similar strain containing
the F´ episome.
pBluescript II phagemids are offered with the IG region in either of two
orientations: pBluescript II (+) is replicated such that the sense strand of the
β-galactosidase gene is secreted within the phage particles; pBluescript II(–)
is replicated such that the antisense strand of the β-galactosidase gene is
secreted in the phage particles.
We offer helper phages that preferentially package pBluescript II
phagemids. Typically, 30–50 pBluescript II molecules are packaged/helper
phage DNA molecule. Yields of single-stranded (ss)DNA depend on the
specific insert sequence. For most inserts, over 1 μg of ssDNA can be
obtained from a 1.5-ml miniprep if grown in XL1-Blue MRF´. A faint
single-strand helper phage band may appear on a gel at ~4 kb for R408 or at
6 kb for VCSM13. This DNA mixture can be sequenced with primers that
are specific for pBluescript II and do not hybridize to the helper phage
genome.
Site-specific mutagenesis is also possible using standard techniques. The
advantages of using pBluescript II phagemids for either purpose are as
follows: (1) pBluescript II phagemids do not replicate via the M13 cycle,
lessening the tendency to delete DNA inserts, therefore it is unlikely that
even 10-kb inserts will be deleted. (2) "Packaging" of pBluescript II
phagemids containing inserts is efficient since the pBluescript II vector is
significantly smaller than wild-type M13. (3) Oligonucleotide mutagenesis
in pBluescript II vectors is advantageous because the mutagenized insert is
located between the T3 and T7 promoters. The resultant mutant transcripts
can be synthesized in vitro without further subcloning.
VCSM13 and R408 helper phage produce the largest amount of singlestrand pBluescript II. R408 (single-strand size ~4 kb) is more stable and can
be grown more easily. VCSM13 (single-strand size ~6 kb), is more efficient
at single-stranded DNA rescue and yields more single-stranded phagemid;
however it is more unstable and reverts to wild-type more frequently. This
difficulty can be addressed by periodically propagating VCSM13 in the
presence of kanamycin. VCSM13 (a derivative of M13KO7) has a
kanamycin gene inserted into the intergenic region, while R408 has a
deletion in that region. We suggest R408 for excision of pBluescript II from
the Lambda ZAP vector and VCSM13 for single-stranded rescue.
+
phenotype (containing an F´ episome), pBluescript II
7, 8
18 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors

Single-Stranded Rescue Protocol
1. Inoculate a single colony into 5 ml of 2× YT containing 100 μg/ml
7
ampicillin and VCM13 or R408 helper phage at 10
–108 pfu/ml
(MOI ~10).
2. Grow the culture at 37°C with vigorous aeration for 16–24 hours, or
until growth has reached saturation.
Note If using VCSM13, after 1–2 hours, add kanamycin to
70
μ
g/ml to select for infected cells.
3. Centrifuge 1.5 ml of the cell culture for 5 minutes in a microcentrifuge.
4. Remove 1 ml of the supernatant to a fresh tube, then add 150 μl of a
solution containing 20% PEG8000 and 2.5 M NaCl. Allow phage
particles to precipitate on ice for 15 minutes.
Note For increased yield, perform the PEG precipitation overnight
at 4°C.
5. Centrifuge for 5 minutes in a microcentrifuge. (A pellet should
be obvious.)
6. Remove supernatant. Centrifuge the PEG pellets a few seconds more to
collect residual liquid, then remove and discard the residual liquid.
7. Resuspend the pellet in 400 μl of 0.3 M NaOAc (pH 6.0) and
1 mM EDTA by vortexing vigorously.
8. Extract with 1 volume phenol–chloroform and centrifuge for
1–2 minutes to separate phases.
9. Transfer the aqueous phase to a fresh tube and add 1 ml of ethanol.
Centrifuge for 5 minutes.
10. Remove ethanol and dry the DNA pellet.
11. Dissolve the pellet in 25 μl of TE buffer.
12. Analyze 1–2 μl on an agarose gel.
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 19

SITE-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS
Isolated single-stranded DNA (see Recovery of Single–Stranded DNA from
Cells Containing pBluescript II Phagemids) can be used for site-directed
oligonucleotide mutagenesis.
1. Phosphorylation of the oligonucleotide with polynucleotide kinase:
100 ng of oligonucleotide
4 μl of 10× ligase buffer
4 μl of 10 mM rATP
2 μl of polynucleotide kinase (10 U)
Water to 40 μl final volume
Incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes.
2. Synthesis of mutant DNA strand
a. Anneal Oligonucleotide
20 μl of oligonucleotide from the kinase reaction (50 ng)
5 μl of salmon sperm DNA (1 μg template)
Incubate at 65°C for 10 minutes, then at room temperature for
5 minutes.
b. Primer Extension Reaction
Add the following to the annealing reaction:
4.0 μl of 10× ligase buffer
2.0 μl of 2.5 mM dNTPs (N = A, C, G and T in equal
4.0 μl of 10 mM rATP
1.0 μg of single-stranded DNA binding protein
1.5 U of Klenow
0.5 μl of T4 DNA ligase (2 U)
Water to 40 μl final volume
Incubate at room temperature for 3–4 hours.
9
The following protocol is recommended:
§
concentration)
§
3. Transform XL1-Blue MRF´ E. coli with 10 μl of synthesis reaction and
plate onto nitrocellulose filters across three plates.
4. Screen as described in Screening Colonies. One percent mutants should
be obtained.
§
See Preparation of Media and Reagents.
20 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors

PLASMID BOILING MINIPREP PROTOCOL
The following protocol yields high-quality dsDNA template simply and
rapidly. (Caution: Escherichia coli strain HB101 and derivatives give low
yields using this protocol.) This DNA is suitable for restriction enzyme
digestion or for enzyme sequencing.
1. Grow a 3-ml culture overnight in LB broth plus ampicillin (100 μg/ml)
from a single colony.
2. Pellet 1.5 ml of the culture in a microcentrifuge at 4°C for 2 minutes.
Remove the supernatant by aspiration.
3. Resuspend the pellet in 110 μl of STETL buffer (see Preparation of
Media and Reagents).
4. Place the tube in a boiling water bath for 30 seconds.
5. Immediately spin the tube in a microcentrifuge for 15 minutes at room
temperature.
6. Remove and discard the pellet with a sterile toothpick. Save the
supernatant. [RNase treatment (20 μg/ml) is optional at this stage.)]
10
7. Add 110 μl of isopropanol to the supernatant and immediately spin the
tube in a microcentrifuge for 15 minutes.
8. Resuspend the pellet in 100 μl of TE buffer.
9. Extract twice with an equal volume of phenol–chloroform [1:1 (v/v)]
and once with chloroform.
Note To purify the sample, StrataClean resin may be used in place
of the phenol–chloroform extraction.
10. Add an equal volume of 7.5 M ammonium acetate and precipitate with
2.5 volumes of ethanol. Incubate on ice 15 minutes and spin at 4°C for
20 minutes.
11. Rinse with 1 ml of 80% (v/v) ethanol and spin in a microcentrifuge for
1 minute.
12. Vacuum dry the pellets.
13. Resuspend the pellets in 15 μl of TE buffer.
14. Use 5 μl of this DNA (about 2.0 μg) for sequencing.
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 21
TROUBLESHOOTING
Observation Suggestion
Digestion with EcoR I produces
multiple bands
Nae I fails to cleave the
pBluescript II vector
Using excess amounts of EcoR I to digest pBluescript II vectors results in EcoR I prime
activity. This appears as cleavage at a non-EcoR I site at the 3´ end of the f1
intergenic region, causing confusion when interpreting results from an agarose gel.
Test whether reducing the units of EcoR I restores a normal restriction pattern
We have observed that the Nae I site in the pBluescript II phagemid presents a
challenging substrate for digestion. Use 16U Nae I enzyme per μg DNA and
increase the digestion period (overnight digestion may be necessary). Even under
these more stringent conditions, Nae I may not produce complete cleavage.
PREPARATION OF MEDIA AND REAGENTS
5× Transcription Buffer
200 mM Tris, pH 8.0
40 mM MgCl
2
10 mM spermidine
250 mM NaCl
M9 Minimal Medium (per Liter)
750 ml of sterile deionized water (cooled to
50°C)
200 ml of 5× M9 salts
Sterile deionized water to 1 liter
20 ml of a 20% solution of the appropriate
carbon source (e.g., 20% glucose)
LB Broth (per Liter)
10 g of NaCl
10 g of tryptone
5 g of yeast extract
Add deionized H
1 liter
Adjust to pH 7.0 with 5 N NaOH
Autoclave
O to a final volume of
2
10× Ligase Buffer
500 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)
70 mM MgCl
2
10 mM dithiothreitol (DTT)
Note rATP is added separately in the ligation
reaction.
20× SSC
175.3 g of NaCl
88.2 g of sodium citrate
800.0 ml of water
10.0 N NaOH
Adjust to pH 7.0 with a few drops of 10.0 N
NaOH
Adjust volume to 1 liter with water
50× Denhardt's Reagent (per 500 ml)
5 g of Ficoll
5 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone
5 g of BSA (Fraction V)
Add deionized H
Filter through a disposable filter
Dispense into aliquots and store at –20°C
O to a final volume of 500 ml
2
1× STE Buffer
100 mM NaCl
20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)
10 mM EDTA
STETL Buffer
8.0% sucrose
0.5% Triton X-100
50.0 mM Tris (pH 8.0)
50.0 mM EDTA
0.5 mg/ml lysozyme
All components except lysozyme can be
prepared and stored indefinitely at 4°C.
The lysozyme is made as a 5 mg/ml stock
and stored in small aliquots at –20°C.
Do not reuse the lysozyme stock after
thawing.
22 pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors
REFERENCES
ENDNOTES
1. Morris, C. E., Klement, J. F. and McAllister, W. T. (1986) Gene 41(2-3):193-200.
2. Studier, F. W. and Moffatt, B. A. (1986) J Mol Biol 189(1):113-30.
3. Jerpseth, B., Greener, A., Short, J. M., Viola, J. and Kretz, P. L. (1992) Strategies
5(3):81–83.
4. Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F. and Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory
Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
5. Short, J. M., Fernandez, J. M., Sorge, J. A. and Huse, W. D. (1988) Nucleic Acids Res
16(15):7583-600.
6. Helfman, D. M., Feramisco, J. R., Fiddes, J. C., Thomas, G. P. and Hughes, S. H.
(1983) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80(1):31-5.
7. Dente, L., Cesareni, G. and Cortese, R. (1983) Nucleic Acids Res 11(6):1645-55.
8. Mead, D. A., Skorupa, E. S. and Kemper, B. (1985) Nucleic Acids Res 13(4):1103-18.
9. Craik, C. S. (1985) Biotechniques 3(1):12-19.
10. Holmes, D. S. and Quigley, M. (1981) Anal Biochem 114(1):193-7.
GenBank® is a registered trademark of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Parafilm
Whatman
Triton
®
is a registered trademark of American Can Company.
®
is a registered trademark of Whatman Ltd.
®
is a registered trademark of Rohm and Haas Co.
MSDS INFORMATION
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) are provided online at http://www.genomics.agilent.com. MSDS
documents are not included with product shipments.
pBluescript II Phagemid Vectors 23
 Loading...
Loading...