Page 1

Operation Manual
TPS52-H33
HT593348 English
Original Operation Manual
Chapter Document-ID
1 Introduction
2 Safety
3 Safety data sheet
4 Product description
HZTL4005_EN_F
HZTL4026_EN_D
HT593348
HZTL4037_EN_E
ABB Turbocharging
Page 2

Operating limits and replacement intervals
The recommended replacement intervals and the corresponding operating limits in chapter 3 are jointly defined
with the enginebuilder. This information is specific to the product.
Non-observance of the recommended replacement intervals and the operating limits increases the risk of unpredictable component failures.
Page 3

Operation Manual / 1 Introduction
Table of contents
Introduction
1 Introduction............................................................................................................ 2
1.1 Purpose of the manual.................................................................................................. 2
1.2 Symbols, definitions...................................................................................................... 3
1.3 Storage of new turbochargers and spare parts...................................................... 5
1.4 Contact information...................................................................................................... 7
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4005_EN Revision F May 2017
Page 4
Operation Manual / 1 Introduction
1 Introduction / 1.1 Purpose of the manual
1 Introduction
1.1 Purpose of the manual
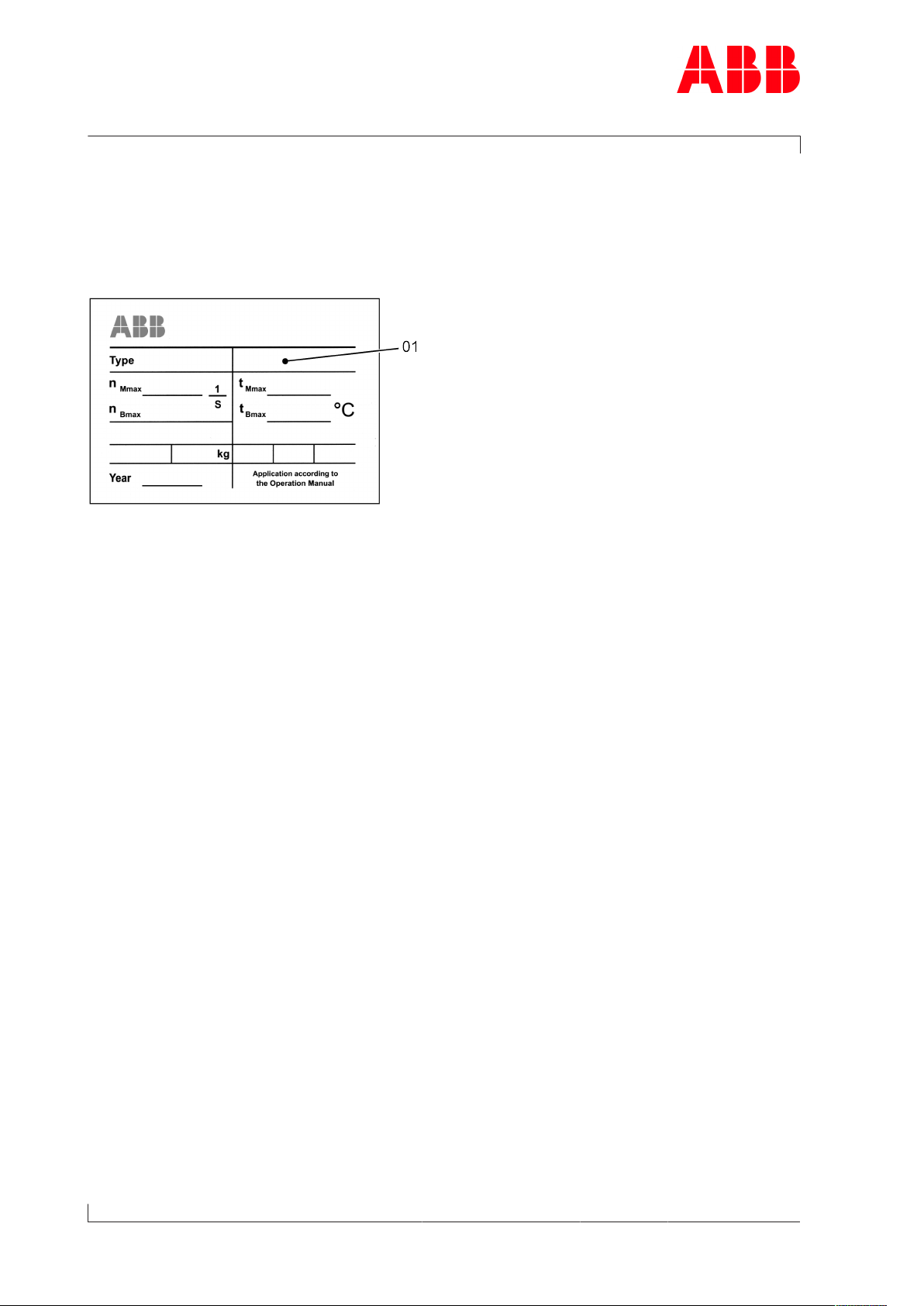
Fig.1: Serial number (01) on the rating plate
This Operation Manual belongs to the turbocharger with the identical serial number (01), see
chapter 3 (Safety data sheet) and the rating plate on the turbocharger.
Operation Manual
The Operation Manual explains the turbocharger and contains instructions for safe opera-
Page 2 / 7
tion.
The Operation Manual is a complement to and expansion of existing national regulations for
occupational safety, accident prevention and environmental protection.
Target group
The Operation Manual is aimed at engineers and trained mechanics responsible for the
proper operation of the engine and for the turbocharger connected to it.
Availability of the Operation Manual
The Operation Manual must be available where the turbocharger is used.
All persons operating or working on the turbocharger must have read and fully understood
the Operation Manual.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4005_EN Revision F May 2017
Page 5

Operation Manual / 1 Introduction
1 Introduction / 1.2 Symbols, definitions
1.2 Symbols, definitions
Symbols
The following symbols are used in this document:
u Indicates an action step.
1. Indicates a numbered action step.
→ Refers to a page number.
Definition of Note
NOTICE
Note
The note provides advice which facilitates the work.
Definition of mandatory signs
Mandatory signs show the protective equipment to be worn for a task. The mandatory signs
are described in chapter Safety and must be complied with.
Definition of Caution / Warning
Caution and warning signs are described in chapter Safety.
ABB Turbo Systems
ABB Turbo Systems Ltd is identified as ABB Turbo Systems in this document.
Official service stations of ABB Turbo Systems
Official service stations are identified in this document as ABB Turbocharging Service Stations. They are regularly audited and certified by ABB Turbo Systems. Also see chapter Con-
tact information →7.
Page 3 / 7
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4005_EN Revision F May 2017
Page 6
Operation Manual / 1 Introduction
1 Introduction / 1.2 Symbols, definitions
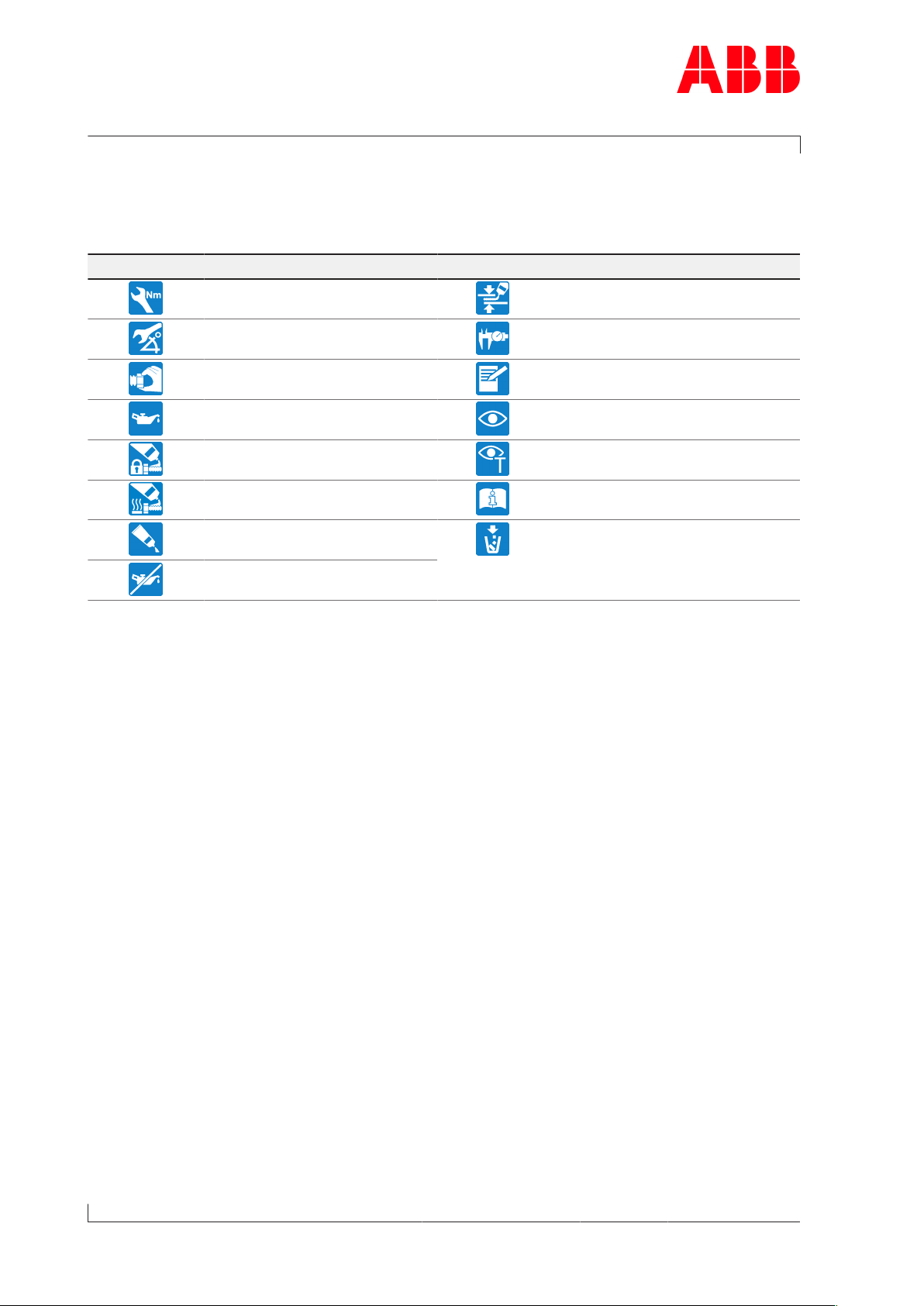
Definition of pictograms
The following pictograms can occur in this document. These point out actions that must be
taken in accordance with the meaning of the relevant pictogram.
Pictogram Meaning Pictogram Meaning
Tighten with specified torque Affix
Tighten over specified tightening angle
Hand-tight, tighten without
tools
Oil Visually inspect
Apply screw locking paste (e.g.
Loctite)
Apply high-temperature grease See document
Apply other paste in accordance with specifications
Oil free, grease free and dry
Table1: Definition of pictograms
Measure
Note
Please note text for numbered
work step
Dispose of in an environmentally
compatible, professional way and
in compliance with locally applicable regulations
Page 4 / 7
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4005_EN Revision F May 2017
Page 7
Operation Manual / 1 Introduction
1 Introduction / 1.3 Storage of new turbochargers and spare parts
1.3 Storage of new turbochargers and spare parts
Storage of new turbochargers and spare parts for up to 6 months
New turbochargers and spare parts can be stored in their closed packages for 6 months
from the date of delivery without additional mothballing measures, indicated by the VCI label on the package.
Fig.2: Volatile Corrosion Inhibitor (VCI)
Only dry rooms with 40...70 % atmospheric humidity, in which no water condensation can
form, are suitable as storage locations.
Storage of new turbochargers and spare parts for more than 6 months
WARNING
Health protection when handling VCI
VCI products are not hazardous in terms of the Ordinance on Hazardous
Substances. Nevertheless, the following points must be observed when
handling VCI:
u Observe information in material safety data sheet
u Ensure proper space ventilation.
u Do not eat, drink or store food at the workplace while working with VCI.
u Clean hands and face after working with VCI.
u For more information, see www.branopac.com.
Wear safety gloves to protect against mechanical hazards.
Every 6 months, the following mothballing measures are required:
u Open package.
u Remove VCI corrosion protection emitter from package and replace with a new VCI corro-
sion protection emitter of the same kind. New VCI corrosion protection emitters can be
obtained from www.branopac.com.
u Old VCI corrosion protection emitters must be disposed of in an environmentally compat-
ible, professional way and in compliance with locally applicable regulations.
Page 5 / 7
u Close package. The more tightly the package is sealed, the longer the protection dura-
tion.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4005_EN Revision F May 2017
Page 8
Operation Manual / 1 Introduction
1 Introduction / 1.3 Storage of new turbochargers and spare parts
Long-term storage of replacement turbochargers or spare parts
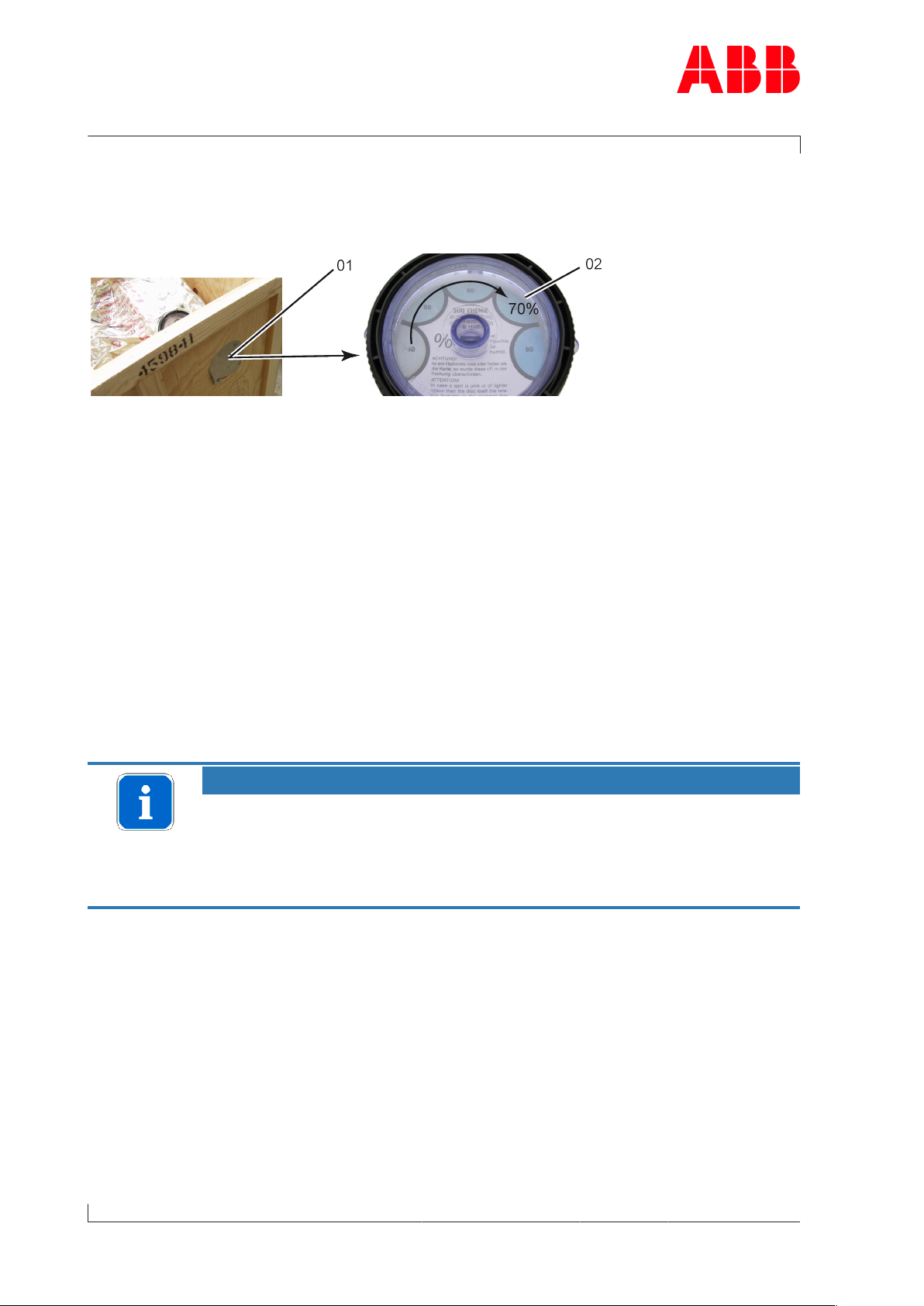
The turbochargers or cartridge groups will be prepared for long-term storage if requested in
the purchase order. The package is equipped with a hygrometer (see illustration).
Fig.3: Package with hygrometer
Every 6 months, the following measures are required:
u Check the hygrometer(02) in the sight-glass. There is an opening(01) in the wooden
crate to enable you to perform this check. If the 70% indicator field has changed colour,
the maximum admissible atmospheric humidity has been exceeded. In this case, the turbocharger or cartridge group must be checked and repackaged by an ABB Turbocharging
Service Station.
u Check the package for damage. If the package is damaged, the turbocharger or cartridge
group must be checked and repackaged by an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
After every 3 years, the following steps must be carried out by an ABB Turbocharging Service
Station:
Page 6 / 7
¡ Checking the component
¡ Replacing the desiccant
¡ Repackaging the component.
NOTICE
Replacement components which are ready for operation
If the 70% field of the hygrometer(02) has not changed colour and the package is not damaged, the replacement turbocharger or replacement cartridge
group can be put into operation without previously having been checked by
an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
Unpackaging replacement turbochargers or spare parts
Once the material has been unpackaged from the VCI package, the corrosion protection is
no longer effective.
To prevent condensation, the temperature of the package contents must be the same as the
ambient temperature.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4005_EN Revision F May 2017
Page 9

Operation Manual / 1 Introduction
1 Introduction / 1.4 Contact information
1.4 Contact information
Contact information for the ABB Turbocharging Service Stations is available online.
u Scan the QR code to access our website.
ABB Turbo Systems Ltd
Bruggerstrasse 71a
CH-5401 Baden
Switzerland
www.abb.com/turbocharging
Page 7 / 7
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4005_EN Revision F May 2017
Page 10

Page 11

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
Table of contents
Safety
1 Safety ...................................................................................................................... 2
1.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................... 2
1.2 CE conformity................................................................................................................. 2
1.3 Definition of mandatory signs .................................................................................... 3
1.4 Definition of safety instructions ................................................................................ 3
1.5 Intended use .................................................................................................................. 4
1.6 Deflagration on gas engines ....................................................................................... 5
1.7 Warning plates on the turbocharger......................................................................... 6
1.8 Turbocharger rating plate............................................................................................ 7
1.9 Periodic check of the pressure vessels..................................................................... 8
1.10 Lifting of loads .............................................................................................................. 9
1.11 Prerequisites for operation and maintenance....................................................... 10
1.12 Hazards during operation and maintenance ......................................................... 11
1.13 Safe operation.............................................................................................................. 13
1.14 Safe maintenance ........................................................................................................ 14
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 12

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.1 Introduction
1 Safety
1.1 Introduction
Turbochargers manufactured by ABB reflect the state of the art. The respective safety and
health protection requirements are met. This ensures safe operation of the turbocharger.
Nevertheless, there may be some residual risks during operation of and work on the turbocharger which:
¡ Are caused by the turbocharger itself or its accessories.
¡ Are caused by the operating equipment used or supplies and materials.
¡ Are a consequence of insufficient compliance with safety instructions.
¡ Are a consequence of insufficient or inappropriate performance of maintenance and in-
spection work.
The operating company is responsible for defining measures that regulate safe access to
and safe handling of the turbocharger.
Page 2 / 17
All instructions contained in this chapter must be observed for safe and trouble-free operation of the turbocharger and during all work on the turbocharger.
All further safety instructions contained and specifically identified in every chapter of this
manual (Definition of safety instructions →3) must also be observed.
1.2 CE conformity
Information
ABB turbochargers comply with the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and are partly completed machinery as defined by Article 2 g in this directive.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 13
Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.3 Definition of mandatory signs
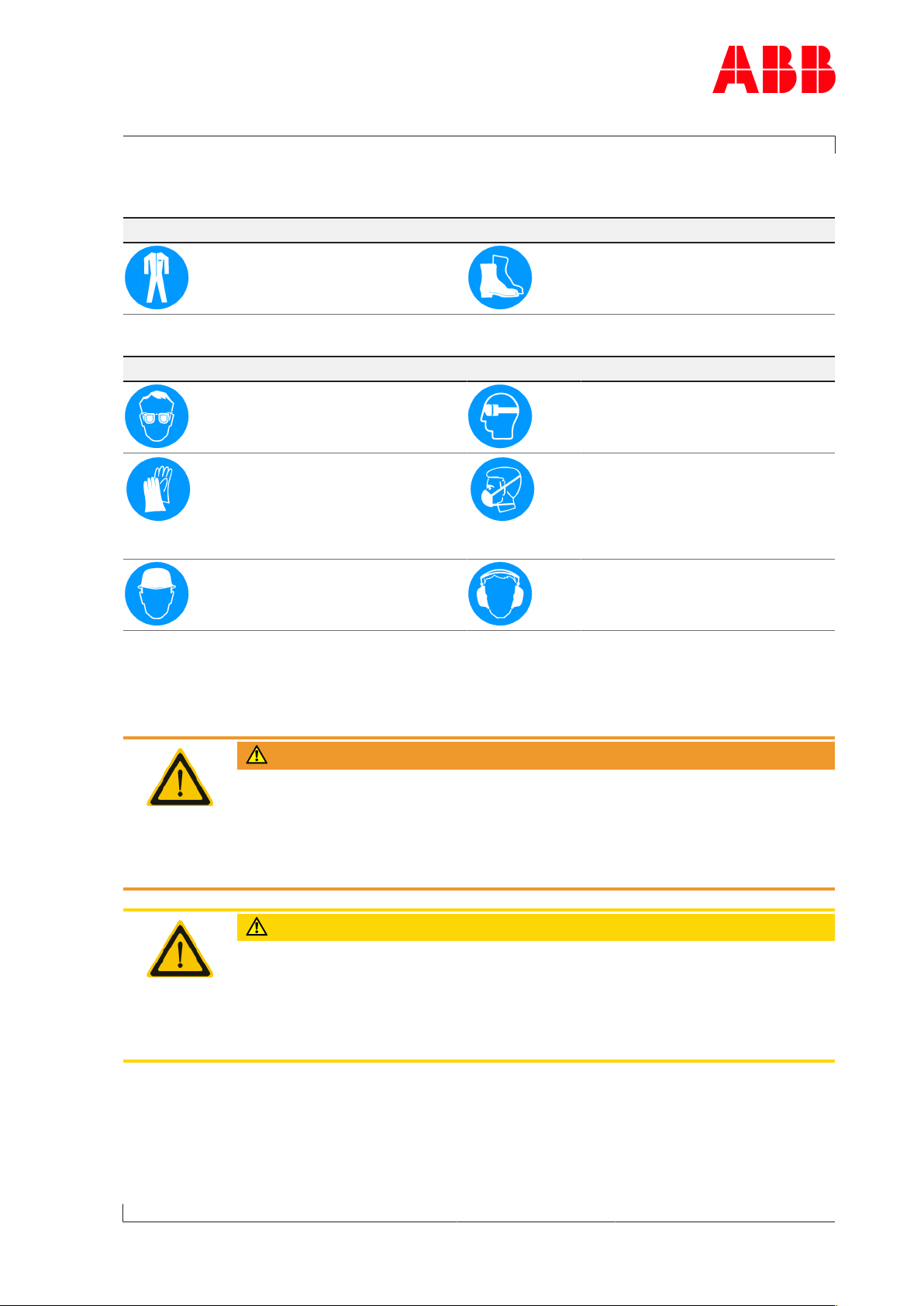
1.3 Definition of mandatory signs
To be worn at all times
Protective clothing Safety footwear to protect
against mechanical hazard and
risk of falling
Table1: Personal protective equipment to be worn at all times
To be worn specific to the respective task
Safety glasses Safety goggles
Safety gloves to protect
against
- Mechanical hazard
- Chemical hazard
- Thermal hazard
Safety helmet Ear protection
Table2: Personal protective equipment to be worn specific to the respective task
Respiratory mask to protect
against
- Dusts
- Gases
1.4 Definition of safety instructions
WARNING
Definition of Warning
Non-compliance or inaccurate compliance with working or operating instructions indicated by this symbol and the word WARNING can lead to serious injuries to personnel and even to fatal accidents.
u Warning signs must always be observed.
Page 3 / 17
CAUTION
Definition of Caution
Non-compliance or inaccurate compliance with working or operating instructions indicated by this symbol and the word CAUTION can lead to serious damage to engine or property with grave consequences.
u Caution signs must always be observed.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 14

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.5 Intended use
1.5 Intended use
Use on internal combustion engines in general
ABB turbochargers are intended for turbocharging internal combustion engines.
To ensure compliance with the machinery directive 2006/42/EC when using on gas engines,
the turbocharger must be operated in an engine room classified as "not at risk of explosion".
This is in accordance with the position paper [2] relating to ATEX issued by EUROMOT[1].
For use on pre-mix gas engines with ignitable propellents in the gas control system, the enginebuilder must implement appropriate safety measures for explosion protection [3] (such
as flame barriers in the inlet system, for example) to assure that there is no transient pressure increase exceeding a maximum of 12 bar before the turbocharger in case of a deflagration.
The turbocharger supplies the engine with the air volume or air/gas mixture and the associated charging pressure required for operation.
Page 4 / 17
The turbocharger is solely intended to be operated with a clockwise direction of rotation as
viewed from the turbine end.
The specific operating limits of the turbocharger were determined on the basis of information from the enginebuilder about the intended use. These data are given on the rating
plate.
ABB accepts no liability and rejects all warranty claims for any non-intended uses.
[1] Euromot = The European Association of Internal Combustion Engine Manufacturers
[2] Directive 94/9/EC concerning equipment and protective systems intended for use in
potentially explosive atmospheres (ATEX) The Euromot Position as of November
2003, ATEX Euromot Position 191103
[3] Guidelines for proper safety design of inlet systems on gas engines, RWTÜV Essen,
1991
WARNING
Unapproved operation
Any operation of the turbocharger outside of its operating limits can be hazardous to personnel.
u Only operate the turbocharger within the operating limits.
u Only trained personnel must operate the turbocharger.
The intended use of the turbocharger includes compliance with all regulations and conditions. In particular, the following must be observed:
¡ Operation Manual
¡ Instructions of the enginebuilder
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 15

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.6 Deflagration on gas engines
State of the art
The turbocharger is designed and manufactured according to the state of the art and is safe
to operate.
Perfect condition
The turbocharger must only be used when it is in a technically flawless condition and operated in compliance with its intended use.
ABB excludes any liability for damage resulting from unauthorized modifications to the turbocharger or improper operation.
1.6 Deflagration on gas engines
ABB turbochargers can tolerate a deflagration with a transient pressure increase of 12bar.
After a deflagration event ABB Turbo Systems recommends verifying the following points on
the turbocharger:
¡ Position of the turbine and compressor casings to the bearing casing
¡ Shifting of the bearing casing in relation to the bracket
¡ Cracks in casings
If during external inspection anomalies are found or if a particularly strong deflagration
event has taken place, it is also recommended to check the bearings of the turbochargers
before the next start. An ABB Turbocharging Service Station should be instructed to carry
out this inspection.
Page 5 / 17
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 16

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.7 Warning plates on the turbocharger
1.7 Warning plates on the turbocharger
Warning plates are attached to the turbocharger, which must be observed. The warning
plates must always be present in the intended locations and must be legible.
Fig.1: Warning plate
If warning plates are not present in the intended locations or are not legible, they must be
replaced with new warning plates. The necessary information can be found in the Operation
Manual, Chapter 4 Product description.
Page 6 / 17
Turbochargers supplied to the enginebuilder without insulation must be equipped later with
warning plates on the insulation. This is the responsibility of the enginebuilder.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 17
Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.8 Turbocharger rating plate
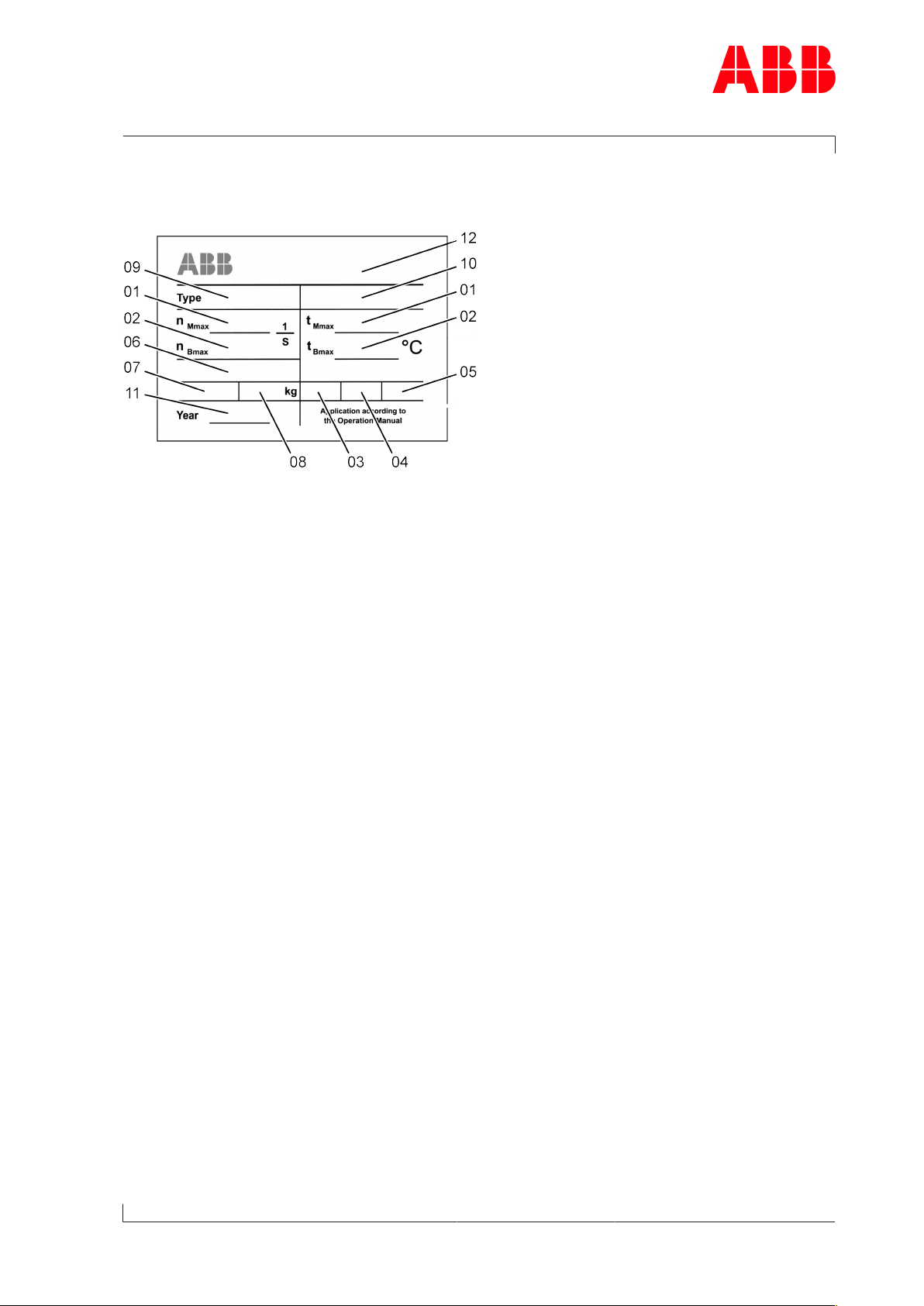
1.8 Turbocharger rating plate
Fig.2: Rating plate
Operating limits
01 Turbocharger operating limits at engine overload (110%).
In test rig operation only, unless otherwise agreed with the enginebuilder.
02 Turbocharger operating limits during operation
Recommended inspection and replacement intervals of turbocharger components
03 Inspection interval of plain bearings in 1000 h
04 Replacement interval of compressor in 1000 h
05 Replacement interval of turbine in 1000 h
Further data
06 Customer part number
07 Designation for special design
08 Weight of turbocharger in kg
09 Turbocharger type
10 Serial number
11 Year of construction of turbocharger
12 Manufacturing plant
Page 7 / 17
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 18

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.9 Periodic check of the pressure vessels
Explanations regarding the rating plate
The recommended inspection and replacement intervals and the corresponding operating
limits are jointly defined with the enginebuilder. This information is specific to the system.
Page 8 / 17
Operation above the indicated values n
Bmax
, t
can considerably shorten the recommended
Bmax
replacement intervals. In such a case, we recommend that you contact the nearest official
service station of ABB Turbo Systems.
n
, t
Mmax
normally apply only when running at overload (110%) during trials on the engine
Mmax
test bed. These limit values can also be permitted during operation for special applications.
Operation above n
Mmax
and t
is not permitted.
Mmax
Non-observance of the recommended inspection and replacement intervals increases the
risk of unpredictable component failures.
Locations of the rating plates
The locations of the rating plates are defined in the Operation Manual, Chapter 4 Product
description.
1.9 Periodic check of the pressure vessels
The pressure vessels used by ABB Turbocharging, such as those for wet or dry cleaning, are
so-called "simple pressure vessels".
¡ The locally applicable legal regulations regarding periodic checks of the pressure vessels
must be observed.
¡ The operating company is responsible for the safe operation of the pressure vessel.
WARNING
Danger due to pressure vessels
The operating company must make sure the pressure vessels are in proper
working condition and monitor them. Necessary repair or maintenance work
must be performed promptly, and the required safety measures must be
taken.
u Pressure equipment must not be operated if defects are present.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 19
Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.10 Lifting of loads
1.10 Lifting of loads
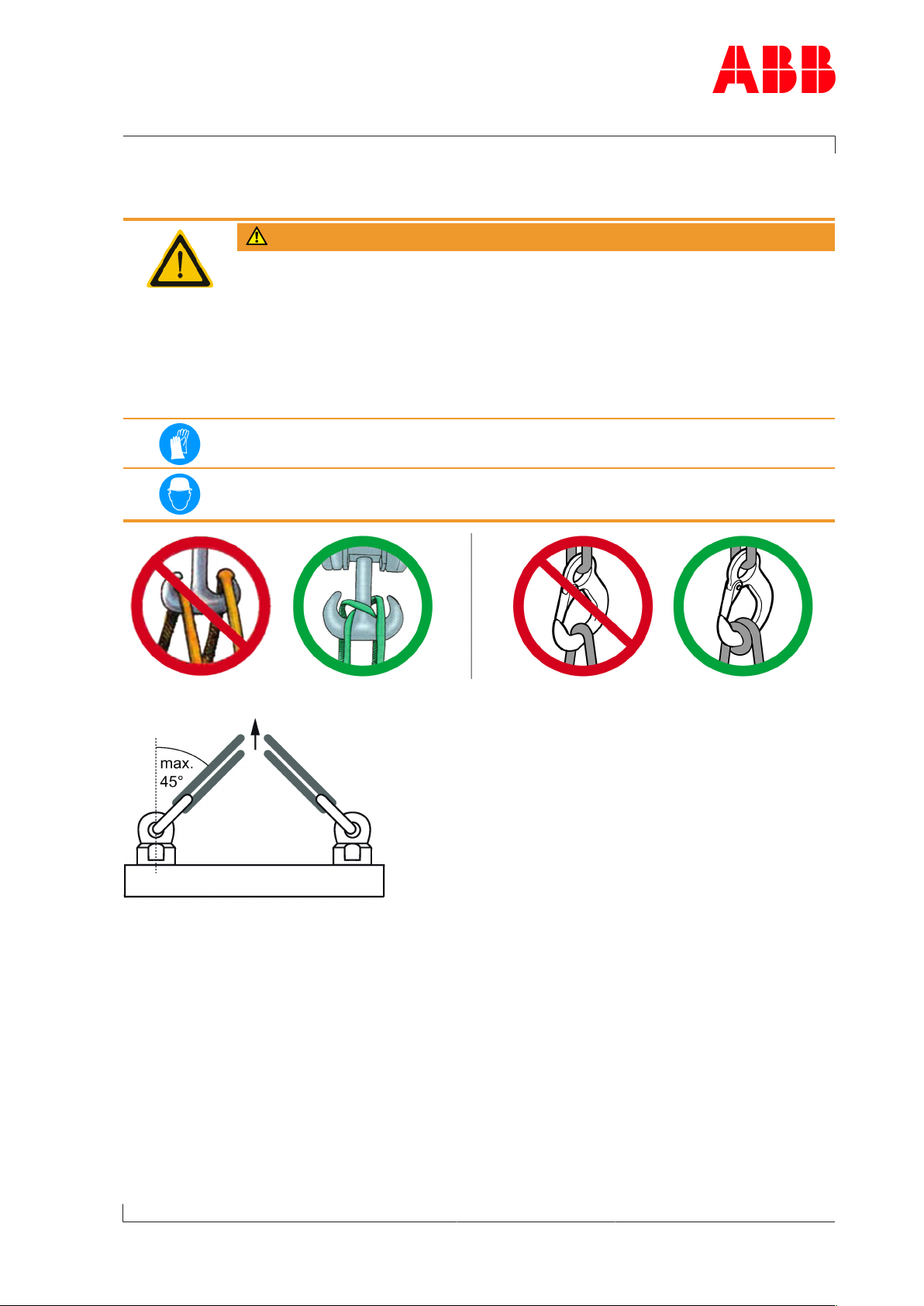
WARNING
Suspended loads
Loads that are not attached according to regulations can cause injury to
personnel or fatal accidents.
u Loads must always be fastened to properly functional lifting gear with a
sufficient load limit.
u Pay attention to the correct attachment of loads on the crane hook.
u People must not stand beneath suspended loads.
Wear safety gloves to protect against mechanical hazards.
Wear safety helmet.
Fig.3: Attachment of loads on the crane hook
Fig.4: Attachment angle
If there are two or more suspension points, the attachment angle of 45° must not be exceeded. This prevents excessive loading due to diagonal pull.
u Before looping around the components of the turbocharger, let them cool down (max-
imum 80°C).
u Attach components of the turbocharger as described in the respective action steps.
u Use a suitable edge guard if there are sharp edges.
u The assembly devices must be completely screwed in and must not unscrew during use.
Page 9 / 17
u Use assembly devices only for the described applications.
u Put down dismantled components of the turbocharger in such a way that they cannot tip
over.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 20

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.11 Prerequisites for operation and maintenance
1.11 Prerequisites for operation and maintenance
Responsibility of the operating company
In awareness of its responsibility, the operating company must ensure that only authorised
personnel work on the turbocharger, who:
¡ Are versed in the general and locally applicable regulations for occupational safety and
accident prevention
¡ Are equipped with the prescribed personal protective equipment
¡ Have read and understood the Operation Manual
¡ Have been instructed in the use of the turbocharger.
The safety-conscious work of the personnel and adherence to the Operation Manual must be
checked periodically.
Suitable working materials and personal protective equipment must be kept in a perfect
condition.
Page 10 / 17
Only authorised personnel may remain in the vicinity of the turbocharger when the engine is
running.
Competence of personnel
The turbocharger must only be operated and serviced by trained and authorised personnel.
Basic mechanical training is a prerequisite.
Modifications to the turbocharger
Modifications to the turbocharger must be approved by ABB Turbo Systems.
WARNING
Use original parts
Operation of the turbocharger with non-original parts can impair the safety
of the turbocharger and can cause serious damage to property and injury to
personnel.
u Only use original parts from ABB Turbo Systems.
Original parts and accessories are specially designed by ABB Turbo Systems for the ABB turbochargers.
ABB accepts no liability for any damage resulting from the use of non-original parts and corresponding accessories.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 21

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.12 Hazards during operation and maintenance
1.12 Hazards during operation and maintenance
Noise hazards
The turbocharger's noise emission during operation is influenced by its installation and operating conditions. A noise level exceeding 85 dB(A) is harmful.
WARNING
Danger due to noise
Exposure to noise can harm the hearing system, impair health and the psychological state and may lead to lack of attention and irritation.
u When the engine is running, always wear ear protection.
u Always wear ear protection if the sound pressure level exceeds 85 dB(A).
Wear ear protection.
Hazards due to hot surfaces
Surfaces of the turbocharger, attached parts and operating fluids (lubricating oil) get hot
during operation. The surface temperature depends on the efficacy of the existing insulation. The temperature may rise to a level that can cause burns.
WARNING
Danger of burns
Touching hot surfaces or contact with hot operating fluids can cause burns.
u Do not touch hot surfaces. Observe the warning plate on the turbochar-
ger.
u Wear heat-resistant safety gloves and protective clothing.
u Wait for the turbocharger to cool down before carrying out any work.
Wear safety gloves to protect against thermal hazards.
Page 11 / 17
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 22

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.12 Hazards during operation and maintenance
WARNING
Hot surfaces on the non-insulated turbocharger
Non-insulated turbochargers can cause serious injuries to personnel (burns).
The turbocharger is supplied with or without insulation in accordance with
the purchase order received from the enginebuilder. If supply is without insulation, the enginebuilder is responsible for providing the turbocharger
with proper insulation and for providing protection against contact with hot
surfaces.
u Compliance with the instructions and specifications given by the en-
ginebuilder to protect against hot turbocharger surfaces is compulsory.
Wear safety gloves to protect against thermal hazards.
Hazards due to rotating parts
Page 12 / 17
WARNING
Physical hazards
Contact with rotating parts can cause severe injury. The turbocharger must
never be used without the filter silencer or the air suction branch. With the
engine stopped, the rotor can rotate due to the stack draught alone.
u Operate the turbocharger in compliance with the specifications.
u Secure the rotor against unintentional rotation during maintenance.
Wear safety gloves to protect against mechanical hazards.
Hazards due to electrical installations (if present)
WARNING
Dangers during work on electrical installations
Electrical installations use voltages that can lead to severe injury to personnel or accidents resulting in fatalities.
At the same time, electrical or electronic components and parts can also be
damaged or destroyed.
u Only specially trained personnel should perform work on, or with, elec-
trical components.
u Observe national regulations.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 23

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.13 Safe operation
WARNING
Absence of grounding on electrical installations
Missing or incorrectly fitted grounding conductors can lead to severe injury
to personnel or accidents resulting in fatalities.
Electric shock or elevated electromagnetic disturbances can damage or destroy electrical and electronic components.
u Ground electrical installations properly with grounding conductors.
u Check the grounding connections on a regular basis and make sure they
are properly connected.
u Switch off the power supply before working on any electrical installations.
u After switching off the power supply, wait for 5 minutes to allow capacitors to discharge
and hot components to cool down.
u Ensure the power supply is switched off when working on electrical installations.
u Do not carry out any tests with regard to insulation resistance or voltage on the electrical
components.
1.13 Safe operation
Mechanical hazards during operation
During standard operation, no mechanical hazards are caused by the turbocharger itself if it
has been properly installed.
Safety during commissioning and operation
u Visually inspect your working environment before starting work.
u Remove any obstacles and objects littering the workplace.
u Check all pipes to and from the turbocharger for damage and leaks before commission-
ing.
u Check turbocharger for recognisable damage or defects every 12 hours of operation or at
least once a day.
u Report any damage and any alterations of operational characteristics to the responsible
department immediately.
u In case of damage, take the turbocharger out of operation immediately and safeguard
against accidental/unauthorised use.
u When switching on operating energy supplies (hydraulics, pneumatics, electricity), pay at-
tention to the risks that may occur as a consequence of this energy input.
Page 13 / 17
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 24

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.14 Safe maintenance
1.14 Safe maintenance
Occupational safety
WARNING
Injuries to persons
Severe injuries to personnel or fatal accidents can be caused by mechanical
influences as a consequence of hazardous and inadequate operational procedures or non-compliance with safety and health standards.
u When working on the turbocharger always wear safety footwear and pro-
tective clothing to protect against mechanical hazards.
u Keep personal protective equipment in perfect condition.
u Obey mandatory signs.
u Observe the general rules for occupational safety and prevention of acci-
dents.
u Only perform operations that are described in this manual.
u Only perform operations for which you have received instruction or train-
ing.
Page 14 / 17
Wear safety footwear to protect against mechanical hazard and risk of falling.
Wear protective clothing.
WARNING
Risk of falling
When working on the turbocharger, there is a risk of falling.
u Do not climb onto the turbocharger or onto attached parts and do not
use them as climbing aids.
u Use suitable climbing aids and working platforms for work above body
height.
u Comply with the general accident prevention regulations.
u Only perform work on the turbocharger when you are in a physically and psychologically
stable condition.
u Only work with suitable tools, equipment and appliances that function properly.
u Power tools must be grounded and cables must be undamaged.
u Keep the workplace clean; clear away any loose objects and obstacles on the floor.
u Keep the floor, equipment, and turbocharger clean.
u Have oil binding agents ready and provide or keep oil pans at hand.
u Clean up any spills.
u Have fire protection means and extinguishing agents available.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 25

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.14 Safe maintenance
Welding work in the vicinity of the turbocharger
u When performing welding work in the vicinity of the turbocharger, always cover the filter
silencer to prevent the filter mat from being damaged.
u Keep flammable objects and substances out of the vicinity of flying sparks.
u Cover all connections on the turbocharger so that no foreign objects can enter the tur-
bocharger.
u Wear personal protective equipment (PPE) for welding operations.
Safety during cleaning
If cleaning agents or solvents are used for cleaning, the corresponding material safety data
sheet and the safety instructions in section Hazards due to operating materials and supplies
must be observed.
u Observe the material safety data sheet for the cleaning agent or solvent.
u Wear personal protective equipment (PPE) according to the material safety data sheet.
u Inspect the electric cables for abrasion and damage before and after your cleaning work.
Safety during disassembly, assembly, maintenance and repair
u Observe the procedures for set-up, service and inspection work and the inspection inter-
vals.
u Inform the operating staff before starting any service or repair work. Make sure the en-
gine is not started while work is being conducted on the turbocharger.
u Before taking off any cover or removing any guard from the turbocharger, switch off the
engine and wait until the turbocharger has come to a standstill.
u Make sure that the oil supply is interrupted, especially with an external oil supply.
u Only restart the engine after all parts have been properly fitted again and oil supply is en-
sured.
CAUTION
Mechanical operations on the turbocharger
Components of the turbocharger can be damaged or destroyed as a result
of improper procedures.
u Only perform operations that are described in this manual.
u Only perform operations for which you have received instruction or train-
ing.
Page 15 / 17
Safety when taking out of operation or preparing for mothballing
u Secure rotor against turning. The rotor can rotate due to the stack draught alone.
u Observe the material safety data sheet for the cleaning and mothballing agents.
u Wear personal protective equipment (PPE) according to the material safety data sheet.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 26

Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.14 Safe maintenance
Mechanical hazards when working on the turbocharger
WARNING
Physical hazards due to rotating parts
The rotor can rotate due to the stack draught alone. Contact with rotating
parts can cause severe injury.
u Secure rotor against turning.
WARNING
Mechanical hazards
Severe injuries to personnel or fatal accidents can be caused by mechanical
influences as a consequence of hazardous and inadequate operational procedures.
u Observe the general rules for occupational safety and prevention of acci-
dents.
u Ensure workplace safety.
u Only perform operations that are described in this chapter.
u Only perform operations for which you have previously received instruc-
tion or training.
Page 16 / 17
Hazards due to operating materials and supplies
Operating materials and supplies are substances required for the operation of the turbocharger or for the performance of maintenance work. Oils, greases, coolants, detergents
and solvents, acids and similar substances can be classified as hazardous substances.
WARNING
Handling operating materials and supplies
Swallowing or inhaling vapours of operating materials and supplies or contact with them may be harmful to health.
u Do not breathe in these substances and avoid contact with the skin.
u Ensure proper ventilation.
u Observe the information in the material safety data sheet for the operat-
ing materials and supplies.
u Wear personal protective equipment (PPE) according to the material
safety data sheet.
u Comply with local legislation.
Wear safety goggles.
Wear safety gloves to protect against chemical hazards.
Wear a respiratory mask to protect against gases.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 27
Operation Manual / 2 Safety / TPS..-H
1 Safety / 1.14 Safe maintenance
WARNING
Danger of fire or explosion
Flammable and combustible operating materials and supplies can catch fire
or resulting vapours can lead to an explosion.
u Observe the information in the material safety data sheet for the operat-
ing materials and supplies.
u Comply with local legislation.
u Do not allow any exposed flame or ignition source during cleaning work.
u Carry out cleaning in the open or provide sufficient ventilation.
CAUTION
Environmental hazard
Improper handling of operating materials and supplies can lead to environmental damage.
u Observe the information in the material safety data sheet for the operat-
ing materials and supplies.
u Comply with local legislation.
Hazards due to the handling of insulation materials
WARNING
Danger from insulation materials
Dust or fibres from insulation materials can have adverse effects on the
health or cause irritations. Unsuitable and combustible insulation materials
are a fire hazard.
u Only use suitable and non-combustible insulation materials.
u Ensure good ventilation at the workplace.
u Avoid whirling up dust.
u Use dust-free tools and working methods.
u Remove package at the workplace only.
u Proceed with particular care when removing old insulation materials.
u Dispose of insulation materials properly and in an environmentally com-
patible manner in compliance with the legal regulations.
Wear safety goggles.
Wear a respiratory mask to protect against dusts.
Page 17 / 17
Wear safety gloves to protect against chemical hazards.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4026_EN Revision D May 2017
Page 28

Page 29

Operation Manual / TPS52-H33 / Safety data sheet
Safety data sheet
TPS52-H33 HT593348
TPS52-H33 HT593348
Page 1 / 1
847 680
805 650
12453772
2020
250 16 60 60
© Copyright 2020 ABB. All rights reserved. HT593348 February 2020
Page 30

Page 31

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
Table of contents
Product description
1 Introduction............................................................................................................ 3
1.1 Essential information.................................................................................................... 3
1.2 Registered trademarks................................................................................................. 3
1.3 Related documents........................................................................................................ 3
1.4 Layout and function of the turbocharger ................................................................ 4
1.5 Position of the rating plate.......................................................................................... 5
1.6 Warning plates on the turbocharger......................................................................... 6
2 Removing and Installing........................................................................................ 7
2.1 Turbocharger weight and transportation ................................................................ 7
2.2 Removing the turbocharger........................................................................................ 8
2.3 Installing the turbocharger........................................................................................ 10
3 Commissioning .................................................................................................... 13
3.1 Oil supply ....................................................................................................................... 13
3.2 Inspection procedures................................................................................................ 14
3.3 Commissioning after taking out of operation....................................................... 16
4 Monitoring operation .......................................................................................... 17
4.1 Oil pressure, oil temperature..................................................................................... 17
4.2 Exhaust gas temperature before turbine ............................................................... 19
4.3 Turbocharger speed.................................................................................................... 19
5 Operation and service ......................................................................................... 23
5.1 Noise emission ............................................................................................................. 23
5.2 Service work ................................................................................................................. 25
5.3 Expected replacement intervals .............................................................................. 28
6 Stopping the engine ............................................................................................ 29
7 Periodic maintenance work ................................................................................ 30
7.1 Foreword to maintenance......................................................................................... 30
7.2 Cleaning components mechanically ....................................................................... 30
8 Eliminating malfunctions.................................................................................... 39
8.1 Malfunctions when starting...................................................................................... 39
8.2 Malfunctions during operation ................................................................................ 40
8.3 Turbocharger is surging............................................................................................ 43
8.4 Malfunctions when stopping.................................................................................... 44
8.5 Speed measurement system.................................................................................... 45
9 Dismantling and fitting....................................................................................... 46
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 32

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
Table of contents
9.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................. 46
9.2 Weights of individual parts....................................................................................... 50
9.3 Removing the gas outlet casing ............................................................................... 51
9.4 Removing air inlets..................................................................................................... 52
9.5 Removing the compressor casing........................................................................... 53
9.6 Removing the cartridge group................................................................................. 55
9.7 Removing nozzle ring ................................................................................................. 58
9.8 Axial clearance A and radial clearance B................................................................. 59
9.9 Nozzle ring compression PD..................................................................................... 60
9.10 Fitting the diffuser ...................................................................................................... 61
9.11 Installing the cartridge group ................................................................................. 62
9.12 Installing nozzle ring .................................................................................................. 64
9.13 Fitting the turbine casing ......................................................................................... 65
9.14 Rotating the turbocharger........................................................................................ 66
9.15 Radial clearances N and R.......................................................................................... 67
9.16 Installing the gas outlet casing ................................................................................ 68
9.17 Installing air inlets ...................................................................................................... 69
9.18 Table of tightening torques...................................................................................... 70
10 Taking out of operation at short notice ........................................................... 71
10.1 Possible emergency repairs....................................................................................... 71
11 Mothballing the turbocharger............................................................................ 72
11.1 Taking the engine out of operation for up to 12months .................................... 72
11.2 Taking the engine out of operation for more than 12months ........................... 73
12 Disposing of turbocharger components .......................................................... 74
13 Spare parts ........................................................................................................... 75
13.1 Spare part overview..................................................................................................... 75
13.2 Ordering spare parts................................................................................................... 75
Figures................................................................................................................... 76
Tables .................................................................................................................... 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 33

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
1 Introduction / 1.1 Essential information
1 Introduction
1.1 Essential information
Design variants
This document is valid for different design variants of turbochargers. There may be sections
and descriptions of components that are not relevant for a specific turbocharger variant.
Please contact an ABB Turbocharging Service Station if you have any questions regarding a
design variant (see Contact information at www.abb.com/turbocharging).
Accuracy of illustrations
The illustrations in this document are general in nature and intended for ease of understanding. Differences in detail are therefore possible.
1.2 Registered trademarks
The trademarks of outside companies are used in this document. These are marked with the
® symbol.
1.3 Related documents
Chapter Document number
Operation Manual / 1 Introduction HZTL4005
Operation Manual / 2 Safety HZTL4026
Operation Manual / 3 Safety data sheet *) Serial number of the turbocharger
Table1: Related documents
*) This chapter is only available in serialised operation manuals.
Page 3 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 34

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
1 Introduction / 1.4 Layout and function of the turbocharger
1.4 Layout and function of the turbocharger
Page 4 / 77
Fig.1: Layout and function of the turbocharger
01 Air suction branch / filter silencer 06 Plain bearing bush
02 Compressor casing 07 Turbine
03 Diffuser 08 Nozzle ring
04 Bearing casing 09 Turbine casing
05 Axial thrust bearing 10 Compressor wheel
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 35

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
1 Introduction / 1.5 Position of the rating plate
Mode of operation
The turbocharger is a turbomachine and consists of the following main components:
¡ Turbine
¡ Compressor.
These components are installed on a common shaft and form the rotor (see Fig.1: Layout
and function of the turbocharger →4).
The exhaust gases of the internal combustion engine flow through the turbine casing (09)
and the nozzle ring (08) onto the turbine (07). The turbine (07) uses the energy contained in
the exhaust gas to drive the rotor and, with this, the compressor wheel (10). The exhaust
gases then reach the atmosphere through the exhaust gas pipe connected to the turbine
casing.
The compressor wheel(10) sucks in air or a mixture of gas and air through the air suction
branch (01) or the filter silencer. In the compressor wheel (10), the energy required for building up the pressure is transferred to the air. By flowing through the diffuser(03) and the
compressor casing(02), the air is compressed further and is then directed to the engine cylinders.
The rotor runs in a radial plain bearing bush (06) that is located in the bearing casing (04)
between the compressor and the turbine. The axial thrust bearing (05) is located in front of
the radial plain bearing bush.
The bearings are connected to a central lubricating oil duct which is normally supplied by the
lubricating oil circuit of the engine. The oil outlet lies at the lowest point of the bearing casing (04).
1.5 Position of the rating plate
The rating plate(01) is attached at the top on the bearing casing of the turbocharger. Explanations regarding the rating plate can be found in the chapter dealing with safety.
Page 5 / 77
Fig.2: Position of the rating plate
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 36

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
1 Introduction / 1.6 Warning plates on the turbocharger
1.6 Warning plates on the turbocharger
Warning plates are affixed at the following locations:
Page 6 / 77
Fig.3: Warning plates on the turbocharger
Turbochargers supplied to the enginebuilder without insulation must be equipped later with
warning plates on the insulation. This is the responsibility of the enginebuilder.
If warning plates are not present in the designated locations or not readable, proceed as follows:
u Order new warning plates (72080) from ABB Turbocharging Service Stations (see chapter
Ordering spare parts →75).
u Remove any warning plates that have become unreadable.
u Clean and degrease the areas designated for the warning plates.
u Fit new warning plates and remove protective sheets.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 37

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
2 Removing and Installing / 2.1 Turbocharger weight and transportation
2 Removing and Installing
2.1 Turbocharger weight and transportation
Lifting gear with a sufficient load limit must be used for removing and installing the turbocharger. The following weight specification applies to the heaviest variant possible. Depending on the specification, the weight specified on the rating plate may be lower than the
standard value specified here.
Product Weights [kg]
TPS44 120
TPS48 180
TPS52 250
Table2: Weight of the turbocharger
One swivel lifting eye (S) is required to safely lift this turbocharger. This is not included in
the ABB Turbo Systems scope of delivery.
Swivel lifting eye (S) to be used Product Thread Length
H[mm]
TPS44 M8 ≤12 ≤25 300
TPS48 M8 ≤12 ≤25 300
TPS52 M10 ≤15 ≤25 400
Table3: Swivel lifting eye (S) to be used
Diameter
D[mm]
Minimum load
limit
[kg]
Page 7 / 77
Fig.4: Turbocharger transport
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 38

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
2 Removing and Installing / 2.2 Removing the turbocharger
2.2 Removing the turbocharger
WARNING
Danger of burns
Touching hot surfaces or contact with hot operating fluids can cause burns.
u Do not touch hot surfaces. Observe the warning plate on the turbochar-
ger.
u Wear heat-resistant safety gloves and protective clothing.
u Wait for the turbocharger to cool down before carrying out any work.
Wear safety gloves to protect against thermal hazards.
CAUTION
Do not strain cables
If you pull the speed measurement cables too hard, contacts can be pulled
out.
u Do not strain the speed measurement cables by pulling.
Page 8 / 77
NOTICE
Gas outlet casing (61001)
The gas outlet casing (61001) can remain fitted in the exhaust gas pipe if the
locking to the turbine casing is accessible. Otherwise the complete turbocharger unit including gas outlet casing must be removed.
u Disconnect all pipes according to the instructions of the enginebuilder.
u Loosen and remove water connections.
u Close the openings of the water connections with screw plugs.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 39

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
2 Removing and Installing / 2.2 Removing the turbocharger
Fig.5: Removing the turbocharger
1. Treat the threads of studs and nuts with penetrating oil and allow to work in.
2. Loosen and remove nuts.
3. If present: Disconnect the plug to the speed sensor (86505) and secure the rolled-up
cable on the turbocharger. This protects the plug from being crushed.
4. Install the swivel lifting eye(S) and attach the lifting gear to it.
5. Lift the turbocharger away from the support vertically. The bracket-turbocharger connection may be in the form of a pin with the TPS52-H.
6. Cover the connections.
Version with water cooling
CAUTION
Freezing of the cooling water in the bearing casing
If cooling water freezes in the bearing casing, this can lead to severe damage.
u For transport and storage of the turbocharger, drain the cooling water
from the bearing casing via one of the two bottom openings of the water
connections.
Page 9 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 40

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
2 Removing and Installing / 2.3 Installing the turbocharger
2.3 Installing the turbocharger
2.3.1 Inserting gaskets
CAUTION
Inserting the gaskets
Gaskets that are forgotten, damaged or improperly inserted will lead to oil
leaks.
u Always use new gaskets and insert them carefully into the slot.
The oil is supplied(02) and drained(03) through the bracket (01).
The necessary sealing is provided by O-rings. The O-rings are not included in the ABB Turbo
Systems scope of delivery.
Page 10 / 77
Fig.6: Inserting O-rings into bracket
01 Bracket
02 Oil supply
03 Oil drain
04 Slot for O-ring
05 O-rings
CE Compressor end
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 41

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
2 Removing and Installing / 2.3 Installing the turbocharger
2.3.2 Fitting threaded rods
Fig.7: Inserting threaded rods into the bracket
1. Lightly oil the surfaces of the threaded rods (02) to be screwed in.
2. Screw the threaded rods into the bracket with the aid of locknuts (01).
3. Remove nuts(01) again.
Requirements for the threaded rods (02)
Fig.8: Requirements for threaded rods
Product Diameter
Threaded rod
[mm]
TPS44 Ø 16 / M16 10.9 / 12.9 ≥ 30 150
TPS48 Ø 16 / M16 10.9 / 12.9 ≥ 30 170
TPS52 Ø 20 / M20 10.9 / 12.9 ≥ 30 195
Table4: Requirements for threaded rods
Material
DIN / ISO 898
(Part 1)
Thread length
L1[mm]
Length of threaded
rod
L2 [mm]
Fastening material scope of delivery
Page 11 / 77
The threaded rods and nuts for fastening the turbocharger on the bracket are not included
in the ABB Turbo Systems scope of delivery. These parts depend on the version of the engine-side bracket.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 42

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
2 Removing and Installing / 2.3 Installing the turbocharger
2.3.3 Attaching the turbocharger to the bracket
Page 12 / 77
Fig.9: Placing the turbocharger on the bracket
Product Through hole in
bearing casing [mm]
Fixing screws [mm] Tightening torque [Nm]
(assumed friction coeffi-
cient µ = 0.12)
TPS44 Ø17 M16 280
TPS48 Ø17 M16 280
TPS52 Ø20 M20 560
Table5: Tightening torque for turbocharger fixing screws
1. Make sure that covers of the oil and water connections are removed.
2. Make sure that the gaskets are not damaged and are positioned correctly in the slots.
3. Install the swivel lifting eye(S) and attach the lifting gear to it.
4. Align the turbocharger over the threaded rods of the bracket.
5. Place the turbocharger on the bracket.
6. Lightly oil the hexagon nuts.
7. Fit the hexagon nuts. Observe the tightening torque.
8. Connect cable to speed sensor (86505).
u Remove the lifting gear.
u Connect all the gas pipes and air lines according to the enginebuilder's instructions.
u If the gas outlet casing from ABB has not been dismantled with the turbocharger, refer to
chapter Installing the gas outlet casing →68.
u Fit the water pipes according to the instructions of the enginebuilder.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 43

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
3 Commissioning / 3.1 Oil supply
3 Commissioning
3.1 Oil supply
3.1.1 Introduction
In all operating states, a functioning and carefully executed oil supply is an important prerequisite for trouble-free operation of the turbocharger.
The lubrication of the turbocharger is usually carried out with oil from the engine oil circulation.
u Comply with the enginebuilder's specifications regarding the selection of lubricating oil
and the oil change intervals.
3.1.2 Pre-lubrication
Pre-lubrication must be carried out as follows:
u Switch on the oil pump.
u Build up oil pressure (see Table6: Lubricating oil pressure at oil inlet before turbocharger
→17).
u Do not exceed a pre-lubrication time of 2 minutes.
u Start the engine.
u Let the oil pump run until the pump driven by the engine generates sufficient pressure.
3.1.3 Oil filtering
Filtering the lubricating oil with a filter mesh width of ≤0.034mm is sufficient for this turbocharger.
3.1.4 Oil pressure
Comply precisely with the oil pressure before the turbocharger for trouble-free operation.
The admissible values are specified in chapter Monitoring operation →17.
Page 13 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 44

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
3 Commissioning / 3.2 Inspection procedures
3.2 Inspection procedures
3.2.1 Introduction
Inspection procedures include preventative visual controls, monitoring and measuring work
before and during commissioning. Inspection procedures enable changes to the turbocharger to be detected. Engine damage can be prevented.
3.2.2 Checks before commissioning
Filter mat (if available)
u Check for damage and contamination.
Lubricating system
Page 14 / 77
CAUTION
Contaminated oil
Serious damage to engine or property can be caused by dirt and solid material particles in the oil.
u For the initial commissioning phase and after all service work, flush the
complete lubricating system with warm oil.
u Use special running-in filters when running in the engine and after all ser-
vice work on the lubricating system.
u Check that the oil filter is clean before commissioning.
u Adhere to lubricating oil pressure at the inlet.
u Adhere to lubricating oil temperature at the inlet.
u For permissible values, see chapter Monitoring operation →17.
Warning plates
u Check whether warning plates are present and legible.
u Check whether the protective sheets have been removed.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 45

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
3 Commissioning / 3.2 Inspection procedures
Version with water-cooled bearing casing
CAUTION
Failure of bearing casing cooling
Any prolonged failure of the water cooling will shorten the lifetime of the
turbocharger.
u Make sure that an uninterrupted supply of cooling water is provided dur-
ing operation.
u Check whether the water pipes are fitted on the bearing casing.
3.2.3 Checks after commissioning (engine in idle mode)
Lubricating system
u Keep to the lubricating oil pressure at the inlet.
u Keep to the lubricating oil temperature at the inlet.
u Refer to chapter Monitoring operation →17 for admissible values.
Leaktightness of pipes
WARNING
Risk of burning from hot gas
Escaping gases are hot and will lead to serious burns in the event of contact.
u Check all pipes for leaks in accordance with the enginebuilder’s instruc-
tions.
3.2.4 Checks when starting up the engine
If present:
u Measure speed, oil pressure and charging pressure at various engine performances.
u Measure the exhaust gas temperature before and after the turbine.
u Measure the air temperature before and after the compressor.
u Compare the measured values with the values of the acceptance report. Different operat-
ing conditions indicate a malfunction (see chapter Eliminating malfunctions →39).
Page 15 / 77
Lubricants and pastes used during assembly can liquefy or vaporise and escape as oily fluids
during the initial hours of operation. Continual escape of an oily fluid indicates an oil leak. If
there is a leak, contact an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 46

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
3 Commissioning / 3.3 Commissioning after taking out of operation
3.3 Commissioning after taking out of operation
If present
u Remove cover plates (blind flanges) from the compressor casing, the gas inlet and the
gas outlet.
u Remove the locking screws on the water connections and fit the water pipe.
General
u Check the exhaust gas pipe before and after the turbine for combustion residues or wa-
ter residues and clean it. Remove any foreign objects that may be present.
u Check and clean filter silencer or air supply line, and remove any foreign objects that may
be present.
u Put engine-side oil circulation to the turbocharger into operation.
u Prepare the turbocharger for operation according to section "Checks before commission-
ing".
Page 16 / 77
u The turbocharger is now ready for operation.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 47

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
4 Monitoring operation / 4.1 Oil pressure, oil temperature
4 Monitoring operation
4.1 Oil pressure, oil temperature
Lubricating oil pressure, oil inlet
To limit the oil flow rate through the turbocharger to the admissible values with the engine
at full load, an oil orifice is mandatory or already fitted at the oil inlet of the bearing casing if
the oil inlet pressure is > 3bar.
CAUTION
Assuring lubricating oil pressure
Serious damage to engine or property can result from missing or insufficient lubricating oil supply.
u The lubricating oil pressure must be monitored during operation and the
necessary pressure assured at the oil inlet.
Status for operation Pressure at oil inlet before tur-
bocharger [bar]
Normal operation 2.0< p
Engine start: Cold oil, admissible for maximal 15 minutes <8.0
Engine idling, admissible for maximal 1 hour 0.5< p
Pre-lubrication and post-lubrication (engine stopped) 0.5< p
Warning signal: (n ≥ 0.5 x n
Alarm signal: Not admissible. Stop the engine immediately. <0.5
Table6: Lubricating oil pressure at oil inlet before turbocharger
) <1.25
Bmax
01 Turbocharger contact surface
02 Oil inlet
03 Oil outlet
M Oil pressure measuring point
T Oil temperature measuring point
≤ 4.5
oil
≤ 2.5
oil
≤ 1.0
oil
For monitoring the lubricating oil pressure, ABB Turbo Systems recommends installing an
"M" manometer immediately before the turbocharger. If the pressure is controlled electronically, the appropriate signals are to be triggered at the warning and alarm values.
*) If the drain pipe is vented, the measuring point for lubricating oil temperature can be installed at the outlet in the vent tank. Otherwise the measurement should be taken in the
drain pipe as close to the turbocharger as possible.
Page 17 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 48

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
4 Monitoring operation / 4.1 Oil pressure, oil temperature
Lubricating oil temperature at the inlet
CAUTION
Machine damage
If the oil temperature at the oil inlet exceeds the admissible range, this may
lead to engine damage.
u Observe oil temperature at the oil inlet according to the following table.
Status for operation Oil temperature at the inlet
T
oil,inlet
Admissible 30…105°C
Temporarily admissible (< 1 h) → alarm >105°C
Not admissible → stop engine >110°C
Not admissible → do not start engine (before start: preheat
oil)
Table7: Lubricating oil temperature at the inlet
<30°C
Page 18 / 77
Lubricating oil temperature at the outlet
The oil temperature at the outlet is mainly dependant on:
¡ Lubricating oil temperature and pressure at the oil inlet
¡ Engine load and turbocharger speed
¡ Exhaust gas temperature
The maximum admissible oil temperature at the outlet is listed in the following table. The
specified oil outlet temperature is to be considered as alarm value for the turbocharger operation and must be monitored according to the current regulations.
Status for operation Oil temperature at the outlet
T
oil,outlet
Admissible ≤160°C
Temporarily admissible → alarm >160°C
Not admissible → stop engine >180°C
Admissible ≤ T
Temporarily admissible → alarm > T
Table8: Lubricating oil temperature at the outlet
oil,inlet
oil,inlet
+ 55K
+ 55K
If the turbocharger was operated for a longer period of time outside of the admissible
range, ABB Turbo Systems recommends to have the turbocharger inspected by an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 49

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
4 Monitoring operation / 4.2 Exhaust gas temperature before turbine
4.2 Exhaust gas temperature before turbine
CAUTION
Factors influencing replacement intervals
Operation above the operating limits defined on the rating plate can
shorten the recommended replacement intervals considerably.
u Measure exhaust gas temperature upstream of turbine.
u Comply with operating limits on rating plate.
u Definition and explanations concerning rating plate: refer to chapter 2 of Operation
Manual / Safety.
u Operating limits: refer to chapter 3 of Operation Manual / Safety data sheet or examine
rating plate.
4.3 Turbocharger speed
4.3.1 Introduction
A speed measuring system enables the constant monitoring of the turbocharger speed.
CAUTION
Do not strain cables
If you pull the speed measurement cables too hard, contacts can be pulled
out.
u Do not strain the speed measurement cables by pulling.
CAUTION
Machine damage
Operation above the operating limits defined on the rating plate can
shorten the recommended replacement intervals considerably and cause
machine damage.
u Measure turbocharger speed.
u Comply with operating limits on rating plate.
u Definition and explanations concerning rating plate: refer to chapter 2 of Operation
Manual / Safety.
Page 19 / 77
u Operating limits: refer to chapter 3 of Operation Manual / Safety data sheet or examine
rating plate.
If no speed measurement system is present, the system below can be ordered from an ABB
Turbocharging Service Station (see chapter Ordering spare parts →75).
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 50

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
4 Monitoring operation / 4.3 Turbocharger speed
4.3.2 Layout and overview
Page 20 / 77
Fig.10: Layout and overview of the speed measurement system
86505 Speed sensor 42188 Screw plug
86515 Cable connector 42189 Gasket
86526 F/I converter 01 Plug with integrated voltage limiter
86528 Tachometer *) Alternative mounting position for speed
sensor
32109 Sealing disc
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 51

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
4 Monitoring operation / 4.3 Turbocharger speed
4.3.3 Speed differences with several turbochargers per engine
The speeds of all turbochargers on an engine vary only slightly from each other in standard
operation.
The difference between the highest and the lowest turbocharger speed must not be more
than 3 %, relative to the speed limit n
If this permissible range of difference is exceeded, the following steps must be carried out:
u Reduce the engine performance immediately to the point at which the maximum tur-
bocharger speed does not exceed 70 % of n
u If the engine cannot be stopped, it can continue to be driven at this reduced engine load
or turbocharger speed.
u If a turbocharger surges continuously, the engine performance must be reduced further.
u Measure the temperatures in the air lines and gas piping from and to the turbochargers
and compare with normal values. If clear deviations of temperature are found, the nearest
ABB Turbocharging Service Station has to be contacted.
Bmax
.
.
Bmax
u Check the pressure loss of the alternative air inlet and compare it with normal values.
If the engine can be stopped temporarily:
u Inspect air lines, gas piping and the turbochargers and remedy any malfunctions.
u In any case, contacting the nearest ABB Turbocharging Service Station is recommended.
4.3.4 Malfunctions on the speed measurement system
In the case of malfunctions of the speed measurement system, refer to the chapter entitled
Troubleshooting/Speed measurement system →45.
Page 21 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 52

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
4 Monitoring operation / 4.3 Turbocharger speed
4.3.5 Replacing the speed sensor
WARNING
Hot speed sensor
Danger of burns. The speed sensor can reach temperatures of more than
100°C during operation.
u Wear safety gloves when disassembling the speed sensor.
Wear safety gloves to protect against thermal hazards.
The speed sensor supplied by ABB is equipped with a sealing lip and an O-ring. No additional
gasket is required during assembly.
Page 22 / 77
Fig.11: Fitting the speed sensor
Part number TPS44 TPS48 TPS52
86505 M12 x 1.5
15Nm
Table9: Tightening torque(86505)
u Reduce the engine performance to idling and then stop the engine. Pay attention to post-
M12 x 1.5
15Nm
M12 x 1.5
15Nm
lubrication (Stopping the engine →29).
u Switch off the lubricating oil supply to the turbocharger.
u Disconnect cable connector (86515) from speed sensor (86505).
u Unscrew and remove defective speed sensor (86505).
u Screw in new speed sensor(86505) as far as it will go and tighten.
u Connect cable connector (86515) to speed sensor (86505).
u Switch on lubricating oil supply to the turbocharger.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 53

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
5 Operation and service / 5.1 Noise emission
5 Operation and service
5.1 Noise emission
WARNING
Danger due to noise
Exposure to noise can harm the hearing system, impair health and the psychological state and may lead to lack of attention and irritation.
u When the engine is running, always wear ear protection.
u Always wear ear protection if the sound pressure level exceeds 85 dB(A).
Wear ear protection.
The emission sound pressure level (A-weighted) is measured at a distance of 1 meter from
the turbocharger.
The highest value of the emission sound pressure level1) reaches a maximum of 105 dB(A)
near the filter silencer. The following prerequisites must be fulfilled with regard to the turbocharger to observe this limit value:
¡ Air-inlet system has been fitted
¡ All standard, noise-reducing measures2) have been fitted
¡ Bellows at the air-outlet has been acoustically insulated by the enginebuilder (see Fig.12:
Noise insulation, bellows →24).
The enginebuilder is responsible for insulating the charge air/scavenging air line and the
charge air cooler.
1) Directive 2006/42/EC, 1.7.4.2 / u / Paragraphs 5 + 7:
A-weighted emission sound pressure level
2) The enginebuilder must provide acoustically equivalent measures in case of deviating in-
sulation versions
Page 23 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 54

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
5 Operation and service / 5.1 Noise emission
Suggestion for noise insulation, bellows
Page 24 / 77
Fig.12: Noise insulation, bellows
01 Compressor casing
02 Bellows
03 Charge air duct / scavenging air duct
04 Insulation cushion
05 Insulation mat (at least 15 mm)
06 Sheet metal cover
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 55

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
5 Operation and service / 5.2 Service work
5.2 Service work
Service work includes visual inspections, monitoring, measuring and inspection work as well
as function checks. Service work enables to detect and rectify changes to the turbocharger
and ensures full operability of the turbocharger.
CAUTION
Service intervals
Any service work on the turbocharger that is omitted or performed too late
can cause excessive contamination, wear and operating failures.
u Carry out the service work at the specified time intervals.
CAUTION
Shortened service intervals
Exceptional stresses such as several starts/stops per day, harsh environmental conditions, poor fuel quality or high system vibrations can lead to
untimely machine damage even if the prescribed service intervals are observed.
u Agree on a shortened service interval with ABB Turbo Systems.
NOTICE
5-year service inspection
To prevent machine damage caused by ageing and downtime, we recommend having an inspection carried out by an ABB Turbocharging Service Station no later than 5 years after the last service.
Page 25 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 56

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
5 Operation and service / 5.2 Service work
5.2.1 Service work every 24 … 48 hours
Pipes
u Check all the inlet and outlet pipes of the turbocharger for leaks.
Operating data
CAUTION
Unknown operational changes
Impairment to the degree of a possible operating failure can be the consequence.
u Have any unknown causes clarified by an ABB Turbocharging Service Sta-
tion.
Page 26 / 77
Monitoring the engine's operating data makes it possible to draw conclusions about the operating behaviour of the turbocharger.
u The following operating data and measured values must be entered every 24 … 48 hours
in the engine logbook of the enginebuilder.
¡ Performance and speed of the engine
¡ Air intake temperature
¡ Charging pressure
¡ Pressure loss in the charge air cooler
¡ Lubricating oil pressure and lubricating oil temperature
If present:
¡ Speed of the turbocharger
¡ Air temperature after the compressor and after the charge-air cooler
¡ Exhaust gas temperature before and after the turbine
¡ Pressure loss in the filter silencer.
u In case of different values, determine the cause.
5.2.2 Service work at 100 hours after commissioning
u Clean or replace the oil filter located in the supply pipe to the turbocharger while the en-
gine is stopped.
5.2.3 Service work according to instructions of enginebuilder
u Clean or replace the oil filter located in the supply pipe to the turbocharger while the en-
gine is stopped.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 57

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
5 Operation and service / 5.2 Service work
5.2.4 Service work according to data on the rating plate
WARNING
Incorrect handling of a cartridge group
Incorrect handling of a cartridge group can damage the turbocharger and
cause injuries to persons.
u Have disassembly and assembly of the cartridge group carried out by an
ABB Turbocharging Service Station only.
NOTICE
Specialist knowledge of an ABB Turbocharging Service Station
Assembly and disassembly of the cartridge group and assessment of the rotor and bearing parts requires the specialist knowledge of an ABB Turbocharging Service Station. The rotor parts turn very fast and are very sensitive to unbalance.
The rotor and bearing parts must be checked and assessed by an ABB Turbocharging Service
Station. The following work can be carried out as preparation.
u Remove turbocharger from engine (see chapter Removing and Installing →7).
u Dismantle the turbocharger and measure the clearances (see chapter Dismantling and fit-
ting →46).
u Mechanically clean the nozzle ring, the turbine casing and compressor casing (see chapter
Periodic maintenance work →30).
u Check the nozzle ring, turbine casing and compressor casing for cracks and erosion/cor-
rosion.
Page 27 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 58

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
5 Operation and service / 5.3 Expected replacement intervals
5.3 Expected replacement intervals
Component GAS / MDO
Turbine casing 25000…50000
Nozzle ring 25000…50000
Heat sheet metal 25000…50000
Rotating components See rating plate information
Bearing parts 12000…24000
Other casings 50000
Table10: Expected replacement intervals [h]
GAS = Gas
MDO = Marine Diesel Oil
1)
The recommended replacement intervals of the compressor and turbine wheels are specified with the aid of the safety concept for rotating parts (SIKO) and dependent on the
operating conditions.
1)
Page 28 / 77
Influencing parameters
The specified values are guideline values and are not guaranteed. The actual values can deviate considerably from the guideline values, for example, due to the following influences:
¡ Fuel quality and fuel treatment
¡ Load profile (thermal cycling, also number of starts/stops, emergency shutdowns, oper-
ating point)
¡ Gas inlet temperature
¡ Turbocharger specification.
¡ System-specific operating conditions (combustion quality, exhaust gas composition)
For bearing parts
¡ Lubricating oil quality (oil filtering, oil condition, oil monitoring)
¡ Load profile (speed, pressure conditions, temperature)
¡ Number of starts/stops
¡ Unbalance of the rotor (degree of contamination).
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 59

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
6 Stopping the engine /
6 Stopping the engine
Water-cooled turbocharger variant
u Post-lubricate as long as the rotor is turning.
u Observe the oil pressure while performing post-lubrication: 0.5 <p
u Switch off post-lubrication as soon as the rotor is stationary or after no more than two
minutes.
Deviating procedures must be coordinated with ABB Turbo Systems.
≤1.0.
oil
CAUTION
Water cooling after stopping the engine
If the heat in the turbocharger is not dissipated after the engine stops, damage may result.
u Allow the water cooling of the turbocharger to continue operating for 15
to 20 minutes after stopping the engine.
Page 29 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 60

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
7 Periodic maintenance work / 7.1 Foreword to maintenance
7 Periodic maintenance work
7.1 Foreword to maintenance
Maintenance work includes regular visual controls and cleaning operations which are intended to ensure the trouble-free functioning of the turbocharger.
Maintenance interval Maintenance work Operating status
Similar to the service interval (usually every 8000…12000h)
Table11: Maintenance table
[h] = Hours of operation
1)
ABB Turbo Systems recommends having mechanical cleaning carried out by an ABB Tur-
bocharging Service Station during the service work.
1)
Cleaning components mechanically →30 Engine stopped
Page 30 / 77
7.2 Cleaning components mechanically
7.2.1 Preparation
CAUTION
Component damage and corrosion
If mechanical cleaning is carried out incorrectly, this can lead to damage and
corrosion on the components.
u Pay attention to the specifications in this chapter pertaining to mechan-
ical cleaning.
CAUTION
Selection of cleaning tools
Turbocharger components are sensitive and easily sustain mechanical damage. The use of needle descalers (for example) or other striking tools damages the components. Depending on the specification, nozzle rings or turbine casings may have protective coatings which can also be damaged.
u Use only soft tools such as rags, brushes or wire brushes.
u In case of heavy contamination, the cleaning methods described in this
chapter (such as soaking, for example) can be repeated until a satisfactory result is achieved.
The disassembly and assembly of the components is described in chapter Dismantling and
fitting →46.
u Contaminated water and cleaning agents must be disposed of in an environmentally
compatible, professional way and in compliance with locally applicable regulations.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 61

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
7 Periodic maintenance work / 7.2 Cleaning components mechanically
7.2.2 Cleaning the filter silencer
Fig.13: Cleaning the filter silencer
81135 Filter silencer body 81266 Cover grid
81136 Absorption segment 81270 Tension band
81137 Sheet-metal covering 81271 Lock
81265 Filter ring
Cleaning the filter ring (if present)
u Remove filter ring (81265).
u Clean filter ring (81265) as required or every 500 hours of operation and replace after the
fifth cleaning process at the latest.
Contamination of the filter ring depends on the degree of purity of the sucked-in air.
u Rinse the filter ring (81265) with water and mild detergent or, in the case of heavy con-
tamination, soak and carefully push through. Rinse in cold water. Avoid high mechanical
loads (water jet).
u Let the filter ring dry completely before assembling.
u Dirty water and mild detergent must be disposed of in compliance with locally applicable
regulations.
Page 31 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 62

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
7 Periodic maintenance work / 7.2 Cleaning components mechanically
Cleaning the absorption segments
(see Fig.13: Cleaning the filter silencer →31)
u Loosen the tension bands (81270).
u Remove the cover grid (81266).
u Pull out and bend up the sheet-metal coverings (81137), and remove the absorption seg-
ments (81136).
u Clean the absorption segments (81136).
When cleaning, note that the absorption segments (81136) must only be cleaned lightly
with compressed air, a soft brush or a moist cleaning cloth.
u Have any heavily contaminated absorption segments replaced by an ABB Turbocharging
Service Station.
Fitting the filter silencer
(see Fig.13: Cleaning the filter silencer →31)
Page 32 / 77
u Insert the absorption segments (81136) into the sheet-metal coverings (81137).
u Bend the sheet-metal coverings (81137) back to their original shape and insert into the
slotted guides in the filter silencer body (81135).
u Fit the cover grid (81266).
u Fit the tension bands (81270) and tighten them at the locks (81271).
u Any tension bands that have become damaged must be replaced.
u Fit the filter ring (81265), if present.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 63

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
7 Periodic maintenance work / 7.2 Cleaning components mechanically
7.2.3 Compressor-end, non-rotating parts
WARNING
Handling operating materials and supplies
Swallowing or inhaling vapours of operating materials and supplies or contact with them may be harmful to health.
u Do not breathe in these substances and avoid contact with the skin.
u Ensure proper ventilation.
u Observe the information in the material safety data sheet for the operat-
ing materials and supplies.
u Wear personal protective equipment (PPE) according to the material
safety data sheet.
u Comply with local legislation.
Wear safety goggles.
Wear safety gloves to protect against chemical hazards.
Wear a respiratory mask to protect against gases.
The following parts, which are relevant in terms of performance, can be cleaned in accordance with the description below.
Fig.14: Cleaning the compressor casing, diffuser mechanically
72000 Compressor casing
79000 Diffuser
u Steam-clean the above-mentioned components or soak in diesel oil or water with house-
hold cleaning agents. After soaking, remove contamination with a brush.
Page 33 / 77
u Dry components completely.
u Spray cleaned surfaces with penetrating oil. Do not spray exterior surfaces of the tur-
bocharger.
u Dispose of contaminated water and cleaning agents in accordance with the information
in the material safety data sheet.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 64

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
7 Periodic maintenance work / 7.2 Cleaning components mechanically
7.2.4 Turbine-end, non-rotating parts
WARNING
Handling operating materials and supplies
Swallowing or inhaling vapours of operating materials and supplies or contact with them may be harmful to health.
u Do not breathe in these substances and avoid contact with the skin.
u Ensure proper ventilation.
u Observe the information in the material safety data sheet for the operat-
ing materials and supplies.
u Wear personal protective equipment (PPE) according to the material
safety data sheet.
u Comply with local legislation.
Wear safety goggles.
Page 34 / 77
Wear safety gloves to protect against chemical hazards.
Wear a respiratory mask to protect against gases.
Baked layers of contamination, for example, from heavy fuel oil or coked oil occur at the turbine end. The following parts, which are relevant in terms of performance, can be cleaned in
accordance with the description below.
Fig.15: Cleaning the nozzle ring, turbine casing mechanically
56001 Nozzle ring
51000 Turbine casing
u Place contaminated parts in hot water or in a liquid such as brake cleaner to soften the
contamination.
u Brush away the contamination or remove with a steam cleaner.
u If necessary, repeat soaking and brushing.
u Use clean water to completely clean parts of any solvents.
u Dry components completely.
u Spray cleaned surfaces with penetrating oil. Do not spray the outer surfaces of the tur-
bocharger.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 65

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
7 Periodic maintenance work / 7.2 Cleaning components mechanically
u Dispose of contaminated water and cleaning agents in accordance with the information
in the material safety data sheet.
7.2.5 Cartridge group, general
CAUTION
Corrosion
If the cartridge group is not put back into operation immediately after cleaning, parts may corrode.
u Immediately after cleaning, install the cartridge group and put it back
into operation.
Compressor wheels can be heavily contaminated due to poorly filtered suction air; turbines
can be heavily contaminated due to coked oil. Contamination such as this must be removed
during the standard service intervals (see service work chapter).
u Remove turbocharger from engine (see chapter Removing and Installing →7).
u Remove cartridge group (see chapter Dismantling and fitting →46).
First clean the compressor end and then the turbine end according to the following description.
7.2.6 Cleaning the cartridge group on compressor end
CAUTION
Selection of the cleaning agent
Cleaning agents which contain chlorine attack metals.
u Use only pH-neutral cleaning agents which do not attack metals.
u Observe safety data sheet.
CAUTION
Water and contamination in the cartridge group
If water or contamination penetrates the cartridge group, this can impair
the function of the turbocharger and damage parts inside the cartridge
group.
u Make sure that no water or contamination can enter into the cartridge
group.
Page 35 / 77
u Clean the compressor wheel with a rag or soft brush which has been soaked in water with
a household cleaning agent. Do not use wire brushes!
u Dry the compressor wheel and the gap between the compressor and the bearing casing
with low-pressure pressurized air.
u Lightly spray the compressor wheel and the gap between the compressor and the bearing
casing with penetrating oil.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 66

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
7 Periodic maintenance work / 7.2 Cleaning components mechanically
u Dispose of dirty water and cleaning agents in accordance with the material safety data
sheet.
7.2.7 Cleaning the cartridge group on turbine end
Soaking the contamination
Baked layers of contamination from fuel residue or coked oil may occur at the turbine end.
The contamination can be removed by soaking and brushing. The procedure for soaking the
layers of contamination as well as for cleaning the turbine are described in the following.
Page 36 / 77
Fig.16: Soaking contamination of the turbine
Product A [mm] B [mm] C [mm]
TPS44 115 20 155
TPS48 115 29 180
TPS52 135 35 215
Table12: Dimensions of the cleaning container
To soak the layers of contamination on the turbine, the cartridge group can be immersed
vertically in a container (02) with fluid.
u Place the container (02) inside a larger container (03) so that the overflowing fluid can be
collected.
CAUTION
Selection of the cleaning agent
Cleaning agents which contain chlorine attack metals.
u Use only pH-neutral cleaning agents which do not attack metals.
u Observe safety data sheet.
u Fill the container (02) with soaking fluid. To shorten the soaking time, the fluid can be
heated up to a maximum of 60 ºC.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 67

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
7 Periodic maintenance work / 7.2 Cleaning components mechanically
WARNING
Heating up of cleaning agents and operating fluids
When cleaning agents or operating fluids are heated up, explosive vapours
can be produced which are hazardous to health.
u Observe the information in the material safety data sheet.
Wear a respiratory mask according to material safety data sheet.
CAUTION
Water and contamination in the cartridge group
If water or contamination penetrates the cartridge group, this can impair
the function of the turbocharger and damage parts inside the cartridge
group.
u Place the cartridge group on suitable supports (01) made of wood or
metal.
u Observe dimension (B) for the supports (01) so that the cartridge group
is not immersed too deeply.
u Let the layers of contamination on the turbine soak for four hours.
Removing dirt
WARNING
Health hazard due to soot particles
If soot particles enter the eyes or respiratory tract, this can be harmful to
health.
u Avoid the formation of dust.
u Vacuum up dust with a suitable vacuum cleaner.
u Wear a respiratory mask to protect against particles (P1 or P2 mask).
u Wear safety goggles.
Wear safety goggles.
Wear a respiratory mask to protect against dusts.
Wear safety gloves to protect against mechanical hazards.
Page 37 / 77
u Lift up the cartridge group and align it horizontally.
u Remove dirt manually using a soft brush or a wire brush.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 68

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
7 Periodic maintenance work / 7.2 Cleaning components mechanically
CAUTION
Water and contamination in the cartridge group
If water or contamination penetrates the cartridge group, this can impair
the function of the turbocharger and damage parts inside the cartridge
group.
u Make sure that no water or dirt enters the gap between the heat sheet
metal and the turbine.
CAUTION
Non-permissible rotor unbalance after cleaning
Unevenly distributed residual contamination deposits lead to rotor unbalance. This can result in bearing or turbocharger damage.
u Remove all traces of contamination from the turbine.
u After brushing off the dirt, fill the container (02) with clean water, not salt water.
Page 38 / 77
u Immerse the turbine of the cartridge group in clean water so that any loose dirt comes
off.
u Lift up the cartridge group and align it horizontally.
u Clamp the heat sheet metal to the bearing casing.
u Dry the turbine and the gap between the turbine and the heat sheet metal with low-pres-
sure pressurized air.
u Lightly spray the turbine and the gap between the turbine and the heat sheet metal with
penetrating oil.
u Dispose of contaminated water and cleaning agents in accordance with the information
in the material safety data sheet.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 69

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
8 Eliminating malfunctions / 8.1 Malfunctions when starting
8 Eliminating malfunctions
8.1 Malfunctions when starting
Delayed start-up
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Turbocharger contaminated Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance
work →30)
Bearing damaged Contact ABB Turbocharging Service StaRotor rubbing
Foreign object in the turbocharger
Table13: Malfunctions when starting – Delayed start-up
Vibrations
tion
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Rotor unbalance Contact ABB Turbocharging Service Sta-
Turbine or compressor damaged
Bearing damaged
Engine Vibrations from engine Contact enginebuilder
Table14: Malfunctions when starting – Vibrations
tion
Rotating parts rubbing
Normal behaviour, not a malfunction
Turbocharger A minimal and uniform wear on the circumference of the rotor components is per-
mitted. This wear can be caused by slight local rubbing against adjacent components. This causes the compressor or turbine blades to be somewhat shortened. To
prevent significant loss of efficiency, specific tolerances must be fulfilled.
¡ If there is any doubt about the extent of the rubbing, contact an ABB Tur-
bocharging Service Station.
¡ Have a dimension check carried out by an ABB Turbocharging Service Sta-
tion.
Table15: Malfunctions when starting - Rotating parts rubbing
Page 39 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 70

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
8 Eliminating malfunctions / 8.2 Malfunctions during operation
8.2 Malfunctions during operation
Lubricating oil pressure too low
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Axial clearance of the rotor excessive Contact ABB Turbocharging Service Sta-
tion
Engine Oil filter heavily contaminated Clean
Oil pump in lubricating system defective Check/replace
Manometer displays incorrectly Replace manometer
Table16: Malfunctions during operation – Lubricating oil pressure too low
Speed reduces
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Turbine and/or nozzle ring severely con-
taminated
Rotor components or bearing damaged Contact ABB Turbocharging Service Sta-
Engine Defects on the connected cylinders in
pulse charging
Pipes Defects, such as leaks, in the exhaust gas
pipes or charge air ducts
Table17: Malfunctions during operation – Speed reduces
Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance
work →30)
tion
Contact enginebuilder
Repair
Page 40 / 77
Speed increases
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Light to medium contamination of the
turbine and/or nozzle ring (with 4-stroke
application)
Table18: Malfunctions during operation – Speed increases
Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance
work →30) or contact an ABB Turbochar-
ging Service Station
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 71

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
8 Eliminating malfunctions / 8.2 Malfunctions during operation
Exhaust gas temperature too high
Engine performance and engine speed unchanged
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Insufficient air, for example, when fil-
ter silencer is blocked by contamination
Compressor/turbine contaminated
Exhaust gas back pressure too high Clean or repair boiler or exhaust gas si-
Turbine damaged or eroded Contact ABB Turbocharging Service Sta-
Engine Malfunction in the injection system Repair or contact manufacturer
Charge air
cooler
Table19: Malfunctions during operation – Exhaust gas temperature too high
Cooler contaminated Clean
Cooling water volume too low Fill
Inlet temperature of cooling water too
high
Insufficient ventilation Improve ventilation
Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance
work →30)
lencer
tion
Check/clean cooling system
Charge air pressure too low
Engine performance and engine speed unchanged, suction condition normal
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Manometer display not correct Replace manometer
Supply pipe to manometer not sealed Repair leak
Filter silencer contaminated, therefore
pressure drop too high
Compressor end and/or turbine end con-
taminated
Compressor/turbine damaged Contact ABB Turbocharging Service Sta-
Exhaust gas back pressure too high Clean or repair boiler or exhaust gas si-
Engine Air receiver not sealed Repair
Gas piping between engine and turbine
leaking
Injection mistimed Set correctly
Valve control misadjusted
Pipes Pipes downstream to the compressor
outlet not sealed.
Table20: Malfunctions during operation – Charge air pressure too low
Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance
work →30)
tion
lencer
Repair.
Page 41 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 72

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
8 Eliminating malfunctions / 8.2 Malfunctions during operation
Charge air pressure too high
Engine performance and engine speed unchanged, suction condition normal
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Manometer display not correct Replace manometer
Increased speed due to contamination of
nozzle ring
Engine Malfunction in the injection system Repair or contact manufacturer
Injection mistimed Set correctly
Engine performance higher than indic-
ated
Table21: Malfunctions during operation – Charge air pressure too high
Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance
work →30) or contact an ABB Turbochar-
ging Service Station
Check engine performance
Reduced compressor performance/efficiency and therefore engine performance
losses
Page 42 / 77
CAUTION
Compressor damage
A severely contaminated or corroded compressor wheel can reduce the compressor wheel’s fatigue endurance limit and result in the turbocharger being
damaged.
u Rectify malfunction in accordance with the following table.
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Compressor components severely con-
taminated by the ventilation gases that
have been fed in
Increased blade vibration, compressor
blade damage due to the ventilation
gases that have been fed in
Material of the compressor wheel corroded due to the feeding in of ventilation
gases containing corrosive components
Material of the compressor wheel corroded due to intake air containing exhaust gases or salt
Table22: Malfunctions during operation – Engine performance losses
Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance
work →30)
Optimize oil separation
Correct the feed of ventilation gases ac-
cording to instructions of enginebuilder.
Correct the feed of ventilation gases according to instructions of enginebuilder.
Prevent exhaust gas leakages in the engine space
Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance
work →30)
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 73

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
8 Eliminating malfunctions / 8.3 Turbocharger is surging
8.3 Turbocharger is surging
WARNING
Hot air escapes from the filter silencer
A surge blow is accompanied by a loud bang and escape of hot air from the
filter silencer. Personal injury can result.
u Keep distance from the filter silencer while the turbocharger is surging.
Turbocharger surges continuously or periodically
CAUTION
Continuous or periodic surging
If the turbocharger surges continuously or periodically, parts of the turbocharger may be damaged.
u Gradually reduce the engine load.
u Have the cause clarified and remedied immediately by an ABB Turbochar-
ging Service Station.
u Have parts assessed for damage and, if necessary, replaced by an ABB
Turbocharging Service Station.
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Filter silencer or diffuser contamin-
ated
Heavy contamination deposits in the
turbine or in the nozzle ring
Engine Protective grating in front of the tur-
bocharger contaminated or damaged
Charge air
cooler
Table23: Malfunction – Turbocharger pumping
Cooler contaminated Clean
Charge air duct blocked
Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance
work →30)
Clean/replace
Sporadic surge blows
Possible causes Remedy
Engine Engine load reduced quickly when
manoeuvring.
When this happens, the flow direction
in the compressor is momentarily reversed. Such sporadic surge blows do
not impair the safe operation of the
turbocharger.
Table24: Malfunction – Sporadic surge blows
- -
Page 43 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 74

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
8 Eliminating malfunctions / 8.4 Malfunctions when stopping
8.4 Malfunctions when stopping
Runout noises
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Turbocharger contaminated Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance work →30)
Bearing damaged Check clearances (see chapter Axial clearance A and
radial clearance B →59). If clearances are outside
the tolerance or if in doubt, contact an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
Rotor rubbing Check clearances (see chapter Radial clearances N
and R →67). If clearances are outside the tolerance
or if in doubt, contact an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
Foreign object in the turbocharger
Table25: Malfunctions when stopping – Runout noises
Dismantle turbocharger (see chapter Dismantling
and fitting →46). In case of damage, replace the
corresponding parts or contact an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
Page 44 / 77
Runout time too short
The runout time must be noted down as a reference. Because the runout time depends on
the oil viscosity, the runout time must always be measured at the same oil temperature.
If the runout time is significantly shorter in comparison to a previous measurement, the following table must be observed.
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Turbocharger contaminated Clean (see chapter Periodic maintenance work →30)
Bearing damaged Check clearances (see chapter Axial clearance A and
radial clearance B →59). If clearances are outside
the tolerance or if in doubt, contact an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
Rotor rubbing Check clearances (see chapter Radial clearances N
and R →67). If clearances are outside the tolerance
or if in doubt, contact an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
Foreign object in the turbocharger
Table26: Malfunctions when stopping – Runout time too short
Dismantle turbocharger (see chapter Dismantling
and fitting →46). In case of damage, replace the
corresponding parts or contact an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 75

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
8 Eliminating malfunctions / 8.5 Speed measurement system
8.5 Speed measurement system
No signal or poor signal amplitude of the speed measurement
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger The speed sensor was acci-
dentally fitted with an additional gasket.
An enlarged distance between
the sensor tip and the signalemitting sealing disc reduces
the voltage amplitude of the
speed signal.
Sensor or cable defective Contact an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
Table27: Malfunction of the speed measurement system – No signal or poor signal amplitude
The screw plug for the sensor is fitted with an additional gasket (copper ring).
For information regarding the disassembly and assembly of the speed sensor, refer to chapter Repla-
cing the speed sensor →22.
Install the speed sensor without the additional gasket (copper ring).
Order new speed sensor(86505) (refer to chapter
Ordering spare parts →75).
Replacing the speed sensor →22.
Measured speed too high
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger Sensor tip contaminated,
since it is magnetic and can
attract metallic particles. This
reduces the distance to the
signal-emitting sealing disc,
which can lead to amplification of the noise component
and, hence, to false triggering.
Table28: Malfunction of the speed measurement system – Measured speed too high
For information regarding the disassembly and assembly of the speed sensor, refer to chapter Repla-
cing the speed sensor →22.
Dismantle the sensor, clean the sensor tip, and fit
the sensor back on with the specified tightening
torque.
Measured speed too low
Possible causes Remedy
Turbocharger - - Contact ABB Turbocharging Service Station
Table29: Malfunction of the speed measurement system – Measured speed too low
If none of the measures described above remedy the malfunction, have the speed measurement system checked by an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
Page 45 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 76

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.1 Introduction
9 Dismantling and fitting
9.1 Introduction
The condition for the work described below is that the turbocharger has been removed from
the engine (see chapter Removing and Installing →7).
WARNING
Danger of burns
Touching hot surfaces or contact with hot operating fluids can cause burns.
u Do not touch hot surfaces. Observe the warning plate on the turbochar-
ger.
u Wear heat-resistant safety gloves and protective clothing.
u Wait for the turbocharger to cool down before carrying out any work.
Page 46 / 77
Wear safety gloves to protect against thermal hazards.
WARNING
Cutting injuries when working on the turbocharger
Some parts on the turbocharger may have sharp edges. There is a risk of a
cutting injury.
u Wear safety gloves against mechanical risks when conducting assembly
and disassembly work.
Wear safety gloves to protect against mechanical hazards.
CAUTION
Further operations
This Operation Manual may be used to carry out only those operations that
are described in it. Further operations that are executed in an incorrect way
can lead to serious damage to the machine.
u ABB Turbo Systems recommends having further operations carried out
only by trained personnel from an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 77

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.1 Introduction
9.1.1 Customer spare part set (97070)
The customer spare part set (97070) is required for the operations described. These parts
are only available in a complete set (see chapter Ordering spare parts →75). The content of
the set can be viewed via the following QR code or URL link.
http://www.abb.com/abblibrary/DownloadCenter/?CategoryID=9AAC179494&View=Result&DocumentKind=Catalogue&QueryText=spare+parts+set&SortBy=Score&CountryCode=CH&AdditionalLanguage=*
Identification of the assembly devices
Not all assembly devices are marked with a part number. Identification is guaranteed by the
tool list. This list is enclosed with the toolbox.
WARNING
Servicing the assembly devices
Assembly devices must be checked for damage before and after use.
u Visually inspect for corrosion, cracks, deformation and wear.
u Damaged assembly devices must no longer be used and must be re-
placed.
Tightening torques for assembly devices
Unless described otherwise, the screws and nuts of the assembly devices supplied by ABB
must be tightened so they rest firmly against the surface.
Page 47 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 78

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.1 Introduction
WARNING
Suspended loads
Loads that are not attached according to regulations can cause injury to
personnel or fatal accidents.
u Only fasten the turbocharger, assemblies or individual parts on properly
functional lifting gear with sufficient load limit.
u Pay attention to the correct attachment of loads on the crane hook.
u People must not stand beneath suspended loads.
Wear safety gloves to protect against mechanical hazards.
Wear safety helmet.
Definition of terms
Page 48 / 77
¡ Suspension point
Defined loading point on a component or an assembly (blind hole thread, eyelet, lug).
¡ Assembly device
Devices that are fitted on the turbocharger in order to obtain a suspension point. Assembly devices are specially constructed and designed for the defined use; they are not
commercially available products. Use assembly devices only for the described applications.
¡ Lifting gear
Equipment for the lifting and transporting of loads (ropes, chain block, crane). Lifting
gear is not supplied by ABB.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 79

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.1 Introduction
One swivel lifting eye (S) is required to safely lift this turbocharger. This is not included in
the ABB Turbo Systems scope of delivery.
Swivel lifting eye (S) to be used Product Thread Length
H[mm]
Diameter
D[mm]
Minimum load
limit
[kg]
TPS44 M8 ≤12 ≤25 300
TPS48 M8 ≤12 ≤25 300
TPS52 M10 ≤15 ≤25 400
Table30: Swivel lifting eye (S) to be used
Two ring nuts are required for safer lifting of the cartridge group, which are not included in
the ABB Turbo Systems scope of delivery.
Ring nuts to be used (VRM) Product Thread
TPS44 M16
TPS48 M16
TPS52 M20
Starpoint ring nut VRM
Table31: Ring nuts to be used
Page 49 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 80

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.2 Weights of individual parts
9.2 Weights of individual parts
The specified weights of the individual parts or assemblies are rounded-up standard values.
Page 50 / 77
Fig.17: Overview of assemblies
Designation TPS44 TPS48 TPS52
01 Radial air suction branch 5 6 8
02 Axial air suction branch 3 4 4
03 Filter silencer 15 - - - 04 Compressor casing 17 30 45
05 Diffuser 2 3 4
06 Cartridge group 24 40 65
07 Nozzle ring 1 2 3
08 Turbine casing 1 inlet 30 45 70
09 Gas outlet casing 16 18 25
Table32: Weights of the assemblies [kg]
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 81

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.3 Removing the gas outlet casing
9.3 Removing the gas outlet casing
u Mark the casing position for assembly.
Note: Gas outlet casings which are not from ABB may also be secured with studs and nuts.
Fig.18: Removing the gas outlet casing
1. Manually secure the gas outlet casing(61001).
2. Loosen and remove screws(51008).
3. Remove the gas outlet casing(61001).
4. Remove the gasket(52400).
Page 51 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 82

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.4 Removing air inlets
9.4 Removing air inlets
u Mark the casing position for assembly.
Page 52 / 77
Fig.19: Removing the air inlets
1. Manually secure the filter silencer (81000) or air suction branch (82000).
2. Loosen and remove V-clamp (72020).
3. Remove the filter silencer(81000) or air suction branch(82000).
4. Remove and dispose of O-ring(81010 / 82010) (refer to Disposing of turbocharger com-
ponents →74).
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 83

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.5 Removing the compressor casing
9.5 Removing the compressor casing
Fig.20: Removing the compressor casing (1/2)
1. Place the turbocharger in a vertical position on a soft underlay.
2. Loosen the hexagon-head screws(72011) and remove them with fastening strips(72012).
Page 53 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 84

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.5 Removing the compressor casing
u Mark the casing position for assembly.
Page 54 / 77
Fig.21: Removing the compressor casing (2/2)
1. Secure lifting gear to compressor casing (72000).
2. Remove the compressor casing(72000) vertically.
3. Rotate the compressor casing(72000) through 180° and put it in place.
4. Remove and dispose of O-ring(42012) (refer to chapter Disposing of turbocharger com-
ponents →74).
5. Remove screw(72041).
6. Remove the diffuser(79000) vertically from the compressor casing.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 85

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.6 Removing the cartridge group
9.6 Removing the cartridge group
Do not remove oil orifice (if present)
42001 Bearing casing
42196 Oil orifice in the oil inlet
To limit the oil flow rate through the bearing casing during operation (engine under load) to
the admissible values, an oil orifice is mandatory at the oil inlet of the bearing casing if the
oil inlet pressure is > 3bar (overpressure).
If an oil orifice is fitted in the oil inlet of the bearing casing, it must not be removed.
Do not loosen screw plugs
CAUTION
Oil leaks
These screw plugs must not be removed for maintenance work. If a screw
plug is loosened, the gasket can be damaged. This can result in an oil leak.
u Do not loosen screw plugs.
u If any screw plugs have been loosened accidentally, have these properly
fitted by an ABB Turbocharging Service Station.
Page 55 / 77
Fig.22: Do not loosen screw plugs
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 86

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.6 Removing the cartridge group
Removing the turbine-end fastening strips
u Mark the casing position for assembly.
Page 56 / 77
Fig.23: Removing the cartridge group (1)
1. Loosen the hexagon nuts(51007).
2. Remove hexagon nuts(51007), Verbus Ripp®discs(51003) and fastening strips(51002).
3. Screw in the swivel lifting eye(S) up to the stop.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 87

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.6 Removing the cartridge group
Removing the cartridge group
Fig.24: Removing cartridge group 2
1. Insert screws from service support into cartridge group.
2. Secure ring nuts (VRM) onto the screws with washers.
3. Secure the lifting gear to the ring nuts and swivel lifting eye as shown.
4. Remove the cartridge group vertically from the turbine casing.
Fig.25: Rotating the cartridge group and fitting the service support
1. Lift the cartridge group and rotate in the horizontal position.
Page 57 / 77
2. Remove the lifting gear from the ring nuts.
3. Remove the ring nuts (VRM) and screws from the service support.
4. Place the cartridge group onto the fitted service support (90012).
5. Fit and hand-tighten nuts.
u Measure: Axial clearance A and radial clearance B →59.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 88

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.7 Removing nozzle ring
9.7 Removing nozzle ring
Page 58 / 77
Fig.26: Removing the nozzle ring
1. Remove the nozzle ring(56001) vertically.
2. Remove the lamellar sealing ring (56005).
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 89

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.8 Axial clearance A and radial clearance B
9.8 Axial clearance A and radial clearance B
u Measure and record clearances A and B after the removal and before the installation of
the cartridge group.
u Attach the dial indicator and align it for the respective clearance as per the illustration.
Fig.27: Measuring clearance A and B
Product A [mm] B [mm]
TPS44 0.10 ... 0.18 0.69 ... 1.27
TPS48 0.11 ... 0.19 0.86 ... 1.52
TPS52 0.13 ... 0.22 0.98 ... 1.68
Table33: Permissible clearances A and B
1. Move the rotor to and fro up to the stop. In order to obtain a correct measurement, elevate the turbine a little.
2. Measure clearance A and compare it with the permissible values in the table.
3. Raise the compressor and push the turbine down at the same time.
4. Raise the turbine and push the compressor down at the same time.
5. Measure clearance B and compare it with the permissible values in the table.
CAUTION
Clearances outside the tolerance
Serious damage to engines or property can be caused by clearances outside
the tolerance and excessively worn parts.
u Have the components assessed and, if necessary, replaced by an ABB Tur-
bocharging Service Station.
Page 59 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 90

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.9 Nozzle ring compression PD
9.9 Nozzle ring compression PD
For the nozzle ring(56001) to be fixed during operation, it must be clamped between the
bearing casing(42001) and the turbine casing(51000).
Page 60 / 77
Fig.28: Measuring nozzle ring compression
42001 Bearing casing
51000 Turbine casing
56001 Nozzle ring
1. Measure dimensions A, B, and C on cleaned surfaces.
2. Calculate the compression (PD) and compare it with the permissible values in the following table.
Product Compression PD [mm]
TPS44 -0.23 ... 0.23
TPS48 -0.23 ... 0.23
TPS52 -0.24 ... 0.24
Table34: Permitted nozzle ring compression PD
u If the calculated value (PD) lies outside the specified range, contact an ABB Turbochar-
ging Service Station.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 91

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.10 Fitting the diffuser
9.10 Fitting the diffuser
Fig.29: Fitting the diffuser
Part number TPS44 TPS48 TPS52
72041 M5
5Nm
Table35: Tightening torque (72041)
M5
5Nm
M6
10Nm
1. Position the diffuser(79000) in the compressor casing(72000).
2. Rotate the diffuser until its bore is aligned with the bore in the compressor casing.
3. Fit and tighten screw(72041).
Page 61 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 92

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.11 Installing the cartridge group
9.11 Installing the cartridge group
Lifting the cartridge group and rotating it by 90°
Page 62 / 77
Fig.30: Lifting the cartridge group and rotating it by 90°
1. Fit a new, high temperature-resisting O-ring (42012, red or green) (see Customer spare
part set (97070) →47).
2. Loosen and remove nuts.
3. Lift the cartridge group out of the service support (90012).
4. Insert the screws of the service support from above and fit ring nuts(VRM) with washers.
5. Attach lifting gear to the ring nuts(VRM).
6. Lift cartridge group at the side of the ring nuts(VRM) and turn it into a vertical position
(compressor wheel facing downwards). Use edge guard between turbines and lifting
gear.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 93

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.11 Installing the cartridge group
Fitting the cartridge group
Fig.31: Fitting the cartridge group
Part number TPS44 TPS48 TPS52
72011 M8
40Nm
Table36: Tightening torque (72011)
M8
40Nm
M10
80Nm
1. Lower cartridge group carefully into the compressor casing.
2. Align cartridge group to the marking.
3. Place first fastening strip (72012) according to illustration.
4. Place remaining fastening strips (72012).
5. Fit and tighten hexalobular-head screws(72011).
Page 63 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 94

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.12 Installing nozzle ring
9.12 Installing nozzle ring
Page 64 / 77
Fig.32: Installing the nozzle ring
1. Fit lamellar sealing ring (56005) in the slot of the nozzle ring. When doing this, pay attention to correct winding of the lamellar sealing ring (see detail A).
2. Secure the lamellar sealing ring (56005) with adhesive tape.
3. Installing the nozzle ring. Ensure correct position according to illustration.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 95

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.13 Fitting the turbine casing
9.13 Fitting the turbine casing
Fitting the turbine casing
Fig.33: Fitting the turbine casing
Part number TPS44 TPS48 TPS52
51007 M8
30Nm
Table37: Tightening torque (51007)
M8
30Nm
M10
60Nm
1. Coat the threads of the studs(51006) with high-temperature grease.
2. Turn the turbine casing (51000) by 180°.
3. Fit two swivel lifting eyes (01) on the turbine casing. Secure lifting gear to the swivel lifting eyes.
4. Place the turbine casing onto the cartridge group.
5. Align turbine casing to the marking.
6. Install the fastening strips(51002) with Verbus Ripp® washers(51003) and hexagon
nuts(51007). Observe the tightening torque.
Page 65 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 96

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.14 Rotating the turbocharger
9.14 Rotating the turbocharger
Rotating the turbocharger
Page 66 / 77
Fig.34: Rotating the turbocharger
1. Fit swivel lifting eye (S).
2. Insert screws from the service support.
3. Fit ring nuts(VRM).
4. Attach lifting gear.
5. Elevate and rotate the turbocharger.
6. Place the turbocharger on a soft underlay.
u Measure: Radial clearances N and R →67.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 97

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.15 Radial clearances N and R
9.15 Radial clearances N and R
Fig.35: Measuring clearances N and R
Product N [mm] R [mm]
TPS44 0.25 ... 0.50 0.40 ... 0.70
TPS48 0.30 ... 0.60 0.50 ... 0.80
TPS52 0.40 ... 0.70 0.60 ... 0.95
Table38: Permissible clearances N and R
1. Push the feeler gauges(01) into the gap such that there is no clearance. The upper direction (N1) and lower direction (N2) must be covered simultaneously.
2. Calculate clearance N and compare it with the permissible values in the table.
3. Push the feeler gauges(01) into the gap such that there is no clearance. The upper direction (R2) and lower direction (R1) must be covered simultaneously.
4. Calculate clearance R and compare it with the permissible values in the table.
CAUTION
Clearances outside the tolerance
Serious damage to engines or property can be caused by clearances outside
the tolerance and excessively worn parts.
u Have the components assessed and, if necessary, replaced by an ABB Tur-
bocharging Service Station.
Page 67 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 98

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.16 Installing the gas outlet casing
9.16 Installing the gas outlet casing
Page 68 / 77
Fig.36: Fitting the gas outlet casing
Part number TPS44 TPS48 TPS52
51008 M8
25Nm
Table39: Tightening torque (51101)
M8
25Nm
M10
50Nm
1. Coat the threads of the hexagon-head screws or studs(51008) with high-temperature
grease.
2. Align the casing position of the gas outlet casing(61001) to the marking.
3. Fit two hexagon-head screws(51008) in the upper area of the gas outlet casing.
4. Position the gasket(52400) on the threads of the hexagon-head screws(51008).
5. Install the gas outlet casing(61001) on the turbine casing with the two screws.
6. Fit the remaining screws(51008), then tighten all the screws.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 99

Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.17 Installing air inlets
9.17 Installing air inlets
Fig.37: Installing the air inlets
Part number TPS44 TPS48 TPS52
72020 M10
30Nm
Table40: Tightening torque (72020)
M10
30Nm
M10
30Nm
1. Fit the new O-ring(81010/ 82010) to the filter silencer(81000) or the air suction
branch(82000).
2. Manually position the filter silencer(81000) or the air suction branch(82000) on the compressor casing(72000).
3. Fit the V-clamp(72020).
4. Align the casing position of the filter silencer(81000) or the air suction branch(82000) to
the marking.
5. Tighten the V-clamp(72020).
Page 69 / 77
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
Page 100

Page 70 / 77
Operation Manual / 4 Product description / TPS44-H.. - TPS52-H..
9 Dismantling and fitting / 9.18 Table of tightening torques
9.18 Table of tightening torques
Fig.38: Overview of tightening torques
Position Part number TPS44 TPS48 TPS52
01 82007 M18 x 1.5
60Nm
02 82005 / 81005 M16 x 1.5
50Nm
03 72020 M10
30Nm
04 72041 M5
5Nm
05 72011 M8
40Nm
06 42188 M12 x 1.5
35Nm
07 51007 M8
30Nm
08 51006 M8
25Nm
09a /
09b
10 61005 M18 x 1.5
11 86505 M12 x 1.5
12 *) - - 90Nm 90Nm 90Nm
Table41: Overview of tightening torques
51008 /
51009
M8
25Nm
60Nm
15Nm
M18 x 1.5
60Nm
M16 x 1.5
50Nm
M10
30Nm
M5
5Nm
M8
40Nm
M12 x 1.5
35Nm
M8
30Nm
M8
25Nm
M8
25Nm
M18 x 1.5
60Nm
M12 x 1.5
15Nm
M18 x 1.5
60Nm
M16 x 1.5
50Nm
M10
30Nm
M6
10Nm
M10
80Nm
M12 x 1.5
35Nm
M10
60Nm
M10
45Nm
M10
50Nm
M18 x 1.5
60Nm
M12 x 1.5
15Nm
*) These screw plugs must not be removed for maintenance work. If the screw plug is
loosened, the tightness is no longer guaranteed.
© Copyright 2017 ABB. All rights reserved. HZTL4037_EN Revision E July 2017
 Loading...
Loading...