Page 1

10/100/1000 Mbps networking solutions
LL AANN SSwwiittcchheess
The only certainty in networks today
is that bandwidth demands will
continue to increase. As more complex and time-sensitive applications
such as voice and video are created
for the desktop, a higher volume of
traffic is generated throughout the
network. This results in network bottlenecks that can cause performance
problems within workgroups, to and
from servers, and across the backbone. Switching technology has
proven to be the most cost-effective,
flexible, and least disruptive way to
add and manage bandwidth at every
level of your network.
3Com has the broadest array of
switching solutions to match your
particular requirements. To safeguard
your investment, we offer a family
of stackable switches that delivers
Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit
Ethernet, ATM technologies, and
Layer 3 switching to solve any
performance problem. No matter
which product you start with today
in one area of your network, you can
be assured of a complete migration
path and compatible solutions to
take you to the next step tomorrow.
And that covers everything from the
desktop to the backbone.
Make any of the SuperStack
®
II
switches part of a 3Com
®
SuperStack
system. The SuperStack II product
family offers scalable multitechnology
connections, integrated management
with a common look and feel, and
optional uninterruptible and
redundant power systems.
For those who require the high
quality, reliability, and robustness of
the 3Com SuperStack II family, but
without management capabilities,
the SuperStack II family of Baseline
switches provides a cost-effective
range of products in a variety of
port densities.
Key Benefits
Protects your investment. The
3Com SuperStack II switching
family protects your investment
by delivering low cost of ownership, end-to-end compatible
solutions, and smooth migration
from lower to higher bandwidth
technologies.
Ships with 3Com Transcend
®
Network Supervisor. PC-based
application providing powerful,
yet easy-to-use network management tuned to the needs of
small-to-medium enterprises.
Delivers the capabilities you
need. Autosensing 10/100
Mbps, advanced stackability,
multimedia, VLAN support,
RMON, and Layer 3 switching
help you to build the most efficient and responsive network for
your company.
Year 2000 compliance. All
SuperStack II switches are Year
2000 compliant.
+5 lifetime limited warranty.
Available on SuperStack II
Switch 610, 1100, 3300,
3300 FX, and 3300 XM.
Free 90-day telephone technical support. 3Com offers
assistance with installation,
configuration, and troubleshooting, in addition to the
3Com Knowledgebase
Web service.
The SuperStack II family of switches
makes high-performance, low-cost
switching a reality at the desktop,
workgroup, and backbone.
data sheet
Switches
Flexible, affordable 10/100/1000 Mbps
stackable switches for boosting performance
at the desktop, workgroup, and backbone
3Com®SuperStack®II
®
Page 2

2
raw bandwidth of Gigabit Ethernet,
ATM provides alternative methods for
delivering effective backbone solutions,
such as Quality of Service (QoS), which
guarantees bandwidth to applications.
The control offered by ATM enables
the deterministic delivery of applications
and services in complex network
environments.
Layer 3 Switching
Intranets and extranets, while proving
indispensable for companies of all sizes,
are also causing new traffic management
problems. Hypertext links between
servers and e-mails create any-to-any
traffic that are overwhelming legacy
LAN routers. As a result, companies are
experiencing more bottlenecks between
subnetworks. Layer 3 switching solves
these intranet bottleneck problems by
embedding classical routing in the
switch hardware that routes traffic at
high speeds while intelligently isolating
faults, containing broadcast traffic, and
providing seamless subnet/VLAN
connections.
SuperStack II
Switches for All Your
Technology Needs
Today, your desktop population
probably requires a mix of 10 Mbps and
100 Mbps service to meet the individual
demands of your users. As you deliver
higher speeds to the desktop, server
connections may become strained, so you
need options to scale to Fast Ethernet,
Gigabit Ethernet, or ATM for high-speed
desktop and server connections as well as
in the backbone. With the SuperStack II
family of switches, you can support all
of your bandwidth requirements with
the appropriate technology and the
appropriate level of control.
Ethernet
Today, Ethernet is the most popular
topology for implementing local area
networks. Ethernet provides bandwidth
that can be either shared across a number
of users using hubs, or dedicated to
workstations using switched technology.
The availability of low-cost Ethernet
switches has also made it possible to
deliver dedicated 10 Mbps full-duplex
links to the desktop, for affordable highperformance, high-functionality, and
highly manageable networks.
Fast Ethernet
Fast Ethernet, based on the Ethernet
standard, is a high-speed technology that
runs over your existing infrastructure,
works with your existing management
systems, and requires no retraining by
your IT staff. Fast Ethernet is one of the
most popular high-speed technologies
because it’s cost effective, stable, and
compatible with existing Ethernet LAN
environments. Fast Ethernet runs over
fiber and copper. For greater performance, full-duplex is also supported.
10/100 Ethernet/Fast Ethernet
10/100 Ethernet/Fast Ethernet with
autosensing capability is one of the
most economical and flexible ways to
add bandwidth immediately—while
maintaining migration options to
higher bandwidth in the future. 10/100
technology combines conventional
10BASE-T and high-speed 100BASETX support in one device, delivering
higher bandwidth to the desktop,
aggregating 10/100 hubs, and
maintaining the status quo for those
who are efficiently served by 10 Mbps
Ethernet. With 10/100 autosensing
functionality, there is no need to
configure individual switched ports.
The switch automatically senses the
speed of the connected end device
(either 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps) and
channels the data through at the
appropriate speed.
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet retains the traditional
simplicity and manageability of
Ethernet and Fast Ethernet, making it
easy to integrate with existing LAN
equipment. It allows a tenfold increase
in backbone bandwidth over Fast
Ethernet with minimal impact on
support staff. The extra bandwidth
helps you deal with unplanned changes
and additions to the network, and
frees you from constantly tuning the
network. Gigabit Ethernet is a powerful
backbone/server solution because it
delivers phenomenal bandwidth cost
effectively, preserves the Ethernet frame
format, and works with your existing
traffic management systems.
ATM
ATM is an established LAN backbone
technology that offers significant
benefits to larger organizations by
providing tight integration between
LAN and WAN environments and
offering high levels of resilience and
redundancy. In the LAN environment,
OC-3c (155 Mbps) and OC-12c
(622 Mbps) connections are used to
communicate across the network. While
these connections do not provide the
In This Guide:
SuperStack II Switches for All Your Technology Needs .......................................................2
Features Supported for SuperStack II Switches .................................................................4
Product Configurations (Diagrams) ................................................................................6–7
New Products
SuperStack II Baseline 10/100 Switches .....................................................................8
SuperStack II Switch 610.............................................................................................9
SuperStack II Switch 1100/3300 Family ...............................................................10-12
SuperStack II Switch 1100 and 3300—Optional High-Speed Accessories ............13-14
SuperStack II Switch 3800.........................................................................................15
SuperStack II Switch 3900 and Switch 9300..............................................................16
SuperStack II Switch 9000.........................................................................................18
SuperStack II Switch 9100.........................................................................................19
SuperStack II Switch 2200.........................................................................................20
SuperStack II Switch 2700.........................................................................................20
Network Management ...............................................................................................21
SuperStack II Switches at a Glance ............................................................................22–23
Specifications.............................................................................................................24–27
Technology Supported for SuperStack II Switches...........................................................25
Ordering Information .......................................................................................................28
Page 3

Backbone WAN/SNA Host
Power Systems
Transcend Network
Management Architecture
RMON-2 Probes
OpenHub
Access Servers
SDLC Converters
Routers
Switches
Hubs
LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
3
SuperStack®II Systems
The 3Com®SuperStack®II system gives you a flexible,
cost-effective connectivity solution for local, wide area,
and SNA networks. You can combine diverse technologies
and network services in one stacked system, strengthen it
with uninterruptible and redundant power systems, and
manage it all with Transcend®network management and
control solutions.
As an important part of the 3Com Transcend Networking
framework, SuperStack II systems will meet your evolving
network needs—future proofing your network investment.
A single SuperStack II system provides connections for a
range of network environments and protocols: Ethernet,
Fast Ethernet, Layer 3 switching, Gigabit Ethernet, Token
Ring, FDDI, ISDN, X.25, Frame Relay, and ATM. Depending
on your needs, you can build SuperStack II systems for
virtually any network environment. Capabilities include:
■
Hubs for flexible workgroup connectivity that feature
SNMP, RMON, and Web-based management
■
Industry-leading physical layer support for Token Ring
networks, including Token Ring switching
■
Full SNMP, RMON, and Web-based management for
Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet switches, as
well as a dedicated RMON-1/RMON-2 probe
■
Full range of switches to increase performance in
high-speed client/server LANs
■
Full, multiprotocol network access for telecommuters or
users at other off-site locations
■
Routing between central site and branch offices
using innovative Boundary Routing®architecture or
conventional routing software for multiple WAN choices,
including ISDN
■
SNA-to-LAN conversion linking local and remote offices
to an SNA host system
■
Choice of power systems to ensure uninterrupted
network operation
For smaller offices of fewer than 20 users, our
OfficeConnect®products can be used to complement
SuperStack II systems.
Page 4

4
Features
Stackability
Four SuperStack II Switch 1100 or
Switch 3300 units can be interconnected
to form a stack that offers unrivaled
performance and management features.
Each unit has a built-in connector at
the rear of the unit called the matrix
port. Two units can be connected backto-back with a SuperStack II Switch
matrix cable. To connect more than two
units, a SuperStack II matrix module can
be inserted into the high-speed module
slot of one of the units in the stack, and
a matrix cable can be used to connect to
each switch in the stack.
Stacking provides the user with a
plethora of benefits. These include the
ability to manage in excess of 100 ports
as a single logical entity. Configuration
is therefore faster and simpler. Stacking
also provides the user with the optional
resilient IP addresses across the stack.
Thus if a failure should occur, the
resilient IP address can be used for
management stacking using the
SuperStack II Switch matrix module
and cable, keeping front panel ports
free and increasing the number of
matrix ports in an aggregated system.
Management
Transcend®network management
All SuperStack II switches are managed
by 3Com Transcend
®
network management and control solutions. Transcend
solutions give you end-to-end visibility
Features Supported for
SuperStack II Switches
Disconnect Unauthorized
Device (Security)
Transcend network
management support
Stackable with matrix
module & cable
Web-based
management
PACE technology
RMON support
Flow control
(IEEE 802.3x)
Roving Analysis Port
IEEE 802.1D
(incorporating 802.1p)
Dual queues
and control over all devices in your
network with two levels of management:
1) technologies, such as embedded
SmartAgent
®
software and RMON,
within 3Com devices throughout the
network, and 2) centralized highly
automated applications at the network
center for monitoring, configuring, and
troubleshooting all devices in the network.
Ships with 3Com Transcend
Network Supervisor
This PC-based application provides
powerful, yet easy-to-use network
management tuned to the needs of smallto-medium enterprises. Network devices
are automatically discovered and network
activity and stress monitored through an
intuitive graphical interface focused on the
tasks and information all managers need
to take control of their network.
Web-based management
Manage your switches with any Web
browser, either through direct or dial-up
connection or across the LAN. This
delivers ease of use and accessibility to
network management personnel and
reduces in-service costs, but still with
full security.
Security—Disconnect Unauthorized
Device (DUD)
LAN security architecture with DUD
automatically disconnects unauthorized
devices from the LAN.
Roving Analysis Port (RAP)
RAP allows a network analyzer attached
to any unit in a stack to monitor any of
the switch ports or virtual LANs
(VLANs) in the stack. It also minimizes
the time required for problem determination and resolution and maximizes
switch uptime, thereby lowering your
cost of ownership.
RMON support
Transcend software’s powerful combination of RMON (Remote Monitoring,
a superset of SNMP MIB II) and
embedded SmartAgent software reduces
the processing burden on your management station, minimizes network traffic,
and saves time by automatically monitoring and analyzing your network.
RMON tells you at a glance how the
network is performing and who is using
it the most. And Transcend software
gives you the added benefit of RMON
features in your network without the
processing and memory costs usually
associated with RMON. See the Ata-Glance RMON Support table on
page 24 for details on RMON groups
supported by SuperStack II switches.
Class of Service (CoS)
CoS can be defined simply as a method
for prioritizing various traffic types.
3Com switches can support two methods
of enabling CoS on Ethernet networks.
The first method is IEEE 802.1D
(incorporating 802.1p), which enables
eight levels of prioritization; and the
second method is 3Com’s innovative
PACE
®
technology, which allows the
user to specify certain applications as
high priority. A hardware feature, dual
queues, is used to exploit these traffic
prioritization schemes; the dual queues
function—required for CoS—will
Half-duplex
Flow Control-I
Ships with Transcend
Network Supervisor
SuperStack II Baseline 10/100 Switch ●●
SuperStack II Switch 610 ●●● ●●●●● ●●●
SuperStack II Switch 2200 ●●●
SuperStack II Switch 2700 ●●
SuperStack II Switch 1100 ●●●●●●●●●●●●
SuperStack II Switch 3300 ●●●●●●●●●●●●
SuperStack II Switch 3300 XM ●●●●●●●●●●●●
SuperStack II Switch 3300 FX ●●●●●●●●●●● ●
SuperStack II Switch 3800 ●●●●●● ● ●
SuperStack II Switch 3900 ●●● ●●●● ●
SuperStack II Switch 9000 ●●●●●● ● ●
SuperStack II Switch 9100 ●●● ●●●● ●●●
SuperStack II Switch 9300 ●●● ●●●● ●
■Optional—Achieved with SuperStack II Switch Layer 3 plug-in module
Page 5

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
5
VLANs
VLANs allow PCs, workstations, and
other resources, including printers and
file servers, to be organized into logical,
broadcast domains so that only devices
within the same domain can communicate with each other. 3Com switches
allow users to implement VLANs on
their network using one of two schemes:
IEEE 802.1Q, including GVRP, which
enables the auto-learning of VLANs, or
3Com’s VLT. Both methods allow for the
configuration of VLANs based on ports
and/or MAC addresses for maximum
flexibility and security. For 802.1Q
VLANs, a port on a switch can be
assigned to a VLAN; all other switches
learn about that VLAN when the
switches automatically communicate that
knowledge via the GVRP protocol.
Switches supporting both VLAN
schemes can be used to provide seamless
migration from VLT to IEEE 802.1Q
environments that preserve investment
in current LAN developments and
equipment.
Layer 3 Support
Multicast filtering using IGMP
snooping
Multicast filtering enables the automatic
configuration of filters for IP multicast
traffic, such as video and audio broadcasts, allowing advanced multimedia
applications to be delivered easily to the
workgroup.
Fast IP
Fast IP is 3Com’s standards-based cutthrough routing solution for all types
of legacy routing network backbones.
This reduces traffic flow through router
bottlenecks and maximizes performance
by utilizing the switched infrastructure.
Layer 3 switching
Layer 3 switching is the implementation
of routing protocols in leading-edge
ASIC technology. Routing performance
is dramatically and cost effectively
boosted to enable the widespread
deployment of intranets (IP-based
networking).
automatically enable a second port
buffer for high-priority traffic thereby
allowing the traffic to bypass lower priority data for faster processing within
the switch.
Traffic Management
Flow control
Flow control is an essential switch
feature that eliminates dropped packets
on congested ports. To provide switch
application flexibility, 3Com switches
support flow control schemes suited to
both full- and half-duplex environments.
Intelligent Flow Management (IFM)
is a solution designed to work in half
duplex, for example, a hub aggregation
application. A solution using IEEE
802.3x is also supported and designed
for full-duplex connections, such as
desktop switching; this method of flow
control is set automatically using the
autosensing features of SuperStack II
switches.
Broadcast traffic control
Traditional Ethernet switches suffer from
the threat of broadcast storms that can
potentially bring networks to a halt.
However, all SuperStack II switches
can be configured with broadcast storm
protection to limit the number of
broadcast packets allowed to be
forwarded by each port. This allows the
SuperStack II switches to offer the
security of broadcast storm protection
normally associated with a router while
also providing the protocol independence
of a switch.
Network Availability
Backup power supplies
3Com gives you all the choices you
need to ensure constant power to your
stackable switches. Both the Advanced
Redundant Power System (ARPS) and
the Uninterruptible Power System
(UPS) work with any SuperStack II
switch. The ARPS is ideally suited as a
backup for individual power supplies in
the SuperStack II units. The UPS fully
protects your SuperStack II system
from the effects of brownouts or spikes
that occur in outside power lines.
Resilient links
3Com’s simple and flexible resilient
links technology ensures fault tolerance
via redundant connections to other
network devices.
Spanning tree
Support for the industry-standard
IEEE 802.1D spanning tree protocol is
provided as an alternative to resilient
links. This protects against network
loops and can be used to provide
redundant network paths.
Port trunking
Port trunking establishes backbone
links by treating multiple parallel links
as a single network pipe. Trunking also
provides link redundancy; traffic on
any failed link comprising a network
trunk automatically switches over to
the other links in the trunk.
Resilient links
UPS backup power
supplies
VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q )
Spanning tree
Broadcast traffic control
Intelligent
switching mode
Layer 3 switching
Trunking
Fast IP
Multicast filtering using
IGMP snooping
Full duplex on all
ports
l-IFM
VLAN (VLT )
●●●
●●●●●●●●●●●●
●●
●●
●●●●●●●●●●●●■
●●● ● ●● ●● ●● ●■
●●● ● ●● ●● ●● ●
●●● ● ●● ●● ●●●■
●● ●●● ●
●● ● ● ●● ● ●
●● ●●● ●
●● ● ●● ●
●●● ● ● ●● ●●
ARPS/Type 2 backup
power supplies
Page 6
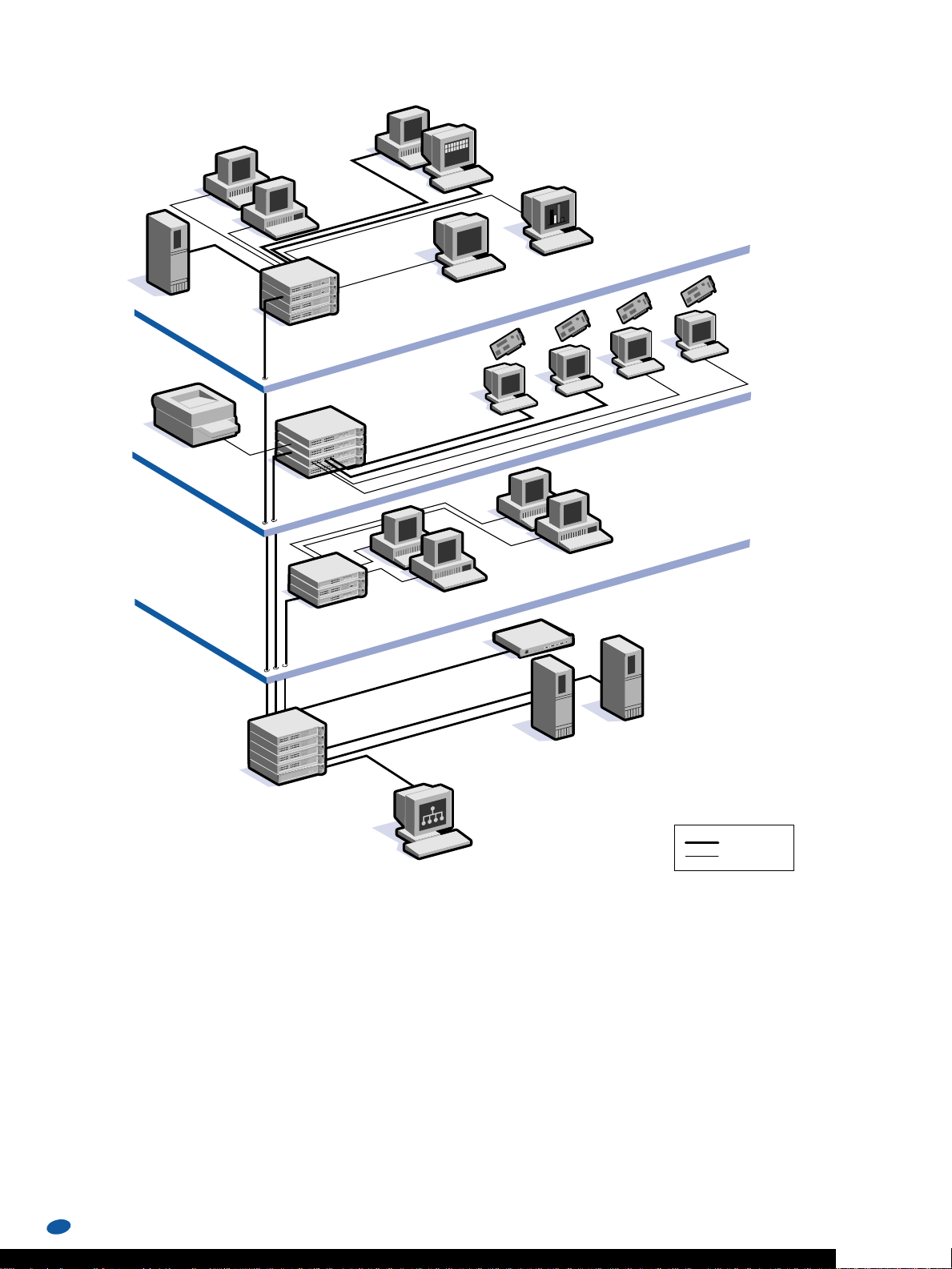
6
Print server on
Fast Ethernet LAN and WAN connectivity
A medium-sized corporation supporting a mixture of switched
and shared workgroups has a central Fast Ethernet backbone.
In the basement, a stack of SuperStack II Switch 3300s provides
Fast Ethernet 10/100 Mbps links to the floors and 10/100
connections for local servers, and it also provides the ability to
scale to Gigabit Ethernet when needed. The entire network is
managed at the Transcend network management console or
via Web-based management at any browser. Intranet traffic
is managed simply and cost effectively when a SuperStack II
Switch Layer 3 module is plugged into a SuperStack II
Switch 3300.
On the first floor, a stack of SuperStack II Switch 1100s provides
dedicated switched 10 Mbps for those users using simple applications such as mail.
On the second floor, the SuperStack II Dual Speed Hub 500 with
a mixture of 100 Mbps and 10 Mbps users is connected to a
switched 100 Mbps backbone via the data center SuperStack II
Switch 3300 stack.
On the third floor, a SuperStack II Switch 1100 and 3300 stack
provides dedicated switched 10 Mbps and 10/100 Mbps to
power users for transferring large files and multimedia traffic.
bps
100 M
bps
Switched 10 M
workgroup
®
II system with
SuperStack
SuperStack II Switch 3300
and 1100
Power users on
dedicated 100 Mbps
Volume intranet
user on dedicated 10 Mbps
User running
ultimedia
m
Floor 3
ixed/shared
M
100 M
and 10 M
bps
bps users
Printer on
10 Mbps
SuperStack II Switch 3300*
Type 2 ARPS and SuperStack II
Switch Layer 3 module
SuperStack II system
with SuperStack II
Switch 3300
SuperStack II system with
SuperStack II Switch 1100
®
Transcend
management console
network
Floor 2
bps workgroup
Switched 10 M
Floor 1
SuperStack II
Enterprise Monitor probe
Basement
Server farm
* For fiber connectivity, use the
SuperStack II Switch 3300 FX.
100 Mbps
10 Mbps
Page 7
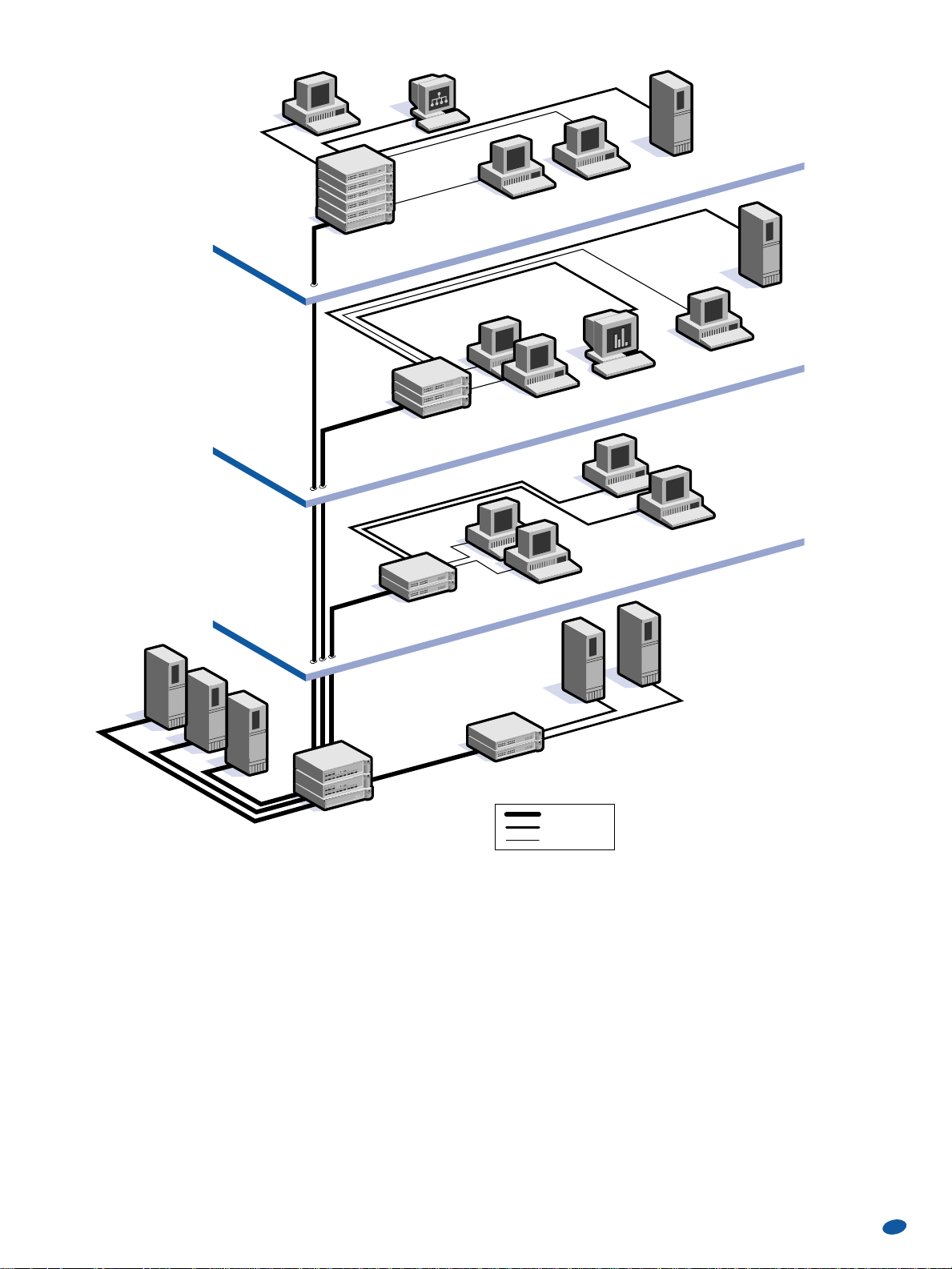
LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
7
SuperStack II Switch 3900
Local server
Switched Fast Ethernet
high-speed power users
Switched
10 M
bps
Volume intranet
user
SuperStack
®
II system with
SuperStack II Switch 3300
and UPS
SuperStack II Switch 9300
**
and Type 2 ARPS
PC running multimedia
videoconferencing
Power users on
switched Fast
Ethernet
Users on
switched Fast
Ethernet
Gigabit
Ethernet
SuperStack II system with
SuperStack II Switch 3900
*
Floor 1
Basement
Floor 2
Floor 3
Gigabit
Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
(1000 Mbps)
server farm
Switched
Ethernet
Transcend
®
network
management console
Existing desktop
Local server using
100 Mbps
Servers using
100 Mbps
SuperStack II Switch 3300
and SuperStack II Switch 1100
and UPS
*
For 10/100/1000 Mbps Layer 3
switching, use the SuperStack II
Switch 3800.
**
For Gigabit Ethernet Layer 3 switching,
use the SuperStack II Switch 9000.
0
5
1
0
1
5
2
0
2
5
3
0
100 Mbps
1000 Mbps
10 Mbps
Gigabit Ethernet LAN and WAN connectivity
An organization supporting a mixture of 10/100 Mbps switched
and shared desktop connections has migrated to a Gigabit
Ethernet backbone.
3Com has taken an early lead in the Gigabit Ethernet market by
providing the ability to utilize this new high-speed technology
while protecting your existing network infrastructure investment.
In this configuration, the SuperStack II system in the basement
comprises a Switch 9300, a Switch 3900, and an Advanced
Redundant Power System for added resilience. The Switch 9300
provides the Gigabit Ethernet switching backbone and links
to Gigabit Ethernet servers while the Switch 3900 provides
unconstrained access to a large Fast Ethernet server farm. This
configuration provides the fastest backbone solution and fastest
server access for all floors.
On the first floor, the SuperStack II Switch 3900 provides linerate services to power users directly connected to switched Fast
Ethernet ports.
On the second floor, the SuperStack II Switch 3300 and Switch
1100 provide network connectivity to switched 10 Mbps and
100 Mbps users, and the use of an optional SuperStack II Switch
1000BASE-SX module provides Gigabit Ethernet support.
On the third floor, the SuperStack II Switch 3300 provides linerate services to power users on switched Fast Ethernet as well
as switched 10 Mbps services to less demanding users, and connects shared 10 Mbps and 10/100 hubs to the Gigabit Ethernet
backbone. The network is managed at the Transcend network
management console.
Page 8

8
The 3Com SuperStack II Baseline
10/100 switches provide the highest
performance product in the SuperStack II
Baseline family. Delivering the power of
switched Fast Ethernet while automatically sensing the speed of the connected
devices, the SuperStack II Baseline
switches are ideal for any environment
where raw power and performance are
needed, but management is not
required. The Baseline 10/100 switches
can be used as an aggregation device
connecting to other switches or hubs,
or to provide cost-effective, highperformance desktop connections.
The Baseline 10/100 switches
provide 12 or 24 10/100BASE-TX
(Fast Ethernet) switched ports that
automatically detect the speed of
connected devices, optimizing network
performance to 100BASE-TX, where
applicable. The SuperStack II Baseline
switches are unmanaged and work
straight out of the box.
Key features include:
■
12 or 24 RJ-45 10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX autosensing ports
provide the ultimate in high-speed
switching connectivity.
■
Autonegotiating full-/half-duplex
operation on each port doubles the
speed of each network connection
to 200 Mbps.
■
MAC addresses support up to
4,000 network devices on your
local area network.
■
IEEE 802.3x Flow Control ensures
network traffic is not lost during
peaks in traffic rates on highthroughput, full-duplex links.
■
19” size for easy installation in a
wiring closet. A rackmounting kit
is supplied. The product can also
be used free-standing.
■
Diagnostic LEDs indicate network
traffic and port status of each port,
making it easy to spot-check faults
and check individual port status.
■
3Com lifetime limited warranty
■
Connection for the SuperStack II
Advanced Redundant Power
System provides ultimate protection against network downtime.
The SuperStack II Advanced
Redundant Power System and
Uninterruptible Power System are
also available from 3Com.
SuperStack II Baseline 10/100 Switches
SuperStack II Baseline 10/100 Switches
Front view of 24 port
Back view
24 ports (RJ-45) LEDs for link status
and network traffic
Advanced RPS
connector
(Type 2)
MDI/MDIX
switch
Front view of 12 port
LEDs for link status
and network traffic
MDI/MDIX
switch
12 ports (RJ-45)
Page 9

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
9
When you need low-cost 10 Mbps and
10/100 Mbps switching coupled with
high levels of performance and manageability, then look no further than
the SuperStack II Switch 610.
The SuperStack II Switch 610 is
based on the high-performance
BRASICA
™
II architecture found in the
SuperStack II Switch 1100 and 3300,
offering high levels of performance and
manageability at an unsurpassed price.
About the Switch
The SuperStack II Switch 610 is perfect
for desktop connectivity and can support up to 6,000 MAC addresses.
Switch 610 is available in a 24-port
version and features two built-in
autosensing 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet
ports. (As with other SuperStack II
switches, the Switch 610 features
autosensing 10/100 Mbps ports that
adjust for 10BASE-T and 100BASETX attached devices.) It automatically
provides full-duplex/half-duplex
capability on all ports to boost
bandwidth for servers and power users.
The SuperStack II Switch 610 supports the following features:
■ Web browser interface to locate
management and configuration
functions
■ Resilient links and spanning tree
■ Optional SuperStack II backup
power supplies
■ Elastic port buffering, enabling
on-the-fly allocation of memory for
automatic performance optimization
based on network traffic
■ RMON - 7 groups and RAP
■ Dual queues to facilitate traffic
prioritization
■ Multicast filtering using IGMP
snooping/GMRP
■ Flow control improves performance
and minimizes packet loss under
heavy network loading
■ VLT VLAN tagging protects
investment infrastructure
■ 802.1Q standard-based VLANs with
GVRP support to facilitate dynamic
VLAN membership
SuperStack II Switch 610 for Ethernet and Fast Ethernet
Back view
Front view of 24 port
SuperStack II Switch 610
24 switched 10BASE-T/RJ-45 ports 2 10/100BASE-TX ports
AC connection
Advanced Redundant Power System connection
Page 10

10
SuperStack II Switch 1100/3300 Family for Ethernet, 10/100 Fast Ethernet, and
Fiber Switching
Companies today realize that the
booming e-business marketplace is providing them with amazing growth
opportunities. To take advantage of
these opportunities and sustain this
growth, IT managers must find a way
to boost network performance in synch
with their evolving e-business requirements. 3Com has developed a family of
modular, stackable switches designed to
help fast-growing companies add power
and performance to their networks
easily, economically, and with minimum disruption.
The SuperStack II Switch
1100/3300 family includes four highperformance switches that can be
mixed and matched to achieve the perfect combination of cost and features
for desktop, workgroup, and backbone
aggregation. This is the first family of
switches that enables IT managers to
create a “virtual stack” of different
switches that act as one logical
switch—providing an easy and affordable way to build performance and
capabilities into the network as needed.
Each switch has a built-in matrix
port connector at the rear of the unit.
Two units can be connected with a
low-cost SuperStack II Switch matrix
cable; three or more units can be
stacked using a SuperStack II Switch
matrix module that delivers highspeed/performance interswitch links—
eliminating bottlenecks between
switches. Stacked switches communicate through matrix ports, so you don’t
consume valuable Fast Ethernet or
Gigabit Ethernet ports. You can mix
and match multiple switches to create
one virtual switch of up to 110
switched ports that is manageable as a
single entity with a single IP address
(note: multiple IP addresses can be supported to provide resilient stack
management).
To make management even easier,
the SuperStack II 1100/3300 family
features Web-based monitoring and
control, so IT staff can troubleshoot or
configure a stack from any location.
Embedded Remote Monitoring
(RMON) support provides detailed
information on network traffic. The
switches also ship with 3Com
Transcend Network Supervisor, an easy
and automatic management solution
specifically designed for small- and
medium-sized businesses.
For added reliability, the switches
support resilient links and spanning
tree, as well as optional redundant
power supplies.
In addition to this easy mix-andmatch scalability, the SuperStack II
Switch 1100/3300 family supports a
broad range of expansion modules
(such as Layer 3 switching, Gigabit
Ethernet, or ATM support) to add connectivity or functionality as needed.
What’s more, all four models share
the same software, reducing training
time and ensuring flawless interoperability. Companies can even bolster
their e-business initiatives by adding
voice and video to their networks with
a rich traffic management feature set,
including:
• Policy enforcement with Fast IP,
IGMP snooping, IEEE 802.1D
(incorporating 802.1p prioritiza-
tion), and IEEE 802.1Q
standards-based VLANs
• Dual queues to help prioritize multimedia traffic
• Multicast filtering using IGMP
snooping/GMRP for more efficient
bandwidth utilization when transporting video traffic
• Elastic port buffering for on-the-fly
port buffer memory allocation,
enabling automatic performance
optimization based on network
traffic
• Flow control to maximize performance and minimize packet loss
under heavy network loading
• Automatic detection of full-/halfduplex operation on all ports to
maximize performance without
manual configuration
• Trunking support to aggregate links
into a single high-speed connection
to other switches or backbone networks
• Optional Layer 3 switching to
increase network performance by
off-loading legacy routers and controlling broadcast/multimedia traffic
All models in the SuperStack II
Switch 1100/3300 family come with
the 3Com lifetime limited warranty,
which includes 5 years of free advance
hardware replacement (3Com will ship
a new switch out to you even before
you return the old one.). For extra
assurance, you’ll also receive 90 days of
free telephone technical support, as
well as free lifetime software upgrades.
Page 11

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
11
About the Switches
The SuperStack II Switch 3300:
The SuperStack II Switch 3300 provides the smoothest migration to Fast
Ethernet with 10/100 autosensing on
all ports to adjust automatically to the
speed of the attached devices. The
SuperStack II Switch 3300 is available
in 12- or 24-port versions and features
an optional expansion modules slot.
The SuperStack II Switch
3300 XM: The SuperStack II Switch
3300 XM delivers the same capabilities
as the SuperStack II Switch 3300, but
without an expansion modules slot. The
24-port version allows you to add additional 10/100 Ethernet/Fast Ethernet
ports to an existing SuperStack II
Switch 1100/3300 in a cost-effective
manner.
The SuperStack II Switch 3300 FX:
The SuperStack II Switch 3300 FX
offers the same capabilities as the
SuperStack II Switch 3300, plus the
added security and redundancy of fiber
cabling support. It features eight multimode fiber Fast Ethernet ports, two
autosensing 10/100 ports, and an
optional expansion modules slot. The
SuperStack II Switch 3300 FX is the
ideal switch for interconnecting remote
hubs and switches over fiber optic
cabling.
*SuperStack II Switch 3300 XM available in 24 port only.
SuperStack II Switch 3300 FX
Front view
Back view
SuperStack II Switch 3300
Front view of 24 port
Back view
Front view of 12 port*
12 switched 10/100BASE-TX ports
24 switched 10/100BASE-TX ports
AC connection RS-232
Advanced
Redundant
Power System
connection
port
Tx
Rx Tx Rx Tx Rx Tx Rx Tx Rx Tx Rx Tx Rx Tx Rx 10BASE-T/100BASETX
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9x 10x
Optional
high-speed
module slot
(not available on
3300 XM model)
3C16982
Matrix
port
SuperStack II
Switch 3300 FX
8 switched 100BASE-FX ports
AC connection RS-232
Advanced
Redundant
Power System
connection
port
Optional
high-speed
module slot
(not available on
3300 XM model)
Matrix
port
Page 12

12
SuperStack II Switch 1100
Front view of 12 port
Back view
Front view of 24 port
The SuperStack II Switch 1100 and Switch 3300 can be
stacked up to four units high by using the SuperStack II
Switch matrix module and SuperStack II Switch matrix cables.
• Mix and match Switch 1100 and Switch 3300 within the
stack to meet customer needs.
• Stack up to four units high—supporting up to 110 switched
ports.
• SuperStack II Switch matrix module supports 4 x 1 Gbps
links between switches to create high-density switches
without wasting Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet ports.
The SuperStack II Switch 1100 and Switch 3300 can be
stacked up to two units high with just the SuperStack II
Switch matrix cable.
• With a low-cost cable, users can double the port density
with a 1 Gbps link between switches.
• Mix and match SuperStack II Switch 1100 and Switch 3300
to meet customer needs.
• Stack up to two units high—supporting up to 56 switched
ports.
The SuperStack II Switch 1100:
The SuperStack II Switch 1100 serves
10 Mbps Ethernet users and provides
two 10/100 Fast Ethernet ports for
high-speed access to servers, high performance workstations, or core
switches. In addition, the switch features a transceiver slot for connecting to
legacy networks. The SuperStack II
Switch 1100 is available in 12- or 24port versions and offers an optional
expansion modules slot.
2 10/100BASE-TX ports
12 switched 10BASE-T/RJ-45 ports
24 switched 10BASE-T/RJ-45 ports
AC
connection
Advanced
Redundant
Power System
connection
Switch
3300 XM
Switch
3300
2 10/100BASE-TX ports
RS-232
port
Optional
high-speed
module slot
Slot for optional
10 Mbps
transceiver
module
Matrix
port
Switch
1100
Switch
3300 XM
Switch
3300 XM
Switch
3300
Page 13

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
13
SuperStack II Switch 1100 and SuperStack II Switch 3300
Optional High-Speed Accessories
SuperStack II Switch Matrix
Module and Matrix Cable
The SuperStack II Switch matrix module
and matrix cable let you mix and match
SuperStack II Switch 1100s and 3300s
to improve throughput, share downlinks,
and ease management. Use the matrix
cable to connect two Switch 1100s or
Switch 3300s and the matrix module
to connect up to four switches* while
conserving Fast Ethernet ports. The
matrix module’s 4 x 1 Gbps backplane
provides a 1 Gbps link between switches.
Ultralow latency (maximum 300
nanoseconds) and hardware flow control
ensure top performance at low cost. The
entire stack can be managed as a single
entity.
■ Any switch port can be configured
to support roving analysis across the
stack for greater visibility into traffic
flows and RMON data; the module
supports IEEE 802.1D and 802.1Q
standards for VLANs and Ethernet
Class of Service (CoS).
*Each unit in a stack requires a matrix cable,
including the unit that holds the matrix module.
SuperStack II Switch
100BASE-FX Modules
The SuperStack II Switch 100BASE-FX
module adds a fiber Fast Ethernet backbone link to your switched workgroup.
The easy-to-install dual module is an
excellent choice for resilient connections
in mission-critical networks or when
multiple fiber backbone connections are
needed to and from the stack. A single
high-speed backbone link can be shared
by multiple units in a stack.
■ Full-duplex Fast Ethernet
provides 200 Mbps throughput
and 2 kilometers distance on fiber.
SuperStack II Switch Gigabit
Ethernet Modules (1000BASE-SX,
1000BASE-LX, 1000BASE-T)
The SuperStack II Switch Gigabit Ethernet modules support highperformance, fault-tolerant interworkgroup and workgroup-to-backbone
connections.The easy-to-install modules
provide full-duplex Gigabit Ethernet up
to 2 Gbps throughput, eliminating network bottlenecks.They support both
802.1D spanning tree and resilient links.
■ The SuperStack II Switch 1000BASE-
SX module offers a multimode fiber
interface over distances up to 550
meters (for 50 micron for MMF).
■ The SuperStack II Switch 1000BASE-
LX module offers multimode and
single-mode fiber interfaces over distances certified by 3Com up to 10
kilometers.
■ The SuperStack II Switch 1000BASE-T
module offers a Category 5 copper
interface over distances up to 100
meters.
SuperStack II Switch matrix module and
SuperStack II Switch matrix cable
SuperStack II Switch 100BASE-FX module
SuperStack II Switch 1000BASE-SX module
SuperStack II Switch 1000BASE-LX module
SuperStack II Switch 1000BASE-T module
Page 14

14
SuperStack II Switch 1100 and SuperStack II Switch 3300
Optional High-Speed Accessories (continued)
SuperStack II Switch
Layer 3 Module
The SuperStack II Switch Layer 3
module lets you cost effectively add
routing capabilities to your switched
10/100/1000 Mbps workgroups to boost
intranet performance and off-load legacy
routers of LAN traffic. SuperStack II
Switch 1100, 3300, and 3300 FX
switches with the easy-to-install Layer 3
module seamlessly route IP traffic
between subnets. IPX, AppleTalk, and
other legacy protocols will be switched
within their subnet (VLAN). One
SuperStack II Layer 3 module can
manage routing for the entire stack.
■ Extensive standards-based routing pro-
tocol support (including RIP and
OSPF) enables the switches to operate
in any networking environment.
■ Distance Vector Multicast Routing
Protocol (DVMRP) optimizes multimedia traffic delivery.
SuperStack II Switch 1100/3300
ATM Expansion Module
The SuperStack II Switch 1100/3300
ATM expansion module provides one
high-speed ATM port for connection to
a high-speed ATM backbone. The port
is software-configurable to run at either
OC-3c (155 Mbps) or OC-12c (622
Mbps) speeds, so you can run at OC-3c
speeds today and upgrade to higher
OC-12c capability in the future with no
additional hardware investment. The
SuperStack II Switch 1100/3300 ATM
expansion module delivers cost-effective
functionality and performance.
Advanced, built-in ATM switching and
Ethernet-to-ATM internetworking features include 802.1Q Ethernet VLANs
to ATM-based ELANs mapping, and
Ethernet 802.1p (amendment to
802.1D) prioritization traffic to ATM
Quality of Service mapping. When
SuperStack II Switch 1100, 3300, or
3300 FX are configured in a stack, multiple expansion modules can provide
resiliency and load sharing across all
ATM ports.
■ The expansion module’s innovative
software-configurable OC-3c/OC12c ATM port accommodates future
backbone bandwidth needs without
additional hardware or software.
■ The module supports industrywide
ATM standards, including UNI
3.0/3.1, and 4.0 signaling and
LAN Emulation (LANE) 1.0
and 2.0 for interoperability in
ATM environments.
SuperStack II Switch Layer 3 module
SuperStack II Switch 1100/3300 ATM
Expansion module
Page 15

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
15
The SuperStack II Switch 3800 offers
affordable leading-edge Layer 3
switching technology for 10 times the
performance of intranets. Wire-speed
Layer 3 switching (IP routing) and
Layer 2 switching are embedded in
ASICs to forward at nonblocking
speed any-to-any intranet traffic while
broadcast/multicast traffic and fault
propagation are kept under control
in appropriate subnetworks.
The SuperStack II Switch 3800
not only aggregates the traffic from
Ethernet and Fast Ethernet workgroups
to a server farm or a corporate backbone
through an optional Gigabit Ethernet
high-speed link, but it removes router
bottlenecks that occur in corporate
networks when high-speed, any-to-any
intranet traffic chokes software-based
legacy routers.
Key features include:
■ 24 10/100 Mbps Ethernet/Fast
Ethernet autosensing ports
■ One Gigabit port (1000BASE-SX)
enabled by an optional SuperStack II
Switch 3800 GBIC (gigabit interface
connector). A second GBIC can be
plugged in to provide additional
physical resilience.
■ Full line-rate nonblocking routing
performance on all ports (over
5 million IP packets per second and
8.7 Gbps throughput)
■ Support for standards-based routing
protocols: RIP/RIP v2
■ Support for up to 12,000 MAC
addresses for handling networks of
virtually any size
■ Elastic port buffering to enable
on-the-fly allocation of memory for
automatic performance optimization
based on network traffic
SuperStack II Switch 3800
10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet Layer 3 Switching
SuperStack II Switch 3800
Front view
24 x 10/100BASE-TX/RJ-45 ports
Physically redundant 1000BASE-SX ports
■ IEEE 802.3x flow control on all full-
duplex ports to improve performance
and minimize packet losses
■ Full VLAN implementation:
– Port and tagged VLANs (802.1Q)
– Protocol-based VLANs to allocate
bandwidth and enforce management policies among different
protocols (e.g., IP, IPX, NetBIOS,
DECnet)
■ User-definable packet filters to
control traffic flows
■ Support for spanning tree per VLAN
■ Class of Service embedded in
ASIC—PACE technology, 802.1D
(incorporating 802.1p)
■ RMON support for four groups
■ Simplicity and scalability of
10/100/1000 Ethernet in the
industry-leading SuperStack II
system architecture
Subnet 4
Subnet 5
Subnet 7
Subnet 6
D
edicated 100 M
bps to pow
er users
Floor 1
SuperStack II
Dual Speed Hub
500 with UPS
Mixed 100 Mbps and 10 Mbps users
with existing segmented 10 Mbps network
Mixed 100 Mbps
and 10 Mbps users
Local server on 100 Mbps
Mixed stack of SuperStack II Dual Speed
Hub 500, SuperStack II PS Hub 40/50
with optional cascade converter, and
SuperStack II Switch 3300
100 Mbps
Trunk
Printer on
10 Mbps
Floor 3
Floor 2
PCs
SuperStack
®
II Switch 1100
Dedicated 10 Mbps
to power user
SuperStack II Hub
1000 SX
SuperStack II Switch
3800 (Layer 3 Sw
itch)
B
asem
ent
W
AN
Legacy router
Gigabit Ethernet
(1000 M
bps) server farm
S
ubnet 1
Subnet 2
Subnet 3
Transcend
®
network
management console
100 Mbps
1000 Mbps
10 Mbps
For a dramatic performance boost in corporate routed networks, the SuperStack II Switch 3800 delivers wire-speed IP
routing embedded in ASIC technology through 10/100/1000 Mbps Layer 3 switching.
It offloads the routing of intranet traffic from slow legacy routers while keeping under control broadcast/multicast traffic
and fault propagation in appropriate subnetworks.
Page 16

16
The SuperStack II Switch 3900 and
the SuperStack II Switch 9300 (Gigabit
Ethernet switch) constitute an industryleading solution for high-density 10/100
Ethernet to Gigabit Ethernet switching.
SuperStack II Switch 3900
The SuperStack II Switch 3900
delivers full line-rate performance
(over 9.8 million pps of switching
performance) for up to 36 10/100 Mbps
ports and from one to three 1000 Mbps
ports. Multiple Gigabit Ethernet
uplinks can be trunked together
to deliver an uplink with 3 Gbps
of bandwidth.
The SuperStack II Switch 3900
is available in two versions: a
24- and 36-port 10/100 Ethernet/
Fast Ethernet switch. Both have one
integral 1000BASE-SX port and two
Gigabit Ethernet expansion slots. The
rear-mounted expansion slots accept
optional Gigabit Ethernet modules
available for either 1000BASE-SX or
1000BASE-LX both via SC connectors.
The 1000BASE-SX option supports
multimode fiber links, while the
1000BASE-LX option supports singlemode fiber. The 1000BASE-LX option
supports multimode fiber when used
in conjunction with a conditioned
launch cable.
Key features include:
■ Supports up to 16,000 MAC
addresses
■ Multicast filtering using IGMP
snooping
■ Multicast throttling limits broadcasts
and multicasts on a per-port basis
■ Support for IEEE 802.3x flow
control on all full-duplex ports
■ Roving Analysis Port (RAP) for
copying data from any port to another
port with a network analyzer attached
■ RMON support for four groups
■ Fully standards-based 802.1Q
VLANs, including GVRP support
for automatic VLAN configuration
distribution
■ IEEE 802.1D (incorporating
802.1p) Class of Service support and
dual priority queuing
SuperStack II
Switch 3900
SuperStack II
Switch 3900
SuperStack II
Switch 3900
SuperStack II
Switch 3900
Gigabit
Ethernet
uplinks
SuperStack II Switch 3900 and SuperStack II Switch 9300 10/100 Mbps
to 1000 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Switching
SuperStack II Switch 3900
3C39024
24 switched 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX RJ-45 ports
Slot for optional
Gigabit Ethernet
modules
Advanced
Redundant
Power System
connection
Built-in
1000BASE-SX
Gigabit Ethernet
port
Console
port
(management)
AC
connection
Back view
Front view of 24 port
Four SuperStack II Switch 3900s equipped
with additional Gigabit Ethernet expansion
modules can be grouped yielding a configuration of 144 10/100 Ethernet ports with
six Gigabit Ethernet uplinks.
• Interconnect four units with dedicated
Gigabit Ethernet links.
• Two additional Gigabit Ethernet option
slots per switch yield six additional
Gigabit Ethernet ports for uplinks or
additional bandwidth.
Front view of 36 port
3C39036
36 switched 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX RJ-45 ports
■ Web browser interface for manage-
ment and configuration functions
■ Full line-rate nonblocking switching
performance (6.6 Gbps throughput
and over 9.8 million pps frame
processing)
■ Support for multiple Gigabit Ethernet
uplinks
■ Support for trunking (multiple
parallel active links) on both Fast
Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet ports
(up to six ports per trunk group and
four trunks per unit)
■ Resilient links
■ Full-duplex support on all Gigabit
and Fast Ethernet ports
■ All Fast Ethernet ports support 10/100
and full-/half-duplex operation with
autonegotiation (IEEE 802.3x)
Page 17

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
17
SuperStack II Switch 9300
The SuperStack II Switch 9300 enables
practical, cost-effective, and highperformance deployment of Gigabit
Ethernet as an effective interswitch,
switch-to-server, and general purpose
backbone technology. As the highest density Gigabit Ethernet (1000/1000 Mbps)
switch available in a SuperStack II
package, the SuperStack II Switch 9300
delivers full line-rate switching between
its 12 Gigabit Ethernet ports to support
17.85 million pps forwarding rate and
12 Gbps full-duplex throughput. Multiple Gigabit Ethernet ports can
be trunked together to deliver up to
6 Gbps interswitch link. Full line-rate
Gigabit Ethernet switching is supported
on all ports via 25.6 Gbps switching
fabric.
The SuperStack II Switch 9300 is
available in three versions: a fixed
12-port fiber optic (12 x 1000BASE-SX)
Gigabit Ethernet switch; a fixed 12-port
fiber optic (10 x 1000BASE-SX and 2 x
1000BASE-LX) Gigabit Ethernet switch;
and a fixed 12-port fiber optic (12 x
1000BASE-LX) Gigabit Ethernet switch.
With the SuperStack II Switch 9300,
you can interconnect high densities of
Fast Ethernet switches that are attached
to either dedicated desktops or shared
segments and high-bandwidth network
resources, such as servers.
Key features include:
■ Supports up to 16,000 MAC
addresses
■ Multicast filtering using IGMP
snooping
■ Multicast throttling limits broadcasts
and multicasts on a per-port basis
■ Support for IEEE 802.3x flow
control on all full-duplex ports
■ Roving Analysis Port (RAP) for
copying data from any port to another
port with a network analyzer attached
■ RMON support for four groups
■ Fully standards-based 802.1Q
VLANs, including GVRP support
for automatic VLAN configuration
distribution
■ IEEE 802.1D (incorporating 802.1p)
Class of Service support and dual pri-
ority queuing
■ Web browser interface for manage-
ment and configuration functions
■ Resilient links
SuperStack II Switch 9300
9 x 1000BASE-SX Gigabit Ethernet ports
Console
port (management)
10BASE-T
Out-of-band management port
1 x 1000BASE-SX
port
2 x 1000BASE-LX
Gigabit Ethernet
ports
AC
connection
Advanced Redundant Power
System connection
Front view of 9300SX/LX
Back view
Front view of 9300 SX
Console
port (management)
10BASE-T
Out-of-band management port
12 x 1000BASE-SX Gigabit Ethernet ports
■ Full line-rate nonblocking switching
performance (12 Gbps throughput and
over 17.8 million pps frame processing)
■ Support for trunking (multiple parallel
active links) on Gigabit Ethernet ports
(up to six ports per trunk group and
four trunks per box)
■ Full-duplex support on all Gigabit
Ethernet ports
Front view of 9300 LX
Console
port (management)
10BASE-T
Out-of-band management port
12 x 1000BASE-LX Gigabit Ethernet ports
Page 18

18
Front view
SuperStack II Switch 9000
SuperStack II Switch 9000
(Layer 3 switch)
SuperStack II Switch 3800
(Layer 3 Switch)
Floor 2
Basement
Floor 1
Floor 3
Subnet 1
Subnet 2
Subnet 3
Subnet 4
Subnet 5
Subnet 6
WAN
Subnet 7
Subnet 8
PCs
SuperStack
®
II Switch 1100 with
Gigabit Ethernet module
Dedicated 10 Mbps
to power user
Dedicated 10 Mbps
and 100 Mbps
Ethernet
100 Mbps
Gigabit
Ethernet
1000
Mbps
1000
Mbps
100 Mbps power users
SuperStack II Switch 3800 (Layer 3 switch)
SuperStack II Switch 3300
with Gigabit Ethernet module
and SuperStack II Switch 3900
Legacy router
Gigabit Ethernet (1000
Mbps) server farm
100 Mbps
1000 Mbps
10 Mbps
Transcend
®
network
management console
For dramatic performance boost in corporate routed networks, the SuperStack II
Switch 9000 delivers wire-speed IP routing
embedded in ASIC technology in addition to
Gigabit Ethernet switching.
It offloads the routing of intranet traffic from
slow legacy routers while keeping under
control broadcast/multicast traffic and fault
propagation in appropriate subnetworks.
The SuperStack II Switch 9000 offers
affordable leading-edge Layer 3
switching technology for 10 times the
performance of intranets. Wire-speed
Layer 3 switching (IP routing) and
Layer 2 switching are embedded in
ASICs to forward at nonblocking speed
any-to-any intranet traffic while broadcast/multicast traffic and fault
propagation are kept under control in
appropriate subnetworks.
The SuperStack II Switch 9000 not
only aggregates at Gigabit speed the
traffic from Ethernet and Fast Ethernet
workgroups, but it removes router
bottlenecks that occur in corporate
networks when high-speed, any-to-any
intranet traffic chokes software-based
legacy routers.
Key features include:
■ Full line-rate nonblocking routing
performance on all ports (over
11.9 million IP packets per second
and 17.7 Gbps throughput)
■ Support for standards-based routing
protocols: RIP/RIP v2
■ Eight 1000BASE-SX Gigabit ports
■ Support for up to 12,000 MAC
addresses for handling networks of
virtually any size
■ Elastic port buffering to enable on-
the-fly allocation of memory for
automatic performance optimization
based on network traffic
SuperStack II Switch 9000
Gigabit Ethernet Layer 3 Switching
■ IEEE 802.3x flow control on all full-
duplex ports to improve performance
and minimize packet losses
■ Full VLAN implementation:
– Port and tagged VLANs (802.1Q)
– Protocol-based VLANs to allocate
bandwidth and enforce management policies among different
protocols (e.g., IP, IPX, NetBIOS,
DECnet)
■ User-definable packet filters to control
traffic flows
■ Support for spanning tree per VLAN
■ Class of Service embedded in ASIC
PACE technology, 802.1D
(incorporating 802.1p)
■ RMON support for four groups
■ Simplicity and scalability of
10/100/1000 Ethernet in the
industry-leading SuperStack II
system architecture
8 x 1000BASE-SX ports
Page 19

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
19
SuperStack II Switch 9100
The SuperStack II Switch 9100 enables
practical, cost-effective, and high-performance deployment of copper Gigabit
Ethernet as an effective interswitch,
switch-to-server, and general-purpose
backbone technology.
Key features include:
■ Supports up to 128,000 MAC
addresses for handling networks of
virtually any size
■ Multicast filtering using IGMP
snooping
■ Port mirroring for copying data from
any port to another port with a network analyzer attached
■ RMON support for four groups
■ IEEE 802.1D (incorporating 802.1p)
Class of Service support and dual priority queuing
■ Web browser interface for manage-
ment and configuration functions
■ Full line-rate nonblocking switching
performance
■ Support for trunking (multiple par-
allel active links) on Gigabit Ethernet
ports (up to four ports per trunk
group)
■ Class of Service embedded in ASIC:
PACE technology and 802.1D
(incorporating 802.1p)
■ Policy-based Quality of Service prior-
itization and allocation for traffic
groups defined by topology or group
of users, individual address, and
physical path
SuperStack II Switch 3300
Local server
Switched Fast Ethernet
high-speed users
Switched
10 Mbps
Volume intranet
user
SuperStack
®
II system with
SuperStack II Switch 3300
SuperStack II Switch 9100
PC running multimedia
videoconferencing
Copper
Gigabit
Ethernet
Basement
Floor 1
Floor 2
Copper
Gigabit
Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
(1000 Mbps)
server farm
Switched Fast
Ethernet
Existing desktop
Local server using
100 Mbps
Servers using
100 Mbps
SuperStack II Switch 3300
and SuperStack II Switch 1100
and UPS
0
5
1
0
1
5
2
0
2
5
3
0
100 Mbps
1000 Mbps
10 Mbps
Transcend
®
network
management console
Console
port (management)
AC connectors
Front view
■ Simplicity and scalability of
100/1000 Ethernet in the industryleading SuperStack II system
architecture
■ IEEE 802.3x flow control on all full-
duplex ports to improve performance
and minimize packet loss
■ Full VLAN implementation:
– Port and tagged VLANs (802.1Q)
– Protocol-based VLANs to allocate
bandwidth and enforce management policies among different
protocols (e.g., IP, IPX, NetBIOS,
DECnet)
Back view
SuperStack II Switch 9100
6 x 100/1000BASE-T ports 2 x 1000BASE-SX ports
(MTRS connectors)
Page 20

20
SuperStack II Switch 2700
The SuperStack II Switch 2700 is a
12-port integrated Ethernet workgroup
switch with the added advantage of an
ATM port for high-speed backbone or
server connections. The switch is ideal
for workgroups that need increased
bandwidth across Ethernet ports
and also require a high-speed ATM
downlink to an ATM campus backbone
now or in the future. SuperStack II
Switch 2700 future proofs your
network with built-in ATM link
capability, making ATM migration
simple and economical. Ethernet
switching operates even if the ATM port
is not configured, allowing you to
implement Ethernet LAN switching
now and connect the LAN to an ATM
backbone later. You get advanced cellbased switching without having to make
changes in existing LAN devices, which
protects your current network
investment. The ATM port
SuperStack II Switch 2700
Back view
Front view
accommodates an OC-3c multimode
155 Mbps SONET/SDH interface for
local and collapsed backbone ATM
connections, or a DS-3 45 Mbps
interface for wide-area links. Singlemode ATM offers support over long-
haul distances greater than 2 kilometers.
Two software-selectable options for
Ethernet switching—cut-through and
store-and-forward modes—offer more
flexibility for network design.
Ethernet-to-ATM Switching
SuperStack II Switch 2200
The SuperStack II Switch 2200 is a
full-featured Ethernet/FDDI switch
that employs state-of-the-art RISC
and ASIC-based technology for highend workgroup performance and
server/backbone connectivity. The
SuperStack II Switch 2200 is the
price/performance leader in its class.
It provides 16 switched 10BASE-T
Ethernet ports and one high-speed
FDDI port for server or backbone
links. The FDDI port can be configured with DAS, allowing you to set up
a resilient LAN. Advanced switching
features include virtual workgroups for
flexible management, user-defined
packet filters to control traffic flow, IP
fragmentation for optimizing Ethernet/
FDDI transfers, and IEEE 802.1D
bridging for optimizing switching in
various LAN environments.
Elastic packet buffering guarantees a
maximum number of buffers for each
port, dynamically allocating additional
buffers as needed to alleviate port
congestion and minimize dropped
packets during high-traffic periods.
Roving Analysis Port (RAP) allows you
to monitor traffic on any Ethernet
port.
Ethernet to FDDI Switching
Back view
SuperStack II Switch 2200
Front view
Console port
FDDI port (DAS/SAS) 16 switched 10BASE-T/RJ-45 ports
AC connection Advanced Redundant Power
System connection
RESET
NMI
INSERTED
ATM port
OC-3c multimodule
AC connection
12 switched 10BASE-T/RJ-45 ports
Advanced Redundant Power System connection
Console port
Page 21

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
21
Network Management
3Com offers a variety of network management applications matched to the
scale and requirements of your network.
3Com Transcend network management
applications are designed to simplify
network management, increasing your
network’s efficiency and increasing your
staff’s productivity. All Transcend applications provide optimal management of
your SuperStack II devices. Which
application you choose will depend on
the size of your network and your
requirements for network management.
Small Enterprise/Small-Business
Solution
3Com provides two options for managing small networks (up to 500 users):
Transcend Network Supervisor and
Transcend WorkGroup Manager for
Windows NT.
Transcend Network Supervisor provides easy-to-use, yet powerful network
monitoring tuned to the needs of small
enterprises and small businesses. Less
experienced network managers will find
the automated operations and intelligent defaults helpful, while more
experienced users will enjoy using the
advanced features. An intuitive user
interface focuses on the tasks and information all managers need to monitor
their network. A discovery wizard finds
IP devices and links. Then, the structure
is automatically mapped to provide a
graphical display of the network.
Working from the map, you can quickly
monitor network stress levels, set thresholds and alerts, view network events,
generate reports, and launch device configuration tools.
Transcend WorkGroup Manager is
designed for similarly sized networks
and provides additional management
capabilities. WorkGroup Manager supports a broader set of 3Com devices,
features agent administration capabilities, and has full integration with
vendor-independent HP OpenView
for Windows.
Medium Enterprise Solution
Recommended for medium networks
(up to 2,500 users), Transcend Enterprise Manager for Windows NT
provides more robust management for
3Com’s full suite of switches, hubs, and
routers in a single application. Colorcoded device icons, audible alarms, and
connectivity testing bring simplicity to
managing your network. Advanced configuration capabilities let you configure
the same parameters across multiple
devices with a single action and quickly
and efficiently distribute new device
agents across the network. A turnkey
management solution, Enterprise Manager includes HP OpenView for
Windows. Other core management
capabilities of Transcend Enterprise
Manager for Windows NT include:
■ Monitoring, analyzing, and trou-
bleshooting using class-leading
RMON management tools, including
packet capture and filter
■ Automatically discovering and con-
figuring network devices
■ Managing stackable products as one
SuperStack II system rather than a
number of separate devices
■ Graphical statistics that help spot
potential problems before they occur
■ Preventing unauthorized access with
user passwords and access levels
■ Receiving automatic notification of a
fault in a SuperStack II ARPS or UPS
Sophisticated Medium and Large
Enterprise Solution
For management of sophisticated
medium and large enterprises, 3Com
offers Transcend Network Control Services. Available for both UNIX and
Windows NT environments, Transcend
Network Control Services delivers a
superset of the functionality of Transcend Enterprise Manager, adding
advanced management capabilities,
such as:
■ Control and configuration of ATM
and VLAN networks, including use
of sophisticated policy-based VLAN
services
■ Flexible Web-based network
management, featuring monitoring,
reporting, and configuring
capabilities
■ Advanced status polling
■ Monitoring, analyzing, and trouble-
shooting using class-leading RMON
management tools, including packet
capture and filter
3Com also offers solutions for policybased management, application flow
monitoring, and service level management that will help you optimize your
e-business and converged applications.
For more information, visit
www.3com.com/transcend.
Transcend Network Supervisor
provides easy-to-use, yet
powerful network monitoring.
Page 22

22
SuperStack II 10/100 SuperStack II SuperStack II SuperStack II SuperStack II SuperStack II
Product name Baseline Switch Switch 610 Switch 2200 Switch 2700 Switch 1100 Switch 3300/33
Switching technology N/A 10/100 Mbps Ethernet/ Ethernet/FDDI/ Ethernet/ATM/ 10/100 Mbps Ethernet/ 10/100 Mbps Et
Fast Ethernet Fast Ethernet ATM/Gigabit Ethernet Fast Ethernet/ATM/ Fast Ethernet/AT
Gigabit Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet
Ethernet ports 24 x 10/100BASE-TX 24 x 10BASE-T 16 x 10BASE-T 12 x 10BASE-T 24 x 10BASE-T 12 x 10/100BAS
(RJ-45 connectors) 12 x 10BASE-T 24 x 10/100BAS
Optional 10 Mbps N/A No No No Yes No
Transceiver Interface
Module
10/100 Mbps Ethernet/ N/A 2 x 10/100BASE-TX N/A N/A 2 x 10/100BASE-TX 24 x 10/100BAS
Fast Ethernet ports 12 x 10/100BASE-TX 2 x 10/100BASE
FDDI connectivity N/A N/A One FDDI (DAS with N/A N/A N/A
two fiber MICs)
5
ATM connectivity N/A N/A N/A One ATM (155 Mbps ATM OC-12c
2
ATM OC-12c
2
OC-3c multimode/ ATM OC-3c ATM OC-3c
single-mode 11 dB SC
connector) one and
DS-3 45 MB
Gigabit Ethernet N/A N/A N/A N/A 1 x 1000BASE-SX 1 x 1000BASE-S
optional per unit optional per uni
Optional extra N/A N/A N/A N/A 100BASE-FX 100BASE-FX
high-speed links 1000BASE-SX 1000BASE-SX
ATM OC-12c
2
ATM OC-12c
2
multimode multimode
Layer 3 switching N/A N/A N/A N/A Optional Layer 3 Optional Layer 3
support module
2
module
2
(RIP, OSPF, DVMRP) (RIP, OS PF, DVM
Forwarding method
4
S&F CT/S&F/Intelligent S&F CT/S&F
6
CT/S&F/Intelligent S&F
Number of MAC 4,000 6,000 8,192 8,192 6,000 12,000
addresses
RMON support N/A Groups 1-6, 9 Roving Analysis Six groups Groups 1-6, 9 Groups 1-6, 9
Port (four groups)
Switching engine N/A BRASICA 2 ISE ZipChip
™
BRASICA 2 BRASICA 2
Height 4.4 cm/1.7 in 4.4 cm/1.7 in 6.4 cm/2 1/2 in 4.4 cm/1 3/4 in 7 cm/2 3/4 in 7 cm/2 3/4 in
Width 44 cm/12 1/4 in 44 cm/17 1/4 in 44 cm/17 1/4 in 44 cm/17 1/4 in 44 cm/17 1/4 in 44 cm/17 1/4 in
Depth 23.5 cm/9 1/4 in 22.4 cm/8 3/5 in 36.8 cm/14 1/2 in 27.5 cm/11 in 30 cm/12 in/ 30 cm/12 in
Weight 2.6 kg/5 4/5 in 4.4 kg/9 2/3 lb 4.5 kg/10 lb 2.5 kg/5 1/2 lb 4.4 kg/9 2/3 lb 4.4 kg/9 2/3 lb
Performance
Aggregate bandwidth Full wire speed Full wire speed Full wire speed Full wire speed Full wire speed Full wire speed
Forwarding rate 1,330,000 pps 1,200,000 pps 193,440 pps 90,000 pps 1,200,000 pps 1,330,000 pps
(packets per second)
Ethernet latency N/A 7 µs (S&F) 30 µs Ethernet to ATM 7 µs (S&F) N/A
35 (CT) 8 µs (S&F) 35 µs (CT)
54 µs (CT)
High-speed N/A 8 µs (S&F) 10/25 µs
3
(S&F) 130 µs (CT) 8 µs (S&F) 8 µs (S&F)
port latency estimated
Packet buffering 32 K static RX per 8 K static RX per 1 MB total 192 KB 8 K static RX per 32 K static RX pe
10/100 Mbps port 10 Mbps port per port per port 10 Mbps port 10/100 Mbps po
12 port: 1600 K 32 K static RX per 32 K static RX per 12 port: 1600 K
dynamic TX shared 10/100 Mbps port 10/100 Mbps port dynamic TX shar
24 port: 2752 K 1216 K dynamic TX 12 port: 800 K 24 port: 2752 K
dynamic TX shared shared across ports dynamic TX shared dynamic TX shar
24 port: 1216 K
dynamic TX shared
Part number 3C16465A-24 port 3C16954 3C220000A 3C32700A
1
3C16950-24 port 3C16980-24 por
3C16464A-12 port 3C16951-12 port 3C16981-12 por
3C16985-24 por
SuperStack II Switches at a Glance
Stackable, versatile switches—ideal solutions for workgroup management and performance
1
See Ordering Information on page 28.
2
Available Q1CY00.
3
Nontranslational/translational
4
CT = Cut-through, S&F = Store and Forward, ISM = intelligent switching mode
5
Each port is also usable as a SAS connection.
6
See page 26 for a full list of connectors.
Page 23

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
23
SuperStack II SuperStack II SuperStack II SuperStack II SuperStack II SuperStack II
No No No No No No
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
ATM OC-12c
2
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
ATM OC-3c
t optional per unit GBIC ports plus 2 option slots ports plus 2 1000BASE-SX ports or 10 1000BASE-
(MTRS connectors) SX+2 1000BASE-LX
100BASE-FX 2 optional/redundant 1000BASE-SX & N/A N/A N/A
1000BASE-SX GBIC ports 1000BASE-LX
ATM OC-12c
2
for option slots
multimode
module
2
S&F S&F S&F S&F S&F S&F
12,000 12,000 16,000 12,000 128,000 16,000
Groups 1-6, 9 Four groups 1-3, 9 Groups 1-3, 9 Four groups 1-3, 9 Four groups 1-3, 9 Groups 1-3, 9
BRASICA 2 Shared memory SAGE Shared memory Shared memory SAGE
7 cm/2 3/4 in 8.8 cm/3 1/2 in 6.6 cm/2 3/5 in 8.8 cm/3 1/2 in 8.8 cm/3 1/2 in 6.6 cm/2 3/5 in
30 cm/12 in 44.5 cm/17 1/2 in 30 cm/12 in 44.5 cm/17 1/2 in 44.5 cm/17 1/2 in 30 cm/12 in
4.4 kg/9 2/3 lb 10 kg/22.3 lb 4.5 kg/12 lb 10 kg/22.3 lb 10 kg/22.3 lb 4.5 kg/12 lb
Full wire speed Full wire speed Full wire speed Full wire speed Full wire speed Full wire speed
1,330,000 pps 5,059,000 pps 9,800,000 pps 11,904,000 pps 11,904,000 pps 17,850,000 pps
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
35 µs (S&F)
8 µs (S&F) 3 µs (S&F) 8 µs (S&F) 3 µs (S&F) 3 µs (S&F) 8 µs (S&F)
estimated 40 µs (CT)
1152 K dynamic TX priority + 64 KB/ high priority; GE: 512 KB/ priority + 64 KB/ priority + 64 KB/ 128 KB/port
port high priority
3C93010-12 LX ports
Page 24

SuperStack II Switches
Switch
1100/
Switch Switch Switch 3300/ Switch Switch Switch Switch Switch Switch
610 2200 2700 3300 XM 3300 FX 3800 3900 9000 9100 9300
Statistics: Total LAN statistics ●●●●●●●●●●
History: Time-based statistics
●● ●●●●●●●
for trend analysis
Alarms: Thresholding ●●●●●●●●●●
Hosts: Statistics by MAC
address
●●●●
HostTopN: Ranked statistics
●●●
by MAC address
Matrix: Traffic matrix showing
●●●
who’s talking to whom
Filter: Packet-selection
mechanism
†
●
Packet Capture: Packet
●
capture against filter
Events: Reporting mechanism ●●●●●●●●●●
24
At-a-Glance
RMON Support
Specifications
SuperStack II High-Performance Stackable Switches
Indicator Chart
Baseline Switch Switch 610 Switch 2200 Switch 2700 Switch 1100/3300,
Switch 3300 XM, and
Switch 3300 FX
Per port status; Per port status; Per port status; Per port status;
Ethernet Port Indicators packet activity packet activity Link, status error packet activity packet activity
FDDI: ATM: Link status,
Non-Ethernet Port Indicators Ring error fail, activity
Transceiver interface module
fitted (1100 only);
Transceiver, Power, fail, High-speed module
Unit Status Indicators Power Power Power activity (Not XM) fitted, power, fault
Page 25

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
25
Switch 3800 Switch 3900 Switch 9000 Switch 9100 Switch 9300
Per port LED Per port LED Per port LED Gigabit ports:
indicators, link Per port status; indicators, link indicators, link Per port status;
status, activity packet activity status, activity status packet activity
Expansion gigabit:
Activity Per port status; packet activity
Power and Power and Power and
management status Power, fault management status management status Power, fault
Autosensing
10/100 Mbps Ethernet/
Fast Ethernet ports
Gigabit Ethernet
ATM
10 Mbps Ethernet ports
100 Mbps
Fast Ethernet only
FDDI
Technology Supported for
SuperStack II Switches
Layer 3 switching
SuperStack II Baseline 10/100 Switch ●●
SuperStack II Switch 610 ●●
SuperStack II Switch 2200 ●●
SuperStack II Switch 2700 ●
SuperStack II Switch 1100 ●●● ● ●
SuperStack II Switch 3300 ●●● ●
SuperStack II Switch 3300 XM ●
SuperStack II Switch 3300 FX ●● ● ●
SuperStack II Switch 3800 ●● ●
SuperStack II Switch 3900 ●●
SuperStack II Switch 9000 ●●
SuperStack II Switch 9100 ●
SuperStack II Switch 9300 ●
Page 26

26
SuperStack II Baseline
10/100 Switch
Standards Compliance
Functional
ISO 8802/3;
IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet);
IEEE 802.3u (Fast Ethernet);
IEEE 802.3x (Flow Control)
Media Interfaces: 12/24
shielded RJ-45 TP; ARPS
connector (Type 2)
Electromagnetic
EN 55022 Class B* and Class A;
FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class A:
ICES-003 Class A; VCCI Class B*
and Class A; AS/NZS 3548
Class B* and Class A; EN 50082-1
Safety
IEC 950; UL 1950;
CSA 22.2 No. 950; EN 60950
SuperStack II Switch 610
Management
The Switch 610 can be managed
locally with a Command Line Interface by connecting a terminal to
the serial port or via Telnet, or
graphically using the resident Web
interface or with Transcend network management.
MIBs supported: Bridge MIB (RFC
1493), BootP (RFC 951).
Plus additional SuperStack II MIBs
for security and resilience.
Standards Compliance
Functional
ISO 8802/3, IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet),
IEEE 802.3u (Fast Ethernet),
IEEE 802.3x (Flow Control), IEEE
802.1D (Bridging) Safety: UL 1950
2nd Edition, EN 60950:1992/
A3:1995 plus ZB/ZC Deviations,
CSA 22.2#950, ECMA 97, TUV GS
Mark will be applied for Mexican
NOM and Russian GOST safety
approval.
Electromagnetic
EN 55022 Class B, FCC part 15
Class A, CSA C108.8-M1983 (A),
VCCI Class 2, EN 50082-1 (IEC 801
Parts 2-4), EN 61000 -3 - 2,
EN 61000 -4 - 5, ENV 50140,
ENV 50141, Russian GOST EMC
approval (Will be obtained after
initial release.) Environmental:
Shock and Vibration: EN 60068
(IEC 68) Protocols: SNMP (RFC
1157), ARP (RFC 826), IP (RFC 791),
ICMP (RFC 792), UDP (RFC 768),
TCP (RFC 793), TFTP (RFC 783)
SuperStack II Switch 2200
Standards Compliance
Electromagnetic
FCC Part 15,
Class A; CISPR22 Class A
Specifications
SuperStack II Switches
Safety
UL 1950; EN 60950;
CSA 22.2 No. 950; TUV
Protocols
SNMP
SNMP protocol (RFC 1157), MIB II
(RFC 1213), SNMP/FDDI MIB (RFC
1512), Ethernet MIB (RFC 1398),
Bridge MIB (RFC 1463)
RFC 1157 SN MP, RFC 1212
Concise, RFC 1212 Traps,
RFC 1213 MIB II
Others
RFC 783 TFTP, VT100
terminal interface protocol
SuperStack II Switch 2700
Standards Compliance
Electromagnetic
EN 55022; FCC Part 15, Class A;
VDE 0871 Part 2; CISPR22
Safety
EN 60950, UL 1950,
CSA 22.2, TUV
Protocols
RFC 826 ARP, RFC 791 IP, RFC 792
ICMP, RFC 768 U DP, RFC 793 TCP.
RFC 1157 SN MP, RFC 1212 Concise, RFC 1213 MIB II, RFC 1212
Traps
Others
VT100 terminal interface protocol
The SuperStack II Switch
Gigabit Ethernet Modules
Management
In-band management over
Ethernet/Fast Ethernet
Supports SNMP and 3Com
Transcend network management
applications.
MIBs supported on Gigabit
Ethernet module: IETF 802.3 1757,
interfaces evolution MIB RFC 1573,
Bridge MIB RFC 1493
Protocols supported on Gigabit
Ethernet module: SNMP RFC 1157,
ARP RFC 826, IP RFC 791, ICMP RFC
792, UDP RFC 768, TCP RFC 793,
TFTP RFC 783, IPX, BootP, Telnet,
and options RFC 854-859
Local management via RS 232 (DB9 port) on SuperStack II Switch
1000/Switch 3000/Desktop Switch
SuperStack II Switch 1100,
SuperStack II Switch 3300,
SuperStack II Switch 3300
XM, and SuperStack II
Switch 3300 FX
Management
All switches support SNMP and
3Com Transcend network
management applications
The Switch 1100, 3300, and 3300
FX can be managed with a Command Line Interface by connecting
a terminal to the serial port or via
Telnet, or graphically using the
resident Web interface.
MIBs supported: New MAU MIB
(RFC 2239), RMON II Probe Config
(RFC 2021), RMON (RFC 1757), RS
232 MIB (RFC 1659), IfStack Table
(RFC 1573), Bridge MIB (RFC
1493), SNMP MIB II (RFC 1213)
Plus additional SuperStack II MIBs
for stacking, security, and
resilience.
Standards Compliance
Functional
ISO 8802/3, IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet),
IEEE 802.3u (Fast Ethernet), IEEE
802.3x (Flow Control), IEEE 802.1D
(incorporating 802.1p), IEEE
802.1Q (Bridging) Safety: UL 1950
2nd Edition, EN 60950:1992/
A3:1995 plus ZB/ZC Deviations,
CSA 22.2#950, ECMA 97, TUV GS
Mark will be applied for Mexican
NOM and Russian GOST safety
approval.
Electromagnetic
EN 55022 Class B, FCC part 15
Class A, CSA C108.8-M1983 (A),
VCCI Class 2, EN 50082-1 (IEC 801
Parts 2-4), EN 61000 -3 - 2, EN
61000 -4 - 5, ENV 50140, ENV
50141, Russian GOST EMC
approval (Will be obtained after initial release.) Environmental: Shock
and Vibration: EN 60068 (IEC 68)
Protocols: SNMP (RFC 1157), ARP
(RFC 826), IP (RFC 791), ICMP
(RFC 792), IGMP (RFC 1112), UDP
(RFC 768), TCP (RFC 793), TFTP
(RFC 783)
SuperStack II Switch Gigabit
Ethernet Modules
Provides support for SuperStack II
Switch 1100, SuperStack II Switch
3300, and SuperStack II Switch
3300 FX.
General
1000BASE-SX
1 single 850 nm fiber optic port
with SC-duplex connectors fullduplex mode
1000BASE-LX
1 single 1300 nm fiber optic port
with SC-duplex connectors fullduplex mode
1000BASE-T
1 single RJ-45 port with 100/1000
autosensing full-duplex mode
Standards Compliance
Functional
ISO 8802/3, IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet), IEEE 802.3x (Flow
Control), IEEE 802.3z (Gigabit
Ethernet), IEEE 802.1Q (VLAN
Tagging), priority bits as per IEEE
802.1p
Electromagnetic
ICES-003 Class A, FCC part 15
Class A, EN 55022 Class B, VCCI
Class 2, AS/NZS 3548 Class B,
CISPR Class B, CNS 13438
Class A, Korean EMC approval;
EN 61000-4-2, EN 61000-4-3,
EN 61000-4-4, EN 61000-4-5, EN
61000-4-6, EN 61000-4-11,
ENV 50204
Safety
UL 1950 3rd Edition, Listed, UL
listed to CSA 22.2 No. 950, TUV GS
to EN 60825-1 and EN
60950:1992/A3:1995 plus ZB/ZC
deviations, IEC 950 Edition 2
Amendment 4 + ALL national deviations; CB Certificate & Report to be
supplied; EN 60825 -1: Class 1
Laser safety
SuperStack II Switch 3800
and Switch 9000
Management
MIBs supported: SNMP MIB II (RFC
1213), Remote Monitoring MIB
(RFC 1571), Bridge MIB (RFC 1493,
Evolution of the interface MIB
(RFC 1573)
Standards Compliance
Electromagnetic
Switch 3800 EN 55022 Class A;
Switch 9000 EN 55022 Class B;
FCC Part 15 Class A, CSA C108.8M1983 (A), VCCI Class 2 EN
50082-1 (IEC801 Parts 2-4),
EN 61000-3-2, EN 61000-4 -3, EN
61000-4 - 5, EN 61000-4 -6, EN
61000-4–11
Safety
UL 1950, EN 60825-1, CSA 22.2
No. 950, Russian GOST and
EN 60950; 1992/A3: 1995 plus
ZB/ZC Deviations.
Protocols
SNMP (RFC 1157), ARP (RFC 826),
IP (RFC 791), ICMP (RFC 792), UDP
(RFC 768), TCP (RFC 793), TFTP
(RFC 783), Telnet (RFC 854), BootP
(RFC 951).
Management Information Bases
(MIBs)
MIB II RFC 1213, Remote Monitoring MIB RFC 1571, Bridge MIB,
RFC 1493, Evolution of the interface MIB RFC 1573
SuperStack II Switch 3900
Standards Compliance
Functional
ISO 8802/3, IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet),
IEEE 802.3u (Fast Ethernet),
IEEE 802.3x (Flow Control),
IEEE 802.1D (Bridging)
Electromagnetic
FCC Part 15 Class A, CISPR22
Class A
Operational shock
10G; operational sine vibration—
5-500 cycles; operational random
vibration—up to 2000 cycles
Safety
UL 1950; EN 60950; CSA 22.2
No. 950, CB Report, TUV GS Mark
Page 27

LL AA NN SS ww ii tt cc hh ee ss
27
Protocols
RFC 826 ARP, RFC 791 IP, RFC 792
ICMP, RFC 768 UDP, RFC 793 TCP,
RFC 783 TFTP IPX, BootP. RFC 1157
SNMP. RFC 854-859
Telnet options, RFC 1213 MIB II.
RFC 1757 RMON; RFC 1493 Bridge
MIB, RFC 1516 IETF 802.3, IfStackTable RFC 1573 MIB V1.
SuperStack II Switch 9100
Management
MIBs supported: SNMP MIB II (RFC
1213), Remote Monitoring MIB
(RFC 1571), Bridge MIB (RFC 1493,
Evolution of the interface MIB
(RFC 1573)
Standards Compliance
Electromagnetic
Switch 3800 EN 55022 Class A;
Switch 9000 EN 55022 Class B;
FCC Part 15 Class A, CSA C108.8M1983 (A), VCCI Class 2 EN
50082-1 (IEC801 Parts 2-4),
EN 61000-3-2, EN 61000-4 -3, EN
61000-4 - 5, EN 61000-4 -6, EN
61000-4–11
Safety
UL 1950, EN 60825-1, CSA 22.2
No. 950, Russian GOST and
EN 60950; 1992/A3: 1995 plus
ZB/ZC Deviations.
Protocols
SNMP (RFC 1157), ARP (RFC 826),
IP (RFC 791), ICMP (RFC 792), UDP
(RFC 768), TCP (RFC 793), TFTP
(RFC 783), Telnet (RFC 854), BootP
(RFC 951).
Management Information Bases
(MIBs)
MIB II RFC 1213, Remote Monitoring MIB RFC 1571, Bridge MIB,
RFC 1493, Evolution of the interface MIB RFC 1573
SuperStack II Switch 9300
Standards Compliance
Functional
IEEE 802.3x (Flow
Control) IEEE 802.1 (Bridging)
Electromagnetic
FCC Part 15 Class A, CISPR22
Class A
Operational shock
10G; operational sine vibration—
5-500 cycles; operational random
vibration—up to 2000 cycles
Safety
UL 1950; EN 60950; CSA 22.2 No.
950, CB Report, TUV GS Mark
Protocols
RFC 826 ARP, RFC 791 IP, RFC 792
ICMP, RFC 768 UDP, RFC 793 TCP,
RFC 783 TFTP IPX, BootP. FC 1157
SNMP. RFC 854-859
Telnet options, RFC 1213 MIB II.
RFC 1757 RMON; RFC 1493 Bridge
MIB, RFC 1516 IETF 802.3, IfStackTable RFC 1573 MIB V1.
SuperStack Switch II
Layer 3 Module
Standards Compliance
Electromagnetic
EN 61000-4-2, EN 61000-4-3,
EN 61000-4-4, EN 61000-4-5, EN
61000-4-6, EN 61000-4-11, ENV
50204, IECS-003 CLASS A,
FCC PART 15 CLA SS A, EN 55022
CLASS A, VCCI CLASS A, AS/NZS
3548 CLASS A, EN 61000-3-2,
EN 61000-3-3, CNS 13438
CLASS A, Korean EMI CLASS A
Safety
EN 60950 1992/A4: 1996 plus
ZB/ZC Deviations, IEC 950
Edition 2 Amendment 4 plus all
national deviations, CB Report to
be upgraded, CSA 22.2 No. 950-95,
UL 1950 3rd edition, NOM-019
SCFI, AS/NZS 3260
Protocols
SNMP (RFC 1157),
MIB II (RFC 1213), BootP
(RFC 951), Telnet (RFC 854), OSPF
(RFC 1253), RIP (RFC 1053),
DVMRP (RFC 1075), IGMP
(RFC 1112), ICMP (RFC 972)
Warranty Summary
The SuperStack II Switch 610,
1100, 3300, and 3300 FX are
covered by 3Com’s +5 lifetime
limited warranty. The +5 lifetime
limited warranty provides a full
5 years of advanced hardware
exchange from your date of
purchase in accordance with the
3Com standard terms and
conditions. To qualify, you must
submit the appropriate product
warranty registration card to 3Com.
After the initial 5-year period, the
warranty reverts to the 3Com
standard lifetime limited warranty.
The +5 lifetime limited warranty is
not offered or is void where
restricted or prohibited by law.
All other SuperStack II switches
and modules are covered by
3Com’s one-year limited
warranty.
Free Telephone Technical
Support for 90 Days
All SuperStack II switches come
with free telephone technical
support for 90 days. For further
information, visit our Web site at
http://suppor
t.3com.com/
warranty/websmeqa.html
.
Knowledgebase Web Service
Provides immediate
around-the-clock access to
technical information on
3Com products. Located at
http://knowledgebase.3com.com.
Page 28

Ordering Information
To learn more about 3Com products and services, visit our World Wide Web site at www.3com.com. 3Com Corporation is publicly
traded on Nasdaq under the symbol COMS.
Copyright © 2000 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. 3Com, the 3Com logo, Boundary Routing, CoreBuilder, OfficeConnect, PACE,
SmartAgent, SuperStack, and Transcend are registered trademarks of 3Com Corporation. B RASICA and ZipChip are trademarks of 3Com
Corporation. OpenView is a trademark of Hewlett-Packard. Windows and Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft. Solstice is a trademark
of Sun Microsystems. UNIX is a trademark of UNIX Laboratories. Other product and brand names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. All specifications are subject to change without notice.
Printed in U.S.A. on recycled paper 400260-016 03/00
SuperStack II Baseline
10/100 Mbps Switch
(12 port) 3C16464A
SuperStack II Baseline
10/100 Mbps Switch
(24 port) 3C16465A
SuperStack II Switch 610
3C16954
SuperStack II Switch 2200
(1 FDDI DAS MIC) 3C220000A
SuperStack II Switch 2700
(OC-3c multimode/single-mode,
short-reach ATM interface)
3C32711A
SuperStack II Switch 2700
(OC-3c multimode
ATM interface) 3C32700A
SuperStack II Switch 2700
(DS-3 ATM interface) 3C32710A
SuperStack II Switch 2700 (TLI)
3C32730A
SuperStack II Switch 1100
(12 port) 3C16951
SuperStack II Switch 1100
(24 port) 3C16950
SuperStack II Switch 3300
(12 port) 3C16981
SuperStack II Switch 3300
(24 port) 3C16980
SuperStack II Switch 3300 XM
(24 port) 3C16985
SuperStack II Switch 3300 FX
3C16982
SuperStack II Switch 3800
3C16910
SuperStack II Switch 3900
(24 port) 3C39024
SuperStack II Switch 3900
(36 port) 3C39036
SuperStack II Switch 9000
3C16990
SuperStack II Switch 9100
3C17705
SuperStack II Switch 9300
(12 Port SX) 3C93012
SuperStack II Switch 9300
(10 SX/2 LX) 3C93011
SuperStack II Switch 9300
(12 port LX) 3C93010
High-Speed Modules and
Accessories for SuperStack II
Switch 1100, Switch 3300,
and Switch 3300 FX
Switch Matrix Module 3C16960
Switch Matrix Cable 3C16965
Switch 100BASE-FX Module
3C16970
Switch 100BASE-FX Dual Module
3C16971
Switch 1000BASE-LX Module
3C16973
Switch 1000BASE-SX Module
3C16975
Switch 1000BASE-T Module
3C16978
SuperStack II Switch 1100/3300
ATM Expansion Module (one
OC-3c/OC-12c multimedia port)
3C16977
Layer 3 Module for SuperStack II
Switch 1100, Switch 3300, and
Switch 3300 FX
SuperStack II Switch
Layer 3 Module 3C16968
High-Speed Interface Connector
for SuperStack II Switch 3800
SuperStack II Switch 3800
(1000BASE-SX Interface
Connector) 3C16911
High-Speed Modules for
SuperStack II Switch 3900
SuperStack II Switch 3900
(1000BASE-SX Module) 3C39001
SuperStack II Switch 3900
(1000BASE-LX Module) 3C39002
Transceiver Interface Modules
for SuperStack II Desktop Switch,
SuperStack II Switch 1000
(12 and 24 Port), Switch 1100
(12 and 24 Port)
AUI Transceiver Interface Module
(one female AUI) 3C1206-0
10 Mbps Fan Out Transceiver
(male AUI) 3C1206-4
10 Mbps Fiber Optic
10BASE-FL (ST) 3C1206-5
10 Mbps Coaxial Transceiver
10BASE2 (BNC) 3C1206-6
10 Mbps TP Transceiver
10BASE-T (RJ-45) 3C12063
10 Mbps Fiber Optic 10BASE-FB
(ST) (10 Mbps) 3C12067
Transcend Management
Transcend Network Control
Services for UNIX 3C27850G
Transcend Network Control
Services for Windows NT
3C81400A
Transcend Enterprise Manager for
Windows NT 3C15010H
Transcend WorkGroup Manager for
Windows 3C15000I
Transcend Network Supervisor
(Shipped with SuperStack II
managed hubs or can be
downloaded from the Web at
www.3com.com/tns)
Power Supply Systems
SuperStack II ARPS 3C16071
SuperStack II ARPS Power
Module Type 2 3C16074
SuperStack II ARPS
Y-Cable Type 2 3C16078
SuperStack II UPS (U.S.)
3C16010
SuperStack II UPS (Int’l)
3C16011
SuperStack II UPS (Japan)
3C16012
3Com Corporation
5400 Bayfront Plaza
P.O. Box 58145
Santa Clara, CA 95052-8145
Phone: 1 800 NET 3Com
or 1 408 326 5000
Fax: 1 408 326 5001
World Wide Web:
http://www.3com.com
®
3Com®SuperStack®II
SuperStack II Switches
 Loading...
Loading...