Page 1

•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
3+0penM MS-DOS '
LAN
Manager
User Reference
o
o
I
00
"f"
.....
V)
...........
...........
...........
.
:::
:
:::::::::::::::
........
. . . . . ..
..
. .
.... ....
..
..
..
.. .. ..
..........
~~~~~~ffi.~~~~~~~~l~~~~~~~~~::~··;·i·I··;·I·~·:·~~·.~·
~
::.f.:::::::::;::::;;:~:::::;~
!
.....
~?~~~~~~~~~~~~§~~:::
. . . . . .
:
:::
::::::"
............
..
. . ............ . . . .
..
................... .
...........................
..
..
..
..
..
.. .. ..
..
.. ..
.. ..
.. ..
..
.. ..
....
..
:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:.:-
........................
..
.. ..
·l:·:~·j··lj·j·j·:·:l···
..••..••
..
. . .
.. .. ..
..
. . .
:-:.:.:-...
..
.... ......................
..
.. .. ..
..
..
................
"
""
.................................
..::
::~~~rrr:~~~~!!!:!:!~~~~
.
.................
..
..
.. ..
.. ..
oo
............
.
as ........ ..
..
..
.........
..... ••••·.·.
. . .
•••••
..
'
:-:~.:-I:-:-:
·
..
. . . . .
•
••
..
.
i·
iii:
>;
<
Page 2

3+0pen
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager
A
member
of
the
User
3+0pen
family
Reference
of
products.
~
Copyright© 3Com Corporation, 1989.
3165
Kifer Road
Santa Clara, CA 95052-8145
Printed in the
Manual Part No. 5148-00
Published August 1989
U.S.A.
All
rights reserved.
Page 3

Copyright
No
part of this manual
derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without permission
Corporation by the
Changes
editions
3Com
including, but not limited
pwpose.
described in this manual at any
of
Corporation provides this guide without warranty
Statement
may
be reproduced
United States Copyright Act
are
made
periodically to
this
publication. Contents are the property
to,
3Com
may
make
the
information herein; these changes
the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness
improvements or changes
time.
in
any
form
of
or
by
any means or used to
1976,
as
amended.
of
3Com
Corporation.
of
any kind, either implied
in
the product(s) and/or
will
make
be
incorporated
All
rights reserved.
or
for
the
program(s)
any
from
3Com
in
new
expressed,
a particular
Portions of
Corporation.
this
manual are reproduced in
whole
or
in
Trademarks
3Com
and
3+
are registered trademarks of
Corporation.
MS,
Microsoft,
IBM and
LaserWriter,
is a registered trademark
Microsoft Word,
osa
are trademarks
and
Macintosh
and
of
International Business Machines Corporation. Apple,
are registered
of
Claris Corporation.
3Com
MS-DOS
trademarks
Corporation. 3+Open
are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Recognition
Writer: Robert Shepherd. Editors: Ruth Hartman
Engineering information: Les Cheong, Ray Marshall,
was
This manual
MacDraw
GD
II
software
produced
with
by
the
3Com
Apple
using
3+GIl
GD
LaserWriterGll
and
for
Macintosh
part
with
permission
of
Apple
Computer, Incorporated.
Nancy Newlin. Production: Cate Lush.
and
Dan Myers.
(3Com), Microsoft Word
Plus
on
a
Macintosh~
from
is
a trademark
netstation.
Microsoft
of
MacDraw
Gll
3Com
3.02, and
Page 4

Table
of
Contents
Preface
Before You Begin xiv
Contents of This Reference xv
Notational
Procedural Conventions xvii
Finding Further
Conventions xvi
Notational
Convention Examples xvi
Text
Examples with Commands
Text Examples with the
Information xviii
xvi
LAN
Manager Screen xvii
Chapter 1: About MS-DOS LAN Manager
MS-DOS
MS-DOS
Startup and Security 1-3
Using
Getting More
LAN
Manager Basic
LAN
Manager Enhanced 1-2
Logging
Automatic Startup 1-4
MS-DOS
LAN
On-Line Help 1-6
Error Messages
On
to the Local Area Network 1-3
MS-DOS
The NET HELP Command 1-6
Help With the LAN Manager Screen 1-7
LAN
Manager 1-4
LAN
Manager Commands 1-5
Manager Screen 1-5
Information 1-6
1-8
1-2
iii
Page 5
Chapter
How to
Using
Abbreviations 2-3
Commands That Start Services Automatically 2-4
Using Passwords with Commands 2-6
Using /yes and /no 2-8
Command Reference Pages 2-8
Basic Commands
LOGOFF 2-12
Syntax 2-12
Comments 2-12
Example 2-13
See
LOGON
Syntax 2-14
Comments 2-16
Automatic Logon 2-22
Example
See
CONTINUE 2-23
NET
Syntax 2-23
Comments 2-24
Example 2-24
See
2:
MS-DOS
Use
This Chapter 2-2
MS-DOS
Service Names
Option Names
Starting the Workstation Service Automatically 2-4
Starting the Messenger Service Automatically 2-5
Logging
Typing a Password 2-6
Using the
General
Logging
Logging
Logging On to the 3+Name Service
Changing Your Password
LAN
On Automatically 2-5
* Option 2-7
Also 2-13
2-14
Usage
On to Mixed Networks 2-18
On to the 3+0pen Network 2-20
2-22
Also 2-22
Also
2-24
Manager Commands
2-11
2-3
2-4
2-17
LAN
Manager
2-3
2-21
Command
2-21
Reference
i\l
Page 6

NET HELP 2-25
Syntax 2-25
Comments 2-26
Example 2-27
See Also 2-27
NET NAME
Syntax 2-28
Comments 2-28
Example
See Also 2-28
NET
PAUSE
Syntax 2-29
Comments 2-30
Example
See Also 2-30
NET PRINT
Syntax
Comments 2-32
Example 2-34
See Also 2-34
NET
START WORKSTATION 2-35
Syntax 2-35
Comments 2-35
Example 2-35
See Also 2-35
NET
USE
Syntax 2-36
Comments 2-37
Example 2-39
See Also 2-40
Enhanced Commands
2-28
2-28
2-29
2-30
2-31
2-31
2-36
NET 2-43
Syntax 2-43
Comments 2-43
Example 2-44
See Also 2-44
2-41
v
Page 7

NET
ACCESS
Syntax
Comments
Example
See
Also
NET
ADMIN
/COMMAND
Syntax
Comments
Example
See
Also
NET
COPY
Syntax
Comments
Example
See
Also
HELP
NET
Syntax
Comments
Example
See
Also
NET
LOAD
Syntax
Comments
About Profile Files
Example
See
Also
NET
LOGOFF
Syntax
Comments 2-64
Example
See
Also
NET
LOGON
Syntax
Comments 2-66
Example
See
Also
2-45
2-45
2-48
2-50
2-50
2-51
2-51
2-51
2-53
2-53
2-54
2-54
2-55
2-57
2-57
2-58
2-58
2-59
2-60
2-60
2-61
2-61
2-62
2-62
2-63
2-63
2-64
2-64
2-65
2-65
2-66
2-66
2-68
2-68
vi
Page 8

NET
MOVE
Syntax
Comments 2-69
Example
See
NET
NAME
Syntax
Comments 2-72
Example
See
NET
PASSWORD
Syntax
Comments 2-75
Example
See
NET
SAVE 2-77
Syntax
Comments 2-78
About Profile Files
Example
See
NET
SEND
Syntax
Comments
Example
See
START MESSENGER
NET
Syntax
Comments 2-83
Example
See
NET
START NETPOPUP
Syntax
Comments 2-85
Example
See
NET
START WORKSTATION 2-87
Syntax
Comments
Example
2-69
2-69
2-70
Also 2-70
2-71
2-71
2-73
Also 2-73
2-74
2-74
2-76
Also 2-76
2-77
2-79
Also 2-79
2-80
2-80
2-81
2-82
Also 2-82
2-83
2-84
Also 2-84
2-85
2-85
Also 2-86
2-87
2-89
2-90
2-78
2-83
2-85
Page 9

NET VIEW
Syntax
Comments 2-92
Example 2-93
See Also 2-93
2-91
2-91
Chapter
Using the
Netstation Information 3-4
Logging
Selecting Menus and Menu
Using Help 3-7
Using Dialog
Menus and Dialog Boxes
View Menu 3-12
View
View
3:
LAN
LAN
Manager Screen 3-3
On 3-5
Box
Elements 3-8
-> Network Servers 3-12
Servers Available on Network 3-13
Listing a Server's Resources 3-14
Resources at (Server) 3-15
Using a Network Resource 3-17
Stop Using a Network Resource 3-17
Use
the Resource (Network Path) 3-18
Connecting to a Shared Resource 3-19
-> This Workstation 3-20
Network Resources in Use at Your Workstation
Adding a New Connection 3-22
Deleting a Connection 3-23
Getting More Information About a Network Resource 3-23
Use
a Network Resource 3-24
Connecting to the Network Resource 3-26
Accessing (Network Path) 3-27
Supplying a Password 3-28
Usage Information for a Network Resource 3-29
Manager
Items 3-6
in
This Chapter
Screen
Reference
3-11
3-21
Page 10

View Menu (continued)
View
-> Print Queues 3-30
Print Queues For
Show
Listing a Server's Printer Queues 3-32
Print Queues for (Server) 3-33
Changing the Status of Your Print Job 3-34
Getting More
Printing Options for Job 3-36
Printing Options for Queue 3-38
Message
Menu
3-40
Message -> Send 3-40
a Message
Send
Sending a Message 3-43
Message
-> Aliases 3-44
Aliases for Messaging 3-44
Adding
an
Deleting a Message Alias 3-45
Add
an
Alias
Config Menu 3-48
Config -> Logon 3-48
Into
Log
Network 3-49
Logging on to
Config -> Load Profile
Load Configuration
Loading a Profile 3-53
See
Also 3-54
Config
-> Save Profile 3-54
Saving Your Current Configuration 3-56
See
Also
Config
-> Change password 3-57
Change Logon Password at a Server 3-57
Changing Your Password 3-59
See
Also 3-59
3-31
Information About a Job or Queue 3-35
3-41
Alias 3-45
3-46
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager 3-50
3-51
3-51
3-57
Page 11

Appendix
LOGON/LOGOFF Error Messages
3+Name Service Error Messages
General
Alerter Service Messages A-9
Net Service Messages A-9
Command Syntax Messages
LAN Manager Application Error Messages A-10
DOS
A:
Error
LAN
Manager Errors A-4
Messages
A-1
A-2
A-10
Index
Page 12

List
of
Figures
Figure
3-1
3-2
3-3
3-4
3-5
3-6
3-7
3-8
3-9
3-10
3-11
3-12
3-13
3-14
3-15
3-16
3-17
3-18
3-19
3-20
3-21
3-22
3-23
Title
LAN
Manager Screen 3-3
Log Into Network Dialog Box 3-5
View Menu 3-6
Using Help Dialog Box 3-7
Sample Dialog Box 3-8
Servers Available on Network Dialog Box 3-13
Resources
Use the Resource (Network Path) Dialog Box 3-18
Network Resources
Use
Accessing (Network Path) Dialog Box 3-27
Usage Information for a Network Resource Dialog Box 3-29
Show Print Queues For Dialog Box
Print Queues for (Server) Dialog Box 3-33
Printing Options for Job Dialog Box 3-36
Printing Options for Queue Dialog Box 3-38
Send a Message Dialog Box
Aliases for Messaging Dialog Box 3-44
Add
Log Into Network Dialog Box 3-49
Load Configuration Dialog Box 3-52
Save Configuration Dialog Box 3-55
Change Logon Password
at
(Server) Dialog Box 3-15
in
Use
at
Your Workstation Dialog Box
a Network Resource Dialog Box 3-24
3-31
3-41
an
Alias Dialog Box 3-46
at
a Server Dialog Box 3-58
3-21
List
Table
2-1
2-2
of
Tables
Title
MS-DOS
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager Basic Commands
LAN
Manager Enhanced Commands
2-11
2-41
xi
Page 13

Page 14

Preface
This
3+
Open MS-DOS
commands and operations for both the Basic and Enhanced versions.
You
should refer to this manual for help with specific tasks
netstation with 3+Open
to a local area network, using network resources
to other computers.
This introduction explains how to use this reference.
other manuals you can
LAN
Manager User Reference describes individual
if
you are using a
MS-DOS LAN Manager. A netstation is a computer linked
but
not offering its
It
also gives an ovelView
turn
to for help
in
using MS-DOS LAN Manager.
own
resources
of
Page 15

Before
Before using this reference, you should read the 3 + Open MS-DOS
User Guide. This manual teaches you how to use MS-DOS
explains concepts, procedures, and terms not reviewed here.
the manual, you should also:
You
Begin
LAN
Manager and
In
addition to reading
IAN
Manager
• Feel comfortable using the MS-DOS
•
Be
able to create and work with files and directories.
• Have MS-DOS
administrator
• Know
Manager.
•
Be
MS-DOS prompt or,
using the
For information about the differences between Basic and Enhanced
Manager, see Chapter
if
you are using the Basic
comfortable either typing MS-DOS
LAN
if
you have questions about this).
LAN
Manager screen.
1:
Manager installed on your computer (see your system
if
you are using MS-DOS
About MS-DOS
or
PC-DOS operating systems.
or
Enhanced version
LAN
Manager commands at the
LAN
Manager.
of
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager Enhanced,
LAN
MS-DOS
LAN
Page 16

Contents
The following list explains the chapters
of
This
Reference
in
this reference.
Chapter
Chapter 1:
AbOut MS-DOS
LAN
Manager versions. This chapter also briefly explains how to
Cha!I5er 2:
MS-
OS
LAN
Manager
Command Reference
Chapter 3:
LAN
Manager Screen
Reference
Appendix A:
Error Messages
Contents
Features
differences between the Basic an Enhanced
start and use 3+Open
how to get help.
MS-
at the
chapter explains Basic commands, which can be
used with either Basic
Manager; the second section explains commands
only available with the Enhanced version. The
commands are listed alphabetically
LAN
boxes. The reference is arranged in the order
menus as they appear across the menu bar. The
dialog boxes are presented in hierarchical order
after
MS-DOS
comments that
prompt
of
MS-DOS
DOS
LAN
MS-DOS prompt. The flrst section in this
Manager screen, its menus, and dialog
their menus.
LAN
or
in LA Manager screen message boxes.
LAN
Manacfer and the
MS-DOS
Manager commands you can type
or
Enhanced MS-DOS
Manager error messages and
m~
appear at the MS-DOS
LAN
Manager and
by
section.
LAN
of
the
xv
Page 17
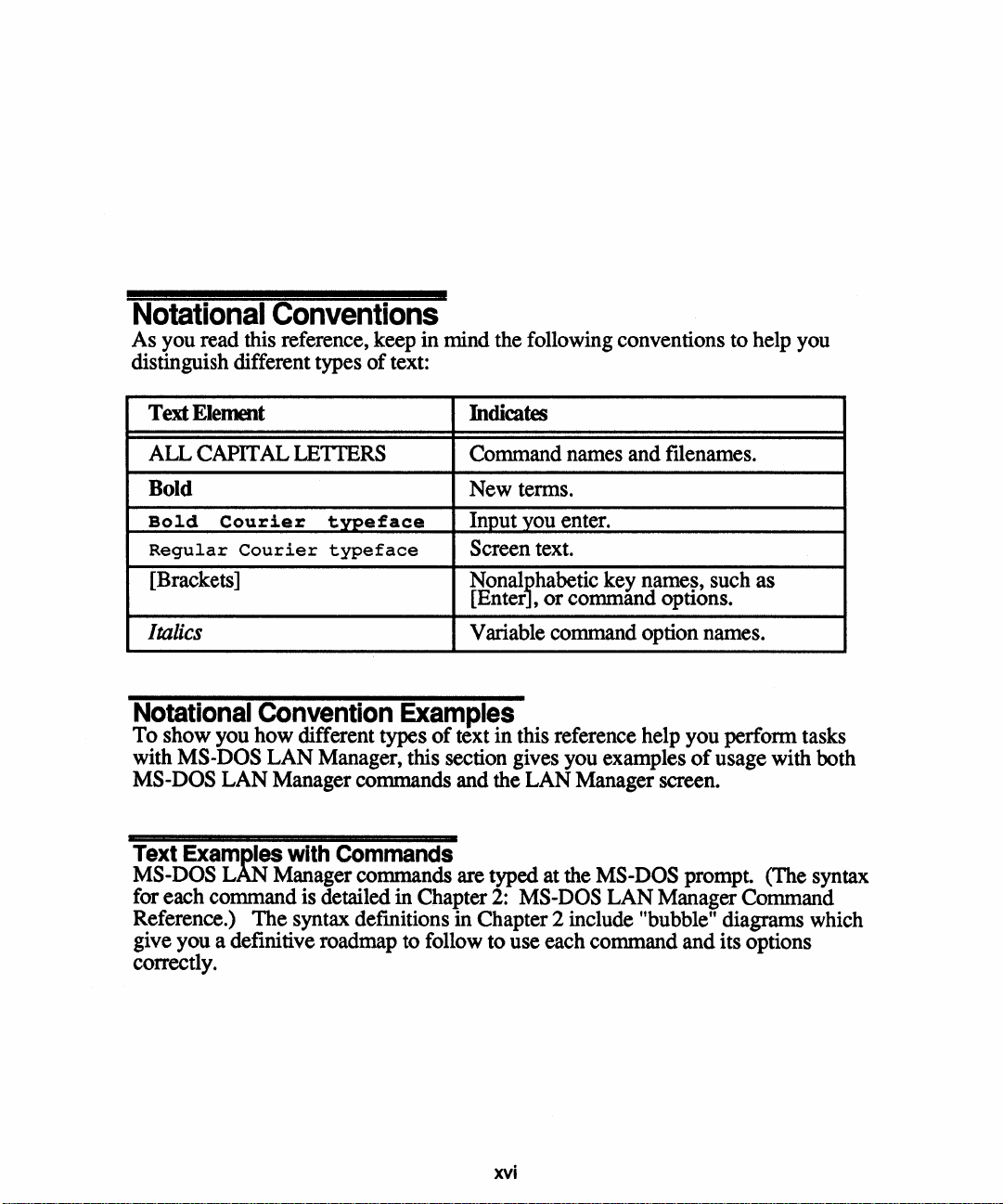
Notational Conventions
As you read this reference, keep
distinguish different types
Text
Element
ALL CAPITAL LETTERS Command names and filenames.
Bold New terms.
Bold
Regular
[Brackets]
Courier
Courier
typeface
typeface
of
in
mind the following conventions to help you
text:
Indicates
Input you enter.
Screen text.
Nonalihabetic key names, such as
[Enter ,
or
command options.
Italics
Notational Convention
To
show you how different types
with
MS-DOS
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager, this section gives you examples
LAN
Manager commands and the LAN Manager screen.
Examples
Variable command option names.
of
text
in
this reference help you perform tasks
of
usage with both
Text Examples with Commands
MS-DOS LAN Manager commands are typed at the MS-DOS prompt. (The syntax
for each command is detailed in Chapter
Reference.)
give you a definitive roadmap to follow to use each command and its options
correctly.
The
syntax defmitions in Chapter 2 include "bubble" diagrams which
2:
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager Command
xvi
Page 18

Text
Examples
From the LAN Manager screen, you peiform tasks by selecting menus and menu
items, which take you to dialog boxes. Dialog boxes have command buttons, text
fields, and other features that let you accomplish a task easily.
To reach a dialog box, you must follow an access path, which begins with a menu
and moves through a menu item to the dialog box. Arrows are used to show the
progression through an access path. For example, the
dialog box is reached through the View menu. Its access path is shown as:
with
the
LAN
Manager
Screen
Use a Network Resource
View->This
Each dialog box reference page in Chapter
shows the access path needed to reach the dialog box.
Procedural
Information you should enter is shown in blue. Terms shown in italics should be
replaced with specific information. For example:
logon
means that you type the command LOOON exactly as shown, and substitute
specific information for the general terms shown in italics. In this example, you
would substitute your own user name where the line shows the word
and your own password where the line shows
of
the command.
workstation->Add
Conventions
username
use
password~
3:
LAN Manager Screen Reference
username,
password.
Press [Enter] at the end
xvii
Page 19

Finding
In
addition to this manual, the following manual is included with MS-DOS
Manager:
Further
Information
LAN
• 3 + Open MS-DOS
MS-DOS
tutorials and instructions for
LAN
LAN
Manager on a netstation. This manual provides you with
Manager User Guide, a procedural guide for using
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager tasks.
xviii
Page 20

About MS-DOS
LAN
Manager
1
1-1
Chapter
3+Open MS-DOS LAN Manager lets you link your computer to a local area
network and use shared resources such as disk drives and printers.
of
MS-DOS
in this reference.
The
capabilities
MS-DOS
at the
does and
you work with menus and dialog boxes at the
typing commands. MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced lets you send and receive
messages, and automatically connect to several shared resources at once.
LAN
MS-DOS prompt. MS-DOS
more-it
1:
About
LAN
Manager are available: Basic and
of
the Basic and Enhanced versions are reflected in their names.
Manager Basic lets you use shared resources
includes commands not found in the Basic version, and also lets
MS-DOS
Enhanced.
LAN
Manager Enhanced does everything Basic
LAN
Manager screen instead
LAN
Each is explained
by
typing commands
Manager
Two
versions
of
Page 21

1
1-2
About MS-DOS
LAN Manager
MS-DOS
With MS-DOS LAN Manager Basic, you can:
• Keep your workgroup's data in a secure and centralized location.
• Add your personal computer to an existing MS-DOS
• Read, revise, and create files on other computers.
• Use
• Use
• Display printer queues.
• Get on-line help.
MS-DOS
With the advanced version
Manager
prompt and using a full-screen interface. MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced gives
you access to all
others.
LAN
applications-such
resources-like
LAN
Enhanced-you
You can:
Manager
disks
Manager
of
the features
Basic
or
OS/2™ network.
as Microsoft
or
printers-attached
Word-with
files on other computers.
to servers.
Enhanced
of
MS-DOS LAN Manager----called MS-DOS LAN
can choose between typing commands at the MS-DOS
of
MS-DOS LAN Manager Basic, plus several
• Work with menus and dialog boxes on the LAN Manager screen instead
typing commands.
• Send and receive messages across the local area network with the Messenger
and N etpopup services.
• Put together a customized set
connect to a number
• Move and copy files from one place to another on the local area network.
of
of
connections----called a
frequently used resources with one command.
profile-so
of
that you can
Page 22

About MS-DOS
LAN Manager
1
1-3
Startup
Regardless
step
in
do this, you need to start the Workstation service, which links your computer
local area network as a netstation.
program puts the following line
startup:
net
start
You
may
prompt. This
you can perform networking tasks using either
if
or,
Startup and Security in the 3 + Open MS-DOS
5:
discussion
AUTOEXEC.BAT.
If
you are using MS-DOS
services
more information about these services, see the
NET
Manager Command Reference.
and
of
using MS-DOS
also start the Workstation service
you have
of
on
START
Security
whether you are using the Basic
LAN
Manager is to start the software
The
3+Open MS-DOS
in
your AUTOEXEC.BAT startup flie to perform
workstation
command
the
starting MS-DOS
your netstation: the Messenger service and the Netpopup service.
NETPOPUP command reference pages
identifIes your computer to the local area network so that
Enhanced version, the
LAN
Manager
LAN
Manager Enhanced, you can also start
or
the Enhanced version, the fIrst
by
typing this command
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager screen.
LAN
Manager User Guide
and
commands you can include in
NET
START
in
Chapter 2: MS-DOS
on
your computer.
LAN
Manager setup
LAN
Manager commands
MESSENGER
at
the MS-DOS
See
also Chapter
two
for
other
to
For
and
LAN
To
the
a
Logging
Once you have identifIed your computer to the local area network, the next step is to
identify yourself.
password.
netstation's AUTOEXEC.BA T file, so that logging
automatically each time you start your netstation.
On
to
The
NETSETUP
the
To
Local
do
this, you
Area
program installed
Network
must
log
on
using your user
the
necessary commands in
on
will be performed
name
and
logon
your
Page 23

About MS-DOS
LAN Manager
1
1-4
For
example, Mary Sullivan's user name is marys, and her logon password
wanderer.
command to log on to the local area network:
Her
netstation's AUTOEXEC.BA T fue contains the following
is
logon
Once you start the Workstation service and log on to the local area network, you are
ready to use local area network resources and perfonn other tasks with
LAN
If
AUTOEXEC.BAT fue accordingly. Refer to the
MS-DOS
Automatic
MS-DOS
instance, when you request use
your user name and password, and automatically sends them along for verification
before logging you
Command Reference and Chapter 3: LAN Manager
details on logging on.
Using
Once you have started the Workstation service, you are ready to perfonn local area
network tasks.
ways to perfonn tasks:
marys
Manager.
your password
wanderer
LAN
Manager Command Reference for more infonnation.
Startup
LAN
Manager perfonns some logon tasks for you automatically.
MS-DOS
If
MS-DOS
or
user name change, you can edit the LOGON line
LOGON
of
a server, MS-DOS
on
to the server. See Chapter 2: MS-DOS
LAN
you are using MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced, there are two
Manager
command in Chapter 2:
LAN
Manager remembers
LAN
Screen Reference for more
in
your
For
Manager
•
•
By
typing MS-DOS
By
selecting options from menus and dialog boxes on the LAN Manager
screen.
LAN
Manager commands at the MS-DOS prompt.
Page 24

About MS-DOS 1
LAN
Manager
1-5
MS-DOS
If
you are using MS-DOS
prompt is the only way you can use the system. Even
version, you
boxes
acquainted with the commands and their options, and
tasks-such
You can use many commands regardless
Enhanced version
available with the Enhanced version. For more information about
Manager commands and how to use them, see Chapter 2: MS-DOS
Command Reference.
fIrst section explains Basic commands, which are available
The
second section explains Enhanced commands.
See also the
about performing local area network tasks using
commands.
that many
To
automate local area network tasks, you can place MS-DOS
commands in batch files, such as your
LAN
The
LAN
LAN
MS-DOS
LAN
on
the
MS-DOS
Manager
Manager screen is a windowed user interface that organizes MS-DOS
Manager commands into a system
LAN
Manager
may
prefer to type commands instead
LAN
Manager screen. It can
as moving
3+0pen
If
you are already familiar with the
files-that
of
MS-DOS
The
MS-DOS
LAN
Commands
LAN
Manager Basic, typing commands at the MS-DOS
cannot be done with the
of
LAN
Manager. However, some commands are only
chapter is divided into an introduction
LAN
Manager User Guide for more information
Manager commands are similar.
AUTOEXEC.BA T file.
Screen
of
Manager Enhanced.
if
you have the Enhanced
of
using the menus and dialog
be
the quicker alternative
it
lets you perform certain
LAN
Manager screen.
whether you have the Basic
to
MS-DOS
3Com
menus. It is available only to users with
LAN
Manager
3+
system, you will notice
LAN
if
you are well
or
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager
and
two
all users,
Manager
the
LAN
sections.
and
the
Menus and dialog boxes provide you with various options from which
choose without having to remember specific commands. Many people
LAN
performing tasks using the
For
typing commands.
see the
For more information about menus and dialog boxes contained within the
Manager screen, see Chapter 3:
3+0pen
MS-DOS
more information about using the
LAN
Manager screen is easier and more convenient than
LAN
Manager screen,
Manager User Guide.
LAN
Manager Screen Reference.
you
fmd
can
that
LAN
Page 25

1
1-6
About MS-DOS
LAN
Manager
Getting
MS-DOS
information
Manager commands and the
On-Line
More
LAN
or
Information
Manager provides more information when you need
error messages and providing on-line help for both MS-DOS
LAN
Manager screen.
Help
Whether you are performing local area network tasks using MS-DOS
Manager commands
or
the
LAN
Manager screen, you can get additional
information to help you as you work.
The NET HELP Command
MS-DOS
MS-DOS
use
Manager command, type
command begins with the word NET, type
second word
using the
net
MS-DOS
LAN
LAN
in
a batch fue).
NET
help
LAN
Manager provides a special help command to assist you in using
Manager commands (commands you type at the MS-DOS prompt
To
get information about using a particular MS-DOS
NET
HELP, followed
of
the command. For example,
by
the command name.
NET
HELP followed only
if
you want more information about
USE command, type:
use
Manager displays the following information:
it
by
LAN
by
displaying
LAN
or
LAN
If
the
the
The
syntax
NET
USE
NET
USE
NET
USE
The
NET
server's
See
the
about
of
[devicename
[devicename]
{devicename
USE
command
shared
MS-DOS
this
command.
this
resource.
LAN
command
I \
\\computername\sharename
I
connects
Manager
is:
\computername\
\\computername\sharename}
a
netstation's
User
Reference
sharename]
local
for
[password]
/DELETE
devicename
more
information
to
a
Page 26

About MS-DOS 1
LAN
Manager
1-7
You can also type
NET
HELP by itself. The following list appears to show you
more about the help command:
The
syntax
NET
HELP
Help
NET
Help
ACCESS
HELP
MOVE
PRINT
VIEW
USE
Help
NAMES
is
on
is
of
[topic]
available
the
following
CONTINUE
LOAD
PASSWORD
SEND
also
available
SYNTAX
this
command
on:
NET
on
is:
commands
COpy
LOGOFF
LOGON
START
these
is
special
available:
topics:
Help With the LAN Manager Screen
If
you are using MS-DOS
LAN
Manager screen, you can press [FI] to get context-sensitive help.
LAN
Manager Enhanced and you are working in the
This means, for example, that
dialog box and press
[FI], information is displayed about using that particular
if
you are working in the Use a Network Resource
dialog box. This information is accompanied by an index from which you can
choose topics
of
interest to you, including general information about how to use
menus and dialog boxes.
Page 27

1
1-8
About MS-DOS
LAN Manager
Error
If
LAN Manager does not recognize, you will see an error message in this form:
NETiiii:
#### is a four-digit number that uniquely identifies the MS-DOS
message.
listing
prompt, see Appendix A: Error Messages.
When you are working in the
message boxes. Some
the
screen. To get more infonnation about a message displayed by the
screen, press
Messages
you type an MS-DOS
Message
Message text is a short message that describes the error.
of
MS-DOS
MS-DOS prompt. Other messages displayed are specific to the
[FI].
LAN
Manager command with an option that MS-DOS
text.
LAN
Manager error messages that may appear at the MS-DOS
LAN
Manager screen, messages are displayed
of
the messages displayed are the same as those displayed at
LAN
For
LAN
LAN
Manager
a complete
Manager
Manager
by
Page 28

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
2-1
Chapter
Command
3+0pen
typing commands at the MS-DOS prompt.
Manager Basic, this is the only way you can operate the system.
If
most
3: LAN Manager
commands is useful if:
• You are familiar with the 3Com 3+ command-line interfaces.
• You are an expert user who feels more comfortable typing commands than
• You want to add MS-DOS LAN Manager commands to batch files.
MS-DOS
you have the Enhanced version
of
the same operations using the
using menus
2:
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager
Reference
LAN
Manager lets you perform
If
of
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager screen, described in Chapter
Screen Reference. The option
in
a full-screen interface (LAN Manager screen).
LAN
Manager operations
you are using MS-DOS
LAN
Manager, you can perform
of
typing MS-DOS
LAN
LAN
by
Manager
Page 29

2
2-2
MS-DOS
Manager Command
Reference
LAN
How
This chapter is divided into three major sections:
• "U sing MS-DOS
• "Basic Commands" describes the commands that are part
• "Enhanced Commands" describes the commands which are part
The command reference sections each begin with a table
applicable to the version
Commands are listed alphabetically within each section; each command reference
explains the usage, syntax, and available options for the command.
to
Use
how to use all
section regardless
MS-DOS
Manager Basic. Users
because
LAN
Manager Enhanced, in addition to the commands included in Basic. Only
users
of
This
MS-DOS
LAN
MS-DOS
the Enhanced version need to use this section.
Chapter
LAN
Manger Commands" provides general information about
LAN
Manager commands. You should read this
of
whether you use MS-DOS
Manager Enhanced.
of
the Enhanced version will also use this section,
LAN
Manager Enhanced includes all the Basic commands.
of
MS-DOS LAN Manager discussed in that section.
LAN
of
Manager Basic
of
MS-DOS
of
the commands
or
LAN
MS-DOS
Page 30

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-3
Using MS-DOS LAN Manager Commands
You should know a few rules and guidelines to help you best use the MS-DOS
LAN
Manager commands described in this chapter.
This section describes abbreviations you can use in some commands, and shows
how to use passwords. Commands that depend
commands that must be run before other
prompts that will help you remember these dependencies.
commands may be used
for doing so.
in batch files; this section provides some useful guidance
commands-are
Abbreviations
You may use abbreviations when typing MS-DOS
Although the command reference pages in this chapter spell out all command
names, option names, and service names,
of
abbreviate many
these for your convenience.
MS-DOS LAN Manager allows you to
on
others-for
LAN
example,
described, along with
MS-DOS
Manager commands.
LAN
Manager
Service Names
MS- DOS
following
LAN
Manager allows you to use abbreviations and synonyms for the
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager services:
Service Abbreviations, synonyms
Workstation
Messenger msg, receiver, rcv
wksta, work, redirector, redir,
rdr
Page 31

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-4
Option Names
MS-DOS
a command option. This means you must type enough letters in the option's name
to distinguish the option you choose from other options for that command.
LAN
Manager also allows you to type any unambiguous abbreviation for
For example,
Isend,
command's options were Iread and Iredo,
accept
The command reference pages in this chapter list command options in alphabetical
order, making
you may type
/r, but would accept either Irea for Iread,
if
you are using a command whose possible options are Iread and
Ir
instead
it
easier for you to compare similar option names.
of
Ire
ad, and
Is
instead
MS-DOS
or
of
Isend.
LAN
Manager would not
Ired for Iredo.
However,
if
the
Commands That Start Services Automatically
Some MS-DOS
service or performed another command
Workstation service before you can display the LAN Manager screen.
In many cases,
prerequisite task.
Starting the Workstation Service Automatically
The
Workstation service must be started before any
run:
NET
NET
NAME
NET
USE
LAN
Manager commands will not work unless you have started a
MS-DOS
NET
NET
NET
LAN
LOAD
PRINT
VIEW
flrst. For example, you must start the
Manager automatically prompts you to perform the
of
the following commands can
NET
LOGON
NET
SEND
Page 32

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-5
When
the Workstation service is running.
you
type
one
of
these commands, MS-DOS
If
it
is not, MS-DOS
LAN
the following prompt:
The
WORKSTATION
Is
it
If
you
type Y (or press [Return], since Y is the default response noted in brackets),
MS-
DOS
you
typed.
service
OK
LAN
or
run the
to
If
is
not
started.
start
it?
(YIN)
[Y]:
Manager first starts the Workstation service, then runs the
you
type N, MS-DOS
command
you typed.
LAN
Manager does
Starting the Messenger Service Automatically
The
Messenger service must be running before you
command.
that service is running.
prompt:
The
MESSENGER
Is
it
If
you
command
command
When
OK
to
type Y, MS-DOS
you typed.
you type
is
start
NET
SEND, MS-DOS
If
it
is not, MS-DOS
not
started.
it?
(YIN)
LAN
If
you type N, MS-DOS
[Y]:
Manager starts the Messenger service, then runs the
you typed, and the Messenger service is
LAN
LAN
LAN
Manager
not
Manager checks
LAN
not
start the Workstation
can
use the
Manager checks
displays the following
Manager
will not run the
started.
to
see
if
Manager displays
command
NET
SEND
to
see
if
Logging On Automatically
When
network first,
Basic) checks to see
Enhanced
Manager
from the LANMAN.INI file
Type
Type
you type a
MS-DOS
runs the
offers
your
your
username,
password:
command
that requires you to
LAN
if
you are logged on.
command
to
log you on to the local area network
or
be
logged
on
to
the local area
Manager Enhanced (but not MS-DOS
If
you typed.
on
your computer:
press
ENTER
you are,
If
you are not logged on, MS-DOS
if
it
MS-DOS
by
reading your user
is
<user
LAN
name>:
LAN
Manager
Manager
LAN
name
Page 33

2
2-6
MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
Automatic logon can log you on to the
to a
3+
network,
LOGON command later in this chapter for more information.
You must be logged
following four commands:
NET
NET
USE
If
you are using MS-DOS Manager Enhanced, using these commands before you
are logged on will cause
you are using MS-DOS LAN Manager Basic, you must use the
before you use these four commands.
Using
Some commands require a password as an option. There are two ways for you to
provide a password.
Passwords
if
you are working in a mixed-network environment. Refer to the
on
to the local area network before you can use any
NET ADMIN /COMMAND
NET VIEW
MS-DOS LAN Manager to automatically log you on.
with
Commands
3+0pen
network only; it cannot log you on
of
the
If
LOGON
command
Typing a Password
The fIrst way to provide a password is to type
itself (remember, your password can be up to 14 characters long).
Mary, whose password is wanderer, wants to use a shared resource plotter
server
admin that requires a password, she types:
it
on
the same line as the command
For
example,
on
a
if
net
use
lptl:
\\admin\plotter
wanderer
Page 34

MS-DOS
Manager
Reference
LAN
Command
2
2-7
Using
You can also ask MS-DOS LAN Manager to prompt you for your password, by
replacing the password with an asterisk
example, Mary could type the following command to connect to the shared resource
the * Option
(*) when you type the command. For
plotter:
net
MS-DOS
When you type a password at this prompt, the password is not displayed as you
use
Type
type. This allows you to keep your password confidential. Although this option
may prove a little less convenient than typing your command and password
together, it provides added security.
You can use the asterisk option with the following commands to cause
LAN Manager to prompt you for a password:
LOGON
NET PASSWORD
Depending on the command you type, MS-DOS
you for other pertinent information, such as your user name.
the
1ptl:
LAN
password
\\admin\p1otter
Manager displays the following prompt:
for
\\ADMIN\PLOTTER:
NET LOGON
NET
USE
*
LAN
Manager
may
also prompt
MS-DOS
NOTE:
to type
MS-DOS
it
with a command that requires one.
LAN
Manager will also prompt you for a password
if
you forget
Page 35

2
2-8
MS-DOS
Manager Command
Reference
LAN
Using
Some
example,
MS-DOS
You
Continuing
Do
You
anticipate and respond to a prompt like the
because when
does
is automatically accepted as your response.
For
respond to the prompt with a Y, you can type the following line:
logoff
The
functions from being interrupted by
feature with
safety, to give you a chance to verify that you want to take an action that has
important consequences (like logging off).
Iyes
and
Ino
commands cause MS-DOS
if
you use the
LAN
Manager displays a prompt similar to the following:
have
you
can use the
example,
Iyes
the
following
LPTl
will
want
to
Iyes
MS-DOS
not
pause to display the corresponding prompt. Instead, the
if
you use the
/yes
and
Ino
options can also be added to commands in batch fues to keep
caution-MS-DOS
LOGOFF
cancel
continue
and
Ino
LAN
LAN
Manager to prompt you for a decision.
command to
remote
the
this
options with any MS-DOS
Manager reads one
LOGOFF
connections:
connections.
operation?
command and know that you want
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager generally prompts you like this for
log
off
(YIN)
one
shown. This expedites the function,
of
LAN
these command options,
Manager prompts.
from the local area network,
[N]:
LAN
Manager command to
Iyes
or
Ino
to
Use
For
it
option
this
Command
Each command reference page
Command
The
top
of
command, followed by a brief description
this description includes information displayed with the command, and the
functions
Reference
Name
each reference page shows the name
it
performs.
and
Pages
in
this chapter includes the following information.
Purpose
of
of
the MS-DOS
what the
command
LAN
Manager
does. Generally,
Page 36

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-9
~b~~agrams
(
NET
USE)
drive:
illustrate command syntax in this manual.
A bold, rounded-comer rectangle surrounds the
The command name is in all capital letters and bold type.
A rectangle surrounds variables.
italic letters. This shape says "substitute something here."
An
oval surrounds arguments that you type exactly as they
appear in this manual.
A circle surrounds punctuation.
The
variable is in lowercase
o
Arrows indicate direction.
A vertical line indicates a return.
be
Each element must
To
read a bubble diagram, start at the command name,
rectangle. You
the direction
freeway interchanges).
the
NET
USE diagram shown next, you could choose to continue to the
without entering any further parameters. Or, you could take one
that tell you to type either a device name,
sharename. After that, you
may
of
the arrows (imagine you are driving a
separated from the next by a space.
in
the bold, rounded-comer
follow any line through the command, as long as you follow
car
through a series
For
example, when you come to the fIrst decision point
or
must
press [Return].
the name
of
a computer and a
command
end
of
the branches
name.
of
in
Page 37

NET
MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
2
Reference
2-10
USE
~~----------------------~~--~
devicename
\ \
computername\sharename
Following the bubble diagrams are explanations
each command. Most option names can be abbreviated.
I-------_~
.......
I
....-.....,
of
all the options you can use with
Comments
The
comments section describes how to use the command, when
why. This section describes the command's options and explains which options
can
be
used in combination. The comments section may also contain warnings
suggestions about using the command.
to
use it, and
or
ExamDle
Exampfes show how the command is used.
Manager
MacroCorp, Inc.
employees.
User
Guide,
The
you were introduced to employees
examples in this chapter also use the names
See Also
At
the end
box reference pages and other publications that you can read for more information
related to the command.
of
each command reference page is a list
In
the 3+0pen MS-DOS
of
a fictitious company,
of
titles
of
command and dialog
IAN
of
MacroCorp
Page 38

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
2-11
Basic
Commands
The following table lists the commands used with MS-DOS LAN Manager Basic.
These commands are available to all users
or
Enhanced. Each command is discussed in detail on its own reference page.
In
the next section
are available only to users with
the LAN Manager screen.
of
this chapter, Enhanced Commands, commands are listed that
MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced, which includes
If
you are uncertain which version
of
MS-DOS LAN Manager, either Basic
of
MS-DOS LAN
Manager you are using, check with your network administrator.
Table 2-1. MS-DOS LAN Manager Basic Commands
Command
LOGOFF
Purpose
Lo~
you off
3+0pen
or
3+
networks (or
bot ).
LOGON
CONTINUE Continues local area network functions
NET
NET HELP
NET NAME
Loe: your user name and password into
or
3+ pen
suspended by the NET
Displa~
use
of
3+ networks (or both).
PAUSE command.
information about the purpose and
S-DOS LAN Manager commands.
Displays the aliases currently defined in a
of
netstauon's list
aliases, and adds
or
deletes
aliases from that list.
NET
PAUSE Suspends the specified MS-DOS LAN
Manager functIons.
NET
PRINT
D~splays
pnnter
and controls the contents
s queue.
of
a shared
START WORKSTATION
NET
NET
USE
Starts MS-DOS LAN Manager services.
Connects users to resources shared by a
server.
Page 39

MS-DOS
Manager
Reference
LAN
Command
2
2-12
LOGOFF
This command ends a computer's connection with the local area network and logs a
user name
both 3+Open and 3+ networks.
command,
Syntax
off
LOGOFF
from the local area network. LOGOFF can be used to log
MS-DOS
NET
LOGOFF, which is used to log
/3plus
LAN
Manager Enhanced has a similar
off
only the
3+0pen
off
from
network.
/30pen
Comments
The LOGOFF command is used to end a user's local area network session. Since
only one user
logging
LOGOFF with no options logs you
message is displayed, confirming each network logged off:
username
username
You can also specify a particular network with the
Adding the
Manager will not prompt you for confirmation before cancelling any connections
currently in effect.
per
netstation can be logged on to the local area network at a time,
off
one user name frees the netstation for use by someone else.
off
successfully
successfully
Iyes
option at the end
logged
logged
both the
off
off
of
the command means that MS-DOS LAN
the
the
3+0pen
3+0pen
3+Name
130pen
and
3+
network
service
and 13plus options.
networks. A
Page 40

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-13
If
you are actively using any shared resources (for example, your current drive
redirected drive), you must stop using those resources before you can log off.
you have any connections to a server's shared resources when you use the
LOGOFF command, MS-DOS
those connections. Messages similar to the following will be displayed:
LAN
Manager warns you that logging
off
deletes
is
If
a
NET2404:
You
have
Continuing
Do
you
If
you respond with Y, your current connections will be broken, and you will see
H:
I:
want
The
the
will
device
following
cancel
to
continue
is
remote
the
being
connections.
this
accessed
connections:
operation?
by
an
(YIN)
active
[N]:
process
messages confmning that you have been logged off.
Once the LOGOFF command has been completed, you no longer have active user
name, password,
or
local area network sessions, and you cannot receive messages
sent to your user name.
Example
At
the end
logoff
See
For more information about this command, see:
Also
of
the day, to log
off
from the local area network, Jenny types:
• The LOGON command in this chapter, for information about logging on.
• The Log Into Network dialog box in Chapter'3:
LAN
Manager Screen
Reference, for information about logging on to MS-DOS LAN Manager
Enhanced.
Page 41

2
MS-DOS
Manager Command
Reference
LAN
2-14
LOGON
This command sets the user name and password for your netstation. The LOGON
command logs you on to either 3+Open
LOOON with NET LOGON (available in MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced),
which logs you on to the
LOGON is quite versatile. The three syntax diagrams below show three different
ways to use
LOGON.
3+0pen
Syntax
or
3+ networks, or both. Do not confuse
network only.
1. Log on to both networks.
2.
Log on to 3+Open network only.
3+0pen
password
3+
password
Page 42

3.
Log
MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
on
to 3+ network with a three-part name.
2-15
Option
usernome
*
3 +
Open
password
3+
password
1'lf1J11e:
domain:org
/pass=
/30pen
/3plus
Abbreviation
/30
/3p,
/3+
Purpose
Specifies the default user name for the local
netstation (up to
You can type an asterisk instead
E:assword
nhanced to prompt you for your password.
Password to
Password to be used
The puee-part name recognized by the 3+Name
service.
Required
for the 3+Name
distinguish the end
Forces LOGON to log
Forces LOGON to log
to cause MS-DOS LAN Manager
if
20 characters long).
of
be
used on
you are
service ( lows LOG N to
3+0pen
on
3+
network.
speci~ng
of
the three-part name).
on
on
a threecfJart name
to
3+0pen
to
3+
only.
your
network.
only.
Page 43

2
2-16
MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
options
may
be
any
or
all
of
the following:
Option
/no_pro
/30pen
/3plus
/yes
!home_server=
computername
/no_time
/help help, I?, ? Displays a help screen for the
/security=
user
or
share
Abbreviation
/np
/30
/3p,
/3+
/y
!hs=
computername
/nt
/SE=
user
or
share
Pur~
Causes
either the
or
Forces
Forces
Skips confinnation prompts as
answered yes.
Sets environment variable used
to computername, to specify the
for
Specifies that net station clock will
from 3+Name server
command.
Sets an environment variable used
establishing the initial
LOGON
the
Start volume users and netstation clock.
3+0pen
3+Name
LOGON
LOGON
to not load profile files for
network
service (PR FILE.SYS).
to
log
on to
to
log
on
or
Start volume connection.
grnTLOGON.PRO)
3+Open
to
3+
if
home server.
LOGON
only.
only.
you had
by
redirector
home
not
for
server
be set
Comments
The
LOOON command is usually put into your netstation's
by
the
NETSETUP
your netstation.
It
network.
networks containing both
works
program. This way, logging
LOGON
on
establishes
networks that contain only
3+0pen
your
and 3+ servers.
user name and password
AUTOEXEC.BAT
on
is handled each time you start
on
the
3+0pen
servers, as well as
file
Page 44

MS-DOS
Manager
Reference
Command
LAN
2
2-17
General
Usage
When you use the LOGON command with no options, you are prompted for a user
if
name and password. Similarly,
you type the LOOON command with just a user
name and no password, it is assumed that no password is required.
Hyou
3+ password,
Enter
Enter
type an asterisk after the user name (in place
or
both), then you are prompted to supply a password:
your
your
3+0pen
3+Name
password:
service
password:
of
either the 3+Open
or
Characters you enter will not be displayed, thereby keeping your password secure.
When you enter just one user name and one password, they are used to attempt to
log on to the
in logging
username
on
successfully
3+0pen
to the
network and to the 3+Name service.
3+0pen
network, it displays the message:
logged
on
the
3+0pen
If
network
LOGON is successful
(username is your user name).
When logging on to the 3+Name service, the user name you supply
or
treated either as an alias
and organization.
If
as a user name under the default Name service domain
3+Name service logon is successful, you will see the message:
LOGON is
3+
User
name:domain:org
supply an alias with the command, the 3+Name service translates
name.
name:domain:org
successfully
logged
on
the
is a three-part name recognized by the 3+Name service.
If
you supply your user name, the three-part name consists
3+Name
it into a three-part
of
your user
name and the default domain and organization associated with your name.
service
If
you
Page 45

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
2
2-18
If
your netstation is already logged on under a different user name
H:
I:
want
LOGON
the
will
to
connections,
You
have
Continuing
Do
you
If
you answer yes (by pressing Y),
your netstation will be logged
your network connections are currently
by
as shown
the MS-DOS prompt, is one
displays the message:
flrst displays a prompt similar to this:
following
cancel
continue
remote
the
connections.
this
off
before
connections:
operation?
LOGON
it
is logged
in
use (for example,
of
cancels these connections. In essence,
your redirected drives),
(yiN):
on
again. However,
and
has remote
if
if
your current drive,
LOGON
any
of
NET2404:
LOGON
The
LOGON
netstation.
Enhanced logs you
Logging On
A mixed network
includes the 3+Name service.
The
device
is
being
accessed
by
an
active
process
cannot continue in this case, and stops.
command also tries to add the specifled user name as an alias for the
If
the user name cannot be added as an alias, MS-DOS
on
to the local area network, but displays a warning message.
to
Mixed Networks
is
one in which there are both
LOGON
is designed to take care
3+0pen
and
LAN
3+
servers, and which
of
logging in to
both networks.
If
your network does not provide the 3+Name service,
LOGON
will detect this
automatically and log you on to the 3+Open network only.
It
is simplest when your user name and password are both the same for both
For
networks.
example,
wanderer, for both networks, use the
logon
marys
wanderer
if
your
user
name is marys, and your password is
LOGON
command like this:
Manager
Page 46

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
If
you have the same user name but different passwords
put
both passwords
LOGON
command would look like:
in
the command.
If
your
3+
password is traveler, then the
2-19
on
both networks, you can
logon
In this example, marys
3+0pen
LOGON
password= lines
located
name for the
on
marys
wanderer
is
your user name
traveler
on
both networks, wanderer
is
your
password, and traveler is your 3+Name service password.
can also take 3+Name service logon infonnation from the name= and
in
your netstation's PROFILE.SYS file. PROFILE.SYS
in
your current directory. This
3+
Name service,
or
may
be convenient
if
you use different user names and/or passwords
if
you use a three-part
must
3+Open and 3+Name service. This will happen automatically unless you
append the option /no-pro to the command, like this:
logon
You can also run
use three-part names
marys
wanderer
LOGON
or
different user names
/no-pro
twice: once for each network. This also allows you to
on
both networks.
The
commands
might look like this:
logon
logon
The
on
If
your user name is registered with the 3+Name service, but your
marys
msmith:finance:macrocorp
wanderer
/30pen
/pass=traveler
options /30pen and /3plus determine which network
to.
LOGON
/3plus
will log you
3+0pen
password is not correct as a 3+ password, you will see the following message:
be
Enter
Enter the correct password at this prompt.
3+Name
service
password:
LOGON
then gives you the opportunity
to change your 3+Name service password to match your
Change
3+0pen
the
3+Name
password?
service
(yiN):
password
to
match
3+0pen
the
password:
Page 47

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
2
Reference
2-20
If
you press Y, you will be asked to type the
partly for security, and partly to ensure you correctly remember the 3+Open
password):
3+0pen
password again (this is done
Enter
If
service and confirm with the following message:
Password
If
the same. This will simplify use
administrator.
Logging
The /30pen (/30) option directs LOGON to log on only to the
For example:
1ogon
You might want to use this form
logged on to both networks, and you wish to change only your
If
database
name and password are sent to the server for verification.
recognizes the user name/password combination you gave, you are allowed to log
on to the local area network.
account,
you log on to the local area network. (This script is contained in a file on the logon
server.)
your
the two passwords match, LOGON will change your password in the 3+Name
your
3+0pen
your
3+0pen
successfully
and 3+ passwords are different, you should consider making them
On
to
marys
3+0pen
of
user names and passwords on one
MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced runs the script on your net station when
password:
changed
the
3+0pen
wanderer
network uses logon security (by keeping a distributed or centralized
Network
If
on
the
3+Name
of
the network for both you and your network
/30pen
of
the LOGON command
or
you have a logon script associated with your
service.
3+0pen
if
you are currently
3+0pen
more servers), then your user
If
the logon server
network.
logon.
Page 48

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
2-21
Logging On
to
the 3+Name Service
The /3plus (J3p, /3+) option directs LOOON to log on only to the 3+Name service.
For example:
1ogon
Like logging on to only the
msmith
trave1er
/3p1us
3+0pen
network, this fonn
of
the LOGON command is
useful to change your logon to 3+ while not changing your logon to 3+Open.
IT
you wish to use a tbree-part name for your 3+ logon you must use a specific
of
fonn
1ogon
Here
because three-part names can contain spaces; /pass= tells
the LOGON command:
name:
name:domain:org
domain:
is your three-part name. The option /pass= is required
org
/pass=password
/3p1us
LOGON where the threepart name ends and the password begins. Note also that you cannot mix a threepart name and a
3+0pen
user name. You must either use LOGON twice, as
described earlier, or put your 3+Name service logon infonnation in the
PROFILE.SYS file.
Changing Your Password
You can use LOGON to change the password currently in effect. You might want
to do this
you have separate passwords for different resources on the network,
or
if
different privilege levels. Note that this is a temporary change; the next time you
start your netstation, the
original password.
LOOON command(s) in AUTOEXEC.BAT will use your
If
you want to change your password permanently, edit the
LOGON command in AUTOEXEC.BAT.
To change only your
1ogon
In
username
this case,
username
password. This fonn
3+0pen
password
password, type the LOGON command like this:
/30pen
is your original user name, and password is the
of
the command won't cancel any current connections, and
will register the new password with the
3+0pen
new
network.
Page 49

2
2-22
MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
Automatic
Certain MS-DOS LAN Manager commands require you to be logged
network before they can be used, as described earlier
"Logging
LOGON
NET
LOGON does not provide the full functionality
mixed networks;
network and the 3+Name service, be sure you have used
attempt any
Logon
on
to the
in this chapter, in the section
On Automatically." These commands automatically run the
command before they proceed with their own functions. Remember that
of
the LOGON command on
if
your network requires you to log on to both the 3+Open
LOGON
of
the commands that require you to be logged on to the network.
NET
before you
Example
For
Jenny to establish
defaults on a netstation, she types:
logon
If
Jenny's network contains both
sees the following prompts as confirmation:
jennyt
jennyt:finance:macrocorp
service.
The
translated by the 3+Name service into a three-part name, containing her name,
domain
jennyt
was
successfully
second line
(macrocorp), and organization (finance).
her
user name,jennyt, and password, babaloo, as the
babaloo
3+0pen
logged
was
of
the message shows that Jenny's user name, jennyt, was
servers and the 3+Name service, she
on
to
the
successfully
3+0pen
logged
network
on
to
the
3+Name
See
Also
For more information about this command, see:
• The NET LOOON command, for information about MS-DOS
Enhanced's
•
The
Config->Logon menu in Chapter
information about the Log Into Network dialog box.
•
The
LOGOFF command, for information about logging
3+0pen
logon capabilities.
3:
LAN
Manager Screen Reference, for
off
the network.
LAN
Manager
Page 50

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
NET CONTINUE
This command continues MS-DOS
PAUSE
Syntax
NET
command.
CONTINUE
Command
2-23
LAN
Manager services suspended by the NET
Option
workstation Continues local area network connections to
prdr
drdr
NET
CONTINUE may
Purpose
ports and disk drives.
Continues local area network connections to printer ports only.
Continues local area network connections to disk drives
be
abbreviated
NET
CONT.
all parallel (LPT)
only_
Page 51

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
2
Reference
2-24
Comments
The
NET CONTINUE command reinstates services
using the
Workstation service,
disk drives only.
When you continue local area network connections to network printers, any local
connections to parallel (LPT) ports are ignored, and connections to local area
network resources are restored.
NET
PAUSE command. Specifically, you can pause and continue the
or
pause and continue connections to parallel (LPT) ports
or
resources that were paused
or
For example, suppose you have a dot-matrix printer connected to
netstation. You may choose to redirect
network, then pause your local area network connections when you want to use the
dot-matrix printer. When you are ready to use the laser printer again, the NET
CONTINUE command causes your netstation to redirect
printer and ignore the local dot-matrix printer connection.
LPTI
to a laser printer on the local area
LPTI
LPTI
to the network laser
of
your
Example
Mike Greenbaum paused the Workstation service on his computer earlier in the day.
Now he wants to use local area network resources, so he continues the Netstation
service by typing NET
CONTINUE WORKSTATION.
See Also
For more information about this command, see:
• The NET PAUSE command in this chapter, for information about pausing
MS-DOS
•
The
LAN
your local area network connections from the
LAN
Manager services.
Network Resources in Use at Your Workstation dialog box, in Chapter 3:
Manager Screen Reference, for information about pausing and continuing
LAN
Manager screen.
Page 52

NET HELP
This
command
MS-DOS
Syntax
LAN
MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
2
2-25
provides infonnation at the MS-DOS prompt about how to use
Manager Basic commands.
( NET
HELP)
1:
'1
command may be one
CONTINUE
PRINT
NAME
START
..
command
of
the following MS-DOS
~
I
r'
PAUSE
USE
LAN
Manager Basic commands:
Page 53

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
2
2-26
Comments
When used without options, the NET HELP command displays a list
MS-DOS
the second word
want help in using the NET
net
In
response,
The
NET
NET
NET
LAN
help
syntax
USE
USE
USE
[devicename
{devicename
Manager commands. You can type NET HELP, followed only by
of
the MS-DOS
LAN
Manager command. For example,
USE command, type:
use
NET
HELP displays information about the NET USE command:
of
this
[devicename]
command
I
\\computername\sharename
I
is:
\\computername\sharename]
\\computername\sharename}
[password]
/DELETE
of
all
if
you
The
NET
USE
server's
See
the
about
NOTE:
command
shared
MS-DOS
this
LAN
command.
You can also see help infonnation for an MS-DOS LAN Manager
connects
resource.
Manager
a
User
netstation's
Reference
for
local
more
devicename
information
command by typing the command in the following fonn:
command
/help
For example, you could see infonnation about the NET LOAD command
of
either
net
net
the following commands:
help
load
load
/help
by
to
a
typing
Page 54

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-27
You can type a command in the following form to see infonnation about syntax for
that command only:
command
For example,
NET
PRINT command is, you could type:
net
print
/?
if
you were interested in seeing only what the proper syntax for the
/?
Example
To
get lielp with options and syntax associated with the
Mike types:
net
See
For more infonnation about the NET HELP command, see:
• The
help
print
Also
NET
HELP command in the third section
NET HELP that displays the commands for MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced.
NET
PRINT command,
of
this chapter, for the version
of
Page 55

NET NAME
Under MS-DOS
name.
Syntax
2
2-28
LAN
Manager Basic,
MS-DOS
Manager
Reference
Command
NET
LAN
NAME displays your netstation's user
(NET
NAME
H
Comments
NET
NAME displays your netstation's user name when you are running MS-DOS
LAN
Manager Basic. When you are running MS-DOS
this command displays more information about aliases at your netstation and allows
you to change them.
LAN
Manager Enhanced,
Example
Jimmy Wilson has forgotten his user name.
net
NET
Name
JIMMYW
The
See
For more infonnation about this command, see:
name
NAME displays his user name:
command
completed
successfully.
Also
To
find out, he types:
• The NET NAME command in the third section
use
of
NET
NAME
if
you are using MS-DOS
of
this chapter, describing the
LAN
Manager Enhanced.
Page 56

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
NET PAUSE
This command suspends an MS-DOS
shared resource, and frees up memory used
Syntax
NET
PAUSE
LAN
2-29
Manager service
by a service.
or
connection to a
Option
workstation
prdr
drdr
Purpose
Pauses local area network connections to
all parallel (LPT) ports
and disk drives.
Pauses local area network connections to printer ports only.
Pauses local area network connections to disk drives only.
Page 57

2
MS-DOS
Manager
Reference
LAN
Command
2-30
Comments
When you pause the Workstation service, you temporarily suspend connections
from your netstation to network printers and disk drives, and free memory
computer for use by other programs you want to run. When you pause a
connection to a shared resource, you temporarily suspend the connection between
your netstation and the shared resource.
For example, you might want to pause the connection between a shared printer and
your netstation's
To
restore a paused resource
LPTI
port
if
you have connected a printer to that port temporarily.
or
service, use the NET CONTINUE command.
on
your
Example
To
pause the connection between a shared printer and his netstation, Ben types:
net
When Ben is ready to resume this local area network connection, he types:
net
pause
continue
workstation
workstation
See Also
For more information about this command, see:
• The NET CONTINUE command in this chapter, for information about
continuing paused services.
Page 58

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
NET PRINT
This command displays and controls the contents
Syntax
NET
PRINT
~---------'~------------~~---'~~r----'~--~~
\
\computername
\ \
computername
1-----'.
\sharename
2-31
of
a shared printer queue.
\\computername\devicename
Option
\\.computername
sharename
Purpose
Specifies the server sharing the printer queue.
Specifies the shared printer queue.
devicename Specifies the local print device connected to the queue.
job# Specifies the identification number assigned to a file
queue.
/hold
/release Releases a held
/delete
Keeps a print
with.
the /hold option stay
until released
Breaks the connection with the printer queue; removes
your print requests in the printer queue. Or,
print Job, removes the print
job
from printing. Print
in
the queue and are not printed
WIth
the /release option.
job
from the queue.
job
jobs
held
if
from the printer queue.
in
in
the queue
you specify a
a
all
of
Page 59

2
MS-DOS
Manager
Reference
LAN
Command
2-32
Comments
When
infonnation about a specific printer queue. For example, the contents
queue
used with the \\.computername option, the
NET
PRINT command displays
in a MacroCorp server \\printl might be displayed as follows:
of
a printer
Printer
Name
FAST
JACKST
JENNYT
JENNYT
The
Queues
PRT
Queue
command
completed
This display lists:
Column
Name
Contents
Sharename
each
Job#
Size
Status
Identification number
Size
Status
the status
\\PRINTI
at
Job#
3
jobs
1
3
4
successfully.
of
job
sent to the queue.
in bytes
of
of
each print
of
each queue and the number
Size
2509
75
75
Status
*Queue
Printing
Waiting
Waiting
Active*
the printer queue and the user name
of
each print job.
each print job.
job
(Printing, Paused, Error)
of
jobs
m it.
on
LPTI
PRT
Queue
of
the owner for
or
Spooling),
or
Page 60

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
2
2-33
When used with the computer name and sharename
redirected device name, the NET
the specified queue. This display includes the status
the
jobs
in the queue, including the size and status
printers controlled by MS
if
heading, as
The status
The
status
(device),
Waiting.
Print
jobs
specified either by the device name, or by the computer name
sharename
redirected to a queue
(identification number 24):
net
print
net
print
net
print
they consisted
of
a printer queue
of
a print
Out
of
paper
to be held
of
the queue. For example,
l.pt2
\
\mis
\
\mis
OS/2
job
can be Spooling, Held, Printing
on
(device), Error on (device), Offline on (device),
or
released (with the !hold and /release options) can be
\\mis\print, any
24
\print
24
PRINT command displays only information about
LAN
Manager servers are listed under a single
of
one large printer queue.
can
be OK, Held, Held until, Pending delete,
if
your netstation's
of
the following commands will hold a
/hol.d
24
/hol.d
/hol.d
of
a queue,
of
the queue itself and a list
of
each job. Print
on
LPTI
or
with the
jobs
for
or
(device), Held on
or
of
the server plus the
device name is
job
of
Error.
Page 61

MS-DOS
Manager
Reference
LAN
Command
2
2-34
Example
Realizing that he sent the wrong monthly budget to a shared printer queue laser on
the
print1 server, Jack wants to delete his print request. First, he types the
following command to see what identification number is assigned to his print
request:
net
print
\\printl\~aser
The following display appears:
Print
Name
LASER
BENS
JACKST
He
net
See
Queues
Queue
at
\\PRINTl
Job#
2
jobs
6
7
Size
2527
3074
Status
*Queue
Printing
Waiting
Active*
on
COMl
sees that his is request number 7. Next, Jack deletes his print request
print
\\printl\laser
7
/delete
Also
For more information about this command, see:
•
The
Printer Queues for (Server) dialog box in Chapter 3:
LAN
Reference, for information about working with printer queues using the
Manager screen
(if
you have MS-DOS
LAN
Manager Enhanced).
by
typing:
Manager Screen
LAN
Page 62

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
NET START WORKSTATION
This command starts the MS-DOS
LAN
Manager Workstation service.
Syntax
2-35
(NET
START WORKSTATION H
Comments
The MS-DOS
no
options
chapter.
AUTOEXEC.BAT
automatically each time you start your netstation.
removed from your AUTOEXEC.BAT file, you can type it at the
LAN
Manager Basic version
on
its command line, unlike the Enhanced version, described later in this
NET
START WORKSTATION is included in your netstation's
flie by the NETSETUP program to start the Workstation service
of
the NET START COMMAND has
If
the command has been
MS-DOS prompt.
Example
John has removed the NET START WORKSTATION command from his
AUTOEXEC.BA T file. When
computer and types the following command to start the Workstation service:
net
start
workstation
he
arrives at work in the morning, he turns on his
See Also
For more information about this command, see:
• The NET START WORKSTATION command for MS-DOS
Enhanced, later
in this chapter.
LAN
Manager
Page 63

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
2
Reference
2-36
NET USE
This command redirects a netstation's local device name to a server's shared
resource.
Syntax
1. Making a connection
NET
USE
devicename
\
\computername\sharename
1ooIr-------
......
2. Deleting a connection
(
NET
USE)-1
3. Getting information about connections
NET
USE
devicename
devicename
\\computername\sharename
J-C:::
/delete
I-------
:>-4
__
~..,
~~-
Page 64

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-37
Option
devicename
\\computername
\sharename
password
Purpose
S~cifies
dIsk drive (for example,
shared printer
the name
or
directory.
of
thed:arallel port (for example,
:)
you are using locally to identify a
LPTl)
Specifies the server controlling the shared resource.
Specifies the shared resource.
For servers with share-level security, this specifies the
password assigned to the shared resource.
For
servers with
user-level security, this specifies the user's password to the
Idelete
server controlling the requested resource,
from the password set with the
&be an asterisk (*) instead
LAN
S
Manager Basic to prompt you for your password.
LOGON command. You can
of
your password to cause MS-
Disconnects a local area network connection.
if
it
is different
Comments
When
connections. The display lists the status, associated device, and sharename
connection. For example:
Status
used without options, the NET USE command lists the netstation's
Local
name
Remote
name
of
or
each
DISCONNECTED
OK
ERROR
The
command
G:
M:
LPTl
completed
\\GENERAL\C
\\MIS\SCRATCH
\\PRINT1\LASER
successfully.
Page 65

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-38
When used with just the device name or just the server's computer name and
sharename, the NET
connection. For example:
net
use
\\admsvc\requests
Local
Remote
Type
Status
Open
Use
The
name R:
name
count
count
command
This display shows:
USE
command displays infonnation about a specific
\\ADMSVC\REQUESTS
Disk
OK
1
1
completed
successfully.
Field
Local
name
Remote
Type
name
Status The status
Open count
Use count
If
you type the NET USE command before
MS-DOS LAN Manager prompts
Contents
The device name of
The sharename
of
the
device connected
the
shared resource.
to
the shared resource.
The type of shared resource being used: Disk or Printer.
of
The number
The number
the connection:
of
times a fue was opened via this connection.
of
connections
you
to
log
OK,
you
have
you
log
on
on.
(This is because
Error, or Disconnected.
to
the shared resource.
to
the
local area network,
MS-DOS
Manager must validate your user name and password before allowing
shared resources.)
You
cannot disconnect a local device name from a server if that
drive. You must
a shared-disk resource
Manager displays a warning message and asks you
frrst change to another drive. Also, if you
when
files are still open
on
the
to
server, MS-DOS LAN
confmn your decision.
is
your current
try
to disconnect from
you
LAN
access to
Page 66

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-39
A connection listed as disconnected means that a server ended your session due to
inactivity. In most cases,
connection the next time you
NET
USE command to reestablish the connection.
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager automatically reestablishes this
try
to use the resource. You
do
not have to retype the
Example
To
connect her netstation's E: device name to a shared directory with the sharename
.
letters controlled by the general server, Debbie types:
net
net
net
net
use
Later, Debbie wishes to connect her netstation's D: device name to a shared
directory with the sharename
the general server.
use
To
connect her netstation's print device LPTI to the shared printer with the
sharename
use
When Debbie is ready to disconnect from this resource, she types:
use
e:
d:
laser2
lptl:
lptl:
\\general\letters
drY
_c,
which shares the entire contents
drY
_c requires the password goddess. Debbie types:
\\general\drv_c
controlled by the print2 server, Debbie types:
\\print2\laser2
/delete
goddess
of
drive
Con
Page 67

MS-DOS
Manager Command
Reference
2
2-40
See Also
For
more information about this command, see:
•
The
LOOON command in this chapter, for information about logging on to the
local area network.
LAN
• The NET SA VE command in this chapter (if you have MS-DOS
Enhanced), for information about saving your netstation's current resource
connections to a profile file.
• The NET LOAD command in this chapter
Enhanced), for information about restoring saved resource connections from a
profile file.
• The Use a Shared Resource dialog box in Chapter 3:
Reference (if you have
about connecting a device to a shared resource using the
MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced), for information
(if
you have MS-DOS
LAN
LAN
LAN
LAN
Manager Screen
Manager screen.
Manager
Manager
Page 68

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-41
Enhanced
The following table lists the commands used with MS-DOS LAN Manager
Enhanced.
commands listed in the previous section
are uncertain which version you are using, check with your network administrator.
Commands
If
you are using the Basic version
of
MS-DOS LAN Manager, only the
of
this chapter are available to you.
If
you
Table 2-2. MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced Commands
Command
NET
NET
ACCESS
NET ADMIN
COpy
NET
HELP-
NET
NET
LOAD
NET LOGOFF
LOGON
NET
MOVE
NET
/COMMAND Allows a network administrator to run a
Purpose
Starts the user version
screen.
Allows a network administrator to change
permissions on a server from a netstation.
command on a server while using a netstation.
Copies files both locally and remotely.
Disp'lays information about the purpose and use
of
MS-DOS LAN Manager commands.
Loads a saved configuration from a file.
Disconnects all 3+0p'en network sessions and
logs a user
Logs a user on to the
the user name and password for the netstation.
Moves files from one place to another on the
local area network.
off
from the
of
the LAN Manager
3+0pen
3+0pen
network.
network and sets
NET NAME
PASSWORD
NET
Sets aliases for the netstation.
Changes the password for logging on to a
server.
Page 69

2
2-42
MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
Table
2-2.
MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced Commands (continued)
Conunand
NET SAVE Saves the current local area network
NET
SEND
NET
START MESSENGER Starts the MS-DOS
NET
START NETPOPUP Starts the MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced
NET
START Starts the Workstation service, registers the
WORKSTATION netstation's user name, and sets various options.
NET VIEW
Purpose
configuration into a file for later use.
Sends
Mes~enger
receive messages.
Netpopup service, displaying messages as they
are received.
Displays the
resources being s ared
messages and files to other users.
LAN
Manager Enhanced
service, allowing you to send and
com~uter
names
by
any server.
of
servers and the
Page 70

NET
This command displays the
Syntax
MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-43
LAN
Manager screen.
(NET
H
Comments
The
LAN
Manager screen lets you perfonn MS-DOS
operations using menus and dialog boxes. You must start the Workstation service
before using this command.
If
you have not logged
box appears with the
the 3+Open network. You
beginning
of
this chapter)
on
to the local area network, the Log Into Network dialog
LAN
Manager screen. This dialog box can only log you
must use the LOGON command (described at the
if
your network includes the 3+Name service.
LAN
Manager Enhanced
on
to
Page 71

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
2
Reference
2-44
Example
To
run the
MS-DOS prompt:
net
The
See
For more information about this command, see:
LAN
Manager screen, Mike types the following command at the
LAN
Manager screen appears.
Also
• Chapter 3:
Manager screen menu and dialog box.
•
The
3 + Open MS-DOS
the LAN Manager screen.
LAN
Manager Screen Reference, for a description
IAN
Manager User Guide, for information about using
of
each
LAN
Page 72

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
2-45
NET ACCESS
This command allows a network administrator to list, create, change, and revoke
permissions for resources at a server.
Syntax
Page 73

2
2-46
MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
Option
resource
account
rights
/delete
/add
/change
/grant
/trail:
[yeslno]
/revoke
/tree
Purpose
Names the resource to be assigned permissions.
can
be a disk, directory, file, printer queue,
Identifies the user name
whose permissions are being
Specifies an account name and permissions to
account:permissions. The name
followed
A,
P, Y, N; these are explained later in this section).
Removes permissions for a resource from the access-control
database.
Adds permissions for a resource to the access-control database.
Changes a user's
Adds
preexlsnng resource record.
Turns audit trailing on
default is yes.)
Revokes a user's
Reports permissions for the resource specified and all
descendants (for example, subdirectones
directory) .
.a
by
the permissions for the resource (R,
or
l).ew
user name and corresponding permissions to a
or
or
group name
mOdified.
of
group's permissions for a resource.
or
off
for a particular resource. (The
group's permissions to use the resource.
of
a specific account
a user
or
of
The
resource
or
pipe.
be
set, in the form
group account is
W,
C,
X,
of
its
a specified
D,
Page 74

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-47
When used without options, the NET ACCESS command displays a list
For
server's shared resources plus their assigned permissions.
Resource
\PRINT
C:\
C:\LANMAN\SPOOL GUEST:R *USERS:R
The
command
completed
This display shows the pathname
Permissions
BENP:W
JACKST:W
MIKEG:WC
GUEST:R *USERS:R
successfully.
of
for that resource. (Group names are preceded by
NOTE:
If
you type the NET ACCESS command for a network resource, the path
Permissions
GUEST:WC
MARYS:WC
*USERS:WC
every resource and the permissions assigned
*.)
example:
in the Resource column is relative to the network server, not to your local
computer.
of
the
Page 75

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-48
Comments
Before you can use the NET ACCESS command, you must:
•
Be
sure that the server is started with user-level security (3+0pen servers only).
• Make sure the resource exists.
• Have existing accounts for the users
permissions.
The NET ACCESS command works only with 3+Open servers; it will not work
with 3+ servers.
When you use the NET ACCESS command to display access permissions, a
comment next to each resource's name shows whether access
being audited.
permitted to use the resource, and the specific permissions. Three types
resources can appear in the list:
• Pathnames
• Sharenames
• Pathnames
Under each resource name are the names
of
drives, directories,
of
printer queues
of
named pipes
or
groups for which you are assigning
of
that resource is
of
users and groups
or
files
of
Page 76

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
2-49
The
NET
ACCESS command can assign up to nine pennissions. These
pennissions apply only when the server is running with user-level security.
pennissions work only with specific types
of
resources:
Some
Utter
R
W
C
X Execute lets users run a command
D Delete allows users to delete files and subdirectories.
A
p
Y Yes allows users to submit files
N
Permission
Read lets users read and copy files
them. This also lets users view the names
Use this pennission by itself
execute programs only.
Write lets users make changes to the files in that directory.
cases,
Create lets users create files and subdirectories in the shared directory.
When used by itself, this pennission lets users create new files
directory and change them while they are creating them; once the
closed, they cannot modify it.
Change attributes lets users
about file attributes, see the
Change permissions lets users change resource pennissions. (This
the same as giving a user administrative privilege for a resource.)
No
exclude a specific person
directory,
it
should
denies users access to a resource, and is useful
or
be
used in combination with read pennission.
chanl5e file attributes. For more infonnation
MS S/2 User Reference.
or
file.
in
that directory,
of
files in a shared directory.
if
you want users to be able
or
program.
or
requests to a printer queue.
persons from using a printer queue,
but
not change
to
look at
In
if
you need to
most
in
the
flie is
or
is
Only users who are assigned the pennission P can change the permissions on a
shared resource using the
privilege
shared from that server can
on
your server account must be obtained before pennissions for resources
NET
ACCESS command. Otherwise, administrative
be
changed.
Page 77

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
2
Reference
2-50
For a resource to be audited, the NET ACCESS command must be used with the
name
of
the resource, and the /trail: option must be set to yes. Since yes is the
default for this option,
turned on.
if
you type the trail option with no value, auditing is
Example
To
add permissions on the files in the bin directory for the user mikeg and the
groups
net
Later, to give Jenny Tibbett read and write permission for the same directory, Mary
types:
pubrel and users, Mary types:
access
c:
\bin
/
add
mikeg:
rwxc
pubrel:rw
users:r
net
See
For more information about this command, see:
• The 3 + Open OS/2
access
c:\bin
/grant
jennyt:rw
Also
LAN
Manager Administrator Guide, for an explanation
how a network administrator can start a server with user-level security
access permissions.
or
of
assign
Page 78

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
NET ADMIN /COMMAND
This command allows a network administrator
3+0pen
Syntax
server.
/ /
computername
\.c------,.I..-r
2
2-51
to
run a command remotely on a
Option
computername
password
Icommand
command
Purpose
S~e~if!es
a mInIstrator
Specifies the network administrator password on the computer
name.
Starts a secondary command processor or runs command at
computer name.
A command that will be run on the accessed server.
the
~omputer.
IS
accessIng.
name
of
the server the network
Comments
When you use the Icommand option without a following command, a command
processor similar to the
and runs at the designated
commands, runs them, and returns the resulting output to your screen.
While using this command processor, you must type the full pathname
command. For example,
then want to see a directory listing for a directory called
type the DIR command, followed by the drive letter and path
dir
f:\macrocorp
MS-DOS COMMAND. COM command processor is started
3+0pen
if
you start a command processor at a network server,
server. This command processor prompts for
of
each
macrocorp on that server,
of
the directory:
Page 79

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
2
Reference
2-52
If
you do not specify a full pathname when you type commands for a network
server,
that server.
To
MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced assumes a path
exit from this command processor, type exit,
or
of
lanman\netprog on
press [Ctrl]+Z.
You can also type the NET ADMIN command
noninteractive command (command) at the
net
admin
\
\computername
[password]
in the following form to run a single,
3+0pen
server:
/command
command
Three rules apply to the command option:
You must type the text
net
If
admin \ \server
command ends with a backslash character (\), be careful to add either an extra
space
or
another backs lash character before the ending quotation mark. For
of
command within quotation marks. For example:
/command
"net
stop
server
/yes"
example, the following command would not work properly:
net
Instead, you could use
net
net
net
admin
admin
admin
admin
If
command includes a multiple-word argument, command must
one set
of
\\server
\\server
\\server
\\server
/command
anyone
/command
/command
/command
"net
of
these commands:
"net
"net
net
share
share
share
share
c=c:\"
c=c:\\"
c=c:\
c=c:\
quotation marks, and the argument must be surrounded by another set.
"
be
surrounded
For example:
by
net
/srvcomment:"Remote
admin \ \server
/command
server
"net
1""
confiq
server
Page 80

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-53
Example
To
start a network administration session for the server print2, where the
administrative password is admiral, Mike types:
net
admin
\\print2
admiral/command
The following message appears:
Type
Exit
or
AZ
to
exit.
The prompt at Mike's netstation changes to include the computer name print2.
Now all
of
the commands Mike types at his netstation run on the server print2.
When he is done working with the network server, Mike types exit and his prompt
reverts to the normal prompt for his netstation.
See
Also
For more information about this command, see:
• The 3 + Open OS/2
LAN
Manager Administrator Guide, for information about
administering a network server.
Page 81

2
2-54
MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
NET
This command copies files, both locally and remotely.
COpy
Syntax
NET
COpy
Option
pathnmnel Names the file being copied.
pathname2
+pathname[ ... ]
/v
pathnamel~--
pathnamel+pathname[
__
--~~
...
__
----~----~~------
]
~--~~----~--~------
Purpose
Specifies
omitted, NE
Appends one
In
pathname2.
Causes
information was properly recorded on the destinatIon drive.
the~athname
COpy
or
more files to pathnamel and places the result
MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced to verify that
the file is copied to.
copies the file Into the current directory.
pathname2
If
pathname2 is
__
~~
/a
/b
Copies files in ASCII (text) format.
Copies files in binary format.
Page 82

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
Comments
The NET
to copy files over the local area network.
COpy
command is similar to the MS-DOS copy command, allowing you
2-55
You can copy files:
• From one location to another
on
your netstation.
• Between a network selVer and your net station.
• From one location to another on a network selVer.
•
From
one
network selVer to another network selVer.
If
you do not specify the pathname2 option, the copy is created in the working
on
directory
the disk in the default drive
same name, creation date, and creation time as the original file
original file is on the default drive and you
COpy
command quits (you are not allowed to copy a file to itself), and MS-DOS
of
your local computer. This copy has the
(pathnamel).
do
not specify pathname2, the
NET
If
LAN Manager displays the following error message:
File
The
causes the
Manager Enhanced must check each entry recorded on the disk.
o
File(s)
cannot
Iv
option lets you verify that critical data has been correctly recorded; it also
copied
NET
be
copied
COpy
onto
itself
command to run more slowly, because MS-DOS
If
MS-DOS
LAN
LAN
Manager cannot verify that the flie was copied successfully, it displays an error
message.
Options
following the source filename
la
and /b perform differently, depending
or
the target filename.
on
whether they are placed
the
Page 83

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-56
When placed after the source filename (pathnamel):
• The
•
When placed after a target filename
• The
•
If
your netstation,
names
to another on a single network server, only the number
the names
You can use full network pathnames, including computer names, with the
COpy
it with the NET
you must have the necessary permissions (that is, read permission) for making
connections.
fa
option causes the file to be treated as an ASCII (text) file. Data in the file
is copied up to but not including the first end-of-file mark. The remainder
the file is not copied.
The!b
marks.
the file.
The!b
you use the NET COPY command to copy files from one place to another on
option causes the entire file to be copied, including any end-of-file
(pathname2):
fa
option causes an end-of-file character to be added as the last character
option does not add an end-of-file character.
or
from one computer to another
of
the files are listed as they are copied. When you copy files from one place
of
the files are not displayed.
command. You do not need to connect to a network file
COpy
command; connections are made automatically. However,
on
the local area network, the
of
files copied is displayed;
or
directory to copy
NET
of
of
U sing NET
quicker than connecting to that network server and then copying files with the
MS-DOS
COpy
COpy
to copy a file from one place to another on a network server is
command.
Page 84

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-57
Example
To
copy a mailing list from the lists directory on the \ \sales server to the address
directory
on
the same server, Olga types:
net
copy
\\sales\lists\mail.txt
\\sales\address\mail.txt
To copy an interoffice memo from one server 0,\humanr) to another 0,\printl), Olga
types:
net
\annual.mtg
This command copies the file MEMOO513.DOC from the olgar directory
copy
\\humanr\olgar\memo0513.doc
\\printl\public
on
the
humanr server, creating a file called ANNUAL.MTG in the public directory on the
printl
See
server.
Also
For more information about this command, see:
• The NET MOVE command in this chapter, to learn how to
move-rather
than
copy-files.
• The MS-DOS User Reference, for information about the MS-DOS
COpy
command.
Page 85

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-58
NET HELP
This command provides information at the MS-DOS prompt about how to use
MS-DOS
commands, since these are also a part
Syntax
LAN
Manager Enhanced commands. This information includes the Basic
of
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager Enhanced.
(NET
command
commands:
ACCESS
COpy
LOOON
PASSWORD
SAVE
USE
Do
provides help
provide help
HELP)
may
not type the word
\
be any
on
the
on
LOGON
'-I
command
of
ADMIN
WAD
MOVE
PAUSE
SEND
VIEW
NET
NET
~
! I
r-'
the following MS-DOS
CONTINUE
LOGOFF
NAME
PRINT
START
as part
LOGOFF
or
LOGOFF.
of
command;
and
NET
LOGON
LAN
Manager Basic
it
is assumed.
commands; it does not
NET
or
Enhanced
HELP
Page 86

Comments
When
MS-DOS
the second
want help in using the
net
used without options, the
LAN
Manager commands.
word
of
the MS-DOS
help
use
MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Command
Reference
NET
NET
LAN
USE
command, type:
HELP
You
command displays a list
can type
Manager command. For example,
2-59
NET
HELP, followed
of
all
by
if
only
you
In response,
The
syntax
NET
USE
NET
USE
NET
USE
The
NET
server's
See
the
about
NOTE:
command
command
For
example, you could see information about the
of
either
net
help
net
load
NET
HELP
of
this
[devicename
[devicename]
{devicename
USE
command
shared
MS-DOS
this
command.
You
can also see help information for an MS-DOS
by
typing the command
/help
displays information about the
command
resource.
LAN
Manager
I
\\computername\sharename]
\\computername\sharename
I
connects
is:
\\computername\sharename}
a
netstation's
User
in
the following form:
the following commands:
load
/help
Reference
NET
[password]
/DELETE
local
for
more
LAN
NET
LOAD command
USE
command:
devicename
information
Manager
by
to
a
typing
Page 87

2
2-60
MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
You can type a command in the following
syntax for that command:
command
For example,
NET
SEND command is, you could type:
net
send
/?
if
you were interested in seeing only what the proper syntax for the
/?
fonn
to see only infonnation about
Example
To get lielp with options and syntax associated with the NET ADMIN command,
Mike types:
net
See
For more infonnation about this command, see:
• The NET HELP reference section earlier in this chapter, for the version
help
admin
Also
HELP that displays the commands for MS-DOS
LAN
Manager Basic.
of
NET
Page 88

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-61
NET LOAD
This command loads a specified profile file that contains MS-DOS
commands to configure the netstation's local area network connections.
Syntax
(
NET
LOAD
)y~-.---
drive:
\path
....
-_._-_
filename
LAN
r'
.....
!
-
Manager
I
Option
drive:\path
filename
When used without options, the NET
\30PEN\DOSWKSTA \LANMAN\PROFILES\NETLOGON.PRO.
Purpaie
Specifies the location
are specified, MS-DOS L Manager Enhanced assumes the
profile file is located in the default directory
\3 open\doswksta\lanman\proJiles.
Specifies the name
of
t~rofile
of
the profile file.
LOAD command loads the default profile file
file.
If
no drive letter and path
Page 89

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-62
Comments
The NET LOAD command loads a profile file for your netstation. A profile file is
like a batch file, containing NET
local area network connections.
USE commands that configure your netstation's
The NET
if
you type the NET LOAD command before logging on to the Workstation service,
MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced offers to log you on to the netstation
automatically:
Workstation
OK
Type Y to log on to the Workstation service and load your profile file.
If
any connections to shared resources exist when NET LOAD is used, MS-DOS
LAN
connections and establishing the ones specified in the profile file.
connections are actually in use when you type the NET
LAN
continue.
About
By
the directory
directory makes it easy for users to create, find, and use profile files.
LAN
specify otherwise. From the
command to create a profile file. Typically, your network administrator will create
a default
connected to the local area network.
profile to fit your specific needs.
LOAD command cannot run
not
started.
to
start
Manager Enhanced prompts for confmnation before canceling the existing
Manager Enhanced displays an error message and asks
Profile
default, MS-DOS
Manager Enhanced also assumes a filename extension
it?
(Y/[N])
If
you do, any existing connections are discontinued.
Files
LAN
Manager Enhanced assumes profile files are stored in
\3open\doswksta\/anman\proji/es. Storing all profile files in one
MS-DOS prompt, you can use the NET SA VE
NETLOGON.PRO file on your netstation when the netstation is first
if
the Workstation service is not started. But
If
any
LOAD command, MS-DOS
if
you want to
MS-DOS
of
.PRO, unless you
If
you wish, you can later modify the default
Page 90

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager
Reference
Command
2-63
Example
Jenny is working
computer room. She uses the NET SAVE command to create a new
called
computer room:
NETPRINT.PRO, that connects her netstation to the line printer in the
on
a new project this week and needs to use the printer in the
profile file,
net
Normally, Jenny has no need to use this printer, so she did not want to alter her
default
she types:
net
See
For more information about this command, see:
save
NETLOGON.PRO file. When Jenny wants to print with the line printer,
10ad
netprint.pro
netprint.pro
Also
• The
• The NET START command in this chapter, for information about how profile
• The Load Configuration dialog box in Chapter 3:
NET
SA VE command in this chapter, for information about creating profile
files.
files are loaded when the netstation is started.
LAN
Manager Screen
Reference, for information about loading profile files using the
screen.
LAN
Manager
Page 91

MS-DOS LAN
2
Manager
Reference
Command
2-64
NET LOGOFF
This command ends a computer's connection with the 3+Open network and logs a
user name
Syntax
off
from the
3+0pen
network.
(NET
LOGOFF
)---
....
Comments
The
NET LOGOFF command is used to end a user's
Since only one user at a time can be logged
netstation, logging
NET
LOGOFF only logs you
command, described at the beginning
network includes the 3+Name service.
If
you are actively using any shared resources (for example, your current drive is a
redirected drive), you must stop using the resources before you can log off.
have any connections to a server's shared resources when you use the
LOGOFF command, MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced warns you that logging
deletes those connections.
If
you confirm your request, you will see the following message
username
successfully
Once the NET LOGOFF command has been completed, you no longer have an
active user name, password,
messages sent to your user name.
off
one user name frees the netstation for use by someone else.
off
the
You
are then asked to confrrrn your request to log off.
logged
off
or
local area network session, and you cannot receive
on
to the local area network from a
3+0pen
of
network; you must use the
this chapter, to log
3+0pen
off
network session.
LOGOFF
the network
on
your screen:
if
If
NET
your
you
off
Page 92

Example
At
the end
of
the day, to log
MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-65
off
from the local area network, Jenny types:
net
logoff
See Also
For more information about this command, see:
• The LOGOFF command earlier in this chapter, for information about logging
from
off
mixed networks (networks that include the 3+Name service).
•
The
NET
LOGON command in this chapter, for information about logging
to the
• The Log Into Network dialog box
Reference, for information about logging on to MS-DOS LAN Manager
Enhanced using the LAN Manager screen.
3+0pen
network.
in
Chapter
3:
LAN
Manager Screen
on
Page 93

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
2
Reference
2-66
NET LOGON
This command logs a user name
the user name and password for the user's netstation.
Syntax
(
NET
WGON
)
~r---u-s-e:-n-a-m-e-V
on
to MS-DOS
LAN
~-p-a-s-~-wo-r-d-j71
Manager Enhanced and sets
Option Abbreviation
username
password
When
password.
used without options,
Purpose
Specifies the default user name for the local
netstation (up to
SEecifies the
1 characters ong).
NET
LOGON
Comments
The
NET
LOGON
by
3+0pen
logs you
3+0pen
NET
command, described earlier in this chapter,
service.
servers to validate requests to use shared resources. This command
on
to the 3+Open network; it does not log you
server.
LOGON
command establishes the user name and password that are used
works only with
3+0pen
servers; you must use the 'LOGON
20 characters long).
~assword
prompts for both the user name and the
if
your network includes the 3+Name
for the netstation (up to
on
to any particular
Page 94

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
2-67
If
your
3+0pen
database
of
name and password are sent to the server for verification.
recognizes the user name/password combination you gave, you are allowed to log
on
to the 3+Open network.
account,
you log
MS-DOS
on
server.)
network uses logon security (by keeping a distributed
user names and passwords on one
or
more servers), then your user
If
If
you have a logon script associated with your
LAN
Manager Enhanced runs the script on your net station when
the logon server
or
centralized
to the 3+Open network. (This script is contained in a file on the logon
When
prompting for a user name, the NET LOGON command displays a default
user name. This name is taken from the username= entry
file.
If
this entry has no value, NET
net station (from the computemame= entry
user
name.
of
Instead
MS-DOS
typing your password, you can type an asterisk (*). This causes
LAN
Manager Enhanced to prompt you for your password.
type your password at the prompt, it is not displayed
LOOON
uses the computer name
in the LANMAN.INI file) as the default
on
to keep your password confidential.
You can use the
name and password. To
NET
LOGON
do
command at any time to change a netstation's user
this, simply type the
NET
LOGON
with the new user name and password.
If
someone is already logged
NET
LOOON
logged
The
off
NET
the netstation.
command displays a prompt saying that that user name must be
before another can
LOGON command also tries to add the specified user name as an alias for
If
the user name cannot be added as an alias, MS-DOS
Manager Enhanced logs you
on
to the
be
logged on.
on
to the
3+0pen
3+0pen
network from your netstation, the
network, but displays a warning
message.
of
the LANMAN.INI
of
the
When
you
the screen. This helps you
command, along
LAN
Page 95

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-68
Example
For
Jenny to establish her user name,jennyt, and password, babaloo, as the default
on
a netstation, she types:
net
1ogon
If
the netstation already had a default user name and password, Jenny would see the
jennyt
baba100
following prompt:
You
are
You
must
Proceed
USERl
JENNYT
currently
logoff
with
logged
logged
logoff?
off
logged
before
successfully
on
successfully.
on
logging
(Y/[N]):
as
USERl
on.
Y
She types Y for yes, and her user name and password become the default for the
netstation.
See
Also
For more information about this command, see:
• The LOGON command at the beginning
logging
on
to mixed networks (networks containing the 3+Name service).
• The NET LOGOFF command in this section
about logging
•
The
NET START WORKSTATION command in this chapter, for information
off
from the
3+0pen
of
this chapter, for information about
network.
of
this chapter, for information
about specifying a user name and password when starting the netstation under
MS-DOS
LAN
Manager Enhanced.
• The Log Into Network dialog box in Chapter
Reference, for information about logging on to the
Manager Screen.
3:
LAN Manager Screen
3+0pen
network using
LAN
Page 96

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
NET MOVE
This command moves files, both locally and remotely.
Syntax
(
NET
MOVE
)-.---1
pathnamel
I
2-69
Option
pat~namel
pathname2 Identifies the directory
Purpose
Names the file(s) to be moved.
wildcard characters (*
or
or
pathnamel will be moved.
are moved to the current directory.
in
pathnamel, then pathname2 must be a directory.
This pathname can include
?).
filename
If
of
the file(s) to which
pathname2 is not specified, the files
If
wildcard characters are used
Comments
The
NET
MOVE
permission to use. You can move files between two network computers.
not have to make connections to servers to move network files; the
command makes the connections for you.
Moving a file is not the same as copying a file. Copying makes a duplicate
specified file and leaves the original in place; moving relocates a file from one place
to another.
To move files, you must have create and delete permission for both the source files
and the destination directory.
command moves files between any two directories you have
You
NET
MOVE
of
do
the
Page 97

MS-DOS LAN
Manager
Reference
Command
2
2-70
Example
To
move all
netstation to the \reports\budget directory on the general server,
of
the document files from the text directory on drive C
of
her
Olga types:
net
All
server and have been deleted from
See
For
•
•
move
of
Olga's files that match the c:\texf\* .doc pathname are now
c:\text\*.doc
\\general\reports\budget
Olga's c:\text directory.
Also
more information about this command, see:
The
NET
COpy
The
MS-DOS User Guide, for information about wildcard characters.
command in this chapter, for information about copying fues.
on
the \\general
Page 98

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
NET NAME
This command displays, adds,
of
net station's list
Syntax
NET
NAME
aliases.
alias
2-71
or
deletes the message aliases defined in a
Option
alias
ladd
Purpose
Specifies an alias you want to add
Adds an alias to the netstation.
or
delete.
Idelete Removes an alias previously added to the netstation.
When used without options, the NET NAME command lists all
on
currently active
Name
JIMMYW
WALTERK
GUEST
The
command
the local netstation. For example:
completed
successfully.
of
the aliases
Page 99

MS-DOS LAN
Manager Command
Reference
2
2-72
Comments
The NET NAME command is also available under MS-DOS
but under Basic
MS-DOS LAN Manager Enhanced, it provides many more options. These options
deal with aliases used for messaging. Therefore, the
Messenger service must be started before you use NET NAME to work with
aliases.
it
only lists the user name established at your netstation. Under
MS-DOS LAN Manager
LAN
Manager Basic,
A netstation can have three types
• One computer name
• One user name
• One
Your netstation can receive messages sent to all three types
The fadd switch is optional (that is, fadd is assumed with no other options); you can
add a new alias by typing NET NAME, along with the alias without the fadd
option. Thus, the following two commands do the same thing, assuming
new alias:
net
net
or
more aliases
name
name
jackst
jackst
/add
of
names:
of
names.
jackst
is a
Page 100

MS-DOS LAN 2
Manager Command
Reference
Example
Jimmy Wilson just started working in the mailroom.
messages for him, until he gets a net station
command at her netstation:
of
his own. Leslie types the following
2-73
He
wants Leslie to receive
net
name
j immyw
Now Leslie's netstation is ready to receive all messages sent to jimmyw. When
Jimmy gets his own netstation, Leslie can stop receiving messages for him by
typing:
net
See
For
• The NET SEND command in this chapter (if you have MS-DOS
name
j immyw /
delete
Also
more information about this command, see:
LAN
Manager
Enhanced), for information about sending messages to other users.
• The Aliases for Messaging dialog box in Chapter 3:
Reference, for information about adding and deleting aliases using the
LAN
Manager Screen
LAN
Manager screen.
 Loading...
Loading...