3Com SuperStack 3 4900 SX, 3C17700, 3C17702, SuperStack 3 4924, SuperStack 3 4950 Getting Started Manual
...Page 1

SuperStack® 3
Switch 4900 Family
Getting Started Guide
Switch 4900 (3C17700)
Switch 4900 SX (3C17702)
Switch 4924 (3C17701)
Switch 4950 (3C17706)
http://www.3com.com/
Part No. DUA1770-0AAA05
Published September 2003
Page 2

3Com Corporation
350 Campus Drive,
Marlborough,
MA 01752-3064
Copyright © 2003, 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced
in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or
adaptation) without written permission from 3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make changes in content from time
to time without obligation on the part of 3Com Corporation to provide notification of such revision or change.
3Com Corporation provides this documentation without warranty, term, or condition of any kind, either
implied or expressed, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties, terms or conditions of
merchantability, satisfactory quality, and fitness for a particular purpose. 3Com may make improvements or
changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this documentation at any time.
If there is any software on removable media described in this documentation, it is furnished under a license
agreement included with the product as a separate document, in the hard copy documentation, or on the
removable media in a directory file named LICENSE.TXT or !LICENSE.TXT. If you are unable to locate a copy,
please contact 3Com and a copy will be provided to you.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
If you are a United States government agency, then this documentation and the software described herein are
provided to you subject to the following:
All technical data and computer software are commercial in nature and developed solely at private expense.
Software is delivered as “Commercial Computer Software” as defined in DFARS 252.227-7014 (June 1995) or
as a “commercial item” as defined in FAR 2.101(a) and as such is provided with only such rights as are
provided in 3Com’s standard commercial license for the Software. Technical data is provided with limited rights
only as provided in DFAR 252.227-7015 (Nov 1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987), whichever is applicable.
You agree not to remove or deface any portion of any legend provided on any licensed program or
documentation contained in, or delivered to you in conjunction with, this User Guide.
Unless otherwise indicated, 3Com registered trademarks are registered in the United States and may or may not
be registered in other countries.
3Com, the 3Com logo, and SuperStack are registered trademarks of 3Com Corporation. XRN is a trademark of
3Com Corporation.
IEEE and 802 are registered trademarks of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows
NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Novell and NetWare are registered trademarks of
Novell, Inc. UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively
through X/Open Company, Ltd.
Netscape Navigator is a registered trademark of Netscape Communications.
JavaScript is a trademark of Sun Microsystems.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are
associated.
ENVIRONMENTAL STATEMENT
It is the policy of 3Com Corporation to be environmentally-friendly in all operations. To uphold our policy, we
are committed to:
Establishing environmental performance standards that comply with national legislation and regulations.
Conserving energy, materials and natural resources in all operations.
Reducing the waste generated by all operations. Ensuring that all waste conforms to recognized environmental
standards. Maximizing the recyclable and reusable content of all products.
Ensuring that all products can be recycled, reused and disposed of safely.
Ensuring that all products are labelled according to recognized environmental standards.
Improving our environmental record on a continual basis.
End of Life Statement
3Com processes allow for the recovery, reclamation and safe disposal of all end-of-life electronic components.
Regulated Materials Statement
3Com products do not contain any hazardous or ozone-depleting material.
Environmental Statement about the Documentation
The documentation for this product is printed on paper that comes from sustainable, managed forests; it is
fully biodegradable and recyclable, and is completely chlorine-free. The varnish is environmentally-friendly, and
the inks are vegetable-based with a low heavy-metal content.
Page 3

CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions 8
Related Documentation 9
Accessing Online Documentation 9
Documentation Comments 10
1 INTRODUCING THE SUPERSTACK 3 SWITCH 4900 FAMILY
About the Switches 12
Summary of Hardware Features 13
Switch — Front View Detail 14
100/1000BASE-T and 10/100/1000BASE-T Ports 16
1000BASE-SX Ports 16
GBIC Ports 16
LEDs 17
Switch — Rear View Detail 18
Unit Information Label 19
Power Socket 19
Redundant Power System Socket 19
Console Port 20
Expansion Module Slot 20
Default Settings 20
2 INSTALLING THE SWITCH
Package Contents 22
Choosing a Suitable Site 22
Rack-mounting 23
Placing Units On Top of Each Other 24
Creating an XRN Distributed Fabric 24
The Power-up Sequence 27
How To Interconnect Units 25
Rules For Interconnecting Units 25
Page 4

Powering-up the Switch 27
Checking for Correct Operation of LEDs 27
Connecting a Redundant Power System 27
Choosing the Correct 10/100/1000BASE-T Cables 28
Choosing the Correct Fiber Cables 29
Switch 4950 — GBIC Operation 29
Approved GBIC Transceivers 29
Inserting a GBIC Transceiver 30
Removing a GBIC Transceiver 31
3 SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
Setting Up Overview 34
IP Configuration 35
Preparing for Management 36
Manually Configuring IP Information 37
Connecting to a Front Panel Port 37
Connecting to the Console Port 40
Viewing Automatically Configured IP Information 43
Using 3Com Network Supervisor 43
Connecting to the Console Port 44
Methods of Managing a Switch 46
Command Line Interface Management 46
Web Interface Management 47
SNMP Management 47
Setting Up Command Line Interface Management 48
CLI Management via the Console Port 48
CLI Management over the Network 48
Setting Up Web Interface Management 49
Pre-requisites 49
Web Management Over the Network 50
Setting Up SNMP Management 51
Pre-requisites 51
Default Users and Passwords 51
Changing Default Passwords 52
4 PROBLEM SOLVING
Solving Problems Indicated by LEDs 54
Page 5

Solving Hardware Problems 55
Solving Communication Problems 57
Solving Software Upgrade Problems 58
A SAFETY INFORMATION
Power Cord Set — Japan 59
Important Safety Information 60
L’information de Sécurité Importante 63
Wichtige Sicherheitsinformationen 66
B PIN-OUTS
Null Modem Cable 69
PC-AT Serial Cable 69
Modem Cable 70
RJ-45 Pin Assignments 70
C TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
D OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR PRODUCT
Register Your Product to Gain Service Benefits 75
Purchase Value-Added Services 75
Troubleshoot Online 75
Access Software Downloads 76
Contact Us 76
Telephone Technical Support and Repair 76
INDEX
REGULATORY NOTICES
Page 6

Page 7
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide provides all the information you need to install and use the
following Switches in their default state:
■ SuperStack
■ SuperStack
■ SuperStack
■ SuperStack
This guide is intended for use with all the 4900 Family Switches listed
above. For illustrative purposes all pictures and example screens show the
4900 model, however, all procedures apply to all the other Switches listed
unless otherwise stated.
®
3 Switch 4900 (3C17700)
®
3 Switch 4900 SX (3C17702)
®
3 Switch 4924 (3C17701)
®
3 Switch 4950 (3C17706)
The guide is intended for use by network administrators who are
responsible for installing and setting up network equipment;
consequently, it assumes a basic working knowledge of LANs (Local Area
Networks).
If the information in the release notes that are shipped with your product
differ from the information in this guide, follow the instructions in the
release notes.
Most user guides and release notes are available in Adobe Acrobat
Reader Portable Document Format (PDF) or HTML on the 3Com
World Wide Web site:
http://www.3com.com/
Page 8

8 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions Tab l e 1 and Ta bl e 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide.
Tab le 1 Notice Icons
Icon Notice Type Description
Information note Information that describes important features or
instructions.
Caution Information that alerts you to potential loss of data or
potential damage to an application, system, or device.
Warning Information that alerts you to potential personal
injury.
Tab le 2 Text Conventions
Convention Description
Screen displays This typeface represents information as it appears on the
screen.
Syntax The word “syntax” means that you must evaluate the syntax
provided and then supply the appropriate values for the
placeholders that appear in angle brackets. Example:
To change your password, use the following syntax:
system password <password>
In this example, you must supply a password for <password>.
Commands The word “command” means that you must enter the
command exactly as shown and then press Return or Enter.
Commands appear in bold. Example:
To display port information, enter the following command:
bridge port detail
The words “enter”
and “type”
Keyboard key names If you must press two or more keys simultaneously, the key
Words in italics Italics are used to:
When you see the word “enter” in this guide, you must type
something, and then press Return or Enter. Do not press
Return or Enter when an instruction simply says “type.”
names are linked with a plus sign (+). Example:
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del
■ Emphasize a point.
■ Denote a new term at the place where it is defined in the
text.
■ Identify menu names, menu commands, and software
button names. Examples:
From the Help menu, select Contents.
Click OK.
Page 9

Related Documentation 9
Related
Documentation
In addition to this guide, each Switch documentation set includes the
following:
■ Management Quick Reference Guide
This guide contains:
■ a list of software features supported by each Switch.
■ a summary of the web interface and command line interface
commands for the Switch.
■ Release Notes
These notes provide information about the current software release,
including new features, modifications, and known problems.
■ Implementation Guide
This guide contains information on the features supported by your
Switch and how they can be used to optimize your network. It is
supplied in PDF format on the CD-ROM that accompanies the Switch.
■ Management Interface Reference Guide
This guide provides detailed information about the web interface and
command line interface that enable you to manage the Switch. It is
supplied in HTML format on the CD-ROM that accompanies the
Switch.
Accessing Online
Documentation
There are other publications you may find useful:
■ Documentation accompanying the Advanced Redundant Power
System.
■ Documentation accompanying the Expansion Modules.
■ Documentation accompanying 3Com Network Supervisor. This is
supplied on the CD-ROM that accompanies the Switch.
The CD-ROM supplied with your Switch contains the following online
documentation:
■ Implementation Guide (PDF format)
■ Management Interface Reference Guide (HTML format)
■ Other documentation relating to the Switch 4900 Family (PDF format)
Page 10
10 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
To access the online documentation from the CD-ROM:
1 Insert the CD-ROM into the relevant CD-ROM drive. If your PC has
auto-run enabled, a splash screen will be displayed automatically.
2 Select the Documentation section from the contents page.
If the online documentation is to be accessed from a local drive or server,
you will need to access the CD-ROM contents via the root directory and
copy the files from the CD-ROM to a suitable directory.
■ The HTML Reference Guide is stored in the Docs/referenceguide
on the CD-ROM. The documentation is accessed using the index.htm
file.
■ The PDF Implementation Guide is stored in the
Docs/implementation directory of the CD-ROM.
3Com recommends that you copy the Docs/referenceguide
directory as a whole to maintain the structure of the files.
Documentation
Comments
Your suggestions are very important to us. They will help make our
documentation more useful to you. Please e-mail comments about this
document to 3Com at:
pddtechpubs_comments@3com.com
Please include the following information when commenting: Document
title, Document part number (on the title page) and Page number (if
appropriate).
Example: Part Number DUA1770-0AAA0x, SuperStack 3 Switch 4900
Family Getting Started Guide, Page 21
Page 11
1
INTRODUCING THE
S
UPERSTACK 3 SWITCH 4900
AMILY
F
This chapter contains introductory information about the Switch 4900,
4900 SX, 4924 and 4950 and how they can be used in your network. It
covers summary information about the hardware.
The information for all the Switches in the Switch 4900 Family is the same
unless otherwise stated.
■ About the Switches
■ Summary of Hardware Features
■ Switch — Front View Detail
■ 100/1000BASE-T and 10/100/1000BASE-T Ports
■ 1000BASE-SX Ports
■ GBIC Ports
■ LEDs
■ Switch — Rear View Detail
■ Unit Information Label
■ Power Socket
■ Redundant Power System Socket
■ Console Port
■ Expansion Module Slot
■ Default Settings
Page 12
12 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE SUPERSTACK 3 SWITCH 4900 FAMILY
About the Switches ■ The Switch 4900 connects your existing 100 Mbps devices and
high-performance workgroups with a 1000 Mbps copper backbone or
server connection.
■ The Switch 4900 SX connects your existing 1000 Mbps devices and
high-performance workgroups with a 1000BASE-SX fiber backbone or
server connection.
■ The Switch 4924 connects your existing 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps
devices and high-performance workgroups to a 1000 Mbps copper
backbone or server connection.
■ The Switch 4950 is a 10/100/1000 Mbps mixed media device that
allows you to connect your existing 10/100/1000 Mbps devices and
high-performance workgroups to a fiber or copper gigabit backbone
or server connection.
You can also interconnect any combination of two Switches from the
®
SuperStack
Distributed Fabric. This allows you to create a highly resilient core around
which you can build your network. For more information about
interconnecting Switches, see “Creating an XRN Distributed Fabric”
page 24
use it in your network, refer to the Implementation Guide on the
CD-ROM that accompanies the Switch.
4900 Family or 3Com Switch 40x0 Family to create an XRN
. For more information about 3Com XRN Technology and how to
on
For information about using the software features of the Switch, refer to
the “SuperStack 3 Switch Management Interface Reference Guide” on
the CD-ROM that accompanies the Switch.
Page 13

About the Switches 13
Summary of
Hardware Features
Tab l e 3 summarizes the hardware features that are supported by the
Switches.
Tab le 3 Hardware features
Feature Switch 4900 Family
Fast Ethernet
and Gigabit
Ethernet Ports
Addresses ■ Up to 12,000 supported
Forwarding
Modes
Duplex Modes ■ Half duplex only supported on
Flow Control Supported on all ports
Smart
auto-sensing
Tra ff ic
Prioritization
Layer 3
Switching
RPS Support Connects to SuperStack 3 Advanced Redundant Power System
XRN Support eXpandable Resilient Networking (XRN) support. Allows
Mounting 19-inch rack or stand-alone mounting
Switch 4900: 12 Auto-negotiating 100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T
ports
Switch 4900 SX: 12 Auto-negotiating 1000BASE-SX ports
Switch 4924: 24 Auto-negotiating
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T ports
Switch 4950: 12 Auto-negotiating
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T, 6 1000BASE-SX and
6 GBIC ports
■ Up to 64 permanent entries
Store and Forward
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T ports in 10/100 Mbps
mode
■ All 1000 Mbps ports are full duplex only
■ Supported on all 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T ports
■ Not supported on 1000BASE-SX and GBIC ports
Supported (IEEE Std 802.1D, 1998 Edition)
Four traffic queues per port
Support for wire-speed IP routing
(ARPS) (3C16071B)
interconnection of two units to create a Distributed Fabric.
Page 14

14 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE SUPERSTACK 3 SWITCH 4900 FAMILY
Switch — Front
View Detail
1x
3C17700
100BASE-TX / 1000BASE-T Ports
Figure 1 Switch 4900 — front view
112
3
Packet
6x
2
3
Status
Port Status LEDs
Module Status LEDs
flashing
green
yellow
4
4
Status
= 1000Mbps
= 100Mbps
on
= enabled,link OK
= disabled
665
5
10
8
9
11
7
10
8
9
11
7
Unit
Module
12
132
12
Power/Self Test
4
Layer 3
Power / Self Test LED
and Layer 3 LED
Unit LEDs
Figure 2 Switch 4900 SX — front view
7x
3C17700 SuperStack 3
100BASE-TX / 1000BASE-T Ports
Switch 4900
12x
Page 15
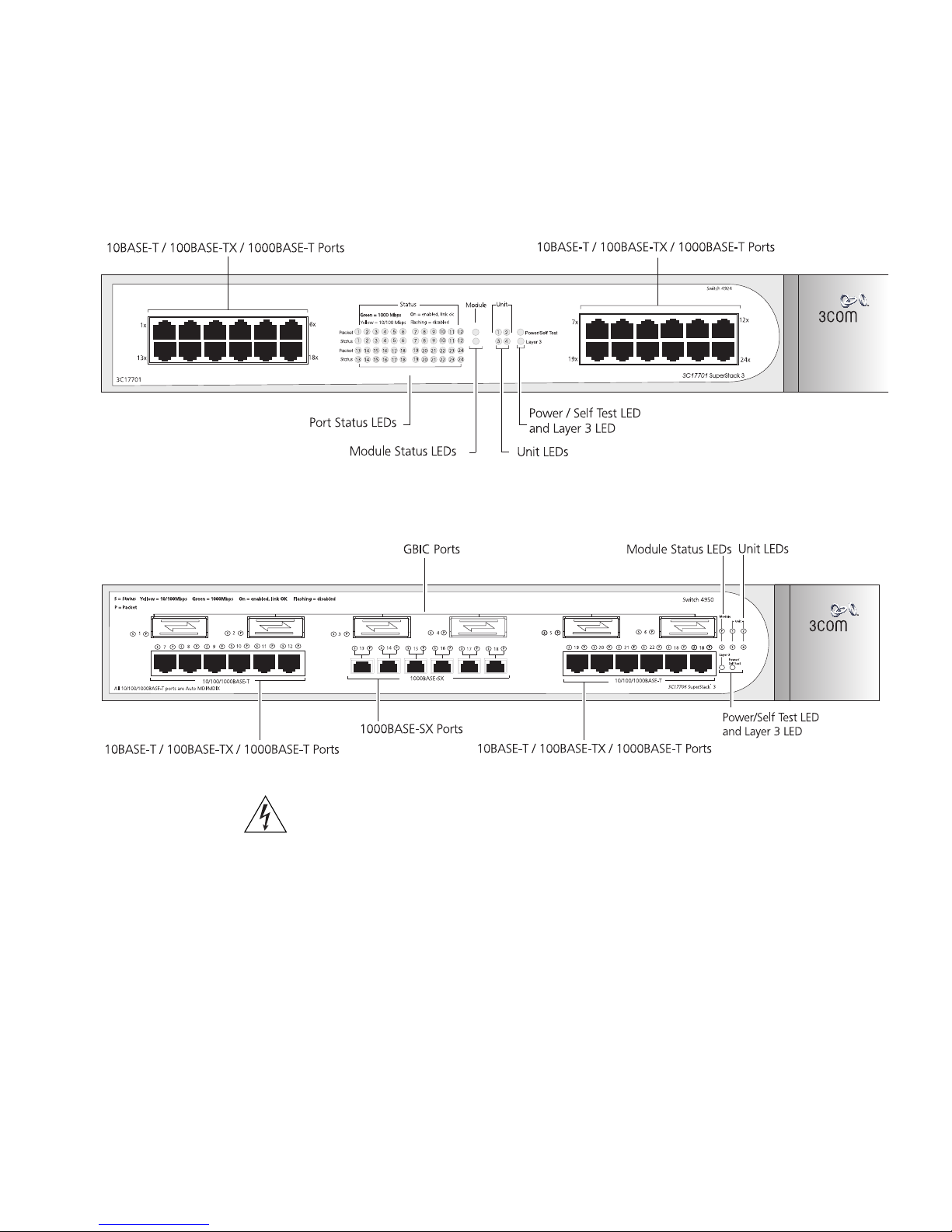
Figure 3 Switch 4924 — front view
Figure 4 Switch 4950 — front view
Switch — Front View Detail 15
WARNING: RJ-45 Ports. These are shielded RJ-45 data sockets. They cannot
be used as standard traditional telephone sockets, or to connect the unit to a
traditional PBX or public telephone network. Only connect RJ-45 data
connectors, network telephony systems, or network telephones to these
sockets.
Either shielded or unshielded data cables with shielded or unshielded
jacks can be connected to these data sockets.
Page 16
16 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE SUPERSTACK 3 SWITCH 4900 FAMILY
100/1000BASE-T and
10/100/1000BASE-T
Ports
The 100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T and 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T
ports have RJ-45 connectors and are configured as Auto MDIX
(cross-over).
The default state for these ports is auto-negotiation enabled, where the
speed, duplex and flow control modes of a link are automatically
detected to provide the highest available bandwidth with the link partner.
Alternatively, auto-negotiation can be disabled. These ports can be
manually configured to 10 Mbps half duplex (if supported), 100 Mbps
half duplex, 10 Mbps full duplex (if supported), or 100 Mbps full duplex.
It is not possible to manually configure a 1000BASE-T link as
auto-negotiation is mandatory in the 1000BASE-T standard.
The maximum segment length is 100 m (328 ft) over Category 5 twisted
pair cable.
1000BASE-T operation only supports full-duplex mode.
10BASE-T (10 Mbps) is only supported on Switch 4924 and 4950.
1000BASE-SX Ports The default state for these ports is auto-negotiation enabled, where the
speed, duplex and flow control modes are negotiated. As the speed and
duplex modes are fixed by the media type, only the flow control is
negotiated with the link partner. Alternatively, auto-negotiation can be
disabled and the flow control setting can be manually configured.
1000BASE-SX ports do not support auto-negotiation of speed and only
support full duplex mode.
GBIC Ports GBIC ports support fiber Gigabit Ethernet short-wave (SX), long-wave
(LX) and long-haul (LH70) GBIC transceivers in any combination. This
offers you the flexibility of using GBIC transceivers to provide connectivity
between the Switch and remote 1000 Mbps workgroups or to create a
high capacity aggregated link backbone connection.
The default state for these ports is auto-negotiation enabled, where the
speed, duplex and flow control modes are negotiated. As the speed and
duplex modes are fixed by the media type, only the flow control is
negotiated with the link partner. Alternatively, auto-negotiation can be
disabled and the flow control setting can be manually configured.
Page 17

Switch — Front View Detail 17
LEDs Ta bl e 4 lists LEDs visible on the front of the Switch, and how to read their
status according to color. For information on using the LEDs for problem
solving, see “Checking for Correct Operation of LEDs”
Tab le 4 LED behavior
LED Color Indicates
Port LEDs
Packet Yellow Packets are being transmitted/received on the port.
Off No packets are being transmitted/received on the port.
Status Green A high speed (1000 Mbps) link is present, and the port
is enabled.
Green flashing A high speed (1000 Mbps) link is present, but the port
is disabled.
Yellow A low speed (100 Mbps on 4900, 10/100 Mbps on
4924/4950) link is present, and the port is enabled.
(Not applicable on 4900 SX.)
Yellow flashing A low speed (100 Mbps on 4900, 10/100 Mbps on
4924/4950) link is present, but the port is disabled.
(Not applicable on 4900 SX.)
Off No link is present.
Module LEDs
Packet Yellow Packets are being transmitted/received on the port.
Off No packets are being transmitted/received on the port.
Status Green The Module is installed and supported. The Link Status
has been determined for a single port Module.
Yellow The Module is installed and supported. The Module
has multi-ports or there is no link for a single port
Module.
Yellow flashing The Module is installed but not supported. Note that
the Switch will continue to operate normally.
Yellow flashing
(fast)
Off The Module is not installed.
Unit LEDs
1–4 Green Determines the identity of the Switch when
Off A fault has occurred.
Power/Self Test LED
Green The Switch is powered-up and operating normally.
A port on the Module has failed POST and has been
automatically disabled.
interconnected to another Switch to create an XRN
Distributed Fabric and that a link is present.
on page 27.
Page 18
18 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE SUPERSTACK 3 SWITCH 4900 FAMILY
LED Color Indicates
Green flashing The Switch is either downloading software or is
initializing (which includes running a Power On Self
Test).
Yellow The Switch has failed its Power On Self Test.
Off The Switch is not receiving power.
Layer 3 LED
Green The Switch software supports Layer 3.
Off The Switch software does not support Layer 3.
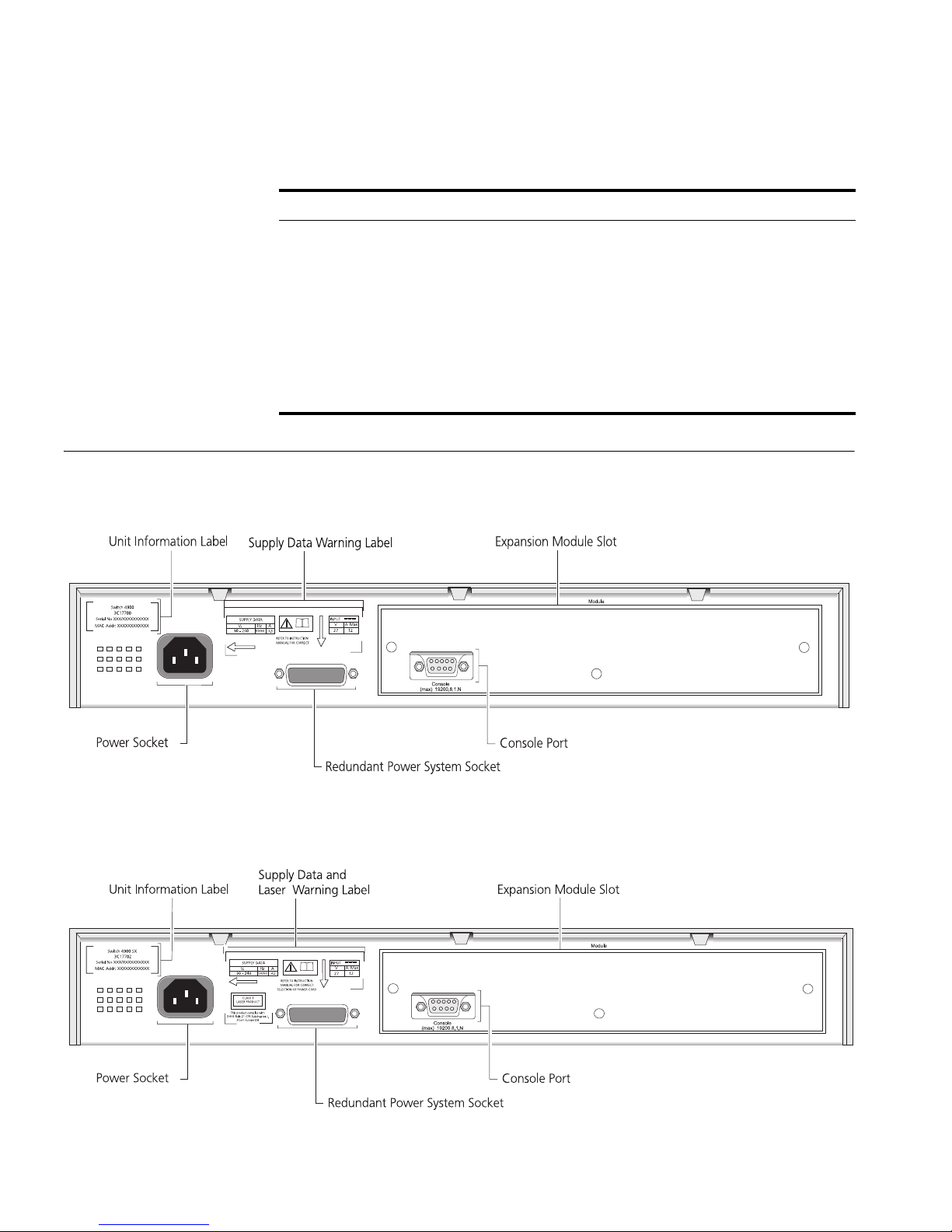
Switch — Rear
View Detail
Figure 5 Switch 4900 — rear view
Figure 6 Switch 4900 SX — rear view
Page 19
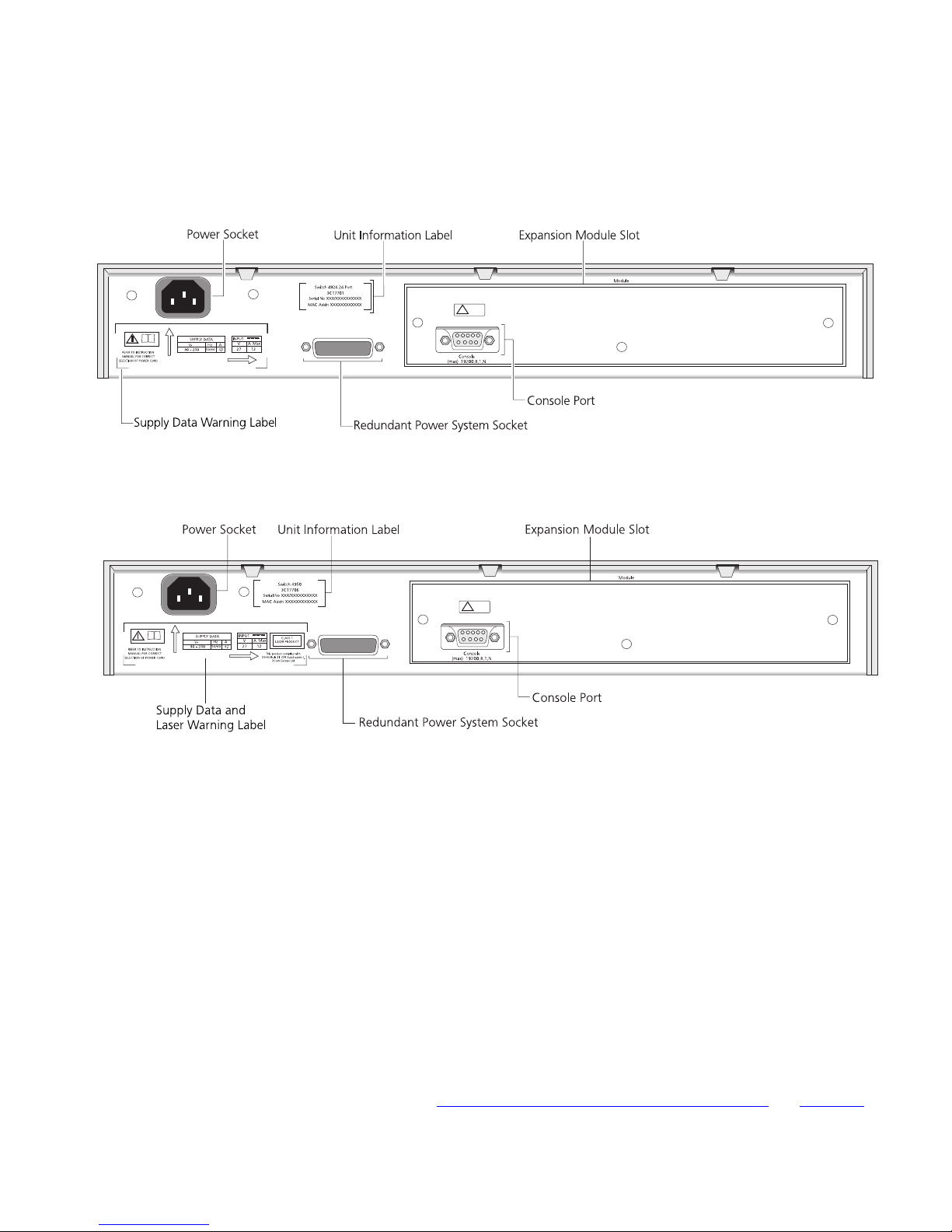
Figure 7 Switch 4924 — rear view
Figure 8 Switch 4950 — rear view
Switch — Rear View Detail 19
Unit Information
Label
This label shows the following:
■ The 3Com product name of the Switch
■ The 3Com 3C number of the Switch
■ The unique MAC address (Ethernet address) of the Switch
■ The serial number of the Switch
You may need this information for fault reporting purposes.
Power Socket The Switch automatically adjusts its power setting to any supply voltage
in the range 90-240 VAC.
Redundant Power
System Socket
To protect against internal power supply failure, you can use this socket
to connect a SuperStack 3 Advanced Redundant Power System (RPS) to
the Switch. See “Connecting a Redundant Power System”
on page 27.
Page 20
20 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING THE SUPERSTACK 3 SWITCH 4900 FAMILY
Console Port The console port allows you to connect a terminal and perform remote or
local out-of-band management. The console port uses a standard null
modem cable and is set to auto-baud (up to a maximum of 19200 baud),
8 data bits, no parity and 1 stop bit.
Expansion Module
Slot
You can use this slot to install an Expansion Module. Contact your
supplier for further information on the range of Expansion Modules
supported by your Switch.
WARNING:
When an Expansion Module is not installed, ensure the
blanking plate is fitted by tightening all screws with a suitable tool.
Default Settings Tab l e 5 shows the default settings for the Switches. If you initialize one of
the Switch units, it is returned to these defaults.
Tab le 5 Default Setting
Feature Switch 4900 Family
Port Status Enabled
Port Speed Auto-negotiated
Duplex Mode Auto-negotiated
Flow Control Auto-negotiated
Broadcast Storm Control Enabled
High threshold: 3000 broadcast frames per
second — Notify and filter
Low threshold: 1500 broadcast frames per
second — Notify and unfilter
Virtual LANs (VLANs) All ports belong to the untagged Default VLAN
(VLAN 1)
Multicast Filtering IGMP filtering enabled
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Enabled
Link Aggregation Control
Protocol (LACP)
Smart Auto-sensing Switch 4900, 4924, and 4950: Enabled
IP Address 169.254.100.100
Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0
Disabled per port
Switch 4900 SX: Not applicable
*
* This default IP address is used if the unit is operating in standalone mode, and/or no other
Switches on the network have this IP address. If this default IP address is already in use then the
Switch detects this and configures itself with an IP address in the range 169.254.1.0 to
169.254.254.255.
Page 21
2
INSTALLING THE SWITCH
This chapter contains the information you need to install and set up the
Switch. It covers the following topics:
■ Package Contents
■ Choosing a Suitable Site
■ Rack-mounting
■ Placing Units On Top of Each Other
■ Creating an XRN Distributed Fabric
■ The Power-up Sequence
■ Switch 4950 — GBIC Operation
WARNING: Safety Information. Before installing or removing any
components from the Switch or carrying out any maintenance
procedures, you must read the safety information provided in Appendix A
of this guide.
AVERTISSEMENT: Consignes de sécurité. Avant d'installer ou d'enlever
tout composant du Switch ou d'entamer une procédure de maintenance,
lisez les informations relatives à la sécurité qui se trouvent dans
l'Appendice A de ce guide.
VORSICHT: Sicherheitsinformationen. Bevor Sie Komponenten aus
dem Switch entfernen oder dem Switch hinzufuegen oder
Instandhaltungsarbeiten verrichten, lesen Sie die
Sicherheitsanweisungen, die in Anhang A in diesem Handbuch
aufgefuehrt sind.
Page 22
22 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE SWITCH
Package Contents ■ Switch unit
■ CD-ROM
■ This Guide
■ Management Quick Reference Guide
■ Release Notes
■ Warranty Flyer
■ Power Cord
■ 2 x securing brackets
■ 6 x screws
■ 4 x rubber feet
Choosing a Suitable
Site
The Switch is suited for use in an internal wiring closet, a network room,
or telecommunications room, where it can be mounted in a standard
19-inch equipment rack, or free-standing.
CAUTION: Ensure that the ventilation holes are not obstructed.
To ensure this product provides optimum performance, high speed fans
are used to provide ventilation. These fans have a high audible output.
When deciding where to position the Switch, ensure that:
■ Cabling is located away from:
■ sources of electrical noise such as radios, transmitters and
broadband amplifiers.
■ power lines and fluorescent lighting fixtures.
■ The Switch is accessible and cables can be connected easily.
■ Water or moisture cannot enter the case of the Switch.
■ Air flow is not restricted around the Switch or through the vents in the
side of the Switch. 3Com recommends that you provide a minimum of
25 mm (1 in.) clearance.
■ Air temperature around the Switch does not exceed 40 °C (104 °F).
If the Switch is installed in a 19-inch rack or closed assembly its local air
temperature may be greater than room ambient temperature.
Page 23

Rack-mounting 23
■ The air is as free from dust as possible.
■ The unit is installed in a clean, air conditioned environment.
■ No more than four Switch units are placed on top of one another, if
the units are free-standing.
■ The Switch is situated away from sources of conductive (electrical)
dust, for example laser printers.
■ The AC supply used by the Switch is separate to that used by units
that generate high levels of AC noise, for example air conditioning
units and laser printers.
Rack-mounting The Switch is 1.5U and will fit in most standard 19-inch racks. However,
as each Switch requires a shelf or runner to support its weight, you may
need to allow a 2U space within the rack for each Switch.
WARNING: The Switch should only be used in a rack if it is mounted on
runners, a shelf, or a tray to support the weight. The rack-mount kits
alone are not sufficient to support the weight of the switch. The rackmount kits must not be used to suspend the Switch from under a table or
desk, or attach it to a wall.
CAUTION: Disconnect all cables from the Switch before continuing.
Remove all self adhesive pads from the underside of the Switch if they
have been fitted.
CAUTION: You must use a shelf or support that will not obstruct the air
flow through the side panels of the Switch.
To rack-mount your Switch:
1 Place the Switch the right way up on a hard flat surface, with the front
facing towards you.
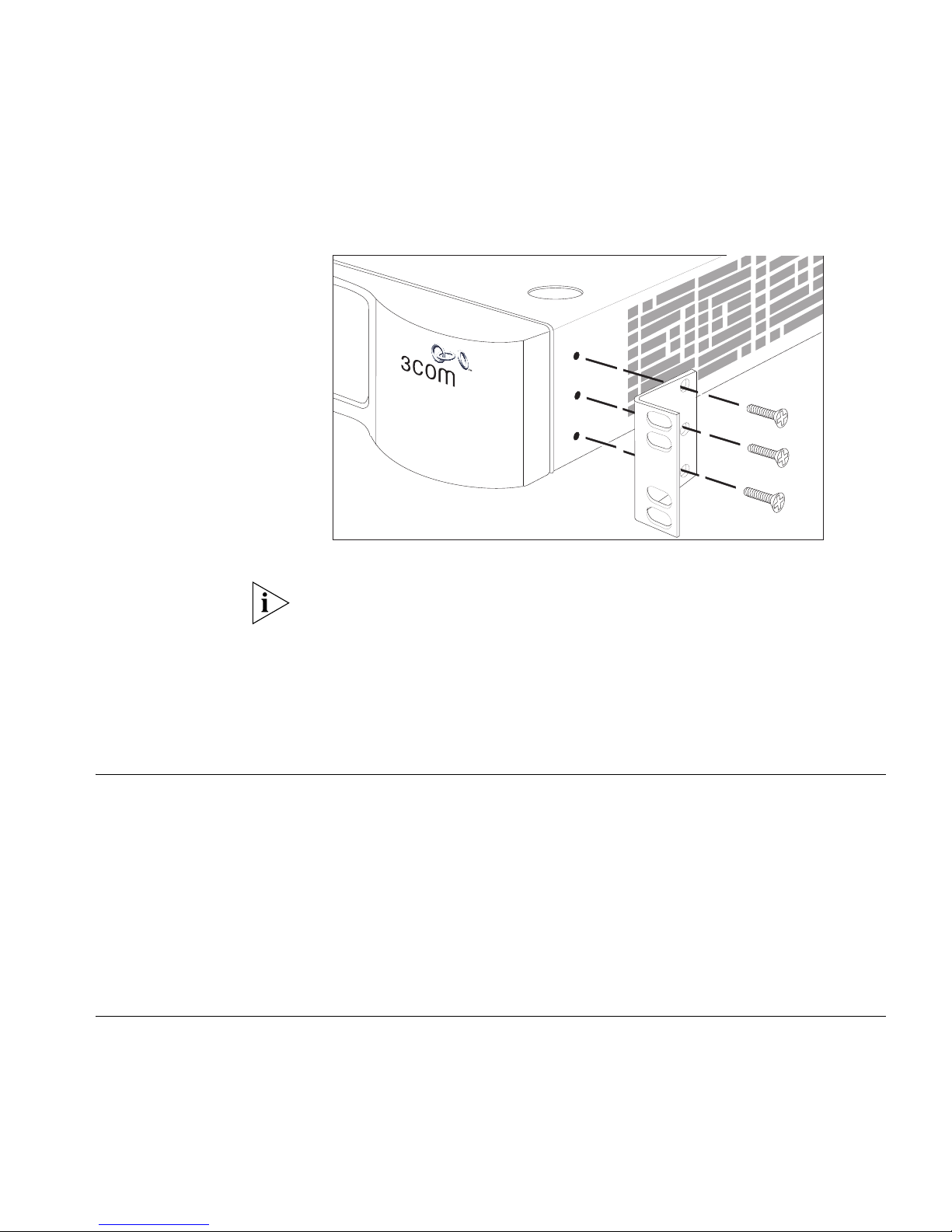
2 Locate a securing bracket over the mounting holes on one side of the
Switch, as shown in Figure 9
.
3 Insert the three screws and tighten with a suitable screwdriver.
Page 24
24 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE SWITCH
Figure 9 Fitting a bracket for rack-mounting
Placing Units On
Top of Each Other
Creating an XRN
Distributed Fabric
You must use the screws supplied with the securing brackets. Damage
caused to the unit by using incorrect screws invalidates your warranty.
4 Repeat steps 2 and 3 for the other side of the Switch.
5 Insert the Switch into the 19-inch rack and secure with suitable screws
(not provided). Ensure that ventilation holes are not obstructed.
6 Connect network cabling.
If the Switch units are free-standing, up to four units can be placed one
®
on top of the other. If you are mixing a variety of SuperStack
3 Switch
and Hub units, the smaller units must be positioned at the top.
If you are placing Switch units one on top of the other, you must use the
self-adhesive rubber pads supplied. Apply the pads to the underside of
each Switch, sticking one in the marked area at each corner. Place the
Switch units on top of each other, ensuring that the pads of the upper
unit line up with the recesses of the lower unit.
SuperStack 3 Switch 4900 Family units and 3Com Switch 40x0 units can
be interconnected to create an XRN Distributed Fabric and then treated as
a single manageable unit with one IP address. A combination of any two
of these units is allowed to be interconnected.
Page 25

Creating an XRN Distributed Fabric 25
S/N: XXXX/7XXXXXXXXX
XRN Interconnect Module (3C17716)
Console
(max) 19200,8,1,N
Unit 1
Unit 2
Activity
Status
S/N: XXXX/7XXXXXXXXX
XRN Interconnect Module (3C17716)
Console
(max) 19200,8,1,N
Unit 1
Unit 2
Activity
Status
How To Interconnect
Units
You can interconnect your Switches to create an XRN Distributed Fabric
using one of the following methods:
■ XRN Interconnect Kit (3C17715) — consists of two XRN Interconnect
Modules and a 1 meter (3.28 feet) Interconnect cable. Should you
wish to connect two Switch units together that are located in separate
racks you can obtain a 5 meter (16.4 feet) Interconnect cable
(3C17722). Contact your
■ SuperStack 3 Switch 4900 Family GBIC Module (3C17714) operating
network supplier for further information.
in XRN mode. Using the GBIC Module in this way means you can have
an Fabric Interconnect extended up to 70 Km (43.5 miles) between
the units, if necessary (dependant upon GBIC transceiver type).
For a detailed description of how to create an XRN Distributed Fabric
using either of these methods, please refer to the user documentation
that accompanies the Kit or the GBIC Module. The documentation can
also be located on the 3Com Web site.
Figure 10 Two Switch 4900 units interconnected using the XRN Interconnect
Kit
Rules For
Interconnecting Units
S
w
i
t
c
h
4
9
0
S
3
e
0
C
r
i
1
a
7
l
N
7
0
o
0
X
M
X
X
A
/
C
X
A
X
X
d
X
d
X
r
:
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SUPPLY DATA
V-
90 - 240
Hz
A
5
0
/6
0
4
.
I
5
I
R
N
E
F
P
E
U
R
T
T
O
M
I
N
A
S
N
T
V
R
U
U
A
C
L
T
F
I
O
O
A
R
N
C
M
O
2
R
a
7
R
x
E
C
T
1
2
(max) 19200,8,1,N
Console
U
n
it 1
U
n
A
it 2
S
/N
:
X
X
ctivity
X
X
/
7
X
X
S
X
ta
X
X
tu
X
s
X
X
X
XRN Interconnect M
odule (3C17716)
S
w
i
t
c
h
4
9
0
S
3
e
0
C
r
i
1
a
7
l
N
7
0
o
0
X
M
X
X
A
/X
C
X
A
X
d
X
d
X
r
:
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
SUPPLY DATA
V-
90 - 240
Hz
A
5
0
/
6
0
4
.
I
5
I
R
N
E
F
P
E
U
R
T
T
O
M
I
N
A
S
N
T
V
R
U
U
A
C
L
T
F
I
O
O
A
R
N
C
M
O
2
R
a
7
R
x
E
C
T
1
2
(max) 19200,8,1,N
Console
U
nit 1
U
n
A
it 2
S
/N
:
X
X
X
ctiv
X
/
7
X
ity
X
S
X
tatu
X
X
X
s
X
X
X
XRN Interconnect Module (3C17716)
This information is also provided in the user documentation that
accompanies the XRN Interconnect Kits or GBIC module.
■ The maximum number of Switch units that can be interconnected is
two.
■ Both Switches must have an unused expansion slot to allow an
Interconnect Module or a GBIC Module to be fitted.
■ The XRN Interconnect Module and the GBIC Module are NOT
hot-swappable or hot-insertable. Ensure that the Switch is powered
off before inserting or removing a Module.
Page 26

26 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE SWITCH
■ Only 3Com XRN Interconnect Cables can be used to connect two XRN
Interconnect Modules.
■ It is not possible to interconnect the SuperStack 3 Switch 4900 Family
and 3Com Switch 40x0 units with any other 3Com device.
■ 3Com strongly recommends that you upgrade all Switches to be
interconnected to the latest software agent.
■ 3Com recommends that you initialize a Switch unit that has previously
been used elsewhere in your network before you interconnect to an
existing unit. If you do not initialize the unit, problems may be caused
by conflicting Switch configurations.
■ When the Switch units are interconnected using the XRN Interconnect
Kit they are assigned a unit number dependent on which XRN
Interconnect Cable end is connected to which Switch. That is, the
Switch with the blue cable end will be assigned the identity of Unit 1
and the Switch with the yellow cable end will be assigned the identity
of Unit 2.
■ When the Switch units are in an XRN Distributed Fabric created using
the GBIC Module, they assume their unit IDs from the MAC address of
the Switch unit within which the GBIC Module is installed. So the unit
with the lowest MAC address will assume Unit 1 ID and the unit with
the highest MAC address will assume Unit 2 ID.
■ To create an XRN Distributed Fabric using a GBIC Module you will
need GMS software version 4.0 or later (Advanced Feature License
3C1770V40) to be installed on both Switch units.
■ Only direct XRN mode to XRN mode connections are supported when
the GBIC Module is operating in XRN mode.
For a detailed description of how XRN Technology operates and
implementation guidelines, please refer to the Implementation Guide on
the CD-ROM that accompanies your Switch or on the 3Com Web site.
Page 27

The Power-up Sequence 27
The Power-up
Sequence
Powering-up the
Switch
Checking for Correct
Operation of LEDs
The following sections describe how to get your Switch powered-up and
ready for operation.
Use the following sequence of steps to power-up the Switch.
1 Plug the power cord into the power socket at the rear of the Switch.
2 Plug the other end of the power cord into your power outlet.
The Switch powers-up and runs through its Power On Self Test (POST),
which takes approximately 10 seconds.
During the Power On Self Test, all ports on the Switch are disabled and
the LEDs light in a rapid sequence.
When the POST has completed, check the Power/Self Test LED to make
sure that your Switch is operating correctly. Ta bl e 6
shows possible colors
for the LED.
Tab le 6 Power/Self Test LED Colors
Connecting a
Redundant Power
System
Color State
Green The Switch is powered-up and operating
normally.
Yellow The Switch has failed its Power On Self Test
(POST) because of an internal problem.
Off The Switch is not receiving power.
If there is evidence of a problem, see “Solving Problems Indicated by
LEDs” on page 54 for a list of suggested solutions.
You can connect a SuperStack 3 Advanced Redundant Power System to
the Switch. This unit, which is also known as an RPS, is designed to
maintain the power to your Switch if a power supply failure occurs.
For normal redundancy, the unit requires one Type 3 Power Module (part
number 3C16075).
For full redundancy, the unit requires two Type 3 Power Modules
combined using a Type 3 Y-Cable (part number 3C16077).
Page 28

28 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE SWITCH
WARNING: If you are connecting the Switch to a Type 3 Power Module,
read the Safety Information section in the Type 3 Power Module User
Guide.
CAUTION: The Switch can only use a SuperStack Advanced Redundant
Power System output.
CAUTION: The Switch has no ON/OFF switch; the only method of
connecting or disconnecting mains power is by connecting or
disconnecting the power cord.
Choosing the Correct
10/100/1000BASE-T
Cables
If your Switch has 10/100/1000BASE-T ports, these ports are Auto-MDIX,
that is they have a cross-over capability. These ports can automatically
detect whether to operate in MDI or MDIX mode. Therefore you can
make a connection to one of the ports with a straight-through (MDI) or a
cross-over cable (MDIX).
The Auto-MDIX feature only operates when auto-negotiation is enabled.
If auto-negotiation is disabled, all the Switch ports are configured as
MDIX (cross-over). If you want to make a connection to another MDIX
port, you need a cross-over cable. Many ports on workstations and
servers are configured as MDI (straight-through). If you want to make a
connection to an MDI port, you need to use a standard straight-through
cable. See Ta bl e 7
.
3Com recommends that you use at least Category 5 twisted pair cable —
the maximum segment length for this type of cable is 100 m (328 ft).
Tab le 7 Cables required to connect the Switch to other devices if
auto-negotiation is disabled
Cross-over Cable Straight-through Cable
Switch to Switch
(MDIX to MDIX)
Switch to Hub
(MDIX to MDIX)
Switch to PC (NIC)
(MDIX to MDI)
✓ ✕
✓ ✕
✕ ✓
CAUTION: If you want to install the Switch using a Category 5E or
Category 6 cable, 3Com recommends that you briefly connect the cable
Page 29

Switch 4950 — GBIC Operation 29
to a grounded port before connecting network equipment. If you do not,
the cable’s Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) may damage the Switch's port.
You can create a grounded port by connecting all wires at one end of a
UTP cable to an earth ground point, and the other end to a female RJ-45
connector located, for example, on a Switch rack or patch panel. The
RJ-45 connector is now a grounded port.
Choosing the Correct
Fiber Cables
If your Switch has fiber ports you can choose from the following cable
options:
■ The 1000BASE-SX ports can be connected to multimode fiber cables
only.
■ The 1000BASE-LX and 1000BASE-LH70 GBIC ports use multimode or
single-mode fiber optic cables.
CAUTION: 3Com recommends that you use MT-RJ cables that do not
contain alignment pins as these are provided by the fiber socket. Cables
that contain alignment pins can cause damage to your Switch.
For detailed information on fiber cable specifications, refer to the
SuperStack 3 Implementation Guide on the CD-ROM that accompanies
your Switch.
If you wish to connect a 1000BASE-SX MT-RJ port to a fiber port with a
different type of connector, for example, SC or ST please contact your
network supplier for a suitable patch cable.
Switch 4950 — GBIC
Operation
The following sections describes how to insert a GBIC transceiver into a
GBIC port on a Switch 4950.
GBIC transceivers are hot-insertable and hot-swappable. You can remove
them from and insert then into any GBIC port without having to power
down the Switch.
Approved GBIC
Transceivers
The following list of approved GBIC transceivers is correct at the time of
publication.
■ 3CGBIC91 GBIC (SX)
■ 3CGBIC92 GBIC (LX)
■ 3CGBIC97 GBIC (LH70)
Page 30

30 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE SWITCH
To access the latest list of approved GBIC transceivers for the Switch on
the 3Com Corporation World Wide Web site, enter this URL into your
internet browser:
http://www.3com.com
Inserting a GBIC
Transceiver
To be recognised as valid, the GBIC transceiver must have the following
characteristics:
■ 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX or 1000BASE-LH70 media type:
■ 1000BASE-SX GBIC transceiver
Use this transceiver to connect the Switch directly to a multimode
fiber-optic cable.
■ 1000BASE-LX GBIC transceiver
Use this transceiver to connect the Switch directly to a single-mode
fiber-optic cable or to multimode fiber using a conditioned launch
cable.
■ 1000BASE-LH70 GBIC transceiver
Use this transceiver to connect the Switch directly to a single-mode
fiber-optic cable or to multimode fiber using a conditioned launch
cable.
■ Fiber SC connector
■ Type 4 GBIC with internal EEPROM fitted.
If the GBIC transceiver is faulty, it will not operate within the Switch. See
“Solving Hardware Problems”
on page 55.
3Com recommends that you only use GBICs supplied by 3Com. If the
GBIC transceiver is invalid it will not be recognised by the Switch.
Use the following sequence of steps to activate the GBIC ports.
1 Hold the transceiver so that the fiber connector (SC) is toward you and
the product label is visible, as shown in Figure 11
2 Gently slide the transceiver into the GBIC port until it clicks into place.
CAUTION: GBIC transceivers are keyed and can be properly inserted only
one way. If the transceiver does not click when you insert it, remove it,
turn it over, and reinsert it.
.
Page 31

Switch 4950 — GBIC Operation 31
Figure 11 Inserting a GBIC Transceiver into a Switch 4950
3 The transceiver connects to the network using a duplex SC connector.
Attach a male duplex SC connector on the network cable into the duplex
SC connector on the transceiver.
Removing a GBIC
Transceiver
4 Connect the other end of the cable to a device fitted with an appropriate
Gigabit Ethernet connection.
5 Check the LEDs on the front of the Switch to ensure that it is operating
correctly. Refer to “LEDs”
on page 17 for more information.
If you wish to remove the transceiver, compress the side tabs and gently
pull the transceiver out of the port.
Page 32

32 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE SWITCH
Page 33

3
SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
Your Switch can operate in its default state, that is, you can install it and
it will work straight away (plug-and-play). However, to make full use of
the features offered by the Switch, and to change and monitor the way it
works, you have to access the management software that resides on the
Switch. This is known as managing the Switch.
Managing the Switch can help you to improve the efficiency of the
Switch and therefore the overall performance of your network.
This chapter explains the initial set up of the Switch and the different
methods of accessing the management software to manage a Switch. It
covers the following topics:
■ Setting Up Overview
■ Manually Configuring IP Information
■ Viewing Automatically Configured IP Information
■ Methods of Managing a Switch
■ Setting Up Command Line Interface Management
■ Setting Up Web Interface Management
■ Setting Up SNMP Management
■ Default Users and Passwords
Page 34

34 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
Setting Up
Overview
This section gives an overview of what you need to do to get your Switch
set up and ready for management when it is in its default state. The
whole setup process is summarised in Figure 12
. Detailed procedural
steps are contained in the sections that follow. In brief, you need to:
■ Configure IP information manually for your Switch or view the
automatically configured IP information
■ Prepare for your chosen method of management
Figure 12 Initial Switch Setup and Management Flow diagram
Power Up the Switch.
Plug and Play Setup
IP Information is automatically configured.
Yes
How do you want to connect to the Switch?
See page 35
Do you want to manually
configure the IP information?
No
How do you want to view the automatically
configured IP information?
Connect to a front
panel port and use the
Initial IP Information Setup
Feature Management
Web Interface or
Command Line Interface.
See page 37
Connect via the
console port.
See page 48
Command Line Interface
Connect to the console
port and use the
Command Line
Interface.
See page 37
How do you want to manage your Switch? See page 46
SNMP
See page 51
Connect over the
network via Telnet.
See page 48
Use 3Com Network
Supervisor (3NS).
See page 43
Connect to the console
Web Interface
Connect over the
network.
See page 50
port and use the
Command Line
Interface.
See page 44
CAUTION: To protect your Switch from unauthorized access, you must
change all three default passwords as soon as possible, even if you do not
intend to actively manage your Switch. For more information on default
Page 35

Setting Up Overview 35
users and changing default passwords, see “Default Users and
Passwords” on page 51.
IP Configuration You can use one of the following methods to allocate IP information to
your Switch (essential if you wish to manage your Switch across the
network).
Manual IP Configuration
You can choose to configure the IP information yourself. The Switch
remembers the information that you enter until you change it again or
set the configuration method to Automatic.
You should use the Manual IP configuration method if:
■ you do not have a DHCP or BootP server on your network, or
■ you want to remove the risk of the IP address ever changing, or
■ your DHCP or BootP server does not allow you to allocate static IP
addresses. (Static IP addresses are necessary to ensure that the Switch
is always allocated the same IP information.)
For most installations, 3Com recommends that you configure the Switch
IP information manually. This makes management simpler and more
reliable as it is not dependent on a DHCP or BootP server, and eliminates
the risk of the IP address changing.
If you wish to manually enter IP information for your Switch, work
through the “Manually Configuring IP Information”
section on page 37.
Automatic IP Configuration
By default the Switch tries to configure itself with IP information without
requesting user intervention. It tries to obtain an IP address from a DHCP
or BootP server on the network.
If neither server is found, the Switch will configure itself with its default IP
address 169.254.100.100 if it is operating in a standalone mode, and/or
no other Switches on the network have this IP address. If this default IP
address is already in use on the network then the Switch detects this and
configures itself with an IP address in the range 169.254.1.0 to
169.254.254.255.
This process is known as Auto-IP and is the same mechanism used by
Windows 98 and Windows 2000. IP addresses configured by Auto-IP are
Page 36

36 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
temporary as they cannot be routed but are useful for small networks
which are not connected to other networks, or for initial configuration.
However, as soon as a DHCP or BootP server is detected, the Switch will
configure itself with the IP address allocated by that server.
When using automatic IP configuration it is important that the IP address
of the Switch is static, otherwise you will not know what the IP address is
and it will be difficult to manage. Most DHCP and BootP servers allow
static IP addresses to be configured so that you know what IP address will
be allocated to the Switch. Refer to the documentation that accompanies
your DHCP/BootP server.
For a detailed description of how automatic IP configuration operates,
please refer to the Implementation Guide on the CD-ROM that
accompanies your Switch or on the 3Com Web site.
You should use the automatic IP configuration method if:
Preparing for
Management
■ your network uses DHCP or BootP to allocate IP information, or
■ flexibility is needed. If the Switch is re-deployed onto a different
subnet, it will automatically reconfigure itself with an appropriate IP
address, instead of you having to manually reconfigure the Switch.
If you use the automatic IP configuration method, you need to discover
the automatically allocated IP information before you can begin
management. Work through the “Viewing Automatically Configured IP
Information” section on page 43.
Once your Switch’s initial set up is complete you can set up your chosen
management method as described in “Methods of Managing a Switch”
on page 46
.
For detailed information about the specific web interface operations and
command line interface commands and problem solving, refer to the
“Management Interface Reference Guide” on the CD-ROM that is
supplied with the Switch or on the 3Com Web site.
Page 37

Manually Configuring IP Information 37
Manually
Configuring IP
Information
Connecting to a Front
Panel Port
You can manually configure the Switch IP information in the following
ways:
■ Connecting to a front panel port — Connect a workstation using an
Ethernet cable to a front panel port of the Switch. You can then
manually enter IP information using the web interface or the
command line interface (CLI).
■ Connecting to the console port — Connect a workstation using a
console cable to the console port of the Switch. You can then
manually enter IP information using the command line interface (CLI).
To set up your Switch manually you can make a connection to a front
panel port. You must do this whilst the Switch is offline, that is, before
you connect the Switch to a network.
The procedure described in this section assumes the unit has been
powered up in standalone mode and has the default IP address of
169.254.100.100.
Pre-requisites
■ A workstation running Windows 95/98/2000 or Windows NT.
■ A Network Interface Card (NIC).
■ A Category 5 twisted pair Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors.
■ A suitable Web browser — refer to “Choosing a Browser”on page 49.
■ You need to have the following so that you can manually set up the
Switch with IP information:
■ IP address
■ subnet mask
■ default gateway
Page 38

38 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
Connecting the Workstation to the Switch
1 Connect the workstation to a front panel port using an Ethernet cable as
shown in Figure 13
Figure 13 Connecting a workstation to the Switch via a front panel port
To connect the cable:
a Attach an RJ-45 connector at one end of the Ethernet cable to the
Network Interface Card (NIC) in the workstation.
b Connect the RJ-45 connector at the other end of the cable to one of
the front panel ports on the Switch.
.
Do not interconnect the Switch to any other unconfigured Switch.
Configuring the Workstation with IP Information
You need to change the IP address and subnet mask of the workstation
that you have connected to the Switch. Make a note of the existing
settings so you can return to them later. Change the workstation to the
following settings:
■ IP address — 169.254.100.99
■ Subnet mask — 255.255.0.0
Setting Up the Switch with IP Information
You are now ready to manually set up the Switch with IP information. You
can do this using the Web interface or the command line interface (CLI)
via telnet.
Using the Web Interface
1 Power-up the Switch. This takes approximately one minute.
2 Open a suitable Web browser and enter 169.254.100.100 in the
Location Address field. This is the default IP address that is automatically
assigned to an offline unit.
Page 39

Manually Configuring IP Information 39
If there is no response, wait for one minute then re-enter the default IP
address.
3 At the login and password prompts, enter admin as your user name and
press Return at the password prompt (default user name and password).
If you have logged on correctly, a set of Getting Started pages are
displayed.
4 The Getting Started pages allow you to enter basic setup information for
the Switch. Select Manual and then enter the IP address, subnet mask,
and default gateway that you want the Switch to use when it is
connected to the network. The final page displays a summary of the
information entered.
The initial set up of your Switch is now complete and the Switch is ready
for you to set up your chosen management method. See “Methods of
Managing a Switch” on page 46.
Using Command Line Interface via Telnet
1 To start a Telnet session to the unit, click Start in Microsoft Windows
95/98/2000/NT.
a Click Run.
b In the dialogue box that appears type the default IP address of the
unit, that is: Telnet 169.254.100.100
c Click OK.
2 Press Enter to open a login prompt.
If the login prompt does not begin immediately, press Return a few times
until it starts.
3 At the login and password prompts, enter admin as your user name and
press Return at the password prompt. If you have logged on correctly, the
top-level menu of the command line interface is displayed as shown in
the example in Figure 14
.
Page 40

40 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
Figure 14 Example top-level command line interface menu
4 At the Select menu option prompt you can either:
■ enter the protocol ip basicConfig command. At the Enter
configuration method prompt enter manual. The screen
prompts you to enter IP information.
or
Connecting to the
Console Port
■ enter the gettingStarted command. At the Enter
configuration method prompt enter manual. The screen
prompts you to enter IP information.
5 Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway IP address for the Switch.
The screen displays a summary of the information entered.
If using the gettingStarted command you will then be prompted to
enter system information, change passwords, and then given the option
to carry out advanced configuration.
The initial set up of your Switch is now complete and the Switch is ready
for you to set up your chosen management method. See “Methods of
Managing a Switch” on page 46.
To set up your Switch manually you can alternatively make a connection
to the console port (this example describes a local connection to the
console port, rather than a remote one via a modem). You can do this
whilst the Switch is offline, that is, before you connect the Switch to a
network, or whilst the Switch is online, that is, connected to a network.
Pre-requisites
■ A workstation with terminal emulation software installed, such as
Microsoft Hyperterminal. This software allows you to communicate
with the Switch via the console port directly, or through a modem.
Page 41

Manually Configuring IP Information 41
■ Documentation supplied with the terminal emulation software.
■ A suitable cable:
■ A standard null modem cable — if you are connecting directly to
the console port, or
■ A standard modem cable — if you are connecting to the console
port using a modem.
You can find pin-out diagrams for both cables in Appendix B
■ You need to have the following so that you can manually set up the
on page 69.
Switch with IP information:
■ IP address
■ subnet mask
■ default gateway
Connecting the Workstation to the Switch
1 Connect the workstation to the console port using a standard null
modem cable as shown in Figure 15.
Figure 15 Connecting a workstation to the Switch via the console port
To connect the cable:
a Attach the female connector on the cable to the male connector on
b Tighten the retaining screws on the cable to prevent it from being
c Connect the other end of the cable to one of the serial ports (also
2 Open your terminal emulation software and configure the COM port
settings to which you have connected the cable. The settings should be
set to match the default settings for the Switch, which are:
■ 19,200 baud
■ 8 data bits
the console port of the Switch.
loosened.
known as a COM port) on your workstation.
Page 42

42 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
■ no parity
■ 1 stop bit
■ no hardware flow control
Refer to the documentation that accompanies the terminal emulation
software for more information.
Setting Up the Switch with IP Information
You are now ready to manually set up the Switch with IP information
using the command line interface.
1 The command line interface login sequence begins as soon as the Switch
detects a connection to its console port.
If the login prompt does not begin immediately, press Return a few times
until it starts.
2 At the login and password prompts, enter admin as your user name and
press Return at the password prompt. If you have logged on correctly, the
top-level menu of the command line interface is displayed as shown in
the example in Figure 16
.
Figure 16 Example top-level command line interface menu
3 At the Select menu option prompt you can either:
■ enter the protocol ip basicConfig command. At the Enter
configuration method prompt enter manual. The screen
prompts you to enter IP information.
or
■ enter the gettingStarted command. At the Enter
configuration method prompt enter manual. The screen
prompts you to enter IP information.
Page 43

Viewing Automatically Configured IP Information 43
4 Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway IP address for the Switch.
The screen displays a summary of the information entered.
If using the gettingStarted command you will then be prompted to
enter system information, change passwords, and then given the option
to carry out advanced configuration.
The initial set up of your Switch is now complete and the Switch is ready
for you to set up your chosen management method. See “Methods of
Managing a Switch” on page 46.
If you do not intend to use the command line interface via the console
port to manage the Switch, you can logout, disconnect the serial cable
and close the terminal emulator software.
Viewing
Automatically
Configured IP
Information
Using 3Com Network
Supervisor
If you allow the Switch to automatically configure its own IP information
you need to discover and view the IP information before you can begin to
manage the Switch. You can discover the IP information in two ways:
■ Using 3Com Network Supervisor — This application will auto-discover
the Switch and display the automatically allocated IP information
assigned to the Switch.
■ Connecting to the Console Port — Connect a workstation using a
console cable to the console port of the Switch. You can then view the
IP information automatically assigned to the Switch using the
command line interface (CLI).
You can use the 3Com Network Supervisor application provided on the
CD-ROM that accompanies your Switch to discover the automatically
allocated IP information.
1 Connect your Switch to the network.
2 Power-up the Switch and wait for two minutes.
3 Launch 3Com Network Supervisor and run the Auto-discovery wizard.
3Com Network Supervisor will auto-discover the new Switch and display
the IP information that has been automatically allocated to the Switch.
Most DHCP and BootP servers allow static IP addresses to be configured
so that you know what IP address the Switch will be given. Refer to the
documentation that accompanies your DHCP or BootP server.
Page 44

44 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
If your network does not have a DHCP or BootP server, the workstation
running 3Com Network Supervisor must be on the same subnet as the
Switch, because Auto-IP addresses are non-routable.
Connecting to the
Console Port
Alternatively, you can view the automatically configured IP information
via the command line interface (CLI) through a connection to the console
port. (This example describes a local connection to the console port,
rather than a remote one via a modem.)
Pre-requisites
■ A workstation with terminal emulation software installed, such as
Microsoft Hyperterminal. This software allows you to communicate
with the Switch via the console port directly, or through a modem.
■ Documentation supplied with the terminal emulation software.
■ A suitable cable:
■ A standard null modem cable — if you are connecting directly to
the console port, or
■ A standard modem cable — if you are connecting to the console
port using a modem.
You can find pin-out diagrams for both cables in Appendix B
■ A Category 5 twisted pair Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors to
on page 69.
connect your Switch to the network.
Connecting the Workstation to the Switch
1 Connect the workstation to the console port using a standard null
modem cable as shown in Figure 17
Figure 17 Connecting a workstation to the Switch via the console port
.
To connect the cable:
a Attach the female connector on the cable to the male connector on
the console port of the Switch.
Page 45

Viewing Automatically Configured IP Information 45
b Tighten the retaining screws on the cable to prevent it from being
loosened.
c Connect the other end of the cable to one of the serial ports (also
known as a COM port) on your workstation.
2 Open your terminal emulation software and configure the COM port
settings to which you have connected the cable. The settings should be
set to match the default settings for the Switch, which are:
■ 19,200 baud
■ 8 data bits
■ no parity
■ 1 stop bit
■ no hardware flow control
Refer to the documentation that accompanies the terminal emulation
software for more information.
Viewing IP Information via the Console Port
You are now ready to view the automatically allocated IP information
using the command line interface.
1 Connect your Switch to the network using an Ethernet cable. As soon as
a network connection is made the Switch begins the automatic IP
configuration process.
The automatic IP configuration process usually completes within one
minute.
If there is no response from a DHCP server within 30 seconds, the Auto-IP
configuration mechanism attempts to allocate the default IP address
169.254.100.100. If this address is not available, it then allocates an IP
address in the range of 169.254.x.y (where x is in the range 1 to 254, and
y is in the range 0 to 255).
2 The command line interface login sequence begins as soon as the Switch
detects a connection to its console port.
If the login prompt does not begin immediately, press Return a few times
until it starts.
3 At the login and password prompts, enter admin as your user name and
press Return at the password prompt. If you have logged on correctly, the
top-level menu of the command line interface is displayed as shown in
the example in Figure 18
.
Page 46

46 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
Figure 18 Example top-level command line interface menu
4 At the Select menu option prompt enter the protocol ip
interface summary command. At the Select IP interfaces
prompt enter all. A summary of the automatically allocated IP
information is displayed. Make a note of the Network IP Address.
Methods of
Managing a Switch
Command Line
Interface
Management
The initial set up of your Switch is now complete and the Switch is ready
for you to set up your chosen management method. See “Methods of
Managing a Switch” on page 46.
If you do not intend to use the command line interface via the console
port to manage the Switch, you can disconnect the serial cable and close
the terminal emulator software.
Once you have completed the initial set up of your Switch, you can
decide how you wish to manage the Switch. You can use one of the
following methods:
■ Command line interface management
■ Web interface management
■ SNMP management
Each Switch has a command line interface (CLI) that allows you to
manage the Switch from a workstation, either locally via a console port
connection (see Figure 19
), or remotely over the network (see Figure 20).
Page 47

Methods of Managing a Switch 47
Figure 19 CLI management via the console port
Figure 20 CLI management over the network
Refer to “Setting Up Command Line Interface Management” on
.
).
Web Interface
Management
page 48
Each Switch has an internal set of web pages that allow you to manage
the Switch using a Web browser remotely over an IP network (see
Figure 21
Figure 21 Web interface management over the network
Refer to “Setting Up Web Interface Management” on page 49.
SNMP Management You can manage a Switch using any network management workstation
running the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) as shown in
Figure 22
. For example, you can use the 3Com Network Supervisor
software that is provided on the CD-ROM that accompanies your Switch.
Page 48

48 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
Figure 22 SNMP management over the network
Refer to “Setting Up SNMP Management” on page 51.
Setting Up
Command Line
Interface
Management
CLI Management via
the Console Port
CLI Management over
the Network
This section describes how you can set up command line interface
management using a local console port connection or over the network.
To manage a Switch using the command line interface via the local
console port connection:
1 Ensure you have connected your workstation to the console port correctly
as described in “Connecting to the Console Port”
on page 40.
2 Your Switch is now ready to continue being managed and/or configured
through the CLI via its console port.
To manage a Switch using the command line interface over a network
using Telnet:
1 Ensure you have already set up the Switch with IP information as
described in “Setting Up Overview”
on page 34.
2 Check that you have the IP protocol correctly installed on your
management workstation. You can check this by trying to browse the
World Wide Web. If you can browse, the IP protocol is installed.
3 Check you can communicate with the Switch by entering a ping
command at the DOS prompt in the following format:
c:\ ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
(where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address of the Switch)
If you get an error message, check that your IP information has been
entered correctly and the Switch is powered up.
4 To open a Telnet session via the DOS prompt, enter the IP address of the
Switch that you wish to manage in the following format:
Page 49

Setting Up Web Interface Management 49
>telnet xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
(where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address of the Switch)
If opening a Telnet session via third party software you will need to enter
the IP address in the format suitable for that software.
5 At the login and password prompts, enter admin as your user name and
press Return at the password prompt (or the password of your choice if
you have already modified the default passwords).
If the login prompt does not display immediately, press Return a few
times until it starts.
6 If you have logged on correctly, the top-level menu of the command line
interface for the Switch you wish to manage is displayed as shown in
Figure 16
on page 42.
Setting Up Web
Interface
Management
Pre-requisites
Netscape 4.76
Netscape 6.2
This section describes how you can set up web interface management
over the network.
■ Ensure you have already set up the Switch with IP information as
described in “Setting Up Overview”
■ Ensure that the Switch is connected to the network using a Category
on page 34.
5 twisted pair Ethernet cable with RJ-45 connectors.
■ A suitable Web browser.
Choosing a Browser
To display the web interface correctly, use one of the following Web
browser and platform combinations:
Tab le 8 Supported Web Browsers and Platforms
Windows NT 4Windows
Windows 95 Windows 98
2000
Windows XP
✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓
✕ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕
Solaris
2.6
Internet Explorer
5.0, 5.5 and 6.0
✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕
Page 50

50 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
For the browser to operate the web interface correctly, JavaScript and
Cascading Style Sheets must be enabled on your browser. These features
are enabled on a browser by default. You will only need to enable them if
you have changed your browser settings.
To enable style sheets in Netscape Navigator 4.76 on Solaris 2.6, open
Netscape Navigator and select Edit > Preferences > Fonts. Select the Use
document-specified fonts, including Dynamic Fonts radio button. You
should also set the font sizes as follows:
■ Variable Width Font - Size 10.0
■ Fixed Width Font - Size 12.0
This ensures that the text spacing is correct. Finally in the Advanced
category ensure that Enable JavaScript and Enable style sheets are
checked.
Web Management
Over the Network
To manage a Switch using the web interface over an IP network:
1 Check that you have the IP protocol correctly installed on your
management workstation. You can check this by trying to browse the
World Wide Web. If you can browse, the IP protocol is installed.
2 Check you can communicate with the Switch by entering a ping
command at the DOS prompt in the following format:
c:\ ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
(where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address of the Switch)
If you get an error message, check that your IP information has been
entered correctly and the Switch is powered up.
3 Open your web browser and enter the IP address of the Switch that you
wish to manage in the URL locator, for example, in the following format:
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
4 At the login and password prompts, enter admin as your user name and
press Return at the password prompt (or the password of your choice if
you have already modified the default passwords).
5 Click on the Device View button to display the web management options.
Page 51

Setting Up SNMP Management 51
Setting Up SNMP
Management
Pre-requisites
Any network management application running the Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP) can manage a Switch if:
■ The correct Management Information Bases (MIBs) are installed on the
management workstation.
■ The management workstation is connected to the Switch using a port
in VLAN 1 (the Default VLAN). By default, all ports on the Switch are in
VLAN 1.
You can use the 3Com Network Supervisor application that is provided on
the CD-ROM that accompanies your Switch to provide SNMP
management for your Switch. If you use 3Com Network Supervisor it
automatically loads the correct MIBs and necessary files onto your
workstation.
■ Documentation supplied with the SNMP network management
application software.
To manage your Switch using an SNMP network management
application, you need to specify SNMP community strings for the users
defined on the Switch. You can do this using the command line interface
system management snmp community command — refer to the
command line interface section of the “Management Interface Reference
Guide” for more information.
Default Users and
Passwords
If you intend to manage the Switch using the web interface or the
command line interface, or to change the default passwords, you need to
log in with a valid user name and password. The Switch has three default
user names, and each user name has a different password and level of
access. These default users are listed in Tab le 9
CAUTION: To protect your Switch from unauthorized access, you must
change all three default passwords as soon as possible, even if you do not
intend to actively manage your Switch
.
Page 52

52 CHAPTER 3: SETTING UP FOR MANAGEMENT
Tab le 9 Default Users
Changing Default
Passwords
User
Name
monitor monitor monitor — the user can view all manageable parameters,
manager manager manager — the user can access and change the
admin (no
Default
Password
password)
Access Level
except special/security features, but cannot change any
manageable parameters.
operational parameters but not special/security features
security — the user can access and change all manageable
parameters
Use the admin default user name (no password) to login and carry out
initial Switch setup.
You can change the default passwords using either:
■ The gettingStarted command on the CLI, or
■ The security device user modify command on the CLI, or
■ The Security > Device > User > Modify operation on the web interface.
For more information about default users and passwords, refer to the
“Management Interface Reference Guide” on the Switch CD-ROM.
Page 53

4
PROBLEM SOLVING
This chapter helps you to diagnose and solve problems you may have
with the operation of your Switch. There is also an explanation of IP
addressing.
The topics covered are:
■ Solving Problems Indicated by LEDs
■ Solving Hardware Problems
■ Solving Communication Problems
■ Solving Software Upgrade Problems
If you experience a problem that is not listed here, it may be included in
the support section of the Superstack 3 Switch Management Interface
Reference Guide on the CD-ROM that accompanies your Switch.
To ensure this product provides optimum performance, high speed fans
are used to provide ventilation. These fans have a high audible output.
For Technical Support information, see Appendix D
.
Page 54

54 CHAPTER 4: PROBLEM SOLVING
Solving Problems
Indicated by LEDs
If the LEDs on the Switch indicate a problem, refer to the list of suggested
solutions below.
The Power LED does not light
Check that the power cable is firmly connected to the Switch and to the
supply outlet. If the connection is secure and there is still no power, you
may have a faulty power cord or an internal fault. Firstly, check the power
cord by:
■ testing it in another device
■ connecting a working power cord to the ‘problem’ device
then contact your supplier for advice.
On powering-up, the Power/Self Test LED lights yellow
The Switch unit has failed its Power On Self Test (POST) because of an
internal problem. The fault type will be indicated on the unit LEDs.
Contact your supplier for advice.
A link is connected and yet the Status LED for the port does not
light
Check that:
■ The Switch and the device at the other end of the link (or cable) are
connected securely.
■ The devices at both ends of the link are powered-up
■ The quality of cable is satisfactory
■ Auto-negotiation settings are the same at both ends.
Auto-negotiation problems will occur with 10BASE-T or 100BASE-T
where auto-negotiation is disabled and incorrect cables are being used
(cross-over or straight)
Auto-negotiation problems will occur with fiber if:
■ The Receiver (RX) and Transceiver (TX) cable connectors are
swapped
■ Fibers are broken
■ Auto-negotiation differs at either end (a link appears at the ‘fixed’
end and not at the auto-negotiation end)
Page 55

Solving Hardware Problems 55
Solving Hardware
Problems
In the rare event of your Switch unit experiencing a hardware failure,
refer to the list of suggested solutions below.
An expansion module is installed and the unit will not power up
Ensure that the expansion module is fully seated in the slot and the
connectors are engaged so that the securing screws can be tightened.
A fan failure warning message is received
Your Switch has a fan monitoring system that will generate fan failure
warning messages. Fan failure could potentially reduce the lifetime of the
Switch. The monitoring system polls the fan status at periodic intervals
while the unit is powered up.
Should one fan failure occur in the Switch, a warning message will be
generated in the following ways:
■ RMON Email Notification — If configured, you will receive
notification of the fan failure via email, SMS (Short Message Service),
or pager.
■ RMON Trap — If configured, an RMON trap is generated and sent to
the management workstation.
For further information about RMON, refer to “Chapter 7: Status
Monitoring and Statistics” in the Switch Implementation Guide supplied
in PDF format on the CD-ROM that accompanies the Switch.
If more than one fan fails in the Switch, a warning message will be
generated by RMON Email Notification, RMON Trap and also in the
following ways:
■ Command Line Interface — An indication of a general hardware
failure is provided through the Top level menu displayed when logging
on to the CLI. For more detailed information about the failure select
the system summary command.
■ Web interface — An indication of fan failure is provided through the
Device Summary table for the specific unit. In addition all Summary
tables turn red to indicate the fan failure.
Page 56

56 CHAPTER 4: PROBLEM SOLVING
If a fan failure warning message is generated:
1 Power off the unit.
2 Check that the air vents are not obstructed.
3 Power cycle the unit. To do this, remove and reconnect the AC mains
supply. If the unit has no AC main supply, remove and reconnect the DC
RPS supply.
4 If another fan failure warning message is generated via the Command
Line Interface or the Web interface, return the unit.
Unit fails, no SNMP fan failure message is received
1 Power cycle the unit. To do this, remove and reconnect the AC mains
supply. If the unit has no AC mains supply, remove and reconnect the DC
RPS supply.
2 Check the command line interface (system summary command) to
determine whether a thermal shutdown has occurred.
3 If no, return the unit:
If yes, check that:
■ The air vents are not obstructed.
■ The ambient temperatures and environmental conditions meet those
specified in Appendix C
.
4 Power cycle the unit. If a further thermal shutdown occurs, and all
environmental conditions are satisfactory, return the unit to 3Com.
Error message indicating that the GBIC transceiver is invalid
The Switch has identified that the GBIC does not meet the minimum
requirements for the Switch and has disabled the port. To correct this
problem, completely remove the GBIC and replace it with a 3Com
approved GBIC. See “Approved GBIC Transceivers”
on page 29.
Error message indicating that the GBIC transceiver is faulty
To correct this problem, completely remove the GBIC and then reinsert it.
If the problem persists, contact 3Com Technical Support.
Page 57

Solving Communication Problems 57
Solving
Communication
Problems
If you experience communication problems with the Switch, ensure that:
■ The Switch IP address has been configured.
■ If the Switch is separated from your management application by a
router, ensure that the default gateway IP address within the Switch is
the same as the IP address of the router.
■ The Switch’s IP address has been entered correctly in your network
management application (for example 3Com Network Supervisor).
The following is an brief overview of IP addressing, and how to obtain a
registered IP address.
IP Addressing
To be managed correctly, each device on your network (for example a
Switch or Hub) must have a unique IP address. IP addresses have the
format n.n.n.n where n is a decimal number between 0 and 255. An
example IP address is 192.168.100.8.
The IP address is split into two parts:
■ The first part (‘192.168.100’ in the example) identifies the network on
which the device resides
■ The second part (‘.8’ in the example) identifies the device within the
network
The natural subnet mask for this example is 255.255.255.0.
If your network has a connection to the external IP network, that is, you
access the Internet, you must apply for a registered IP address.
How do you obtain a registered IP Address?
The IP registration system ensures that every IP address used is unique; if
you do not have a registered IP address, you may be using an identical
address to someone else and your network will not operate correctly.
InterNIC Registration Services is the organization responsible for
supplying registered IP addresses. The following contact information is
correct at time of publication:
World Wide Web site: http://www.internic.net
Page 58

58 CHAPTER 4: PROBLEM SOLVING
If your IP network is internal to your organization only, that is, you do not
access the Internet, you may use any arbitrary IP address as long as it is
not being used by another device on your network. 3Com suggests you
use addresses in the range 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 with a
subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
These suggested IP addresses are part of a group of IP addresses that
have been set aside specially for use ‘in house’ only.
Solving Software
Upgrade Problems
You can upgrade the management software of the Switch by using the
System > Control > Software Upgrade operation in the Web Interface, or
the system control softwareUpgrade command in the
command line interface.
For details on these options, refer to the Management Interface
Reference Guide supplied in HTML format on the CD-ROM that
accompanies your Switch.
If you have problems with your software upgrade, refer to the Problem
Solving section in the Management Interface Reference Guide.
Page 59

A
SAFETY INFORMATION
You must read the following safety information before carrying out any
installation or removal of components, or any maintenance procedures
on the Switch 4900, 4900 SX, 4924, or 4950.
WARNING: Warnings contain directions that you must follow for your
personal safety. Follow all directions carefully.
You must read the following safety information carefully before you
install or remove the unit.
AVERTISSEMENT: Les avertissements présentent des consignes que vous
devez respecter pour garantir votre sécurité personnelle. Vous devez
respecter attentivement toutes les consignes.
Nous vous demandons de lire attentivement les consignes suivantes de
sécurité avant d’installer ou de retirer l’appareil.
Power Cord Set —
Japan
VORSICHT: Vorsicht enthalten Anweisungen, die Sie zu Ihrer eigenen
Sicherheit befolgen müssen. Alle Anweisungen sind sorgfältig zu
befolgen.
Sie müssen die folgenden Sicherheitsinformationen’ sorgfältig
durchlesen, bevor Sie das Gerät installieren oder ausbauen.
Page 60

60 APPENDIX A: SAFETY INFORMATION
Important Safety Information
WARNING: Installation and removal of the unit must be carried out by
qualified personnel only.
WARNING: If installing the Switch in a stack with SuperStack 3 units that
are narrower than the Switch, the Switch unit must be installed below
the narrower units.
WARNING: The unit must be earthed (grounded).
WARNING: Connect the unit to an earthed power supply to ensure
compliance with safety standards.
WARNING: Power Cord Set:
This must be approved for the country where it is used:
U.S.A. and
Canada
■ The cord set must be UL-approved and CSA certified.
■ The minimum specification for the flexible cord is:
No. 18 AWG
Type SV or SJ
3-conductor
■ The cord set must have a rated current capacity of at least
10A.
■ The attachment plug must be an earth-grounding type
with a NEMA 5-15P (15A, 125V) or NEMA 6-15P (15A,
250V) configuration.
United
Kingdom only
■ The supply plug must comply with BS1363 (3-pin 13 amp)
and be fitted with a 5A fuse which complies with BS1362.
■ The mains cord must be <HAR> or <BASEC> marked and
be of type H03VVF3GO.75 (minimum).
Europe only: ■ The supply plug must comply with CEE 7/7 (“SCHUKO”).
■ The mains cord must be <HAR> or <BASEC> marked and
be of type H03VVF3GO.75 (minimum).
Denmark ■ The supply plug must comply with section 107-2-D1,
standard DK2-1a or DK2-5a.
Switzerland ■ The supply plug must comply with SEV/ASE 1011.
WARNING: The appliance coupler (the connector to the unit and not the
wall plug) must have a configuration for mating with an EN60320/IEC320
appliance inlet.
Page 61

Important Safety Information 61
WARNING: The socket outlet must be near to the unit and easily
accessible. You can only remove power from the unit by disconnecting
the power cord from the outlet.
WARNING: This unit operates under SELV (Safety Extra Low Voltage)
conditions according to IEC 60950. The conditions are only maintained if
the equipment to which it is connected also operates under SELV
conditions.
WARNING: France and Peru only:
†
This unit cannot be powered from IT
supplies. If your supplies are of IT
type, this unit must be powered by 230V (2P+T) via an isolation
transformer ratio 1:1, with the secondary connection point labelled
Neutral, connected directly to earth (ground).
†
Impédance à la terre.
WARNING: U.K. only:
If connecting a modem to the console port of the Switch, only use a
modem which is suitable for connection to the telecommunications
system.
WARNING: RJ-45 Ports. These are shielded RJ-45 data sockets. They
cannot be used as standard traditional telephone sockets, or to connect
the unit to a traditional PBX or public telephone network. Only connect
RJ-45 data connectors, network telephony systems, or network
telephones to these sockets.
Either shielded or unshielded data cables with shielded or unshielded
jacks can be connected to these data sockets.
WARNING: The switch should only be used in a rack if it is mounted on
runners, a shelf, or a tray to support the weight. The rack mount kits
alone are not sufficient to support the weight of the switch. The rack
mount kits must not be used to suspend the switch from under a table or
desk, or attach it to a wall.
WARNING: If you are connecting the Switch to a Type 3 Power Module,
read the Safety Information section in the Type 3 Power Module User
Guide.
WARNING: When an Expansion Module is not installed ensure the
blanking panel is fited by tightening all screws with a suitable tool.
Page 62

62 APPENDIX A: SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: Fiber Optic ports - Optical Safety
Never look at the transmit laser while it is powered-up. Never look
directly at the fiber ports and fiber cable ends when they are
powered-up.
WARNING: Use of controls or adjustments of performance or procedures
other than those specified herein may result in hazardous laser emissions.
Page 63

L’information de Sécurité Importante
AVERTISSEMENT: L'installation et la dépose de ce groupe doivent être
confiés à un personnel qualifié.
AVERTISSEMENT: Si vous entassez l'unité Switch avec les unités
SuperStack 3 Hub, l'unité Switch doit être installée en dessous des unités
Hub plus étroites.
AVERTISSEMENT: Vous devez mettre l’appareil à la terre (à la masse) ce
groupe.
AVERTISSEMENT: Brancher l’unité à une source de courant mise à la
terre pour assurer la conformité aux normes de sécurité.
AVERTISSEMENT: Cordon électrique:
Il doit être agréé ans le pays d'utilisation:
Etats-Unis et
Canada
L’information de Sécurité Importante 63
■ Le cordon doit avoir reçu l'homologation des UL et un
certificat de la CSA
■ Le cordon souple doit respecter, à titre minimum, les
spécifications suivantes :
■ calibre 18 AWG
■ type SV ou SJ
■ à 3 conducteurs
■ Le cordon doit être en mesure d'acheminer un courant
nominal d'au moins 10 A
■ La prise femelle de branchement doit être du type à mise à la
terre (mise à la masse) et respecter la configuration NEMA
5-15P (15 A, 125 V) ou NEMA 6-15P (15 A, 250 V)
Danemark ■ La prise mâle d'alimentation doit respecter la section 107-2
D1 de la norme DK2 1a ou DK2 5a
Europe ■ La prise secteur doit être conforme aux normes CEE 7/7
(“SCHKO”)
■ LE cordon secteur doit porter la mention <HAR> ou
<BASEC> et doit être de type HO3VVF3GO.75 (minimum).
Suisse ■ La prise mâle d'alimentation doit respecter la norme SEV/ASE
1011
AVERTISSEMENT: Le coupleur d'appareil (le connecteur du groupe et
non pas la prise murale) doit respecter une configuration qui permet un
branchement sur une entrée d'appareil EN60320/CEI 320.
Page 64

64 APPENDIX A: SAFETY INFORMATION
AVERTISSEMENT: La prise secteur doit se trouver à proximité de
l’appareil et son accès doit être facile. Vous ne pouvez mettre l’appareil
hors circuit qu'en débranchant son cordon électrique au niveau de cette
prise.
AVERTISSEMENT: L’appareil fonctionne à une tension extrêmement
basse de sécurité qui est conforme à la norme CEI 60950. Ces conditions
ne sont maintenues que si l'équipement auquel il est raccordé fonctionne
dans les mêmes conditions.
AVERTISSEMENT: France et Pérou uniquement:
Ce groupe ne peut pas être alimenté par un dispositif à impédance à la
terre. Si vos alimentations sont du type impédance à la terre, ce groupe
doit être alimenté par une tension de 230 V (2 P+T) par le biais d'un
transformateur d'isolement à rapport 1:1, avec un point secondaire de
connexion portant l'appellation Neutre et avec raccordement direct à la
terre (masse).
AVERTISSEMENT: Points d’accès RJ-45. Ceux-ci sont protégés par des
prises de données. Ils ne peuvent pas être utilisés comme prises de
téléphone conventionnelles standard, ni pour la connection de l’unité à
un réseau téléphonique central privé ou public. Raccorder seulement
connecteurs de données RJ-45, systèmes de réseaux de téléphonie ou
téléphones de réseaux à ces prises.
Il est possible de raccorder des câbles protégés ou non protégés avec des
jacks protégés ou non protégés à ces prises de données.
AVERTISSEMENT: Le commutateur doit être utilisé en rack uniquement
s’il est monté sur des rails à glissières, une étagère ou un plateau pour
supporter son poids. Les kits de montage en rack ne suffisent pas à eux
seuls pour supporter le poids du commutateur.
AVERTISSEMENTS: Si vous connectez le commutateur Switch à un
moduled'alimentation de Type 3, consultez les informations de sécurité
qui se trouvent dans le guide del'utilisateur du module d'alimentation de
type 3.
AVERTISSEMENTS: Si le module d’expansion nest pas installé, veillez à
bien installer la plaque d’obturation et serrez toutes les vis à l’aide d’un
outil approprié.
Page 65

L’information de Sécurité Importante 65
AVERTISSEMENT: Ports pour fibres optiques – sécurité sur le plan
optique
Ne regardez jamais le laser tant qu'il est sous tension. Ne regardez jamais
directement le port à fibres optiques et les embouts de câbles à fibres
optiques tant qu'ils sont sous tension.
AVERTISSEMENT: L'utilisation de contrôles, de réglages de
performances ou de procédures autres que ceux qui sont spécifiés au sein
du présent document risquent d'entraîner l'exposition à des
rayonnements laser dangereux.
Page 66

66 APPENDIX A: SAFETY INFORMATION
Wichtige Sicherheitsinformationen
VORSICHT: Die Installation und der Ausbau des Geräts darf nur durch
Fachpersonal erfolgen.
VORSICHT: Wenn die Switch Einheit in einer Stapel mit anderen
SuperStack 3 Hub Einheiten eingebaut werden soll, muß die Switch
Einheit unter die schmaleren Hub Einheiten eingebaut werden.
VORSICHT: Das Gerät muß geerdet sein.
VORSICHT: Das Gerät muß an eine geerdete Steckdose angeschlossen
werden, die europäischen Sicherheitsnormen erfüllt.
VORSICHT: Der Anschlußkabelsatz muß mit den Bestimmungen des
Landes übereinstimmen, in dem er verwendet werden soll.
VORSICHT: Der Gerätestecker (der Anschluß an das Gerät, nicht der
Wandsteckdosenstecker) muß eine passende Konfiguration für einen
Geräteeingang gemäß EN60320/IEC320 haben.
VORSICHT: Die Netzsteckdose muß in der Nähe des Geräts und leicht
zugänglich sein. Die Stromversorgung des Geräts kann nur durch
Herausziehen des Gerätenetzkabels aus der Netzsteckdose unterbrochen
werden.
VORSICHT: Europe
■ Das Netzkabel muß vom Typ HO3VVF3GO.75 (Mindestanforderung)
sein und die Aufschrift <HAR> oder <BASEC> tragen.
■ Der Netzstecker muß die Norm CEE 7/7 erfüllen (”SCHUKO”).
VORSICHT: Der Betrieb dieses Geräts erfolgt unter den
SELV-Bedingungen (Sicherheitskleinstspannung) gemäß IEC 60950. Diese
Bedingungen sind nur gegeben, wenn auch die an das Gerät
angeschlossenen Geräte unter SELV-Bedingungen betrieben werden.
Page 67

Wichtige Sicherheitsinformationen 67
VORSICHT: RJ-45-Porte. Diese Porte sind geschützte Datensteckdosen.
Sie dürfen weder wie normale traditionelle Telefonsteckdosen noch für
die Verbindung der Einheit mit einem traditionellem privatem oder
öffentlichem Telefonnetzwerk gebraucht werden. Nur
RJ-45-Datenanscluße, Telefonnetzsysteme or Netztelefone an diese
Steckdosen anschließen.
Entweder geschützte oder ungeschützte Buchsen dürfen an diese
Datensteckdosen angeschlossen werden.
VORSICHT: Der Switch darf nur dann in einem Einschub montiert
werden, wenn dieser zur Tragkraftverstärkung auf einer Laufschiene, in
einem Regal oder einem Träger montiert ist. Der Einschubmontagesatz
alleine reicht nicht aus, um das Gewicht des Switch zu tragen.
VORSICHT: Ist kein Erweiterungsmodul installiert, überprüfen Sie bitte
den Sitz der Stanzplatte, indem Sie alle Schrauben mit einem geeigneten
Werkzeug anziehen.
VORSICHT: Bevor Sie den Schalter an das Stromversorgungsmodul Typ 3
anschließen, lesen Sie bitte die Sicherheitshinweise in der
Bedienungsanleitung für das Stromversorgungsmodul Typ 3.
VORSICHT: Faseroptikanschlüsse – Optische Sicherheit
Niemals ein Übertragungslaser betrachten, während dieses eingeschaltet
ist. Niemals direkt auf die Faseransnchlüsse und auf die Faserkabelenden
schauen, während diese eingeschaltet sind.
VORSICHT: Die Verwendung von Steuerelementen oder die Anpassung
von Leistungen und Verfahren in anderer als der hierin genannten Weise
kann zu gefährlichen Laseremissionen führen.
Page 68

68 APPENDIX A: SAFETY INFORMATION
Page 69

PIN-OUTS
B
Null Modem Cable 9-pin to RS-232 25-pin
PC-AT Serial Cable 9-pin to 9-pin
Page 70

70 APPENDIX B: PIN-OUTS
Modem Cable 9-pin to RS-232 25-pin
RJ-45 Pin
Assignments
Pin assignments are identical for 10/100BASE-T and 1000BASE-T RJ-45
connectors.
Table 10 Pin assignments
Pin Number 10/100BASE-T 1000BASE-T
Ports configured as MDI
1 Transmit Data + Bidirectional Data A+
2 Transmit Data - Bidirectional Data A3 Receive Data + Bidirectional Data B+
4 Not assigned Bidirectional Data C+
5 Not assigned Bidirectional Data C6 Receive Data – Bidirectional Data B7 Not assigned Bidirectional Data D+
8 Not assigned Bidirectional Data D-
Page 71

RJ-45 Pin Assignments 71
Table 11 Pin assignments
Pin Number 10/100BASE-T 1000BASE-T
Ports configured as MDIX
1 Receive Data + Bidirectional Data B+
2 Receive Data - Bidirectional Data B3 Transmit Data + Bidirectional Data A+
4 Not assigned Bidirectional Data D+
5 Not assigned Bidirectional Data D6 Transmit Data - Bidirectional Data A7 Not assigned Bidirectional Data C+
8 Not assigned Bidirectional Data C-
Page 72

72 APPENDIX B: PIN-OUTS
Page 73

C
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
The technical specifications for the Switches in the Switch 4900 Family
are the same unless otherwise stated.
Physical Dimensions
Environmental Requirements
Operating Temperature 0 ° to 40 °C (32 ° to 104 °F)
Storage Temperature –10 ° to +70 °C (14 ° to 158 °F)
Operating Humidity 10–95% relative humidity, non-condensing
Standards EN60068 to 3Com schedule (Package testing: paras 2.1, 2.2, 2.30, and 2.32.
Safety
Agency Certifications UL 1950 / UL60950, EN60950, CSA 22.2 No. 950 / CSA 22.2 No. 60950,
EMC
Emissions CISPRR 22 Class A, EN55022 Class A, FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class A,
Immunity EN 55024
Power Consumption Switch 4900: 308 watts maximum
Switch 4900: Switch Height: 65.8 mm (2.59 in.) x Width: 440 mm (17.3 in.) x
Depth: 363.4 mm (14.30 in.) (not including bulge). Weight: 6.3 Kg (13.88 lbs)
Switch 4900 SX: Height: 65.8 mm (2.59 in.) x Width: 440 mm (17.3 in.) x
Depth: 363.4 mm (14.30 in.) (not including bulge). Weight: 6.0 Kg (13.22 lbs)
Switch 4924: Height: 65.8 mm (2.59 in.) x Width: 440 mm (17.3 in.) x Depth:
413 mm (16.27 in.) (not including bulge). Weight: 6.4 Kg (14.10 lbs)
Switch 4950: Height: 65.8 mm (2.59 in.) x Width: 440 mm (17.3 in.) x Depth:
413 mm (16.27 in.) (not including bulge). Weight: 6.91 Kg (15.23 lbs)
Operational testing: paras 2.1, 2.2, 2.30 and 2.13).
IEC 60950, IEC 825-1 (4900 SX and 4950 only), EN 60825-1 (4900 SX and 4950
only)
ICES-003 Class A, VCCI Class A, AS/NZS 3548 Class A, EN61000-3-2
Switch 4900 SX: 162 watts maximum
Switch 4924: 254 watts maximum
Switch 4950: 200 watts maximum
Page 74

74 APPENDIX C: TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Heat Dissipation Switch 4900:1050 BTU/hour maximum
Switch 4900 SX: 560 BTU/hour maximum
Switch 4924: 870 BTU/hour maximum
Switch 4950: 685 BTU/hour maximum
Power Supply
AC Line Frequency 50/60 Hz
Input Voltage Options 90–240 VAC
Current Rating Switch 4900: 4 A (amps) (maximum)
Switch 4900 SX: 3 A (amps) (maximum)
Switch 4924 and 4950: 4.5 A (amps) (maximum)
Page 75

D
OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR
PRODUCT
Register Your
Product to Gain
Service Benefits
Purchase
Value-Added
Services
To take advantage of warranty and other service benefits, you must first
register your product at
services are based on accounts that you create or have authorization to
access. First time users must apply for a user name and password that
provides access to a number of eSupport features including Product
Registration, Repair Services, and Service Request.
To enhance response times or extend warranty benefits, contact 3Com or
your authorized 3Com reseller. Value-added services can include 24x7
telephone technical support, software upgrades, onsite assistance or
advance hardware replacement. Experienced engineers are available to
manage your installation with minimal disruption to your network. Expert
assessment and implementation services are offered to fill resource gaps
and ensure the success of your networking projects. More information on
3Com Extended Warranty and Professional Services is available at
http://www.3com.com/
Contact your authorized 3Com reseller or 3Com for additional product
and support information.
http://eSupport.3com.com/. 3Com eSupport
Troubleshoot
Online
You will find support tools posted on the 3Com web site at
http://www.3com.com/
■ 3Com Knowledgebase helps you troubleshoot 3Com products. This
query-based interactive tool is located at
http://knowledgebase.3com.com and contains thousands of
technical solutions written by 3Com support engineers.
Page 76

76 APPENDIX D: OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR PRODUCT
■ Connection Assistant helps you install, configure and troubleshoot
3Com desktop and server NICs, wireless cards and Bluetooth devices.
This diagnostic software is located at:
http://www.3com.com/prodforms/software/connection_assistan
t/ca_thankyou.html
Access Software
Downloads
Software Updates are the bug fix / maintenance releases for the version
of software initially purchased with the product. In order to access these
Software Updates you must first register your product on the 3Com web
site at
http://eSupport.3com.com/.
First time users will need to apply for a user name and password. A link to
software downloads can be found at
under the Product Support heading at
http://eSupport.3com.com/, or
http://www.3com.com/
Software Upgrades are the software releases that follow the software
version included with your original product. In order to access upgrades
and related documentation you must first purchase a service contract
from 3Com or your reseller.
Contact Us 3Com offers telephone, e-mail and internet access to technical support
and repair services. To access these services for your region, use the
appropriate telephone number, URL or e-mail address from the list below.
You will find a current directory of support telephone numbers posted on
the 3Com web site at
http://csoweb4.3com.com/contactus/
Telephone Technical
Support and Repair
To obtain telephone support as part of your warranty and other service
benefits, you must first register your product at
http://eSupport.3com.com/
When you contact 3Com for assistance, please have the following
information ready:
■ Product model name, part number, and serial number
■ A list of system hardware and software, including revision level
■ Diagnostic error messages
■ Details about recent configuration changes, if applicable
Page 77

Telephone Technical Support and Repair 77
To send a product directly to 3Com for repair, you must first obtain a
return authorization number (RMA). Products sent to 3Com, without
authorization numbers clearly marked on the outside of the package, will
be returned to the sender unopened, at the sender’s expense. If your
product is registered and under warranty, you can obtain an RMA
number online at
http://eSupport.3com.com/. First time users will
need to apply for a user name and password.
Telephone numbers are correct at the time of publication. Find a current
directory of support telephone numbers posted on the 3Com web site at
http://csoweb4.3com.com/contactus/
Country Telephone Number Country Telephone Number
Asia, Pacific Rim Telephone Technical Support and Repair
Australia
Hong Kong
India
Indonesia
Japan
Malaysia
New Zealand
Pakistan
You can also obtain support in this region using the following e-mail: apr_technical_support@3com.com
Or request a repair authorization number (RMA) by fax using this number: + 65 543 6348
Europe, Middle East, and Africa Telephone Technical Support and Repair
From anywhere in these
regions, call:
From the following countries, you may use the numbers shown:
Austria
Belgium
Denmark
Finland
France
Germany
Hungary
Ireland
Israel
Italy
You can also obtain support in this region using the following URL:
http://emea.3com.com/support/email.html
1 800 678 515
800 933 486
+61 2 9424 5179 or
000800 650 1111
001 803 61009
00531 616 439 or
03 5977 7991
1800 801 777
0800 446 398
+61 2 9937 5083
+44 (0)1442 435529
01 7956 7124
070 700 770
7010 7289
01080 2783
0825 809 622
01805 404 747
06800 12813
01407 3387
1800 945 3794
199 161346
Philippines
P. R. o f Chi n a
Singapore
S. Korea
Ta iw a n
Thailand
Luxembourg
Netherlands
Norway
Poland
Portugal
South Africa
Spain
Sweden
Switzerland
U.K.
1235 61 266 2602 or
1800 1 888 9469
10800 61 00137 or
021 6350 1590 or
00800 0638 3266
80
0 6161 463
080 333 3308
00801 611 261
001 800 611 2000
342 0808128
0900 777 7737
815 33 047
00800 441 1357
707 200 123
0800 995 014
9 021 60455
07711 14453
08488 50112
0870 909 3266
Page 78

78 APPENDIX D: OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR PRODUCT
Country Telephone Number Country Telephone Number
Latin America Telephone Technical Support and Repair
Antigua
Argentina
Aruba
Bahamas
Barbados
Belize
Bermuda
Bonaire
Brazil
Cayman
Chile
Colombia
Costa Rica
Curacao
Ecuador
Dominican Republic
1 800 988 2112
0 810 444 3COM
1 800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
52 5 201 0010
1 800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
0800 13 3COM
1 800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
Guatemala
Haiti
Honduras
Jamaica
Martinique
Mexico
Nicaragua
Panama
Paraguay
Peru
Puerto Rico
Salvador
Trinidad and Tobago
Uruguay
Venezuela
Virgin Islands
AT&T +800 998 2112
57 1 657 0888
AT&T +800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
571 657 0888
01 800 849CARE
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
54 11 4894 1888
AT&T +800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
1 800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
AT&T +800 998 2112
57 1 657 0888
You can also obtain support in this region using the following:
Spanish speakers, enter the URL:
http://lat.3com.com/lat/support/form.html
Portuguese speakers, enter the URL:
http://lat.3com.com/br/support/form.html
English speakers in Latin America should send e-mail to:
lat_support_anc@3com.com
US and Canada Telephone Technical Support and Repair
1 800 876 3266
Page 79

INDEX
Numbers
3C number 19
A
access levels of default users 51
approved GBIC transceivers 29
automatic setup 43
3Com Network Supervisor 43
console port 44
C
cable
10/100/1000BASE-T 28
fiber 29
pin-outs 69
CD-ROM 9
command line interface
management 46
conventions
notice icons, About This Guide 8
text, About This Guide 8
cross-over configuration 28
D
default
settings 20
users 51
H
hardware features 13
I
installing the Switch 21
prerequisites 23
interconnect cable 25
IP addressing
registered 57
IP configuration 35
L
LEDs 17
logging in as a default user 51
M
MAC address of the Switch 19
management
methods 46
preparing for 36
setting up 33, 34
manual setup
console port 40
front panel port 37
MDI configuration 28
MDIX configuration 28
E
Ethernet address of the Switch 19
F
factory defaults 20
G
GBIC
ports 16
P
passwords
of default users 51
pin assignments
modem cable 70
null modem cable 69
RJ-45 70
serial cable 69
pin-outs 69
ports
10/100/1000BASE-T 16
1000BASE-SX 16
Page 80

80 INDEX
GBIC 16
power socket 19
powering-up a Switch 27
problem solving 11, 53
communication problems 57
hardware problems 55
IP addressing 55
LEDs 54
product name 19
R
rack mounting a Switch 23
Redundant Power System. See RPS
RPS 19
socket 19
S
safety information
English 60
French 63
German 66
serial number of the Switch 19
Simple Network Management Protocol. See SNMP
SNMP 51
SNMP management 47
setting up 51
socket
power 19
RPS 19
specifications, system 73
straight-through configuration 28
Switch
3C number 19
automatic setup 43
dimensions 73
Ethernet address 19
features 13
installation 21, 23
interconnecting 24
MAC address 19
power socket 19
powering-up 27
product name 19
rack mounting 23
RPS socket 19
serial number 19
size 73
unit information label 19
weight 73
XRN Distributed Fabric 24
system specifications 73
T
troubleshooting 11, 53
U
unit information label 19
W
web interface management 47
setting up 49
X
XRN
Distributed Fabric 24
interconnecting 24
Page 81

REGULATORY NOTICES
FCC STATEMENT This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause harmful interference to radio communications, in which case the user will be required to
correct the interference at their own expense.
INFORMATION TO THE USER If this equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of
the following measures:
■ Reorient the receiving antenna.
■ Relocate the equipment with respect to the receiver.
■ Move the equipment away from the receiver.
■ Plug the equipment into a different outlet so that equipment and receiver are on different branch circuits.
If necessary, the user should consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for additional
suggestions. The user may find the following booklet prepared by the Federal Communications Commission
helpful:
How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems
This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402, Stock No.
004-000-00345-4.
In order to meet FCC emissions limits, this equipment must be used only with cables which comply with IEEE
802.3.
CSA STATEMENT This Class A digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment
Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur
du Canada.
CE STATEMENTS (EUROPE) This product complies with the European Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC and EMC Directive 89/336/EEC as
amended by European Directive 93/68/EEC.
Warning: This is a class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
You must only insert a 3Com approved GBIC transceiver into the Switch. These are listed in the “Approved
GBIC Transceivers” section of the Getting Started Guide.
VCCI STATEMENT
Page 82

 Loading...
Loading...