Page 1
3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Free-Fall Tube with 6 Induction Coils U8511200
Instruction sheet
12/09 SP/ALF
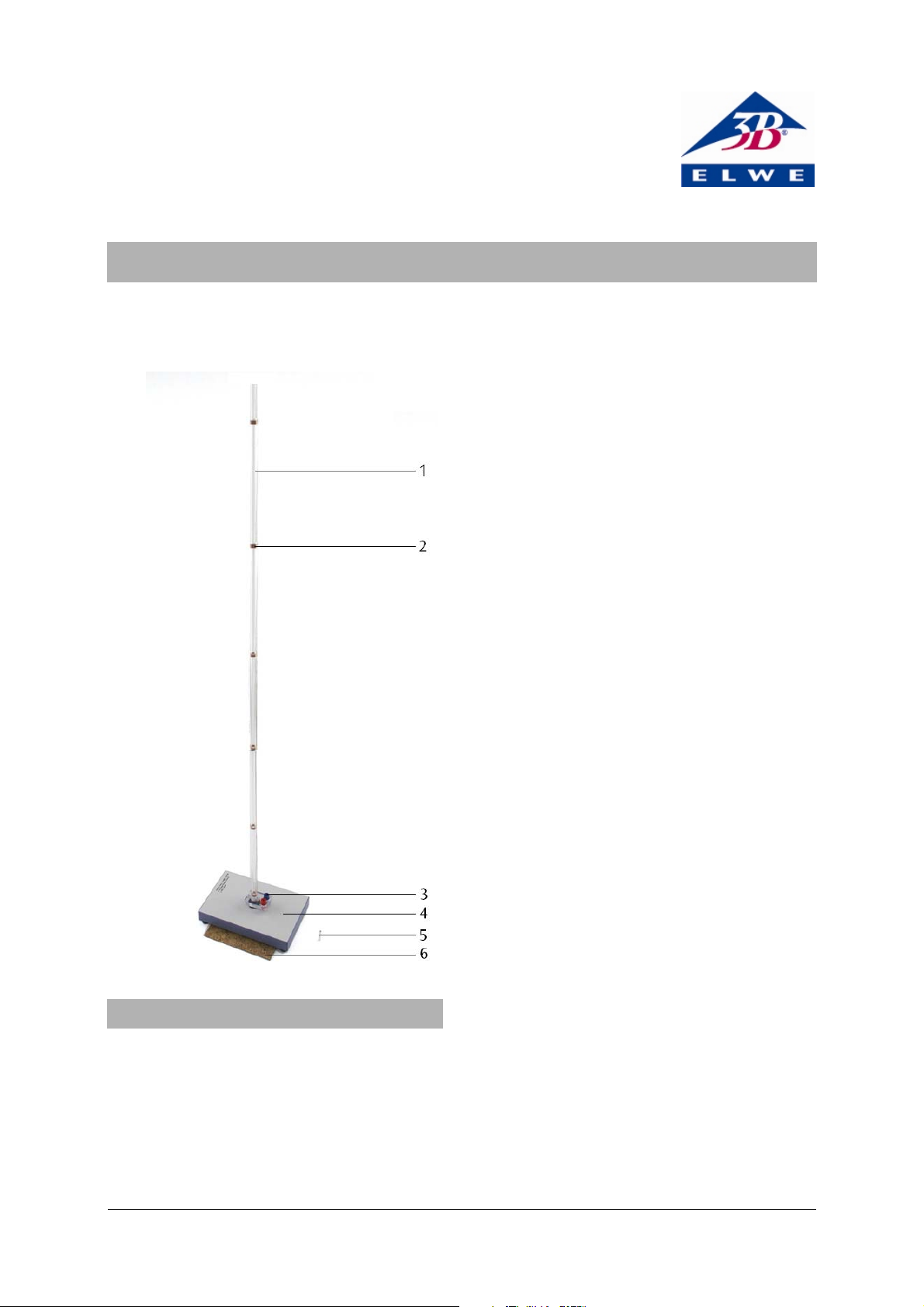
1 Free-fall tube
2 Coil
3 Connector sockets
4 Plinth with socket
5 Bar magnet
6 Cork mat
1. Description
The free-fall tube with 6 induction coils is used to
illustrate the principles of induced voltages.
The free-fall tube is a plastic tube that is mounted
upright on a plinth and has six identical induction
coils connected in series with one another. Within
the clamp socket of the plinth there is a rubber
washer, which prevents the falling body (a bar
magnet) from bouncing back up the tube after the
impact.
If the bar magnet is allowed to fall through the
tube, a voltage is induced in each of the coils in
turn. Since the velocity of the magnet increases with
time as it falls, the amplitudes of the voltage peaks
also increase as time passes, while their widths
decrease. The area under each of the voltage peaks
remains constant.
1
Page 2

By using the 3B NETlogTM unit as an interface or by
means of a storage oscilloscope it is possible to
display the voltage curve graphically. Two 4 mm
sockets are provided for making the connections.
After falling, the magnet is held in the rubber
washer and can be retrieved when the plinth is
tilted sideways. The cork mat serves to protect the
magnet and the table top from damage by the
impact.
2. Technical data
Coil width: 5 mm
Distance between coils: 180 mm
Number of turns: 13 in each coil
Overall dimensions: 130x200x1020 mm
3
approx.
Weight: 500 g approx.
3. Assembly
• Set up the tube in the socket of the plinth using
gentle pressure.
Bumps, knocks or any lateral forces acting on the
tube may damage the instrument.
• Do not subject the tube to any mechanical
stress.
4. Operation
Also required:
1 3B NETlog
or
1 3B NETlog
1 3B NETlab
TM
U11300-230
TM
U11300-115
TM
U11310
Experiment leads
• Set up the experiment as shown in fig. 1.
• Connect leads between the connector sockets of
the tube and the voltage input U
IN
on the
A
interface.
• Connect the interface to the computer.
• Start the software program.
• Hold the bar magnet over the top opening of
the tube.
• Start a measurement in the program and allow
the bar magnet to fall.
• Evaluate the voltage curve.
Alternatively, the measurement may be carried out
with an oscilloscope.
Fig. 1 Experiment set-up
2
Page 3

Fig. 2 Trace of induced voltage as a function of time
Elwe Didactic GmbH ▪ Steinfelsstr. 6 ▪ 08248 Klingenthal ▪ Germany ▪ www.elwedidactic.com
3B Scientific GmbH ▪ Rudorffweg 8 ▪ 21031 Hamburg ▪ Germany ▪ www.3bscientific.com
Subject to technical amendments
© Copyright 2009 3B Scientific GmbH
Page 4

 Loading...
Loading...