Page 1
3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
U14320 Standgefäß mit drei Glasröhren
Bedienungsanleitung
1/03 ALF
1
®
2
3
2
Das Standgefäß mit drei Glasröhren dient zur Demonstration des Wasserstands in kommunizierenden Röhren, ist aber auch als Überlaufgefäß zur Volumen- und
Dichtebestimmung fester Körper geeignet.
1. Sicherheitshinweise
• Glaskörper vorsichtig behandeln. Bruch- und damit Verletzungsgefahr!
• Apparatur keinen mechanischen Belastungen aussetzen.
• Austausch der Glasröhren vorsichtig vornehmen.
• Bei Benutzung von gefärbtem Wasser darauf ach-
ten, dass z.B. Kleidung nicht bespritzt wird.
2. Beschreibung, technische Daten
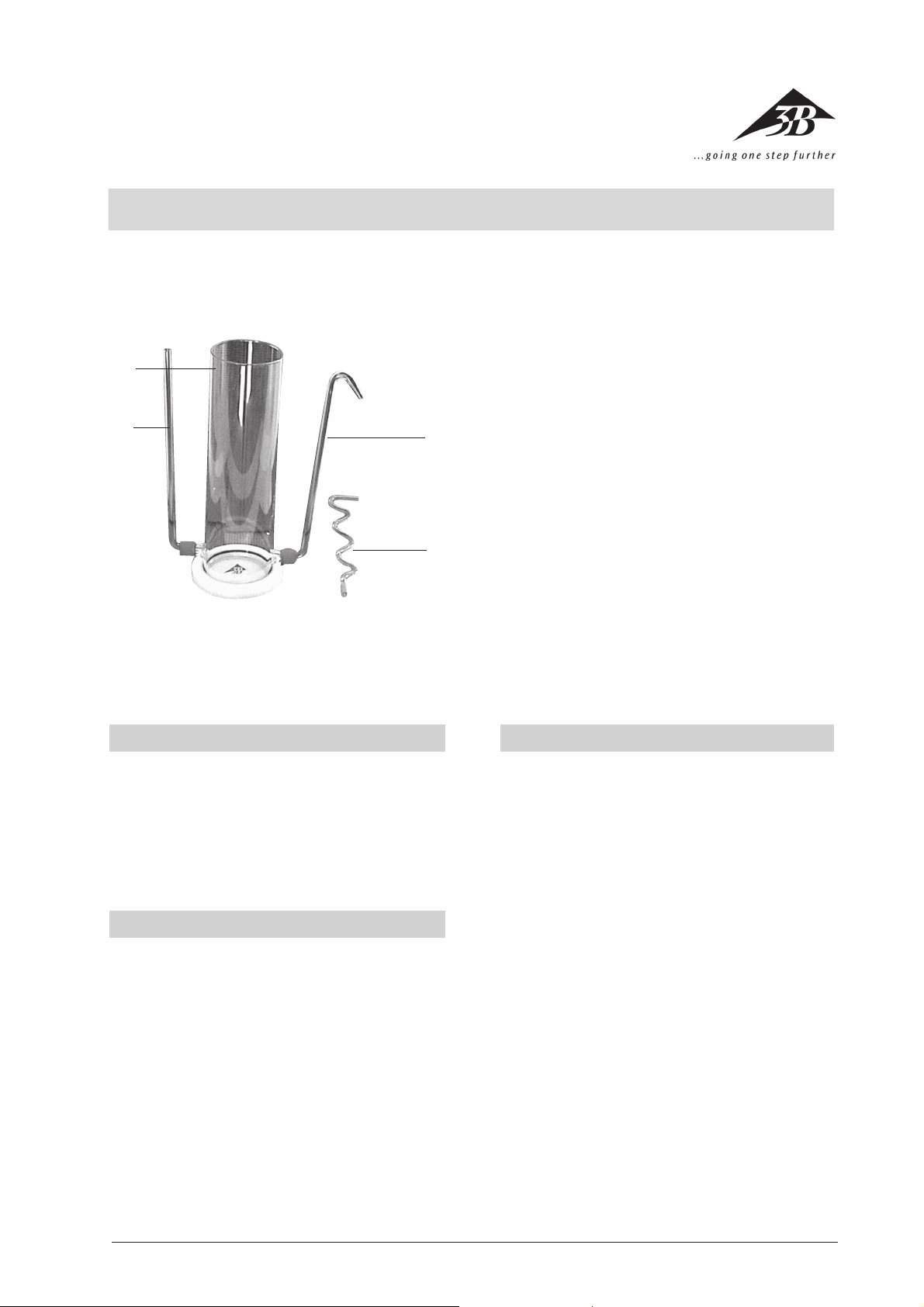
Das Standgefäß besteht aus einem Glaszylinder in
einer Kunststoff-Bodenplatte. Unten befinden sich
zwei Ausflussöffnungen mit GL-Verschraubung zur
Aufnahme von zwei verschieden geformten Glasröhren oder der Blindverschraubung und des Überlaufrohres.
Höhe: ca. 300 mm
Durchmesser: 90 mm
Durchmesser der Röhren: 10 mm
Verschraubung: GL-17
2.1 Lieferumfang
1 Standgefäß mit Kunststoff-Bodenplatte
Standgefäß
1
2 Glasröhren
3 Überlaufrohr
2 verschieden geformte Glasröhren
1 Überlaufrohr mit Tropföffnung
1 Blindverschraubung
3. Bedienung
• Bei Versuchen ist es zweckmäßig gefärbtes Wasser zu verwenden.
• Für den Versuch Flüssigkeitsstand in kommunizierenden Röhren beide Verschraubungen am Standzylinder lösen.
• Die zwei verschieden geformten Glasröhren einsetzen und festschrauben.
• Standzylinder zu ca. 2/3 mit Wasser füllen.
• Wasserstand in allen drei Gefäßen prüfen.
• Zur Demonstration die Apparatur nach beiden
Seiten kippen und den jeweiligen Pegelstand prüfen.
• Für den Versuch Volumenbestimmung fester Körper Blindverschraubung und das Überlaufrohr mit
Tropföffnung einsetzen und festschrauben.
• Messzylinder unter die Tropföffnung positionieren.
• Standzylinder soweit mit Wasser füllen, bis das
Wasser durch das Überlaufrohr abfließt.
• Wasser aus dem Messzylinder abgießen.
• Probekörper ins Wasser geben.
• Zur Volumenbestimmung Wasserstand des über-
gelaufenen Wassers im Messzylinder ablesen.
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Deutschland • www.3bscientific.com • Technische Änderungen vorbehalten
1
Page 2
3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
U14320 Upright vessel with three glass tubes
Operating instructions
1/03 ALF
1
®
2
3
2
The upright vessel with three glass tubes is used to observe water levels in connected tubes, and also serves
as an overflow vessel for measurements of the volume
and density of solid bodies.
1. Safety instructions
• Handle the glass vessel carefully to avoid breakage
and resulting injury.
• Avoid exerting mechanical loads on the apparatus.
• Proceed carefully when interchanging the glass
tubes.
• Be careful when using coloured water not to let it
splash on your clothes, for example.
2. Description, technical data
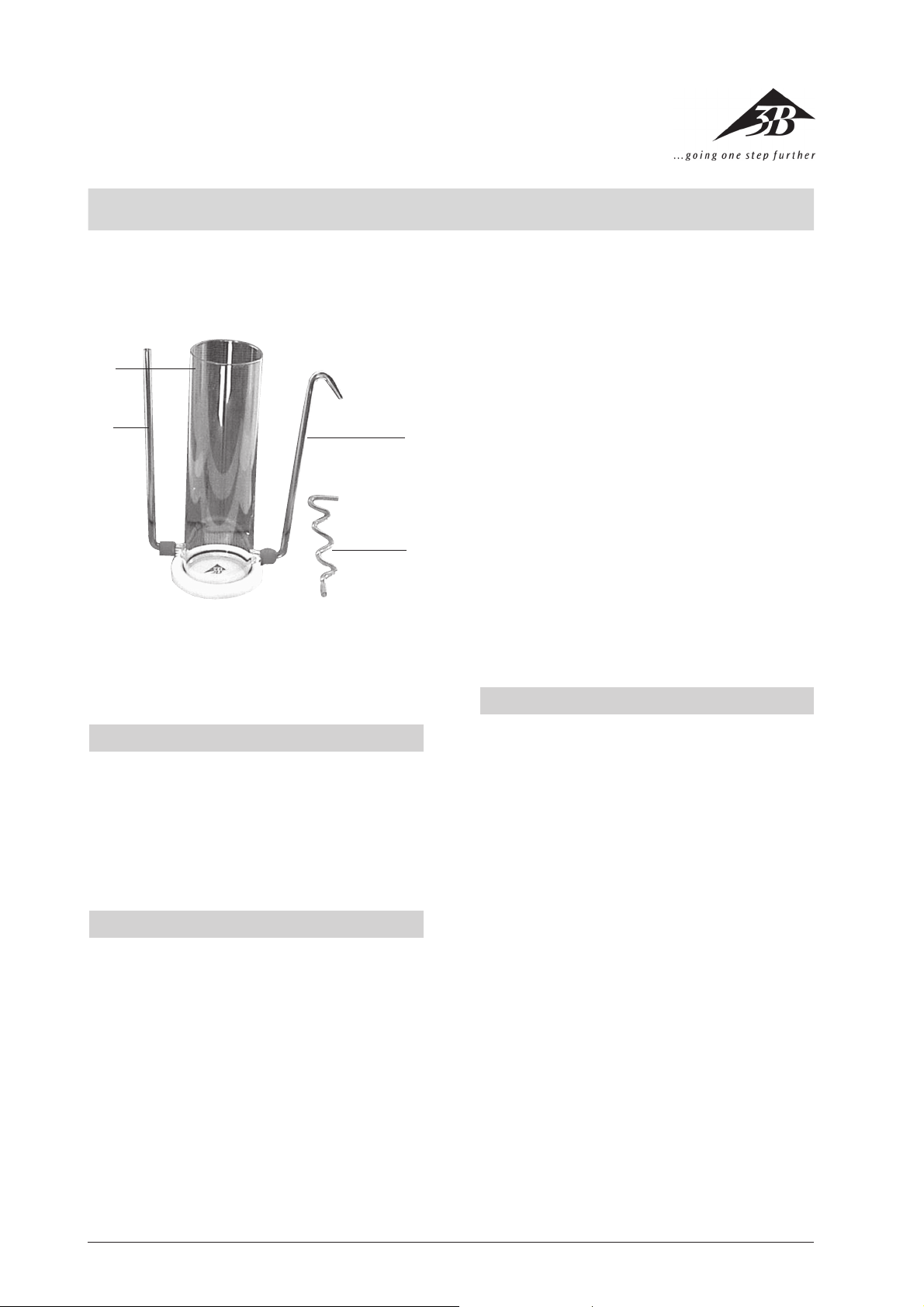
The upright vessel consists of a glass cylinder in a plastic base plate. Two outlets each with a GL screw connection are located at the bottom for the purpose of
mounting either two differently shaped glass tubes, or
a dummy joint and an overflow tube.
Height: Approximately 300 mm
Diameter: 90 mm
Tube diameter: 10 mm
Screw connection: GL-17
2.1 Scope of delivery
1 upright vessel with a plastic base plate
2 differently shaped glass tubes
1
Upright vessel
2 Glass tubes
3 Overflow tube
1 overflow tube with a drop outlet
1 dummy screw joint
3. Procedure
• It is practical to use coloured water during the experiments.
• For experiments to observe liquid levels in connected tubes, undo both the screw connections on
the upright cylinder.
• Mount the two differently shaped glass tubes and
screw them tightly into place.
• Fill the upright cylinder to approximately 2/3 with
water.
• Check the water level in all three vessels.
• As a demonstration, tilt the apparatus toward ei-
ther side and check the water level again in each
case.
• For experiments to determine the volume of solid
bodies, mount the dummy connection and the overflow tube with the drop outlet, and screw them
tightly into place.
• Position the measuring cylinder under the drop outlet.
• Fill the upright cylinder with water until it starts to
flow out of the overflow tube.
• Empty the measuring cylinder of water.
• Immerse the sample body into the water vessel.
• To determine the volume of the body, read the level
of the displaced water which has overflowed into
the measuring cylinder.
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Germany • www.3bscientific.com • Technical amendments are possible
2
Page 3

3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
U14320 Vase à trois tubes en verre
Instructions d’utilisation
1/03 ALF
1
2
3
1
Vase
2 Tubes en verre
®
2
Le vase avec les trois tubes en verre permet d’illustrer le
niveau d’eau dans des vases communicants, mais peut
aussi être utilisé comme réservoir de trop-plein pour
déterminer le volume et la densité de corps solides.
1. Consignes de sécurité
• Manipuler les corps en verre avec précaution. Risque de cassure et ainsi de blessure !
• Ne pas exposer l’appareil à des charges mécaniques.
• Echanger les tubes en verre avec précaution.
• En cas d’utilisation d’eau colorée, veiller à ne pas
mouiller par ex. les vêtements.
2. Description, caractéristiques techniques
Le vase est constitué d’un cylindre en verre monté dans
une plaque d’assise en plastique. Au-dessous se trouvent deux orifices d’écoulement à vissage GL permettant de loger deux tubes en verre de formes différentes ou du vissage aveugle et du tube de trop-plein.
Hauteur : env. 300 mm
Diamètre : 90 mm
Diamètre des tubes : 10 mm
Raccord à vis : GL-17
2.1 Matériel fourni
1 vase avec plaque d’assise en plastique
3 Trop-plein
2 tubes en verre de formes différentes
1 tube de trop-plein avec orifice d’égouttement
1 raccord à vis aveugle
3. Manipulation
• Pour les expériences, il est recommandé d’utiliser
de l’eau colorée.
• Pour l’expérience portant sur le niveau de liquide
dans des vases communicants, desserrer les deux
raccords à vis du cylindre à pied.
• Installer et visser les deux tubes de verre de différentes formes.
• Remplir le cylindre à pied de 2/3 d’eau.
• Vérifier le niveau d’eau dans les trois récipients.
• Aux fins de démonstration, basculer le dispositif
des deux côtés et vérifier le niveau respectif.
• Pour l’expérience destinée à déterminer le volume
de corps solides, visser le raccord aveugle et le tube
de trop-plein avec l’orifice d’égouttement.
• Placer le cylindre de mesure sous l’orifice d’égouttement.
• Remplir le cylindre à pied avec de l’eau, jusqu’à ce
que celle-ci s’écoule à travers le trop-plein.
• Déverser l’eau du cylindre de mesure.
• Mettre l’échantillon dans l’eau.
• Pour déterminer le volume, lire dans le cylindre
de mesure le niveau de l’eau qui a débordé.
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Allemagne • www.3bscientific.com • Sous réserve de modifications techniques
3
Page 4

3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
U14320 Cilindro di vetro con tre tubi
Istruzioni per l’uso
1/03 ALF
1
®
2
3
2
Il cilindro di vetro con tre tubi serve per la dimostrazione del livello dell’acqua nei vasi comunicanti, ma
viene utilizzato anche come vaso di troppopieno per
la determinazione di volume e densità dei solidi.
1. Norme di sicurezza
• Manipolare gli oggetti di vetro con cautela. Pericolo di rottura e quindi di lesioni!
• Non sottoporre l’apparecchiatura a sollecitazioni
meccaniche.
• Prestare attenzione nel sostituire i tubi di vetro.
• Nel caso si utilizzi di acqua colorata fare attenzio-
ne ad es. che i vestiti non vengano schizzati.
2. Descrizione, dati tecnici
Il recipiente è costituito da un cilindro di vetro inserito in una piastra di base in plastica. In basso si trovano
due luci di efflusso con un raccordo a vite GL per l’inserimento di due tubi di vetro di forma diversa oppure
del raccordo di chiusura a vite e del tubo di
troppopieno.
Altezza: ca. 300 mm
Diametro: 90 mm
Diametro dei tubi: 10 mm
Attacco a vite: GL-17
Cilindro di vetro
1
2 Tubi di vetro
3 Tubo di troppopieno
2.1 Dotazione di serie
1 cilindro di vetro con piastra di base in plastica
2 tubi di vetro di forma diversa
1 tubo di troppopieno con apertura di gocciolamento
1 raccordo di chiusura a vite
3. Comandi
• Per l’esperimento è opportuno utilizzare acqua colorata.
• Per l’esperimento sul livello dei liquidi in vasi comunicanti allentare entrambi i raccordi a vite nel
cilindro di vetro.
• Inserire i due tubi di vetro di forma diversa e avvitarli.
• Riempire con acqua il cilindro di vetro per ca. 2/3.
• Verificare il livello dell’acqua nei tre recipienti.
• Procedere alla dimostrazione inclinando l’apparec-
chiatura da entrambi i lati e verificando di volta in
volta il livello dell’acqua.
• Per l’esperimento relativo alla determinazione del
volume dei solidi applicare e serrare il raccordo di
chiusura a vite e il tubo di troppopieno con apertura di gocciolamento.
• Posizionare il cilindro graduato sotto l’apertura di
gocciolamento.
• Riempire il cilindro di vetro con l’acqua finché
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Germania • www.3bscientific.com • Con riserva di modifiche tecniche
4
Page 5

3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
U14320 Recipiente de fondo plano con tres tubos de vidrio
Instrucciones de uso
1/03 ALF
1
®
2
3
2
El recipiente de fondo plano con tres tubos de vidrio
sirve para la demostración del nivel de agua en vasos
comunicantes, pero es también apto, como recipiente
de rebose, para la determinación del volumen y la densidad de los cuerpos sólidos.
1. Aviso de seguridad
• Trate con cuidado las piezas de cristal. ¡Peligro de
que se quiebren y ocasionen heridas!
• No someta el equipo a ninguna carga mecánica.
• Tenga cuidado al intercambiar los tubos de vidrio.
• Cuando use agua coloreada, tenga cuidado de que,
por ejemplo, no salpique la ropa.
2. Descripción, datos técnicos
El recipiente de fondo plano consta de un cilindro de
vidrio montado sobre una base de plástico. En la parte
inferior se encuentran dos aberturas de salida con
atornilladuras GL para el alojamiento de dos tubos de
vidrio de diferente forma, o del racor con tapón
roscado, y del tubo de rebose.
Altura: aprox. 300 mm
Diámetro: 90 mm
Diámetro de los tubos: 10 mm
Atornilladuras: GL-17
2.1 Volumen de suministro
1 Recipiente de fondo plano con soporte base de plástico
Recipiente de fondo plano
1
2 Tubos de vidrio
3 Tubo de rebose
2 tubos de cristal de diferente diseño
1 tubo de rebose con abertura de goteo
1 racor con tapón roscado
3. Servicio
• Para la experimentación se debe usar, preferentemente, agua coloreada.
• Para el experimento de nivel de líquidos en los vasos comunicantes, desatornillar las dos
atornilladuras del cilindro.
• Insertar los dos tubos de cristal de diferente diseño y atornillarlos fijamente.
• Llenar de agua el cilindro hasta aproximadamente
2/3 de su volumen.
• Comprobar el nivel del agua en los tres recipientes.
• Para fines de demostración, inclinar el conjunto
hacia ambos lados y comprobar en cada caso el
nivel del líquido.
• Para el experimento de determinación del volumen
de un cuerpo sólido, insertar y atornillar fijamente
el racor con tapón roscado y el tubo de rebose con
abertura de goteo.
• Posicionar el cilindro de medición debajo de la
abertura de goteo.
• Llenar de agua el recipiente de fondo plano hasta
que ésta se derrame por el tubo de rebose.
• Verter el agua del cilindro graduado.
• Introducir en el agua el cuerpo de prueba.
• Para la determinación del volumen, leer el nivel
alcanzado por el agua en el cilindro de medición.
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Al emania • www.3bscientific.com • Se reservan las modificaciones técnicas
5
Page 6

3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
U14320 Vaso de medição com 3 tubos de vidro
Instruções para o uso
1/03 ALF
1
®
2
3
2
O vaso de medição com três tubos de vidro serve para
demonstrar o equilíbrio do nível de líquidos em vasos
comunicados, mas também pode servir como vaso recipiente para determinar o volume e a densidade de
corpos sólidos.
1. Indicações de segurança
• Manipular os objetos de vidro com cuidado. Perigo
de quebra e de ferida.
• Não submeter a aparelhagem a cargas ou pressão
mecânica.
• Trocar os tubos de vidro com máximo cuidado.
• Quando usada água tingida, tomar cuidado para
não respingar, por exemplo, na roupa.
2. Descrição, dados técnicos
O vaso de medição é composto de um cilindro de vidro e uma placa de apoio de material plástico. Abaixo
encontram-se dois orifícios de evacuação com rosca
GL para a recepção de dois tipos diferentes de tubo de
vidro ou da rosca de obstrução e do tubo de extravasão.
Altura: aprox. 300 mm
Diâmetro: 90 mm
Diâmetro dos tubos: 10 mm
Rosca: GL-17
2.1 Conteúdo da entrega
1 vaso de medição com placa de apoio de material plástico
1
Vaso de medição
2 Tubos de vidro
3 Tubo de extravasão
2 tubos de vidro de diferentes formas
1 tubo de extravasão com abertura para goteio
1 rosca de obstrução
3. Utilização
• É de utilidade utilizar água tingida para as experiências.
• Para a experiência do nível do líquido em vasos comunicados, soltar as duas roscas no cilindro.
• Aplicar os dois tubos de vidro de formas diferentes
e fixar apertando-os nas roscas.
• Encher o cilindro até aproximadamente 2/3 com
água.
• Verificar o nível da água nos três recipientes.
• Para a demonstração, inclinar a aparelhagem para
ambos lados e verificar cada nível da água.
• Para a experiência de determinação do volume e
da densidade de corpos sólidos, aplicar a rosca de
obstrução e o tubo de extravasão com abertura para
goteio e apertar nas roscas.
• Posicionar o cilindro de medida debaixo da abertura para goteio.
• Encher o cilindro até que a água comece a vazar
pelo tubo de extravasão.
• Esvaziar a água do cilindro de medição.
• Por os corpos da experiência na água.
• Para determinar o volume, ler o nível da água que
vazou para o cilindro de medição.
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Alemanha • www.3bscientific.com • Sob reserva de modificações técnicas
6
 Loading...
Loading...