CHAPTER 12
WAN
R1
R2
A
R3
LAN
Static Route
12.1 Overview
The ZyXEL Device usually uses the default gateway to route outbound tr affic from
computers on the LAN to the Internet. To have the ZyXEL Device send data to
devices not reachable through the default gateway, use static routes.
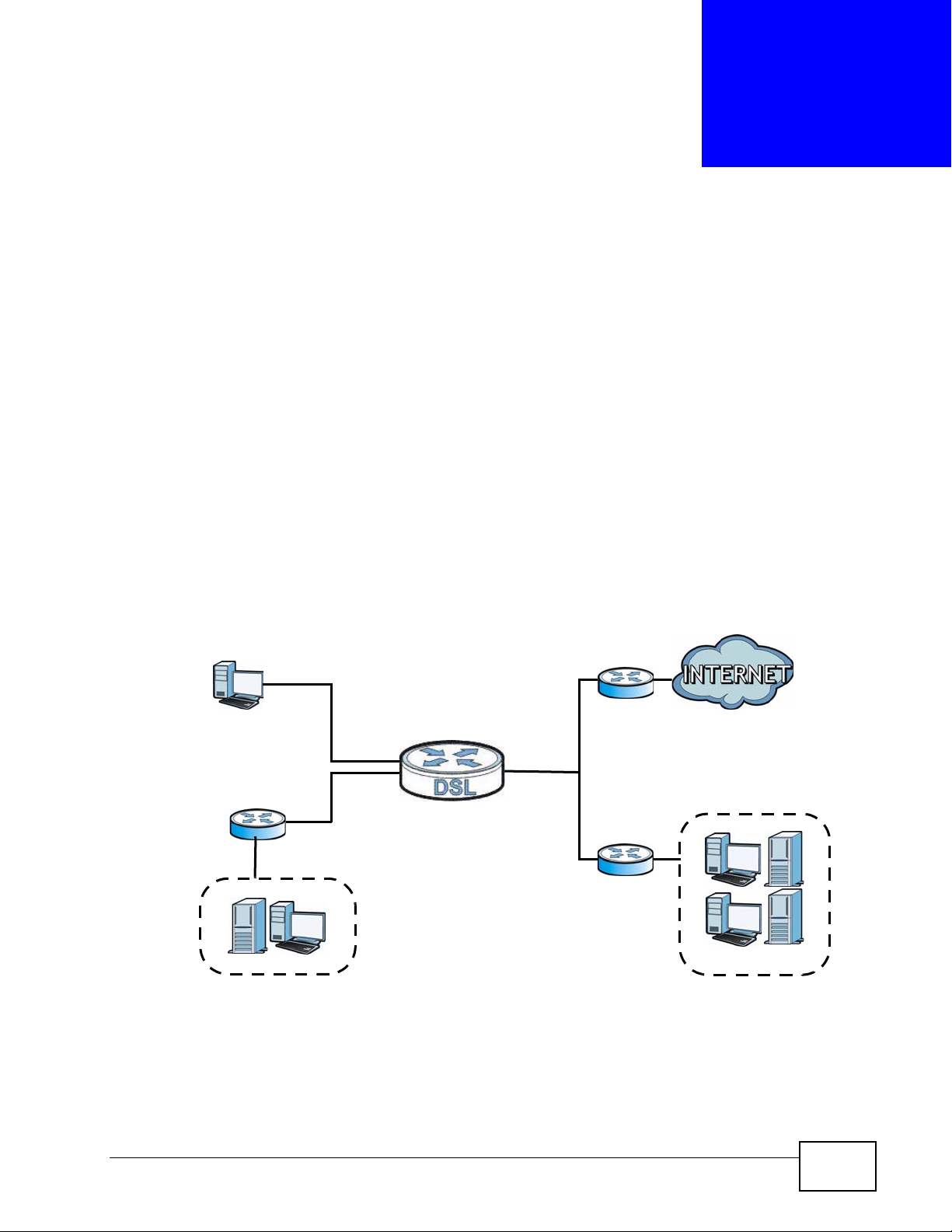
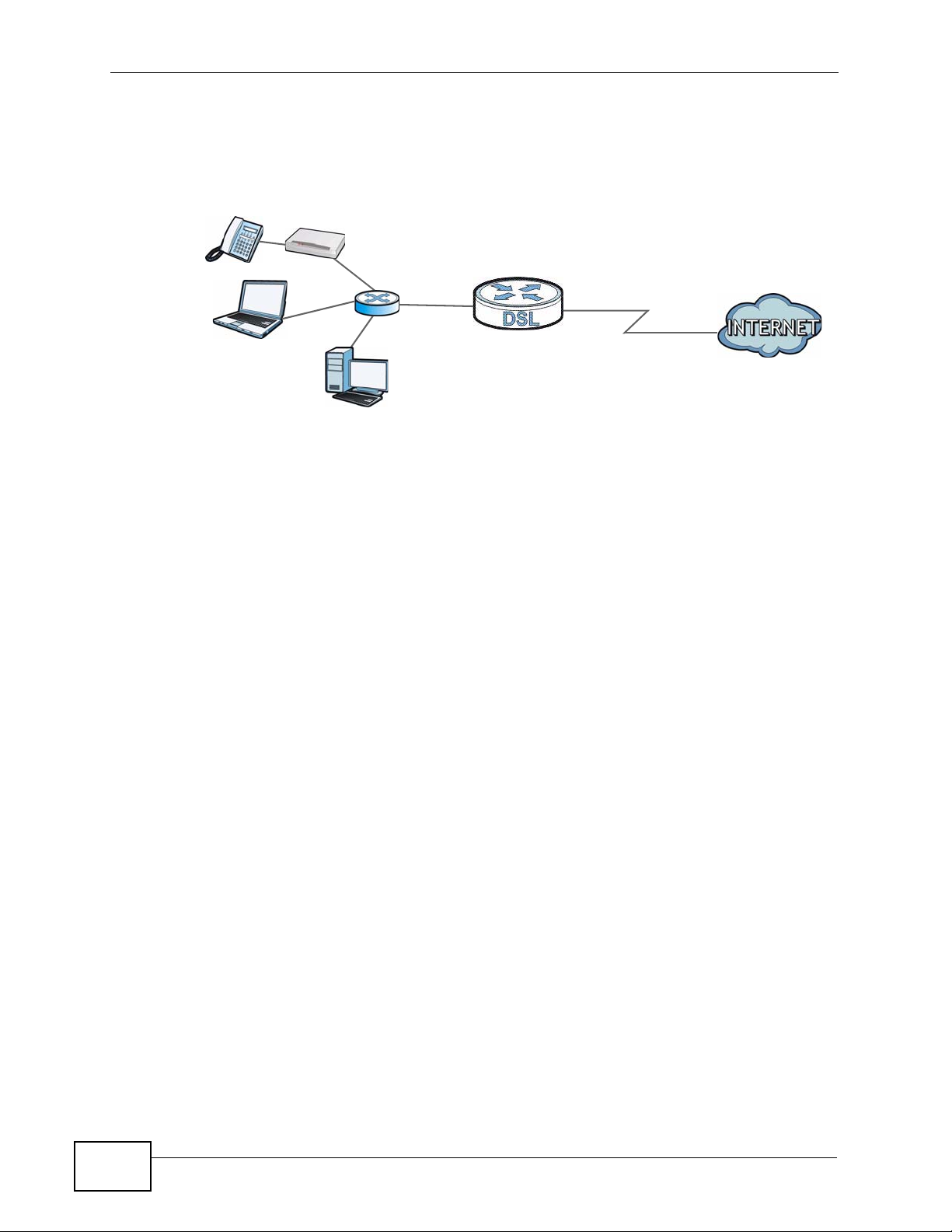
For example, the next figure shows a computer (A) connected to the ZyXEL
Device’s LAN interface. The ZyXEL Device routes most traffic from A to the
Internet through the ZyXEL Device’s default gateway (R1). You create one static
route to connect to services offered by your ISP behind router R2. You create
another static route to communicate with a separate network behind a router R3
connected to the LAN.
Figure 77 Example of Static Routing Topology
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
161
Chapter 12 Static Route
12.1.1 What You Can Do in the Static Route Screens
Use the Static Route screens (Section 12.2 on page 162) to view and configure
IP static routes on the ZyXEL Device.
12.2 The Static Route Screen
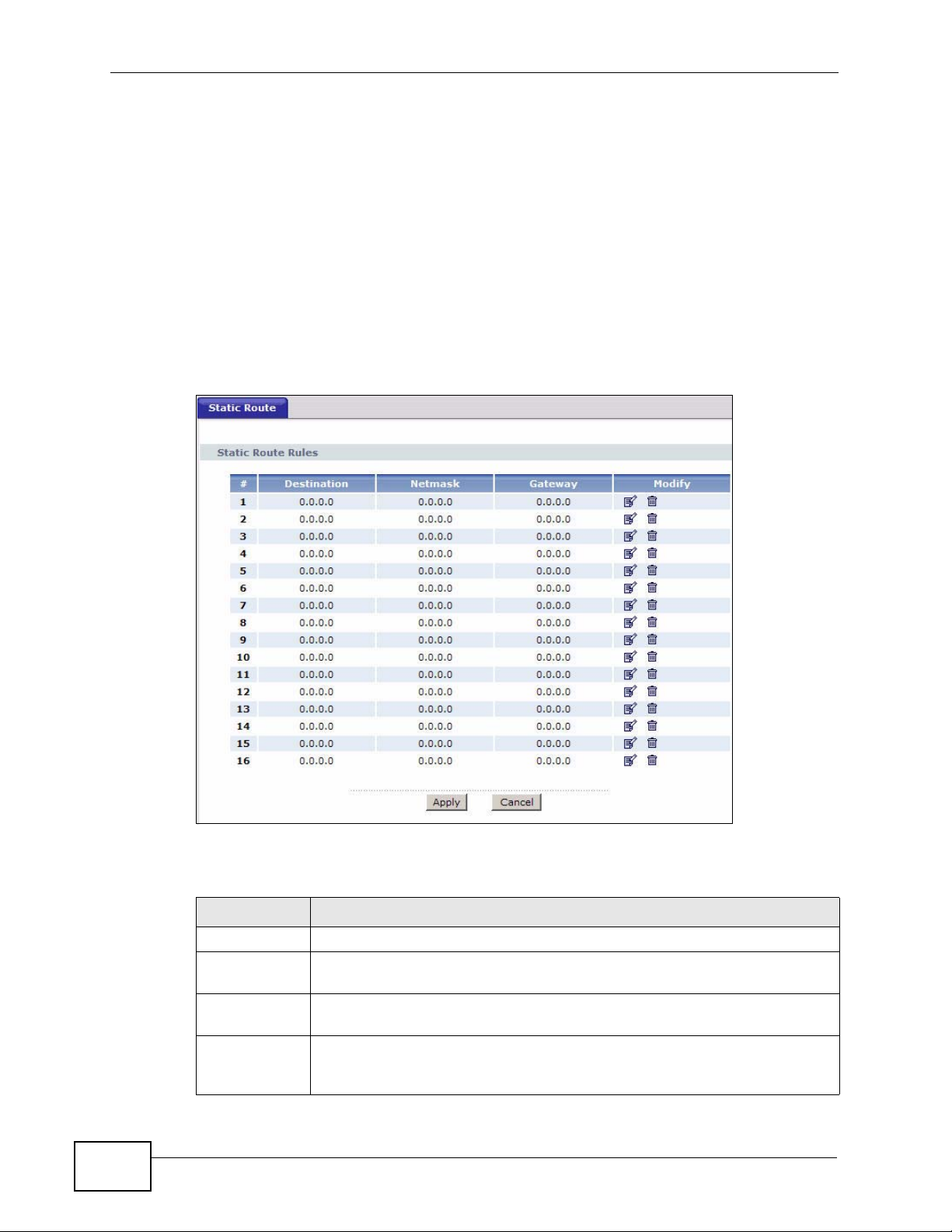
Use this screen to view the static route rules. Click Advanced > Static Route to
open the Static Route screen.
Figure 78 Advanced > Static Route
162
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 53 Advanced > Static Route
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the number of an individual static route.
Destination This parameter specifies the IP network address of the final destination.
Routing is always based on network number.
Netmask This parameter specifies the IP network subnet mask of the final
destination.
Gateway This is the IP address of the gateway. The gateway is a router or switch
on the same network segment as the device's LAN or WAN port. The
gateway helps forward packets to their destinations.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
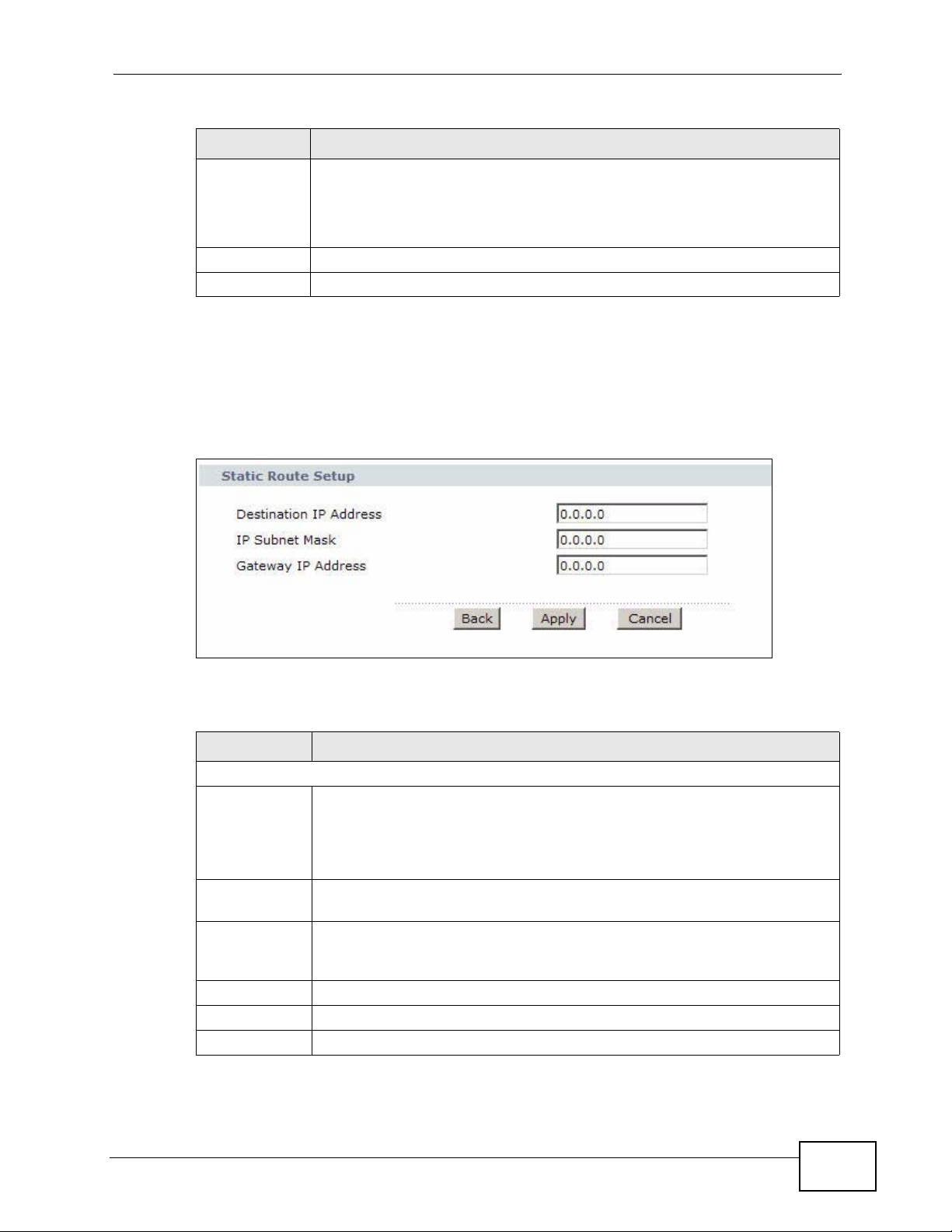
Table 53 Advanced > Static Route
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Modify Click the Edit icon to go to the screen where you can set up a static route
on the ZyXEL Device.
Click the Remove icon to remove a static route from the ZyXEL Device. A
window displays asking you to confirm that you want to delete the route.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
12.2.1 Static Route Edit
Use this screen to configure the required information for a static route. Select a
static route index number and click Edit. The screen shown next appears.
Figure 79 Advanced > Static Route: Edit
Chapter 12 Static Route
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 54 Advanced > Static Route: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static Route Setup
Destination IP
Address
IP Subnet
Mask
Gateway IP
Address
Back Click this to return to the previous screen without saving.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
This parameter specifies the IP network address of the final destination.
Routing is always based on network number. If you need to specify a
route to a single host, use a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255 in the
subnet mask field to force the network number to be identical to the host
ID.
Enter the IP subnet mask here.
Enter the IP address of the gateway. The gateway is a router or switch on
the same network segment as the device's LAN or WAN port. The
gateway helps forward packets to their destinations.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
163

Chapter 12 Static Route
164
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
CHAPTER 13
Ports
VLAN Groups
Priority Levels
802.1Q
802.1P
802.1Q/1P
13.1 Overview
This chapter describes how to configure the 802.1Q/1P settings.
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) allows a physical network to be partitioned
into multiple logical networks. A VLAN group can be treated as an individual
device. Each group can have its own rules about where and how to forward traffic.
You can assign any ports on the ZyXEL Device to a VLAN group and configure the
settings for the group. You may also set the priority level for traffic trasmitted
through the ports.
Figure 80 802.1Q/1P
13.1.1 What You Can Do in the 802.1Q/1P Screens
•Use the Group Setting screen (Section 13.2 on page 166) to activate 802.1Q/
1P, specify the management VLAN group, display the VLAN groups and
configure the settings for each VLAN group.
•Use the Port Setting screen (Section 13.3 on page 169) to configure the PVID
for each port.
13.1.2 What You Need to Know About 802.1Q/1P
IEEE 802.1P Priority
IEEE 802.1P specifies the user priority field and defines up to eight separate tr affic
types by inserting a tag into a MAC-layer fr ame that contains bits to define class of
service.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
165

Chapter 13 802.1Q/1P
IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN
Tagged VLAN uses an explicit tag (VLAN ID) in the MAC header to identi fy the
VLAN membership of a frame across bridges - they are not confined to the device
on which they were created. The VLA N ID associates a fr ame with a speci fic VLAN
and provides the information that devices need to process the frame across the
network.
PVC
A virtual circuit is a logical point-to-point circuit between customer sites.
Permanent means that the circuit is preprogrammed by the carrier as a path
through the network. It does not need to be set up or torn down for each session.
Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames
Each port on the device is capable of passing tagged or untagged frames. To
forward a frame from an 802.1Q VLAN-aware devi ce t o an 802. 1Q VLAN- unaw are
device, the ZyXEL Device first decides where to f orward the frame and then strips
off the VLAN tag. To forward a frame from an 802.1Q VLAN-unaware device to an
802.1Q VLAN-aware switch, the ZyXEL Device first decides where to forward the
frame, and then inserts a VLAN tag reflecting the ingress port's default VID. The
default PVID is VLAN 1 for all ports, but this can be changed.
Whether to tag an outgoing frame depends on the setting of the egress port on a
per-VLAN, per-port basis (recall that a port can belong to multiple VLANs). If the
tagging on the egress port is enabled for the VID of a frame, then the frame is
transmitted as a tagged frame; otherwise, it is transmitted as an untagged frame.
13.2 The 802.1Q/1P Group Setting Screen
Use this screen to activate 802.1Q/1P and display the VLAN groups. Click
Advanced > 802.1Q/1P to display the following screen.
166
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide

Chapter 13 802.1Q/1P
Note: If the WAN interface in the VLAN group is not the default router, you need to
create a static route to communicate with the WAN.
Figure 81 Advanced > 802.1Q/1P > Group Setting
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 55 Advanced > 802.1Q/1P > Group Setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
802.1Q/1P
Active Select this check box to activate the 802.1P/1Q feature.
Summary
# This field displays the index number of the VLAN group.
Active This field displays whether 802.1P/1Q is active for the VLAN group.
VID This field displays the ID number of the VLAN group.
Port Number These columns display the VLAN’s settings for each port. A tagged
port is marked as T, an untagged port is marked as U and ports not
participating in a VLAN are marked as “–“.
Modify Click the Edit button to configure the the ports in the VLAN group.
Click the Remove button to delete the VLAN group.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
167
Chapter 13 802.1Q/1P
13.2.1 Editing 802.1Q/1P Group Setting
Use this screen to configure the settings for each VLAN group.
In the 802.1Q/1P screen, click the Edit button from the Modify filed to display
the following screen.
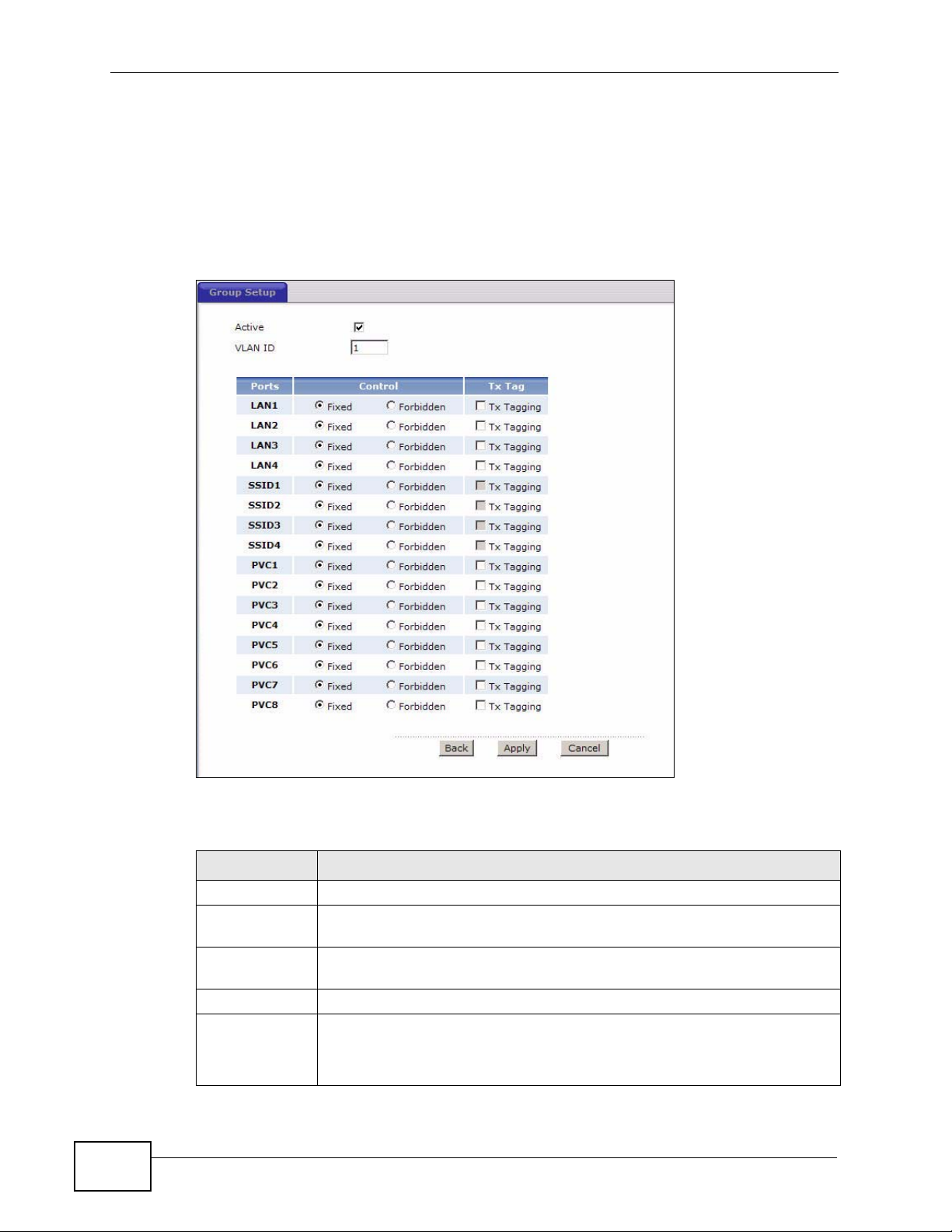
Figure 82 Advanced > 802.1Q/1P > Group Setting > Edit
168
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 56 Advanced > 802.1Q/1P > Group Setting > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Select this check box to activate the group setting.
VLAN ID Assign a VLAN ID for the VLAN group. The valid VID range is between 1
and 4094.
Default
Gateway
Ports This field displays the types of ports available to join the VLAN group.
Control Select Fixed for the port to be a permanent member of the VLAN group.
Select the default gateway for the VLAN group.
Select Forbidden if you want to prohibit the port from joining the VLAN
group.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
Chapter 13 802.1Q/1P
Table 56 Advanced > 802.1Q/1P > Group Setting > Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Tx Tag Select Tx Tagging if you want the port to tag all outgoing traffic
trasmitted through this VLAN. Y ou select this if you want to create VLANs
across different devices and not just the ZyXEL Device.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen without saving.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
13.3 The 802.1Q/1P Port Setting Screen
Use this screen to configure the PVID for each port. Click Advanced > 802.1Q/
1P > Port Setting to display the following screen.
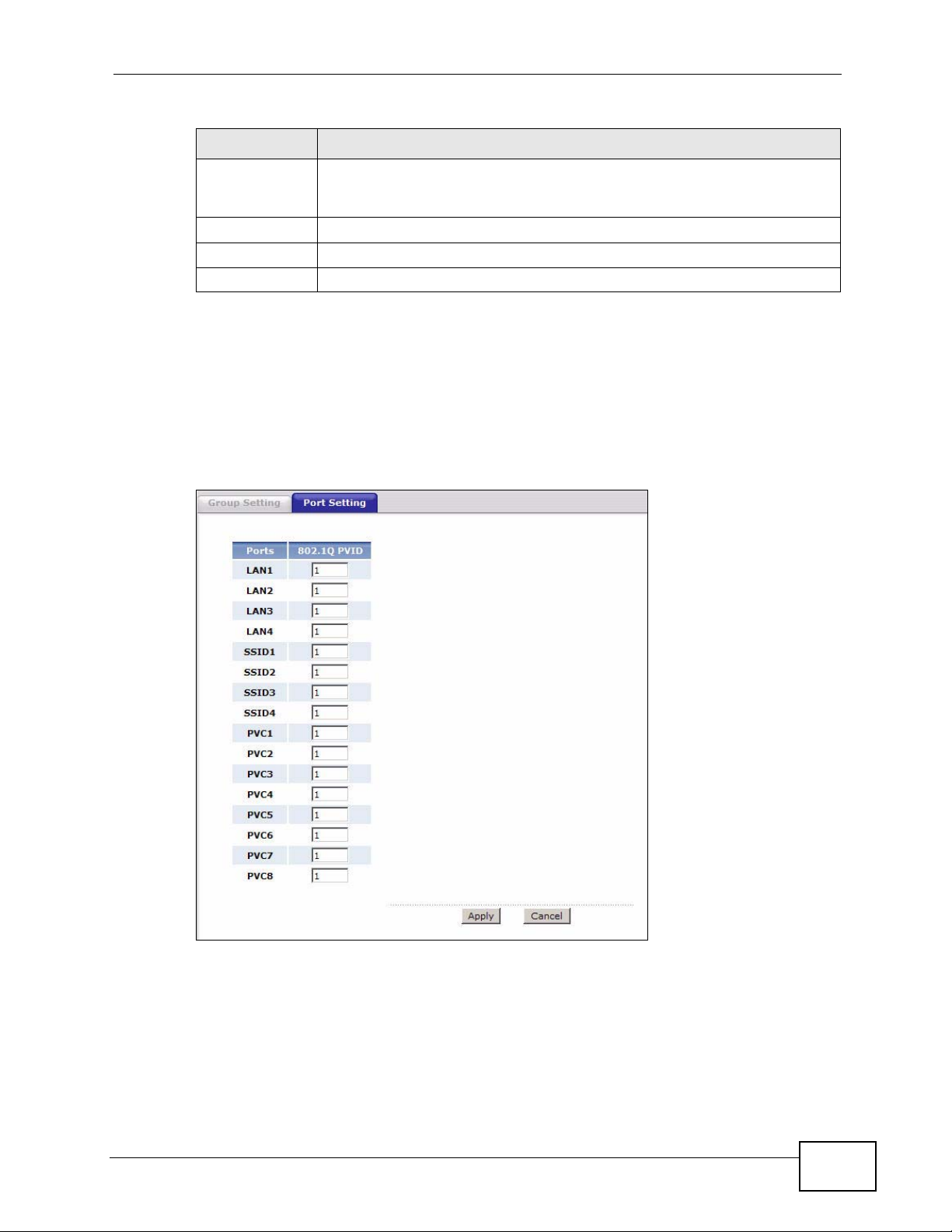
Figure 83 Advanced > 802.1Q/1P > Port Setting
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
169

Chapter 13 802.1Q/1P
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 57 Advanced > 802.1Q/1P > Port Setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ports This field displays the types of ports available to join the VLAN group.
802.1Q PVID Assign a VLAN ID for the port. The valid VID range is between 1 and
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
4094. The ZyXEL Device assigns the PVID to untagged frames or
priority-tagged frames received on this port.
170
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide

CHAPTER 14
Quality of Service (QoS)
14.1 Overview
Use the QoS screen to set up your ZyXEL Device to use QoS for traffic
management.
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to both a network’s ability to deliver data with
minimum delay, and the networking methods used to control bandwidth. QoS
allows the ZyXEL Device to group and prioritize application traffic and fine-tune
network performance.
Without QoS, all traffic data are equally likely to be dropped when the network is
congested. This can cause a reduction in network performance and make the
network inadequate for time-critic al applications such as video-on-demand.
The ZyXEL Device assigns each packet a priority and then queues the packet
accordingly. Packets assigned with a hi gh priority are processed more quickly than
those with low priorities if there is congestion, allowing time-sensitive applications
to flow more smoothly. Time-sensitive applications include both those that require
a low level of latency (delay) and a low level of jitter (variations in delay) such as
Voice over IP (VoIP) or Internet gaming, and those for which jitter alone is a
problem such as Internet radio or streaming video.
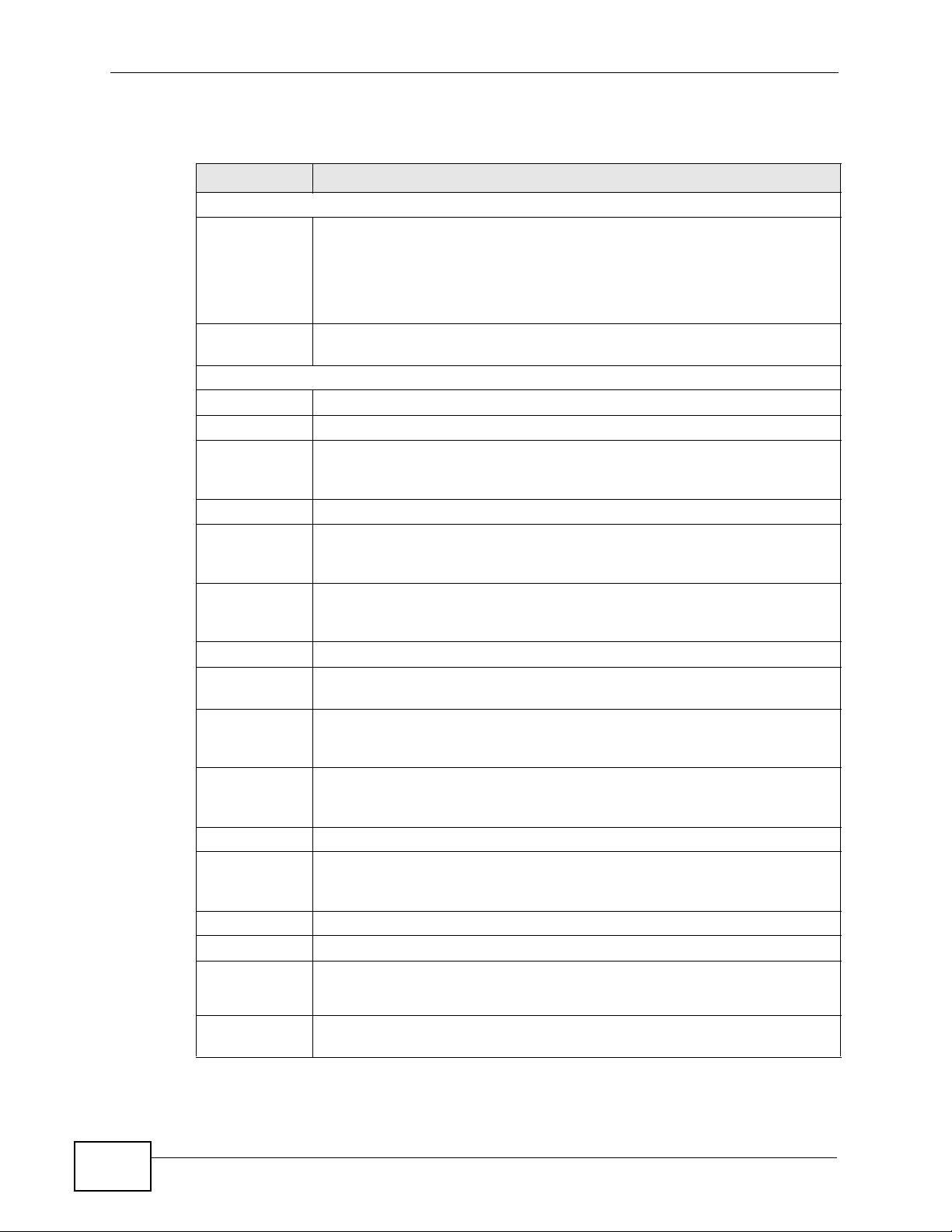
In the following figure, your Internet connection has an upstream transmission
speed of 50 Mbps. You configure a classifier to assign the highest priority queue
(6) to VoIP traffic from the LAN interface, so that voice traffic would not get
delayed when there is network congestion. Traffic from the boss’s IP address
(192.168.1.23 for example) is mapped to queue 5. Traffic that does not match
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
171
Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
50 Mbps
DSL
VoIP: Queue 6
Boss: Queue 5
IP=192.168.1.23
these two classes are assigned priority queue based on the internal QoS mapping
table on the ZyXEL Device.
Figure 84 QoS Example
14.1.1 What You Can Do in the QoS Screens
•Use the QoS screen (Section 14.2 on page 173) to configure QoS settings on
the ZyXEL Device.
•Use the QoS Settings Summary screen (Section 14.2.1 on page 175) to check
the summary of QoS rules and actions you configured for the ZyXEL Device.
14.1.2 What You Need to Know About QoS
802.1p
QoS is used to prioritize source-to-destination tr affic flows. All packets in the same
flow are given the same priority. 802.1p is a way of managing traffic in a network
by grouping similar types of traffic together and treating each type as a class. You
can use 802.1p to give different priorities to different packet types.
Tagging and Marking
In a QoS class, you can configure whether to add or change the DiffServ Code
Point (DSCP) value, IEEE 802.1p priority level and VLAN ID number in a matched
packet. When the packet passes through a compatible network, the networking
device, such as a backbone switch, can provide specific treatment or service
based on the tag or marker.
Finding Out More
172
See Section 14.3 on page 176 for advanced technical information on QoS.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
14.2 The QoS Screen
Use this screen to enable or disable QoS and have the ZyXEL Device assign
priority levels to traffic according to the port range, IEEE 802.1p prio rity level and/
or IP precedence.
Click Advanced Setup > QoS to open the screen as shown next.
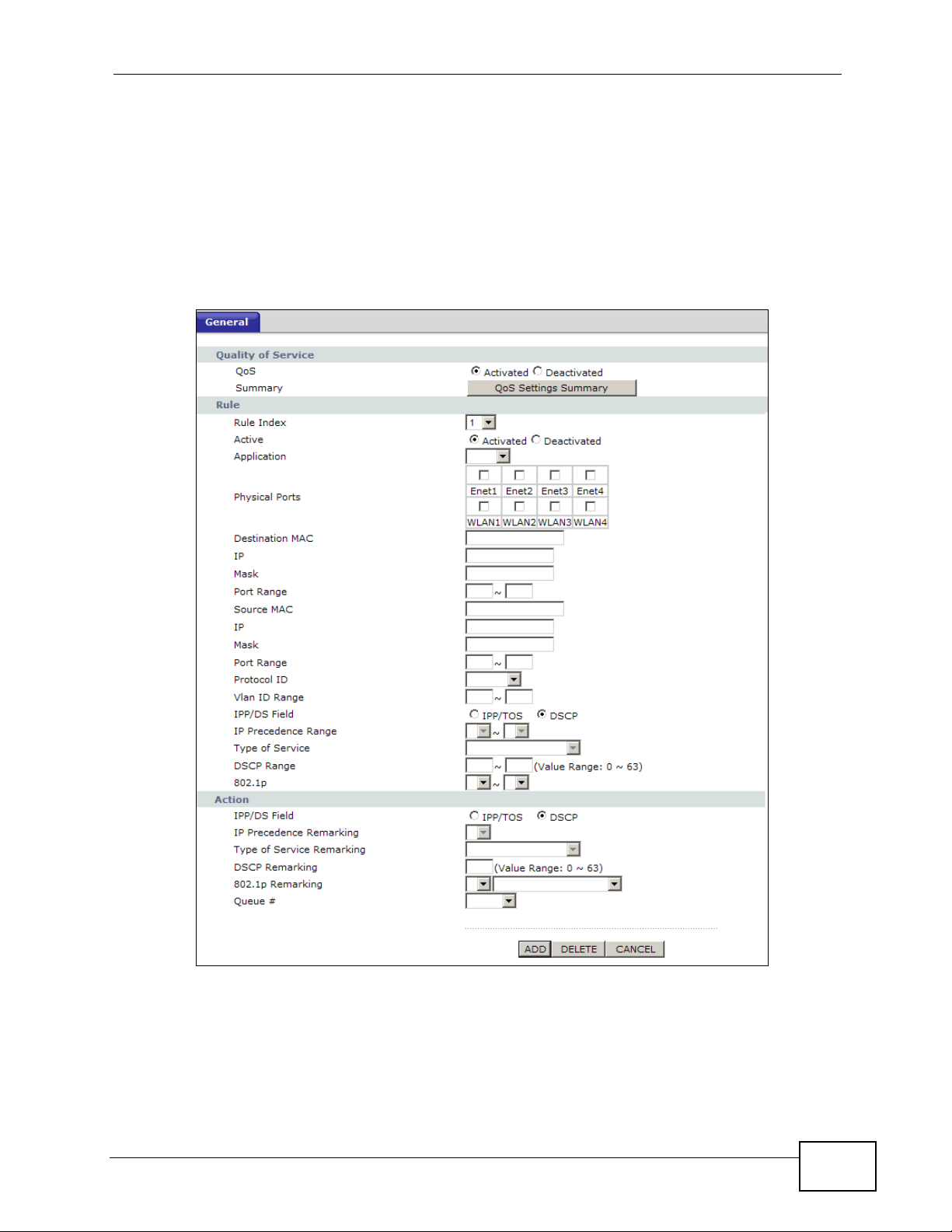
Figure 85 Advanced Setup > QoS
Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
173
Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 58 Advanced Setup > QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Quality of Service
QoS Use this field to turn on QoS to improve your network performance.
You can give priority to traffic that the ZyXEL Device forwards out
through the WAN interface. Give high priority to voice and video to make
them run more smoothly. Similarly, give low priority to many large file
downloads so that they do not reduce the quality of other applications.
Summary Click this to open a summary table showing the QoS settings. See
Section 14.2.1 on page 175 for more details.
Rule
Rule Index Select the rule’s index number from the drop-down list box.
Active Use this field to enable or disable the rule.
Application Select an application from the drop-down list box. The Destination Port
Range and Protocol ID fields may change depending on the type of
applications you choose.
Physical Ports Select Enet1 to apply the rule to the Ethernet port.
Destination
MAC
IP Enter a destination IP address in dotted decimal notation. QoS is then
Mask Enter a destination subnet mask here.
Port Range Either use the default value set by the application you choose, or enter
Source MAC T ype a source MAC address here. QoS is then applied to traffic containing
IP Enter a source IP address in dotted decimal notation. QoS is then applied
Mask Enter a source subnet mask here.
Port Range Enter the port number to which the rule should be applied. 0 means any
Protocol ID Select an IP protocol type from the drop-down list box.
Vlan ID Range Enter the source VLAN ID in this field.
IPP/DS Field Select IPP/TOS to specify an IP precedence range and type of services.
Type a destination MAC address here. QoS is then applied to traffic
containing this destination MAC address. Leave it blank to apply the rule
to all MAC addresses.
applied to traffic containing this destination IP address. A blank
destination IP address means any destination IP address.
the port number to which the rule should be applied.
this source MAC address. Leave it blank to apply the rule to all MAC
addresses.
to traffic containing this source IP address. A blank source IP address
means any source IP address.
source port number. See Appendix E on page 307 for some common
services and port numbers.
174
IP Precedence
Range
Select DSCP to specify a DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) range.
Enter a range from 0 to 7 for IP precedence. Zero is the lowest priority
and seven is the highest.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide

Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
Table 58 Advanced Setup > QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Type of
Service
DSCP Range Specify a DSCP number between 0 and 63 in this field.
802.1p Select a priority level (0 to 7) from the drop-down list box.
Action
IPP/DS Field Select IPP/TOS to specify an IP precedence range and type of services.
IP Precedence
Remarking
Type of
Service
Remarking
DSCP
Remarking
802.1p
Remarking
Queue # Specify a Low, Medium, High or Highest queue tag to matched traffic.
ADD Click this to add the rule.
DELETE Click this to remove the rule.
CANCEL Click this to restore previously saved settings.
Select a type of service from the drop-down list box.
Available options are: Normal service, Minimize delay, Maximize
throughput, Maximize reliability and Minimize monetary cost.
Select DSCP to specify a DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) range.
Enter a range from 0 to 7 to re-assign IP precedence to matched traffic.
Zero is the lowest priority and seven is the highest.
Select a type of service to re-assign the priority level to matched traffic.
Available options are: Normal service, Minimize delay, Maximize
throughput, Maximize reliability and Minimize monetary cost.
Specify a DSCP number between 0 and 63 to re-assign the priority level
to matched traffic.
Select a priority level (0 to 7) to re-assign the priority level to matched
traffic.
Traffic assigned to a higher queue gets through faster while traffic in
lower queues is dropped when there is network congestion.
14.2.1 The QoS Settings Summary Screen
Use this screen to display a summary of rules and actions configured for the
ZyXEL Device. I n the Advanced > QoS screen, click the QoS Settings
Summary button to open the following screen.
Figure 86 Advanced Setup > QoS > QoS Settings Summary
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
175
Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 59 Advanced Setup > QoS > QoS Settings Summary
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rules
# This is the rule’s index number.
Active This shows whether the rule is enabled or disabled.
Physical Ports This is the physical port associated with the rule.
Destination MAC
and IP/Mask
Port Ranges
Source MAC and
IP/Mask Port
Ranges
Protocol ID This is the protocol ID associated with the rule.
VLAN ID This is the VLAN ID associated with the rule.
IPP/TOS (DSCP) This shows the IPP/TOS or DSCP settings.
802.1p This is the 802.1p priority level.
Actions
IPP/TOS (DSCP)
Remarking
802.1p
Remarking
Queue # The ZyXEL Device assigns the queue level specified in this field to
This is the port range for destination MAC address and IP address.
This is the port range for source MAC address and IP address.
The ZyXEL Device re-assigns the priority values specified in this field
to matched traffic.
The ZyXEL Device re-assigns the priority levels specified in this field
to matched traffic.
matched traffic.
14.3 QoS Technical Reference
This section provides some technical background information about the topics
covered in this chapter.
14.3.1 IEEE 802.1p
IEEE 802.1p specifies the user priority field and defines up to eight separ ate traffic
types. The following table describes the traffic types defined in the IEEE 802.1d
standard (which incorporates the 802.1p).
Table 60 IEEE 802.1p Priority Level and Traffic Type
PRIORITY
LEVEL
Level 7 Typically used for network control traffic such as router configuration
Level 6 Typically used for voice traffic that is especially sensitive to jitter (jitter is the
176
TRAFFIC TYPE
messages.
variations in delay).
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
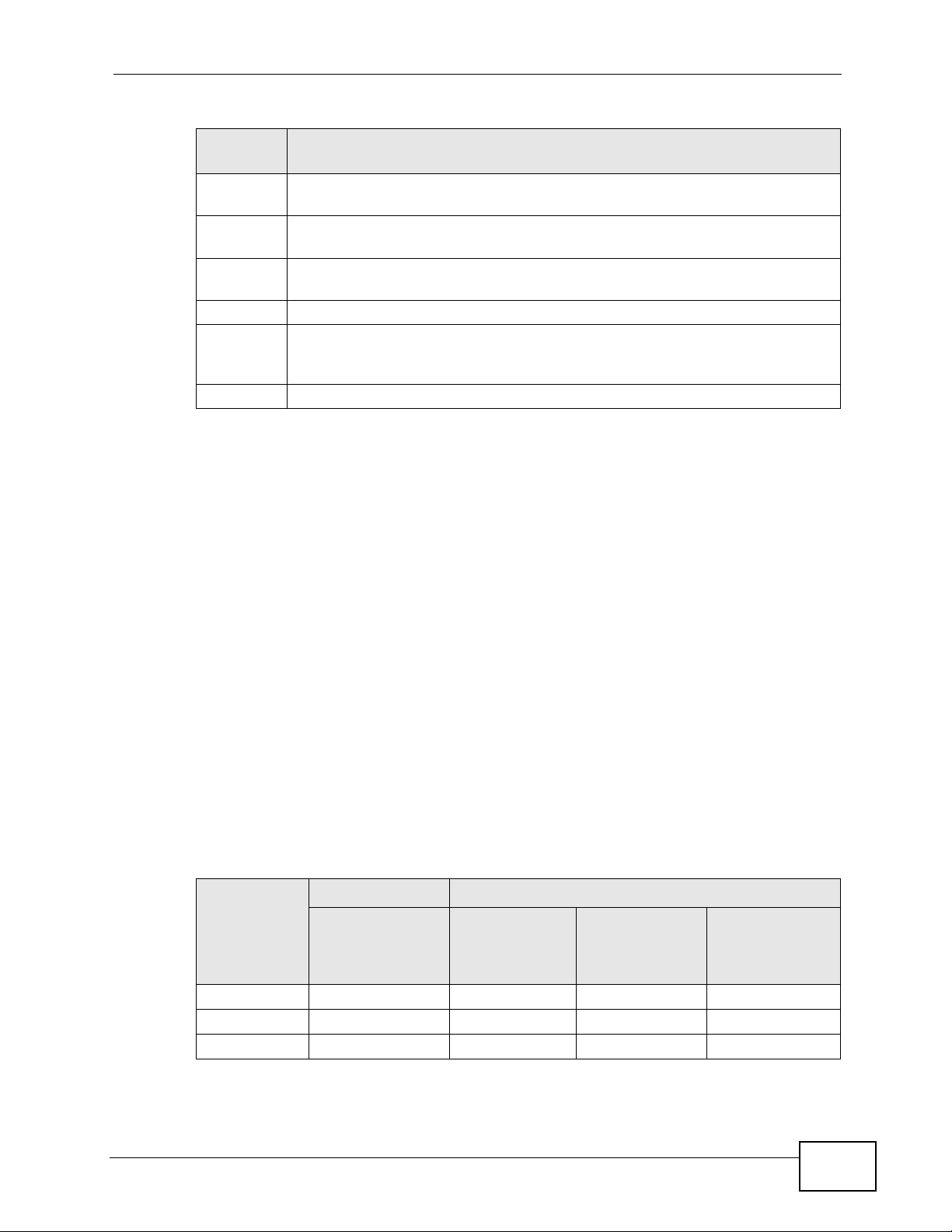
Table 60 IEEE 802.1p Priority Level and Traffic Type
PRIORITY
LEVEL
Level 5 Typically used for video that consumes high bandwidth and is sensitive to
Level 4 Typically used for controlled load, latency-sensitive traffic such as SNA
Level 3 Typically used for “excellent effort” or better than best effort and would
Level 2 This is for “spare bandwidth”.
Level 1 This is typically used for non-critical “background” traffic such as bulk
Level 0 Typically used for best-effort traffic.
TRAFFIC TYPE
jitter.
(Systems Network Architecture) transactions.
include important business traffic that can tolerate some delay.
transfers that are allowed but that should not affect other applications and
users.
14.3.2 IP Precedence
Similar to IEEE 802.1p prioritization at layer-2, you can use IP precedence to
prioritize packets in a layer-3 network. IP precedence uses three bits of the eightbit ToS (Type of Service) field in the IP header. There are eight classes of services
(ranging from zero to seven) in IP precedence. Zero is the lowes t priority level and
seven is the highest.
Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
14.3.3 Automatic Priority Queue Assignment
If you enable QoS on the ZyXEL Device, the ZyXEL Device can automatically base
on the IEEE 802.1p priority level, IP precedence and/or packet length to assign
priority to traffic which does not match a class.
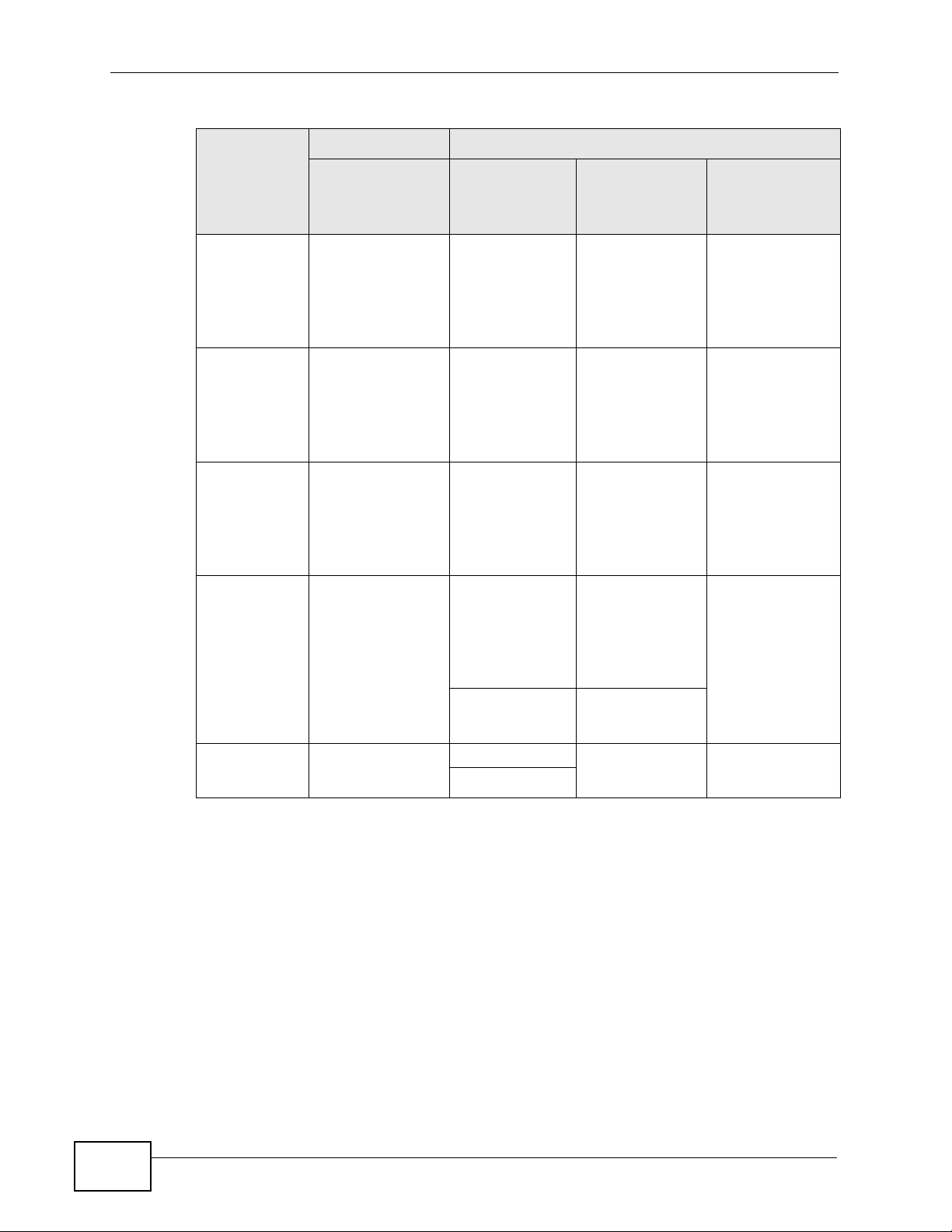
The following table shows you the internal layer-2 and layer-3 QoS mapping on
the ZyXEL Device. On the ZyXEL Device, traffic assigned to higher priority queues
gets through faster while traffic in lower index queues is dropped if the network is
congested.
Table 61 Internal Layer2 and Layer3 QoS Mapping
LAYER 2 LAYER 3
PRIORITY
QUEUE
0 1 0 000000
12
2 0 0 000000 >1100
IEEE 802.1P
USER PRIORITY
(ETHERNET
PRIORITY)
TOS (IP
PRECEDENCE)
DSCP
IP PACKET
LENGTH (BYTE)
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
177
Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
Table 61 Internal Layer2 and Layer3 QoS Mapping
LAYER 2 LAYER 3
PRIORITY
QUEUE
IEEE 802.1P
USER PRIORITY
(ETHERNET
TOS (IP
PRECEDENCE)
DSCP
PRIORITY)
3 3 1 001110
001100
001010
001000
4 4 2 010110
010100
010010
010000
5 5 3 011110
011100
011010
011000
6 6 4 100110
100100
IP PACKET
LENGTH (BYTE)
250~1100
<250
100010
100000
5 101110
101000
7 7 6 110000
7
111000
178
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide

CHAPTER 15
Dynamic DNS Setup
15.1 Overview
Dynamic DNS allows you to update your current dynamic IP address with one or
many dynamic DNS services so that anyone can contact you (in NetMeeting, CUSeeMe, etc.). You can also access your FTP server or Web site on your own
computer using a domain name (for instance myhost.dhs.org, where myhost is a
name of your choice) that will never change instead of using an IP address that
changes each time you reconnect. Your friends or relatives will always be able to
call you even if they don't know your IP address.
First of all, you need to have registered a dynamic DNS account with
www.dyndns.org. This is for people with a dynamic IP from their ISP or DHCP
server that would still like to have a domain name. The Dynamic DNS service
provider will give you a password or key.
15.1.1 What You Can Do in the DDNS Screen
Use the Dynamic DNS screen (Section 15.2 on page 180) to enable DDNS and
configure the DDNS settings on th e ZyXEL Device.
15.1.2 What You Need To Know About DDNS
DYNDNS Wildcard
Enabling the wildcard feature for your host causes *.yourhost.dyndns.org to be
aliased to the same IP address as yourhost.dyndns.org. This feature is useful if
you want to be able to use, for example, www.yourhost.dyndns. org and still reach
your hostname.
If you have a pri va t e WAN I P address, then you cannot use Dyn amic DNS.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
179
Chapter 15 Dynamic DNS Setup
15.2 The Dynamic DNS Screen
Use this screen to change your ZyXEL Device’s DDNS. Click Advanced >
Dynamic DNS. The screen appears as shown.
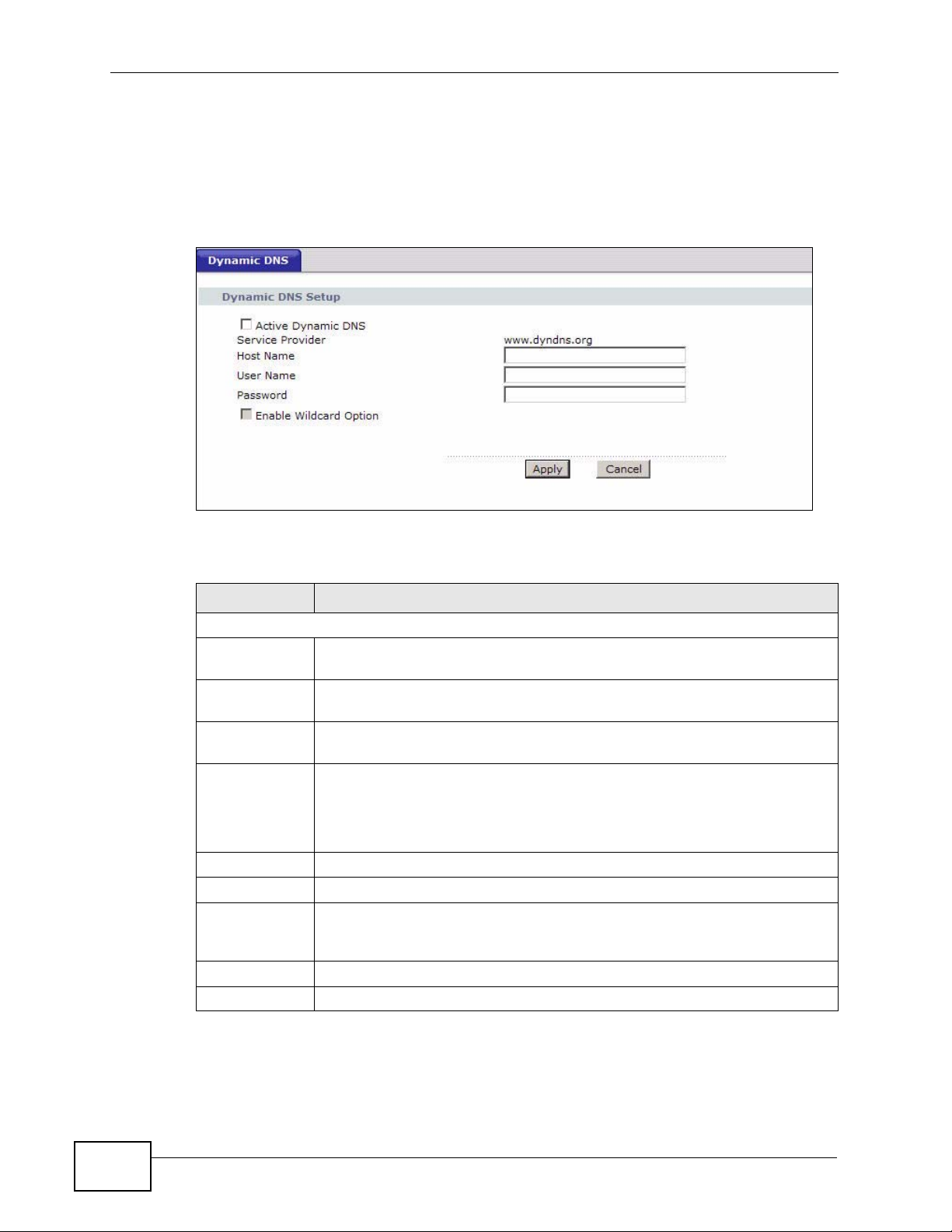
Figure 87 Advanced > Dynamic DNS
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 62 Advanced > Dynamic DNS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Dynamic DNS Setup
Active
Dynamic DNS
Service
Provider
Dynamic DNS
Type
Host Name Type the domain name assigned to your ZyXEL Device by yo ur Dynamic
User Name Type your user name.
Password Type the password assigned to you.
Enable
Wildcard
Option
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Select this check box to use dynamic DNS.
This is the name of your Dynamic DNS service provider.
Select the type of service that you are registered for from your Dynamic
DNS service provider.
DNS provider.
You can specify up to two host names in the field separ ated by a comma
(",").
Select the check box to enable DynDNS Wildcard.
180
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
CHAPTER 16
LAN
WAN
HTTP
Telnet
Remote Management
16.1 Overview
Remote management allows you to determine which services/ protocols can access
which ZyXEL Device interface (if any) from which computers.
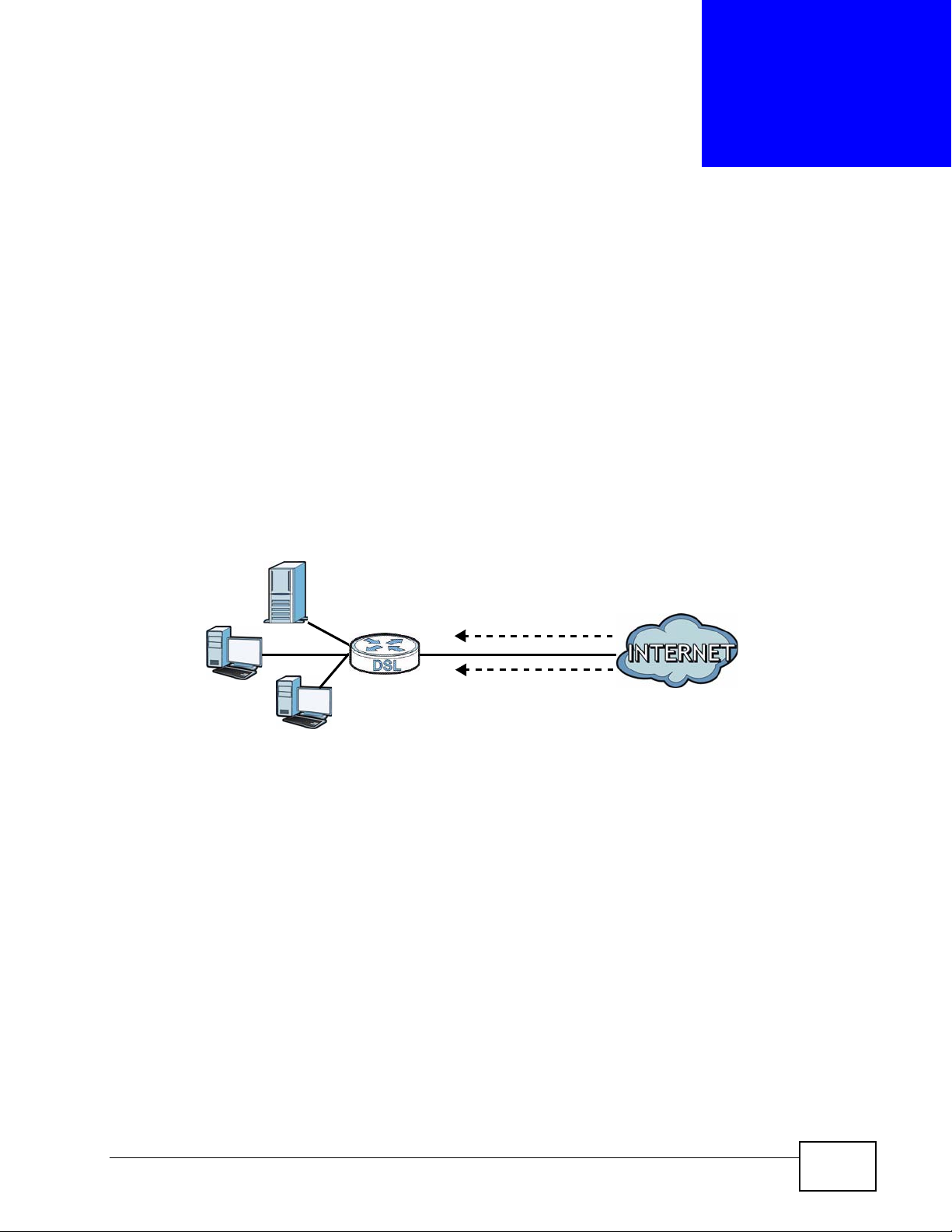
The following figure shows remote management of the ZyXEL Device coming in
from the WAN.
Figure 88 Remote Management From the WAN
Note: When you configure remote management to allow management from the WAN,
you still need to configure a firewall rule to allow access.
You may manage your ZyXEL Device from a remote location via:
•Internet (WAN only)
•LAN only
•LAN and WAN
• None (Disable)
To disable remote management of a service, select Disable in the corresponding
Service Access field.
You ma y only have one remote management session running at a time. The ZyXEL
Device automatically disconnects a remote management session of lower priority
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
181

Chapter 16 Remote Management
when another remote management session of higher priority starts. The priorities
for the different types of remote management sessions are as follows.
1 Telnet
2 HTTP
16.1.1 What You Can Do in the Remote Management Screens
•Use the WWW screen (Section 16.2 on page 183) to configure through which
interface(s) and from which IP address(es) users can use HTTP to manage the
ZyXEL Device.
•Use the Telnet screen (Section 16.3 on page 184) to configure through which
interface(s) and from which IP address(es) users can use Telnet to manage the
ZyXEL Device.
•Use the FTP screen (Section 16.4 on page 185) to configure through which
interface(s) and from which IP address(es) users can use FTP to access the
ZyXEL Device.
• Your ZyXEL Device can act as an SNMP agent, which allows a manager station to
manage and monitor the ZyXEL Device through the network. Use the SNMP
screen (see Section 16.5 on page 186) to configure through which interface(s)
and from which IP address(es) users can use SNMP to access the ZyXEL Device.
•Use the DNS screen (Section 16.6 on page 188) to configure through which
interface(s) and from which IP address(es) users can send DNS queries to the
ZyXEL Device.
•Use the ICMP screen (Section 16.7 on page 189) to set whether or not your
ZyXEL Device will respond to pings and probes for services that you have not
made available.
16.1.2 What You Need to Know About Remote Management
Remote Management Limitations
Remote management does not work when:
• You have not enabled that service on the interface in the corresponding remote
management screen.
• You have disabled that service in one of the remote management screens.
• The IP address in the Secured Client IP Address field does not match the
client IP address. If it does not match, the ZyXEL Device will disconnect the
session immediately.
182
• There is already another remote management session with an equal or higher
priority running. You may only have one remote management session running
at one time.
• There is a firewall rule that blocks it.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
Remote Management and NAT
When NAT is enabled:
• Use the ZyXEL Device’s WAN IP address when configuring from the WAN.
• Use the ZyXEL Device’s LAN IP address when configuring from the LAN.
System Timeout
There is a default system management idle timeout of five minutes (three
hundred seconds). The ZyXEL Device automatically logs you out if the
management session remains idle for longer than this timeout period. The
management session does not time out when a statistics screen is polling.
16.2 The WWW Screen
Use this screen to specify how to connect to the ZyXEL Device from a web
browser, such as Internet Explorer.
Chapter 16 Remote Management
Note: If you disable the WWW service in the Remote MGMT > WWW screen, then
the ZyXEL Device blocks all HTTP connection attempts.
16.2.1 Configuring the WWW Screen
Click Advanced > Remote MGMT to display the WWW screen.
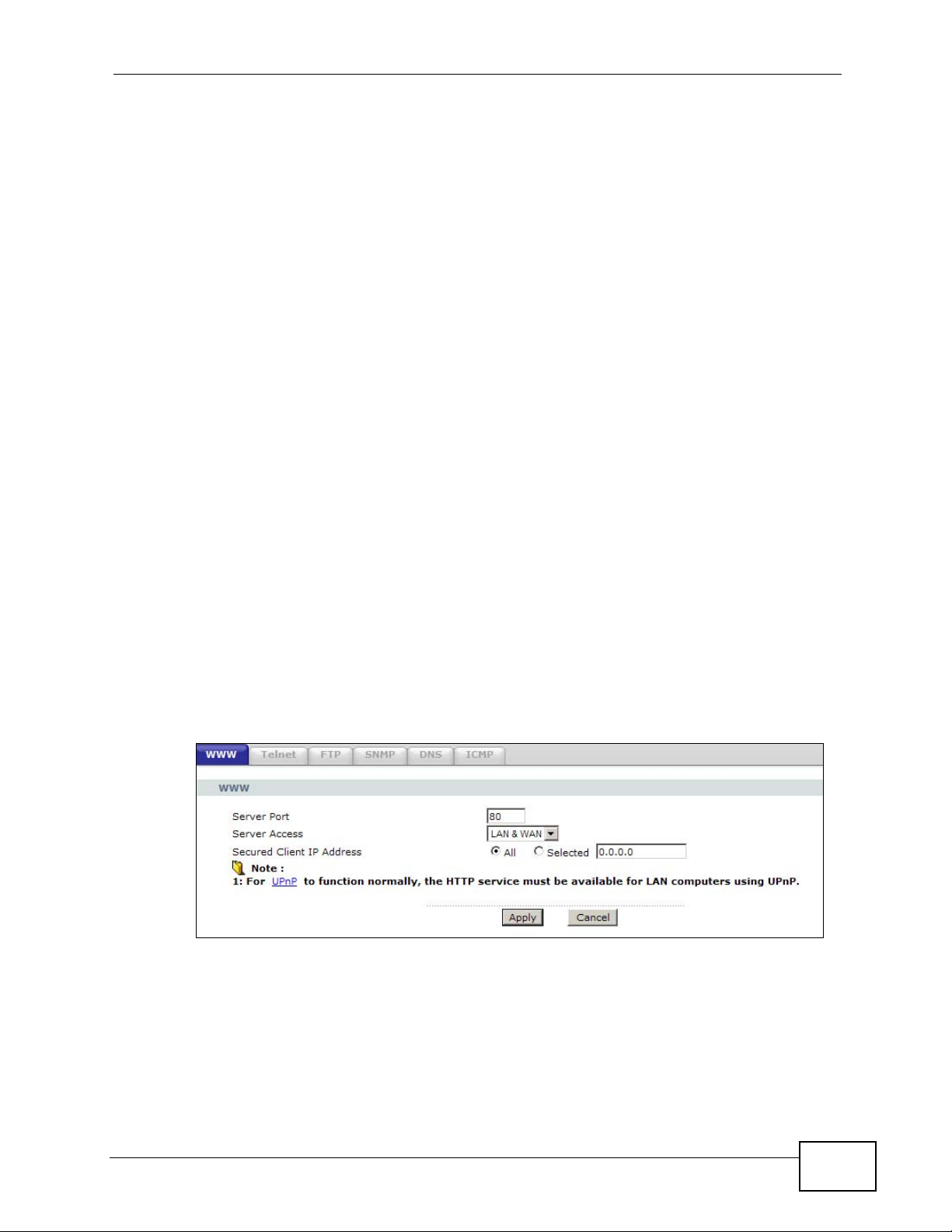
Figure 89 Advanced > Remote MGMT > WWW
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
183

Chapter 16 Remote Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 63 Advanced > Remote Management > WWW
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port You may change the server port number for a service, if needed.
However, you must use the same port number in order to use that
service for remote management.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the ZyXEL
Device using this service.
Secured Client
IP Address
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate
with the ZyXEL Device using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the ZyXEL Device using this
service.
Choose Selected to just allow the computer with the IP address that
you specify to access the ZyXEL Device using this service.
16.3 The Telnet Screen
You can use Telnet to access the ZyXEL Device’s command line interface. Specify
which interfaces allow Telnet access and from which IP address the access can
come.
Click Advanced > Remote MGMT > Telnet tab to display the screen as shown.
Figure 90 Advanced > Remote MGMT > Telnet
184
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
Chapter 16 Remote Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 64 Advanced > Remote Management > Telnet
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port You may change the server po rt number for a service if needed, however
you must use the same port number in order to use that service for
remote management.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the ZyXEL
Device using this service.
Secured Client
IP Address
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate
with the ZyXEL Device using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the ZyXEL Device using this
service.
Choose Selected to just allow the computer with the IP address that you
specify to access the ZyXEL Device using this service.
16.4 The FTP Screen
You can use FTP (File Transfer Protocol) to upload and download the ZyXEL
Device’s firmware and configuration files. Please see the User ’s Guide chapter on
firmware and configuration file maintenance for details. To use this feature, your
computer must have an FTP client.
Use this screen to specify which interfaces allow FTP access and from which IP
address the access can come. To change your ZyXEL Device’s FTP settings, click
Advanced > Remote MGMT > FTP. The screen appears as shown.
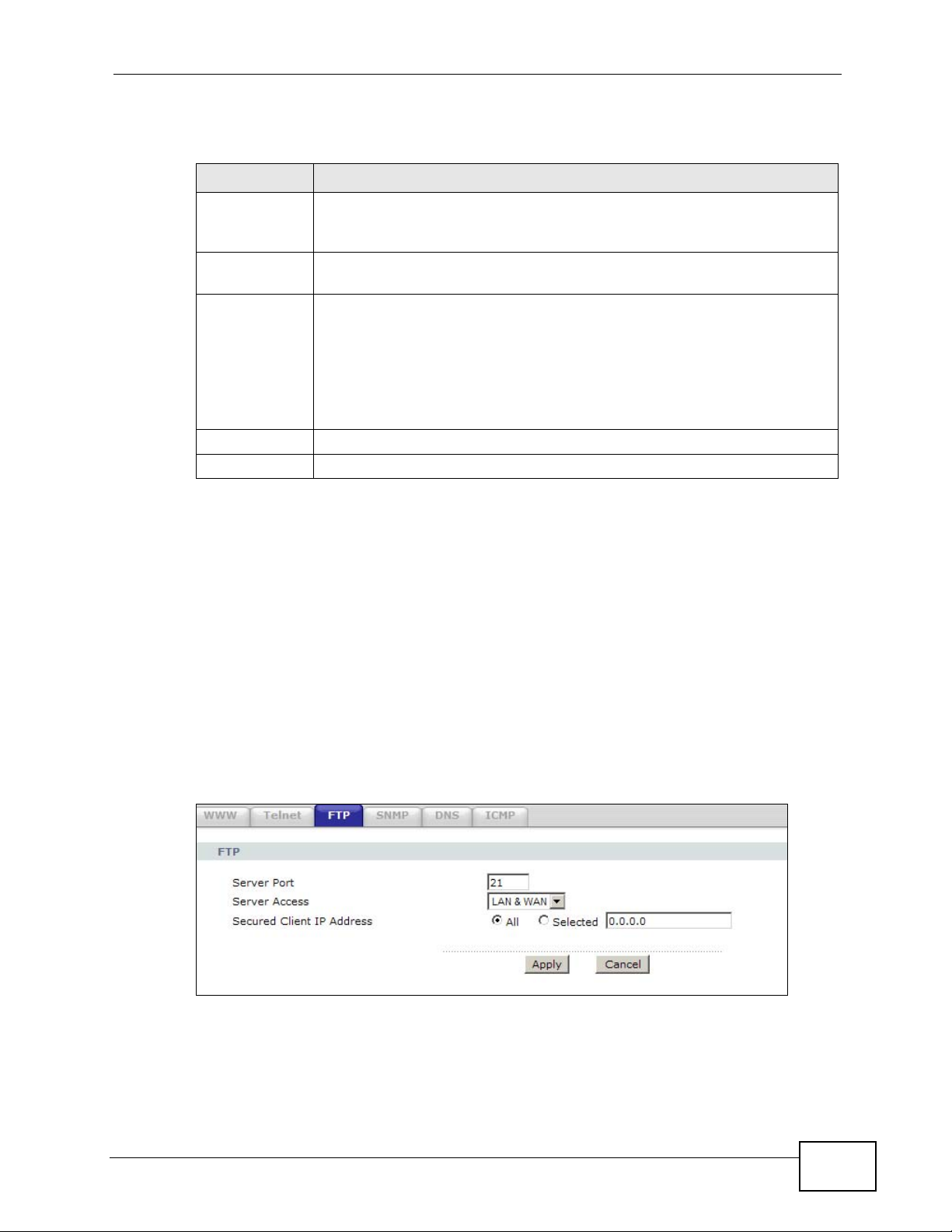
Figure 91 Advanced > Remote MGMT > FTP
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
185
Chapter 16 Remote Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 65 Advanced > Remote MGMT > FTP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port You may change the server port number for a service, if needed.
However, you must use the same port number in order to use that
service for remote management.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the ZyXEL
Device using this service.
Secured Client
IP Address
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate
with the ZyXEL Device using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the ZyXEL Device using this
service.
Choose Selected to just allow the computer with the IP address that
you specify to access the ZyXEL Device using this service.
16.5 The SNMP Screen
Simple Network Management Protocol is a protocol used for exchanging
management information between network devices. Your ZyXEL Device supports
SNMP agent functionality, which allows a manager station to manage and monitor
the ZyXEL Device through the network. The ZyXEL Device supports SNMP version
one (SNMPv1) and version two (SNMPv2c). The next figure illustrates an SNMP
management operation.
Figure 92 SNMP Management Model
186
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
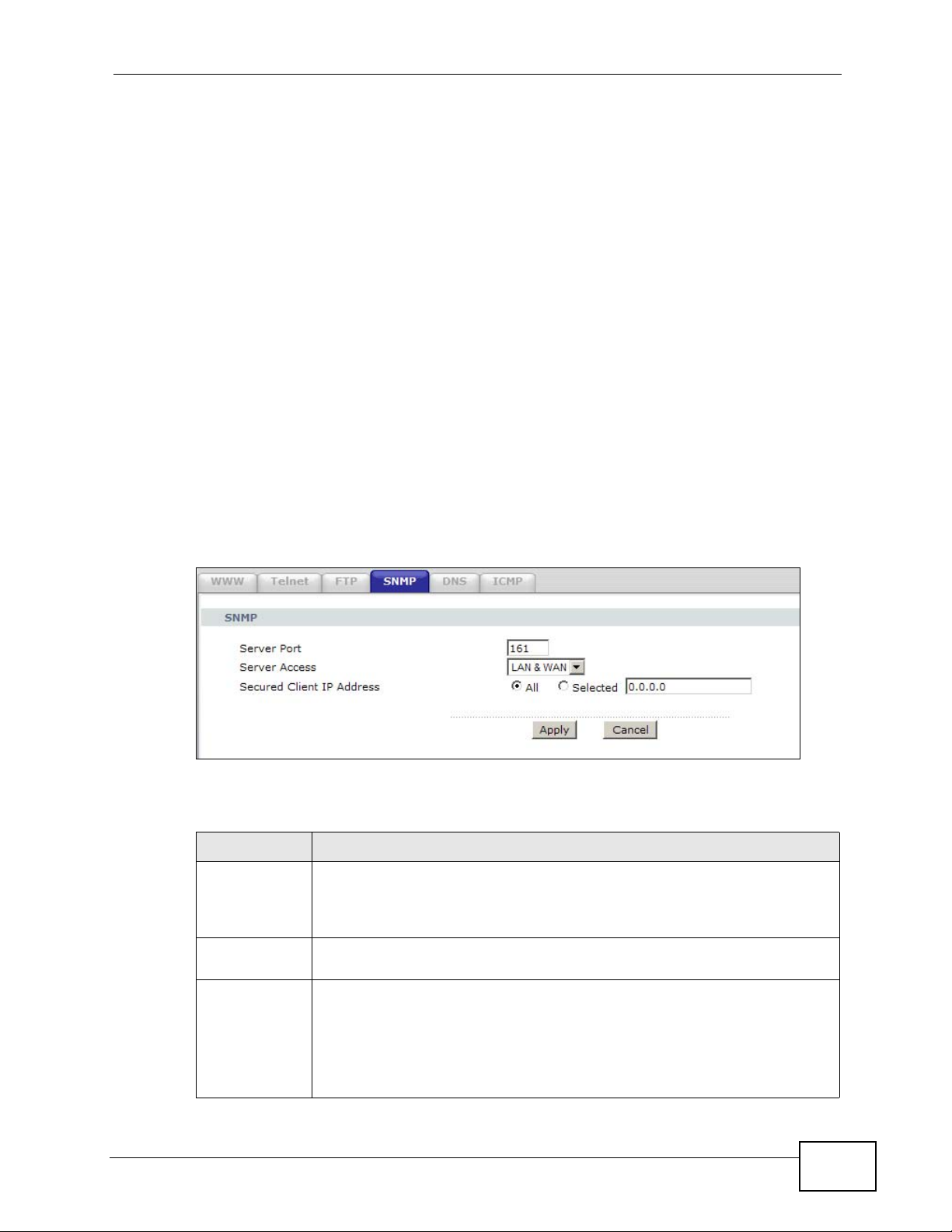
An SNMP managed network consists of two main types of component: agents and
a manager.
An agent is a management software module that resides in a managed device (the
ZyXEL Device). An agent translates the local management information from the
managed device into a form compatible with SNMP. The manager is the console
through which network administrators perform network management functions. It
executes applications that control and monitor managed devices.
The managed devices contain object variables/managed objects that define each
piece of information to be collected about a device. Examples of variables include
such as number of packets received, node port status etc. A Management
Information Base (MIB) is a collection of managed objects. SNMP allows a
manager and agents to communicate for the purpose of accessing these objects.
16.5.1 Configuring SNMP
To change your ZyXEL Device’s SNMP settings, click Advanced > Remote MGMT
> SNMP tab. The screen appears as shown.
Chapter 16 Remote Management
Figure 93 Advanced > Remote MGMT > SNMP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 66 Advanced > Remote MGMT > SNMP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port The SNMP agent listens on port 161 by default. If you change the SNMP
server port to a different number on the ZyXEL Device, for example
8161, then you must notify people who need to access the ZyXEL Device
SNMP agent to use the same port.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the ZyXEL
Device using this service.
Secured Client
IP Address
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to access the
SNMP agent on the ZyXEL Device.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
Select All to allow any computer to access the SNMP agent.
Choose Selected to just allow the computer with the IP address that you
specify to access the SNMP agent.
187
Chapter 16 Remote Management
Table 66 Advanced > Remote MGMT > SNMP (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
16.6 The DNS Screen
Use DNS (Domain Name System) to map a domain name to its corresponding IP
address and vice versa. Refer to Chapter 7 on page 89 for background
information.
Use this screen to set from which IP address the ZyXEL Device will accept DNS
queries and on which interface it can send them your ZyXEL Device’s DNS
settings. This feature is not available when the ZyXEL Device is set to bridge
mode. Click Advanced > Remote MGMT > DNS to change your ZyXEL Device’s
DNS settings.
Figure 94 Advanced > Remote Management > DNS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 67 Advanced > Remote Management > DNS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port The DNS service port number is 53 and cannot be changed here.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may send DNS queries
to the ZyXEL Device.
Secured Client
IP Address
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to send DNS
queries to the ZyXEL Device.
Select All to allow any computer to send DNS queries to the ZyXEL
Device.
188
Choose Selected to just allow the computer with the IP address that
you specify to send DNS queries to the ZyXEL Device.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
16.7 The ICMP Screen
To change your ZyXEL Device’ s security settings, click Advanced > Remote
MGMT > ICMP. The screen appears as shown.
If an outside user attempts to probe an unsupported port on your ZyXEL Device,
an ICMP response packet is automatically returned. T his allows the outside user to
know the ZyXEL Device exists. Your ZyXEL Device supports anti-probing, which
prevents the ICMP response packet from being sent. This keeps outsiders from
discovering your ZyXEL Device when unsupported ports are probed.
Note: If you want your device to respond to pings and requests for unauthorized
services, you may also need to configure the firewall anti probing settings to
match.
Figure 95 Advanced > Remote Management > ICMP
Chapter 16 Remote Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 68 Advanced > Remote Management > ICMP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol is a message control and error-
reporting protocol between a host server and a gateway to the Internet.
ICMP uses Internet Protocol (IP) datagrams, but the messages are
processed by the TCP/IP software and directly apparent to the
application user.
Respond to
Ping on
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
The ZyXEL Device will not respond to any incoming Ping requests when
Disable is selected. Select LAN to reply to incoming LAN Ping requests.
Select WAN to reply to incoming WAN Ping requests. Otherwise select
LAN & WAN to reply to both incoming LAN and WAN Ping requests.
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
189

Chapter 16 Remote Management
190
P-660HN-TxA User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...