ZyXEL P3202HNBA Installation guide
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
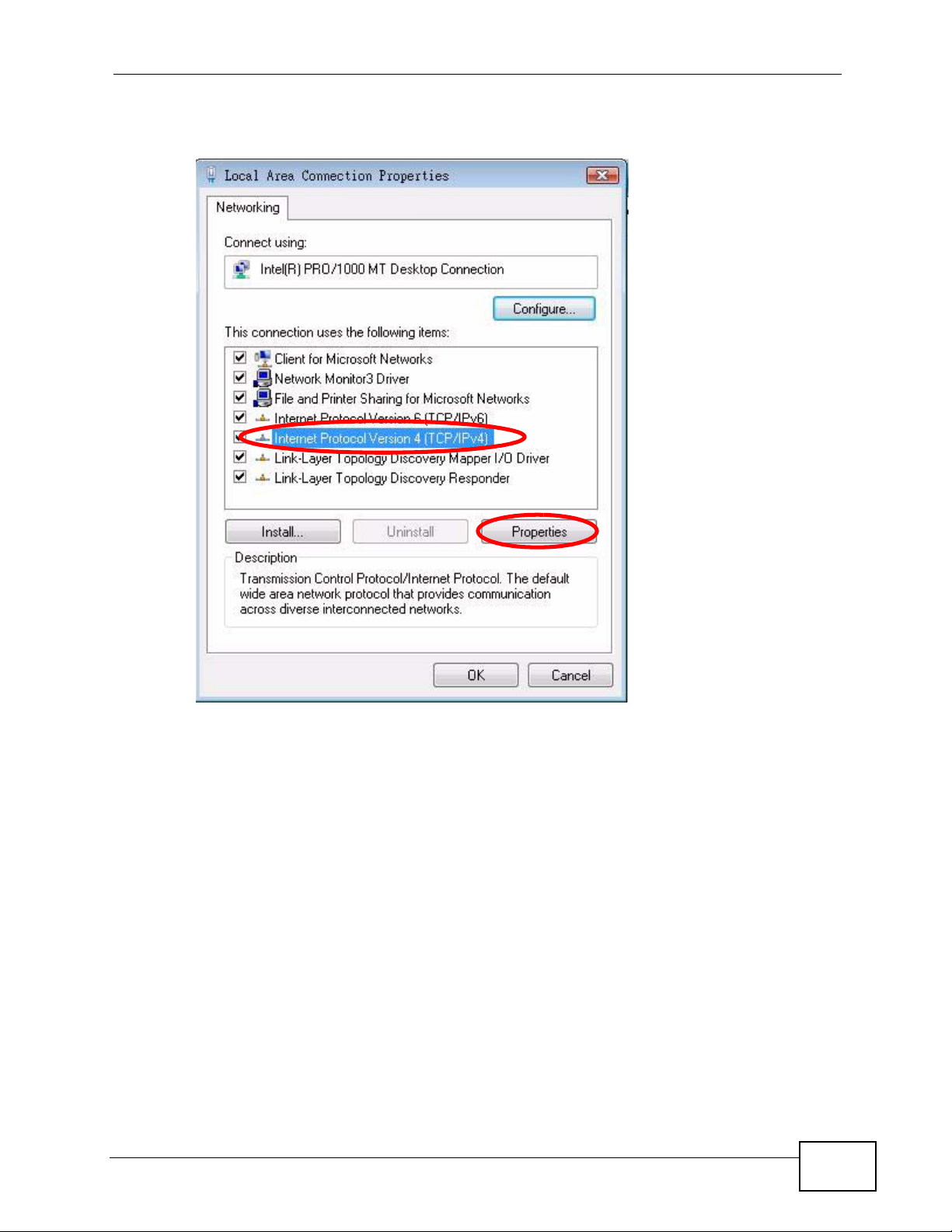
6 Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then select Properties.
Figure 131 Windows Vista: Local Area Connection Properties
IAD User’s Guide
251
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
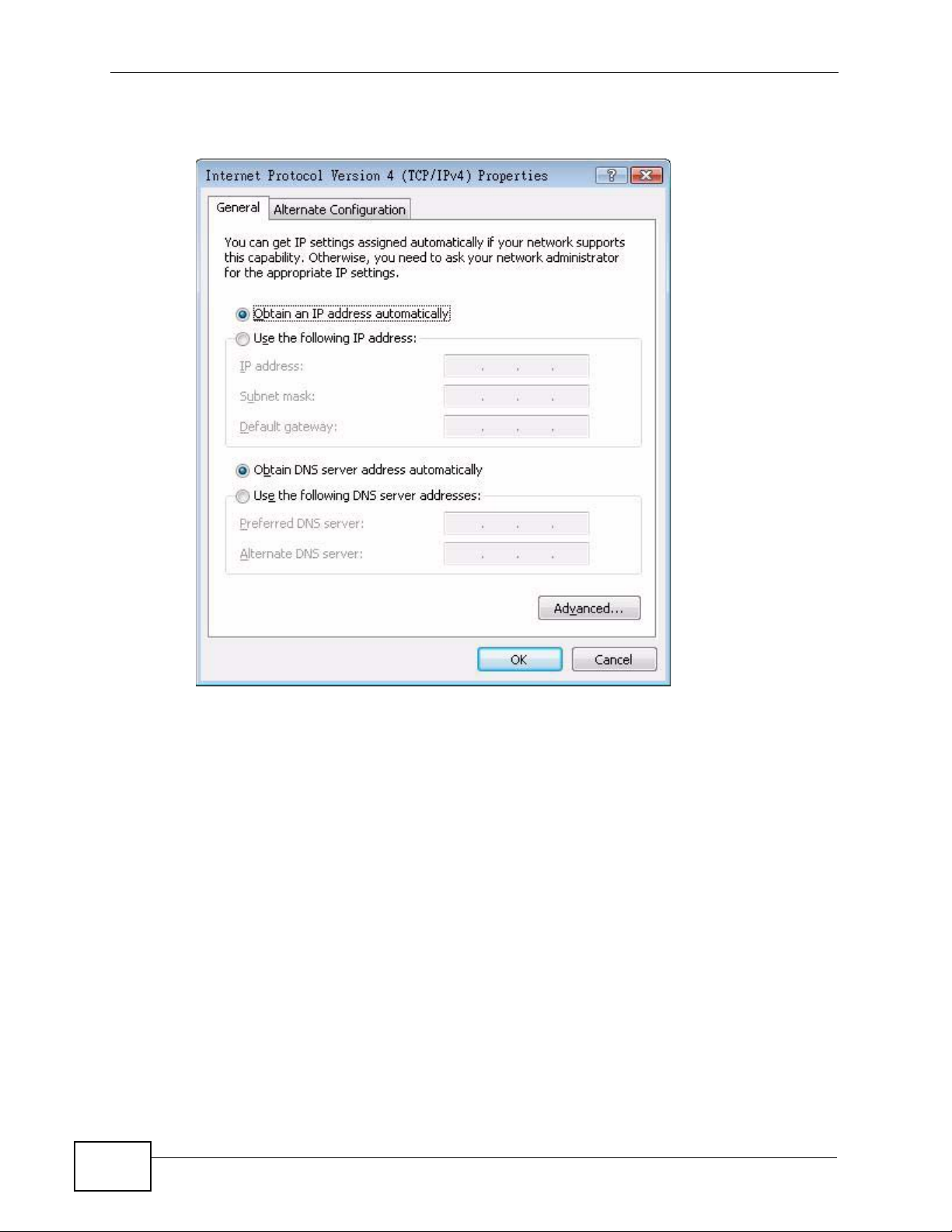
7 The Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window opens.
Figure 132 Windows Vista: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
8 Select Obtain an IP addr ess automatically if your network administr ator or ISP
assigns your IP address dynamically.
Select Use the following IP Address and fill in the IP address, Subnet mask,
and Default gateway fields if you have a static IP address that was assigned to
you by your network administrator or ISP. You may also ha ve to enter a Preferred
DNS server and an Alternate DNS server, if that information was
provided.Click Advanced.
9 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
10 Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
252
IAD User’s Guide
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER].
You can also go to Start > Control Panel > Network Connections, right-click a
network connection, click Status and then click the Support tab to view your IP
address and connection information.
Windows 7
This section shows screens from Windows 7 Enterprise.
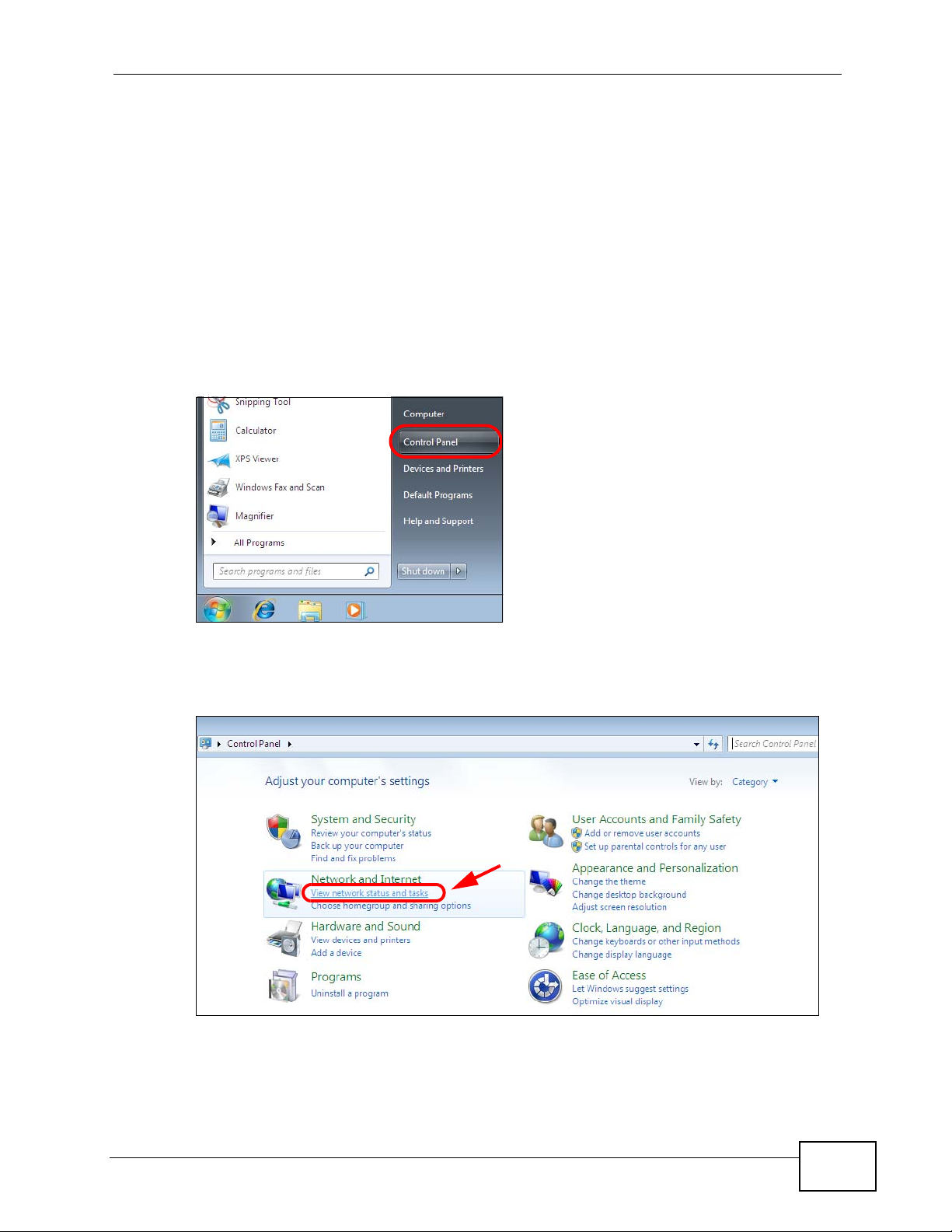
1 Click Start > Control Panel.
Figure 133 Windows 7: Start Menu
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
2 In the Control Panel, click View network status and tasks under the
Network and Internet category.
Figure 134 Windows 7: Control Panel
IAD User’s Guide
253
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
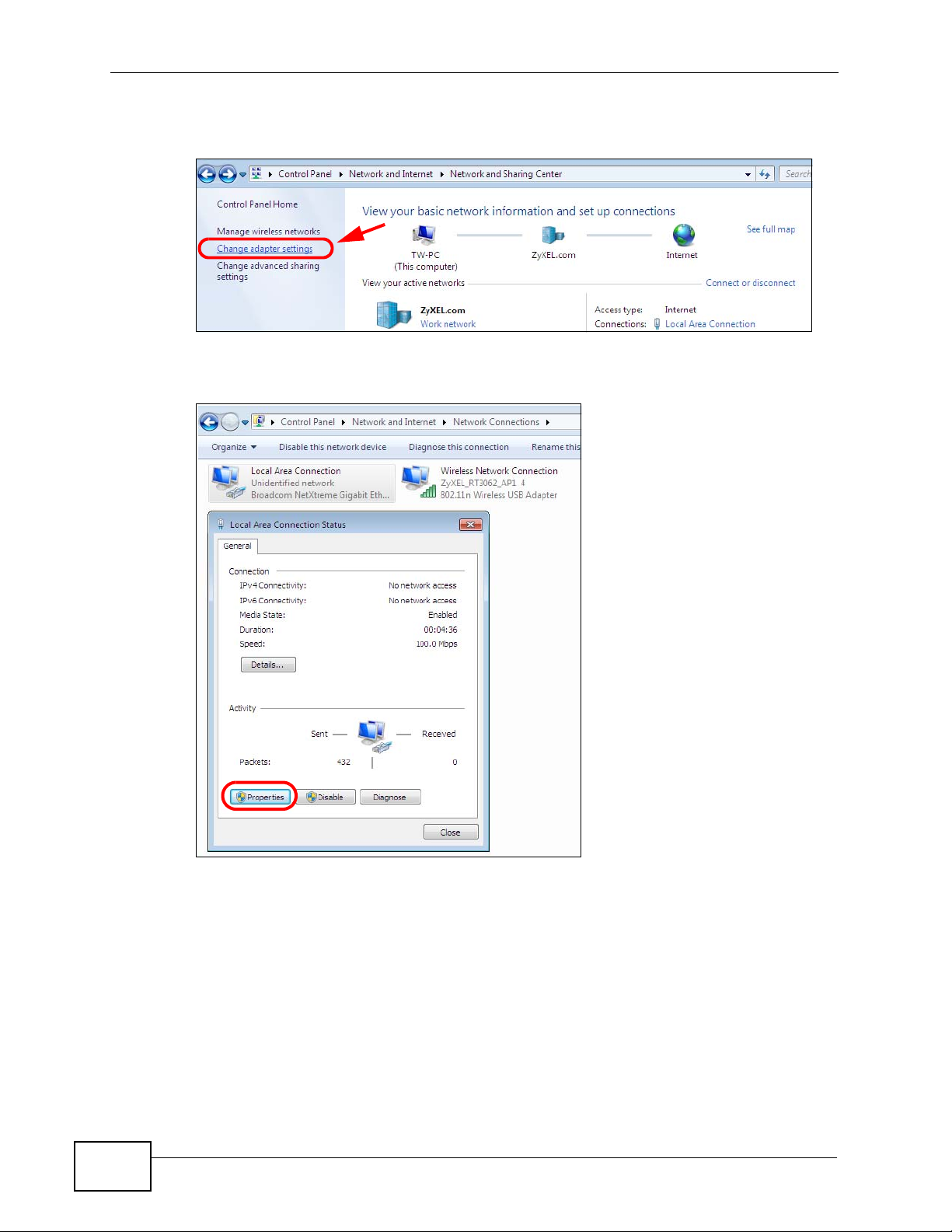
3 Click Change adapter settings.
Figure 135 Windows 7: Network And Sharing Center
4 Double click Local Area Connection and then select Properties.
Figure 136 Windows 7: Local Area Connection Status
254
Note: During this procedure, click Continue whenever Windows displays a screen
saying that it needs your permission to continue.
IAD User’s Guide
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
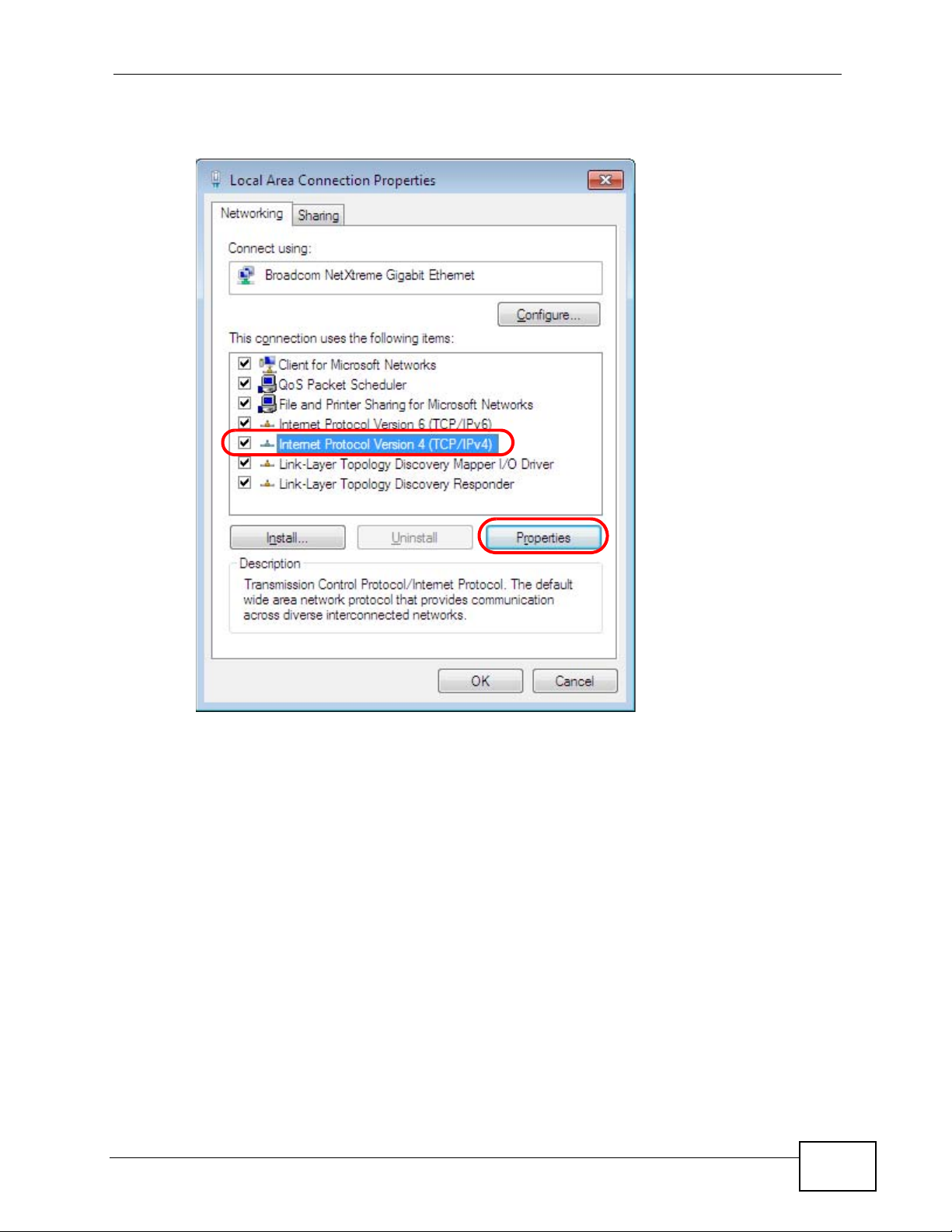
5 Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then select Properties.
Figure 137 Windows 7: Local Area Connection Properties
IAD User’s Guide
255
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
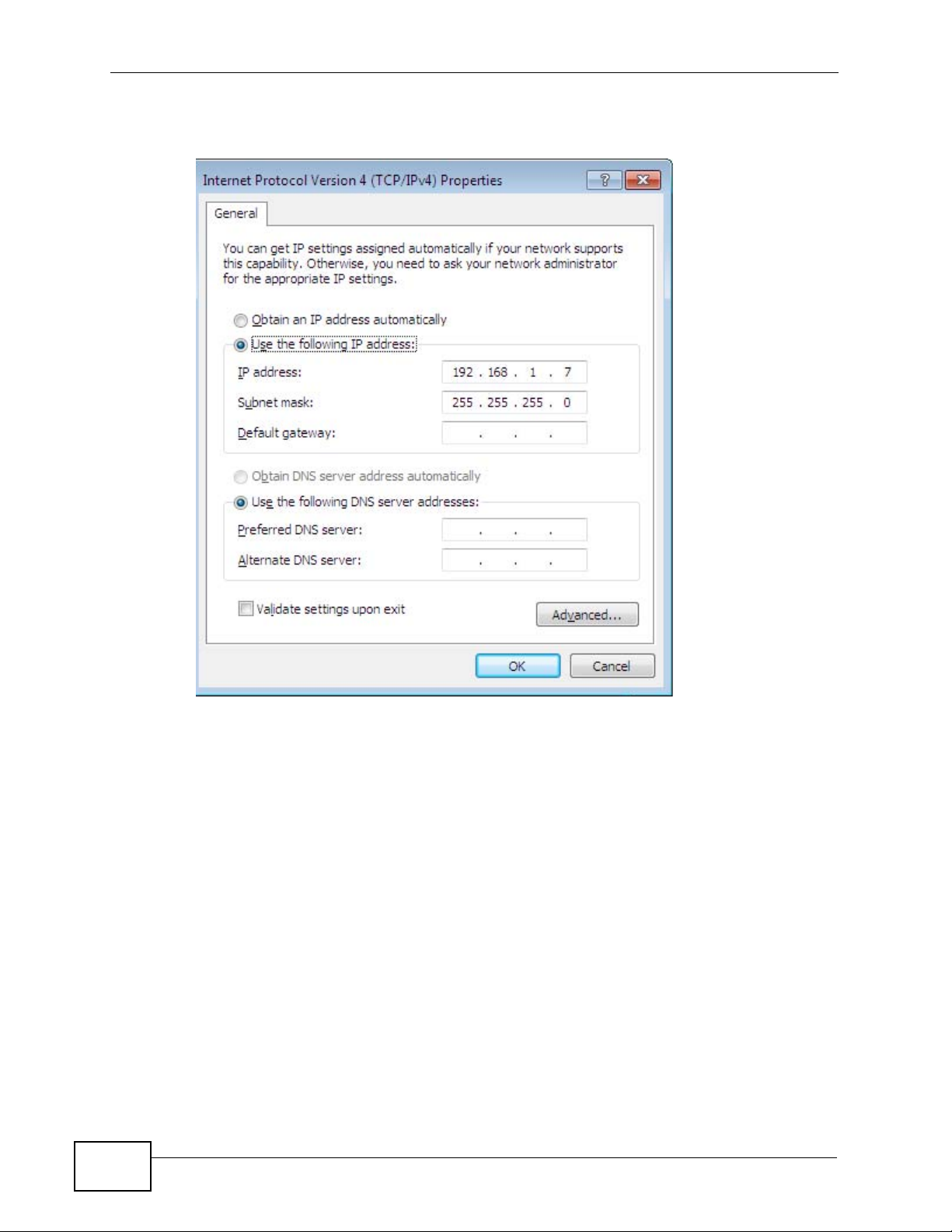
6 The Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window opens.
Figure 138 Windows 7: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
7 Select Obtain an IP addr ess automatically if your network administr ator or ISP
assigns your IP address dynamically.
Select Use the following IP Address and fill in the IP address, Subnet mask,
and Default gateway fields if you have a static IP address that was assigned to
you by your network administrator or ISP. You may also ha ve to enter a Preferred
DNS server and an Alternate DNS server, if that information was provided.
Click Advanced if you want to configure advanced settings for IP, DNS and WINS.
8 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
9 Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER].
256
IAD User’s Guide
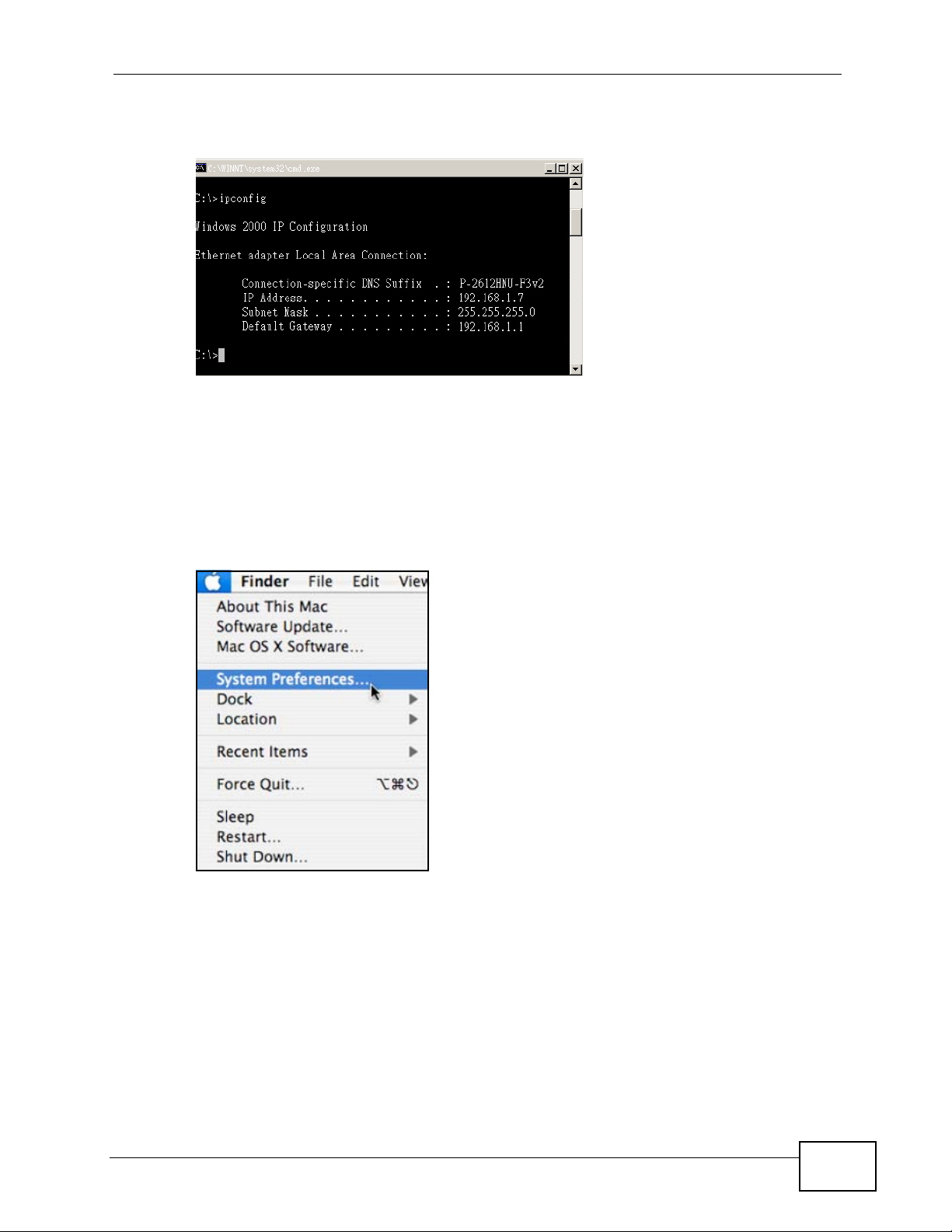
3 The IP settings are displayed as follows.
Figure 139 Windows 7: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
Mac OS X: 10.3 and 10.4
The screens in this section are from Mac OS X 10.4 but can also apply to 10.3.
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
1 Click Apple > System Preferences.
Figure 140 Mac OS X 10.4: Apple Menu
IAD User’s Guide
257
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
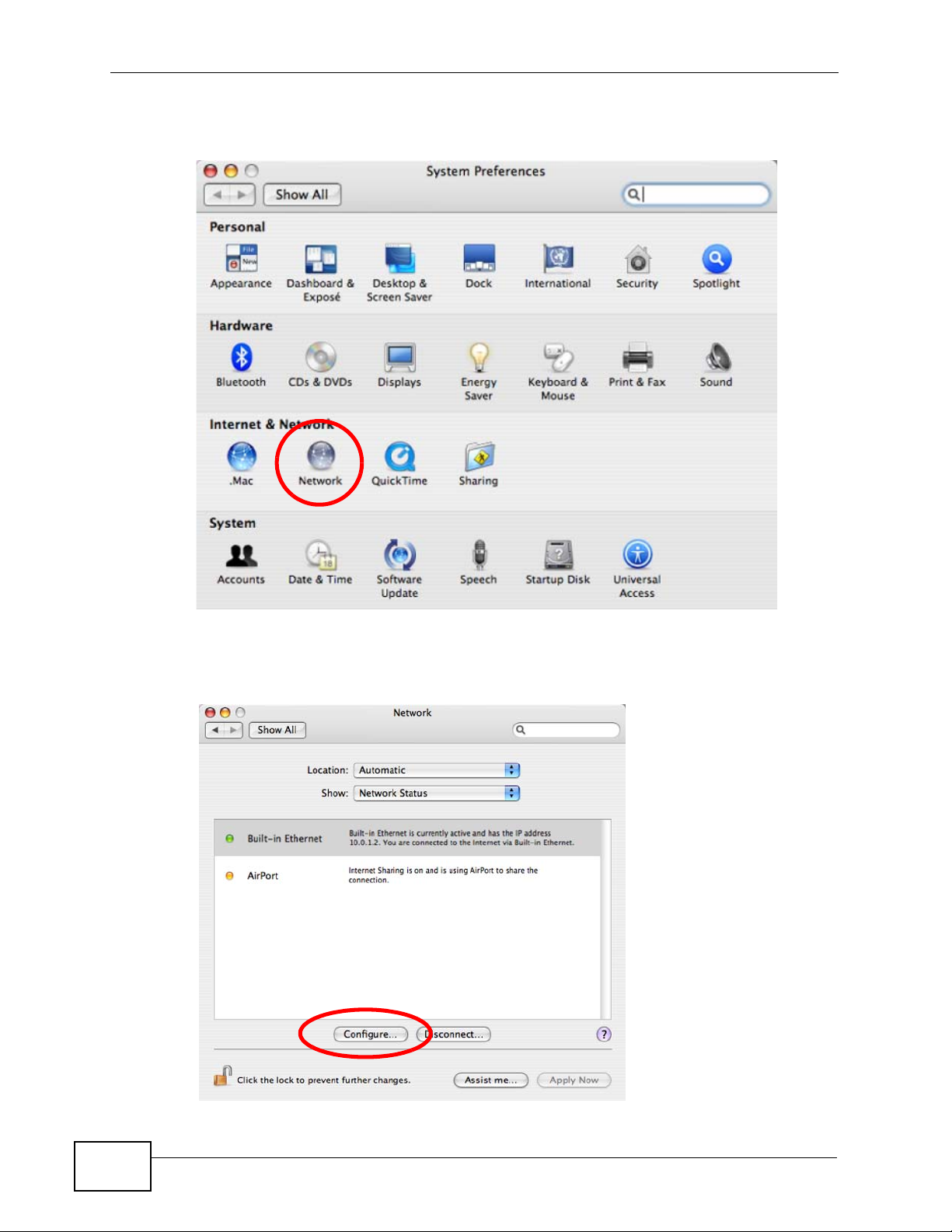
2 In the System Preferences window, click the Network icon.
Figure 141 Mac OS X 10.4: System Preferences
3 When the Network preferences pane opens, select Built-in Ethernet from the
network connection type list, and then click Configure.
Figure 142 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences
258
IAD User’s Guide
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
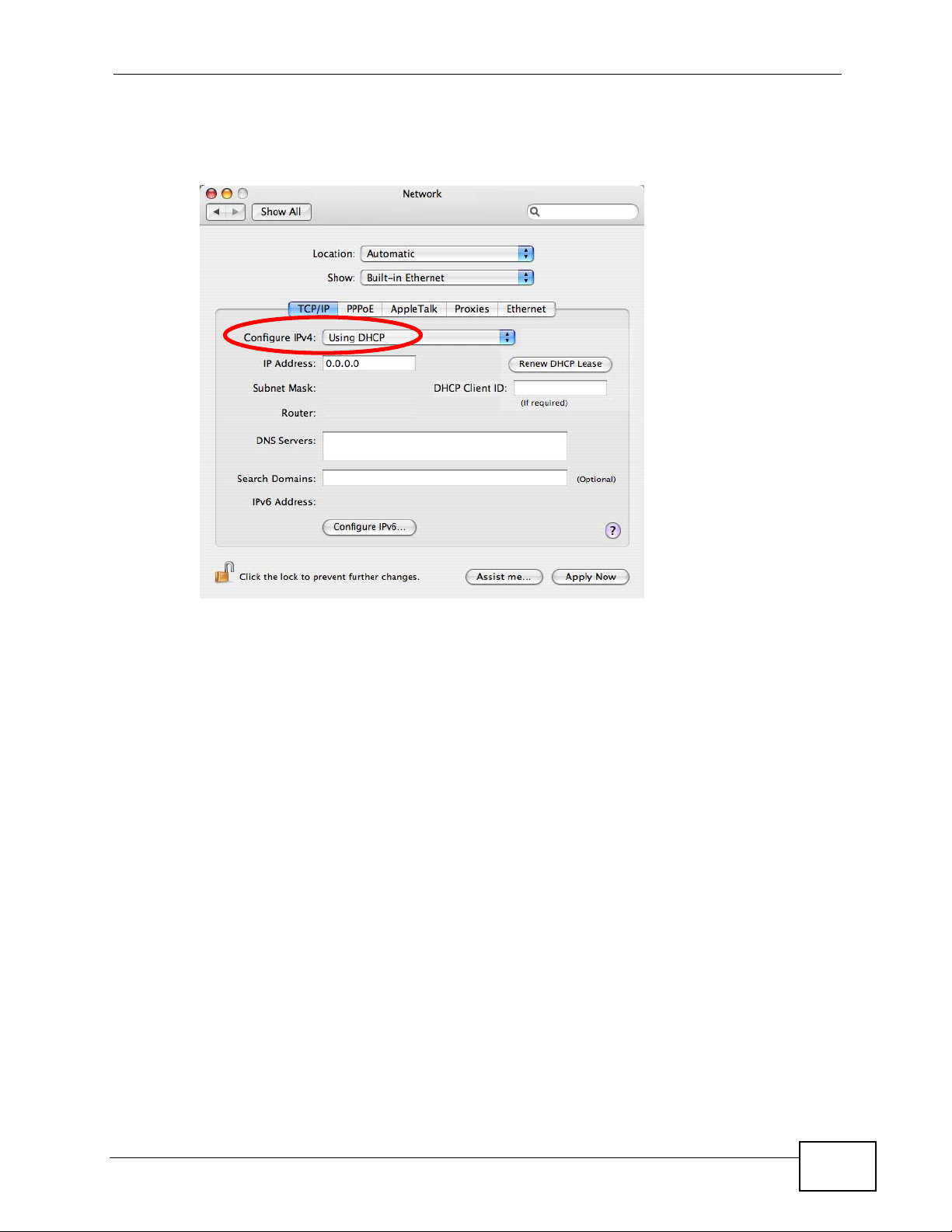
4 For dynamically assigned settings, select Using DHCP from the Configure IPv4
list in the TCP/IP tab.
Figure 143 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences > TCP/IP Tab.
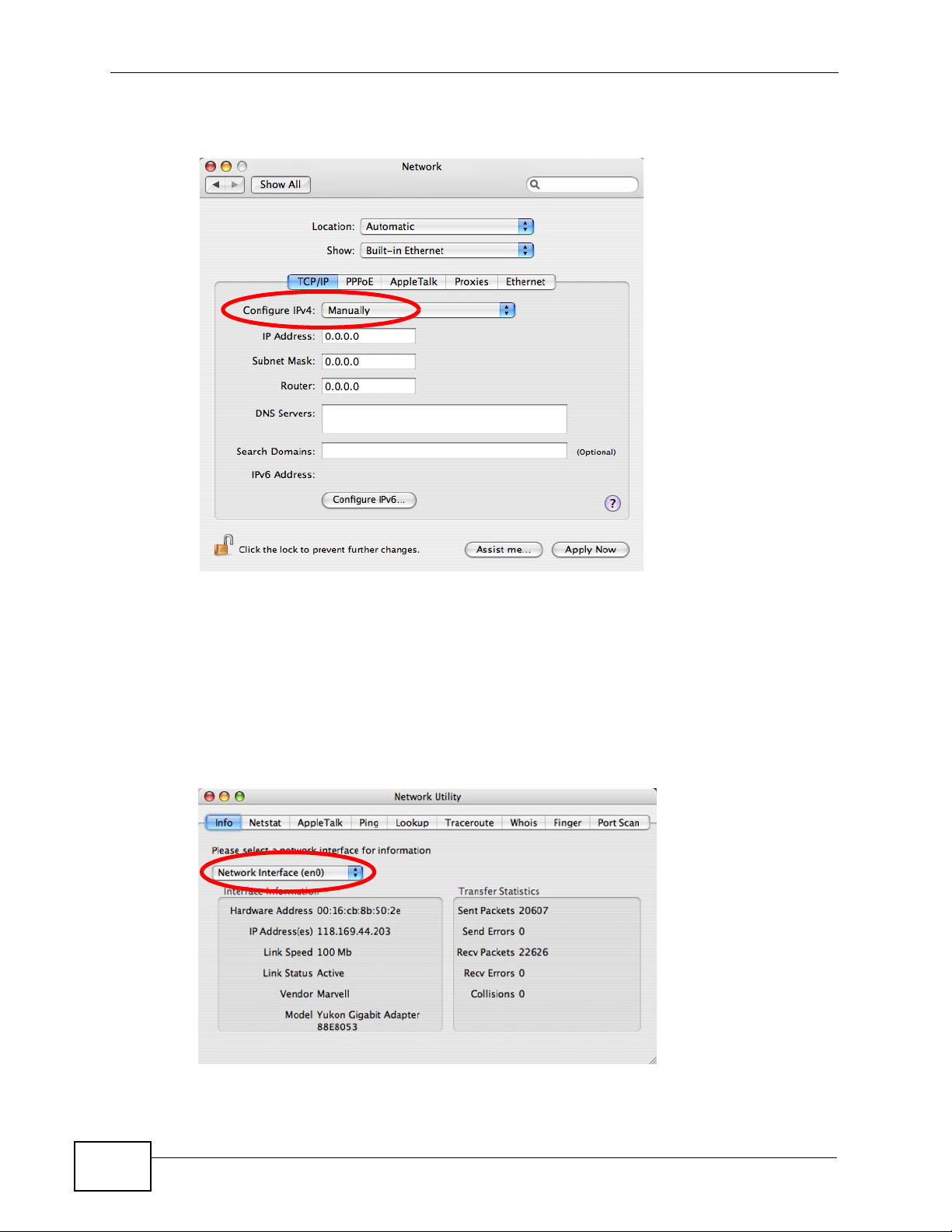
5 For statically assigned settings, do the following:
•From the Configure IPv4 list, select Manually.
•In the IP Address field, type your IP address.
•In the Subnet Mask field, type your subnet mask.
IAD User’s Guide
259
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
•In the Router field, type the IP address of your device.
Figure 144 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences > Ethernet
6 Click Apply Now and close the window.
Verifying Settings
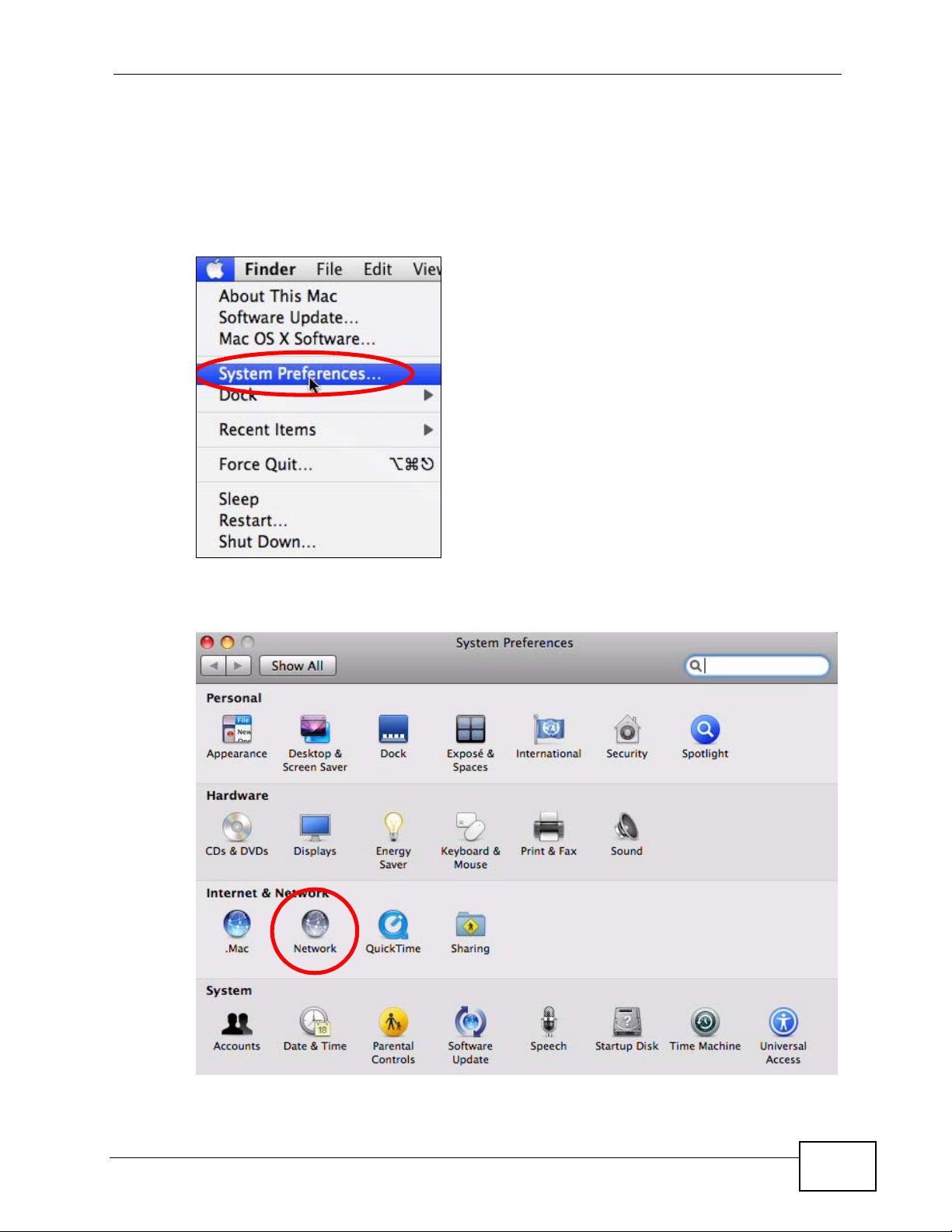
Check your TCP/IP properties by clicking Applications > Utilities > Network
Utilities, and then selecting the appropriate Network Interface from the Info
tab.
Figure 145 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Utility
260
IAD User’s Guide
Mac OS X: 10.5 and 10.6
The screens in this section are from Mac OS X 10.5 but can also apply to 10.6.
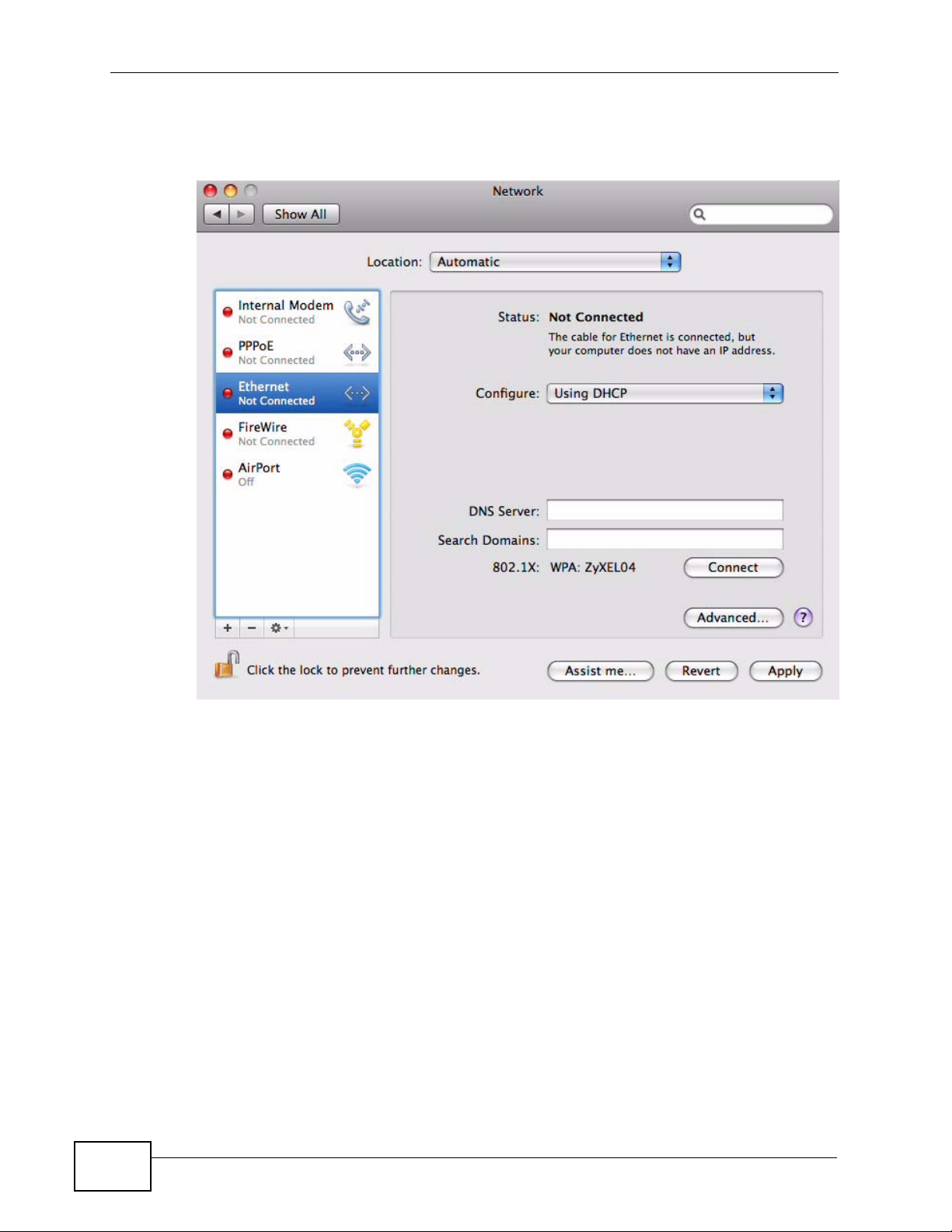
1 Click Apple > System Preferences.
Figure 146 Mac OS X 10.5: Apple Menu
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
2 In System Preferences, click the Network icon.
Figure 147 Mac OS X 10.5: Systems Preferences
IAD User’s Guide
261
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
3 When the Network preferences pane opens, select Ethernet from the list of
available connection types.
Figure 148 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Preferences > Ethernet
262
4 From the Configure list, select Using DHCP for dynamically assigned settings.
5 For statically assigned settings, do the following:
•From the Configure list, select Manually.
•In the IP Address field, enter your IP address.
•In the Subnet Mask field, enter your subnet mask.
IAD User’s Guide
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
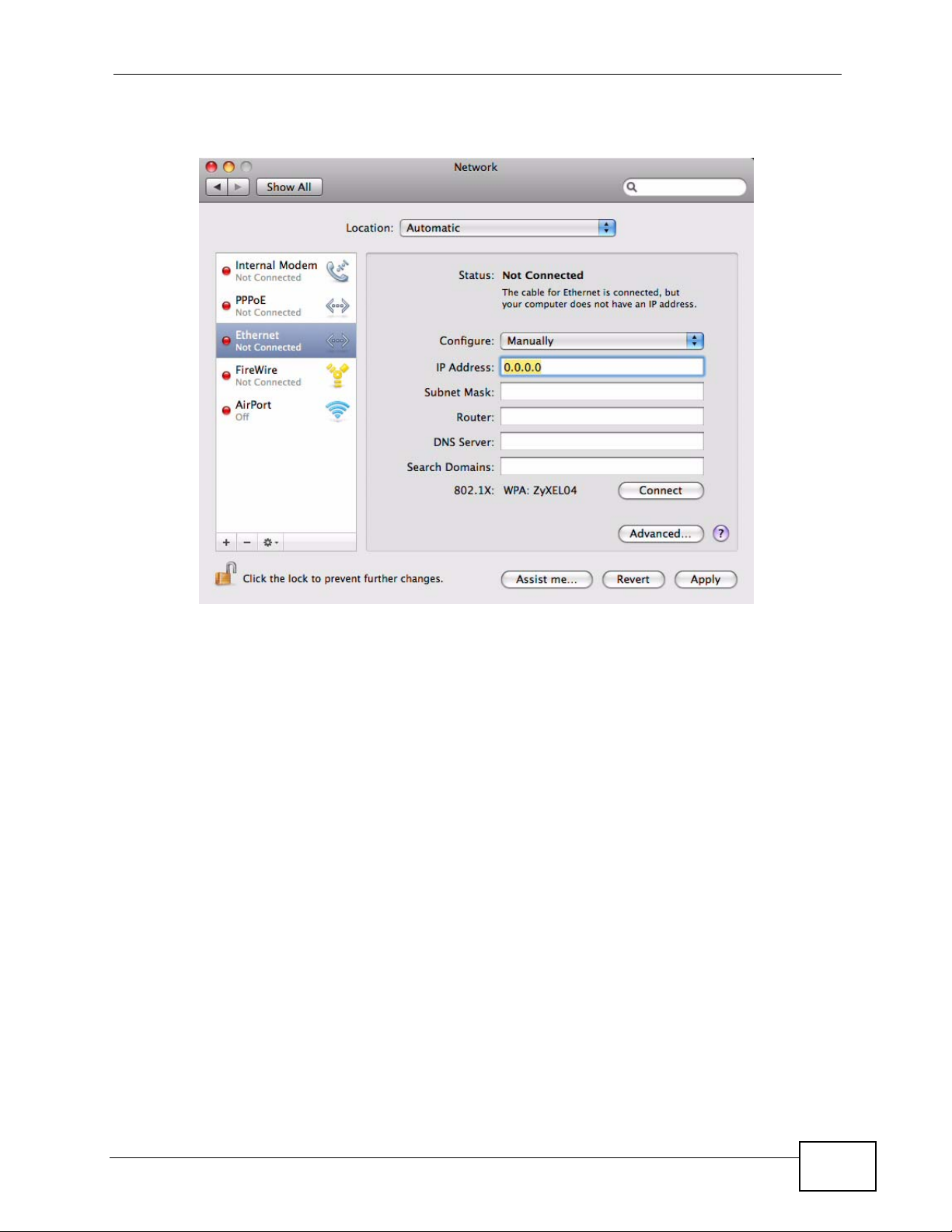
•In the Router field, enter the IP address of your IAD.
Figure 149 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Preferences > Ethernet
6 Click Apply and close the wind ow.
IAD User’s Guide
263
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
Verifying Settings
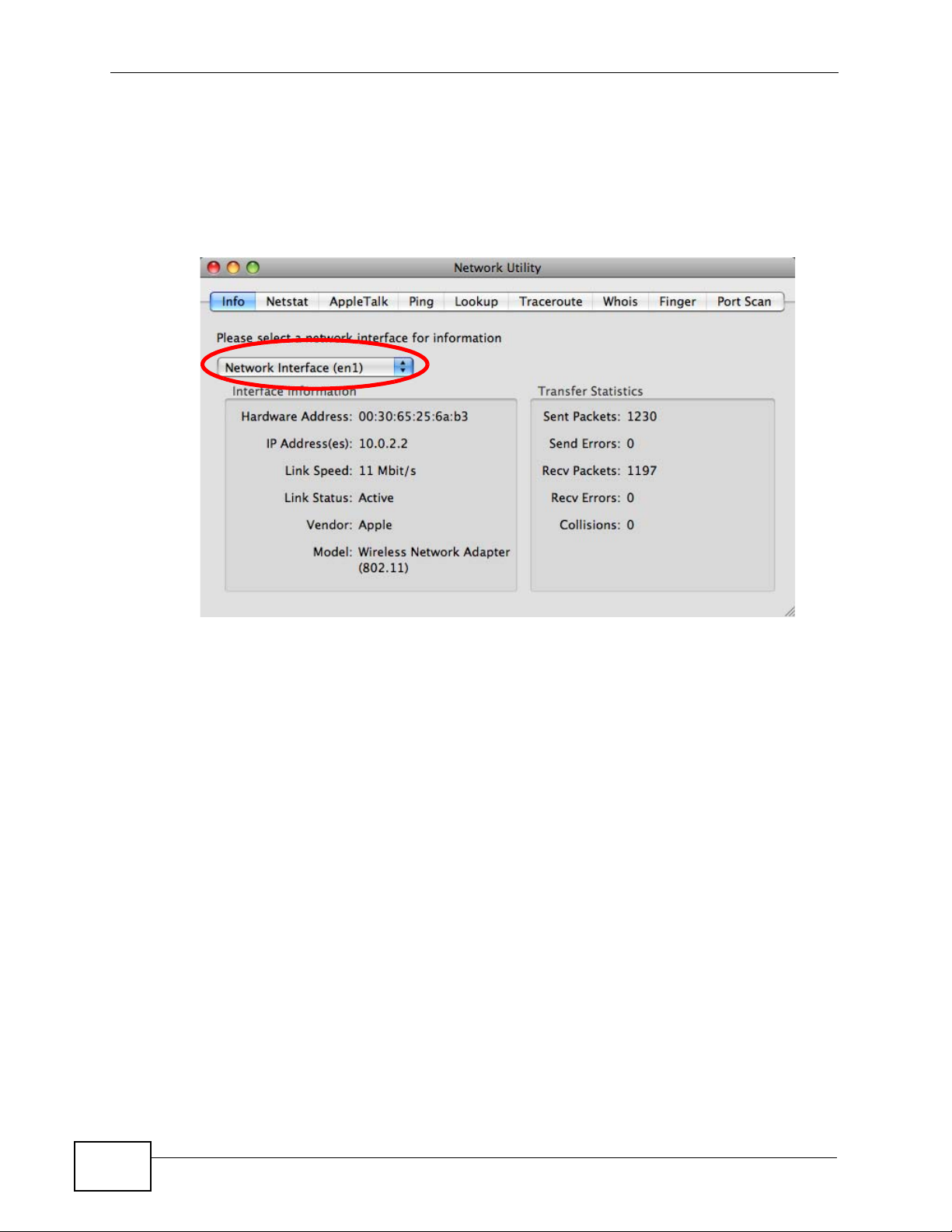
Check your TCP/IP properties by clicking Applications > Utilities > Network
Utilities, and then selecting the appropriate Network interface from the Info
tab.
Figure 150 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Utility
Linux: Ubuntu 8 (GNOME)
This section shows you how to configure your computer’s TCP/IP settings in the
GNU Object Model Environment (GNOME) using the Ubuntu 8 Linux distribution.
The procedure, screens and file locations may vary depending on your specific
distribution, release version, and individual configuration. The following screens
use the default Ubuntu 8 installation.
Note: Make sure you are logged in as the root administrator.
Follow the steps below to configure your computer IP address in GNOME:
264
IAD User’s Guide
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
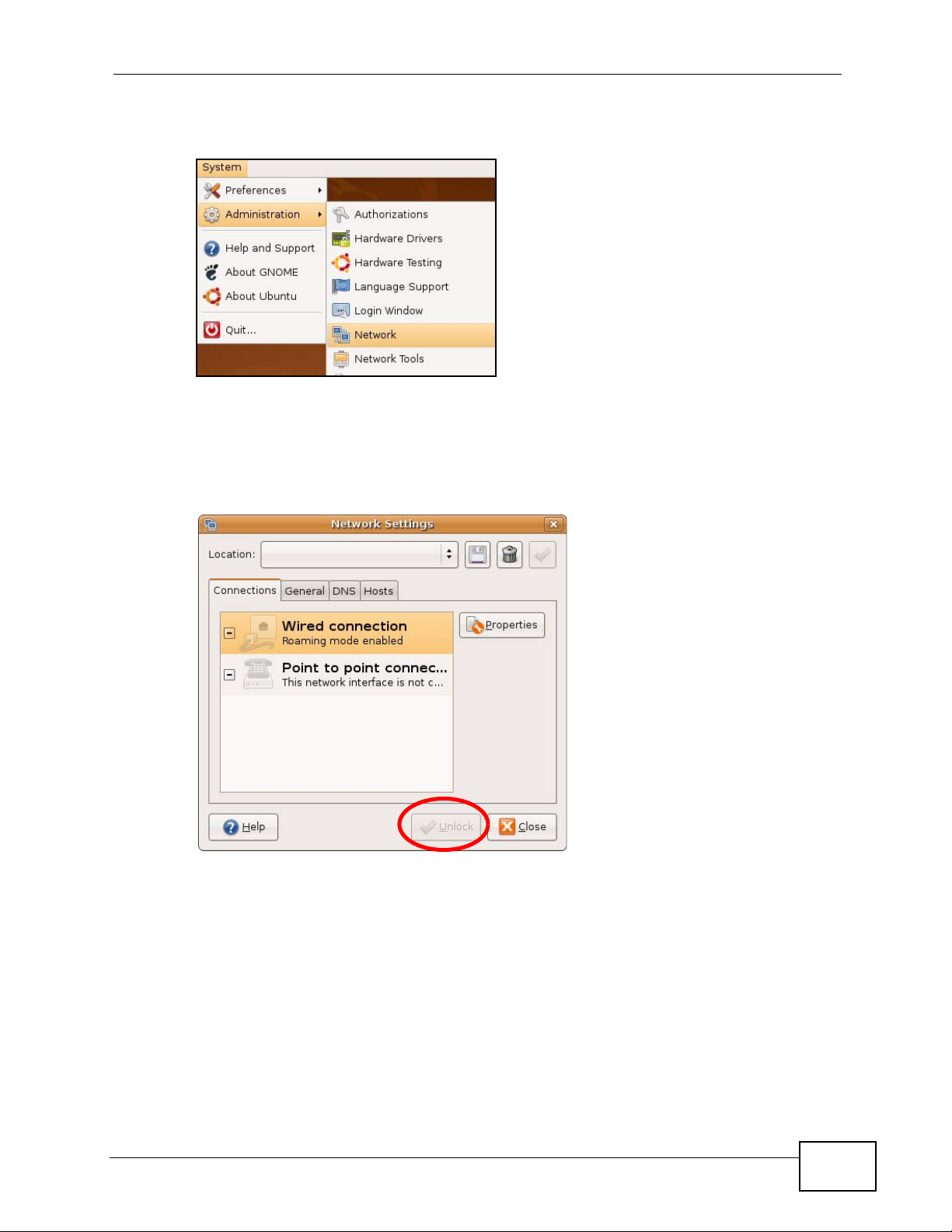
1 Click System > Administration > Network.
Figure 151 Ubuntu 8: System > Administration Menu
2 When the Network Settings window opens, click Unlock to open the
Authenticate window. (By default, the Unlock button is greyed out until clicked.)
You cannot make changes to your configuration unless you first enter your admin
password.
Figure 152 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Connections
IAD User’s Guide
265
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
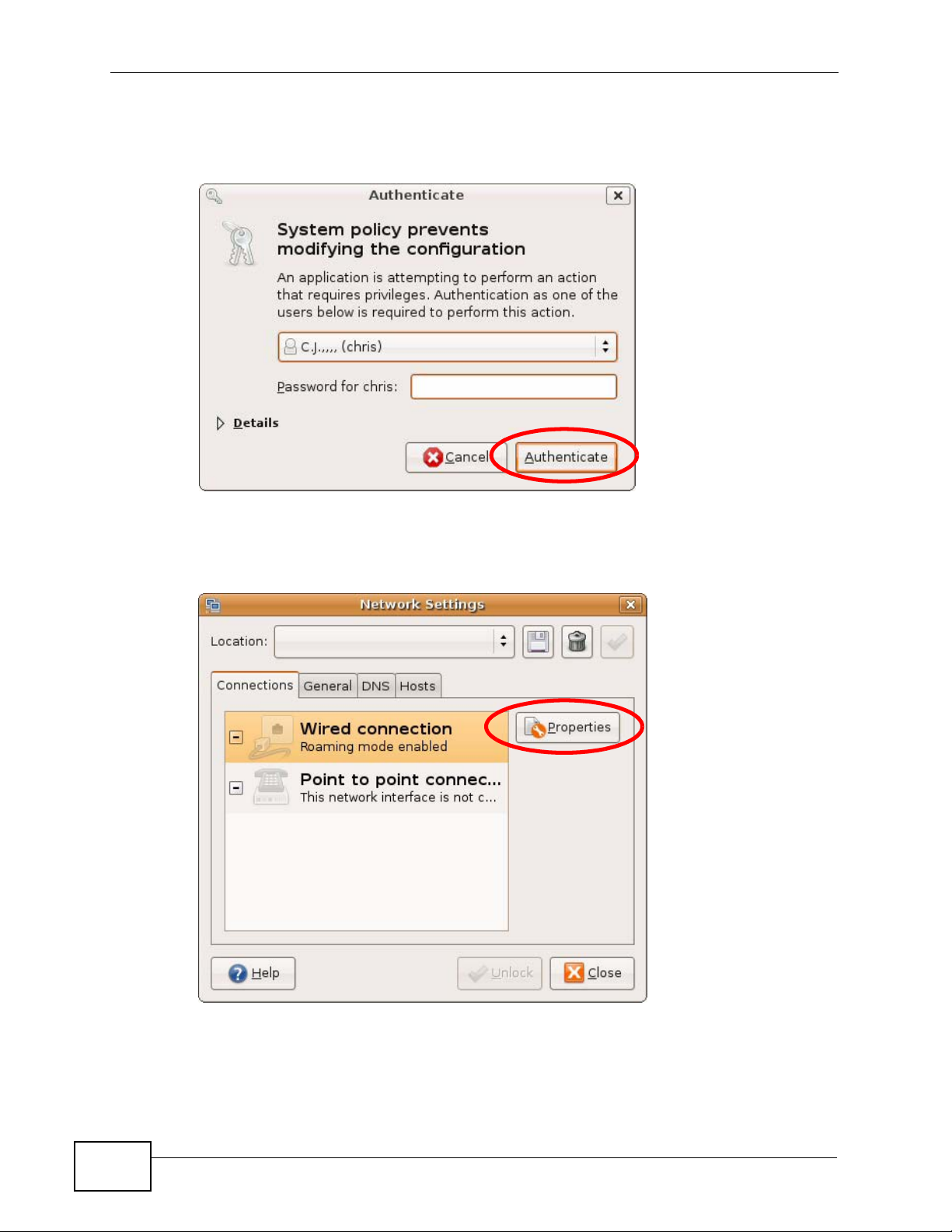
3 In the Authenticate window, enter y our admin account name and password t hen
click the Authenticate button.
Figure 153 Ubuntu 8: Administrator Account Authentication
4 In the Network Settings window, select the connection that you want to
configure, then click Properties.
Figure 154 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Connections
266
IAD User’s Guide
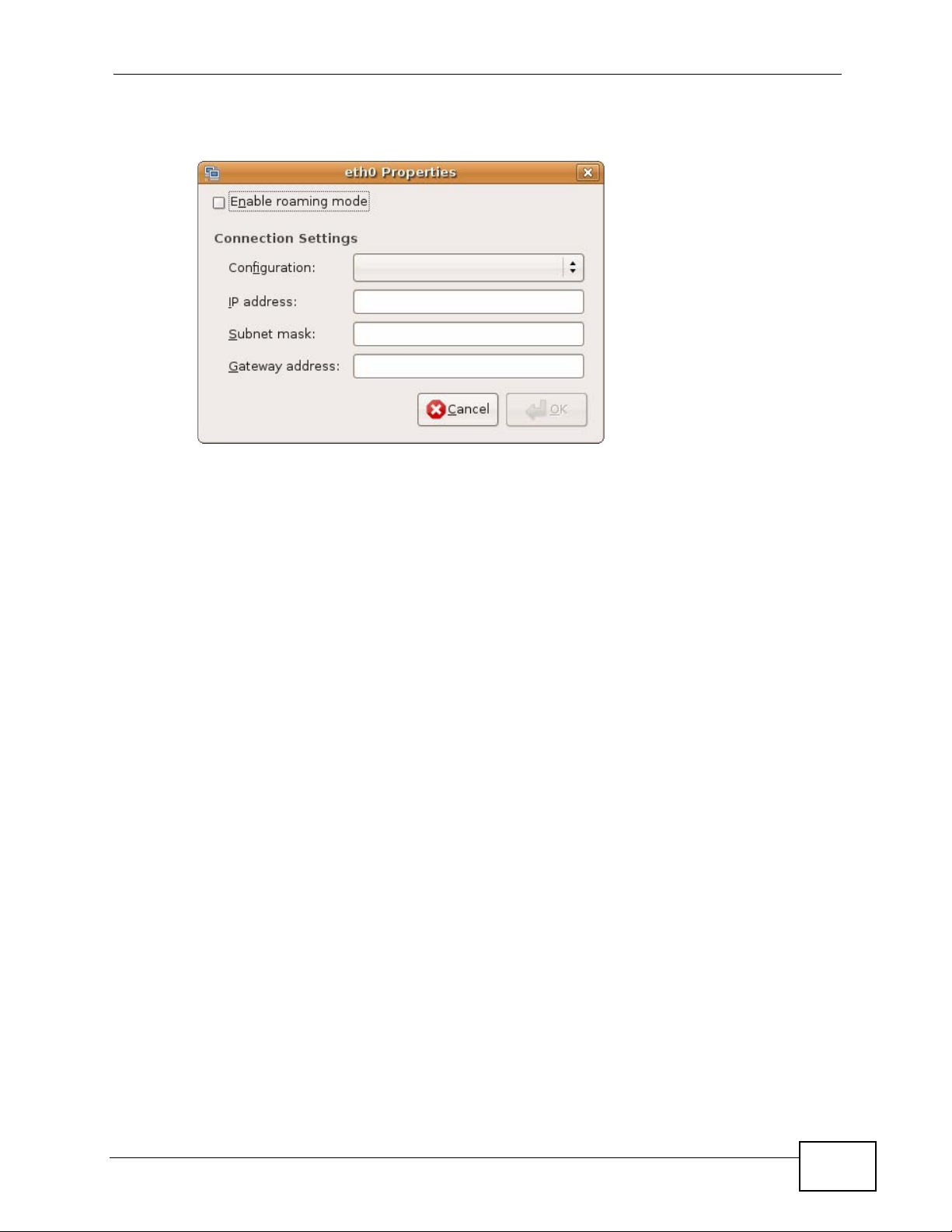
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
5 The Properties dialog box opens.
Figure 155 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Properties
•In the Configuration list, select Automatic Configuration (DHCP) if you
have a dynamic IP address.
•In the Configuration list, select Static IP address if you have a static IP
address. Fill in the IP address, Subnet mask, and Gateway address fields.
6 Click OK to save the changes and close the Properties dialog box and return to
the Network Settings screen.
IAD User’s Guide
267
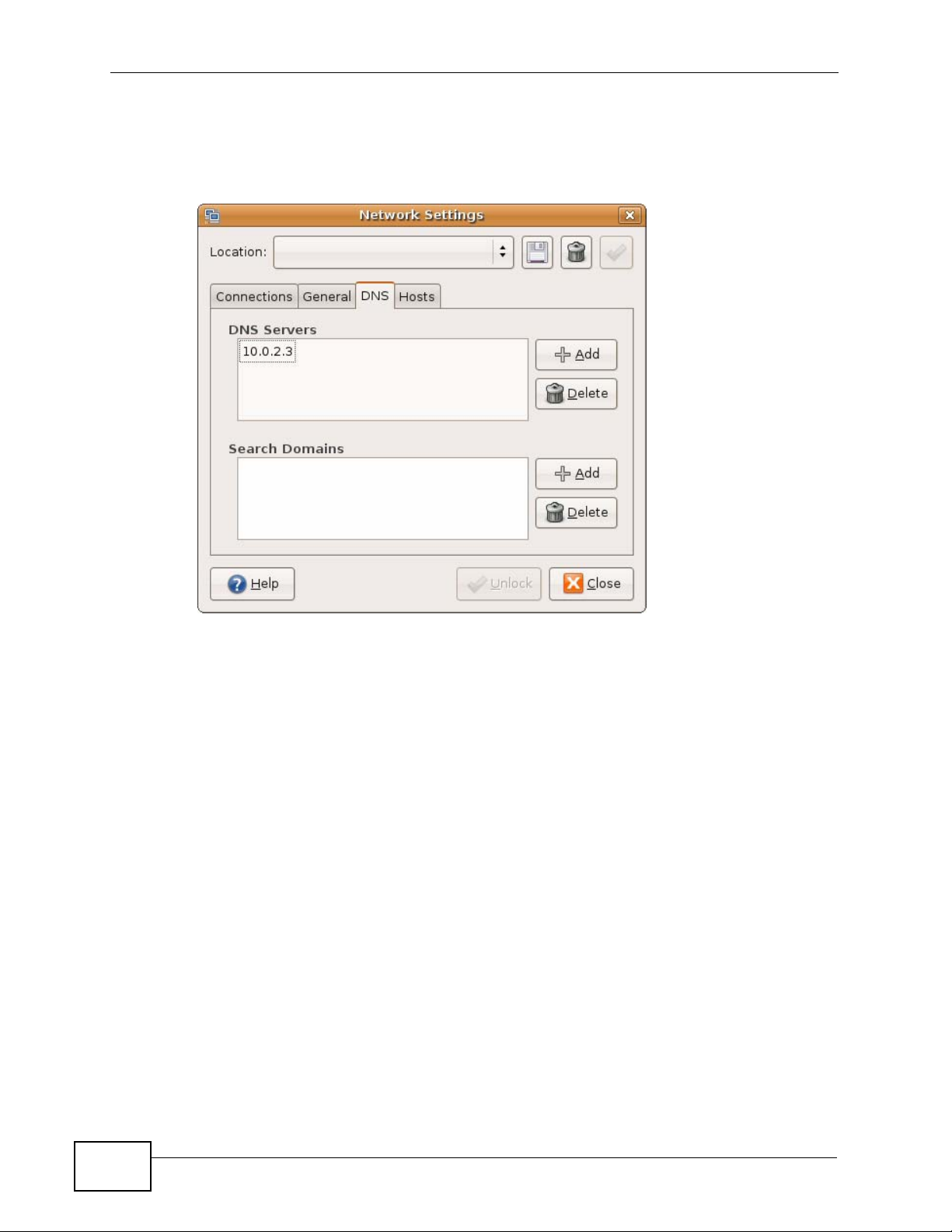
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
7 If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click the DNS tab in the Network
Settings window and then enter the DNS server information in the fields
provided.
Figure 156 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > DNS
8 Click the Close button to apply the changes.
Verifying Settings
Check your TCP/IP properties by clicking System > Administration > Network
Tools, and then selecting the appropriate Network device from the Devices
268
IAD User’s Guide
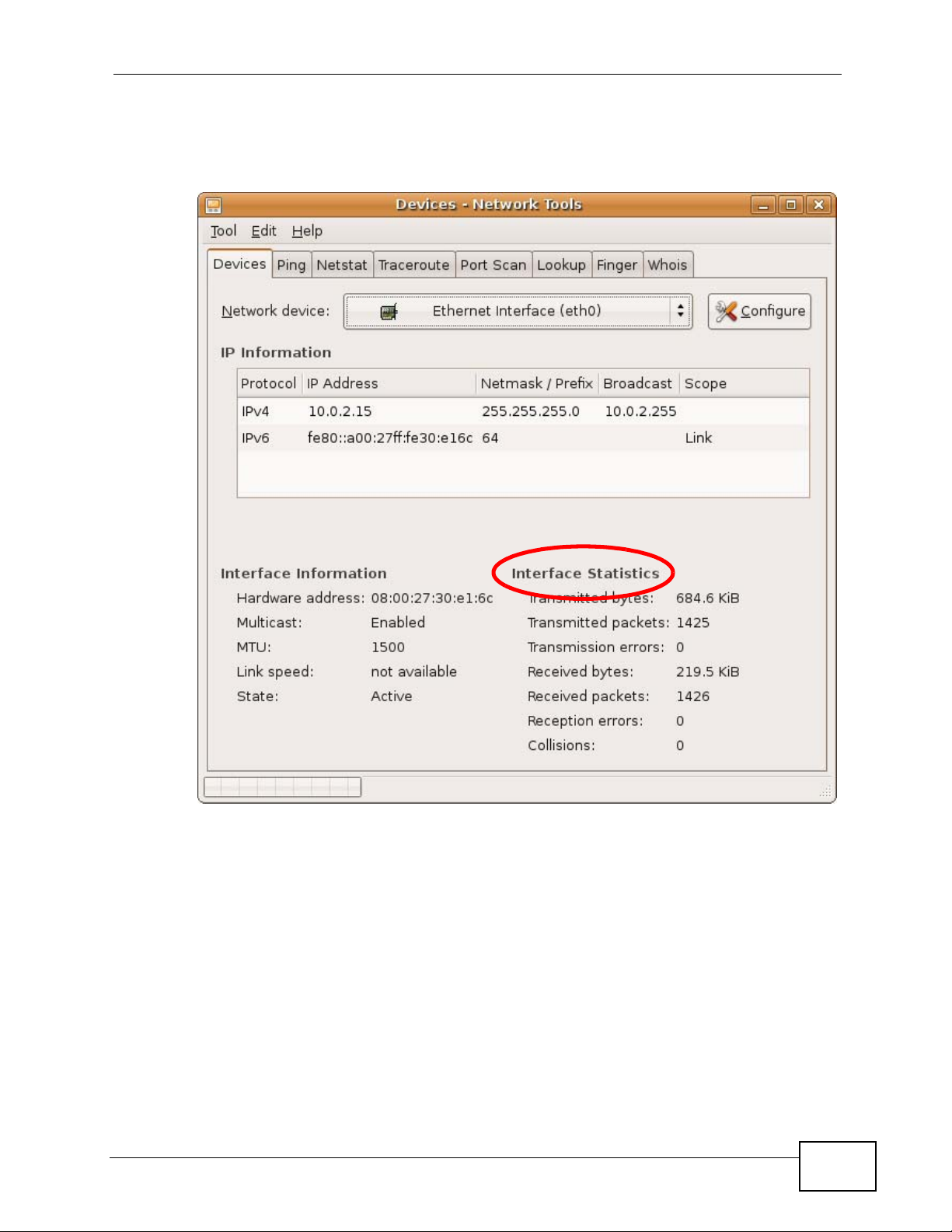
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
tab. The Interface Statistics column shows data if your connection is working
properly.
Figure 157 Ubuntu 8: Network Tools
Linux: openSUSE 10.3 (KDE)
This section shows you how to configure your computer’s TCP/IP settings in the K
Desktop Environment (KDE) using the openSUSE 10.3 Linux distribution. The
procedure, screens and file locations may vary depending on your specific
distribution, release version, and individual configuration. The following screens
use the default openSUSE 10.3 installation.
Note: Make sure you are logged in as the root administrator.
Follow the steps below to configure your computer IP address in the KDE:
IAD User’s Guide
269
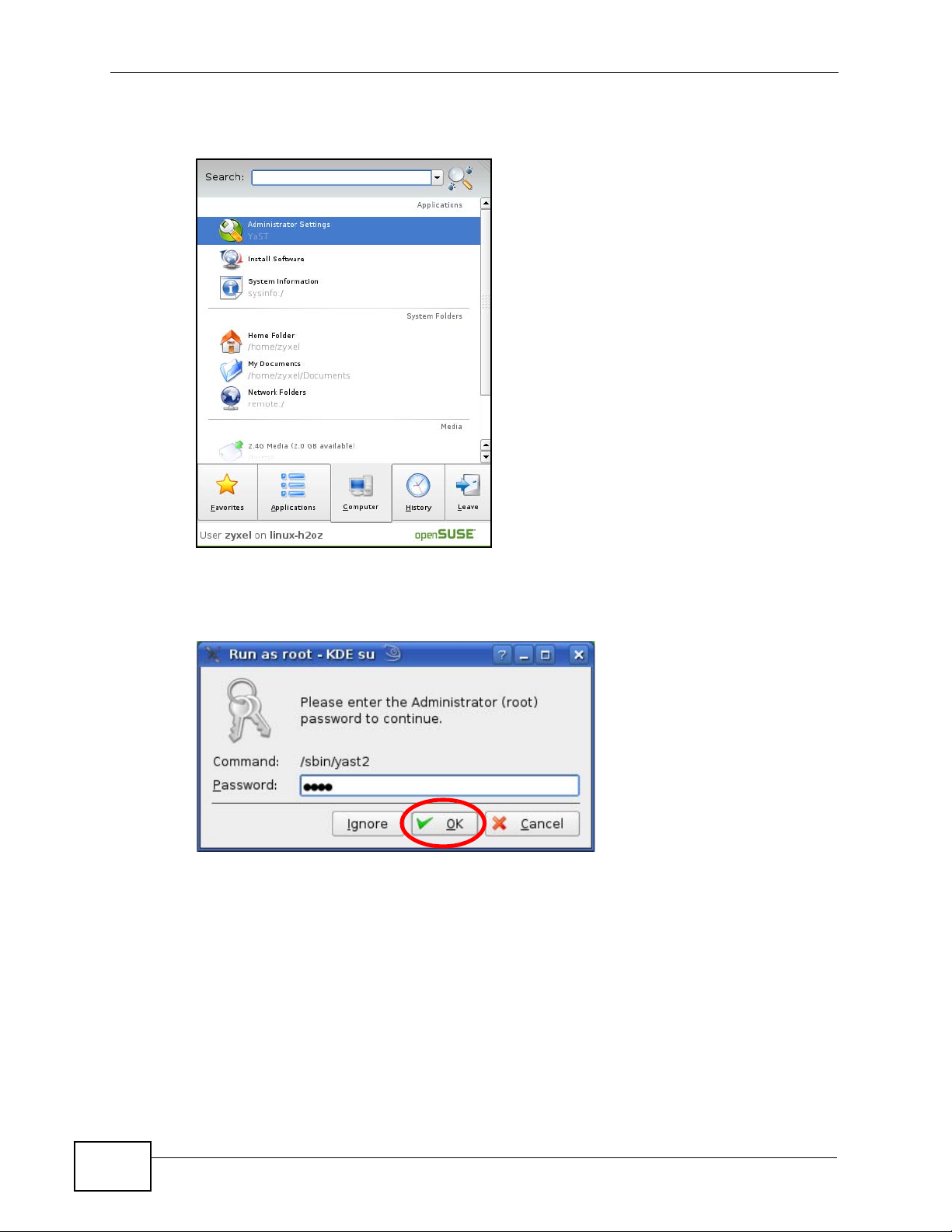
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
1 Click K Menu > Computer > Administrator Settings (YaST).
Figure 158 openSUSE 10.3: K Menu > Computer Menu
2 When the Run as Root - KDE su dialog opens, enter the admin password and
click OK.
Figure 159 openSUSE 10.3: K Menu > Computer Menu
270
IAD User’s Guide
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
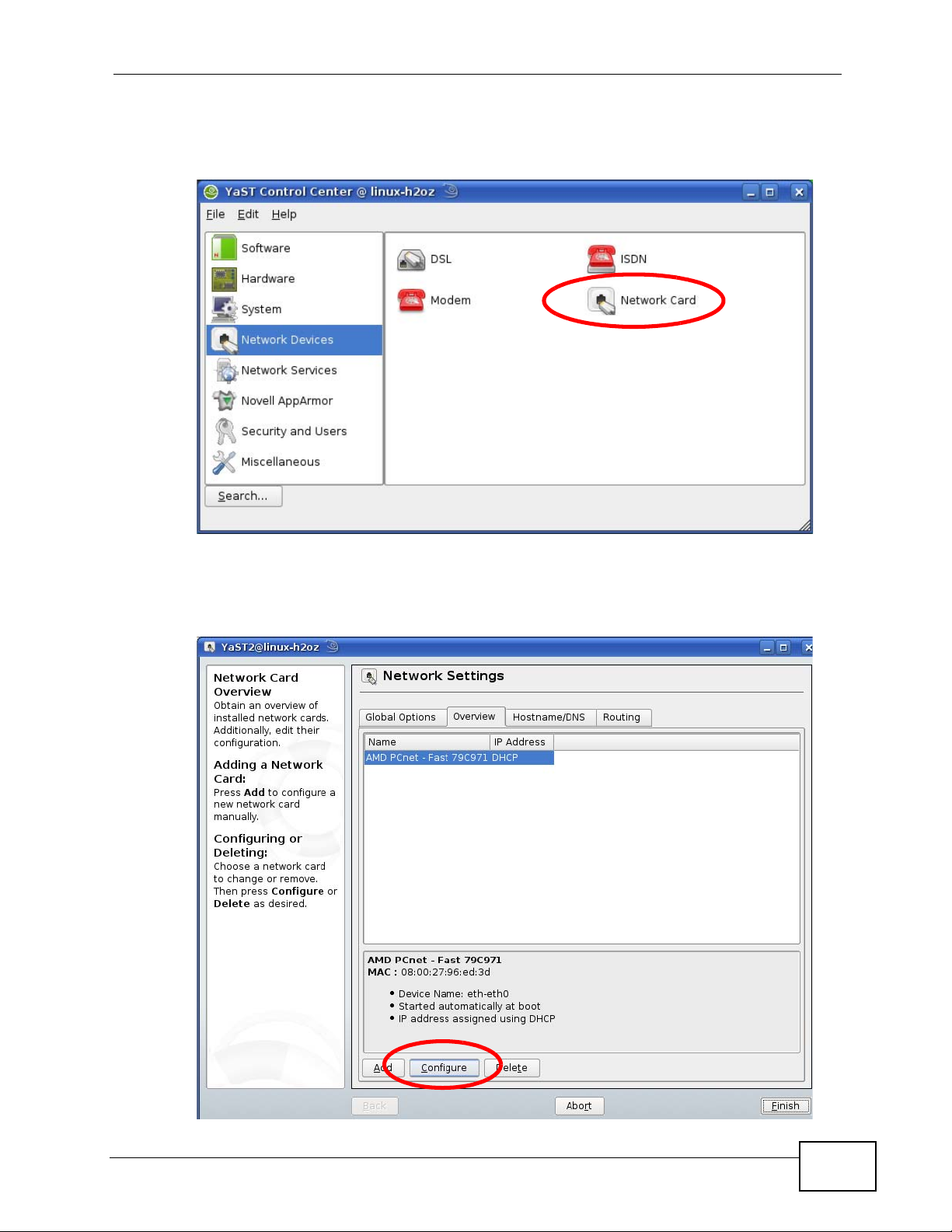
3 When the YaST Control Center window opens, select Network Devices and
then click the Network Card icon.
Figure 160 openSUSE 10.3: YaST Control Center
4 When the Network Settings window opens, click the Overview tab, select the
appropriate connection Name from the list, and then click the Configure button.
Figure 161 openSUSE 10.3: Network Settings
IAD User’s Guide
271
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
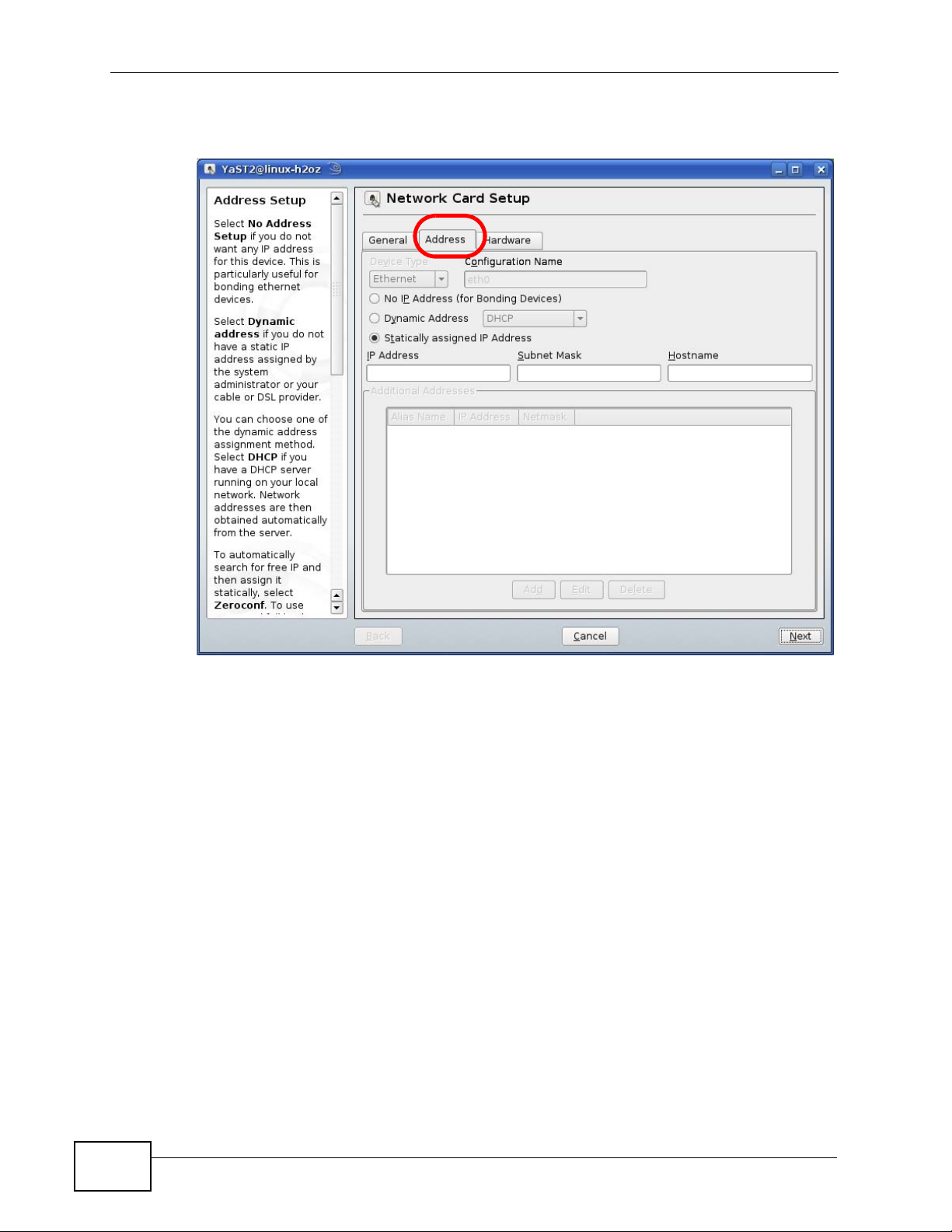
5 When the Network Card Setup window opens, click the Address tab
Figure 162 openSUSE 10.3: Network Card Setup
6 Select Dynamic Address (DHCP) if you have a dynamic IP address.
Select Statically assigned IP Address if you have a static IP address. Fill in the
IP address, Subnet mask, and Hostname fields.
7 Click Next to save the changes and close the Network Card Setup window.
272
IAD User’s Guide
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
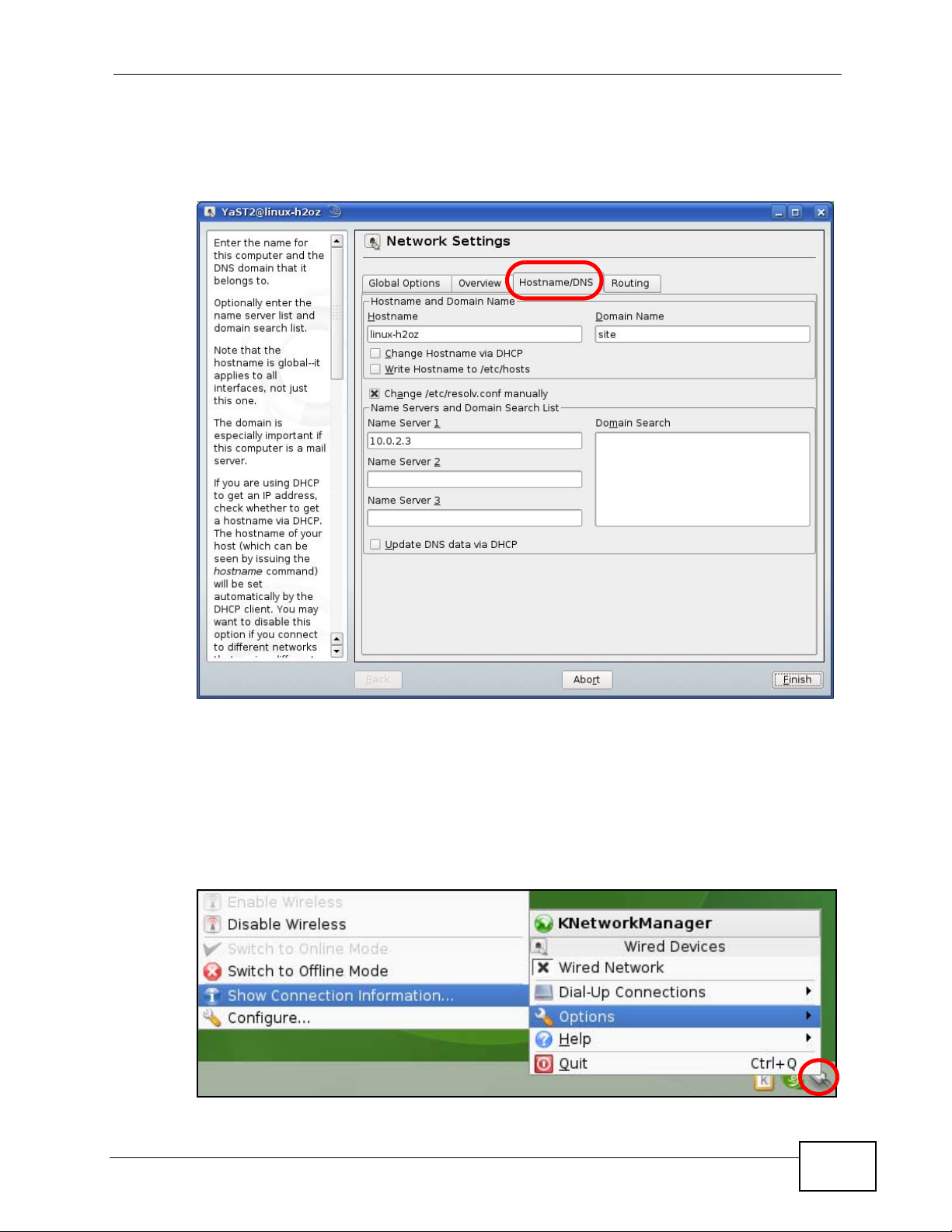
8 If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click the Hostname/DNS tab in
Network Settings and then enter the DNS server information in the fields
provided.
Figure 163 openSUSE 10.3: Network Settings
9 Click Finish to save your settings and close the window.
Verifying Settings
Click the KNetwork Manager icon on the Task bar to check your TCP/IP
properties. From the Options sub-menu, select Show Connection Information.
Figure 164 openSUSE 10.3: KNetwork Manager
IAD User’s Guide
273
 Loading...
Loading...