Page 1
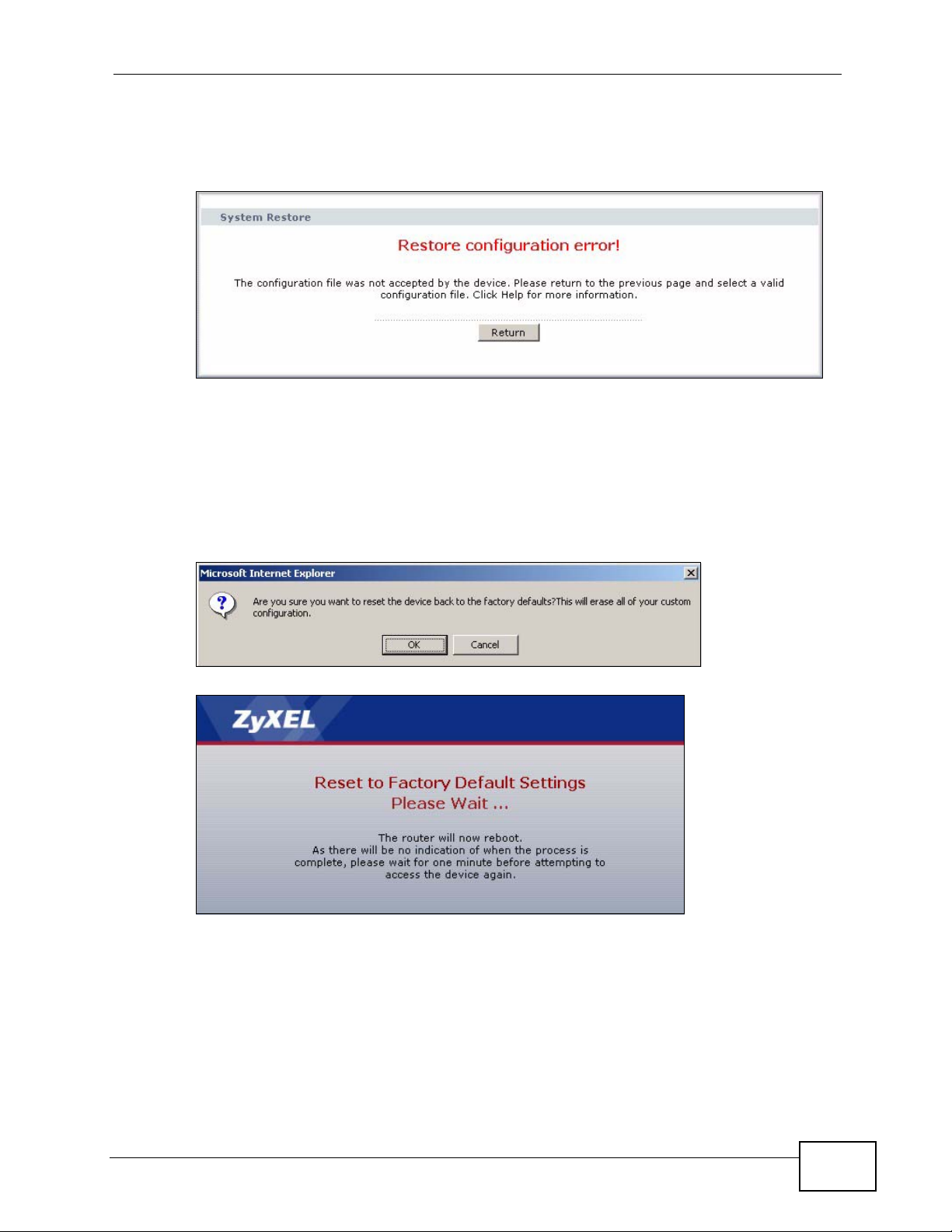
If the upload was not successful, the following screen will appear. Click Return to
go back to the Configuration screen.
Figure 295 Configuration Upload Error
27.3.1 Reset to Factory Defaults
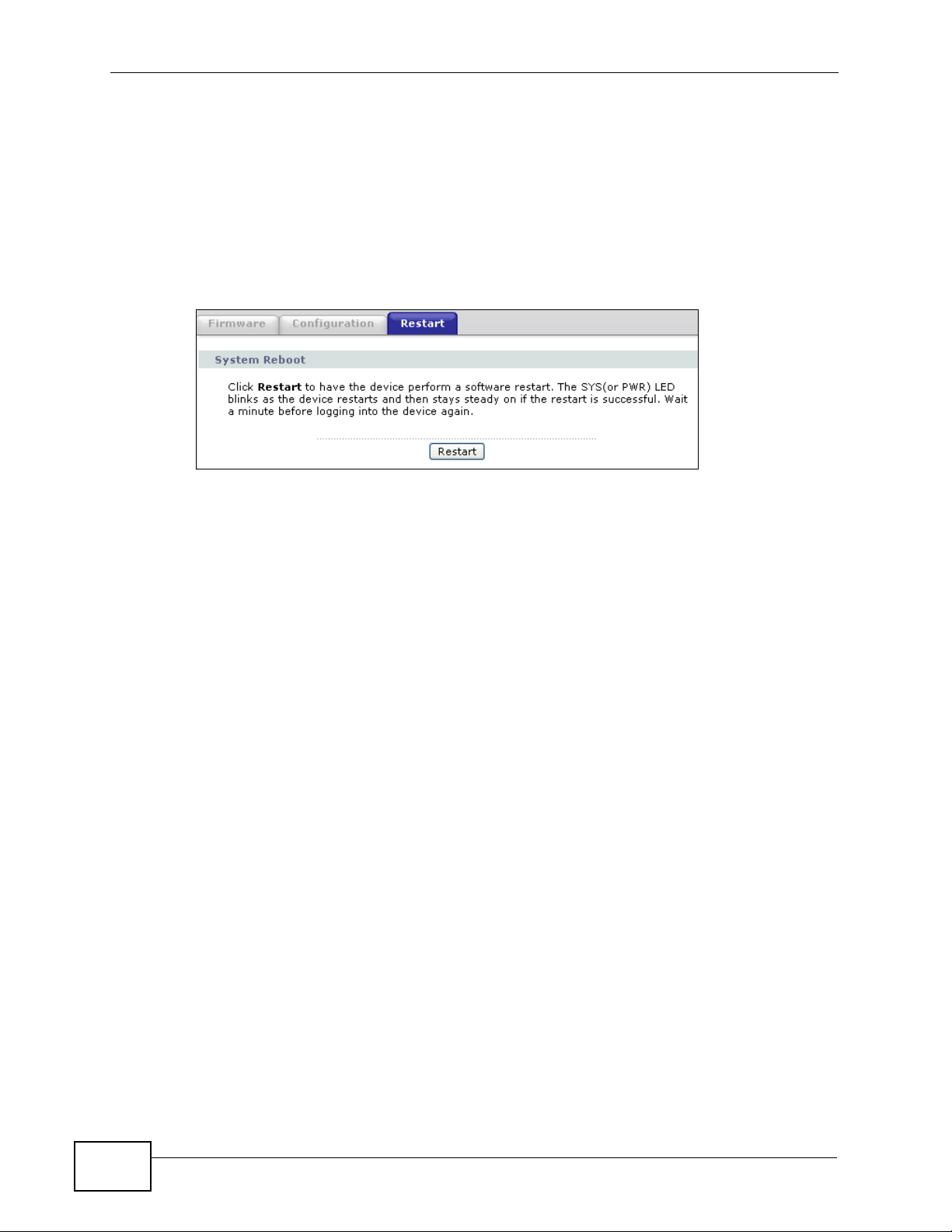
Click the Reset button to clear all user-entered configuration information and
return the ZyXEL Device to its factory defaults. The following warning screen
appears.
Chapter 27 Tools
Figure 296 Reset Warning Message
Figure 297 Reset In Process Message
You can also press the RESET button on the rear panel to reset the factory
defaults of your ZyXEL Device. Refer to Section 1.5 on page 30 for more
information on the RESET button.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
451
Page 2
Chapter 27 Tools
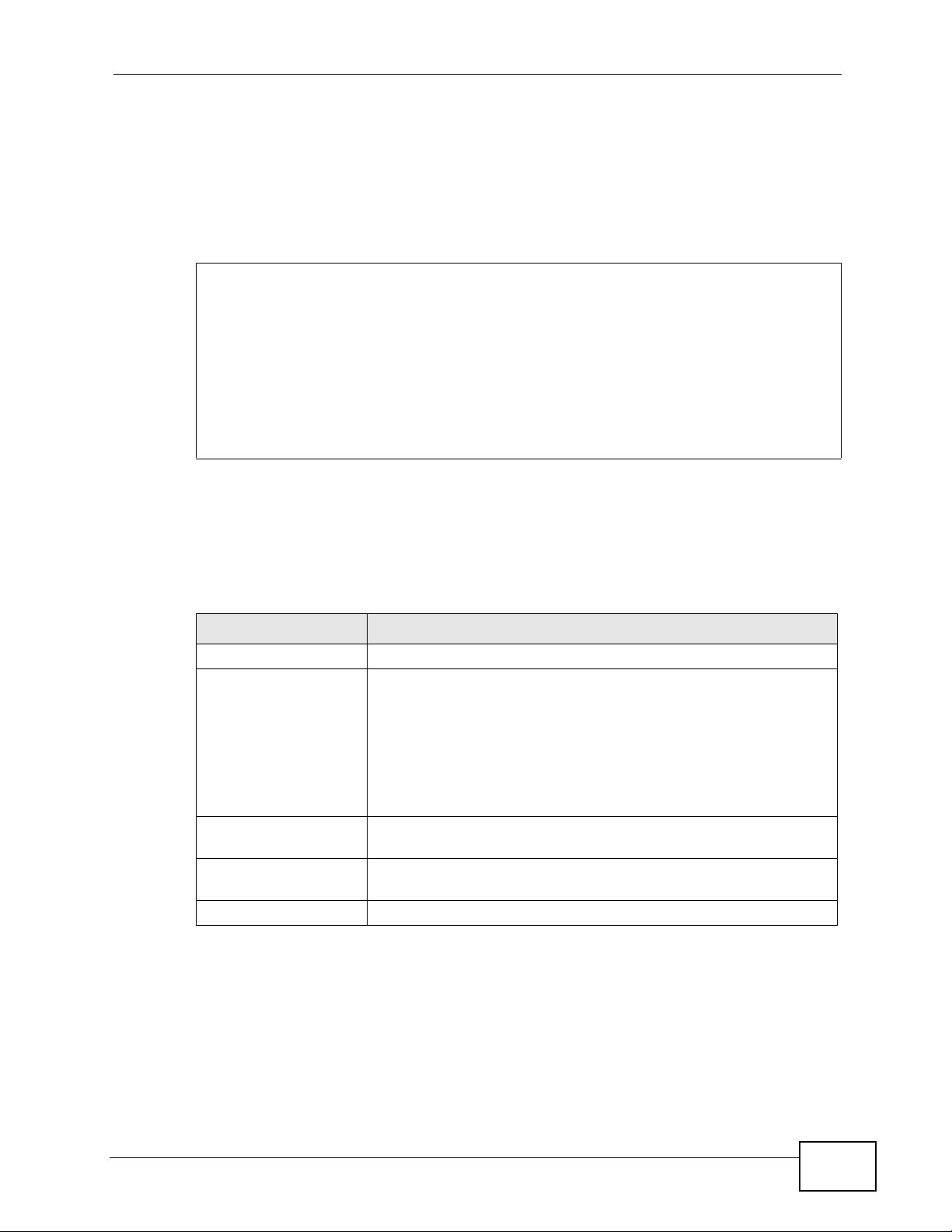
27.4 Restart
System restart allows you to reboot the ZyXEL Device without turning the power
off.
Click Maintenance > Tools > Restart. Click Restart to have the ZyXEL Device
reboot. This does not affect the ZyXEL Device's configuration.
Figure 298 Maintenance > Tools > Restart Screen
27.5 Using FTP or TFTP to Back Up
Configuration
This section covers how to use FTP or TFTP to save your device’s config urati on file
to your computer.
27.5.1 Using the FTP Commands to Back Up Configuration
1 Launch the FTP client on your computer.
2 Enter “open”, followed by a space and the IP address of your ZyXEL Device.
3 Enter your username as requested (the default is “admin”).
4 Press [ENTER] when prompted for a password.
5 Enter “bin” to set transfer mode to binary.
6 Use “get” to transfer files from the ZyXEL Device to the computer, for example,
“get rom-0 config.rom” transfers the configuration file on the ZyXEL Device to
your computer and renames it “config.rom”. See earlier in this chapter for more
information on filename conventions.
452
7 Enter “quit” to exit the ftp prompt.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 3
Chapter 27 Tools
27.5.2 FTP Command Configuration Backup Example
This figure gives an example of using FTP commands from the DOS command
prompt to save your device’s configuration onto your computer.
Figure 299 FTP Session Example
331 Enter PASS command
Password:
230 Logged in
ftp> bin
200 Type I OK
ftp> get rom-0 zyxel.rom
200 Port command okay
150 Opening data connection for STOR ras
226 File received OK
ftp: 16384 bytes sent in 1.10Seconds 297.89Kbytes/sec.
ftp> quit
27.5.3 Configuration Backup Using GUI-based FTP Clients
The following table describes some of the commands that you may see in GUIbased FTP clients.
Table 163 General Commands for GUI-based FTP Clients
COMMAND DESCRIPTION
Host Address Enter the address of the host server.
Login Type Anonymous.
This is when a user I.D. and password is automatically supplied
to the server for anonymous access. Anonymous logins will work
only if your ISP or service administrator has enabled this option.
Normal.
The server requires a unique User ID and Password to login.
Transfer Type Transfer files in either ASCII (plain text format) or in binary
mode.
Initial Remote
Directory
Initial Local Directory Specify the default local directory (path).
Specify the default remote directory (path).
27.5.4 Backup Configuration Using TFTP
The ZyXEL Device supports the up/downloading of the firmware and the
configuration file using TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) over LAN. Although
TFTP should work over WAN as well, it is not recommended.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
453
Page 4

Chapter 27 Tools
T o use TFTP, your computer must have both telnet and TFTP clients. To backup the
configuration file, follow the procedure sh own next.
1 Use telnet from your computer to connect to the ZyXEL Device and log in. Because
TFTP does not have any security checks, the ZyXEL Device records the IP address
of the telnet client and accepts TFTP requests only from this address.
2 Enter command “sys stdio 0” to disable the management idle timeout, so the
TFTP transfer will not be interrupted. Enter command “sys stdio 5” to restore
the five-minute management idle timeout (default) when the file transfer is
complete.
3 Launch the TFTP client on your computer and connect to the ZyXEL Device. Set
the transfer mode to binary before starting data transfer.
4 Use the TFTP client (see the example below) to transfer files between the ZyXEL
Device and the computer. The file name for the configuration file is “rom-0” (rom-
zero, not capital o).
Note that the telnet connection must be active before and during the TFTP
transfer. For details on TFTP commands (see following example), please consult
the documentation of your TFTP client program. For UNIX, use “get” to transfer
from the ZyXEL Device to the computer and “binary” to set binary transfer mode.
27.5.5 TFTP Command Configuration Backup Example
The following is an example TFTP command:
tftp [-i] host get rom-0 config.rom
where “i” specifies binary image transfer mode (use this mode when transferring
binary files), “host” is the ZyXEL Device IP address, “get” transf ers the file source
on the ZyXEL Device (rom-0, name of the configuration file on the ZyXEL Device)
to the file destination on the computer and renames it config.rom.
454
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 5
Chapter 27 Tools
27.5.6 Configuration Backup Using GUI-based TFTP Clients
The following table describes some of the fields that you may see in GUI-based
TFTP clients.
Table 164 General Commands for GUI-based TFTP Clients
COMMAN
D
Host Enter the IP address of the ZyXEL Device. 192.168.1.1 is the ZyXEL Device’s
Send/
Fetch
Local File Enter the path and name of the firmware file (*.bin extension) or
Remote
File
Binary Transfer the file in binary mode.
Abort Stop transfer of the file.
DESCRIPTION
default IP address when shipped.
Use “Send” to upload the file to the ZyXEL Device and “Fetch” to back up the
file on your computer.
configuration file (*.rom extension) on your computer.
This is the filename on the ZyXEL Device. The filename for the firmware is
“ras” and for the configuration file, is “rom-0”.
Refer to Section on page 440 to read about configurations that disallow TFTP and
FTP over WAN.
27.6 Using FTP or TFTP to Restore Configuration
This section shows you how to restore a previously sa ved configur ation. Note that
this function erases the current configuration before restoring a previous back up
configuration; please do not attempt to restore unless you have a backup
configuration file stored on disk.
FTP is the preferred method for restoring your current computer configuration to
your device since FTP is faster. Please note that you must wait for the system to
automatically restart after the file transfer is complete.
Do not interrupt the file transfer process as this may
PERMANENTLY DAMAGE your device. When the Restore
Configuration process is complete, the device automatically
restarts .
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
455
Page 6
Chapter 27 Tools
27.6.1 Restore Using FTP Session Example
Figure 300 Restore Using FTP Session Example
ftp> put config.rom rom-0
200 Port command okay
150 Opening data connection for STOR rom-0
226 File received OK
221 Goodbye for writing flash
ftp: 16384 bytes sent in 0.06Seconds 273.07Kbytes/sec.
ftp>quit
Refer to Section on page 440 to read about configurations that disallow TFTP and
FTP over WAN.
27.7 FTP and TFTP Firmware and Configuration
File Uploads
This section shows you how to upload firmware and configuration files.
Do not interrupt the file transfer process as this may
PERMANENTLY DAMAGE your device.
FTP is the preferred method for uploading the firmware and configuration. To use
this feature, your computer must have an FTP client. The following sections give
examples of how to upload the firmware and the configuration files.
27.7.1 FTP File Upload Command from the DOS Prompt
Example
1 Launch the FTP client on your computer.
2 Enter “open”, followed by a space and the IP address of your device.
3 Enter your username as requested (the default is “admin”).
4 Press [ENTER] when prompted for a password.
456
5 Enter “bin” to set transfer mode to binary.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 7
Chapter 27 Tools
6 Use “put” to transfer files from the computer to the device, for example, “put
firmware.bin ras” transfers the firmware on your computer (firmware.bin) to the
device and renames it “ras”. Similarly, “put config.rom rom-0” transfers the
configuration file on your computer (config.rom) to the device and renames it
“rom-0”. Likewise “get rom-0 config.rom” transfers the configuration file on the
device to your computer and renames it “config.rom.” See earlier in this chapter
for more information on filename conventions.
7 Enter “quit” to exit the ftp prompt.
27.7.2 FTP Session Example of Firmware File Upload
Figure 301 FTP Session Example of Firmware File Upload
331 Enter PASS command
Password:
230 Logged in
ftp> bin
200 Type I OK
ftp> put firmware.bin ras
200 Port command okay
150 Opening data connection for STOR ras
226 File received OK
ftp: 1103936 bytes sent in 1.10Seconds 297.89Kbytes/sec.
ftp> quit
More commands (found in GUI-based FTP clients) are listed earlier in this chapter.
Refer to Section on page 440 to read about configurations that disallow TFTP and
FTP over WAN.
27.7.3 TFTP File Upload
The device also supports the uploading of firmware files using TFTP (Trivial File
Transfer Protocol) over LAN. Although TFTP should work over WAN as well, it is not
recommended.
To use TFTP, your computer must have both telnet and TFTP clients. To transfer
the firmware and the configuration file, follow the procedure shown next.
1 Use telnet from your computer to connect to the device and log in. Because TFTP
does not have any security checks, the device records the IP address of the telnet
client and accepts TFTP requests only from this address.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
457
Page 8

Chapter 27 Tools
2 Enter the command “sys stdio 0” to disable the management idle timeout, so the
TFTP transfer will not be interrupted. Enter “command sys stdio 5” to restore the
five-minute management idle timeout (default) when the file transfer is complete.
3 Launch the TFTP client on your computer and connect to the device. Set the
transfer mode to binary before starting data transfer.
4 Use the TFTP client (see the example below) to transfer files between the device
and the computer. The file name for the firmware is “ras”.
Note that the telnet connection must be active and the device in CI mode before
and during the TFTP transfer. For details on TFTP commands (see following
example), please consult the documentation of your TFTP client program. For
UNIX, use “get” to transfer from the device to the computer, “put” the other way
around, and “binary” to set binary transfer mode.
27.7.4 TFTP Upload Command Example
The following is an example TFTP command:
tftp [-i] host put firmware.bin ras
Where “i” specifies binary image transfer mode (use this mode when transferring
binary files), “host” is the device’s IP address, “put” transfers the file source on
the computer (firmware.bin – name of the firmware on the computer) to the file
destination on the remote host (ras - name of the firmware on the device).
Commands that you may see in GUI-based TFTP clients are listed earlier in this
chapter.
458
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 9
CHAPTER 28
Diagnostic
28.1 Overview
These read-only screens display information to help you identify problems with the
ZyXEL Devic e.
28.1.1 What You Can Do in the Diagnostic Screens
Use the General Diagnostic screen (Section 28.2 on page 459) to ping an IP
address.
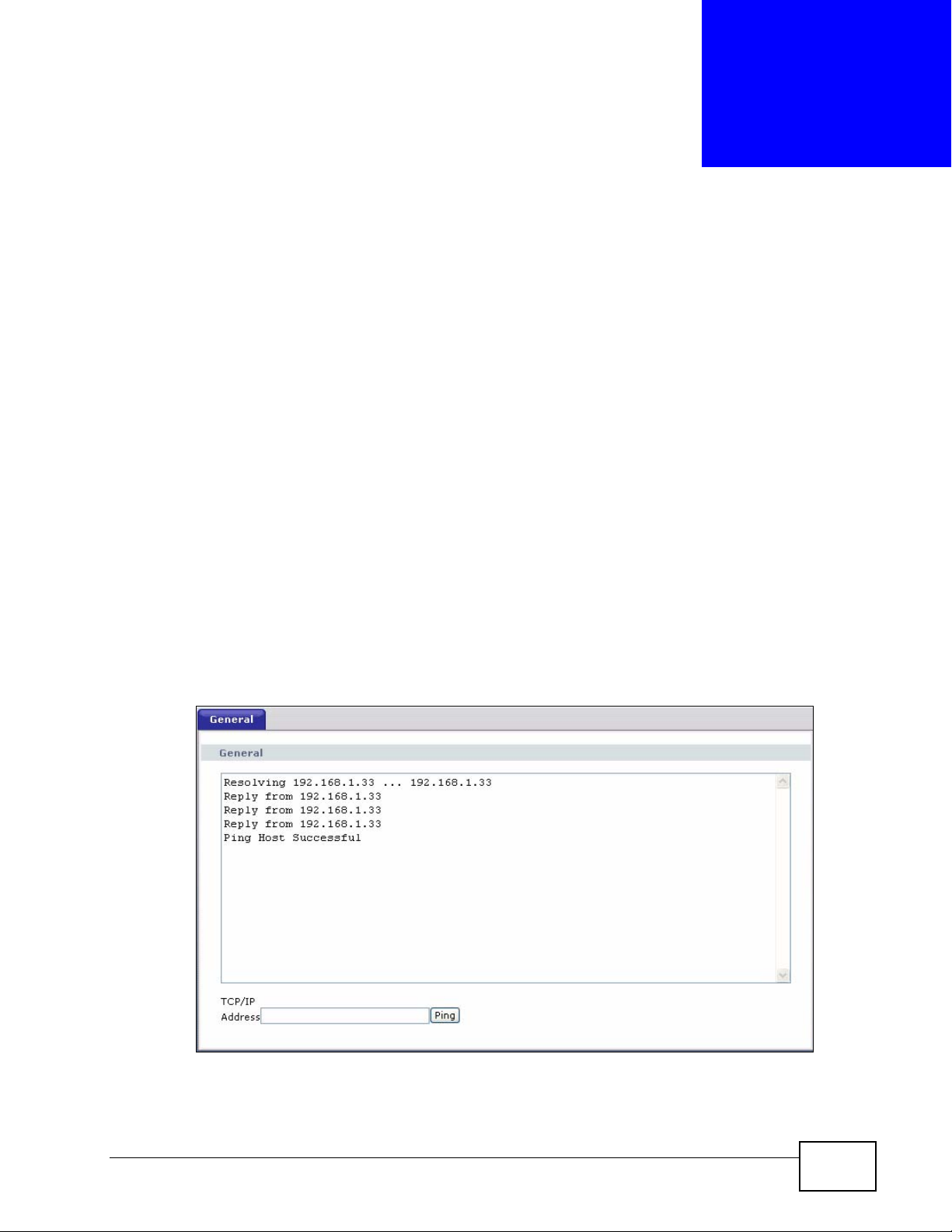
28.2 The General Diagnostic Screen
Click Maintenance > Diagnostic to open the screen shown next.
Figure 302 Maintenance > Diagnostic > General
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
459
Page 10

Chapter 28 Diagnostic
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 165 Maintenance > Diagnostic > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
TCP/IP
Address
Ping Click this button to ping the IP address that you entered.
Type the IP address of a computer that you want to ping in order to test a
connection.
460
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 11

CHAPTER 29
Troubleshooting
29.1 Overview
This chapter offers some suggestions to solve problems you might encounter. The
potential problems are divided into the following categories.
• Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
• ZyXEL Device Access and Login
• Internet Access
• Phone Calls and VoIP
• Multiple SIP Accounts
• USB Device Connection
29.2 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
The ZyXEL Device does not turn on. None of the LEDs turn on.
1 Make sure the ZyXEL Device is turned on.
2 Make sure you are using the power adaptor or cord included with the ZyXEL
Device.
3 Make sure the power adaptor or cord is connected to the ZyXEL Device and
plugged in to an appropriate power source. Make s ure the power source is turned
on.
4 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
5 If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
461
Page 12
Chapter 29 Troubleshooting
One of the LEDs does not behave as expected.
1 Make sure you understand the normal behavior of the LED. See Section 1.4 on
page 28.
2 Check the hardware connections. See the Quick Start Guide.
3 Inspect your cables for damage. Contact the vendor to replace any damaged
cables.
4 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
5 If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
29.3 ZyXEL Device Access and Login
I forgot the IP address for the ZyXEL Device.
1 The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
2 If you changed the IP address and have forgotten it, you might get the IP address
of the ZyXEL Device by looking up the IP address of the default gateway for your
computer. To do this in most Windows computers, click Start > Run, enter cmd,
and then enter ipconfig. The IP address of the Default Gateway might be the IP
address of the ZyXEL Device (it depends on the network), so enter this IP add ress
in your Internet browser.
3 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See
Section 1.5 on page 30.
I cannot see or access the Login screen in the web configurator.
462
1 Make sure you are using the correct IP address.
• The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
• If you changed the IP address (Section on page 127), use the new IP
address.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 13

Chapter 29 Troubleshooting
• If you changed the IP address and have forgotten it, see the troubleshooting
suggestions for I forgot the IP address for the ZyXEL Device.
2 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as
expected. See the Quick Start Guide.
3 Make sure your Internet bro wser does not block pop-up windows and has
JavaScripts and Jav a enabled. See Appendix B on page 511.
4 If you disabled Any IP (Section 7.2.1 on page 120), make sure your computer is
in the same subnet as the ZyXEL Device. (If you know that there are routers
between your computer and the ZyXEL Device, skip this step.)
• If there is a DHCP server on your network, make sure your computer is using
a dynamic IP address. See Appendix A on page 485. Your ZyXEL Device is a
DHCP server by default.
• If there is no DHCP server on your network, make sure your co mputer’s IP
address is in the same subnet as the ZyXEL Device. See Appendix A on page
485.
5 Reset the device to its factory defaults, and try to access the ZyXEL Device with
the default IP address. See Section 1.5 on page 30.
6 If the problem continues, contact the network administrator or vendor, or try one
of the advanced suggestions.
Advanced Suggestions
• Try to access the Z yXEL Device using another service, such as Telnet. If you can
access the ZyXEL Device, check the remote management settings and firewall
rules to find out why the ZyXEL Device does not respond to HTTP.
• If your computer is connected to the WAN port or is connected wirelessly, use a
computer that is connected to a ETHERNET port.
I can see the Login screen, but I cannot log in to the ZyXEL Device.
1 Make sure you have entered the user name and password correctly. The default
user name is admin. These fields are case-sensitiv e , so make sure [Caps Lock] is
not on.
2 You cannot log in to the web configurator while someone is using Telnet to access
the ZyXEL Device. Log out of the ZyXEL Device in the other session, or ask the
person who is logged in to log out.
3 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
463
Page 14
Chapter 29 Troubleshooting
4 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See
Section 29.2 on page 461.
I cannot Telnet to the ZyXEL Device.
See the troubleshooting suggestions for I cannot see or access the Login screen in
the web configurator. Ignore the suggestions about your browser.
I cannot use FTP to upload / download the configuration file. / I cannot use FTP to
upload new firmware.
See the troubleshooting suggestions for I cannot see or access the Login screen in
the web configurator. Ignore the suggestions about your browser.
29.4 Internet Access
I cannot access the Internet.
1 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as
expected. See the Quick Start Guide and Section 1.4 on page 28.
2 Make sure you entered your ISP account information correctly in the wizard. These
fields are case-sensitive, so make sure [Caps Lock] is not on.
3 If you are trying to access the Internet wirelessly, make sure the wireless settings
in the wireless client are the same as the settings in the AP.
4 Disconnect all the cables from your device, and follow the directions in the Quick
Start Guide again.
5 If the problem continues, contact your ISP.
464
I cannot access the Internet anymore. I had access to the Internet (with the ZyXEL
Device), but my Internet connection is not available anymore.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 15
Chapter 29 Troubleshooting
1 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as
expected. See the Quick Start Guide and Section 1.4 on page 28.
2 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
3 If the problem continues, contact your ISP.
The Internet connection is slow or intermittent.
1 There might be a lot of traffic on the network. Look at the LEDs, and check Section
1.4 on page 28. If the ZyXEL Device is sending or receiving a lot of information,
try closing some programs that use the Internet, especially peer-to-peer
applications.
2 Check the signal strength. If the signal strength is low, try moving the ZyXEL
Device closer to the AP if possible, and look around to see if there are any devices
that might be interfering with the wireless network (for example, microwaves,
other wireless networks, and so on).
3 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
4 If the problem continues, contact the network administrator or vendor, or try one
of the advanced suggestions.
Advanced Suggestions
• Check the settings for bandwidth management. If it is disabled, you might
consider activating it. If it is enabled, you might consider changing the
allocations.
• Check the settings for QoS. If it is disabled, you might consi der activating it. If it
is enabled, you might consider raising or lowe ri ng the priority for some
applications.
29.5 Phone Calls and VoIP
The telephone port won’t work or the telephone lacks a dial tone.
1 Check the telephone connections and telephone wire.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
465
Page 16

Chapter 29 Troubleshooting
I can access the Internet, but cannot make VoIP calls.
1 The PHONE light should come on. Make sure that your telephone is connected to
the PHONE port.
2 You can also check the VoIP status in the Status screen.
3 If the VoIP settings are correct, use speed dial to make peer-to-peer calls. If you
can make a call using speed dial, there may be something wrong with the SIP
server, contact your VoIP service provider.
29.6 Multiple SIP Accounts
You can set up two SIP accounts on your ZyXEL Device and your ZyXEL Device is
equipped with two phone ports. By default yo ur ZyXEL Device uses SIP account 1
with both phone ports for outgoing calls, and it uses SIP accounts 1 and 2 for
incoming calls. With this setting, you always use SIP account 1 for your outgoing
calls and you cannot distinguish which SIP account the calls are coming in
through. If you want to control the use of different dialing plans for accounting
purposes or other reasons, you need to configure your phone ports in order to
control which SIP account you are using when placing or receiving calls.
466
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 17
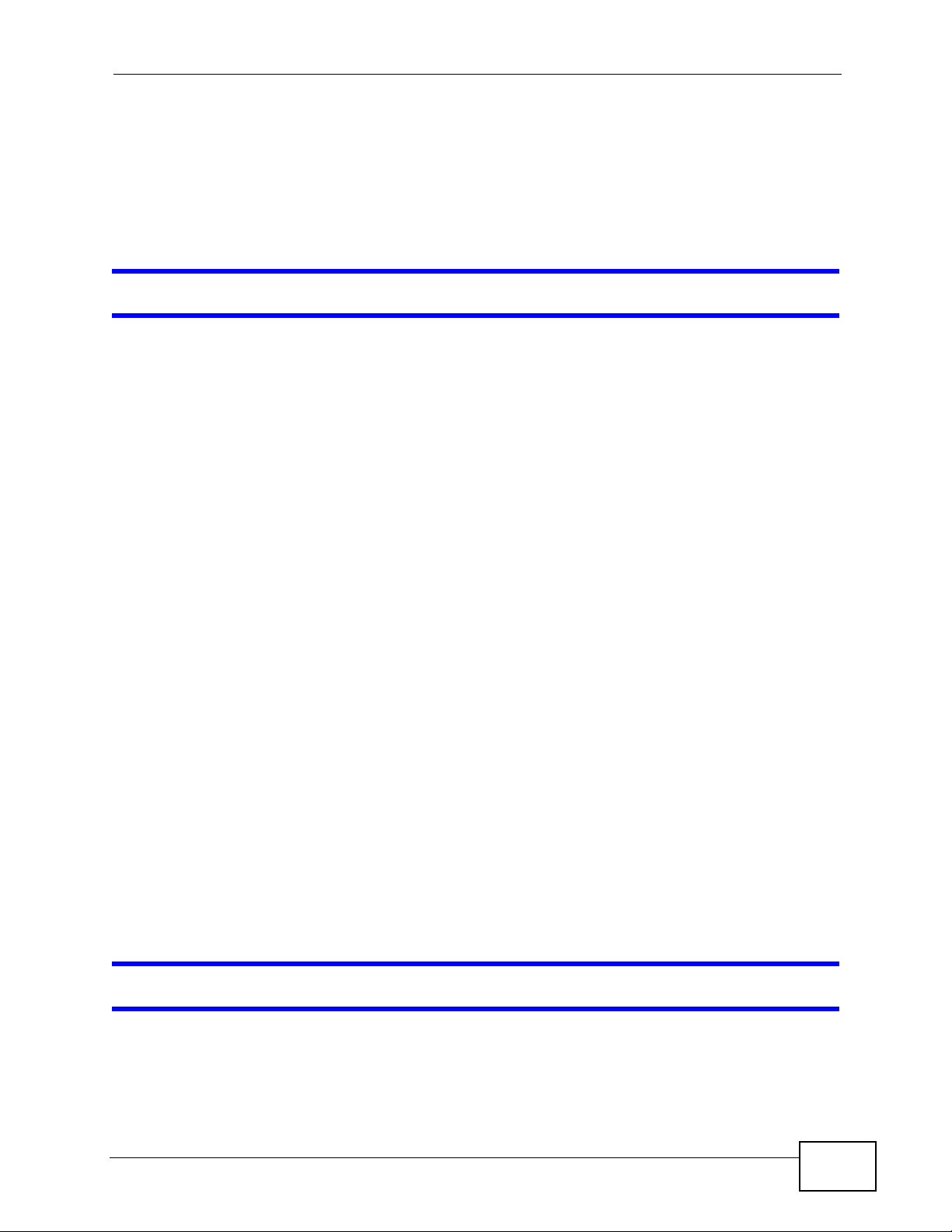
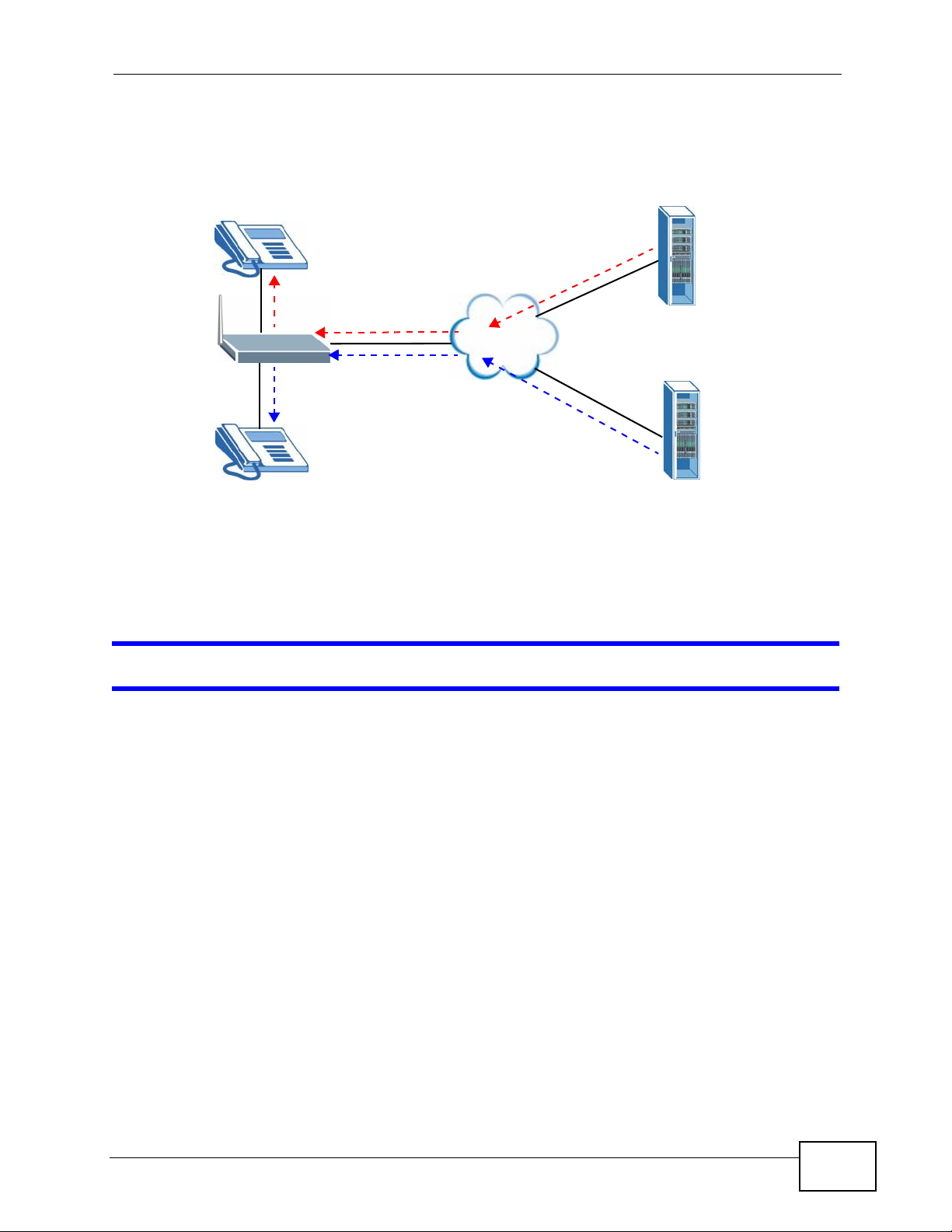
29.6.1 Outgoing Calls
The following figure represents the default behavior of your ZyXEL Device when
two SIP accounts are configured and you are using two phones. When you place a
call from phone port 1 or phone port 2, the ZyXEL Device will use SIP account 1.
Figure 303 Outgoing Calls: Default
PHONE 1
Chapter 29 Troubleshooting
SIP 1
Internet
PHONE 2
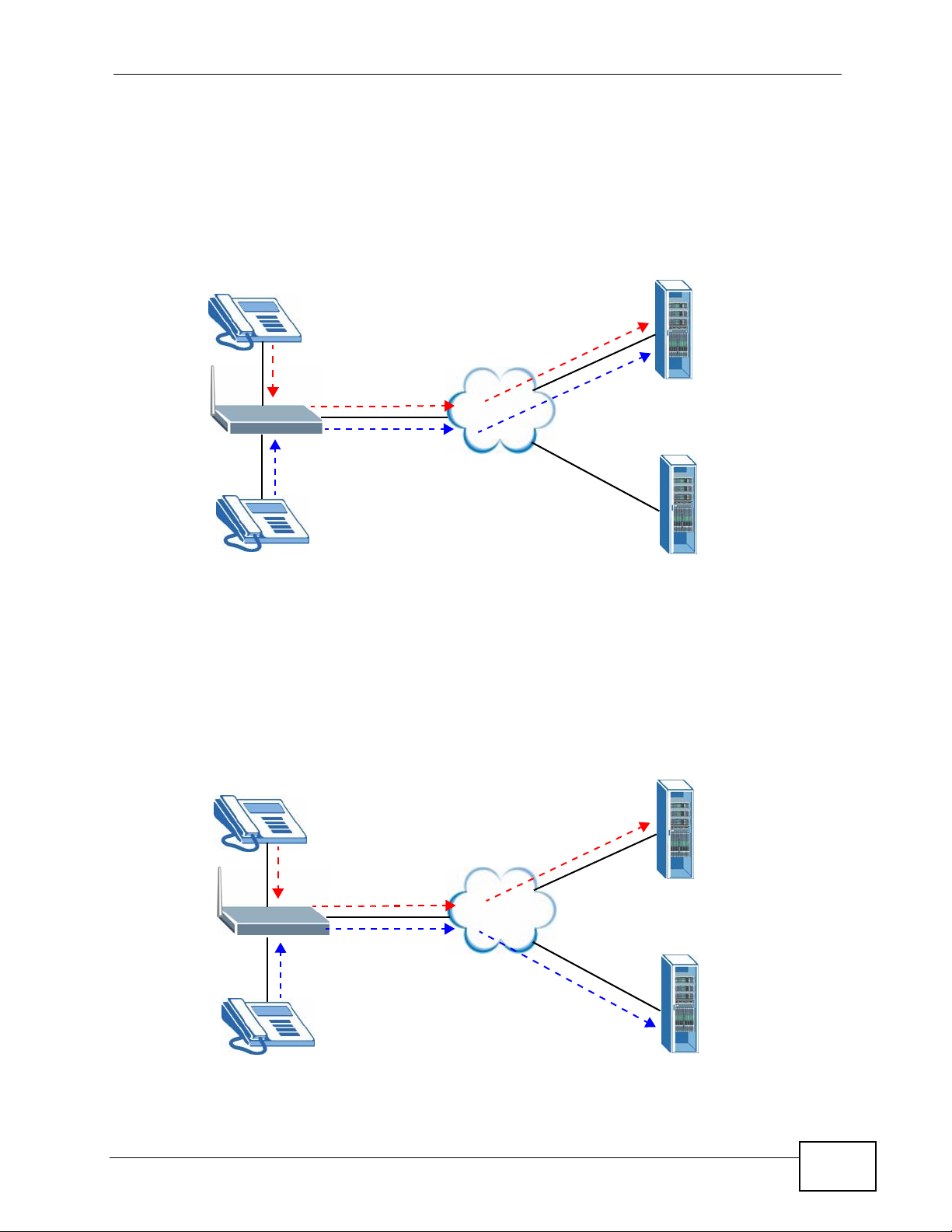
In the next example, phone port 1 is configured to use SIP account 1 and phone
port 2 is configured to use SIP account 2. In this case, every time you place a call
through phone port 1, you are using your SIP account 1. Similarly, every time you
place a call through phone port 2, you are using your SIP account 2. To apply
these configuration changes you need to configure the Analog Phone screen. See
Section 10.5 on page 190.
SIP 2
Figure 304 Outgoing Calls: Individual Configuration
PHONE 1
SIP 1
Internet
PHONE 2
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
SIP 2
467
Page 18
Chapter 29 Troubleshooting
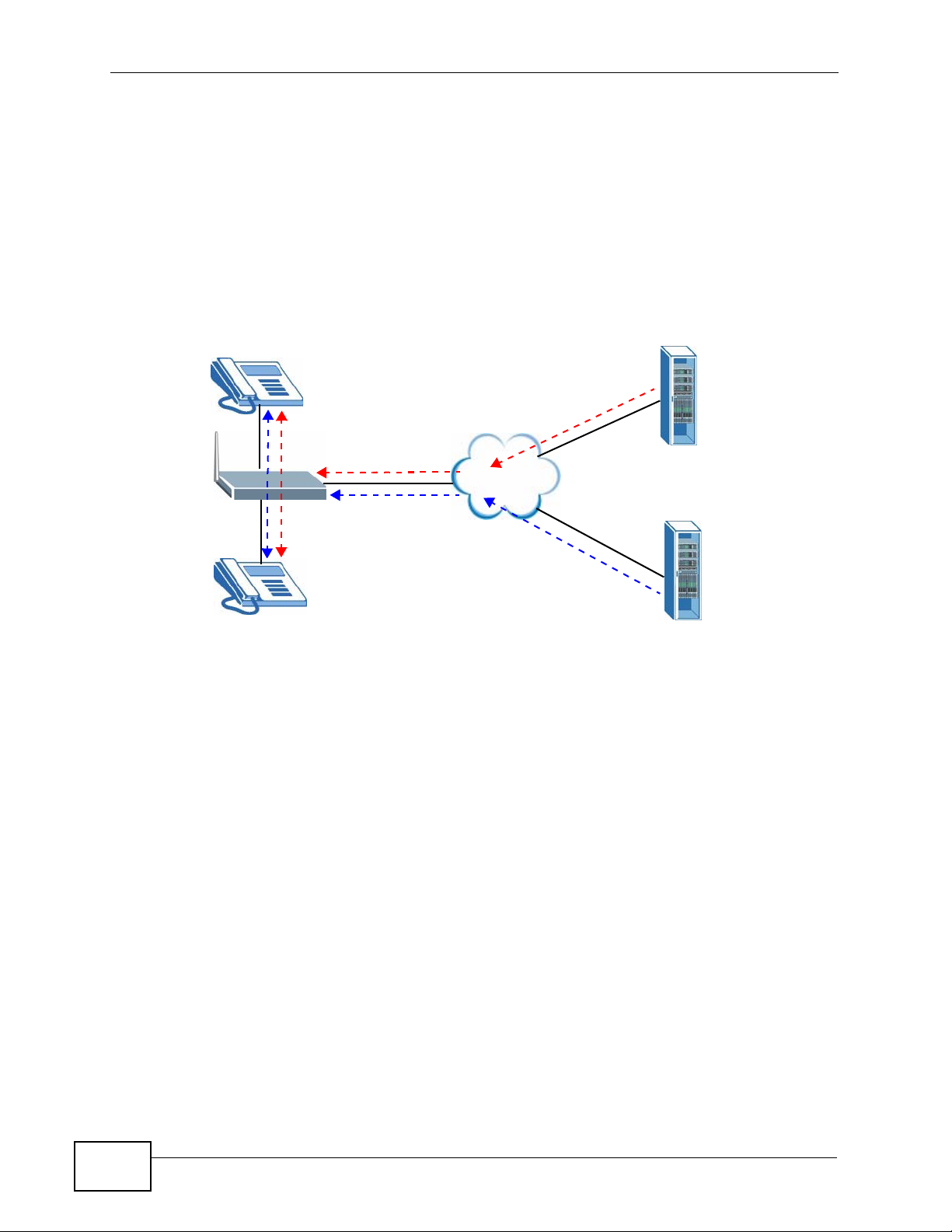
29.6.2 Incoming Calls
The following example shows the default behavior of your ZyXEL Device for
incoming calls when two SIP accounts are configured and you are using two
phones. When a call comes in from your SIP account 1, the phones connected to
both phone port 1 and phone port 2 ring. Similarly, when a call comes in from your
SIP account 2, the phones connected to both phone port 1 and phone port 2 ring.
In either case you are not sure which SIP account the call is coming from.
Figure 305 Incoming Calls: Default
PHONE 1
SIP 1
Internet
PHONE 2
In the next example, phone port 1 is configured to use SIP account 1 and phone
port 2 is configured to use SIP account 2 for incoming calls. In this case, every
time you receive a call from your SIP account 1, the phone connected to phone
port 1 rings. Similarly, every time you receive a call from your SIP account 2,
SIP 2
468
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 19
Chapter 29 Troubleshooting
phone port 2 rings. To apply these configuration changes you need to configure
the Analog Phone screen. See Section 10.5 on page 190.
Figure 306 Incoming Calls: Individual Configuration
PHONE 1
SIP 1
Internet
PHONE 2
29.7 USB Device Connection
The ZyXEL Device fails to detect my USB device.
1 Disconnect the USB device.
2 Reboot the ZyXEL Device.
3 If you are connecting a USB hard drive that comes with an external power supply,
make sure it is connected to an appropriate power source that is on.
4 Re-connect your USB device to the ZyXEL Device.
SIP 2
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
469
Page 20

Chapter 29 Troubleshooting
470
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 21

CHAPTER 30
Product Specifications
The following tables summarize the ZyXEL Device’s hardware and firmware
features.
Hardware Specifications
Table 166 Hardware Specifications
Dimensions (218 W) x (144 D) x (40 H) mm
Weight 460 g
Power Specification 18V 1A DC
Built-in Switch Four auto-negotiating, auto MDI/MDI-X 10/100 Mbps RJ-45
Ethernet ports
DSL Port One RJ11 DSL port
WAN Port One RJ45 WAN port
PHONE Ports 2 RJ-11 FXS POTS ports
RESET Button Restores factory defaults
WLAN Button 1 second: Turn on or off WLAN
USB Port One USB v2.0 port for file sharing or print server setup
Antenna One attached external dipole antenna, 2.9 dBi
Operation
Temperature
Storage Temperature -20º ~ 60º C
Operation Humidity 20% ~ 85% RH
Storage Humidity 20% ~ 90% RH
Distance between the
centers of the holes
(for wall-mounting)
on the device’s back
Screw size for wallmounting
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
5 seconds: Start WPS
0º C ~ 40º C
137.20mm
M4 tap
471
Page 22
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
Firmware Specifications
Table 167 Firmware Specifications
Default IP Address 192.168.1.1
Default Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 (24 bits)
Default User Name adminpldt
Default Password 1234567890
DHCP Server IP Pool Starting Address: 192.168.1.33
Size: 32
Static DHCP
Addresses
Content Filtering Web page blocking by URL keyword.
Static Routes 16
Device Management Use the web configurator to easily configure the rich range of
Wireless
Functionality
(wireless devices
only)
Firmware Upgrade Download new firmware (when available) from the Z yXEL web site
10
features on the ZyXEL Device.
Allow the IEEE 802.11b and/or IEEE 802.11g wireless clients to
connect to the ZyXEL Device wirelessly. Enable wireless security
(WEP, WPA(2), WPA(2)-PSK) and/or MAC filtering to protect your
wireless network.
and use the web configurator, an FTP or a TFTP tool to put it on
the ZyXEL Device.
Note: Only upload firmware for your specific model!
Configuration Backup
& Restoration
Network Address
Translation (NAT)
Port Forwarding If you have a server (mail or web server for example) on your
IEEE 802.1Q and
IEEE 802.1P
DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration
Protocol)
Make a copy of the ZyXEL Device’s configuration. You can put it
back on the ZyXEL Device later if you decide to revert back to an
earlier configuration.
Each computer on your network must have its own unique IP
address. Use NAT to convert your public IP address(es) to multiple
private IP addresses for the computers on your network.
network, you can use this feature to let people access it from the
Internet.
Use IEEE 802.1Q VLAN and IEEE 802.1P priority tags in
implementing QoS. Configure VLANs based on port, PVC, and
SSID. Specify a PVID to assign to untagged frames or prioritytagged frames received on this port, SSID, or PVC. Assign a
priority for the traffic transmitted through a port, SSID, or PVC.
Use this feature to have the ZyXEL Device assign IP addresses, an
IP default gateway and DNS servers to computers on your
network. Your device can also act as a surrogate DHCP server
(DHCP Relay) where it relays IP address assignment from the
actual real DHCP server to the clients.
472
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 23
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
Table 167 Firmware Specifications (continued)
Dynamic DNS
Support
IP Multicast IP multicast is used to send traffic to a specific group of
Time and Date Get the current time and date from an external server when you
Logs Use logs for troubleshooting. You can send logs from the ZyXEL
Universal Plug and
Play (UPnP)
Firewall Your device has a stateful inspection firewall with DoS (Denial of
Content Filtering Content filtering allows you to block access to Internet web sites
QoS (Quality of
Service)
Remote Management This allows you to decide whether a service (HT TP or FTP traffic for
Any IP The Any IP feature allows a computer to access the Internet and
PPPoE Support
(RFC2516)
IPSec VPN Capability Establish a Virtual Priv ate Network (VPN) to connect with business
With Dynamic DNS (Domain Name System) support, you can use
a fixed URL, www.zyxel.com for example, with a dynamic IP
address. You must register for this service with a Dynamic DNS
service provider.
computers. The ZyXEL Device supports versions 1 and 2 of IGMP
(Internet Group Management Protocol) used to join multicast
groups (see RFC 2236).
turn on your ZyXEL Device. You can also set the time manually.
These dates and times are then used in logs.
Device to an external syslog server.
A UPnP-enabled device can dynamically join a network, obtain an
IP address and convey its capabilities to other devices on the
network.
Service) protection. By default, when the firewall is activated, all
incoming traffic from the WAN to the LAN is blocked unless it is
initiated from the LAN. The firewall supports TCP/UDP inspection,
DoS detection and prevention, real time alerts, reports and logs.
that contain key words (that you specify) in the URL. You can also
schedule when to perform the filtering and give trusted LAN IP
addresses unfiltered Internet access.
You can efficiently manage traffic on your network by reserving
bandwidth and giving priority to certain types of traffic and/or to
particular computers.
example) from a computer on a network (LAN or WAN for
example) can access the ZyXEL Device.
the ZyXEL Device without changing the network settings (such as
IP address and subnet mask) of the computer, when the IP
addresses of the computer and the ZyXEL Device are not in the
same subnet.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) emulates a dial-up
connection. It allows your ISP to use their existing network
configuration with newer broadband technologies such as ADSL.
The PPPoE driver on your device is transparent to the computers
on the LAN, which see only Ethernet and are not aware of PPPoE
thus saving you from having to manage PPP oE clients on individual
computers.
partners and branch offices using data encryption and the Internet
to provide secure communications without the expense of leased
site-to-site lines. The ZyXEL Device VPN is based on the IPSec
standard and is interoperable with other IPSec-based VPN
products.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
The ZyXEL Device supports up to two simultaneous IPSec
connections.
473
Page 24
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
Table 167 Firmware Specifications (continued)
Other PPPoE Features PPPoE idle time out
Multiple PVC
(Permanent Virtual
Circuits) Support
IP Alias IP alias allows you to partition a physical network into logical
Packet Filters Your device’s packet filtering function allows added network
ADSL Standards Support ITU G.992.1 G.dmt
PPPoE dial on demand
Your device supports one Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs).
networks over the same Ethernet interface. Your device supports
three logical LAN interfaces via its single physical Ethernet
interface with the your device itself as the gateway for each LAN
network.
security and management.
EOC specified in ITU-T G.992.1
ADSL2 G.dmt.bis (G.992.3)
ADSL2 G.lite.bis (G.992.4)
ADSL 2/2+ AnnexM
ADSL2+ (G.992.5)
Reach-Extended ADSL (RE ADSL)
SRA (Seamless Rate Adaptation)
Auto-negotiating rate adaptation
ADSL physical connection AAL5 (ATM Adaptation Layer type 5)
Multi-protocol over AAL5 (RFC 2684/1483)
PPP over ATM AAL5 (RFC 2364)
PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516)
Multiple PPPoE
VC-based and LLC-based multiplexing
I.610 F4/F5 OAM
474
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 25
Table 167 Firmware Specifications (continued)
Other Protocol
Support
Management Embedded Web Configurator
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) link layer protocol
Transparent bridging for unsupported network layer protocols
RIP I/RIP II
ICMP
ATM QoS
SNMP v1 and v2c with MIB II support (RFC 1213)
IP Multicasting IGMP v1 and v2
IGMP Proxy
CLI (Command Line Interpreter)
SNMP v1 & v2c with MIB II
Embedded FTP/TFTP Server for firmware upgrade and
configuration file backup and restore
Telnet for remote management
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
Voice Specifications
Note: To take full advantage of the supplementary phone services available through
the ZyXEL Device's phone port, you may need to subscribe to the se rvices from
your VoIP service provider.
Note: Not all features are supported by all service providers. Consult your service
provider for more information.
Remote Management Control: Telnet, FTP, Web, SNMP and DNS.
Remote Firmware Upgrade
Syslog
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
475
Page 26
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
Table 168 Voice Features
Call Park and
Pickup
Call Return With call return, you can place a call to the last number that called
Country Code Phone standards and settings differ from one country to another, so
Do not Disturb
(DnD)
Auto Dial You can set the ZyXEL Device to automatically dial a specified number
Phone config The phone config table allows you to customize the phone keypad
HTTP pincode If your service provider uses an auto provisioning server , y ou need to
Firmware update
enable / disable
Call waiting This feature allows you to hear an alert when you are already using
Call park and pickup lets you put a call on hold (park) and then
continue the call (pickup). The caller must still pay while the call is
parked.
When you park the call, you enter a number of your choice (up to
eight digits), which you must enter again when you pick up the call. If
you do not enter the correct number, you cannot pickup the call. This
means that only someone who knows the number you have chosen
can pick up the call.
You can have more than one call on hold at the same time, but you
must give each call a different number.
you (either answered or missed). The last incoming call can be
through either SIP or PSTN.
the settings on your ZyXEL Device must be configured to match those
of the country you are in. The country code feature allows you to do
this by selecting the country from a list rather than changing each
setting manually . Configu re the country code feature when you move
the ZyXEL Device from one country to another.
This feature allows you to set your phone not to ring when someone
calls you. You can set each phone independently using its keypad, or
configure global settings for all phones using the command line
interpreter.
immediately whenever you lift a phone off the hook. Use the Web
Configurator to set the specified number. Use the command line
interpreter to have the ZyXEL Device wait a specified length of time
before dialing the number.
combinations you use to access certain features on the ZyXEL Device,
such as call waiting, call return, and call forward. The phone config
table is configurable in command interpreter mode.
enter a personal identification number (supplied by your service
provider) before you first use the feature.
If your service provider uses this feature, you hear a recorded
message when you pick up the phone when new firmware is available
for your ZyXEL Device . Enter *99# in your phone’s keypad to have
the ZyXEL Device upgrade the firmware, or enter #99# to not
upgrade. If your service provider gave you different numbers to use,
enter them instead. If you enter the code to not upgrade, you can
make a call as normal. You will hear the recording again each time
you pick up the phone, until you upgrade.
the phone and another person calls you. You can then either reject
the new incoming call, put your current call on hold and receive the
new incoming call, or end the current call and receive the new
incoming call.
476
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 27
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
Table 168 Voice Features
Call forwarding With this feature, you can set the ZyXEL Device to forward calls to a
specified number, either unconditionally (always), when your number
is busy, or when you do not answer. You can also forward incoming
calls from one specified number to another.
Caller ID The ZyXEL Device supports caller ID, which allows you to see the
originating number of an incoming call (on a phone with a suitable
display).
REN A Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) is used to determine the number
of devices (like telephones or fax machines) that may be connected
to the telephone line. Your device has a REN of three, so it can
support three devices per telephone port.
Dynamic Jitter
Buffer
Multiple SIP
Accounts
Multiple Voice
Channels
Voice Activity
Detection/Silence
Suppression
Comfort Noise
Generation
Echo Cancellation You device supports G.168, an ITU-T standard for eliminating the
QoS (Quality of
Service)
The built-in adaptive buffer helps to smooth out the variations in
delay (jitter) for voice traffic. This helps ensure good voice quality for
your conversations.
You can simultaneously use multiple voice (SIP) accounts and assign
them to the telephone port.
Your device can simultaneously handle multiple voice channels
(telephone calls). Additionally you can answer an incoming phone call
on a VoIP account, even wh ile someone else is using the account for a
phone call.
Voice Activity Detection (V AD) reduces the bandwidth that a call uses
by not transmitting when you are not speaking.
Your device generates background noise to fill moments of silence
when the other device in a call stops transmitting because the other
party is not speaking (as total silence could easily be mistaken for a
lost connection).
echo caused by the sound of your voice reverberating in the
telephone receiver while you talk.
Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms help to provide better service
on a per-flow basis. Your device supports Type of Service (ToS)
tagging and Differentiated Services (DiffServ) tagging. This allows
the device to tag voice frames so they can be prioritized over the
network.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
477
Page 28
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
Table 168 Voice Features
SIP ALG Your device is a SIP Application Layer Gateway (ALG). It allows VoIP
Other Voice
Features
calls to pass through NAT for devices behind it (such as a SIP-based
VoIP software application on a computer).
SIP version 2 (Session Initiatiion Protocol RFC 3261)
SDP (Session Description Protocol RFC 2327)
RTP (RFC 1889)
RTCP (RFC 1890)
Voice codecs (coder/decoders) G.711, G.729
Fax and data modem discrimination
DTMF Detection and Generation
DTMF: In-band and Out-band traffic (RFC 2833),(PCM), (SIP INFO)
Point-to-point call establishment between two IADs
Quick dialing through predefined phone book, which maps the phone
dialing number and destination URL.
Flexible Dial Plan (RFC3525 section 7.1.14)
Wireless Features
Table 169 Wireless Features
External Antenna The ZyXEL Device is equipped with an attached antenna to
Multiple SSID Multiple SSID allows the ZyXEL Device to operate up to 4
WDS WDS (Wireless Distribution System) lets the ZyXEL Device
Wireless LAN MAC Address
Filtering
WEP Encryption WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encrypts data frames before
Wi-Fi Protected Access Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i
WPA2 WPA 2 is a wireless security standard that defines stronger
provide a clear radio signal between the wireless stations and
the access points.
different wireless networks simultaneously, each with
independently configurable wireless and security settings.
act as a bridge with other ZyXEL access points.
Your device can check the MAC addresses of wireless stations
against a list of allowed or denied MAC addresses.
transmitting over the wireless network to help keep network
communications private.
security standard. Key differences between WPA and WEP
are user authentication and improved data encryption.
encryption, authentication and key management than WPA.
478
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 29
Table 169 Wireless Features
WPS Wi-Fi Protected Setup
Other Wireless Features IEEE 802.11g Compliance
Frequency Range: 2.4 GHz ISM Band
Advanced Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
(OFDM)
Data Rates: 54Mbps, 11Mbps, 5.5Mbps, 2Mbps, and 1 Mbps
Auto Fallback
T urn on-off WLAN by WLAN button (press the WLAN button
for one second to turn the WLAN on or turn off; five seconds
to turn on WPS)
IEEE 802.11i
IEEE 802.11e
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Data Encryption 64/128/256
bit.
WLAN bridge to LAN
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
Up to 32 MAC Address filters
IEEE 802.1x
External RADIUS server using EAP-MD5, TLS, TTLS
Scheduling lets you set when the WLAN is on.
The following list, which is not exhaustive, illustrates the standards supported in
the ZyXEL Device.
Table 170 Standards Supported
STANDARD DESCRIPTION
RFC 867 Daytime Protocol
RFC 868 Time Protocol.
RFC 1058 RIP-1 (Routing Information Protocol)
RFC 1112 IGMP v1
RFC 1157 SNMPv1: Simple Network Management Protocol version 1
RFC 1305 Network Time Protocol (NTP version 3)
RFC 1441 SNMPv2 Simple Network Management Protocol version 2
RFC 1483 Multiprotocol Encapsulation over ATM Adaptation Layer 5
RFC 1631 IP Network Address Translator (NAT)
RFC 1661 The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
RFC 1723 RIP-2 (Routing Information Protocol)
RFC 1901 SNMPv2c Simple Network Management Protocol version 2c
RFC 2236 Internet Group Management Protocol, Version 2.
RFC 2364 PPP over AAL5 (PPP over ATM over ADSL)
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
479
Page 30
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
Table 170 Standards Supported (continued)
STANDARD DESCRIPTION
RFC 2408 Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol
RFC 2516 A Me thod for Transmitting PPP Over Ethernet (PPPoE)
RFC 2684 Multiprotocol Enca psulation over ATM Adaptation Layer 5.
RFC 2766 Network A ddress Translation - Protocol
IEEE 802.11 Also known by the brand Wi-Fi, denotes a set of Wireless LAN/
IEEE 802.11b Uses the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band
IEEE 802.11g Uses the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band
IEEE 802.11d Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks: Media
IEEE 802.11x Port Based Network Access Control.
IEEE 802.11e QoS IEEE 802.11 e Wireless LAN for Quality of Service
ANSI T1.413, Issue 2 Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) standard.
G dmt(G.992.1) G.992.1 Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
ITU G.992.1 (G.DMT) ITU standard for ADSL using discrete multitone modulation.
ITU G.992.2 (G. Lite) ITU standard for ADSL using discrete multitone modulation.
ITU G.992.3
(G.dmt.bis)
ITU G.992.4
(G.lite.bis)
ITU G.992.5 (ADSL2+) ITU standard (also referred to as ADSL2+) that extends the
Microsoft PPTP MS PPTP (Microsoft's implementation of Point to Point Tunneling
RFC 2383 ST 2+ over ATM Protocol Specification - UNI 3.1 Version
TR-069 TR-069 DSL Forum Standard for CPE Wan Management.
1.363.5 Compli ant AAL5 SAR (Segmentation And Re-assembly)
(ISAKMP)
WLAN standards developed by working group 11 of the IEEE
LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802).
Access Control (MAC) Bridges
Transceivers
ITU standard (also referred to as ADSL2) that extends the
capability of basic ADSL in data rates.
ITU standard (also referred to as ADSL2) that extends the
capability of basic ADSL in data rates.
capability of basic ADSL by doubling the number of downstream
bits.
Protocol)
Power Adaptor Specifications
Table 171 Power Adaptor Specifications
NORTH AMERICAN PLUG
STANDARDS
AC Power Adapter Model MT18-Y180100-A1
Input Power 120V~60Hz 0.5A
480
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 31

Table 171 Power Adaptor Specifications (continued)
EUROPEAN PLUG
STANDARDS
AC Power Adapter Model MV18-Y180100-C5
Input Power 230V~50Hz 0.5A
UNITED KINGDOM PLUG
STANDARDS
AC Power Adapter Model MV18-Y180100-B2
Input Power 230V~50Hz 0.5A
Wall-mounting Instructions
Do the following to hang your ZyXEL Device on a wall.
Note: See Table 166 on page 471 for the size of screws to use and how far apart to
place them.
Chapter 30 Product Specifications
1 Locate a high position on a wall that is free of obstructions. Use a sturdy wall.
2 Drill two holes for the screws. Make sure the distance between the centers of the
holes matches what is listed in the product specifications appendix.
Be careful to avoid damaging pipes or cables located inside the
wall when drilling holes for the screws.
3 Do not screw the screws all the way into the wall. Leave a small gap of about 0.5
cm between the heads of the screws and the wall.
4 Make sure the screws are snugly fastened to the wall. They need to hold the
weight of the ZyXEL Device with the connection cables.
5 Align the holes on the back of the ZyXEL Device with the screws on the wall. Hang
the ZyXEL Device on the screws.
Figure 307 Wall-mounting Example
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
481
Page 32

Chapter 30 Product Specifications
The following are dimensions of an M4 tap screw and masonry plug used for wall
mounting. All measurements are in millimeters (mm).
Figure 308 Masonry Plug and M4 Tap Screw
482
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 33

PART IV
Appendices and
Index
Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
(485)
Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java
Permissions (511)
IP Addresses and Subnetting (521)
Wireless LANs (533)
Common Services (557)
Legal Information (561)
Index (565)
483
Page 34

484
Page 35

APPENDIX A
Setting Up Your Computer’s IP
Address
Note: Your specific ZyXEL Device may not support all of the operating systems
described in this appendix. See the product specifications for more information
about which operating systems are supported.
This appendix shows you how to configure the IP settings on your computer in
order for it to be able to communicate with the other devices on your network.
Windows Vista/XP/2000, Mac OS 9/OS X, and all versions of UNIX/LINUX include
the software components you need to use TC P/IP on your computer.
If you manually assign IP information instead of using a dynamic IP, make sure
that your network’s computers have IP addresses that place them in the same
subnet.
In this appendix, you can set up an IP address for:
• Windows XP/NT/2000 on page 485
• Windows Vista on page 489
• Mac OS X: 10.3 and 10.4 on page 493
• Mac OS X: 10.5 on page 497
• Linux: Ubuntu 8 (GNOME) on page 500
• Linux: openSUSE 10.3 (KDE) on page 505
Windows XP/NT/2000
The following example uses the default Windows XP display theme but can also
apply to Windows 2000 and Windows NT.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
485
Page 36

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
1 Click Start > Control Panel.
Figure 309 Windows XP: Start Menu
2 In the Control Panel, click the Network Connections icon.
Figure 310 Windows XP: Control Panel
486
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 37

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
3 Right-click Local Area Connection and then select Properties.
Figure 311 Windows XP: Control Panel > Network Connections > Properties
4 On the General tab, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then click
Properties.
Figure 312 Windows XP: Local Area Connection Properties
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
487
Page 38

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
5 The Internet Protocol TCP/IP Properties window opens.
Figure 313 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
6 Select Obtain an IP addr ess automatically if your network administr ator or ISP
assigns your IP address dynamically.
Select Use the following IP Address and fill in the IP address, Subnet mask,
and Default gateway fields if you have a static IP address that was assigned to
you by your network administrator or ISP. Y ou may also have to enter a Preferred
DNS server and an Alternate DNS server, if that information was provided.
7 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
8 Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
488
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 39

2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER].
You can also go to Start > Control Panel > Network Connections, right-click a
network connection, click Status and then click the Support tab to view your IP
address and connection information.
Windows Vista
This section shows screens from Windows Vista Professional.
1 Click Start > Control Panel.
Figure 314 Windows Vista: Start Menu
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
2 In the Control Panel, click the Network and Internet icon.
Figure 315 Windows Vista: Control Panel
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
489
Page 40

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
3 Click the Network and Sharing Center icon.
Figure 316 Windows Vista: Network And Internet
4 Click Manage network connections.
Figure 317 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
5 Right-click Local Area Connection and then select Properties.
Figure 318 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
Note: During this procedure, click Continue whenever Windows displays a screen
saying that it needs your permission to continue.
490
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 41

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
6 Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then select Properties.
Figure 319 Windows Vista: Local Area Connection Properties
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
491
Page 42

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
7 The Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window opens.
Figure 320 Windows Vista: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
8 Select Obtain an IP addr ess automatically if your network administr ator or ISP
assigns your IP address dynamically.
Select Use the following IP Address and fill in the IP address, Subnet mask,
and Default gateway fields if you have a static IP address that was assigned to
you by your network administrator or ISP. Y ou may also have to enter a Preferred
DNS server and an Alternate DNS server, if that information was
provided.Click Advanced.
9 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
10 Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
492
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 43

2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER].
You can also go to Start > Control Panel > Network Connections, right-click a
network connection, click Status and then click the Support tab to view your IP
address and connection information.
Mac OS X: 10.3 and 10.4
The screens in this section are from Mac OS X 10.4 but can also apply to 10.3.
1 Click Apple > System Preferences.
Figure 321 Mac OS X 10.4: Apple Menu
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
493
Page 44

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
2 In the System Preferences window, click the Network icon.
Figure 322 Mac OS X 10.4: System Preferences
3 When the Network preferences pane opens, select Built-in Ethernet from the
network connection type list, and then click Configure.
Figure 323 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences
494
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 45

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
4 For dynamically assigned settings, select Using DHCP from the Configure IPv4
list in the TCP/IP tab.
Figure 324 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences > TCP/IP Tab.
5 For statically assigned settings, do the following:
•From the Configure IPv4 list, select Manually.
•In the IP Address field, type your IP address.
•In the Subnet Mask field, type your subnet mask.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
495
Page 46

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
•In the Router field, type the IP address of your device.
Figure 325 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Preferences > Ethernet
6 Click Apply Now and close the window.
Verifying Settings
Check your TCP/IP properties by clicking Applications > Utilities > Network
Utilities, and then selecting the appropriate Network Interface from the Info
tab.
Figure 326 Mac OS X 10.4: Network Utility
496
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 47

Mac OS X: 10.5
The screens in this section are from Mac OS X 10.5.
1 Click Apple > System Preferences.
Figure 327 Mac OS X 10.5: Apple Menu
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
2 In System Preferences, click the Network icon.
Figure 328 Mac OS X 10.5: Systems Preferences
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
497
Page 48

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
3 When the Network preferences pane opens, select Ethernet from the list of
available connection types.
Figure 329 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Preferences > Ethernet
498
4 From the Configure list, select Using DHCP for dynamically assigned settings.
5 For statically assigned settings, do the following:
•From the Configure list, select Manually.
•In the IP Address field, enter your IP address.
•In the Subnet Mask field, enter your subnet mask.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 49

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
•In the Router field, enter the IP address of your Zy XEL Device.
Figure 330 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Preferences > Ethernet
6 Click Apply and close the wind ow.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
499
Page 50

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
Verifying Settings
Check your TCP/IP properties by clicking Applications > Utilities > Network
Utilities, and then selecting the appropriate Network interface from the Info
tab.
Figure 331 Mac OS X 10.5: Network Utility
Linux: Ubuntu 8 (GNOME)
This section shows you how to configure your computer’s TCP/IP settings in the
GNU Object Model Environment (GNOME) using the Ubuntu 8 Linux distribution.
The procedure, screens and file locations may vary depending on your specific
distribution, release version, and individual configuration. The following screens
use the default Ubuntu 8 installation.
Note: Make sure you are logged in as the root administrator.
Follow the steps below to configure your computer IP address in GNOME:
500
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 51

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
1 Click System > Administration > Network.
Figure 332 Ubuntu 8: System > Administration Menu
2 When the Network Settings window opens, click Unlock to open the
Authenticate window. (By default, the Unlock button is greyed out until clicked.)
You cannot make changes to your configuration unless you first enter your admin
password.
Figure 333 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Connections
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
501
Page 52

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
3 In the Authenticate window, enter y our admin account name and password t hen
click the Authenticate button.
Figure 334 Ubuntu 8: Administrator Account Authentication
4 In the Network Settings window, select the connection that you want to
configure, then click Properties.
Figure 335 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Connections
502
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 53

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
5 The Properties dialog box opens.
Figure 336 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > Properties
•In the Configuration list, select Automatic Configuration (DHCP) if you
have a dynamic IP address.
•In the Configuration list, select Static IP address if you have a static IP
address. Fill in the IP address, Subnet mask, and Gateway address fields.
6 Click OK to save the changes and close the Properties dialog box and return to
the Network Settings screen.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
503
Page 54

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
7 If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click the DNS tab in the Network
Settings window and then enter the DNS server information in the fields
provided.
Figure 337 Ubuntu 8: Network Settings > DNS
8 Click the Close button to apply the changes.
Verifying Settings
Check your TCP/IP properties by clicking System > Administration > Network
Tools, and then selecting the appropriate Network device from the Devices
504
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 55

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
tab. The Interface Statistics column shows data if your connection is working
properly.
Figure 338 Ubuntu 8: Network Tools
Linux: openSUSE 10.3 (KDE)
This section shows you how to configure your computer’s TCP/IP settings in the K
Desktop Environment (KDE) using the openSUSE 10.3 Linux distribution. The
procedure, screens and file locations may vary depending on your specific
distribution, release version, and individual configuration. The following screens
use the default openSUSE 10.3 installation.
Note: Make sure you are logged in as the root administrator.
Follow the steps below to configure your computer IP address in the KDE:
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
505
Page 56

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
1 Click K Menu > Computer > Administrator Settings (YaST).
Figure 339 openSUSE 10.3: K Menu > Computer Menu
2 When the Run as Root - KDE su dialog opens, enter the admin password and
click OK.
Figure 340 openSUSE 10.3: K Menu > Computer Menu
506
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 57

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
3 When the YaST Control Center window opens, select Network Devices and
then click the Network Card icon.
Figure 341 openSUSE 10.3: YaST Control Center
4 When the Network Settings window opens, click the Overview tab, select the
appropriate connection Name from the list, and then click the Configure button.
Figure 342 openSUSE 10.3: Network Settings
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
507
Page 58

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
5 When the Network Card Setup window opens, click the Address tab
Figure 343 openSUSE 10.3: Network Card Setup
6 Select Dynamic Address (DHCP) if you have a dynamic IP address.
Select Statically assigned IP Address if you have a static IP address. Fill in the
IP address, Subnet mask, and Hostname fields.
7 Click Next to save the changes and close the Network Card Setup window.
508
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 59

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
8 If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click the Hostname/DNS tab in
Network Settings and then enter the DNS server information in the fields
provided.
Figure 344 openSUSE 10.3: Network Settings
9 Click Finish to save your settings and close the window.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
509
Page 60

Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
Verifying Settings
Click the KNetwork Manager icon on the Task bar to check your TCP/IP
properties. From the Options sub-menu, select Show Connection Information.
Figure 345 openSUSE 10.3: KNetwork Manager
When the Connection Status - KNetwork Manager window opens, click the
Statistics tab to see if your connection is working properly.
Figure 346 openSUSE: Connection Status - KNetwork Manager
510
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 61

APPENDIX B
Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts
and Java Permissions
In order to use the web configurator you need to allow:
• Web browser pop-up windows from your device.
• JavaScripts (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
Note: Internet Explorer 6 screens are used here. Screens for other Internet Explorer
versions may vary.
Internet Explorer Pop-up Blockers
You may have to disable pop-up blocking to log into your device.
Either disable pop-up blocking (enabled by default in Windows XP SP (Service
Pack) 2) or allow pop-up blocking and create an exception for your device’s IP
address.
Disable Pop-up Blockers
1 In Internet Explorer, select Tools, Pop-up Blocker and then select Turn Off
Pop-up Blocker.
Figure 347 Pop-up Blocker
You can also check if pop-up blocking is disabl ed in the Pop-up Blocker section in
the Privacy tab.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
511
Page 62

Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
1 In Internet Explorer, select Tools, Internet Options, Privacy.
2 Clear the Block pop-ups check box in the Pop-up Blocker section of the screen.
This disables any web pop-up blockers you may have enabled.
Figure 348 Internet Options: Privacy
3 Click Apply to save this setting.
Enable Pop-up Blockers with Exceptions
Alternatively, if you only want to allow pop-up windows from your device, see the
following steps.
1 In Internet Explorer, select Tools, Internet Options and then the Privacy tab.
512
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 63

Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
2 Select Settings…to open the Pop-up Blocker Settings screen.
Figure 349 Internet Options: Privacy
3 Type the IP address of your device (the web page that you do not want to have
blocked) with the prefix “http://”. For example, http://192.168.167.1.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
513
Page 64

Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
4 Click Add to move the IP address to the list of Allowed sites.
Figure 350 Pop-up Blocker Settings
5 Click Close to return to the Privacy screen.
6 Click Apply to save this setting.
JavaScripts
If pages of the web configurator do not display properly in Internet Explorer, check
that JavaScripts are allowed.
514
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 65

Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
1 In Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options and then the Security tab.
Figure 351 Internet Options: Security
2 Click the Custom Level... button.
3 Scroll down to Scripting.
4 Under Active scripting make sure that Enable is selected (the default).
5 Under Scripting of Java applets make sure that Enable is selected (the
default).
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
515
Page 66

Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
6 Click OK to close the window.
Figure 352 Security Settings - Java Scripting
Java Permissions
1 From Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options and then the Security
tab.
2 Click the Custom Level... button.
3 Scroll down to Microsoft VM.
4 Under Java permissions make sure that a safety level is selected.
516
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 67

Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
5 Click OK to close the window.
Figure 353 Security Settings - Java
JAVA (Sun)
1 From Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options and then the Advanced
tab.
2 Make sure that Use Java 2 for <applet> under Java (Sun) is selected.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
517
Page 68

Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
3 Click OK to close the window.
Figure 354 Java (Sun)
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox 2.0 screens are used here. Scre ens fo r other versions may vary.
You can enable Java, Javascripts and pop-ups in one screen. Click Tools, then
click Options in the screen that appears.
Figure 355 Mozilla Firefox: Tools > Options
518
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 69

Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
Click Content.to show the screen below. Select the check boxes as shown in the
following screen.
Figure 356 Mozilla Firefox Content Security
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
519
Page 70

Appendix B Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions
520
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 71

APPENDIX C
IP Addresses and Subnetting
This appendix introduces IP addresses and subnet masks.
IP addresses identify individual devices on a network. Every networking device
(such as computers, servers, routers, and printers) needs an IP address to
communicate across the network. These networking devices are also known as
hosts.
Subnet masks determine the maximum number of possible hosts on a network.
You can also use subnet masks to divide one network into multiple sub-networks.
Introduction to IP Addresses
One part of the IP address is the network number, and the other part is the host
ID. In the same way that houses on a street share a common street name, the
hosts on a network share a common network number. Similarly, as each house
has its own house number, each host on the network has its own unique
identifying number - the hos t ID. R outers use the network nu mber to send packets
to the correct network, while the host ID determines to which host on the network
the packets are delivered.
Structure
An IP address is made up of four parts, w rit ten in dotted decimal notation (f or
example, 192.168.1.1). Each of these four parts is known as an octet. An octet is
an eight-digit binary number (for example 11000000, which is 192 in decimal
notation).
Therefore, each octet has a possible range of 00000000 to 1111111 1 in binary, or
0 to 255 in decimal.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
521
Page 72

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
The following figure shows an example IP address in which the first three octets
(192.168.1) are the network number, and the fourth octet (16) is the host ID.
Figure 357 Network Number and Host ID
How much of the IP address is the network number and how much is the host ID
varies according to the subnet mask.
Subnet Masks
A subnet mask is used to determine which bits are part of the network number,
and which bits are part of the host ID (using a logical AND operation). The term
“subnet” is short for “sub-network”.
A subnet mask has 32 bits. If a bit in the subnet mask is a “1” then the
corresponding bit in the IP address is part of the network number. If a bit in the
subnet mask is “0” then the corresponding bit in the IP address is part of the host
ID.
The following example shows a subnet mask identifying the network number (in
bold text) and host ID of an IP address (192.168.1.2 in decimal).
Table 172 IP Address Network Number and Host ID Example
1ST
OCTET:
2ND
OCTET:
3RD
OCTET:
4TH
OCTET
522
(192)
IP Address (Binary) 11000000 10101000 00000001 00000010
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000
Network Number 11000000 10101000 00000001
Host ID 00000010
(168)
(1)
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
(2)
Page 73

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
By convention, subnet masks always consist of a continuous sequence of ones
beginning from the leftmost bit of the mask, followed by a continuous sequence of
zeros, for a total number of 32 bits.
Subnet masks can be referred to by the size of the network number part (the bits
with a “1” value). For example, an “8-bit mask” means that the first 8 bits of the
mask are ones and the remaining 24 bits are zeroes.
Subnet masks are expressed in dotted decimal notation just like IP addresses. The
following examples show the binary and decimal notation for 8-bit, 16-bit, 24-bit
and 29-bit subnet masks.
Table 173 Subnet Masks
BINARY
1ST
OCTET
8-bit mask 11111111 00000000 00000000 00000000 255.0.0.0
16-bit mask 11111111 11111111 00000000 00000000 255.255.0.0
24-bit mask 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000 255.255.255.0
29-bit mask 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111000 255.255.255.248
2ND
OCTET
3RD
OCTET
4TH
OCTET
DECIMAL
Network Size
The size of the network number determines the maximum number of possible
hosts you can have on your network. The larger the number of network number
bits, the smaller the number of remaining host ID bits.
An IP address with host IDs of all zeros is the IP address of the network
(192.168.1.0 with a 24-bit subnet mask, for example). An IP address with host
IDs of all ones is the broadcast address for that network (192.168.1.255 with a
24-bit subnet mask, for example).
As these two IP addresses cannot be used for individual hosts, calculate the
maximum number of possible hosts in a network as follows:
Table 174 Maximum Host N um bers
SUBNET MASK HOST ID SIZE
8 bits 255.0.0.0 24 bits 224 – 2 16777214
16 bits 255.255.0.0 16 bits 2
24 bits 255.255.255.0 8 bits 2
29 bits 255.255.255.248 3 bits 2
MAXIMUM NUMBER OF
HOSTS
16
– 2 65534
8
– 2 254
3
– 2 6
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
523
Page 74

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
Notation
Since the mask is always a continuous number of ones beginning from the left,
followed by a continuous number of zeros for the remainder of the 32 bit mask,
you can simply specify the number of ones instead of writing the value of each
octet. This is usually spec if i e d by wri t ing a “/” followed by the number of bits in
the mask after the address.
For example, 192.1.1.0 /25 is equivalent to saying 192.1.1.0 with subnet mask
255.255.255.128.
The following table shows some possible subnet masks using both notations.
Table 175 Alternative Subnet Mask Notation
SUBNET MASK
255.255.255.0 /24 0000 0000 0
255.255.255.128 /25 1000 0000 128
255.255.255.192 /26 1100 0000 192
255.255.255.224 /27 1110 0000 224
255.255.255.240 /28 1111 0000 240
255.255.255.248 /29 1111 1000 248
255.255.255.252 /30 1111 1100 252
ALTERNATIVE
NOTATION
LAST OCTET
(BINARY)
LAST OCTET
(DECIMAL)
Subnetting
You can use subnetting to divide one network into multiple sub-networks. In the
following example a network administrator creates two sub-networks to isolate a
group of servers from the rest of the company network for security reasons.
In this example, the company network address is 192.168.1.0. The first three
octets of the address (192.168.1) are the network number, and the remaining
octet is the host ID, allowing a maximum of 2
8
– 2 or 254 possible hosts.
524
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 75

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
The following figure shows the company network before subnetting.
Figure 358 Subnetting Example: Before Subnetting
You can “borrow” one of the host ID bits to divide the network 192.168.1.0 into
two separate sub-networks. The subnet mask is now 25 bits (255.255.255.128 or
/25).
The “borrowed” host ID bit can have a value of either 0 or 1, allowing two
subnets; 192.168.1.0 /25 and 192.168.1.128 /25.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
525
Page 76

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
The following figure shows the company network after subnetting. There are now
two sub-networks, A and B.
Figure 359 Subnetting Example: After Subnetting
In a 25-bit subnet the host ID has 7 bits, so each sub-network has a maximum of
7
2
– 2 or 126 possible hosts (a host ID of all zeroes is the subnet’s address itself,
all ones is the subnet’s broadcast address).
192.168.1.0 with mask 255.255.255.128 is subnet A itself, and 192.168.1.127
with mask 255.255.255.128 is its broadcast address. Therefore, the lowest IP
address that can be assigned to an actual host for subnet A is 192.168.1.1 and
the highest is 192.168.1.126.
Similarly, the host ID range for subnet B is 192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.254.
Example: Four Subnets
The previous example illustrated using a 25-bit subnet mask to divide a 24-bit
address into two subnets. Similarly, to divide a 24-bit address into four subnets,
you need to “borrow” two host ID bits to give four possible combinations (00, 01,
10 and 11). The subnet mask is 26 bits
(11111111.11111111.11111111.11000000) or 255.255.255.192.
526
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 77

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
Each subnet contains 6 host ID bits, giving 26 - 2 or 62 hosts for each subnet (a
host ID of all zeroes is the subnet itself, all ones is the subnet’s broadcast
address).
Table 176 Subnet 1
IP/SUBNET MASK NETWORK NUMBER
IP Address (Decimal) 192.168.1. 0
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001. 00000000
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111. 11000000
Subnet Address:
192.168.1.0
Broadcast Address:
192.168.1.63
Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.1
Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.62
LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
Table 177 Subnet 2
IP/SUBNET MASK NETWORK NUMBER
IP Address 192.168.1. 64
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001. 01000000
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111. 11000000
Subnet Address:
192.168.1.64
Broadcast Address:
192.168.1.127
Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.65
Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.126
LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
Table 178 Subnet 3
IP/SUBNET MASK NETWORK NUMBER
IP Address 192.168.1. 128
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001. 10000000
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111. 11000000
Subnet Address:
192.168.1.128
Broadcast Address:
192.168.1.191
Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.129
Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.190
LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
Table 179 Subnet 4
IP/SUBNET MASK NETWORK NUMBER
IP Address 192.168.1. 192
IP Address (Binary) 11000000.10101000.00000001. 11000000
Subnet Mask (Binary) 11111111.11111111.11111111. 11000000
Subnet Address:
192.168.1.192
Broadcast Address:
192.168.1.255
Lowest Host ID: 192.168.1.193
Highest Host ID: 192.168.1.254
LAST OCTET BIT
VALUE
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
527
Page 78

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
Example: Eight Subnets
Similarly, use a 27-bit mask to create eight subnets (000, 001, 010, 011, 100,
101, 110 and 111).
The following table shows IP address last octet values for each subnet.
Table 180 Eight Subnets
SUBNET
1 0 1 30 31
2 32 33 62 63
3 64 65 94 95
4 96 97 126 127
5 128 129 158 159
6 160 161 190 191
7 192 193 222 223
8 224 225 254 255
SUBNET
ADDRESS
FIRST ADDRESS
LAST
ADDRESS
BROADCAST
ADDRESS
Subnet Planning
The following table is a summary for subnet planning on a network with a 24-bit
network number.
Table 181 24-bit Network Number Subnet Planning
NO. “BORROWED”
HOST BITS
1 255.255.255.128 (/25) 2 126
2 255.255.255.192 (/26) 4 62
3 255.255.255.224 (/27) 8 30
4 255.255.255.240 (/28) 16 14
5 255.255.255.248 (/29) 32 6
6 255.255.255.252 (/30) 64 2
7 255.255.255.254 (/31) 128 1
The following table is a summary for subnet planning on a network with a 16-bit
network number.
Table 182 16-bit Network Number Subnet Planning
NO. “BORROWED”
HOST BITS
1 255.255.128.0 (/17) 2 32766
2 255.255.192.0 (/18) 4 16382
SUBNET MASK NO. SUBNETS
SUBNET MASK NO. SUBNETS
NO. HOSTS PER
SUBNET
NO. HOSTS PER
SUBNET
528
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 79

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
Table 182 16-bit Network Number Subnet Planning (continued)
NO. “BORROWED”
HOST BITS
3 255.255.224.0 (/19) 8 8190
4 255.255.240.0 (/20) 16 4094
5 255.255.248.0 (/21) 32 2046
6 255.255.252.0 (/22) 64 1022
7 255.255.254.0 (/23) 128 510
8 255.255.255.0 (/24) 256 254
9 255.255.255.128 (/25) 512 126
10 255.255.255.192 (/26) 1024 62
11 255.255.255.224 (/27) 2048 30
12 255.255.255.240 (/28) 4096 14
13 255.255.255.248 (/29) 8192 6
14 255.255.255.252 (/30) 16384 2
15 255.255.255.254 (/31) 32768 1
SUBNET MASK NO. SUBNETS
NO. HOSTS PER
SUBNET
Configuring IP Addresses
Where you obtain your network number depends on your particular situation. If
the ISP or your network administrator assigns you a block of registered IP
addresses, follow their instructions in selecting the IP addresses and the subnet
mask.
If the ISP did not explicitly give you an IP network number, then most likely you
have a single user account and the ISP will assign you a dynamic IP address when
the connection is established. If this is the case, it is recommended that you select
a network number from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.0. The Internet Assigned
Number Authority (IANA) reserved this block of addresses specifically for private
use; please do not use any other number unless you are told otherwise. Y ou must
also enable Network Address Translation (NAT) on the ZyXEL Device.
Once you have decided on the network number, pick an IP address for your ZyXEL
Device that is easy to remember (for instance, 192.168.1.1) but make sure that
no other device on your network is using that IP address.
The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your
ZyXEL Device will compute the subnet mask automatically based on the IP
address that you entered. Y ou don't need to change the subnet mask computed by
the ZyXEL Device unless you are instructed to do otherwise.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
529
Page 80

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
Private IP Addresses
Every machine on the Internet must have a unique address. If your networks are
isolated from the Internet (running only between two branch offices, for example)
you can assign any IP addresses to the hosts without problems. However, the
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three
blocks of IP addresses specifically for private networks:
• 10.0.0.0 — 10.255.255.255
• 172.16.0.0 — 172.31.255.255
• 192.168.0.0 — 192.168.255.255
You can obtain your IP address from the IANA, from an ISP, or it can be assigned
from a private network. If you belong to a small organization and your Internet
access is through an ISP, the ISP can provide you with the Internet addresses for
your local networks. On the other hand, if you are part of a much larger
organization, you should consult your network administrator for the appropriate IP
addresses.
Regardless of your particular situation, do not create an arbitrary IP address;
always follow the guidelines above. For more information on address assignment,
please refer to RFC 1597, Address Allocation for Private Internets and RFC 1466,
Guidelines for Management of IP Address Space.
IP Address Conflicts
Each device on a network must have a unique IP address. Devices with duplicate
IP addresses on the same network will not be able to access the Internet or other
resources. The devices may also be unreachable through the network.
Conflicting Computer IP Addresses Example
More than one device can not use the same IP address. In the following example
computer A has a static (or fixed) IP address that is the same as the IP address
that a DHCP server assigns to computer B which is a DHCP client. Neither can
access the Internet. This problem can be solved by assigning a different static IP
530
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 81

address to computer A or setting computer A to obtain an IP address
automatically.
Figure 360 Conflicting Computer IP Ad dresses Example
Conflicting Router IP Addresses Example
Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
Since a router connects different networks, it must have interfaces using different
network numbers. For example, if a router is set between a LAN and the Internet
(WAN), the router’ s LAN and WAN addresses must be on different subnets. In the
following example, the LAN and WAN are on the same subnet. The LAN computers
cannot access the Internet because the router cannot route between networks.
Figure 361 Conflicting Computer IP Ad dresses Example
Conflicting Computer and Router IP Addresses Example
More than one device can not use the same IP address. In the following example,
the computer and the router’s LAN port both use 192.168.1.1 as the IP address.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
531
Page 82

Appendix C IP Addresses and Subnetting
The computer cannot access the Internet. This problem can be solved by
assigning a different IP address to the computer or the router’s LAN port.
Figure 362 Conflicting Computer and Router IP Addresses Example
532
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 83

APPENDIX D
Wireless LANs
Wireless LAN Topologies
This section discusses ad-hoc and infrastructure wireless LAN topologies.
Ad-hoc Wireless LAN Configuration
The simplest WLAN configuration is an independent (Ad-hoc) WLAN that connects
a set of computers with wireless adapters (A, B, C) . Any time two or more wireless
adapters are within range of each other, they can set up an independent network,
which is commonly referred to as an ad-hoc network or Independent Basic Service
Set (IBSS). The following diagram shows an example of notebook computers
using wireless adapters to form an ad-hoc wireless LAN.
BSS
Figure 363 Peer-to-Peer Communication in an Ad-hoc Network
A Basic Service Set (BSS) exists when all communications between wireless
clients or between a wireless client and a wired network client go through one
access point (AP).
Intra-BSS traffic is traffic between wireless clients in the BSS. When Intra-BSS is
enabled, wireless client A and B can access the wired network and communicate
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
533
Page 84

Appendix D Wireless LANs
with each other. When Intra-BSS is disabled, wireless client A and B can still
access the wired network but cannot communicate with each other.
Figure 364 Basic Service Set
ESS
An Extended Service Set (ESS) consists of a series of overlapping BSSs, each
containing an access point, with each access point connected together by a wired
network. This wired connection between APs is called a Distribution S ystem (DS).
This type of wireless LAN topology is called an Infrastructure WLAN. The Access
Points not only provide communication with the wired network but also mediate
wireless network traffic in the immediate neighborhood.
534
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 85

Appendix D Wireless LANs
An ESSID (ESS IDentification) uniquely identifies each ESS. All access points and
their associated wireless clients within the same ESS must have the same ESSID
in order to communicate.
Figure 365 Infrastructure WLAN
Channel
A channel is the radio frequency(ies) used by wireless devices to transmit and
receive data. Channels available depend on your geogr aphical area. You may have
a choice of channels (for your region) so you should use a channel different from
an adjacent AP (access point) to reduce interference. Interference occurs when
radio signals from different access points overlap causing interference and
degrading performance.
Adjacent channels partially overlap however. T o avoid interference due to overlap,
your AP should be on a channel at least five channels away from a channel that an
adjacent AP is using. For example, if yo ur region has 11 channels and an adjacent
AP is using channel 1, then you need to select a channel between 6 or 11.
RTS/CTS
A hidden node occurs when two stations are within range of the same access
point, but are not within range of each other. The following figure illustrates a
hidden node. Both stations (STA) are within range of the access point (AP) or
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
535
Page 86

Appendix D Wireless LANs
wireless gateway, but out-of-range of each other, so they cannot "h ear" each
other, that is they do not know if the channel is currently being used. Therefore,
they are considered hidden from each other.
Figure 366 RTS/CTS
When station A sends data to the AP, it might not know that the station B is
already using the channel. If these two stations send data at the same time,
collisions may occur when both sets of data arrive at the AP at the same time,
resulting in a loss of messages for both stations.
RTS/CTS is designed to prevent collisions due to hidden nodes. An RTS/CTS
defines the biggest size data frame you can send before an RTS (Request To
Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake is invoked.
When a data frame exceeds the RTS/CTS value you set (between 0 to 2432
bytes), the station that wants to transmit th is frame mus t fi rs t s end an RTS
(Request To Send) message to the AP for permission to send it. The AP then
responds with a CTS (Clear to Send) message to all other stations within its range
to notify them to defer their transmission. It also reserves and confirms with the
requesting station the time frame for the requested transmission.
Stations can send frames smaller than the specified RTS/CTS directly to the AP
without the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake.
You should only configure RTS/CTS if the possibility of hidden nodes exists on
your network and the "cost" of resending large frames is more than the extra
network overhead involved in the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send)
handshake.
If the RTS/CTS value is greater than the Fragmentation Threshold value (see
next), then the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send) handshake will never
occur as data frames will be fragmented before they reach RTS/CTS size.
536
Note: Enabling the RTS Threshold causes redundant network overhead that could
negatively affect the throughput performance instead of providing a remedy.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 87

Fragmentation Threshold
A Fragmentation Threshold is the maximum data fragment size (between 256
and 2432 bytes) that can be sent in the wireless network before the AP will
fragment the packet into smaller data frames.
A large Fragmentation Threshold is recommended for networks not prone to
interference while you should set a smaller threshold for busy networks or
networks that are prone to interference.
If the Fragmentation Threshold value is smaller than the RTS/CTS value (see
previously) you set then the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear to Send)
handshake will never occur as data frames will be fragmented before they reach
RTS/CTS size.
Preamble Type
Appendix D Wireless LANs
Preamble is used to signal that data is coming to the receiver. Short and long refer
to the length of the synchronization field in a packet.
Short preamble increases performance as less time sending preamble means
more time for sending data. All IEEE 802.11 compliant wireless adapters support
long preamble, but not all support short preamble.
Use long preamble if you are unsure what preamble mode other wireless devices
on the network support, and to provide more reliable communications in busy
wireless networks.
Use short preamble if you are sure all wireless devices on the network support it,
and to provide more efficient communications.
Use the dynamic setting to automatically use short preamble when all wireless
devices on the network support it, otherwise the ZyXEL Device uses long
preamble.
Note: The wireless devices MUST use the same preamble mode in order to
communicate.
IEEE 802.11g Wireless LAN
IEEE 802.11g is fully compatible with the IEEE 802.11b standard. This means an
IEEE 802.11b adapter can interface directly with an IEEE 802.11g access point
(and vice versa) at 11 Mbps or lower depending on range. IEEE 802.11g has
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
537
Page 88

Appendix D Wireless LANs
several intermediate rate steps between the maximum and minimum data rates.
The IEEE 802.11g data rate and modulation are as follows:
Table 183 IEEE 802.11g
DATA RATE
(MBPS)
1 DBPSK (Differential Binary Phase Shift Keyed)
2 DQPSK (Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying)
5.5 / 11 CCK (Complementary Code Keying)
6/9/12/18/24/36/
48/54
MODULATION
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)
Wireless Security Overview
Wireless security is vital to your network to protect wireless communication
between wireless clients, access points and the wired network.
Wireless security methods available on the ZyXEL Device are data encryption,
wireless client authentication, restricting access by device MAC address and hiding
the ZyXEL Device identity.
The following figure shows the relative effectiveness of these wireless security
methods available on your ZyXEL Device.
Table 184 Wireless Security Levels
SECURITY
LEVEL
Least
Secure
Most Secure
SECURITY TYPE
Unique SSID (Default)
Unique SSID with Hide SSID Enabled
MAC Address Filtering
WEP Encryption
IEEE802.1x EAP with RADIUS Server
Authentication
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
WPA2
Note: You must enable the same wireless security settings on the ZyXEL Device and
on all wireless clients that you want to associate with it.
538
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 89

IEEE 802.1x
In June 2001, the IEEE 802.1x standard was designed to extend the features of
IEEE 802.11 to support extended authentication as well as providing additional
accounting and control features. It is supported by Windows XP and a number of
network devices. Some advantages of IEEE 802.1x are:
• User based identification that allows for roaming.
• Support for RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service, RFC 2138,
2139) for centralized user profile and accounting management on a network
RADIUS server.
• Support for EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol, RFC 2486) that allows
additional authentication methods to be deployed with no changes to the access
point or the wireless clients.
RADIUS
Appendix D Wireless LANs
RADIUS is based on a client-server model that supports authentication,
authorization and accounting. The access point is the client and the server is the
RADIUS server. The RADIUS server handles the following tasks:
• Authentication
Determines the identity of the users.
• Authorization
Determines the network services available to authenticated users once they are
connected to the network.
•Accounting
Keeps track of the client’s network activity.
RADIUS is a simple package exchange in which your AP acts as a message relay
between the wireless client and the network RADIUS server.
Types of RADIUS Messages
The following types of RADIUS messages are exchanged between the access point
and the RADIUS server for user authentication:
• Access-Request
Sent by an access point requ es ti ng authentication.
• Access-Reject
Sent by a RADIUS server rejecting access.
• Access-Accept
Sent by a RADIUS server allowing access.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
539
Page 90

Appendix D Wireless LANs
• Access-Challenge
Sent by a RADIUS server requesting more information in order to allow access.
The access point sends a proper response from the user and then sends another
Access-Request message.
The following types of RADIUS messages are exchanged between the access point
and the RADIUS server for user accounting:
•Accounting-Request
Sent by the access point requesting accounting.
• Accounting-Response
Sent by the RADIUS server to indicate that it has started or stopped accounting.
In order to ensure network security , the access point and the RADIUS serv er use a
shared secret key, which is a password, they both know. The key is not sent over
the network. In addition to the shared key, password information exchanged is
also encrypted to protect the network from unauthorized access.
Types of EAP Authentication
This section discusses some popular authentication types: EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS,
EAP-TTLS, PEAP and LEAP. Your wireless LAN device may not support all
authentication types.
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is an authentication protocol that runs on
top of the IEEE 802.1x transport mechanism in order to support multiple types of
user authentication. By using EAP to in teract with an EAP-compatible RADIUS
server, an access point helps a wireless station and a RADIUS server perform
authentication.
The type of authentication you use depends on the RADIUS server and an
intermediary AP(s) that supports IEEE 802.1x. .
For EAP-TLS authentication type, you must first have a wired connection to the
network and obtain the certificate(s) from a certificate authority (CA). A certificate
(also called digital IDs) can be used to authenticate users and a CA issues
certificates and guarantees the identity of each certificate owner.
EAP-MD5 (Message-Digest Algorithm 5)
540
MD5 authentication is the simplest one-way authentication method. The
authentication server sends a challenge to the wireless client. The wireless client
‘proves’ that it knows the password by encrypting the password with the challenge
and sends back the information. Password is not sent in plain text.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 91

However, MD5 authentication has some weaknesses. Since the authentication
server needs to get the plaintext passwords, the passwords must be stored. Thus
someone other than the authentication server may access the password file. In
addition, it is possible to impersonate an authentication server as MD5
authentication method does not perform mutual authentication. Finally, MD5
authentication method does not support data encryption with dynamic session
key. You must configure WEP encryption keys for data encryption.
EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security)
With EAP- TLS, digi tal certifications are needed by both the server and the wireless
clients for mutual authentication. T he s erver presents a certificate to the client.
After validating the identity of the server, the client sends a different certificate to
the server. The exchange of certificates is done in the open before a secured
tunnel is created. This makes user identity vulnerable to passive attacks. A digital
certificate is an electronic ID card that authenticates the sender’s identity.
However, to implement EAP-TLS, you need a Certificate Authority (CA) to handle
certificates, which imposes a management overhead.
Appendix D Wireless LANs
EAP-TTLS (Tunneled Transport Layer Service)
EAP-TTLS is an extension of the EAP-TLS authentication that uses certificates for
only the server-side authentications to establish a secure connection. Client
authentication is then done by sending username and password through the
secure connection, thus client identity is protected. For client authentication, EAPTTLS supports EAP methods and legacy authentication methods such as PAP,
CHAP, MS-CHAP and MS-CHAP v2.
PEAP (Protected EAP)
Like EAP-TTLS, server-side certificate authentication is used to establish a secure
connection, then use simple username and password methods through the
secured connection to authenticate the clients, thus hiding client identity.
However, PEAP only supports EAP methods, such as EAP-MD5, EAP-MSCHAPv2
and EAP-GTC (EAP-Generic Token Card), for client authentication. EAP-GTC is
implemented only by Cisco.
LEAP
LEAP (Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol) is a Cisco implementation of
IEEE 802.1x.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
541
Page 92

Appendix D Wireless LANs
Dynamic WEP Key Exchange
The AP maps a unique key that is generated with the RADIUS server. This key
expires when the wireless connection times out, disconnects or reauthentication
times out. A new WEP key is generated each time reauthentication is performed.
If this feature is enabled, it is not necessary to configure a default encryption key
in the wireless security configuration screen. You may still configure and store
keys, but they will not be used while dynamic WEP is enabled.
Note: EAP-MD5 cannot be used with Dynamic WEP Key Exchange
For added security, certificate-based authentications (EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS and
PEAP) use dynamic keys for data encryption. They are often deployed in corporate
environments, but for public deployment, a simple user name and password pair
is more practical. The following table is a comparison of the features of
authentication types.
Table 185 Comparison of EAP Authentication Types
EAP-MD5 EAP-TLS EAP-TTLS PEAP LEAP
Mutual Authentication No Yes Yes Yes Yes
Certificate – Client No Yes Optional Optional No
Certificate – Server No Yes Yes Yes No
Dynamic Key Exchange No Yes Yes Yes Yes
Credential Integrity None Strong Strong Strong Moder ate
Deployment Difficulty Easy Hard Moderate Moderate Moderate
Client Identity
Protection
No No Yes Yes No
WPA and WPA2
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA2
(IEEE 802.11i) is a wireless security standard that defines stronger encryption,
authentication and key management than WPA.
Key differences between WP A or WPA2 and WEP are improved data encryption and
user authentication.
If both an AP and the wireless clients support WPA2 and you have an external
RADIUS server, use WPA2 for stronger data encryption. If you don't have an
external RADIUS server, you should use WPA2-PSK (WPA2-Pre-Shared Key) that
only requires a single (identical) password entered into each access point, wireless
gateway and wireless client. As long as the passwords match, a wireless client will
be granted access to a WLAN.
542
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 93

If the AP or the wireless clients do not support WPA2, just use WPA or WPA-PSK
depending on whether you have an external RADIUS server or not.
Select WEP only when the AP and/or wireless clients do not support WP A or WPA2.
WEP is less secure than WPA or WPA2.
Encryption
Both WPA and WPA2 improve data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity
Protocol (TKIP), Message Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1x. WPA and WPA2
use Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) in the Counter mode with Cipher block
chaining Message authentication code Protocol (CCMP) to offer stronger
encryption than TKIP.
TKIP uses 128-bit keys that are dynamically generated and distributed by the
authentication server. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a block cipher that
uses a 256-bit mathematical algorithm called Rijndael. They both include a perpacket key mixing function, a Message Integrity Check (MIC) named Michael, an
extended initialization vect or (IV) with sequencing rules, and a re-keying
mechanism.
Appendix D Wireless LANs
WPA and WPA2 regularly change and rotate the encryption keys so that the same
encryption key is never used twice.
The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that
then sets up a key hierarchy and management system, using the PMK to
dynamically generate unique data encryption keys to encrypt every data packet
that is wirelessly communicated between the AP and the wireless clients. This all
happens in the background automatically.
The Message Integrity Check (MIC) is designed to prevent an attacker from
capturing data packets, altering them and resending them. The MIC provides a
strong mathematical function in which the receiver and the transmitter each
compute and then compare the MIC. If they do not match, it is assumed that the
data has been tampered with and the packet is dropped.
By generating unique data encryption keys for ev ery data pack et and by creating
an integrity checking mechanism (MIC), with TKIP and AES it is more difficult to
decrypt data on a Wi-Fi network than WEP and difficult for an intruder to break
into the network.
The encryption mechanisms used for WPA(2) and WPA(2)-PSK are the same. The
only difference between the two is that WPA(2)-PSK uses a simple common
password, instead of user-specific credentials. The common-password approach
makes WPA(2)-PSK susceptible to brute-force password-guessing attacks but it’s
still an improvement over WEP as it employs a consistent, single, alphanumeric
password to derive a PMK which is used to generate unique temporal encryption
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
543
Page 94

Appendix D Wireless LANs
keys. This prevent all wireless devices sharing the same encryption keys. (a
weakness of WEP)
User Authentication
WPA and WPA2 apply IEEE 802.1x and Extens ible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to
authenticate wireless clients using an external RADIUS database. WPA2 reduces
the number of key exchange messages from six to four (CCMP 4- w a y handsh ak e)
and shortens the time required to connect to a network. Other WPA2
authentication features that are different from WPA include key caching and preauthentication. These two features are optional and may not be supported in all
wireless devices.
Key caching allows a wireless client to store the PMK it derived thro ugh a
successful authentication with an AP. The wireless client uses the PMK when it tries
to connect to the same AP and does not need to go with the authentication
process again.
Pre-authentication enables fast roaming by allowing the wireless client (already
connecting to an AP) to perform IEEE 802.1x authentication with another AP
before connecting to it.
Wireless Client WPA Supplicants
A wireless client supplicant is the software that runs on an operating system
instructing the wireless client how to use WPA. At the time of writing, the most
widely available supplicant is the WPA patch for Windows XP, Funk Software's
Odyssey client.
The Windows XP patch is a free download that adds WPA capability to Windows
XP's built-in "Zero Configur ation" wireless client . However, you must run Windows
XP to use it.
WPA(2) with RADIUS Application Example
To set up WPA(2), you need the IP address of the RADIUS server, its port number
(default is 1812), and the RADIUS shared secret. A WPA(2) application example
with an external RADIUS server looks as follows. "A" is the RADIUS server. "DS" is
the distribution system.
1 The AP passes the wireless client's authentication request to the RADIUS server.
2 The RADIUS server then checks the user's identification against its datab as e and
grants or denies network access accordingly.
544
3 A 256-bit Pairwise Master K ey (PMK) is derived from the authentication process by
the RADIUS server and the client.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 95

Appendix D Wireless LANs
4 The RADIUS server distributes the PMK to the AP. The AP then sets up a key
hierarchy and management system, using the PMK to dynamically generate
unique data encryption keys. The keys are used to encrypt every data packet that
is wirelessly communicated between the AP and the wireless clients.
Figure 367 WPA(2) with RADIUS Application Example
WPA(2)-PSK Application Example
A WPA(2)-PSK application looks as follows.
1 First enter identical passwords into the AP and all wireless clients. The Pre-Shared
Key (PSK) must consist of between 8 and 63 ASCII characters or 64 hexadecimal
characters (including spaces and symbols).
2 The AP checks each wireless client's password and allows it to join the network
only if the password matches.
3 The AP and wireless clients generate a common PMK (Pairwise Master Key). The
key itself is not sent over the network, but is derived from the PSK and the SSID.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
545
Page 96

Appendix D Wireless LANs
4 The AP and wireless clients use the TKIP or AES encryption process, the PMK and
information exchanged in a handshake to create temporal encryption keys. They
use these keys to encrypt data exchanged between them.
Figure 368 WPA(2)-PSK Authentication
Security Parameters Summary
Refer to this table to see what other security parameters you should configure for
each authentication method or key management protocol type. MAC address
filters are not dependent on how you configure these security features.
Table 186 Wireless Security Relational Matrix
AUTHENTICATION
METHOD/ KEY
MANAGEMENT
PROTOCOL
Open None No Disable
Open WEP No Enable with Dynamic WEP Key
Shared WEP No Enable with Dynamic WEP Key
WPA TKIP/AES No Enable
WPA-PSK TKIP/AES Yes Disable
WPA2 TKIP/AES No Enable
WPA2-PSK TKIP/AES Yes Disable
ENCRYPTIO
N METHOD
ENTER
MANUAL KEY
Yes Enable without Dynamic WEP
Yes Disable
Yes Enable without Dynamic WEP
Yes Disable
IEEE 802.1X
Enable without Dynamic WEP
Key
Key
Key
546
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 97

Antenna Overview
An antenna couples RF signals onto air. A transmitter within a wireless device
sends an RF signal to the antenna, which propagates the signal through the air.
The antenna also operates in reverse by capturing RF signals from the air.
Positioning the antennas properly increases the range and coverage area of a
wireless LAN.
Antenna Characteristics
Frequency
An antenna in the frequency of 2.4GHz (IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11g) or 5GHz
(IEEE 802.11a) is needed to communicate efficiently in a wireless LAN
Radiation Pattern
Appendix D Wireless LANs
A radiation pattern is a diagram that allows you to visualize the shape of the
antenna’s coverage area.
Antenna Gain
Antenna gain, measured in dB (decibel), is the increase in coverage within the RF
beam width. Higher antenna gain improves the range of the signal for better
communications.
For an indoor site, each 1 dB increase in a nt e nna gain results in a range increas e
of approximately 2.5%. For an unobstructed outdoor site, each 1dB increase in
gain results in a range increase of approximately 5%. Actual results may vary
depending on the network environment.
Antenna gain is sometimes specified in dBi, which is how much the antenna
increases the signal power compared to using an isotropic antenna. An isotropic
antenna is a theoretical perfect antenna that sends out radio signals equally well
in all directions. dBi represents the true gain that the antenna provides.
Types of Antennas for WLAN
There are two types of antennas used for wireless LAN applications.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
547
Page 98

Appendix D Wireless LANs
• Omni-directional antennas send the RF signal out in all directions on a horizontal
plane. The coverage area is torus-shaped (like a donut) which makes these
antennas ideal for a room environment. With a wide coverage area, it is possible
to make circular overlapping coverage areas with multiple access points.
• Directional antennas concentrate the RF signal in a beam, like a flashlight does
with the light from its bulb. The angle of the beam determines the width of the
coverage pattern. Angles typically range from 20 degrees (very directional) to
120 degrees (less directional). Directional antennas are ideal for hallways and
outdoor point-to-point applications.
Positioning Antennas
In general, antennas should be mounted as high as practically possible and free of
obstructions. In point-to–point application, position both antennas at the same
height and in a direct line of sight to each other to attain the best performance.
For omni-directional antennas mounted on a table, desk, and so on, point the
antenna up. For omni-directional antennas mounted on a wal l or ceiling, point the
antenna down. For a single AP application, place omni-directional antennas as
close to the center of the coverage area as possible.
For directional antennas, point the antenna in the direction of the desired
coverage area.
WiFi Protected Setup
Your ZyXEL Device supports WiFi Protected Setup (WPS), which is an easy way to
set up a secure wireless network. WPS is an industry standard specification,
defined by the WiFi Alliance.
WPS allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without
having to configure security settings manually. Each WPS connection works
between two devices. Both devices must support WPS (check each device’s
documentation to make sure).
Depending on the devices you have, you can either press a button (on the device
itself , or in its configuration utility) or enter a PIN (a unique P ersonal Identification
Number that allows one device to authenticate the other) in each of the two
devices. When WPS is activated on a device, it has two minutes to find another
device that also has WPS activated. Then, the two devices connect and set up a
secure network by themselves.
548
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
Page 99

Push Button Configuration
WPS Push Button Configuration (PBC) is in itiated by pressing a button o n ea c h
WPS-enabled device, and allowing them to connect automatically. You do not need
to enter any information.
Not every WPS-enabled device has a physical WPS button. Some may have a WPS
PBC button in their configuration utilities instead of or in addition to the physical
button.
Take the following steps to set up WPS using the button.
1 Ensure that the two devices you want to set up are within wireless range of one
another.
2 Look for a WPS button on each device. If the device does not have one, log into its
configuration utility and locate the button (see the device’s User’ s Guide for how to
do this - for the ZyXEL Device, see Section 8.6 on page 149).
Appendix D Wireless LANs
3 Press the button on one of the devices (it doesn’t matter which).
4 Within two minutes, press the button on the other device. The registrar sends the
network name (SSID) and security key throug h an secure connection to the
enrollee.
If you need to make sure that WPS worked, check the list of associated wireless
clients in the AP’s configuration utility. If you see the wireless client in the list,
WPS was successful.
PIN Configuration
Each WPS-enabled device has its own PIN (Personal Identification Number). This
may either be static (it cannot be changed) or dynamic (you can change it to a
new random number by clicking on a button in the configuration interface).
When you use the PIN method, you must enter the enrollee’s PIN into the
registrar. Then, when WPS is activated on the enrollee, it presents its PIN to the
registrar. If the PIN matches, the registrar sends the network and security
information to the enrollee, allowin g it to joi n the network.
The advantage of using the PIN method rather than the PBC method is that you
can ensure that the connection is established between the devices you specify, not
just the first two devices to activate WPS in the area. Howeve r, you need to log
into the configuration interfaces of both devices.
Take the following steps to set up WPS using the PIN method.
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
549
Page 100

Appendix D Wireless LANs
1 Decide which device you want to be the registrar (usually the AP) and which you
want to be the enrollee (usually the client).
2 Look for the enrollee’s WPS PIN; it may be displayed on the device. If you don’t
see it, log into the enrollee’s configuration interface and locate the PIN. Select the
PIN connection mode (not PBC connection mode). See the device’s User’s Guide
for how to do this - for the ZyXEL Device, see Section 8.5 on page 148.
3 Log into the configuration utility of the registrar. Select the PIN connection mode
(not the PBC connection mode). Locate the place where you can enter the
enrollee’s PIN (if you are using the ZyXEL Device, see Section 8.6 on page 149).
Enter the PIN from the enrollee device.
4 Activate WPS on both devices within two minutes.
Note: Use the configuration utility to activate WPS, not the push-button on the device
itself.
5 On a computer connected to the wireless client, try to connect to the Internet. If
you can connect, WPS was successful.
If you cannot connect, check the list of associated wireless clients in the AP’s
configuration utility. If you see the wireless client in the list, WPS was successful.
550
P-2612HWU-F1 User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...