Page 1

OLT-1308 Series
Optical Line Terminal
User’s Guide
Version 3.60
1/2007
Edition 1
www.zyxel.com
Page 2

Page 3
About This User's Guide
About This User's Guide
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for people who want to configure the OLT using the web configurator.
You should have at least a basic knowledge of TCP/IP networking concepts and topology.
Related Documentation
• Web Configurator Online Help
Embedded web help for descriptions of individual screens and supplementary
information.
• Command Reference Guide
The Command Reference Guide explains how to use the Command-Line Interface (CLI)
and CLI commands to configure the OLT.
" It is recommended you use the web configurator to configure the OLT.
• Supporting Disk
Refer to the included CD for support documents.
• ZyXEL Web Site
Please refer to www.zyxel.com
certifications.
User Guide Feedback
Help us help you. Send all User Guide-related comments, questions or suggestions for
improvement to the following address, or use e-mail instead. Thank you!
The Technical Writing Team,
ZyXEL Communications Corp.,
6 Innovation Road II,
Science-Based Industrial Park,
Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan.
E-mail: techwriters@zyxel.com.tw
for additional support documentation and product
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
3
Page 4

Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this User’s Guide.
1 Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
" Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may
need to configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• The OLT-1308 and OLT-1308H may be referred to as the “OLT”, the “device” or the
“system” in this User’s Guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A key stroke is denoted by square brackets and uppercase text, for example, [ENTER]
means the “enter” or “return” key on your keyboard.
• “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters and then press the [ENTER] key.
“Select” or “choose” means for you to use one of the predefined choices.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example,
Maintenance > Log > Log Setting means you first click Maintenance in the navigation
panel, then the Log sub menu and finally the Log Setting tab to get to that screen.
• Units of measurement may denote the “metric” value or the “scientific” value. For
example, “k” for kilo may denote “1000” or “1024”, “M” for mega may denote “1000000”
or “1048576” and so on.
• “e.g.,” is a shorthand for “for instance”, and “i.e.,” means “that is” or “in other words”.
4
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 5
Document Conventions
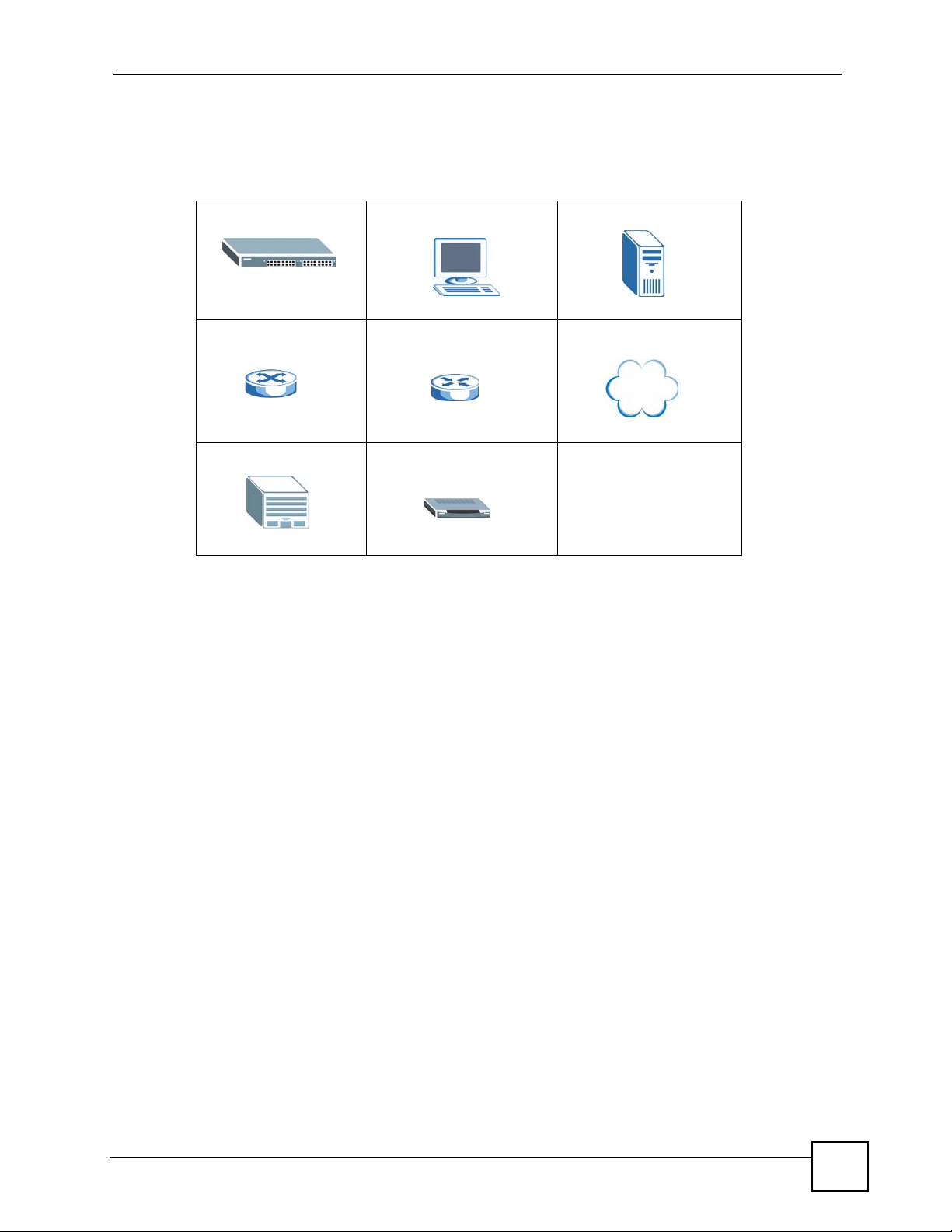
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this User’s Guide may use the following generic icons. The OLT icon is not an exact
representation of your device.
OLT Computer Server
Switch Router Internet
Central Office/ISP ONU
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Safety Warnings
Safety Warnings
1 For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
• Do NOT use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming
pool.
• Do NOT expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do NOT store things on the device.
• Do NOT install, use, or service this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk
of electric shock from lightning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• Do NOT open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to
dangerous high voltage points or other risks. ONLY qualified service personnel should
service or disassemble this device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
• Always disconnect all cables from this device before servicing or disassembling.
• Use ONLY an appropriate power adaptor or cord for your device.
• Connect the power adaptor or cord to the right supply voltage (for example, 110V AC in
North America or 230V AC in Europe).
• Do NOT allow anything to rest on the power adaptor or cord and do NOT place the
product where anyone can walk on the power adaptor or cord.
• Do NOT use the device if the power adaptor or cord is damaged as it might cause
electrocution.
• If the power adaptor or cord is damaged, remove it from the power outlet.
• Do NOT attempt to repair the power adaptor or cord. Contact your local vendor to order a
new one.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a
remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Do NOT obstruct the device ventilation slots, as insufficient airflow may harm your
device.
6
This product is recyclable. Dispose of it properly.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 7
Safety Warnings
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Safety Warnings
8
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 9

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 29
Introducing the OLT ................................................................................................................... 31
Hardware Installation and Connection ....................................................................................... 35
Hardware Overview ................................................................................................................... 39
Basic Setup ............................................................................................................................ 43
The Web Configurator ............................................................................................................... 45
Initial Setup Example ................................................................................................................. 55
System Status and Port Statistics ..............................................................................................59
Basic Setting ............................................................................................................................. 73
Advanced: Switch .................................................................................................................. 95
VLAN ......................................................................................................................................... 97
Static MAC Forward Setup ...................................................................................................... 107
Filtering .................................................................................................................................... 109
Spanning Tree Protocol ............................................................................................................ 111
Bandwidth Control ....................................................................................................................117
Broadcast Storm Control ..........................................................................................................119
Mirroring .................................................................................................................................. 121
Link Aggregation ...................................................................................................................... 123
Port Security ............................................................................................................................ 127
Queuing Method ...................................................................................................................... 129
Classifier .................................................................................................................................. 133
Policy ...................................................................................................................................... 139
Multicast .................................................................................................................................. 145
DHCP Relay ............................................................................................................................ 155
Advanced: EPON .................................................................................................................157
Classification Filter Profile ....................................................................................................... 159
VLAN Profile ............................................................................................................................ 163
Priority Profile .......................................................................................................................... 173
Static MAC Forward Setup ...................................................................................................... 179
Destination Filter ...................................................................................................................... 181
Port Authentication .................................................................................................................. 185
IP and Management .............................................................................................................189
Static Route ............................................................................................................................. 191
Maintenance ............................................................................................................................ 193
Access Control ........................................................................................................................ 201
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Contents Overview
Diagnostic ................................................................................................................................ 213
Syslog ...................................................................................................................................... 215
Cluster Management ............................................................................................................... 219
MAC Table ............................................................................................................................... 225
ARP Table ................................................................................................................................ 229
IGMP Table .............................................................................................................................. 231
Commands and Troubleshooting ....................................................................................... 233
Introducing the Commands ..................................................................................................... 235
Command Examples ...............................................................................................................271
Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................... 287
Appendix and Index .............................................................................................................295
10
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 11

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
About This User's Guide ..........................................................................................................3
Document Conventions............................................................................................................4
Safety Warnings........................................................................................................................6
Contents Overview ................................................................................................................... 9
Table of Contents.................................................................................................................... 11
List of Figures ......................................................................................................................... 21
List of Tables...........................................................................................................................25
Part I: Introduction................................................................................. 29
Chapter 1
Introducing the OLT ................................................................................................................31
1.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................. 31
1.2 Ways to Manage the OLT .................................................................................................... 31
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the OLT ..................................................................................... 32
1.4 LEDs .................................................................................................................................... 32
Chapter 2
Hardware Installation and Connection .................................................................................35
2.1 Freestanding Installation ..................................................................................................... 35
2.2 Mounting the OLT on a Rack ............................................................................................... 35
2.2.1 Rack-mounted Installation Requirements ................................................................. 35
2.2.2 Attaching the Mounting Brackets to the OLT ............................................................. 36
2.2.3 Mounting the OLT on a Rack ..................................................................................... 36
Chapter 3
Hardware Overview................................................................................................................. 39
3.1 Hardware Connection ......................................................................................................... 39
3.1.1 Fiber Connections ...................................................................................................... 40
3.1.2 Gigabit Ethernet Ports ................................................................................................ 40
3.1.3 Mini-GBIC Slots ........................................................................................................40
3.1.4 Console Port .............................................................................................................. 41
3.1.5 Power Connector ....................................................................................................... 42
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
11
Page 12

Table of Contents
Part II: Basic Setup ................................................................................ 43
Chapter 4
The Web Configurator ............................................................................................................45
4.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................... 45
4.2 System Login ....................................................................................................................... 45
4.3 The Status Screen ............................................................................................................... 46
4.3.1 Change Your Password ............................................................................................. 51
4.4 Device Lockout .................................................................................................................... 52
4.5 Resetting the OLT ................................................................................................................ 52
4.5.1 Reload the Configuration File ..................................................................................... 52
4.6 Logging Out of the Web Configurator .................................................................................. 53
4.7 Help ..................................................................................................................................... 54
Chapter 5
Initial Setup Example..............................................................................................................55
5.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................. 55
5.2 Connecting the Devices ....................................................................................................... 55
5.3 Creating a Service Profile .................................................................................................... 56
5.4 Testing the Internet Connection ........................................................................................... 57
Chapter 6
System Status and Port Statistics .........................................................................................59
6.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................. 59
6.2 Port Status Summary .......................................................................................................... 59
6.2.1 EPON Info ................................................................................................................. 62
6.2.2 EPON Details ............................................................................................................63
6.2.3 Ethernet Port Details ................................................................................................. 68
Chapter 7
Basic Setting .......................................................................................................................... 73
7.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................. 73
7.2 System Information ............................................................................................................. 73
7.3 General Setup .................................................................................................................... 75
7.4 Introduction to VLANs ......................................................................................................... 77
7.5 Switch Setup Screen .......................................................................................................... 77
7.6 IP Setup .............................................................................................................................. 79
7.6.1 Management IP Address ............................................................................................ 79
7.7 Port Setup ........................................................................................................................... 82
7.8 IGMP Snooping ................................................................................................................... 85
7.9 DBA (Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation) ................................................................................. 85
7.10 EPON Setup .................................................................................................................... 85
7.10.1 Profile Setup ............................................................................................................ 87
12
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 13

Table of Contents
7.10.2 Service Setup ..........................................................................................................91
Part III: Advanced: Switch..................................................................... 95
Chapter 8
VLAN ........................................................................................................................................ 97
8.1 Introduction to IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN ........................................................................ 97
8.1.1 Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames ............................................................... 97
8.2 Automatic VLAN Registration .............................................................................................. 98
8.2.1 GARP ........................................................................................................................ 98
8.2.2 GVRP ......................................................................................................................... 98
8.3 Port VLAN Trunking ........................................................................................................... 98
8.4 Select the VLAN Type ........................................................................................................ 99
8.5 Static VLAN ......................................................................................................................... 99
8.5.1 Static VLAN Status .................................................................................................... 99
8.5.2 Configure a Static VLAN ......................................................................................... 100
8.5.3 Configure VLAN Port Setting .................................................................................. 102
8.6 Port-based VLAN .............................................................................................................. 103
8.6.1 Configure a Port-based VLAN .................................................................................. 103
Chapter 9
Static MAC Forward Setup...................................................................................................107
9.1 Static MAC Forwarding Overview ..................................................................................... 107
9.2 Configuring Static MAC Forwarding ............................................................................... 107
Chapter 10
Filtering..................................................................................................................................109
10.1 Filtering Overview ........................................................................................................... 109
10.2 Configure a Filtering Rule ..............................................................................................109
Chapter 11
Spanning Tree Protocol........................................................................................................ 111
11.1 STP/RSTP Overview ....................................................................................................... 111
11.1.1 STP Terminology ....................................................................................................111
11.1.2 How STP Works .....................................................................................................112
11.1.3 STP Port States .......................................................................................................112
11.2 STP Status .......................................................................................................................112
11.3 Configure STP .................................................................................................................114
Chapter 12
Bandwidth Control................................................................................................................ 117
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
13
Page 14

Table of Contents
12.1 Configuring Bandwidth Control ........................................................................................117
Chapter 13
Broadcast Storm Control ..................................................................................................... 119
13.1 Broadcast Storm Control Overview .................................................................................119
13.2 Broadcast Storm Control Setup .......................................................................................119
Chapter 14
Mirroring ................................................................................................................................ 121
14.1 Mirroring Overview ......................................................................................................... 121
14.2 Port Mirroring Configuration ............................................................................................ 121
Chapter 15
Link Aggregation .................................................................................................................. 123
15.1 Link Aggregation Overview ............................................................................................. 123
15.1.1 Dynamic Link Aggregation ..................................................................................... 123
15.1.2 Link Aggregation ID ................................................................................................ 123
15.2 Link Aggregation Status ..................................................................................................124
15.3 Link Aggregation Setup .................................................................................................. 124
Chapter 16
Port Security.......................................................................................................................... 127
16.1 Port Security Overview ..................................................................................................127
16.2 Port Security Setup .......................................................................................................... 127
Chapter 17
Queuing Method.................................................................................................................... 129
17.1 Queuing Method Overview ............................................................................................. 129
17.1.1 Strict Priority Queuing (SPQ) ................................................................................. 129
17.1.2 Weighted Round Robin Scheduling (WRR) ........................................................... 130
17.2 Configuring Queuing ........................................................................................................ 130
Chapter 18
Classifier................................................................................................................................133
18.1 Classifier Overview ......................................................................................................... 133
18.2 Configuring a Classifier ................................................................................................... 133
18.3 Classifier Example ........................................................................................................... 136
Chapter 19
Policy .................................................................................................................................... 139
14
19.1 Policy Overview .............................................................................................................. 139
19.1.1 DiffServ .................................................................................................................. 139
19.1.2 DSCP and Per-Hop Behavior ................................................................................. 139
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 15

Table of Contents
19.2 Configuring a Policy ......................................................................................................... 139
19.3 Policy Example ................................................................................................................ 142
Chapter 20
Multicast ................................................................................................................................ 145
20.1 Multicast Overview ......................................................................................................... 145
20.1.1 IP Multicast Addresses ........................................................................................... 145
20.1.2 IGMP Filtering ........................................................................................................ 145
20.1.3 IGMP Snooping ...................................................................................................... 145
20.2 Multicast Status ............................................................................................................... 146
20.3 Multicast Setup ............................................................................................................... 146
20.4 IGMP Filtering Profile ..................................................................................................... 147
20.5 MVR Overview ................................................................................................................ 148
20.5.1 Types of MVR Ports ............................................................................................... 149
20.5.2 MVR Modes ........................................................................................................... 149
20.5.3 How MVR Works .................................................................................................... 149
20.6 General MVR Configuration ........................................................................................... 150
20.7 MVR Group Configuration ............................................................................................... 152
20.7.1 MVR Configuration Example .................................................................................. 153
Chapter 21
DHCP Relay ...........................................................................................................................155
21.1 DHCP Relay Overview ................................................................................................... 155
21.1.1 DHCP “Relay Agent Information Option” ............................................................... 155
21.1.2 DHCP Relay Agent Circuit ID Sub-option Format .................................................. 155
21.2 DHCP Relay Configuration ............................................................................................. 155
Part IV: Advanced: EPON .................................................................... 157
Chapter 22
Classification Filter Profile...................................................................................................159
22.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 159
22.2 Classification Filter Profile Setup .................................................................................... 159
22.2.1 Example: Classification Filter Profile ...................................................................... 161
Chapter 23
VLAN Profile.......................................................................................................................... 163
23.1 Introduction to IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLANs ................................................................... 163
23.1.1 Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames ............................................................ 163
23.2 VLAN Stacking ................................................................................................................. 164
23.2.1 VLAN Stacking Example ........................................................................................ 164
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
15
Page 16

Table of Contents
23.3 VLAN Tag Format ............................................................................................................ 165
23.3.1 Frame Format ........................................................................................................ 165
23.4 Configuring a VLAN Profile ............................................................................................. 166
23.4.1 VLAN Profile: Example ........................................................................................... 169
23.4.2 VLAN Profile: Example 2 ........................................................................................ 170
Chapter 24
Priority Profile ....................................................................................................................... 173
24.1 Priority Profile Overview .................................................................................................. 173
24.2 Configuring a Priority Profile ...........................................................................................173
24.2.1 Example: Priority Profile ......................................................................................... 178
Chapter 25
Static MAC Forward Setup...................................................................................................179
25.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 179
25.2 Static MAC Forwarding Status ........................................................................................ 179
25.3 Configuring Static MAC Forwarding .............................................................................. 180
Chapter 26
Destination Filter................................................................................................................... 181
26.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 181
26.2 Destination Filter Status .................................................................................................. 181
26.3 Destination Filter Setup .................................................................................................. 181
26.3.1 Example: Destination Filter .................................................................................... 183
Chapter 27
Port Authentication............................................................................................................... 185
27.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 185
27.1.1 RADIUS .................................................................................................................185
27.2 Configuring Port Authentication ...................................................................................... 186
27.2.1 Activating IEEE 802.1x Security ............................................................................ 186
27.2.2 Configuring RADIUS Server Settings .................................................................... 187
Part V: IP and Management................................................................. 189
Chapter 28
Static Route ........................................................................................................................... 191
28.1 Configuring Static Route .................................................................................................191
Chapter 29
Maintenance .......................................................................................................................... 193
16
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 17

Table of Contents
29.1 The Main Maintenance Screen ....................................................................................... 193
29.2 Load Factory Defaults .....................................................................................................193
29.3 Reboot System ................................................................................................................ 194
29.4 Remote ONU Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................... 194
29.5 Chip Reset ...................................................................................................................... 195
29.6 Remote Device Reset ..................................................................................................... 196
29.7 OLT Firmware Upgrade .................................................................................................. 196
29.8 Restore Configuration ..................................................................................................... 197
29.9 Backup Configuration .....................................................................................................197
29.10 FTP Command Line ...................................................................................................... 198
29.10.1 Filename Conventions ......................................................................................... 198
29.10.2 FTP Command Line Procedure .......................................................................... 199
29.10.3 GUI-based FTP Clients ........................................................................................ 199
29.10.4 FTP Restrictions ................................................................................................... 199
Chapter 30
Access Control...................................................................................................................... 201
30.1 About Access Control ....................................................................................................201
30.2 The Access Control Main Screen .................................................................................... 201
30.3 About SNMP ................................................................................................................... 202
30.3.1 Supported MIBs ..................................................................................................... 203
30.3.2 SNMP Traps ........................................................................................................... 203
30.3.3 Configuring SNMP ................................................................................................ 203
30.4 Login Accounts .............................................................................................................. 204
30.5 SSH Overview ................................................................................................................. 205
30.6 How SSH works ............................................................................................................... 206
30.7 SSH Implementation on the OLT ..................................................................................... 207
30.7.1 Requirements for Using SSH ................................................................................. 207
30.8 Introduction to HTTPS .....................................................................................................207
30.9 HTTPS Example .............................................................................................................. 208
30.9.1 Internet Explorer Warning Messages ..................................................................... 208
30.9.2 Netscape Navigator Warning Messages ................................................................ 208
30.9.3 The Main Screen .................................................................................................... 209
30.10 Service Access Control ................................................................................................ 210
30.11 Remote Management ....................................................................................................211
Chapter 31
Diagnostic.............................................................................................................................. 213
31.1 Diagnostic ....................................................................................................................... 213
31.2 Saving Logs ..................................................................................................................... 214
Chapter 32
Syslog .................................................................................................................................... 215
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
17
Page 18

Table of Contents
32.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 215
32.2 Syslog Setup ................................................................................................................. 215
32.3 Syslog Server Setup ....................................................................................................... 216
Chapter 33
Cluster Management.............................................................................................................219
33.1 Introduction to Cluster Management .............................................................................. 219
33.2 Cluster Management Status ............................................................................................ 220
33.2.1 Cluster Member Switch Management .................................................................... 220
33.3 Cluster Management Configuration ................................................................................ 222
Chapter 34
MAC Table..............................................................................................................................225
34.1 MAC Table Overview ...................................................................................................... 225
34.2 Viewing the MAC Table ................................................................................................... 226
Chapter 35
ARP Table ..............................................................................................................................229
35.1 Introduction to ARP Table ............................................................................................... 229
35.1.1 How ARP Works .................................................................................................... 229
35.2 Viewing ARP Table .......................................................................................................... 229
Chapter 36
IGMP Table.............................................................................................................................231
36.1 Displaying IGMP Table .................................................................................................. 231
Part VI: Commands and Troubleshooting ......................................... 233
Chapter 37
Introducing the Commands .................................................................................................235
37.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 235
37.1.1 Configuration File ................................................................................................... 235
37.2 Accessing the CLI .......................................................................................................... 235
37.2.1 Multiple Login ......................................................................................................... 236
37.2.2 The Console Port ................................................................................................... 236
37.2.3 Telnet ..................................................................................................................... 237
37.2.4 SSH ........................................................................................................................ 237
37.3 The Login Screen ........................................................................................................... 238
37.4 Command Syntax Conventions ....................................................................................... 238
37.5 Changing the Password .................................................................................................. 238
37.6 Command Modes ............................................................................................................ 238
18
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 19

Table of Contents
37.7 Getting Help ..................................................................................................................... 239
37.7.1 List of Available Commands ................................................................................... 239
37.7.2 Detailed Command Information ............................................................................. 240
37.8 Using Command History .................................................................................................. 241
37.9 Saving Your Configuration ............................................................................................... 241
37.9.1 Logging Out ............................................................................................................ 241
37.10 Command Summary ...................................................................................................... 241
37.10.1 User Mode ............................................................................................................ 241
37.10.2 Enable Mode ........................................................................................................ 243
37.10.3 General Configuration Mode ................................................................................ 248
37.10.4 classifier-filter-profile Commands ......................................................................... 259
37.10.5 epon-common Commands ................................................................................... 260
37.10.6 epon-profile Commands ....................................................................................... 261
37.10.7 interface Commands ............................................................................................ 263
37.10.8 mvr Commands .................................................................................................... 265
37.10.9 onu Commands .................................................................................................... 266
37.10.10 priority-profile Commands .................................................................................. 267
37.10.11 vlan Commands ................................................................................................. 268
37.10.12 vlan-profile Commands ...................................................................................... 269
Chapter 38
Command Examples.............................................................................................................271
38.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 271
38.2 show Commands .............................................................................................................271
38.2.1 show epon .............................................................................................................. 271
38.2.2 show epon-counter ................................................................................................. 272
38.2.3 show epon-counter onu .......................................................................................... 272
38.2.4 show hardware-monitor .......................................................................................... 273
38.2.5 show ip ................................................................................................................... 274
38.2.6 show system-information ....................................................................................... 274
38.3 ping ................................................................................................................................. 275
38.4 traceroute ........................................................................................................................ 275
38.5 epon-common Commands .............................................................................................. 276
38.6 epon-profile Commands .................................................................................................. 277
38.7 Configuration File Maintenance ...................................................................................... 278
38.7.1 Backing up Configuration ....................................................................................... 278
38.7.2 Restoring Configuration ........................................................................................ 279
38.7.3 Resetting to the Factory Default ............................................................................. 279
38.8 no Command Examples .................................................................................................. 280
38.8.1 no port-access-authenticator .................................................................................. 280
38.8.2 no ssh ..................................................................................................................... 280
38.9 priority-profile Commands ............................................................................................... 281
38.10 onu Commands .............................................................................................................282
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
19
Page 20

Table of Contents
38.11 vlan-profile Commands .................................................................................................. 283
Chapter 39
Troubleshooting....................................................................................................................287
39.1 Problems Starting Up the OLT ......................................................................................... 287
39.2 Problems Accessing the OLT .......................................................................................... 287
39.2.1 Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions ........................................... 288
39.3 Problems with the Password ........................................................................................... 293
Part VII: Appendix and Index .............................................................. 295
Appendix A Product Specifications ................................................................................. 297
Appendix B Legal Information......................................................................................... 299
Appendix C Customer Support .......................................................................................303
Index....................................................................................................................................... 307
20
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 21

List of Figures
List of Figures
Figure 1 Network Example .................................................................................................................... 31
Figure 2 LEDs (OLT-1308H) .................................................................................................................. 32
Figure 3 LEDs (OLT-1308) .................................................................................................................... 32
Figure 4 Attaching the Mounting Brackets ............................................................................................. 36
Figure 5 Mounting the OLT on a Rack .................................................................................................. 37
Figure 6 Front Panel ............................................................................................................................. 39
Figure 7 Transceiver Installation Example ............................................................................................. 41
Figure 8 Installed Transceiver ............................................................................................................. 41
Figure 9 Opening the Transceiver’s Latch Example ..............................................................................41
Figure 10 Transceiver Removal Example .............................................................................................. 41
Figure 11 Web Configurator: Login ........................................................................................................ 46
Figure 12 Web Configurator: Home Screen (Status): OLT-1308 .......................................................... 46
Figure 13 Change Administrator Login Password .................................................................................52
Figure 14 Resetting the Device: Via the Console Port ..........................................................................53
Figure 15 Web Configurator: Logout Screen ......................................................................................... 53
Figure 16 Initial Setup: Network Example ............................................................................................. 55
Figure 17 Status: OLT-1308 ................................................................................................................... 59
Figure 18 Status: OLT-1308H ................................................................................................................ 61
Figure 19 Status: EPON Info ................................................................................................................. 62
Figure 20 Status: EPON Info: EPON Details ........................................................................................ 64
Figure 21 Status: Port Details ................................................................................................................ 69
Figure 22 System Info ........................................................................................................................... 74
Figure 23 General Setup ....................................................................................................................... 76
Figure 24 Switch Setup ......................................................................................................................... 78
Figure 25 IP Setup: OLT-1308 ............................................................................................................... 80
Figure 26 IP Setup: OLT-1308H ............................................................................................................ 82
Figure 27 Port Setup: OLT-1308 ............................................................................................................ 83
Figure 28 Port Setup: OLT-1308H ......................................................................................................... 84
Figure 29 EPON Setup: OLT-1308H .................................................................................................... 86
Figure 30 EPON Setup: Profile Setup ................................................................................................... 88
Figure 31 EPON Setup: Service Setup (or ONU Setup) ....................................................................... 92
Figure 32 Port VLAN Trunking ............................................................................................................... 99
Figure 33 Switch Setup: Select VLAN Type .......................................................................................... 99
Figure 34 VLAN: VLAN Status ............................................................................................................ 100
Figure 35 VLAN: Static VLAN ............................................................................................................. 101
Figure 36 VLAN: Static VLAN: VLAN Port Setting ............................................................................... 102
Figure 37 Port Based VLAN Setup (All Connected) ............................................................................ 104
Figure 38 Port Based VLAN Setup (Port Isolation) ............................................................................. 104
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
21
Page 22

List of Figures
Figure 39 Static MAC Forwarding ........................................................................................................ 107
Figure 40 Filtering ................................................................................................................................ 109
Figure 41 Spanning Tree Protocol: Status ............................................................................................113
Figure 42 Spanning Tree Protocol: Configuration .................................................................................114
Figure 43 Bandwidth Control ................................................................................................................117
Figure 44 Broadcast Storm Control ......................................................................................................119
Figure 45 Mirroring .............................................................................................................................. 121
Figure 46 Link Aggregation Control Protocol Status ...........................................................................124
Figure 47 Link Aggregation Control Protocol: Configuration ............................................................... 125
Figure 48 Port Security ........................................................................................................................ 127
Figure 49 Queuing Method .................................................................................................................. 130
Figure 50 Classifier .............................................................................................................................. 134
Figure 51 Classifier: Example .............................................................................................................. 137
Figure 52 Policy .................................................................................................................................. 140
Figure 53 Policy Example .................................................................................................................... 143
Figure 54 Multicast Status . .................................................................................................................. 146
Figure 55 Multicast .............................................................................................................................. 146
Figure 56 Multicast: IGMP Filtering Profile .......................................................................................... 148
Figure 57 MVR Network Example ....................................................................................................... 149
Figure 58 MVR Multicast Television Example ..................................................................................... 150
Figure 59 MVR .................................................................................................................................... 151
Figure 60 MVR: Group Configuration .................................................................................................. 152
Figure 61 MVR Configuration Example ............................................................................................... 153
Figure 62 MVR Configuration Example ............................................................................................... 154
Figure 63 MVR Group Configuration Example ................................................................................... 154
Figure 64 DHCP Relay ........................................................................................................................ 156
Figure 65 Classification Filter Profile Setup ......................................................................................... 159
Figure 66 Classification Filter Profile: Example ................................................................................... 161
Figure 67 VLAN Stacking Example ..................................................................................................... 165
Figure 68 EPON VLAN Profile Setup .................................................................................................. 167
Figure 69 VLAN Network Example 1 .................................................................................................... 170
Figure 70 VLAN Profile: Example 1 ..................................................................................................... 170
Figure 71 VLAN Network Example 2 ................................................................................................... 170
Figure 72 VLAN Profile: Example 2 ..................................................................................................... 171
Figure 73 VLAN Profile: Example 2: Classification Filter Profile ......................................................... 171
Figure 74 Priority Profile: OLT-1308 .................................................................................................... 174
Figure 75 Priority Profile: OLT-1308H .................................................................................................. 176
Figure 76 Priority Profile: Example ...................................................................................................... 178
Figure 77 Static MAC Forwarding Status .............................................................................................. 179
Figure 78 Static MAC Forwarding ........................................................................................................ 180
Figure 79 Destination Filter Status ...................................................................................................... 181
Figure 80 Destination Filter: DA Filter ................................................................................................. 182
Figure 81 Destination Filter: Example ................................................................................................. 183
22
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 23

List of Figures
Figure 82 RADIUS Server Network Example .................................................................................... 185
Figure 83 Port Authentication .............................................................................................................. 186
Figure 84 Port Authentication: 802.1x ................................................................................................. 186
Figure 85 Port Authentication: RADIUS .............................................................................................. 187
Figure 86 Static Routing ...................................................................................................................... 191
Figure 87 Maintenance ....................................................................................................................... 193
Figure 88 Load Factory Default: Conformation ................................................................................... 193
Figure 89 Load Factory Default: Start .................................................................................................. 194
Figure 90 Reboot System: Confirmation ............................................................................................. 194
Figure 91 Reboot System: Start .......................................................................................................... 194
Figure 92 Maintenance: Remote Firmware Upgrade .......................................................................... 195
Figure 93 Maintenance: Chip Reset .................................................................................................... 195
Figure 94 Maintenance: Remote Device Reset ................................................................................... 196
Figure 95 Firmware Upgrade .............................................................................................................. 197
Figure 96 Restore Configuration ......................................................................................................... 197
Figure 97 Backup Configuration .......................................................................................................... 197
Figure 98 Access Control .................................................................................................................... 202
Figure 99 SNMP Management Model ................................................................................................. 202
Figure 100 Access Control: SNMP ...................................................................................................... 204
Figure 101 Access Control: Logins ...................................................................................................... 205
Figure 102 SSH Communication Example ...........................................................................................206
Figure 103 How SSH Works ................................................................................................................. 206
Figure 104 HTTPS Implementation ...................................................................................................... 207
Figure 105 Security Alert Dialog Box (Internet Explorer) ...................................................................... 208
Figure 106 Security Certificate 1 (Netscape) ........................................................................................ 209
Figure 107 Security Certificate 2 (Netscape) ........................................................................................ 209
Figure 108 Example: Lock Denoting a Secure Connection ................................................................. 210
Figure 109 Access Control: Service Access Control ........................................................................... 210
Figure 110 Access Control: Remote Management ...............................................................................211
Figure 111 Diagnostic .......................................................................................................................... 213
Figure 112 Syslog ................................................................................................................................ 216
Figure 113 Syslog: Server Setup ......................................................................................................... 216
Figure 114 Clustering Application Example ......................................................................................... 219
Figure 115 Cluster Management Status .............................................................................................. 220
Figure 116 Cluster Management Status ............................................................................................... 220
Figure 117 Cluster Member Web Configuration Screen ...................................................................... 221
Figure 118 Example: Uploading Firmware to a Cluster Member Switch ............................................. 221
Figure 119 Configuring Cluster Management ...................................................................................... 222
Figure 120 MAC Table Flowchart ........................................................................................................ 226
Figure 121 MAC Table: OLT-1308 ....................................................................................................... 226
Figure 122 MAC Table: OLT-1308H .................................................................................................... 227
Figure 123 ARP Table ......................................................................................................................... 230
Figure 124 IGMP Table ........................................................................................................................ 231
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
23
Page 24

List of Figures
Figure 125 Pop-up Blocker ................................................................................................................... 288
Figure 126 Internet Options ................................................................................................................. 289
Figure 127 Internet Options .................................................................................................................. 290
Figure 128 Pop-up Blocker Settings ..................................................................................................... 290
Figure 129 Internet Options .................................................................................................................. 291
Figure 130 Security Settings - Java Scripting ....................................................................................... 292
Figure 131 Security Settings - Java ...................................................................................................... 292
Figure 132 Java (Sun) .......................................................................................................................... 293
24
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 25

List of Tables
List of Tables
Table 1 LEDs ......................................................................................................................................... 32
Table 2 Port Connection ........................................................................................................................ 39
Table 3 Navigation Panel Sub-links Overview: OLT-1308 ..................................................................... 47
Table 4 Navigation Panel Sub-links Overview: OLT-1308H ................................................................... 48
Table 5 Web Configurator Screen Sub-links Details .............................................................................. 49
Table 6 Navigation Panel Links ............................................................................................................. 50
Table 7 Status: OLT-1308 ...................................................................................................................... 60
Table 8 Status: OLT-1308H .................................................................................................................... 61
Table 9 Status: EPON Info ..................................................................................................................... 62
Table 10 Status: EPON Info: EPON Details ........................................................................................... 65
Table 11 Status: Port Details .................................................................................................................. 69
Table 12 System Info ............................................................................................................................. 74
Table 13 General Setup ......................................................................................................................... 76
Table 14 Switch Setup ........................................................................................................................... 78
Table 15 IP Setup: OLT-1308 ................................................................................................................ 80
Table 16 IP Setup: OLT-1308H .............................................................................................................. 82
Table 17 Port Setup: OLT-1308 ............................................................................................................. 83
Table 18 Port Setup: OLT-1308H ........................................................................................................... 84
Table 19 EPON Setup ........................................................................................................................... 86
Table 20 EPON Setup: Profile Setup ..................................................................................................... 89
Table 21 EPON Setup: Service Setup (or ONU Setup) ......................................................................... 92
Table 22 IEEE 802.1Q Terminology ....................................................................................................... 98
Table 23 VLAN: VLAN Status .............................................................................................................. 100
Table 24 VLAN: Static VLAN ............................................................................................................... 101
Table 25 VLAN: Static VLAN: VLAN Port Setting ................................................................................ 102
Table 26 Port Based VLAN Setup ....................................................................................................... 105
Table 27 Static MAC Forwarding ......................................................................................................... 107
Table 28 FIltering ................................................................................................................................. 109
Table 29 STP Path Costs .....................................................................................................................111
Table 30 STP Port States .....................................................................................................................112
Table 31 Spanning Tree Protocol: Status ..............................................................................................113
Table 32 Spanning Tree Protocol: Configuration ..................................................................................114
Table 33 Bandwidth Control ..................................................................................................................117
Table 34 Broadcast Storm Control ....................................................................................................... 120
Table 35 Mirroring ................................................................................................................................ 122
Table 36 Link Aggregation ID: Local Switch ........................................................................................ 123
Table 37 Link Aggregation ID: Peer Switch ......................................................................................... 124
Table 38 Link Aggregation Control Protocol: Status ............................................................................124
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
25
Page 26

List of Tables
Table 39 Link Aggregation Control Protocol: Configuration ................................................................. 125
Table 40 Port Security ......................................................................................................................... 128
Table 41 Physical Queue Priority ......................................................................................................... 129
Table 42 Queuing Method ................................................................................................................... 131
Table 43 Classifier ............................................................................................................................... 134
Table 44 Common Ethernet Type Number ..........................................................................................136
Table 45 Common Protocol Port Number ............................................................................................ 136
Table 46 Policy .................................................................................................................................... 141
Table 47 Multicast Status ..................................................................................................................... 146
Table 48 Multicast ................................................................................................................................ 147
Table 49 Multicast: IGMP Filtering Profile ............................................................................................ 148
Table 50 MVR ...................................................................................................................................... 151
Table 51 MVR: Group Configuration .................................................................................................... 153
Table 52 DHCP Relay .......................................................................................................................... 156
Table 53 Classification Filter Profile Setup .......................................................................................... 160
Table 54 VLAN Tag Format ................................................................................................................. 165
Table 55 Single and Double Tagged 802.11Q Frame Format ............................................................. 165
Table 56 802.1Q Frame ....................................................................................................................... 166
Table 57 EPON VLAN Profile Setup .................................................................................................... 167
Table 58 Priority Profile: OLT-1308 ...................................................................................................... 174
Table 59 Priority Profile: OLT-1308H ................................................................................................... 176
Table 60 Common Ethernet Types Numbers ....................................................................................... 177
Table 61 Common Protocol Names and Numbers .............................................................................. 177
Table 62 Static MAC Forwarding Status .............................................................................................. 179
Table 63 Static MAC Forwarding ......................................................................................................... 180
Table 64 Destination Filter Status ........................................................................................................ 181
Table 65 Destination Filter: DA Filter ................................................................................................... 182
Table 66 Port Authentication: 802.1x ................................................................................................... 186
Table 67 Port Authentication: RADIUS ................................................................................................ 187
Table 68 Static Routing ........................................................................................................................ 191
Table 69 Filename Conventions .......................................................................................................... 198
Table 70 Access Control Overview ...................................................................................................... 201
Table 71 SNMP Commands ................................................................................................................ 203
Table 72 SNMP Traps .......................................................................................................................... 203
Table 73 Access Control: SNMP ......................................................................................................... 204
Table 74 Access Control: Logins ......................................................................................................... 205
Table 75 Access Control: Service Access Control ...............................................................................210
Table 76 Access Control: Remote Management ..................................................................................211
Table 77 Diagnostic ............................................................................................................................. 213
Table 78 Syslog Severity Levels .......................................................................................................... 215
Table 79 Syslog ................................................................................................................................... 216
Table 80 Syslog: Server Setup ............................................................................................................ 217
Table 81 ZyXEL Clustering Management Specifications ..................................................................... 219
26
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 27

List of Tables
Table 82 FTP Upload to Cluster member Example ............................................................................. 221
Table 83 Configuring Cluster Management ......................................................................................... 222
Table 84 MAC Table: OLT-1308 ........................................................................................................... 227
Table 85 MAC Table: OLT-1308H ........................................................................................................ 227
Table 86 ARP Table ............................................................................................................................. 230
Table 87 IGMP Table ........................................................................................................................... 231
Table 88 Sub Configuration Modes ..................................................................................................... 239
Table 89 Command Summary: User Mode ........................................................................................ 241
Table 90 Command Summary: Enable Mode ...................................................................................... 243
Table 91 Command Summary: Configuration Mode ............................................................................ 248
Table 92 classifier-filter-profile Commands .......................................................................................... 259
Table 93 epon-common Commands .................................................................................................... 260
Table 94 epon-profile Commands ........................................................................................................ 261
Table 95 interface port-channel Commands ........................................................................................ 263
Table 96 mvr Commands ..................................................................................................................... 265
Table 97 onu Commands ..................................................................................................................... 266
Table 98 priority-profile Commands ..................................................................................................... 267
Table 99 vlan Commands .................................................................................................................... 268
Table 100 vlan-profile Commands ....................................................................................................... 269
Table 101 Troubleshooting the Start-Up of Your OLT .......................................................................... 287
Table 102 Troubleshooting Accessing the OLT ...................................................................................287
Table 103 Troubleshooting the Password ............................................................................................ 293
Table 104 General Product Specifications ........................................................................................... 297
Table 105 Management Specifications ................................................................................................ 298
Table 106 Physical and Environmental Specifications ......................................................................... 298
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
27
Page 28

List of Tables
28
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 29

PART I
Introduction
Introducing the OLT (31)
Hardware Installation and Connection (35)
Hardware Overview (39)
29
Page 30

30
Page 31

CHAPTER 1
Introducing the OLT
This chapter introduces the main applications and features of the OLT. It also introduces the
ways you can manage the OLT.
1.1 Overview
The OLT-1308 series is a manageable optical line terminal with eight fiber ports, eight Gigabit
uplink interfaces, one 10/100Mbps Ethernet management port and a console port. The OLT1308 series is capable of providing network access to customers at distances up to 20km.
The OLT allows service providers to easily implement FTTH (Fiber To The Home)
infrastructure offering reliable high-speed network access to their subscribers over optical
fiber through ONUs (Optical Network Units).
The following shows an example network.
Figure 1 Network Example
Ethernet
Two OLT models are discussed in this guide. The OLT-1308H comes with 8 uplink ports for
each fiber connection. The OLT-1308 has a built-in 4-port switch. Switch features discussed in
this guide are for the OLT-1308 only.
With its built-in web configurator, managing and configuring the OLT is easy. In addition, the
OLT can also be managed via Telnet, any terminal emulator program on the console port, or by
third-party SNMP management.
1.2 Ways to Manage the OLT
Use any of the following methods to manage the OLT.
• Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the OLT using a
(supported) web browser.
• Command Line Interface. Line commands are mostly used for troubleshooting by service
engineers.
• FTP for firmware upgrades and configuration backup/restore.
• SNMP. The device can be monitored by an SNMP manager. See the SNMP chapter in this
User’s Guide.
Fiber
Internet
Ethernet
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 1 Introducing the OLT
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the OLT
Do the following things regularly to make the OLT more secure and to manage the OLT more
effectively.
• Change the password. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that consists of
different types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an
earlier working configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even
crashes. If you forget your password, you will have to reset the OLT to its factory default
settings. If you backed up an earlier configuration file, you would not have to totally reconfigure the OLT. You could simply restore your last configuration.
1.4 LEDs
The following figure shown the LED labels on the OLT.
Figure 2 LEDs (OLT-1308H)
Figure 3 LEDs (OLT-1308)
The following table describes the LEDs.
Table 1 LEDs
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR Green On The OLT is receiving power.
Off The OLT is not receiving power.
SYS/ALM Green On The OLT is ready and is functioning properly.
Blinking The OLT is rebooting.
Red On The OLT failed the system test.
Off The OLT is not ready.
PON
LINK Green On The PON port is initialized and ready.
Off The PON port is not initialized or not ready.
Gigabit Ethernet Ports (OLT-1308)
32
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 33

Chapter 1 Introducing the OLT
Table 1 LEDs (continued)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
Green On The link to a 10 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
Blinking The port is receiving or transmitting data. at 10 Mbps.
Off This port is not connected to an Ethernet device.
Amber On The link to a 100 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
Blinking The port is receiving or transmitting data. at 100 Mbps.
Off This port is not connected to an Ethernet device.
Green +
Amber
Gigabit Ethernet Ports (OLT-1308H)
1000 Green Blinking The port is sending/receiving data.
Mini-GBIC ports (OLT-1308)
LNK Green On The port has a successful connection.
ACT Green Blinking The port is sending or receiving data.
MGMT Port (OLT-1308)
10 Green On The link to a 10 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
100 Amber On The link to a 100 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
MGMT Port (OLT-1308H)
10 Amber On The link to a 10 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
100 Green On The link to a 100 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
On The link to a 1000 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
Blinking The port is receiving or transmitting data. at 1000 Mbps.
Off This port is not connected to an Ethernet device.
On The link to a 1000 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
Off No Ethernet device is connected to this port.
Off No Ethernet device is connected to this port.
Off The port is not sending or receiving data.
Blinking The port is receiving or transmitting data. at 10 Mbps.
Off This port is not connected to an Ethernet device.
Blinking The port is receiving or transmitting data. at 100 Mbps.
Off This port is not connected to an Ethernet device.
Blinking The port is receiving or transmitting data. at 10 Mbps.
Off This port is not connected to an Ethernet device.
Blinking The port is receiving or transmitting data. at 100 Mbps.
Off This port is not connected to an Ethernet device.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 1 Introducing the OLT
34
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 35

CHAPTER 2
Hardware Installation and
Connection
This chapter shows you how to install the hardware and make port connections.
" Example graphics are shown.
2.1 Freestanding Installation
1 Make sure the OLT is clean and dry.
2 Set the OLT on a smooth, level surface strong enough to support the weight of the OLT
and the connected cables. Make sure there is a power outlet nearby.
3 Make sure there is enough clearance around the OLT to allow air circulation and the
attachment of cables and the power cord.
4 Remove the adhesive backing from the rubber feet.
5 Attach the rubber feet to each corner on the bottom of the OLT. These rubber feet help
protect the OLT from shock or vibration and ensure space between devices when
stacking.
" Do NOT block the ventilation holes. Leave space between devices when
stacking.
For proper ventilation, allow at least 4 inches (10 cm) of clearance at the front
and 3.4 inches (8 cm) at the back of the OLT. This is especially important for
enclosed rack installations.
2.2 Mounting the OLT on a Rack
This section lists the rack mounting requirements and precautions and describes the
installation steps.
2.2.1 Rack-mounted Installation Requirements
• Two mounting brackets.
• Eight M3 flat head screws and a #2 Philips screwdriver.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
• Four M5 flat head screws and a #2 Philips screwdriver.
" Failure to use the proper screws may damage the unit.
2.2.1.1 Precautions
• Make sure the rack will safely support the combined weight of all the equipment it
contains.
• Make sure the position of the OLT does not make the rack unstable or top-heavy. Take all
necessary precautions to anchor the rack securely before installing the unit.
2.2.2 Attaching the Mounting Brackets to the OLT
1 Position a mounting bracket on one side of the OLT, lining up the four screw holes on
the bracket with the screw holes on the side of the OLT.
Figure 4 Attaching the Mounting Brackets
2 Using a #2 Philips screwdriver, install the M3 flat head screws through the mounting
bracket holes into the OLT.
3 Repeat steps 1 and 2 to install the second mounting bracket on the other side of the OLT.
4 You may now mount the OLT on a rack. Proceed to the next section.
2.2.3 Mounting the OLT on a Rack
1 Position a mounting bracket (that is already attached to the OLT) on one side of the rack,
lining up the two screw holes on the bracket with the screw holes on the side of the rack.
36
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 37

Figure 5 Mounting the OLT on a Rack
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
2 Using a #2 Philips screwdriver, install the M5 flat head screws through the mounting
bracket holes into the rack.
3 Repeat steps 1 and 2 to attach the second mounting bracket on the other side of the rack.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
37
Page 38

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
38
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 39

CHAPTER 3
Hardware Overview
This chapter describes the front panel and rear panel of the OLT and shows you how to make
the hardware connections.
3.1 Hardware Connection
The figure below shows the front panel of the OLT.
Figure 6 Front Panel
The following table describes the port labels on the front panel.
Table 2 Port Connection
PORT DESCRIPTION
PON Ports Connect a port to an Optical Network Unit (ONU) using a fiber optic cable with an
SC/UPC connector.
To connect more than one ONU to a port, use an optical splitter.
RJ-45 Gigabit
Ethernet Ports
(OLT-1308H)
Gigabit/Mini-GBIC
Ports (OLT-1308)
CONSOLE Only connect this port if you want to configure the OLT using the command line
MGMT Connect to a computer using an RJ-45 Ethernet cable for local configuration of the
Connect these uplink ports to a computer, a server, a switch or router. The port
number corresponds to the PON port number. For example, Gigabit Ethernet port
1 is the uplink port for PON port 1.
Note: The Gigabit Ethernet ports connect at 1000 Mbps only.
Connect only Gigabit Ethernet devices to these ports.
Connect these switch ports to a computer, a server, a switch or router.
interface (CLI) via the console port.
Note: On the OLT-1308, the CONSOLE port is on the rear
panel.
OLT.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
3.1.1 Fiber Connections
" To avoid possible eye injury, do NOT look into an operating fiber-optic module’s
connectors.
Connect a PON port to an ONU using a fiber cable with an SC/UPC connector. Insert the
cable into the port and push the shutter in until the connector snaps into the port.
The shutter protects the cable from being accidentally disconnected.
Do NOT use excessive force to twist or bend the connector into the port. This will damage the
fiber port and/or fiber connector.
3.1.1.1 Removing a Fiber Cable
To remove the fiber cable from a PON port, pull out the shutter until you hear a click sound
and then disconnect the cable.
You cannot disconnect the cable without first releasing the shutter. Do NOT forcibly pull out a
fiber cable. This will damage the fiber port and/or the fiber connector.
3.1.2 Gigabit Ethernet Ports
The OLT-1308H has eight Gigabit Ethernet ports that work as uplink ports for the
corresponding PON ports. The Gigabit port number corresponds to the PON port number. For
example, Gigabit Ethernet port 1 is the uplink port for PON port 1. The Gigabit Ethernet ports
connect at 1000 Mbps only. Connect only Gigabit Ethernet devices to these ports.
On the OLT-1308, there are four pairs of Gigabit Ethernet/mini-GBIC ports for switching. The
mini-GBIC ports have priority over the Gigabit Ethernet ports. This means that if a mini-GBIC
port and the corresponding Gigabit port are connected at the same time, the Gigabit Ethernet
port will be disabled.
3.1.2.1 Default Gigabit Ethernet Settings
The factory default negotiation settings for the Gigabit Ethernet ports on the OLT are:
• Speed: 1000 Mbps
• Duplex: Full
• Flow control: on
3.1.3 Mini-GBIC Slots
The mini-GBIC slots are available on the OLT-1308. These are slots for mini-GBIC (Gigabit
Interface Converter) transceivers. A transceiver is a single unit that houses a transmitter and a
receiver. The switch does not come with transceivers. You must use transceivers that comply
with the Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) Transceiver MultiSource Agreement (MSA). See
the SFF committee’s INF-8074i specification Rev 1.0 for details.
40
The mini-GBIC ports have priority over the Gigabit ports. This means that if a mini-GBIC port
and the corresponding Gigabit port are connected at the same time, the Gigabit port will be
disabled.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 41

You can change transceivers while the switch is operating. You can use different transceivers
to connect to Ethernet switches with different types of fiber-optic connectors.
• Type: SFP connection interface
• Connection speed: 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps)
3.1.3.1 Transceiver Installation
Use the following steps to install a mini-GBIC transceiver (SFP module).
1 Insert the transceiver into the slot with the exposed section of PCB board facing down.
Figure 7 Transceiver Installation Example
2 Press the transceiver firmly until it clicks into place.
3 The switch automatically detects the installed transceiver. Check the LEDs to verify that
it is functioning properly.
Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
Figure 8 Installed Transceiver
3.1.3.2 Transceiver Removal
Use the following steps to remove a mini-GBIC transceiver (SFP module).
1 Open the transceiver’s latch (latch styles vary).
Figure 9 Opening the Transceiver’s Latch Example
2 Pull the transceiver out of the slot.
Figure 10 Transceiver Removal Example
3.1.4 Console Port
For local management using the CLI (Command Line Interface) commands, you can use a
computer with terminal emulation software configured to the following parameters:
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 3 Hardware Overview
• VT100 terminal emulation
• 9600 bps
• No parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit
• No flow control
Connect the male 9-pin end of the console cable to the console port of the OLT. Connect the
female end to a serial port (COM1, COM2 or other COM port) of your computer.
3.1.5 Power Connector
Make sure you are using the correct power source as shown on the panel.
42
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 43

PART II
Basic Setup
The Web Configurator (45)
Initial Setup Example (55)
System Status and Port Statistics (59)
Basic Setting (73)
43
Page 44

44
Page 45

CHAPTER 4
The Web Configurator
This chapter introduces the configuration and functions of the web configurator.
4.1 Introduction
The web configurator is an HTML-based management interface that allows easy OLT setup
and management via Internet browser. Use Internet Explorer 6.0 and later or Netscape
Navigator 7.0 and later versions. The recommended screen resolution is 1024 by 768 pixels.
In order to use the web configurator you need to allow:
• Web browser pop-up windows from your device. Web pop-up blocking is enabled by
default in Windows XP SP (Service Pack) 2.
• JavaScript (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
" Web configurator screens are similar for the OLT models described in this
guide. Screens for the OLT-1308 are used as examples.
4.2 System Login
1 Connect your computer to the MGMT port and set your computer IP address to the same
subnet as the out-of-band management IP address of the OLT.
" On the OLT-1308, you can also access the web configurator through a switch
port.
2 Start your web browser.
3 Type “http://” and the management IP address of the OLT (the default is 192.168.0.1) in
the Location or Address field. Press [ENTER].
4 The login screen appears. The default username is admin and associated default
password is 1234. The date and time display as shown if you have not configured a time
server nor manually entered a time and date in the General Setup screen.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
Figure 11 Web Configurator: Login
5 Click OK to view the first web configurator screen.
4.3 The Status Screen
The Status screen is the first screen that displays when you access the web configurator.
The following figure shows the navigating components of a web configurator screen.
Figure 12 Web Configurator: Home Screen (Status): OLT-1308
46
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 47

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
In the navigation panel, click a main link to reveal a list of submenu links.
Table 3 Navigation Panel Sub-links Overview: OLT-1308
BASIC SETTING
ADVANCED
APPLICATION: SWITCH
ADVANCED
APPLICATION: EPON
ROUTING PROTOCOL MANAGEMENT
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
47
Page 48

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
Table 4 Navigation Panel Sub-links Overview: OLT-1308H
BASIC SETTING
ADVANCED
APPLICATION
MANAGEMENT
48
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 49

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
The following table lists the various web configurator screens within the sub-links.
Table 5 Web Configurator Screen Sub-links Details
BASIC SETTING ADVANCED APPLICATION ROUTING PROTOCOL MANAGEMENT
System Info
General Setup
Switch Setup
IP Setup
Port Setup
EPON Setup
Profile Setup
Service Setup
(or ONU
Setup)
Switch Advance (OLT-1308 only):
VLAN
VLAN Status
VLAN Port Setting
Static VLAN
Static MAC Forwarding
Filtering
Spanning Tree Protocol
Status
Spanning Tree Protocol
Configuration
Bandwidth Control
Broadcast Storm Control
Mirroring
Link Aggregation
Link Aggregation Protocol
Status
Configuration
Port Security
Queuing Method
Classifier
Policy Rule
Multicast
Status
Multicast Setting
IGMP Filtering Profile
MVR
Group Configuration
DHCP Relay
Static Routing Maintenance
Remote Firmware Upgrade
OLT Chip Reset
ONU Device Reset
Firmware Upgrade
Restore Configuration
Backup Configuration
Load Factory Default
Reboot System
Access Control (OLT-1308
only)
SNMP
Logins
Service Access Control
Remote Management
Diagnostic
Syslog
Syslog Server Setup
Cluster Management
Status
Cluster Management
Configuration
MAC Table
ARP Table
IGMP Table
EPON Advance:
Classification Filter Profile
VLAN Profile
Priority Profile
Static MAC Forwarding Status
Static MAC Forwarding
Destination Filter Status
DA Filter
Port Authentication
RADIUS
802.1x
Access Control (OLT-1308H only)
SNMP
Logins
Service Access Control
Remote Management
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
The following table describes the links in the navigation panel.
Table 6 Navigation Panel Links
LINK DESCRIPTION
Basic Settings
System Info This link takes you to a screen that displays general system and hardware
monitoring information.
General Setup This link takes you to a screen where you can configure general identification
information about the OLT.
Switch Setup This link takes you to a screen where you can set up global switch parameters such
as VLAN type, MAC address learning, GARP and priority queues.
IP Setup This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the IP address, subnet
Port Setup This link takes you to screens where you can configure settings for the Gigabit
EPON Setup This link takes you to screens where you can configure the filter ports, create
Advanced Application: Switch Advance (OLT-1308 only)
VLAN This link takes you to screens where you can configure port-based or 802.1Q VLAN
Static MAC
Forwarding
Filtering This link takes you to a screen to set up filtering rules.
Spanning Tree
Protocol
Bandwidth
Control
Broadcast Storm
Control
Mirroring This link takes you to screens where you can copy traffic from one port or ports to
Link Aggregation This link takes you to a screen where you can logically aggregate physical links to
Port Security This link takes you to a screen where you can activate MAC address learning and
Queuing Method This link takes you to a screen where you can configure SPQ or WFQ with
Multicast This link takes you to a screen where you can configure various multicast features
DHCP Relay This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the DHCP relay settings for
Advanced Application: EPON
Classification
Filter Profile
VLAN Profile This link takes you to screens where you can configure VLAN profiles to control
Priority Profile This link takes you to a screen where you can configure priority profiles for packet
mask and default gateway necessary for management.
Ethernet ports.
profiles and service settings for ONUs.
(depending on what you configured in the Switch Setup menu).
This link takes you to screens where you can configure static MAC addresses for a
port. These static MAC addresses do not age out.
This link takes you to screens where you can configure the STP/RSTP to prevent
network loops.
This link takes you to screens where you can cap the maximum bandwidth allowed
from specified source(s) to specified destination(s).
This link takes you to a screen to set up broadcast filters.
another port in order that you can examine the traffic from the first port without
interference
form one logical, higher-bandwidth link.
set the maximum number of MAC addresses to learn on a port.
associated queue weights for each port.
and create multicast VLANs.
the network on the OLT.
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure classifiers to group traffic
streams and specify actions on the traffic.
VLAN traffic.
prioritization.
50
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 51

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
Table 6 Navigation Panel Links (continued)
LINK DESCRIPTION
Static MAC
Address
Forwarding
Destination Filter
Profile Status
Port
Authentication
IP Application
Static Route This link takes you to screens where you can configure static routes. A static route
Management
Maintenance This link takes you to screens where you can perform device firmware and
Access Control This link takes you to screens where you can change the system login password
Diagnostic This link takes you to screens where you can view system logs and test port(s).
Syslog This link takes you to screens where you can enable syslog logging and configure
Cluster
Management
MAC Table This link takes you to a screen where you can view the MAC addresses (and types)
IGMP Table This link takes you to a screen where you can view information collected by IGMP
ARP Table This link takes you to a screen where you can view the MAC addresses – IP
This link takes you to screens where you can view the number of static MAC
address forwarding rules and configure static MAC addresses for each fiber port.
These static MAC addresses do not age out.
This link takes you to screens where you can view and configure the actions on
traffic from specified ONUs.
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure RADIUS (Remote
Authentication Dial-In User Service), a protocol for user authentication that allows
you to use an external server to validate an unlimited number of users.
defines how the switch should forward traffic by configuring the TCP/IP parameters
manually.
configuration file maintenance as well as reboot the system. You can also perform
remote ONU firmware upgrade and reset the ONU or connection.
and configure SNMP and remote management.
syslog server settings.
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure clustering management
and view its status.
of devices attached to what ports and VLAN IDs.
snooping.
address resolution table.
4.3.1 Change Your Password
After you log in for the first time, it is recommended you change the default administrator
password. Click Management > Access Control > Logins in the OLT-1308 or Advanced
Application > Access Control > Logins in the OLT-1308H to display the following screen.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
Figure 13 Change Administrator Login Password
4.4 Device Lockout
You can be locked out from managing the OLT if another administrator is currently logged in
with the admin user name. You must wait until the other administrator has logged out before
you can log in.
Any of the following could also lock you and others out from using out-of-band management
(managing through the console port or management port).
1 Misconfiguring the text configuration file.
2 Forgetting the password and/or management IP address.
3 Preventing all services from accessing the OLT.
4 Incorrectly configuring the access control settings.
5 Changing a service port number but forgetting it.
" Be careful not to lock yourself and others out of the OLT.
4.5 Resetting the OLT
If you lock yourself (and others) from the OLT or forget the administrator password, you will
need to reload the factory-default configuration file or reset the OLT back to the factory
defaults.
4.5.1 Reload the Configuration File
Uploading the factory-default configuration file replaces the current configuration file with the
factory-default configuration file. This means that you will lose all previous configurations
and the speed of the console port will be reset to the default of 9600bps with 8 data bit, no
parity, one stop bit and flow control set to none. The password will also be reset to 1234 and
the default out-of-band management IP address to 192.168.0.1.
52
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 53

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
To upload the configuration file, do the following:
1 Connect to the console port using a computer with terminal emulation software. See
Section 3.1.4 on page 41 for details.
2 Disconnect and reconnect the OLT’s power to begin a session. When you reconnect the
OLT’s power, you will see the initial screen.
3 When you see the message “
seconds ...
4 Type
atlc after the “Enter Debug Mode” message.
5 Wait for the “
” press any key to enter debug mode.
Starting XMODEM upload” message before activating XMODEM
Press any key to enter Debug Mode within 3
upload on your terminal.
6 After a configuration file upload, type
Figure 14 Resetting the Device: Via the Console Port
Bootbase Version: VAIJ100 | 04/13/2006 18:25:19
RAM:Size = 64 Mbytes
FLASH: Intel 64M
ZyNOS Version: V3.60(AIJ.0) | 05/10/2006 18:10:56
atgo to restart the OLT.
Press any key to enter debug mode within 3 seconds.
....................
Enter Debug Mode
sysname> atlc
Starting XMODEM upload (CRC mode)....
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
Total 393216 bytes received.
Erasing..
................................................................
OK
sysname> atgo
The OLT is now reinitialized with a default configuration file including the default
administrator login password of 1234 and the out-of-band management IP address of
192.168.0.1.
4.6 Logging Out of the Web Configurator
Click Logout in a screen to exit the web configurator. You have to log in with your password
again after you log out. This is recommended after you finish a management session for
security reasons.
Figure 15 Web Configurator: Logout Screen
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
53
Page 54

Chapter 4 The Web Configurator
4.7 Help
The web configurator’s online help has descriptions of individual screens and some
supplementary information.
Click the Help link from a web configurator screen to view an online help description of that
screen.
54
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 55

CHAPTER 5
Initial Setup Example
This chapter shows how to set up the OLT to provide Internet access to an ONU using the
default service profiles.
5.1 Overview
You need to test the connection between an ONU and the OLT in your network before
deploying your PON. You should already have a network with Internet access, a DHCP server
and a Gigabit switch.
In this example, you set up a simple PON network using an OLT, an ONU and a computer.
Once connected, the default profile settings on the OLT allows you to can access the Internet
through the ONU. For the test network, you create a service profile on the OLT with the predefined 100Mbps bandwidth limit and apply it to the ONU.
Figure 16 Initial Setup: Network Example
ONU
PON 1
The following outlines the procedure for the initial setup.
• Connect the devices to set up a simple network.
• Create a service profile with the pre-defined bandwidth setting.
• Test the Internet connection from the ONU.
5.2 Connecting the Devices
Follow the steps below to connect the devices for the simple test network.
1 For OLT-1308H: Connect Gigabit Ethernet port 1 on the OLT to a Gigabit port on a
switch that has access to the Internet.
For OLT-1308: Connect a switch port to a router/switch that has access to the Internet.
OLT
MGMT
Ethernet 1
Internet
" On OLT-1308H, the Gigabit Ethernet port connects only at 1000 Mbps.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
2 Connect an ONU to PON port 1 on the OLT.
3 Turn on the connected devices and check the LEDs on the OLT. The LEDs for PON 1
and the Ethernet port should be on.
5.3 Creating a Service Profile
Log into the OLT for management and create a service profile for the ONU. The service
profile is to use a pre-defined connection profile to limit the upstream and downstream
bandwidths to 100 Mbps.
1 Connect your computer to the MGMT port and set your computer to use a static IP
address in the range 192.168.0.2 ~ 192.168.0.254 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
2 Open a web browser and enter the management IP address of the OLT. The default is
192.168.0.1.
3 Enter the login username (“admin” is the default) and password (“1234” is the default)
and Click OK.
4 The Status screen displays. Click
port 1 to display the EPON Info
screen and write down the MAC
address of the ONU.
5 Click Basic Setting > EPON Setup
and the Service Setup (or ONU
Setup) link.
6 In the EPON Service Setup (or
EPON ONU Setup) screen, create a
service profile for the ONU. Select
Active and enter a descriptive name
in the ONU Name field (for
example, “TestSetup”).
7 Select Port 1 and enter the MAC address of the ONU in the MAC Address field.
56
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 57

Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
8 Select 100M in the EPON Profile field to apply the bandwidth settings and click Add.
9 The OLT automatically applies the settings to the ONU. Display the EPON Info screen
again to check the settings (click Status > port 1).
You should see that the upstream and downstream bandwidths for the ONU are set to
100 Mbps.
5.4 Testing the Internet Connection
In this section, you test Internet access through the ONU as a subscriber.
1 Connect your computer to the Ethernet port on the ONU.
" Make sure the computer is set to use a dynamic IP address.
2 Open a web browser and enter any web site address (for example, www.zyxel.com).
When the web site displays, you have successfully accessed the Internet through the
PON.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 5 Initial Setup Example
58
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 59

CHAPTER 6
System Status and Port
Statistics
This chapter describes the system status (web configurator home page) and port details
screens.
6.1 Overview
The home screen of the web configurator displays a port statistical summary with links to each
port showing statistical details.
6.2 Port Status Summary
To view the port statistics, click Status in any web configurator screen. The Status screen as
shown next.
Figure 17 Status: OLT-1308
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
59
Page 60

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 7 Status: OLT-1308
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System up Time This field shows how long the system has been running since the last time it was
Port This identifies the fiber port. Click a port number to display the EPON Info screen
OLT This field indicates whether the PON port is ready (Up) or not (Down).
Number of LLID This field displays the number of logical links (or ONUs) on this port.
TxPkts This field shows the number of transmitted frames on this port.
RxPkts This field shows the number of received frames on this port.
Errors This field shows the number of received errors on this port.
Tx KB/s This field shows the number of kilobytes per second transmitted on this port.
Rx KB/s This field shows the number of kilobytes per second received on this port.
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time in hours, minutes and seconds the port has
Port This identifies the Gigabit Ethernet port. Click a port number to display the Port
Link This field displays whether a device is connected to the Gigabit Ethernet port or not.
State This field displays the STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) state of the port. See the
LACP This fields displays whether LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) has been
TxPkts This field shows the number of transmitted frames on this port.
RxPkts This field shows the number of received frames on this port.
Errors This field shows the number of received errors on this port.
Tx KB/s This field shows the number of kilobytes per second transmitted on this port.
Rx KB/s This field shows the number of kilobytes per second received on this port.
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time in hours, minutes and seconds the port has
Poll Interval(s) The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may change
Stop Click Stop to halt system statistic polling.
Port Select a port and click Clear Counter to reset the counters for that port.
started.
(refer to Figure 19 on page 62).
been up.
Details screen (refer to Figure 21 on page 69).
chapter on STP for details on STP states.
enabled on the port.
been up.
the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then clicking Set
Interval.
Select All and click Clear Counter to reset counters for all ports.
60
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 61

Figure 18 Status: OLT-1308H
Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 Status: OLT-1308H
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System up Time This field shows how long the system has been running since the last time it was
started.
Port This identifies the fiber port. Click a port number to display the EPON Info screen
(refer to Figure 19 on page 62).
Status This field indicates whether the PON port is ready (Up) or not (Down).
Number of LLID This field displays the number of logical links (or ONUs) on this port.
TxGoodBytes This field displays the number of bytes transmitted on this port without errors.
RxGoodByets This field displays the number of bytes received on this port without errors.
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time in hours, minutes and seconds the port has
been up.
Uplink Port This identifies the Gigabit Ethernet port. Click a port number to display the Port
Link This field displays whether a device is connected to the Gigabit Ethernet port or not.
TxPkts This field shows the number of transmitted frames on this port.
RxPkts This field shows the number of received frames on this port.
Errors This field shows the number of packets with errors on this port.
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time in hours, minutes and seconds the port has
Details screen (refer to Figure 21 on page 69).
been up.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
61
Page 62

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
Table 8 Status: OLT-1308H (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Poll Interval(s) The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may change
the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then clicking Set
Interval.
Stop Click Stop to halt system statistic polling.
6.2.1 EPON Info
Click a number (1 to 8) in the Port column in the Status screen to display general fiber port
information. Use this screen to check the status and general performance data on connections
to the ONUs.
Figure 19 Status: EPON Info
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 9 Status: EPON Info
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status Click this link to return to the main Status screen.
Port No This field displays the EPON port index number.
Number of
LLID
LLID This field displays the index number of a logical link. Each LLID (Logical Link ID)
Status This field shows the logical link status.
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of the ONU on this logical link.
This field displays the number of connections to the client devices on this port.
denotes a connection to an ONU.
This field displays Up if an ONU is connected.
This field displays Down if an ONU is not connected or is not ready.
This field displays Test ing if you are performing s diagnostic test on the link (using the
Diagnostic screen).
The following lists the five Up states:
Normal - when the ONU is transmitting traffic.
Queuing - when the ONU is waiting for the firmware upgrade.
Upgrading - when the ONU is upgrading its firmware.
Upgrade Fail - ONU firmware upgrade has failed. In this case, reset the ONU.
Upgrade Success - ONU firmware upgrade is completed without errors. The ONU will
restart automatically and the state changes to Normal.
62
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 63

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
Table 9 Status: EPON Info (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Min Us BW This field displays the minimum upstream bandwidth.
Max Us BW This field displays the maximum upstream bandwidth.
Max Ds BW This field displays the maximum downstream bandwidth.
RTT This field displays the round trip time (RTT) in nanoseconds (ns). The RTT is the time
it takes a packet to travel from the OLT, to the ONU and back.
ONU SW This field displays the software version the ONU is using.
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time the connection has been up.
Reregister Click Reregister to reset connections to the ONU. This allows you to set the profile
settings to the ONU or troubleshoot link problems.
The ONU entry will disappear from the screen temporarily. Once the connection is re-
established, you will see the LLID information again.
Poll
Interval(s)
Stop Click Stop to stop port statistic polling.
The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may change
the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then clicking Set
Interval.
6.2.2 EPON Details
To view detailed EPON statistics, click an LLID number in the EPON Info screen to display
the EPON Details screen.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
63
Page 64

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
Figure 20 Status: EPON Info: EPON Details
64
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 65

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 10 Status: EPON Info: EPON Details
LABEL DESCRIPTION
LLID Info
LLID No This field displays the index number of the logical link.
Status This field shows the logical link status.
This field displays Up if an ONU is connected.
This field displays Down if an ONU is not connected or is not ready.
This field displays Testing if you are performing s diagnostic test on the link
(using the Diagnostic screen).
The following lists the five Up states:
Normal - when the ONU is transmitting traffic.
Queuing - when the ONU is waiting for the firmware upgrade.
Upgrading - when the ONU is upgrading its firmware.
Upgrade Fail - ONU firmware upgrade has failed. In this case, reset the
ONU.
Upgrade Success - ONU firmware upgrade is completed without errors.
The ONU will restart automatically and the state changes to Normal.
EAP State This field displays the IEEE 802.1x supplicant EAP status.
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of the ONU on this logical link.
Minimum Upstream
Bandwidth
Maximum Upstream
Bandwidth
Maximum
Downstream
Bandwidth
RTT This field displays the Round Trip Time (RTT) in nanoseconds.
OLT SW Version This field displays the firmware version the OLT uses.
This field displays the minimum upstream bandwidth in Mbps.
This field displays the maximum upstream bandwidth in Mbps.
This field displays the maximum downstream bandwidth in Mbps.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
Table 10 Status: EPON Info: EPON Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ONU SW Version This field displays the firmware version the ONU uses.
Up Time This field displays how long the link connection has been up.
UNI Status This field displays whether the UNI (User Network Interface) connection is
established and auto-negotiation is enabled.
Link Speed This field displays the connection speed and the duplex mode (half or full) for
this link.
ONU HW This field displays the ONU hardware model.
OLT PON Octets
Tx OK This field displays the number of octets transmitted successfully through the
OLT PON Frames
Tx OK This field displays the number of frames transmitted successfully through the
Total Tx Dropped This field displays the number of transmitted frames dropped on the PON.
Total Rx Dropped This field displays the number of received frames dropped on the PON.
Rx FCS Error This is the number of packets received from the PON with one or more FCS
Rx Multicast This field displays the number of multicast packets received.
Tx Multicast This field displays the number of multicast packets transmitted.
Rx Broadcast This field displays the number of broadcast packets received.
Tx Broadcast This field displays the number of broadcast packets transmitted.
ONU Sys Frames
Tx OK This field displays the number of frames transmitted successfully to the
Total Tx Dropped This field displays the number of transmitted frames dropped from the
Rx OK This field displays the number of frames received successfully by the UNI
Rx Err This field displays the number of errored frames received by the UNI port.
Rx Oversized This field displays the number of oversized frames received by the UNI port.
ONU Sys Octets
Tx OK This field displays the number of octets transmitted successfully to the
Rx OK This field displays the number of octets received successfully by the UNI
Rx Err This field displays the number of errored octets received by the UNI port.
ONU PON Octets
Tx OK This field displays the number of octets transmitted successfully to the ONU.
Rx OK This field displays the number of octets received successfully by the ONU.
ONU PON Frames
Total Tx Dropped This field displays the number of transmitted frames dropped on the ONU.
PON.
PON.
errors.
system.
downlink queue due to queue overflow.
port.
system.
port.
66
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 67

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
Table 10 Status: EPON Info: EPON Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rx FCS Error This field displays the number of received packets with one or more FCS
errors on the ONU.
Rx Multicast This field displays the number of multicast frames received by the ONU.
Tx Multicast This field displays the number of multicast frames transmitted by the ONU.
Rx Broadcast This field displays the number of broadcast frames received by the ONU.
Tx Broadcast This field displays the number of broadcast frames transmitted by the ONU.
P0 Tx Frames This field displays the number of priority 0 frames transmitted to the ONU.
P1 Tx Frames This field displays the number of priority 1 frames transmitted to the ONU.
P2 Tx Frames This field displays the number of priority 2 frames transmitted to the ONU.
P3 Tx Frames This field displays the number of priority 3 frames transmitted to the ONU.
P2P Frames
Received OK This field displays the number of peer-to-peer frames received.
Dropped by Policier This field displays the number of peer-to-peer frames dropped by a policy.
Dropped Due To Tx
Buffer Full
Transmitted OK This field displays the number of peer-to-peer frames transmitted.
MPCP Info
Administration State This field indicates whether access is allowed for management.
Mode This field displays the mode of the device on this network.
Unsupported
Frames
MAC Ctrl Frames
Transmitted
MAC Ctrl Frames
Received
Max Pending
Grants
Register Request
Transmitted OK
Register Received OKThis field displays the number of registration request received.
This field displays the number of peer-to-peer frames dropped because the
transmission buffer is full.
This field displays then number of frames that were not supported/
recognized.
This field displays the number of MAC control frames transmitted.
This field displays the number of MAC control frames received.
The field displays the maximum number of grants an ONU can store.
This field displays the number of registration request transmitted.
Register Ack
Transmitted OK
Grant Frames
Transmitted OK
Grant Frames
Received OK
OLT Gate Frames
Transmitted OK
ONU Gate Frames
Received OK
Report Frames
Transmitted OK
Report Frames
Received OK
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
This field displays the number of registration request acknowledgement
transmitted.
This field displays the number of grant frames transmitted.
This field displays the number of grant frames received.
This field displays the number of gate frames transmitted from the OLT.
This field displays the number of gate frames received by the ONU.
This field displays the number of report frames transmitted.
This field displays the number of report frames received.
67
Page 68

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
Table 10 Status: EPON Info: EPON Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
OAM Frames Counter
Unsupported Codes RXThis field displays the number of received frames with unsupported OAM
Information TX This field displays the number of OAM frames transmitted.
Information RX This field displays the number of OAM frames received.
Event Notification TxThis field displays the number of event notification transmitted.
functions.
Unique Event
Notification Rx
Duplicate Event
Notification Rx
Loopback Control TxThis field displays the number of loopback control packets transmitted.
Loopback Control RxThis field displays the number of loopback packets received.
Frames Lost Due to
OAM Error
Alarm
BER This field indicates whether a Bit Error Rate (BER) alarm has occurred.
FER This field indicates whether a Frame Error Rate (FER) alarm has occurred.
Dying Gasp This field indicates whether a Dying Gasp alarm has occurred.
Errored Symbol
Period
Errored Frame This field indicates whether an Errored Frames alarm has occurred.
Errored Frame
Period
Errored Frames
Second Summary
OAM Link
Disconnection
Bad Encryption Key This field indicates whether a bad encryption key alarm has occurred.
Poll Interval(s) The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may
Stop Click Stop to stop port statistic polling.
Counter Click Clear to reset the counters.
This field displays the number of event notifications with a sequence number
not equal to the last event notification received. The sequence number is
increased by one for each unique event notification received.
This field displays the number of event notifications with a sequence number
that is equal to the last event notification received.
This field displays the number of frames lost due to OAM errors.
This field indicates whether an Errored Symbol Period alarm has occurred.
This field indicates whether an Errored Frames Period alarm has occurred.
This field indicates whether an Errored Frames Second Summary alarm has
occurred.
This field indicates whether an OAM link disconnection alarm has occurred.
change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then
clicking Set Interval.
6.2.3 Ethernet Port Details
Click a number (9-12) in the Port column or a number (1-8) in the Uplink Port column in the
Status screen to display Ethernet port statistics. Use this screen to check status and detailed
performance data about an Ethernet uplink port on the OLT.
68
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 69

Figure 21 Status: Port Details
Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Tabl e 11 Status: Port Details
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Info
Link This field displays the speed (either 10M for 10Mbps, 100M for 100Mbps or 1000M for
1000Mbps) and the duplex (F for full duplex or H for half duplex).
Status This field shows the training state of the ports. The states are FORWARDING
(forwarding), which means the link is functioning normally or STOP (the port is stopped
to break a loop or duplicate path).
LACP This field shows if LACP is enabled on this port or not.
TxPkts This field shows the number of transmitted frames on this port
RxPkts This field shows the number of received frames on this port
Errors This field shows the number of received errors on this port.
Tx KB/s This field shows the number kilobytes per second transmitted on this port.
Rx KB/s This field shows the number of kilobytes per second received on this port.
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time the connection has been up.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
Tabl e 11 Status: Port Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Tx Packet
The following fields display detailed information about packets transmitted.
TX Packets This field shows the number of good packets (unicast, multicast and broadcast)
transmitted.
Multicast This field shows the number of good multicast packets transmitted.
Broadcast This field shows the number of good broadcast packets transmitted.
Pause This field shows the number of 802.3x Pause packets transmitted.
Rx Packet
The following fields display detailed information about packets received.
RX Packets This field shows the number of good packets (unicast, multicast and broadcast)
Multicast This field shows the number of good multicast packets received.
Broadcast This field shows the number of good broadcast packets received.
Pause This field shows the number of 802.3x Pause packets received.
Control This field shows the number of control packets received (including those with CRC
TX Collision
The following fields display information on collisions while transmitting.
Single This is a count of successfully transmitted packets for which transmission is inhibited
Multiple This is a count of successfully transmitted packets for which transmission was inhibited
Excessive This is a count of packets for which transmission failed due to excessive collisions.
Late This is the number of times a late collision is detected, that is, after 512 bits of the
Error Packet The following fields display detailed information about packets received that were in
RX CRC This field shows the number of packets received with CRC (Cyclic Redundant Check)
Length This field shows the number of packets received with a length that was out of range.
Runt This field shows the number of packets received that were too short (shorter than 64
Distribution
64 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received that were 64
65-127 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
128-255 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
256-511 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
512-1023 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
received.
error) but it does not include the 802.3x Pause packets.
by exactly one collision.
by more than one collision.
Excessive collision is defined as the number of maximum collisions before the
retransmission count is reset.
packets have already been transmitted.
error.
error(s).
octets), including the ones with CRC errors.
octets in length.
between 65 and 127 octets in length.
between 128 and 255 octets in length.
between 256 and 511 octets in length.
between 512 and 1023 octets in length.
70
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 71

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
Tabl e 11 Status: Port Details (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
1024-1518 This field shows the number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
Giant This field shows the number of packets received that are bigger than the maximum
Poll Interval(s) The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may change
Stop Click Stop to stop port statistic polling.
between 1024 and 1518 octets in length.
frame size.
the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then clicking Set
Interval.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
71
Page 72

Chapter 6 System Status and Port Statistics
72
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 73

CHAPTER 7
Basic Setting
This chapter describes how to configure the screens in Basic Setting menu.
7.1 Overview
The System Info screen displays general OLT information (such as firmware version number)
and hardware polling information. The General Setup screen allows you to configure general
OLT identification information. The General Setup screen also allows you to set the system
time manually or get the current time and date from an external server when you turn on your
OLT. The real time is then displayed in the logs. The IP Setup screen allows you to configure
the management IP settings (such as the IP address and subnet mask). Use the EPON Setup
screens to configure general PON settings and create service and profiles to associate to each
ONU.
7.2 System Information
In the navigation panel, click Basic Setting > System Info to display the screen as shown. You
can check the firmware version number and monitor the OLT temperature, fan speeds and
voltage in this screen.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Figure 22 System Info
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 System Info
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Name This field displays the descriptive name of the OLT for identification purposes.
ZyNOS F/W
Version
(or F/W
Version)
Ethernet
Address
Hardware Monitor
Temperature
Unit
Temperature SWITCH, GPHY and SERDES refer to the location of the temperature sensors on the
Current This shows the current temperature in degrees centigrade at this sensor.
MAX This field displays the maximum temperature measured at this sensor.
MIN This field displays the minimum temperature measured at this sensor.
Threshold This field displays the upper temperature limit at this sensor.
Status This field displays Normal for temperatures below the threshold and Error for those
This field displays the version number of the OLT 's current firmware including the
date created.
This field refers to the Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control) address of the OLT.
The OLT has temperature sensors that are capable of detecting and reporting if the
temperature rises above the threshold. You may choose the temperature unit
(Centigrade or Fahrenheit) in this field.
circuit board.
above.
If Error displays, check that the fans are working and make sure that you do not block
ventilation holes on the OLT.
74
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 75

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Table 12 System Info (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Fan Speed
(RPM)
Current This field displays this fan's current speed in Revolutions Per Minute (RPM).
MAX This field displays this fan's maximum speed measured in Revolutions Per Minute
MIN This field displays this fan's minimum speed measured in Revolutions Per Minute
Threshold This field displays the minimum speed at which a normal fan should work.
Status Normal indicates that this fan is functioning above the minimum speed. Error
Voltage(V) The power supply for each voltage has a sensor that is capable of detecting and
Current This is the current voltage reading.
MAX This field displays the maximum voltage measured at this point.
MIN This field displays the minimum voltage measured at this point.
Threshold This field displays the percentage tolerance of the voltage with which the OLT still
Status Normal indicates that the voltage is within an acceptable operating range at this
Poll Interval(s) The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may change
Stop Click Stop to halt statistic polling.
A properly functioning fan is an essential component (along with a sufficiently
ventilated, cool operating environment) in order for the device to stay within the
temperature threshold. Each fan has a sensor that is capable of detecting and
reporting if the fan speed falls below the threshold shown.
(RPM).
(RPM).
indicates that this fan is functioning below the minimum speed.
If Error displays, it is recommended that the fan(s) on the OLT be replaced by a
qualified technician.
reporting if the voltage falls out of the tolerance range.
works.
point; otherwise Error is displayed.
If Error displays, an electronic component might be defective. Have the OLT serviced
by a qualified technician.
the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then clicking Set
Interval.
7.3 General Setup
Click Basic Setting > General Setup in the navigation panel to display the screen as shown.
Use this screen to configure the system name, the system time and date or set the OLT to save
system logs.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
75
Page 76

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Figure 23 General Setup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 General Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Name Choose a descriptive name for identification purposes. This name consists of up to
30 characters; spaces are allowed.
Location Enter the geographic location (up to 30 characters) of your OLT.
Contact Person's
Name
Save System
Log
Use Time Server
when Bootup
Time Server IP
Address
Enter the name (up to 30 characters) of the person in charge of this OLT.
By default, system logs are stored in versatile memory. This means logs are erased
after you restart the OLT).
To save logs in non-versatile memory, select this option. The OLT automatically
saves the logs every one hour. You can store up to 1000 log entries on the OLT.
Once full, the OLT wraps around and delete the old logs.
You can view logs in the Diagnostic screen (see Figure 111 on page 213).
Enter the time service protocol that a timeserver sends when you turn on the OLT.
Not all time servers support all protocols, so you may have to use trial and error to
find a protocol that works. The main differences between them are the time format.
When you select the Daytime (RFC 867) format, the OLT displays the day, month,
year and time with no time zone adjustment. When you use this format it is
recommended that you use a Daytime timeserver within your geographical time
zone.
Time (RFC-868) format displays a 4-byte integer giving the total number of
seconds since 1970/1/1 at 0:0:0.
NTP (RFC-1305) is similar to Time (RFC-868).
None is the default value. Enter the time manually. Each time you turn on the OLT,
the time and date will be reset to 2000-1-1 0:0.
Enter the IP address of your timeserver. The OLT searches for the timeserver for
up to 60 seconds. If you select a timeserver that is unreachable, then this screen
will appear locked for 60 seconds. Please wait.
76
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 77

Table 13 General Setup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Current Time This field displays the time you open this menu (or refresh the menu).
New Time
(hh:min:ss)
Current Date This field displays the date you open this menu.
New Date (yyyymm-dd)
Time Zone Select the time difference between UTC (Universal Time Coordinated), formerly
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
Enter the new time in hour, minute and second format. The new time then appears
in the Current Time field after you click Apply.
Enter the new date in year, month and day format. The new date then appears in
the Current Date field after you click Apply.
known as GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) and your time zone from the drop-down list
box.
7.4 Introduction to VLANs
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a physical network to be partitioned into
multiple logical networks. Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can
belong to more than one group. With VLAN, a device cannot directly talk to or hear from
devices that are not in the same group(s); the traffic must first go through a router.
Chapter 7 Basic Setting
In MTU (Multi-Tenant Unit) applications, VLAN is vital in providing isolation and security
among the subscribers. When properly configured, VLAN prevents one subscriber from
accessing the network resources of another on the same LAN, thus a user will not see the
printers and hard disks of another user in the same building.
VLAN also increases network performance by limiting broadcasts to a smaller and more
manageable logical broadcast domain. In traditional switched environments, all broadcast
packets go to each and every individual port. With VLAN, all broadcasts are confined to a
specific broadcast domain.
Note: VLAN is unidirectional; it only governs outgoing traffic.
See Chapter 8 on page 97 for information on port-based and IEEE 802.1Q tagged VLANs.
7.5 Switch Setup Screen
Click Basic Setting and then Switch Setup in the navigation panel to display the screen as
shown. The VLAN setup screens change depending on whether you choose 802.1Q or Port
Based in the VLAN Type field in this screen. Refer to the chapter on VLAN.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
77
Page 78

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Figure 24 Switch Setup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 Switch Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VLAN Type Choose 802.1Q or Port Based. The VLAN Setup screen changes depending on
whether you choose 802.1Q VLAN type or Port Based VLAN type in this screen.
See Chapter 8 on page 97 for more information.
Bridge Control
Protocol
Transparency
MAC Address
Learning
Aging Time Enter a time from 10 to 3000 seconds. This is how long all dynamically learned MAC
GARP Timer: Switches join VLANs by making a declaration. A declaration is made by issuing a Join
message using GARP. Declarations are withdrawn by issuing a Leave message. A Leave All message
terminates all registrations. GARP timers set declaration timeout values. See the chapter on VLAN
setup for more background information.
Join Timer Join Timer sets the duration of the Join Period timer for GVRP in milliseconds. Each
Leave Timer Leave Time sets the duration of the Leave Period timer for GVRP in milliseconds.
Leave All
Timer
Select Active to allow the switch to handle bridging control protocols (STP for
example). You also need to define how to treat a BPDU in the Port Setup screen.
MAC address learning reduces outgoing traffic broadcasts. For MAC address
learning to occur on a port, the port must be active.
addresses remain in the MAC address table before they age out (and must be
relearned).
port has a Join Period timer. The allowed Join Time range is between 100 and
65535 milliseconds; the default is 200 milliseconds. See the chapter on VLAN setup
for more background information.
Each port has a single Leave Period timer. Leave Timer must be two times larger
than Join Timer; the default is 600 milliseconds.
Leave All Timer sets the duration of the Leave All Period timer for GVRP in
milliseconds. Each port has a single Leave All Period timer. Leave All Timer must be
larger than Leave Timer; the default is 10000 milliseconds.
78
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 79

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Table 14 Switch Setup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Priority Queue Assignment
IEEE 802.1p defines up to 8 separate traffic types by inserting a tag into a MAC-layer frame that
contains bits to define class of service. Frames without an explicit priority tag are given the default
priority of the ingress port. Use the next two fields to configure the priority level-to-physical queue
mapping.
The switch has eight physical queues that you can map to the 8 priority levels. On the switch, traffic
assigned to higher index queues gets through faster while traffic in lower index queues is dropped if the
network is congested.
Priority Level (The following descriptions are based on the traffic types defined in the IEEE 802.1d
standard (which incorporates the 802.1p).
Level 7 Typically used for network control traffic such as router configuration messages.
Level 6 Typically used for voice traffic that is especially sensitive to jitter (jitter is the
Level 5 Typically used for video that consumes high bandwidth and is sensitive to jitter.
Level 4 Typically used for controlled load, latency-sensitive traffic such as SNA (Systems
Level 3 Typically used for “excellent effort” or better than best effort and would include
Level 2 This is for “spare bandwidth”.
Level 1 This is typically used for non-critical “background” traffic such as bulk transfers that
Level 0 Typically used for best-effort traffic.
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
variations in delay).
Network Architecture) transactions.
important business traffic that can tolerate some delay.
are allowed but that should not affect other applications and users.
7.6 IP Setup
Use the IP Setup screen to configure the IP address, subnet mask and the default gateway for
management purposes. Click Basic Setting > IP Setup to display the configuration screen.
7.6.1 Management IP Address
The switch needs an IP address for it to be managed over the network. The factory default inband IP address is 192.168.1.1 and out-of-band management IP is 192.168.0.1. The subnet
mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. The factory default subnet mask
is 255.255.255.0.
On the OLT-1308, you can configure up to 128 IP addresses which are used to access and
manage the switch from the ports belonging to the pre-defined VLAN(s).
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
79
Page 80

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Figure 25 IP Setup: OLT-1308
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 15 IP Setup: OLT-1308
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Domain Name
Server
Default
Management
In-band Management IP Address
DHCP Client Select this option if you have a DHCP server that can assign the switch an IP
Enter the IP address of the domain name server in dotted decimal notation, for
example 192.168.1.20.
Select which traffic flow (In-Band or Out-of-band) the switch is to use to send
packets with an unknown source or that originated from the switch itself (such as
SNMP traps).
Select Out-of-band to have the switch send the packets to the out-of-band
management port. This means that device(s) connected to the other port(s) do not
receive these packets.
Select In-Band to have the switch send the packets to all ports except the out-ofband management port. This means that device(s) connected to out-of-band
management port do not receive these packets.
address and subnet mask, a default gateway IP address and a domain name server
IP address.
80
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 81

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Table 15 IP Setup: OLT-1308 (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static IP Address Select this option if you don't have a DHCP server or if you wish to assign static IP
IP Address Enter the IP address of your switch in dotted decimal notation for example
IP Subnet
Mask
Default
Gateway
VID Enter the VLAN identification number associated with the switch IP address. This is
Out-of-band Management IP Address
IP Address Enter the IP address of your switch in dotted decimal notation for example
IP Subnet
Mask
Default
Gateway
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
In-band IP Addresses
You can create up to 128 IP addresses, which are used to access and manage the switch from the
ports belonging to the pre-defined VLAN(s). You must configure a VLAN first.
IP Address Enter the IP address for managing the switch by the members of the VLAN specified
IP Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask in dotted decimal notation.
VID Type the VLAN group identification number.
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the default outgoing gateway in dotted decimal notation.
Add Click Add to save the new rule to the switch. It then displays in the summary table at
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
Index This field displays the index number of the rule. Click an index number to edit the
IP Address This field displays the IP address.
IP Subnet Mask This field displays the subnet mask.
VID This field displays the ID number of the VLAN group.
Default Gateway This field displays the IP address of the default gateway.
Delete Check the rule(s) that you want to remove in the Delete column, then click the
Cancel Click Cancel to clear the selected checkboxes in the Delete column.
address information to the switch. You need to fill in the following fields when you
select this option.
192.168.1.1.
Enter the IP subnet mask of your switch in dotted decimal notation for example
255.255.255.0.
Enter the IP address of the default outgoing gateway in dotted decimal notation, for
example 192.168.1.254
the VLAN ID of the CPU and is used for management only. The default is "1". All
ports, by default, are fixed members of this "management VLAN" in order to manage
the device from any port. If a port is not a member of this VLAN, then users on that
port cannot access the device. To access the switch make sure the port that you are
connected to is a member of Management VLAN.
192.168.0.1.
Enter the IP subnet mask of your switch in dotted decimal notation for example
255.255.255.0.
Enter the IP address of the default outgoing gateway in dotted decimal notation, for
example 192.168.1.254
in the VID field below.
the bottom of the screen.
rule.
Delete button.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
On the OLT-1308H, you can use this screen to configure the IP settings on the MGMT port.
Figure 26 IP Setup: OLT-1308H
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 16 IP Setup: OLT-1308H
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Out-of-band Management IP Address
IP Address Enter the IP address of your switch in dotted decimal notation for example
IP Subnet
Mask
Default
Gateway
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
192.168.0.1.
Enter the IP subnet mask of your switch in dotted decimal notation for example
255.255.255.0.
Enter the IP address of the default outgoing gateway in dotted decimal notation, for
example 192.168.1.254
7.7 Port Setup
Use the Port Setup screen to configure the uplink and/or the switch ports. Click Basic Setting
> Port Setup in the navigation panel to display the configuration screen.
On the OLT-1308, the Gigabit/Mini-GBIC switch ports are labeled 9 through 12 on the device
front panel.
82
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 83

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Figure 27 Port Setup: OLT-1308
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17 Port Setup: OLT-1308
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This is the port index number. This number corresponds to the port label on the front
Active Select this check box to enable a port. The factory default for all ports is enabled. A
Name Enter a descriptive name (up to nine printable characters and spaces allowed) that
Type This field displays 10/100/1000M for the Gigabit/Mini-GBIC switch ports or 1000M for
Speed/Duplex This field is applicable on the Ethernet ports.
Flow Control This field is applicable on the Ethernet ports.
802.1P Priority This priority value is added to incoming frames without a (802.1p) priority queue tag.
panel.
port must be enabled for data transmission to occur.
identifies this port.
the Gigabit uplink ports.
Select the speed and the duplex mode of the connection on this port. Choices are
Auto, 10M/Half Duplex, 10M/Full Duplex, 100M/Half Duplex, 100M/Full Duplex
and 1000M/Full Duplex.
Selecting Auto (auto-negotiation) allows one port to negotiate with a peer port
automatically to obtain the connection speed and duplex mode that both ends
support. When auto-negotiation is turned on, a port on the switch negotiates with the
peer automatically to determine the connection speed and duplex mode. If the peer
port does not support auto-negotiation or turns off this feature, the switch determines
the connection speed by detecting the signal on the cable and using half duplex
mode. When the switch’s auto-negotiation is turned off, a port uses the pre-configured
speed and duplex mode when making a connection, thus requiring you to make sure
that the settings of the peer port are the same in order to connect.
A concentration of traffic on a port decreases port bandwidth and overflows buffer
memory causing packet discards and frame losses. Flow control is used to regulate
transmission of signals to match the bandwidth of the receiving port.
The OLT uses IEEE802.3x flow control in full duplex mode and back pressure flow
control in half duplex mode.
IEEE802.3x flow control is used in full duplex mode to send a pause signal to the
sending port, causing it to temporarily stop sending signals when the receiving port
memory buffers fill.
See Priority Queue Assignment in Table 14 on page 78 for more information.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
83
Page 84

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Table 17 Port Setup: OLT-1308 (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
BPDU Control Configure the way to treat BPDUs received on this port. You must activate bridging
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
On the OLT-1308H, the Gigabit uplink ports are labeled 1 through 8 on the device front panel.
Figure 28 Port Setup: OLT-1308H
control protocol transparency in the Switch Setup screen first.
Select Peer to process any BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Units) received on this port.
Select Tunn el to forward BPDUs received on this port.
Select Discard to drop any BPDU received on this port.
Select Network to process a BPDU with no VLAN tag and forward a tagged BPDU.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18 Port Setup: OLT-1308H
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Uplink Port This is the uplink port index number. This number corresponds to the port label on the
front panel.
Active Select this check box to enable a port. The factory default for all ports is enabled. A
port must be enabled for data transmission to occur.
Name Enter a descriptive name (up to nine printable characters and spaces allowed) that
Speed/Duplex This field displays 1000M/Full Duplex.
identifies this port.
Note: The Gigabit Ethernet ports connect at 1000 Mbps only. Connect
only Gigabit Ethernet devices to these ports.
Flow Control A concentration of traffic on a port decreases port bandwidth and overflows buffer
memory causing packet discards and frame losses. Flow control is used to regulate
transmission of signals to match the bandwidth of the receiving port.
The OLT uses IEEE802.3x flow control in full duplex mode and back pressure flow
control in half duplex mode.
IEEE802.3x flow control is used in full duplex mode to send a pause signal to the
sending port, causing it to temporarily stop sending signals when the receiving port
memory buffers fill.
84
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 85

Table 18 Port Setup: OLT-1308H (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
7.8 IGMP Snooping
The OLT can passively snoop on IGMP Query, Report and Leave (IGMP version 2) packets
transferred between IP multicast routers/switches and IP multicast hosts to learn IP multicast
group membership information. It checks IGMP packets passing through it, picks out the
group registration information, and configures multicasting accordingly. IGMP snooping
allows the OLT to learn multicast groups without you having to manually configure them.
The OLT forwards multicast traffic destined for multicast groups (that it has learned from
IGMP snooping or that you have manually configured) to ports that are members of that
group. The OLT discards multicast traffic destined for multicast groups that it does not know.
IGMP snooping generates no additional network traffic, allowing you to significantly reduce
multicast traffic passing through your OLT.
Chapter 7 Basic Setting
7.9 DBA (Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation)
When network congestion occurs, dynamic bandwidth allocation allows the OLT to quickly
re-assign unused bandwidth based on traffic requirements. Bandwidth re-assignment can be
for an ONU or for the priority-level queues. In addition to reassigning bandwidth on the go,
DBA helps to ensure quality of service on the network.
By default, the OLT uses the Plato DBA algorithm that allows you to fully utilize bandwidth in
your network environment. With Plato DBA algorithm, the OLT assigns bandwidth based on
link priority and delay tolerance. In addition, the OLT guarantees a minimum upstream
bandwidth and provides the best-effort maximum upstream bandwidth.
7.10 EPON Setup
Use the EPON Setup screen to configure general PON (or fiber) interface settings. Click
Basic Setting > EPON Setup. Not all fields are available on all models.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Figure 29 EPON Setup: OLT-1308H
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 EPON Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
p2p Access Peer-to-peer (p2p) access allows ONUs on the same port to send packets to each
other directly (without having to route through the uplink ports).
Select the port(s) you want to allow peer-to-peer communication.
Clear the check box to disable this feature. In this case, all packets from the ONUs on
the same port are sent to the uplink interface. ONUs cannot communicate with each
other.
DBA Mode The OLT uses the Plato mode to assign bandwidth dynamically based on the priority
Aging Time This is how long all dynamically learned MAC addresses remain in the MAC address
Upstream/Downstream Priority Queue Assignment
IEEE 802.1p defines up to 8 separate traffic types by inserting a tag into a MAC-layer frame that
contains bits to define class of service. Frames without an explicit priority tag are given the default
priority of the ingress port. Use the next two fields to configure the priority level-to-physical queue
mapping.
On the OLT, traffic assigned to higher index queues gets serviced faster while traffic in lower index
queues may be dropped if the network is congested.
and delay tolerance settings.
You can configure bandwidth settings in the Profile Setup screen.
table before they age out (and must be relearned).
Enter a time from 10 to 86400 seconds.
86
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 87

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Table 19 EPON Setup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Priority Level (The following descriptions are based on the traffic types defined in the IEEE 802.1d
standard (which incorporates IEEE 802.1p).
Priority 7 Typically used for network control traffic such as router configuration messages.
Priority 6 Typically used for voice traffic that is especially sensitive to jitter (jitter is the variations
in delay).
Priority 5 Typically used for video that consumes high bandwidth and is sensitive to jitter.
Priority 4 Typically used for controlled load, latency-sensitive traffic such as SNA (Systems
Network Architecture) transactions.
Priority 3 Typically used for “excellent effort” or better than best effort and would include
Priority 2 This is for “spare bandwidth”.
Priority 1 This is typically used for non-critical “background” traffic such as bulk transfers that
Priority 0 Typically used for best-effort traffic.
IGMP
Snooping
IGMP Query
Timeout Count
IGMP Last
Member
IGMP Last
Member
Query Count
IGMP Last
Member
Query Interval
Upstream
Multicast
forwarding
Downstream
Multicast
Forwarding
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
important business traffic that can tolerate some delay.
are allowed but that should not affect other applications and users.
Select this option to enable IGMP snooping.
Select a query timeout count. When the ONU snoops the first query, it starts the count
down. For each query the ONU snoops, this timeout count is decreased by 1. When
this number reaches zero, a group member is removed from the group if no report
message is received.
Select this option to set the ONU to query all group members when a group leave
message is received. This is to confirm that all group members wish to leave that
IGMP group.
Clear this option to disable this feature. When a group leave message is received, all
group members are removed from an IGMP group without confirmation checks.
Select the number of times the ONU sends a group-leave query.
Select the time interval the ONU waits before sending another group-leave query.
Select Pass to forward upstream packets with a matching multicast MAC address in
the range shown.
Select Discard to drop upstream packets with a matching multicast MAC address in
the range shown.
Select Pass to forward downstream packets with a matching multicast MAC address
in the range shown.
Select Discard to drop downstream packets with a matching multicast MAC address
in the range shown.
7.10.1 Profile Setup
Use the Profile Setup screen to configure upstream/downstream bandwidth limit, priority
level, delay priority and the MAC address learning settings. Once you have set the profile
settings, you can apply it to the ONU in the Service Setup (or ONU Setup) screens (refer to
Section 7.10.2 on page 91).
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
87
Page 88

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Your OLT comes with a “Default” profile contains the settings that work in most network
environment.
When you create a profile having the same name as an existing profile, the previous settings
will be replaced in the existing profile. Current field settings are displayed in bold text labels.
Click Basic Setting > EPON Setup > Profile Setup to display the configuration screen. Not
all fields are available on all models.
Figure 30 EPON Setup: Profile Setup
88
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 89

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 20 EPON Setup: Profile Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Select this option to activate this profile.
Clear this check box to disable the profile.
Name Enter a descriptive name (up to 20 alphanumerical characters) to identify this
Upstream DBA
Priority Class Select a traffic priority level for a logical link.
Delay Specify the delay tolerance of a logical link for bandwidth allocation when
Minimum Upstream
Bandwidth
Maximum Upstream
Bandwidth
Upstream Policing per Queue
Active Select Active to apply the bandwidth limit to the upstream traffic on the queues
Maximum Queue 0
Bandwidth
Maximum Queue 1
Bandwidth
Maximum Queue 2
Bandwidth
Maximum Queue 3
Bandwidth
Upstream Priority Queue Size
Active Select Active to set the queue size for the upstream traffic.
Queue 0 Size Specify the size (in byte) for queue 0.
Queue 1 Size Specify the size (in byte) for queue 1.
Queue 2 Size Specify the size (in byte) for queue 2.
Queue 3 Size Specify the size (in byte) for queue 3.
Downstream Policing
Active Select Active to control the downstream traffic (from the OLT to the ONU).
profile.
The higher the priority (larger number), the more likely that the ONU gets the
unused upstream bandwidth (up to the maximum bandwidth setting) after the
minimum bandwidth requirement is met.
network congestion occurs.
Select Low Delay for the packets to get serviced faster. This is recommended
when you have real-time applications (such as VoIP) on the network.
Select High Delay to get less service time slots. Packets are serviced slower.
Specify the minimum upstream bandwidth guaranteed to the ONU. Upstream
traffic refers to traffic from the ONU to the OLT.
The number you entered is multiplied by 64.
Specify the maximum upstream bandwidth guaranteed to the ONU. Upstream
traffic refers to traffic from the ONU to the OLT.
The number you entered is multiplied by 64.
then configure the settings in the field below. Upstream traffic refers to traffic
from the ONU to the OLT.
Specify the maximum upstream bandwidth for packets in queue 0.
The number you entered is multiplied by 100.
Specify the maximum upstream bandwidth for packets in queue 1.
The number you entered is multiplied by 100.
Specify the maximum upstream bandwidth for packets in queue 2.
The number you entered is multiplied by 100.
Specify the maximum upstream bandwidth for packets in queue 3.
The number you entered is multiplied by 100.
The number you entered is multiplied by 128.
The number you entered is multiplied by 128.
The number you entered is multiplied by 128.
The number you entered is multiplied by 128.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Table 20 EPON Setup: Profile Setup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Maximum
Downstream
Bandwidth
Maximum
Downstream Burst
Size
Downstream Policing per Queue
Active Select Active to apply the bandwidth limit to the upstream traffic on the queues
Maximum Queue 0
Bandwidth
Maximum Queue 1
Bandwidth
Maximum Queue 2
Bandwidth
Maximum Queue 3
Bandwidth
Downstream Priority Queue Size
Active Select Active to set the queue size for the downstream traffic.
Queue 0 Size Specify the size (in byte) for queue 0.
Queue 1 Size Specify the size (in byte) for queue 1.
Queue 2 Size Specify the size (in byte) for queue 2.
Queue 3 Size Specify the size (in byte) for queue 3.
ONU PHY Configuration
Power Down Select this option to disable the connection to the ONU.
Speed/Duplex Select the link speed and duplex mode (10M/Half, 10M/Full, 100M/Half, 100M/
Auto-negotiation Select this option to establish the connection to the ONU using auto-negotiation
Flow Control IEEE802.3x flow control is used in full duplex mode to send a pause signal to
Address Learning MAC address learning reduces outgoing broadcast traffic. For MAC address
This field is applicable when you select Downstream Policing. Downstream
traffic refers to traffic from the OLT to the ONU.
Specify the maximum downstream bandwidth allowed for the ONU.
The number you entered is multiplied by 64.
This field is applicable when you select Downstream Policing. Downstream
traffic refers to traffic from the OLT to the ONU.
Specify the maximum downstream burst size that an ONU is allowed to send
for a single traffic burst. This assigns more bandwidth to the ONU for a short
burst period without changing the profile settings.
then configure the settings in the field below. Downstream traffic refers to traffic
from the OLT to the ONU.
Specify the maximum downstream bandwidth for packets in queue 0.
The number you entered is multiplied by 100.
Specify the maximum downstream bandwidth for packets in queue 1.
The number you entered is multiplied by 100.
Specify the maximum downstream bandwidth for packets in queue 2.
The number you entered is multiplied by 100.
Specify the maximum downstream bandwidth for packets in queue 3.
The number you entered is multiplied by 100.
The number you entered is multiplied by 128.
The number you entered is multiplied by 128.
The number you entered is multiplied by 128.
The number you entered is multiplied by 128.
Full or 1000M/Full) for the connection to the ONU.
for the link speed and duplex mode.
the sending port, causing it to temporarily stop sending signals when the
receiving port memory buffers fill.
Select this option to enable flow control for the connection to the ONU.
learning to occur on a port, the port itself must be active with address learning
enabled.
90
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 91

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Table 20 EPON Setup: Profile Setup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Limited Number of
Learned MAC
Addresses
Encryption Mode You can set the OLT to encrypt data using AES128 to provide secure
Add Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
Clear Click Clear to reset the fields to the default settings.
Name This field displays the descriptive name of a profile.
Active This field displays whether the priority profile is active or not.
Max Upstream This field displays the maximum upstream bandwidth.
Max Downstream This field displays the maximum amount of downstream bandwidth.
Addr Learning This field displays the maximum number of MAC addresses is allowed.
Delete Click Delete to remove the selected entry from the summary table.
Cancel Click Cancel to clear the Delete check boxes.
Use this field to limit the number of (dynamic) source MAC addresses that may
be learned on the ONU.
For example, if you set this field to "8", then only the devices with these eight
learned MAC addresses may access through the ONU at any one time. A ninth
device would have to wait until one of the eight learned MAC addresses aged
out. MAC address aging time can be set in the EPON Setup screen.
Select the number of MAC address an ONU can learn.
communication through the ONUs.
Specify the direction of the traffic to which the OLT encrypts. Data encryption
may affect transmission performance.
Select Disabled if you do not want to encrypt data.
7.10.2 Service Setup
Use the Service Setup (or ONU Setup) screen to associate profiles to an ONU. When the
ONU has successfully registered (or connected) to the OLT, settings in the associated profiles
are set to the ONU.
Click Basic Setting > EPON Setup and the Service Setup (or ONU Setup) link to display the
configuration screen.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
91
Page 92

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Figure 31 EPON Setup: Service Setup (or ONU Setup)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 21 EPON Setup: Service Setup (or ONU Setup)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Select this option to activate this profile.
ONU Name Enter a descriptive name (up to 20 alpha-numerical characters) to identify the ONU to
Port Select the port to which the ONU is connected.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of the ONU to which this service is to be applied.
Clear this check box to disable the profile.
which this service is applied.
Note: The MAC address setting is ignored in default services.
EPON Profile Select the EPON profile to apply to the ONU. You can configure EPON profiles in the
Profile Setup screen (refer to Section 7.10.1 on page 87).
Classifier Filter
Profile
VLAN Profile Select the VLAN profile to apply to the ONU. You can configure VLAN profiles in the
Priority Profile Select the packet priority profile to apply to the ONU. Refer to Section 7.10.1 on page
Add Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to reset the fields to your previous configuration.
Clear Click Clear to reset the fields to the default settings.
Port This field displays the port index number.
Active This field displays whether the service is enabled or not.
ONU Name This field displays the name of the ONU on this port. Click a name to configure the
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of the ONU allowed to use the service on this
EPON Profile This field displays the name of the EPON profile the ONU on this port uses. Click a
Select the packet classification filter profile to apply to the ONU. Refer to Section 22.2
on page 159 for more information on classification filter profile setup.
VLAN Profile screen (refer to Section 23.4 on page 166).
87 for more information on priority profile setup.
service profile.
port. ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff means that any ONU is allowed on the port.
name to configure the EPON profile.
92
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 93

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
Table 21 EPON Setup: Service Setup (or ONU Setup) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Classification
Filter Profile
VLAN Profile This field displays the name of the VLAN profile the ONU on this port uses. Click a
Priority Profile This field displays the name of the priority profile the ONU on this port uses. Click a
Delete Click Delete to remove the selected entry from the summary table.
This field displays the name of the classification filter profile the ONU on this port
uses. Click a name to configure the classification filter profile.
name to configure the VLAN profile.
name to configure the priority profile.
Note: You cannot delete the default services.
Cancel Click Cancel to clear the Delete check boxes.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
93
Page 94

Chapter 7 Basic Setting
94
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 95

PART III
Advanced: Switch
VLAN (97)
Static MAC Forward Setup (107)
Filtering (109)
Spanning Tree Protocol (111)
Bandwidth Control (117)
Broadcast Storm Control (119)
Mirroring (121)
Link Aggregation (123)
Port Security (127)
Queuing Method (129)
Classifier (133)
Policy (139)
Multicast (145)
DHCP Relay (155)
95
Page 96

96
Page 97

CHAPTER 8
VLAN
The type of screen you see here depends on the VLAN Type you selected in the Switch Setup
screen. This chapter shows you how to configure 802.1Q tagged and port-based VLANs.
8.1 Introduction to IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN
A tagged VLAN uses an explicit tag (VLAN ID) in the MAC header to identify the VLAN
membership of a frame across bridges - they are not confined to the switch on which they were
created. The VLANs can be created statically by hand or dynamically through GVRP. The
VLAN ID associates a frame with a specific VLAN and provides the information that switches
need to process the frame across the network. A tagged frame is four bytes longer than an
untagged frame and contains two bytes of TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier), residing within the
type/length field of the Ethernet frame) and two bytes of TCI (Tag Control Information), starts
after the source address field of the Ethernet frame).
The CFI (Canonical Format Indicator) is a single-bit flag, always set to zero for Ethernet
switches. If a frame received at an Ethernet port has a CFI set to 1, then that frame should not
be forwarded as it is to an untagged port. The remaining twelve bits define the VLAN ID,
giving a possible maximum number of 4,096 VLANs. Note that user priority and VLAN ID
are independent of each other. A frame with VID (VLAN Identifier) of null (0) is called a
priority frame, meaning that only the priority level is significant and the default VID of the
ingress port is given as the VID of the frame. Of the 4096 possible VIDs, a VID of 0 is used to
identify priority frames and value 4095 (FFF) is reserved, so the maximum possible VLAN
configurations are 4,094.
TPID
2 Bytes
8.1.1 Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames
Each port on the switch is capable of passing tagged or untagged frames. To forward a frame
from an 802.1Q VLAN-aware switch to an 802.1Q VLAN-unaware switch, the switch first
decides where to forward the frame and then strips off the VLAN tag. To forward a frame from
an 802.1Q VLAN-unaware switch to an 802.1Q VLAN-aware switch, the switch first decides
where to forward the frame, and then inserts a VLAN tag reflecting the ingress port's default
VID. The default PVID is VLAN 1 for all ports, but this can be changed.
User Priority
3 Bits
CFI
1 Bit
VLAN ID
12 bits
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
97
Page 98

Chapter 8 VLAN
8.2 Automatic VLAN Registration
GARP and GVRP are the protocols used to automatically register VLAN membership across
switches.
8.2.1 GARP
GARP (Generic Attribute Registration Protocol) allows network switches to register and deregister attribute values with other GARP participants within a bridged LAN. GARP is a
protocol that provides a generic mechanism for protocols that serve a more specific
application, for example, GVRP.
8.2.1.1 GARP Timers
Switches join VLANs by making a declaration. A declaration is made by issuing a Join
message using GARP. Declarations are withdrawn by issuing a Leave message. A Leave All
message terminates all registrations. GARP timers set declaration timeout values.
8.2.2 GVRP
GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol) is a registration protocol that defines a way for
switches to register necessary VLAN members on ports across the network. Enable this
function to permit VLANs groups beyond the local switch.
Table 22 IEEE 802.1Q Terminology
VLAN PARAMETER TERM DESCRIPTION
VLAN Type Permanent VLAN This is a static VLAN created manually.
Dynamic VLAN This is a VLAN configured by a GVRP registration/
VLAN Administrative
Control
VLAN Tag Control Tagged Ports belonging to the specified VLAN tag all outgoing
VLAN Port Port VID This is the VLAN ID assigned to untagged frames that
Registration Fixed Fixed registration ports are permanent VLAN members.
Registration
Forbidden
Normal Registration Ports dynamically join a VLAN using GVRP.
Untagged Ports belonging to the specified don't tag all outgoing
Acceptable frame
type
Ingress filtering If set, the switch discards incoming frames for VLANs
8.3 Port VLAN Trunking
Enable VLAN Trunking on a port to allow frames belonging to unknown VLAN groups to
pass through that port. This is useful if you want to set up VLAN groups on end devices
without having to configure the same VLAN groups on intermediary devices.
deregistration process.
Ports with registration forbidden are forbidden to join the
specified VLAN.
frames transmitted.
frames transmitted.
this port received.
You may choose to accept both tagged and untagged
incoming frames or just tagged incoming frames on a
port.
that do not have this port as a member
98
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
Page 99

Refer to the following figure. Suppose you want to create VLAN groups 1 and 2 (V1 and V2)
on devices A and B. Without VLAN Trunking, you must configure VLAN groups 1 and 2 on
all intermediary switches C, D and E; otherwise they will drop frames with unknown VLAN
group tags. However, with VLAN Trunking enabled on a port(s) in each intermediary switch
you only need to create VLAN groups in the end devices (A and B). C, D and E automatically
allow frames with VLAN group tags 1 and 2 (VLAN groups that are unknown to those
switches) to pass through their VLAN trunking port(s).
Figure 32 Port VLAN Trunking
8.4 Select the VLAN Type
Select a VLAN type in the Switch Setup screen.
Chapter 8 VLAN
Figure 33 Switch Setup: Select VLAN Type
8.5 Static VLAN
Use a static VLAN to decide whether an incoming frame on a port should be
• sent to a VLAN group as normal depends on its VLAN tag.
• sent to a group whether it has a VLAN tag or not.
• blocked from a VLAN group regardless of its VLAN tag.
You can also tag all outgoing frames (that were previously untagged) from a port with the
specified VID.
8.5.1 Static VLAN Status
Click Advanced Application, VLAN from the navigation panel to display the VLAN Status
screen as shown next.
Use this screen to view the current static VLAN group(s) you have configured. Refer to
Section 8.1 on page 97 for background information.
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
99
Page 100

Chapter 8 VLAN
Figure 34 VLAN: VLAN Status
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 23 VLAN: VLAN Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
The Number of
VLAN
Index This is the VLAN index number.
VID This is the VLAN identification number that was configured in the Static VLAN
Port Number This field shows how this VLAN was added to the switch; dynamic - using GVRP,
Elapsed Time This field shows how long it has been since a normal VLAN was registered or a
Status This field shows how this VLAN was added to the switch; dynamically using GVRP
Poll Interval(s) The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may change
Stop Click Stop to halt polling statistics.
Change Pages Click Previous Page or Next Page to show the previous/next screen if all status
This is the number of VLANs configured on the switch.
screen.
static - added as a permanent entry or other - added using Multicast VLAN
Registration (MVR).
static VLAN was set up.
or statically, that is, added as a permanent entry.
the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then clicking Set
Interval.
information cannot be seen in one screen.
8.5.2 Configure a Static VLAN
To configure a static VLAN, click Static VLAN in the VLAN Status screen to display the
screen as shown next.
Use a static VLAN to decide whether an incoming frame on a port should be
• sent to a VLAN group as normal depends on its VLAN tag.
100
OLT-1308 Series User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...