Page 1

IES-1248-51/51A/53
ADSL2+ IP DSLAM
User’s Guide
Version 3.52 (ABQ.0), (ABR.0)
Edition 1
7/2006
Page 2

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
2
Page 3

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Copyright
Copyright © 2006 by ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, transcribed, stored in a
retrieval system, translated into any language, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, photocopying, manual, or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Published by ZyXEL Communications Corporation. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
ZyXEL does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any products, or software
described herein. Neither does it convey any license under its patent rights nor the patent rights of others.
ZyXEL further reserves the right to make changes in any products described herein without notice. This
publication is subject to change without notice.
Trademarks
ZyNOS (ZyXEL Network Operating System) is a registered trademark of ZyXEL Communications, Inc.
Other trademarks mentioned in this publication are used for identification purposes only and may be
properties of their respective owners.
Copyright 3
Page 4

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Certifications
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Interference Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference.
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operations.
FCC Warning
This device has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital switch, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a commercial environment. This device generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this device in a residential area is likely to cause
harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
CE Mark Warning:
This is a class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which
case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Taiwanese BSMI (Bureau of Standards, Metrology and Inspection) A Warning:
Notices
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the
user's authority to operate the equipment.
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Viewing Certifications
1 Go to http://www.zyxel.com.
2 Select your product from the drop-down list box on the ZyXEL home page to go to that product's
page.
3 Select the certification you wish to view from this page.
4 Certifications
Page 5

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Safety Warnings
For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
• Do NOT use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming pool.
• Do NOT expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do NOT store things on the device.
• Do NOT install, use, or service this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk of electric
shock from lightning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• ONLY qualified service personnel should service or disassemble this device.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
• Always disconnect all cables from this device before servicing or disassembling.
• Use ONLY an appropriate power adaptor or cord for your device.
• Connect the power adaptor or cord to the right supply voltage (for example, 110V AC in North
America or 230V AC in Europe).
• Do NOT allow anything to rest on the power adaptor or cord and do NOT place the product where
anyone can walk on the power adaptor or cord.
• Do NOT use the device if the power adaptor or cord is damaged as it might cause electrocution.
• If the power adaptor or cord is damaged, remove it from the power outlet.
• Do NOT attempt to repair the power adaptor or cord. Contact your local vendor to order a new one.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a remote risk of
electric shock from lightning.
• CAUTION: RISK OF EXPLOSION IF BATTERY (on the motherboard) IS REPLACED BY AN
INCORRECT TYPE. DISPOSE OF USED BATTERIES ACCORDING TO THE INSTRUCTIONS.
Dispose them at the applicable collection point for the recycling of electrical and electronic
equipment. For detailed information about recycling of this product, please contact your local city
office, your household waste disposal service or the store where you purchased the product.
• Do NOT obstruct the device ventilation slots, as insufficient airflow may harm your device.
• Use only No. 26 AWG (American Wire Gauge) or larger telecommunication line cord.
• Fuse Warning! Replace a fuse only with a fuse of the same type and rating.
• Warning! To avoid risk of electric shock, remove only one card at a time and do not place fingers or
objects inside the chassis. Cover empty slots with slot covers.
• The length of exposed (bare) power wire should not exceed 7mm.
• Fan Module Warning! Use the fan module handle when pulling out or pushing in the fan module. Be
careful not to put fingers or objects inside the fan module.
Safety Warnings 5
Page 6

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
This product is recyclable. Dispose of it properly.
6 Safety Warnings
Page 7

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
ZyXEL Limited Warranty
ZyXEL warrants to the original end user (purchaser) that this product is free from any defects in materials
or workmanship for a period of up to two years from the date of purchase. During the warranty period, and
upon proof of purchase, should the product have indications of failure due to faulty workmanship and/or
materials, ZyXEL will, at its discretion, repair or replace the defective products or components without
charge for either parts or labor, and to whatever extent it shall deem necessary to restore the product or
components to proper operating condition. Any replacement will consist of a new or re-manufactured
functionally equivalent product of equal or higher value, and will be solely at the discretion of ZyXEL.
This warranty shall not apply if the product has been modified, misused, tampered with, damaged by an act
of God, or subjected to abnormal working conditions.
Note
Repair or replacement, as provided under this warranty, is the exclusive remedy of the purchaser. This
warranty is in lieu of all other warranties, express or implied, including any implied warranty of
merchantability or fitness for a particular use or purpose. ZyXEL shall in no event be held liable for
indirect or consequential damages of any kind to the purchaser.
To obtain the services of this warranty, contact ZyXEL's Service Center for your Return Material
Authorization number (RMA). Products must be returned Postage Prepaid. It is recommended that the unit
be insured when shipped. Any returned products without proof of purchase or those with an out-dated
warranty will be repaired or replaced (at the discretion of ZyXEL) and the customer will be billed for parts
and labor. All repaired or replaced products will be shipped by ZyXEL to the corresponding return address,
Postage Paid. This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights that vary
from country to country.
Registration
Register your product online to receive e-mail notices of firmware upgrades and information at
www.zyxel.com for global products, or at www.us.zyxel.com for North American products.
ZyXEL Limited Warranty 7
Page 8
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
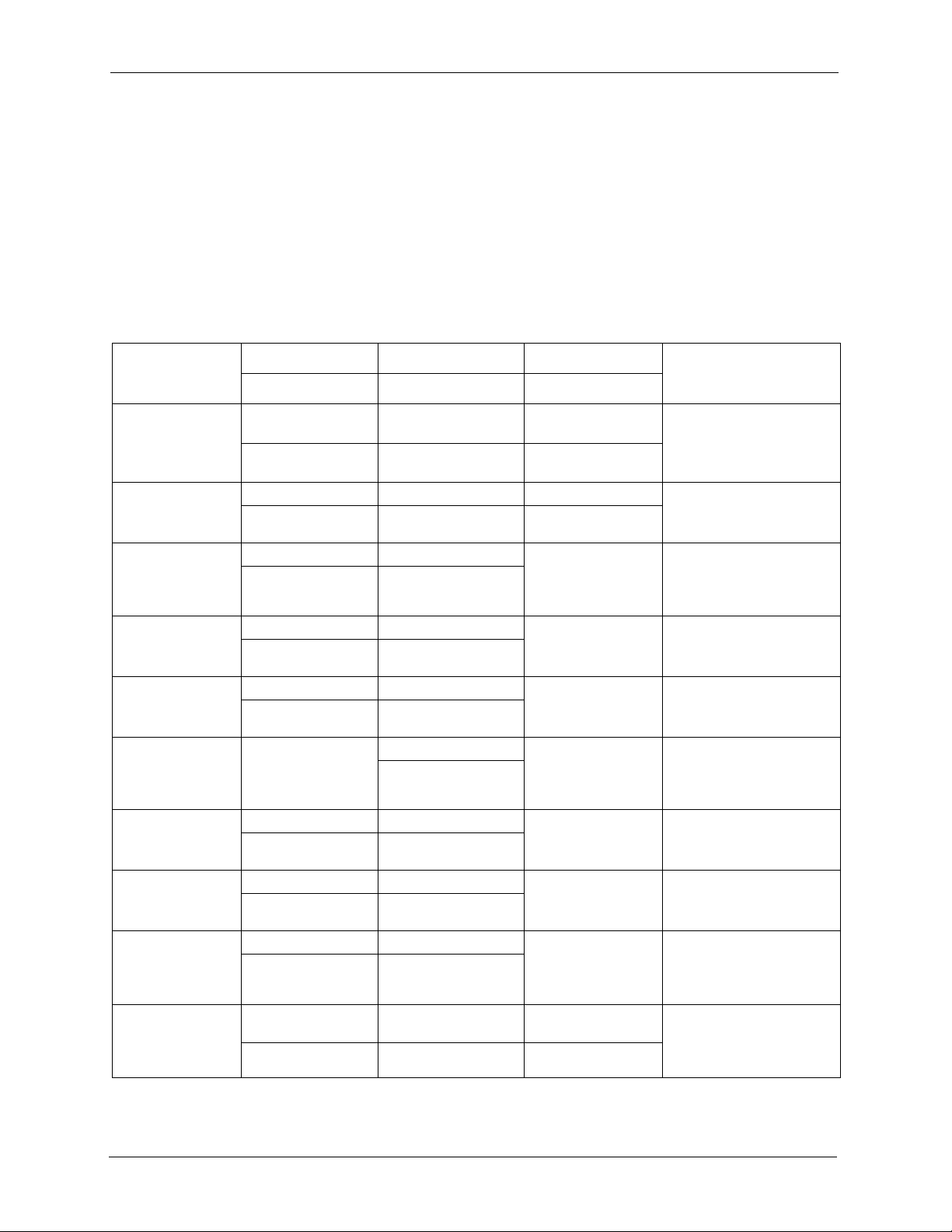
Customer Support
Please have the following information ready when you contact customer support.
• Product model and serial number.
• Warranty Information.
• Date that you received your device.
• Brief description of the problem and the steps you took to solve it.
METHOD
LOCATION
CORPORATE
HEADQUARTERS
(WORLDWIDE)
COSTA RICA
CZECH REPUBLIC
DENMARK
FINLAND
FRANCE
GERMANY
HUNGARY
KAZAKHSTAN
NORTH AMERICA
SUPPORT E-MAIL TELEPHONE WEB SITE
SALES E-MAIL FAX FTP SITE
support@zyxel.com.tw +886-3-578-3942 www.zyxel.com
www.europe.zyxel.com
sales@zyxel.com.tw +886-3-578-2439 ftp.zyxel.com
ftp.europe.zyxel.com
soporte@zyxel.co.cr +506-2017878 www.zyxel.co.cr ZyXEL Costa Rica
sales@zyxel.co.cr +506-2015098 ftp.zyxel.co.cr
info@cz.zyxel.com +420-241-091-350 www.zyxel.cz ZyXEL Communications
info@cz.zyxel.com +420-241-091-359
support@zyxel.dk +45-39-55-07-00 www.zyxel.dk ZyXEL Communications A/S
sales@zyxel.dk +45-39-55-07-07
support@zyxel.fi +358-9-4780-8411 www.zyxel.fi ZyXEL Communications Oy
sales@zyxel.fi +358-9-4780 8448
info@zyxel.fr +33-4-72-52-97-97 www.zyxel.fr ZyXEL France
+33-4-72-52-19-20
support@zyxel.de +49-2405-6909-0 www.zyxel.de ZyXEL Deutschland GmbH.
sales@zyxel.de +49-2405-6909-99
support@zyxel.hu +36-1-3361649 www.zyxel.hu ZyXEL Hungary
info@zyxel.hu +36-1-3259100
http://zyxel.kz/support +7-3272-590-698 www.zyxel.kz ZyXEL Kazakhstan
sales@zyxel.kz +7-3272-590-689
support@zyxel.com 1-800-255-4101
+1-714-632-0882
sales@zyxel.com +1-714-632-0858 ftp.us.zyxel.com
www.us.zyxel.com ZyXEL Communications Inc.
REGULAR MAIL
ZyXEL Communications Corp.
6 Innovation Road II
Science Park
Hsinchu 300
Ta iw a n
Plaza Roble Escazú
Etapa El Patio, Tercer Piso
San José, Costa Rica
Czech s.r.o.
Modranská 621
143 01 Praha 4 - Modrany
Ceská Republika
Columbusvej
2860 Soeborg
Denmark
Malminkaari 10
00700 Helsinki
Finland
1 rue des Vergers
Bat. 1 / C
69760 Limonest
France
Adenauerstr. 20/A2 D-52146
Wuerselen
Germany
48, Zoldlomb Str.
H-1025, Budapest
Hungary
43, Dostyk ave.,Office 414
Dostyk Business Centre
050010, Almaty
Republic of Kazakhstan
1130 N. Miller St.
Anaheim
CA 92806-2001
U.S.A.
8 Customer Support
Page 9
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
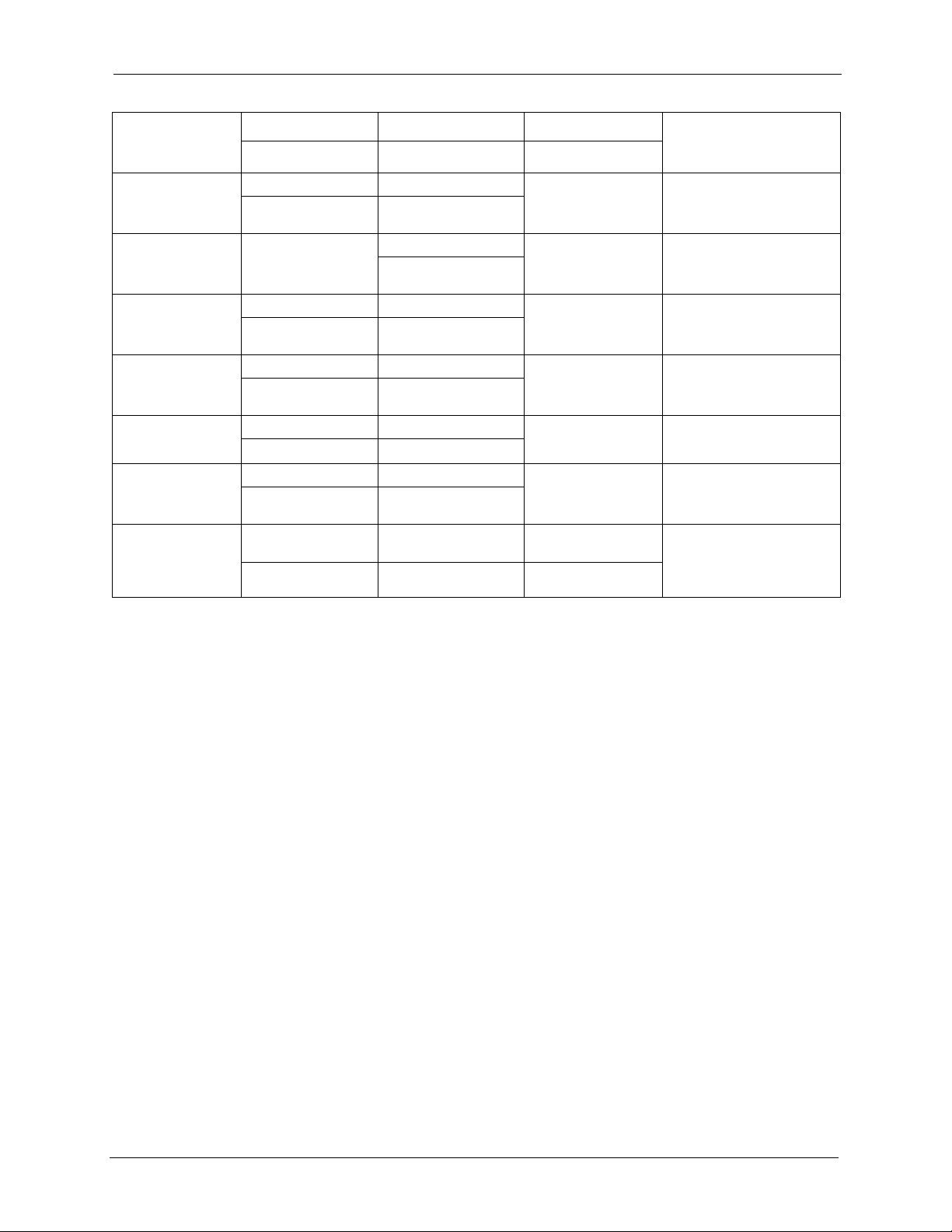
METHOD
LOCATION
NORWAY
POLAND
RUSSIA
SPAIN
SWEDEN
UKRAINE
UNITED KINGDOM
SUPPORT E-MAIL TELEPHONE WEB SITE
SALES E-MAIL FAX FTP SITE
support@zyxel.no +47-22-80-61-80 www.zyxel.no ZyXEL Communications A/S
sales@zyxel.no +47-22-80-61-81
info@pl.zyxel.com +48 (22) 333 8250 www.pl.zyxel.com ZyXEL Communications
+48 (22) 333 8251
http://zyxel.ru/support +7-095-542-89-29 www.zyxel.ru ZyXEL Russia
sales@zyxel.ru +7-095-542-89-25
support@zyxel.es +34-902-195-420 www.zyxel.es ZyXEL Communications
sales@zyxel.es +34-913-005-345
support@zyxel.se +46-31-744-7700 www.zyxel.se ZyXEL Communications A/S
sales@zyxel.se +46-31-744-7701
support@ua.zyxel.com +380-44-247-69-78 www.ua.zyxel.com ZyXEL Ukraine
sales@ua.zyxel.com +380-44-494-49-32
support@zyxel.co.uk +44-1344 303044
08707 555779 (UK only)
sales@zyxel.co.uk +44-1344 303034 ftp.zyxel.co.uk
www.zyxel.co.uk ZyXEL Communications UK
REGULAR MAIL
Nils Hansens vei 13
0667 Oslo
Norway
ul. Okrzei 1A
03-715 Warszawa
Poland
Ostrovityanova 37a Str.
Moscow, 117279
Russia
Arte, 21 5ª planta
28033 Madrid
Spain
Sjöporten 4, 41764 Göteborg
Sweden
13, Pimonenko Str.
Kiev, 04050
Ukraine
Ltd.,11 The Courtyard,
Eastern Road, Bracknell,
Berkshire, RG12 2XB,
United Kingdom (UK)
+” is the (prefix) number you enter to make an international telephone call.
Customer Support 9
Page 10

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
10 Customer Support
Page 11

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table of Contents
Copyright ..................................................................................................................3
Certifications ............................................................................................................4
Safety Warnings ....................................................................................................... 5
ZyXEL Limited Warranty.......................................................................................... 7
Customer Support.................................................................................................... 8
Table of Contents ................................................................................................... 11
List of Figures ........................................................................................................ 27
List of Tables .......................................................................................................... 35
Preface ....................................................................................................................39
Chapter 1
Getting to Know the IES-1248 ............................................................................... 41
1.1 System Description ............................................................................................41
1.2 Applications ........................................................................................................45
1.2.1 MTU Application .......................................................................................45
1.2.2 Curbside Application .................................................................................46
Chapter 2
Hardware Installation............................................................................................. 47
2.1 General Installation Instructions .........................................................................47
2.2 Installation Scenarios .........................................................................................47
2.2.1 Desktop Installation Procedure .................................................................47
2.2.2 Rack-Mounted Installation ........................................................................48
2.2.2.1 Rack-mounted Installation Requirements .......................................48
2.2.2.2 Rack-Mounted Installation Procedure .............................................49
2.3 Connecting the Frame Ground ...........................................................................50
Chapter 3
Front Panel Connections....................................................................................... 53
3.1 Front Panel .........................................................................................................53
3.1.1 Front Panel Ports ......................................................................................53
3.1.2 LEDs .........................................................................................................54
3.2 1000/100M Auto-Sensing Ethernet ....................................................................55
Table of Contents 11
Page 12

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
3.2.1 Ethernet Default Settings ..........................................................................55
3.3 SFP Mini GBIC Slots ..........................................................................................55
3.3.1 Transceiver Installation ............................................................................56
3.3.2 Transceiver Removal ................................................................................57
3.4 Console Port Connection ...................................................................................58
3.5 ALARM Connections ..........................................................................................58
3.6 ADSL Connections .............................................................................................59
Chapter 4
MDF Connections................................................................................................... 61
4.1 MDF Connections Overview ..............................................................................61
4.2 MDF (Main Distribution Frame) ..........................................................................61
4.3 Telco-50 Cables .................................................................................................62
4.4 Telco-50 Connections ........................................................................................62
4.5 MDF Scenarios ..................................................................................................63
4.6 Typical MDF Scenarios .....................................................................................63
4.6.1 Installation Scenario A .............................................................................63
4.6.1.1 Procedure to Connect to an MDF ...................................................64
4.6.2 Installation Scenario B ..............................................................................64
4.6.2.1 Procedure to Connect to MDFs .......................................................65
4.6.3 Installation Scenario C ..............................................................................66
4.6.3.1 Procedure to Connect to MDFs .......................................................67
Chapter 5
Power Connections................................................................................................ 69
5.1 Power Connections Overview ............................................................................69
5.2 Power Connections ............................................................................................69
5.2.1 AC Power Connections (IES-1248-51A only) ...........................................69
5.2.2 DC Power Connections (IES-1248-51, IES-1248-53) ...............................70
5.3 Procedure to Turn on the IES-1248 Power ........................................................70
Chapter 6
Fan Maintenance .................................................................................................... 71
6.1 Fan Maintenance Introduction ............................................................................71
6.2 Removing and Installing the Fan Module ...........................................................71
Chapter 7
Introducing the Web Configurator........................................................................ 73
7.1 Web Configurator Overview ...............................................................................73
7.2 Screen Privilege Levels ......................................................................................73
7.3 Accessing the Web Configurator ........................................................................73
7.4 Navigation Panel ................................................................................................75
7.5 Changing Your Password ...................................................................................77
12 Table of Contents
Page 13

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
7.6 Saving Your Configuration ..................................................................................78
7.7 Logging Out of the Web Configurator ................................................................78
Chapter 8
Initial Configuration ............................................................................................... 81
8.1 Initial Configuration Overview ............................................................................81
8.2 Initial Configuration ............................................................................................81
Chapter 9
Home and Port Statistics Screens........................................................................ 87
9.1 Home Screen .....................................................................................................87
9.1.1 Ethernet Port Statistics Screen .................................................................88
9.1.2 ADSL Port Statistics Screen .....................................................................91
9.1.3 RMON Statistics Screen ...........................................................................93
9.1.4 RMON History Screen ..............................................................................95
9.1.5 RMON History Detail Screen ....................................................................96
Chapter 10
System Information................................................................................................ 99
Chapter 11
General Setup....................................................................................................... 103
Chapter 12
User Account........................................................................................................ 105
12.1 User Account Screen .....................................................................................105
12.2 Authentication Screen ....................................................................................106
Chapter 13
Switch Setup......................................................................................................... 109
13.1 GARP Timer Setup .........................................................................................109
13.2 Switch Modes .................................................................................................109
13.2.1 Standalone Switch Mode ......................................................................109
13.2.2 Port Isolation with Standalone Switch Mode Example ..........................110
13.2.3 Daisychain Switch Mode ....................................................................... 110
13.2.4 Port Isolation with Daisychain Switch Mode Example .......................... 111
13.3 Switch Setup Screen ...................................................................................... 111
Table of Contents 13
Page 14

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Chapter 14
IP Setup................................................................................................................. 115
Chapter 15
ENET Port Setup .................................................................................................. 117
Chapter 16
xDSL Port Setup................................................................................................... 119
16.1 ADSL Standards Overview ............................................................................. 119
16.2 Downstream and Upstream ...........................................................................119
16.3 Profiles ...........................................................................................................120
16.4 Interleave Delay .............................................................................................120
16.4.1 Fast Mode .............................................................................................120
16.5 Configured Versus Actual Rate ......................................................................120
16.6 Default Settings ..............................................................................................121
16.7 xDSL Port Setup Screen ................................................................................121
16.7.1 xDSL Port Setting Screen .....................................................................123
16.8 Virtual Channels .............................................................................................127
16.8.1 Super Channel ......................................................................................127
16.8.2 LLC .......................................................................................................128
16.8.3 VC Mux .................................................................................................128
16.8.4 Virtual Channel Profile ..........................................................................128
16.9 VC Setup Screen ...........................................................................................128
16.10 Priority-based PVCs .....................................................................................132
16.11 PPVC Setup Screen .....................................................................................133
16.11.1 PPVC Setup Members Screen ...........................................................134
Chapter 17
xDSL Profiles Setup............................................................................................. 137
17.1 Port Profile Screen .........................................................................................137
17.2 ATM QoS ........................................................................................................140
17.3 Traffic Shaping ...............................................................................................140
17.3.1 ATM Traffic Classes ..............................................................................140
17.3.1.1 Constant Bit Rate (CBR) .............................................................140
17.3.1.2 Variable Bit Rate (VBR) ...............................................................140
17.3.1.3 Unspecified Bit Rate (UBR) .........................................................141
17.3.2 Traffic Parameters ................................................................................141
17.3.2.1 Peak Cell Rate (PCR) .................................................................141
17.3.2.2 Sustained Cell Rate (SCR) ..........................................................141
17.3.2.3 Maximum Burst Size (MBS) ........................................................141
17.3.2.4 Cell Delay Variation Tolerance (CDVT) .......................................142
17.3.2.5 Burst Tolerance (BT) ...................................................................142
17.3.2.6 Theoretical Arrival Time (TAT) .....................................................142
17.4 Upstream Policing ..........................................................................................143
14 Table of Contents
Page 15

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
17.5 VC Profile Screen ...........................................................................................143
17.6 Alarm Profile Screen ......................................................................................145
17.7 IGMP Filtering ................................................................................................147
17.8 IGMP Filter Profile Screen .............................................................................148
Chapter 18
xDSL Line Data..................................................................................................... 151
18.1 xDSL Line Rate Info Screen ...........................................................................151
18.2 xDSL Performance Screen ............................................................................153
18.3 xDSL Line Data Screen ..................................................................................155
Chapter 19
VLAN ..................................................................................................................... 157
19.1 Introduction to VLANs ....................................................................................157
19.2 Introduction to IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN ...................................................157
19.2.1 Forwarding Tagged and Untagged Frames ..........................................158
19.3 VLAN Status Screen ......................................................................................158
19.4 Static VLAN Setting Screen ...........................................................................160
19.5 VLAN Port Setting Screen ..............................................................................161
Chapter 20
IGMP ...................................................................................................................... 165
20.1 IGMP ..............................................................................................................165
20.2 IP Multicast Addresses ...................................................................................165
20.2.1 IGMP Snooping ....................................................................................165
20.2.2 IGMP Proxy ..........................................................................................165
20.3 IGMP Status Screen .......................................................................................166
20.4 IGMP Bandwidth Screen ................................................................................168
20.4.1 Bandwidth Port Setup Screen ...............................................................169
20.5 IGMP Setup Screen .......................................................................................170
20.6 IGMP Filter Setup Screen ..............................................................................171
20.7 IGMP Count Screen .......................................................................................171
20.8 IGMP Port Info Screen ...................................................................................172
20.9 IGMP Port Group Screen ...............................................................................173
Chapter 21
Static Multicast.....................................................................................................175
21.1 Static Multicast ...............................................................................................175
21.2 Static Multicast Screen ...................................................................................175
Chapter 22
Multicast VLAN..................................................................................................... 177
22.1 Multicast VLAN Overview ...............................................................................177
Table of Contents 15
Page 16

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
22.2 MVLAN Status Screen ...................................................................................177
22.3 MVLAN Setup Screen ....................................................................................178
22.4 MVLAN Group Screen ...................................................................................180
Chapter 23
Filtering ................................................................................................................. 183
23.1 Packet Filter Screen .......................................................................................183
Chapter 24
MAC Filter ............................................................................................................. 185
24.1 MAC Filter Introduction ..................................................................................185
24.2 MAC Filter Screen ..........................................................................................185
Chapter 25
Spanning Tree Protocol ....................................................................................... 187
25.1 RSTP and STP ...............................................................................................187
25.2 Spanning Tree Protocol Status Screen ..........................................................189
25.3 Spanning Tree Protocol Screen .....................................................................191
Chapter 26
Port Authentication.............................................................................................. 193
26.1 Introduction to Authentication .........................................................................193
26.1.1 RADIUS ................................................................................................193
26.1.2 Introduction to Local User Database ....................................................193
26.2 RADIUS Screen .............................................................................................194
26.3 802.1x Screen ................................................................................................195
Chapter 27
Port Security......................................................................................................... 197
27.1 Port Security Overview ...................................................................................197
27.2 Port Security Screen ......................................................................................197
Chapter 28
DHCP Relay .......................................................................................................... 199
28.1 DHCP Relay ...................................................................................................199
28.2 DHCP Relay Agent Information Option (Option 82) .......................................199
28.2.1 DHCP Relay Agent Circuit ID and Remote ID Sub-option Formats .....199
28.3 DHCP Relay Screen ......................................................................................200
Chapter 29
DHCP Snoop......................................................................................................... 203
29.1 DHCP Snoop Overview ..................................................................................203
29.2 DHCP Snoop Screen .....................................................................................203
16 Table of Contents
Page 17

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
29.3 DHCP Snoop Status Screen ..........................................................................204
29.4 DHCP Counter Screen ...................................................................................205
Chapter 30
2684 Routed Mode ............................................................................................... 207
30.1 2684 Routed Mode .........................................................................................207
30.1.1 2684 Routed Mode Example ................................................................207
30.2 2684 Routed PVC Screen ..............................................................................208
30.3 2684 Routed Domain Screen .........................................................................210
30.4 RPVC Arp Proxy Screen ................................................................................211
30.5 2684 Routed Gateway Screen .......................................................................212
Chapter 31
PPPoA to PPPoE .................................................................................................. 215
31.1 PPPoA to PPPoE Overview ...........................................................................215
31.2 PPPoA to PPPoE Screen ...............................................................................215
31.3 PPPoA to PPPoE Status Screen ....................................................................218
Chapter 32
DSCP ..................................................................................................................... 221
32.1 DSCP Overview .............................................................................................221
32.2 DSCP Setup Screen ......................................................................................221
32.3 DSCP Map Screen .........................................................................................222
Chapter 33
TLS PVC ................................................................................................................ 223
33.1 Transparent LAN Service (TLS) Overview .....................................................223
33.1.1 TLS Network Example ..........................................................................223
33.2 TLS PVC Screen ............................................................................................224
Chapter 34
ACL........................................................................................................................ 227
34.1 Access Control Logic (ACL) Overview ...........................................................227
34.1.1 ACL Profile Rules .................................................................................227
34.1.2 ACL Profile Actions ...............................................................................228
34.2 ACL Setup Screen .........................................................................................228
34.3 ACL Profile Setup Screen ..............................................................................230
34.4 ACL Profile Map Screen .................................................................................232
Chapter 35
Downstream Broadcast ....................................................................................... 233
35.1 Downstream Broadcast ..................................................................................233
35.2 Downstream Broadcast Screen .....................................................................233
Table of Contents 17
Page 18

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Chapter 36
Syslog ................................................................................................................... 235
36.1 Syslog ............................................................................................................235
36.2 SysLog Screen ...............................................................................................235
Chapter 37
Access Control..................................................................................................... 237
37.1 Access Control Screen ...................................................................................237
37.2 Access Control Overview ...............................................................................237
37.3 SNMP .............................................................................................................237
37.3.1 Supported MIBs ....................................................................................239
37.3.2 SNMP Traps .........................................................................................239
37.4 SNMP Screen ................................................................................................241
37.5 Service Access Control Screen ......................................................................242
37.6 Remote Management Screen ........................................................................243
Chapter 38
Static Routing....................................................................................................... 245
Chapter 39
Alarm ..................................................................................................................... 247
39.1 Alarm ..............................................................................................................247
39.2 Alarm Status Screen ......................................................................................247
39.3 Alarm Descriptions .........................................................................................248
39.4 Alarm Event Setup Screen .............................................................................249
39.4.1 Edit Alarm Event Setup Screen ............................................................251
39.5 Alarm Port Setup Screen ...............................................................................252
Chapter 40
Maintenance ......................................................................................................... 255
40.1 Maintenance Screen ......................................................................................255
40.2 Firmware Upgrade Screen .............................................................................255
40.3 Restore Configuration Screen ........................................................................256
40.4 Backing Up a Configuration File .....................................................................256
40.5 Load Factory Defaults ....................................................................................257
40.6 Reboot System ...............................................................................................257
40.7 Command Line FTP .......................................................................................258
Chapter 41
Diagnostic............................................................................................................. 259
41.1 Diagnostic Screen ..........................................................................................259
41.2 Log Format .....................................................................................................261
41.2.1 Log Messages ......................................................................................262
18 Table of Contents
Page 19

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
41.3 LDM Test Parameters ....................................................................................263
41.4 ToneDiag Parameters ....................................................................................264
Chapter 42
MAC Table ............................................................................................................. 265
42.1 Introduction to MAC Table ..............................................................................265
42.2 MAC Table Screen .........................................................................................266
Chapter 43
ARP Table.............................................................................................................. 267
43.1 Introduction to ARP Table ..............................................................................267
43.1.1 How ARP Works ...................................................................................267
43.2 ARP Table Screen ..........................................................................................267
Chapter 44
Commands............................................................................................................ 269
44.1 Command Line Interface Overview ................................................................269
44.2 Command Privilege Levels ............................................................................269
44.3 Saving Your Configuration ..............................................................................270
44.4 Commands .....................................................................................................270
Chapter 45
Command Examples............................................................................................ 289
45.1 Command Examples Overview ......................................................................289
45.2 Sys Commands ..............................................................................................289
45.2.1 Log Show Command ............................................................................289
45.3 Log Format .....................................................................................................289
45.3.1 Log Messages ......................................................................................290
45.3.2 Log Clear Command .............................................................................292
45.3.3 Info Show Command ............................................................................292
45.4 Isolation Commands ......................................................................................293
45.4.1 Isolation Show Command .....................................................................293
45.4.2 Isolation Enable Command ...................................................................293
45.4.3 Isolation Disable Command ..................................................................294
45.5 Statistics Monitor Command ..........................................................................294
45.6 Statistics Port Command ................................................................................295
Chapter 46
Alarm Commands ................................................................................................297
46.1 Alarm Commands ..........................................................................................297
46.2 General Alarm Command Parameters ...........................................................297
46.3 Alarm Show Command ..................................................................................297
46.4 Alarm Port Show Command ...........................................................................298
Table of Contents 19
Page 20

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
46.5 Alarm Port Set Command ..............................................................................299
46.6 Alarm Tablelist Command ..............................................................................300
46.7 Log Format .....................................................................................................301
46.8 Alarm History Show Command ......................................................................301
46.9 Alarm History Clear Command ......................................................................302
46.10 Alarm XEdit Command .................................................................................302
46.11 Alarm Cutoff Command ................................................................................303
46.12 Alarm Clear Command .................................................................................303
Chapter 47
DHCP Commands ................................................................................................ 305
47.1 DHCP Relay Commands ...............................................................................305
47.1.1 Show Command ...................................................................................305
47.1.2 Enable Command .................................................................................305
47.1.3 Disable Command ................................................................................306
47.1.4 Server Set Command ...........................................................................306
47.1.5 Server Delete Command ......................................................................306
47.1.6 Server Active Command .......................................................................307
47.1.7 Relaymode Command ..........................................................................307
47.2 DHCP Relay Option 82 (Agent Information) Sub-option 1 (Circuit ID) ...........307
47.2.1 Option 82 Sub-option 1 Enable Command ...........................................308
47.2.2 Option 82 Sub-option 1 Disable Command ..........................................308
47.2.3 Option 82 Sub-option 1 Set Command .................................................308
47.3 DHCP Relay Option 82 (Agent Information) Sub-option 2 (Remote ID) ........308
47.3.1 Option 82 Sub-option 2 Enable Command ...........................................308
47.3.2 Option 82 Sub-option 2 Disable Command ..........................................309
47.3.3 Option 82 Sub-option 2 Set Command .................................................309
47.4 DHCP Snoop Commands ..............................................................................309
47.4.1 DHCP Snoop Enable Command ..........................................................309
47.4.2 DHCP Snoop Disable Command ..........................................................310
47.4.3 DHCP Snoop Flush Command .............................................................310
47.4.4 DHCP Snoop Show Command ............................................................. 311
47.4.5 DHCP Counter Statistics Command ..................................................... 311
47.4.6 DHCP Snoop Statistics Command .......................................................312
Chapter 48
IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN Commands ............................................................. 313
48.1 Introduction to VLANs ....................................................................................313
48.2 IEEE 802.1Q Tagging Types ..........................................................................313
48.3 Filtering Databases ........................................................................................313
48.3.1 Static Entries (SVLAN Table) ................................................................313
48.4 IEEE VLAN1Q Tagged VLAN Configuration Commands ...............................314
48.4.1 VLAN Port Show Command .................................................................314
20 Table of Contents
Page 21

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
48.4.2 VLAN PVID Command .........................................................................314
48.4.3 VLAN Priority Command .......................................................................315
48.4.4 VLAN Set Command ............................................................................315
48.4.4.1 Modify a Static VLAN Table Example ..........................................316
48.4.4.2 Forwarding Process Example .....................................................316
48.4.5 VLAN Frame Type Command ...............................................................317
48.4.6 VLAN CPU Show Command ................................................................317
48.4.7 VLAN CPU Set Command ....................................................................318
48.4.8 Configuring Management VLAN Example ............................................318
48.4.9 VLAN Delete Command .......................................................................319
48.5 VLAN Enable ..................................................................................................319
48.6 VLAN Disable .................................................................................................319
48.6.1 VLAN Show Command .........................................................................320
Chapter 49
MAC Commands ..................................................................................................321
49.1 MAC Commands Overview ............................................................................321
49.2 MAC Filter Commands ...................................................................................321
49.2.1 MAC Filter Show Command .................................................................321
49.2.2 MAC Filter Enable Command ...............................................................322
49.2.3 MAC Filter Disable Command .............................................................322
49.2.4 MAC Filter Mode Command ................................................................322
49.2.5 MAC Filter Set Command .....................................................................323
49.2.6 MAC Filter Delete Command ................................................................323
49.3 MAC Count Commands .................................................................................324
49.3.1 MAC Count Show Command ................................................................324
49.3.2 MAC Count Enable Command .............................................................325
49.3.3 MAC Count Disable Command ............................................................325
49.3.4 MAC Count Set Command ...................................................................326
Chapter 50
IGMP Commands .................................................................................................327
50.1 Multicast Overview .........................................................................................327
50.2 IGMP Snoop Commands ...............................................................................327
50.2.1 IGMP Snoop Show Command ..............................................................327
50.2.2 IGMP Snoop Enable Command ...........................................................327
50.2.3 IGMP Snoop Disable Command ...........................................................328
50.3 IGMP Filter Commands ..................................................................................328
50.3.1 IGMP Filter Show Command ................................................................328
50.3.2 IGMP Filter Set Command ....................................................................329
50.3.3 IGMP Filter Profile Set Command ........................................................329
50.3.4 IGMP Filter Profile Delete Command ...................................................330
50.3.5 IGMP Filter Profile Show Command ....................................................330
Table of Contents 21
Page 22

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
50.4 IGMP Bandwidth Commands .........................................................................331
50.4.1 IGMP Bandwidth Default Command .....................................................331
50.4.2 IGMP Bandwidth Set Command ...........................................................332
50.4.3 IGMP Bandwidth Delete Command ......................................................332
50.5 IGMP Bandwidth Port Commands .................................................................332
50.5.1 IGMP Bandwidth Port Disable Command .............................................332
50.5.2 IGMP Bandwidth Port Enable Command .............................................333
50.5.3 IGMP Bandwidth Port Set Command ...................................................333
50.5.4 IGMP Bandwidth Port Show Command ................................................333
50.6 IGMP Count Limit Commands .......................................................................334
50.6.1 IGMP Count Disable Command ...........................................................334
50.6.2 IGMP Count Enable Command ............................................................335
50.6.3 IGMP Count Set Command ..................................................................335
50.6.4 IGMP Count Show Command ..............................................................336
50.7 IGMP Snoop Statistics Commands ................................................................336
50.7.1 IGMP Snoop Info Statistics Command .................................................336
50.7.2 IGMP Group Statistics Command .........................................................337
50.7.3 IGMP Port Info Statistics Command .....................................................337
50.7.4 IGMP Port Group Statistics Command .................................................338
50.8 Multicast VLAN Commands ...........................................................................338
50.8.1 Multicast VLAN Set Command .............................................................338
50.8.2 Multicast VLAN Delete Command ........................................................339
50.8.3 Multicast VLAN Disable Command .......................................................339
50.8.4 Multicast VLAN Enable Command .......................................................340
50.8.5 Multicast VLAN Show Command ..........................................................340
50.8.6 Multicast VLAN Group Set Command ..................................................341
50.8.7 Multicast VLAN Group Delete Command .............................................341
50.8.8 Multicast VLAN Group Show Command ...............................................341
Chapter 51
Packet Filter Commands ..................................................................................... 343
51.1 Packet Filter Commands ................................................................................343
51.1.1 Packet Filter Show Command ..............................................................343
51.1.2 Packet Filter Set Command ..................................................................344
51.1.3 Packet Filter PPPoE Only Command ...................................................345
Chapter 52
IP Commands ....................................................................................................... 347
52.1 IP Commands Introduction .............................................................................347
52.2 IP Settings and Default Gateway ...................................................................347
52.3 General IP Commands ...................................................................................348
52.3.1 Show .....................................................................................................348
52.3.2 Ping Command .....................................................................................348
22 Table of Contents
Page 23

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
52.3.3 Route Set Command ............................................................................349
52.3.4 Route Delete Command .......................................................................349
52.3.5 Route Show Command .........................................................................349
52.3.6 ARP Show Command ...........................................................................350
52.3.7 ARP Flush Command ...........................................................................350
52.4 Statistics IP Command ...................................................................................350
Chapter 53
Firmware and Configuration File Maintenance ................................................. 353
53.1 Firmware and Configuration File Maintenance Overview ..............................353
53.2 Filename Conventions ...................................................................................353
53.3 Editable Configuration File .............................................................................354
53.3.1 Editable Configuration File Backup ......................................................354
53.3.2 Edit Configuration File .........................................................................355
53.3.3 Editable Configuration File Upload .......................................................356
53.4 Firmware File Upgrade ..................................................................................357
Chapter 54
SNMP.....................................................................................................................359
54.1 SNMP Commands .........................................................................................359
54.1.1 Get Community Command ...................................................................359
54.1.2 Set Community Command ....................................................................359
54.1.3 Trusted Host Set Command .................................................................359
54.1.4 Trap Community Command ..................................................................360
54.1.5 Trap Destination Set Command ...........................................................360
54.1.6 Show SNMP Settings Command ..........................................................360
Chapter 55
ADSL Commands................................................................................................. 363
55.1 ADSL Commands ..........................................................................................363
55.1.1 ADSL Show Command .........................................................................363
55.1.2 ADSL Enable Command .......................................................................363
55.1.3 ADSL Disable Command ......................................................................364
55.1.4 ADSL Profile Show Command ..............................................................364
55.1.5 ADSL Profile Set Command .................................................................365
55.1.6 ADSL Profile Delete Command ............................................................367
55.1.7 ADSL Profile Map Command ................................................................368
55.1.8 ADSL Name Command ........................................................................369
55.1.9 ADSL Tel Command .............................................................................369
55.1.10 ADSL Loopback Command ................................................................370
55.1.11 ADSL Upstream PSD Command ........................................................370
55.1.12 ADSL Downstream PSD Command ...................................................371
55.1.13 ADSL Upstream Carrier Command ....................................................371
Table of Contents 23
Page 24

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
55.1.14 ADSL Downstream Carrier0 Command ..............................................372
55.1.15 ADSL Downstream Carrier1 Command ..............................................373
55.1.16 PMM Parameters Command ..............................................................375
55.1.17 Impulse Noise Protection Command ..................................................376
55.1.18 Annex L Enable Command .................................................................377
55.1.19 Annex L Disable Command ................................................................377
55.1.20 Annex M Enable Command ................................................................378
55.1.21 Annex M Disable Command ...............................................................378
55.1.22 Annex I Enable Command ..................................................................379
55.1.23 Annex I Disable Command .................................................................379
55.2 Statistics ADSL Commands ...........................................................................379
55.2.1 ADSL Show Command .........................................................................380
55.2.2 Linedata Command ..............................................................................380
55.2.3 Lineinfo Command ................................................................................381
55.2.4 Lineperf Command ...............................................................................383
55.2.5 15 Minute Performance Command .......................................................384
55.2.6 1 Day Performance Command .............................................................386
55.2.7 Line Diagnostics Set Command ...........................................................387
55.2.8 Line Diagnostics Get Command ...........................................................388
55.2.9 Line Diagnostics Get 992.3 Command .................................................389
55.2.10 SELT Diagnostic Set Command .........................................................391
55.2.11 SELT Diagnostic Get Command .........................................................392
55.2.12 Tone Diagnostics 992.3 Command .....................................................392
55.3 Alarm Profile Commands ...............................................................................394
55.3.1 Alarm Profile Show Command ..............................................................394
55.3.2 Alarm Profile Set Command .................................................................395
55.3.3 Alarm Profile Delete Command ............................................................397
55.3.4 Alarm Profile Map Command ................................................................397
55.3.5 Alarm Profile Showmap Command .......................................................397
Chapter 56
Virtual Channel Management.............................................................................. 399
56.1 Virtual Channel Management Overview .........................................................399
56.2 Virtual Channel Profile Commands ................................................................399
56.2.1 Show Virtual Channel Profile Command ..............................................399
56.2.2 Set Virtual Channel Profile Command .................................................399
56.2.3 Delete Virtual Channel Profile Command ............................................401
56.3 PVC Channels ................................................................................................401
56.3.1 PVC Show Command ...........................................................................401
56.3.2 PVC Set Command ..............................................................................402
56.3.3 PVC Delete Command .........................................................................403
56.4 Priority-based PVCs .......................................................................................403
56.4.1 PPVC Set Command ............................................................................404
24 Table of Contents
Page 25

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
56.4.2 PPVC Member Set Command ..............................................................404
56.5 PPVC Member Delete Command ..................................................................405
56.6 PPVC Member Show Command ....................................................................406
56.6.1 PPVC Show Command ........................................................................407
56.6.2 PPVC Delete Command .......................................................................407
56.7 2684 Routed Mode Commands .....................................................................408
56.7.1 2684 Routed Mode Example ................................................................409
56.7.2 RPVC Gateway Set Command .............................................................410
56.7.3 RPVC Gateway Show Command .........................................................410
56.7.4 RPVC Gateway Delete Command ........................................................ 411
56.7.5 RPVC Set Command ............................................................................411
56.7.6 RPVC Show Command ........................................................................412
56.7.7 RPVC Delete Command .......................................................................413
56.7.8 RPVC Route Set Command .................................................................414
56.7.9 RPVC Route Show Command ..............................................................414
56.7.10 RPVC Route Delete Command ..........................................................415
56.7.11 RPVC ARP Agingtime Set Command .................................................416
56.7.12 RPVC ARP Agingtime Show Command .............................................416
56.7.13 RPVC ARP Show Command ..............................................................417
56.7.14 RPVC ARP Flush Command ..............................................................417
56.8 PPPoA to PPPoE (PAE) Commands .............................................................417
56.8.1 PAE PVC Delete Command .................................................................417
56.8.2 PAE PVC Set Command ......................................................................418
56.8.3 PAE PVC Show Command ...................................................................419
56.8.4 PAE PVC Session Command ...............................................................419
56.8.5 PAE PVC Counter Command ...............................................................420
56.9 Transparent LAN Service (TLS) Commands ..................................................421
56.9.1 TLS PVC Delete Command ..................................................................421
56.9.2 TLS PVC Set Command .......................................................................422
56.9.3 TLS PVC Show Command ...................................................................422
Chapter 57
ACL Commands ................................................................................................... 425
57.1 ACL Profile Commands ..................................................................................425
57.1.1 ACL Profile Set Command ....................................................................425
57.1.2 ACL Profile Delete Command ...............................................................427
57.1.3 ACL Profile Show Map Command ........................................................427
57.1.4 ACL Profile Show Command ................................................................427
57.2 ACL Assignment Commands .........................................................................428
57.2.1 ACL Assignment Set Command ...........................................................428
57.2.2 ACL Assignment Delete Command ......................................................429
57.2.3 ACL Assignment Show Command .......................................................429
Table of Contents 25
Page 26

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Chapter 58
Troubleshooting ................................................................................................... 431
58.1 The SYS or PWR LED Does Not Turn On .....................................................431
58.2 The ALM LED Is On .......................................................................................431
58.3 SFP LNK LEDs Do Not Turn On ....................................................................432
58.4 100/1000 LEDs Do Not Turn On ....................................................................432
58.5 100/1000 Ethernet Port Data Transmission ...................................................432
58.6 DSL Data Transmission .................................................................................433
58.7 There Is No Voice on an ADSL Connection ...................................................433
58.8 Testing Wiring .................................................................................................434
58.9 Local Server ...................................................................................................436
58.10 Data Rate ....................................................................................................436
58.11 Configured Settings ......................................................................................437
58.12 Password .....................................................................................................437
58.13 System Lockout ............................................................................................437
58.14 SNMP ...........................................................................................................437
58.15 Telnet ............................................................................................................438
58.16 Resetting the Defaults ..................................................................................438
58.16.1 Resetting the Defaults Via Command .................................................438
58.16.2 Uploading the Default Configuration File ............................................439
58.17 Recovering the Firmware .............................................................................440
Appendix A
Default Settings.................................................................................................... 443
Appendix B
IES-1248 Specifications....................................................................................... 445
Appendix C
Pin Assignments .................................................................................................. 449
Appendix D
Removing and Installing a Fuse ........................................................................ 453
Index...................................................................................................................... 455
26 Table of Contents
Page 27

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
List of Figures
Figure 1 MTU Application .......................................................................................45
Figure 2 Curbside Application ................................................................................ 46
Figure 3 Attaching Rubber Feet ............................................................................. 48
Figure 4 Attaching Mounting Brackets and Screws ................................................ 49
Figure 5 Rack Mounting ......................................................................................... 50
Figure 6 IES-1248 Frame Ground .......................................................................... 51
Figure 7 IES-1248 Front Panel ............................................................................... 53
Figure 8 IES-1248-51A Front Panel ....................................................................... 53
Figure 9 SFP Mini GBIC Slot .................................................................................. 56
Figure 10 Transceiver Installation ........................................................................... 56
Figure 11 Installed Transceivers .............................................................................57
Figure 12 Opening the Transceiver Latch .............................................................. 57
Figure 13 Removing the Transceiver ...................................................................... 58
Figure 14 ALARM Pins Layout ............................................................................... 59
Figure 15 MDF (Main Distribution Frame) Wiring ................................................... 61
Figure 16 Telco-50 Cable with RJ-11 Connectors ..................................................62
Figure 17 Installation Overview Example ...............................................................63
Figure 18 Installation Scenario A ............................................................................64
Figure 19 One MDF for End-user and CO Connections ......................................... 64
Figure 20 Installation Scenario B ............................................................................65
Figure 21 Two Separate MDFs for End-user and CO Connections ........................ 66
Figure 22 Installation Scenario C ............................................................................ 67
Figure 23 Fan Module Thumbscrews ..................................................................... 71
Figure 24 Removing the Fan Module .....................................................................72
Figure 25 Fan Module Removed ............................................................................ 72
Figure 26 Login ....................................................................................................... 74
Figure 27 Home ......................................................................................................74
Figure 28 User Account .......................................................................................... 77
Figure 29 User Account .......................................................................................... 78
Figure 30 Logout .................................................................................................... 79
Figure 31 IP Setup ..................................................................................................81
Figure 32 xDSL Port Setup ..................................................................................... 82
Figure 33 VC Setup ................................................................................................ 83
Figure 34 VC Setup, Delete .................................................................................... 83
Figure 35 Select Ports ............................................................................................ 84
Figure 36 VC Setup ................................................................................................ 84
Figure 37 VC Setup ................................................................................................ 85
Figure 38 Select Ports ............................................................................................ 85
List of Figures 27
Page 28

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 39 VC Setup ................................................................................................ 86
Figure 40 Config Save ............................................................................................ 86
Figure 41 Config Save, Save Successful ............................................................... 86
Figure 42 Home ......................................................................................................87
Figure 43 Port Statistics (Ethernet) ......................................................................... 89
Figure 44 Port Statistics (ADSL) ............................................................................. 92
Figure 45 Port Statistics (RMON) ...........................................................................94
Figure 46 Port Statistics (RMON History)) .............................................................. 96
Figure 47 Port Statistics (RMON History Detail)) ....................................................97
Figure 48 System Info ............................................................................................ 100
Figure 49 General Setup ........................................................................................ 103
Figure 50 User Account .......................................................................................... 105
Figure 51 Authentication .........................................................................................106
Figure 52 Port Isolation with Standalone Switch Mode Example ...........................110
Figure 53 Port Isolation with Daisychain Switch Mode Example ............................ 111
Figure 54 Switch Setup .......................................................................................... 112
Figure 55 IP Setup ..................................................................................................115
Figure 56 ENET Port Setup .................................................................................... 117
Figure 57 xDSL Port Setup ..................................................................................... 121
Figure 58 Select Ports ............................................................................................ 122
Figure 59 xDSL Port Setting ................................................................................... 124
Figure 60 VC Setup ................................................................................................ 129
Figure 61 Basic Setting, xDSL Port Setup, VC Setup, Delete ................................ 131
Figure 62 Select Ports ............................................................................................ 131
Figure 63 Select Ports ............................................................................................ 132
Figure 64 PPVC Setup ...........................................................................................133
Figure 65 PPVC Setup, Edit ................................................................................... 135
Figure 66 Port Profile ..............................................................................................137
Figure 67 PCR, SCR and MBS in Traffic Shaping .................................................. 142
Figure 68 TAT, CDVT and BT in Traffic Shaping .................................................... 142
Figure 69 VC Profile ............................................................................................... 144
Figure 70 Alarm Profile ........................................................................................... 146
Figure 71 IGMP Filter Profile ..................................................................................149
Figure 72 xDSL Line Rate Info ............................................................................... 151
Figure 73 xDSL Performance .................................................................................153
Figure 74 xDSL Line Data ......................................................................................155
Figure 75 VLAN Status ........................................................................................... 159
Figure 76 Static VLAN Setting ................................................................................ 160
Figure 77 VLAN Port Setting ..................................................................................162
Figure 78 Select Ports ............................................................................................ 163
Figure 79 IGMP Proxy Network Example ............................................................... 166
Figure 80 IGMP (Status) ......................................................................................... 167
Figure 81 IGMP Bandwidth .................................................................................... 168
28 List of Figures
Page 29

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 82 Bandwidth Port Setup ............................................................................. 170
Figure 83 IGMP Setup ............................................................................................171
Figure 84 IGMP Count ............................................................................................ 172
Figure 85 IGMP Port Info ........................................................................................ 173
Figure 86 IGMP Port Group .................................................................................... 173
Figure 87 Static Multicast ....................................................................................... 175
Figure 88 MVLAN Status ........................................................................................ 177
Figure 89 MVLAN Setup ......................................................................................... 179
Figure 90 MVLAN Group ........................................................................................180
Figure 91 Packet Filter ........................................................................................... 183
Figure 92 MAC Filter .............................................................................................. 185
Figure 93 STP Root Ports and Designated Ports ...................................................188
Figure 94 Spanning Tree Protocol Status ............................................................... 189
Figure 95 Spanning Tree Protocol ..........................................................................191
Figure 96 RADIUS Server ...................................................................................... 193
Figure 97 RADIUS ..................................................................................................194
Figure 98 802.1x ..................................................................................................... 195
Figure 99 Port Security ........................................................................................... 197
Figure 100 Select Ports .......................................................................................... 198
Figure 101 DHCP Relay Agent Circuit ID Sub-option Format ................................ 199
Figure 102 DHCP Relay Agent Remote ID Sub-option Format .............................. 200
Figure 103 DHCP Relay ......................................................................................... 200
Figure 104 DHCP Snoop ........................................................................................ 203
Figure 105 DHCP Snoop Status ............................................................................. 204
Figure 106 DHCP Counter ..................................................................................... 205
Figure 107 2684 Routed Mode Example ................................................................ 208
Figure 108 2684 Routed PVC ................................................................................ 209
Figure 109 2684 Routed Domain ........................................................................... 210
Figure 110 RPVC Arp Proxy ................................................................................... 212
Figure 111 2684 Routed Gateway ..........................................................................213
Figure 112 Mixed PPPoA-to-PPPoE Broadband Network Example ...................... 215
Figure 113 PPPoA to PPPoE ..................................................................................216
Figure 114 PPPoA to PPPoE Status ....................................................................... 218
Figure 115 DSCP Setup ......................................................................................... 221
Figure 116 DSCP Map ............................................................................................222
Figure 117 Transparent LAN Service Network Example ....................................... 224
Figure 118 TLS PVC ...............................................................................................225
Figure 119 ACL Setup ............................................................................................ 229
Figure 120 ACL Profile Setup ................................................................................. 230
Figure 121 ACL Profile Map ...................................................................................232
Figure 122 Downstream Broadcast ........................................................................233
Figure 123 SysLog ................................................................................................. 235
Figure 124 Access Control .....................................................................................237
List of Figures 29
Page 30

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 125 SNMP Management Model .................................................................. 238
Figure 126 SNMP ................................................................................................... 241
Figure 127 Service Access Control ........................................................................242
Figure 128 Remote Management (Secured Client Setup) ..................................... 243
Figure 129 Static Routing ....................................................................................... 245
Figure 130 Alarm Status ......................................................................................... 247
Figure 131 Alarm Event Setup ............................................................................... 250
Figure 132 Alarm Event Setup Edit ........................................................................251
Figure 133 Alarm Port Setup .................................................................................. 252
Figure 134 Maintenance ......................................................................................... 255
Figure 135 Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................255
Figure 136 Restore Configuration .......................................................................... 256
Figure 137 Restore Default Configuration .............................................................. 257
Figure 138 Restore Factory Default Settings, Reboot ............................................ 257
Figure 139 Reboot System ..................................................................................... 258
Figure 140 Diagnostic ............................................................................................. 259
Figure 141 MAC Table Filtering Flowchart ............................................................. 265
Figure 142 MAC Table ............................................................................................266
Figure 143 ARP Table ............................................................................................ 268
Figure 144 Log Show Command Example ............................................................. 289
Figure 145 Info Show Example .............................................................................. 293
Figure 146 Isolation Show Example ....................................................................... 293
Figure 147 Statistics Monitor Command Example .................................................. 294
Figure 148 Statistics Port Command Example ....................................................... 295
Figure 149 Alarm Show Command Example ......................................................... 298
Figure 150 Alarm Port Show Command Example ..................................................299
Figure 151 Alarm Port Set Command Example ..................................................... 300
Figure 152 Alarm Tablelist Command Example ..................................................... 300
Figure 153 Alarm History Show Command Example ............................................. 302
Figure 154 Alarm History Clear Command Example ..............................................302
Figure 155 Alarm Xedit Command Example .......................................................... 303
Figure 156 Show Command Example .................................................................... 305
Figure 157 DHCP Snoop Enable Command Example ........................................... 310
Figure 158 DHCP Snoop Show Command Example ............................................. 311
Figure 159 DHCP Counter Statistics Command Example ......................................311
Figure 160 DHCP Snoop Statistics Command Example ........................................312
Figure 161 VLAN Port Show Command Example .................................................. 314
Figure 162 VLAN PVID Command Example .......................................................... 315
Figure 163 VLAN CPU Set Command Example ....................................................315
Figure 164 Modifying the Static VLAN Example ..................................................... 316
Figure 165 VLAN Frame Type Command Example ............................................... 317
Figure 166 VLAN CPU Set Command Example ....................................................318
Figure 167 VLAN CPU Set Command Example ....................................................318
30 List of Figures
Page 31

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 168 CPU VLAN Configuration and Activation Example ..............................318
Figure 169 Deleting Default VLAN Example .......................................................... 319
Figure 170 VLAN Delete Command Example ........................................................ 319
Figure 171 VLAN Show Command Example ......................................................... 320
Figure 172 MAC Filter Show Command Example ..................................................321
Figure 173 MAC Filter Enable Command Example ................................................ 322
Figure 174 MAC Filter Disable Command Example ...............................................322
Figure 175 MAC Filter Mode Command Example .................................................. 323
Figure 176 MAC Filter Set Command Example ..................................................... 323
Figure 177 MAC Filter Delete Command Example ................................................ 324
Figure 178 MAC Count Show Command Example ................................................ 324
Figure 179 MAC Count Enable Command Example ..............................................325
Figure 180 MAC Count Disable Command Example .............................................325
Figure 181 MAC Count Set Command Example .................................................... 326
Figure 182 IGMP Snoop Show Command Example .............................................. 327
Figure 183 IGMP Snoop Enable Command Example ............................................ 328
Figure 184 IGMP Snoop Disable Command Example ........................................... 328
Figure 185 IGMP Filter Show Command Example ................................................. 329
Figure 186 IGMP Filter Set Command Example .................................................... 329
Figure 187 IGMP Filter Profile Set Command Example ......................................... 330
Figure 188 IGMP Filter Profile Delete Command Example .................................... 330
Figure 189 IGMP Filter Show Command Example ................................................. 331
Figure 190 IGMP Bandwidth Port Show Command Example ................................ 334
Figure 191 IGMP Count Disable Command Example ............................................ 335
Figure 192 IGMP Count Enable Command Example .............................................335
Figure 193 IGMP Count Set Command Example ................................................... 336
Figure 194 IGMP Count Show Command Example ............................................... 336
Figure 195 IGMP Snoop Info Statistics Command Example .................................337
Figure 196 IGMP Group Statistics Command Example ........................................ 337
Figure 197 IGMP Port Info Statistics Command Example ..................................... 338
Figure 198 IGMP Port Group Statistics Command Example ................................. 338
Figure 199 Multicast VLAN Disable Command Example ...................................... 340
Figure 200 Multicast VLAN Show Command Example ......................................... 340
Figure 201 Multicast VLAN Group Set Command Example ..................................341
Figure 202 Packet Filter Show Command Example ...............................................343
Figure 203 Packet Filter Set Command Example .................................................. 345
Figure 204 Packet Filter PPPoE Only Command Example .................................... 345
Figure 205 IP Settings and Default Gateway Address Commands ........................347
Figure 206 IP Settings and Default Gateway Address Command Example ........... 348
Figure 207 Route Show Command Example ......................................................... 350
Figure 208 ARP Show Command Example ...........................................................350
Figure 209 Statistics IP Command Example .......................................................... 351
Figure 210 FTP Put Configuration File Example .................................................... 353
List of Figures 31
Page 32

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 211 FTP Get Configuration File Example .................................................... 353
Figure 212 Example: Use an FTP Client to Connect to the IES-1248 .................... 354
Figure 213 Example: Enter the Management Password ........................................ 355
Figure 214 Example: Get the Configuration File config-0 ....................................... 355
Figure 215 Example: Close FTP Client ..................................................................355
Figure 216 Configuration File Example .................................................................. 356
Figure 217 Example: Use an FTP Client to Connect to the IES-1248 .................... 356
Figure 218 Example: Enter the Management Password ........................................ 357
Figure 219 Example: Upload the Configuration File config-0 ................................. 357
Figure 220 Example: Close FTP Client ..................................................................357
Figure 221 Example: Use an FTP Client to Connect to the IES-1248 .................... 357
Figure 222 Example: Enter the Management Password ........................................ 357
Figure 223 Example: Transfer the Firmware File ................................................... 358
Figure 224 Example: Close FTP Client ..................................................................358
Figure 225 ADSL Show Command Example ......................................................... 363
Figure 226 ADSL Profile Show Command Example ..............................................365
Figure 227 ADSL Profile Set Command Example 1 ............................................... 367
Figure 228 ADSL Profile Set Command Example 2 ............................................... 367
Figure 229 ADSL Profile Delete Command Example .............................................367
Figure 230 ADSL Profile Delete Command Example .............................................368
Figure 231 ADSL Name Command Example ......................................................... 369
Figure 232 ADSL Tel Command Example .............................................................. 369
Figure 233 ADSL Loopback Command Example ...................................................370
Figure 234 ADSL Upstream PSD Command Example ...........................................371
Figure 235 ADSL Downstream PSD Command Example ......................................371
Figure 236 ADSL Upstream Carrier Command Example ....................................... 372
Figure 237 ADSL Upstream Carrier Command Display Example .......................... 372
Figure 238 ADSL Downstream Carrier0 Command Example 1 ............................. 373
Figure 239 ADSL Downstream Carrier0 Command Display Example ................... 373
Figure 240 ADSL Downstream Carrier0 Command Example 2 ............................. 373
Figure 241 ADSL Downstream Carrier1 Command Example 1 ............................. 374
Figure 242 ADSL Downstream Carrier1 Command Example 2 ............................. 374
Figure 243 ADSL Downstream Carrier1 Command Display Example ................... 375
Figure 244 PMM Parameters Command Example ................................................. 376
Figure 245 Impulse Noise Protection Command Example .....................................377
Figure 246 Annex L Enable Command Example ..................................................377
Figure 247 Annex L Disable Command Example .................................................. 378
Figure 248 Annex M Enable Command Example ..................................................378
Figure 249 Annex M Disable Command Example .................................................. 378
Figure 250 Annex I Enable Command Example ....................................................379
Figure 251 Annex I Disable Command Example .................................................... 379
Figure 252 ADSL Show Command Example ......................................................... 380
Figure 253 Linedata Command Example ............................................................... 381
32 List of Figures
Page 33

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 254 Lineinfo Command Example ................................................................382
Figure 255 Lineperf Command Example ................................................................ 383
Figure 256 15 Minute Performance Command Example ....................................... 385
Figure 257 1Day Performance Command Example ...............................................387
Figure 258 Line Diagnostics Set Command Example ............................................ 387
Figure 259 Line Diagnostics Get Command Example ............................................388
Figure 260 Line Diagnostics Get 992.3 Command Example .................................. 390
Figure 261 SELT Diagnostic Set Command Example ............................................ 392
Figure 262 Line Diagnostics Get Command Example ............................................392
Figure 263 Tone Diagnostics Command Example .................................................393
Figure 264 Alarm Profile Show Command Example .............................................. 395
Figure 265 Alarm Profile Set Command Example .................................................. 396
Figure 266 Alarm Profile Delete Command Example .............................................397
Figure 267 Alarm Profile Map Command Example ................................................ 397
Figure 268 Alarm Profile Showmap Command Example ....................................... 398
Figure 269 Set Virtual Channel Profile Command Example 1 ................................ 400
Figure 270 Set Virtual Channel Profile Command Example 2 ................................ 400
Figure 271 Set Virtual Channel Profile Command Example 3 ................................ 401
Figure 272 Delete Virtual Channel Profile Command Example .............................. 401
Figure 273 PVC Set Command Example ............................................................... 403
Figure 274 PPVC Set Command Example .............................................................404
Figure 275 PPVC Member Set Command Example .............................................. 405
Figure 276 PPVC Member Delete Command Example ......................................... 406
Figure 277 PPVC Member Show Command Example ...........................................407
Figure 278 PPVC Show Command Example ......................................................... 407
Figure 279 PPVC Delete Command Example ........................................................ 408
Figure 280 2684 Routed Mode Example ................................................................ 409
Figure 281 2684 Routed Mode Commands Example ............................................410
Figure 282 RPVC Gateway Set Command Example .............................................410
Figure 283 RPVC Gateway Show Command Example .......................................... 411
Figure 284 RPVC Gateway Delete Command Example ........................................ 411
Figure 285 RPVC Set Command Example ............................................................ 412
Figure 286 RPVC Show Command Example ......................................................... 413
Figure 287 RPVC Delete Command Example ....................................................... 413
Figure 288 RPVC Route Set Command Example .................................................. 414
Figure 289 RPVC Route Show Command Example .............................................. 415
Figure 290 RPVC Route Delete Command Example .............................................416
Figure 291 RPVC ARP Agingtime Command Example .........................................416
Figure 292 RPVC ARP Agingtime Show Command Example ............................... 416
Figure 293 RPVC ARP Agingtime Show Command Example ............................... 417
Figure 294 PAE PVC Set Command Example ...................................................... 418
Figure 295 PAE PVC Show Command Example ................................................... 419
Figure 296 PAE PVC Session Command Example ............................................... 420
List of Figures 33
Page 34

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 297 PAE PVC Counter Command Example ...............................................420
Figure 298 TLS PVC Set Command Example ......................................................422
Figure 299 TLS PVC Show Command Example ...................................................423
Figure 300 ACL Profile Set Command Example .................................................... 427
Figure 301 ACL Profile Show Map Command Example ........................................ 427
Figure 302 ACL Profile Show Command Example ................................................ 428
Figure 303 ACL Assignment Set Command Example ............................................ 429
Figure 304 ACL Assignment Show Command Example ........................................ 429
Figure 305 Testing In-house Wiring ........................................................................ 435
Figure 306 Resetting the Switch Via Command ..................................................... 439
Figure 307 Example Xmodem Upload .................................................................... 440
Figure 308 Example Xmodem Upload .................................................................... 441
Figure 309 USER Telco-50 Pin Assignments ......................................................... 449
Figure 310 CO Telco-50 Pin Assignments ..............................................................450
Figure 311 Console Cable RJ-11 Male Connector ................................................. 451
Figure 312 Console Cable DB-9 Female Connector .............................................. 451
34 List of Figures
Page 35

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
List of Tables
Table 1 IES-1248 Front Panel Ports ...................................................................... 53
Table 2 LED Descriptions ...................................................................................... 54
Table 3 Navigation Panel Submenu Links ............................................................. 75
Table 4 Web Configurator Screens ........................................................................75
Table 5 Home ........................................................................................................87
Table 6 Port Statistics (Ethernet) ...........................................................................89
Table 7 Port Statistics (ADSL) ...............................................................................92
Table 8 Port Statistics (RMON) .............................................................................. 94
Table 9 Port Statistics (RMON History) .................................................................. 96
Table 10 Port Statistics (RMON History Detail) ......................................................97
Table 11 System Info ............................................................................................. 100
Table 12 General Setup ......................................................................................... 103
Table 13 User Account .......................................................................................... 105
Table 14 User Account .......................................................................................... 107
Table 15 Switch Setup ........................................................................................... 112
Table 16 IP Setup .................................................................................................. 115
Table 17 ENET Port Setup .................................................................................... 117
Table 18 ADSL Standards Maximum Transfer Rates ............................................ 119
Table 19 xDSL Port Setup .....................................................................................121
Table 20 xDSL Port Setting ................................................................................... 124
Table 21 VC Setup ................................................................................................. 129
Table 22 IEEE 802.1p Priority to PPVC Mapping ..................................................132
Table 23 PPVC Setup ............................................................................................ 133
Table 24 PPVC Setup, Edit ....................................................................................135
Table 25 Port Profile .............................................................................................. 138
Table 26 VC Profile ................................................................................................144
Table 27 Alarm Profile ........................................................................................... 146
Table 28 IGMP Filter Profile ................................................................................... 149
Table 29 xDSL Line Rate Info ................................................................................ 151
Table 30 xDSL Performance ..................................................................................154
Table 31 xDSL Line Data ....................................................................................... 156
Table 32 VLAN Status ............................................................................................ 159
Table 33 Static VLAN Setting ................................................................................. 161
Table 34 VLAN Port Setting ................................................................................... 162
Table 35 IGMP (Status) ......................................................................................... 167
Table 36 IGMP Bandwidth ..................................................................................... 169
Table 37 Bandwidth Port Setup .............................................................................170
Table 38 IGMP Setup ............................................................................................171
List of Tables 35
Page 36

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 39 IGMP Count ............................................................................................ 172
Table 40 IGMP Port Info ........................................................................................ 173
Table 41 IGMP Port Group .................................................................................... 174
Table 42 Static Multicast ........................................................................................ 175
Table 43 MVLAN Status ......................................................................................... 178
Table 44 MVLAN Setup ......................................................................................... 179
Table 45 MVLAN Group ......................................................................................... 181
Table 46 Packet Filter ............................................................................................ 183
Table 47 MAC Filter ............................................................................................... 185
Table 48 Path Cost ................................................................................................ 187
Table 49 RSTP Port States .................................................................................... 188
Table 50 Spanning Tree Protocol Status ................................................................ 190
Table 51 Spanning Tree Protocol ........................................................................... 191
Table 52 RADIUS .................................................................................................194
Table 53 802.1x ..................................................................................................... 196
Table 54 Port Security ........................................................................................... 197
Table 55 DHCP Relay ............................................................................................ 201
Table 56 DHCP Snoop .......................................................................................... 203
Table 57 DHCP Snoop Status ...............................................................................204
Table 58 DHCP Counter ........................................................................................205
Table 59 2684 Routed PVC ...................................................................................209
Table 60 2684 Routed Domain ..............................................................................211
Table 61 RPVC Arp Proxy ..................................................................................... 212
Table 62 2684 Routed Gateway ............................................................................213
Table 63 PPPoA to PPPoE .................................................................................... 216
Table 64 PPPoA to PPPoE Status .........................................................................218
Table 65 DSCP Setup ............................................................................................ 221
Table 66 DSCP Map .............................................................................................. 222
Table 67 TLS PVC ................................................................................................. 225
Table 68 ACL Setup ............................................................................................... 229
Table 69 ACL Profile Setup ................................................................................... 231
Table 70 ACL Profile Map ...................................................................................... 232
Table 71 Downstream Broadcast ........................................................................... 233
Table 72 SysLog .................................................................................................... 235
Table 73 Access Control Summary ....................................................................... 237
Table 74 SNMP Commands ..................................................................................238
Table 75 SNMPv2 Traps ........................................................................................ 239
Table 76 SNMP ...................................................................................................... 242
Table 77 Service Access Control ........................................................................... 242
Table 78 Remote Management (Secured Client Setup) ........................................ 243
Table 79 Static Routing .......................................................................................... 245
Table 80 Alarm Status ............................................................................................ 247
Table 81 Alarm Descriptions .................................................................................. 248
36 List of Tables
Page 37

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 82 Alarm Event Setup ..................................................................................250
Table 83 Alarm Event Setup Edit ........................................................................... 251
Table 84 Alarm Port Setup ..................................................................................... 253
Table 85 Diagnostic ............................................................................................... 260
Table 86 Log Format .............................................................................................. 261
Table 87 Log Messages ......................................................................................... 262
Table 88 LDM Test Parameters .............................................................................263
Table 89 ToneDiag Parameters ............................................................................. 264
Table 90 MAC Table ..............................................................................................266
Table 91 ARP Table ............................................................................................... 268
Table 92 Commands .............................................................................................. 270
Table 93 Log Format .............................................................................................. 289
Table 94 Log Messages ......................................................................................... 290
Table 95 General Alarm Command Parameters .................................................... 297
Table 96 Log Format .............................................................................................. 301
Table 97 Filename Conventions ............................................................................354
Table 98 Line Performance Counters .................................................................... 383
Table 99 15 Minute Performance Counters ........................................................... 385
Table 100 Line Diagnostics Get Command ...........................................................389
Table 101 Line Diagnostics Get 992.3 Command ................................................. 391
Table 102 ToneDiag Command .............................................................................393
Table 103 SYS LED Troubleshooting .................................................................... 431
Table 104 ALM LED Troubleshooting .................................................................... 431
Table 105 SFP LNK LED Troubleshooting ............................................................ 432
Table 106 100/1000 LED Troubleshooting ............................................................ 432
Table 107 Troubleshooting Data Transmission ......................................................432
Table 108 DSL Data Transmission Troubleshooting .............................................. 433
Table 109 ADSL Voice Troubleshooting ................................................................ 433
Table 110 Wiring Tests ...........................................................................................434
Table 111 Testing In-house Wiring .........................................................................435
Table 112 Troubleshooting a Local Server ............................................................ 436
Table 113 Troubleshooting the SYNC-rate ............................................................436
Table 114 Troubleshooting the IES-1248’s Configured Settings ............................ 437
Table 115 Troubleshooting the SNMP Server ........................................................437
Table 116 Troubleshooting Telnet .......................................................................... 438
Table 117 Default Settings ..................................................................................... 443
Table 118 Wire Gauge Specifications .................................................................... 445
Table 119 Power Input Specifications ....................................................................446
Table 120 Power Input Specifications ....................................................................446
Table 121 Fuse Specifications (IES-1248-51A only) ............................................. 446
Table 122 Fuse Specifications (IES-1248-51, IES-1248-53) ................................. 446
Table 123 Hardware Telco-50 Connector Port and Pin Numbers ..........................450
Table 124 Console Cable Connector Pin Assignments ......................................... 451
List of Tables 37
Page 38

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
38 List of Tables
Page 39

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Preface
Congratulations on your purchase of the IES-1248.
This preface introduces you to the IES-1248 and discusses the conventions of this User’s
Guide. It also provides information on other related documentation.
About This User's Guide
This manual is designed to guide you through the configuration of your IES-1248 for its
various applications.
Related Documentation
• ZyXEL Glossary and Web Site
Please see www.zyxel.com
documentation.
for an online glossary of networking terms and additional support
Syntax Conventions
• “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters. “Select” or “Choose” means for
you to use one of the predefined choices.
• Command and arrow keys are enclosed in square brackets.
carriage return key;
• Mouse action sequences are denoted using a comma. For example, “In Windows, click
Start, Programs, Acrobat Reader” means first click the Start button, then move your
mouse pointer to Programs and then click Acrobat Reader.
• “e.g.,” is a shorthand for “for instance”, and “i.e.,” means “that is” or “in other words”.
• The IES-1248 may be referred to as the “IES-1248”, the “IES”, the “device” or the
“system” in this User’s Guide.
• “IES-1248” refers to the IES-1248-51 for ADSL over POTS (Annex A), the
IES-1248-51A for ADSL over POTS that uses AC power, and the IES-1248-53 for
ADSL over ISDN (Annex B). Differentiation is made where needed.
[ESC] means the Escape key and [SPACE BAR] means the Space Bar.
[ENTER] means the Enter, or
Preface 39
Page 40

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Graphics Icons Key
IES-1248 Computer Server
Computer DSLAM Gateway
Central Office/ ISP Internet Hub/Switch
Firmware Naming Conventions
A firmware version includes the model code and release number as shown in the following
example.
Firmware Version: V3.52 (ABQ.0)
"ABQ" is the model code.
• “ABQ” denotes the IES-1248-51 for ADSL over POTS (Annex A).
• “ABR” denotes the IES-1248-53 for ADSL over ISDN (Annex B).
"0" is this firmware's release number. This varies as new firmware is released. Your
firmware's release number may not match what is displayed in this User's Guide.
User Guide Feedback
Help us help you. E-mail all User Guide-related comments, questions or suggestions for
improvement to techwriters@zyxel.com.tw or send regular mail to The Technical Writing
Team, ZyXEL Communications Corp., 6 Innovation Road II, Science-Based Industrial Park,
Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan. Thank you.
40 Preface
Page 41

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 1
Getting to Know the IES-1248
This chapter describes the system features, specifications and applications of your IES-1248.
The IES-1248 is an IP-based DSLAM (Internet Protocol Digital Subscriber Line Access
Multiplexer) that connects ADSL subscribers to the Internet. As a high-performance but yet
compact platform, it can conveniently deliver broadband Internet access to telephone company
central offices, multi-tenant units (MTUs), hospitals, hotels, schools, university campuses and
ISPs. The IES-1248’s low cost and easy management make it a perfect DSL-provider solution.
The IES-1248 platform allows for convenient management and support of ADSL technology.
Up to 48 ADSL subscribers can simultaneously utilize a wide range of powerful broadband
services.
1.1 System Description
Four Telco-50 Connectors
There are four Telco-50 connectors for ADSL and POTS connections.
1000/100 Mbps Ethernet Ports
The IES-1248 has two 1000/100Mbps auto-sensing Ethernet ports.
They allow you to:
• Connect the IES-1248 to a second-level switch
• Daisy-chain other IES-1248
Two Slots for Mini GBIC Modules
The mini GBIC (Gigabit Interface Converter) module transceivers allow flexibility in
connection options. You can use mini GBIC transceivers for fiber connections to backbone
Ethernet switches.
Stacking
Daisy-chain up to three IES-1248 (or other Ethernet devices).
Chapter 1 Getting to Know the IES-1248 41
Page 42

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Integrated Splitters
The integrated DSL splitter eliminates the need to use external splitters that separate the voiceband and ADSL signals.
Console Port
Use the console port for local management of the IES-1248.
Fans
The fans cool the IES-1248 sufficiently to allow reliable operation of the IES-1248 in even
poorly ventilated rooms or basements. To conserve energy and reduce noise, the fan speed
depends on the temperature.
IP Protocols
• IP Host (No routing)
• Telnet for configuration and monitoring
• SNMP for management
• SNMP MIB II (RFC 1213)
• SNMP v1 RFC 1157
• SNMPv2, SNMPv2c or later version
• Bridge MIBs (RFC 1493, 2674)
• SMI RFC 1155
• ADSL Line MIB (RFC 2662)
• ADSL Extension Line MIB (RFC2449)
•Private MIBs
ADSL Encapsulation
Multiple Protocols over AAL5 (RFC 1483)
ADSL Compliance
• Multi-Mode ADSL standard (some IES-1248 models do not support all of these)
• G.dmt (ITU-T G.992.1)
• G.lite (ITU-T G.992.2)
• G.hs (ITU-T G.994.1)
• ETSI
• ANSI T1.413 issue 2
• ADSL2: G.992.3, G.992.4
• ADSL2+: G.992.5
• Rate adaptation support
42 Chapter 1 Getting to Know the IES-1248
Page 43

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
IEEE 802.1p Priority
Your IES-1248 uses IEEE 802.1p Priority to assign priority levels to individual PVCs.
Multiple PVC and ATM QoS
The IES-1248 allows you to use different channels (also called Permanent Virtual Circuits or
PVCs) for different services or subscribers. Define channels
services or levels of service and assign each channel a priority. ATM Quality of Service (QoS)
allows you to regulate the average rate and fluctuations of data transmission. This helps
eliminate congestion to allow the transmission of real time data (such as audio and video).
1
on each DSL port for different
IEEE 802.1x Port-based Authentication
The IES-1248 supports the IEEE 802.1x standard for centralized user authentication and
accounting management through an optional network authentication (RADIUS) server.
2684 Routed Mode
The IES-1248 can handle 2684 routed mode traffic.
Downstream Broadcast
The IES-1248 can block downstream broadcast packets from being sent to specified VLANs
on specified ports.
Management
• Remote configuration backup/restore and firmware upgrade
•SNMP manageable
• Text-based management locally via console port and remotely via telnet
• Editable plain text based configuration file
Security
• Password protection for system management
•VLAN
MAC (Media Access Control) Filter
Use the MAC filter to accept or deny incoming frames based on MAC (Media Access Control)
address(es) that you specify. You may enable/disable the MAC filter on specific ports. You
may specify up to ten MAC addresses per port.
1. Up to eight channels on each DSL port at the time of writing.
Chapter 1 Getting to Know the IES-1248 43
Page 44

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
MAC (Media Access Control) Count Filter
You can limit the number of MAC addresses that may be dynamically learned on a port. You
may enable/disable the MAC count filter on individual ports.
Static Multicast
Use static multicast to allow incoming frames based on multicast MAC address(es) that you
specify. This feature can be used in conjunction with IGMP snooping and IGMP proxy to
allow multicast MAC address(es) that are not learned by IGMP snooping or IGMP proxy.
IGMP Proxy
In a simple tree network, the system can proxy multicast traffic in order to improve network
performance.
IGMP Snooping
With IGMP snooping, group multicast traffic is only forwarded to ports that are members of
that group. IGMP Snooping generates no additional network traffic, allowing you to
significantly reduce multicast traffic passing through your IES-1248.
System Monitoring
• System status (link status, rates, statistics counters)
• Temperatures, voltage reports and alarms.
System Error Logging
The IES-1248’s system error log will record error logs locally. These logs may be viewed
again after a warm restart.
Alarm LED
An ALM (alarm) LED lights when the IES-1248 is overheated, the fans are not working
properly, the voltage readings are outside the tolerance levels or an alarm has been detected on
the ALARM input pins.
Bandwidth Control
The IES-1248 supports rate limiting in 32 Kbps increments allowing you to create different
service plans
Quality of Service
• Four priority queues for ENET and eight priority queues for downstream PVC so you can
ensure mission-critical data gets delivered on time.
• Follows the IEEE 802.1p priority setting standard.
44 Chapter 1 Getting to Know the IES-1248
Page 45

STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) / RSTP (Rapid STP)
(R)STP detects and breaks network loops and provides backup links between switches,
bridges or routers. It allows a switch to interact with other (R)STP -compliant switches in your
network to ensure that only one path exists between any two stations on the network.
1.2 Applications
These are the main applications for the IES-1248:
• Internet access and multimedia services for Multiple Tenant Units (MTU).
• Other applications include telemedicine, surveillance systems, remote servers systems,
cellular base stations and high-quality teleconferencing.
1.2.1 MTU Application
The following diagram depicts a typical application of the IES-1248 with ADSL modems, in a
large residential building, or multiple tenant unit (MTU), that leverages existing phone line
wiring to provide Internet access to all tenants. Note that ADSL service can coexist with voice
service on the same line.
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 1 MTU Application
Chapter 1 Getting to Know the IES-1248 45
Page 46

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
1.2.2 Curbside Application
The IES-1248 can also be used by an Internet Service Provider (ISP) in a street cabinet to form
a “mini POP (Point-of-Presence)” to provide broadband services to residential areas that are
too far away from the ISP to avail of DSL services. Residents need an ADSL modem,
connected as shown in the previous figure.
Figure 2 Curbside Application
46 Chapter 1 Getting to Know the IES-1248
Page 47

CHAPTER 2
Hardware Installation
This chapter explains how to install the IES-1248.
2.1 General Installation Instructions
Before you begin, read all the safety warnings in Safety Warnings on page 5, and make sure
you follow them.
Perform the installation as follows:
1 Make sure the IES-1248 power switch is in the OFF position.
2 Install the hardware. See Section 2.2 on page 47.
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
3 Connect the frame ground. See Section 2.3 on page 50.
4 See Chapter 3 on page 53 for instructions on making front panel connections.
5 See Chapter 4 on page 61 for instructions on connecting the Telco-50 connectors.
6 See Chapter 5 on page 69 for instructions on making power connections and turning on
the IES-1248.
2.2 Installation Scenarios
The IES-1248 can be placed on a desktop or rack-mounted on a standard EIA rack. Use the
rubber feet in a desktop installation and the brackets in a rack-mounted installation.
For proper ventilation, allow at least 4 inches (10 cm) of clearance at the front and 3.4 inches
(8 cm) at the back of the IES-1248. This is especially important for enclosed rack installations.
2.2.1 Desktop Installation Procedure
1 Make sure the IES-1248 is clean and dry.
2 Set the IES-1248 on a smooth, level surface strong enough to support the weight of the
IES-1248 and the connected cables. Make sure there is a power outlet nearby.
3 Make sure there is enough clearance around the IES-1248 to allow air circulation and the
attachment of cables and the power cord.
4 Remove the adhesive backing from the rubber feet.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation 47
Page 48

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
5 Attach the rubber feet to each corner on the bottom of the IES-1248. These rubber feet
help protect the IES-1248 from shock or vibration and ensure space between IES-1248
when stacking.
Figure 3 Attaching Rubber Feet
Note: Do not block the ventilation holes. Leave space between IES-1248 when
stacking.
2.2.2 Rack-Mounted Installation
2.2.2.1 Rack-mounted Installation Requirements
The IES-1248 can be mounted on an EIA standard size, 19-inch rack or in a wiring closet with
other equipment. Follow the steps below to mount your IES-1248 on a standard EIA rack
using a rack-mounting kit.
Note: Make sure the rack will safely support the combined weight of all the equipment
it contains.
Note: Make sure the position of the IES-1248 does not make the rack unstable or top-
heavy. Take all necessary precautions to anchor the rack securely before
installing the unit.
• Use a #2 Philips screwdriver to install the screws.
• See Appendix B on page 445 for the gauge of wire to use for the frame ground
connections.
• See Appendix B on page 445 for the hardware that is required to mount the IES-1248.
Note: Failure to use the proper screws may damage the unit.
Note: Do not block the ventilation holes. Leave space between IES-1248 when
stacking.
48 Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
Page 49

2.2.2.2 Rack-Mounted Installation Procedure
1 Align one bracket with the holes on one side of the IES-1248 and secure it with the
bracket screws smaller than the rack-mounting screws.
2 Attach the other bracket in a similar fashion.
Figure 4 Attaching Mounting Brackets and Screws
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
3 After attaching both mounting brackets, position the IES-1248 in the rack by lining up the
holes in the brackets with the appropriate holes on the rack. Secure the IES-1248 to the
rack with the rack-mounting screws.
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation 49
Page 50

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 5 Rack Mounting
2.3 Connecting the Frame Ground
Follow the directions in this section for the IES-1248-51 and IES-1248-53. This section is not
applicable for the IES-1248-51A.
Note: See Appendix B on page 445 for the ground wire gauge.
• The IES-1248 frame ground is on the lower left corner of the front panel.
• Connect the frame grounds to a building’s protective earthing terminals using a greenand-yellow frame ground wire.
Note: Warning! Connect the frame ground before you connect any other cables or
wiring.
50 Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
Page 51

Figure 6 IES-1248 Frame Ground
Frame Ground
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation 51
Page 52

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
52 Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
Page 53

The following table briefly describes the ports on the front panel. Then, the rest of this chapter
explains how to make connections to the IES-1248’s front panel.
3.1 Front Panel
The following figure shows the front panel of the IES-1248.
Figure 7 IES-1248 Front Panel
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 3
Front Panel Connections
Figure 8 IES-1248-51A Front Panel
3.1.1 Front Panel Ports
The following table describes the ports on the front panel of the IES-1248.
Table 1 IES-1248 Front Panel Ports
CONNECTOR DESCRIPTION
CONSOLE Connect this mini-RJ-11 port to a computer for local management.
1000/100 1/2 Use these RJ-45 ports for subtending. You can daisy chain more IES-1248’s or
other Ethernet switches.
This is an electrical Ethernet interface for use with the following copper Ethernet
cables:
• 100Base-Tx 2 pair UTP Cat. 5, up to 100m
• 1000Base-T 4-pair UTP Cat. 5, up to 100m
Note: For better performance and lower radiation noise, use
shielded Ethernet cables.
Chapter 3 Front Panel Connections 53
Page 54

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 1 IES-1248 Front Panel Ports (continued)
CONNECTOR DESCRIPTION
ALARM This DB9 connector has alarm input pins and alarm output pins.
SFP 1, 2 Each of these Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) slots can house a mini GBIC
USER 1-24, 25-48 Connect these Telco-50 connectors to subscribers 1-24 and 25-48 respectively.
CO 1-24, 25-48 Connect these Telco-50 connectors to the telephone company for subscribers 1-
3.1.2 LEDs
The following table describes the LED indicators on the IES-1248.
Table 2 LED Descriptions
Connect the alarm input pins to alarm output terminals on other pieces of
equipment.
Connect the alarm output pins to an alarm input terminal on another piece of
equipment.
(Gigabit Interface Converter) transceiver.
24 and 25-48 respectively.
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR Green On The power is turned on.
Off The power is off.
SYS Green Blinking The system is rebooting and performing self-diagnostic tests.
On The system is on and functioning properly.
Off The system is not ready/malfunctioning.
ALM Red On There is a hardware failure, or there is ALM input.
Off The system is functioning normally.
1000/100 1,2 Yellow On The link to a 100 Mbps Ethernet network is up.
Blinking The link is transmitting/receiving 100 Mbps Ethernet traffics.
Off The link to a 100 Mbps Ethernet network is down.
Green On The link to a 1000 Mbps (1Gbps) Ethernet network is up.
Blinking The link is transmitting/receiving 1000 Mbps (1Gbps) Ethernet
traffics.
Off The link to a 1000 Mbps (1Gbps) Ethernet network is down.
SFP 1,2 LNK Green On The link to a 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps) Ethernet network is up.
Off There is not a link to a 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps) Ethernet network
SFP 1,2 ACT Green Blinking The system is transmitting/receiving Ethernet traffic.
Off The system is not transmitting/receiving Ethernet traffic.
or the 1000 Mbps network link is down.
54 Chapter 3 Front Panel Connections
Page 55

3.2 1000/100M Auto-Sensing Ethernet
The IES-1248 has two 1000/100Mbps auto-sensing Ethernet ports. There are two factors
related to Ethernet: speed and duplex mode. In 1000/100Mbps Fast Ethernet, the speed can be
100Mbps or 1000Mbps and the duplex mode can be half duplex or full duplex. The autonegotiation capability makes one Ethernet port able to negotiate with a peer automatically to
obtain the connection speed and duplex mode that both ends support.
When auto-negotiation is turned on, an Ethernet port on the IES-1248 negotiates with the peer
automatically to determine the connection speed and duplex mode. If the peer Ethernet port
does not support auto-negotiation or turns off this feature, the IES-1248 determines the
connection speed by detecting the signal on the cable and using half duplex mode. When the
IES-1248’s auto-negotiation is turned off, an Ethernet port uses the pre-configured speed and
duplex mode when making a connection, thus requiring you to make sure that the settings of
the peer Ethernet port are the same in order to connect.
Use the Ethernet ports for subtending. You can daisy chain more IES-1248 or other Ethernet
switches.
Use with the following copper Ethernet cables: 1000Base-T 4-pair UTP Cat. 5, up to 100m.
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Note: For better performance and lower radiation noise, use shielded Ethernet
cables.
Each 1000/100M port is paired with a mini GBIC slot. The IES-1248 uses up to one
connection for each pair for a total of two possible gigabit connections (one from each of the
two pairs). The IES-1248 uses the mini GBIC transceiver whenever it has a connection.
3.2.1 Ethernet Default Settings
• Speed: Auto
• Duplex: Auto
3.3 SFP Mini GBIC Slots
The SFP slots can each house a mini GBIC (Gigabit Interface Converter) transceiver. A
transceiver is a single unit that houses a transmitter and a receiver. The IES-1248 does not
come with a transceiver. You must use a transceiver that complies with the Small Form-factor
Pluggable (SFP) Transceiver MultiSource Agreement (MSA). See the SFF committee’s INF8074i specification Rev 1.0 for details.
You can change transceivers while the IES-1248 is operating. You can use different
transceivers to connect to Ethernet switches with different types of fiber-optic connectors.
Note: To avoid possible eye injury, do not look directly into an operating fiber-optic
module’s connectors.
Chapter 3 Front Panel Connections 55
Page 56

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 9 SFP Mini GBIC Slot
• Type: SFP connection interface
• Connection speed: 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps)
3.3.1 Transceiver Installation
Use the following steps to install a mini GBIC transceiver (SFP module) in the SFP slot.
Note: The SFP slot is at an angle. Do not attempt to straighten it.
1 Remove the dust cover from the transceiver.
2 For transceivers with a flip-up or flip-down latch, close the latch.
3 Insert the fiber-optic cables into the transceiver (you may need to remove cable dust
covers).
4 Insert the transceiver into the IES-1248’s SFP slot with the exposed section of PCB board
facing down.
5 Press the transceiver firmly until it clicks into place.
Figure 10 Transceiver Installation
56 Chapter 3 Front Panel Connections
Page 57

Figure 11 Installed Transceivers
3.3.2 Transceiver Removal
Use the following steps to remove a mini GBIC transceiver (SFP module) from the IES-1248.
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
1 Remove the fiber-optic cables from the transceiver.
2 Unlock the transceiver’s latch (latch styles vary).
3 Pull the transceiver out of the slot.
4 Put the transceiver’s dust cover on the transceiver.
Figure 12 Opening the Transceiver Latch
Chapter 3 Front Panel Connections 57
Page 58

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 13 Removing the Transceiver
3.4 Console Port Connection
For local management, you can use a computer with terminal emulation software configured
to the following parameters:
• VT100 terminal emulation
• 9600 bps
• No parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit
• No flow control
Connect the mini-RJ-11 male end of the console cable to the console port of the IES-1248.
Connect the female end to a serial port (COM1, COM2 or other COM port) of your computer.
3.5 ALARM Connections
A closed circuit on the ALARM input pins indicates an alarm. Pins 7 and 3 are alarm input
one. Pins 8 and 4 are alarm input two. Pins 9 and 5 are alarm input 3.
The IES-1248 signals an alarm when it detects an alarm on the ALARM input pins or the IES-
1248.
To signal an alarm, the IES-1248 opens the circuit for pins 1 and 6 (the common pin) and
closes the circuit for pins 2 and 6.
Examples of an alarm on the IES-1248 are when the IES-1248’s voltage or temperature is
outside of the normal range.
58 Chapter 3 Front Panel Connections
Page 59

Figure 14 ALARM Pins Layout
Pin 5
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Pin 1
3.6 ADSL Connections
Connect the lines from the user equipment (ADSL modems) to the USER Telco-50 connector
and the lines from the central office switch or PBX (Private Branch Exchange) to the
Telco-50 connector. Make sure that the
MDF (Main Distribution Frame).
The line from the user carries both the ADSL and the voice signals. For each line, the IES1248 has a built-in splitter that separates the high frequency ADSL signal from the voice band
signal and feeds the ADSL signal to the IES-1248, while the voice band signal is diverted to
the CO port. See Chapter 4 on page 61 for more information on the Telco-50 connections.
Pin 9
Pin 6
CO
USER line and the CO lines are not shorted on the
Chapter 3 Front Panel Connections 59
Page 60

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
60 Chapter 3 Front Panel Connections
Page 61

MDF Connections
This chapter shows you how to connect the Telco-50 connectors to an MDF.
4.1 MDF Connections Overview
Observe the following before you start:
• See Appendix B on page 445 for the gauge of telephone wire to use.
• Follow the pin assignments shown in Appendix C on page 449 to wire Telco-50 cables to
Telco-50 connectors.
• See Chapter 1 on page 41 and Appendix C on page 449 for details on how to make the
management connections.
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 4
4.2 MDF (Main Distribution Frame)
An MDF is usually installed between subscribers’ equipment and the telephone company
(CO) in a basement or telephone room. The MDF is the point of termination for the outside
telephone company lines coming into a building and the telephone wiring in the building.
Figure 15 MDF (Main Distribution Frame) Wiring
• Connect wiring to end-user equipment to the lower ports of an MDF and connect wiring
from the telephone company to the upper ports of an MDF (see the previous figure).
• Some MDFs have surge protection circuitry built in between the two banks; thus, do not
connect telephone wires from the telephone company directly to your IES-1248.
Chapter 4 MDF Connections 61
Page 62

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
• Use a punch-down tool to seat telephone lines into MDF blocks.
• Multiple upper and lower MDF port connections are shown as one line in the following
figures.
4.3 Telco-50 Cables
Telco-50 cables are used for data and voice applications with MDFs (Main Distribution
Frame), patch panels and distribution boxes. They can also be used as extension cables. Telco50 cables are made up of 25 twisted-pair copper wires.
Connect a Telco-50 connector to one end of the cable (see Appendix C on page 449 for pin
assignments) and connect the other end directly to an MDF; alternatively attach RJ-11
connectors and connect directly to DSL modem(s).
Figure 16 Telco-50 Cable with RJ-11 Connectors
4.4 Telco-50 Connections
The internal DSL splitters separate the voice signals from the DSL signals. They feed the DSL
signals to the IES-1248 and divert the voice signals to the CO Telco-50 connectors.
Connect the CO Telco-50 connectors to the PBX or PSTN/ISDN switch.
Connect the USER Telco-50 connectors to the subscribers’ telephone wiring. In most multitenant unit applications, the USER pins connect to the subscribers’ telephone wiring via Main
Distribution Frame (MDF).
62 Chapter 4 MDF Connections
Page 63

See the pin assignments in Appendix C on page 449 and Section 4.5 on page 63 for details on
Telco-50 connections.
4.5 MDF Scenarios
The following figure gives an overview on a possible installation scenario for the IES-1248.
Data and voice signals can coexist on the same telephone wiring.
Figure 17 Installation Overview Example
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
You can also attach RJ-11 connectors to the Telco-50 cable and connect directly to a DSL
modem(s) or patch panel. This chapter discusses connections using MDFs.
4.6 Typical MDF Scenarios
This section describes typical installation scenarios.
4.6.1 Installation Scenario A
You want to install the IES-1248 in an environment where there are no previously installed
MDFs. There is no phone service and you want to install the IES-1248 for data-access only.
You may connect using an MDF or attach RJ-11 connectors to the non-IES-1248 end of the
Telco-50 cable and then connect to DSL modems directly.
Chapter 4 MDF Connections 63
Page 64

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 18 Installation Scenario A
4.6.1.1 Procedure to Connect to an MDF
1 Connect the Telco-50 connector end of the cable to the Telco-50 connector labeled
USER.
2 Connect the wiring on the other end of the Telco-50 cable to the upper ports of the MDF
using a punch-down tool.
3 Connect the telephone wiring from each end-user’s DSL modem to the lower ports of the
MDF.
4.6.2 Installation Scenario B
Phone service is available. There is one MDF from which end-users CO connections are made
(see the next figure).
Figure 19 One MDF for End-user and CO Connections
This installation scenario requires three MDFs. Please see the following figure for the
connection schema.
64 Chapter 4 MDF Connections
Page 65

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
• MDF 1 is the original MDF used for telephone connections only.
• MDF 2 is used for telephone connections only.
• MDF 3 is for DSL service connections.
Note: Change the wiring from MDF 1 to MDF 3 for telephone subscribers who want
DSL service.
Figure 20 Installation Scenario B
4.6.2.1 Procedure to Connect to MDFs
1 Connect the Telco-50 connector end of the cable you want for DSL service to the Telco-
50 connector labeled USER.
2 Connect the wiring on the other side of the Telco-50 cable to the upper ports of MDF 3
using a punch-down tool.
3 Connect the telephone wiring from the end-user’s DSL modem(s) to the lower ports of
MDF 3.
4 Connect the Telco-50 connector end of the cable you want for phone service to the Telco-
50 connector labeled CO.
5 Connect the wiring on the other side of the Telco-50 cable to the lower ports of MDF 2
using a punch-down tool.
6 Connect the upper ports of MDF 2 to the lower ports of MDF 1 using telephone wires.
7 Connect the upper ports of MDF 1 to the telephone company.
8 Telephone subscribers only (non-DSL subscribers) retain connections to the lower ports
of MDF 1.
Chapter 4 MDF Connections 65
Page 66

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
9 Change the wiring from MDF 1 to MDF 3 for telephone subscribers who want DSL
service.
4.6.3 Installation Scenario C
Phone service is also available but there are two MDFs; one for end-user telephone line
connections and the other one for CO telephone wiring connections (see the following figure).
Note: Users A and B have telephone (only) service.
Figure 21 Two Separate MDFs for End-user and CO Connections
This installation scenario requires four MDFs. Please see the following figure for the DSL
connection schema.
• MDFs 1 and 2 are the two original MDFs.
• MDFs 3 and 4 are two additional MDFs you need.
Note: User A still has telephone service only. User B now has telephone and DSL
service (see the following figure)
66 Chapter 4 MDF Connections
Page 67

Figure 22 Installation Scenario C
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
4.6.3.1 Procedure to Connect to MDFs
1 Connect the Telco-50 connector end of the cable you want for DSL service to the Telco-
50 connector labeled USER.
2 Connect the wiring on the other side of the Telco-50 cable to the upper ports of MDF 3
using a punch-down tool.
3 Connect the lower ports of MDF 3 to the upper ports of MDF 2 for those users that want
DSL service. (Users who want telephone service only, retain the original connection from
the top port of MDF 2 to the bottom port of MDF 1.)
4 Connect the telephone wiring from the end-user’s DSL equipment to the lower ports of
MDF 2.
5 Connect the Telco-50 connector end of the cable you want for phone service to the Telco-
50 connector labeled CO.
6 Connect the wiring on the other side of the Telco-50 cable to the lower ports of MDF 4
using a punch-down tool.
7 Connect the top ports of MDF 4 to the bottom ports of MDF 1 using telephone wires.
8 Connect the top ports of MDF 1 to the telephone company.
Chapter 4 MDF Connections 67
Page 68

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
68 Chapter 4 MDF Connections
Page 69

Power Connections
This chapter shows you how to connect the IES-1248 to a power source.
5.1 Power Connections Overview
Use the following procedures to connect the IES-1248 to a power source after you have
installed it in a rack.
Note: Check the power supply requirements in Appendix B on page 445, and make
sure you are using an appropriate power source.
Observe the following before you start:
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 5
• See Appendix B on page 445 for the gauge of wire to use for the IES-1248 power
connections.
• (IES-1248-51A only) Use the included power cord for the IES-1248’s power
connections.
• Keep the IES-1248 power switch in the OFF position until you come to the procedure for
turning on the power.
• Keep the power supply switch in the OFF position until you come to the procedure for
turning on the power.
Note: Use only power wires of the required diameter for connecting the IES-1248 to a
power supply (see Appendix B on page 445 for the required wire diameter).
5.2 Power Connections
The IES-1248 power connections are at the lower-left corner of the front panel.
5.2.1 AC Power Connections (IES-1248-51A only)
Connect the female end of the power cord to the power socket of your IES-1248. Connect the
other end of the cord to a power outlet. Make sure that no objects obstruct the airflow of the
fans.
Chapter 5 Power Connections 69
Page 70

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
5.2.2 DC Power Connections (IES-1248-51, IES-1248-53)
Note: When installing the IES-1248 power wire, push the wire firmly into the terminal
as deep as possible and make sure that no exposed (bare) wire can be seen or
touched.
1 Connect one end of a power wire to the – power terminal on the front panel of your IES-
1248 and tighten the terminal screw.
2 Connect the other end of the power wire to the -36 to -72 VDC terminal on the power
supply.
3 Repeat the previous step for the terminal labeled +.
5.3 Procedure to Turn on the IES-1248 Power
1 Turn on the power supply.
2 Move the IES-1248 power switch to the ON position.
70 Chapter 5 Power Connections
Page 71

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 6
Fan Maintenance
This chapter describes how to change a fan module.
6.1 Fan Maintenance Introduction
The IES-1248 has a hot-swappable fan module. Use the following procedures to remove the
fan module. Replace the entire fan module. Return any malfunctioning fan modules to the
manufacturer.
6.2 Removing and Installing the Fan Module
The IES-1248 fan module is at the left on the front panel. Perform the following procedure to
remove the fan module.
1 Loosen the thumbscrew on the front of the fan module.
2 Slide out the fan module.
3 Use a different fan module from the manufacturer.
4 Slide the fan module into the fan module slot.
5 Tighten the thumbscrew.
Figure 23 Fan Module Thumbscrews
Chapter 6 Fan Maintenance 71
Page 72

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 24 Removing the Fan Module
Figure 25 Fan Module Removed
72 Chapter 6 Fan Maintenance
Page 73

Introducing the Web
This chapter tells how to access and navigate the web configurator.
7.1 Web Configurator Overview
The web configurator allows you to use a web browser to manage the IES-1248.
7.2 Screen Privilege Levels
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 7
Configurator
There is a high or low privilege level for each screen.
High privilege screens are only available to administrators with high privilege access. High
privilege screens include things like creating administrator accounts, restarting the system,
saving changes to the nonvolatile memory and resetting to factory defaults. Nonvolatile
memory refers to the IES-1248’s storage that remains even if the IES-1248’s power is turned
off. Administrators with high privilege access can use all screens including the lower privilege
screens.
Administrators with the low privilege level are restricted to using only low privilege screens.
Low privilege screens are read only.
7.3 Accessing the Web Configurator
Use Internet Explorer 6 and later versions with JavaScript enabled.
Use the following instructions to log on to the web configurator.
1 Launch your web browser, and enter the IP address of the IES-1248 (default: 192.168.1.1
is the factory default) in the Location or Address field. Press Enter. The Login screen
appears.
Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator 73
Page 74

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 26 Login
2 Type admin in the User Name field and your password (default: 1234) in the Password
field. Click OK. The main screen appears.
This is the web configurator’s main screen.
Figure 27 Home
B
C
A
A - Click the menu items to open submenu links, and then click on a submenu link to open the
screen in the main window. See Section 7.4 on page 75 for more information.
B - Click this to open the Home screen. (This is the same screen that is displayed above.) See
Chapter 9 on page 87 for more information.
C - Click this to log out of the web configurator.
74 Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator
Page 75

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
7.4 Navigation Panel
In the navigation panel, click a menu item to reveal a list of submenu links. Click a submenu
link to go to the corresponding screen.
Table 3 Navigation Panel Submenu Links
BASIC SETTING ADVANCED APPLICATION ROUTING PROTOCOL
ALARM MANAGEMENT CONFIG SAVE
The following table briefly describes the functions of the screens that you open by clicking the
navigation panel’s sub-links.
Table 4 Web Configurator Screens
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Basic Setting
System Information Use this screen to display general system and hardware monitoring information.
General Setup Use this screen to configure general identification information about the device
and the time and date settings.
Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator 75
Page 76

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 4 Web Configurator Screens (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
User Account Use this screen to configure system administrator accounts.
Switch Setup Use this screen to set up system-wide parameters such as MAC address
IP Setup Use this screen to configure the system and management IP addresses and
ENET Port Setup Use this screen to configure settings for the Ethernet ports.
xDSL Port Setup Use these screens for configuring settings for individual DSL ports.
xDSL Profiles Setup Use these screens for configuring profiles for the DSL ports.
xDSL Line Data Use these screens for viewing DSL line operating values, bit allocation and
Advanced
Application
VLAN Use these screens for viewing and configuring the VLAN settings.
IGMP Use these screens to view IGMP status information and configure IGMP settings
Static Multicast Use this screen to configure static multicast entries.
Multicast VLAN Use these screens to set up multicast VLANs that can be shared among
Filtering Use this screen to configure packet filtering.
MAC Filter Use this screen to configure MAC filtering for each port.
Spanning Tree
Protocol
Port Authentication Use these screens to configure RADIUS and IEEE 802.1x security settings.
Port Security Use this screen to limit the number of MAC address that can be learned on a
DHCP Relay Use this screen to configure the DHCP relay settings.
DHCP Snoop Use these screens to drop traffic from IP addresses not assigned by the DHCP
2684 Routed Mode Use this screen to configure the IES-1248 to handle 2684 routed mode traffic.
PPPoA to PPPoE Use this screen to enable PPPoA-to-PPPoE conversions on each port.
DSCP Use this screen to set up DSCP on each port and to convert DSCP values to
TLS PVC Use this screen to set up Transparent LAN Service (VLAN stacking, Q-in-Q) on
ACL Use this screen to set up Access Control Logic profiles and to assign them to
Downstream
Broadcast
SysLog Use this screen to configure the syslog settings.
Access Control Use this screen to configure service access control and configure SNMP and
Routing Protocol
learning and priority queues.
subnet masks.
performance counters.
and IGMP filters. You can also use these screens to set up bandwidth
requirements by multicast group or port and to set up limits on the number of
multicast groups to which a port can subscribe.
different subscriber VLANs on the network.
Use these screens to display Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) information
and configure RSTP settings.
port.
server and to look at a summary of the DHCP packets on each port.
IEEE 802.1p values.
each port.
each PVC.
Use this screen to block downstream broadcast packets from being sent to
specified VLANs on specified ports.
remote management.
76 Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator
Page 77

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 4 Web Configurator Screens (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static Routing Use this screen to configure static routes. A static route defines how the IES-
1248 should forward traffic by configuring the TCP/IP parameters manually.
Alarm
Alarm Status Use these screens to view the alarms that are currently in the system.
Alarm Event Setup Use these screens to view and set the severity levels of the alarms and where
the system is to send them.
Alarm Port Setup Use this screen to set the alarm severity threshold for recording alarms on an
individual port(s).
Management
Maintenance Use this screen to perform firmware and configuration file maintenance as well
as restart the system.
Diagnostic Use this screen to view system logs and test port(s).
MAC Table Use this screen to view the MAC addresses of devices attached to what ports.
ARP Table Use this screen to view the MAC address to IP address resolution table.
Config Save
Config Save Use this screen to save the device’s configuration into the nonvolatile memory
(the IES-1248’s storage that remains even if the IES-1248’s power is turned off).
7.5 Changing Your Password
After you log in for the first time, it is recommended you change the default administrator
password. Click Basic Setting and then User Account to display the User Account screen.
Figure 28 User Account
Click the index number 1 to edit the default administrator account settings.
Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator 77
Page 78

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 29 User Account
Enter the new password in the Password and Retype Password to confirm fields, and click
Modify. Do not forget to click Config Save before you exit the web configurator. See Section
7.6 on page 78.
7.6 Saving Your Configuration
Click Apply in a configuration screen when you are done modifying the settings in that screen
to save your changes back to the run-time memory. Settings in the run-time memory are lost
when the IES-1248’s power is turned off.
Click Config Save in the navigation panel to save your configuration to nonvolatile memory.
Nonvolatile memory refers to the IES-1248’s storage that remains even if the IES-1248’s
power is turned off.
Note: Use Config Save when you are done with a configuration session.
7.7 Logging Out of the Web Configurator
Click Logout in any screen to exit the web configurator. You have to log in with your
password again after you log out. This is recommended after you finish a management session
both for security reasons and so you do not lock out other device administrators.
78 Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator
Page 79

Figure 30 Logout
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator 79
Page 80

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
80 Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator
Page 81

Initial Configuration
This chapter describes initial configuration for the IES-1248. See Appendix A on page 443 for
various default settings of the IES-1248.
8.1 Initial Configuration Overview
This chapter shows what you first need to do to provide service to ADSL subscribers.
8.2 Initial Configuration
This chapter uses the web configurator for initial configuration. See the CLI chapters for
information on the commands. Use Internet Explorer 6 and later versions with JavaScript
enabled.
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 8
1 Log in to the web configurator. See Section 7.3 on page 73 for instructions.
2 In the navigation panel, click Basic Setting, IP Setup. The IP Setup screen appears.
Figure 31 IP Setup
3 Use this screen to change the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway IP address for
your network. Apply the settings.
Note: If you change the IP address of the IES-1248, after you click Apply IP setting,
you have to use the new IP address to log into the web configurator again.
4 If your subscribers use VPI 0 and VCI 33 (the default for all of the ADSL ports), go to
step 13. Otherwise, use the following steps to change the VPI and VCI settings for all of
the ADSL ports.
Chapter 8 Initial Configuration 81
Page 82

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
First, you will delete the default virtual channel from all of the ADSL ports. (You cannot edit
it). Then, you will configure a new virtual channel for a port and copy it to the other ADSL
ports.
Adding another virtual channel without deleting the default virtual channel is not
recommended since you cannot set the new channel to be the port’s super channel. The super
channel can forward frames belonging to multiple VLAN groups (that are not assigned to
other channels). A channel that is not the super channel can only forward frames with a single
VLAN ID (that is configured on that channel). In this case, the IES-1248 drops any frames
received from the subscriber that are tagged with another VLAN ID.
5 In the navigation panel, click Basic Setting, xDSL Port Setup. The xDSL Port Setup
screen appears.
Figure 32 xDSL Port Setup
6 Click VC Setup. The following screen appears.
82 Chapter 8 Initial Configuration
Page 83

Figure 33 VC Setup
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
7 Select any virtual channel’s Select radio button, and click Delete. The following screen
appears.
Figure 34 VC Setup, Delete
8 Click OK. The following screen appears.
Chapter 8 Initial Configuration 83
Page 84

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 35 Select Ports
9 Click All, and then click Apply. The VC Setup screen is updated.
Figure 36 VC Setup
10Select Super Channel to allow the channel to forward frames belonging to multiple
VLAN groups (that are not assigned to other channels). Then, enter the VPI and VCI that
you use. Leave the other default settings, and click Add. The VC Setup screen is
updated.
84 Chapter 8 Initial Configuration
Page 85

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 37 VC Setup
11Select the new channel’s Select radio button. Click Copy, and then click Paste. The
following screen appears. The following screen appears.
Figure 38 Select Ports
12Click All, and then click Apply. The VC Setup screen is updated.
Chapter 8 Initial Configuration 85
Page 86

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 39 VC Setup
13Click Config Save, Config Save. The Config Save screen appears.
Figure 40 Config Save
14Click Save. The following screen should appear.
Figure 41 Config Save, Save Successful
You can now use the device (with the other settings set to the defaults) to provide service to
ADSL subscribers. See Appendix A on page 443 for information on other default settings.
86 Chapter 8 Initial Configuration
Page 87

Home and Port Statistics
This chapter describes the Home (status), Port Statistics, and RMON screens.
9.1 Home Screen
The Home screen of the web configurator displays a port statistical summary with links to
each port showing statistical details.
To open this screen, click Home in any web configurator screen.
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 9
Screens
Figure 42 Home
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 5 Home
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System up Time This field shows how long the system has been running since the last time it was
started.
The following fields are related to the Ethernet ports.
ENET This field displays the number of the Ethernet port. Click a port number to
display that port’s statistics screen. The Ethernet Port Statistics Screen appears.
See Section 9.1.1 on page 88.
Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens 87
Page 88

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 5 Home (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status This field displays whether the Ethernet port is connected (Up) or not (Down).
Port Name This field displays the name of the Ethernet port.
Media This field displays the type of media that this Ethernet port is using for a
Duplex This field displays whether the port is using half or full-duplex communication. “-“
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time in hours, minutes and seconds the
xDSL This identifies the ADSL port. Click a port number to display that port’s statistics
Status This field shows whether the port is connected (Up) or not (Down).
Mode This field shows which ADSL operational mode the port is set to use. “-“ displays
Up/Down stream This field shows the number of kilobits per second that a port is set to transmit
Interleave/Fast This field shows the port’s ADSL latency mode (fast or interleave).
Up Time This field shows the total amount of time in hours, minutes and seconds the
Poll Interval(s)
Set Interval
Stop Click Stop to halt system statistic polling.
Port
Clear Counter
Reset Click this to set the Poll Interval(s) and Port fields to their default values and to
connection (Copper or Fiber). “-“ displays when the port is disabled or not
connected.
displays when the port is disabled or not connected.
port’s connection has been up. “--:--:--“ displays when the port is disabled or not
connected.
The following fields are related to the ADSL ports.
screen. The ADSL Port Statistics Screen appears. See Section 9.1.2 on page
91.
when the port is not connected.
and receive.
port’s connection has been up. “-“ displays when the port is not connected.
The following fields and buttons apply to the whole screen.
The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may
change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then
clicking Set Interval.
Select a port from the Port drop-down list box and then click Clear Counter to
erase the recorded statistical information for that port.
refresh the screen.
9.1.1 Ethernet Port Statistics Screen
Use this screen to display statistics about an Ethernet port. To open this screen, click an
Ethernet port’s number in the Home screen.
88 Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens
Page 89

Figure 43 Port Statistics (Ethernet)
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 6 Port Statistics (Ethernet)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RMON Click this to open the RMON Statistics screen.
Return Click this to go back to the Home screen.
Port Use this drop-down list box to select a port for which you wish to view statistics.
This field identifies the port described in this screen.
Port Name This field displays the name that you have configured for the port.
Rx bytes This field shows the number of octets of Ethernet frames received that are from
0 to 1518 octets in size, counting the ones in bad packets, not counting framing
bits but counting FCS (Frame Check Sequence) octets. An octet is an 8-bit
binary digit (byte).
Rx packets This field shows the number of packets received on this port (including multicast,
unicast, broadcast and bad packets).
Rx error fcs This field shows the number of frames received with an integral length of 64 to
1518 octets and containing a Frame Check Sequence error.
Rx multicast This field shows the number of good multicast frames received of 64 to 1518
octets in length (for non VLAN) or 1522 octets (for VLAN), not including
Broadcast frames. Frames with range or length errors are also not taken into
account.
Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens 89
Page 90

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 6 Port Statistics (Ethernet) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rx broadcast This field shows the number of good broadcast frames received of 64 to 1518
Rx mac pause This field shows the number of valid IEEE 802.3x Pause frames received on this
Rx fragments This field shows the number of frames received that were less than 64 octets
Rx error overrun This field shows how many times an Ethernet transmitter overrun occurred.
Rx error mru This field shows the number of received frames that were dropped due to
Rx dropped This field shows the number of received frames that were received into the IES-
Rx jabber This field shows the number of frames received that were longer than 1518
Rx error alignment This field shows the number of frames received that were 64 to 1518 (non
Rx oversize This field shows the number of frames received that were bigger than 1518 (non
Rx undersize This field shows the number of frames received that were less than 64 octets
Tx bytes This field shows the number of bytes that have been transmitted on this port.
Tx packets This field shows the number of packets transmitted on this port.
Tx multicast This field shows the number of good multicast frames transmitted on this port
Tx broadcast This field shows the number of broadcast frames transmitted on this port (not
Tx mac_pause This field shows the number of valid IEEE 802.3x Pause frames transmitted on
Tx fragments This field shows the number of transmitted frames that were less than 64 octets
Tx frames This field shows the number of complete good frames transmitted on this port.
Tx error underrun This field shows the number of outgoing frames that were less than 64 octets
Tx undersize This field shows the number of frames transmitted that were less than 64 octets
Tx jabber This field shows the number of frames transmitted that were longer than 1518
Tx oversize This field shows the number of frames transmitted that were bigger than 1518
packet(<=64) This field shows the number of frames received and transmitted (including bad
octets in length (for non VLAN) or 1522 octets (for VLAN), not including multicast
frames. Frames with range or length errors are also not taken into account.
port.
long, and contained an invalid FCS, including non-integral and integral lengths.
exceeding the Maximum Receive Unit frame size.
1248, but later dropped because of a lack of system resources.
octets (non VLAN) or 1522 octets (VLAN) and contained an invalid FCS,
including alignment errors.
VLAN) or 1522 (VLAN) octets long but contained an invalid FCS and a nonintegral number of octets.
VLAN) or 1522 (VLAN) octets and contained a valid FCS.
long and contained a valid FCS.
This includes collisions but not jam signal or preamble/SFD (Start of Frame
Delimiter) bytes.
(not including broadcast frames).
including multicast frames).
this port.
long, and with an incorrect FCS value.
long.
long and contained a valid FCS.
octets (non VLAN) or 1522 octets (VLAN) and contained an incorrect FCS value.
octets (non VLAN) or 1522 (VLAN) and contained a valid FCS.
frames) that were 64 octets or less in length (this includes FCS octets but
excludes framing bits).
90 Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens
Page 91

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 6 Port Statistics (Ethernet) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
packet(65-127) This field shows the number of frames received and transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 65 to 127 octets in length (this includes FCS octets but
excludes framing bits).
packet(128-255) This field shows the number of frames received and transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 128 to 255 octets in length (this includes FCS octets but
excludes framing bits).
packet(256-511) This field shows the number of frames received and transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 256 to 511 octets in length (this includes FCS octets but
excludes framing bits).
packet(512-1023) This field shows the number of frames received and transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 512 to 1023 octets in length (this includes FCS octets but
excludes framing bits).
packet(1024-1518) This field shows the number of frames received and transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 1024 to 1518 octets in length (this includes FCS octets but
excludes framing bits).
packet(1522) This field shows the number of frames received and transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 1519 to 1522 octets in length (this includes FCS octets but
excludes framing bits).
packet(total) This field shows the total number of received and transmitted packets.
broadcast(total) This field shows the total number of received and transmitted broadcast frames.
multicast(total) This field shows the total number of received and transmitted multicast frames.
octet(total) This field shows the total number of received and transmitted octets (unicast,
multicast and broadcast).
Poll Interval(s)
Set Interval
Stop Click Stop to halt system statistic polling.
Port
Clear Counter
Reset Click this to set the Poll Interval(s) and Port fields to their default values and to
The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may
change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then
clicking Set Interval.
Select a port from the Port drop-down list box and then click Clear Counter to
erase the recorded statistical information for that port.
refresh the screen.
9.1.2 ADSL Port Statistics Screen
Use this screen to display statistics about an ADSL port. To open this screen, click an ADSL
port’s number in the Home screen.
Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens 91
Page 92

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 44 Port Statistics (ADSL)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 7 Port Statistics (ADSL)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
RMON Click this to open the RMON Statistics screen.
Return Click this to go back to the Home screen.
xDSL Port Use this drop-down list box to select a port for which you wish to view statistics.
Port Name This field displays the name that you have configured for the port. If you have not
Tx packets This field shows the number of packets transmitted on this port.
Rx packets This field shows the number of packets received on this port.
Tx broadcast
packets
Rx broadcast
packets
Tx discard packets This field shows the number of outgoing packets that were dropped on this port.
This field identifies the port described in this screen.
configured a name, it is blank.
This field shows the number of broadcast packets transmitted on this port.
This field shows the number of broadcast packets received on this port.
The “Tx discard packets” counter always displays “0” because the IES-1248
does not discard packets that it sends.
92 Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens
Page 93

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 7 Port Statistics (ADSL) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rx discard packets This field shows the number of received packets that were dropped on this port.
Some of the possible reasons for the discarding of received (rx) packets are:
• The packet filter is enabled and the packets matched a packet filter.
• The MAC filter is enabled and the IES-1248 dropped the packets according
to the MAC filter’s configuration.
• The packets contained frames with an invalid VLAN ID.
Errors This field shows the number of AAL5 frames received with CRC errors.
Tx rate This field shows the number of kilobytes per second transmitted on this port.
Rx rate This field shows the number of kilobytes per second received on this port.
Tx bytes This field shows the number of bytes that have been transmitted on this port.
Rx bytes This field shows the number of bytes that have been received on this port.
VPI/VCI This field displays the Virtual Path Identifier (VPI) and Virtual Circuit Identifier
Tx Packets This field shows the number of packets transmitted on each channel.
Rx Packets This field shows the number of packets received on each channel.
Tx rate This field shows the number of bytes per second transmitted on each channel.
Rx rate This field shows the number of bytes per second received on each channel.
Tx cells This field shows the number of ATM cells transmitted on each channel.
Rx cells This field shows the number of ATM cells received on each channel.
Errors This field shows the number of error packets on each channel.
Poll Interval(s)
Set Interval
Stop Click Stop to halt system statistic polling.
Port
Clear Counter
Reset Click this to set the Poll Interval(s) and Port fields to their default values and to
(VCI) of channels on this port.
The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You may
change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box and then
clicking Set Interval.
Select a port from the Port drop-down list box and then click Clear Counter to
erase the recorded statistical information for that port.
refresh the screen.
9.1.3 RMON Statistics Screen
Use this screen to display RMON statistics about a port. To open this screen, click RMON in
the ADSL Port Statistics screen or Ethernet Port Statistics screen.
Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens 93
Page 94

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 45 Port Statistics (RMON)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 Port Statistics (RMON)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Statistics Click this to go back to the previous screen.
Enet1 Click this to look at the RMON history for this port.
Enet2 Click this to look at the RMON history for this port.
EtherStatsDropEvents This field displays the total number of packets that were dropped on
this port.
EtherStatsOctets This field displays the total number of octets received/transmitted on
EtherStatsPkts This field displays the total number of good packets received/
EtherStatsBroadcastPkts This field displays the total number of broadcast packets received/
EtherStatsMulticastPkts This field displays the total number of multicast packets received/
EtherStatsCRCAlignErrors This field displays the total number of CRC (Cyclical Redundancy
this port.
transmitted on this port.
transmitted on this port.
transmitted on this port.
Check) alignment errors on this port.
94 Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens
Page 95

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 8 Port Statistics (RMON) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
EtherStatsUndersizePkts This field displays the total number of packets that were too small
received/transmitted on this port.
EtherStatsOversizePkts This field displays the total number of packets that were too big
received/transmitted on this port.
EtherStatsFragments This is the number of frames received/transmitted that were less than
64 octets long, and contained an invalid FCS, including non-integral
and integral lengths.
EtherStatsJabbers This is the number of frames received/transmitted that were longer than
1518 octets (non VLAN) or 1522 octets (VLAN) and contained an
invalid FCS, including alignment errors.
EtherStatsCollisions This is the number of frames for which transmission failed due to
excessive collisions. Excessive collision is defined as the number of
maximum collisions before the retransmission count is reset.
EtherStats64Octets This is the number of frames received/transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 64 octets or less in length (this includes FCS octets
but excludes framing bits).
EtherStats65to127Octets This is the number of frames received/transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 65 to 127 octets in length (this includes FCS octets
but excludes framing bits).
EtherStats128to255Octets This is the number of frames received and transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 128 to 255 octets in length (this includes FCS octets
but excludes framing bits).
EtherStats256to511Octets This is the number of frames received/transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 256 to 511 octets in length (this includes FCS octets
but excludes framing bits).
EtherStats512to1023Octets This is the number of frames received/transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 512 to 1023 octets in length (this includes FCS octets
but excludes framing bits).
EtherStats1024to1518Octets This is the number of frames received/transmitted (including bad
frames) that were 1024 to 1518 octets in length (this includes FCS
octets but excludes framing bits).
Poll Interval(s)
Set Interval
Stop Click Stop to halt system statistic polling.
Port
Clear Counter
Reset Click this to set the Poll Interval(s) and Port fields to their default
The text box displays how often (in seconds) this screen refreshes. You
may change the refresh interval by typing a new number in the text box
and then clicking Set Interval.
Select a port from the Port drop-down list box and then click Clear
Counter to erase the recorded statistical information for that port.
values and to refresh the screen.
9.1.4 RMON History Screen
Use this screen to display general information (such as sample time) on history samples. To
open this screen, click any port number in the RMON Statistics screen.
Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens 95
Page 96

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 46 Port Statistics (RMON History))
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 9 Port Statistics (RMON History)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Index:Interval Select the index of the sample interval and the desired data sampling time (in
seconds).
Apply Click this to use the selected data sampling time.
Refresh Click this to update this screen.
Sample Index This field display the sample number.
Interval Start This field displays the data sampling time.
Pkts This field displays the number of packets received or transmitted since the last
sample time.
BroadcastPkts This field displays the number of broadcast packets received or transmitted
MulticastPkts This field displays the number of multicast packets received/transmitted since
Utilization This field displays the port utilization status.
since the last sample time.
the last sample time.
9.1.5 RMON History Detail Screen
Use this screen to display detailed RMON history. To open this screen, click any index
number in the RMON History screen.
96 Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens
Page 97

Figure 47 Port Statistics (RMON History Detail))
IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 10 Port Statistics (RMON History Detail)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
UP Click this to return to the previous screen.
Refresh Click this to update this screen.
Index This field displays the index of the sample interval.
Sample Index This field displays the sample number.
Interval Start This field displays the data sampling time.
Drop Events This field displays the total number of packets that were dropped in the sampling
period.
Octets This field displays the total number of octets received/transmitted in the
Pkts This field displays the total number of good packets received/transmitted in the
BroadcastPkts This field displays the total number of broadcast packets received/transmitted in
MulticastPkts This field displays the total number of multicast packets received/transmitted in
CRCAlignErrors This field displays the total number of CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check)
UndersizePkts This field displays the total number of packets that were too small received/
OversizePkts This field displays the total number of packets that were too big received/
sampling period.
sampling period.
the sampling period.
the sampling period.
alignment errors in the sampling period.
transmitted in the sampling period.
transmitted in the sampling period.
Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens 97
Page 98

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Table 10 Port Statistics (RMON History Detail) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Fragments This is the number of frames received/transmitted that were less than 64 octets
Jabbers This is the number of frames received/transmitted that were longer than 1518
Collisions This is the number of frames for which transmission failed due to excessive
Utilizations This field displays the port utilization status in the sampling period.
long, and contained an invalid FCS, including non-integral and integral lengths.
octets (non VLAN) or 1522 octets (VLAN) and contained an invalid FCS,
including alignment errors.
collisions. Excessive collision is defined as the number of maximum collisions
before the retransmission count is reset.
98 Chapter 9 Home and Port Statistics Screens
Page 99

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 10
System Information
The System Information screen displays general device information (such as firmware
version number) and hardware polling information (such as fan status). You can check the
firmware version number and monitor the hardware status in this screen.
To open this screen, click Basic Setting, System Information.
Chapter 10 System Information 99
Page 100

IES-1248-51/51A/53 User’s Guide
Figure 48 System Info
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 11 System Info
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Name This field displays the device 's model name.
ZyNOS F/W Version This field displays the version number of the device’s current firmware including
100 Chapter 10 System Information
the date created.
 Loading...
Loading...