Page 1

G-320H
802.11g Wireless High Power PCI Adapter
User’s Guide
Version 1.00
10/2006
Edition 1
www.zyxel.com
Page 2

Page 3

About This User's Guide
About This User's Guide
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for people who want to configure the G-320H using the ZyXEL
utility. You should have at least a basic knowledge of TCP/IP networking concepts and
topology.
Related Documentation
• Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide is designed to help you get up and running right away. It contains
information on setting up your network and configuring for Internet access.
• Online Help
Embedded web help for descriptions of individual screens and supplementary
information.
• Supporting Disk
Refer to the included CD for support documents.
• ZyXEL Web Site
Please refer to www.zyxel.com
certifications.
for additional support documentation and product
User Guide Feedback
Help us help you. Send all User Guide-related comments, questions or suggestions for
improvement to the following address, or use e-mail instead. Thank you!
The Technical Writing Team,
ZyXEL Communications Corp.,
6 Innovation Road II,
Science-Based Industrial Park,
Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan.
E-mail: techwriters@zyxel.com.tw
G-320H User’s Guide
3
Page 4

Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this User’s Guide.
1 Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
" Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may
need to configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• The G-320H may be referred to as the “G-320H” or the “device” in this User’s Guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A key stroke is denoted by square brackets and uppercase text, for example, [ENTER]
means the “enter” or “return” key on your keyboard.
• “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters and then press the [ENTER] key.
“Select” or “choose” means for you to use one of the predefined choices.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example,
Maintenance > Log > Log Setting means you first click Maintenance in the navigation
panel, then the Log sub menu and finally the Log Setting tab to get to that screen.
• Units of measurement may denote the “metric” value or the “scientific” value. For
example, “k” for kilo may denote “1000” or “1024”, “M” for mega may denote “1000000”
or “1048576” and so on.
• “e.g.,” is a shorthand for “for instance”, and “i.e.,” means “that is” or “in other words”.
4
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 5
Document Conventions
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this User’s Guide may use the following generic icons. The G-320H icon is not an
exact representation of your device.
AP Computer Notebook computer
Server Wireless Signal Modem or Router
Internet Cloud
G-320H User’s Guide
5
Page 6
Safety Warnings
Safety Warnings
1 For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
• Do NOT use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming
pool.
• Do NOT expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do NOT store things on the device.
• Do NOT install, use, or service this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk
of electric shock from lightning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• ONLY qualified service personnel should service or disassemble this device.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a
remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Antenna Warning! This device meets FCC certification requirements when using the
included antenna(s). Only use the included antenna(s).
This product is recyclable. Dispose of it properly.
6
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 7

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
Getting Started ........................................................................................................................... 19
Tutorial ....................................................................................................................................... 25
Wireless LAN Network ............................................................................................................... 33
Wireless Station Mode Configuration ........................................................................................ 41
Access Point Mode Configuration ............................................................................................. 59
Maintenance .............................................................................................................................. 65
Troubleshooting ......................................................................................................................... 69
G-320H User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Contents Overview
8
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 9

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
About This User's Guide ..........................................................................................................3
Document Conventions............................................................................................................4
Safety Warnings........................................................................................................................6
Contents Overview ...................................................................................................................7
Table of Contents...................................................................................................................... 9
List of Figures ......................................................................................................................... 13
List of Tables...........................................................................................................................17
Chapter 1
Getting Started........................................................................................................................ 19
1.1 About Your G-320H ........................................................................................................... 19
1.2 Application Overview .......................................................................................................... 19
1.2.1 Station Mode .............................................................................................................. 19
1.2.2 Access Point Mode ................................................................................................... 20
1.2.3 Changing G-320H Mode ........................................................................................... 21
1.3 G-320H Hardware and Utility Installation ............................................................................. 22
1.3.1 ZyXEL Utility Icon ......................................................................................................22
1.4 Configuration Methods ....................................................................................................... 22
1.4.1 Enabling WZC ............................................................................................................ 23
1.4.2 Accessing the ZyXEL Utility ....................................................................................... 23
Chapter 2
Tutorial .....................................................................................................................................25
2.1 Connecting to a Wireless LAN ............................................................................................. 25
2.2 Creating and Using a Profile ................................................................................................ 27
2.3 Configuring the G-320H as an AP ....................................................................................... 30
Chapter 3
Wireless LAN Network............................................................................................................33
3.1 Wireless LAN Overview ...................................................................................................... 33
3.2 Wireless LAN Security ........................................................................................................ 34
3.2.1 Hide SSID .................................................................................................................. 34
3.2.2 MAC Address Filter .................................................................................................... 34
3.2.3 User Authentication and Encryption ........................................................................... 35
3.3 Introduction to OTIST ...................................................................................................... 36
G-320H User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Table of Contents
3.3.1 Enabling OTIST .......................................................................................................... 37
3.3.2 Starting OTIST ..........................................................................................................38
3.3.3 Notes on OTIST ......................................................................................................... 39
Chapter 4
Wireless Station Mode Configuration ................................................................................... 41
4.1 Wireless Station Mode Overview ........................................................................................ 41
4.1.1 ZyXEL Utility Screen Summary .................................................................................. 41
4.2 The Link Info Screen ........................................................................................................... 42
4.2.1 Trend Chart ................................................................................................................ 43
4.3 The Site Survey Screen ....................................................................................................... 43
4.3.1 Security Settings ........................................................................................................45
4.3.2 Confirm New Settings ................................................................................................ 49
4.4 The Profile Screen ............................................................................................................... 50
4.4.1 Adding a New Profile .................................................................................................. 51
4.5 The Adapter Screen ............................................................................................................ 55
Chapter 5
Access Point Mode Configuration ........................................................................................ 59
5.1 Access Point Mode Introduction ......................................................................................... 59
5.1.1 ZyXEL Utility Screen Summary .................................................................................. 59
5.1.2 Additional Setup Requirements .................................................................................. 59
5.2 The Link Info Screen ........................................................................................................... 60
5.3 The Configuration Screen .................................................................................................... 61
5.4 The MAC Filter Screen ........................................................................................................ 63
Chapter 6
Maintenance ............................................................................................................................ 65
6.1 The About Screen ............................................................................................................... 65
6.2 Uninstalling the ZyXEL Utility .............................................................................................. 65
6.3 Upgrading the ZyXEL Utility ...............................................................................................66
Chapter 7
Troubleshooting...................................................................................................................... 69
Appendix A Product Specifications.........................................................................................71
Appendix B Access Point Mode Setup Example .................................................................... 73
Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration .................................................. 77
Appendix D Wireless Security ................................................................................................91
Appendix E Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address.............................................................. 97
Appendix F Legal Information ..............................................................................................109
10
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 11

Table of Contents
Appendix G Customer Support ............................................................................................ 113
Index....................................................................................................................................... 117
G-320H User’s Guide
11
Page 12

Table of Contents
12
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 13

List of Figures
List of Figures
Figure 1 Application: Infrastructure ........................................................................................................ 20
Figure 2 Application: Ad-Hoc ................................................................................................................. 20
Figure 3 Application: Access Point Mode .............................................................................................. 21
Figure 4 ZyXEL Utility: Change Modes .................................................................................................. 21
Figure 5 ZyXEL Utility: System Tray Icon .............................................................................................. 22
Figure 6 Enable WZC ............................................................................................................................. 23
Figure 7 Infrastructure Network .............................................................................................................. 25
Figure 8 ZyXEL Utility: Site Survey ........................................................................................................ 26
Figure 9 ZyXEL Utility: Security Setting ................................................................................................. 26
Figure 10 ZyXEL Utility: Confirm New Settings ..................................................................................... 27
Figure 11 ZyXEL Utility: Link Info .......................................................................................................... 27
Figure 12 ZyXEL Utility: Profile ............................................................................................................... 28
Figure 13 ZyXEL Utility: Add New Profile ............................................................................................... 28
Figure 14 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Security ................................................................................................. 28
Figure 15 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Encryption ............................................................................................. 29
Figure 16 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Confirm New Settings ........................................................................... 29
Figure 17 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Activate ................................................................................................. 30
Figure 18 ZyXEL Utility: AP: Link Info .................................................................................................... 31
Figure 19 ZyXEL Utility: AP: Configuration ............................................................................................ 31
Figure 20 Example of a Wireless Network ............................................................................................. 33
Figure 21 ZyXEL Utility Menu Summary: Station Mode ........................................................................ 41
Figure 22 Station Mode: Link Info .......................................................................................................... 42
Figure 23 Station Mode: Link Info: Trend Chart ..................................................................................... 43
Figure 24 Station Mode: Site Survey ..................................................................................................... 44
Figure 25 Station Mode: Security Setting: WEP ................................................................................... 45
Figure 26 Station Mode: Security Setting: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK .......................................................... 46
Figure 27 Station Mode: Security Setting: WPA/WPA2 ......................................................................... 47
Figure 28 Station Mode: Security Setting: IEEE 802.1x ........................................................................ 48
Figure 29 Station Mode: Confirm New Settings ..................................................................................... 49
Figure 30 Station Mode: Profile ............................................................................................................ 50
Figure 31 Station Mode: Profile: Add a New Profile .............................................................................. 52
Figure 32 Station Mode: Profile: Select a Channel ................................................................................ 53
Figure 33 Station Mode: Profile: Security Settings ................................................................................ 54
Figure 34 Station Mode: Profile: Security Settings ................................................................................ 54
Figure 35 Station Mode: Profile: Confirm New Settings ........................................................................ 55
Figure 36 Station Mode: Profile: Activate the Profile ............................................................................. 55
Figure 37 Station Mode: Adapter ........................................................................................................... 56
Figure 38 ZyXEL Utility Menu Summary: AP Mode ............................................................................... 59
G-320H User’s Guide
13
Page 14

List of Figures
Figure 39 Access Point Mode: Link Info ................................................................................................ 60
Figure 40 Access Point Mode: Configuration ........................................................................................ 61
Figure 41 Access Point Mode: MAC Filter ............................................................................................. 63
Figure 42 About ..................................................................................................................................... 65
Figure 43 Uninstall: Confirm ................................................................................................................. 66
Figure 44 Uninstall: Finish ..................................................................................................................... 66
Figure 45 Windows 2000: Start ............................................................................................................. 73
Figure 46 Windows 2000: Network and Dial-up Connections ............................................................... 74
Figure 47 Windows 2000: Network Properties ...................................................................................... 74
Figure 48 WIndows 2000: Network Properties: Select Network Adapter .............................................. 75
Figure 49 Windows 2000: Local Network .............................................................................................. 75
Figure 50 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Network Connection Status ....................................................... 77
Figure 51 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection Status ....................................................... 78
Figure 52 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Network Connection Properties ................................................. 78
Figure 53 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection Properties ................................................. 79
Figure 54 Windows XP SP2: WZC Not Available ................................................................................... 79
Figure 55 Windows XP SP2: System Tray Icon .....................................................................................80
Figure 56 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection Status ....................................................... 80
Figure 57 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Network Connection Status ....................................................... 81
Figure 58 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection .................................................................. 81
Figure 59 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Network Connection Properties ................................................. 82
Figure 60 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection: WEP or WPA-PSK .................................. 83
Figure 61 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection: No Security ............................................ 83
Figure 62 Windows XP: Wireless (network) properties: Association ...................................................... 84
Figure 63 Windows XP: Wireless (network) properties: Authentication ................................................. 85
Figure 64 Windows XP: Protected EAP Properties ................................................................................ 86
Figure 65 Windows XP: Smart Card or other Certificate Properties ....................................................... 87
Figure 66 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Networks: Preferred Networks .................................................. 88
Figure 67 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Networks: Preferred Networks .................................................. 89
Figure 68 WPA-PSK Authentication ....................................................................................................... 95
Figure 69 WPA(2) with RADIUS Application Example ........................................................................... 95
Figure 70 WIndows 95/98/Me: Network: Configuration .......................................................................... 98
Figure 71 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: IP Address .............................................................. 99
Figure 72 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: DNS Configuration ................................................ 100
Figure 73 Windows XP: Start Menu ...................................................................................................... 101
Figure 74 Windows XP: Control Panel ................................................................................................. 101
Figure 75 Windows XP: Control Panel: Network Connections: Properties ........................................... 102
Figure 76 Windows XP: Local Area Connection Properties ................................................................. 102
Figure 77 Windows XP: Advanced TCP/IP Settings ............................................................................ 103
Figure 78 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties ............................................................ 104
Figure 79 Macintosh OS 8/9: Apple Menu ............................................................................................ 105
Figure 80 Macintosh OS 8/9: TCP/IP ................................................................................................... 105
Figure 81 Macintosh OS X: Apple Menu .............................................................................................. 106
14
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 15

List of Figures
Figure 82 Macintosh OS X: Network .................................................................................................... 107
G-320H User’s Guide
15
Page 16

List of Figures
16
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 17

List of Tables
List of Tables
Table 1 ZyXEL Utility: System Tray Icon ................................................................................................ 22
Table 2 ZyXEL Utility Menu Summary: Station Mode ............................................................................ 41
Table 3 Station Mode: Link Info ............................................................................................................. 42
Table 4 Station Mode: Link Info: Trend Chart ........................................................................................ 43
Table 5 Station Mode: Site Survey ......................................................................................................... 44
Table 6 Station Mode: Security Setting: WEP ........................................................................................ 45
Table 7 Station Mode: Security Setting: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK ............................................................ 47
Table 8 Station Mode: Security Setting: WPA/WPA2 ............................................................................. 47
Table 9 Station Mode: Security Setting: IEEE 802.1x ............................................................................ 48
Table 10 Station Mode: Confirm New Settings ...................................................................................... 49
Table 11 Station Mode: Profile ............................................................................................................... 51
Table 12 Station Mode: Profile: Add a New Profile ................................................................................ 52
Table 13 Station Mode: Profile: Select a Channel ................................................................................. 53
Table 14 Station Mode: Adapter ............................................................................................................ 56
Table 15 ZyXEL Utility Menu Summary: AP Mode ................................................................................ 59
Table 16 Access Point Mode: Link Info .................................................................................................. 60
Table 17 Access Point Mode: Configuration .......................................................................................... 61
Table 18 Access Point Mode: MAC Filter .............................................................................................. 63
Table 19 About ....................................................................................................................................... 65
Table 20 Product Specifications ............................................................................................................. 71
Table 21 Windows XP SP2: System Tray Icon ...................................................................................... 80
Table 22 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection ................................................................... 82
Table 23 Windows XP: Wireless Networks ............................................................................................ 83
Table 24 Windows XP: Wireless (network) properties: Association ...................................................... 84
Table 25 Windows XP: Wireless (network) properties: Authentication .................................................. 85
Table 26 Windows XP: Protected EAP Properties .................................................................................86
Table 27 Windows XP: Smart Card or other Certificate Properties ....................................................... 87
Table 28 Comparison of EAP Authentication Types .............................................................................. 92
Table 29 Wireless Security Relational Matrix ........................................................................................ 96
G-320H User’s Guide
17
Page 18

List of Tables
18
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 19

CHAPTER 1
Getting Started
This chapter introduces the G-320H and prepares you to use the ZyXEL utility.
1.1 About Your G-320H
The G-320H is an IEEE 802.11b/g compliant wireless LAN adapter. You can also use the
ZyXEL utility to turn your G-320H into an access point (AP). The ZyXEL utility is a tool that
helps you configure your G-320H. See the appendix for detailed product specifications.
1.2 Application Overview
This section describes some network applications for the G-320H.
1.2.1 Station Mode
The G-320H acts as a wireless LAN adapter (station mode) by default. In station mode, you
can either set the network type to Infrastructure and connect to an AP or use Ad-Hoc mode
and connect to a peer computer (another wireless device in Ad-Hoc mode) without an AP. See
Section 4.4 on page 50 for how to configure the network type.
1.2.1.1 Infrastructure
To connect to a network via an access point (AP), set the G-320H network type to
Infrastructure. Through the AP, you can access the Internet or the wired network behind the
AP.
G-320H User’s Guide
19
Page 20
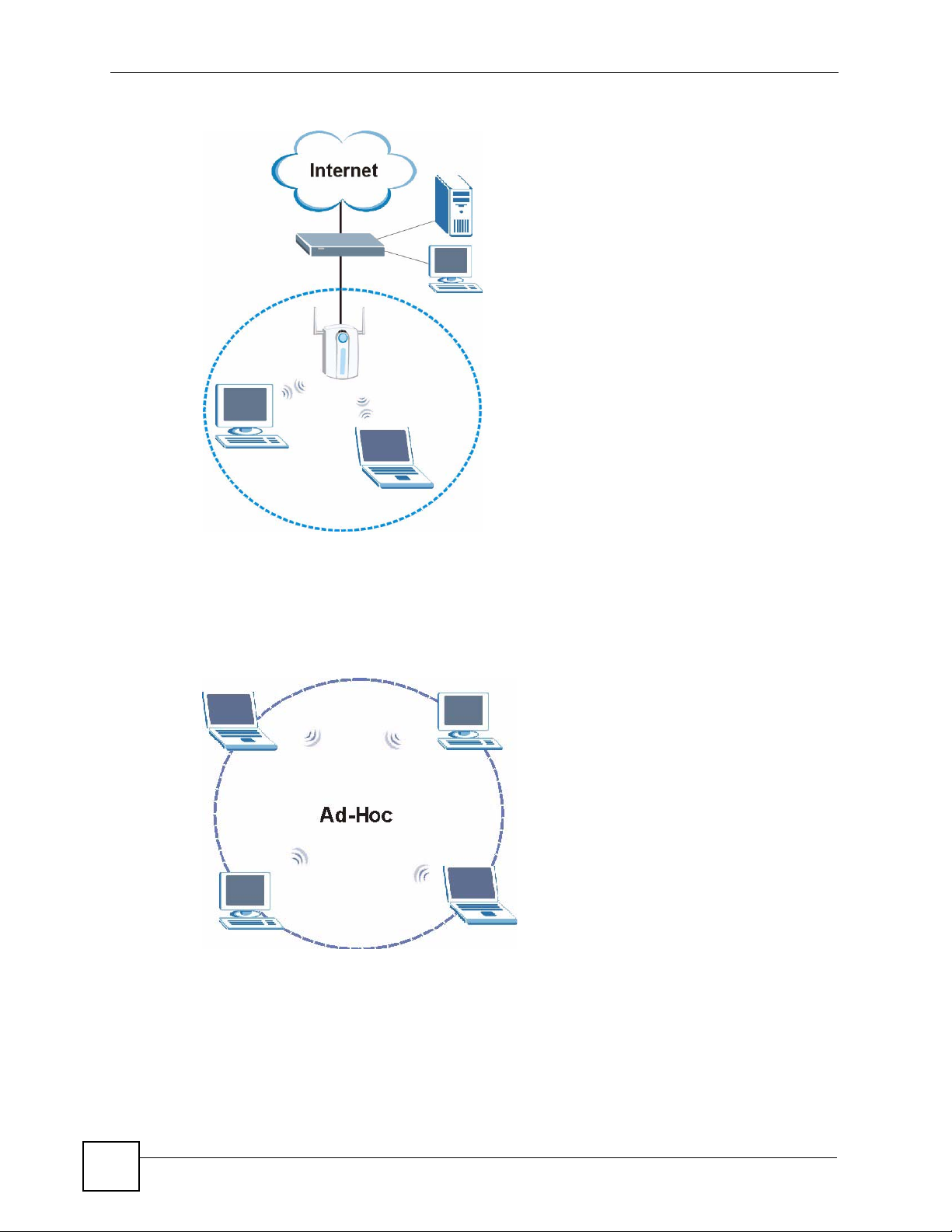
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Figure 1 Application: Infrastructure
1.2.1.2 Ad-Hoc
To set up a small independent wireless workgroup without an AP, use Ad-Hoc.
Ad-Hoc does not require an AP or a wired network. Two or more wireless clients (wireless
stations) communicate directly to each other.
Figure 2 Application: Ad-Hoc
1.2.2 Access Point Mode
20
In access point mode, your G-320H functions as an access point. This allows you to set up a
wireless network without using a dedicated AP. The following figure shows a network
example.
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 21
Chapter 1 Getting Started
Figure 3 Application: Access Point Mode
In the example, the G-320H is installed on computer A and set to operate in access point
mode. Computer A provides an Internet connection to the wireless LAN, so wireless stations
B and C can access the Internet.
" If the computer in which the G-320H is installed uses WZC (Wireless Zero
Configuration), the G-320H cannot function as an AP.
1.2.3 Changing G-320H Mode
To change between the modes, select either Station Mode or AP Mode in any ZyXEL utility
screens.
Figure 4 ZyXEL Utility: Change Modes
G-320H User’s Guide
21
Page 22

Chapter 1 Getting Started
" Wait for about five seconds for the ZyXEL utility to complete the mode change.
" The current mode is indicated by the color of the check box, see Table 1 on
page 22.
1.3 G-320H Hardware and Utility Installation
Follow the instructions in the Quick Start Guide to install the ZyXEL utility and make
hardware connections.
1.3.1 ZyXEL Utility Icon
After you install and start the ZyXEL utility, an icon for the ZyXEL utility appears in the
system tray.
" The ZyXEL utility system tray icon displays only when the G-320H is installed
properly.
Figure 5 ZyXEL Utility: System Tray Icon
The color of the ZyXEL utility system tray icon indicates the status of the G-320H. Refer to
the following table for details.
Table 1 ZyXEL Utility: System Tray Icon
COLOR DESCRIPTION
Red The G-320H is operating in wireless station mode but is not connected to a wireless
network.
Green The G-320H is operating in wireless station mode and connected to a wireless network.
Pale Blue The G-320H is operating in access point mode.
1.4 Configuration Methods
To configure your G-320H, use one of the following applications:
22
• ZyXEL Utility (required when you want to use the G-320H as an access point)
• Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) (the Windows XP wireless configuration tool)
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 23
Chapter 1 Getting Started
1.4.1 Enabling WZC
" When you use the ZyXEL utility, it automatically disables WZC.
If you want to use WZC to configure the G-320H, you need to disable the ZyXEL utility by
right-clicking the utility icon ( ) in the system tray and selecting Use Windows to configure
my wireless network settings.
Figure 6 Enable WZC
Refer to the appendices for information on how to use WZC to manage the G-320H.
To re-activate the ZyXEL utility, double-click the ( ) icon on your desktop or click Start,
(All) Programs, ZyXEL G-320H Utility, ZyXEL G-320H Utility.
1.4.2 Accessing the ZyXEL Utility
Double-click on the ZyXEL wireless LAN utility icon in the system tray to open the ZyXEL
utility. The ZyXEL utility screens are similar in all Microsoft Windows versions. Screens for
Windows 2000 are shown in this User’s Guide.
" Click the icon (located in the top right corner) to display the online help
window.
G-320H User’s Guide
23
Page 24

Chapter 1 Getting Started
24
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 25
CHAPTER 2
Tutorial
The following sections show you how to join a wireless network using the ZyXEL utility, as in
the following diagrams. The wireless client is labeled C and the access point is labeled AP.
Figure 7 Infrastructure Network
There are three ways to connect the wireless client (the G-320H in station mode) to a network.
• Configure nothing and leave the wireless client to automatically scan for and connect to
any available network that has no wireless security configured.
• Manually connect to a network (see Section 2.1 on page 25).
• Configure a profile to have the wireless client automatically connect to a specific network
or peer computer (see Section 2.2 on page 27).
This chapter also includes a simple example of how to configure the G-320H as an AP using
the ZyXEL utility. See Section 2.3 on page 30 for more information.
2.1 Connecting to a Wireless LAN
This example illustrates how to manually connect your wireless client to an access point (AP)
which is configured for WPA-PSK security and connected to the Internet. Before you connect
to the access point, you must know its Service Set IDentity (SSID) and WPA-PSK pre-shared
key. In this example, the SSID is “SSID_Example3” and the pre-shared key is
“ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey” in the AP.
After you install the ZyXEL utility and then insert the wireless client, follow the steps below
to connect to a network using the Site Survey screen.
1 Open the ZyXEL utility and click the Site Survey tab to open the screen as shown next.
G-320H User’s Guide
25
Page 26
Chapter 2 Tutorial
Figure 8 ZyXEL Utility: Site Survey
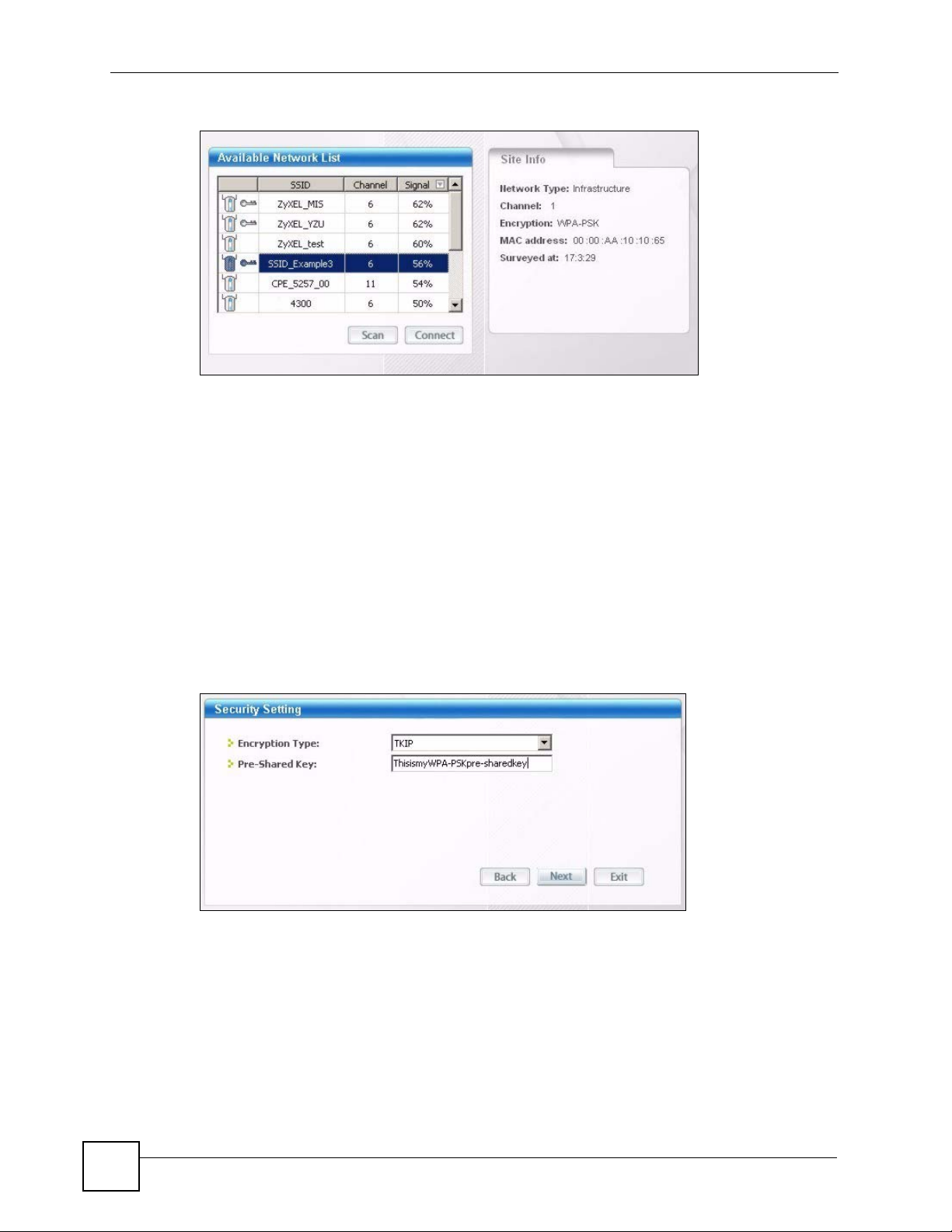
2 The wireless client automatically searches for available wireless networks. Click Scan if
3 To connect to an AP or peer computer, either click an entry in the list and then click
4 When you try to connect to an AP with security configured, a window will pop up
you want to search again. If no entry displays in the Available Network List, that means
there is no wireless network available within range. Make sure the AP or peer computer
is turned on, or move the wireless client closer to the AP or peer computer. See Table 5
on page 44 for detailed field descriptions.
Connect or double-click an entry (with a SSID of SSID_Examples3 in this example).
prompting you to specify the security settings. Enter the pre-shared key and leave the
encryption type at the default setting.
Use the Next button to move on to the next screen. You can use the Back button at any
time to return to the previous screen, or the Exit button to return to the Site Survey
screen.
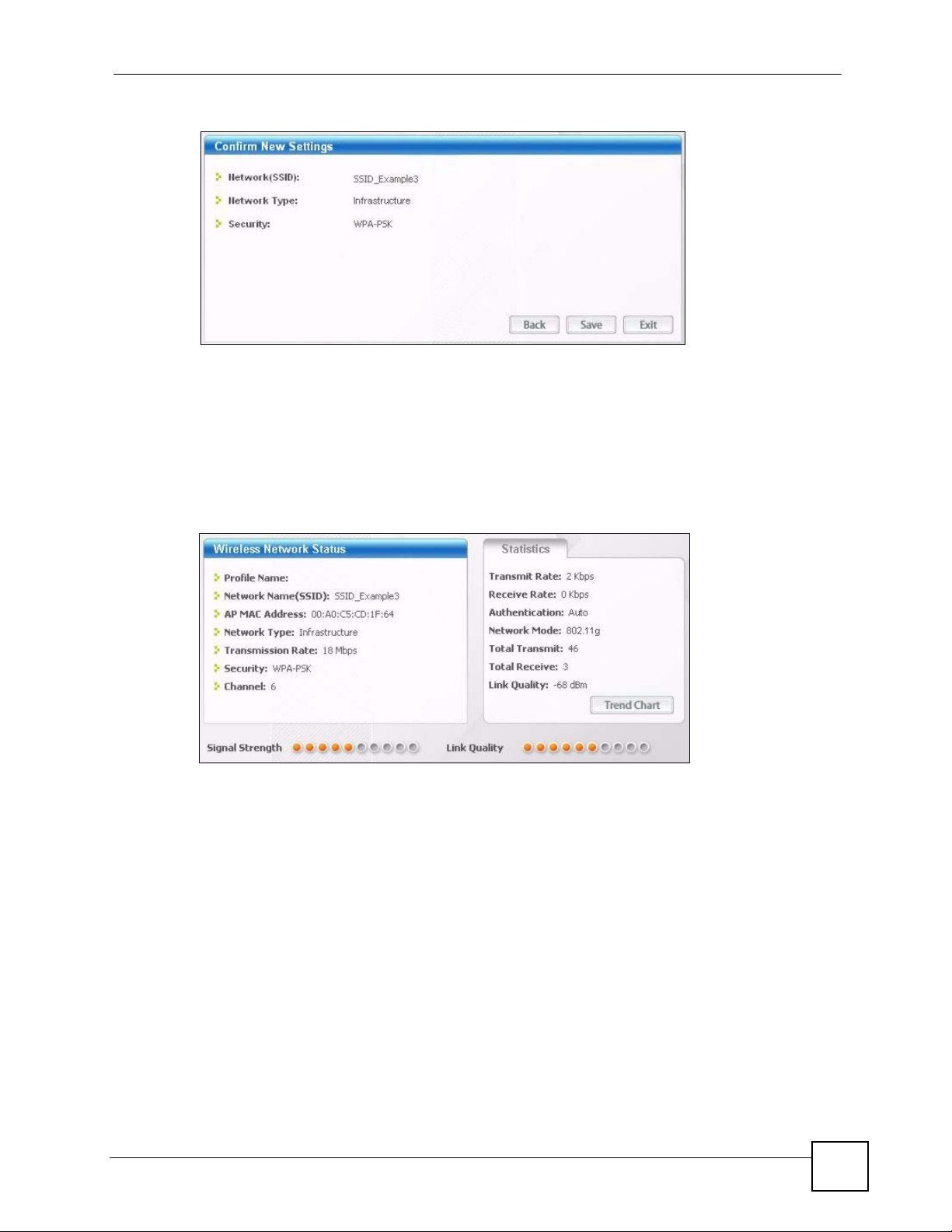
Figure 9 ZyXEL Utility: Security Setting
5 The Confirm New Settings window appears. Check your settings and click Save to
continue.
26
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 27
Chapter 2 Tutorial
Figure 10 ZyXEL Utility: Confirm New Settings
6 The ZyXEL utility returns to the Link Info screen while it connects to the wireless
network using your settings. When the wireless link is established, the ZyXEL utility
icon in the system tray turns green and the Link Info screen displays details of the active
connection. Check the network information in the Link Info screen to verify that you
have successfully connected to the selected network. If the wireless client is not
connected to a network, the fields in this screen remain blank. See Table 3 on page 42 for
detailed field descriptions.
Figure 11 ZyXEL Utility: Link Info
7 Open your Internet browser and enter http://www.zyxel.com or the URL of any other
web site in the address bar. If you are able to access the web site, your wireless
connection is successfully configured. If you cannot access the web site, check the
Troubleshooting section of this User's Guide or contact your network administrator if
necessary.
2.2 Creating and Using a Profile
A profile lets you automatically connect to the same wireless network every time you use the
ZyXEL utility. You can also configure different profiles for different networks, for example if
you connect a notebook computer to wireless networks at home and at work.
This example illustrates how to set up a profile and connect the wireless client to an access
point configured for WPA-PSK security. In this example, the SSID is “SSID_Example3” and
the pre-shared key is “ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey” in the AP. You have chosen the
profile name “PN_Example3”.
G-320H User’s Guide
27
Page 28
Chapter 2 Tutorial
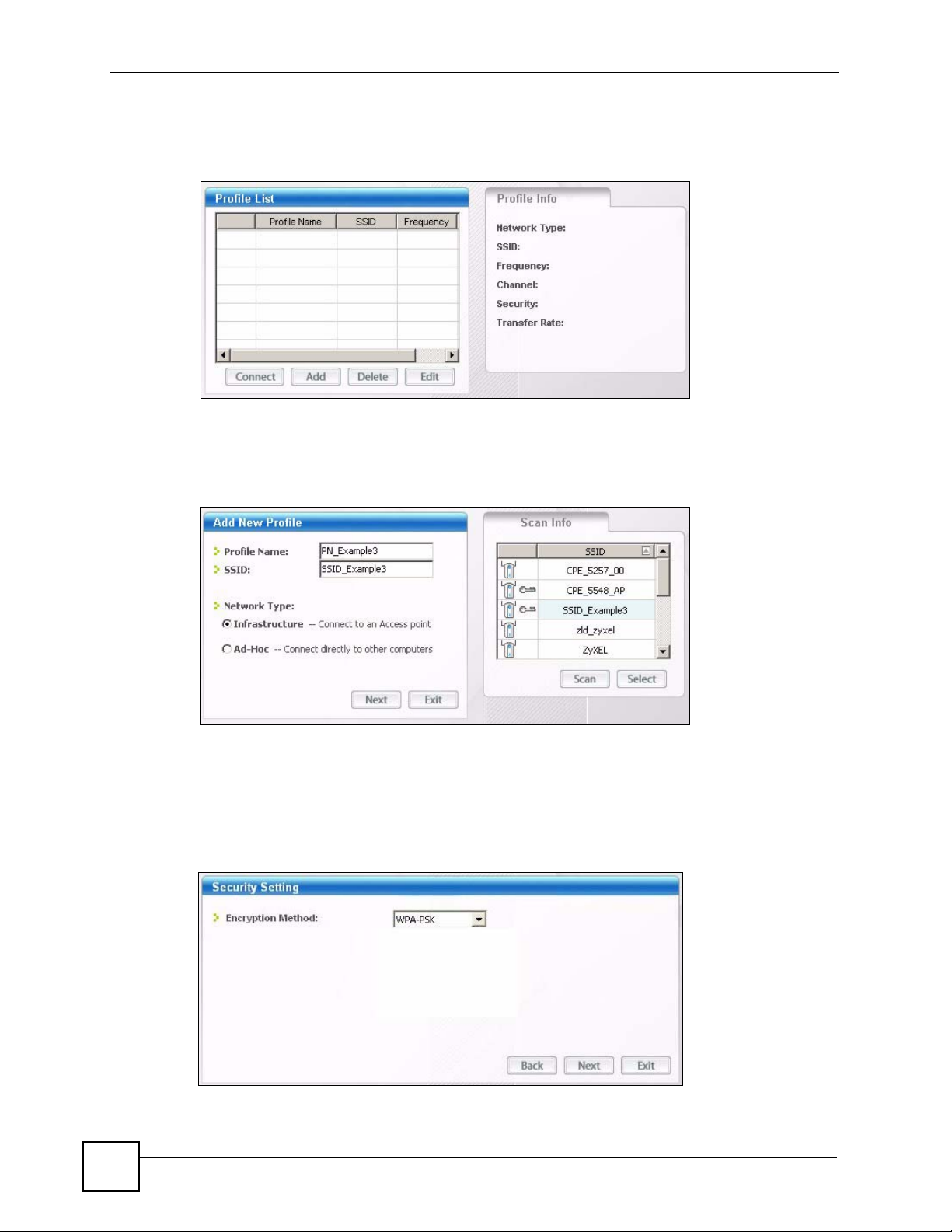
1 Open the ZyXEL utility and click the Profile tab to open the screen as shown. Click Add
Figure 12 ZyXEL Utility: Profile
2 The Add New Profile screen appears. The wireless client automatically searches for
Figure 13 ZyXEL Utility: Add New Profile
to configure a new profile.
available wireless networks, which are displayed in the Scan Info box. You can also
configure your profile for a wireless network that is not in the list.
28
3 Give the profile a descriptive name (of up to 32 printable ASCII characters). Select
Infrastructure and either manually enter or select the AP's SSID in the Scan Info table
and click Select.
4 Choose the same encryption method as the AP to which you want to connect (In this
example, WPA-PSK).
Figure 14 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Security
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 29
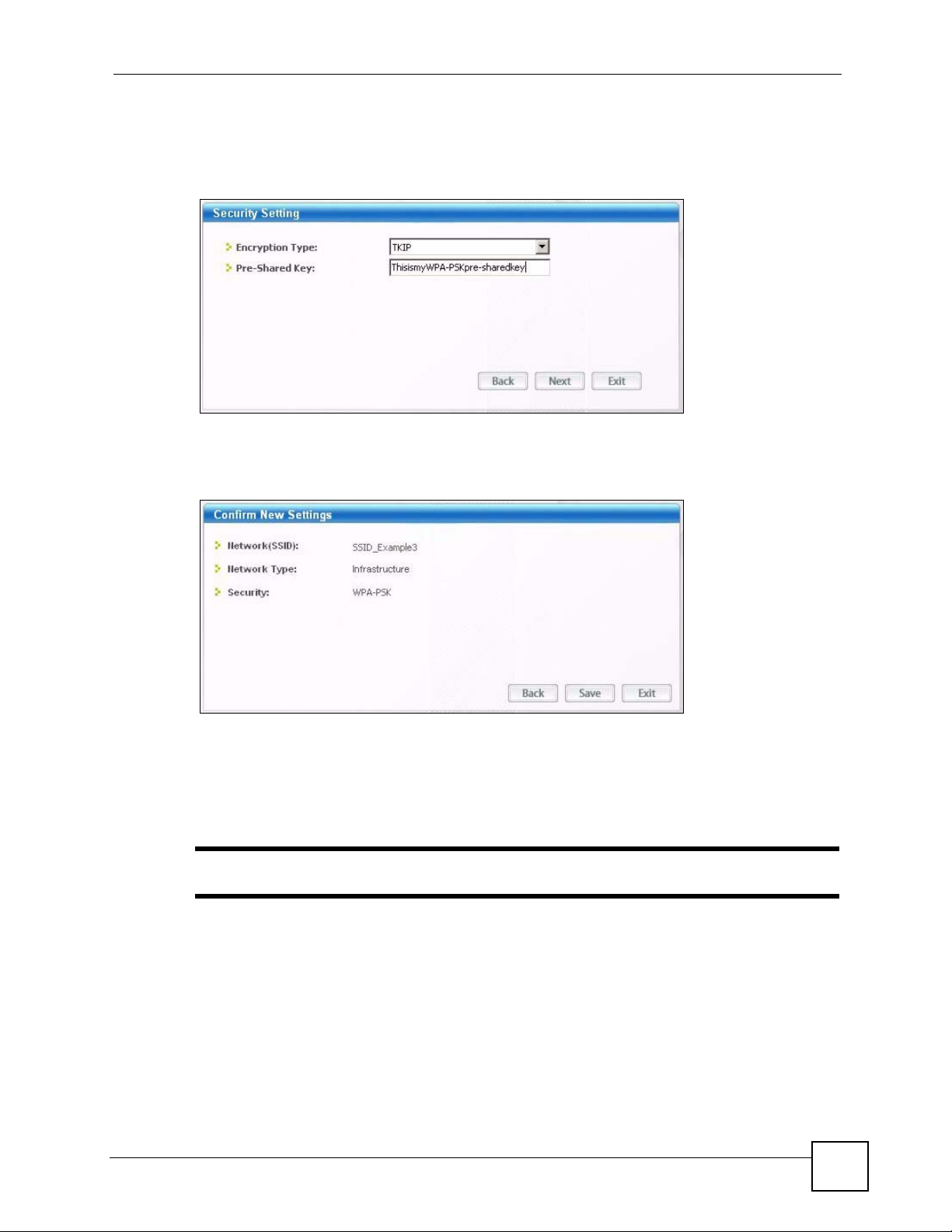
Chapter 2 Tutorial
5 This screen varies depending on the encryption method you selected in the previous
screen. In this example, enter the pre-shared key and leave the encryption type at the
default setting.
Figure 15 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Encryption
6 Verify the profile settings in the ready-only screen. Click Save to save and go to the next
screen.
Figure 16 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Confirm New Settings
7 Click Activate Now to use the new profile immediately. Otherwise, click the Activate
Later button to go back to the Profile List screen.
If you clicked Activate Later you can select the profile from the list in the Profile
screen and click Connect to activate it.
" Only one profile can be activated and used at any given time.
G-320H User’s Guide
29
Page 30
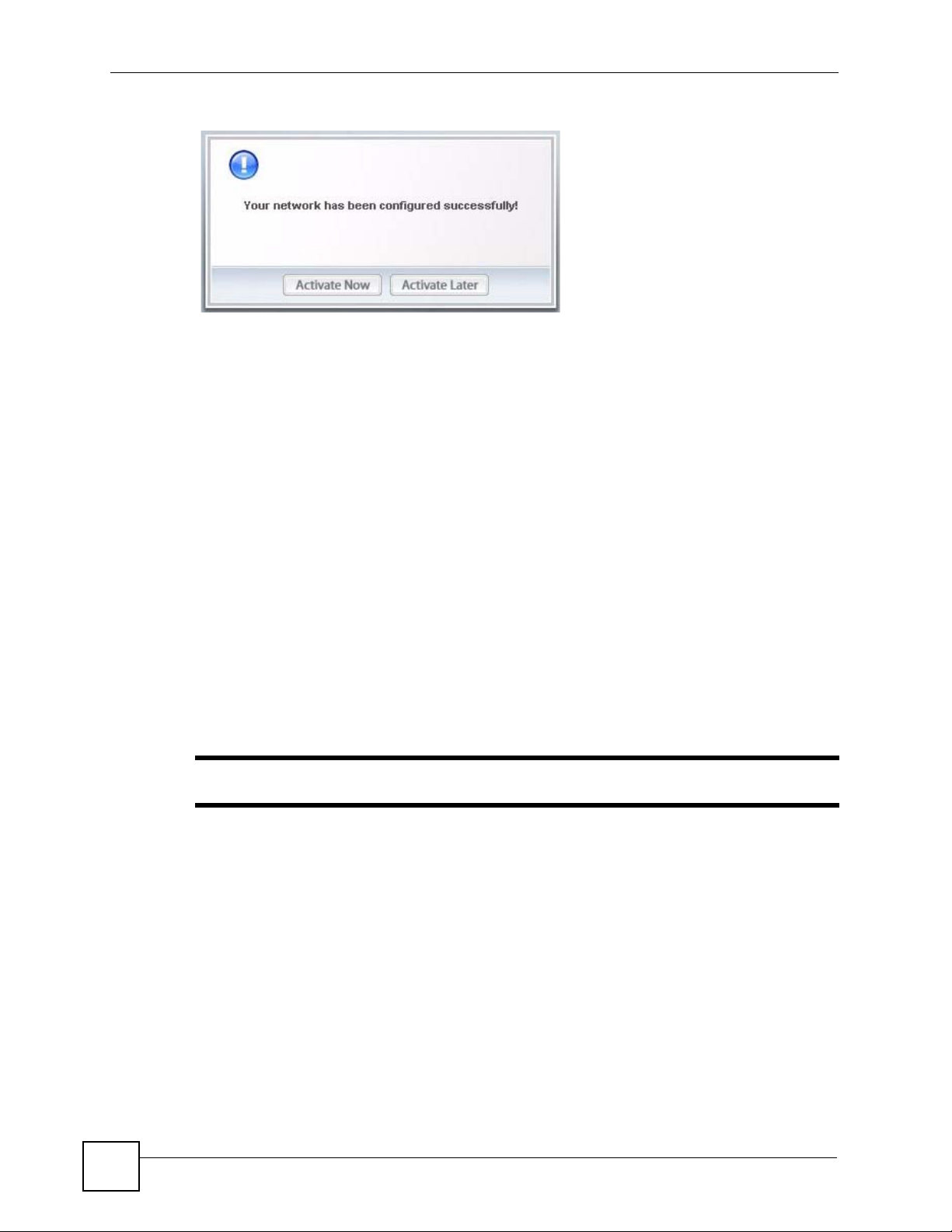
Chapter 2 Tutorial
Figure 17 ZyXEL Utility: Profile Activate
8 When you activate the new profile, the ZyXEL utility goes to the Link Info screen while
9 Make sure the selected AP in the active profile is connected to the Internet. Open your
10 If you cannot access the Internet, go back to the Profile screen. Select the profile you are
it connects to the AP using your settings. When the wireless link is established, the
ZyXEL utility icon in the system tray turns green and the Link Info screen displays
details of the active connection.
Internet browser, enter http://www.zyxel.com or the URL of any other web site in the
address bar and press ENTER. If you are able to access the web site, your new profile is
successfully configured.
using and click Edit. Check the details you entered previously. Also, refer to the
Troubleshooting section of this User's Guide or contact your network administrator if
necessary.
2.3 Configuring the G-320H as an AP
In access point mode, your G-320H allows you to set up your wireless network without using
a dedicated AP. Refer to Section 1.2.3 on page 21 and Chapter 5 on page 59 for more
information.
" With WZC, you cannot use the G-320H as an access point.
After you install the ZyXEL utility and then insert the G-320H, follow the steps below to set
up your G-320H as an AP.
1 Select AP Mode in any utility screen and wait for five seconds. The screen changes and
displays as next. Under Status, you can view the current settings on the G-320H. In the
Association List, you can see if any wireless clients have connected to your G-320H.
30
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 31

Figure 18 ZyXEL Utility: AP: Link Info
Chapter 2 Tutorial
2 If you want to change the SSID and enable wireless security for your G-320H, click the
Configuration tab and refer to Section 5.3 on page 61 for detailed field descriptions.
" You can only use WEP when the G-320H is in AP mode.
Figure 19 ZyXEL Utility: AP: Configuration
G-320H User’s Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 2 Tutorial
32
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 33

CHAPTER 3
Wireless LAN Network
This chapter provides background information on wireless LAN network.
3.1 Wireless LAN Overview
The following figure provides an example of a wireless network with an AP. See Figure 2 on
page 20 for an Ad Hoc network example.
Figure 20 Example of a Wireless Network
The wireless network is the part in the blue circle. In this wireless network, devices A and B
are called wireless clients. The wireless clients use the access point (AP) to interact with other
devices (such as the printer) or with the Internet
Every wireless network must follow these basic guidelines.
• Every device in the same wireless network must use the same SSID.
The SSID is the name of the wireless network. It stands for Service Set IDentity.
• If two wireless networks overlap, they should use a different channel.
Like radio stations or television channels, each wireless network uses a specific channel,
or frequency, to send and receive information.
G-320H User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 3 Wireless LAN Network
• Every device in the same wireless network must use security compatible with the AP or
peer computer.
Security stops unauthorized devices from using the wireless network. It can also protect
the information that is sent in the wireless network.
3.2 Wireless LAN Security
Wireless LAN security is vital to your network to protect wireless communications.
Configure the wireless LAN security using the Configuration or the Profile Security Setting
screen. If you do not enable any wireless security on your G-320H, the G-320H’s wireless
communications are accessible to any wireless networking device that is in the coverage area.
" You can only use WEP encryption if you set the G-320H to Ad-hoc mode.
See the appendices for more detailed information about wireless security.
3.2.1 Hide SSID
Normally, the G-320H in AP mode acts like a beacon and regularly broadcasts the SSID in the
area. You can hide the SSID instead, in which case the G-320H in AP mode does not
broadcast the SSID. In addition, you should change the default SSID to something that is
difficult to guess.
This type of security is fairly weak, however, because there are ways for unauthorized wireless
devices to get the SSID. In addition, unauthorized wireless devices can still see the
information that is sent in the wireless network.
3.2.2 MAC Address Filter
Every device that can use a wireless network has a unique identification number, called a
MAC address.
example, 00A0C5000002 or 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. To get the MAC address for each device in
the wireless network, see the device’s User’s Guide or other documentation.
You can use the MAC address filter to tell the G-320H in AP mode which devices are allowed
or not allowed to use the wireless network. If a device is allowed to use the wireless network,
it still has to have the correct information (SSID, channel, and security). If a device is not
allowed to use the wireless network, it does not matter if it has the correct information.
This type of security does not protect the information that is sent in the wireless network.
Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized wireless devices to get the MAC address of an
authorized device. Then, they can use that MAC address to use the wireless network.
1
A MAC address is usually written using twelve hexadecimal characters2; for
34
1. Some wireless devices, such as scanners, can detect wireless networks but cannot use wireless networks.
These kinds of wireless devices might not have MAC addresses.
2. Hexadecimal characters are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F.
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 35

3.2.3 User Authentication and Encryption
You can make every user log in to the wireless network before they can use it. This is called
user authentication. However, every wireless client in the wireless network has to support
IEEE 802.1x to do this.
Wireless networks can use encryption to protect the information that is sent in the wireless
network. Encryption is like a secret code. If you do not know the secret code, you cannot
understand the message.
3.2.3.1 WEP
3.2.3.1.1 Data Encryption
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption scrambles all data packets transmitted between
the G-320H and the AP or other wireless stations to keep network communications private.
Both the wireless stations and the access points must use the same WEP key for data
encryption and decryption.
There are two ways to create WEP keys in your G-320H.
• Automatic WEP key generation based on a “password phrase” called a passphrase. The
passphrase is case sensitive. You must use the same passphrase for all WLAN adapters
with this feature in the same WLAN.
For WLAN adapters without the passphrase feature, you can still take advantage of this
feature by writing down the four automatically generated WEP keys from the Security
Setting or the Configuration screen of the ZyXEL utility and entering them manually as
the WEP keys in the other WLAN adapter(s).
• Enter the WEP keys manually.
Your G-320H allows you to configure up to four 64-bit, 128-bit or 256-bit WEP keys and
only one key is used as the default key at any one time.
Chapter 3 Wireless LAN Network
3.2.3.1.2 Authentication Type
The IEEE 802.11 b/g standard describes a simple authentication method between the wireless
stations and AP. Three authentication types are defined: Auto, Open System and Shared
Key.
• Open System mode is implemented for ease-of-use and when security is not an issue.
The wireless station and the AP or peer computer do not share a secret key. Thus the
wireless stations can associate with any AP or peer computer and listen to any transmitted
data that is not encrypted.
• Shared Key mode involves a shared secret key to authenticate the wireless station to the
AP or peer computer. This requires you to enable the wireless LAN security and use same
settings on both the wireless station and the AP or peer computer.
• Auto authentication mode allows the G-320H to switch between the open system and
shared key modes automatically. Use the auto mode if you do not know the authentication
mode of the other wireless stations.
3.2.3.2 IEEE 802.1x
The IEEE 802.1x standard outlines enhanced security methods for both the authentication of
wireless stations and encryption key management. Authentication can be done using an
external RADIUS server.
G-320H User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 3 Wireless LAN Network
3.2.3.2.1 EAP Authentication
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is an authentication protocol that runs on top of the
IEEE 802.1x transport mechanism in order to support multiple types of user authentication. By
using EAP to interact with an EAP-compatible RADIUS server, an access point helps a
wireless station and a RADIUS server perform authentication.
The type of authentication you use depends on the RADIUS server and an intermediary AP(s)
that supports IEEE 802.1x. The G-320H supports EAP-TLS and EAP-PEAP. Refer to
Appendix D on page 91 for descriptions.
For EAP-TLS authentication type, you must first have a wired connection to the network and
obtain the certificate(s) from a certificate authority (CA). A certificate (also called digital IDs)
can be used to authenticate users and a CA issues certificates and guarantees the identity of
each certificate owner.
3.2.3.3 WPA and WPA2
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA2 (IEEE
802.11i) is a wireless security standard that defines stronger encryption, authentication and
key management than WPA.
Key differences between WPA(2) and WEP are improved data encryption and user
authentication.
Both WPA and WPA2 improve data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
(TKIP), Message Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1x. WPA and WPA2 use Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES) in the Counter mode with Cipher block chaining Message
authentication code Protocol (CCMP) to offer stronger encryption than TKIP.
If both an AP and the wireless clients support WPA2 and you have an external RADIUS
server, use WPA2 for stronger data encryption. If you don't have an external RADIUS server,
you should use WPA2-PSK (WPA2-Pre-Shared Key) that only requires a single (identical)
password entered into each access point, wireless gateway and wireless client. As long as the
passwords match, a wireless client will be granted access to a WLAN.
If the AP or the wireless clients do not support WPA2, just use WPA or WPA-PSK depending
on whether you have an external RADIUS server or not.
Select WEP only when the AP and/or wireless clients do not support WPA or WPA2. WEP is
less secure than WPA or WPA2.
3.3 Introduction to OTIST
In a wireless network, the wireless clients must have the same SSID and security settings as
the access point (AP) or wireless router (we will refer to both as “AP” here) in order to
associate with it. Traditionally this meant that you had to configure the settings on the AP and
then manually configure the exact same settings on each wireless client.
36
OTIST (One-Touch Intelligent Security Technology) allows you to transfer your AP’s SSID
and WEP or WPA-PSK security settings to wireless clients that support OTIST and are within
transmission range. You can also choose to have OTIST generate a WPA-PSK key for you if
you didn’t configure one manually.
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 37
Chapter 3 Wireless LAN Network
3.3.1 Enabling OTIST
You must enable OTIST on both the AP and wireless client before you start transferring
settings.
We use the P-334U in this guide as the example AP. Screens may vary slightly for your
ZyXEL devices.
" The AP and wireless client(s) MUST use the same Setup key.
3.3.1.1 AP
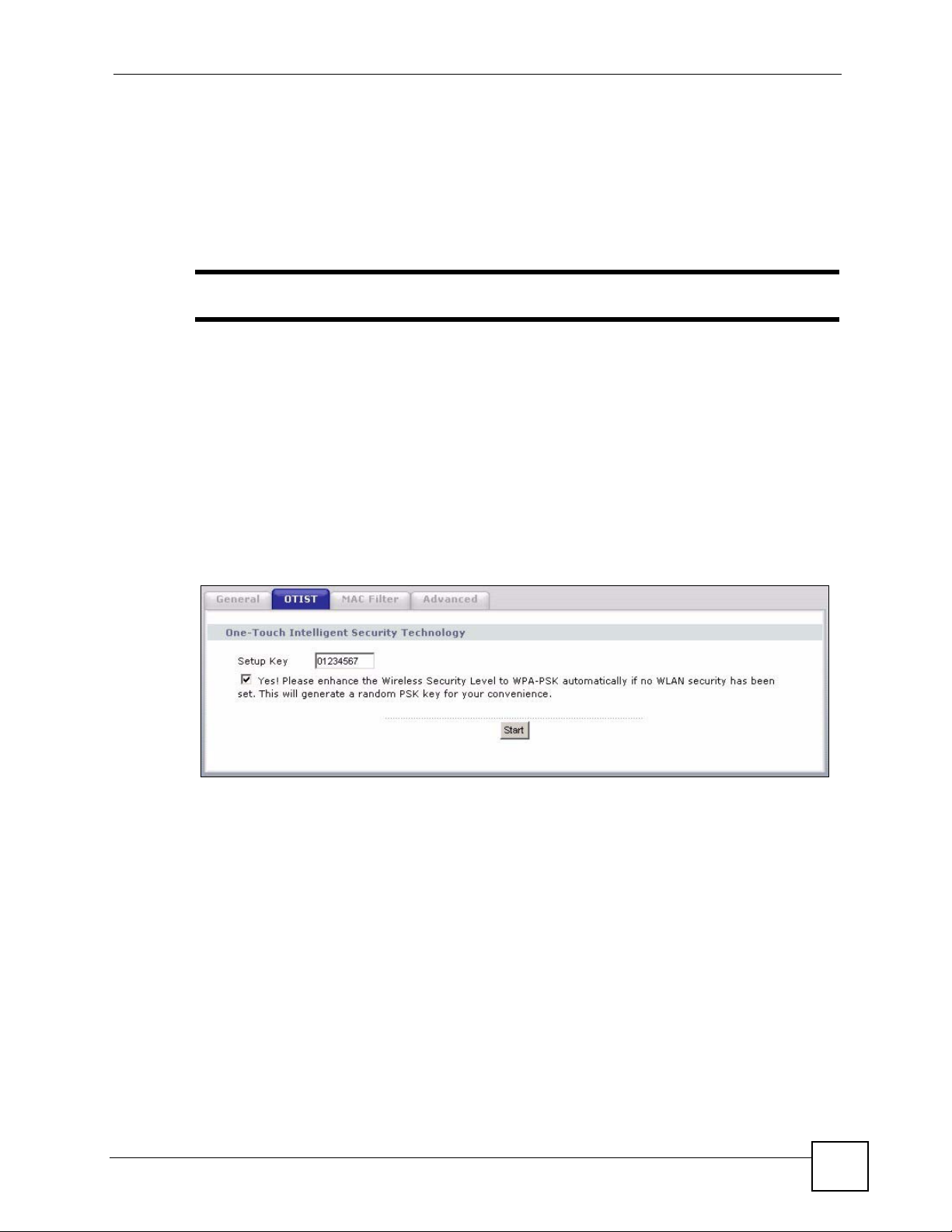
On the P-334U, you can enable OTIST using the OTIST button or the web configurator. If
you use the OTIST button, the default (01234567) or previous saved (through the web
configurator) Setup key is used to encrypt the settings that you want to transfer.
Hold in the OTIST button for about two seconds.
In the web configurator, go to the Wireless LAN main screen and then select OTIST. To
change the Setup key, enter zero to eight printable characters. To have OTIST automatically
generate a WPA-PSK key, select the Yes check box. If you manually configured a WEP key
or a WPA-PSK key and you also selected this check box, then the key you manually
configured is used.
G-320H User’s Guide
37
Page 38

Chapter 3 Wireless LAN Network
3.3.1.2 Wireless Client
Start the ZyXEL utility and click the Adapter tab. Select the OTIST check box, enter the
same Setup Key as your AP’s and click Save.
3.3.2 Starting OTIST
You must click Start in the AP OTIST web configurator screen and in the
wireless client(s) Adapter screen all within three minutes (at the time of
writing). You can start OTIST in the wireless clients and AP in any order
but they must all be within range and have OTIST enabled.
1 In the AP, a web configurator screen pops
up showing you the security settings to
transfer. After reviewing the settings, click
OK.
2 This screen appears while OTIST settings are being transferred. It closes when the
transfer is complete.
38
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 39
• In the wireless client, you see this screen if it
can't find an OTIST-enabled AP (with the
same Setup key). Click OK to go back to
the ZyXEL utility main screen.
• If there is more than one OTIST-enabled AP within range, you see a screen asking you to
select one AP to get settings from.
3.3.3 Notes on OTIST
1 If you enabled OTIST in the wireless client, you see this screen each time you start the
utility. Click Ye s for it to search for an OTIST-enabled AP.
Chapter 3 Wireless LAN Network
2 If an OTIST-enabled wireless client loses its wireless connection for more than ten
seconds, it will search for an OTIST-enabled AP for up to one minute. (If you manually
have the wireless client search for an OTIST-enabled AP, there is no timeout; click
Cancel in the OTIST progress screen to stop the search.)
3 When the wireless client finds an OTIST-enabled AP, you must still click Start in the
AP OTIST web configurator screen or hold in the OTIST button (for about two
seconds) for the AP to transfer settings.
4 If you change the SSID or the keys on the AP after using OTIST, you need to run OTIST
again or enter them manually in the wireless client(s).
5 If you configure OTIST to generate a WPA-PSK key, this key changes each time you
run OTIST. Therefore, if a new wireless client joins your wireless network, you need to
run OTIST on the AP and ALL the wireless clients again.
G-320H User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 3 Wireless LAN Network
40
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 41
CHAPTER 4
Wireless Station Mode
Configuration
This chapter shows you how to use the ZyXEL utility to configure your G-320H in wireless
station mode. See Chapter 5 on page 59 for how to configure the G-320H in access point
mode.
4.1 Wireless Station Mode Overview
To set your G-320H to wireless station mode, select Station Mode in any utility screen (refer
to Section 1.2.3 on page 21).
4.1.1 ZyXEL Utility Screen Summary
This section describes the ZyXEL utility screens when the G-320H is in station mode.
Figure 21 ZyXEL Utility Menu Summary: Station Mode
The following table describes the menus.
Table 2 ZyXEL Utility Menu Summary: Station Mode
TAB DESCRIPTION
Station Mode
Link Info Use this screen to see your current connection status, configuration and data rate
statistics.
Site Survey Use this screen to
• scan for a wireless network
• configure wireless security (if activated on the selected network).
• connect to a wireless network.
Profile Use this screen to add, delete, edit or activate a profile with a set of wireless and
security settings.
Adapter Use this screen to configure a transfer rate, enable power saving and use OTIST
(One-Touch Intelligent Security Technology).
G-320H User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
4.2 The Link Info Screen
When the ZyXEL utility starts, the Link Info screen displays, showing the current
configuration and connection status of your G-320H.
Figure 22 Station Mode: Link Info
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 3 Station Mode: Link Info
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Network
Security
Profile Name This is the name of the profile you are currently using.
Network Name
(SSID)
AP MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of the AP or peer computer to which the G-
Network Type This field displays the network type (Infrastructure or Ad-Hoc) of the wireless
Transmission
Rate
Security This field displays whether data encryption is activated (WEP (WEP or 802.1x),
Channel This field displays the radio channel the G-320H is currently using.
Statistics
Transmit Rate This field displays the current data transmission rate in kilobits per second (Kbps).
Receive Rate This field displays the current data receiving rate in kilobits per second (Kbps).
The SSID identifies the wireless network to which a wireless station is associated.
This field displays the name of the wireless device to which the G-320H is
associated.
320H is associated.
network.
This field displays the current transmission rate of the G-320H in megabits per
second (Mbps).
TKIP (WPA/WPA-PSK/WPA2/WPA2-PSK), AES (WPA /WPA -PSK/ WPA2 /WPA2-
PSK)) or inactive (None).
42
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 43

Table 3 Station Mode: Link Info (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Authentication This field displays the authentication method of the G-320H.
Network Mode This field displays the wireless standard ( 802.11b or 802.11g) of the AP or peer
Total Transmit This field displays the total number of data frames transmitted.
Total Receive This field displays the total number of data frames received.
Link Quality This field displays the signal strength of the G-320H.
Trend Chart Click this button to display the real-time statistics of the data rate in kilobits per
Signal Strength The status bar shows the strength of the signal. The signal strength is mainly
Link Quality The status bar shows the quality of wireless connection. This refers to the
4.2.1 Trend Chart
Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
computer.
second (Kbps).
depending on the antenna output power and the distance between your G-320H
and the AP or peer computer.
percentage of packets transmitted successfully. If there are too many wireless
stations in a wireless network, collisions may occur which could result in a loss of
messages even though you have high signal strength.
Click Trend Chart in the Link Info screen to display a screen as shown below. Use this
screen to view real-time data traffic statistics.
Figure 23 Station Mode: Link Info: Trend Chart
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 4 Station Mode: Link Info: Trend Chart
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Transmit This field displays the current data transmission rate in kilobits per second (Kbps).
Receive This field displays the current data receiving rate in kilobits per second (Kbps).
4.3 The Site Survey Screen
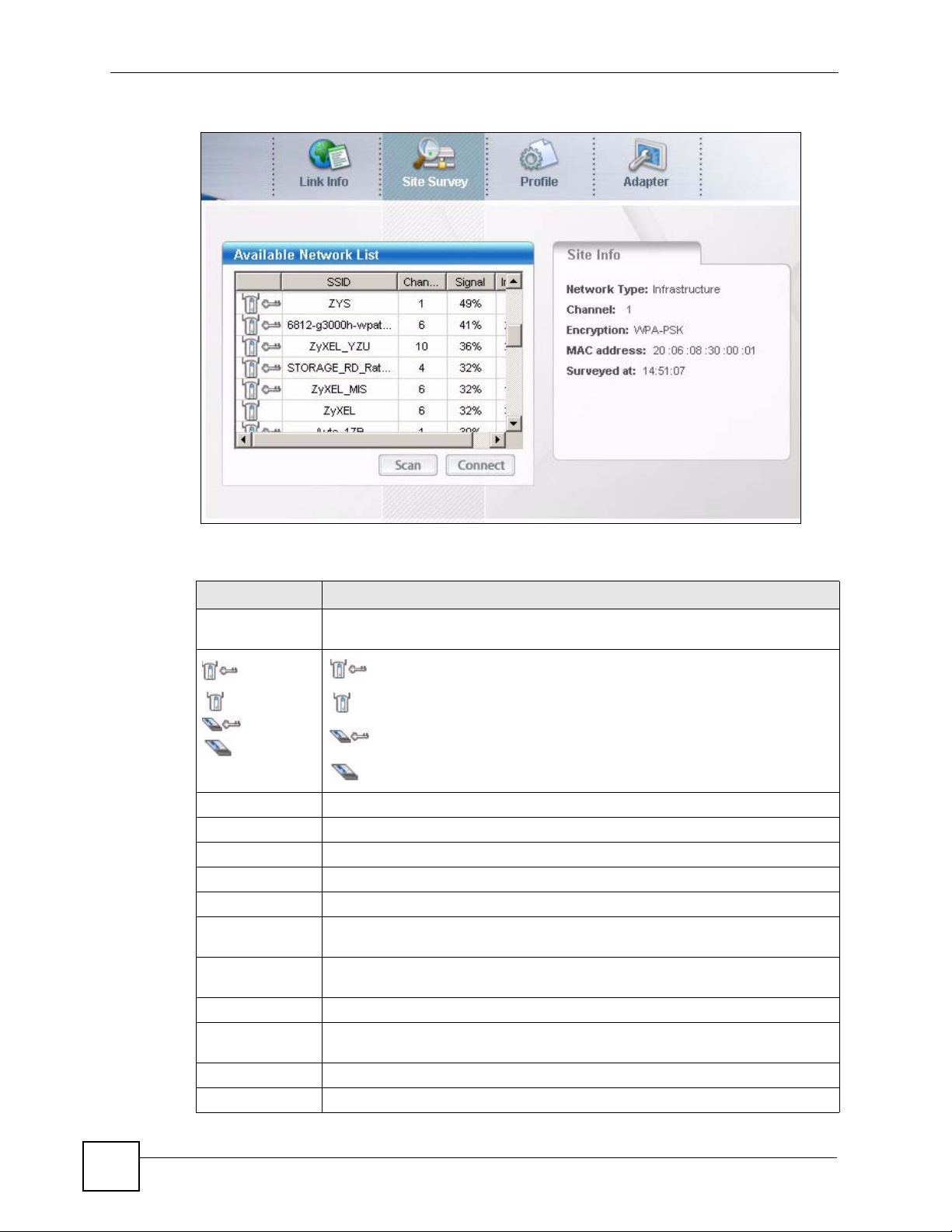
Use the Site Survey screen to scan for and connect to a wireless network automatically.
G-320H User’s Guide
43
Page 44
Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Figure 24 Station Mode: Site Survey
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 5 Station Mode: Site Survey
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Available Network
List
,
,
or
SSID This field displays the SSID (Service Set IDentifier) of each wireless device.
Channel This field displays the channel number used by each wireless device.
Signal This field displays the signal strength of each wireless device.
Scan Click Scan to search for available wireless devices within transmission range.
Connect Click Connect to associate to the selected wireless device.
Site Info Click an entry in the Available Network List table to display the information of the
Network Type This field displays the network type (Infrastructure or Ad-Hoc) of the wireless
Channel This field displays the channel number used by each wireless device.
Encryption This field shows whether data encryption is activated (WEP, WPA-PSK, WPA,
MAC address This field displays the MAC address of the wireless device.
Surveyed at This field displays the time when the wireless device is scanned.
Click a column heading to sort the entries.
denotes that the wireless device is in infrastructure mode and the wireless
security is activated.
denotes that the wireless device is in infrastructure mode but the wireless
security is deactivated.
denotes that the wireless device is in Ad-Hoc mode and the wireless
security is activated.
denotes that the wireless device is in Ad-Hoc mode but the wireless
security is deactivated.
selected wireless device.
device.
802.1x, WPA2, WPA2-PSK) or inactive (Disabled).
44
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 45
4.3.1 Security Settings
When you configure the G-320H to connect to a network with wireless security activated and
the security settings are different on the G-320H, the screen varies according to the encryption
method used by the selected network.
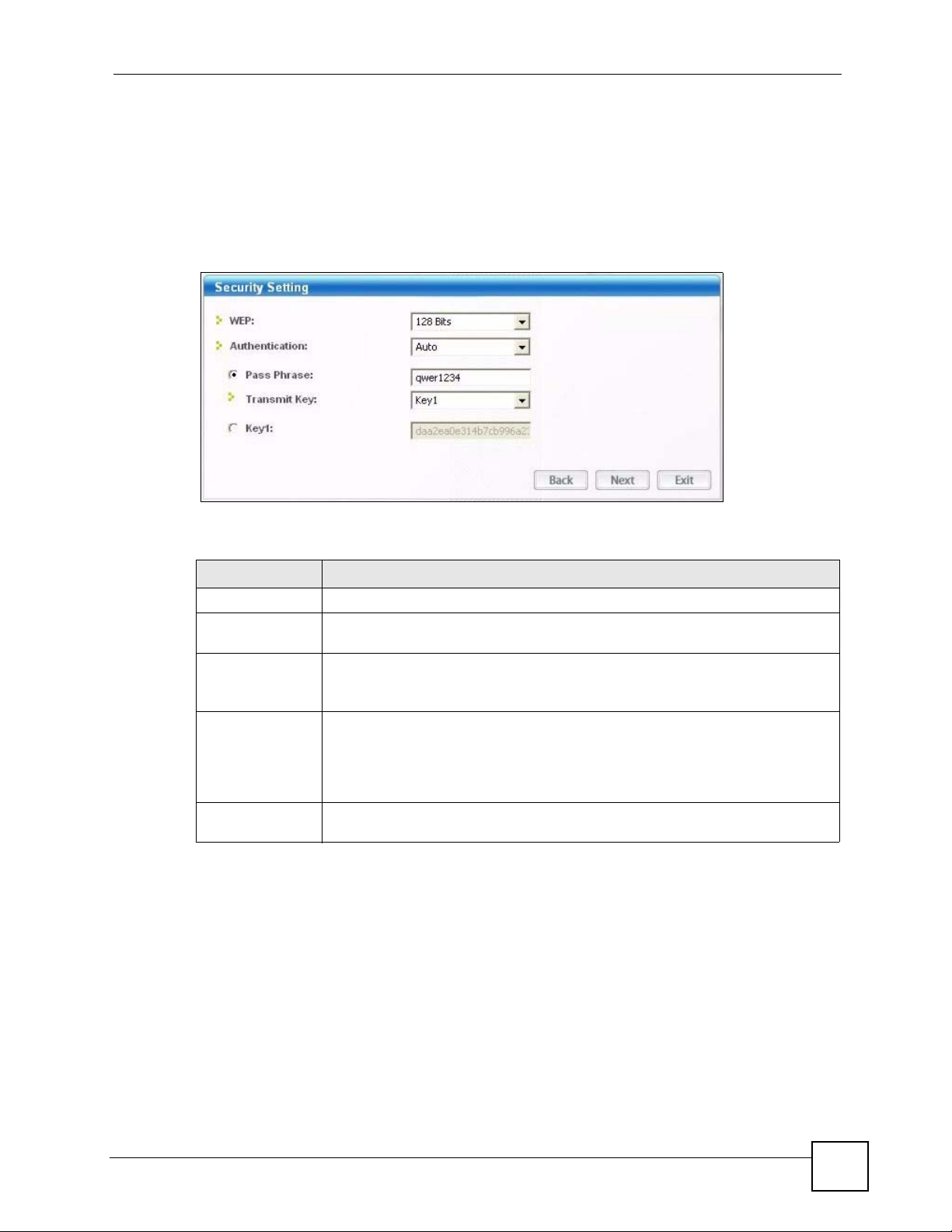
4.3.1.1 WEP Encryption
Figure 25 Station Mode: Security Setting: WEP
Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 6 Station Mode: Security Setting: WEP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Setting
WEP Select 64 Bits, 128 Bits or 256 Bits to activate WEP encryption and then fill in the
related fields.
Encryption Type Select an authentication method. Choices are Auto, Open System and Shared
Pass Phrase Enter a passphrase of up to 63 case-sensitive printable characters. As you enter
Transmit Key Select a default WEP key to use for data encryption. The key displays in the field
Key.
Refer to Section 3.2.3.1.2 on page 35 for more information.
the passphrase, the G-320H automatically generates four different WEP keys and
displays one of them in the key field below. Refer to Section 3.2.3.1.1 on page 35
for more information.
At the time of writing, you cannot use passphrase to generate 256-bit WEP keys.
below.
G-320H User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Table 6 Station Mode: Security Setting: WEP (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Key x (where x is
a number
between 1 and 4)
Select this option if you want to manually enter the WEP keys. Enter the WEP key
in the field provided.
If you select 64 Bits in the WEP field.
Enter either 10 hexadecimal digits in the range of “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” (for
example, 11AA22BB33) for HEX key type.
or
Enter 5 ASCII characters (case sensitive) ranging from “a-z”, “A-Z” and “0-9”
(for example, MyKey) for ASCII key type.
If you select 128 Bits in the WEP field,
Enter either 26 hexadecimal digits in the range of “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” (for
example, 00112233445566778899AABBCC) for HEX key type
or
Enter 13 ASCII characters (case sensitive) ranging from “a-z”, “A-Z” and “0-9”
(for example, MyKey12345678) for ASCII key type.
If you select 256 Bits in the WEP field,
Enter either 58 hexadecimal digits in the range of "A-F", "a-f" and "0-9" (for
example,
0000111122223333444455556666777788889999AAAABBBBCCCC000011)
for HEX key type
or
Enter 29 ASCII characters (case sensitive) ranging from "a-z", "A-Z" and "0-9"
(for example , MyKey 111122 223333444455556678) for ASCII key type.
Note: The values for the WEP keys must be set up exactly the
Note: ASCII WEP keys are case sensitive.
Back Click Back to go to the Site Survey screen to select and connect to another
network.
Next Click Next to confirm your selections and advance to the Confirm New Settings
screen. Refer to Section 4.3.2 on page 49.
Exit Click Exit to return to the Site Survey screen without saving.
4.3.1.2 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Figure 26 Station Mode: Security Setting: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
same on all wireless devices in the same wireless LAN.
46
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 47

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 7 Station Mode: Security Setting: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Encryption Type The encryption mechanisms used for WPA/WPA2 and WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK are
Pre-Shared Key Type a pre-shared key (same as the AP or peer device) of between 8 and 63
Back Click Back to go to the Site Survey screen to select and connect to another
Next Click Next to confirm your selections and advance to the Confirm New Settings
Exit Click Exit to return to the Site Survey screen without saving.
4.3.1.3 WPA/WPA2
Figure 27 Station Mode: Security Setting: WPA/WPA2
Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
the same. The only difference between the two is that WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK uses
a simple common password, instead of user-specific credentials.
Select the encryption type (TKIP or AES) for data encryption.
Refer to Section 3.2.3.3 on page 36 for more information.
case-sensitive ASCII characters (including spaces and symbols) or 64
hexadecimal characters.
network.
screen. Refer to Section 4.3.2 on page 49.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 Station Mode: Security Setting: WPA/WPA2
LABEL DESCRIPTION
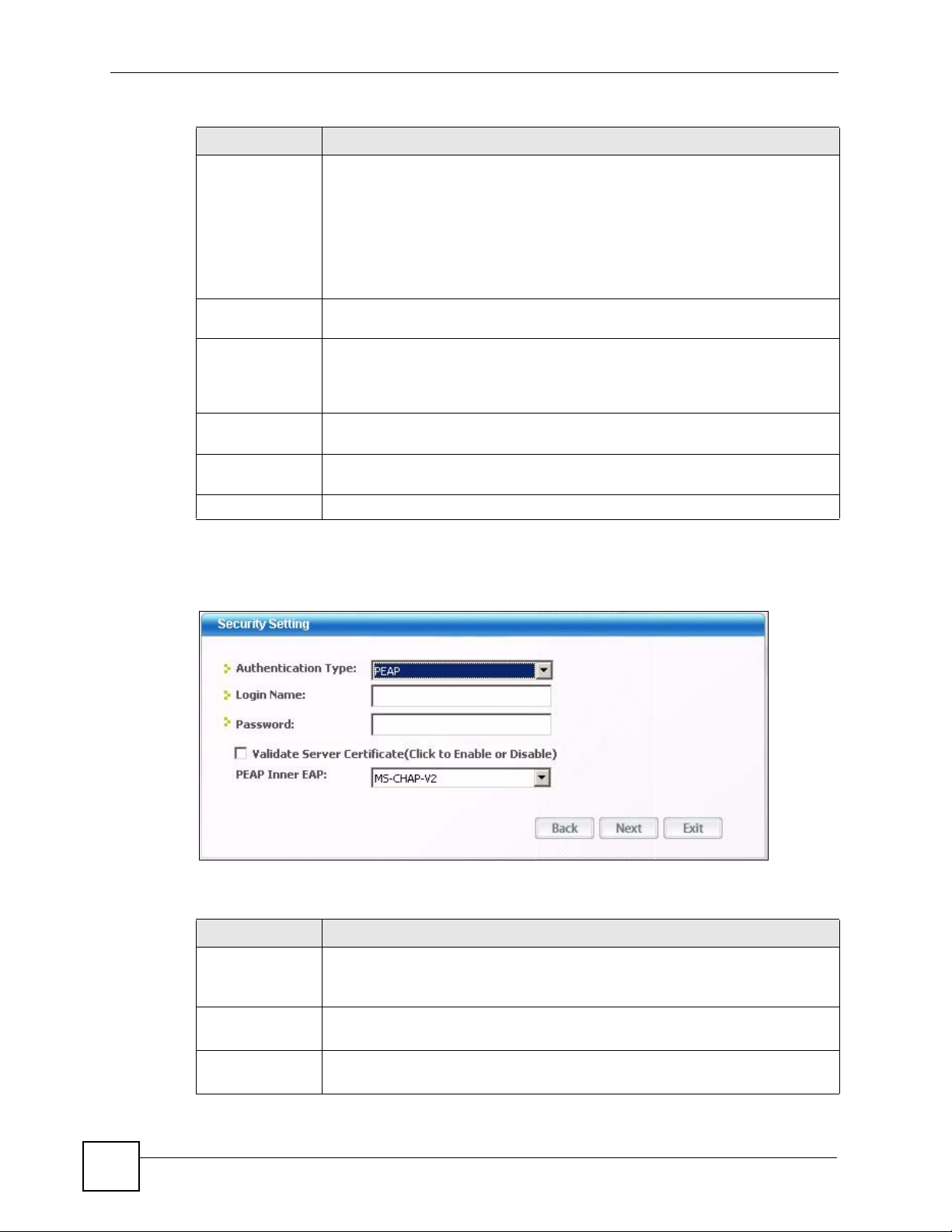
Encryption Type The encryption mechanisms used for WPA/WPA2 and WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK are
Authentication
Type
Login Name Enter a user name.
Password This field is not available when you select TLS in the Authentication Type field.
G-320H User’s Guide
the same. The only difference between the two is that WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK uses
a simple common password, instead of user-specific credentials.
Select the encryption type (TKIP or AES) for data encryption.
Refer to Section 3.2.3.3 on page 36 for more information.
The type of authentication you use depends on the RADIUS server or AP.
Select an authentication method from the drop down list. Options are TLS and
PEAP.
This is the user name that you or an administrator set up on a RADIUS server.
Enter the password associated with the user name above.
47
Page 48
Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Table 8 Station Mode: Security Setting: WPA/WPA2
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Certificate This field is only available when you select TLS in the Authentication Type field.
Select a certificate used by the authentication server to authenticate the G-320H.
Note: You must first have a wired connection to a network and
obtain the certificate(s) from a certificate authority (CA).
Consult your network administrator for more
information.
Validate Server
Certificate
PEAP Inner EAP This field is only available when you select PEAP in the Authentication Type
Back Click Back to go to the Site Survey screen to select and connect to another
Next Click Next to confirm your selections and advance to the Confirm New Settings
Exit Click Exit to return to the Site Survey screen without saving.
Select the check box to check the certificate of the authentication server.
field.
The PEAP method used by the RADIUS server or AP for client authentication is
MS CHAP v2.
network.
screen. Refer to Section 4.3.2 on page 49.
4.3.1.4 IEEE 802.1x
Configure IEEE 802.1x security with various authentication methods in this screen.
Figure 28 Station Mode: Security Setting: IEEE 802.1x
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 9 Station Mode: Security Setting: IEEE 802.1x
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Authentication
Type
Login Name Enter a user name.
Password This field is not available when you select TLS in the Authentication Type field.
The type of authentication you use depends on the RADIUS server or AP.
Select an authentication method from the drop down list. Options are TLS and
PEAP.
This is the user name that you or an administrator set up on a RADIUS server.
Enter the password associated with the user name above.
48
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 49

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Table 9 Station Mode: Security Setting: IEEE 802.1x
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Certificate This field is only available when you select TLS in the Authentication Type field.
Select a certificate used by the authentication server to authenticate the G-320H.
Note: You must first have a wired connection to a network and
obtain the certificate(s) from a certificate authority (CA).
Consult your network administrator for more
information.
Validate Server
Certificate
PEAP Inner EAP This field is only available when you select PEAP in the Authentication Type
Back Click Back to go to the Site Survey screen to select and connect to another
Next Click Next to confirm your selections and advance to the Confirm New Settings
Exit Click Exit to return to the Site Survey screen without saving.
Select the check box to check the certificate of the authentication server.
field.
The PEAP method used by the RADIUS server or AP for client authentication is
MS CHAP v2.
network.
screen. Refer to Section 4.3.2 on page 49.
4.3.2 Confirm New Settings
Use this screen to confirm and save the security settings.
Figure 29 Station Mode: Confirm New Settings
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 10 Station Mode: Confirm New Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Network(SSID) This field displays the SSID previously entered.
Network Type This field displays the network type (Infrastructure or Ad-Hoc) of the wireless
device.
Security This field shows whether data encryption is active (WEP, WPA-PSK, WPA,
802.1x, WPA2, WPA2-PSK) or inactive (Disabled).
Channel This field displays the channel number used by the profile.
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
G-320H User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Table 10 Station Mode: Confirm New Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Save Click Save to save the changes back to the G-320H and display the Link Info
screen.
Exit Click Exit to discard changes and return to the Site Survey screen.
4.4 The Profile Screen
A profile is a set of wireless parameters that you need to connect to a wireless network. With a
profile activated, each time you start the G-320H, it automatically scans for the specific SSID
and joins that network with the pre-defined wireless security settings. If the specified network
is not available, the G-320H cannot connect to a network.
If you do not configure and activate a profile, each time you start the G-320H, the G-320H
uses the default profile to connect to any available network with security disabled.
The default profile is a profile that allows you to connect to any SSID without security.
Click the Profile tab in the ZyXEL utility program to display the Profile screen as shown next.
The profile function allows you to save the wireless network settings in this screen, or use one
of the pre-configured network profiles.
Figure 30 Station Mode: Profile
50
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 51

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Tabl e 11 Station Mode: Profile
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Profile List Click a column heading to sort the entries.
denotes that the wireless device is in infrastructure mode and the wireless
,
,
or
Profile Name This is the name of the pre-configured profile.
SSID This is the SSID of the wireless network to which the selected profile associates.
Frequency This is the wireless LAN mode of the wireless network to which the selected profile
associates.
Connect To use and activate a previously saved network profile, select a pre-configured
profile name in the table and click Connect.
Add To add a new profile into the table, click Add.
Delete To delete an existing wireless network configuration, select a profile in the table
and click Delete.
Edit To edit an existing wireless network configuration, select a profile in the table and
click Edit.
Profile Info The following fields display detail information of the selected profile in the Profile
List table.
Network Type This field displays the network type (Infrastructure or Ad-Hoc) of the profile.
SSID This field displays the SSID (Service Set IDentifier) of the profile.
Frequency This field displays the wireless LAN mode of the profile.
Channel This field displays the channel number used by the profile.
Security This field shows whether data encryption is activated (WEP, WPA-PSK, WPA,
802.1x, WPA2, WPA2-PSK) or inactive (Disable).
Transfer Rate This field displays the transmission speed of the selected profile in megabits per
second (Mbps).
security is activated.
denotes that the wireless device is in infrastructure mode but the wireless
security is deactivated.
denotes that the wireless device is in Ad-Hoc mode and the wireless
security is activated.
denotes that the wireless device is in Ad-Hoc mode but the wireless
security is deactivated.
4.4.1 Adding a New Profile
Follow the steps below to add a new profile.
1 Click Add in the Profile screen. An Add New Profile screen displays as shown next.
Click Next to continue.
G-320H User’s Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Figure 31 Station Mode: Profile: Add a New Profile
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 Station Mode: Profile: Add a New Profile
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add New Profile
Profile Name Enter a descriptive name in this field.
SSID Select an available wireless device in the Scan Info table and click Select, or
enter the SSID of the wireless device to which you want to associate in this field
manually.
Network Type Select Infrastructure to associate to an AP. Select Ad-Hoc to associate to a peer
computer.
Next Click Next to go to the next screen.
Exit Click Exit to go back to the previous screen without saving.
Scan Info This table displays the information of the available wireless networks within the
transmission range.
denotes that the wireless device is in infrastructure mode and the wireless
,
,
or
SSID This field displays the SSID (Service Set IDentifier) of each AP or peer device.
Scan Click Scan to search for available wireless devices within transmission range.
Select Select an available wireless device in the table and click Select to add it to this
profile.
Whenever you activate this profile, the G-320H associates to the selected wireless
network only.
security is activated.
denotes that the wireless device is in infrastructure mode but the wireless
security is deactivated.
denotes that the wireless device is in Ad-Hoc mode and the wireless
security is activated.
denotes that the wireless device is in Ad-Hoc mode but the wireless
security is deactivated.
52
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 53

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
2 If you select the Infrastructure network type in the previous screen, skip to step 3. If
you select the Ad-Hoc network type in the previous screen, a screen displays as follows.
Select a channel number and click Next to continue.
" To associate to an ad-hoc network, you must use the same channel as the peer
computer.
Figure 32 Station Mode: Profile: Select a Channel
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 Station Mode: Profile: Select a Channel
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Settings
Channel Select a channel number from the drop-down list box. To associate with an ad-hoc
Wireless Mode This displays b+g and allows the G-320H to connect to either an IEEE 802.11g or
3 If you select Infrastructure network type in the first screen, select WEP, WPA-PSK,
WPA, WPA2-PSK, WPA2 or 802.1x from the drop-down list box to enable data
encryption. If you select Ad-Hoc network type in the first screen, you can only use WEP
encryption method. Otherwise, select Disabled to allow the G-320H to communicate
with the access points or other peer wireless computers without any data encryption and
skip to step 5.
G-320H User’s Guide
network, you must use the same channel as the peer computer.
IEEE 802.11b wireless device.
53
Page 54

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Figure 33 Station Mode: Profile: Security Settings
4 The screen varies depending on the encryption method you selected in the previous
screen. The settings must be exactly the same on the APs or other peer wireless
computers as they are on the G-320H. Refer to Section 4.3.1 on page 45 for detailed
information on wireless security configuration.
Figure 34 Station Mode: Profile: Security Settings
5 This read-only screen shows a summary of the new profile settings. Verify that the
settings are correct. Click Save to save and go to the next screen. Click Back to return to
the previous screen. Otherwise, click Exit to go back to the Profile screen without
saving.
54
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 55

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Figure 35 Station Mode: Profile: Confirm New Settings
6 To use this network profile, click the Activate Now button. Otherwise, click the
Activate Later button. You can activate only one profile at a time.
" Once you activate a profile, the ZyXEL utility will use that profile the next time it
is started.
Figure 36 Station Mode: Profile: Activate the Profile
4.5 The Adapter Screen
To set the advanced features on the G-320H, click the Adapter tab.
G-320H User’s Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Figure 37 Station Mode: Adapter
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 Station Mode: Adapter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Adapter Setting
Transfer Rate In most networking scenarios, the factory default Fully Auto setting is the most
efficient and allows your G-320H to operate at the highest possible transmission
(data) rate.
If you want to select a specific transmission rate, select one that the AP or peer
wireless device supports.
Preamble Type Preamble is used to signal that data is coming to the receiver. Select the preamble
type that the AP uses.
Short Preamble increases performance as less time sending preamble means
more time for sending data. All IEEE 802.11b/g compliant wireless adapters
support Long Preamble, but not all support short preamble.
Select Auto to have the G-320H automatically use short preamble when all
access point or wireless stations support it; otherwise the G-320H uses long
preamble.
Note: The G-320H and the access point or wireless stations
MUST use the same preamble mode in order to
communicate.
Power Saving
Mode
WMM QoS WMM (Wi-Fi MultiMedia) QoS (Quality of Service) allows you to prioritize wireless
Select Enabled to save power (especially for notebook computers). This forces
the G-320H to go to sleep mode when it is not transmitting data.
When you select Disabled, the G-320H will never go to sleep mode.
traffic according to the delivery requirements of individual services. To do this, you
must enable WMM QoS on both the AP and wireless clients.
Select this check box to enable WMM QoS on the G-320H.
56
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 57

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
Table 14 Station Mode: Adapter (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
OTIST (OneTouch Intelligent
Security
Technology)
Setup Key Enter the same setup key (up to eight printable characters) as the ZyXEL AP or
Select this check box to enable OTIST.
wireless router to which you want to associate. The default OTIST setup key is
"01234567".
Note: If you change the OTIST setup key on the ZyXEL AP or
wireless router, you must also make the same change
here.
Start Click Start to encrypt the wireless security data using the setup key and have the
ZyXEL AP or wireless router set your G-320H to use the same wireless settings as
the ZyXEL AP or wireless router. You must also activate and start OTIST on the
ZyXEL AP or wireless router all within three minutes. See Section 3.3 on page 36
for more information.
Save Click Save to save the changes to the G-320H and return to the Link Info screen.
G-320H User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 4 Wireless Station Mode Configuration
58
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 59
CHAPTER 5
Access Point Mode
Configuration
This chapter shows you how to configure your G-320H in access point mode.
5.1 Access Point Mode Introduction
To use your G-320H as an Access Point (AP), select AP Mode in any utility screen (refer to
Section 1.2.3 on page 21).
In access point mode, your G-320H allows you to set up your wireless networks without using
a dedicated AP.
5.1.1 ZyXEL Utility Screen Summary
This section describes the ZyXEL utility screens when the G-320H is in AP mode.
Figure 38 ZyXEL Utility Menu Summary: AP Mode
The following table describes the menus.
Table 15 ZyXEL Utility Menu Summary: AP Mode
TAB DESCRIPTION
AP Mode
Link Info Use this screen to see your current connection status, configuration and data rate
statistics.
Configuration Use this screen to configure wireless LAN settings.
MAC Filter Use this screen to configure which computer(s) you want to access the wireless
LAN through the G-320H.
5.1.2 Additional Setup Requirements
To bridge your wired and wireless network using the G-320H, the following requirements
must be met:
G-320H User’s Guide
59
Page 60

Chapter 5 Access Point Mode Configuration
1 The G-320H must be installed on a computer connected to the wired network.
2 Either configure network sharing (refer to Appendix B on page 66 for an example) or
bridge the two interfaces (wireless and wired) on the computer.
3 Set the wireless station’s IP address to be dynamic if you want the wireless stations to
access the wired network or the Internet through the G-320H. Refer to Appendix E on
page 97 for how to configure your computer’s IP address.
5.2 The Link Info Screen
Select the AP Mode check box and wait for about five seconds to display the screen as shown.
Figure 39 Access Point Mode: Link Info
60
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 16 Access Point Mode: Link Info
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status
SSID This field displays the name that identifies your G-320H in the wireless LAN
network.
Current Channel This field displays the radio channel the G-320H is currently using.
Transmission
Rate
Security This field shows whether data encryption is activated (WEP) or inactive
MAC This field displays the MAC address of the G-320H.
Output Power This field shows the strength of the G-320H’s antenna gain or transmission power.
Association List This table lists up to 16 wireless clients that are currently connected to the G-
This field displays the current transmission rate of the G-320H in megabits per
second (Mbps).
(Disabled).
320H.
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 61

Table 16 Access Point Mode: Link Info (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
or denotes a wireless client without WEP security.
denotes a wireless client with WEP security enabled.
MAC Address This field displays the MAC addresses of a wireless client that is currently
connected to the G-320H.
Refresh Click Refresh to update this screen.
5.3 The Configuration Screen
Click Configuration in the ZyXEL utility screen to display the screen as shown.
Figure 40 Access Point Mode: Configuration
Chapter 5 Access Point Mode Configuration
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17 Access Point Mode: Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Settings
SSID The SSID identifies the wireless network to which a wireless station is associated.
Hide SSID Select this check box to hide the SSID so an intruder cannot obtain the SSID
Channel Set the operating frequency/channel depending on your geographical region.
G-320H User’s Guide
Wireless stations associating to the access point (the G-320H) must have the
same SSID.
Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable 7-bit ASCII characters) for the
wireless LAN.
through scanning using a site survey tool.
61
Page 62

Chapter 5 Access Point Mode Configuration
Table 17 Access Point Mode: Configuration (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Output Power Set this field if you need to conserve power consumption (especially for notebook
computers). This control changes the strength of the G-320H’s antenna gain or
transmission power. Antenna gain, measured in dBm (decibel relative units
compared to milliwatts), is the increase in coverage. Higher antenna gain
improves the range of the signal for better communications.
Select High to set the G-320H’s antenna to transmit at 17-dBm.
Select Medium-High to set the G-320H’s antenna to transmit at 15-dBm.
Select Medium-Low to set the G-320H’s antenna to transmit at 13-dBm.
Select Low to set the G-320H’s antenna to transmit at 11-dBm. This allows for the
least power consumption.
Security Settings
WEP Select 64 Bits, 128 Bits or 256 Bits to activate WEP encryption and then fill in the
related fields.
Select Disable to deactivate the WEP encryption.
Authentication
Type
Pass Phrase When you select the radio button, enter a passphrase of up to 63 case-sensitive
Transmit Key Select a default WEP key to use for data encryption. The key displays in the field
Key x (where x is
a number
between 1 and 4)
Select an authentication method. Choices are Auto, Shared Key and Open
System.
Refer to Section 3.2.3.1.2 on page 35 for more information.
printable characters. As you enter the passphrase, the G-320H automatically
generates four different WEP key and displays it in the key field below. Refer to
Section 3.2.3.1 on page 35 for more information.
At the time of writing, you cannot use passphrase to generate 256-bit WEP keys.
below.
Select this option if you want to manually enter the WEP keys.
Enter the WEP key in the field provided.
If you select 64 Bits in the WEP field.
Enter either 10 hexadecimal digits in the range of “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” (for
example, 11AA22BB33) for HEX key type
or
Enter 5 ASCII characters (case sensitive) ranging from “a-z”, “A-Z” and “0-9”
(for example, MyKey) for ASCII key type.
If you select 128 Bits in the WEP field,
Enter either 26 hexadecimal digits in the range of “A-F”, “a-f” and “0-9” (for
example, 00112233445566778899AABBCC) for HEX key type
or
Enter 13 ASCII characters (case sensitive) ranging from “a-z”, “A-Z” and “0-9”
(for example, MyKey12345678) for ASCII key type.
If you select 256 Bits in the WEP field,
Enter either 58 hexadecimal digits in the range of "A-F", "a-f" and "0-9" (for
example,
0000111122223333444455556666777788889999AAAABBBBCCCC000011)
for HEX key type
or
Enter 29 ASCII characters (case sensitive) ranging from "a-z", "A-Z" and "0-9"
(for example , MyKey 111122 223333444455556678) for ASCII key type.
62
Note: The values for the WEP keys must be set up exactly the
same on all wireless devices in the same wireless LAN.
Note: ASCII WEP keys are case sensitive.
Save Click Save to save the changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 63

5.4 The MAC Filter Screen
The MAC Filter screen allows you to configure the G-320H to give exclusive access to
(Accept) devices or exclude devices from (Reject) connecting to the G-320H. The MAC
address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of hexadecimal characters, for
example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. You need to know the MAC address of the device(s) to
configure this screen. See Section 3.2.2 on page 34 for more information.
Figure 41 Access Point Mode: MAC Filter
Chapter 5 Access Point Mode Configuration
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18 Access Point Mode: MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Filter Type Define the filter action for the list of MAC addresses in the MAC address filter
Filter MAC
Address 1-16
Save Click Save to save the changes back to the G-320H.
Cancel Click Cancel to discard the changes.
table.
Select Disable to deactivate the MAC filter feature.
Select Reject to block access to the G-320H, MAC addresses not listed will be
allowed to access the G-320H.
Select Accept to permit access to the G-320H, MAC addresses not listed will be
denied access to the G-320H.
Specify the MAC address(es) of the wireless station(s) that is allowed or denied
association to the G-320H.
Enter six pairs of hexadecimal digits (separated by colons) in the range of “A-F”,
“a-f” and “0-9” (for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02).
If you enter an invalid MAC address, once you click Save to save the values, a
warning screen will be displayed.
G-320H User’s Guide
63
Page 64

Chapter 5 Access Point Mode Configuration
64
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 65

CHAPTER 6
Maintenance
This chapter describes how to uninstall or upgrade the ZyXEL utility.
6.1 The About Screen
The About screen displays driver and utility version numbers of the G-320H. To display the
screen as shown below, click the about ( ) button.
Figure 42 About
The following table describes the read-only fields in this screen.
Table 19 About
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Driver version This field displays the version number of the G-320H driver.
Utility version This field displays the version number of the ZyXEL utility.
6.2 Uninstalling the ZyXEL Utility
Follow the steps below to remove (or uninstall) the ZyXEL utility from your computer.
1 Click Start, (All) Programs, ZyXEL G-320H Utility, Uninstall ZyXEL G-320H
Software.
2 When prompted, click OK or Yes to remove the driver and the utility software.
G-320H User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 6 Maintenance
Figure 43 Uninstall: Confirm
3 Click Finish to complete uninstalling the software and restart the computer when
prompted.
Figure 44 Uninstall: Finish
6.3 Upgrading the ZyXEL Utility
" Before you uninstall the ZyXEL utility, take note of your current wireless
configurations.
To perform the upgrade, follow the steps below.
1 Download the latest version of the utility from the ZyXEL web site and save the file on
your computer.
2 Follow the steps in Section 6.2 on page 65 to remove the current ZyXEL utility from
your computer.
3 Restart your computer when prompted.
4 Disconnect the G-320H from your computer.
66
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 67

Chapter 6 Maintenance
5 Double-click on the setup program for the new utility to start the ZyXEL utility
installation.
6 Insert the G-320H and check the version numbers in the About screen to make sure the
new utility is installed properly.
G-320H User’s Guide
67
Page 68

Chapter 6 Maintenance
68
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 69

CHAPTER 7
Troubleshooting
This chapter offers some suggestions to solve problems you might encounter.
V The ZyXEL utility icon does not display.
1 If you install the Funk Odyssey Client software on the computer, uninstall (remove) both
the Funk Odyssey Client software and ZyXEL utility, and then install the ZyXEL utility
again after restarting the computer.
V I Cannot start the ZyXEL utility.
1 Make sure the G-320H is properly inserted and the LED(s) is on. Refer to the Section
1.3.1 on page 22 for the LED descriptions.
2 Use the Device Manager to check for possible hardware conflicts. Click Start, Settings,
Control Panel, System, Hardware and Device Manager. Verify the status of the G-
320H under Network Adapter. (Steps may vary depending on the version of Windows)
3 Install the G-320H in another computer.
4 If the error persists, you may have a hardware problem. In this case, you should contact
your local vendor.
V When using the Windows XP configuration tool, cannot scan for or connect to
any access points.
1 The G-320H might still be operating in access point mode. This results when you set the
G-320H to operate in access point mode using the ZyXEL utility, close the ZyXEL
utility and then use the Windows XP configuration tool.
Before you use the Windows XP configuration tool, make sure you set the G-320H to
operate in station mode before you close and exit the ZyXEL utility.
G-320H User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
V The link quality and/or signal strength is poor all the time.
1 Search and connect to another AP with a better link quality using the Site Survey
screen.
2 Move your computer closer to the AP or the peer computer(s) within the transmission
range.
3 There may be too much radio interference (for example microwave or another AP using
the same channel) around your wireless network. Lower the output power of each AP.
4 Make sure there are not too many wireless stations connected to a wireless network.
V In wireless station mode, the computer with the G-320H installed cannot
communicate with the other computer(s).
In Infrastructure Mode
1 Make sure that the AP and the associated computers are turned on and working properly.
2 Make sure the G-320H computer and the associated AP use the same SSID.
3 Change the AP and the associated wireless clients to use another radio channel if
interference is high.
4 Make sure that the computer and the AP share the same security option and key. Verify
the settings in the Profile Security Setting screen.
5 If you are using WPA(2) or WPA(2)-PSK security, try changing your encryption type
from TKIP to AES or vice versa.
In Ad-Hoc (IBSS) Mode
1 Verify that the peer computer(s) is turned on.
2 Make sure the G-320H computer and the peer computer(s) are using the same SSID and
channel.
3 Make sure that the computer and the peer computer(s) share the same security settings.
4 Change the wireless clients to use another radio channel if interference is high.
V In access point mode, the wireless station(s) cannot associate to the G-320H.
1 Verify that the computer with the G-320H installed is turned on.
2 Make sure the wireless station(s) uses the same SSID as the G-320H.
3 Make sure the wireless station(s) uses the same security settings.
4 Verify that the wireless station(s) is not blocked in the MAC Filter screen.
70
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 71

APPENDIX A
Product Specifications
Table 20 Product Specifications
PHYSICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL
Product Name ZyXEL G-320H 802.11g Wireless High Power PCI Adapter
Interface 3.3V 32-bit PCI V2.2
Standards IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
Network Architectures Infrastructure
Ad-Hoc
Antenna One 5 dBi Detachable Antenna
Operating Temperature 0 ~ 50 degrees Centigrade
Storage Temperature -30 ~ 60 degrees Centigrade
Operating Humidity 20 ~ 95% (non-condensing)
Storage Humidity 20 ~ 95% (non-condensing)
Vol tage 3.3V
Weight 123 g
Dimension (W) 80 mm × (L) 120 mm × (H) 10 mm
RADIO SPECIFICATIONS
Media Access Protocol IEEE 802.11
Operating Frequencies IEEE 802.11b: 2.412~2.462GHz (North America and Taiwan)
Operating Channels IEEE 802.11b: 11 Channels (North America and Taiwan)
Data Rate IEEE 802.11b: 11, 5.5, 2, 1Mbps
Modulation IEEE 802311b: PBCC, Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (CCK, DQPSK,
Output Power (Average) IEEE 802.11b: 21+/-1.5 dBm at 11 Mbps CCK, QPSK, BPSK
RX Sensitivity 54 Mbps (OFDM): < -72 dBm
SOFTWARE SPECIFICATIONS
Device Drivers Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows XP 64-bit
G-320H User’s Guide
IEEE 802.11g: 2.412~2.462GHz (North America and Taiwan)
IEEE 802.11g: 11 Channels (North America and Taiwan)
IEEE 802.11g: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, 6 Mbps
DBPSK).
IEEE 802.11g: Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (64QAM,
16QAM, QPSK and BPSK)
IEEE 802.11g: 19+/-1.5 dBm at 54 Mbps OFDM
11 Mbps (CCK): < -85 dBm
71
Page 72

Appendix A Product Specifications
Table 20 Product Specifications (continued)
ZyXEL Utility ZyXEL Wireless Configuration Tool
Security 64/128/256-bit WEP
WPA/WPA-PSK/WPA2/WPA2-PSK
IEEE 802.1x
72
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 73

APPENDIX B
Access Point Mode Setup
Example
This example uses the network sharing feature in Windows 2000 to bridge the wired and
wireless network when you set the G-320H in access point (AP) mode.
Refer to Chapter 5 on page 59 for setup methods and requirements.
Steps may vary depending on your Windows version. You may need to install additional
software in Windows 98 Second Edition and Windows ME.
Configuring the Computer on Which You Install the G-320H
1 Refer to Section 1.2.3 on page 21 to set the G-320H to operate in AP mode.
2 Click Start, Settings, Network and Dial-up Connections (or click Start, Settings,
Control Panel and double-click Network and Dial-up Connections).
Figure 45 Windows 2000: Start
3 Right-click on the icon for your wired Ethernet adapter and click Properties.
G-320H User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Appendix B Access Point Mode Setup Example
Figure 46 Windows 2000: Network and Dial-up Connections
4 A Properties screen displays. Click the Sharing tab and select Enable Internet
Connection Sharing for this connection. Click OK.
Figure 47 Windows 2000: Network Properties
74
If there is more than one network adapter on the computer, select Enable Internet
Connection Sharing for this connection and select the network adapter to which you
want to share network access.
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 75

Appendix B Access Point Mode Setup Example
Figure 48 WIndows 2000: Network Properties: Select Network Adapter
5 A notice screen displays. Click Ye s .
Figure 49 Windows 2000: Local Network
Configuring the Wireless Station Computer
Refer to Appendix E on page 97 for more information on how to set up the wireless station
computer(s) IP address.
G-320H User’s Guide
75
Page 76

Appendix B Access Point Mode Setup Example
76
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 77

APPENDIX C
Management with Wireless Zero
Configuration
This appendix shows you how to manage your G-320H using the Windows XP wireless zero
configuration tool.
Be sure you have the Windows XP service pack 2 installed on your computer. Otherwise, you
should at least have the Windows XP service pack 1 already on your computer and download
the support patch for WPA from the Microsoft web site.
Windows XP SP2 screen shots are shown unless otherwise specified. Click the help icon ( )
in most screens, move the cursor to the item that you want the information about and click to
view the help.
Activating Wireless Zero Configuration
1 Click Start, Control Panel and double-click Network Connections.
2 Double-click on the icon for wireless network connection.
3 The status window displays as shown below. Click Properties.
Figure 50 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Network Connection Status
G-320H User’s Guide
77
Page 78

Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
Figure 51 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection Status
4 The Wireless Network Connection Properties screen displays. Click the Wireless
Networks tab.
Make sure the Use Windows to configure my wireless network settings check box is
selected.
Figure 52 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Network Connection Properties
78
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 79

Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
Figure 53 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection Properties
If you see the following screen, refer to article 871122 on the Microsoft web site for
information on starting WZC.
Figure 54 Windows XP SP2: WZC Not Available
Connecting to a Wireless Network
1 Double-click the network icon for wireless connections in the system tray to open the
Wireless Network Connection Status screen.
G-320H User’s Guide
79
Page 80
Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
Figure 55 Windows XP SP2: System Tray Icon
The type of the wireless network icon in Windows XP SP2 indicates the status of the G-320H.
Refer to the following table for details.
Table 21 Windows XP SP2: System Tray Icon
ICON DESCRIPTION
The G-320H is connected to a wireless network.
The G-320H is in the process of connecting to a wireless network.
The connection to a wireless network is limited because the network did not assign a
network address to the computer.
The G-320H is not connected to a wireless network.
2 Windows XP SP2: In the Wireless Network Connection Status screen, click View
Wireless Networks to open the Wireless Network Connection screen.
Figure 56 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection Status
80
Windows XP SP1: In the Wireless Network Connection Status screen, click
Properties and the Wireless Networks tab to open the Wireless Network Connection
Properties screen.
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 81
Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
Figure 57 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Network Connection Status
3 Windows XP SP2: Click Refresh network list to reload and search for available
wireless devices within transmission range. Select a wireless network in the list and click
Connect to join the selected wireless network.
Figure 58 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection
G-320H User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
The following table describes the icons in the wireless network list.
Table 22 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection
ICON DESCRIPTION
This denotes that wireless security is activated for the wireless network.
This denotes that this wireless network is your preferred network. Ordering your
preferred networks is important because the G-320H tries to associate to the preferred
network first in the order that you specify. Refer to the section on ordering the preferred
networks for detailed information.
This denotes the signal strength of the wireless network.
Move your cursor to the icon to see details on the signal strength.
Windows XP SP1: Click Refresh to reload and search for available wireless devices
within transmission range. Select a wireless network in the Available networks list,
click Configure and set the related fields to the same security settings as the associated
AP to add the selected network into the Preferred networks table. Click OK to join the
selected wireless network. Refer to the section on security settings (discussed later) for
more information.
Figure 59 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Network Connection Properties
82
4 4.Windows XP SP2: If the wireless security is activated for the selected wireless
network, the Wireless Network Connection screen displays. You must set the related
fields in the Wireless Network Connection screen to the same security settings as the
associated AP and click Connect. Refer to the section about security settings for more
information. Otherwise click Cancel and connect to another wireless network without
data encryption. If there is no security activated for the selected wireless network, a
warning screen appears. Click Connect Anyway if wireless security is not your concern.
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 83

Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
Figure 60 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection: WEP or WPA-PSK
Figure 61 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Network Connection: No Security
5 Verify that you have successfully connected to the selected network and check the
connection status in the wireless network list or the connection icon in the Preferred
networks or Available networks list.
The following table describes the connection icons.
Table 23 Windows XP: Wireless Networks
ICON DESCRIPTION
Security Settings
When you configure the G-320H to connect to a secure network but the security settings are
not yet enabled on the G-320H, you will see different screens according to the authentication
and encryption methods used by the selected network.
Association
Select a network in the Preferred networks list and click Properties to view or configure
security.
This denotes the wireless network is an available wireless network.
This denotes the G-320H is associated to the wireless network.
This denotes the wireless network is not available.
G-320H User’s Guide
83
Page 84

Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
Figure 62 Windows XP: Wireless (network) properties: Association
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 24 Windows XP: Wireless (network) properties: Association
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Network name
(SSID)
This field displays the SSID (Service Set IDentifier) of each wireless network.
Network
Authentication
Data Encryption This field automatically shows the encryption type (TKIP, WEP or Disable) used
Network Key Enter the pre-shared key or WEP key.
Confirm network
key
Key index
(advanced)
The key is
provided for me
automatically
This is a
computer-tocomputer (ad hoc)
network; wireless
access points are
not used
OK Click OK to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to leave this screen without saving any changes you may have
This field automatically shows the authentication method (Share, Open, WPA or
WPA-PSK) used by the selected network.
by the selected network.
The values for the keys must be set up exactly the same on all wireless devices in
the same wireless LAN.
Enter the key again for confirmation.
Select a default WEP key to use for data encryption.
This field is available only when the network use WEP encryption method and the
The key is provided for me automatically check box is not selected.
If this check box is selected, the wireless AP assigns the G-320H a key.
If this check box is selected, you are connecting to another computer directly.
made.
84
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 85

Authentication
Click the Authentication tab in the Wireless (network) properties screen to display the
screen shown next. The fields on this screen are grayed out when the network is in Ad-Hoc
mode or data encryption is disabled.
Figure 63 Windows XP: Wireless (network) properties: Authentication
Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 25 Windows XP: Wireless (network) properties: Authentication
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable IEEE
802.1x
authentication for
this network
EAP Type Select the type of EAP authentication. Options are Protected EAP (PEAP) and
Properties Click this button to open the properties screen and configure certificates. The
Authenticate as
computer when
computer
information is
available
Authenticate as
guest when user
or computer
information is
unavailable
OK Click OK to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to leave this screen without saving any changes you may have
This field displays whether the IEEE 802.1x authentication is active.
If the network authentication is set to Open in the previous screen, you can
choose to disable or enable this feature.
Smart Card or other Certificate.
screen varies depending on what you select in the EAP type field.
Select this check box to have the computer send its information to the network for
authentication when a user is not logged on.
Select this check box to have the computer access to the network as a guest when
a user is not logged on or computer information is not available.
made.
G-320H User’s Guide
85
Page 86

Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
Authentication Properties
Select an EAP authentication type in the Wireless (network) properties: Authentication
screen and click the Properties button to display the following screen.
Protected EAP Properties
Figure 64 Windows XP: Protected EAP Properties
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26 Windows XP: Protected EAP Properties
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Validate server
certificate
Connect to these
servers
Trusted Root
Certification
Authorities:
Select the check box to verify the certificate of the authentication server.
Select the check box and specify a domain in the field below to have your
computer connect to a server which resides only within this domain.
Select a trusted certification authority from the list below.
Note: You must first have a wired connection to a network and
obtain the certificate(s) from a certificate authority (CA).
Consult your network administrator for more
information.
Do not prompt
user to authorize
new server or
trusted
certification
authorities.
Select
Authentication
Method:
Enable Fast
Reconnect
Select this check box to verify a new authentication server or trusted CA without
prompting.
This field is available only if you installed the Windows XP server pack 2.
Select an authentication method from the drop-down list box and click Configure
to do settings.
Select the check box to automatically reconnect to the network (without reauthentication) if the wireless connection goes down.
86
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 87
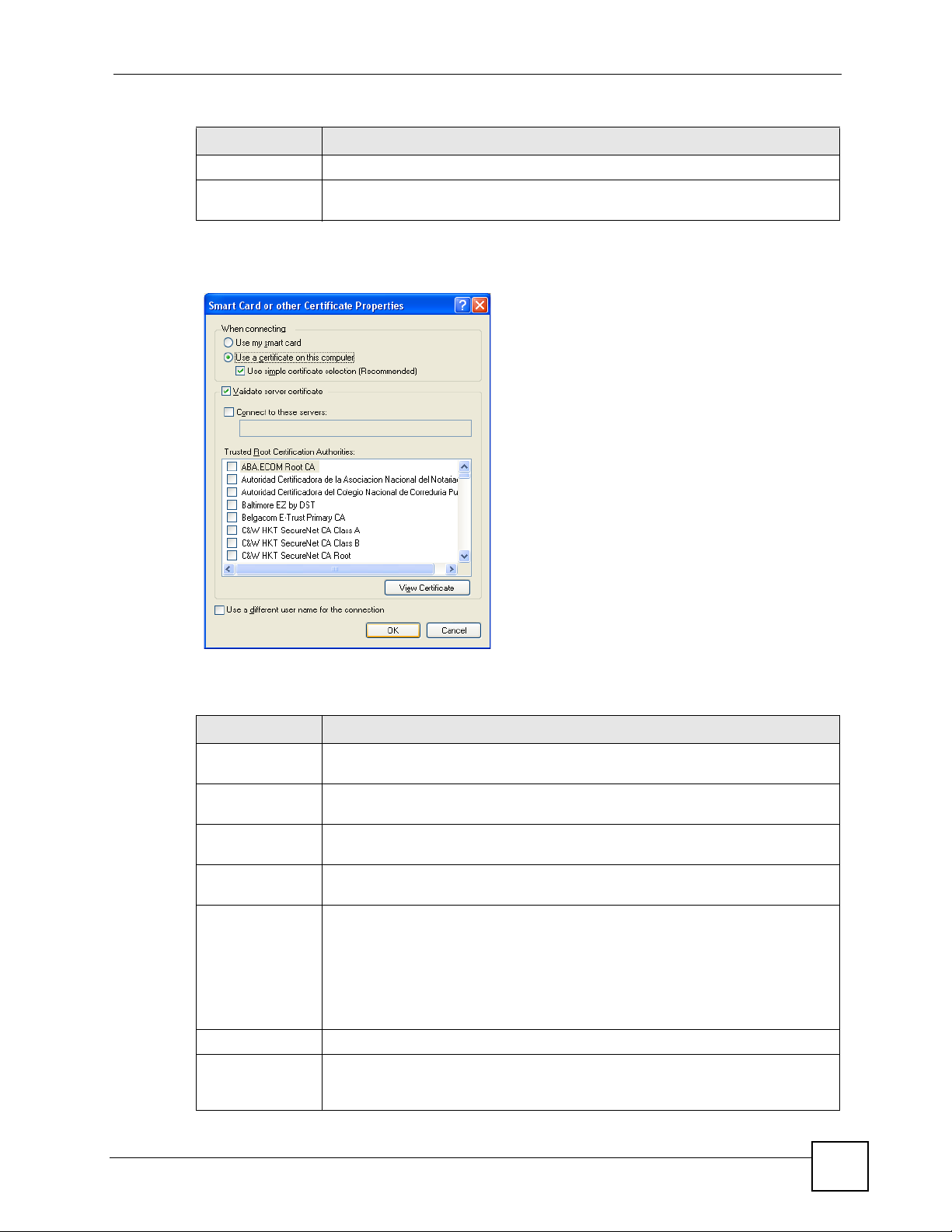
Table 26 Windows XP: Protected EAP Properties
LABEL DESCRIPTION
OK Click OK to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to leave this screen without saving any changes you may have
made.
Smart Card or other Certificate Properties
Figure 65 Windows XP: Smart Card or other Certificate Properties
Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 27 Windows XP: Smart Card or other Certificate Properties
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Use my smart
card
Use a certificate
on this computer
Validate server
certificate
Connect to these
servers
Trusted Root
Certification
Authorities:
Select this check box to use the smart card for authentication.
Select this check box to use a certificate on your computer for authentication.
Select the check box to check the certificate of the authentication server.
Select the check box and specify a domain in the field below to have your
computer connect to a server which resides only within this domain.
Select a trusted certification authority from the list below.
Note: You must first have a wired connection to a network and
obtain the certificate(s) from a certificate authority (CA).
Consult your network administrator for more
information.
View Certificate Click this button if you want to verify the selected certificate.
Use a different
user name for the
connection:
Select the check box to use a different user name when the user name in the
smart card or certificate is not the same as the user name in the domain that you
are logged on to.
G-320H User’s Guide
87
Page 88

Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
Table 27 Windows XP: Smart Card or other Certificate Properties
LABEL DESCRIPTION
OK Click OK to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to leave this screen without saving any changes you may have
made.
Ordering the Preferred Networks
Follow the steps below to manage your preferred networks.
1 Windows XP SP2: Click Change the order of preferred networks in the Wireless
Network Connection screen (see Figure 58 on page 81). The screen displays as shown.
Figure 66 Windows XP SP2: Wireless Networks: Preferred Networks
88
Windows XP SP1: In the Wireless Network Connection Status screen, click
Properties and the Wireless Networks tab to open the screen as shown.
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 89
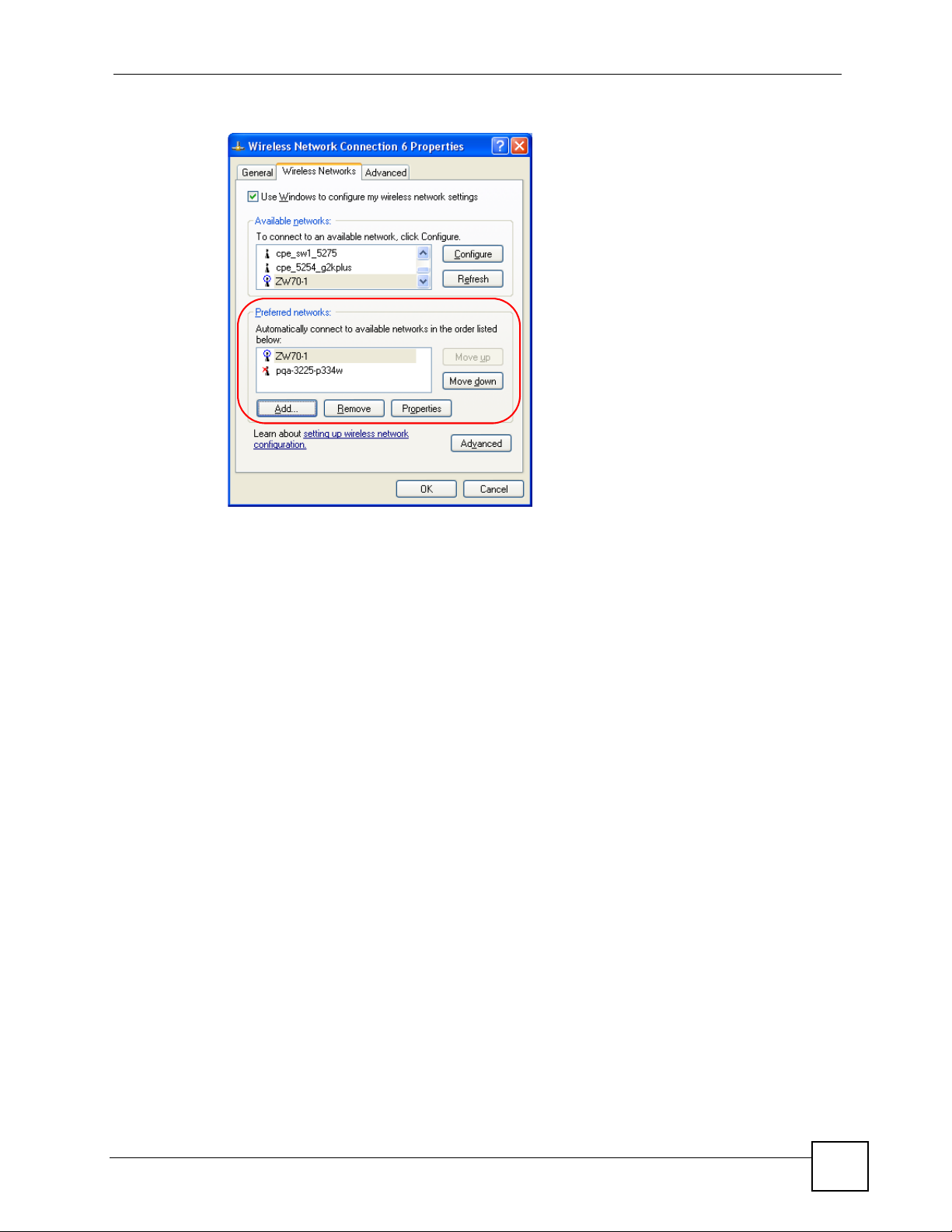
Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
Figure 67 Windows XP SP1: Wireless Networks: Preferred Networks
2 Whenever the G-320H tries to connect to a new network, the new network is added in
the Preferred networks table automatically. Select a network and click Move up or
Move down to change it's order, click Remove to delete it or click Properties to view
the security, authentication or connection information of the selected network. Click
Add to add a preferred network into the list manually.
G-320H User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Appendix C Management with Wireless Zero Configuration
90
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 91

APPENDIX D
Wireless Security
Types of EAP Authentication
This section discusses some popular authentication types: EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS,
PEAP and LEAP. Your wireless LAN device may not support all authentication types.
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) is an authentication protocol that runs on top of the
IEEE 802.1x transport mechanism in order to support multiple types of user authentication. By
using EAP to interact with an EAP-compatible RADIUS server, an access point helps a
wireless station and a RADIUS server perform authentication.
The type of authentication you use depends on the RADIUS server and an intermediary AP(s)
that supports IEEE 802.1x. .
For EAP-TLS authentication type, you must first have a wired connection to the network and
obtain the certificate(s) from a certificate authority (CA). A certificate (also called digital IDs)
can be used to authenticate users and a CA issues certificates and guarantees the identity of
each certificate owner.
EAP-MD5 (Message-Digest Algorithm 5)
MD5 authentication is the simplest one-way authentication method. The authentication server
sends a challenge to the wireless station. The wireless station ‘proves’ that it knows the
password by encrypting the password with the challenge and sends back the information.
Password is not sent in plain text.
However, MD5 authentication has some weaknesses. Since the authentication server needs to
get the plaintext passwords, the passwords must be stored. Thus someone other than the
authentication server may access the password file. In addition, it is possible to impersonate an
authentication server as MD5 authentication method does not perform mutual authentication.
Finally, MD5 authentication method does not support data encryption with dynamic session
key. You must configure WEP encryption keys for data encryption.
EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security)
With EAP-TLS, digital certifications are needed by both the server and the wireless stations
for mutual authentication. The server presents a certificate to the client. After validating the
identity of the server, the client sends a different certificate to the server. The exchange of
certificates is done in the open before a secured tunnel is created. This makes user identity
vulnerable to passive attacks. A digital certificate is an electronic ID card that authenticates the
sender’s identity. However, to implement EAP-TLS, you need a Certificate Authority (CA) to
handle certificates, which imposes a management overhead.
G-320H User’s Guide
91
Page 92

Appendix D Wireless Security
EAP-TTLS (Tunneled Transport Layer Service)
EAP-TTLS is an extension of the EAP-TLS authentication that uses certificates for only the
server-side authentications to establish a secure connection. Client authentication is then done
by sending username and password through the secure connection, thus client identity is
protected. For client authentication, EAP-TTLS supports EAP methods and legacy
authentication methods such as PAP, CHAP, MS-CHAP and MS-CHAP v2.
PEAP (Protected EAP)
Like EAP-TTLS, server-side certificate authentication is used to establish a secure connection,
then use simple username and password methods through the secured connection to
authenticate the clients, thus hiding client identity. However, PEAP only supports EAP
methods, such as EAP-MD5, EAP-MSCHAPv2 and EAP-GTC (EAP-Generic Token Card),
for client authentication. EAP-GTC is implemented only by Cisco.
LEAP
LEAP (Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol) is a Cisco implementation of IEEE
802.1x.
Dynamic WEP Key Exchange
The AP maps a unique key that is generated with the RADIUS server. This key expires when
the wireless connection times out, disconnects or reauthentication times out. A new WEP key
is generated each time reauthentication is performed.
If this feature is enabled, it is not necessary to configure a default encryption key in the
Wireless screen. You may still configure and store keys here, but they will not be used while
Dynamic WEP is enabled.
" EAP-MD5 cannot be used with Dynamic WEP Key Exchange
For added security, certificate-based authentications (EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS and PEAP) use
dynamic keys for data encryption. They are often deployed in corporate environments, but for
public deployment, a simple user name and password pair is more practical. The following
table is a comparison of the features of authentication types.
Table 28 Comparison of EAP Authentication Types
EAP-MD5 EAP-TLS EAP-TTLS PEAP LEAP
Mutual Authentication No Ye s Yes Yes Yes
Certificate – Client No Ye s Optional Optional No
Certificate – Server No Yes Ye s Yes No
Dynamic Key Exchange No Yes Ye s Yes Ye s
Credential Integrity None Strong Strong Strong Moderate
92
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 93

Table 28 Comparison of EAP Authentication Types
Deployment Difficulty Easy Hard Moderate Moderate Moderate
Client Identity Protection No No Yes Yes No
WPA and WPA2
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard. WPA2 (IEEE
802.11i) is a wireless security standard that defines stronger encryption, authentication and
key management than WPA.
Key differences between WPA(2) and WEP are improved data encryption and user
authentication.
If both an AP and the wireless clients support WPA2 and you have an external RADIUS
server, use WPA2 for stronger data encryption. If you don't have an external RADIUS server,
you should use WPA2-PSK (WPA2-Pre-Shared Key) that only requires a single (identical)
password entered into each access point, wireless gateway and wireless client. As long as the
passwords match, a wireless client will be granted access to a WLAN.
Appendix D Wireless Security
EAP-MD5 EAP-TLS EAP-TTLS PEAP LEAP
If the AP or the wireless clients do not support WPA2, just use WPA or WPA-PSK depending
on whether you have an external RADIUS server or not.
Select WEP only when the AP and/or wireless clients do not support WPA or WPA2. WEP is
less secure than WPA or WPA2.
Encryption
Both WPA and WPA2 improve data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
(TKIP), Message Integrity Check (MIC) and IEEE 802.1x. WPA and WPA2 use Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES) in the Counter mode with Cipher block chaining Message
authentication code Protocol (CCMP) to offer stronger encryption than TKIP.
TKIP uses 128-bit keys that are dynamically generated and distributed by the authentication
server. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a block cipher that uses a 256-bit
mathematical algorithm called Rijndael. They both include a per-packet key mixing function,
a Message Integrity Check (MIC) named Michael, an extended initialization vector (IV) with
sequencing rules, and a re-keying mechanism.
WPA and WPA2 regularly change and rotate the encryption keys so that the same encryption
key is never used twice.
The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that then sets up
a key hierarchy and management system, using the PMK to dynamically generate unique data
encryption keys to encrypt every data packet that is wirelessly communicated between the AP
and the wireless stations. This all happens in the background automatically.
The Message Integrity Check (MIC) is designed to prevent an attacker from capturing data
packets, altering them and resending them. The MIC provides a strong mathematical function
in which the receiver and the transmitter each compute and then compare the MIC. If they do
not match, it is assumed that the data has been tampered with and the packet is dropped.
G-320H User’s Guide
93
Page 94

Appendix D Wireless Security
By generating unique data encryption keys for every data packet and by creating an integrity
checking mechanism (MIC), with TKIP and AES it is more difficult to decrypt data on a Wi-Fi
network than WEP and difficult for an intruder to break into the network.
The encryption mechanisms used for WPA(2) and WPA(2)-PSK are the same. The only
difference between the two is that WPA(2)-PSK uses a simple common password, instead of
user-specific credentials. The common-password approach makes WPA(2)-PSK susceptible to
brute-force password-guessing attacks but it’s still an improvement over WEP as it employs a
consistent, single, alphanumeric password to derive a PMK which is used to generate unique
temporal encryption keys. This prevent all wireless devices sharing the same encryption keys.
(a weakness of WEP)
User Authentication
WPA and WPA2 apply IEEE 802.1x and Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to
authenticate wireless stations using an external RADIUS database. WPA2 reduces the number
of key exchange messages from six to four (CCMP 4-way handshake) and shortens the time
required to connect to a network. Other WPA2 authentication features that are different from
WPA include key caching and pre-authentication. These two features are optional and may not
be supported in all wireless devices.
Key caching allows a wireless client to store the PMK it derived through a sucessful
authentication with an AP. The wireless client uses the PMK when it tries to connect to the
same AP and does not need to go with the authentication process again.
Pre-authentication enables fast roaming by allowing the wireless client (already connecting to
an AP) to perform IEEE 802.1x authentication with another AP before connecting to it.
WPA(2)-PSK Application Example
A WPA(2)s-PSK application looks as follows.
1 First enter identical passwords into the AP and all wireless clients. The Pre-Shared Key
(PSK) must consist of between 8 and 63 ASCII characters or 64 hexadecimal characters
(including spaces and symbols).
2 The AP checks each client's password and (only) allows it to join the network if it
matches its password.
3 The AP and wireless clients use the pre-shared key to generate a common PMK.
4 The AP and wireless clients use the TKIP or AES encryption process to encrypt data
exchanged between them.
94
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 95

Figure 68 WPA-PSK Authentication
WPA(2) with RADIUS Application Example
You need the IP address of the RADIUS server, its port number (default is 1812), and the
RADIUS shared secret. A WPA(2) application example with an external RADIUS server
looks as follows. "A" is the RADIUS server. "DS" is the distribution system.
1 The AP passes the wireless client's authentication request to the RADIUS server.
2 The RADIUS server then checks the user's identification against its database and grants
or denies network access accordingly.
3 The RADIUS server distributes a Pairwise Master Key (PMK) key to the AP that then
sets up a key hierarchy and management system, using the pair-wise key to dynamically
generate unique data encryption keys to encrypt every data packet that is wirelessly
communicated between the AP and the wireless clients.
Appendix D Wireless Security
Figure 69 WPA(2) with RADIUS Application Example
G-320H User’s Guide
95
Page 96
Appendix D Wireless Security
Security Parameters Summary
Refer to this table to see what other security parameters you should configure for each
Authentication Method/ key management protocol type. MAC address filters are not
dependent on how you configure these security features.
Table 29 Wireless Security Relational Matrix
AUTHENTICATION
METHOD/ KEY
MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL
Open None No Disable
Open WEP No Enable with Dynamic WEP Key
Shared WEP No Enable with Dynamic WEP Key
WPA TKIP/AES No Enable
WPA-PSK TKIP/AES Ye s Disable
WPA2 TKIP/AES No Enable
WPA2-PSK TKIP/AES Ye s Disable
ENCRYPTIO
N METHOD
ENTER
MANUAL KEY
Yes Enable without Dynamic WEP Key
Yes Disable
Yes Enable without Dynamic WEP Key
Yes Disable
IEEE 802.1X
Enable without Dynamic WEP Key
96
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 97

APPENDIX E
Setting up Your Computer’s IP
Address
All computers must have a 10M or 100M Ethernet adapter card and TCP/IP installed.
Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP, Macintosh OS 7 and later operating systems and all
versions of UNIX/LINUX include the software components you need to install and use TCP/
IP on your computer. Windows 3.1 requires the purchase of a third-party TCP/IP application
package.
TCP/IP should already be installed on computers using Windows NT/2000/XP, Macintosh OS
7 and later operating systems.
After the appropriate TCP/IP components are installed, configure the TCP/IP settings in order
to "communicate" with your network.
Windows 95/98/Me
Click Start, Settings, Control Panel and double-click the Network icon to open the Network
window
G-320H User’s Guide
97
Page 98

Appendix E Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 70 WIndows 95/98/Me: Network: Configuration
Installing Components
The Network window Configuration tab displays a list of installed components. You need a
network adapter, the TCP/IP protocol and Client for Microsoft Networks.
If you need the adapter:
1 In the Network window, click Add.
2 Select Adapter and then click Add.
3 Select the manufacturer and model of your network adapter and then click OK.
If you need TCP/IP:
1 In the Network window, click Add.
2 Select Protocol and then click Add.
3 Select Microsoft from the list of manufacturers.
4 Select TCP/IP from the list of network protocols and then click OK.
If you need Client for Microsoft Networks:
1 Click Add.
2 Select Client and then click Add.
3 Select Microsoft from the list of manufacturers.
4 Select Client for Microsoft Networks from the list of network clients and then click
OK.
5 Restart your computer so the changes you made take effect.
98
G-320H User’s Guide
Page 99
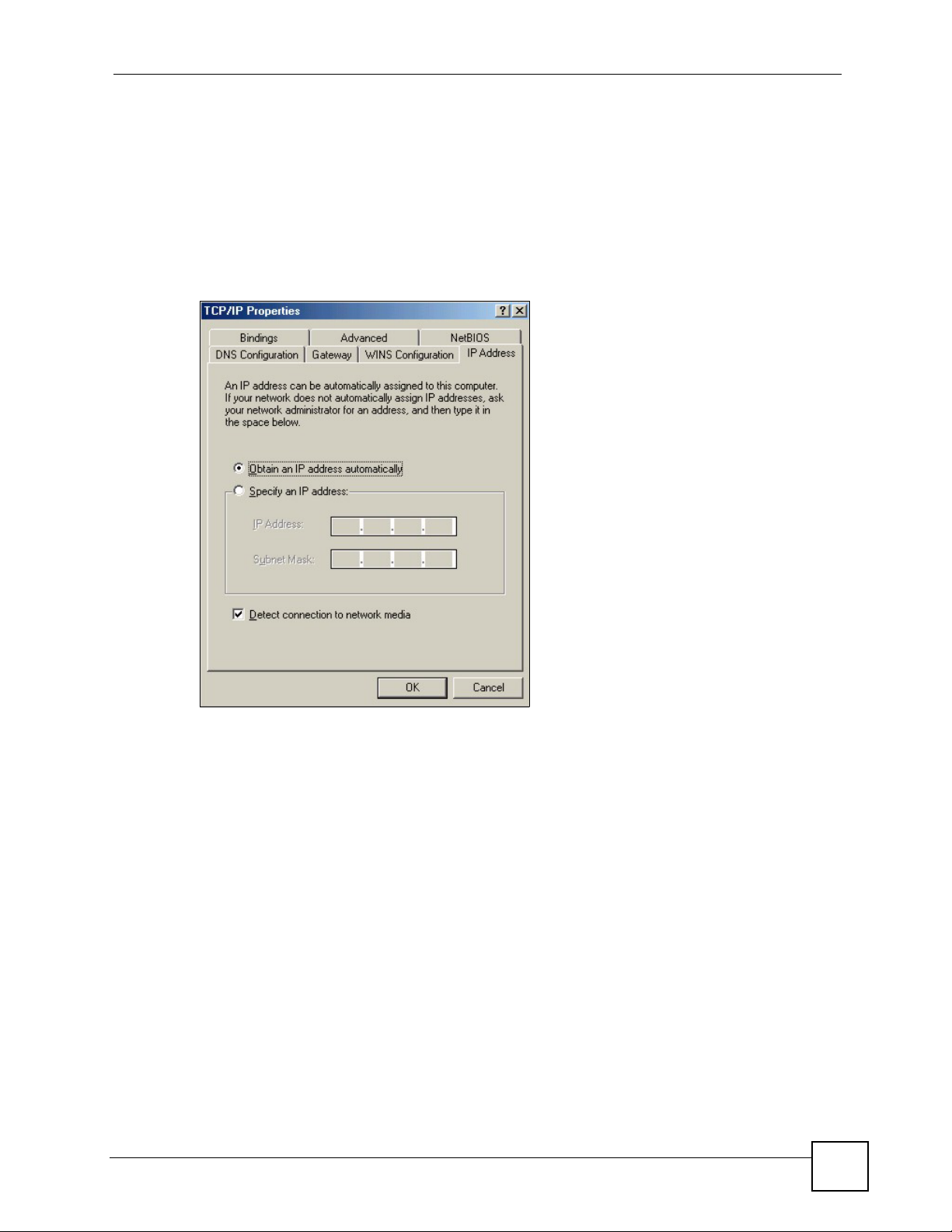
Configuring
Figure 71 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: IP Address
Appendix E Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
1 In the Network window Configuration tab, select your network adapter's TCP/IP entry
and click Properties
2 Click the IP Address tab.
• If your IP address is dynamic, select Obtain an IP address automatically.
• If you have a static IP address, select Specify an IP address and type your
information into the IP Address and Subnet Mask fields.
3 Click the DNS Configuration tab.
• If you do not know your DNS information, select Disable DNS.
• If you know your DNS information, select Enable DNS and type the information in
G-320H User’s Guide
the fields below (you may not need to fill them all in).
99
Page 100
Appendix E Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 72 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: DNS Configuration
4 Click the Gateway tab.
• If you do not know your gateway’s IP address, remove previously installed gateways.
• If you have a gateway IP address, type it in the New gateway field and click Add.
5 Click OK to save and close the TCP/IP Properties window.
6 Click OK to close the Network window. Insert the Windows CD if prompted.
7 Restart your computer when prompted.
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start and then Run.
2 In the Run window, type "winipcfg" and then click OK to open the IP Configuration
window.
3 Select your network adapter. You should see your computer's IP address, subnet mask
and default gateway.
Windows 2000/NT/XP
1 For Windows XP, click start, Control Panel. In Windows 2000/NT, click Start,
Settings, Control Panel.
100
G-320H User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...