Page 1
12.1 Overview
S2
S1
R1
R1
R1
MOD
VoIP
Data
PVC0
PVC2
PVC1
This chapter describes how to configure the port binding settings.
Port binding allows you to aggregate port connections into logical groups. You may bind WAN PVCs
to Ethernet ports and WLANs to specify how traffic is forwarded. Different ATM QoS settings can be
specified for each WAN PVC to meet bandwidth requirements for the type of traffic to be
transferred.
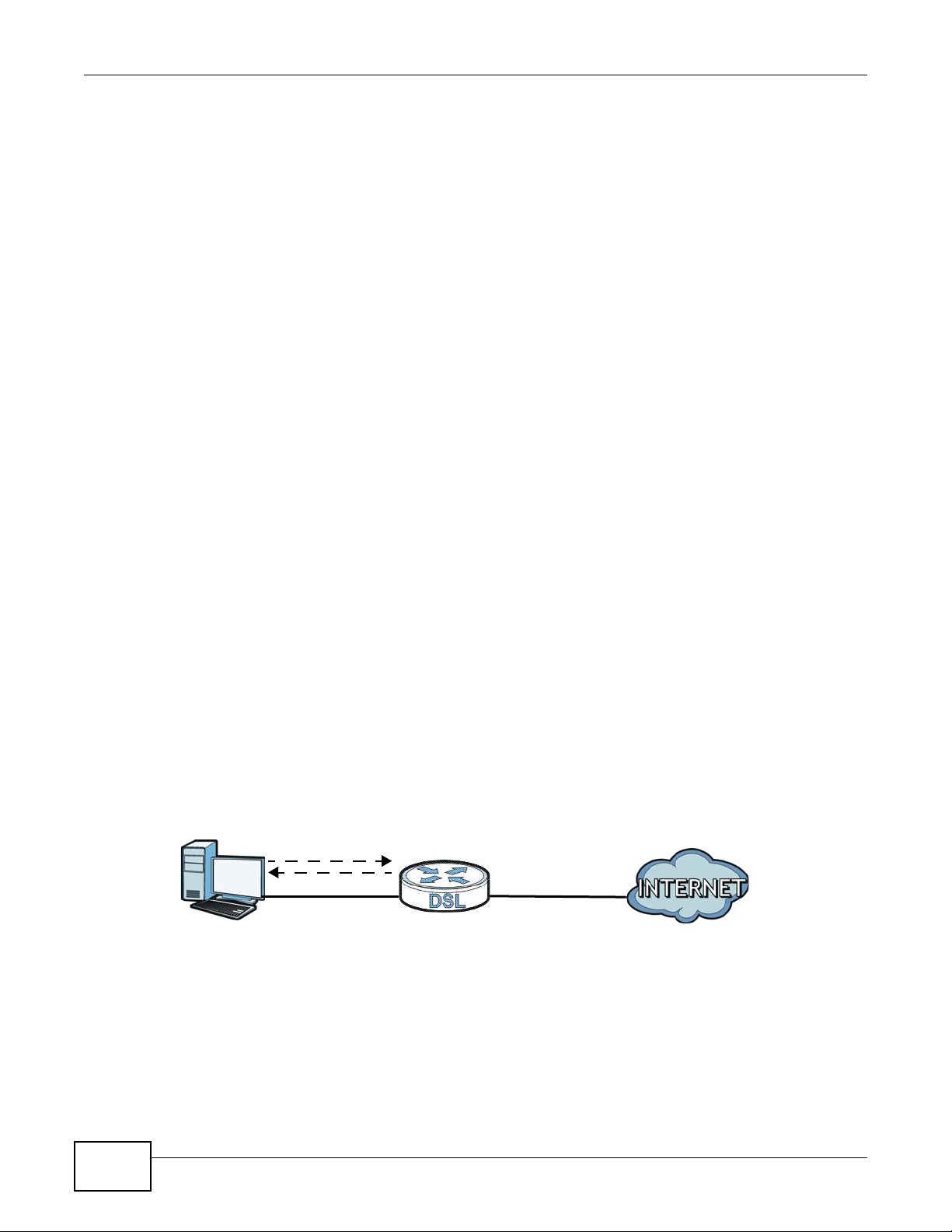
For example, three port binding groups could be created on the device (R1) for three different WAN
PVC connections. The first PVC (PVC0) is for non time-sensitive data traffic. The second and third
PVCs (PVC1 and PVC2) are for time sensitive Media-On-Demand (MOD) video traffic and VoIP
traffic, respectively.
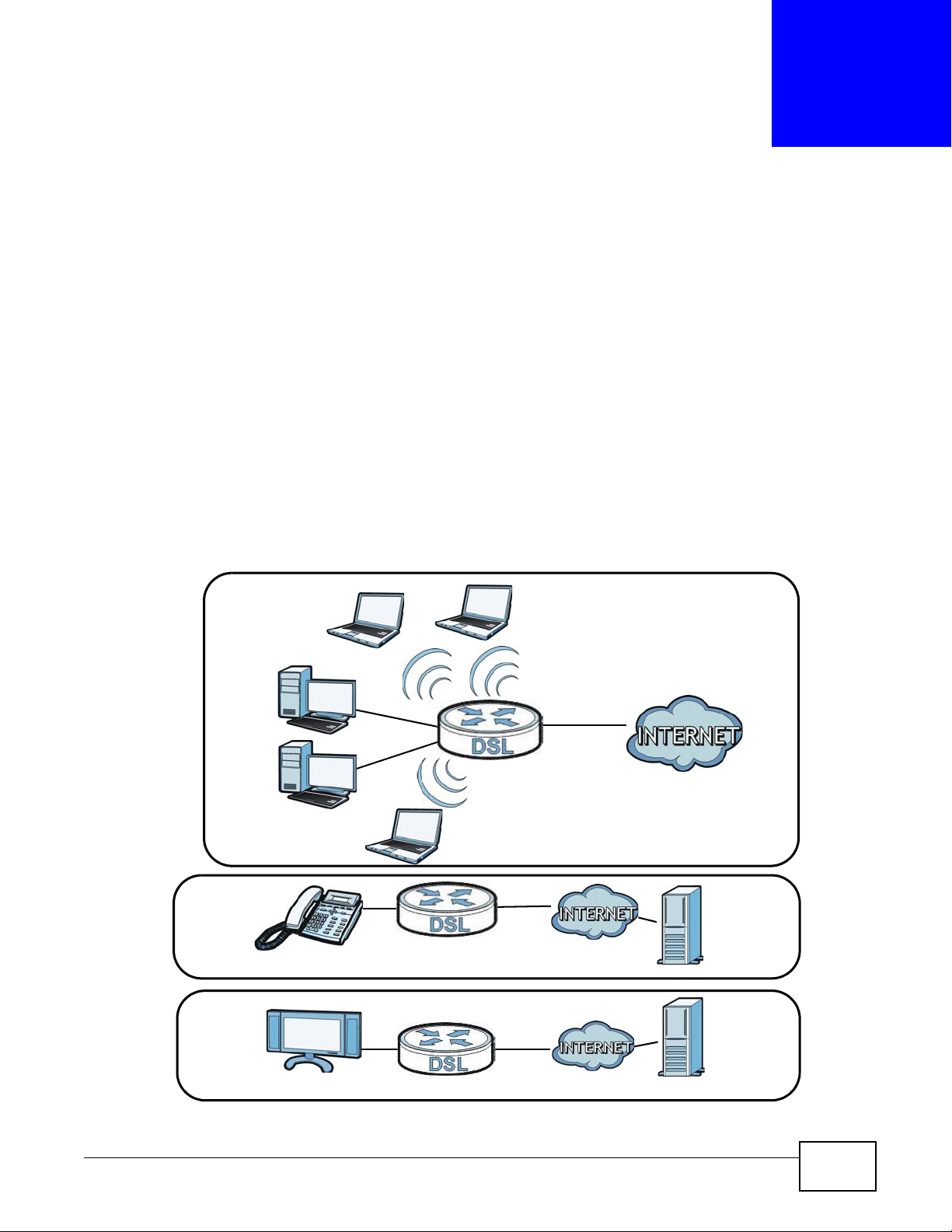
Figure 73 Port Binding Groups
CHAPTER 12
Port Binding
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 161
Page 2

Chapter 12 Port Binding
If a WAN PVC is bound to an ethernet port, traffic from the ethernet port will only be forwarded
through the specified WAN PVC and vice versa. If a port is not in a port binding group, traffic to and
from the port will be forwarded according to the routing table. See the tutorial section (Section on
page 37) for more details on configuring port binding for multiple WAN connections.
12.1.1 What You Can Do in the Port Binding Screens
•Use the General screen (Section 12.3 on page 162) to activate port binding.
•Use the Port Binding screen (Section 12.3 on page 162) to set up port binding groups.
•Use the Port Binding Summary screen (Section 12.3.1 on page 163) to view configured port
binding groups.
12.2 The Port Binding General Screen
Use this screen to activate port binding and set up port binding groups. Click Network Setting >
Port Binding to display the following screen.
Figure 74 Network Setting > Port Binding
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 54 Network Setting > Port Binding
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Activated Port Binding Activate or deactivate the port binding feature.
Apply Add the selected port binding group configuration.
12.3 The Port Binding Screen
Use this screen to set up port binding groups. Click Network Setting > Port Binding > Port
Binding to display the following screen.
162
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 3
Chapter 12 Port Binding
E
x
a
m
p
l
e
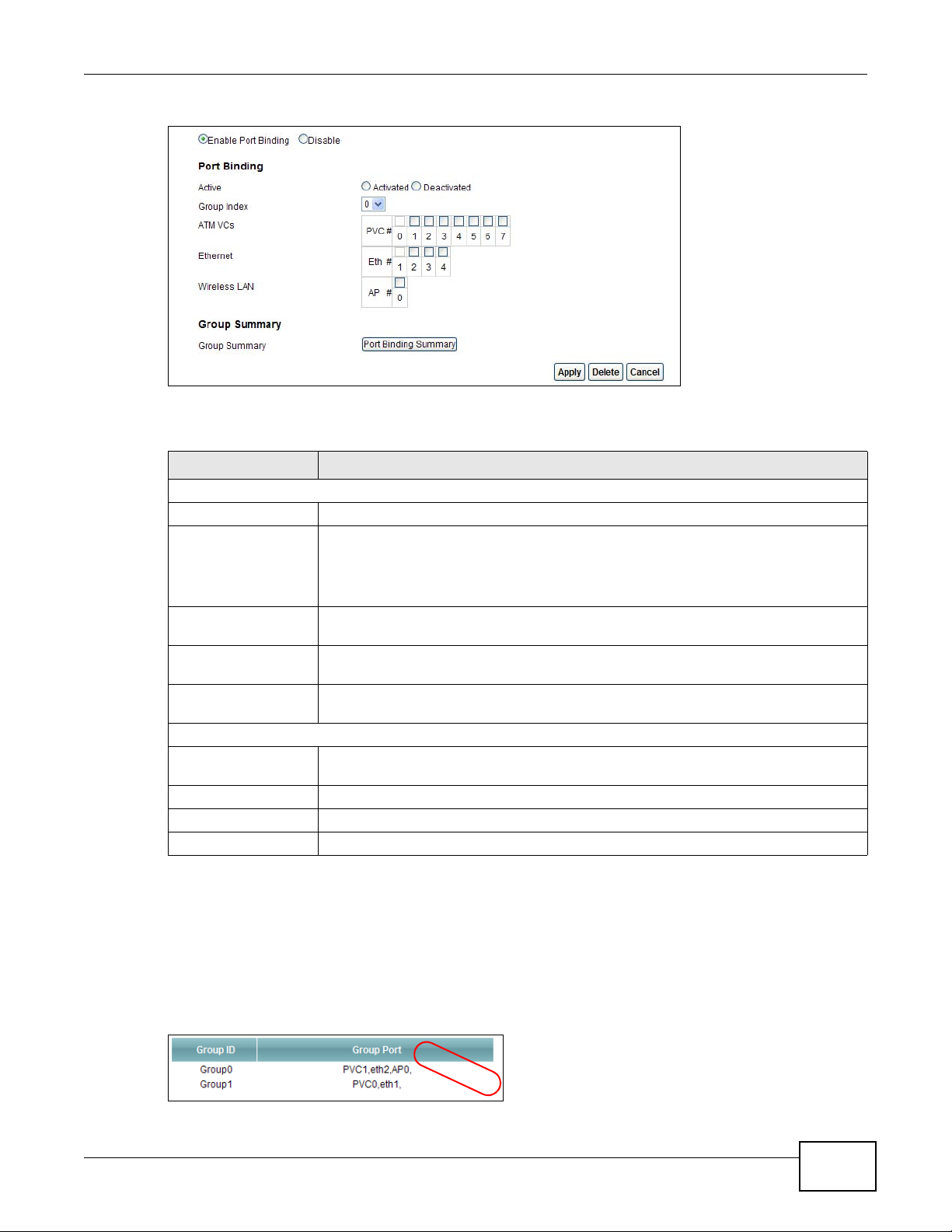
Figure 75 Network Setting > Port Binding > Port Binding
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 55 Network Setting > Port Binding > Port Binding
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Binding
Active Activate or deactivate port binding for the port binding group.
Group Index Select the index number for the port binding group.
When a port is assigned to a port binding group, traffic will be forwarded to the other
ports in the group, but not to ports in other groups. If a port is not included in any
groups, traffic will be forwarded according to the routing table.
ATM VCs Select the ATM VC (PVC) to include in the port binding group. Each ATM VC can only
be bound to one group.
Ethernet Select the Ethernet (Eth) ports to include in the port binding group. Each Ethernet
port can only be bound to one group.
Wireless LAN Select the WLAN (AP) connection to include in the port binding group. Additional APs
Group Summary
Port Binding
Summary
Apply Add the selected port binding group configuration.
Delete Delete the selected port binding group configuration.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
can be enabled on the More AP screen (Section 7.3 on page 98).
Click this to view a summary of configured port binding groups.
12.3.1 Port Binding Summary Screen
Use this screen to view configured port binding groups.
In the Port Binding screen, click the Port Binding Summary button in the Group Summary
section to display the following screen.
Figure 76 Network Setting > Port Binding > Port Binding Summary
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
163
Page 4

Chapter 12 Port Binding
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 56 Network Setting > Port Binding > Port Binding Summary
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Group ID This field displays the group index number.
Group port This field displays the ports included in the group.
164
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 5

CHAPTER 13
Dynamic DNS Setup
13.1 Overview
Dynamic DNS allows you to update your current dynamic IP address with one or many dynamic
DNS services so that anyone can contact you (in NetMeeting, CU-SeeMe, etc.). You can also access
your FTP server or Web site on your own computer using a domain name (for instance
myhost.dhs.org, where myhost is a name of your choice) that will never change instead of using an
IP address that changes each time you reconnect. Your friends or relatives will always be able to
call you even if they don't know your IP address.
First of all, you need to have registered a dynamic DNS account with www.dyndns.org. This is for
people with a dynamic IP from their ISP or DHCP server that would still like to have a domain name.
The Dynamic DNS service provider will give you a password or key.
13.1.1 What You Can Do in the DDNS Screen
Use the Dynamic DNS screen (Section 13.2 on page 165) to enable DDNS and configure the DDNS
settings on the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
13.1.2 What You Need To Know About DDNS
DYNDNS Wildcard
Enabling the wildcard feature for your host causes *.yourhost.dyndns.org to be aliased to the same
IP address as yourhost.dyndns.org. This feature is useful if you want to be able to use, for example,
www.yourhost.dyndns.org and still reach your hostname.
If you have a private WAN IP address, then you cannot use Dynamic DNS.
13.2 The Dynamic DNS Screen
Use this screen to change your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s DDNS. Click Network Setting >
Dynamic DNS. The screen appears as shown.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 165
Page 6
Chapter 13 Dynamic DNS Setup
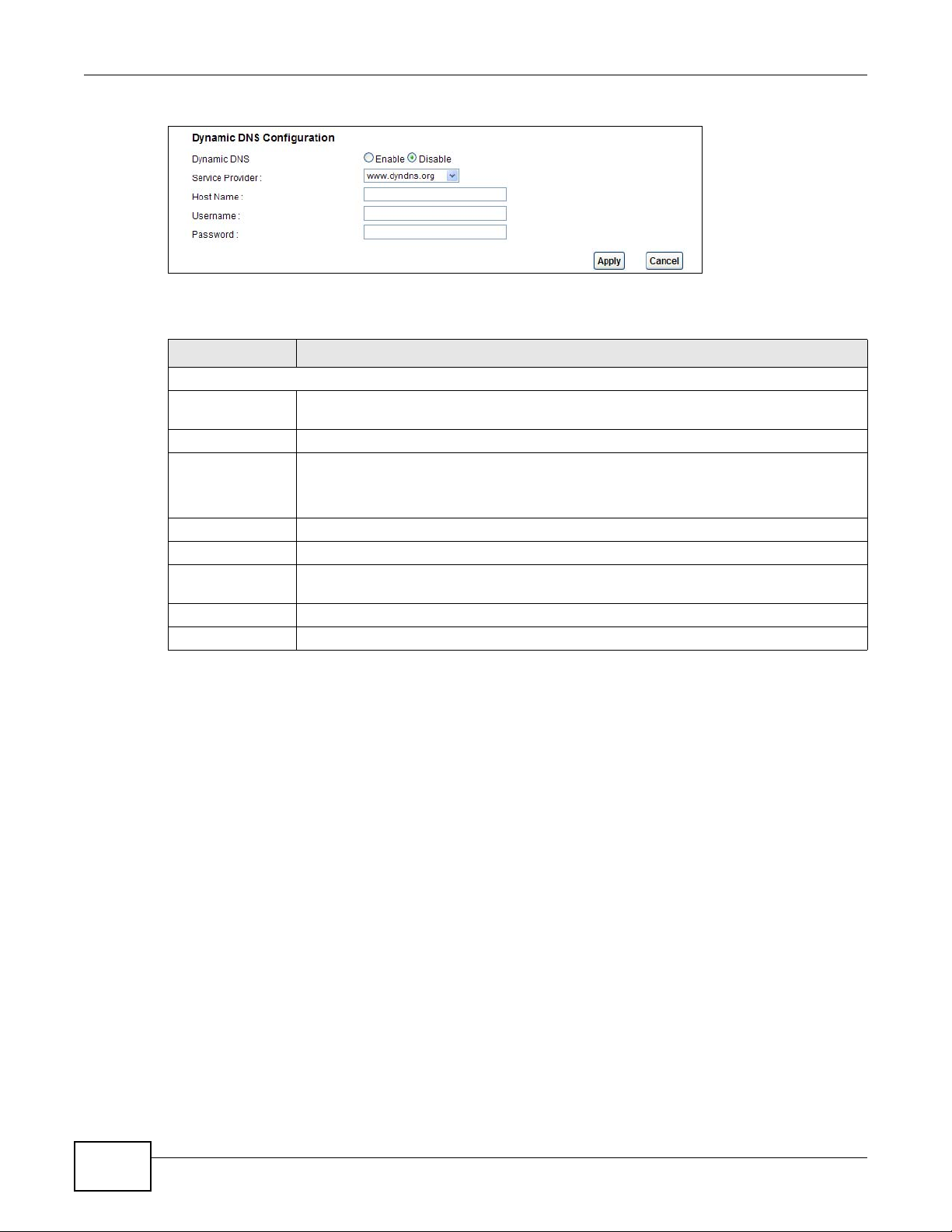
Figure 77 Network Setting > Dynamic DNS
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 57 Network Setting > Dynamic DNS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Dynamic DNS Setup
Active Dynamic
DNS
Service Provider This is the website of your Dynamic DNS service provider.
Host Name Type the domain name assigned to your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries by your Dynamic
Username Type your user name.
Password Type the password assigned to you.
Enable Wildcard
Option
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Select this check box to use dynamic DNS.
DNS provider.
You can specify up to two host names in the field separated by a comma (",").
Select the check box to enable DynDNS Wildcard.
166
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 7

CHAPTER 14
14.1 Overview
This chapter introduces three types of filters supported by the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. You can
configure rules to restrict traffic by IP addresses, MAC addresses, IPv6 addresses and/or URLs.
14.1.1 What You Can Do in the Filter Screens
•Use the IP/MAC Filter screen (Section 14.2 on page 167) to create IP and MAC filter rules.
•Use the IPv6/MAC Filter screen (Section 14.3 on page 170) to create IPv6 and MAC filter rules.
14.1.2 What You Need to Know About Filtering
Filters
URL
The URL (Uniform Resource Locator) identifies and helps locates resources on a network. On the
Internet the URL is the web address that you type in the address bar of your Internet browser, for
example “http://www.zyxel.com”.
URL and IP Filter Structure
The URL, IP and IPv6 filters have individual rule indexes. The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries allows
you to configure each type of filter with its own respective set of rules.
14.2 The IP/MAC Filter Screen
Use this screen to create and apply IP and MAC filters. Click Security > Filter > IP/MAC Filter.
The screen appears as shown.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 167
Page 8
Chapter 14 Filters
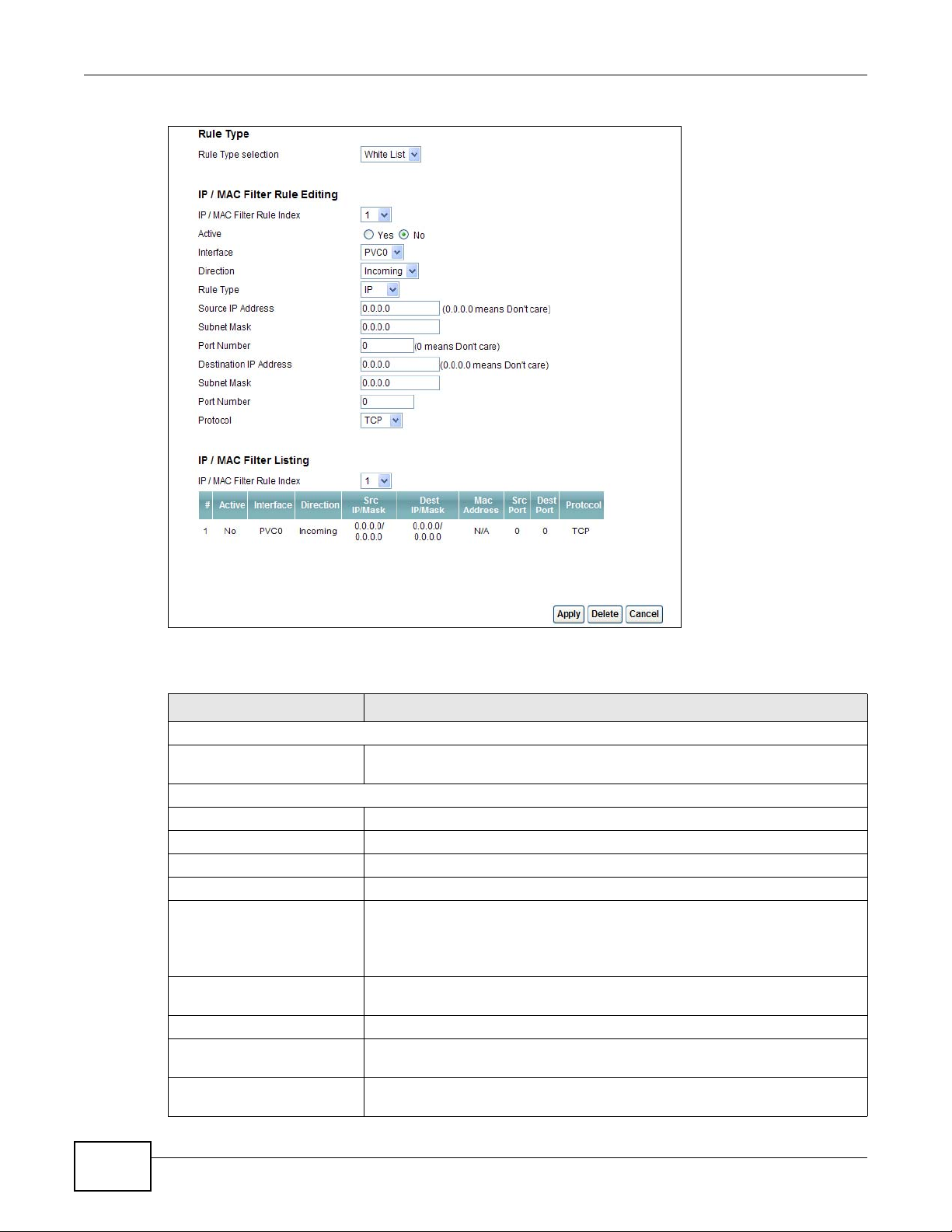
Figure 78 Security > Filter > IP/MAC Filter
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 58 Security > Filter > IP/MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rule Type
Rule Type selection Select White List to specify traffic to allow and Black List to specify traffic to
disallow.
IP / MAC Filter Rule Editing
IP / MAC Filter Rule Index Select the index number of the filter rule.
Active Use this field to enable or disable the filter rule.
Interface Select the PVC to which to apply the filter.
Direction Apply the filter to Incoming or Outgoing traffic direction.
Rule Type Select IP or MAC type to configure the rule.
Use the IP Filter to block or allow traffic by IP addresses.
Use the MAC Filter to block or allow traffic by MAC address.
Source IP Address Enter the source IP address of the packets you wish to filter. This field is
Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask for the source IP address
Port Number Enter the source port of the packets that you wish to filter. The range of this
Destination IP Address Enter the destination IP address of the packets you wish to filter. This field is
ignored if it is 0.0.0.0.
field is 0 to 65535. This field is ignored if it is 0.
ignored if it is 0.0.0.0.
168
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 9
Chapter 14 Filters
Table 58 Security > Filter > IP/MAC Filter (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask for the destination IP address.
Port Number Enter the destination port of the packets that you wish to filter. The range of
this field is 0 to 65535. This field is ignored if it is 0.
Protocol Select ICMP, TCP or UDP for the upper layer protocol.
IP / MAC Filter Listing
IP / MAC Filter Rule Index Select the index number of the filter set from the drop-down list box.
# This is the index number of the rule in a filter set.
Active This field shows whether the rule is activated.
Interface This is the interface that the filter set applies to.
Direction The filter set applies to this traffic direction.
Src IP/Mask This is the source IP address and subnet mask when you select IP as the rule
type.
Dest IP/Mask This is the destination IP address and subnet mask.
Mac Address This is the MAC address of the packets being filtered.
Src Port This is the source port number.
Dest Port This is the destination port number.
Protocol This is the upper layer protocol.
Apply Click this to apply your changes.
Delete Click this to remove the filter rule.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
169
Page 10
Chapter 14 Filters
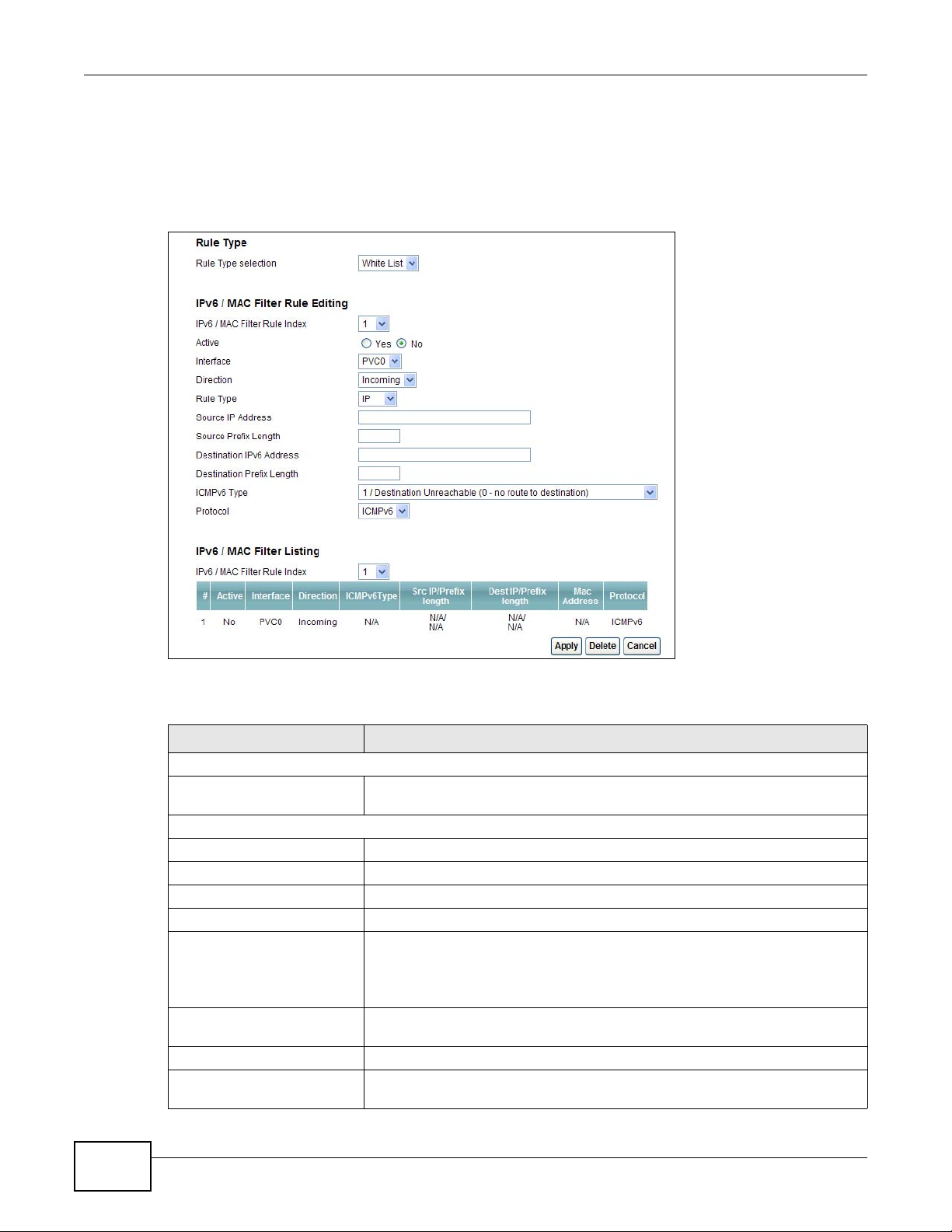
14.3 IPv6/MAC Filter
Use this screen to create and apply IPv6 filters. Click Security > Filter > IPv6/MAC Filter. The
screen appears as shown.
Figure 79 Security > Filter > IPv6/MAC Filter
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 59 Security > Filter > IPv6/MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rule Type
Rule Type selection Select White List to specify traffic to allow and Black List to specify traffic to
IPv6 / MAC Filter Rule Editing
IPv6 / MAC Filter Rule Index Select the index number of the filter rule.
Active Use this field to enable or disable the filter rule.
Interface Select the PVC to which to apply the filter.
Direction Apply the filter to Incoming or Outgoing traffic direction.
Rule Type Select IP or MAC type to configure the rule.
Source IP Address Enter the source IPv6 address of the packets you wish to filter. This field is
Source Prefix Length Enter the prefix length for the source IPv6 address
Destination IPv6 Address Enter the destination IPv6 address of the packets you wish to filter. This field is
block.
Use the IP Filter to block or allow traffic by IPv6 addresses.
Use the MAC Filter to block or allow traffic by MAC address.
ignored if it is ::.
ignored if it is ::.
170
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 11
Chapter 14 Filters
Table 59 Security > Filter > IPv6/MAC Filter (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Destination Prefix Length Enter the prefix length for the destination IPv6 address.
ICMPv6 Type Select the ICMPv6 message type to filter. The following message types can be
selected:
1 / Destination Unreachable: 0 - no route to destination; 1 -
communication with destination administratively prohibited; 3 - address
unreachable; 4 - port unreachable
2 / Packet Too Big
3 / Time Exceeded: 0 - hop limit exceeded in transit; 1 - fragment
reassembly time exceeded
4 / Parameter Problem: 0 - erroneous header field encountered; 1 -
unrecognized Next Header type encountered; 2 - unrecognized IPv6 option
encountered
128 / Echo Request
129 / Echo Response
130 / Listener Query - Multicast listener query
131 / Listener Report - Multicast listener report
132 / Listener Done - Multicast listener done
143 / Listener Report v2 - Multicast listener report v2
133 / Router Solicitation
134 / Router Advertisement
135 / Neighbor Solicitation
136 / Neighbor Advertisement
137 / Redirect - Redirect message
Protocol This is the (upper layer) protocol that defines the service to which this rule
IPv6 / MAC Filter Listing
IPv6 / MAC Filter Rule Index Select the index number of the filter set from the drop-down list box.
# This is the index number of the rule in a filter set.
Active This field shows whether the rule is activated.
Interface This is the interface that the rule applies to.
Direction The filter set applies to this traffic direction.
ICMPv6 Type The ICMPv6 message type to filter.
Src IP/PrefixLength This displays the source IPv6 address and prefix length.
Dest IP/PrefixLength This displays the destination IPv6 address and prefix length.
Mac Address This is the MAC address of the packets being filtered.
Protocol This is the (upper layer) protocol that defines the service to which this rule
Apply Click this to apply your changes.
Delete Click this to remove the filter rule.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
applies. By default it is ICMPv6.
applies. By default it is ICMPv6.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
171
Page 12

Chapter 14 Filters
172
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 13
15.1 Overview
WAN
LAN
3
4
1
2
A
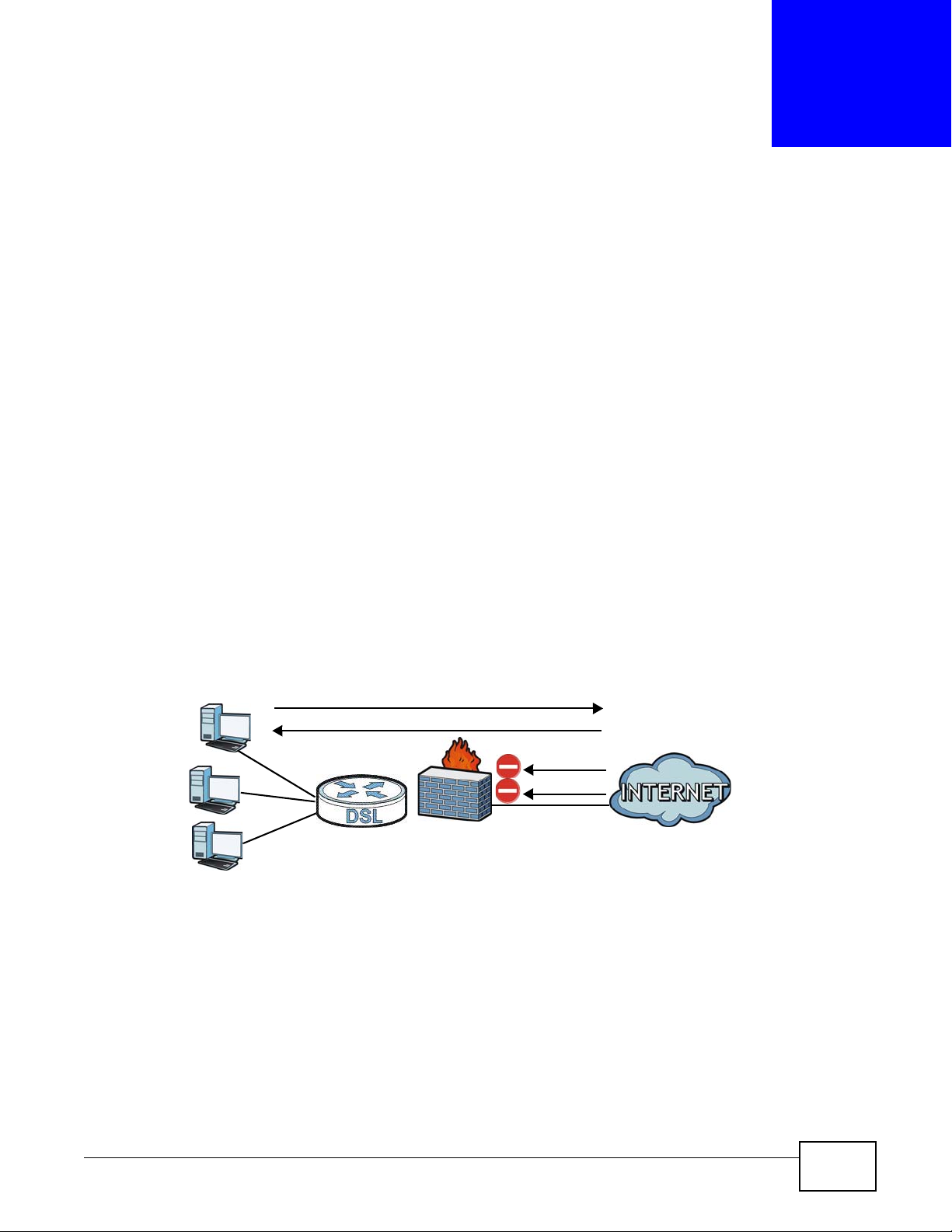
This chapter shows you how to enable the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries firewall. Use the firewall to
protect your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries and network from attacks by hackers on the Internet and
control access to it. The firewall:
• allows traffic that originates from your LAN computers to go to all other networks.
• blocks traffic that originates on other networks from going to the LAN.
• blocks SYN and port scanner attacks.
By default, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries blocks DDOS, LAND and Ping of Death attacks whether
the firewall is enabled or disabled.
The following figure illustrates the firewall action. User A can initiate an IM (Instant Messaging)
session from the LAN to the WAN (1). Return traffic for this session is also allowed (2). However
other traffic initiated from the WAN is blocked (3 and 4).
CHAPTER 15
Firewall
Figure 80 Default Firewall Action
15.1.1 What You Can Do in the Firewall Screens
•Use the General screen (Section 15.2 on page 175) to select the firewall protection level on the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
•Use the Default Action screen (Section 15.3 on page 176) to set the default action that the
firewall takes on packets that do not match any of the firewall rules.
•Use the Rules screen (Section 15.4 on page 178) to view the configured firewall rules and add,
edit or remove a firewall rule.
•Use the Dos screen (Section 15.5 on page 184) to set the thresholds that the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries uses to determine when to start dropping sessions that do not become fully
established (half-open sessions).
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 173
Page 14

Chapter 15 Firewall
15.1.2 What You Need to Know About Firewall
SYN Attack
A SYN attack floods a targeted system with a series of SYN packets. Each packet causes the
targeted system to issue a SYN-ACK response. While the targeted system waits for the ACK that
follows the SYN-ACK, it queues up all outstanding SYN-ACK responses on a backlog queue. SYNACKs are moved off the queue only when an ACK comes back or when an internal timer terminates
the three-way handshake. Once the queue is full, the system will ignore all incoming SYN requests,
making the system unavailable for legitimate users.
DoS
Denials of Service (DoS) attacks are aimed at devices and networks with a connection to the
Internet. Their goal is not to steal information, but to disable a device or network so users no longer
have access to network resources. The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries is pre-configured to
automatically detect and thwart all known DoS attacks.
DDoS
A Distributed DoS (DDoS) attack is one in which multiple compromised systems attack a single
target, thereby causing denial of service for users of the targeted system.
LAND Attack
In a Local Area Network Denial (LAND) attack, hackers flood SYN packets into the network with a
spoofed source IP address of the target system. This makes it appear as if the host computer sent
the packets to itself, making the system unavailable while the target system tries to respond to
itself.
Ping of Death
Ping of Death uses a "ping" utility to create and send an IP packet that exceeds the maximum
65,536 bytes of data allowed by the IP specification. This may cause systems to crash, hang or
reboot.
SPI
Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) tracks each connection crossing the firewall and makes sure it is
valid. Filtering decisions are based not only on rules but also context. For example, traffic from the
WAN may only be allowed to cross the firewall in response to a request from the LAN.
RFC 4890 SPEC T raffic
174
RFC 4890 specifies the filtering policies for ICMPv6 messages. This is important for protecting
against security threats including DoS, probing, redirection attacks and renumbering attacks that
can be carried out through ICMPv6. Since ICMPv6 error messages are critical for establishing and
maintaining communications, filtering policy focuses on ICMPv6 informational messages.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 15

Chapter 15 Firewall
Anti-Probing
If an outside user attempts to probe an unsupported port on your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries, an
ICMP response packet is automatically returned. This allows the outside user to know the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries exists. The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries supports anti-probing, which
prevents the ICMP response packet from being sent. This keeps outsiders from discovering your
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries when unsupported ports are probed.
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a message control and error-reporting protocol
between a host server and a gateway to the Internet. ICMP uses Internet Protocol (IP) datagrams,
but the messages are processed by the TCP/IP software and directly apparent to the application
user.
DoS Thresholds
For DoS attacks, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries uses thresholds to determine when to drop
sessions that do not become fully established. These thresholds apply globally to all sessions. You
can use the default threshold values, or you can change them to values more suitable to your
security requirements.
15.2 The Firewall General Screen
Use this screen to select the firewall protection level on the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. Click
Security > Firewall > General to display the following screen.
Figure 81 Security > Firewall > General
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
175
Page 16

Chapter 15 Firewall
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 60 Security > Firewall > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
High This setting blocks all traffic to and from the Internet. Only local network traffic and LAN to WAN
Medium This is the recommended setting. It allows traffic to the Internet but blocks anyone from the
Low This setting allows traffic to the Internet and also allows someone from the Internet to access
Custom This setting allows the customer to create and edit individual firewall rules.
Off This setting is not recommended. It disables firewall protection for your network and could
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
service (Telnet, FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, POP3, SMTP) is permitted.
Internet from accessing any services on your local network.
services on your local network. This would be used with Port Forwarding, Default Server.
Firewall rules can be created in the Default Action screen (Section 15.3 on page 176) and Rules
screen (Section 15.4 on page 178).
potentially expose your network to significant security risks. This option should only be used for
troubleshooting or if you intend using another firewall in conjunction with your ZyXEL router.
15.3 The Default Action Screen
Use this screen to set the default action that the firewall takes on packets that do not match any of
the firewall rules. Click Security > Firewall > Default Action to display the following screen.
Figure 82 Security > Firewall > Default Action
176
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 17

Chapter 15 Firewall
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 61 Security > Firewall > Default Action
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Packet Direction This is the direction of travel of packets (LAN to Router , LAN to WAN, WAN to Router,
Default Action Use the drop-down list boxes to select the default action that the firewall is to take on
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
WAN to LAN).
Firewall rules are grouped based on the direction of travel of packets to which they apply.
For example, LAN to Router means packets traveling from a computer/subnet on the
LAN to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries itself.
packets that are traveling in the selected direction and do not match any of the firewall
rules.
Select Drop to silently discard the packets without sending a TCP reset packet or an ICMP
destination-unreachable message to the sender.
Select Reject to deny the packets and send a TCP reset packet (for a TCP packet) or an
ICMP destination-unreachable message (for a UDP packet) to the sender.
Select Permit to allow the passage of the packets.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
177
Page 18

Chapter 15 Firewall
15.4 The Rules Screen
Click Security > Firewall > Rules to display the following screen. This screen displays a list of the
configured firewall rules. Note the order in which the rules are listed.
Note: The firewall configuration screen shown in this section is specific to the following
devices: P-The ordering of your rules is very important as rules are applied in turn.
Figure 83 Security > Firewall > Rules
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 62 Security > Firewall > Rules
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Firewall Rules Storage
Space in Use
Packet Direction Use the drop-down list box to select a direction of travel of packets for which you
Create a new rule
after rule number
# This is your firewall rule number. The ordering of your rules is important as rules are
Active This field displays whether a firewall is turned on or not. Select the check box to
Source IP Address This column displays the source addresses or ranges of addresses to which this
Destination IP Address This column displays the destination addresses or ranges of addresses to which this
Service This column displays the services to which this firewall rule applies. See Appendix F
Action This field displays whether the firewall silently discards packets (Drop), discards
Source Interface This column displays the source interface to which this firewall rule applies. This is
This read-only bar shows how much of the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries's memory for
recording firewall rules it is currently using. When you are using 80% or less of the
storage space, the bar is green. When the amount of space used is over 80%, the
bar is red.
want to configure firewall rules.
Select an index number and click Add to add a new firewall rule after the selected
index number. For example, if you select “6”, your new rule becomes number 7 and
the previous rule 7 (if there is one) becomes rule 8.
The following read-only fields summarize the rules you have created that apply to
traffic traveling in the selected packet direction. The firewall rules that you configure
(summarized below) take priority over the general firewall action settings in the
General screen.
applied in turn.
enable the rule. Clear the check box to disable the rule.
firewall rule applies. Please note that a blank source or destination address is
equivalent to Any.
firewall rule applies. Please note that a blank source or destination address is
equivalent to Any.
on page 305 for more information.
packets and sends a TCP reset packet or an ICMP destination-unreachable message
to the sender (Reject) or allows the passage of packets (Permit).
the interface through which the traffic entered the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Please note that a blank source interface is equivalent to Any.
178
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 19
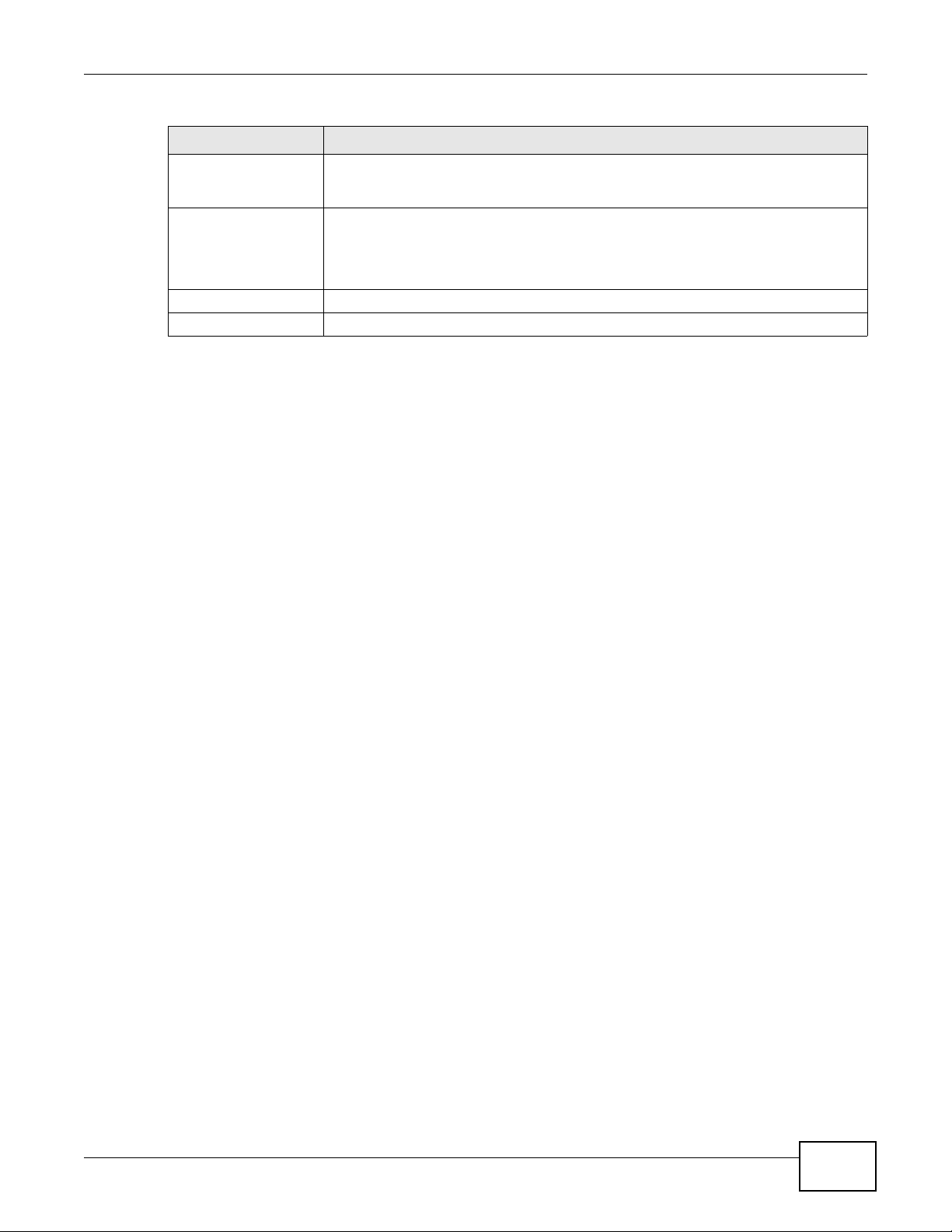
Table 62 Security > Firewall > Rules
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Destination Interface This column displays the destination interface to which this firewall rule applies. This
is the interface through which the traffic is destined to leave the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries. Please note that a blank source interface is equivalent to Any.
Modify Click the Edit icon to go to the screen where you can edit the rule.
Click the Remove icon to delete an existing firewall rule. A window displays asking
you to confirm that you want to delete the firewall rule. Note that subsequent firewall
rules move up by one when you take this action.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
15.4.1 The Rules Add Screen
Use this screen to configure firewall rules. In the Rules screen, select an index number and click
Add or click a rule’s Edit icon to display this screen and refer to the following table for information
on the labels.
Chapter 15 Firewall
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
179
Page 20
Chapter 15 Firewall
Figure 84 Security > Firewall > Rules > Add
180
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 63 Security > Firewall > Rules > Add
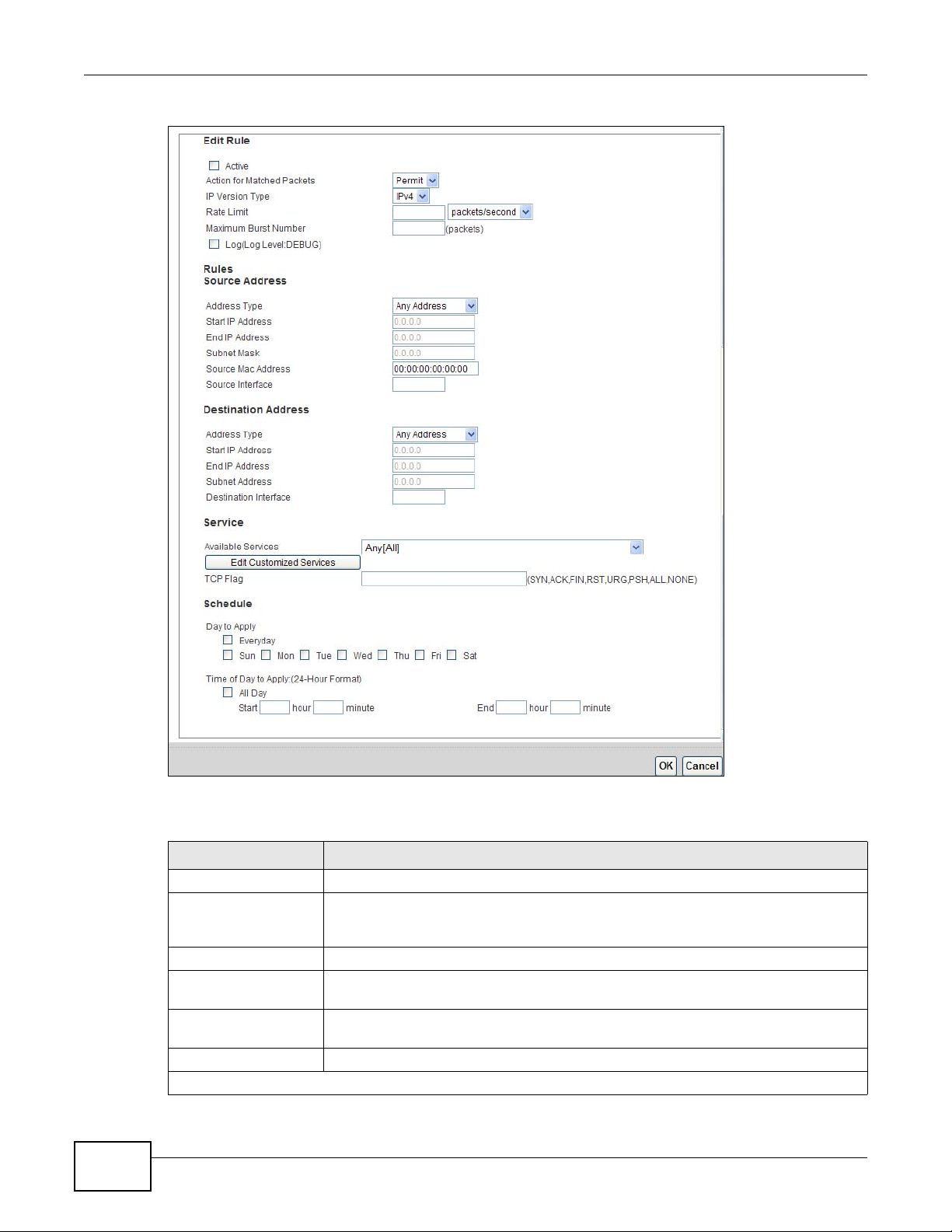
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Select this option to enable this firewall rule.
Action for Matched
Packets
IP Version Type Select the IP version, IPv4 or IPv6, to apply this firewall rule to.
Rate Limit Set a maximum number of packets per second, minute, or hour to limit the
Maximum Burst
Number
Log This field determines if a log for packets that match the rule is created or not.
Rules/Destination Address
Use the drop-down list box to select whether to discard (Drop), deny and send an
ICMP destination-unreachable message to the sender of (Reject) or allow the
passage of (Permit) packets that match this rule.
throughput of traffic that matches this rule.
Set the maximum number of packets that can be sent at the peak rate.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 21
Chapter 15 Firewall
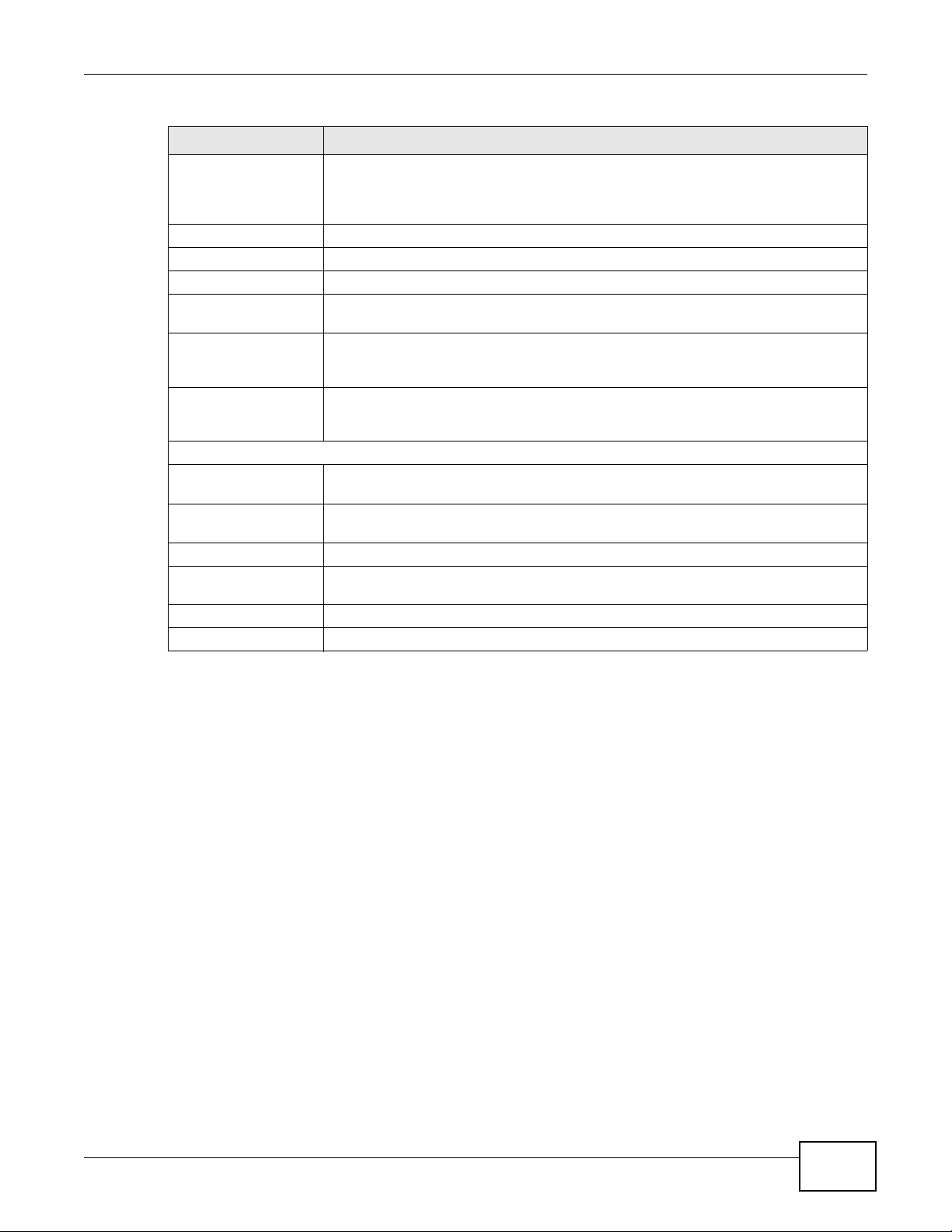
Table 63 Security > Firewall > Rules > Add
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Address Type Do you want your rule to apply to packets with a particular (single) IP, a range of IP
addresses (for instance, 192.168.1.10 to 192.169.1.50), a subnet or any IP address?
Select an option from the drop-down list box that includes: Single Address, Range
Address, Subnet Address and Any
Start IP Address Enter the single IP address or the starting IP address in a range here.
End IP Address Enter the ending IP address in a range here.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask here, if applicable.
Source Mac Address Specify a source MAC address of traffic to which to apply this firewall rule applies.
Please note that a blank source MAC address is equivalent to any.
Source Interface Specify a source interface to which this firewall rule applies. This is the interface
through which the traffic entered the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. Please note that a
blank source interface is equivalent to any.
Destination Interface Specify a destination interface to which this firewall rule applies. This is the interface
through which the traffic is destined to leave the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. Please
note that a blank source interface is equivalent to any.
Services
Available Services Please see Appendix F on page 305 for more information on services available. Select
Edit Customized
Service
TCP Flag Specify any TCP flag bits the firewall rule is to check for.
Schedule Select the days and time during which to apply the rule. Select Everyday and All
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
a service from the Available Services box.
Click the Edit Customized Service button to bring up the screen that you use to
configure a new custom service that is not in the predefined list of services.
Day to always apply the rule.
Address.
15.4.2 Customized Services
Configure customized services and port numbers not predefined by the AMG1302/AMG1202TSeries. For a comprehensive list of port numbers and services, visit the IANA (Internet Assigned
Number Authority) website. See Appendix F on page 305 for some examples. Click the Edit
Customized Services button while editing a firewall rule to configure a custom service port. This
displays the following screen.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
181
Page 22
Chapter 15 Firewall
Figure 85 Security > Firewall > Rules: Edit: Edit Customized Services
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
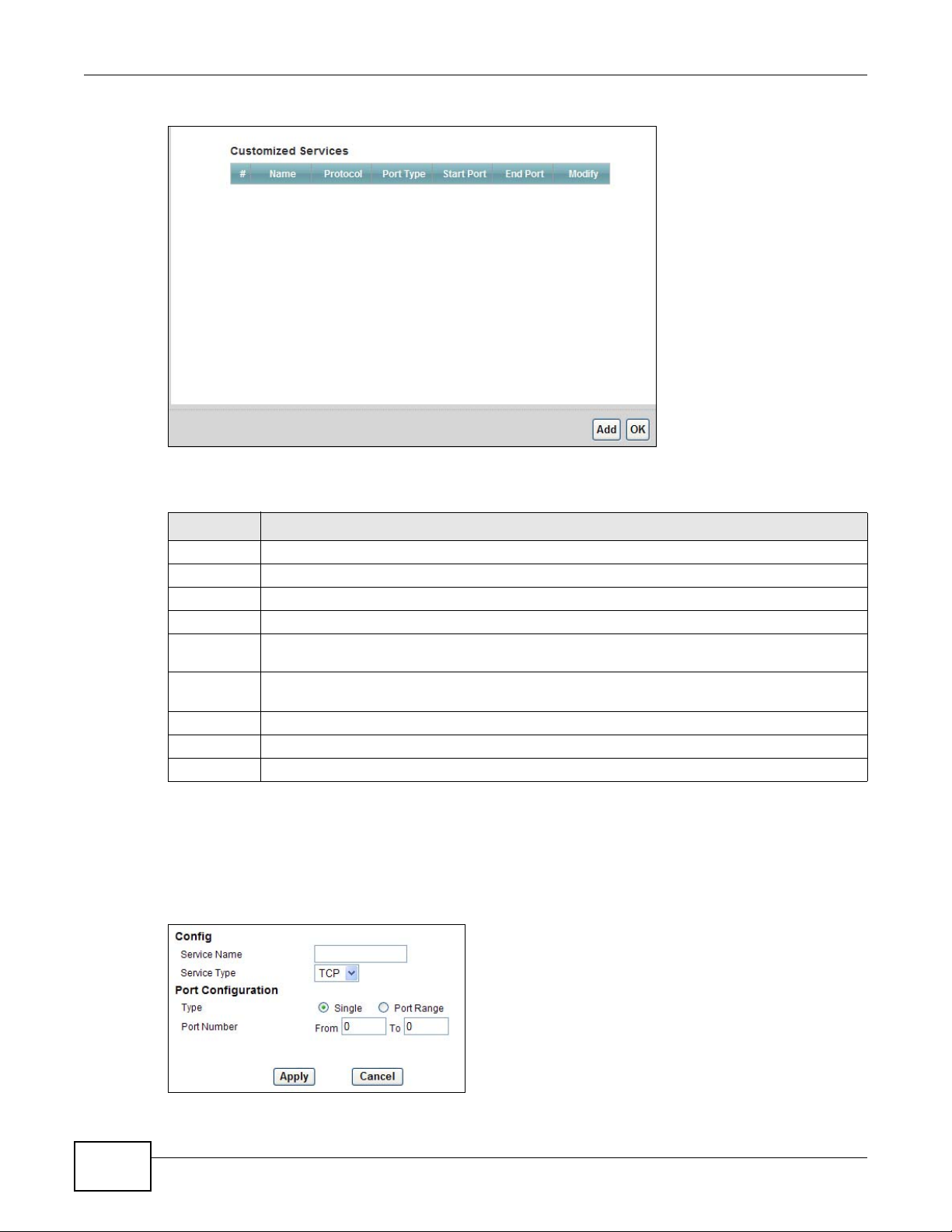
Table 64 Security > Firewall > Rules: Edit: Edit Customized Services
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the number of your customized port.
Name This is the name of your customized service.
Protocol This shows the IP protocol (TCP or UDP) that defines your customized service.
Port Type This is the port number or range that defines your customized service.
Start Port This is a single port number or the starting port number of a range that defines your
End Port This is a single port number or the ending port number of a range that defines your customized
Modify Click this to edit a customized service.
Add Click this to configure a customized service.
Back Click this to return to the Firewall Edit Rule screen.
customized service.
service.
15.4.3 Customized Service Add/Edit
Use this screen to add a customized rule or edit an existing rule. Click Add or the Edit icon next to
a rule number in the Firewall Customized Services screen to display the following screen.
Figure 86 Security > Firewall > Rules: Edit: Edit Customized Services: Add/Edit
182
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 23
Chapter 15 Firewall
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 65 Security > Firewall > Rules: Edit: Edit Customized Services: Add/Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Config
Service Name Type a unique name for your custom port.
Service Type Choose the IP port (TCP or UDP) that defines your customized port from the drop down list
Port Configuration
Type Click Single to specify one port only or Port Range to specify a span of ports that define
Port Number Type a single port number or the range of port numbers that define your customized
Back Click this to return to the previous screen without saving.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Delete Click this to delete the current rule.
box.
your customized service.
service.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
183
Page 24
Chapter 15 Firewall
15.5 The DoS Screen
Use this screen to enable DoS protection. Click Security > Firewall > Dos to display the following
screen.
Figure 87 Security > Firewall > Dos
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 66 Security > Firewall > Dos
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Denial of Services Enable this to protect against DoS attacks. The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries will drop
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Advanced Click this to go to a screen to specify maximum thresholds at which the AMG1302/
sessions that surpass maximum thresholds.
AMG1202-TSeries will start dropping sessions.
15.5.1 The DoS Advanced Screen
For DoS attacks, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries uses thresholds to determine when to start
dropping sessions that do not become fully established (half-open sessions). These thresholds
apply globally to all sessions.
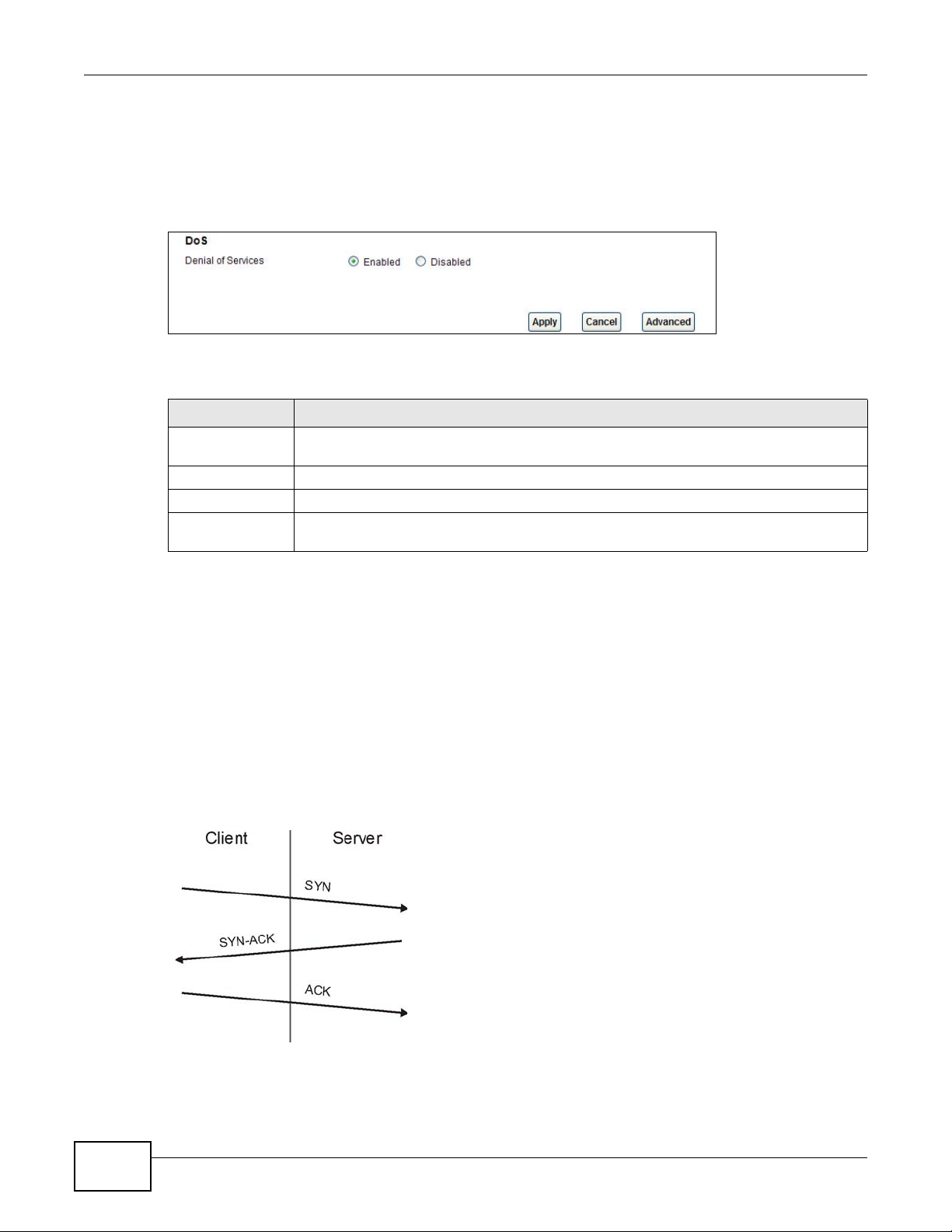
For TCP, half-open means that the session has not reached the established state-the TCP three-way
handshake has not yet been completed. Under normal circumstances, the application that initiates
a session sends a SYN (synchronize) packet to the receiving server. The receiver sends back an ACK
(acknowledgment) packet and its own SYN, and then the initiator responds with an ACK
(acknowledgment). After this handshake, a connection is established.
Figure 88 Three-Way Handshake
184
For UDP, half-open means that the firewall has detected no return traffic. An unusually high number
(or arrival rate) of half-open sessions could indicate a DOS attack.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 25
15.5.1.1 Threshold Values
If everything is working properly, you probably do not need to change the threshold settings as the
default threshold values should work for most small offices. Tune these parameters when you
believe the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries has been receiving DoS attacks that are not recorded in
the logs or the logs show that the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries is classifying normal traffic as DoS
attacks. Factors influencing choices for threshold values are:
1 The maximum number of opened sessions.
2 The minimum capacity of server backlog in your LAN network.
3 The CPU power of servers in your LAN network.
4 Network bandwidth.
5 Type of traffic for certain servers.
Reduce the threshold values if your network is slower than average for any of these factors
(especially if you have servers that are slow or handle many tasks and are often busy).
• If you often use P2P applications such as file sharing with eMule or eDonkey, it’s recommended
that you increase the threshold values since lots of sessions will be established during a small
period of time and the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries may classify them as DoS attacks.
Chapter 15 Firewall
15.5.2 Configuring Firewall Thresholds
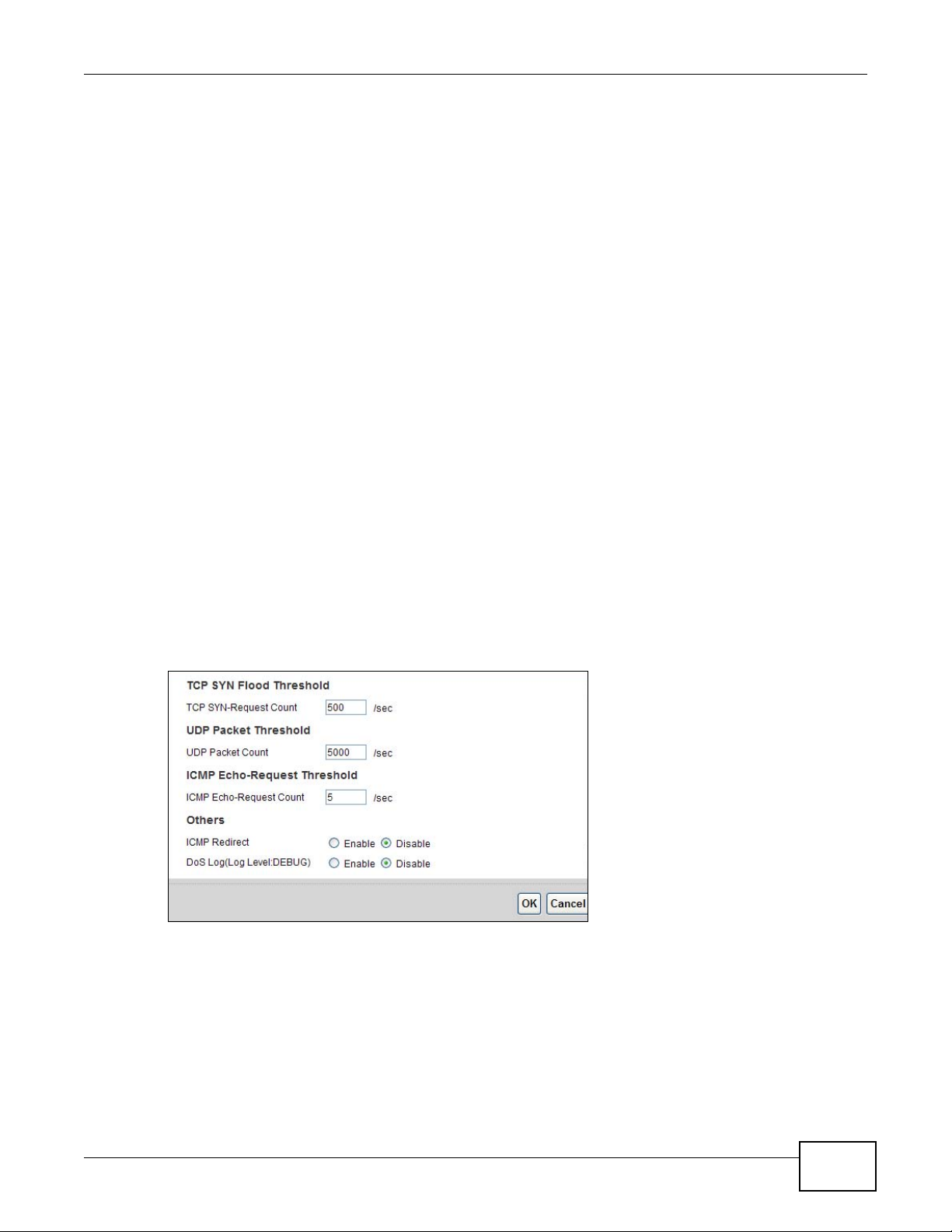
Click Security > Firewall > DoS > Advanced to display the following screen.
Figure 89 Security > Firewall > DoS > Advanced
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
185
Page 26
Chapter 15 Firewall
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 67 Security > Firewall > DoS > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
TCP SYN-Request
Count
UDP Packet Count This is the rate of new UDP half-open sessions per second that causes the firewall to
ICMP Echo-Request
Count
Back Click this button to return to the previous screen.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
This is the rate of new TCP half-open sessions per second that causes the firewall to
start deleting half-open sessions. When the rate of new connection attempts rises
above this number, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries deletes half-open sessions as
required to accommodate new connection attempts.
start deleting half-open sessions. When the rate of new connection attempts rises
above this number, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries deletes half-open sessions as
required to accommodate new connection attempts.
This is the rate of new ICMP Echo-Request half-open sessions per second that causes
the firewall to start deleting half-open sessions. When the rate of new connection
attempts rises above this number, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries deletes half-open
sessions as required to accommodate new connection attempts.
15.6 Firewall Technical Reference
This section provides some technical background information about the topics covered in this
chapter.
15.6.1 Firewall Rules Overview
Your customized rules take precedence and override the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s default
settings. The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries checks the source IP address, destination IP address and
IP protocol type of network traffic against the firewall rules (in the order you list them). When the
traffic matches a rule, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries takes the action specified in the rule.
Firewall rules are grouped based on the direction of travel of packets to which they apply:
•LAN to Router •WAN to LAN
• LAN to WAN • WAN to Router
Note: The LAN includes both the LAN port and the WLAN.
By default, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s stateful packet inspection allows packets traveling in
the following directions:
•LAN to Router
These rules specify which computers on the LAN can manage the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries
(remote management).
186
Note: You can also configure the remote management settings to allow only a specific
computer to manage the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 27

Chapter 15 Firewall
•LAN to WAN
These rules specify which computers on the LAN can access which computers or services on the
WAN.
By default, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s stateful packet inspection drops packets traveling in
the following directions:
•WAN to LAN
These rules specify which computers on the WAN can access which computers or services on the
LAN.
Note: You also need to configure NAT port forwarding (or full featured NAT address
mapping rules) to allow computers on the WAN to access devices on the LAN.
•WAN to Router
By default the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries stops computers on the WAN from managing the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. You could configure one of these rules to allow a WAN computer to
manage the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Note: You also need to configure the remote management settings to allow a WAN
computer to manage the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
You may define additional rules and sets or modify existing ones but please exercise extreme
caution in doing so.
For example, you may create rules to:
• Block certain types of traffic, such as IRC (Internet Relay Chat), from the LAN to the Internet.
• Allow certain types of traffic, such as Lotus Notes database synchronization, from specific hosts
on the Internet to specific hosts on the LAN.
• Allow everyone except your competitors to access a web server.
• Restrict use of certain protocols, such as Telnet, to authorized users on the LAN.
These custom rules work by comparing the source IP address, destination IP address and IP
protocol type of network traffic to rules set by the administrator. Your customized rules take
precedence and override the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s default rules.
15.6.2 Guidelines For Enhancing Security With Your Firewall
6 Change the default password via web configurator.
7 Think about access control before you connect to the network in any way.
8 Limit who can access your router.
9 Don't enable any local service (such as telnet or FTP) that you don't use. Any enabled service could
present a potential security risk. A determined hacker might be able to find creative ways to misuse
the enabled services to access the firewall or the network.
10 For local services that are enabled, protect against misuse. Protect by configuring the services to
communicate only with specific peers, and protect by configuring rules to block packets for the
services at specific interfaces.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
187
Page 28
Chapter 15 Firewall
1
2
WAN
LAN
11 Protect against IP spoofing by making sure the firewall is active.
12 Keep the firewall in a secured (locked) room.
15.6.3 Security Considerations
Note: Incorrectly configuring the firewall may block valid access or introduce security
risks to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries and your protected network. Use caution
when creating or deleting firewall rules and test your rules after you configure
them.
Consider these security ramifications before creating a rule:
1 Does this rule stop LAN users from accessing critical resources on the Internet? For example, if IRC
is blocked, are there users that require this service?
2 Is it possible to modify the rule to be more specific? For example, if IRC is blocked for all users, will
a rule that blocks just certain users be more effective?
3 Does a rule that allows Internet users access to resources on the LAN create a security
vulnerability? For example, if FTP ports (TCP 20, 21) are allowed from the Internet to the LAN,
Internet users may be able to connect to computers with running FTP servers.
4 Does this rule conflict with any existing rules?
Once these questions have been answered, adding rules is simply a matter of entering the
information into the correct fields in the web configurator screens.
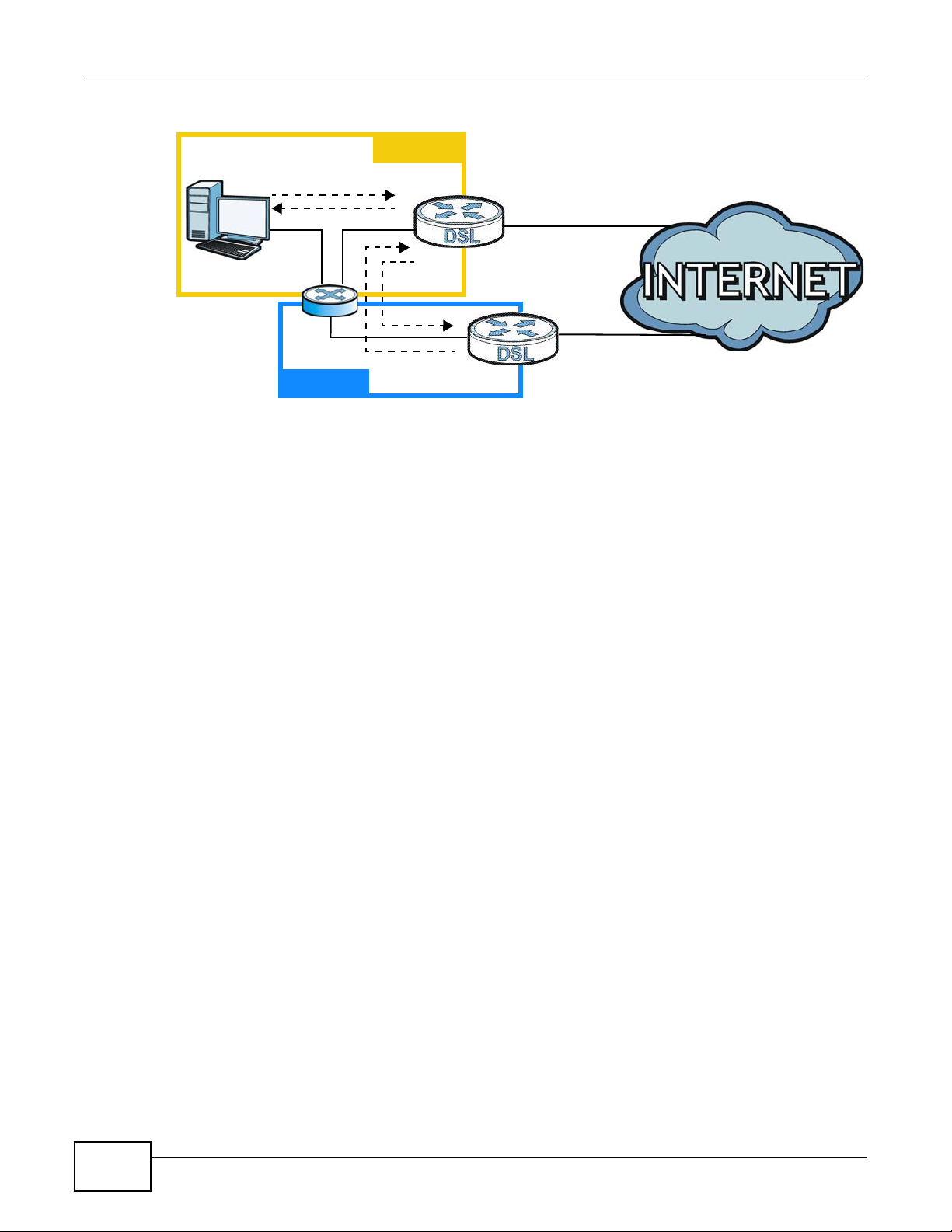
15.6.4 Triangle Route
When the firewall is on, your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries acts as a secure gateway between your
LAN and the Internet. In an ideal network topology, all incoming and outgoing network traffic
passes through the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to protect your LAN against attacks.
Figure 90 Ideal Firewall Setup
15.6.4.1 The “Triangle Route” Problem
A traffic route is a path for sending or receiving data packets between two Ethernet devices. You
may have more than one connection to the Internet (through one or more ISPs). If an alternate
gateway is on the LAN (and its IP address is in the same subnet as the AMG1302/AMG1202TSeries’s LAN IP address), the “triangle route” (also called asymmetrical route) problem may occur.
The steps below describe the “triangle route” problem.
188
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 29
Chapter 15 Firewall
1
2
3
WAN
LAN
A
ISP 1
ISP 2
1 A computer on the LAN initiates a connection by sending out a SYN packet to a receiving server on
the WAN.
2 The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries reroutes the SYN packet through Gateway A on the LAN to the
WAN.
3 The reply from the WAN goes directly to the computer on the LAN without going through the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
As a result, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries resets the connection, as the connection has not been
acknowledged.
Figure 91 “Triangle Route” Problem
15.6.4.2 Solving the “Triangle Route” Problem
If you have the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries allow triangle route sessions, traffic from the WAN can
go directly to a LAN computer without passing through the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries and its
firewall protection.
Another solution is to use IP alias. IP alias allows you to partition your network into logical sections
over the same Ethernet interface. Your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries supports up to three logical
LAN interfaces with the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries being the gateway for each logical network.
It’s like having multiple LAN networks that actually use the same physical cables and ports. By
putting your LAN and Gateway A in different subnets, all returning network traffic must pass
through the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to your LAN. The following steps describe such a scenario.
1 A computer on the LAN initiates a connection by sending a SYN packet to a receiving server on the
WAN.
2 The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries reroutes the packet to Gateway A, which is in Subnet 2.
3 The reply from the WAN goes to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
4 The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries then sends it to the computer on the LAN in Subnet 1.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
189
Page 30
Chapter 15 Firewall
1
2
3
LAN
A
ISP 1
ISP 2
4
WAN
Subnet 1
Subnet 2
Figure 92 IP Alias
190
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 31

CHAPTER 16
16.1 Overview
Parental control allows you to block web sites with the specific URL. You can also define time
periods and days during which the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries performs parental control on a
specific user.
16.2 The Parental Control Screen
Use this screen to enable parental control, view the parental control rules and schedules.
Click Security > Parental Control to open the following screen.
Parental Control
Figure 93 Security > Parental Control
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 68 Security > Parental Control
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Parental Control Use this field to activate or deactivate parental control.
Add new PCP Click this to create a new parental control rule.
# This is the index number of the rule.
Status This indicates whether the rule is active or not.
A yellow bulb signifies that this rule is active. A gray bulb signifies that this rule is not
active.
PCP Name This shows the name of the rule.
Home Network User This shows the MAC address of the LAN user’s computer to which this rule applies.
Internet Access
Schedule
Network Service This shows whether the network service is configured. If not, None will be shown.
This shows the day(s) and time on which parental control is enabled.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 191
Page 32

Chapter 16 Parental Control
Table 68 Security > Parental Control (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Website Blocked This shows whether the website block is configured. If not, None will be shown.
Modify Click the Edit icon to go to the screen where you can edit the rule.
Click the Delete icon to delete an existing rule.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to restore your previously saved settings.
16.2.1 Add/Edit Parental Control Rule
Click Add new PCP in the Parental Control screen to add a new rule or click the Edit icon next to
an existing rule to edit it. Use this screen to configure a restricted access schedule and/or URL
filtering settings to block the users on your network from accessing certain web sites.
Figure 94 Add/Edit Parental Control Rule
192
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 69 Parental Control: Add/Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General
Active Select the checkbox to activate this parental control rule.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 33

Chapter 16 Parental Control
Table 69 Parental Control: Add/Edit (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Parental Control
Profile Name
Home Network User
Internet Access Schedule
Day Select check boxes for the days that you want the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to
Time of Day to Apply Enter the starting and ending time that the LAN user is allowed access.
Network Service
Network Service
Setting
Add new service Click this to show a screen in which you can add a new service rule. You can configure
Active This shows whether a configured service is activated or not.
Service Name This shows the name of the rule.
Protocol This shows the protocol of the rule.
Port This shows the port of the rule.
Modify Click the Edit icon to go to the screen where you can edit the rule.
Blocked Site/URL Enter the URL of web sites or URL keywords to which the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving.
Enter a descriptive name for the rule.
Select the LAN user that you want to apply this rule to from the drop-down list box. If
you select Custom, enter the LAN user’s MAC address. If you select All, the rule
applies to all LAN users.
perform parental control.
If you select Block, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries prohibits the users from viewing
the Web sites with the URLs listed below.
If you select Access, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries blocks access to all URLs except
ones listed below.
the Service Name, Protocol, and Name of the new rule.
Click the Delete icon to delete an existing rule.
blocks access.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
193
Page 34

Chapter 16 Parental Control
194
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 35

CHAPTER 17
17.1 Overview
The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries can use certificates (also called digital IDs) to authenticate users.
Certificates are based on public-private key pairs. A certificate contains the certificate owner’s
identity and public key. Certificates provide a way to exchange public keys for use in authentication.
17.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•Use the Local Certificates screen to view and import the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s CA-
signed certificates (Section 17.3 on page 195).
•The Trusted CA screen lets you save the certificates of trusted CAs to the AMG1302/AMG1202-
TSeries (Section 17.4 on page 197).
Certificate
17.2 What You Need to Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
Certification Authority
A Certification Authority (CA) issues certificates and guarantees the identity of each certificate
owner. There are commercial certification authorities like CyberTrust or VeriSign and government
certification authorities. The certification authority uses its private key to sign certificates. Anyone
can then use the certification authority's public key to verify the certificates. You can use the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to generate certification requests that contain identifying information
and public keys and then send the certification requests to a certification authority.
Certificate File Format
The certification authority certificate that you want to import has to be in one of these file formats:
• PEM (Base-64) encoded X.509: This Privacy Enhanced Mail format uses 64 ASCII characters to
convert a binary X.509 certificate into a printable form.
17.3 Local Certificates
Use this screen to view the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s summary list of certificates and
certification requests. You can import the following certificates to your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries:
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 195
Page 36

Chapter 17 Certificate
• Web Server - This certificate secures HTTP connections.
• SSH - This certificate secures remote connections.
Click Security > Certificates to open the Local Certificates screen.
Figure 95 Security > Certificates > Local Certificates
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 70 Security > Certificates > Local Certificates
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WebServer Click Browse... to find the certificate file you want to upload.
Current File This field displays the name used to identify this certificate. It is recommended
Subject This field displays identifying information about the certificate’s owner, such as
Issuer This field displays identifying information about the certificate’s issuing
Valid From This field displays the date that the certificate becomes applicable. The text
Valid To This field displays the date that the certificate expires. The text displays in red
Cert Click this button and then Save in the File Download screen. The Save As
SSH Type in the location of the SSH certificate file you want to upload in this field or
Current File This field displays the name used to identify this certificate. It is recommended
Key Type This field applies to the SSH certificate.
that you give each certificate a unique name.
CN (Common Name), OU (Organizational Unit or department), O (Organization
or company) and C (Country). It is recommended that each certificate have
unique subject information.
certification authority, such as a common name, organizational unit or
department, organization or company and country.
displays in red and includes a Not Yet Valid! message if the certificate has not
yet become applicable.
and includes an Expiring! or Expired! message if the certificate is about to
expire or has already expired.
screen opens, browse to the location that you want to use and click Save.
click Browse to find it.
that you give each certificate a unique name.
196
This shows the file format of the current certificate.
Replace Click this to replace the certificate(s) and save your changes back to the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Reset Click this to clear your settings.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 37

17.4 The Trusted CA Screen
Use this screen to view a summary list of certificates of the certification authorities that you have
set the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to accept as trusted. The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries accepts
any valid certificate signed by a certification authority on this list as being trustworthy; thus you do
not need to import any certificate that is signed by one of these certification authorities.
Click Security > Certificates > Trusted CA to open the Trusted CA screen.
Figure 96 Security > Certificates > Trusted CA
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 71 Security > Certificates > Trusted CA
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Import Certificate Click this button to open a screen where you can save the certificate of a certification
authority that you trust to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Name This field displays the name used to identify this certificate.
Subject This field displays information that identifies the owner of the certificate, such as
Common Name (CN), OU (Organizational Unit or department), Organization (O), State
(ST) and Country (C). It is recommended that each certificate have unique subject
information.
Type This field displays general information about the certificate. ca means that a
Certification Authority signed the certificate.
Action Click View to open a screen with an in-depth list of information about the certificate.
Chapter 17 Certificate
Click Remove to delete the certificate.
17.5 Trusted CA Import
Click Import Certificate in the Trusted CA screen to open the Import Certificate screen. You
can save a trusted certification authority’s certificate to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
197
Page 38

Chapter 17 Certificate
Note: You must remove any spaces from the certificate’s filename before you can import
Figure 97 Trusted CA > Import
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 72 Security > Certificates > Trusted CA > Import
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Certificate File
Path
Browse Click Browse to find the certificate file you want to upload.
Apply Click Apply to save the certificate on the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
the certificate.
Type in the location of the file you want to upload in this field or click Browse to
find it.
17.6 View Certificate
Use this screen to view in-depth information about the certification authority’s certificate, change
the certificate’s name and set whether or not you want the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to check a
certification authority’s list of revoked certificates before trusting a certificate issued by the
certification authority.
198
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 39

Chapter 17 Certificate
Click Security > Certificates > Trusted CA to open the Trusted CA screen. Click the View icon
to open the View Certificate screen.
Figure 98 Trust e d C A : V i e w
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 73 Trusted CA: Vi e w
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Certificate Name This field displays the identifying name of this certificate. If you want to
Certificate Detail This read-only text box displays the certificate or certification request in
Back Click this to return to the previous screen.
change the name, type up to 31 characters to identify this key certificate. You
may use any character (not including spaces).
Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) format. PEM uses 64 ASCII characters to convert
the binary certificate into a printable form.
You can copy and paste the certificate into an e-mail to send to friends or
colleagues or you can copy and paste the certificate into a text editor and save
the file on a management computer for later distribution (via floppy disk for
example).
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
199
Page 40

Chapter 17 Certificate
200
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 41

CHAPTER 18
18.1 Overview
The web configurator allows you to choose which categories of events and/or alerts to have the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries log and then display the logs or have the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries
send them to an administrator (as e-mail) or to a syslog server.
18.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•Use the Log screen to see the system logs for the categories that you select (Section 18.2 on
page 202).
18.1.2 What You Need To Know
Logs
The following terms and concepts may help as you read this chapter.
Alerts and Logs
An alert is a type of log that warrants more serious attention. They include system errors, attacks
(access control) and attempted access to blocked web sites. Some categories such as System
Errors consist of both logs and alerts. You may differentiate them by their color in the View Log
screen. Alerts display in red and logs display in black.
Syslog Overview
The syslog protocol allows devices to send event notification messages across an IP network to
syslog servers that collect the event messages. A syslog-enabled device can generate a syslog
message and send it to a syslog server.
Syslog is defined in RFC 3164. The RFC defines the packet format, content and system log related
information of syslog messages. Each syslog message has a facility and severity level. The syslog
facility identifies a file in the syslog server. Refer to the documentation of your syslog program for
details. The following table describes the syslog severity levels.
Table 74 Syslog Severity Levels
CODE SEVERITY
0 Emergency: The system is unusable.
1 Alert: Action must be taken immediately.
2 Critical: The system condition is critical.
3 Error: There is an error condition on the system.
4 Warning: There is a warning condition on the system.
5 Notice: There is a normal but significant condition on the system.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 201
Page 42

Chapter 18 Logs
Table 74 Syslog Severity Levels
CODE SEVERITY
6 Informational: The syslog contains an informational message.
7 Debug: The message is intended for debug-level purposes.
18.2 The System Log Screen
Click System Monitor > Log to open the System Log screen. Use the System Log screen to see
the system logs for the categories that you select in the upper left drop-down list box.
Figure 99 System Monitor > Log > System Log
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 75 System Monitor > Log > System Log
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Level Select a severity level from the drop-down list box. This filters search results according to
the severity level you have selected. When you select a severity, the AMG1302/AMG1202-
TSeries searches through all logs of that severity or higher.
Refresh Click this to renew the log screen.
Clear Logs Click this to delete all the logs.
Export Click this to download logs to a file on your computer.
Email Log Now
# This field is a sequential value and is not associated with a specific entry.
Time This field displays the time the log was recorded.
Level This field displays the severity level of the logs that the device is to send to this syslog
Message This field states the reason for the log.
Click this to send logs to a specified e-mail address.
server.
202
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 43

CHAPTER 19
19.1 Overview
Use the Traffic Status screens to look at network traffic status and statistics of the WAN, LAN
interfaces and NAT.
19.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•Use the WAN screen to view the WAN traffic statistics (Section 19.2 on page 203).
•Use the LAN screen to view the LAN traffic statistics (Section 19.3 on page 204).
•Use the NAT screen to view the NAT status of the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s client(s)
(Section 19.4 on page 205).
Traffic Status
19.2 The WAN Status Screen
Click System Monitor > Traffic Status to open the WAN screen. You can view the WAN traffic
statistics in this screen.
Figure 100 System Monitor > Traffic Status > WAN
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 76 System Monitor > Traffic Status > WAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status This shows the number of bytes received and sent through the WAN interface of the
Refresh Interval Select how often you want the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to update this screen from the
Connected
Interface
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
drop-down list box.
This shows the name of the WAN interface that is currently connected.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 203
Page 44

Chapter 19 Traffic Status
Table 76 System Monitor > Traffic Status > WAN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Packets Sent
Data This indicates the number of transmitted packets on this interface.
Error This indicates the number of frames with errors transmitted on this interface.
Drop This indicates the number of outgoing packets dropped on this interface.
Packets Received
Data This indicates the number of received packets on this interface.
Error This indicates the number of frames with errors received on this interface.
Drop This indicates the number of received packets dropped on this interface.
19.3 The LAN Status Screen
Click System Monitor > Traffic Stat us > LAN to open the following screen. You can view the LAN
traffic statistics in this screen.
Figure 101 System Monitor > Traffic Status > LAN
204
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 77 System Monitor > Traffic Status > LAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh
Interval(s)
Set Interval
Stop Click Stop to stop refreshing statistics.
Interface This shows the LAN or WLAN interface.
Bytes Sent This indicates the number of bytes transmitted on this interface.
Bytes Received This indicates the number of bytes received on this interface.
Interface This shows the LAN or WLAN interface.
Sent (Packet)
Select how often you want the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to update this screen
from the drop-down list box.
Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in the Refresh
Interval field.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 45

Table 77 System Monitor > Traffic Status > LAN (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Data This indicates the number of transmitted packets on this interface.
Error This indicates the number of frames with errors transmitted on this interface.
Drop This indicates the number of outgoing packets dropped on this interface.
Received (Packet)
Data This indicates the number of received packets on this interface.
Error This indicates the number of frames with errors received on this interface.
Drop This indicates the number of received packets dropped on this interface.
19.4 The NAT Screen
Click System Monitor > Traffic Status > NAT to open the following screen. You can view the NAT
status of the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s client(s) in this screen.
Figure 102 System Monitor > Traffic Status > NAT
Chapter 19 Traffic Status
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 78 System Monitor > Traffic Status > NAT
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh Interval Select how often you want the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to update this screen from the
drop-down list box.
Set Interval
Stop Click Stop to stop refreshing statistics.
Device Name This shows the name of the client.
IP Address This shows the IP address of the client.
MAC Address This shows the MAC address of the client.
No. of Open
Session
Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in the Refresh Interval field.
This shows the number of NAT sessions used by the client.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
205
Page 46

Chapter 19 Traffic Status
206
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 47

CHAPTER 20
20.1 Overview
You can configure system password for different user accounts in the User Account screen.
20.2 The User Account Screen
Use the User Account screen to configure system password.
Click Maintenance > User Account to open the following screen.
Figure 103 Maintenance > User Account
User Account
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 79 Maintenance > User Account
LABEL DESCRIPTION
User Name You can configure the password for the Power User and Admin accounts.
Old Password Type the default password or the existing password you use to access the system in this
New Password
Retype to
Confirm
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to restore your previously saved settings.
field.
Type your new system password (up to 30 characters). Note that as you type a password,
the screen displays a (*) for each character you type. After you change the password, use
the new password to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Type the new password again for confirmation.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 207
Page 48

Chapter 20 User Account
208
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 49

21.1 Overview
MSZD
The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries supports TR-069 Amendment 1 (CPE WAN Management Protocol
Release 2.0) and TR-069 Amendment 2 (CPE WAN Management Protocol v1.1, Release 3.0).
TR-069 is a protocol that defines how your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries (ZD) can be managed via a
management server (MS) such as ZyXEL’s Vantage Access.
Figure 104 LAN and WAN
CHAPTER 21
TR-069 Client
An administrator can use a management server to remotely set up the AMG1302/AMG1202TSeries, modify settings, perform firmware upgrades as well as monitor and diagnose the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
In order to use CWMP, you need to configure the following steps:
1 Activate CWMP
2 Specify the URL, username and password.
3 Activate periodic inform and specify an interval value.
21.2 The TR-069 Client Screen
Use this screen to configure your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to be managed by a management
server. Click Maintenance > TR-069 Client to display the following screen.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 209
Page 50

Chapter 21 TR-069 Client
Figure 105 Maintenance > TR-069 Client
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 80 Maintenance > TR-069 Client
LINK DESCRIPTION
CWMP Select Enable to allow the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to be managed by a management
ACS URL Type the IP address or domain name of the management server. If the AMG1302/AMG1202-
ACS User Name The user name is used to authenticate the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries when making a
ACS Password The password is used to authenticate the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries when making a
Connection
Request Path
Connection
Request Port
Connection
Request
UserName
Connection
Request
Password
Inform Select Enable to have the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries periodically send information to the
Inform Interval The interval is the duration in seconds for which the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries must
server or select Disable to not allow the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries to be managed by a
management server.
TSeries is behind a NAT router that assigns it a private IP address, you will have to
configure a NAT port forwarding rule on the NAT router.
connection to the management server. This user name on the management server and the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries must be the same. Type a user name of up to 255 printable
characters found on an English-language keyboard. Spaces and characters such as
@#$%^&*()_+ are allowed.
connection to the management server. This password on the management server and the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries must be the same. Type a password of up to 255 printable
characters found on an English-language keyboard.
Type the IP address or domain name of the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. The management
server uses this path to verify the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
The default port for access to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries from the management server
is port 7547. If you change it, make sure it does not conflict with another port on your
network and it is recommended to use a port number above 1024 (not a commonly used
port). The management server should use this port to connect to the AMG1302/AMG1202TSeries. You may need to alter your NAT port forwarding rules if they were already
configured.
The user name is used to authenticate the management server when connecting to the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. Type a user name of up to 255 printable characters found on
an English-language keyboard. Spaces and characters such as @#$%^&*()_+ are allowed.
The password is used to authenticate the management server when connecting to the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. Type a password of up to 255 printable characters found on an
English-language keyboard. Spaces are not allowed.
management server (recommended if CWMP is enabled) or select Disable to not have the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries periodically send information to the management server
attempt to connect with the management server to send information and check for
configuration updates. Enter a value between 1 and 86400 seconds.
210
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 51

Table 80 Maintenance > TR-069 Client (continued)
LINK DESCRIPTION
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Chapter 21 TR-069 Client
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
211
Page 52

Chapter 21 TR-069 Client
212
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 53

CHAPTER 22
System Settings
22.1 Overview
This chapter shows you how to configure system related settings, such as system time, password,
name, the domain name and the inactivity timeout interval.
22.1.1 What You Can Do in the System Settings Screens
•Use the System screen (Section 22.2 on page 213) to configure system settings.
•Use the Time Setting screen (Section 22.3 on page 213) to set the system time.
22.2 The System Screen
Use this screen to configure system admin password.
Click Maintenance > System to open the screen as shown.
Figure 106 Maintenance > System
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 81 Maintenance > System
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Administrator
Inactivity Timer
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Type how many seconds a management session (either via the web configurator) can be
left idle before the session times out and you have to log in again. Very long idle timeouts
may have security risks. A value of "0" means a management session never times out, no
matter how long it has been left idle (not recommended).
22.3 The Time Screen
Use this screen to configure the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s time based on your local time zone.
To change your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s time and date, click Maintenance > System >
Time Setting. The screen appears as shown.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 213
Page 54

Chapter 22 System Settings
Figure 107 Maintenance > System > Time Setting
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 82 Maintenance > System > Time
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Current Date/Time
Current Time This field displays the time and date of your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Each time you reload this page, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries synchronizes the time
and date with the time server.
Time and Date Setup
Manual Select this radio button to enter the time and date manually. If you configure a new
time and date, Time Zone and Daylight Saving at the same time, the new time and date
you entered has priority and the Time Zone and Daylight Saving settings do not affect
it.
Current Date/Time This field displays the last updated time (in hh:mm:ss format) from the time server or
the last time configured manually.
When you set Time and Date Setup to Manual, enter the new time in this field and
then click Apply.
Current Time This field displays the last updated date (in yyyy/mm/dd format) from the time server
or the last date configured manually.
When you set Time and Date Setup to Manual, enter the new date in this field and
then click Apply.
Get from Time
Server
Time Server
Address 1/2
Time Zone Setup
Time Zone Choose the time zone of your location. This will set the time difference between your
Select this radio button to have the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries get the time and date
from the time server you specified below.
Enter the IP address or URL (up to 20 extended ASCII characters in length) of your time
server. Check with your ISP/network administrator if you are unsure of this information.
time zone and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
214
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 55

Chapter 22 System Settings
Table 82 Maintenance > System > Time (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Daylight Savings Daylight saving is a period from late spring to early fall when many countries set their
clocks ahead of normal local time by one hour to give more daytime light in the
evening.
Select this option if you use Daylight Saving Time.
Start Date Configure the day and time when Daylight Saving Time starts if you selected Enable
Daylight Saving. The o'clock field uses the 24 hour format. Here are a couple of
examples:
Daylight Saving Time starts in most parts of the United States on the second Sunday of
March. Each time zone in the United States starts using Daylight Saving Time at 2 A.M.
local time. So in the United States you would select Second, Sunday, March and type
2 in the o'clock field.
Daylight Saving Time starts in the European Union on the last Sunday of March. All of
the time zones in the European Union start using Daylight Saving Time at the same
moment (1 A.M. GMT or UTC). So in the European Union you would select Last,
Sunday, March. The time you type in the o'clock field depends on your time zone. In
Germany for instance, you would type 2 because Germany's time zone is one hour
ahead of GMT or UTC (GMT+1).
End Date Configure the day and time when Daylight Saving Time ends if you selected Enable
Daylight Saving. The o'clock field uses the 24 hour format. Here are a couple of
examples:
Daylight Saving Time ends in the United States on the first Sunday of November. Each
time zone in the United States stops using Daylight Saving Time at 2 A.M. local time. So
in the United States you would select First, Sunday, November and type 2 in the
o'clock field.
Daylight Saving Time ends in the European Union on the last Sunday of October. All of
the time zones in the European Union stop using Daylight Saving Time at the same
moment (1 A.M. GMT or UTC). So in the European Union you would select Last,
Sunday, October. The time you type in the o'clock field depends on your time zone.
In Germany for instance, you would type 2 because Germany's time zone is one hour
ahead of GMT or UTC (GMT+1).
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
215
Page 56

Chapter 22 System Settings
216
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 57

23.1 Overview
This chapter explains how to upload new firmware to your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. You can
download new firmware releases from your nearest ZyXEL FTP site (or www.zyxel.com) to use to
upgrade your device’s performance.
Only use firmware for your device’s specific model. Refer to the label on
the bottom of your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
23.2 The Firmware Screen
CHAPTER 23
Firmware Upgrade
Click Maintenance > Firmware Upgrade to open the following screen. The upload process uses
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and may take up to two minutes. After a successful upload, the
system will reboot.
Do NOT turn off the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries while firmware upload
is in progress!
Figure 108 Maintenance > Firmware Upgrade
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 83 Maintenance > Firmware Upgrade
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Current Firmware
Version
File Path Type in the location of the file you want to upload in this field or click Browse... to find it.
Browse... Click this to find the .bin file you want to upload. Remember that you must decompress
Upload Click this to begin the upload process. This process may take up to two minutes.
This is the present Firmware version.
compressed (.zip) files before you can upload them.
After you see the firmware updating screen, wait two minutes before logging into the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries again.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 217
Page 58

Chapter 23 Firmware Upgrade
Figure 109 Firmware Uploading
The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries automatically restarts in this time causing a temporary network
disconnect. In some operating systems, you may see the following icon on your desktop.
Figure 110 Network Temporarily Disconnected
After two minutes, log in again and check your new firmware version in the Status screen.
If the upload was not successful, an error screen will appear. Click OK to go back to the Firmware
Upgrade screen.
Figure 111 Error Message
218
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 59

CHAPTER 24
24.1 Overview
The Backup/Restore screen allows you to backup and restore device configurations. You can also
reset your device settings back to the factory default.
24.2 The Backup/Restore Screen
Click Maintenance > Backup/Restore. Information related to factory defaults, backup
configuration, and restoring configuration appears in this screen, as shown next.
Figure 112 Maintenance > Backup/Restore
Backup/Restore
Backup Configuration
Backup Configuration allows you to back up (save) the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s current
configuration to a file on your computer. Once your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries is configured and
functioning properly, it is highly recommended that you back up your configuration file before
making configuration changes. The backup configuration file will be useful in case you need to
return to your previous settings.
Click Backup to save the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s current configuration to your computer.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 219
Page 60

Chapter 24 Backup/Restore
Restore Configuration
Restore Configuration allows you to upload a new or previously saved configuration file from your
computer to your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Table 84 Restore Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
File Path Type in the location of the file you want to upload in this field or click Browse... to find it.
Browse... Click this to find the file you want to upload. Remember that you must decompress
Upload Click this to begin the upload process.
Reset Click this to reset your device settings back to the factory default.
Do not turn off the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries while configuration file
upload is in progress.
After the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries configuration has been restored successfully, the login screen
appears. Login again to restart the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries automatically restarts in this time causing a temporary network
disconnect. In some operating systems, you may see the following icon on your desktop.
compressed (.ZIP) files before you can upload them.
Figure 113 Network Temporarily Disconnected
If you restore the default configuration, you may need to change the IP address of your computer
to be in the same subnet as that of the default device IP address (192.168.1.1). See Appendix A on
page 245 for details on how to set up your computer’s IP address.
If the upload was not successful, an error screen will appear. Click OK to go back to the
Configuration screen.
Reset to Factory Defaults
Click the Reset button to clear all user-entered configuration information and return the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries to its factory defaults. The following warning screen appears.
Figure 114 Reset Warning Message
220
Wait until the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s login screen appears. You can also press the RESET
button on the rear panel to reset the factory defaults of your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. Refer to
Section 1.7 on page 19 for more information on the RESET button.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 61

24.3 The Reboot Screen
System restart allows you to reboot the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries remotely without turning the
power off. You may need to do this if the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries hangs, for example.
Click Maintenance > Reboot. Click the Reboot button to have the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries
reboot. This does not affect the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries's configuration.
Figure 115 Maintenance > Reboot
Chapter 24 Backup/Restore
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
221
Page 62

Chapter 24 Backup/Restore
222
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 63

25.1 Overview
LAN
WAN
HTTP
Telnet
Remote management allows you to determine which services/protocols can access which
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries interface (if any) from which computers.
The following figure shows remote management of the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries coming in from
the WAN.
Figure 116 Remote Management From the WAN
CHAPTER 25
Remote Management
Note: When you configure remote management to allow management from the WAN, you
still need to configure a IP filter rule to allow access.
You may manage your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries from a remote location via:
• Internet (WAN only)
•LAN only
•LAN and WAN
• None (Disable)
To disable remote management of a service, select Disable in the corresponding Service Access
field.
25.1.1 What You Can Do in the Remote Management Screens
•Use the WWW screen (Section 25.2 on page 224) to configure through which interface(s) and
from which IP address(es) users can use HTTP to manage the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
•Use the Telnet screen (Section 25.3 on page 226) to configure through which interface(s) and
from which IP address(es) users can use Telnet to manage the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
•Use the FTP screen (Section 25.4 on page 226) to configure through which interface(s) and from
which IP address(es) users can use FTP to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 223
Page 64

Chapter 25 Remote Management
• Your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries can act as an SNMP agent, which allows a manager station to
manage and monitor the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries through the network. Use the SNMP
screen (see Section 25.5 on page 227) to configure through which interface(s) and from which IP
address(es) users can use SNMP to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
•Use the DNS screen (Section 25.6 on page 230) to configure through which interface(s) and
from which IP address(es) users can send DNS queries to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
•Use the ICMP screen (Section 25.7 on page 230) to set whether or not your AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries will respond to pings and probes for services that you have not made available.
•Use the SSH screen (Section 25.8 on page 231) to configure through which interface(s) and from
which IP address(es) users can use SSH to manage the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
25.1.2 What You Need to Know About Remote Management
Remote Management Limitations
Remote management does not work when:
• You have not enabled that service on the interface in the corresponding remote management
screen.
• You have disabled that service in one of the remote management screens.
• The IP address in the Secured Client IP Address field does not match the client IP address. If
it does not match, the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries will disconnect the session immediately.
• There is a firewall rule that blocks it.
Remote Management and NAT
When NAT is enabled:
• Use the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s WAN IP address when configuring from the WAN.
• Use the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s LAN IP address when configuring from the LAN.
25.2 The WWW Screen
Use this screen to specify how to connect to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries from a web browser,
such as Internet Explorer.
25.2.1 Configuring the WWW Screen
Click Maintenance > RemoteMGMT to display the WWW screen.
224
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 65

Figure 117 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > WWW
Chapter 25 Remote Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 85 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > WWW
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port This displays the service port number for accessing the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the AMG1302/AMG1202-
using HTTP or HTTPS. If the number is grayed out, it is not editable.
TSeries using this service.
Note: It is recommended if you are allowing WAN access even temporarily to change the
default password (in Maintenance > User Account). T o allow access from the
WAN, you will need to configure a WAN to Router firewall rule. See Section 4.1 on
page 37 for information on configuring firewall rules.
Secured Client IP
Address
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate with the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this
service.
Choose Range to just allow the computer(s) with an IP address in the range that you
specify to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this service.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
225
Page 66

Chapter 25 Remote Management
25.3 The Telnet Screen
You can use Telnet to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s command line interface. Specify
which interfaces allow Telnet access and from which IP address the access can come.
Click Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > Telnet tab to display the screen as shown.
Figure 118 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > Telnet
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 86 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > Telnet
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port This displays the service port number for accessing the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. If
the number is grayed out, it is not editable.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the AMG1302/AMG1202-
TSeries using this service.
Note: It is recommended if you are allowing WAN access even temporarily to change the
default password (in Maintenance > User Account). To allow access from the
WAN, you will need to configure a WAN to Router firewall rule. See Firewall Section
on page 173 for information on configuring firewall rules.
Secured Client IP
Address
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate with the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this
service.
Choose Range to just allow the computer(s) with an IP address in the range that you
specify to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this service.
25.4 The FTP Screen
You can use FTP (File Transfer Protocol) to upload and download the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s
firmware and configuration files. Please see the User’s Guide chapter on firmware and configuration
file maintenance for details. To use this feature, your computer must have an FTP client.
226
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 67

Chapter 25 Remote Management
Use this screen to specify which interfaces allow FTP access and from which IP address the access
can come. To change your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s FTP settings, click Maintenance >
RemoteMGMT > FTP. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 119 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > FTP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 87 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > FTP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port This displays the service port number for accessing the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. If
the number is grayed out, it is not editable.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the AMG1302/AMG1202-
Secured Client IP
Address
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
TSeries using this service.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate with the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this
service.
Choose Range to just allow the computer(s) with an IP address in the range that you
specify to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this service.
25.5 The SNMP Screen
Simple Network Management Protocol is a protocol used for exchanging management information
between network devices. Your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries supports SNMP agent functionality,
which allows a manager station to manage and monitor the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries through
the network. The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries supports SNMP version one (SNMPv1) and version
two (SNMPv2c). The next figure illustrates an SNMP management operation.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
227
Page 68

Chapter 25 Remote Management
Figure 120 SNMP Management Model
An SNMP managed network consists of two main types of component: agents and a manager.
An agent is a management software module that resides in a managed device (the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries). An agent translates the local management information from the managed
device into a form compatible with SNMP. The manager is the console through which network
administrators perform network management functions. It executes applications that control and
monitor managed devices.
The managed devices contain object variables/managed objects that define each piece of
information to be collected about a device. Examples of variables include such as number of
packets received, node port status etc. A Management Information Base (MIB) is a collection of
managed objects. SNMP allows a manager and agents to communicate for the purpose of accessing
these objects.
25.5.1 Configuring SNMP
To change your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s SNMP settings, click Maintenance > RemoteMGMT
> SNMP tab. The screen appears as shown.
228
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 69

Figure 121 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > SNMP
Chapter 25 Remote Management
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 88 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > SNMP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port This displays the port the SNMP agent listens on. If the number is grayed out, it is not
editable.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the AMG1302/AMG1202-
Secured Client IP
Address
Get Community Enter the Get Community, which is the password for the incoming Get and GetNext
Set Community Enter the Set community, which is the password for incoming Set requests from the
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
TSeries using this service.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to access the SNMP agent on the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Select All to allow any computer to access the SNMP agent.
Choose Range to just allow the computer(s) with an IP address in the range that you
specify to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this service.
requests from the management station. The default is public and allows all requests.
management station. The default is public and allows all requests.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
229
Page 70

Chapter 25 Remote Management
25.6 The DNS Screen
Use DNS (Domain Name System) to map a domain name to its corresponding IP address and vice
versa.
Use this screen to set from which IP address the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries will accept DNS
queries and on which interface it can send them your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s DNS settings.
This feature is not available when the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries is set to bridge mode. Click
Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > DNS to change your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s DNS
settings.
Figure 122 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > DNS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 89 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > DNS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port This displays the service port number for accessing the AMG1302/AMG1202-
Access Status Select the interface(s) through which a computer may send DNS queries to the
Secured Client IP
Address
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
TSeries. If the number is grayed out, it is not editable.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to send DNS queries to
the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Select All to allow any computer to send DNS queries to the AMG1302/AMG1202-
TSeries.
Choose Range to just allow the computer(s) with an IP address in the range that
you specify to send DNS queries to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
25.7 The ICMP Screen
To change your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s security settings, click Maintenance >
RemoteMGMT > ICMP. The screen appears as shown.
230
If an outside user attempts to probe an unsupported port on your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries, an
ICMP response packet is automatically returned. This allows the outside user to know the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 71

Chapter 25 Remote Management
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries exists. Your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries supports anti-probing, which
prevents the ICMP response packet from being sent. This keeps outsiders from discovering your
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries when unsupported ports are probed.
Note: If you want your device to respond to pings and requests for unauthorized services,
you will also need to configure the firewall accordingly by disabling SPI.
Figure 123 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > ICMP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 90 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > ICMP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Respond to Ping on The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries will not respond to any incoming Ping requests when
Disable is selected. Select LAN to reply to incoming LAN Ping requests. Select WAN to
reply to incoming WAN Ping requests. Otherwise select LAN & WAN to reply to both
incoming LAN and WAN Ping requests.
Secured Client IP
Address
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to send Ping requests to the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
Select All to allow any computer to send Ping requests to the AMG1302/AMG1202TSeries.
Choose Range to just allow the computer(s) with an IP address in the range that you
specify to send Ping requests to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
25.8 The SSH Screen
You can use Secure SHell (SSH) to securely access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries’s command line
interface. Specify which interfaces allow SSH access and from which IP address the access can
come. SSH is a secure communication protocol that combines authentication and data encryption to
provide secure encrypted communication between two hosts over an unsecured network.
Click Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > SSH tab to display the screen as shown.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
231
Page 72

Chapter 25 Remote Management
Figure 124 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > SSH
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 91 Maintenance > RemoteMGMT > SSH
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port This displays the service port number for accessing the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. If
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the AMG1302/AMG1202-
the number is grayed out, it is not editable.
TSeries using this service.
Secured Client IP
Address
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
25.8.1 SSH Example
This section shows an example using a graphical interface SSH client program to remotely access
the ZyXEL Device. The configuration and connection steps are similar for most SSH client programs.
Refer to your SSH client program user’s guide.
1 Enter the IP address and port number. Select SSH.
Note: It is recommended if you are allowing WAN access even temporarily to change the
default password (in Maintenance > User Account). To allow access from the
WAN, you will need to configure a WAN to Router firewall rule. See Firewall Section
on page 173 for information on configuring firewall rules.
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate with the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this
service.
Choose Range to just allow the computer(s) with an IP address in the range that you
specify to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using this service.
232
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 73

Chapter 25 Remote Management
2 A window displays prompting you to store the host key in your computer. Click Yes to continue.
3 Enter your user name and password.
4 The command line interface displays.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
233
Page 74

Chapter 25 Remote Management
234
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 75

CHAPTER 26
26.1 Overview
These read-only screens display information to help you identify problems with the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries.
26.1.1 What You Can Do in the Diagnostic Screens
•Use the Ping screen (Section 26.2 on page 235) to ping an IP address.
•Use the DSL Line screen (Section 26.3 on page 236) to view the DSL line statistics and reset the
ADSL line.
Diagnostic
26.2 The General Screen
Use this screen to ping an IP address. Click Maintenance > Diagnostic > Ping to open the screen
shown next.
Figure 125 Maintenance > Diagnostic > Ping
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 92 Maintenance > Diagnostic > Ping
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Type the IP address of a computer that you want to ping in order to test a connection.
Ping Click this to ping the IP address that you entered.
PingV6 Click this to ping the IPv6 address that you entered.
Tra cerou teV6 Click this to display the route path and transmission delays between the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries to the IPv6 address that you entered.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 235
Page 76

Chapter 26 Diagnostic
26.3 The DSL Line Screen
Use this screen to view the DSL line statistics and reset the ADSL line. Click Maintenance >
Diagnostic > DSL Line to open the screen shown next.
Figure 126 Maintenance > Diagnostic > DSL Line
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 93 Maintenance > Diagnostic > DSL Line
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ATM Status Click this to view your DSL connection’s Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) statistics.
ATM is a networking technology that provides high-speed data transfer. ATM uses fixedsize packets of information called cells. With ATM, a high QoS (Quality of Service) can be
guaranteed.
The (Segmentation and Reassembly) SAR driver translates packets into ATM cells. It also
receives ATM cells and reassembles them into packets.
These counters are set back to zero whenever the device starts up.
inPkts is the number of good ATM cells that have been received.
inDiscards is the number of received ATM cells that were rejected.
inF4Pkts is the number of ATM Operations, Administration, and Management (OAM) F4
cells that have been received. See ITU recommendation I.610 for more on OAM for ATM.
inF5Pkts is the number of ATM OAM F5 cells that have been received.
outPkts is the number of ATM cells that have been sent.
outDiscards is the number of ATM cells sent that were rejected.
outF4Pkts is the number of ATM OAM F4 cells that have been sent.
outF5Pkts is the number of ATM OAM F5 cells that have been sent.
ATM Loopback
Test
Click this to start the ATM loopback test. Make sure you have configured at least one PVC
with proper VPIs/VCIs before you begin this test. The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries sends
an OAM F5 packet to the DSLAM/ATM switch and then returns it (loops it back) to the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries. The ATM loopback test is useful for troubleshooting
problems with the DSLAM and ATM network.
236
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 77

Chapter 26 Diagnostic
Table 93 Maintenance > Diagnostic > DSL Line (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
DSL Line Status Click this to view statistics about the DSL connections.
noise margin downstream is the signal to noise ratio for the downstream part of the
connection (coming into the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries from the ISP). It is measured in
decibels. The higher the number the more signal and less noise there is.
output power upstream is the amount of power (in decibels) that the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries is using to transmit to the ISP.
attenuation downstream is the reduction in amplitude (in decibels) of the DSL signal
coming into the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries from the ISP.
Discrete Multi-Tone (DMT) modulation divides up a line’s bandwidth into sub-carriers
(sub-channels) of 4.3125 KHz each called tones. The rest of the display is the line’s bit
allocation. This is displayed as the number (in hexadecimal format) of bits transmitted for
each tone. This can be used to determine the quality of the connection, whether a given
sub-carrier loop has sufficient margins to support certain ADSL transmission rates, and
possibly to determine whether particular specific types of interference or line attenuation
exist. Refer to the ITU-T G.992.1 recommendation for more information on DMT.
The better (or shorter) the line, the higher the number of bits transmitted for a DMT tone.
The maximum number of bits that can be transmitted per DMT tone is 15. There will be
some tones without any bits as there has to be space between the upstream and
downstream channels.
Reset ADSL Line Click this to reinitialize the ADSL line. The large text box above then displays the progress
and results of this operation, for example:
"Start to reset ADSL
Loading ADSL modem F/W...
Reset ADSL Line Successfully!"
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
237
Page 78

Chapter 26 Diagnostic
238
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 79

CHAPTER 27
Troubleshooting
This chapter offers some suggestions to solve problems you might encounter. The potential
problems are divided into the following categories.
• Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
• AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries Access and Login
• Internet Access
27.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
The AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries does not turn on. None of the LEDs turn on.
1 Make sure the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries is turned on.
2 Make sure you are using the power adaptor or cord included with the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
3 Make sure the power adaptor or cord is connected to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries and plugged
in to an appropriate power source. Make sure the power source is turned on.
4 Turn the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries off and on.
5 If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
One of the LEDs does not behave as expected.
1 Make sure you understand the normal behavior of the LED. Section 1.5 on page 17
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WPS LED Green: successful connection
Off: connection failure
WIFI LED Green: WIFI active
Off: WIFI inactive
2 Check the hardware connections.
3 Inspect your cables for damage. Contact the vendor to replace any damaged cables.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 239
Page 80

Chapter 27 Troubleshooting
4 Turn the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries off and on.
5 If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
27.2 AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries Access and Login
I forgot the IP address for the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
1 The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
2 If you changed the IP address and have forgotten it, you might get the IP address of the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries by looking up the IP address of the default gateway for your computer. To do this
in most Windows computers, click Start > Run, enter cmd, and then enter ipconfig. The IP
address of the Default Gateway might be the IP address of the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries (it
depends on the network), so enter this IP address in your Internet browser.
3 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See Section 1.7 on page
19.
I forgot the password.
1 The default admin user name and password can be found on the cover of this User’s Guide.
2 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See Section 1.7 on page
19.
I cannot see or access the Login screen for the web configurator.
1 Make sure you are using the correct IP address.
• The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
• If you changed the IP address (Section 8.2 on page 123), use the new IP address.
• If you changed the IP address and have forgotten it, see the troubleshooting suggestions for I
forgot the IP address for the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
2 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as expected. See the Quick
Start Guide.
3 Make sure your Internet browser does not block pop-up windows and has JavaScripts and Java
enabled. See Appendix C on page 273.
240
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 81

Chapter 27 Troubleshooting
4 Reset the device to its factory defaults, and try to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries with the
default IP address. See Section 1.7 on page 19.
5 If the problem continues, contact the network administrator or vendor, or try one of the advanced
suggestions.
Advanced Suggestions
• Try to access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries using another service, such as Telnet. If you can
access the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries, check the remote management settings and firewall
rules to find out why the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries does not respond to HTTP.
• If your computer is connected to the DSL port or is connected wirelessly, use a computer that is
connected to a ETHERNET port.
I can see the Login screen, but I cannot log in to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
1 Make sure you have entered the password correctly. The default user and default admin password
can be found on the cover page of this User’s Guide. The field is case-sensitive, so make sure [Caps
Lock] is not on.
2 You cannot log in to the web configurator while someone is using Telnet to access the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries. Log out of the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries in the other session, or ask the
person who is logged in to log out.
3 Turn the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries off and on.
4 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See Section 1.7 on page
19.
I cannot Telnet to the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries.
See the troubleshooting suggestions for I cannot see or access the Login screen for the web
configurator. Ignore the suggestions about your browser.
I cannot use FTP to upload / download the configuration file. / I cannot use FTP to upload
new firmware.
See the troubleshooting suggestions for I cannot see or access the Login screen for the web
configurator. Ignore the suggestions about your browser.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
241
Page 82

Chapter 27 Troubleshooting
27.3 Internet Access
I cannot access the Internet.
1 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as expected. See the Quick
Start Guide and Section 27.1 on page 225.
2 Make sure you entered your ISP account information correctly in the wizard. These fields are case-
sensitive, so make sure [Caps Lock] is not on.
3 If you are trying to access the Internet wirelessly, make sure the wireless settings in the wireless
client are the same as the settings in the AP.
4 If you are trying to access the Internet wirelessly, make sure you enabled the wireless LAN and
have selected the correct country and channel in which your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries operates
in the Wireless LAN > AP screen.
5 Disconnect all the cables from your device, and follow the directions in the Quick Start Guide again.
6 If the problem continues, contact your ISP.
I cannot access the Internet anymore. I had access to the Internet (with the AMG1302/
AMG1202-TSeries), but my Internet connection is not available anymore.
1 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as expected. See the Quick
Start Guide and Section 27.1 on page 225.
2 Turn the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries off and on.
3 If the problem continues, contact your ISP.
The Internet connection is slow or intermittent.
1 There might be a lot of traffic on the network. Look at the LEDs, and check Section 27.1 on page
225. If the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries is sending or receiving a lot of information, try closing
some programs that use the Internet, especially peer-to-peer applications.
2 Check the signal strength. If the signal strength is low, try moving your computer closer to the
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries if possible, and look around to see if there are any devices that might
be interfering with the wireless network (for example, microwaves, other wireless networks, and so
on).
3 Turn the AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries off and on.
242
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 83

Chapter 27 Troubleshooting
4 If the problem continues, contact the network administrator or vendor, or try one of the advanced
suggestions.
Advanced Suggestions
• Check the settings for QoS. If it is disabled, you might consider activating it. If it is enabled, you
might consider raising or lowering the priority for some applications.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
243
Page 84

Chapter 27 Troubleshooting
244
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 85

APPENDIX A
Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
All computers must have a 10M or 100M Ethernet adapter and TCP/IP installed.
Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP/Vista, Macintosh OS 7 and later operating systems and all versions
of UNIX/LINUX include the software components you need to install and use TCP/IP on your
computer. Windows 3.1 requires the purchase of a third-party TCP/IP application package.
TCP/IP should already be installed on computers using Windows NT/2000/XP, Macintosh OS 7 and
later operating systems.
After the appropriate TCP/IP components are installed, configure the TCP/IP settings in order to
"communicate" with your network.
If you manually assign IP information instead of using dynamic assignment, make sure that your
computers have IP addresses that place them in the same subnet as the AMG1302/AMG1202TSeries’s LAN port.
Windows 95/98/Me
Click Start, Settings, Control Panel and double-click the Network icon to open the Network
window.
Figure 127 WIndows 95/98/Me: Network: Configuration
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide 245
Page 86

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Installing Component s
The Network window Configuration tab displays a list of installed components. You need a
network adapter, the TCP/IP protocol and Client for Microsoft Networks.
If you need the adapter:
1 In the Network window, click Add.
2 Select Adapter and then click Add.
3 Select the manufacturer and model of your network adapter and then click OK.
If you need TCP/IP:
1 In the Network window, click Add.
2 Select Protocol and then click Add.
3 Select Microsoft from the list of manufacturers.
4 Select TCP/IP from the list of network protocols and then click OK.
If you need Client for Microsoft Networks:
1 Click Add.
2 Select Client and then click Add.
3 Select Microsoft from the list of manufacturers.
4 Select Client for Microsoft Networks from the list of network clients and then click OK.
5 Restart your computer so the changes you made take effect.
Configuring
1 In the Network window Configuration tab, select your network adapter's TCP/IP entry and click
Properties
2 Click the IP Address tab.
• If your IP address is dynamic, select Obtain an IP address automatically.
• If you have a static IP address, select Specify an IP address and type your information into
the IP Address and Subnet Mask fields.
246
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 87

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 128 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: IP Address
3 Click the DNS Configuration tab.
• If you do not know your DNS information, select Disable DNS.
• If you know your DNS information, select Enable DNS and type the information in the fields
below (you may not need to fill them all in).
Figure 129 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: DNS Configuration
4 Click the Gateway tab.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
247
Page 88

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
• If you do not know your gateway’s IP address, remove previously installed gateways.
• If you have a gateway IP address, type it in the New gateway field and click Add.
5 Click OK to save and close the TCP/IP Properties window.
6 Click OK to close the Network window. Insert the Windows CD if prompted.
7 Turn on your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries and restart your computer when prompted.
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start and then Run.
2 In the Run window, type "winipcfg" and then click OK to open the IP Configuration window.
3 Select your network adapter. You should see your computer's IP address, subnet mask and default
gateway.
Windows 2000/NT/XP
The following example figures use the default Windows XP GUI theme.
1 Click start (Start in Windows 2000/NT), Settings, Control Panel.
Figure 130 Windows XP: Start Menu
2 In the Control Panel, double-click Network Connections (Network and Dial-up Connections
in Windows 2000/NT).
248
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 89

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 131 Windows XP: Control Panel
3 Right-click Local Area Connection and then click Properties.
Figure 132 Windows XP: Control Panel: Network Connections: Properties
4 Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) (under the General tab in Win XP) and then click Properties.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
249
Page 90

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 133 Windows XP: Local Area Connection Properties
5 The Internet Protocol TCP/IP Properties window opens (the General tab in Windows XP).
• If you have a dynamic IP address click Obtain an IP address automatically.
• If you have a static IP address click Use the following IP Address and fill in the IP addres s,
Subnet mask, and Default gateway fields.
• Click Advanced.
Figure 134 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
250
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 91

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
6 If you do not know your gateway's IP address, remove any previously installed gateways in the IP
Settings tab and click OK.
Do one or more of the following if you want to configure additional IP addresses:
•In the IP Settings tab, in IP addresses, click Add.
•In TCP/IP Address, type an IP address in IP address and a subnet mask in Subnet mask,
and then click Add.
• Repeat the above two steps for each IP address you want to add.
• Configure additional default gateways in the IP Settings tab by clicking Add in Default
gateways.
•In TCP/IP Gateway Address, type the IP address of the default gateway in Gateway. To
manually configure a default metric (the number of transmission hops), clear the Automatic
metric check box and type a metric in Metric.
• Click Add.
• Repeat the previous three steps for each default gateway you want to add.
• Click OK when finished.
Figure 135 Windows XP: Advanced TCP/IP Properties
7 In the Internet Protocol TCP/IP Properties window (the General tab in Windows XP):
• Click Obtain DNS server address automatically if you do not know your DNS server IP
address(es).
• If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click Use the following DNS server
addresses, and type them in the Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server fields.
If you have previously configured DNS servers, click Advanced and then the DNS tab to order
them.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
251
Page 92

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 136 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
8 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
9 Click Close (OK in Windows 2000/NT) to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
10 Close the Network Connections window (Network and Dial-up Connections in Windows
2000/NT).
11 Turn on your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries and restart your computer (if prompted).
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start, All Programs, Accessories and then Command Prompt.
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER]. You can also open
Network Connections, right-click a network connection, click Status and then click the Support
tab.
Windows Vista
This section shows screens from Windows Vista Enterprise Version 6.0.
1 Click the Start icon, Control Panel.
252
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 93

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 137 Windows Vista: Start Menu
2 In the Control Panel, double-click Network and Internet.
Figure 138 Windows Vista: Control Panel
3 Click Network and Sharing Center.
Figure 139 Windows Vista: Network And Internet
4 Click Manage network connections.
Figure 140 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
253
Page 94

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
5 Right-click Local Area Connection and then click Properties.
Note: During this procedure, click Continue whenever Windows displays a screen saying
that it needs your permission to continue.
Figure 141 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
6 Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
Figure 142 Windows Vista: Local Area Connection Properties
7 The Intern et Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window opens (the General tab).
• If you have a dynamic IP address click Obtain an IP address automatically.
254
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 95

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
• If you have a static IP address click Use the following IP address and fill in the IP address,
Subnet mask, and Default gateway fields.
• Click Advanced.
Figure 143 Windows Vista: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
8 If you do not know your gateway's IP address, remove any previously installed gateways in the IP
Settings tab and click OK.
Do one or more of the following if you want to configure additional IP addresses:
•In the IP Settings tab, in IP addresses, click Add.
•In TCP/IP Address, type an IP address in IP address and a subnet mask in Subnet mask,
and then click Add.
• Repeat the above two steps for each IP address you want to add.
• Configure additional default gateways in the IP Settings tab by clicking Add in Default
gateways.
•In TCP/IP Gateway Address, type the IP address of the default gateway in Gateway. To
manually configure a default metric (the number of transmission hops), clear the Automatic
metric check box and type a metric in Metric.
• Click Add.
• Repeat the previous three steps for each default gateway you want to add.
• Click OK when finished.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
255
Page 96

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 144 Windows Vista: Advanced TCP/IP Properties
9 In the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window, (the General tab):
• Click Obtain DNS server address automatically if you do not know your DNS server IP
address(es).
• If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click Use the following DNS server
addresses, and type them in the Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server fields.
If you have previously configured DNS servers, click Advanced and then the DNS tab to order
them.
256
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 97

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 145 Windows Vista: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
10 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window.
11 Click Close to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
12 Close the Network Connections window.
13 Turn on your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries and restart your computer (if prompted).
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start, All Programs, Accessories and then Command Prompt.
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER]. You can also open
Network Connections, right-click a network connection, click Status and then click the Support
tab.
Macintosh OS 8/9
1 Click the Apple menu, Control Panel and double-click TCP/IP to open the TCP/IP Control
Panel.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
257
Page 98

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 146 Macintosh OS 8/9: Apple Menu
2 Select Ethernet built-in from the Connect via list.
Figure 147 Macintosh OS 8/9: TCP/IP
3 For dynamically assigned settings, select Using DHCP Server from the Configure: list.
4 For statically assigned settings, do the following:
258
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
Page 99

•From the Configure box, select Manually.
• Type your IP address in the IP Address box.
• Type your subnet mask in the Subnet mask box.
• Type the IP address of your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries in the Router address box.
5 Close the TCP/IP Control Panel.
6 Click Save if prompted, to save changes to your configuration.
7 Turn on your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries and restart your computer (if prompted).
Verifying Settings
Check your TCP/IP properties in the TCP/IP Control Panel window.
Macintosh OS X
1 Click the Apple menu, and click System Preferences to open the System Preferences window.
Figure 148 Macintosh OS X: Apple Menu
Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
2 Click Network in the icon bar.
•Select Automatic from the Location list.
•Select Built-in Ethernet from the Show list.
• Click the TCP/IP tab.
3 For dynamically assigned settings, select Using DHCP from the Configure list.
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
259
Page 100

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Figure 149 Macintosh OS X: Network
4 For statically assigned settings, do the following:
•From the Configure box, select Manually.
• Type your IP address in the IP Address box.
• Type your subnet mask in the Subnet mask box.
• Type the IP address of your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries in the Router address box.
5 Click Apply Now and close the window.
6 Turn on your AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries and restart your computer (if prompted).
Verifying Settings
Check your TCP/IP properties in the Network window.
Linux
This section shows you how to configure your computer’s TCP/IP settings in Red Hat Linux 9.0.
Procedure, screens and file location may vary depending on your Linux distribution and release
version.
Note: Make sure you are logged in as the root administrator.
260
AMG1302/AMG1202-TSeries User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...