Zte Unitrans ZXMP M600 Technical Instructions

ZXMP M600 (V1.0)
Metro CWDM Equipment
Technical Manual
ZTE CORPORATION

ZXMP M600 (V1.0)
Technical Manual
Manual Version 20050425-R1.0
Product Version V1.0
Copyright © ZTE Corporation
All rights reserved.
No part of this documentation may be excerpted, reproduced, translated, annotated or
duplicated, in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of ZTE
Corporation.
ZTE CORPORATION
ZTE Plaza, Keji Road South, Hi-Tech Industrial Park, Nanshan District, Shenzhen, P.R. China
Website: http://www.zte.com.cn
Postcode: 518057
Customer Support Center: (+86755) 26771900 800-9830-9830
Fax: (+86755) 26770801
Email: support@zte.com.cn
* * * *
S.N.: sjzl20041373
FAX: +86-755-26770160
Suggestions and Feedback
To improve the quality of ZTE product documentation and offer better services to our customers, we hope
you can give us your suggestions and comments on our documentation and fax this form to
+86-755-26770160; or mail to “Marketing center 3rd floor ZTE Plaza, Keji Road South, Hi-Tech Industrial
Park, Nanshan District, Shenzhen, P. R. China”. Our postcode is 518057.
Document name Unitrans ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Metro CWDM Equipment Technical Manual
Product version V1.0 Document version 20050425-R1.0
Equipment installation time
Your information
Name Company
Postcode Company address
Telephone E-mail
Presentation: How is information presented? (Introductions, procedures, illustrations, others)
Good Fair Average Poor Bad
Your evaluation
of this
documentation
Your suggestions
for improvement
of this
documentation
Your other
suggestions on
ZTE product
documentation
Accessibility: Can you find the information you want? (Table of contents, Index, headings,
numbering, others)
Good Fair Average Poor Bad
Intelligibility: Can you understand it when you find it? (Language, vocabulary, readability, others)
Good Fair Average Poor Bad
Presentation:
Accessibility:
Intelligibility:


Preface
About This Manual
This manual is applicable to Unitrans ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Metro CWDM Equipment
(ZXMP M600 for short).
The ZXMP M600 is a wavelength division equipment belonging to the metropolitan
area optical network product series developed by ZTE. This equipment is capable of
transparently transmitting signals at various rates and services. It features high optical
transmission capacity and fully satisfies users’ requirements on networking and
management. Therefore, this equipment is applicable to various layers in
small-/medium-sized Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), the convergence layer and
access layer of a large-sized MAN.
The equipment has four accompanying manual, including:
Unitrans ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Metro CWDM Equipment Technical Manual
Unitrans ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Metro CWDM Equipment Hardware Manual
Unitrans ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Metro CWDM Equipment Installation Manual
Unitrans ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Metro CWDM Equipment Maintenance Manual
How to Use This Manual
Unitrans ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Metro CWDM Equipment Technical Manual deals
with the architecture, technical indices, system functions, configuration and networking
of the ZXMP M600. It enables users to get a comprehensive understanding of the
ZXMP M600 and serves as a basis for the users to read other relevant documents.
Chapter 1 System Overview briefs the background, applicable standards, system
structure and features of the ZXMP M600.
Chapter 2 Technical Indices describes various technical indices of the ZXMP-M600
in detail.
Conventions
Chapter 3 System Functions deals with the functions of the ZXMP M600 and their
implementation, including the transmission function, Service multiplexing function and
protection function.
Chapter 4 System Configurations and Networking Modes introduces the
networking modes supported by the ZXMP M600, the system configuration
requirements and networking examples. It enables the users to understand the
networking capability and service providing capability of the equipment.
Appendix A Explanation of Terms provides a brief explanation to some terms
adopted to facilitate understanding the manual.
Appendix B Abbreviations summarizes the English abbreviations and terms in the
manual for readers’ reference.
1. Notational convention
Angular brackets “<and>” identify names of keys and buttons, and the
information typed by an operator from a terminal
Square brackets “[and]” indicate a man-machine interface, menu item, data list
or field name. The symbol “→” separates a multi-level menu, e.g., [File→
New→ Folder] indicates the [Folder] menu item under the [New] submenu of
the menu [File].
2. Keyboard Operation Convention
Format Description
Characters within
angular brackets
<Key 1+Key 2> Press Key 1 and Key 2 at the same time.
<Key 1, Key 2> Press Key1 first. Then release Key 1 and press Key 2
Indicate a key or button name, e.g., <Enter>, <Tab>, <Backspace>, and
<a>
3. Mouse Operation Convention
Format Description
Click
Double-click
Right-click
Drag Refers to pressing and holding a mouse button and move the mouse
Refers to clicking the primary mouse button (usually the left mouse
button) once
Refers to quickly clicking the primary mouse button (usually the left
mouse button) twice
Refers to clicking the secondary mouse button (usually the right mouse
button) once.
4. Danger, Warning, Caution and Note Statements
Danger, Warning, Caution and Note statements are
used throughout this manual to emphasize important and critical information. You must
read these statements to help ensure safety and to prevent product damage. The
statements are defined below.
Danger:
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death
or serious injury. This signal word is to be limited to the most extreme situations.
Warning:
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
Caution:
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided, could result in minor or
moderate injury. It may also be used to alert against unsafe practices.

Note:
A Note statement is used to notify people of installation, operation, or maintenance
information that is important, but not hazard-related.
Tips:
Indicates a suggestion or hint to make things easier or more productive for the reader
Statement: The actual product may differ from what is described in this
manual due to frequent update of ZTE products and fast development of
technologies. Please contact the local ZTE office for the latest updating
information of the product.

Contents
1 System Overview.....................................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 System Background .......................................................................................................................1-1
1.1.1 MAN ...................................................................................................................................1-1
1.1.2 Wavelength Division Multiplexing Technique....................................................................1-4
1.2 System Structure ............................................................................................................................ 1-6
1.2.1 Structure of Hardware System ............................................................................................1-6
1.2.2 Structure of Network Management Software System......................................................... 1-9
1.3 System Features ...........................................................................................................................1-12
1.4 Applicable Standards/Recommendations.....................................................................................1-14
2 Technical Indices .....................................................................................................................................2-1
2.1 System Indices ...............................................................................................................................2-1
2.2 Structure Indices.............................................................................................................................2-2
2.3 Power Indices................................................................................................................................. 2-3
2.3.1 Voltage Requirements .........................................................................................................2-3
2.3.2 Power Consumption Requirements.....................................................................................2-3
2.4 Environment Requirements............................................................................................................ 2-4
2.4.1 Grounding Requirements.................................................................................................... 2-4
2.4.2 Temperature and Humidity Requirements...........................................................................2-4
2.4.3 Cleanness Requirements .....................................................................................................2-5
2.4.4 Dustproof and Anti-corrosion Requirements ......................................................................2-5
2.5 Working Wavelengths ....................................................................................................................2-5
2.6 Reliability.......................................................................................................................................2-6
-i-

2.7 Optical safety and electrical safety ................................................................................................ 2-6
2.8 Indices of System Component Parts .............................................................................................. 2-7
2.8.1 Performance Indices of OMD............................................................................................. 2-7
2.8.2 Performance Indices of OAD Units.................................................................................... 2-8
2.8.3 OTU Interface Indices ...................................................................................................... 2-10
2.8.4 Performance Indices of Optical Supervisor Channel........................................................ 2-13
2.8.5 SRM42 Interface Indices .................................................................................................. 2-13
3 System Function...................................................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1 Line Transmission Function .......................................................................................................... 3-1
3.2 Service Functions........................................................................................................................... 3-2
3.2.1 Service Access Function..................................................................................................... 3-2
3.2.2 Service Convergence Function ........................................................................................... 3-2
3.3 Communication and Monitoring Functions................................................................................... 3-3
3.3.1 Communication between EMS and Access Point............................................................... 3-3
3.3.2 Communication between Nodes ......................................................................................... 3-5
3.3.3 Intra-node Communication and Monitoring ....................................................................... 3-6
3.4 Power Input and Output Functions ................................................................................................ 3-7
3.5 Grounding Function....................................................................................................................... 3-7
3.6 Alarm Output Function.................................................................................................................. 3-7
3.7 Protection Function........................................................................................................................ 3-8
3.7.1 Ring Network Protection .................................................................................................... 3-8
4 System Configurations and Networking Modes................................................................................... 4-1
4.1 System Configuration.................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1.1 Board Slot Resources.......................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1.2 Metro Optical Terminal Equipment (OTM)........................................................................ 4-2
-ii-

4.1.3 Metro OADM Equipment (OADM) ...................................................................................4-2
4.2 Networking Mode .......................................................................................................................... 4-2
4.2.1 Point-to-point Networking ..................................................................................................4-2
4.2.2 Chain Networking...............................................................................................................4-2
4.2.3 Ring Networking.................................................................................................................4-2
4.2.4 Ring-to-chain Networking ..................................................................................................4-2
4.3 Configuration Example..................................................................................................................4-2
4.3.1 Configuration Implementation ............................................................................................ 4-2
4.3.2 Application Features............................................................................................................4-2
Appendix A Term Description..................................................................................................................A-2
Appendix B Abbreviations ....................................................................................................................... B-2
-iii-


List of Figures
Fig. 1.1-1 Basic Structure of MAN...................................................................................................1-3
Fig. 1.2-1 Functional Structure of the ZXMP M600 Equipment ......................................................1-6
Fig. 1.2-2 Functional Structure of OTM Equipment.........................................................................1-8
Fig. 1.2-3 Functional Structure of OADM Equipment .....................................................................1-8
Fig. 1.2-4 Structure of the Network Management Software System.................................................1-9
Fig. 2.8-1 Optical Interfaces of OMD Units .....................................................................................2-7
Fig. 2.8-2 Optical Interfaces of OAD Units......................................................................................2-8
Fig. 3.3-1 Connection between the Access Point and the EMS (through an Ethernet interface)...... 3-3
Fig. 3.3-2 Connection with the EMS Through SDH Equipment ......................................................3-4
Fig. 3.3-3 Connection with the EMS through RS232 .......................................................................3-5
Fig. 3.3-4 Intra-node Communication and Monitoring Channel.......................................................3-6
Fig. 3.7-1 1+1 Protection of Optical Channel on a Ring Network.................................................... 3-8
Fig. 4.1-1 Slot Distribution in the CWU Shelf..................................................................................4-1
Fig. 4.1-2 Slot Distribution in the SMU Shelf ..................................................................................4-2
Fig. 4.1-3 Board Configuration of OTM Equipment (which adds/drops 8 wavelengths).................4-2
Fig. 4.1-4 Fiber Connection of OTM Equipment (1310nm monitoring channel)............................. 4-2
Fig. 4.1-5 Board Configuration of OADM Equipment (which adds/drops 3 wavelengths)..............4-2
Fig. 4.1-6 Fiber Connections of OADM (which adds/drops 3 wavelengths)....................................4-2
Fig. 4.2-1 Application of Point-to-point Networking........................................................................4-2
Fig. 4.2-2 Application of Chain Networking ....................................................................................4-2
Fig. 4.2-3 Application of Ring Networking ...................................................................................... 4-2
Fig. 4.2-4 Application of Ring-to-chain Networking........................................................................4-2
-i-

Fig. 4.3-1 Networking in a Typical Configuration Example ............................................................ 4-2
Fig. 4.3-2 Service Requirements....................................................................................................... 4-2
Fig. A.9-1 Optical Transmission Over Interface Made of Uneven Media....................................... A-2
Fig. A.9-2 Optical Dispersion Over a Fiber..................................................................................... A-2
-ii-

List of Tables
Table 2.2-1 Outline Dimensions and Weight Indices of the ZXMP M600 Component Parts...........2-2
Table 2.3-1 Power Consumption Indices of the ZXMP M600 Boards/Units....................................2-3
Table 2.4-1 Temperature and Humidity Requirements .....................................................................2-5
Table 2.5-1 Wavelength Distribution of the ZXMP M600 Equipment (with ordinary fibers adopted)
.............................................................................................................................................................2-6
Table 2.8-1 Performance Indices of OMD........................................................................................ 2-8
Table 2.8-2 Performance Indices of OAD Units ............................................................................... 2-9
Table 2.8-3 Indices of the Line End Optical Transmitting Port ......................................................2-10
Table 2.8-4 Indices of the Line End Optical Receiving Port...........................................................2-11
Table 2.8-5 Indices of Client Optical Transceiving Module ...........................................................2-12
Table 2.8-6 Major Performance Indices of Optical Monitoring Channel........................................2-13
Table 2.8-7 Indices of Client Optical Transceiving Module ...........................................................2-14
Table 4.1-1 Relation between the Boards and Slots in the CWU Shelf ............................................4-1
Table 4.1-2 Relation between the Boards and Slots in the SMU Shelf.............................................4-2
Table 4.3-1 Equipment Configuration...............................................................................................4-2
-i-


1 System Overview
This chapter introduces the background, architecture, system features and applicable
standards/recommendations. It aims at laying a basis for readers to understand the
equipment.
1.1 System Background
The ZXMP M600 is the metro CDWM system developed by ZTE. It features large
optical transmission capacity and can implement transparent transmission of various
services at multiple rates. It can be applied to the convergence and access layers of
large MANs as well as various layers of middle- and small-sized MANs.
In the following, the Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) and Wavelength Division
Multiplexing (WDM) will be introduced briefly.
1.1.1 MAN
1.1.1.1 Concept
As data services such as IP and Ethernet services develop rapidly in recent years, a data
network that can provide wide coverage, high-speed bandwidth and convenient
services is required for providing services such as Internet access, IP-based virtual
private network, IP phone, multimedia application and e-commerce. Meanwhile, as a
metropolis features prosperous economy, dense population, compact coverage area and
frequent information exchange, the information-oriented construction keeps developing
rapidly. Thus, the requirements on MAN also becomes higher and higher.
Generally a MAN is considered as a broadband network that has a unified protocol and
connects government departments, educational and scientific institutions, companies
and home users. It provides data services as well as integrated multimedia services
such as packet voice, graphic and video services, and covers local public networks in
metropolitan and suburb areas.
Based on the statistics and packet technology, the MAN boasts of a clear network
structure, perfect expandability and high reliability. The products and technologies
1-1

ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Technical Manual
adopted in it are widely used for commercial purposes, while the user and service
management is flexibly and convenient. The MAN features broadband capacity and
rate, efficient transmission of information and diversified access methods. It obtains the
contents locally, offers user-defined access, provides characteristic services and can
deploy new services quickly. In addition, its capacity can be expanded flexibly and its
upgrade and development can be predicted.
1.1.1.2 Basic Structure
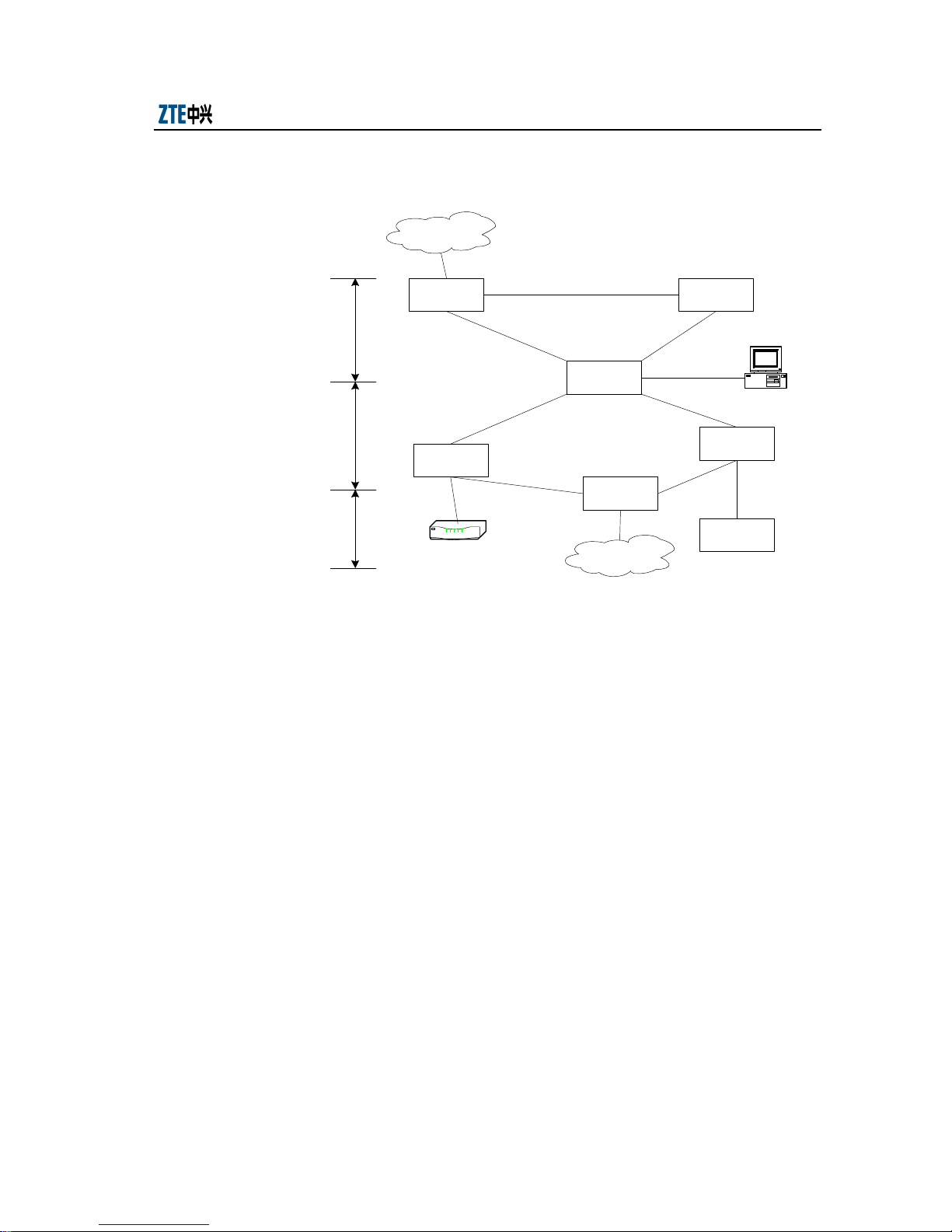
The MAN can either be divided vertically or horizontally:
1. Vertical division
The MAN can be vertically divided into the access layer, convergence layer and
core layer.
The access layer accesses different types of subscribers such as routers and LAN.
The convergence layer converges sporadic access points, implements data
multiplexing, transmitting and switching, and provides traffic control and user
management functions. It includes Multi-Service Transmit Platform (MSTP) and
Metro OADM. The core layer implements high-speed information exchange on
the whole network as well as interconnection between backbone networks. It
generally consists of OADM equipment.
1-2
Chapter 1 System Overview
Fig. 1.1-1 shows the basic structure of a MAN.
Backbone layer
MOADMMOADM
Core layer
MOADM
Convergence
layer
MSTP
MSTP
Access layer
Router
MSTP: multi-service transmit platform OADM: metro OADM
Fig. 1.1-1 Basic Structure of MAN
LAN
MSTP
ATM
2. Horizontal division
A MAN can also be horizontally divided into the service layer and transmission
layer.
The service layer can implement multiple services such as narrowband voice
service, Internet service, remote calculation and transaction processing,
e-commerce, video conference, multimedia integrated information service,
remote communication and control through computer and leased line service. It
consists of various ATM and IP devices. The transmission layer indicates the
metro optical network that carries the services at the service layer. It provides an
efficient and a unified transmission platform that features large capacity and low
cost and consists of WDM and SDH devices.
Service and
management
center
1-3

ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Technical Manual
1.1.1.3 Features of Metro Optical Network
1. Large service access capacity
The rapid development of MAN service causes the acute increase in the demand
for bandwidth. This demand can only be met by large-capacity metro optical
network. Thus, the core layer of the metro optical network should have large
service access capacity and should be capable of continuous upgrading.
2. Multi-service convergence and transparent transmission
To make full use of the existing network resources, the core layer should be able
to converge various low-rate services and encapsulate services of different rates
and with different protocols into a single wavelength. This helps save the
wavelength resources and economize network construction. On the other hand,
to avoid extra overhead due to protocol conversion and frame format matching
and to make full use of the bandwidth resources, the core layer is also required
to transmit the carried services in the original mode.
3. High reliability and powerful network protection capability
The network security and reliability guarantee normal service transmission.
Thus, redundancy protection measures should be provided for the hardware on
the equipment. Besides, channel protection and multiplex section protection
should also be provided at various levels on the network.
4. Low networking cost
1.1.2 Wavelength Division Multiplexing Technique
As MAN services become increasingly abundant, the requirement on the MAN
capacity becomes higher and higher. As a result, the multi-service broadband MAN
gradually becomes a hotspot in the telecom and network construction. To use the
existent optical fiber resources to increase the bandwidth capacity, the Wavelength
Division Multiplexing (WDM) technique is adopted in the MAN.
WDM can be divided into Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)
technique and Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing technique.
1.1.2.1 DWDM Technique
The DWDM technique adopts an Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA), a high
wavelength stability laser and dense wavelength division multiplexing/ demultiplexing
1-4

Chapter 1 System Overview
equipment to transmit optical signal service and implement balanced management of
optical power on the whole line. In the DWDM system, the selection of wavelength
and the frequency intervals should conform to ITU-T Recommendation G.692.
The working wavelength range of the DWDM system is 1528.77nm~1560.61nm and
the corresponding working frequency range is 196.1THz~192.1THz.
The channel interval of the system is a multiple of 100GHz (about 0.8nm). The smaller
the channel interval is, the higher the resolution of the optical demultiplexer should be.
The channel interval commonly used at present is either 200GHz (about 1.6nm) or
100GHz (about 0.8nm).
While saving the cost of the electrical relay, EDFA technique adopted in the DWDM
equipment presents much higher requirements on the wavelength stability, dispersion
tolerance and chirp performance of the laser.
Therefore, if the DWDM equipment that suitable for long distance transmission is used
in a MAN that features short transmission distance and diversified service interfaces,
the network construction cost will greatly increase.
1.1.2.2 CWDM Technique
The CWDM technique is developed to improve the utility of optical fibers on the MAN,
to provide multiple service interfaces and to cut the network construction cost at the
same time.
The working principle of CWDM is similar to that of DWDM. At the transmitting end
of the link, an optical multiplexer is used to multiplex the wavelengths transmitted in
different fibers into one fiber for transmission, while at the receiving end, a
demultiplexer is used to recover the original wavelengths from the combined
wavelength.
The wavelength selection and channel interval of the CWDM conforms to ITU-T
Recommendation G694.2. The wavelength interval is 20 nm, while the working
wavelength range is determined by the adopted fiber type. If an ordinary fiber type
G.652 A&B is adopted, then the working wavelength range is 1470nm~1610 nm; if
full-wave fibers, that is, G.652 C&D fibers are adopted, then the working wavelength
range is 1270 nm~1610 nm.
1-5

ZXMP M600 (V1.0) Technical Manual
The CWDM system adopts uncooled laser and multiplexer/demultiplexer. Compared to
DWDM, it boasts shorter transmission distance and lower cost and is suitable for the
construction of MAN.
1.2 System Structure
The structure of the ZXMP M600 equipment is shown in Fig. 1.2-1.
Fig. 1.2-1 Functional Structure of the ZXMP M600 Equipment
The ZXMP M600 equipment can be divided into the hardware system and network
management software system. The two systems are independent of each other but will
also work together.
1.2.1 Structure of Hardware System
1.2.1.1 Platform Functions
The hardware system of the ZXMP M600 includes an optical transfer platform, service
convergence system, multiplexing/demultiplexing platform, monitor platform and
power supply platform.
1. Optical transfer platform
It adopts the optical/ electrical/ optical conversion mode to implement
wavelength conversion of service signals and line signals.
The service signals include multi-service signals with a rate lower than 2.5Gbit/s
and with the maximum rate being 2.5Gbit/s.
1-6

Chapter 1 System Overview
The line signals meet the requirements specified in ITU-T recommendation
G.694.2.
2. Service convergence platform
It converges multiple channels of low rate signals into one wavelength for
transmission and implements the reserve process.
The low rate signals include standard STM-1, STM-4 signals with the maximum
rate being 2.5Gbit/s on the line.
3. Multiplexing/demultiplexing platform
It includes a multiplexing part and a demultiplexing part.
1) Multiplexing part: It couples multiple channels of optical signals with different
wavelengths from the optical transfer platform and service convergence platform
to a piece of optical fiber for transmission.
2) Demultiplexing part: It divides the multiplexing optical signals from the line
side according to their different wavelengths and sends them to different optical
transfer platform and service convergence platform.
4. Monitor platform
1) Collecting, processing and reporting the configuration, alarm and performance
information of the various platforms
2) Receiving the command from the EMS and transferring it to the destination
board
3) Using a specified monitoring optical channel to transparently transmit the
network management information. The wavelength of the monitoring channel
can be either 1310nm or 1510nm.
5. Power supply platform
It converts in DC input into +5V or -48V DC power to provide power for
various platforms.
Options –48V, +24V and –60V are available for DC power supply, and 1+1
warm backup are practicable.
1-7
 Loading...
Loading...