
3
0 °
P
RELIMINARY
P
RODUCT
S
PECIFICATION
FEATURES
ROM
Part
Z87100 1 124 18-pin DIP & SOIC
Note: *General-Purpose
■
3.0V to 5.5V Operating Range
■
On-Chip PN Modulator for Spread Spectrum
Communications
■
ROM-Programmable PN Codes, up to 256 Bits ("Chips")
■
Fast Instruction Pointer - 1.0 µ s @ 12 MHz
■
Two Standby Modes - STOP and HALT
12 Input/Output Lines (One with Comparator Input)
■
(Kbytes)
RAM*
(Bytes)
Package
Information
Z87100
PN M
W
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
ODULATOR
IRELESS
Two Programmable 8-Bit Counter/Timers
6-Bit Programmable Prescaler
Six Vectored, Priority Interrupts (Two External, One
Software Generated)
Maximum Clock Speed of 12 MHz
Watch-Dog/Power-On Reset Timer
Analog Comparator with Programmable Interrupt
Polarity
On-Chip Oscillator that Accepts a RC, or External Clock
Drive
Low EMI Noise Mode
to +70 ° C Ultra-Low Power Operation at 10 kHz
T
RANSMITTER
3
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Z87100 Wireless Controller is a member of the Z8
single-chip microcontroller family and is manufactured in
CMOS technology. Zilog’s CMOS Z87100 microcontroller
offers fast execution, efficient use of memory, sophisticated interrupts, input/output bit manipulation capabilities,
and easy hardware/software system expansion along with
low cost and low power consumption.
The Z87100 architecture is based on Zilog’s 8-bit microcontroller core with the addition of an Expanded Register
File which allows access to register mapped peripheral
and I/O circuits. The Z87100 offers a flexible I/O scheme
and a number of ancillary features that are useful in many
consumer, industrial, automotive, and advanced scientific
applications.
The Z87100 is designed with specific features for wireless
spread spectrum applications using direct sequence pseudo-noise (PN) modulation. With up to 256 bits (“chips”) of
DS96WRL0700
P R E L I M I N A R Y
®
specially designated “PN ROM”, one or more PN code sequences may be stored and used to PN-modulate data
generated by the Z87100. PN modulation is synchronous
with the data, using an integer number of PN chips per data
bit.
The Z87100 features an Internal Time Base Counter which
provides a real time clock for Stop-Mode Recovery or interrupt at programmable intervals of 0.25 seconds, one second, one minute and one hour. This requires an external
clock oscillator signal at 32.768 kHz.
Special PN modulator control registers allow the user to
select the desired PN modulator outputs, to choose the PN
clock source and PN sequence start address in PN ROM,
to stop/start and enable/disable the PN modulator, and to
determine whether a complete PN code sequence is modulated against a single bit or an integer fraction or multiple
of a single bit. The PN-modulated data may then be used
3-1
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
GENERAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
with an external modulator and RF section to form a complete wireless spread spectrum transmitter.
The device's many applications demand powerful I/O capabilities. The Wireless Controller fulfills this with 12 pins
dedicated to input and output. These lines are grouped into
two ports, and are configurable under software control to
provide timing, status signals, or parallel I/O.
Three basic address spaces are available to support this
wide range of configurations; Program Memory, Register
InputOutput
Port 3
VCC GND
File, and Expanded Register File. The Register File is
composed of 124 bytes of General-Purpose Registers, two
I/O Port registers and fifteen Control and Status registers.
The Expanded Register File consists of two port registers,
four control registers and six PN modulator registers.
With powerful peripheral features such as on-board comparators, counter/timers, Watch-Dog Timer, and PN modulator, the Z87100 meets the needs for most sophisticated
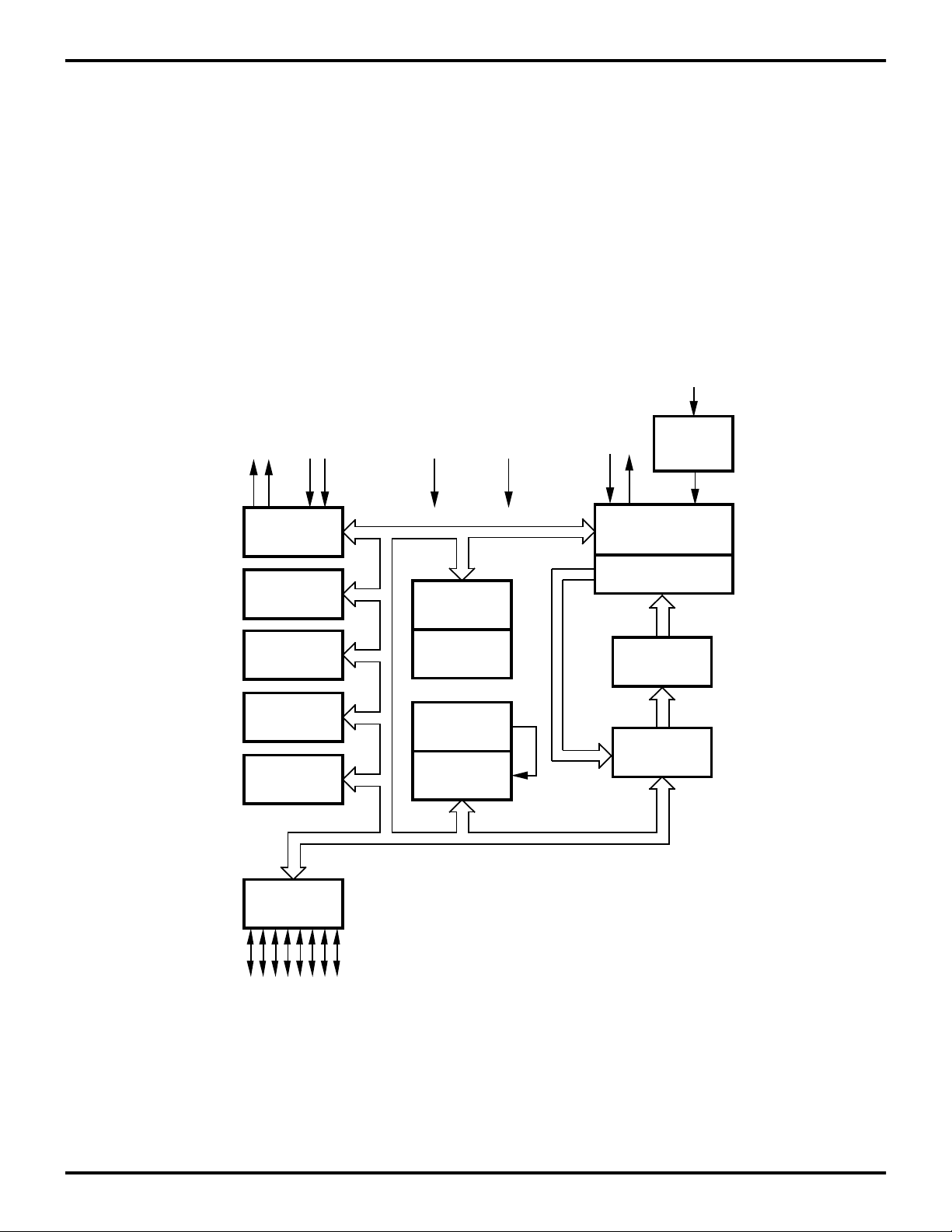
wireless and low-power controller applications (Figure 1).
TMBASE
RC
Machine Timing &
Instruction Control
Time Base
Generator
Counter/
Timers (2)
Interrupt
Control
Analog
Comparator
PN
Modulator
Port 2
I/O
(Bit Programmable)
ALU
FLAG
Register
Pointer
Register File
144 x 8-Bit
WDT, POR
Prg. Memory
1024 x 8-Bit
Program
Counter
3-2
Figure 1. Functional Block Diagram
P R E L I M I N A R Y
DS96WRL0700
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Z87100
PIN DESCRIPTION
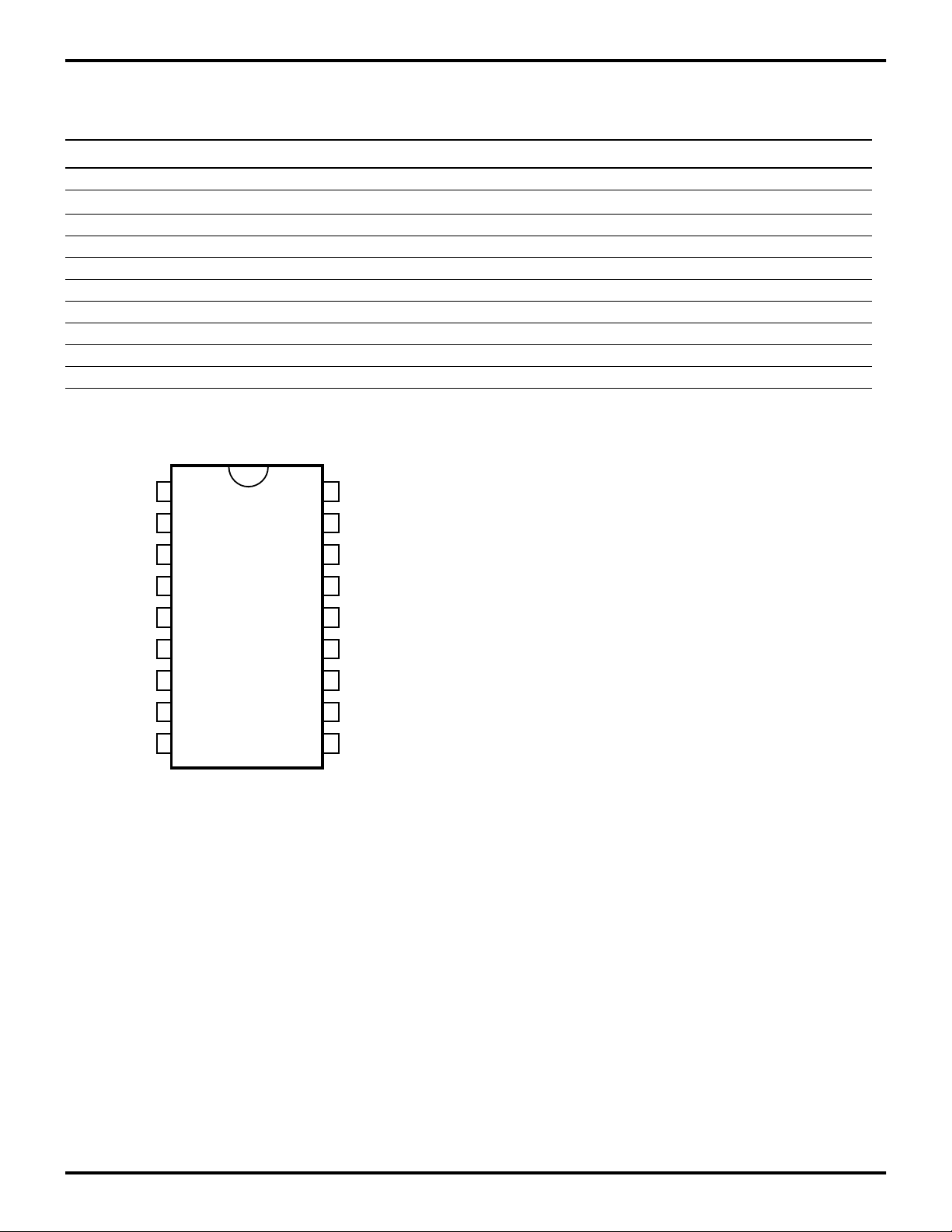
Table 1. 18-Pin DIP/SOIC Pin Identification
No Symbol Function Direction
1-4 P24-27 Port 2, Pins 4, 5, 6, 7 In/Output
5V
6 RC2 RC Oscillator Clock Output
7 RC1 RC Oscillator Clock Input
8-9 P31, P33 Port 3, Pins 1, 3 Fixed Input
10 TMBASE Time Base Clock Input
11 GND Ground Input
12-13 P35-36 Port 3, Pins 5, 6 Fixed Output
14 GND Ground Input
15-18 P20-23 Port 2, Pins 0, 1, 2, 3 In/Output
P24
P25
P26
P27
1
2
3
4
CC
18
17
16
15
Power Supply Input
P23
P22
P21
P20
Z87100
VCC
RC2
RC1
P31
P33
Figure 2. 18-Pin DIP/SOIC Pin Configuration
5
6
7
8
9
14
13
12
11
10
GND
P36
P35
GND
TMBASE
DS96WRL0700
P R E L I M I N A R Y
3-3
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATING
Sym Description Min Max Units
V
T
T
Supply V oltage* –0.3 +7.0 V
CC
Storage Temp –65 +150 C
STG
Oper Ambient
A
†C
Temp
Notes:
1. *Voltage on all pins with respect to GND.
2. † See Ordering Information
STANDARD TEST CONDITIONS
The characteristics listed below apply for standard test
conditions as noted. All voltages are referenced to ground.
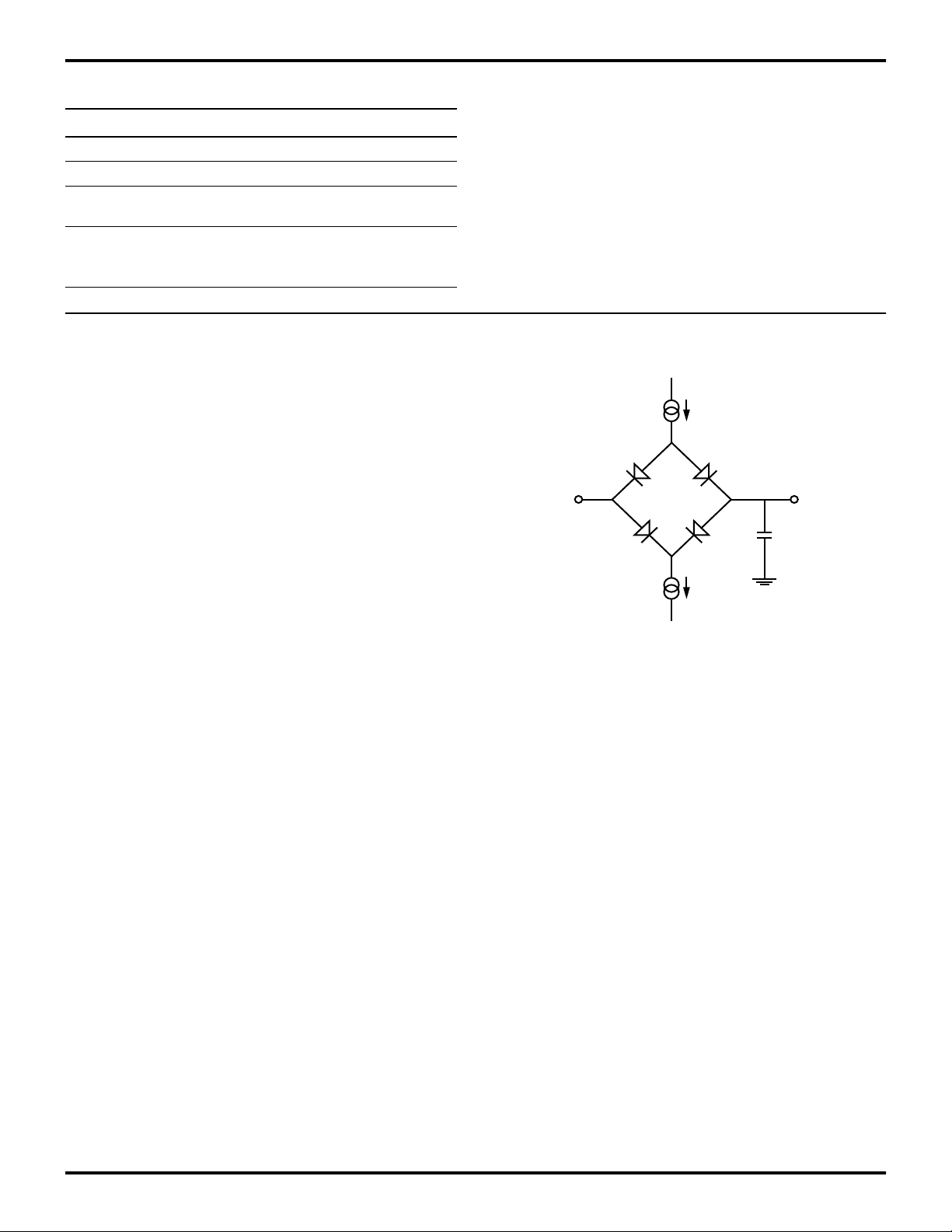
Positive current flows into the referenced pin (Figure 3).
Stresses greater than those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; operation of the device at
any condition above those indicated in the operational sections of these specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended period may
affect device reliability.
IoL
Threshold
Voltage
Output
Under
Test
50pF
IoH
Figure 3. Test Load Configuration
3-4
P R E L I M I N A R Y
DS96WRL0700

3
≤
≤
Z87100
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
T
Sym Parameter
Max Input
Voltage
V
CH
Clock Input
High V oltage
V
CL
Clock Input
Low V oltage
V
IH
Input High
Voltage
V
IL
Input Low
Voltage
V
OH
Output High
Voltage
V
OL1
Output Low
Voltage
V
OL2
Output Low
Voltage
V
OFFSET
Comparator
Input Offset
Voltage
I
IL
Input Leakage
(Input bias
current of
comparator)
V
CC
3.0V
5.5V
3.0V
5.5V
3.0V
5.5V
3.0V
5.5V
3.0V
5.5V
3.0V
5.5V
3.0V
5.5V
3.0V
5.5V
3.0V
5.5V
3.0V
5.5V
= 0 ° C to +70 ° C
A
Min Max @ 25 ° C Units Conditions Notes
12
12
0.9 V
0.9 V
V
SS
V
SS
0.7 V
0.7 V
V
SS
V
SS
V
CC
V
CC
CC
CC
–0.3
–0.3
CC
CC
–0.3
–0.3
–0.4
–0.4
V
CC
V
CC
0.2 V
0.2 V
V
CC
V
CC
0.2 V
0.2 V
+0.3
+0.3
CC
CC
+0.3
+0.3
CC
CC
0.8
0.4
1.0
1.0
25
25
–1.0
–1.0
1.0
1.0
Typical
2.4
3.9
1.6
2.7
1.8
2.8
1.0
1.5
3.1
4.8
0.2
0.1
0.4
0.5
10
10
VVI
IN
I
IN
250 µ A
250 µ A
VVDriven by External Clock
Generator
VVDriven by External Clock
Generator
V
V
V
V
VVI
VVI
VVI
= –2.0 mA
OH
I
= –2.0 mA
OH
=+4.0 mA
OL
I
=+4.0 mA
OL
= 6 mA, 3 Pin Max
OL
I
= +12 mA, 3 Pin Max
O
mV
mV
µAµAVIN = OV, V
VIN = OV, V
CC
CC
DS96WRL0700
P R E L I M I N A R Y
3-5

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
TA= 0°C to +70°C
Sym Parameter
I
OL
Output
Leakage
I
CC
Supply Current 3.0V
V
CC
3.0V
5.5V
Min Max @ 25°C Units Conditions Notes
–1.0
–1.0
5.5V
4.5V
I
CC1
Standby
Current
3.0V
5.5V
(HALT mode)
3.0V
5.5V
I
CC2
Standby
Current
3.0V
5.5V
(STOP mode)
3.0V
5.5V
5.5V 12 5 µA STOP mode;
T
V
POR
LV
Power-On
Reset
VCC Low
3.0V
5.5V
7
3
1.50 2.65 2.1 V 2 MHz max Ext. CLK
Voltage
Notes:
1. V
increases as the temperature decreases.
LV
2. All outputs unloaded, I/O pins floating,
inputs at either rail, TMBASE clock input grounded.
3. CL1 = CL2 = 100 pF
= 5.5V.
CC
CC
.
4. Same as note 2 except inputs at V
5. Low EMI oscillator selected; SCLK = RC1/2;
10 kHz external oscillator with the comparator not enabled 10 µA.
10 kHz external oscillator with the comparator enabled 310 µA
RC selected for WDT; 10 kHz RC oscillator
(corresponding to R = 1.2MΩ C~ 68 pF), comparator is off.
6. Z8 in STOP moderate off; Z8 in STOP mode; WDT off.
TMBASE selected; as Z8 system clock source
Time base counter enabled; V
7. Analog Comparator disabled
1.0
1.0
8.0
15
15
4.5
7.0
2.0
4.5
10
10
TBD
TBD
24
13
Typical
4.5
9.0
10
2.0
4.0
1.0
2.5
1.0
3.0
160
200
13
7
µAµAVIN = OV, V
VIN = OV, V
mA
@ 12 MHz
mA
@ 12 MHz
µA
10 kHz; external RC
CC
CC
mAmAHALT mode VIN=0V, VCC
@12 MHz
HALT mode V
V
@ 12 MHz
CC
IN
=0V,
mAmAClock Divide-by-16
@12 MHz
Clock Divide-by-16
@ 12 MHz
µAµASTOP mode VIN = OV,
V
WDT is not Running
CC
STOP mode V
V
WDT is not Running
CC
µAµASTOP mode V
V
WDT is Running
CC
STOP mode V
V
WDT is Running
CC
= OV,
IN
= OV,
IN
= OV,
IN
TMBASE=32.768 kHz;
WDT is not Running
ms
ms
Freq.
2,3
2,3
2,3
2,3
2,3
2,3
2,3
4,7
4,7
4,7
4,7
6,7
1
3-6 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700
Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
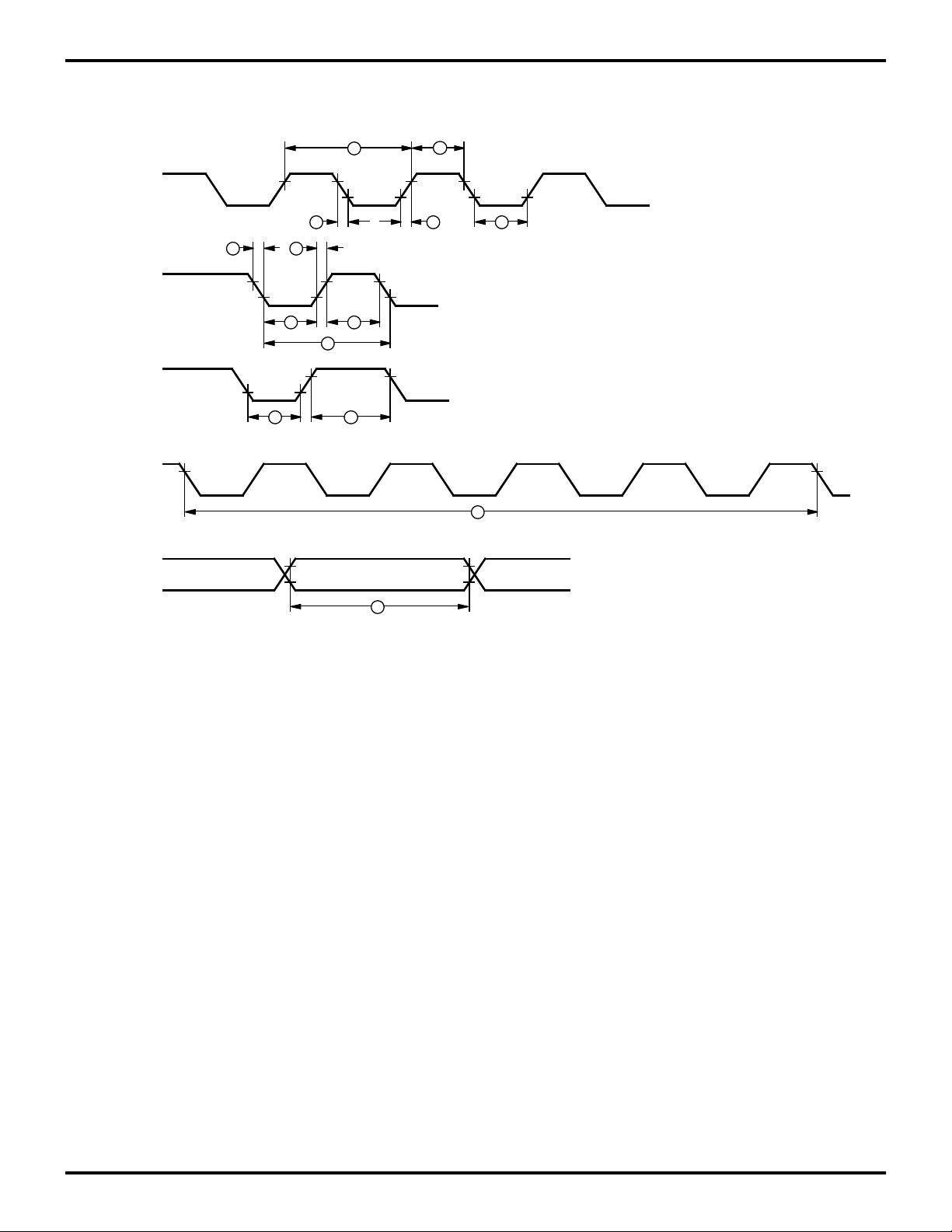
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Clock
TIN
IRQN
Clock
Setup
Stop-Mode
Recovery
Source
7 7
8
1
2 2 3
4
5
6
9
10
3
11
Figure 4. Additional Timing
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-7

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
TA=0°C to +70°C
12 MHz
No Sym Parameter
1 TpC Input Clock Period 3.3V
2 TrC,TfC Clock Input Rise
and Fall Times
3 TwC Input Clock Width 3.3V
4 TwTinL Timer Input
Low Width
5 TwTinH Timer Input
High Width
6 TpTi Timer Input Period 3.3V
7 TrTin,
TtTin
Timer Input Rise
and Fall Timer
8 TwIL Int. Request
Low Time
9 TwIH Int. Request High
Time
10 Twsm Stop-Mode
Recovery
Width Spec
11 Tost RC Oscillator
Start-up Time
Twdt Watch-Dog Timer
Refresh Time
Notes:
1. Timing Reference uses 0.9 V
2. Interrupt request through Port 3 (P33-P31)
3. 5.0V ±0.5V, 3.3V ±0.3V
4. SMR-D5 = 0
5. WDT Oscillator only.
for a logic 1 and 0.1 VCC for a logic 0.
CC
V
CC
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
3.3V
5.0V
Min Max Units Notes
83
83
26
26
100
70
3TpC
3TpC
8TpC
8TpC
100
70
3TpC
3TpC
12
12
15
5
30
16
60
25
250
120
100,000
100,000
15
15
100
100
5TpC
5TpC
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
ms
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1,2
1,2
1,2
1,2
Reg.4
D0=0 5
D1=05
D0=15
D1=05
D0=05
D1=15
D0=15
D1=15
3-8 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
PIN FUNCTIONS
RC1 (RC Oscillator input). This pin connects an external
RC network or an external single-phase clock to the onchip RC oscillator.
RC2 (RC Oscillator output). This pin connects an external RC network to the on-chip RC oscillator.
P27
P26
P25
P24
Z87100
P23
P22
TMBASE (Time Base Counter Clock Input). This pin
connects an external 32 kHz clock signal to the input of an
on-chip Time Base Counter.
As a mask option, the Z87100 can be configured to initialize ("cold start") using either RC or TMBASE. Consequently, the Z87100 can be operated with either or both RC and
TMBASE clock sources.
Port 2 (I/O)
Open-Drain
P21-P26 OE
P21-P26 OUT
P21-P26 IN
P21
P20
Port 2
P21-P26
PAD
1.5 2.3 Hysteresis
Figure 5. Port 2 Configuration (P21-P26)
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-9
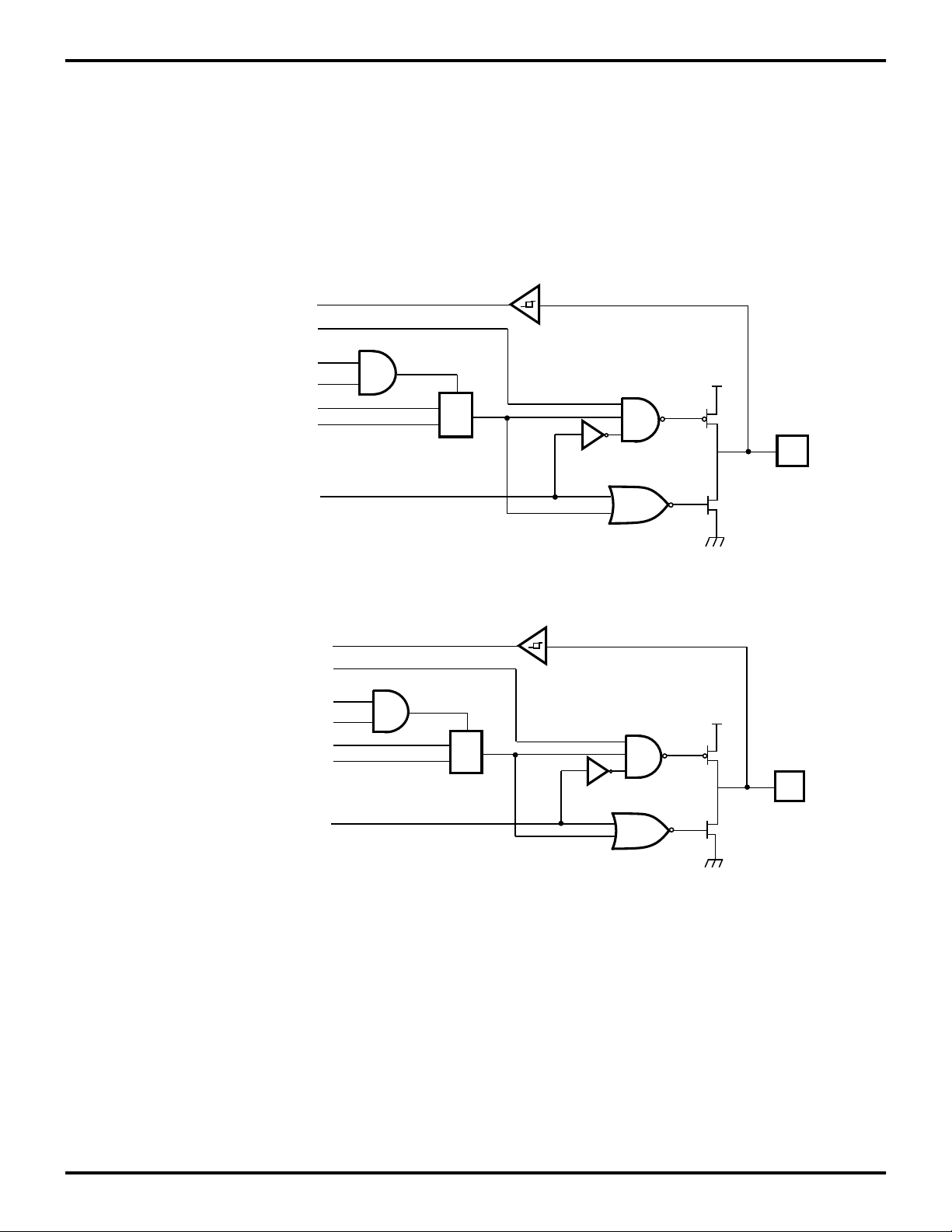
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
PIN FUNCTIONS (Continued)
Port 2 (P27-P20). Port 2 is an 8-bit, bidirectional, CMOS
compatible I/O port. These 8 I/O lines can be configured
under software control to be an input or output, independently. Input buffers are Schmitt-triggered. Pins programmed as outputs may be globally programmed as either push-pull or open-drain (Figure 6). In addition, when
P20 IN
Open-Drain
PN _ ENABLE (PNCON1 D0)
PNDOUT _ ENABLE (PNCON D4)
PNDOUT
P20 OUT
P20 OE
MUX
the PN modulator is enabled, and the appropriate pins are
programmed as outputs, P20 may be programmed as the
unspread data-out from the PN modulator. To provide a
monitor of this unspread data signal, P27 may similarly be
programmed as the data clock output.
P20
PAD
P27 IN
Open-Drain
PN _ ENABLE (PNCON1 D0)
PNDCLKOUT _ ENABLE (PNCON1 D5)
PNDCLKOUT
P27 OUT
P27 OE
MUX
Figure 6. Port 2 Configuration (P20-P27)
P27
PAD
3-10 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700
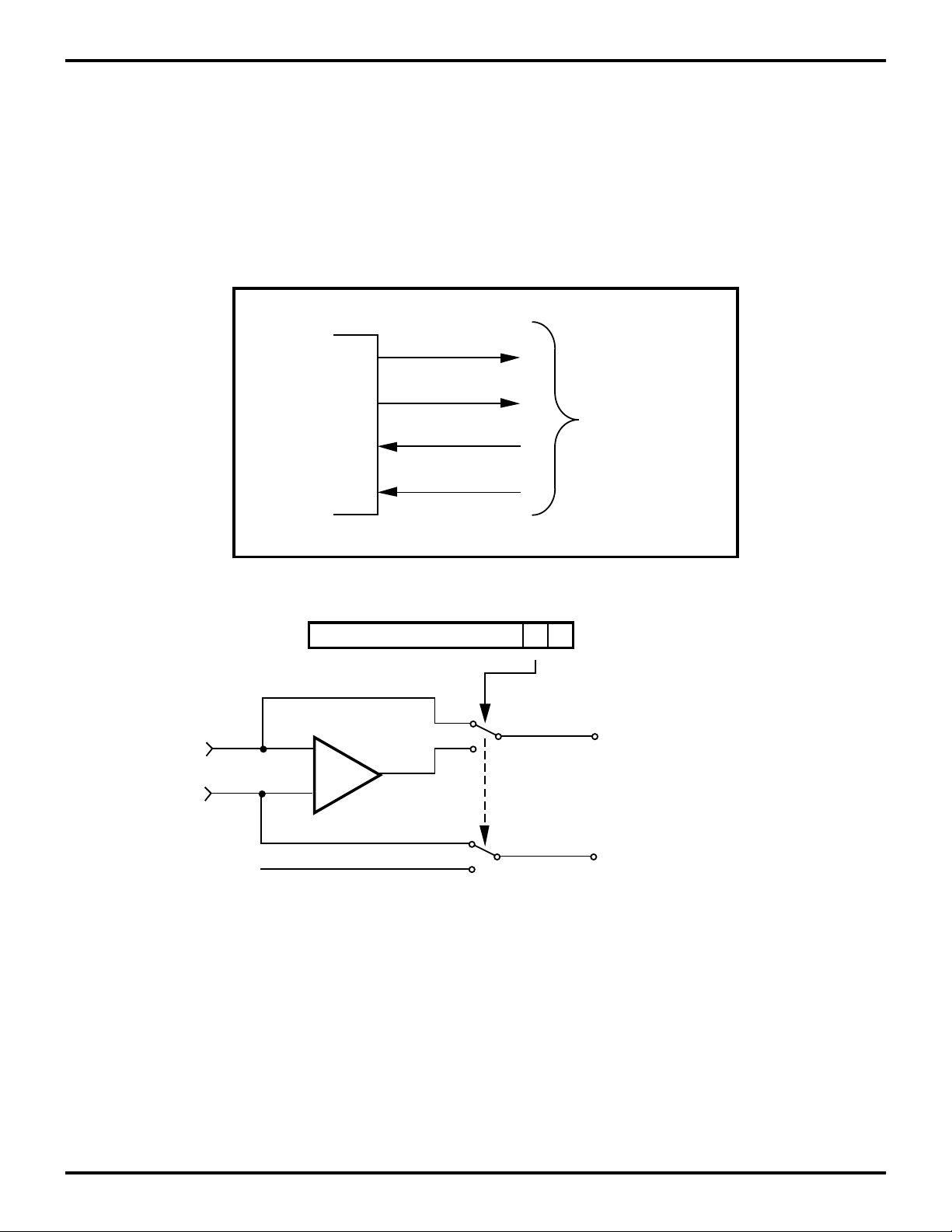
Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Port 3 (P36-P31). Port 3 is a 4-bit, CMOS-compatible port.
These four lines consist of two fixed inputs (P31, P33) and
two fixed outputs (P36-P35). P31 and P33 are standard
CMOS inputs (no auto latch) and P35 and P36 are pushpull outputs. An on-board comparator can process analog
signals on P31 with reference to the voltage on P33, where
this analog function is enabled by programming Port 3
Mode Register (bit 1). P31 is programmable as falling, ris-
P36
P35
Z87100
P33
P31
Port 3
ing, or both edge triggered interrupts (IRQ register bits 6
and 7). Access to Counter/Timer 1 is made through P31
(TIN) and P36 (T
OUT
).
When the PN modulator is enabled, P35 is automatically
configured as the output for the PN spread data, and, if desired, P36 may be programmed as the PN clock output
(Figures 7 and 8).
Port 3
(I/O or Control)
P31 (AN1)
+
P33 (REF)
-
Stop Mode Recovery Source
Figure 7. Port 3 Configuration (P31, P33)
R247 = P3M
DIG.
AN.
D1
1 = Analog
0 = Digital
IRQ2, TIN, P31 Data Latch
IRQ1, P33 Data Latch
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-11
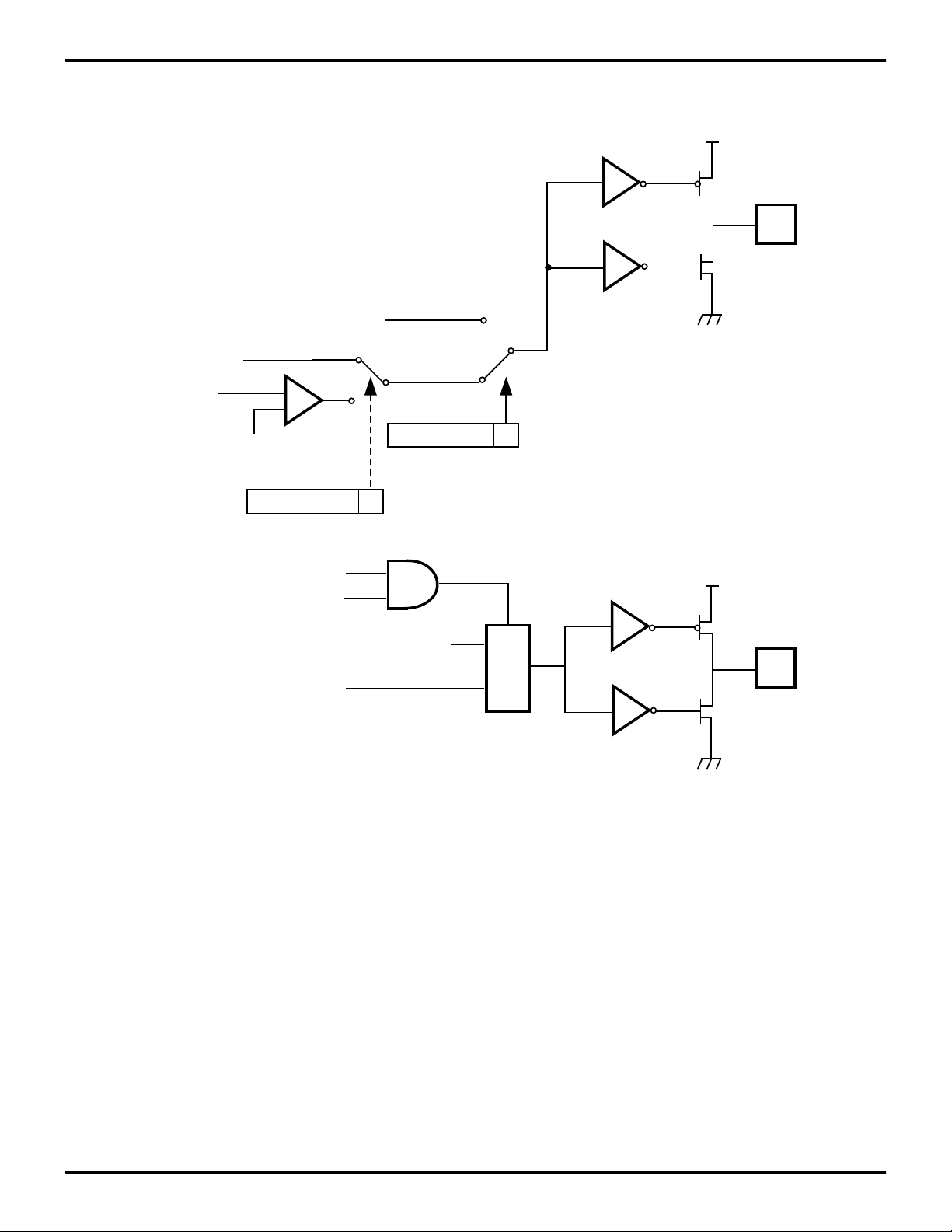
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
PIN FUNCTIONS (Continued)
P35
PAD
P35 OUT
P31
REF
PN_ENABLE (PNCON D0)
PNCLKOUT _ENABLE (PNCON D3)
PCON
+
-
P36 OUT
PNMODOUT
0
1
D0
PNCLKOUT
1
0
PNCON
D0
0 P35 Standard Output
1 P35 Comparator Output
MUX
0 PN Modulator Disabled
1 PN Modulator Enabled (P35 PNMODOUT)
P36
PAD
Figure 8. Port 3 Configuration (P35,P36)
3-12 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Comparator
Output PORT 3
0 P35 Standard Output
*
1 P35 Comparator Output
Low EMI Noise **
PORT 3
0 Low EMI Noise
1 Standard
*
Low EMI Noise **
PORT 2
0 Low EMI Noise
1 Standard
*
Reserved (Must be 1)
PCON (F) 00
Low EMI RC Oscillator **
0 Low EMI Noise
1 Standard
*
*
Default Setting After Power-On Reset Only.
** Will not be reset after a Stop-Mode Recovery.
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
PORT Configuration Register (PCON). The PORT Con-
figuration Register (PCON) configures the ports to support
comparator output on Port 3, low EMI noise on Ports 2 and
3, and low EMI noise oscillator. The PCON Register is located in the Expanded Register File at bank F, location 00
(Figure 7). Bit 0 controls the comparator use in Port 3. A 1
in this location brings the comparator output to P35 (Figure
9), and a 0 releases the port to its standard I/O configuration. Bits 5 and 6 of this register configure ports 2 and 3,
respectively, for low EMI operation. A 1 in these locations
configures the corresponding port for standard operation,
and a 0 configures the port for low EMI operation. Finally,
bit 7 of the PCON Register controls the low EMI noise oscillator. A 1 in this location configures the oscillator with
standard drive, while a 0 configures the oscillator with low
noise drive.
Low EMI Option. The Z87100 can be programmed to operate in a low EMI emission mode by the PCON register.
The RC oscillator and all I/O ports can be programmed as
low EMI emission mode independently. Use of this feature
results in:
■ Less than 1 mA current consumption during the HALT
mode.
Comparator Inputs. Port 3, P31 has a comparator front
end where the comparator reference voltage is provided
by P33. In analog mode, the P33 input functions as a reference voltage to the comparators. The internal P33 register and its corresponding IRQ1 are connected to the StopMode Recovery source selected by the SMR. In this mode,
any of the Stop-Mode Recovery sources are used to toggle
the P33 bit or generate IRQ1. In digital mode, P33 can be
used as a P33 register input or IRQ1 source (Figure 9).
When P3M is programmed for analog inputs on port 3 (Bit
D1=1) that power to the comparator is on and the current
used is 300 µA if V
is VCC, and , 50 µA if V
REF
REF
is VDD.
When comparator is digital (Bit D1=0) the comparator is
off.
■ The pre-drivers slew rate reduced to10 ns typical.
■ Low EMI output drivers have resistance of 200 ohms
(typical).
■ Internal SLCK/TCLK operation limited to a maximum of
4 MHz (250 ns cycle time).
With bit 7 of the PCON register, the gain of the RC oscillator may be selected: standard gain is intended for high performance, high speed circuits, while the low gain option is
intended for low speed, low EMI, and low current consumption applications.
Figure 9. PORT Configuration Register (PCON)
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-13
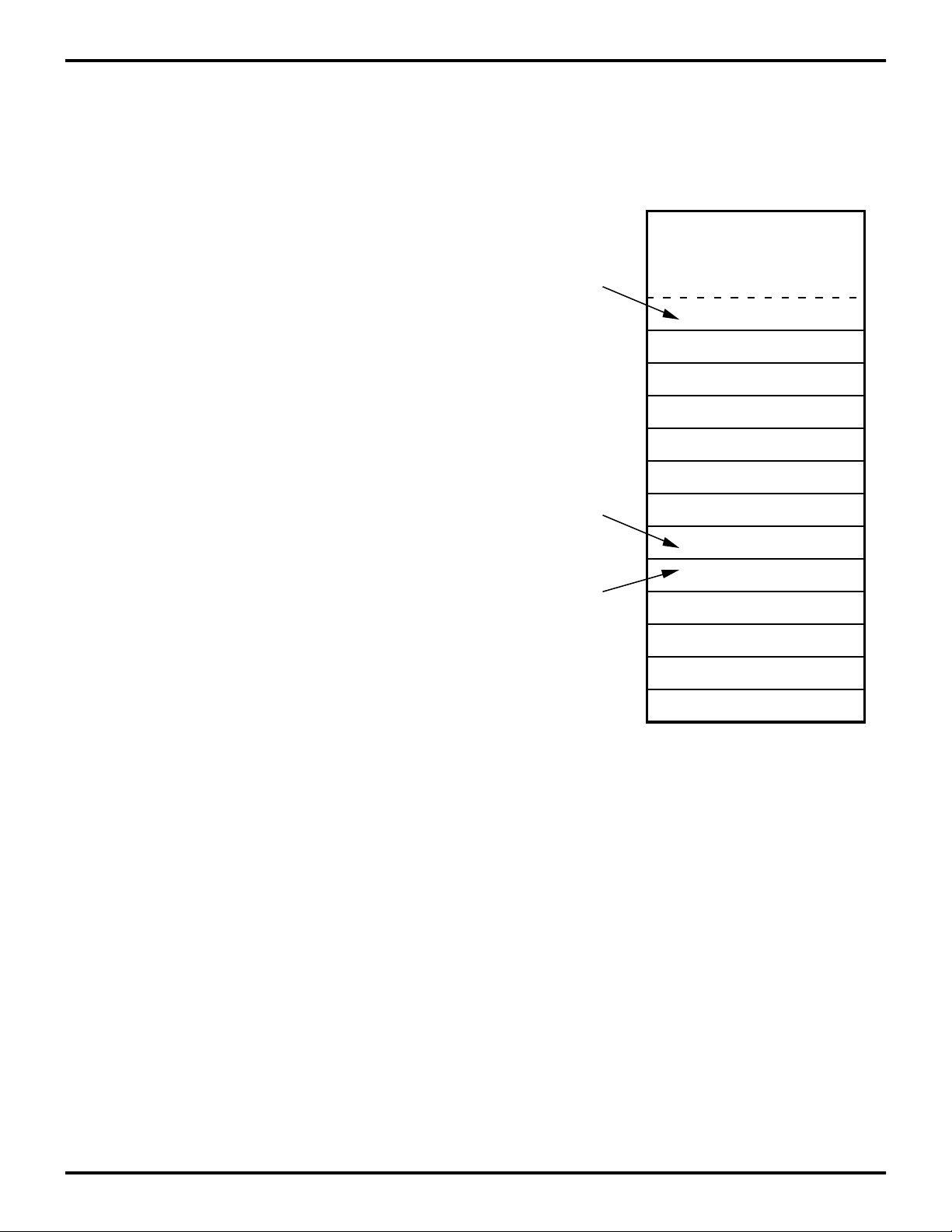
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The Z8® Wireless Controller incorporates special functions to enhance the Z8’s application in consumer, automotive, industrial, scientific research, and advanced technology applications.
RESET. The device can be reset through one of the following mechanisms:
■ Power-On Reset
■ Watch-Dog Timer
■ Stop-Mode Recovery Source
The device does not re-initialize the WDTMR, SMR, P2M,
or P3M registers to their reset values on a Stop-Mode Recovery operation.
Program Memory. The Z87100 can address up to 1
Kbytes of internal program memory (Figure 10). The first
12 bytes of program memory are reserved for the interrupt
vectors. These locations contain six 16-bit vectors that correspond to the six available interrupts. Byte 13 to byte
1023 consists of on-chip, mask-programmed ROM.
ROM Protect. The 1 Kbytes of Program Memory are mask
programmable. A ROM protect feature will prevent “dumping” of the ROM contents by inhibiting execution of the
LDC and LDCI instructions to program memory in all
modes.
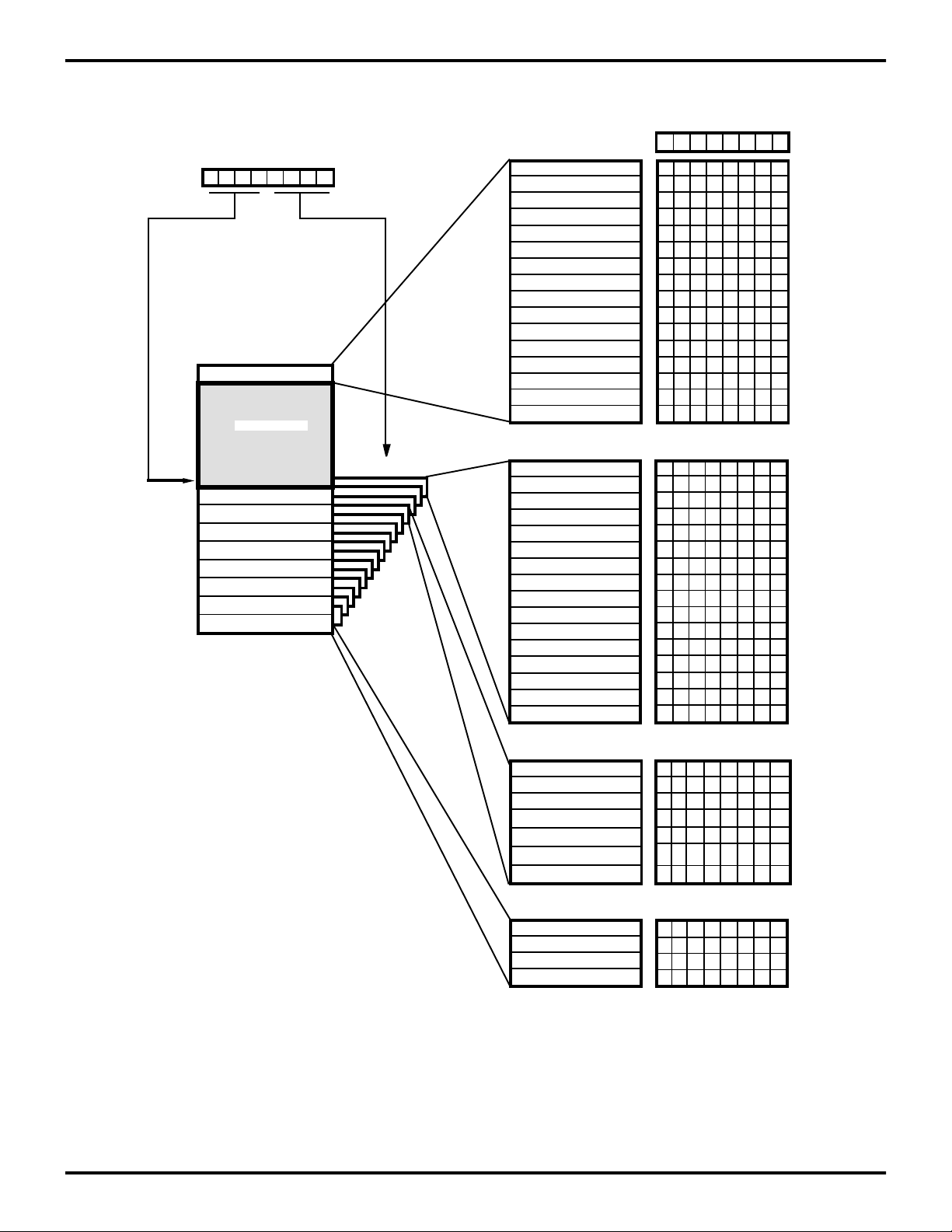
Expanded Register File. The register file has been expanded to allow for additional system control registers and
for mapping of additional peripheral devices and input/output ports into the register address area. The Z8 register
address space R0 through R15 is implemented as 16
groups of 16 registers per group. These register groups
are known as the ERF (Expanded Register File). Bits 3-0
of the Register Pointer (RP) select the active ERF group.
Bits 7-4 of register RP select the working register group
(Figure 11). Three system configuration registers reside in
the Expanded Register File address space in Bank F,
while six PN modulator registers reside in Bank C. The rest
of the Expanded Register addressing space is not physically implemented and is open for future expansion. To
write to the ERF, the upper nibble of the RP must be zero.
To write to the rest of the register file, the lower nibble must
be zero.
Antiheroine using Zilog's cross assembler Version 2.1 or
earlier, use theLD RP, #0X instruction rather than the SRP
#0X instruction to access the ERF.
1023
Location of
First Byte of
Instruction
Executed
After RESET
Interrupt
Vector
(Lower Byte)
Interrupt
Vector
(Upper Byte)
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
On-Chip
ROM
IRQ5
IRQ5
IRQ4
IRQ4
IRQ3
IRQ3
IRQ2
IRQ2
IRQ1
IRQ1
IRQ0
IRQ0
Figure 10. Program Memory Map
3-14 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700
Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Z8 STANDARD CONTROL REGISTERS
RESET CONDITION
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
0
U
U
U
0
U
U
U
U
U
U
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
0
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
RESET CONDITION
UUU01101
0010 00 00
UUUU0
1*
1*
1*
UUU0**00 0
00000000
UUUUUUU
U
UUUUUUUU
UUUUUUUU
UUUUUUUU
0000000 0
RESET CONDITION
†11† U†
UUUUUUUU
UUUUUUUU
UUUUUUUU
U
†
U
U
0
U
U
0
U
U
0
1
0
U
0
U
0
7
Working Register
Group Pointer
%FF
%FO
%7F
%0F
%00
Legend:
**
REGISTER POINTER
6543210
Expanded Register
Group Pointer
Z8 Reg. File
Not Implemented
U = Unknown
† = Reserved
Will not be reset with a
*
STOP-Mode Recovery
Resets upon power-on according
to RC/TMBASE mask option.
REGISTER
% FF
% FE
% FD
% FC
% FB
% FA
% F9
% F8
% F7
*
% F6
*
% F5
% F4
% F3
% F2
% F1
% F0
SPL
GPR
RP
FLAGS
IMR
IRQ
IPR
P01M
P3M
P2M
PRE0
T0
PRE1
T1
TMR
Reserved
EXPANDED REG. GROUP (F)
REGISTER
% (F) 0F
*
% (F) 0E
% (F) 0D
% (F) 0C
% (F) 0B
*
% (F) 0A
% (F) 09
% (F) 08
% (F) 07
% (F) 06
% (F) 05 Reserved
% (F) 04 Reserved
% (F) 03
% (F) 02
% (F) 01
% (F) 00
WDTMR
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
SMR
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
PCON
EXPANDED REG. GROUP (C)
REGISTER RESET CONDITION
% (C) 06 TMBAS
*
% (C) 05 DCLK
*
% (C) 04
*
% (C) 03 TxBUFL
*
% (C) 02 PNLEN
*
% (C) 01
*
% (C) 00
*
TxBUFH
PNADDR
PNCON
REG. GROUP (0)
REGISTER
% (0) 03 P3
% (0) 02 P2
% (0) 01 Reserved
% (0) 00
Reserved
Figure 11. Expanded Register File Architecture
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-15

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
support of the PN modulator. The instructions can access
R253 RP
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Expanded Register File Pointer
Working Register Pointer
Figure 12. Register Pointer
Register File. The Register File consists of two I/O port
registers, 124 general-purpose registers, 15 control and
status registers, and ten system configuration registers in
the Expanded Register Group, including six registers in
registers directly or indirectly through an 8-bit address
field, allowing use of a short 4-bit register address with the
Register Pointer. In the 4-bit mode, the Register File is divided into 16 working register groups, each occupying 16
continuous locations. The Register Pointer addresses the
starting location of the active working-register group.
Caution: D4 of Control Register P01M (R248) must be
0. If the Z87100 is emulated by Z86C90, D4 of P01M
has to change to 0 before submission to ROM code.
GPR. The Z87100 has one extra general-purpose register
located at %FE(R254).
r7 r6 r5 r4 R253 (%FD)
The upper nibble of the register file address
provided by the register pointer specifies
the active working-register group.
7F
70
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
2F
20
1F
10
0F
Register Group F
Specified Working
Register Group
Register Group 1
Register Group 0
r3 r2 r1 r0
•
•
•
(Register Pointer)
R127 to R111
The lower nibble
of the register
file address
provided by the
instruction points
to the specified
register.
R31 to R16
R15 to R4
00
I/O Ports
R3 to R0
Figure 13. Register Pointer
3-16 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Stack. The Z87100 has an 8-bit Stack Pointer (R255) used
for the internal stack that resides within the 124 generalpurpose registers.
OSC
÷2
0
÷16
1
(SMR) D0
(SMR) D1
1
0
Internal
Clock
(SCLK)
Write Write Read
Initial Value
Register
÷4
Counter/Timers. There are two 8-bit programmable
counter/timers (T0-T1), each driven by its own 6-bit programmable prescaler. The T1 prescaler can be driven by
internal or external clock sources, however, the T0 prescaler is driven by the internal clock only (Figure 14).
Internal Data Bus
PRE0
6-Bit
Down
Counter
T0
Initial Value
Register
8-Bit
Down
Counter
T0
Current Value
Register
IRQ4
Clock
Logic
TIN
P31
External Clock
÷4
Internal Clock
Gated Clock
Triggered Clock
6-Bit
Down
Counter
PRE1
Initial Value
Register
Write Write Read
8-Bit
Down
Counter
T1
Initial Value
Register
Internal Data Bus
Figure 14. Counter/Timer Block Diagram
÷2
Current Value
Register
TOUT
P36
IRQ5
T1
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-17

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
The 6-bit Prescaler divide the input frequency of the clock
source by any integer number from 1 to 64. Each prescaler
drives its counter, which decrements the value (1 to 256)
that has been loaded into the counter. When the counter
reaches the end of count, a timer interrupt request, IRQ4
(T0) or IRQ5 (T1), is generated.
The counters are programmed to start, stop, restart to continue, or restart from the initial value. The counters can
also be programmed to stop upon reaching zero (singlepass mode) or to automatically reload the initial value and
continue counting (modulo-n continuous mode).
The counters, but not the Prescaler, may be read at any
time without disturbing their value or count mode. The
clock source for T1 is user-definable and can be either the
internal microprocessor clock divided by four, or an exter-
nal signal input through Port 3. The Timer Mode register
configures the external timer input (P31) as an external
clock, a trigger input that can be retriggerable or non-retriggerable, or as a gate input for the internal clock. Port 3, line
P36 serves as a timer output (T
) through which T0, T1
OUT
or the internal clock can be output. The counter/timers can
be cascaded by connecting the T0 output to the input of
T1.
Interrupts. The Z87100 has six different interrupts from
six different sources. The interrupts are maskable and prioritized (Figure 15). The six sources are divided as follows;
two sources are claimed by Port 3 lines P31 and P33, two
sources in the counter/timers, one source for the PN modulator and one source for the time base generator. The Interrupt Mask Register globally or singularly enables or disables the six interrupt requests (Table 2).
IRQ0 IRQ2
IRQ1, 3, 4, 5
Interrupt
Edge
Select
IRQ (D6, D7)
Interrupt
Request
Global
Interrupt
Enable
PRIORITY
Vector Select
Figure 15. Interrupt Block Diagram
IRQ
IMR
6
IPR
LOGIC
3-18 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Table 2. Interrupt Types, Sources, and Vectors
Vector
Name Source
IRQ0 Time Base 0, 1 Internal,
IRQ1 IRQ1 2, 3 External (P33),
IRQ2 IRQ2, TIN 4, 5 External (P31),
IRQ3 Software/PN
Modulator
IRQ4 T0 8, 9 Internal
IRQ5 TI 10, 11 Internal
Notes:
*When the PN Modulator is enabled, IRQ3 is an internal
interrupt.
When more than one interrupt is pending, priorities are resolved by a programmable priority encoder that is controlled by the Interrupt Priority register. An interrupt machine cycle is activated when an interrupt request is
granted. This disables all subsequent interrupts, saves the
Program Counter and Status Flags, and then branches to
the program memory vector location reserved for that interrupt. All Z87100 interrupts are vectored through locations in the program memory. This memory location and
the next byte contain the 16-bit starting address of the interrupt service routine for that particular interrupt request.
Location Comments
Rising/Falling Edge
Triggered
Falling Edge
Triggered
Rising/Falling Edge
Triggered
6, 7 Software
Generated/Internal*
An interrupt resulting from AN1 (P31) is mapped into IRQ2,
and an interrupt from the time base generator is mapped
into IRQ0. Interrupts IRQ2 and IRQ0 may be rising, falling,
or both-edge triggered, and are programmable by the user. The software can poll to identify the state of the pin. For
IRQ0 and the time base generator, selection of the trigger
edge is not critical but should not be changed once selected.
The programming bits for the INTERRUPT EDGE SELECT are located in the IRQ register (R250), bits D7 and
D6. The configuration is shown in Table 3.
Table 3. IRQ0 and IRQ2 Interrupt Edge
Programming
Interrupt
IRQ
Register D7
00FF
01FR
10RF
1 1 R/F R/F
Notes:
F = Falling Edge
R = Rising Edge
Clock. The Z87100 derives its timing from an on-board RC
oscillator referenced as RC or an external clock source applied to the time base counter input referenced as TMBASE. The RC clock source is made of an internal oscillator and an external resistor and an optional external
capacitor (See Figure 14).
IRQ
Register D6 P31
Edge Time
Base
To accommodate polled interrupt systems, interrupt inputs
are masked and the interrupt request register is polled to
determine which of the interrupt requests needs services.
When the PN modulator is disabled, IRQ3 has no hardware source but can be invoked by software by setting bit
D3 of the IRQ register to 1. When the PN modulator is enabled, an interrupt will be mapped to IRQ3 after the contents of the PN modulator's data hold register have been
loaded into the modulator's data shift register.
The 2 terminals that are part of the RC oscillator are referenced as RC1 and RC2. The frequency of the clock signal
generated by the RC oscillator cannot exceed 6 MHz. RC1
can also be driven by an external clock source, while RC2
remains unconnected. In this configuration the Z87100
can be clocked up to 12 MHz, when not in Low EMI mode.
(4 MHz in Low EMI mode).
Both clock sources, RC and TMBASE, can be selected to
drive the internal Z8 system clock, depending on the setting of a mask-programmed option bit.
The TMBASE clock input requires a 32.768 kHz clock signal when the TMBASE is enabled or when the TMBASE is
selected to be the default oscillator. As a special feature of
the Z87100, ICC current consumption is significantly reduced at a clock frequency of 10 kHz in low EMI noise
mode.
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-19
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
R
Standard Mode
SCLK=RC1/2
Ext Clock 12 MHz
(SCLK=6 MHz)
RC 6 MHz
(SCLK = 3 MHz)
RC1
RC1
C
R
RC2
RC2
RC Oscillator
Figure 16. RC Oscillator Configuration
Table 4. Maximum Clock Value in Different Modes
Standard Mode
SCLK=RC1
6 MHz
(SCLK = 6 MHz)
3 MHz
(SCLK = 3 MHz)
Low EMI
SCLK= RC1/2
4 MHz
(SCLK = 2 MHz)
1 MHz
(SCLK = 500 kHz)
RC1
RC2
External Clock
Low EMI
SCLK=RC1
2 MHz
(SCLK = 2 MHz)
500 kHz
(SCLK = 500 kHz)
Recovery Timer Circuit. A timer circuit clocked by a dedicated on-board WDT oscillator or by the RC oscillator or
TMBASE clock oscillator is used as a recovery timer. The
timer allows VCC and the oscillator circuit to stabilize before instruction execution begins. The recovery timer circuit is a one-shot timer triggered by one of the three conditions:
■ Power Fail to Power OK status
■ Stop-Mode Recovery (If D5 of SMR=1)
■ WDT Time-Out
The recovery time is a nominal 5 ms using the internal
WDT oscillator or, if used with the WDT, 256 clock cycles
of the selected externally referenced oscillator. Bit 5 of the
Stop Mode Register determines whether the recovery timer is bypassed after Stop-Mode Recovery.
HALT. The HALT instruction turns off the internal CPU
clock but not the selected RC oscillator or TMBASE clock.
The counter/timers and external interrupts IRQ0 and IRQ2
remain active. The device is recovered by interrupts, either
externally or internally generated. After the interrupt, execution proceeds to the next instruction following the HALT
instruction.
STOP. This instruction turns off the internal clock and the
RC oscillation and reduces the standby current to 10 µA or
less. The STOP mode is terminated by either WDT timeout, POR, or SMR recovery. Either of these events causes
the processor to restart the application program at address
000C (HEX). Note that the selected clock source, RC oscillator or TMBASE clock, remains active if bits 3 and 4 of
the WDTMR are set. In this mode, only the watch-dog timer runs and the time base generator always remain on.
3-20 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
In order to enter STOP (or HALT) mode, it is necessary to
first flush the instruction pipeline to avoid suspending execution in mid-instruction. To do this, the user executes a
NOP (opcode=FFH) immediately before the appropriate
sleep instruction; i.e.,
FF NOP; clear the pipeline
6F STOP; enter STOP mode
or
FF NOP; clear the pipeline
7F HALT; enter HALT mode
PN Modulator. The Z87100 incorporates a PN modulator
to allow generation of a direct sequence spread spectrum
data stream. Coupled with the appropriate transmitter circuitry, the Z87100 can support wireless and power line
spread spectrum transmission.
The PN modulator of the Z87100 is shown in Figure 15.
Major elements of the PN modulator include the PN ROM,
the PN modulator control logic, the data hold and data
shift registers, and the clock select multiplexor and PN and
data clock generator.
As part of the PN modulator, a specially designated area
of ROM (PN ROM) provides space for 256 bits (“chips”) of
one or more pseudorandom noise sequences. The PN
modulator control logic accesses the PN ROM as a circular
buffer and synchronously exclusive-or’s (XORs) each chip
of the sequence with the data bits loaded in the PN modulator's data shift register, thereby PN modulating the data.
The PN code is accessed from the PN ROM beginning at
a specified relative address (PNADDR, register %02 in
bank C of the Expanded Register Group) until the chip corresponding to the PN code length (PNLEN, register %03 in
bank C of the Expanded Register Group) is reached, at
which point access continues again from the specified relative address.
The limits of the PN ROM address space are automatically
resolved by the control logic so that the PN ROM is effectively a large circular buffer from which smaller circular
buffers defined by PNLEN and PNADDR can be accessed. Operation and control of the circular buffer is transparent to the user. As long as the sum of code lengths is less
than or equal to 256 chips, more than one PN sequence
may be ROM programmed, with the choice of code or even
a concatenation of codes to be used for transmission controlled by Z8 software and the values of PNADDR and PNLEN.
Contents of PN ROM are shifted out and XOR’ed with the
contents of the data shift register. The rates at which the
two streams are shifted are controlled by the PN and data
clocks so that one or more PN chips are XOR’ed against a
single data bit, where the number of PN chips is determined by the value of PNLEN. The reference clock for the
PN modulator may be selected from the internal system
clock (SCLK) or either of the two counter/timers (T0 and
T1).
In nominal operation, the PN clock is defined by the selected reference clock, and the data clock is then generated as
an integer fraction of the PN clock, where the integer is
specified by PNLEN. In this way, each data bit can be synchronously modulated by a full PN code sequence as defined by PNLEN, PNADDR, and the contents of PN ROM.
As a practical matter, this type of symbol-synchronous PN
modulation allows the corresponding spread spectrum receiver to be designed with improved acquisition performance — since the PN and data modulation are synchronously related at the transmitter, PN acquisition at the
receiver can simultaneously establish bit synchronization.
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-21

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
While nominal operation assumes that a single PN sequence of PNLEN chips corresponds to a single data bit as
described above, the PN modulator additionally supports
modes which allow 2 or 4 bits per PN sequence or 2 or 4
PN sequences per bit or an arbitrary relationship between
the PN and data clocks. The specific relationship between
the selected reference clock, the PN clock, and the data
clock then depends upon the values of the PNLEN and
DCLK registers.
The Z8 loads the data shift register of the PN modulator by
writing to the PN modulator’s 16-bit data hold register, TxBUFL and TxBUFH. As the last bit of the data shift register
is shifted to be XOR’ed, the PN modulator’s control logic
loads the contents of the data hold register into the data
shift register and triggers interrupt IRQ3. Loading of the
next byte of data to TxBUFL and TxBUFH can thus be controlled by Z8 software through interrupts or through polling
by using IRQ3.
Initiation of PN modulation is controlled by three control
bits in the PNCON and TMBASE control registers:
PN_ENABLE,PN_MODULATE,and
MODULATE_SELECT.
PN _ENABLE (PNCON D0) enables the PN modulator by
providing its circuitry with clock signals and configures
IRQ3 and P35 of Port 3.
PN_MODULATE (PNCON D6) initializes the PN ROM address counter to the start of the PN sequence, loads the
data shift register with the contents of the data hold register, TxBUFH and TxBUFL, and, depending on the value of
MODULATE_SELECT, either begins PN modulation of the
data or begins transmission of the unmodulated PN sequence.
MODULATE_SELECT (TMBASE D4) controls whether
the contents of the data hold register are clocked out to be
PN modulated. If MODULATE_SELECT is set to 0, the
contents of PN ROM and the data hold register will then be
clocked out to be XOR'ed together; otherwise, if
MODULATE_SELECT is set to 1, only the contents of PN
ROM will be clocked out.
Typically, one would enable the PN modulator with
PN_ENABLE, select the desired PN code sequence from
PN ROM using PNLEN and PNADDR, configure the desired PN and data clocks using REF_CLOCK_SELECT,
DATA_CLOCK_MODE and DCLK, and select the desired
outputs using PNCLKOUT_ENABLE, PNDOUT_ENABLE
and PNDCLKOUT_ENABLE. With the first data to be
transmitted loaded in the data hold register TxBUFL and
TXBUFH, transmission of PN modulated data or just the
PN code sequence can then begin under control of
PN_MODULATE and MODULATE_SELECT.
PN Modulator I/O. The Z87100 PN modulator outputs and
inputs are multiplexed with the pins of Ports 2 and 3 according to Table 4. By enabling the PN modulator with
PN_ENABLE (D0 of PN Modulator Control Register 1,
PNCON1), the PN-modulated data output, PNMODOUT,
is automatically multiplexed to P35. Selection of the other
PN modulator outputs, however, requires explicit enabling
of the associated control bits in PNCON as well as
PN_ENABLE. In that way, as few as one or as many as
four I/O pins may be used in operation of the PN modulator, depending upon the application’s requirements.
3-22 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
SCLK
CPU
DATA
BUS
T0
T1
clk select
TMBAS
DCLK
PNLEN
PNADDR
PNCON
IRQ3
PNLEN
PNADDR
pnclk
CLOCK
SELECT
PN MODULATOR
CONTROL
LOGIC
pnload
refclk
SHIFT CTL
8
8
ROM
Address
Counter
8
PN ROM
256 x 1
PNCLKOUT
(P36)
pnclk
CLOCK
GENERATOR
clk ctrl
dataclk
DATA SHIFT REGISTER
D0 D1 D14 D15
XOR
PNMODOUT
(P35)
PNDCLKOUT
(P27)
PNDOUT
(P20)
data load
DATA HOLD REGISTER
Tx BUFL Tx BUFH
Figure 17. Z87100 PN Modulator Conceptual Block Diagram
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-23

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Table 5. PN Modulator Registers
Pin Name Location I/O Function
PNDOUT P20 output unspread data
output
PNDCLKOUT P27 output data clock
output
PNMODOUT P35 output PN spread data
output
PNCLKOUT P36 output PN clock output
PN Modulator Registers
The PN modulator is supported by six read/write registers
located in bank (C) of the Expanded Register Group: the
PN modulator control register (PNCON) at %(C)00; the PN
relative address register (PNADDR) at %(C)01; the PN
code length register (PNLEN) at %(C)02; the PN modulator low-byte data hold register (TxBUFL) at %(C)03; the
high-byte data hold register (TxBUFH) at %(C)04; and the
data clock control register (DCLK) at %(C)05. Internally,
the PN modulator also contains the data shift register for
the chips and data bits to be XOR’ed.
PNCON
The PN control register, PNCON, shown in Figure 18 and
located at %(C)00, controls the operation and configuration of the Z87100’s PN modulator. PNCON provides the
following control functions:
PN_ENABLE (PNCON D0) disables or enables the PN
modulator. When disabled (PN_ENABLE=0), clock signals
to the PN modulator circuitry are discontinued, reducing
the overall Z87100 power requirements. When enabled
(PN_ENABLE=1), the PN-spread output PNMODOUT is
automatically directed to P35 of Port 3 and the pins indicated in Table 4 may, under program control, be selected as
indicated.
Enabling the PN modulator further configures interrupt
IRQ3 to monitor the status of the PN modulator's data shift
register. IRQ3 will initially be cleared (set to 0) but will be
set to 1 after the last bit of the data shift register's contents
has been PN-modulated and the current contents of TxBUFL and TxBUFH have been automatically transferred to
the data shift register. The user then has at most 16 data
bit intervals in which to update TxBUFL and TxBUFH.
IRQ3 may be used to control data input to the PN modulator either as an interrupt or as a polled flag, depending on
whether the EI instruction has been invoked. As an interrupt, IRQ3 will be automatically cleared as the interrupt is
serviced; as a polled flag, IRQ3 must be cleared each time
by manually setting bit 3 of the register to 0.
REF_CLOCK_SELECT (PNCON D1:D2) selects which of
three sources (SCLK, T0, or T1) is used as the PN clock.
PNCLKOUT_ENABLE (PNCON D3) when enabled
(D3=1), selects P36 of Port 3 as the output pin for the PN
modulator’s PN clock. PN_ENABLE must be set.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
PN_ENABLE
0 Disable
1 Enable
REF_CLOCK_SELECT
00 SCLK
01 T0
1X T1
PNCLKOUT_ENABLE
0 P36 I/O
1 P36 PNCLKOUT
PNDOUT_ENABLE
0 P20 I/O
1 P20 DCLKOUT
PNDCLKOUT_ENABLE
0 P27 I/O
1 P27 PNDCLKOUT
PN_MODULATE
0 STOP
1 START
DATA_CLOCK MODE
0 PNLEN-Dependent Data Clock
1 Independent Data Clock
Figure 18. PN Modulator Control Register (PNCON)
PNDOUT_ENABLE (PNCON D4), when enabled (D5=1),
selects P20 of Port 2 as the output pin for the unspread
data stream. PN_ENABLE must be set, and P20 must be
configured as an output pin using P20OE of the P2M Port
2 Mode Register.
PNDCLKOUT_ENABLE (PNCON D5), when enabled
(D6=1), selects P27 of Port 2 as the output pin for the unspread data’s clock. PN_ENABLE must be set, and P27
must be configured as an output pin using P27OE of the
P2M Port 2 Mode Register.
PN_MODULATE (PNCON D6) turns the PN modulation
function on and off, starting and stopping its operation
once enabled by PN_ENABLE. Setting PN_MODULATE
to 1 from 0 loads the data shift register with the current
contents of the data hold register, TxBUFL and TxBUFH,
and initializes the PN ROM address counter to the start of
the PN sequence according to the value set in PNADDR.
If MODULATE_SELECT is set to 0, the contents of PN
ROM and the data hold register will then be clocked out to
be XOR'ed together; otherwise, if MODULATE_SELECT
is set to 1, only the contents of PN ROM will be clocked
out.
3-24 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Resetting PN_MODULATE to 0 from 1 stops PN modulation after the current data byte is completely modulated;
i.e., after either the high or low byte of the current contents
of the 16-bit data shift register is completely modulated.
The timing of the command to reset PN_MODULATE must
be monitored by the user, based on the number of cycles
after IRQ3 was last raised, in order to insure that the desired byte is the last byte transmitted.
When instructed to stop, the contents of TxBUFL and TxBUFH will not be transferred to the data shift register. Setting PN_MODULATE to 1 will then completely reinitiate PN
modulation beginning with the PN sequence starting at
PNADDR (i.e., the PN sequence will be reset) and with the
data word to be modulated as currently stored in the PN
modulator's data hold register, TxBUFL and TxBUFH. In
effect, the data shift register contents are flushed when PN
modulation is stopped.
DATA_CLOCK_MODE (PNCON D7) controls whether the
data and PN clocks are integrally related. When
DATA_CLOCK_MODE equals 0, the data and PN clocks
are integrally related as determined by bits D0, D1, and D2
of register DCLK and the value of PNLEN. When
DATA_CLOCK_MODE equals 1, the PN clock is determined by the selected reference clock and PNLEN while
the data clock is independently determined by the reference clock and DCLK.
PNADDR
The PN relative address register, PNADDR at %(C)01, indicates the starting address within PN ROM to access the
PN sequence to be used in modulation. Addressing is relative, with PNADDR=00H corresponding to the first PN
chip contained in PN ROM, PNADDR=FFH corresponding
to the last. The value of PNADDR must be set prior to starting operation of the PN modulator; writing to PNADDR
while PN modulation is in process will give indeterminate
results.
PNLEN
The PN code length register, PNLEN at %(C)02, indicates
the number of PN chips to be accessed from PN ROM and
modulated against each data bit. If the value of PNLEN
plus PNADDR exceeds FFH, the PN modulator’s control
logic will automatically cycle through PN ROM so that a total of PNLEN chips are utilized. In some modes, the value
of PNLEN also determines the data rate, where the PN
modulator’s data shift register is clocked by an integer multiple or fraction of the selected reference clock divided by
PNLEN. The value of PNLEN must be set prior to starting
operation of the PN modulator; writing to PNLEN while PN
modulation is in process will give indeterminate results.
TxBUFL and TxBUFH
The PN modulator’s data hold register, TxBUFL at %(C)03
and TxBUFH at %(C)04, supports the loading of data bytes
by the Z8 core for PN modulation. Data loading may be
controlled either through software polling or interrupt using
IRQ3. The time available to load data depends upon the
transmit data rate, itself a function of the speed of the selected reference clock and the value of PNLEN, and, of
course, upon the Z87100 clock.
Note that the data shift register is clocked by the dataclk.
Data is shifted for PN modulation D15 first, D0 last in terms
of the data loaded into TxBUFL and TxBUFH. The data
shift register, as opposed to TxBUFL and TxBUFH, is not
accessible by the CPU.
DCLK
The data clock control register, DCLK at %(C)05, determines the relationship within the PN modulator among the
PN clock controlling the PN shift register (pnclk), the data
clock controlling the data shift register (dataclk), and the
selected reference clock (SCLK, or one of the two Z8
counter/timers). A conceptual drawing of the PN modulator’s timing generator is shown in Figure 17, while Table 5
summarizes the following discussion of the various data
clock modes.
When DATA_CLOCK_MODE (PNCON D7) is set to 0, the
first three bits of DCLK (D2, D1, D0) establish an integral
relationship between the data clock and the PN code sequence.
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-25

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Nominal operation corresponds to DCLK D2=0, D1=0, and
D0=0: the PN clock (pnclk) is then equal to the reference
clock (refclk), and the data clock is equal to refclk divided
by the value of PNLEN. In this way, a complete PN code
sequence as defined by PNLEN corresponds to a single
data bit. The PN modulator output is thus the PN sequence
with its polarity determined by the value of the data bit.
With D2=0, non-zero values of D1 and D0 determine if refclk/PNLEN is further divided by 2D1 D0 to form the data
clock. In other words,
pnclk = refclk,
dataclk = pnclk/(PNLEN x 2D1 D0),
As can be seen, a single data bit may correspond to 2, 4,or
8 PN sequences in this mode.
With D2=1, the PN clock is formed by dividing refclk by 4.
The values of D1 and D0 then determine the relationship
DCLK D2
PNCON D7
÷ 4
SCLK
T0
T1
Clock
Select
(DATA_CLOCK_MODE)
refclk
of dataclk to refclk and can allow a single PN sequence to
correspond to 2 or 4 data bits:
pnclk = refclk/4,
dataclk = refclk/(PNLEN x 2D1 D0)
or, equivalently,
dataclk = (4/2D1 D0) x pnclk/PNLEN.
When DATA_CLOCK_MODE (PNCON D7) is set to 1, the
number of complete PN code sequences per data bit or
number of data bits per single PN code sequence is not
necessarily an integer. The PN clock is defined by refclk,
while the data clock is determined as refclk/DCLK, using
all 8 bits of DCLK. Although not likely to be used, DCLK =
00H corresponds to a value of 256. The transition edges of
a single chip are still aligned with that of a bit transition, but
the PN code cycle is not necessarily synchronous with
data transitions.
0
pnclk
(to PN ROM)
1
DCLK
D1 D0
0
1
PNCON
D7
DATA_CLOCK_MODE
dataclk
(to DATA SHIFT
REGISTER)
0 dataclk
integrally related
to pnclk
1 independent
dataclk
÷ PNLEN
÷ DCLK
÷2
D1 D0
Figure 19. Conceptual Block Diagram of PN Modulator Timing Generator
3-26 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Table 6. Data and PN Clock Configuration
DATA_CLOCKMODE DCLK PNCLK DATACLK
0 xxxxx000 refclk pnclk/PNLEN
0 xxxxx001 refclk pnclk/(PNLENx2)
0 xxxxx010 refclk pnclk/(PNLENx4)
0 xxxxx011 refclk pnclk/(PNLENx8)
0 xxxxx100 refclk/4 4xpnclk/PNLEN
0 xxxxx101 refclk/4 2xpnclk/PNLEN
0 xxxxx110 refclk/4 pnclk/PNLEN
0 xxxxx111 refclk/4 pnclk/(PNLENx2)
1 DCLK refclk pnclk/DCLK
Time Base Generator. The time base generator can be
used while the Z8 is in stop mode to initiate a stop-mode
recovery or while the Z8 is operating to generate IRQ0 interrupts as a time-keeping pulse. If used while the Z8 is in
stop mode, time-out will trigger a stop-mode recovery
("warm start") and reset the processor to address 000C
(hex). Otherwise, time-out of the time base generator will
set IRQ0 to 1. This mode can be used while the Z8 continues operation and a regular time base is desired, where
IRQ0 can either be polled as a flag and manually cleared
by the user or enabled as an interrupt and automatically
cleared. The time base generator is programmable and
can provide clock signals every .25 seconds, one second,
one minute, or one hour, with control of the time base generator provided through the TMBASE register at %(C)06.
TMBASE
The time base generator control register, located at
%(C)06 and depicted in Figure 18, allows the time base to
be selected and its actions controlled.
TIMEOUT_SELECT. (TMBASE D0-D1) determines the
time base. A value of D1=0, D0=0 selects .25 seconds; 01
selects one second; 10 selects one minute; and 11 selects
one hour.
TIMEOUT_ENABLE. (TMBASE D2) enables and disables
the time base generator. When set to 0,
TIMEOUT_ENABLE stops current operation of the time
base generator. When set to 1, TIMEOUT_ENABLE resets and starts the time base generator. Reading
TIMEOUT_ENABLE provides an indication of the time
base generator's status: if set to 0, the time base generator
is off; if set to 1, the generator is currently operating.
CLOCK_SELECT. (TMBASE D3) selects either RC or
TMBASE as the clock for the Z8. If set to 0, RC will be the
clock for the Z87100; if set to 1, TMBASE will be the clock.
Determination of which clock is used upon Power-On Reset ("cold start") is mask-programmable, to be selected by
the customer at the time ROM code is submitted. Upon a
Stop-Mode Recovery warm start, however, the value of
this bit (as is true for all the values of this register) is not
reset. As a result, a customer could, for example, maskprogram the Z87100 to power-up using RC and then, under software control, switch. Depending on the application,
operation during the wake cycle could then be conducted
using either RC or TMBASE.
If the external time base clock input is not connected to an
external clock source, pin 10 should be connected to
ground.
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-27
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
The time base generator, if mask-optioned, are always on,
but RC is off when not selected. When switching from TMBASE to RC, internal circuitry waits for 128 valid clock cycles of TMBASE (4 msec @ 32 kHz) before effecting the
switch from TMBASE to RC to insure that RC has stabilized. Internal circuitry also insures that the switch from RC
to TMBASE or TMBASE to RC is glitch-free. It is recommended that any command to switch oscillators be followed by a loop that tests the value of CLOCK_SELECT:
the value of CLOCK_SELECT will only change when the
transition has fully taken place.
MODULATE_SELECT. (TMBASE D4) controls the clocking out of data from the PN modulator's data shift register.
If MODULATE_SELECT is set to 0, the contents of PN
ROM and the data hold register will be clocked out to be
XOR'ed together; otherwise, if MODULATE_SELECT is
set to 1, only the contents of PN ROM will be clocked out.
Timing of this operation depends on whether the data and
PN clocks are integrally related, as determined by
DATA_CLOCK_MODE, and whether PN modulation has
Table 7. PN Modulation Stop/Start Control
begun, as determined by PN_MODULATE, as shown in
Table 7.
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
TIMEOUT_SELECT
0 0 0.25 Second
0 1 1.0 Second
1 0 1 Minute
1 1 1 Hour
TIMEOUT_ENABLE
0 Disabled (stop)
1 Enabled (reset and start)
CLOCK_SELECT
0 RC
1 TMBASE
MODULATE_SELECT
0 PN-modulated data
1 PN sequence only
Reserved
Figure 20. Time Base Generator Control Register
PN_MODULATE
0→ 1
MODULATE_SELECT=0
(PN-Modulated Data)
MODULATE_SELECT=1
(PN Sequence Only)
PN_MODULATE=1
MODULATE_SELECT 1→0
(PN Only → PN + Data)
MODULATE_SELECT 0 →1
(PN + Data → PN Only)
First data bit and first PN chip of the PN code sequence will be clocked out
together at the next edge of the data clock (dclk).
First PN chip of the PN chip sequence will be clocked out at the next edge
of the data clock (dclk).
If DATA_CLOCK_MODE=0 (integer number of PN code sequences per
bit), then the first data bit will be clocked out with the next repetition of the
first PN chip of the PN code sequence.
If DATA_CLOCK_MODE=1 (independent PN code sequence length and
data bit duration). then the first data bit will be clocked out at the the next
edge of the data clock (dclk) together with the ongoing PN sequence.
Last data bit will be clocked out with the immediately preceding edge of the
data clock (dclk); code sequence output will continue according to the PN
clock (pnclk).
3-28 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Table 8. Stop-Mode Recovery Source
SMR (F) 0B
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
* Default setting after RESET
SCLK/TCLK Divide by 16
0 OFF
*
1 ON
Clock Divide
0 SCLK = RC1/2*
1 SCLK = RC1
Stop-Mode Recovery Source
000 POR Only
001 POR Only
010 P31
011 Time Base Generator
100 P33
101 P27
110 P2 NOR 0:3
111 P2 NOR 0:7
Stop Delay
0 OFF
1 ON
Stop Recovery Level
0 Low Level
1 High Level
Stop Flag
0 POR
1 Stop Recovery
*
*
*
*
SMRD4SMRD3SMR
D2
Operation
Description of Action
0 0 0 POR recovery only
0 0 1 POR recovery only
0 1 0 P31 transition
0 1 1 Time Base Generator
1 0 0 P33 transition
1 0 1 P27 transition
1 1 0 Logical NOR of Port 2 bits 0-3
1 1 1 Logical NOR of Port 2 bits 0-7
P31 and P33 cannot wake up from STOP mode if the input
lines are configured as analog inputs.
Stop-Mode Recovery Delay Select (D5). This bit disables the nominal 5 ms RESET delay provided by the recovery timer circuit after Stop-Mode Recovery. The default
condition of this bit is 1, enabling the delay. If this bit is 0,
the extra delay is disabled, limiting the recovery delay to 18
cycles of RC1.
Stop-Mode Recovery Level Select (D6). A 1 in this bit
position indicates that a high level on any one of the recov-
Figure 21. Stop-Mode Register
ery sources wakes the device from STOP mode. A 0 indicates low level recovery. The default is 0 on POR (Figure
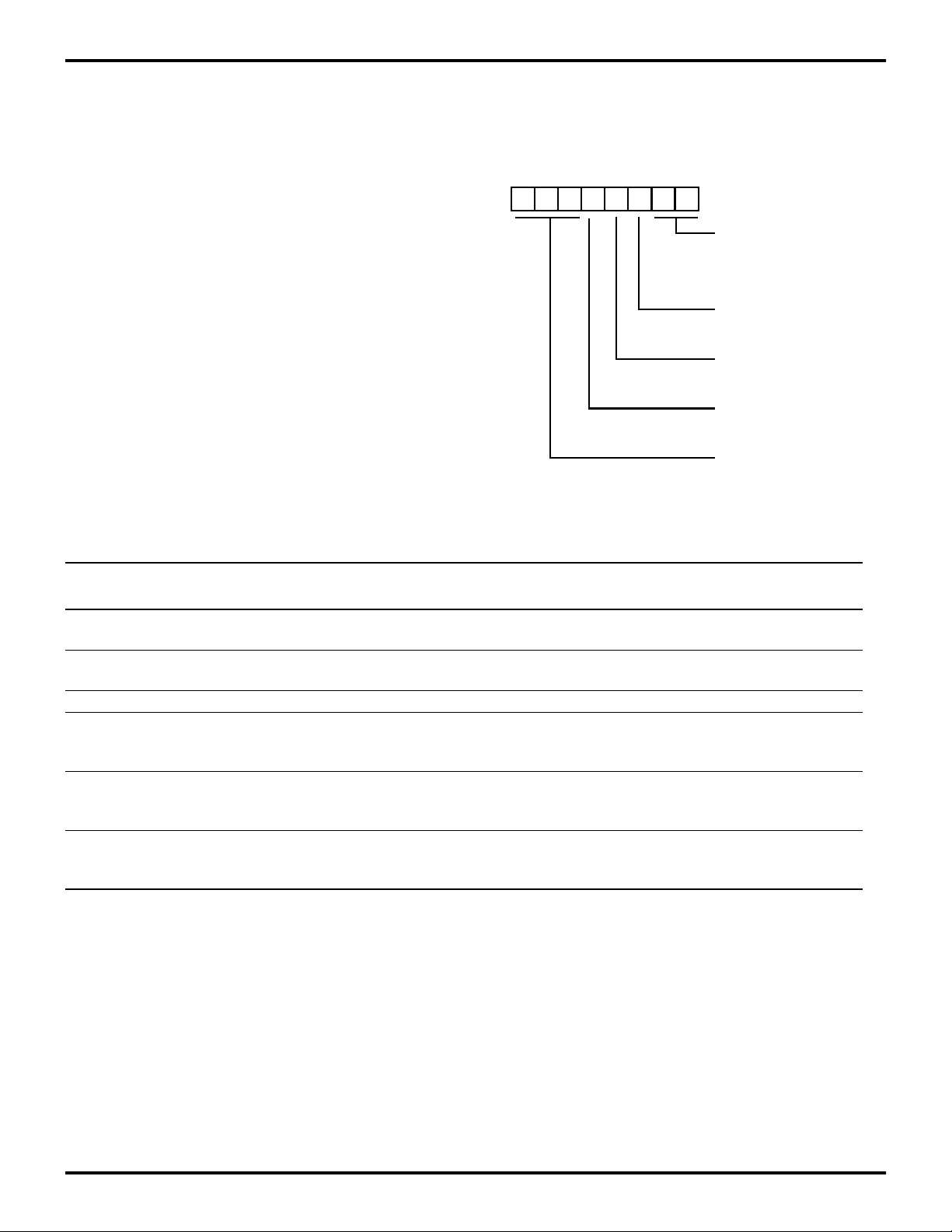
Stop-Mode Recovery Register (SMR). This register se-
19).
lects the clock divide value and determines the mode of
Stop-Mode Recovery (Figure 19). All bits are write only except bit 7, which is read only. Bit 7 is a flag bit that is hardware set on the condition of a STOP recovery and reset on
a power-on cycle. Bit 6 controls whether a low level or high
level is required from the recovery source. Bit 5 controls
the reset delay after recovery. Bits 2, 3, and 4 of the SMR
specify the source of the Stop-Mode Recovery signal. Bit
1 determines whether the selected oscillator, RC or TM-
Cold or Warm Start (D7). This bit is READ only. When the
device enters STOP mode, D7 will be set to 1. D7 will only
be reset to 0 to indicate "cold" start if the device is reset by
either a Power-On Reset or by a Watch-Dog Timer Reset
when the part is in normal operation. Otherwise, if the device is reset by a Watch-Dog Timer Reset when the part is
in STOP mode or by any other SMR source, then this bit
will continue to be set to 1 to indicate a "warm" start.
BASE, is divided by 1 or 2. Bit 0 controls the divide-by-16
prescaler of SCLK/TCLK.
Reset Upon Power-On. Upon applying power to the
Z87100, an internal reset pulse is generated which triggers
SCLK/TCLK divide-by-16 select (D0). D0 of the SMR
controls a divide-by-16 prescaler of SCLK/TCLK. The purpose of this control is to selectively reduce device power
consumption during normal processor execution (SCLK
the timing recovery circuit illustrated in Figure 22. Poweron reset (POR) behavior is different, however, depending
on whether RC or TMBASE has been selected as the clock
that drives the Z8
®
.
control) and/or HALT mode (where TCLK sources the
counter/timers and interrupt logic).
When RC is mask-selected to be the Z8 system clock, the
recovery counter is clocked by an internal WDT (Watch-
RC1 Clock divide-by-two (D1). This bit determines
whether the RC1 clock is divided by two or one. When this
bit is set to 1, the SCLK/TCLK is equal to the RC1 clock.
This option can work together with the low EMI options in
PCON register to reduce the EMI noise. Maximum clock
Dog Timer) oscillator. The system reset initiated by POR
takes 5 ms and guarantees that the RC oscillations are
stabilized before the first instruction is executed by the Z8.
Subsequently, the recovery counter is used as the WatchDog Timer.
frequency is 6 MHz when divide-by-one selection is active.
When TMBASE is mask-selected to be the default Z8 sys-
Stop-Mode Recovery Source (D2,D3,D4). These three
bits of the SMR specify the wake-up source of the Stop-
tem clock upon power-on, recovery timing is controlled by
the time base generator.
Mode Recovery (Figure 21 and Table 8).
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-29

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Watch-Dog Timer Mode Register (WDTMR). The WDT
is a retriggerable one-shot timer that resets the Z8 if it
reaches its terminal count. The WDT is initially enabled by
executing the WDT instruction and retriggered on subsequent executions of the WDT instruction. The WDT timer
circuit is driven by an on-board WDT oscillator or external
clock source RC. The WDT does not use TMBASE. The
WDT timer clock source is selected with bit 4 of the WDTMR to use either the internal WDT oscillator and a reset
delay of 5 ms, or RC1 and a reset delay of 512 RC1 clock
cycles. Note that the WDT instruction may affect the zero,
sign, and overflow flags.
Bits 0 and 1 control a tap circuit that determines the WDT
time-out period. Bit 2 determines whether the WDT is active during HALT and bit 3 determines WDT activity during
SMR D4
VDD
SMR D40D31D2
XTALB
Time Base
Generator
SMR D40D31D2
P31
D3
D2
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
P20
P27
0
P20
P23
SMR D41D31D2
SMR D41D31D2
STOP. If bits 3 and 4 of this register are both set to 1, only
the WDT is only driven by the external clock during STOP
mode. This feature makes it possible to wake up from
STOP mode from an internal source. Bits 5 through 7 of
the WDTMR are reserved (Figure 23).
The WDTMR register is accessible only during the first 64
processor cycles (128 oscillator clocks) from the execution
of the first instruction after Power-On-Reset, Watch Dog
Reset or a Stop-Mode Recovery (Figure 22). After this
point, the register cannot be modified by any means, intentional or otherwise. The WDTMR cannot be read and is located in bank F of the Expanded Register Group at address location 0FH, as shown in Figure 23.
To POR
Reset
Stop Mode Recovery
Edge Select (SMR)
To P33 Data
1
P33 From Pads
Digital/Analog Mode
Select (P3M)
0
Latch and IRQ1
MUX
SMR D41D30D2
1
P33
SMR D41D30D2
0
P27
Figure 22. Stop-Mode Recovery Source
Note: The POR, with TMBASE the default Z8 clock
source, takes 1.5 seconds the first instruction is executed by the Z8.
3-30 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
WDT Time Select (D1,D0). Selects the WDT time-out pe-
riod. It is configured as shown in Table 9.
Table 9. WDT Time Select
Time-out of
D1 D0
internal WDT
OSC
Time-out of
RC7 clock
0 0 5 ms min 512TpC
0 1 15 ms min 1024TpC
1 0 25 ms min 2048TpC
1 1 100 ms min 8192TpC
Note: The default on a WDT initiated RESET is 15 ms.
WDT During HALT (D2). This bit determines whether or
not the WDT is active during HALT mode. A 1 indicates active during HALT. The default is 1.
WDT During STOP (D3). This bitdetermines whether or
not the WDT is active during STOP mode. A 1 indicates
active during STOP. The default is 1. If bits D3 and D4 are
both set to 1, then only the WDT is driven by the external
clock during STOP mode.
On-Board WDT Oscillator or RC Oscillator Select (D4).
This bit determines which oscillator source is used to clock
the internal recovery and WDT counter chain. If the bit is a
1, the internal WDT oscillator is bypassed and the recovery
and WDT clock source is driven from RC1. The default
configuration of this bit is 0, which selects the internal WDT
oscillator.
Voltage Comparator. An on-board Voltage Compar-
V
CC
ator checks that VCC is at the required level to ensure correct operation of the device. Reset is globally driven if V
CC
is below the specified voltage (typically 2.1V).
Notes: The internal clock frequency is one half the
external clock frequency, unless the device is divide-byone mode.
The device functions normally at or above 3.0V under all
conditions. Below 3.0V, the device functions normally until
the Low-Voltage Protection trip point (V
) is reached, for
LV
the temperatures and operating frequencies described
above. The device is guaranteed to function normally at
supply voltages above the low voltage trip point. The actual low voltage trip point is a function of temperature and
process parameters (Figure 23).
ROM Protect. ROM protect is mask-programmable. It is
selected by the customer at the time the ROM code is submitted. The selection of ROM protect disables the LDC and
LDCI instructions.
WDTMR (F) 0F
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
WDT TAP INT WDT OSC RC7 CLK
00 5 512 TpC
01 15 1024 TpC*
10 25 2048 TpC
11 100 8192 TpC
WDT During HALT
0 OFF
*
1 ON
WDT During STOP
0 OFF
1 ON
*
RC/WDT OSC Select for WDT
*
Default setting after RESET
0 WDT Oscillator
1 RC7 Oscillator
Reserved (Must be 0)
*
Figure 23. Watch-Dog Timer Mode Register
Low-Voltage Protection (VLV). The low voltage trip volt-
age (VLV) will be less than 3 volts and above 1.4 volts under the following conditions.
Maximum (VLV) Conditions:
TA = 0°, +70°C, Internal Clock Frequency
equal or less than 2 MHz
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-31
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Z87100 Mask Options. The following summarizes the
mask options to be selected by the customer at the time of
ROM code submittal:
RC/TMBASE
Clear
CLK
WDT Select
(WDTMR) D1-D0
CLK Select
(WDTMR) D4
RC7
WDT
OSC
M
U
X
5 ms Recovery
CLK
Determine whether "cold start" Initialization: uses RC or
TMBASE as base clock.
ROM Protect Selects ROM protect.
On/Off:
18 Clock RESET
Generator
WDT TAP SELECT
5 ms 15 ms 25 ms 100 ms
WDT/Recovery Counter Chain
CLR
RESET
Internal
RESET
VCC
2V REF
WDT
From
Stop Mode
Recovery Source
+
-
12 ns
Glitch
Filter
Stop Delay Select (SMR D5)
TMBASE
Figure 24. Timing Recovery Circuit (POR, WDT)
1
0
Power-On Recovery
Time Base Counter
(.25s, 1s, 1 min, 1 hr)
3-32 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
VCC
2.80
(Volts)
2.60
2.40
2.20
2.00
1.80
1.60
1.40
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Figure 25. Typical Z87100 VLV V oltage vs T emperature
EXPANDED REGISTER FILE CONTROL REGISTERS
V (Typical)
LV
Temperature (°C)
SMR (F) 0B
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
SCLK/TCLK Divide by 16
0 OFF *
1 ON
Clock Divide
0 RC/2
1 RC
Stop-Mode Recovery Source
000 POR Only
001 POR Only
010 P31
011 Time Base
100 P33
101 P27
110 P2 NOR 0:3
111 P2 NOR 0:7
Stop Delay
0 OFF
1 ON *
Stop Recovery Level
0 Low Level *
1 High Level
Stop Flag (Read Only)
* Default setting after RESET
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
0 POR *
1 Stop Recovery
WDTMR (F) 0F
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
WDT TAP WDT OSC RC CLK
00 5 512 TpC
01 15 1024 TpC *
10 25 2048 TpC
11 100 8192 TpC
WDT During HALT
0 OFF
1 ON*
*
*
Default setting after RESET
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
WDT During STOP
0 OFF
1 ON*
RC/WDT OSC Select for WDT
0 WDT Oscillator
1 RC Oscillator
Reserved (Must be 0)
*
Figure 27. Watch-Dog Timer Mode Register
((F) 0FH: Write Only)
Figure 26. Stop-Mode Recovery Register
((F) 0BH: Write Only)
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-33
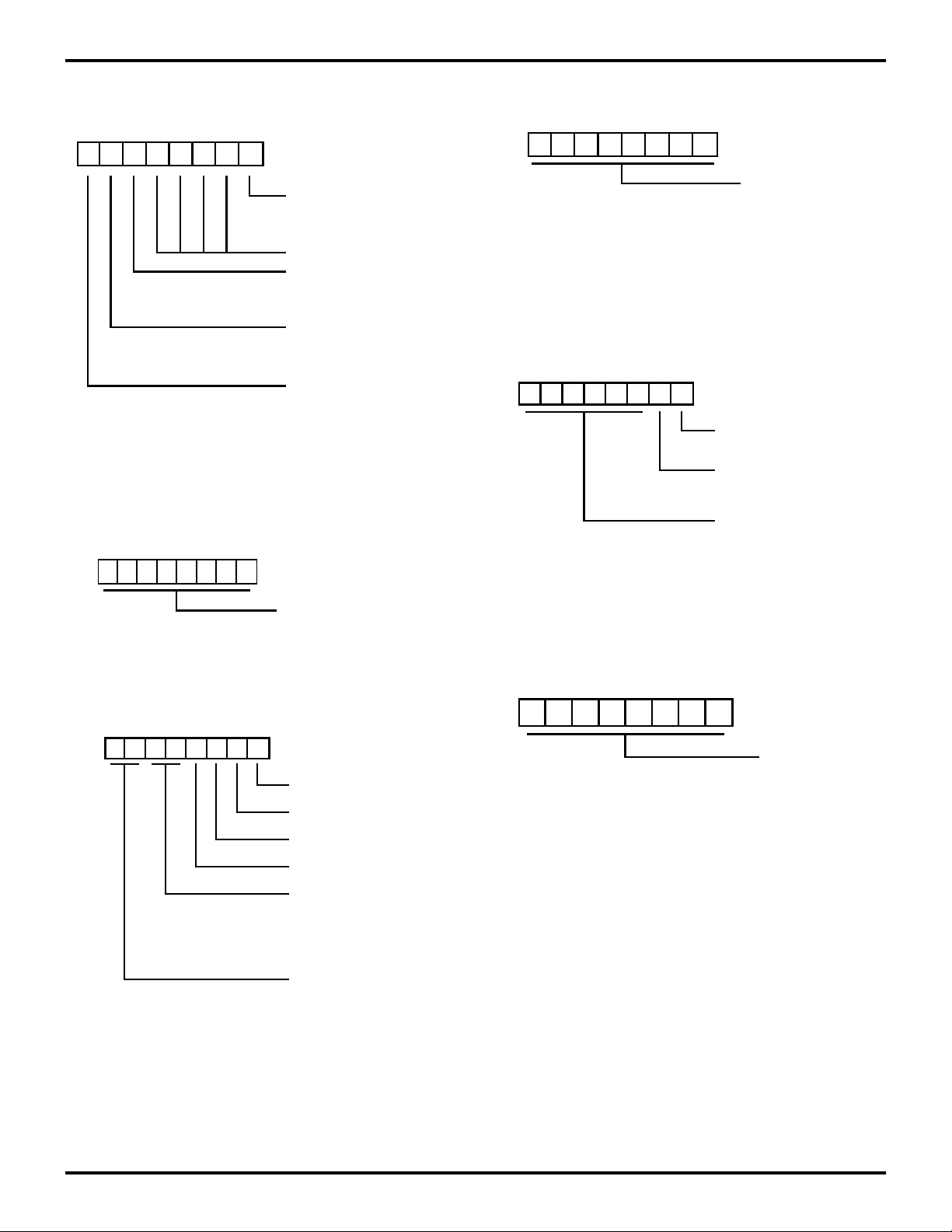
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
EXPANDED REGISTER FILE CONTROL REGISTERS (Continued)
PCON (F) 00
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Default Setting After Reset.
*
Figure 28. PORT Control Register
((F) 00H: Write Only)
R 240
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Comparator
Output PORT 3
0 P34, P35 Standard Output
1 P34, P35 Comparator Output
Reserved (Must be 1)
Low EMI Noise
PORT 2
0 Low EMI Noise
1 Standard
Low EMI Noise
PORT 3
0 Low EMI Noise
1 Standard
Low EMI RC Oscillator
0 Low EMI Noise
1 Standard
*
*
*
R244 T0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
T0 Initial Value
(When Written)
*
(Range: 1-256 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
T0 Current Value
(When READ)
Figure 31. Counter Timer 1 Register
(F2H: Read/Write)
R243 PRE1
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Count Mode
0 T1 Single Pass
1 T1 Modulo-N
Clock Source
1 T1 Internal
0 T1 External Timing Input
(TIN ) Mode
Prescaler Modulo
(Range: 1-64 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
Figure 29. Reserved
R241 TMR
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Reserved (Must be 0)
0 No Function
1 Load T0
0 Disable T0 Count
1 Enable T0 Count
0 No Function
1 Load T1
0 Disable T1 Count
1 Enable T1 Count
TIN Modes
00 External Clock Input
01 Gate Input
10 Trigger Input
(Non-retriggerable)
11 Trigger Input
(Retriggerable)
TOUT Mode
00 Not Used
01 T0 OUT
10 T1 OUT
11 Internal Clock Out (P36)
Figure 32. Prescaler 1 Register
(F3H: Write Only)
R244 T0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
T0 Initial Value
(When Written)
(Range: 1-256
Decimal
01-00 HEX)
T0 Current Value
(When READ)
Figure 33. Counter/Timer 0 Register
(F4H: Read/Write)
Figure 30. Timer Mode Register
(F1H: Read/Write)
3-34 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
R245 PRE0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 34. Prescaler 0 Register
(F5H: Write Only)
PNCON (C) 00
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
PN_ENABLE
0 Disable
1 Enable
REF_CLOCK_SELECT
00 SCLK
01 T0
1X T1
PNCLKOUT_ENABLE
0 P36 I/O
1 P36 PNCLKOUT
PNDOUT_ENABLE
0 P20 I/O
1 P20 DCLKOUT
PNDCLKOUT_ENABLE
0 P27 I/O
1 P27 PNDCLKOUT
PN_MODULATE
0 STOP
1 START
DATA_CLOCK_MODE
0 PNLEN-dependent data clock
1 Independent data clock
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
Count Mode
0 T0 Single Pass
1 T0 Modulo N
X
Prescaler Modulo
(Range: 1-64 Decimal
01-00 HEX)
PNLEN (C) 02
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
PNLEN = PN sequence length
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
Figure 37. PN Code Length Register
((C) 02H: Read/Write)
TxBUFH (C) 04
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
TxBUFH = X
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
Figure 38. PN Modulator Low-Byte
Data Hold Register ((C) 03H: Write Only)
TxBUFH (C) 04
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
TxBUFH = X
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
Figure 39. PN Modulator High-Byte
Data Hold Register ((C) 04H: Write Only)
DCLK (C) 05
Figure 35. PN Modulator Control Register
((C) 00H: Read/Write)
PNADDR (C) 01
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
PNADDR = PN sequence
starting address
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
When DATA_CLOCK_MODE
(PNCON D7) = 0,
dataclk = refclk/2
D2 = 0: pnclk = refclk
D2 = 1: pnclk = refclk/4
When DATA_CLOCK_MODE
(PNCON D7) = 1,
pnclk = refclk
dataclk = refclk/DCLK
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
D1-D0
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
Figure 36. PN ROM Relative Address Register
((C) 01H: Read/Write)
Figure 40. Data Clock Control Register
((C) 05H: Read/Write)
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-35

Z87100
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
X
Must be 0
X
R248 P01M
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
EXPANDED REGISTER FILE CONTROL REGISTERS (Continued)
TMBAS (C) 06
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
TIMEOUT_SELECT
0 0 0.25 second
0 1 1.0 second
1 0 1 minute
1 1 1 hour
TIMEOUT_ENABLE
0 Disabled (stop)
1 Enabled (reset and start)
CLOCK_SELECT
0 RC
1 TMBASE
MODULATE_SELECT
0 PN modulated data
1 PN sequence only
Reserved
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
Figure 41. Time Base Generator
Control Register ((C) 06H: Read/Write)
R246 P2M
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
P2 - P2 I/O Definition
70
0 Defines Bit as OUTPUT
1 Defines Bit as INPUT
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
Figure 42. Port 2 Mode Register
(F6H; Write Only)
Figure 44. Port 0 and 1 Mode Register
(F8H: Write Only)
R249 IPR
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Interrupt Group Priority
000 Reserved
001 C > A > B
010 A > B > C
011 A > C > B
100 B > C > A
101 C > B > A
110 B > A > C
111 Reserved
IRQ1, IRQ4 Priority (Group C)
0 IRQ1 > IRQ4
1 IRQ4 > IRQ1
IRQ0, IRQ2 Priority (Group B)
0 IRQ2 > IRQ0
1 IRQ0 > IRQ2
IRQ3, IRQ5 Priority (Group A)
0 IRQ5 > IRQ3
1 IRQ3 > IRQ5
0
Figure 45. Interrupt Priority Register
(F9H: Write Only)
R247 P3M
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Note: Register settings are not reset upon Stop-Mode Recovery.
Figure 43. Port 3 Mode Register
(F7H: Write Only)
3-36 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700
0 Port 2 Open-Drain
1 Port 2 Push-Pull
Port 3 Inputs
0 Digital
1 Analog
0 Reserved
R250 IRQ
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
IRQ0 = XTALB Time Base Generator
IRQ1 = P33 Input
IRQ2 = P31 Input
IRQ3 = Software Controlled/PN Modulator
IRQ4 = T0
IRQ5 = T1
Interrupt On Edge
00 P31 ↓ XTALB Time Base ↓
01 P31 ↓ XTALB Time Base ↑
10 P31 ↑ XTALB Time Base ↓
11 P31 ↑↓ XTALB Time Base ↑↓
Figure 46. Interrupt Request Register
(FAH: Read/Write)

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
R251 IMR
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 47. Interrupt Mask Register
(FBH: Read/Write)
R252 Flags
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 48. Flag Register
(FCH: Read/Write)
1 Enables IRQ5-IRQ0
(D0= IRQ0)
0 Reserved
1 Enables Interrupts
User Flag F1
User Flag F2
Half Carry Flag
Decimal Adjust Flag
Overflow Flag
Sign Flag
Zero Flag
Carry Flag
R253 RP
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Expanded Register File Pointer
Working Register Pointer
Figure 49. Register Pointer
(FDH: Read/Write)
R254 GPR
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 50. General-Purpose Register
(FEH: Read/Write)
R255 SPL
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Stack Pointer Lower
Byte (SP0- SP7 )
Figure 51. Stack Pointer
(FFH: Read/Write)
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-37

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
DEVICE CHARACTERISTICS
Current
(mA)
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0246810121416
Frequency (MHz)
Figure 52. Typical ICC vs Frequency
Icc at 5V
Icc at 3.3V
Icc1 at 5V
Icc1 at 5V
(SCLK divided by 16)
Icc1 at 3.3V
Icc1 at 3.3V
(SCLK divided by 16)
Note:RC is divided by 2
Vcc
(Volts)
2.0
1.0
0.0
-60 120
Legend:
A = VIL at Vcc = 3.3V
B = VIL at Vcc = 5.5V
C = VOL at Vcc = 3.0V
D = VOL at Vcc = 5.5V
-20 0 40 60 80
100-40 20 140
Temperature (°C)
Figure 53. Typical VOL, VIL vs Temperature
B
A
C
D
3-38 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Vcc
(Volts)
8.0
6.0
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Temperature (°C)
Figure 54. Typical VOH, VIH vs Temperature
VOH at Vcc 5.5V
VIH at Vcc = 5.5V
VOH at Vcc 3.0V
VIH at Vcc = 3.0V
Note: STD Mode
(Not Low EMI Mode)
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-39

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
DEVICE CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
V (Volts)
OH
-1.0
-2.0
-3.0
-4.0
-5.0
0
1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0
Vcc = 3.0V
Vcc = 5.0V
Vcc = 5.5V
7.0 8.00
IOH
(mA)
-6.0
-7.0
-8.0
A B C D E FGH I
-9.0
Legend:
A = 125°C
B = 25°C
C = -55°C
D = 125°C
E = 25°C
F = -55°C
G = 125°C
H = 25°C
I = -55°C
Figure 55. Typical VOH vs IOH Over Temperature
Note: STD Mode
(Not Low EMI Mode)
3-40 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
24.0
IOL
(mA)
22.0
20.0
18.0
16.0
14.0
12.0
10.0
8.0
6.0
4.0
2.0
0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8
AB CD
E
F
Legend:
A = -55°C
B = 25°C
C = 125°C
D = -55°C
E = 25°C
F = 125°C
Vcc = 5.5V
Vcc = 3.0V
Figure 56. Typical IOL vs VOL Over Temperature
V (Volts)
OL
Note: STD Mode
(Not Low EMI Mode)
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-41
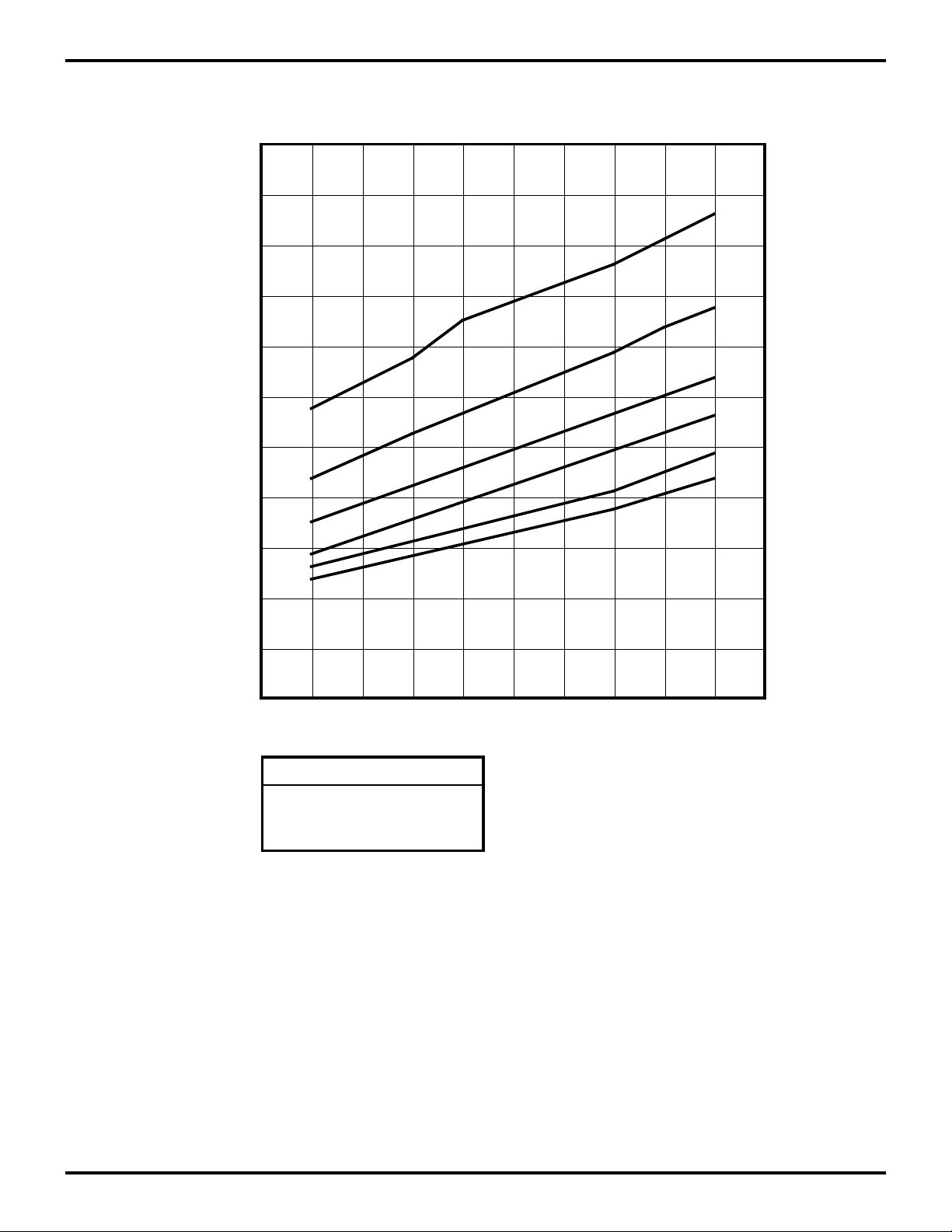
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
DEVICE CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
Time
(ms)
22.0
20.0
18.0
16.0
14.0
12.0
10.0
8.0
6.0
A
B
C
D
E
F
4.0
2.0
0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Temperature (°C)
Legend:
A - Vcc = 3.0V
B - Vcc = 3.5V
C - Vcc = 4.0V
D - Vcc = 4.5V
E - Vcc = 5.0V
F - Vcc = 5.5V
Note: Using WDT Oscillator
Figure 57. Typical Power-On Reset Time vs Temperature
140
3-42 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700

Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Time
(ms)
45.0
40.0
35.0
30.0
25.0
20.0
15.0
10.0
5.0
A
B
C
D
E
F
0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Temperature (°C)
Legend:
A - Vcc = 3.0V
B - Vcc = 3.5V
C - Vcc = 4.0V
D - Vcc = 4.5V
E - Vcc = 5.0V
F - Vcc = 5.5V
Note: Using WDT Oscillator
Figure 58. Typical 5 ms WDT Setting vs Temperature
140
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-43

Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
DEVICE CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
85
Time
(ms)
80
A
75
70
65
B
60
55
C
50
Legend:
A - Vcc = 3.0V
B - Vcc = 3.5V
C - Vcc = 4.0V
D - Vcc = 4.5v
E - Vcc = 5.0V
F - Vcc = 5.5V
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
D
E
F
140
Temperature (°C)
Note: Using WDT Oscillator
Figure 59. Typical 15 ms WDT Setting vs Temperature
3-44 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700
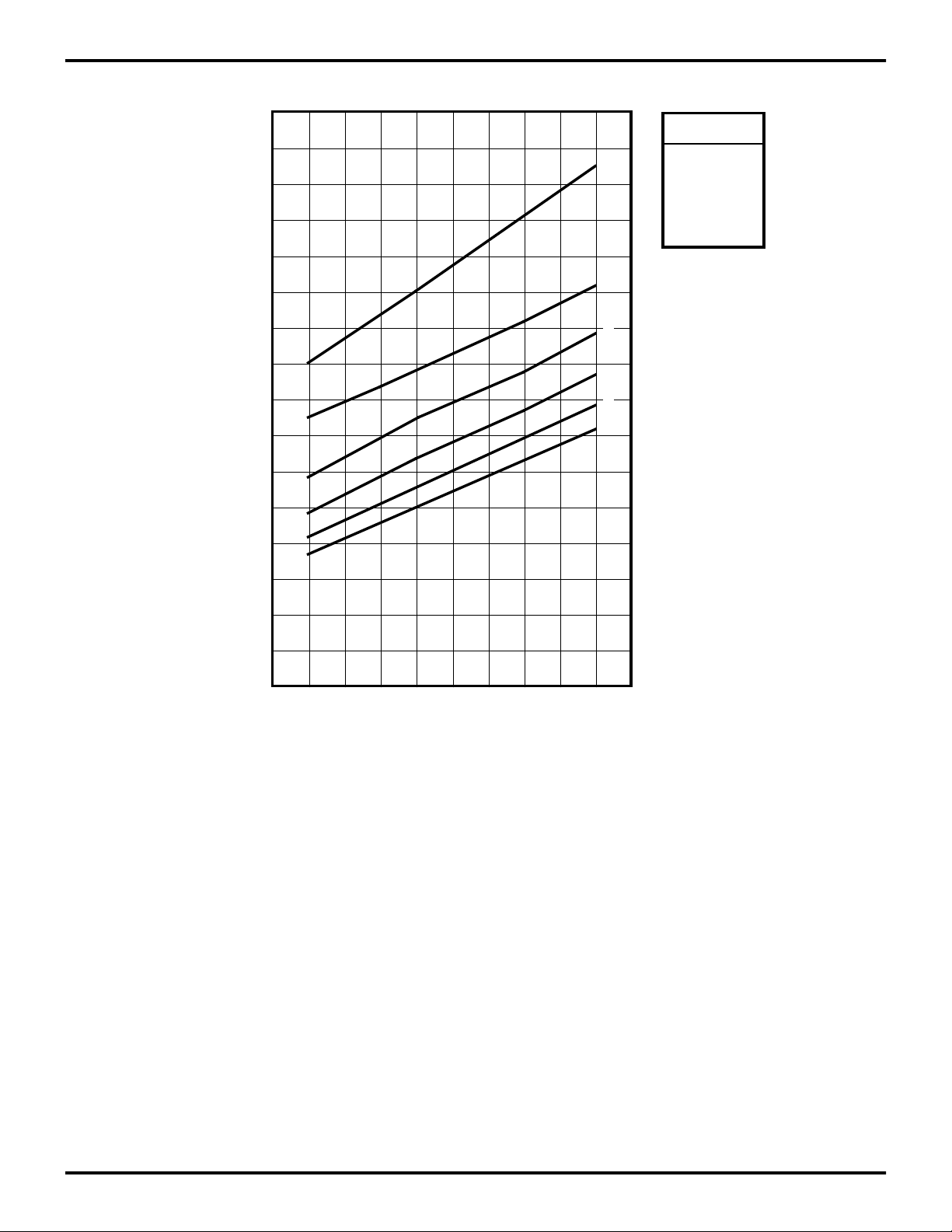
Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Time
(ms)
170
160
150
140
130
120
110
90
80
70
60
50
40
Legend:
A
B
C
D
E
F
A - Vcc = 3.0V
B - Vcc = 3.5V
C - Vcc = 4.0V
D - Vcc = 4.5v
E - Vcc = 5.0V
F - Vcc = 5.5V
30
20
10
0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Temperature (°C)
Note: Using WDT Oscillator
Figure 60. Typical 25 ms WDT Setting vs Temperature
140
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-45
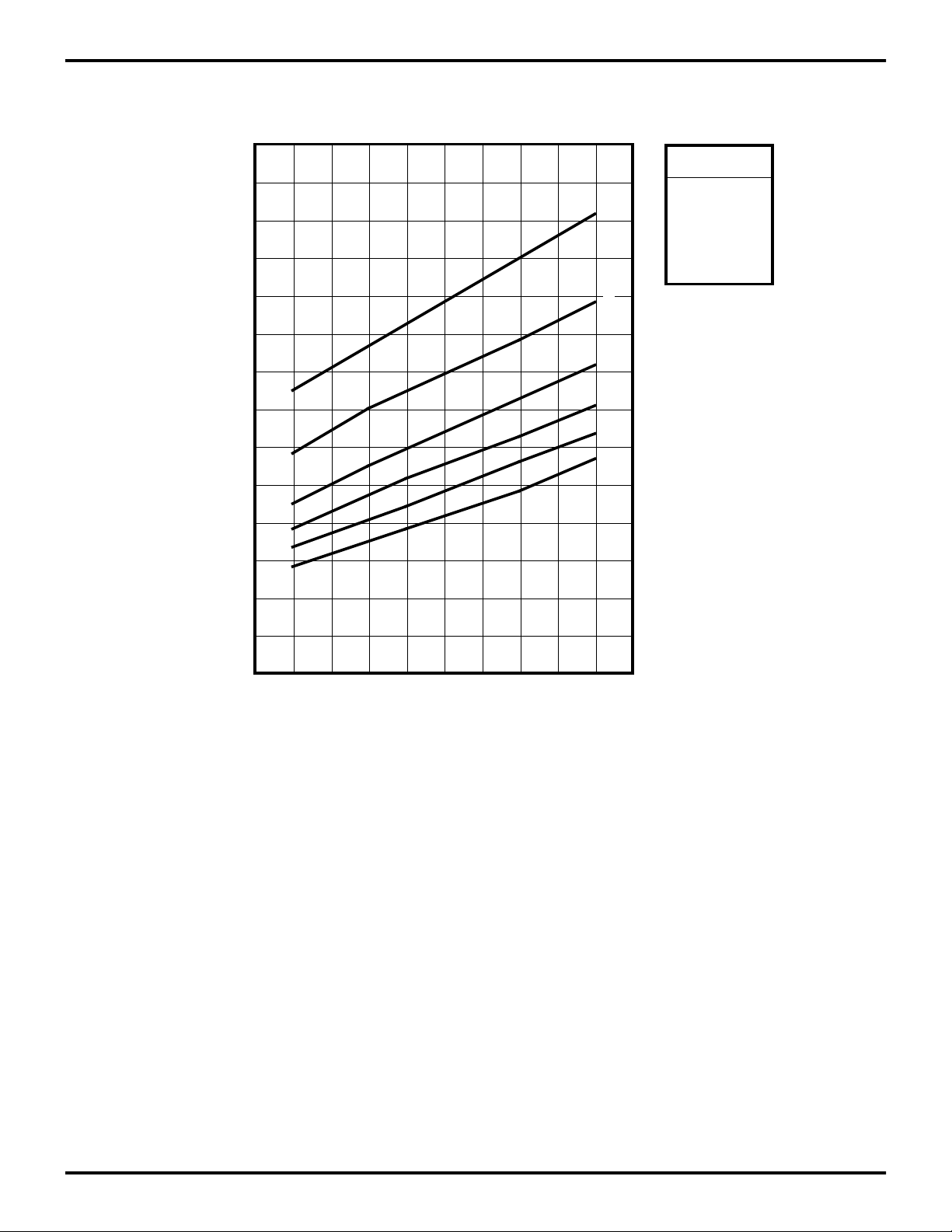
Z87100
Wireless Transmitter Zilog
DEVICE CHARACTERISTICS (Continued)
Time
(ms)
700
650
600
550
500
450
400
350
300
250
200
150
Legend:
A - Vcc = 3.0V
A
B
C
D
E
F
B - Vcc = 3.5V
C - Vcc = 4.0V
D - Vcc = 4.5v
E - Vcc = 5.0V
F - Vcc = 5.5V
100
50
0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Temperature (°C)
Note: Using WDT Oscillator
Figure 61. Typical 100 ms WDT Setting vs Temperature
140
3-46 P R E L I M I N A R Y DS96WRL0700
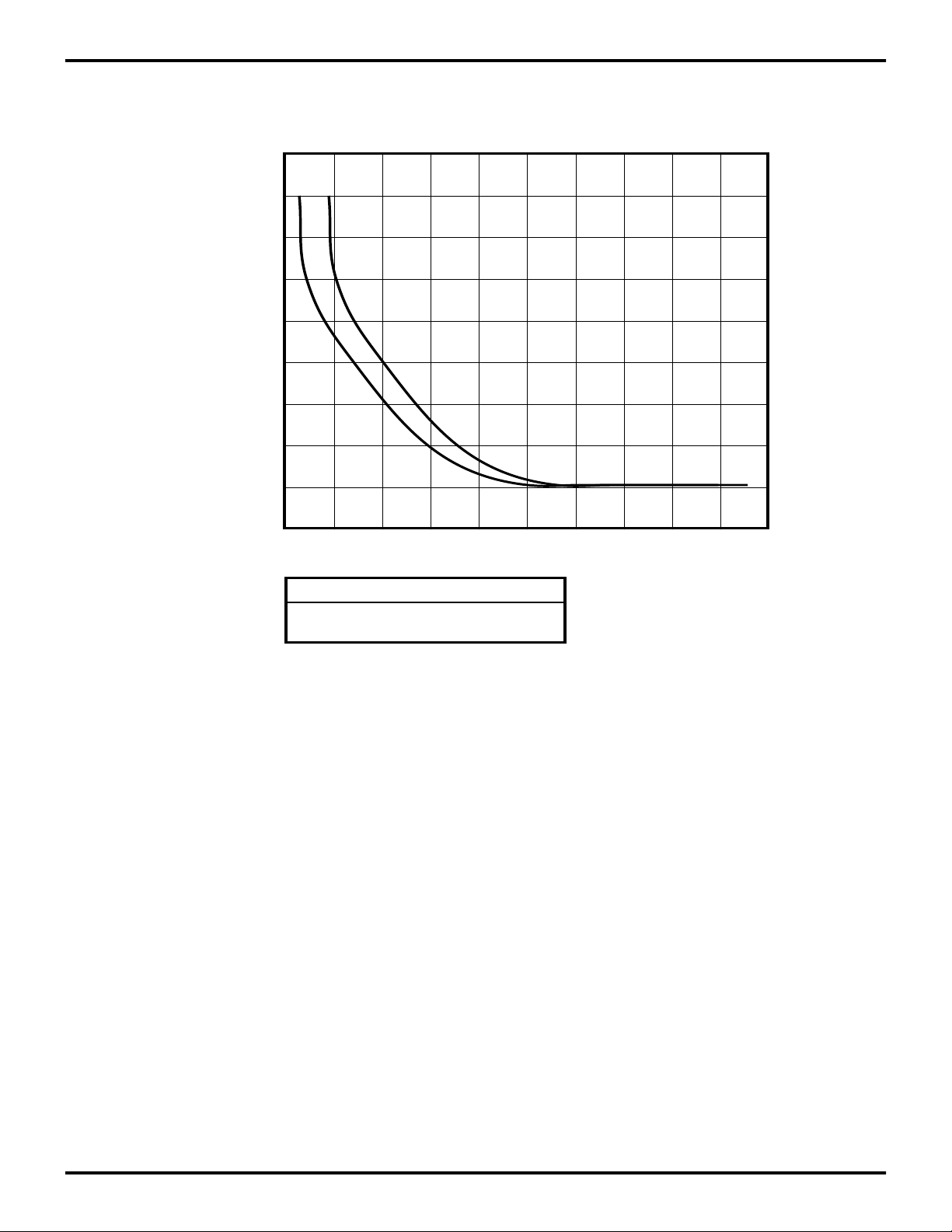
Z87100
3
Zilog Wireless Transmitter
Frequency
(MHz)
10
A
B
0
0
Legend:
A - VCC = 5.0V ±10%; no external capacitor
B - VCC = 5.0V ±10%; external capacitor = 22 pF
40
Resistance (Kohms)
Figure 62. Typical Frequency vs RC Resistance
DS96WRL0700 P R E L I M I N A R Y 3-47

 Loading...
Loading...