Page 1

Page 2

Page 3

FORE WORD
This man ual con tains Pro gram ming in for ma tion for Ze bra Se ries Card Print ers man u fac tured by
Ze bra Tech nol o gies Cor po ra tion, Camarillo, Cal i for nia.
Pro pri etary State ment
This man ual con tains pro pri etary in for ma tion of the man u fac turer. It is in tended solely for the in for ma tion and use of par ties op er at ing and main tain ing the equip ment de scribed herein. Such pro pri etary in for ma tion may not be used, re pro duced, or dis closed to any other par ties for any other
pur pose with out the ex pressed writ ten per mis sion of the man u fac turer.
Prod uct Im prove ments
Con tin u ous im prove ment of prod ucts is a pol icy of the man u fac turer. All spec i fi ca tions and signs
are sub ject to change with out no tice.
Li a bil ity Dis claimer
The man u fac turer takes steps to as sure that its pub lished En gi neer ing spec i fi ca tions and Man u als
are cor rect; how ever, er rors do oc cur. The man u fac turer re serves the right to cor rect any such er rors and dis claims li a bil ity re sult ing there from.
No Li a bil ity for Con se quen tial Dam age
In no event shall the man u fac turer or any one else in volved in the cre ation, pro duc tion, or de liv ery
of the ac com pa ny ing prod uct (in clud ing hard ware and soft ware) be li a ble for any dam ages what so ever (in clud ing, with out lim i ta tion, dam ages for loss of busi ness prof its, busi ness in ter rup tion,
loss of busi ness in for ma tion, or other pe cu ni ary loss) aris ing out of the use of or the re sults of use of
or in abil ity to use such prod uct, even if the man u fac turer has been ad vised of the pos si bil ity of such
dam ages. Be cause some states do not al low the ex clu sion or lim i ta tion of li a bil ity for con se quen tial
or in ci den tal dam ages, the above lim i ta tion may not ap ply to you.
Trade marks and Copy rights
The Ze bra logo and the ze bra head de sign are both reg is tered trade marks of ZIH Corp.
Win dows and MS-DOS are reg is tered trade marks of Microsoft Corp.
Soft ware® Ze bra Tech nol o gies Cor po ra tion; all rights re served world wide.
All other marks are trade marks or reg is tered trade marks of their re spec tive hold ers.
This copy righted man ual and the software de scribed herein are owned by the man u fac turer. All
rights are re served. Copy right vi o la tors may be sub ject to civil li a bil ity.
©2006 ZIH Corp. All rights re served.
i
Page 4

ii
Page 5

Ta ble of Con tents
IN TRO DUC TION .........................1-1
......................................1-2
Com mon Fea tures ............................1-2
Pro gram ming Ob jec tives .........................1-2
Ba sic Com mand Syn tax .........................1-7
Com mand Ed i tor.............................1-8
Im age Mem ory Ar range ments ......................1-8
Bit-Map Com pres sion Al go rithm .....................1-9
Data-to-Card Map ping .........................1-13
Con trol Com mands ...........................1-19
Card Han dling Pro cess .........................1-20
Com mand Link ing ...........................1-20
Sam ple Card ..............................1-21
Par al lel Port Sig nals...........................1-22
Er ror Line Cod ing............................1-22
COM MAND REF ER ENCE .....................2-1
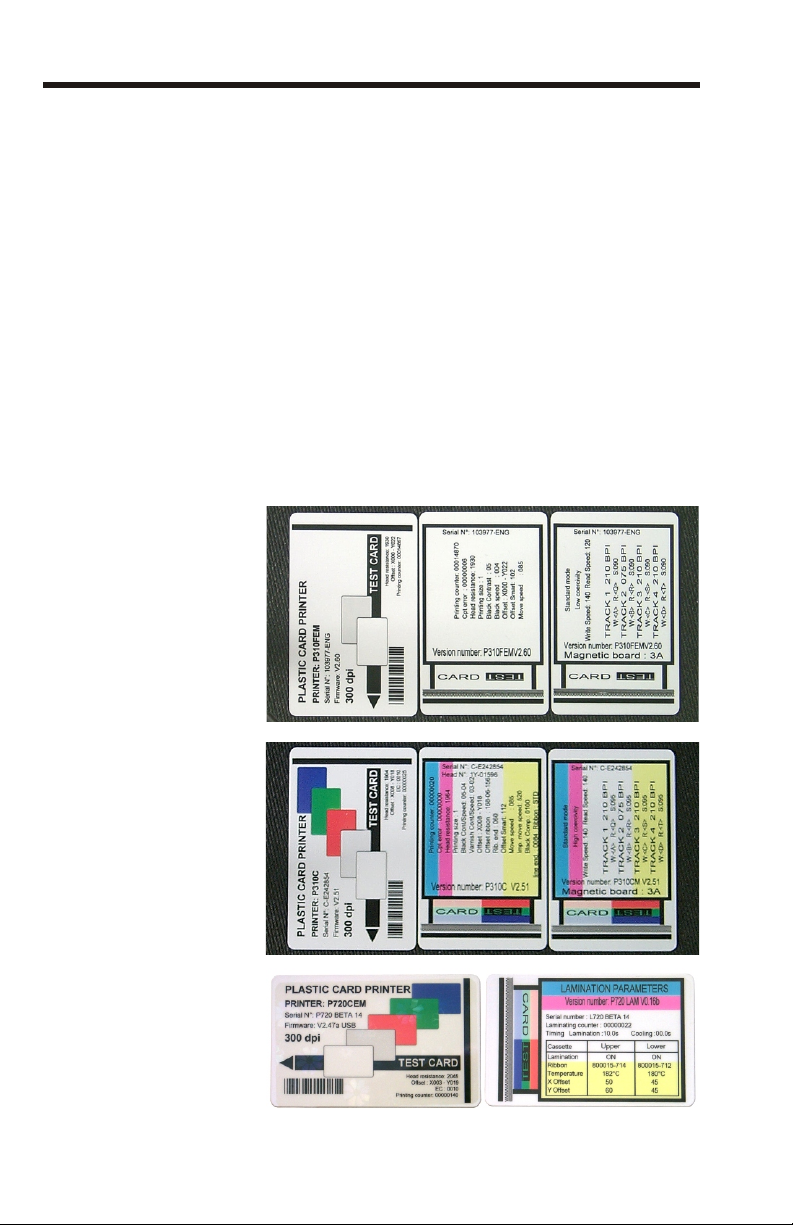
A - Print Test Card............................2-6
!AO - Check Patch Sen sors .......................2-7
!AT - Check Heat Off set .........................2-8
ATM - Set Card Feed ing Mode .....................2-9
&B - Load Mag netic En coder Track Write Buffer ............2-10
+B - Se rial In ter face Rate .......................2-12
+BS - Set Black Syn chro........................2-13
B/vB - Write Bar Code .........................2-14
&C - Set Coercivity ..........................2-16
+C - Ad justs Mono chrome In ten sity ..................2-17
+$C - Ad just Color Con trast ......................2-18
!CC - Get Num ber of Cards Printed ..................2-19
!CCLN - Check Clean ing Pa ram e ters .................2-20
+CCLN - Set Clean ing Pa ram e ters ..................2-21
%CDER - Get Mag netic En coder Read Set tings ............2-22
&CDER - Set Mag netic En coder Track Read En code Pa ram e ters ...2-23
&CDEW - Set Mag netic En coder Track Write En code Pa ram e ters ...2-25
+CDOTS - Im age Print Qual ity Com pen sa tion Fac tor .........2-27
+CH - Ad just Ho lo gram In ten sity ...................2-28
CHECK - Re turn Checksum ......................2-29
CLEAN - Set Clean ing Card Se quence.................2-30
!CLEAN - Clean the Laminator ....................C-31
%CLN - Check Due-for-Clean ing Pa ram e ters .............2-32
CLNCARD - Set Clean ing Pa ram e ters .................2-33
CRB - Set Re ject Box Card Count Warn ing Thresh old .........2-34
!CT - Check Cool ing Time .......................2-35
+CT - Set Cool ing Time ........................2-36
+CV - Ad just Clear Var nish In ten sity..................2-37
C/vC - Write Box (Mono chrome)....................2-38
!D - Move Print Head Down ......................2-39
&D - Change Track Den sity ......................2-40
iii
Page 6

+DLAMI - Set Lam i na tion Con fig u ra tion ...............2-41
+DLAMI - Set Lam i na tion Con fig u ra tion (Con tin ued) ........2-42
+DLAMI - Set Lam i na tion Con fig u ra tion (Con tin ued) ........2-43
+DLAMI - Set Lam i na tion Con fig u ra tion (Con tin ued) ........2-44
D/vD - Draw Di ag o nal Line (Mono chrome/Over lay)..........2-45
E - Re trans mit Last Re sponse .....................2-46
&E - Write Sin gle Track .......................2-47
&E* - Write Track Buff ers ......................2-48
+EC - End of Print ..........................2-49
$F - Clear Color Im age Buff ers ....................2-50
!FF - Set Rib bon Color Se quence ..................2-51
$FP - Clear Spec i fied Bit-Maps ....................2-52
FS - Con trol Use of Card Feed Sen sor ................2-53
F/vF - Clear Mono chrome Im age Buff ers ...............2-54
GS - Down load Color Graphic ....................2-55
G/vG - Ini tial ize Mono chrome Graphic (B/W).............2-56
%HEAD - Get Print Head Se rial Num ber ...............2-57
I - Print Mono chrome Panel .....................2-58
IH - Print Ho lo gram Over lay .....................2-59
IM - Print Color Test Card ......................2-60
IMB - Print Gray Test Card ......................2-61
IS - Print Card Panel .........................2-62
IV - Print Clear Var nish ........................2-63
+ISC - Set Smart Card Se rial Port Data Rate.............2-64
+ISC2 - Set Smart Card Se rial Port Data Rate (Ad vanced)......2-65
ISERIES - i-Se ries Printer Test ....................2-66
J - Print Mul ti ple Mono chrome Cards .................2-67
!L - Check Sta tus: P720 Laminator Sen sor Lev els ..........2-68
!L - Check Sta tus of Printer Sen sors .................2-69
$L - Draw a Hor i zon tal Line/Rect an gle in a Color Buffer .......2-71
&L - Read Sin gle Track .......................2-72
+$L - Ad just Spec i fied Color In ten sity ................2-74
!LC - Check Lam i na tion Coun ter ..................2-75
$LD - Ini tial ize a Color Buffer to a Spec i fied In ten sity Level .....2-76
!LT - Check Lam i na tion Tem per a ture ................2-77
+LT - Set Lam i na tion Tem per a ture .................2-78
!LTI - Check Lam i na tion Time ....................2-79
+LTI - Set Lam i na tion Time .....................2-80
L/vL - Draw Hor i zon tal Line (Mono chrome/Over lay) .........2-81
!M - Move Print Head Up .......................2-82
MB - Re turn Card To Card Feeder ..................2-83
MC - Clear Me dia Path ........................2-84
MCL - Move Contactless .......................2-85
ME - Exit Card To Out put Hop per ..................2-86
MF - Flip Card ............................2-87
MI - Move Card Into Print Ready Po si tion ..............2-88
MIB - Move Card Back To Print Ready Po si tion ...........2-89
MM - Move Card Through Printer ..................2-90
M/m - Mul ti ple Com mand .......................2-91
MO - Move Card To Out put Hop per .................2-92
MR - Check for Card Pres ence ....................2-93
iv
Page 7

MRB - Move Card to Re ject Box ....................2-94
MS - Move Card To Smart Card Pro gram mer .............2-95
MS - Move Card To Smart Card Pro gram mer .............2-96
&– Se lect Mag netic En cod ing Stan dard ................2-97
!NL - Get Printer Im pres sion and Er ror Coun ters ............2-98
!O - Check Card Off set .........................2-99
+O - Print Off set X-Axis .......................2-100
+OCL - Off set Contactless ......................2-101
!OFP - Check X-Axis Patch Off set ..................2-102
+OFP - Ad just X-Axis Laminator Patch Off set ............2-103
+OLP - Off set Overlaminate Patch ..................2-104
!OP - Check Patch Off sets ......................2-105
+OP - Ad just Laminator Patch X and Y Off set ............2-106
+OS - Smart Card X-axis Off set ...................2-107
O/vO - Load Sin gle Line Bit-map (Mono chrome) ...........2-108
+OY - Print Off set Y-axis .......................2-110
!P - Move Card For ward 8 cm ....................2-111
&P - Check Card Pres ent - En coder .................2-112
+PRF - Pre-Feed a Card Close to the Print Area ...........2-113
PS - Down load Color Im age Buffer ..................2-114
P/vP - Draw Sin gle Dot (Mono chrome/Over lay) ............2-115
R - Re set ...............................2-116
!R - Print Head Re sis tance ......................2-117
&R - Re set Mag netic En coder ....................2-118
>R - Read Data From Smart Card Se rial In ter face ..........2-119
+RB - Set Re ject Box Us age .....................2-120
>RB - Read Data From Smart Card Se rial In ter face in ASCII hex Form
....................................2-121
RCBC - Re set Re jected Card Box Coun ter ..............2-122
>RG - Con tact In ter nal Gemplus Smart Card Read Com mand....2-123
+RIB - Set Rib bon Type .......................2-124
!RIB BON - Check Rib bon Type ...................2-125
!RIB BON - Get rib bon type in stalled..................2-126
+RIB BON - Set Rib bon Type ....................2-127
!RIBPN- Get rib bon part num ber ...................2-128
!RIBLEN- Get num ber of re main ing pan els on rib bon . 2-129
+RO - X-Axis Off set, Rel a tive.....................2-130
+ROY - Y-Axis Offet, Rel a tive ....................2-131
!SA - Self Ad just ...........................2-132
!SAN - Per form pre-cal i bra tion base line test ing ............2-134
!SB - Check Stand-By Mode Set tings .................2-135
+SB - Con fig ure Laminator Stand-By Mode .............2-136
SDATA - Force im me di ate save of pa ram e ters ............2-137
!SERIE - Get Laminator Se rial Num ber ................2-138
%SERIE - Get Printer Se rial Num ber .................2-139
SF - Syn chro nize Film (Overlaminate) ................2-140
!SIDE - Check Lam i na tion Mode ...................2-141
+SIDE - Set Lam i na tion Mode ....................2-142
&SVM - Dis able/En able Mag netic En cod ing Ver i fi ca tions .......2-143
&T - Mag netic En coder Card Eject ..................2-144
+TC - Set Laminator Head Tem per a ture ...............2-145
v
Page 8
TF - Film Type ...........................2-146
T/vT - Draw Text (Mono chrome/Over lay) ..............2-147
T/vT - ASCII Text (Con tin ued) ....................2-148
V - Check Printer Type/Ver sion ...................2-149
!V - Re turn Op er a tional Pa ram e ter .................2-150
+V - Black Print Speed .......................2-151
+VL - Set Lam i na tion Speed ....................2-152
!W - Move Card Back ward 8 cm ..................2-153
&W - Change En cod ing Di rec tion .................2-154
>W - Write Data To Smart Card Se rial Port.............2-155
>WB - Write Data For mat ted in ASCII HEX To Smart Card Se rial Port
...................................2-156
>WG - Con tact In ter nal Gemplus Smart Card Write Com mand ..2-157
!X - Check Com mand Ini ti a tor....................2-158
+X - Change Com mand Ini ti a tion Char ac ter ............2-159
!Z - Re-Syn chro nize Card ......................2-160
Z/vZ - Load Bit-map (Mono chrome) .................2-161
. - Clear Er ror Sta tus Lines .....................2-163
Ap pen dix A ............................A-1
Res i dent Fonts ..............................A-2
Code 39
(Code 3 of 9) ..............................A-2
Stan dard 2 of 5
(Code 2/5) ................................A-4
In ter leaved 2 of 5
(Code I 2/5) ...............................A-5
UPC-A ..................................A-6
EAN-8 ..................................A-7
EAN-13 .................................A-8
Code 128
Sub sets B & C ..............................A-9
EAN In ter na tional Reg u la tion Agen cies .................A-11
Ap pen dix B ............................B-1
Par al lel Port Printer Data Hand shake Sig nal Lines.............B-1
Par al lel Port Printer Er ror Re sponse ....................B-1
Se rial Port Printer Data Hand shake ....................B-1
Se rial Port Printer
Er ror Re sponse .............................B-2
Ap pen dix C ............................C-1
Mag netic Encoders............................C-1
En coder Op er a tion ...........................C-1
Data Er rors ...............................C-3
En coder De fault Con fig u ra tion......................C-3
Ba sic Com mands ............................C-4
Ad vanced En coder Com mands .....................C-4
Re set ting The En coder To ANSI/ISO Track De faults ............C-5
Change Track Den sity ..........................C-5
vi
Page 9

Chang ing Read Con fig u ra tion ......................C-5
Chang ing Write Con fig u ra tions .....................C-5
Cus tom ISO Data ............................C-6
Unique Cus tom Data For mats ......................C-7
vii
Page 10

viii
Page 11
IN TRO DUC TION
This man ual de scribes pro gram ming com mands that
con trol op er a tions and de liver data for the fol low ing
card printer mod els:
Mod els
P110i • •
P120i • • •
P205
P210 • •
P310F
P310C •
P310i • •
P320i • • •
P330i • •
P420 • •
P420i • • • •
P430i • • •
P520 • • •*
P520i • • • •* •
P720 • • • •†
* Model that laminates duplex using same lamination patch type for both card sides
† Model ca pa ble of ap ply ing different upper and lower lamination patch types onto cards
RFID
Color
Print ing
Fea tures
Du plex
Print ing
Du plex
Lam i na tion
Log-On
Se cu rity
All mod els em ploy a Com mon Com mand Set plus
ad di tional Com mand Sets for any model-specific
fea tures. All mod els ship with Win dows driv ers.
As so ci ated pro gram ming for use in the Win dows
en vi ron ment is not nec es sary.
1-1
Page 12

Common Features All cov ered mod els can print bar-codes in sev eral for mats
and have res i dent scal able font de scrip tions. Also, all
mod els can in clude a Smart-Card Docking Sta tion. P310
and P420 vari ants can have a Prox im ity Card dock ing
Sta tion. All mod els are of fered with or with out a Mag netic
Stripe En coder. A Se rial Host In ter face is op tional on the
P205, P210, P310, and P420 vari ants, where an
as so ci ated RS-232C Setup Com mand ex ists. All mod els
can have USB Ports, ei ther stan dard or as an option.
The pro gram ming com mands con trol the print ing pro cess
by color and by rib bon ma te rial, al low ing over print ing
and sep a rate con trol of var i ous pro tec tive cov er ings.
Pro gramming
Objectives
The Es cape Com mands al low printer set ups, many of
which de ter mine how a Printer Mod ule El e ment re acts
upon re ceiv ing an in com ing card. For ex am ple, a data
down load must oc cur be fore the Printer Mod ule can print
a card or en code a mag netic stripe.
Ex cept for the Card Feeder, each mod ule has an In put
Sen sor that trig gers the re sponses de ter mined pre vi ously
by setup com mands.
Card Sen sors also al low the Firm ware to keep track of the
po si tion of the card in the Card Path. There fore, the need
for card po si tion ing oc curs as an au to matic re sponse to
re lated com mands. For ex am ple, with no card in the
Card Path, a Print Com mand pro duces a Card Feed.
Sim i larly, if a Print Com mand oc curs af ter a card has
passed be yond the Print Head, the card first re turns to the
Print Head.
Rib bons come in dif fer ent panel con fig u ra tions, and how
the printer re sponds to a Print Com mand var ies
ac cord ing to the Rib bon Type Com mand Pa ram e ters
spec i fied. For each rib bon type, a re lated print se quence
ex ists. How ever, all mod els equipped with the RFID
fea ture sense the rib bon type, and firm ware takes care of
this pa ram e ter.
While some com mands af fect just one printer mod ule,
oth ers can pro duce re sponses from more than one. Also,
some com mands serve as set ups for a par tic u lar printer
and, there fore, need not be re es tab lished for each print
job. No ta bly, all com mand pa ram e ters end up in Flash
mem ory.
1-2
Page 13

Rib bons Rib bon types ex ist in the fol low ing con fig u ra tions:
• Con tin u ously Coated Mono chrome Rib bons are
Ther mal Trans fer Rib bons hav ing a resin coat ing and no
panel sep a ra tions. Ze bra of fers these in sev eral rib bon
col ors along with a Scratch-Off Gray, us able in all mod els but an ob vi ous choice for use in Mono chrome
Printers.
• Black Sublimination Dye al ter nated with Var -
nish Panels that im age black and white gray-scale el e ments. An ex cel lent choice for im ag ing black-and-white
photo im ages, fol lowed by an ap pli ca tion of a UV pro tec tive coat ing.
• Black Resin al ter nated with Var nish Panels that
im age fully sat u rated black and ap ply a pro tec tive coat ing. Ideal for im ag ing solid graphic el e ments such as
Text and Bar Codes.
• Yel low, Ma genta, and Cyan Panels for im ag ing
only Dye Sublimination Color. Typically used in print ers
with no re quire ment for Resin or Var nish. No ta bly, Yel low, Ma genta, and Cyan Panels can com bine to pro duce Black, and a Laminator re moves a need for
Var nish.
• Yel low, Ma genta, and Cyan Panels for im ag ing
Dye Sublimination Color fol lowed by Black
Resin and Var nish Panels. Dye Sublimination Im -
ages should have a pro tec tive coat ing, and Black Resin
serves as an ex cel lent choice for Text and Bar Codes.
Thus, Color Printers with out Laminators typ i cally use
these rib bons.
• Yel low, Ma genta, and Cyan Panels for im ag ing
Dye Sublimination Color fol lowed by a sin gle
Black Resin Panel. While a Laminator pre cludes the
need for var nish, a solid resin black pro duces the best
Bar Codes and of fers an other, some times better, way to
im age Black Text and other black graphic el e ments.
• Yel low, Ma genta, and Cyan Panels for im ag ing
Dye Sublimination Color fol lowed by a two
Black Resin Panels. This rib bon of fers im ag ing for
color plus resin on one card side and only resin on the
other side while us ing sin gle set of rib bon pan els.
1-3
Page 14
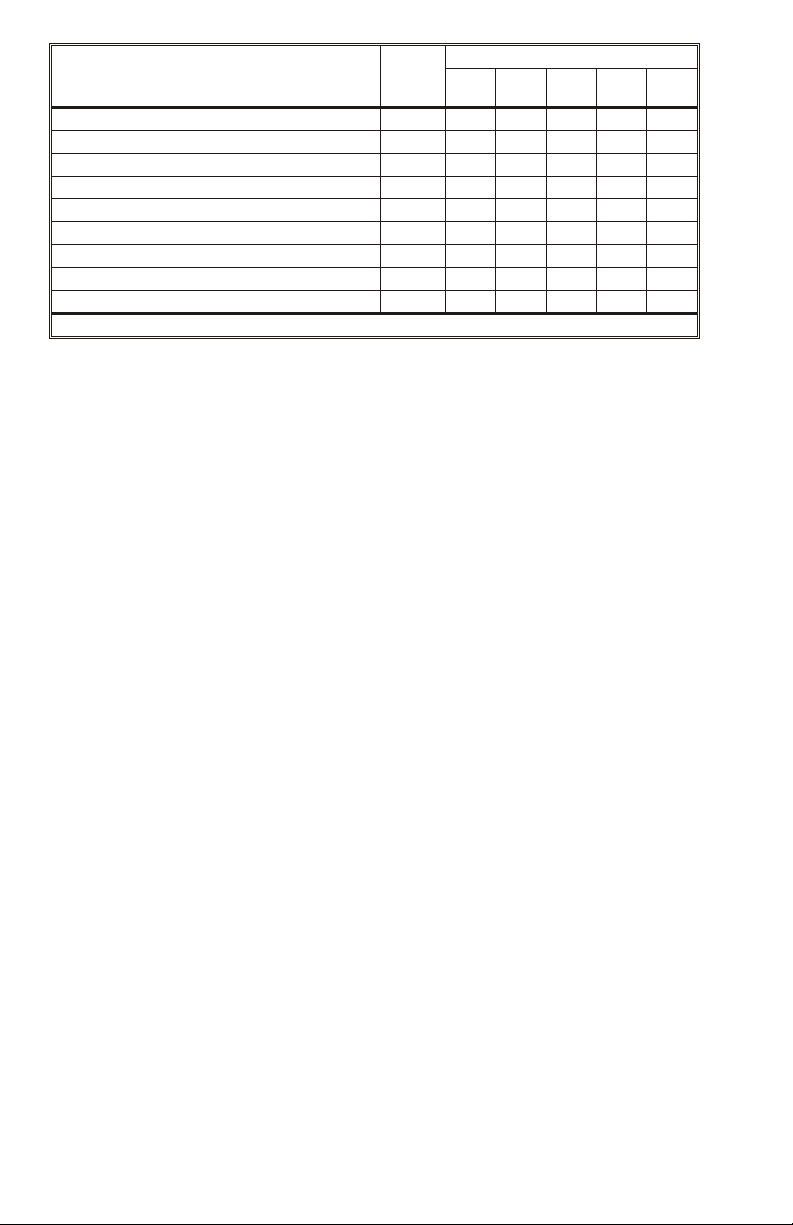
Printer Rib bons
K
(all monochrome colors) 1 • • • • •
resin
Scratch-off Gray 1 • • • •
K
O 2 • • •
resin
K
O 2 • • •
dye
YMC 3 • •
YMCK 4 • •
YMCK
YMCK
YMCK
* P310 monochrome and P205 printers only use 1-panel ribbons.
O 5 • • •
resin
resinKresin
resinOKresin
*Panel
Count
P205
P210
5 • •
6 •
Mod els
P310
P420 P520 P720
P320
Mod u lar El e ments:
• Print En gine—Be ing the pri mary con trol ling el e ment in
all printer mod els, the Print En gine CPU re ceives Host
Com mands. Re ceived com mands can en com pass op er a tions that di rectly con trol the Print En gine and op er a tions that draw on other Printer El e ments for ex e cu tion.
Whereas some el e ments have their own CPUs, the Print
En gine CPU ex er cises com plete con trol over other el e ments. Only in P520s and P720s can a com mand be di rected to an other el e ment (the Laminator CPU). An
as so ci ated El e ment-Spe cific Com mand Pre fix ex ists for
this pur pose. Be sides its print func tion, Print Engines
have Op tions that in clude a Mag netic Stripe En coder
and/or a Smart Card Docking Sta tion. Some Models also
of fer Prox im ity (Contactless) Card Docking as an al ter na tive to Smart Card Docking.
• Card Feeder—This el e ment de livers cards placed in the
Card In put Hop per to the Card Path in side the Printer un der con trol of the Print En gine CPU.
• Card Flip—Printers with this el e ment can flip cards in
prep a ra tion for du plex print ing or, in the case of a P520,
Sec ond Side Lam i na tion. Card Flip Sta tions can also de liver cards with sensed flaws to the Re jected Card Box.
This el e ment has its own CPU that car ries out the de tails
of in struc tions re ceived.
• Sin gle Side Laminator—P520 Printers can place a
pro tec tive trans par ent patch on one card sur face at a
time. This el e ment also has its own CPU that car ries out
the de tails of in struc tions re ceived.
• Du plex Laminator—Printers with this el e ment lam i -
nate both card sur faces in a sin gle lam i na tion pass. This
el e ment also has its own CPU that car ries out the de tails
of in struc tions re ceived.
• Op er a tor LCD Con trol Panel—Printers with this el e -
ment con vey mes sages to op er a tors via a 1- or 2-line by
1-4
Page 15

16- char ac ter LCD screen and al low op er a tor re sponses
and Printer Con trol. Power and Alert LEDs also ap pear.
This el e ment also has its own CPU that car ries out the
de tails of in struc tions re ceived.
Sig nif i cant model/con fig u ra tion dif fer ences
re lated to pro gram ming in clude the fol low ing:
• P310 Mono chrome card print ers have a smaller com -
mand set along with an im age buffer suf fi cient for a
one-bit im age map ping depth. Im aging us ing Ther mal
Trans fer Meth od ol ogy oc curs, sup ported by Ther mal
Trans fer Printer Rib bons. (Only fully-saturated dots im age in a sin gle print pass.) Any gray-scale im ag ing re quires host data mapped into mul ti ple-dot ma trixes,
sized for the de sired gray-scale range (e.g., a
four-by-four dot pixel ma trix can pro duce 16 lev els of
gray plus white, [(4 x 4)2/16 + white]). Gray Levels de rive from the num ber of dots im aged in side the ma trix.
• P310 Color card print ers em ploy dye sub li ma tion
meth od ol ogy for color im ag ing and ther mal trans fer
meth od ol ogy for im ag ing from Resin Mono chrome Rib bons or Rib bon Panels. A yel low, ma genta, and cyan
im ag ing se quence oc curs. Each rib bon panel pro duces
im ages from five-bit-per-dot data.
The black pan els on Ze bra-sup plied rib bons with color
pan els have a resin coat ing that par tic u larly suits
bar-code and other solid im age print ing (i.e., no gray
scale). How ever, resin re sponds poorly as a dye sub li ma tion print me dium. There fore, the black used for
gray-scale im ag ing co mes from for mu la tions of yel low,
ma genta, and cyan (YMC), which means
dye-sublimation black also has a five-bit-per-dot range
(32 lev els of gray). If the need for a
resin-panel-generated gray scale should ever be come
nec es sary, as so ci ated host data must be mapped into
mul ti ple-dot pixel ma trixes as noted in the P310 Mono chrome de scrip tion.
1-5
Page 16

• P310 Color Card Print ers have five im age buff -
ers—three for color and an other for two for mono chrome. The color buffer re ceives down loads of Cyan,
Ma genta, and Yel low im age data, each five bits deep.
The Mono chrome Buffer re ceives black and/or var nish
data one bit deep. Sep a rate data for Resin Black and
Over lay Var nish can of ten be avoided. Be cause of its du ra bil ity, card ar eas with resin im ages may not re quire var nish for the as so ci ated ul tra vi o let pro tec tion. There fore,
by us ing a re verse im ag ing for var nish, the same bit-map
used for resin pro duces a var nish over lay that omits the
ar eas with resin. Also, through re verse im ag ing, a Clear
Com mand can pre pare Mono chrome Mem ory for a
full-cov er age var nish.
• P420s em ploy the same Print Engines as the P310 Color
de scribed above. Be cause P420s also have a Card-Flip
as sem bly and a Re jected Card Box, these mod els have
some ad di tional re lated com mands. P420s also have an
in ter face that sup ports the pro gram ming of Prox im ity
Cards (also called Contactless Cards). Mem ory size is
dou bled to sup port two-sided print ing.
• P520s have all the same im ple men ta tions as a P420, in -
clud ing Smart Card sta tions, and Mag netic Encoders as
op tions. How ever, P520s also have a Card Laminator
Sta tion. Laminators serve as heat-transfer de vices for
ma te rial or pan els con tained on Lam i na tion Rib bons. A
va ri ety of these kinds of rib bons ex ist, as fol lows:
• Rib bons with trans par ent die-cut patches that of fer
near edge-to-edge card cov er age
• Die cuts with cut outs for Smart Card Con tacts, and
smaller die cuts that serve to avoid Mag netic Stripes
• Preprinted Patches that con tain se cu rity de vices such
as graph ics, ho lo grams, or other op ti cally-encoded
safe guards
1-6
P520 Laminators can also serve a heat-transfer func tion for rib bons con tain ing a coat ing in stead of
die-cut pan els. How ever, only a to tal card ap pli ca tion
can oc cur. Be cause the Print Sta tion can have a Dye
Sub li ma tion Rib bon with Var nish Panels, many
choices ex ist for se lec tion of pro tec tive coat ings. Ad di tional com mands ex ist to im ple ment Laminator
use.
• In stead of just an <Esc>, a P520 Com mand meant
for the Laminator needs a pre ced ing:
<Esc>#<Space>1<Space>
Page 17

• P720s have P420 el e ments plus a Laminator mod ule
<Esc>T p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6 p7 data<Rtn>
Command Name
Command
Parameters
WRITE TEXT
ASCII Programming Code
Text
Hexadecimal Programming Code
Escape (Command Initiator)
Carriage Return (Command Terminator)
1B54203130302031303020302031203230203330203120546578740D
<Esc>T 100 100 0 1 20 30 1 Text<Rtn>
Space (Delimiters)
that fully im ple ments si mul ta neous near edge-to-edge
patch ap pli ca tions from above and be low the Card
Path. In te gral sen sors as sure ac cu rate patch place ments
and sig nal the Rib bon Types in use and the amount re main ing on their cores.
Basic Command
Syntax
Each com mand be gins with a Com mand Ini ti a tor (the
Es cape Char ac ter). For P520s, di rect ing char ac ters can
fol low the Es cape Char ac ter.
The Com mand Ini ti a tor serves to mark the char ac ter(s)
im me di ately fol low ing as com mand char ac ters.
Com mand char ac ters vary be tween one and seven
char ac ters (or up to seven bytes of hex a dec i mal data).
Some Com mands then have one or more Pa ram e ters to
sup ply the printer with in for ma tion nec es sary to
com plete the com mand. A Space Char ac ter de lin eates
in di vid ual Com mand Con trol Pa ram e ters. The fol low ing
Text Com mand shows a typ i cal ex am ple.
Each Com mand Line re quires a Car riage Re turn
Char ac ter (13 dec. or 0D hex.). The Printer ig nores a
sin gle Line Feed (LF) char ac ter (Dec. 10 or 0A Hex.)
when it im me di ately fol lows the com mand ter mi nat ing
Car riage Re turn. Most PC Based Sys tems send a CR/LF
when the En ter Key is pressed.
1-7
Page 18

Command Editor Any ASCII based Text Ed i tor can serve to cre ate sim ple
com mand files. In the DOS en vi ron ment, MS-DOS EDIT
of fers a good choice. To ex e cute the file, use the Print
Com mand from the ed i tor, or from DOS, the COPY
Com mand, to send the file to the printer. Ex am ples us ing
the COPY Com mand are:
COPY file name.ext LPT1
For more in for ma tion on the use of the COPY com mand,
re fer to a DOS Soft ware Man ual.
Some text ed it ing pro grams can cause printer er rors by add ing ex tra char ac ters or by chang ing ex ist ing char ac ters
when gen er at ing a near ASCII for mat ted file.
Ex am ple: A com mon ASCII ed i tor, BRIEF, changes all NUL
char ac ters to the SPACE or TAB char ac ters with a File
Save. The graphic data for print in ten sity level “0" is the
NUL char ac ter. This causes the re sult ing file to print with
hor i zon tal lines in all graph ics with solid white (i.e.,
no-print) ar eas. Other ed i tors may add a SUB char ac ter
(Dec. 26 or 1A Hex.), which causes the printer to er ror.
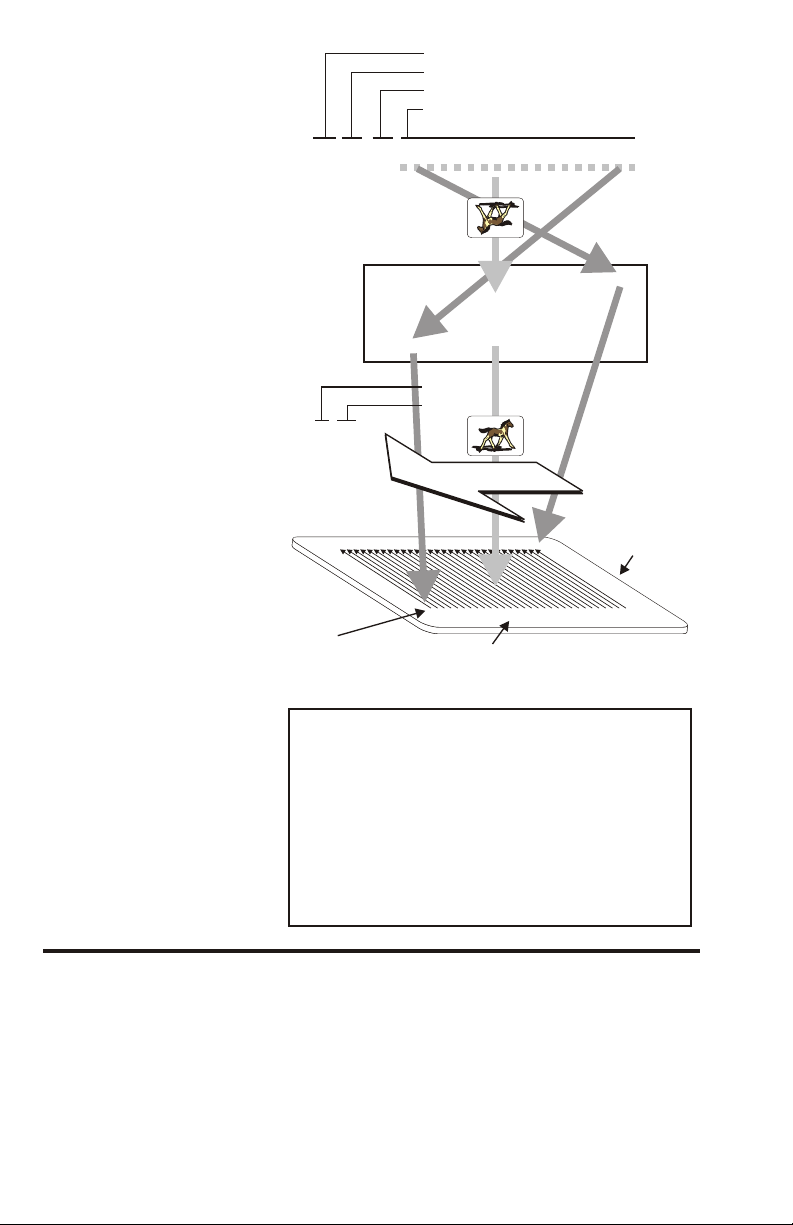
Image Mem ory
Ar range ments
1-8
Fig ure 1-1 shows el e ments in volved in im age data flow.
Note that two Im age Mem ory Con fig u ra tions ex ist and
that Im age Mem ory al ways con tains com pressed data.
Ideally, hosts should send com pressed data, which
re quires a com pat i ble com pres sion al go rithm. This can
sub stan tially re duce the data trans fer times of most im age
files.
Mono chrome Print ers need no Color Buff ers and of fer
less mem ory ca pac ity. Color Print ers may need as many
as five buff ers and, there fore, have a greater mem ory
ca pac ity. In most cases, com pressed data for an en tire
card im age fits into avail able mem ory in a sin gle
down load se quence.
Color-sep a rated data en ters re lated buff ers due to a
buffer-spec i fy ing pa ram e ter in the Color Data Com mand.
Page 19
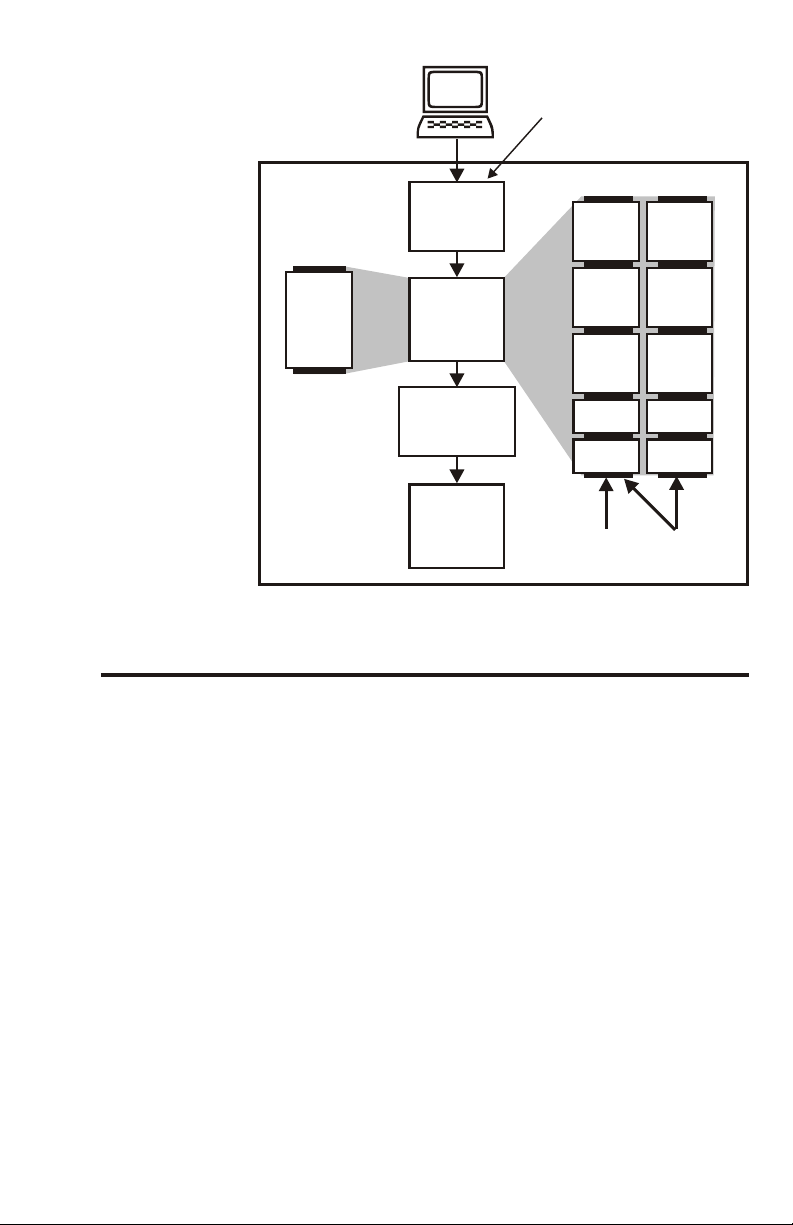
Host Computer
Image Data
Compression
Algorithm
Image
Buffers
Image Data
Decompression
Algorithm
Print Head
Registers
CARD PRINTER
Bypassed
when Host
Compressed
Color Printer
Memory
Monochrome
Printer Memory
Mono.
Buffer
Yellow
Buffer
Magenta
buffer
Cyan
Buffer
Black
Buffer
Varnish
Buffer
Yellow
Buffer
Magenta
buffer
Cyan
Buffer
Black
Buffer
Varnish
Buffer
SINGLE
DUPLEX
Figure 1-1
Image Memory
Arrangements
Bit- Map
Com pres sion
Al go rithm
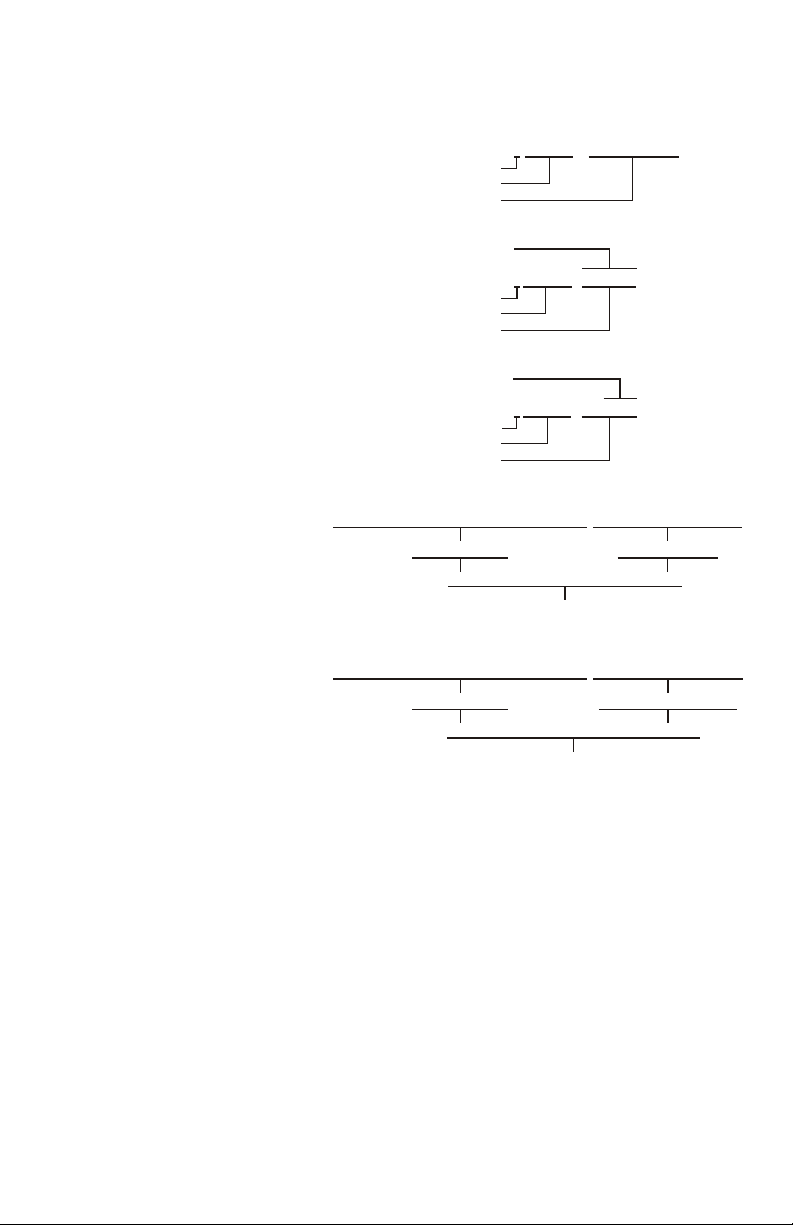
Char ac ter is tically, a Bit-Map Com pres sion Al go rithm
flags data seg ments as ei ther re peat ing or non-repeating,
spec i fies the bytes re peated, and the num ber of re peats.
For these card print ers, com pres sion ap plies to
byte-wide bit-map seg ments, which the host sends with
the PS, GS, Z, and vZ com mands. The PS and GS
com mands in clude pa ram e ters spec i fy ing a buffer
(YMCK). Mono chrome com mands Z and vZ send
as so ci ated bit-map data to the Black (K) and Var nish
Buffers, re spec tively. All of these com mands in clude
pa ram e ters that spec ify whether or not the com mand
ap plies to com pressed data. For rec og ni tion by the card
printer, com pressed data must con form to the fol low ing
rules:
Rule 1. When high, the most sig nif i cant bit (the Flag
Bit) of a two-byte se quence in di cates that the sec ond
byte re peats. The re main ing seven bits of the first byte
spec ify the num ber of re peats, al low ing a
field-specification range of from zero to 127 re peats.
1-9
Page 20

Rule 2. When low, the Flag Bit of a data se quence
in di cates that the re main ing seven bits of the byte spec ify
the num ber of fol low ing bytes that rep re sent
non-re peat ing im age data. Here, how ever, the range
al lows a spec i fi ca tion of from zero to 31 bytes of data.
Rule 3. The first byte in the Data Field of any com mand
spec i fy ing a Com pressed Bit-Map must have the
Com pres sion Flag high, even if a one must be en tered as
the num ber of bytes re peated.
Rule 4. No other al go rithm can be used to com press
im age data for this card printer.
Fig ure 1-2 in cludes ex am ples of data strings em ploy ing
com pres sion.
1-10
Page 21
1XXX XXXX XXXX XXXX
Data Compression Flag Set
No. of Repeats (1~127)
Data Byte Repeated
Dye Sub. Panel 1-Dot Data Field
1XXX XXXX XXXX XXXX
Data Compression Flag Set
No. of Repeats (1~127)
Data Byte Repeated
Mono. Panel 8-Dot Data Field
0XXX XXXX
Data Compression Flag Off
No. of Non-Compressed Bytes
Non-Compressed Data
---Bytes (0~31)---
0001 1111 0001 1111 0001 1111 0001 1111 0001 1111 0000 0011 0000 0011 0000 0011
1F Hex (5 repeats) 03 Hex (3 repeats)
85 1F 83 03
Compressed Data
1000 0101 0001 1111 1000 0011 0000 0011
Compression Example 1
0001 1111 0001 1111 0001 1111 0001 1111 0001 1111 0000 0100 0000 1011 0000 0011
1F Hex (5 repeats) 04 0B 03 Hex (0 repeats)
85 1F 03 04 0B 03
Compressed Data
1000 0101 0001 1111 0000 0011 0000 0100 0000 1011 0000 0011
Compression Example 2
Figure 1-2
Bit-Map
Compression
1-11
Page 22
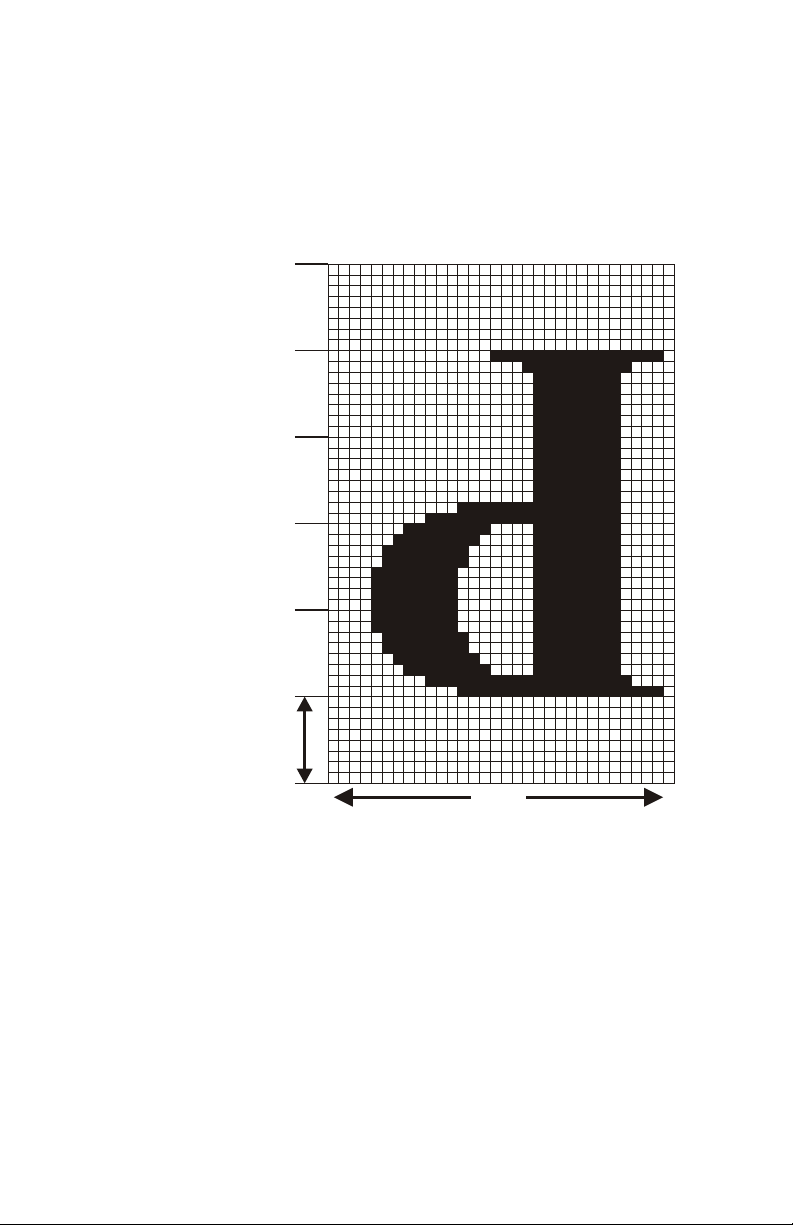
Fig ure 1-3 shows how a bit-map re lates to as so ci ated
1B 5A
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 03 F0 00 00 00
00 0F FC 00 00 00
00 1F FE 00 00 00
00 3F FF 00 00 00
00 3F FF 00 00 00
00 7F FF 80 00 00
00 7F FF 80 00 00
00 7F FF 80 00 00
00 FC 0F C0 00 00
00 F0 03 C0 00 00
00 E0 01 C0 00 00
00 C0 00 C0 01 00
00 C0 00 C0 01 00
00 C0 00 C0 01 00
00 C0 00 C0 03 00
00 FF FF FF FF 00
00 FF FF FF FF 00
00 FF FF FF FF 00
00 FF FF FF FF 00
00 FF FF FF FF 00
00 FF FF FF FF 00
00 FF FF FF FF 00
00 FF FF FF FF 00
00 C0 00 00 03 00
00 80 00 00 01 00
00 80 00 00 01 00
00 80 00 00 01 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
0D
1 Byte
x axis
non-compressed data. Fig ure 1-4 shows the same
bit-map in as so ci a tion with com pressed data.
Figure 1-3
Non-Compressed
Bit-Map
1-12
Page 23

1B 5A
99 00 02
03 F0 84 00 02
0F FC 84 00 02
1F FE 84 00 02
3F FF 84 00 02
3F FF 84 00 3C
7F FF 80 00 00
00 7F FF 80 00 00
00 7F FF 80 00 00
00 FC 0F C0 00 00
00 F0 03 C0 00 00
00 E0 01 C0 00 00
00 C0 00 C0 01 00
00 C0 00 C0 01 00
00 C0 00 C0 01 00
00 C0 00 C0 03 00
00 84 FF 02 00
00 84 FF 02 00
00 84 FF 02 00
00 84 FF 02 00
00 84 FF 02 00
00 84 FF 02 00
00 84 FF 02 00
00 84 FF 18 00
00 C0 00 00 03 00
00 80 00 00 01 00
00 80 00 00 01 00
00 80 00 00 01 87
00
0D
1 Byte
Figure 1-4
Compressed
Bit-Map
Data- to-Card
Map ping
Fig ure 1-5 shows a card con sis tent with the ori en ta tion
of a card trav el ing right to left in the Card Path of a
printer. From this per spec tive, the data field of the PS,
GS, Z, and vZ com mands first be comes a
mem ory-res i dent im age in a des ig nated im age buffer.
The Im age Buffer, as shown, fills from top to bot tom and
from right to left. Be cause the Im age Buffer has a
last-in-first-out (LIFO) ar range ment, card im ages build
from bot tom to top and from left to right. This suits the
front-to-back load ing of Print Head Reg is ters and the
right-to-left card move ment dur ing print cy cles. As noted
in the fig ure, an ob ject mir rored in both axis in the data
sent to the buffer would print nor mally on the card.
1-13
Page 24
PS p1 p2 data.............................data
Download Buffer Data Command
Buffer Select (YMCK) Parameter
Compressed vs. Uncompressed Parameter
Data Downloaded (300dpi/11,8dpmm)
Last In
First Out
MAXIMUM CARD IMAGING
646 Line Bytes by 1030 Lines
Image Buffer
IS p1
Print Buffer Command
Buffer Select (CMYK) Parameter
Print Direction
Card Size
3.375 x 2.125 in
85,7 x 53,9 mm
PartialImage
Origin
ASSOCIATED COMMANDS
Monochrome
G
O
Z
P
L*
C*
D*
T
B
I
Overlay
IH
IV
vZ
vP
vL*
vC*
vD*
vT
vB
Color
PS
GS
IS
* Objects drawn with these commands have an upper-left origin.
Figure 1-5
Data Sent verses
Card Mapping
Laminator Data
Considerations
1-14
As so ci ated print ers have no need to print var nish.
How ever, the Var nish Buffer stores mono chrome data.
There fore, all data com mands for mono chrome data
re quire the “v” pref ace. A sub se quent “I” com mand
prints data stored in the Var nish Buffer. Note that the IV
Com mand serves to in di cate the pres ence of a rib bon
with var nish pan els that then get by passed.
Page 25

Color Printer Data
Con sid era tions
When con vert ing from another color sys tem to CMY, the
best pos si ble re sults oc cur when a ta ble maps each
source color to a vi su ally equiv a lent CMY printer color.
Such a ta ble must convert all pos si ble printer col ors.
Also, the con ver sions must be fine-tuned to produce
optimum re sults. How ever, for RGB data, a sim ple
con ver sion can oc cur via the fol low ing:
Y = 255 - B
M = 255 - G
C = 255 - R.
Color data al ways en ters a color im age buffer, ei ther as
Yel low, Ma genta, or Cyan. This is also true for K
rib bon, which im ages with black dye. The com mand
des ig nates the buffer dif fer ently ac cord ing to the Buffer
Spec i fi ca tion Pa ram e ter in the com mand. Note that the
spec i fi ca tion for Dye Sub li ma tion only ap plies to im ages
pro duced us ing a Dye Sub li ma tion Black Rib bon. All
data as so ci ated with these com mands rep re sent im ag ing
con sist ing of five-bits-per-dot.
Whether down loading data for a par tial im age (GS
com mand) or for a com plete card im age (PS com mand)
the data must match the as so ci ated card area. For par tial
im ages (some times called lo gos be cause of a typ i cal
ap pli ca tion) the GS Com mand Pa ram e ters spec ify the
area im aged. This as sures proper line breaks. Any ei ther
over- or un der-flow pro duces an er ror. For proper
ap pear ance, color im ages should not over print other
card print ing.
dye
O
1-15
Page 26

Mono chrome Data
Considerations
P-Series Printers al ways down load mono chrome data
into a Mono chrome Im age Buffer. In print ers with out
Laminators, mono chrome data com mands pref aced with
a “v” des ig nate the Var nish Buffer. Com mands with out
the “v” pref ace des ig nate the buffer used for resin
print ing. If only one Mono chrome Im age Buffer ex ists, the
com mand des ig nates the buffer dif fer ently de pend ing on
the as so ci ated data.
How ever, most color im ag ing does not need a
pre-established Var nish Buffer to ap ply the var nish
coat ing. If no Var nish Buffer is down loaded, the printer
de faults to the Resin Buffer for the ap pli ca tion of var nish.
This works for three rea sons. First, color rib bons have
resin black fol lowed by var nish pan els, both lim ited to
mono chrome data. Sec ond, the pri mary use of var nish is
to pro tect the dye sub li ma tion im ag ing from ul tra vi o let
ra di a tion. Third, be cause resin may need no var nish
pro tec tion, an in verted-resin bit-map can ap ply var nish.
The IV com mand has a pa ram e ter set ting to pro duce an
in verted data print. There fore, when suit able, leave the
Resin Buffer un changed af ter print ing resin. Then, is sue
an IV com mand to print the var nish.
Note that full-coverage var nish, as re quired for ul tra vi o let
pro tec tion us ing dye-sublimation black rib bons, re quires
only a buffer clear com mand (F) fol lowed by the in verted
print com mand (IV).
A wa ter mark sim u la tion can re sult by, in ef fect, punch ing
holes in the var nish im age. Sim i larly, suit able holes in the
var nish ap pli ca tion are nec es sary to pre vent cov er age
over Mag netic Stripes or Smart Card Con tacts. How ever,
this con cern can be avoided by lim it ing im ages re quir ing
var nish to the card sides with out con tacts or stripes.
A ho lo gram trans fer from an as so ci ated rib bon oc curs by
print ing a Var nish Buffer that im ages the area of the
rib bon con tain ing the ho lo gram. Both of these im ages
re quire data pre vi ously down loaded into the Var nish
Buffer.
1-16
Page 27

Mono chrome graphic ob jects can down load into
ei ther a Resin or Var nish Buffer. As with the pre ced ing,
a “v” pref ace des ig nates a buffer that prints with the
“IV” Com mand, and com mands with out the “v” pref ace
des ig nate a buffer that prints with the “I” Com mand.
Com mands ex ist for down loads of the fol low ing graphic
ob jects:
P/vP Write Dot
L/vL Write Line
C/vC Write Box
D/vD Write Di ag o nal Line
T/vT Write Text
B/vB Write Bar-Code
The fol low ing Graphic Com mands have Ro ta tional
Pa ram e ters (clock wise):
D/vD (Di ag o nal Line) 0, 90, or 180°
Cen ter of Ro ta tion lower-left
T/vT (Text) 90° In cre ments (0~270)
Cen ter of Ro ta tion lower-left or ob ject cen ter
B/vB (Bar Code) 90° In cre ments (0~270)
Cen ter of Ro ta tion lower-left or ob ject cen ter
Mono chrome bit-maps re quire en try of two
com mands—first an initializing com mand (G) and then
an as so ci ated data com mand. The “G” Com mand
spec i fies im age place ments as so ci ated with the fol low ing
com mands:
O/vO Down load Sin gle Line
Z/vZ Down load Mul ti ple Lines
Fig ure 1-5 shows the re la tion ship be tween data sent by
“O” or “Z” com mands and an area pre vi ously
es tab lished by a “G” com mand. The “G” com mand can
also de fine data as sin gle bits (i.e., im age dots).
With dots se lected as the Data Mode in the G
Com mand, data sent to the printer must, nev er the less,
fin ish on an even byte bound ary. When nec es sary, fill in
zero bits to bytes that do not reach the bound ary
spec i fied in the G Com mand.
Data is han dled in bytes dec i mal (0~255) or
hex a dec i mal (00~FF) by the printer.
1-17
Page 28

Bar Codes Bar Codes vary in ca pac ity, size, char ac ter sets, and
den sity. Sev eral in dus tries have adopted spe cific cod ing
and bar code for mats. A se lected Bar Code must match a
code sup ported by the scan ning equip ment.
All the Bar Codes of fered by the card print ers have the
data char ac ters, 2 quiet zones, and Start and Stop
Char ac ters. The Bar Codes can in clude Text as part of
the Printed Bar Code. Some of the Bar Codes in clude a
printer-generated Check Digit (or Data Check Sum)
Char ac ter au to mat i cally or as an op tion.
A com mand er ror con di tion oc curs when Im age Data
ex tends be yond the ad dress able range of the Im age Buffer.
The Bar Code and Text Fields must re main within the ad dress able area of the Im age Buffer. Each of the Bar Codes,
in the Com mand B and Ap pen dix-A De scrip tions have a
for mula to de ter mine a Bar Code Length.
Se lecting a larger Bar Code Width Mul ti plier and a higher
ra tio of the nar row to wide bars (and spaces, where ap pli ca ble) im proves the gen eral read abil ity of a Bar Code. Also,
wider bars and spaces in crease the depth of field for im proved per for mance with Moving-Beam La sers and other
non-contact scan ning de vices.
1-18
Page 29

Control
Commands
The card print ers can per form a va ri ety of print, card,
rib bon, head move ment, and other con trol com mand
op er a tions.
Print Controls
Card Movement
In ten sity—Ad justs the amount of heat used to trans fer
Max i mum In ten sity Color or Mono chrome Dots.
Con trast (Color Only)—Ad justs the min i mum
amount of heat used to print dots at the low est color
set ting.
Im age Po si tioning—Lo cates the print able im age on
the card.
Head—Raises the Print Head for card moves and
low ers the head to print. These com mands are nested
within Print Com mands and typ i cally only sup port
test ing.
Print Test Cards—Ini ti ates a print se quence us ing
printer-resident data.
Print Ready Po si tion—The card moves to a po si tion
just prior to the Card Edge Sen sor.
Exit Card—The printer sends the card to the Out put
Hop per. For print ers with mul ti ple sta tions, cards exit to
the next sta tion.
Du plex—Flips cards us ing the Card-Flip Sta tion,
ini ti ated by the MF com mand.
Ready Smart Card—Po si tions a Smart Card un der the
Smart Card Docking Sta tion, where Smart Card Chip
Con tacts make con tact and be come avail able at a
rear-mounted printer con nec tor.
En code Ready po si tion—The card moves to a
po si tion just prior to the Read Write Head of the
Mag netic En coding Sta tion.
Re ject Card—Sends a card to the Re jected Card Box
Ribbon
Re set Rib bon—Ad vances rib bon to pre pare for the
first im ag ing pass (for color, Yel low) or cy cles a
con tin u ous color Mono chrome Rib bon.
Se lect Panel—Re sets, then ad vances rib bon to a
com mand-specified panel.
1-19
Page 30

Card Handling
Process
The fol low ing out lines a rec om mended card han dling
se quence:
1. Smart Card Pro gram ming - Op tion
2. Mag net i cally En code Card - Op tion
3. Print Card
For color, print:
Yel low
Ma genta
Cyan
Black
Clear Var nish
4. Du plex - Flip Card - Op tion
5. Print Card Back side - Op tion
For color, print:
Yel low
Ma genta
Cyan
Black
Clear Var nish
Ho lo gram Lam i na tion
6. Eject Card
Never im age or lam i nate over mag netic stripes or Smart
Card Con tacts. En coding and/or Smart Card Pro gramming
Er rors can result. Those with lamination capabilities can
order patches that leave these ar eas un cov ered.
Command Linking The “M” and “m” Com mands serve as Com mand
Linking Op er a tors. A string of linked com mands may
ex e cute one or mul ti ple times. The “[” char ac ter serves as
the de lim iter for Linked Com mands in the as so ci ated
syn tax.
For the com plete “M” Com mand Syn tax, and an
ex am ple, see M/m in the Com mand Ref er ence.
1-20
Page 31

Sam ple Card Fig ure 5-6 shows a printed card along with the
Commands
Descriptions
+RIB
+C 4
F
B 512 600 4 0 2 4 100 1 TEST
T 512 75 4 0 0 35 1 Company Name, Incorporated
T 200 200 0 1 0 50 1 FIRST NAME
T 200 300 0 1 0 50 1 LAST NAME
T 200 400 0 1 0 50 1 ACCOUNT NUMBER
T 65 320 7 1 0 50 0 Reverse text
L 15 80 970 4 1
I
Ribbon Type, Monochrome
Thermal Intensity
Clear Mono. Buffer
Write Bar Code
Write Text
Write Text
Write Text
Write Text
Write Text
Write Line
Print Monochrome
Figure 1-6
Sample Monochrome
Card
com mands used.
1-21
Page 32

Parallel Port Signals P205, P210, P310 and P420 Printers have a Se rial Port
Op tion. Se rial equipped print ers com mu ni cate with the
host over an RS-232C in ter face us ing ACK/NAK flow
con trol. Par al lel Ports are stan dard. The other card printer
mod els have no Se rial Port Op tion.
Card print ers with Par al lel Ports com mu ni cate with the
host us ing the fol low ing sig nal lines:
DATA (0~7) Eight bits of par al lel data.
STROBE (Pin 1) A host sig nal that in di cates sta ble data.
ACK/ (Pin 10) A printer sig nal that in di cates data re ceived. The
host drops the STROBE sig nal in re sponse.
BUSY (Pin 11) A printer sig nal that in di cates an in abil ity to ac cept
com mands due to on go ing pro cess ing. In print ers
with more than one pro ces sor, a BUSY re sponse
from one pro ces sor does not im ply a BUSY at the
an other pro ces sor.
READY (Pin 13) A printer sig nal that in di cates its avail abil ity to re -
ceive Host Com mands.
PAPER ER ROR (Pin 12)
Card print ers re port er rors to the host by en cod ing
the PAPER ER ROR and ER ROR lines (see Er ror
Line Coding be low).
ER ROR/ (Pin 15) Card print ers re port er rors to the host by en cod ing
the PAPER ER ROR and ER ROR lines (see Er ror
Line Coding be low).
INIT (Pin 14) Not used.
Er ror Line Cod ing
1-22
Pa per Er ror Er ror De scrip tion
0 1 No Error
0 0 Syn tax Error
1 1 Rib bon End/Empty Feeder
1 0 Me chani cal Error
Page 33

Esc
#
Space
Enter
Command Initiator—Press <Esc> to
indicate Command String follows.
Command String Delimiter—Use Spaces
<Sp> between Commands and Parameters.
Send Key—Press <Rtn> to send Command
String to Printer.
Placed after and followed by number (n)
(<Esc>#<sp>n<Sp>) directs Command
to Station n.
P1~Pn
{P1~Pn}
data
Indicates Required Parameter(s) in String
Indicates Optional Parameter(s) in String
Indicates Data Position in String
Figure 2-1
Command Entry
COM MAND REF ER ENCE
This sec tion con tains in di vid ual com mand de scrip tions
for data down loads, print ing, lam i na tion, mag netic
en codes, and card move ment con trol. An in cluded
command list groups com mands by func tion and shows
the as so ci ated ap pli ca ble printer models.
2-1
Page 34

Com mand List
DNA MMOC
DE SCRIP TION
Setup Com mands
+BS Set Black Speed
+C Ad justs Monochrome In ten sity 2-17
+$C Ad just Color Con trast 2-18
+CCLN Set Cleaning Parameters 2-21
+CDOTS Image Print Quality Compensation Factor 2-27
+CH Ad just Holo gram In ten sity 2-28
CRB Set Card Count Warning Threshold 2-34
+CT Set Cooling Time 2-36
+CV Ad just Clear Varnish In ten sity 2-37
+EC End of Print 2-49
!FF Set Rib bon Color Se quence 2-51
+$L Ad just Specified Color In ten sity 2-74
+LC Set Lamination Counter
+LT Set Lamination Roller Temperature 2-78
+LTI Set Lamination Time 2-80
MCL Move Contactless 2-85
+O Print Off set X- axis 2-100
+OCL Offset Contactless 2-101
+OFP Adjust X-Axis Laminator Patch Offset 2-102
+OLP Offset Overlaminate Patch 2-104
+OP Adjust Laminator Patch X and Y Offset 2-106
+OS Smart Card X- axis Off set 2-107
+OY Print Off set Y- axis 2-110
!R Print Head Re sis tance 2-117
+RB Set Reject Box Usage 2-120
+RIB Set Rib bon Type 2-124
+RIB BON Set Ribbon Type 2-127
+RO Set X-Axis Offset, Relative 2-130
+ROY Set Y-Axis Offset, Relative 2-131
+SB Configure Laminator Stand-By Mode 2-136
+SIDE Set Lamination Mode 2-142
SXY Center Image Maps
+V Black Print Speed 2-151
A Print Test Card 2-6
IM Print Color Test Card 2-60
egaP
2-2
Page 35

DNA MMOC
DE SCRIP TION
Tests
IMB Print Gray Test Card 2-61
!SA Self Adjust 2-132
ISERIE i-Se ries Printer Test 2-66
Ini tial ize Com mands
ATM Set Card Feeding Mode 2-9
+B Se rial In ter face Rate 2-12
+DLAMI Set Lami na tion Con figu ra tion 2-41
FS Set Mag netic En coder Track Write En code Pa ram e ters 2-53
F/vF Clear Mono chrome Im age Buff ers 2-54
$LD Ini tial ize a Color Buffer to a Spec i fied In ten sity Level 2-76
R Re set 2-116
RCBC Reset Rejected Card Box Counter 2-122
SF Syn chro nize Film (Overlaminate) 2-140
+TC Set Laminator Head Tem pera ture 2-145
TF Film Type 2-146
+VL Set Lami na tion Speed 2-152
+X Change Command Initiation Character 2-159
Printer Query Com mands
!AO Check Patch Sensors 2-7
!AT Check Heat Offset 2-8
!CCLN Check Cleaning Parameters 2-20
CHECK Return Checksum 2-29
%CLN Check Due-for-Cleaning Parameters 2-32
!CC Get Number of Cards Printed 2-19
!CT Check Cooling Time 2-35
E Re trans mit Last Re sponse 2-46
%F Return Font Names
!L Check Status: P720 Laminator Sensor Levels 2-68
!L Check Status of Printer Sensor 2-68
!LC Check Lamination Counter 2-75
!LT Check Lamination Temperatures 2-77
!LTI Check Lamination Time 2-79
%N Return Number of Loaded Fonts
!NL Get Printer Impression and Error Counter 2-98
!O Get State of Cover Sensor
!O Check Card Offset 2-99
!OFP Check X-Axis Patch Offset 2-102
!OP Check Patch Offsets 2-105
&P Check Card Pre sent - En coder 2-112
egaP
2-3
Page 36
DNA MMOC
!RIB BON Check Ribbon Type 2-125
!RLEVEL Check Patches Remaining
!SB Check Stand-By Mode Settings 2-135
%SERIE Get Printer Serial Number 2-139
%HEAD Get Print Head Serial Number 2-57
!SERIE Get Laminator Serial Number 2-138
!SIDE Check Laminator Mode 2-141
V Check Printer Type/Ver sion 2-149
!V Return Operational Parameter 2-150
!W Move Card Backward 8 cm 2-153
!X Check Com mand Ini tia tor 2-158
DE SCRIP TION
Im age Data Down load Com mands
B/vB Write Bar Code 2-14
C/vC Write Box (Monochrome) 2-38
D/vD Draw Di ago nal Line (Monochrome) 2-45
G/vG Ini tial ize Mono chrome Graphic (B/W) 2-56
GS Down load Color Graphic 2-55
$L Draw a Horizontal Line/Rectangle in a Color Buffer 2-71
L/vL Draw Horizontal Line (Monochrome/Overlay) 2-81
O/vO Load Sin gle Line Bitmap (Monochrome) 2-108
PS Down load Color Im age Buffer 2-114
P/vP Draw Single Dot (Monochrome/Overlay) 2-115
T/vT Draw Text (Monochrome/overlay) 2-147
Z/vZ Load Bitmap (Monochrome) 2-161
Card Po si tioning Com mands
egaP
!M Move Print Head Up 2-82
MB Return Card to Card Feeder 2-83
MC Clear Me dia Path 2-84
MCL Move Contactless 2-85
ME Exit Card to Out put Hop per 2-86
MF Flip Card 2-87
MI Move Card to Print Ready Po si tion 2-88
MIB Move Card Back to Print Ready Position 2-89
MM Move Card Through Printer 2-90
MO Move Card to Out put Hopper 2-92
MR Check for CArd Presence 2-93
MRB Move Card to Reject Box 2-94
MS Move Card to Smart Card Programmer 2-96
!P Move Card Forward 8 cm 2-111
SF Synchronize Film (Overlaminate) 2-140
&T Mag netic En coder Card Eject 2-144
2-4
Page 37

DNA MMOC
DE SCRIP TION
Print Com mands
I Print Mono chrome Panel 2-58
IH Print Holo gram Over lay 2-59
IS Print Card Panel 2-62
IV Print Clear Var nish 2-151
J Print Mul ti ple Monochrome Cards 2-67
!Z Re-Synchronize Card 2-160
Mag netic Stripe En coder Com mands
&B Load Magnetic En coder Track Write Buffer 2-11
&C Set Coercivity 2-16
&CDER Set Magnetic Encoder Track Read Encode Parameters 2-24
&CDEW Set Mag netic En coder Track Write En code Pa ram e ters 2-25
&D Change Track Den sity 2-40
&E Write Sin gle Track 2-47
&E* Write Track Buffers 2-48
$F Clear Color Image Buffers 2-50
$FP Clear Specified Bit Maps 2-52
&L Read Sin gle Track 2-73
&N Select Magnetic Encoding Standard 2-97
&R Re set Magnetic En coder 2-118
&SVM Disable/Enable Magnetic Encoding Verifications 2-143
&W Change En cod ing Di rec tion 2-154
Smart Card Com mands
egaP
+ISC Set Smart Card Se rial Port Data Rate 2-64
+ISC2 Set Smart Card Se rial Port Data Rate (Advanced) 2-65
>R Read Data From Smart Card Serial Interface 2-119
>RB Read Data From Smart Card Serial Interface in ASCII hex Form 2-121
>W Write Data From Smart Card Serial Port 2-155
>WB Write Data From Smart Card Serial Port in ASCII hex Form 2-156
Mis cel la neous Com mands
. Clear Er ror Sta tus Lines 2-126
CLEAN Start Cleaning Card Se quence 2-30
CLNCARD Set Cleaning Card Parameters 2-33
!D Move Print Head Down 2-39
M/m Multiple Command 2-91
2-5
Page 38
A - Print Test Card
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Prints a Stan dard Test Card with Printer Pa ram e ters,
Ver sion Num ber, and Test Pat tern. Sys tems with
Laminators print two cards—one for the Printer the other
for the Laminator (if con nected).
Syntax <Esc>A{ p1}
Parameters p
= Test Card
1
Where:
None =
Stan dard Test Card(s)
1 = Printer Test Card
2 = Mag netic En coder Test Card
3 = Lam i na tion Test Card
Figure 2-2
Standard
Monochrome
Test Cards
Color Test Cards
2-6
Figure 2-3
Standard
Figure 2-4
Printer and
Laminator
Card Sides
Page 39

!AO - Check Patch Sen sors
Models Supported P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion Re turns val ues for se lected laminator patch po si tion
sen sor
Syn tax <Esc>#-1-!AO p1{ p2}
Pa ram e ters p
= Card Side
1
Where:
0 = Up per laminator patch po si tion sen sors
1 = Lower laminator patch po si tion sen sors
p2 = laminator patch po si tion sen sor se lec tion
Where:
None = De fault set tings
0 = X-Axis Sen sor
1 = Y-Axis Sen sor
2-7
Page 40

!AT - Check Heat Off set
Models Supported P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion Re turns any vari a tion from the Fac tory Set Laminator
Roller Heat. For ex am ple, for a Fac tory Set ting of 180°
and a Roller Heat of 190°, the !AT Com mand re turns a
+10.
Syn tax <Esc>#-1-!AT p
Pa ram e ters p
= Roller Se lec tion
1
Where:
0 = Top Heat Roller
1 = Bot tom Heat Roller
1
2-8
Page 41

ATM - Set Card Feed ing Mode
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P330i, P430i
Description Se lect card feed ing mode and con trol how printer re acts
to an out-of-card con di tion.
Syntax <Esc>ATM p
Parameters p
= Feed Mode as fol lows:
1
0 = Nor mal mode (de fault). This mode is in tended for
use with print ers equipped with a card feeder hop per.
When the hop per is empty, the printer will sig nal that it
is out of cards and wait for the user to add more. The
printer will not en ter a ready state (and re sume print ing)
un til the er ror state is cleared by press ing the <se lect>
but ton.
1 = ATM Mode (de fault). This mode is in tended for use
with print ers equipped with a front sin gle-card feed ing
slot. In this mode, the printer will sig nal that it is out of
cards as mode 0 does, but will au to mat i cally clear this
er ror sta tus when a card is fed in; the user does not have
to press <se lect> to clear the er ror.
ATM mode, when en abled, is most ef fec tive when used in
con junc tion with an en abled card feed sen sor (con trolled
by the FS com mand).
1
2-9
Page 42

&B - Load Magnetic En coder Track Write Buffer
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Load data into the write buffer for a sin gle se lected track
of en cod ing
Syntax <Esc>&B p1 data
Parameters p
= Track Num ber and data for mat
1
Where:
1 = Track 1 ASCII data
2 = Track 2 ASCII data
3 = Track 3 ASCII data
11= Track 1 hex a dec i mal data*
12= Track 2 hex a dec i mal data*
13= Track 3 hex a dec i mal data*
data =
Each track has unique char ac ter and length
lim i ta tions due to for mat ting, and each has its own
data buffer. When <p1> = 1..3, <data> should be
ex pressed as a sim ple string of ASCII char ac ters. If
<p1> = 11..13, <data> should be ex pressed as a
vari able length se quence of 2-digit ASCII
hex a dec i mal num bers.
In hex mode, only dig its 0..9 and up per case al pha
char ac ters A..F are al lowed. No er ror check ing is
per formed on the <data> field; the data loaded into
the track write buffer will be in de ter mi nate if the
<data> string con tains in valid char ac ters. The
printer au to mat i cally in serts the re quired ISO Con trol
Char ac ters (start and stop sen ti nel, lon gi tu di nal
re dun dancy check char ac ter, etc.) into the data.
2-10
The ac tual data en coded onto the card is con verted from
ASCII to an ISO track-spec i fied en cod ing for mat. See Ap pen dix C for de fault ANSI/ISO data for mats and cus tom
data en cod ing com mands.
Page 43

&B - Load Mag En coder Track Write Buffer (Con tin ued)
Track
1
2 0 through 9 = 37
3 0 through 9 = 104
11* Hexa deci mal N/A *
12* Hexa deci mal N/A *
13* Hexa deci mal N/A *
* - See Ap pen dix C for Ex tended En coder Com mand Set and
Cus tom Track Data and Con trol Pa rame ters.
Char ac ters
(De fault ANSI/ISO)
<Sp> $ ( ) - . /
0 through 9
A through Z (All Caps)
Field
Sep a ra tor
^ 76
Length
2-11
Page 44

+B - Se rial In ter face Rate
The card printer re sponds to com mands (with data or er ror
codes) via the bi-di rec tional se rial in ter face only. Print ers
with par al lel in ter faces can not re spond to this com mand,
(other than flag ging an er ror). In a test en vi ron ment, card
print ers can op er ate with both in ter faces at tached and com mu ni cat ing with the printer. The printer CPU board has as so ci ated con nec tors.
Models Supported P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P420c, P420i
Description This com mand changes the bit rate (Baud) of print ers
with RS232 se rial in ter faces. RFID-equipped mod els may
not of fer the RS232 op tion.
NOTE: Baud set ting re mains in ef fect un til power is
cy cled, af ter which printer re turns to de fault.
Syntax <Esc>+B p1{ p2}
Parameters p
= Se rial In ter face baud rate op tions
1
Where:
0 = 9600 (De fault)
1 = 19200
2 = 38400
3 = 57600
p2 = Com mand re ply time
Where:
None = ACK af ter Baud switch
1 = ACK be fore Baud switch
2-12
Page 45

+BS - Set Black Synchro
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Sets the ac cu racy of card po si tion ing, when set to high
qual ity, the printer print po si tion ing is more ac cu rate.
Syntax <Esc>+BS p
Parameters p
= Speed
1
Where:
0 = High speed print ing
1 = High qual ity print ing
1
2-13
Page 46

B/vB - Write Bar Code
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description This com mand down loads stan dard bar codes. See
Ap pen dix A for char ac ter maps and unique pa ram e ter
set tings for each bar code type. The B com mand writes to
the mono chrome buffer, while the vB com mand writes to
the var nish buffer.
Syntax <Esc>B p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6 p7 p8 data
Parameters p
= Hor i zon tal (X-axis) Start Po si tion, in dots
1
p2 = Ver ti cal (Y-axis) start po si tion, in dots
p3 = Ro ta tion:
Where:
Value De scrip tion Or i gin
0 No ro ta tion Lower Left
1 90 de grees Lower Left
2 180 de grees Lower Left
3 270 de grees Lower Left
4 No ro ta tion Cen tered
5 90 de grees Cen tered
6 180 de grees Cen tered
7 270 de grees Cen tered
Figure 2-5
Bar Code Rotation
Samples
2-14
p4 = Bar Code se lec tion - See Ap pen dix A
Where:
0 = Code 39 (3 of 9—Al pha nu meric)
1 = 2/5 In ter leaved (Nu meric, Even No Count
2 = 2/5 In dus trial (Nu meric) no Check Digit
3 = EAN8 (Nu meric, 12 dig its en coded)
4 = EAN13 (Nu meric, 12 dig its en coded)
5 = UPC - A (Nu meric, 12 dig its en coded)
6 = Re served for MON ARCH
7 = Code 128 C w/o Check Dig its* (Nu meric
only, Even Num ber Printed)
8 = Code 128 B w/o Check Dig its*
(Al pha nu meric)
s
Page 47

B/vB - Write Bar Code (Con tin ued)
107 = Code 128 C w/Check Dig its*
* Not sup ported in some Mono chrome Printerp5 = Bar
NOTE: Some bar code types have a selectable bar code
width ra tio. See Ap pen dix A for sup ported ra tio and
set tings.
p6 = Bar Code Bar Width Mul ti plier. Range 3~9 for all
p7 = Bar Code Height in dots
(Nu meric only, Even Num ber printed)
108 = Code 128 B w/Check Dig its*
(Al pha nu meric)
Width Ra tio
Where:
Value Nar row Bar Wide Bar Ra tio
0 1 dot 2 dots 2:1
1 1 dot 3 dots 3:1
2 2 dots 5 dots 2.5:1 or 2:5
Ze bra card bar codes ex cept UPC-A, EAN-8 and
EAN-13 which have a range of 4~7. For a se lected
bar width ra tio of 2:5, the range is 2~4.
Note: Each bar code type has a spec i fied stan dard
for the width range of a nar row bar width. See
Ap pen dix A for op ti mal val ues.
Note: Each Bar Code Type has an in dus try
spec i fied min i mum height stan dard. See Ap pen dix
A for op ti mal val ues.
p8 = Print Text ver sion of Bar Code un der Bar Code
Where:
1 = yes
0 = no.
data =
Rep re sents a fixed data field. Each bar code type
has a dif fer ing data field length and al low able
char ac ter re quire ments. See Ap pen dix A.
A printer er ror oc curs when a bar code ex tends be yond the
ad dress able area of the im age buffer. See Ap pen dix A for
field size cal cu la tions for to tal bar code length and height.
2-15
Page 48

&C - Set Coercivity
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion This com mand sets the en coder for high- or
low-coercivity mag netic stripe re cord ing.
Syn tax <Esc>&C p
Pa rame ters p
Where:
= Coercivity
1
0 = Low
1 = High
1
2-16
Page 49

+C - Ad justs Mono chrome In ten sity
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Sets the mono chrome rib bon trans fer in ten sity (heat)
level. Vary ing the in ten sity level af fects the dot gain, or
the size of the dot and the den sity (opaque ness) of the
trans ferred ma te rial. note that higher val ues raise the
trans fer heat.
Syntax <Esc>+C p
Parameters p
Where:
= In ten sity
1
5 = Printer de fault
0~10 = range
1
2-17
Page 50

+$C - Ad just Color Con trast
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i, P330i,
P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Sets the range from the max i mum to min i mum color
in ten sity (heat) level ap plied to a se lected dye sub li ma tion
rib bon panel
Syntax <Esc>+$C p1 p
Parameters p
= 4 : Set con trast for all col ors (0 - 3)
1
Where:
0 = Yel low (Y)
1 = Ma genta (M)
2 = Cyan ©)
3 = Dye Sub li ma tion Black (K
p2 = Con trast:
Where:
5 = Printer de fault
0~10 = p2 range
2
)
dye
2-18
Page 51

!CC - Get Num ber of Cards Printed
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P210i, P310i, P320i, P330i, P420i, P430i,
P520i
De scrip tion Ev ery time the printer fin ishes print ing an en tire card, it
in cre ments its cards printed coun ter. This coun ter is
saved in non-vol a tile mem ory. This com mand will
re turn the to tal num ber of cards that have been printed
since the printer en tered ser vice. The value is re ported
to the host as an ASCII dec i mal num ber.
Syn tax <Esc>!CC
Pa ram e ters None
2-19
Page 52

!CCLN - Check Clean ing Pa ram e ters
Models Supported P720c
De scrip tion Re turns Card Count and Max i mum Heat Val ues set by
Syn tax <Esc>#-1-!CCLN
Pa ram e ters None
the +CCLN Com mand
2-20
Page 53

+CCLN - Set Clean ing Pa ram e ters
Models Supported P720c
De scrip tion Es tab lishes lam i na tion count and max i mum tem per a ture
value for laminator cleanings
Syn tax <Esc>#-1-+CCLN p1 p
Pa ram e ters p
= Num ber of cards lam i nated
1
p2 = Tem per a ture be low which clean ing is al lowed
2
De fault +CCLN 1000 60
2-21
Page 54

%CDER - Get Mag netic En coder Read Set tings
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Re turns the mag netic en coder read set tings that are pres ently in
ef fect, as set by the &CDER com mand. The string re turned is
for mat ted like this:
“TRACK 1”* “TRACK 2”# “TRACK 3”*
where * and # are sub sti tuted with the de code set tings
that take the same form as those used by the &CDER
com mand. the ex am ple be low shows the string that
would be re turned if tracks 1 and 3 were set to the de fault
ISO de code set tings, and the set tings for track 2 had been
changed by ex e cut ing the com mand: &CDER 2 V 6 :
“TRACK 1”A “TRACK 2”V 6 “TRACK 3”C
Syntax <Esc>%CDER
Parameters None
2-22
Page 55

&CDER - Set Mag netic En coder Track Read En code Pa ram e ters
The card printer re sponds to com mands (with data or er ror
codes) via the bi-di rec tional se rial in ter face only. The card
printer can not re spond to this com mand, (other than flag ging an er ror), through a par al lel in ter face. In a test en vi ron ment, card print ers can op er ate with both in ter faces
at tached and com mu ni cat ing with the printer. The printer
CPU board has as so ci ated con nec tors.
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion Set the en coder to read a se lected data for mat
Syntax <Esc>&CDER p1 p2
<Esc>&CDER p1 p2
Parameters p
= Track Se lect: (val ues 1, 2, 3, or 0 (zero)
1
Where:
0 = Re set of ALL tracks to ISO de fault
con fig u ra tion pa ram e ters
p2 = Cus tom Data Se lect, as fol lows:
Value De scrip tion - ISO For mat Data
Re sets ALL tracks to ISO de fault con figu ra tion
0
pa rame ters.
De fault For mat Se lect
Q ISO Track 1 Data For mat to Track 1
R ISO Track 2 Data For mat to Track 2
S ISO Track 3 Data For mat to Track 3
Cus tom ISO Track For mat Lo ca tion
qX Track 1 with ISO Track “X” For mat
rX Track 2 with ISO Track “X” For mat
sX Track 3 with ISO Track “X” For mat
X = 1, 2, or 3 as the ISO de fault track for mat ap plied to the
se lected track (e.g., Q=q1, R=r2, and S=s3.
2-23
Page 56

&CDER - Set Mag netic En coder Track Read En code Pa ram e ters (Con tin ued)
p2 = Cus tom Data Se lect, as fol lows:
Value De scrip tion - Raw Data For mat
Read For ward - “Raw” Data
U Track 1
U_ Track 1 read data with NULs in data string
V Track 2
V_ Track 2 read data with NULs in data string
W Track 3
W_ Track 3 read data with NULs in data string
Read Re verse - “Raw” Data
u Track 1
u_ Track 1 read data with NULs in data string
v Track 2
v_ Track 2 read data with NULs in data string
w Track 3
w_ Track 3 read data with NULs in data string
2-24
p3 = Data Block Size Se lect in Bits
Where:
Ac cept able val ues = 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7
The en coder can not de code and con vert raw data into
ASCII data. The en coder only re ports data read af ter the
pro cess has com pleted.
Page 57

&CDEW - Set Mag netic En coder Track Write En code Pa ram e ters
The card printer re sponds to com mands (with data or er ror
codes) via the bi-di rec tional se rial in ter face only. The card
printer can not re spond to this com mand (other than flag ging an er ror) through a par al lel in ter face. In a test en vi ron ment, card print ers can op er ate with both in ter faces
at tached and com mu ni cat ing with the printer. The printer
CPU board has as so ci ated con nec tors.
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Con fig ure the write data to en code a sin gle, se lected
track of data
Syntax <Esc>&CDEW p1 p2
<Esc>&CDEW p1 p2 p3
Parameters p
= Track Se lect: (val ues 1, 2, 3 or 0 (zero)
1
Where:
0 = Re set of ALL tracks to ISO de fault
con fig u ra tion pa ram e ters
p2 = Data For mat Se lect, as fol lows:
Value De scrip tion - ISO For mat Data
Re set ALL tracks to ISO de fault con figu ra tion
0
pa rame ters.
De fault For mat Se lect
A ISO Track 1 Data For mat to Track 1
B ISO Track 2 Data For mat to Track 2
C ISO Track 3 Data For mat to Track 3
Cus tom ISO Track For mat Se lect
aX Track 1 with ISO Track “X” For mat
bX Track 2 with ISO Track “X” For mat
cX Track 3 with ISO Track “X” For mat
X = ISO de fault track for mat ap plied to the se lected track
(e.g., A=a1, B=b2, and C=c3.
2-25
Page 58

&CDEW - Write Cus tom Track Data (Con tin ued)
p2 = Cus tom Data Se lect, as fol lows:
Value De scrip tion - Raw Data For mat
Read For ward - “Raw” Data
E Track 1
E_ Track 1 write data with NULs in data string
F Track 2
F_ Track 2 write data with NULs in data string
G Track 3
G_ Track 3 write data with NULs in data string
p3 = Data Block Size Se lect in Bits
Where:
Ac cept able val ues = 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7
The en coder can not en code and con vert ASCII data into
raw data. The en coder only re ports that a data write pro cess
has com pleted.
2-26
Page 59

+CDOTS - Im age Print Qual ity Com pen sa tion
Fac tor
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion Card de sign el e ments that run the length of a card side
can some times ap pear with den sity vari a tions. An ID
badge con tain ing a por trait and a solid, card length, bar
at a side can ex hibit these vari a tions.
Any changes should oc cur in small in cre ments fol lowed by
card prints us ing trial-and-er ror as a ba sis. Ze bra Tech ni cal
Sup port guid ance is rec om mended.
Syn tax <Esc>CDOTS p1{ p2}
Pa ram e ters p
= Com pen sa tion Fac tor (0 ~ 50)
1
Where:
0 = No change
1 ~ 50 = Com pen sa tion fac tor
p2 = 1 = Re turn cur rent com pen sa tion fac tor
2-27
Page 60

+CH - Ad just Ho lo gram In ten sity
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Sets the ho lo gram ma te rial trans fer in ten sity (heat) level.
Vary ing the in ten sity level af fects the dot gain or size of
the dot and the den sity (opaque ness) of the trans ferred
ma te rial.
Syntax <Esc>+CH p
Parameters p
= In ten sity
1
Where:
5 = Printer de fault
0~10= range
1
2-28
Page 61

CHECK - Re turn Checksum
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
De scrip tion Re turns firm ware checksum value
Syn tax <Esc>CHECK
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
2-29
Page 62

CLEAN - Set Clean ing Card Se quence
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion This com mand re quires the prior re moval of any rib bon
and all cards ex cept for a sin gle Clean ing Card. The
fol low ing oc curs:
• Raise Print Head
• Feed a card to a po si tion un der Print Head
• Lower Print Head
• Move card back and forth the num ber of times spec i fied by CLNCARD Com mand
• Raise Print Head
• Exit card
Non P720 Syntax <Esc>CLEAN
Non P720 Parameters None
P720 Syn tax <Esc>CLEAN p
P720 Pa ram e ters p
= Sta tion Cleaned
1
Where:
1 = Printer
2 = Mag netic En coder Head
3 = Printer and Laminator (this com mand will be
ig nored)
4 = Laminator (this com mand will be ig nored)
1
2-30
Page 63

!CLEAN - Clean the Laminator
Models Supported P720c
De scrip tion This com mand will clean the laminator on the P720c
Parameters None
Syn tax <Esc>+CLEAN
printer
C-31
Page 64

%CLN - Check Due-for-Clean ing Pa ram e ters
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Re ports cur rent val ues for the print ing, clean ing and
clean ing pass coun ters
Syntax (sent) <Esc>%CLN
Syntax (received) Cpt imp:p
Where:
next clean Prn:p2 nb pass:p
1
p1 = To tal num ber of Head-down Im age Passes
made by printer since new (note that each
rib bon panel used counts as a pass)
p2 = Cur rent set ting for im age passes that trig ger a
clean ing alert (de fault = 00005000—see
CLNCARD Com mand)
p3 = Cur rent set ting for passes per formed us ing
Clean ing Card (de fault = 5—see
CLNCARD Com mand)
3
Ex am ple Cpt imp:00025000 next clean Prn:00005000 nb pass:5
2-32
Page 65

CLNCARD - Set Clean ing Pa ram e ters
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion Al lows set tings for a Time-to-Clean Alert and the cy cling
of clean ing card in Card Path
Syntax <Esc>#-1-CLNCARD p1 p
Parameters p
= Rib bon Panel Count to Clean ing No ti fi ca tion
1
(De fault = 5000)
p2 = Num ber of Clean ing Card Passes Through Printer
(De fault = 5)
2
2-33
Page 66

CRB - Set Re ject Box Card Count Warn ing Thresh old
Models Supported P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion P420, P520, and P720 Print ers have a coun ter that keeps
track of the num ber of cards sent to the Re jected Card
Box. This com mand al lows se lec tion of a card count that
pro duces the RE JECTED BOX FULL mes sage on the
LCD. Note that, af ter re mov ing the cards, us ers press the
Panel But ton. For this com mand, re lease of the Panel
But ton re sets the coun ter. The box can safely hold twenty
30-mil cards, and P420, P520, and P720 Print ers ship
with this set ting. Us ers of less thick cards may wish to
in crease the count.
Syn tax <Esc>CRB p
Pa ram e ters p
= Re ject Box card count warn ing thresh old
1
Where:
10 = De fault
1
2-34
Page 67

!CT - Check Cool ing Time
Models Supported P720c
De scrip tion Re turns the Tran si tion Time Set ting for cards pass ing
be tween the Lam i na tion Roll ers and the Out put Hop per
Syn tax <Esc># 1 !CT{ p1}
Pa ram e ters p
= De fault, if p1 is other than 0
1
2-35
Page 68

+CT - Set Cool ing Time
Models Supported P720c
De scrip tion Ad justs the tran si tion time for cards pass ing be tween the
lam i na tion roll ers and the out put hop per
Syn tax <Esc># 1 +CT p
Pa ram e ters p
= Cool ing time in sec onds
1
Where:
De fault = 0
1
2-36
Page 69

+CV - Ad just Clear Var nish In ten sity
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Sets the clear ve neer rib bon trans fer in ten sity (heat)
level. vary ing the in ten sity level af fects the den sity
(amount) of the trans ferred ma te rial.
Syntax <Esc>+CV p
Parameters p
= In ten sity
1
Where:
5 = De fault
0~10 = Range
1
2-37
Page 70

C/vC - Write Box (Mono chrome)
0
D
o
t
s
Lines
Hollow Box
Image Origin
p5
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Writes a hol low-box rect an gle graphic to the
mono chrome im age buffer by de fin ing the height, width,
line thick ness (width) and or i gin. The C com mand writes
to the buffer used for resin print ing. The vC com mand
writes to the buffer used for var nish print ing.
Syntax <Esc>C p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p
<Esc>vC p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p
Parameters p
= Hor i zon tal (X-axis) start po si tion in dots
1
p2 = Ver ti cal (Y-axis) start po si tion in dots
p3 = Hor i zon tal (X-axis) width of graphic line in dots (i.e.
hor i zon tal lines)
p4 = Ver ti cal (Y-axis) height of graphic line in dots
p5 = Thick ness/width of di ag o nal graphic line in dots
p6 = Graphic Mode
Where:
0 = Re verse Bit Map—Clear Print Area and load
1 = Stan dard Bit Map—Clear Print Area and load
2 = Merge Bit Map—Over write Back ground Bit
Map Im age with Print able Dot
Lo ca tions,
Lo ca tions alone
Re verse Bit Map Im age
Bit Map Im age
leav ing Non-print ing Dot
6
6
Hollow Box
Image Positioning
2-38
Figure 2-1
Page 71

!D - Move Print Head Down
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
Description Moves the Print Head as sem bly down to the card (and
Syntax <Esc>!D
Parameters None
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
platen roller)
2-39
Page 72

&D - Change Track Den sity
The card printer re sponds to com mands (with data or er ror
codes) via the bi-di rec tional se rial in ter face only. Print ers
with par al lel in ter faces can not re spond to this com mand,
(other than flag ging an er ror). In a test en vi ron ment, card
print ers can op er ate with both in ter faces at tached and com mu ni cat ing with the printer. The printer CPU board has as so ci ated con nec tors.
Models Supported P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i, P330i, P420c,
P420i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Changes the data en cod ing and de cod ing den sity of an
in di vid ual track
Syntax <Esc>&D p1 p
Parameters p
= Track Se lect, as fol lows:
1
Where:
p2 = Den sity Se lect, as fol lows:
Where:
1 = Tracks 1 and 3
2 = Track 2
3 = Tracks 1 and 3
75 = 75 bpi
210 = 210 bpi
2
2-40
Page 73

+DLAMI - Set Lam i na tion Con fig u ra tion
Models Supported P520c, P520i
Description En ables or dis ables print sta tion var nish or laminator
sta tion lam i na tion. The as so ci ated ap pli ca tion oc curs
with is su ance of an IV com mand, or in some in stances,
an I com mand (In the fol low ing ex am ples, look for the
+DLAMI that pre cedes an I or IV)
NOTE 1: This com mand ap plies to printer and,
there fore, re quires no <Esc>#<Sp>1 pref ace.
Syntax <Esc>+DLAMI p1 p
Parameters p
Ex am ples Using
= Print sta tion var nish
1
Where:
0 = Dis able
1 = En able
p2 = Laminator
.000n
Where:
0 = Dis able
1 = En able
2 = En able and flip to lam i nate (ap plies to
YMCKO and YMCK rib bons to lam i nate the
color side af ter im ag ing K
mono chrome side)
Print YMCK on both sides then lam i nate first side:
2
on the
resin
YMCKO Ribbon
+DLAMI 0 1 Lam i nate en abled (side-1 de fault)
IS 0 Print Y (side 1)
IS 1 Print M (side 1)
IS 2 Print C (side 1)
I Print K (side 1)
IV 10 No var nish, just a re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 0 0 Dis able both var nish & lam i na tion
IS 0 Print Y (side 2)
IS 1 Print M (side 2)
IS 2 Print C (side 2)
I Print K (side 2)
IV Flip card, lam i nate, eject (no var nish)
2-41
Page 74

+DLAMI - Set Lam i na tion Con fig u ra tion (Con tin ued)
On first side, print YMCK then lam i nate. On sec ond
side, print YMCKO pan els (no lam i nate):
+DLAMI 0 1 Lam i nate en abled (side-1 de fault)
IS 0 Print Y (side 1)
IS 1 Print M (side 1)
IS 2 Print C (side 1)
I Print K (side 1)
IV 10 No var nish, just a re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 1 0 Var nish en abled
IS 0 Print Y (side 2)
IS 1 Print M (side 2)
IS 2 Print C (side 2)
I Print K (side 2)
IV Print O (side 2), flip, lam i nate, & eject
Print all rib bon pan els on both sides with out lam i na tion:
+DLAMI 1 0 Var nish en abled
IS 0 Print Y (side 1)
IS 1 Print M (side 1)
IS 2 Print C (side 1)
I Print K (side 1)
IV 10 Print O (side 1) & re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 1 0 Var nish en abled
IS 0 Print Y (side 2)
IS 1 Print M (side 2)
IS 2 Print C (side 2)
I Print K (side 2)
IV Print O (side 2) & eject)
Ex am ples Using
YMCKOK Ribbon
2-42
On first side, print YMCK pan els then lam i nate. On
sec ond side, print last K panel then lam i nate:
+RIB 10 YMCKOK rib bon in use
+DLAMI 0 1 Lam i nate en abled (side-1 de fault)
IS 0 Print Y (side 1)
IS 1 Print M (side 1)
IS 2 Print C (side 1)
I Print K (side 1)
IV 10 No var nish, just a re turn
MF Flip Card
+DLAMI 0 0 Lam i nate en abled
I 20 Print K (side 2)
MO Flip Card, Lam i nate, & Eject
Page 75

+DLAMI - Set Lam i na tion Con fig u ra tion (Con tin ued)
On first side, print YMCK pan els then lam i nate. On
sec ond side, print just last K panel:
+RIB 10 YMCKOK rib bon in use
+DLAMI 1 0 Lam i nate en abled (side-1 de fault)
IS 0 Print Y (side 1)
IS 1 Print M (side 1)
IS 2 Print C (side 1)
I Print K (side 1)
IV 10 No var nish, just a re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 0 0 Var nish en abled
I 20 Print K (side 2) & re turn
MO Flip card, lam i nate, & eject
On first side, print YMCKO pan els (no lam i na tion). On
sec ond side, print just last K panel (No lam i na tion):
+RIB 10 YMCKOK rib bon in use
+DLAMI 1 0 Var nish en abled
IS 0 Print Y (side 1)
IS 1 Print M (side 1)
IS 2 Print C (side 1)
I Print K (side 1)
IV 10 Print O & re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 1 0 Var nish en abled
I 20 Print K (side 2) & re turn
MO Eject card
Ex am ples Using
K
O Ribbon
dye
Print K
+DLAMI 0 1 Lam i nate en abled (side-1 de fault)
IS 3 Print K (side 1)
IV 10 No var nish, just a re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 0 0 Dis able both var nish & lam i nate
IS 3 Print K (side 2)
IV Flip card, lam i nate, & eject
and lam i nate K
dye
on side two:
dye
2-43
Page 76

+DLAMI - Set Lam i na tion Con fig u ra tion (Con tin ued)
On first side, print K and lam i nate. On sec ond side, print
K and var nish:
+DLAMI 0 1 Lam i nate en abled (side-1 de fault)
IS 3 Print K (side 1)
IV 10 No var nish, just a re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 1 0 Var nish en abled
IS 3 Print K (side 2)
IV Print O, flip card, & lam i nate
Print K
+DLAMI 1 0 Var nish en abled
IS 3 Print K (side 1)
IV 10 Print O (side 2) & re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 1 0 Var nish en abled
IS 3 Print K (side 2)
IV Print O (side 2) & eject
O on both sides with out lam i na tion:
dye
Ex am ples Using
Mono chrome Ribbon
Print K and lam i nate side one:
+DLAMI 0 1 Lam i nate en abled (side-1 de fault)
I 10 Place at print ready
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 0 0 Dis able both var nish & lam i nate
I Print K, flip card, lam i nate eject
On first side, print K and lam i nate. On sec ond side just
print K:
+DLAMI 0 1 Lam i nate en abled (side-1default)
I 10 Print K (side 1), & re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 0 1 Var nish en abled
I Print K, flip card, & eject
Print K on both sides with out lam i na tion:
+DLAMI 1 0 Var nish en abled
I 10 Print K & re turn
MF Flip Card & re turn
+DLAMI 0 0 Dis able both var nish & lam i nate
I Print K & eject card
2-44
Page 77

D/vD - Draw Di ag o nal Line (Mono chrome/Over lay)
0
D
o
t
s
(y)
Lines (x)
Diagonal Line
Image Origin
P
1
P
2
P
3
P
4
P
5
P-1
6
P- 2
6
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Write a mono chrome di ag o nal line graphic by de fin ing
the to tal height, to tal width, line thick ness (width) and
po si tion in the Mono chrome Im age Buffer. The “D”
Com mand writes to the Resin buffer, and the “vD”
com mand writes to the Var nish buffer. The ac tual im age
placed is a rect an gle.
Syntax <Esc>D p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6 p
Parameters p
= Hor i zon tal (X-axis) Start Po si tion, in dots
1
p2 = Ver ti cal (Y-axis) Start Po si tion, in dots
p3 = Hor i zon tal (X-axis) Width of Graphic, in dots
p4 = Ver ti cal (Y-axis) Height of Graphic, in dots
p5 = Thick ness/width of the Line, in dots
p6 = Ro ta tion & Or i gin
Where:
Value De scrip tion Or i gin
1 90 de grees Lower Left
2 180 de grees Lower Left
p7 = Graphic Mode:
7
Where:
0 = Re verse Bit Map—Clear Print Area and load
Re verse Bit Map Im age
1 = Stan dard Bit Map—Clear Print Area and load
Bit Map Im age
2 = Merge Bit Map—Over write Back ground Bit
Map Im age with Print able Dot Lo ca tions,
leav ing Non-print ing Dot Lo ca tions alone
Figure 2-2
Diagonal Line Values
2-45
Page 78

E - Re trans mit Last Re sponse
The card printer re sponds to com mands (with data or er ror
codes) via the bi-di rec tional se rial in ter face only. Print ers
with par al lel in ter faces can not re spond to this com mand,
(other than flag ging an er ror). In a Test En vi ron ment, card
print ers can op er ate with both in ter faces at tached and com mu ni cat ing with the printer. The Printer CPU Board has as so ci ated con nec tors.
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i, P330i, P420c,
P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Models SupportedDescription This com mand di rects the printer to re peat the last Sta tus
Mes sage.
Syntax <Esc>E{ p1}
Pa rame ters p
= Port se lec tion/mode
1
Where:
1 = Par al lel Port in Re verse Se rial mode (al lows
host to pull se ri al ized data from printer over
the Par al lel Port—please con tact Tech ni cal
Sup port for re lated in for ma tion).
2= Use USB Port. Up date Printer Out put Buffer
with re sponse to com mands re ceived.
2-46
Page 79

&E - Write Sin gle Track
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description En code, write and read (ver ify) a sin gle track of data.
The printer feeds a card (if a card is not loaded) and
mag net i cally writes data to the se lected ISO Track. The
card au to mat i cally read-ver i fies the en coded data. The
card then moves to the print-ready po si tion.
Syntax <Esc>&En data
<Esc>&e n data
Parameters p
= En cod ing Track Num ber (1~3)
1
data = ISO track
n = track #
The <data> field is op tional; if it is omit ted, the data last
loaded into the mag en coder write buffer for track
<p1> will be writ ten to the spec i fied track. If a <data>
field is spec i fied, it overwrites any pre vi ous data in the
track write buffer; the new data pro vided is used in the
sub se quent track write op er a tion. The for mat of the
<data> pa ram e ter is an ASCII string, fol low ing the
same con ven tions as those that ap ply to the <data>
field for the &B (Load Mag En coder Track Write Buffer)
com mand.
The ac tual data en coded onto the card is con verted from
ASCII to the en cod ing for mat pre vi ously spec i fied for the
as so ci ated ISO card track. See Ap pen dix C for de fault
ANSI/ISO data for mats and cus tom en cod ing com mands.
2-47
Page 80

&E* - Write Track Buff ers
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description En codes, Writes, and Reads (ver i fies) for all tracks of data
stored in Printer Mem ory.
The printer po si tions a card at the En coder Sta tion and
mag net i cally writes data (pre vi ously en tered in mem ory)
to the pre-se lected ISO track(s). If no card is pres ent in
the Card Path, a card is sent from the Card Feeder.
Fol low ing the En coder Write Op er a tion, the card re turns
to the Write-Ready Po si tion, and a read-ver i fi ca tion of
En coded Card Data fol lows. The card then trav els to the
Print-Ready Po si tion, and an En coder Data Buffer Clear
oc curs in prep a ra tion for the next op er a tion.
Syntax <Esc>&E*
Parameters None
2-48
Page 81

+EC - End of Print
P310
X and EC
Origin
Start of
Printing
P210
X and EC
Origin
Start of
Printing
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion Spec i fies a point, be yond which, no card print ing oc curs.
Print sta tions have stor age for 1030 lines of im ag ing,
which ex ceeds the x-axis im age area on the cards.
The pa ram e ter for end of print causes the print head to
raise at the end-of-card point, not the end of data. If left
down be yond the end of card, the print head can shear
the rib bon as the print head abruptly drops be low the
sur face of the card. Note that higher val ues of p1 re sult in
short ened line counts.
Note that the print di rec tion of P205/P210 en gines is the
op po site of other en gines. In all en gines, EC off sets
shorten the bitmap at the end of the printed area.
There fore, EC in creases shorten the left side of
P205/P210 im ages and the right side of other printer
im ages.
Pa rame ters p
Syn tax <Esc>+EC p
= line count for end-of-print
1
Where:
10 = de fault (stan dard)
0~48 = range
Ex am ple The fol low ing ex am ple sets the End of Print to 10 (the
de fault value).
1
<Esc>+EC 10
2-49
Page 82

$F - Clear Color Im age Buff ers
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
Description Clears the yel low, cyan, and ma genta color panel im age
Syntax <Esc>$F
Parameters None
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
buff ers to the de fault (all pix els off) state.
2-50
Page 83

!FF - Set Rib bon Color Se quence
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Re sets and moves the rib bon to a se lected panel
The printer first aligns on the Cyan (and Black) Pan els
and then counts rib bon panel po si tions from the Yel low
“0" Panel.
Syntax <Esc>!FF p
Parameters p
= Panel de tec tion num ber
1
The P330i and P430i printers will re spond to !FF 0 only.
Any other pa ram e ter will cause the rib bon to con tin u ously
feed.
Where:
p1 = 0 Moves rib bon to Sync Po si tion, as fol lows:
Rib bon Sync Po si tion
YMCK
YMCK
YMCK
1
YMC Yel low Panel
resin
O Yel low Panel
resin
resinOKresin
K
O Mid Over lay Var nish
dye
K
O Mid Over lay Var nish
resin
Yel low Panel
Yel low Panel
p1 = 1 Moves rib bon to next Trans par ent Panel, un less
al ready there. For P210, moves rib bon to next
panel.
p1 = 2 Moves rib bon to next Non-trans par ent Panel,
un less al ready there. For P210, moves rib bon to
next panel.
p1 = 3 Moves rib bon to be gin ning of Black (for
YMCK
O rib bons only)
resin
2-51
Page 84

$FP - Clear Spec i fied Bit-Maps
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i, P330i,
P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion Al lows Mem ory Clears of ar eas re served for spec i fied
col ors
Syntax <Esc>$FP p
Parameters p
= Buffer Area Cleared
1
Where:
0 = Yel low
1 = Ma genta
2 = Cyan
3 = Dye Black (Us ing K
1
O Rib bon)
dye
2-52
Page 85

FS - Con trol Use of Card Feed Sen sor
Models Supported P330i, P430i
Description The printer pro vides a sen sor lo cated near the card feed
slot that can de tect when a card has been in serted into
the slot by the user. When the card feed sen sor is
en abled (and the ‘ATM’ fea ture is en abled - see ATM
com mand) the printer can ac cept a card fed by the user
with out re quir ing the user to ac tu ally start a print job on
the host or press a but ton on the printer - the printer
ac cepts a card for print ing in much the same way that a
ATM ma chine ac cepts a card, hence, “ATM mode”.
In some en vi ron ments, it may be pref er a ble to have the
printer act like ear lier sin gle card mod els, where the
printer card feed mech a nism is ac ti vated when a print
job is started, rather than the mere pres ence of a card in
the card feed slot. This com mand, in con junc tion with
the “ATM” com mand, con trols how the printer han dles
card feed ing..
Syntax <Esc>FS P
Pa rame ters P
= Card feed sen sor mon i tor
1
0: Sen sor dis abled. User must start a print job
be fore the printer will ac cept a card.
1: Sen sor en abled. Printer will au to mat i cally feed a
card pre sented at the card feed slot into the print
mech a nism (as sum ing that a card has not al ready
been fed in).
1
2-53
Page 86

F/vF - Clear Mono chrome Im age Buff ers
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
Description Clears Mono chrome Im age Buff ers of bit-maps and
Syntax <Esc>F
Parameters None
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
print able data (lines, text, bar codes, etc.)
2-54
Page 87

GS - Down load Color Graphic
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P210i, P310c, P310i, P320i, P330i,
P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Initializes, down loads, and po si tions in di vid ual
color-sep a rated data (C,M,Y, or K) for a par tial im age.
De fines the height, width and po si tion of the graphic.
Syntax <Esc>GS p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6 data
Parameters p
= Color Im age Buffer Num ber
1
Where:
0 = Yel low (Y)
1 = Ma genta (M)
2 = Cyan ©)
3 = Dye Sub li ma tion Black (Ks)
p2 = Data Mode:
Where:
32 = Un com pressed Data - 256 lev els
(00~FF Hex.)
30 = Com pressed Data - 32 lev els (00-1F Hex.)
p3 = Hor i zon tal (X-axis) Start Po si tion, in dots
p4 = Ver ti cal (Y-axis) Start Po si tion, in dots
p5 = Hor i zon tal (X-axis) Width of graphic, in dots (i.e.
hor i zon tal lines)
p6 = Ver ti cal (Y-axis) Height of graphic, in bytes
data =
Un com pressed or com pressed color bit-map
data for a sin gle sep a rated color
2-55
Page 88
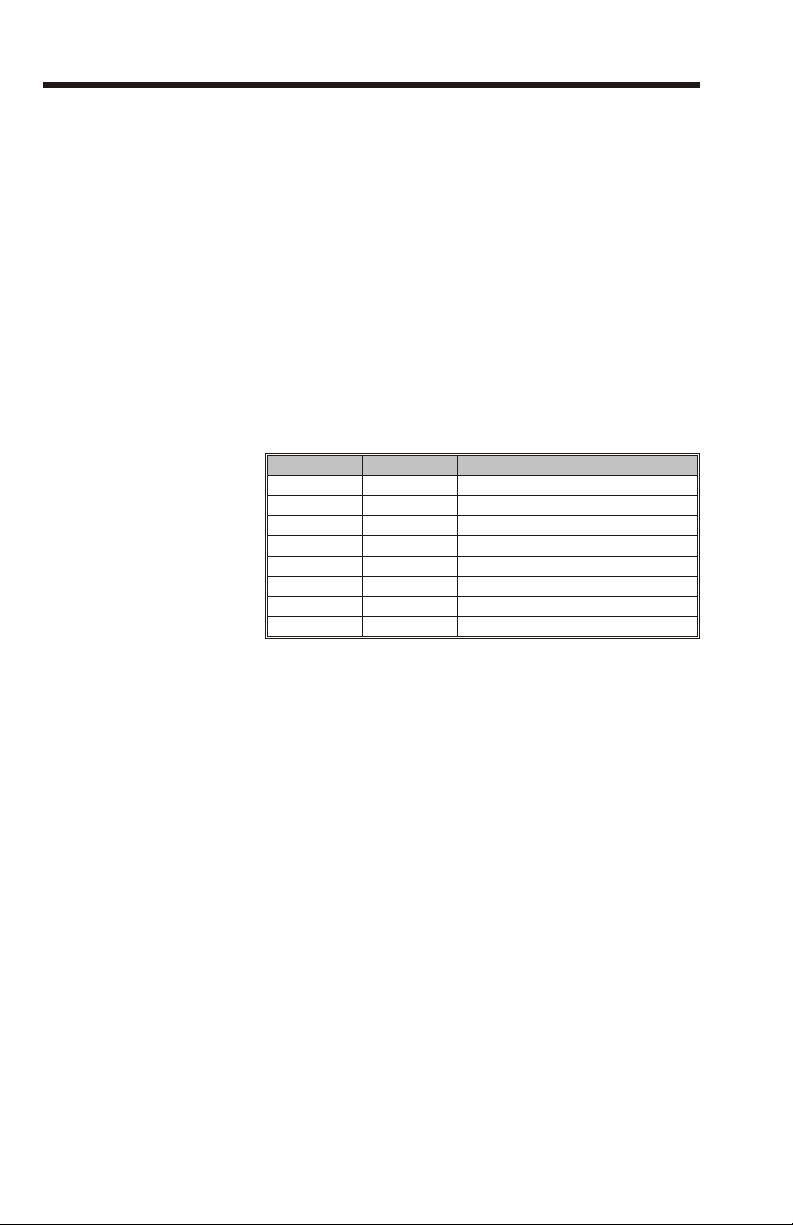
G/vG - Ini tial ize Mono chrome Graphic (B/W)
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Initializes Mono chrome Graphic Area us ing height, width
and po si tion
Syntax <Esc>G p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p
Parameters p
= Hor i zon tal (X-axis) Start Po si tion (X) in dots
1
p2 = Ver ti cal (Y-axis) Start Po si tion (Y) in dots
p3 = Down load Mode for Graphic (Bit-map):
When us ing bytes, the byte count must be rounded
up ward to the next near est whole byte.
Ex am ple:
25 dots = 3 bytes + 1 dot = 4 bytes
Value Data De scrip tion
0 Byte Stan dard
1 Byte Stan dard with Check sum
2 Byte Com pressed
3 Byte Com pressed with Check sum
10 Dot Stan dard
11 Dot Stan dard with Check sum
12 Dot Com pressed
13 Dot Com pressed with Check sum
p4 = Ver ti cal (Y-axis) Height of graphic in bytes.
Round up the num ber of bytes load ing in mul ti ples
of 8 bits (i.e. Mono chrome Dots)
6
2-56
p5 = Hor i zon tal (X-axis) Width of graphic in dots (i.e.
hor i zon tal lines)
p6 = Graphic Mode:
Where:
0 = Re verse Bit Map—Clear Print Area and load
Re verse Bit Map Im age
1 = Stan dard Bit Map—Clear Print Area and load
Bit Map Im age
2 = Merge Bit Map—Over write Back ground Bit
Map Im age with Print able Dot
Lo ca tions,
leav ing Non-print ing Dot
Lo ca tions alone
Page 89

%HEAD - Get Print Head Se rial Num ber
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion Both the printer as a whole and the print head
sub as sem bly are as signed a unique se rial num ber af ter
pass ing post-man u fac tur ing qual ity and func tional tests.
The se rial num ber as signed to the print head mech a nism
is sep a rate from that as signed to the printer as a whole.
This com mand is used to re trieve the se rial num ber
as signed to the print head mech a nism.
Syn tax <Esc>%HEAD
Pa ram e ters None
2-57
Page 90

I - Print Mono chrome Panel
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description This com mand serves to print a Mono chrome Graphic
Panel from a card im age pre vi ously stored in the buffer
des ig nated for Resin im ages.
Af ter print com ple tion, the card may be ejected to the
Out put Hop per or re po si tioned to print an other im age
(rib bon panel). Typ i cally the Clear Var nish, or for some
mod els, the Ho lo gram Lam i na tion prints next. Then, a
du plex printer may pro duce ad di tional print ing af ter
flip ping the card to the op po site side.
Rib bon pan els ad vance dur ing print ing, mak ing the
in stalled rib bon the over rid ing fac tor in choos ing buff ers
for im ag ing.
Syntax <Esc>I{ p1}
Parameters p
= Op tional Com mand Pa ram e ter
1
Where:
None =
Mono chrome Buffer Print and card eject
10 = Card Print and re turn to Print Ready Po si tion
20 = For Kr or Ks Rib bons—Prints card and
re turns card to Print Ready Po si tion. When
ap pro pri ate, syn chro nizes rib bon
For P520s us ing YMCKrOKr Rib bon—Ejects
card af ter last ap pli ca tion of ei ther Kr or
lam i nate. A prior +DLAMI Com mand
de ter mines when the I 20 Com mand in vokes
lam i na tion.
30 = Print card but leave in place—used when
next Sta tion is BUSY.
2-58
P520 with KrO Rib bon Ex am ple:
I 20
IV
MF
I 20
IV
MO
Page 91

IH - Print Ho lo gram Over lay
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i, P330i,
P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i
Description This com mand serves to print the en tire ad dress able
Var nish Im age Buffer or to re verse print any im age data
(line, rect an gles, graphics, text, etc.) pre vi ously stored in
the Resin Im age Buffer.
Af ter print ing is com plete, the card may be ejected to the
Out put Hop per or re po si tioned to print form sub se quent
rib bon pan els for mod els that sup port the du plex
print ing.
The rib bon ad vances po si tion a panel for print ing af ter
com ple tion of print ing from the pre vi ous panel.
Syntax <Esc>IH{ p1}
Parameters p
= Op tional Print Pa ram e ter
1
Where:
None =
Prints 100% of Im age Buffer as Ho lo gram
Lam i na tion and ejects card
1 = Prints in verse of Im age Data to card and
ejects card
10 = Prints card and re turns card to Print-Ready
Po si tion
2-59
Page 92

IM - Print Color Test Card
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P210i, P310c, P310i, P320i, P330i, P420c,
P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Prints a card with a Color Test Pat tern
NOTE: The K
panel is not used in this im age.
resin
Syntax <Esc>IM
Parameters None
Figure 2-3
Color Test Card
2-60
Page 93

IMB - Print Gray Test Card
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
Description Prints an all gray card. Typ i cally this card serves as a
ba sis for Print Head Ad just ments. Note that a black
rib bon is re quired (Ref er ence ta ble below).
Printer Model Rib bon Re quired
P205 mono chrome rib bon 800015-221
P210i mono chrome rib bon 800015-201
P310c mono chrome rib bon 800015-301
P320i, P330i, P420c, P420i,
P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
mono chrome rib bon
800015-101
Syntax <Esc>IMB
Parameters None
Figure 2-4
Print Black Test Card
2-61
Page 94

IS - Print Card Panel
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P210i, P310c, P310i, P320i, P330i, P420c,
P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion This com mand serves to print from a se lected color dye
sub li ma tion rib bon panel us ing data from an as so ci ated
im age buffer.
Af ter com plet ing a print ing pass, the card is re po si tioned
to print the next rib bon panel.
The rib bon panel ad vances dur ing print ing such that
com ple tion of one panel leaves the rib bon ready to print
the next panel.
NOTE: Print ing for Dye Sub li ma tion Black oc curs us ing
data from a color buffer in con junc tion with a K
rib bon.
Syntax <Esc>IS p
Parameters p
Where:
NOTE: Card im ag ing us ing the YMCKOK rib bon re quires
the fol low ing com mand se quence:
IS 0 Im age Yel low
IS 1 Im age Ma genta
IS 2 Im age Cyan
I Im age Black and Re turn
IV 10 Im age Var nish and Re turn
I 20 Im age Black and Re turn
MO Eject Card
1
= Color im age buffer num ber:
1
0 = Yel low (Y)
1 = Ma genta (M)
2 = Cyan ©)
3 = Dye Sub li ma tion Black (K
(YMCKOK only)
dye
)
dye
O
2-62
Page 95

IV - Print Clear Var nish
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P210i, P310c, P310i, P320i, P330i,
P420c, P420i, P430i
Description This com mand serves ei ther to print the en tire
ad dress able im age buffer or to re verse print with the
clear var nish or any im age data (line, rect an gles,
graphics, text, etc.) pre vi ously stored in a Mono chrome
Im age Buffer.
Af ter print ing is com plete, the card may be ejected to the
Out put Hop per or re po si tioned to print more rib bon
pan els for mod els that sup port the Ho lo gram,
Lam i na tion, or Du plex Op er a tions.
The rib bon pan els ad vance dur ing print ing such that
com ple tion of print ing from one rib bon panel leaves the
rib bon ready to print the next panel.
Syntax <Esc>IV{ p1}
Parameters p
= Op tional Print Pa ram e ter
1
Where:
None =
Buffer and
eject card
1 = Print Var nish us ing In verted Im age Buffer data
and eject card
10 = Print card and re turn card to Print Ready
11 = Print Var nish us ing In verted Im age Buffer
Ready Po si tion
30 = Print card but leave in place (used when
31 = Sim i lar to 30, but in verts Im age data
Print Var nish from all of Im age
Po si tion
data and re turn card to Print
next Sta tion is BUSY
2-63
Page 96

+ISC - Set Smart Card Se rial Port Data Rate
Models Supported P330i, P430i
De scrip tion The Smart Card in ter face on the P330i printer pro vides
an asyn chron ous com mu ni ca tion port that can be used to
com mu ni cate with an ex ter nal smart card pro gram ming
de vice. This com mand (or the more flex i ble +ISC2
vari ant) is used to con fig ure the com mu ni ca tion
pa ram e ters used by the smartcard se rial port.
Syn tax <Esc>+ISC p
Pa ram e ters p
= Se rial port baud rate, from the fol low ing ta ble:
1
The word size, par ity and stop bit con fig u ra tion of the smart
card se rial port are set to 8/None/1 when this com mand is
used. Use the +ISC2 com mand if these pa ram e ters need to
be changed.
0=9600, 1=19200, 2=38400, 3=57600,
4=112500
1
2-64
Page 97
+ISC2 - Set Smart Card Se rial Port Data Rate
(Ad vanced)
Models Supported P330i, P430i
De scrip tion The Smart Card in ter face on the P330i printer pro vides
an asyn chron ous com mu ni ca tion port that can be used
to com mu ni cate with an ex ter nal smart card
pro gram ming de vice. This com mand (or the more ba sic
+ISC vari ant) is used to con fig ure the com mu ni ca tion
pa ram e ters used by the smartcard se rial port.
Syn tax <Esc>+ISC2 p1 p2 p3 p
Pa ram e ters P
- Se rial port baud rate, from the fol low ing ta ble:
1
0=9600, 1=19200, 2=38400, 3=57600, 4=112500
P2 - Par ity set ting: 0=Even, 1=Odd, 2=None
P3 - Word size: 5, 6, 7 or 8
P4 - Stop bits: 0 or 1=1 stop bit, 2=2 stop bits
The +ISC com mand can also be used to ini tial ize the smart
card in ter face se rial port. When +ISC is used, the
wordsize, par ity and stop bit set tings are fixed at 8/None/1.
4
2-65
Page 98

ISERIES - i-Se ries Printer Test
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P210i, P310i, P320i, P330i, P420i, P430i,
P520i,
Description This com mand sim ply re turns a <Ack> re sponse when
ex e cuted on an i-Se ries printer. Ear lier printer mod els
(such as the C se ries) will sig nal a er ror when this
com mand is ex e cuted. The re sponse to this com mand
can be used to de ter mine if the printer at tached is an
i-Se ries (or later) gen er a tion.
Syntax <Esc>ISERIES
Pa ram e ters None
2-66
Page 99

J - Print Mul ti ple Mono chrome Cards
Models Supported P110i, P120i, P205, P210i, P310c, P310f, P310i, P320i,
P330i, P420c, P420i, P430i, P520c, P520i, P720c
De scrip tion NOTE: This com mand only ap plies to mono chrome
print ing us ing a Mono chrome Rib bon hav ing a sin gle
con tinuos color and ma te rial; i.e., all black, all red, all
green, etc.
This com mand serves to print sev eral mono chrome
cards from an im age pre vi ously stored in the Resin
Im age Buffer.
NOTE: Er ror re cov ery is not pos si ble from this
com mand.
Syntax <Esc>J p
Parameters p
= Num ber of cards to print
1
1
2-67
Page 100

!L - Check Sta tus: P720 Laminator Sen sor Lev els
Models Supported P720c
De scrip tion Al lows a P720 Laminator Sen sor Level Check
Syn tax <Esc># 1 !L{ p1}
Parameters p
= Sen sor
1
Where:
None = All sen sors
0 = Rib bon Top (0~255)
1 = Rib bon Bot tom (0~255)
2 = Tem per a ture Top (0~255)
3 = Tem per a ture Bot tom (0~255)
4 = Decurling (0~255)
5 = En try (0~255)
6 = X Top (0~255)
7 = Y Top (0~255)
8 = X Bot tom (0~255)
9 = Y Bot tom (0~255)
10 = Top Rib bon De tect (0~7)
11 = Bot tom Rib bon De tect (0~7)
2-68
 Loading...
Loading...