YAMAHA YFM660FP SERVICE MANUAL

YFM660FP
SERVICE MANUAL
LIT-11616-15-01 5KM-28197-E0

EB001000
NOTICE
This manual was produced by the Yamaha Motor Company primarily for use by Yamaha dealers
and their qualified mechanics. It is not possible to include all the knowledge of a mechanic in one
manual, so it is assumed that anyone who uses this book to perform maintenance and repairs on
Yamaha machine has a basic understanding of the mechanical ideas and the procedures of
machine repair. Repairs attempted by anyone without this knowledge are likely to render the
machine unsafe and unfit for use.
Yamaha Motor Company, Ltd. is continually striving to improve all its models. Modifications and significant changes in specifications or procedures will be forwarded to all authorized Yamaha dealers
and will appear in future editions of this manual where applicable.
OTE:
Designs and specifications are subject to change without notice.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Particularly important information is distinguished in this manual by the following notations.
The Safety Alert Symbol means ATTENTION! BECOME ALERT! YOUR
SAFETY IS INVOLVED!
WARNING
CAUTION:
NOTE:
Failure to follow WARNING instructions could result in severe injury or death
to the machine operator, a bystander or a person inspecting or repairing the
machine.
A CAUTION indicates special precautions that must be taken to avoid damage to the machine.
A NOTE provides key information to make procedures easier or clearer.
EB002000
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
MANUAL ORGANIZATION
This manual consists of chapters for the main categories of subjects. (See “Illustrated symbols”)
1st title 1: This is the title of the chapter with its symbol in the upper right corner of each page.
2nd title 2: This title indicates the section of the chapter and only appears on the first page of each
section. It is located in the upper left corner of the page.
3rd title 3: This title indicates a sub-section that is followed by step-by-step procedures accompanied by corresponding illustrations.
EXPLODED DIAGRAMS
To help identify parts and clarify procedure steps, there are exploded diagrams at the start of each
removal and disassembly section.
1. An easy-to-see exploded diagram 4 is provided for removal and disassembly jobs.
2. Numbers 5 are given in the order of the jobs in the exploded diagram. A number that is enclosed
by a circle indicates a disassembly step.
3. An explanation of jobs and notes is presented in an easy-to-read way by the use of symbol marks
6. The meanings of the symbol marks are given on the next page.
4. A job instruction chart 7 accompanies the exploded diagram, providing the order of jobs, names
of parts, notes in jobs, etc.
5. For jobs requiring more information, the step-by-step format supplements 8 are given in addition
to the exploded diagram and the job instruction chart.
12
GEN
INFO
34
SPEC
CHK
ENG
ADJ
56
COOL
78
CARB
EB003000
ILLUSTRATED SYMBOLS
Illustrated symbols 1 to 0 are printed on the
top right of each page and indicate the subject
of each chapter.
1 General information
2 Specifications
3 Periodic checks and adjustments
4 Engine
5 Cooling system
6 Carburetion
7 Drive train
8 Chassis
9 Electrical
0 Troubleshooting
DRIV
90
–+
ELEC
AB
CD
EF
T
.
R
.
GH
CHAS
TRBL
SHTG
Illustrated symbols A to H are used to identify
the specifications appearing in the text.
A Can be serviced with engine mounted
B Filling fluid
C Lubricant
D Special tool
E Torque
F Wear limit, clearance
G Engine speed
Ω, V, A
H
IJK
LS
G
M
M
New
E
LMN
B
OP
LT
Illustrated symbols I to N in the exploded
diagrams indicate the types of lubricants and
lubrication points.
I Apply engine oil
J Apply gear oil
K Apply molybdenum disulfide oil
L Apply wheel bearing grease
M Apply lightweight lithium-soap base grease
N Apply molybdenum disulfide grease
Illustrated symbols O to P in the exploded
diagrams indicate where to apply a locking
agent O and when to install a new part P.
O Apply the locking agent (LOCTITE
P Replace
)

TABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL INFORMATION
SPECIFICATIONS
PERIODIC CHECKS AND
ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE
COOLING SYSTEM
GEN
INFO
SPEC
CHK
ADJ
ENG
COOL
1
2
3
4
5
CARBURETION
DRIVE TRAIN
CHASSIS
ELECTRICAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
CARB
DRIV
CHAS
–+
ELEC
TRBL
SHTG
6
7
8
9
10

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1.
GENERAL INFORMATION
MACHINE IDENTIFICATION
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER ................................................. 1-1
MODEL LABEL ...................................................................................... 1-1
FEATURES
FRONT DIFFERENTIAL ........................................................................ 1-2
TRANSMISSION ...................................................................................1-9
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
PREPARATION FOR REMOVAL PROCEDURES .............................1-10
REPLACEMENT PARTS ..................................................................... 1-10
GASKETS, OIL SEALS AND O-RINGS ..............................................1-10
LOCK WASHERS/PLATES AND COTTER PINS ............................... 1-11
BEARINGS AND OIL SEALS .............................................................. 1-11
CIRCLIPS ............................................................................................1-11
CHECKING OF CONNECTIONS
SPECIAL TOOLS
...................................................................................................1-2
........................................................................................1-13
........................................................................1-1
.....................................................................1-10
................................................................ 1-12
CHAPTER 2.
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
MAINTENANCE SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE .................................................................................................2-4
CHASSIS ............................................................................................. 2-14
ELECTRICAL ......................................................................................2-18
HOW TO USE THE CONVERSION TABLE
GENERAL TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
......................................................................2-1
............................................................. 2-4
............................................... 2-20
................................................... 2-20

LUBRICATION POINTS AND LUBRICANT TYPES .................................. 2-21
ENGINE ...............................................................................................2-21
COOLANT FLOW DIAGRAMS ................................................................... 2-22
OIL FLOW DIAGRAMS .............................................................................. 2-24
CABLE ROUTING ....................................................................................... 2-27
CHAPTER 3.
PERIODIC CHECKS AND ADJUSTMENTS
INTRODUCTION ...........................................................................................3-1
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE/LUBRICATION INTERVALS ..........................3-1
SEAT, CARRIERS, FENDERS AND FUEL TANK .......................................3-3
SEAT AND SIDE PANELS .................................................................... 3-3
FRONT CARRIER, FRONT BUMPER AND FRONT GRILL ................. 3-4
HANDLEBAR COVER, FUEL TANK COVER AND FRONT FENDER . 3-5
REAR CARRIER AND REAR FENDER ................................................ 3-7
ENGINE SKID PLATE (CENTER) AND ENGINE SKID PLATE
(REAR) ..............................................................................................3-9
FUEL TANK ......................................................................................... 3-10
FOOTREST BOARDS ................................................................................ 3-12
ENGINE ....................................................................................................... 3-13
ADJUSTING THE VALVE CLEARANCE ............................................ 3-13
ADJUSTING THE TIMING CHAIN ...................................................... 3-16
ADJUSTING THE IDLING SPEED ......................................................3-16
ADJUSTING THE THROTTLE LEVER FREE PLAY .......................... 3-17
ADJUSTING THE SPEED LIMITER .................................................... 3-19
ADJUSTING THE STARTER CABLE ................................................. 3-21
CHECKING THE SPARK PLUG ......................................................... 3-22
CHECKING THE IGNITION TIMING ................................................... 3-23
MEASURING THE COMPRESSION PRESSURE .............................. 3-24
CHECKING THE ENGINE OIL LEVEL ................................................ 3-26
CHANGING THE ENGINE OIL ...........................................................3-27
CLEANING THE AIR FILTER .............................................................. 3-29
CHECKING THE COOLANT LEVEL ...................................................3-31
CHANGING THE COOLANT ............................................................... 3-32
CHECKING THE COOLANT TEMPERATURE WARNING LIGHT ..... 3-36
CHECKING THE V-BELT ....................................................................3-36
CLEANING THE SPARK ARRESTER ................................................3-37

CHASSIS ....................................................................................................3-39
ADJUSTING THE REAR BRAKE ........................................................ 3-39
CHECKING THE BRAKE FLUID LEVEL ............................................. 3-41
CHECKING THE FRONT BRAKE PAD .............................................. 3-43
CHECKING THE REAR BRAKE PAD ................................................. 3-43
CHECKING THE BRAKE HOSE ......................................................... 3-43
BLEEDING THE HYDRAULIC BRAKE SYSTEM ............................... 3-44
ADJUSTING THE SELECT LEVER CONTROL CABLE
AND SHIFT ROD ............................................................................. 3-46
ADJUSTING THE REAR BRAKE LIGHT SWITCH ............................. 3-47
CHECKING THE FINAL GEAR OIL LEVEL ........................................ 3-48
CHANGING THE FINAL GEAR OIL ....................................................3-48
CHECKING THE DIFFERENTIAL GEAR OIL .....................................3-49
CHANGING THE DIFFERENTIAL GEAR OIL .................................... 3-50
CHECKING THE CONSTANT VELOCITY JOINT DUST BOOT ........ 3-51
CHECKING THE STEERING SYSTEM .............................................. 3-51
ADJUSTING THE TOE-IN ...................................................................3-51
ADJUSTING THE FRONT SHOCK ABSORBER ................................3-53
ADJUSTING THE REAR SHOCK ABSORBER .................................. 3-54
CHECKING THE TIRE ........................................................................ 3-54
CHECKING THE WHEEL .................................................................... 3-56
CHECKING AND LUBRICATING THE CABLE ................................... 3-57
LUBRICATING THE LEVERS, PEDAL, ETC. ..................................... 3-57
ELECTRICAL .............................................................................................. 3-58
CHECKING THE BATTERY ................................................................ 3-58
CHECKING THE FUSE .......................................................................3-63
ADJUSTING THE HEADLIGHT BEAM ............................................... 3-65
CHANGING THE HEADLIGHT BULB ................................................. 3-65
CHAPTER 4.
ENGINE
ENGINE REMOVAL ...................................................................................... 4-1
AIR DUCTS, MUFFLER AND EXHAUST PIPE .................................... 4-1
SELECT LEVER UNIT AND COOLANT RESERVOIR ......................... 4-3
HOSES AND LEADS ............................................................................. 4-4
ENGINE MOUNTING BOLTS ...............................................................4-5
INSTALLING THE ENGINE ................................................................... 4-7
CYLINDER HEAD COVER ........................................................................... 4-8
REMOVING THE CYLINDER HEAD COVER .....................................4-10
CHECKING THE CYLINDER HEAD COVER ..................................... 4-10
CHECKING THE TAPPET COVER ..................................................... 4-11
INSTALLING THE CYLINDER HEAD COVER ................................... 4-11

ROCKER ARMS ......................................................................................... 4-12
REMOVING THE ROCKER ARM .......................................................4-14
CHECKING THE ROCKER ARM ........................................................ 4-14
INSTALLING THE ROCKER ARM ...................................................... 4-15
CAMSHAFT AND CYLINDER HEAD ......................................................... 4-16
REMOVING THE CAMSHAFT AND CYLINDER HEAD .....................4-18
CHECKING THE CAMSHAFT ............................................................. 4-19
CHECKING THE CAMSHAFT SPROCKET ........................................ 4-19
CHECKING THE DECOMPRESSION SYSTEM ................................. 4-19
CHECKING THE TIMING CHAIN GUIDE ........................................... 4-20
CHECKING THE TIMING CHAIN TENSIONER .................................. 4-20
CHECKING THE CYLINDER HEAD ................................................... 4-20
INSTALLING THE CAMSHAFT AND CYLINDER HEAD .................... 4-21
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS ............................................................... 4-24
REMOVING THE VALVE AND VALVE SPRING ................................4-25
CHECKING THE VALVE AND VALVE SPRING ................................. 4-26
INSTALLING THE VALVE AND VALVE SPRING ............................... 4-30
CYLINDER AND PISTON ........................................................................... 4-32
REMOVING THE PISTON ..................................................................4-33
CHECKING THE CYLINDER AND PISTON ....................................... 4-33
CHECKING THE PISTON RING ......................................................... 4-35
CHECKING THE PISTON PIN ............................................................ 4-36
INSTALLING THE PISTON ................................................................. 4-36
INSTALLING THE CYLINDER ............................................................ 4-37
RECOIL STARTER AND AC MAGNETO ................................................... 4-38
REMOVING THE AC MAGNETO ........................................................ 4-41
DISASSEMBLING THE RECOIL STARTER .......................................4-41
CHECKING THE AC MAGNETO ........................................................ 4-41
CHECKING THE STARTER CLUTCH ................................................ 4-42
CHECKING THE STARTER PULLEY ................................................. 4-43
CHECKING THE RECOIL STARTER ................................................. 4-43
ASSEMBLEING THE RECOIL STARTER ..........................................4-43
INSTALLING THE AC MAGNETO ...................................................... 4-44
BALANCER GEARS AND OIL PUMP GEARS .......................................... 4-47
REMOVING THE BALANCER DRIVE GEAR
AND BALANCER DRIVEN GEAR ................................................... 4-48
REMOVING THE BALANCER DRIVE GEAR
AND BUFFER BOSS ....................................................................... 4-48
CHECKING THE OIL PUMP DRIVE ................................................... 4-48

CHECKING THE BALANCER DRIVE ................................................. 4-49
INSTALLING THE BALANCER DRIVE GEAR
AND BALANCER DRIVEN GEAR ................................................... 4-49
PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SHEAVES ................................................. 4-51
PRIMARY SHEAVE ............................................................................. 4-53
SECONDARY SHEAVE ...................................................................... 4-54
REMOVING THE PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SHEAVES ............. 4-55
DISASSEMBLING THE SECONDARY SHEAVE ................................4-55
CHEKING THE PRIMARY SHEAVE ................................................... 4-56
CHECKING THE SECONDARY SHEAVE .......................................... 4-56
ASSEMBLING THE PRIMARY SHEAVE ............................................ 4-57
ASSEMBLING THE SECONDARY SHEAVE ......................................4-57
INSTALLING THE PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SHEAVES ............ 4-59
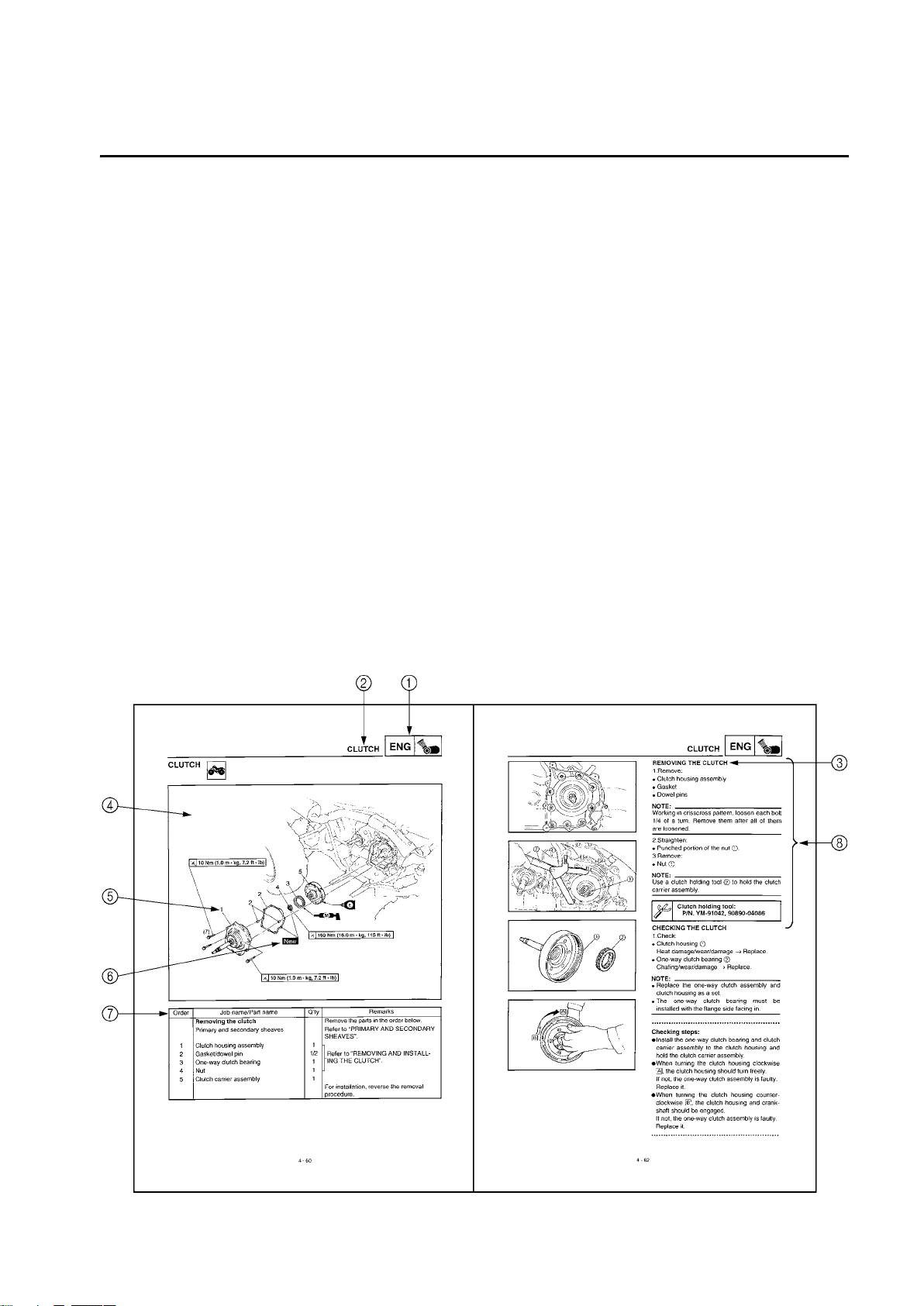
CLUTCH ...................................................................................................... 4-60
REMOVING THE CLUTCH ................................................................. 4-62
CHECKING THE CLUTCH ..................................................................4-62
INSTALLING THE CLUTCH ................................................................4-63
CRANKCASE ..............................................................................................4-65
STARTER MOTOR, TIMING CHAIN AND OIL FILTER ...................... 4-65
CRANKCASE ......................................................................................4-67
CRANKCASE BEARING ..................................................................... 4-68
SEPARATING THE CRANKCASE ...................................................... 4-69
CHECKING THE TIMING CHAIN AND GUIDE ................................... 4-69
CHECKING THE OIL DELIVERY PIPE ............................................... 4-69
CHECKING THE CRANKCASE .......................................................... 4-70
CHECKING THE BEARINGS .............................................................. 4-70
ASSEMBLING THE CRANKCASE ...................................................... 4-70
INSTALLATING THE SHIFT LEVER ................................................... 4-71
CRANKSHAFT AND OIL PUMP ................................................................ 4-72
OIL PUMP ........................................................................................... 4-73
REMOVING THE CRANKSHAFT .......................................................4-74
CHECKING THE OIL PUMP ............................................................... 4-74
CHECKING THE RELIEF VALVE ....................................................... 4-75
CHECKING THE OIL STRAINER .......................................................4-75
ASSEMBLING THE OIL PUMP ...........................................................4-75
CHECKING THE CRANKSHAFT ........................................................ 4-76
INSTALLING THE CRANKSHAFT AND BALANCER ......................... 4-77

TRANSMISSION .........................................................................................4-78
REMOVING THE TRANSMISSION ....................................................4-81
CHECKING THE SHIFT FORK ........................................................... 4-81
CHECKING THE SHIFT CAM ............................................................. 4-82
CHECKING THE DRIVE AXLE ...........................................................4-82
CHECKING THE HIGH WHEEL GEAR
AND MIDDLE DRIVE GEAR ........................................................... 4-82
CHECKING THE SECONDARY SHAFT
AND DRIVEN SPROCKET .............................................................. 4-83
CHECKING THE CHAIN ..................................................................... 4-83
CHECKING THE STOPPER LEVER
AND STOPPER WHEEL ................................................................. 4-83
ASSEMBLING THE SHIFT FORK ASSEMBLY ..................................4-84
INSTALLING THE TRANSMISSION .................................................... 4-84
MIDDLE GEAR ...........................................................................................4-85
MIDDLE DRIVE SHAFT ...................................................................... 4-85
MIDDLE DRIVEN SHAFT .................................................................... 4-86
REMOVING THE MIDDLE DRIVE SHAFT ......................................... 4-88
REMOVING THE MIDDLE DRIVEN SHAFT ....................................... 4-88
CHECKING THE PINION GEAR ......................................................... 4-91
MIDDLE DRIVE AND DRIVEN GEAR SHIM SELECTION ................. 4-91
INSTALLING THE MIDDLE DRIVEN SHAFT ..................................... 4-94
INSTALLING THE MIDDLE DRIVE SHAFT ........................................ 4-96
MEASURING THE MIDDLE GEAR BACKLASH ................................. 4-97
CHAPTER 5.
COOLING SYSTEM
RADIATOR .................................................................................................... 5-1
CHECKING THE RADIATOR ................................................................5-3
INSTALLING THE RADIATOR ..............................................................5-4
THERMOSTAT ..............................................................................................5-5
CHECKING THE THERMOSTAT .......................................................... 5-6
INSTALLING THE THERMOSTAT ........................................................ 5-6
WATER PUMP ..............................................................................................5-7
DISASSEMBLING THE WATER PUMP ................................................ 5-9
CHECKING THE WATER PUMP .......................................................... 5-9
ASSEMBLING THE WATER PUMP .................................................... 5-10

CHAPTER 6.
CARBURETION
CARBURETOR
DISASSEMBLING THE CARBURETOR ...............................................6-4
CHECKING THE CARBURETOR ......................................................... 6-4
ASSEMBLING THE CARBURETOR .....................................................6-6
ADJUSTING THE FUEL LEVEL ............................................................ 6-7
.............................................................................................6-1
CHAPTER 7.
DRIVE TRAIN
TROUBLESHOOTING
FRONT CONSTANT VELOCITY JOINTS
AND DIFFERENTIAL GEAR
DISASSEMBLING THE UNIVERSAL JOINT ........................................ 7-9
REMOVING THE RING GEAR ............................................................ 7-10
CHECKING THE CONSTANT VELOCITY JOINT .............................. 7-10
CHECKING THE DIFFERENTIAL GEAR ............................................ 7-10
CHECKING THE GEAR MOTOR ........................................................7-11
ASSEMBLING THE FRONT CONSTANT VELOCITY JOINT ............. 7-11
ASSEMBLING THE DIFFERENTIAL GEAR ....................................... 7-12
INSTALLING THE UNIVERSAL JOINT ............................................... 7-14
MEASURING AND ADJUSTING
THE DIFFERENTIAL GEAR LASH ................................................. 7-15
CHECKING THE DIFFERENTIAL GEAR OPERATION ..................... 7-17
..................................................................................7-1
.................................................................... 7-4
REAR CONSTANT VELOCITY JOINT/FINAL DRIVE GEAR
AND DRIVE SHAFT
ASSEMBLING THE REAR CONSTANT VELOCITY JOINT ............... 7-22
REMOVING AND DISASSEMBLING
THE FINAL DRIVE ROLLER BEARING ..........................................7-23
POSITIONING THE FINAL DRIVE PINION GEAR
AND RING GEAR ............................................................................ 7-24
CHECKING THE DRIVE SHAFT ......................................................... 7-29
CHECKING THE FINAL DRIVE GEAR ............................................... 7-29
MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTING THE FINAL GEAR LASH ..........7-30
ASSEMBLING THE FINAL DRIVE GEAR ........................................... 7-32
INSTALLING THE FINAL DRIVE GEAR ............................................. 7-32
................................................................................7-18

CHAPTER 8.
CHASSIS
FRONT WHEELS AND BRAKE DISCS
FRONT WHEELS .................................................................................. 8-1
CHECKING THE FRONT WHEEL ........................................................ 8-3
CHECKING THE FRONT WHEEL HUB ................................................ 8-3
CHECKING THE FRONT BRAKE DISC ............................................... 8-4
INSTALLING THE FRONT WHEEL HUB .............................................. 8-4
INSTALLING THE FRONT WHEEL ...................................................... 8-4
REAR WHEELS AND BRAKE DISC
REAR WHEELS ....................................................................................8-6
REAR BRAKE DISC .............................................................................. 8-7
CHECKING THE REAR WHEEL ........................................................... 8-8
CHECKING THE REAR WHEEL HUB .................................................. 8-8
CHECKING THE REAR BRAKE DISC .................................................. 8-8
INSTALLING THE REAR WHEEL HUB ................................................ 8-9
INSTALLING THE REAR WHEEL ......................................................... 8-9
FRONT AND REAR BRAKES
FRONT BRAKE PADS ........................................................................ 8-10
REAR BRAKE PADS ........................................................................... 8-11
REPLACING THE FRONT BRAKE PAD .............................................8-12
REPLACING THE REAR BRAKE PAD ............................................... 8-14
FRONT BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER ................................................ 8-16
REAR BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER ..................................................8-18
CHECKING THE MASTER CYLINDER .............................................. 8-21
ASSEMBLING THE FRONT BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER ............... 8-22
ASSEMBLING THE REAR BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER ..................8-22
INSTALLING THE FRONT BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER .................. 8-23
INSTALLING THE REAR BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER .................... 8-24
FRONT BRAKE CALIPER ................................................................... 8-26
REAR BRAKE CALIPER ..................................................................... 8-28
DISASSEMBLING THE BRAKE CALIPER ......................................... 8-30
DISASSEMBLING THE REAR BRAKE CALIPER .............................. 8-30
CHECKING THE FRONT AND REAR BRAKE CALIPER ................... 8-31
ASSEMBLING THE FRONT BRAKE CALIPER .................................. 8-32
INSTALLING THE FRONT BRAKE CALIPER .................................... 8-32
ASSEMBLING THE REAR BRAKE CALIPER .................................... 8-34
INSTALLING THE REAR BRAKE CALIPER ....................................... 8-35
....................................................................8-10
....................................................... 8-1
............................................................ 8-6

STEERING SYSTEM .................................................................................. 8-36
HANDLEBAR ....................................................................................... 8-36
REMOVING THE REAR BRAKE SWITCH ......................................... 8-37
CHECKING THE HANDLEBAR ..........................................................8-37
INSTALLING THE HANDLEBAR ........................................................8-37
INSTALLING THE REAR BRAKE LEVER .......................................... 8-37
INSTALLING THE MASTER CYLINDER ASSEMBLY ........................ 8-38
STEERING STEM ............................................................................... 8-39
REMOVING THE BEARING RETAINER ............................................ 8-41
CHECKING THE STEERING STEM ................................................... 8-41
INSTALLING THE BEARING RETAINER ........................................... 8-41
INSTALLING THE STEERING STEM ................................................. 8-41
INSTALLING THE CABLE GUIDE ...................................................... 8-42
TIE ROD AND STEERING KNUCKLE ................................................ 8-43
REMOVING THE STEERING KNUCKLE ........................................... 8-44
CHECKING THE TIE ROD ..................................................................8-44
CHECKING THE STEERING KNUCKLE ............................................ 8-44
CHECKING THE BALL JOINT ............................................................ 8-45
CHECKING THE TIE ROD ..................................................................8-45
FRONT ARMS AND FRONT SHOCK ABSORBER ................................... 8-46
REMOVING THE FRONT ARMS ........................................................ 8-48
CHECKING THE FRONT ARM ........................................................... 8-48
CHECKING THE FRONT SHOCK ABSORBER ................................. 8-48
INSTALLING THE FRONT ARMS
AND FRONT SHOCK ABSORBER .................................................8-49
REAR KNUCKLE AND STABILIZER ......................................................... 8-50
CHECKING THE REAR KNUCKLE .................................................... 8-51
CHECKING THE STABILIZER ............................................................8-51
REAR ARMS AND REAR SHOCK ABSORBER ....................................... 8-52
CHECKING THE REAR ARM .............................................................8-53
CHECKING THE REAR SHOCK ABSORBER .................................... 8-53
CHECKING THE REAR ARMS
AND REAR SHOCK ABSORBER ................................................... 8-53

CHAPTER 9.
ELECTRICAL
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
CHECKING THE SWITCH
CHECKING THE SWITCH .................................................................... 9-2
CHECKING A SWITCH SHOWN IN THE MANUAL ............................. 9-2
CHECKING THE SWITCH CONTINUITY ............................................. 9-4
CHECKING THE BULBS AND BULB SOCKETS
TYPES OF BULBS ................................................................................ 9-6
CHECKING THE CONDITION OF THE BULBS ................................... 9-6
CHECKING THE CONDITION OF THE BULB SOCKETS ................... 9-8
CHECKING THE LEDs .......................................................................... 9-8
IGNITION SYSTEM
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM .............................................................................. 9-9
TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................................................9-10
ELECTRIC STARTING SYSTEM
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ............................................................................ 9-15
STARTING CIRCUIT OPERATION ..................................................... 9-16
TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................................................9-17
.......................................................................................9-9
..................................................................... 9-1
............................................................................9-2
........................................ 9-6
............................................................... 9-15
STARTER MOTOR ............................................................................. 9-21
CHECKING THE STARTER MOTOR ................................................. 9-22
ASSEMBLING THE STARTER MOTOR .............................................9-23
CHARGING SYSTEM
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ............................................................................ 9-24
TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................................................9-25
LIGHTING SYSTEM
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ............................................................................ 9-27
TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................................................9-28
CHECKING THE LIGHTING SYSTEM ................................................ 9-30
SIGNAL SYSTEM
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ............................................................................ 9-32
TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................................................9-34
CHECKING THE SIGNAL SYSTEM ...................................................9-36
.................................................................................9-24
....................................................................................9-27
.......................................................................................9-32
9-21

COOLING SYSTEM ....................................................................................9-47
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ............................................................................ 9-47
TROUBLESHOOTING ....................................................................... 9-48
2WD/4WD SELECTING SYSTEM .............................................................. 9-52
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ............................................................................ 9-52
TROUBLESHOOTING ........................................................................9-53
CHAPTER 10.
TROUBLESHOOTING
STARTING FAILURE/HARD STARTING ................................................... 10-1
FUEL SYSTEM .................................................................................... 10-1
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM ....................................................................... 10-1
COMPRESSION SYSTEM .................................................................. 10-2
POOR IDLE SPEED PERFORMANCE ......................................................10-2
POOR IDLE SPEED PERFORMANCE ............................................... 10-2
POOR MEDIUM AND HIGH-SPEED PERFORMANCE ............................. 10-2
POOR MEDIUM AND HIGH-SPEED PERFORMANCE ..................... 10-2
FAULTY DRIVE TRAIN .............................................................................. 10-3
FAULTY GEAR SHIFTING ......................................................................... 10-4
HARD SHIFTING ................................................................................. 10-4
SHIFT LEVER DOES NOT MOVE ...................................................... 10-4
JUMPS OUT OF GEAR ....................................................................... 10-4
FAULTY CLUTCH PERFORMANCE .........................................................10-4
ENGINE OPERATES BUT MACHINE WILL NOT MOVE ...................10-4
CLUTCH SLIPPING ............................................................................ 10-4
POOR STARTING PERFORMANCE ..................................................10-4
POOR SPEED PERFORMANCE ........................................................10-5
OVERHEATING .......................................................................................... 10-5
OVERHEATING ..................................................................................10-5
FAULTY BRAKE .........................................................................................10-5
POOR BRAKING EFFECT ..................................................................10-5

SHOCK ABSORBER MALFUNCTION ....................................................... 10-6
MALFUNCTION ...................................................................................10-6
UNSTABLE HANDLING ............................................................................. 10-6
UNSTABLE HANDLING ...................................................................... 10-6
LIGHTING SYSTEM ....................................................................................10-6
HEADLIGHT DARK ............................................................................. 10-6
BULB BURNT OUT ............................................................................. 10-6
MACHINE IDENTIFICATION
GENERAL INFORMATION
MACHINE IDENTIFICATION
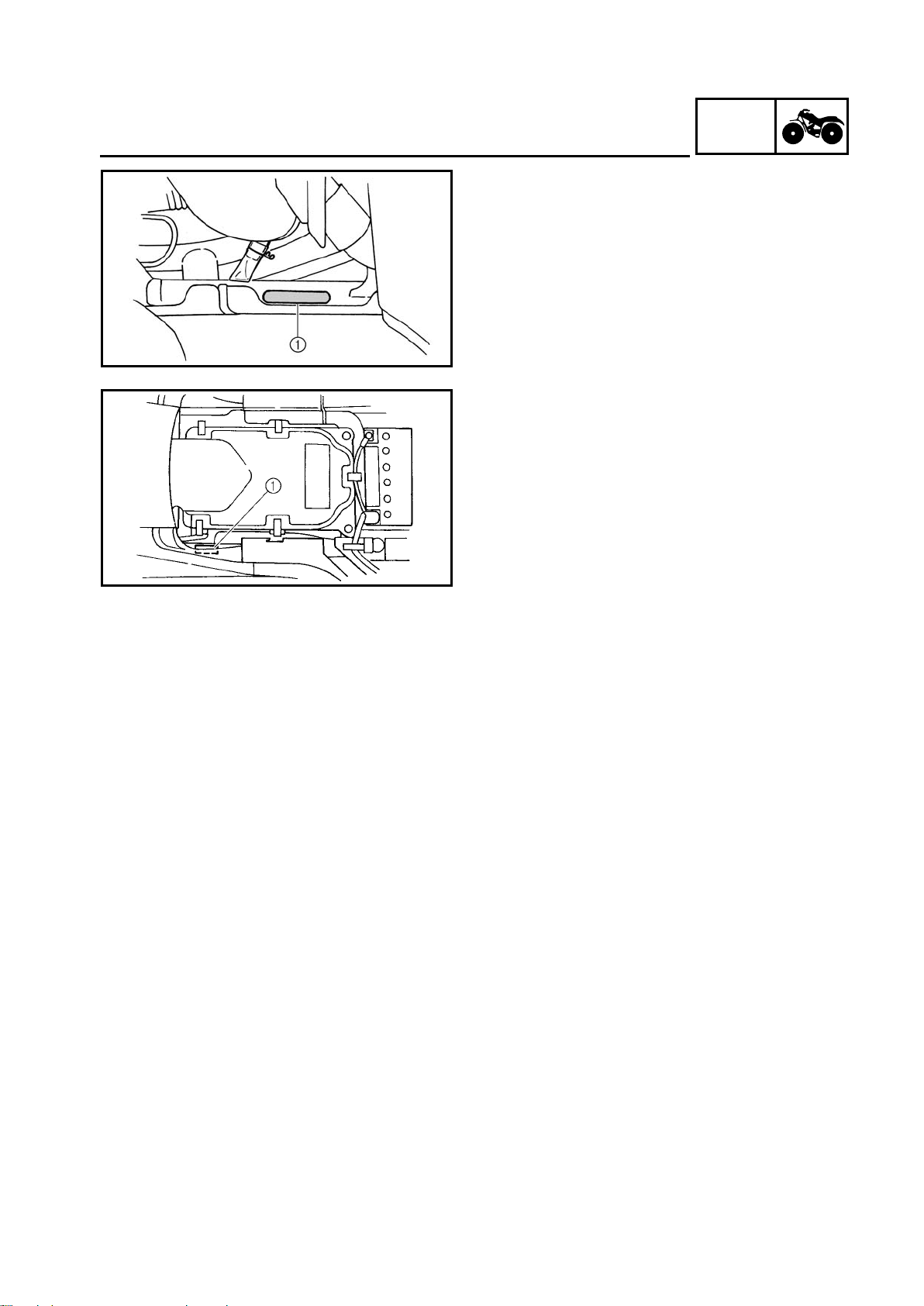
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
The vehicle identification number 1 is
stamped into the left side of the frame.
MODEL LABEL
The model label 1 is affixed to the frame. This
information will be needed to order spare
parts.
GEN
INFO
1 - 1
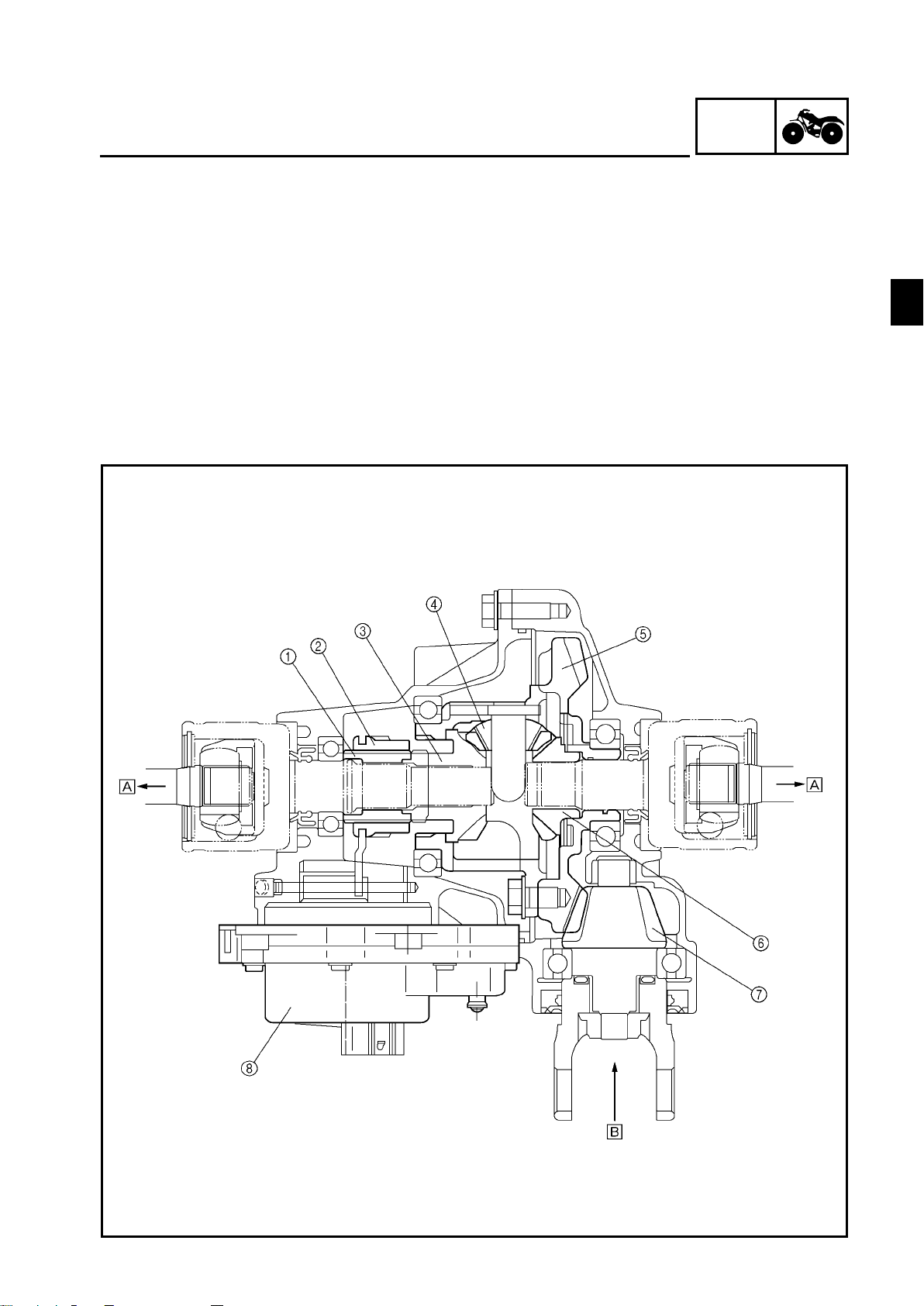
FEATURES
FRONT DIFFERENTIAL
1 Adapter
2 Drive clutch
3 Differential side gear (left)
4 Differential pinion gear
5 Ring gear
6 Differential side gear (right)
FEATURES
7 Drive pinion gear
8 Gear motor
È To front wheel
É From the middle gear
GEN
INFO
1
1 - 2
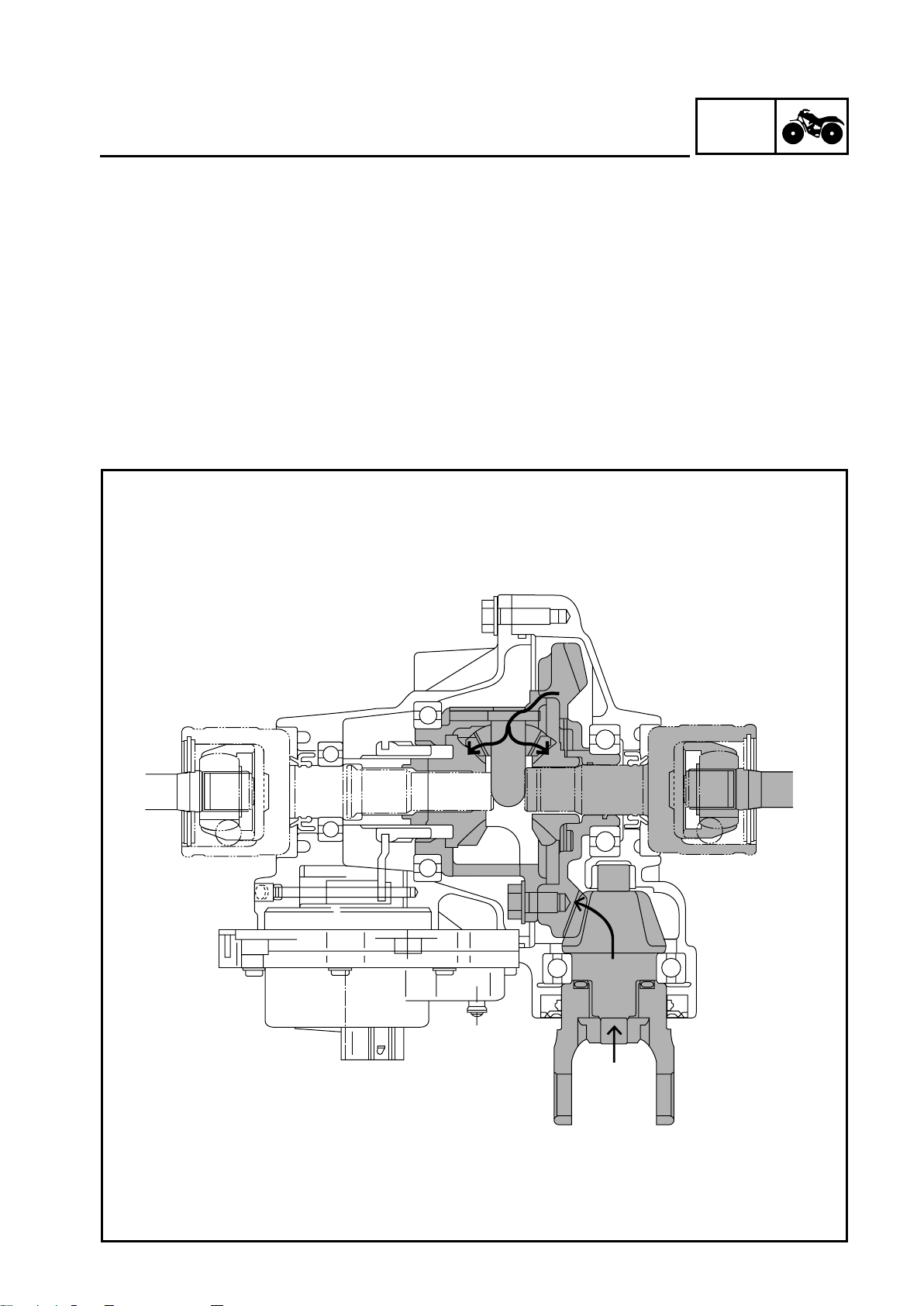
GEN
FEATURES
2WD
Power is transmitted as follows: middle gear → front drive shaft → drive pinion gear 7 → ring gear
5 → differential pinion gear 4. In the 2WD mode, the left differential side gear 3 and the drive
clutch 2 are not engaged, therefore, the left side gear runs idle and does not transmit power to the
left front constant velocity joint.
INFO
1 - 3

GEN
FEATURES
4WD
When the 4WD mode is selected, the gear motor is operated, and the drive clutch 2 moves to the
right and engages with the left differential side gear 3. Accordingly, power is transmitted as follows:
ring gear 5 → differential pinion gear 4 → left differential side gear 3 → drive clutch 2 → adapter
1 → left front constant velocity joint.
Meanwhile, power from the differential pinion gear 4 is transmitted to the right front constant velocity joint via the right differential side gear 6.
The ring gear 5 and the drive clutch 2 are not engaged at this time. Therefore, the rotational difference that occurs between the right and left wheels, while the handlebar is being turned, is absorbed
by the difference in the rotational speeds of the ring gear 5 and the left differential side gear 3.
INFO
1 - 4
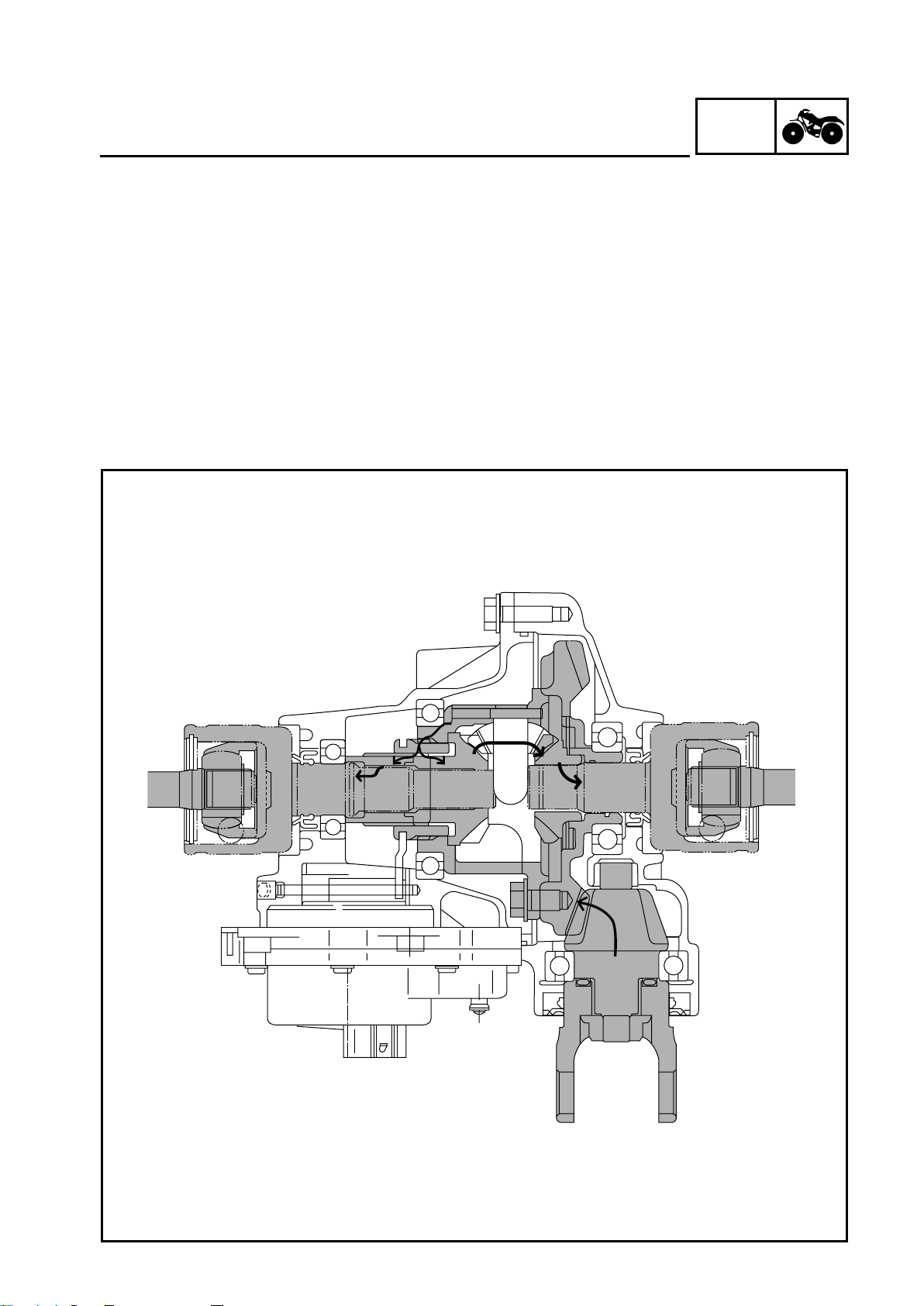
GEN
FEATURES
4WD (Diff-Lock)
When the 4WD (Diff-Lock) mode is selected, the gear motor moves the drive clutch 2 further to the
right, which causes the ring gear 5 and the drive clutch 2 to engage. As a result, power is transmitted directly from the ring gear 5 to the drive clutch 2, then to the left front constant velocity joint via
the adapter 1.
Meanwhile, because the ring gear 5 and the drive clutch 2 are engaged, the ring gear 5, the drive
clutch 2, and the right differential side gear 6 become locked coaxially. Thus, power is transmitted
as follows: differential pinion gear 4 → right differential pinion gear 6 → right front constant velocity joint.
When the ATV is in the 4WD (Diff-Lock) mode, the right and left wheels rotate constantly at the
same speed, which affects the maneuverability of the ATV (e.g., making it difficult to steer). Therefore, the maximum traveling speed is limited to 35 km/h (22 mph).
INFO
1 - 5

GEN
FEATURES
In addition, the 4WD (Diff-Lock) mode can be engaged only when the ATV is stopped. Even if an
attempt is made to select this mode when the ATV is traveling, it will only result in a standby condition (i.e., when the differential lock select switch and the differential gear are not matched).
(1) When the ATV is traveling
Even if the 4WD (Diff-Lock) mode is selected, the gear motor will stand by, instead of operating.
Therefore, the ATV can be driven in the normal 4WD mode. When this occurs, the differential gear
lock indicator light “ ” in the speedometer unit will flash to alert the driver that the control is on
standby. When the ATV is stopped, the control transfers to the condition described in (2).
(2) When the ATV is stopped
The gear motor operates to connect the drive clutch to the differential case, thus resulting in the
differential lock condition. When this occurs, the differential gear lock indicator light “ ” in the
speedometer unit changes to a constant illumination.
* Until the drive clutch and the differential case mesh together (i.e., the splines are unmeshed) the
engine misfires to control the engine speed. During this time, the differential gear lock indicator light
in the speedometer unit continues to flash.
DIFF.
LOCK
INFO
DIFF.
LOCK
1 - 6
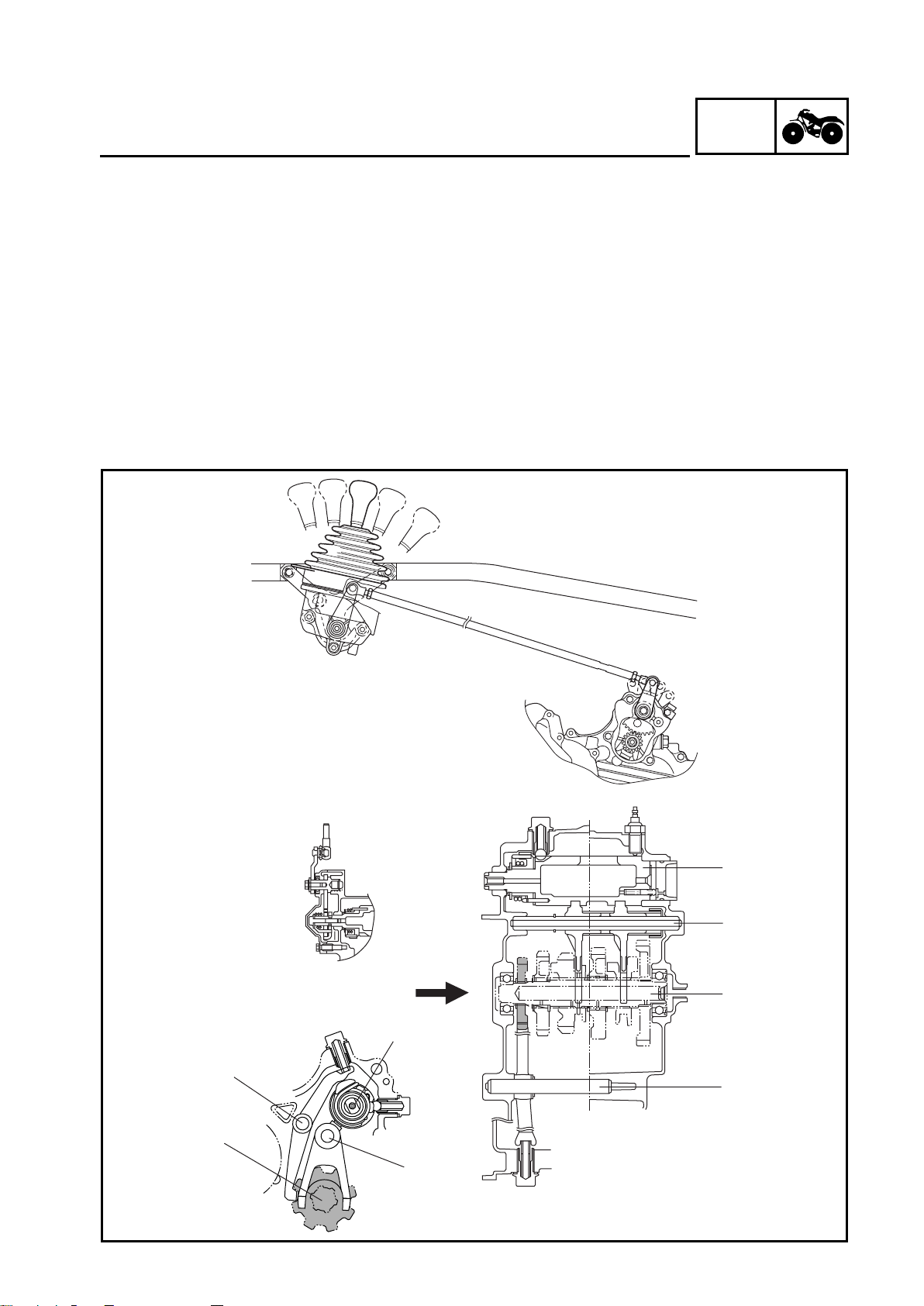
FEATURES
Shift mechanism
A new shift mechanism with a parking position has been added to the YFM660F.
1.Shift cam
2.Shift fork guide bar
3.Drive axle
4.Stopper lever shaft
H
L
N
R
P
GEN
INFO
H
N
L
R
P
1
2
3
1
4
4
3
2
1 - 7
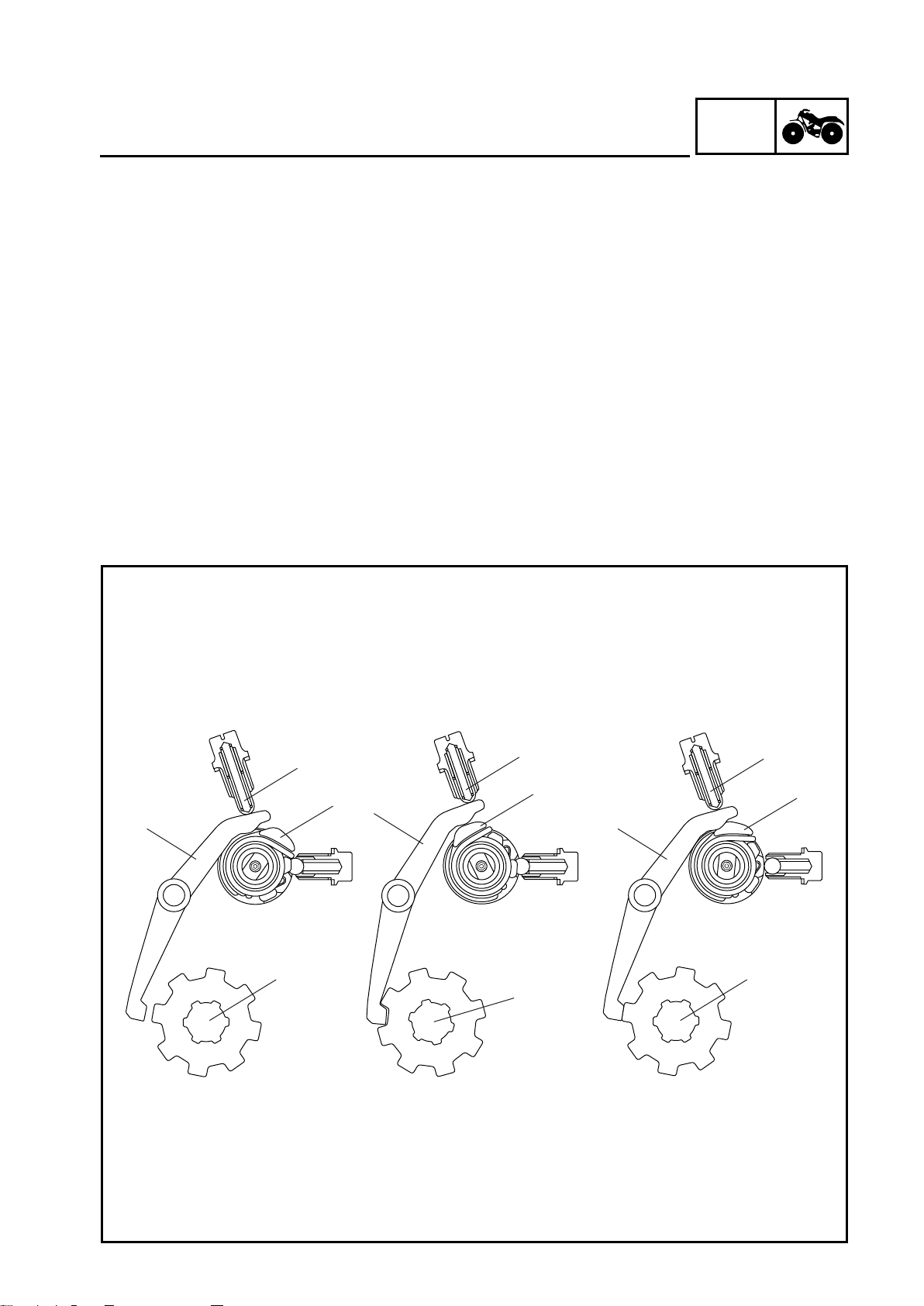
GEN
FEATURES
Parking
(1) L (Low), H (High), N (Neutral), and R (Reverse) positions
The end of the stopper lever is held by the return spring 1. Then, the stopper lever tab is sepa-
rated from the drive axle stopper to free the drive axle.
(2) P (Park) position
When the drive select lever is shifted to the “P” position, the cam lever of the shift cam pushes
up on the end of the stopper lever. Then, the stopper lever tab pushes against the drive axle
stopper to lock the drive axle.
(3) Not synchronized
If the stopper lever tab and the drive axle stopper are not synchronized, the torsion spring is
compressed. As a result, the spring pushes the stopper lever tab against the drive axle stopper
and waits until the synchronization is completed. When the stop lever tab and the drive axle are
synchronized, the stop lever tab pushes against the drive axle stopper in order to lock the drive
axle.
1 Stopper lever
2 Return spring
3Shift cam
4Drive axle
INFO
2
3
1
4
(1) (2) (3)
1
2
3
1
4
2
3
4
1 - 8
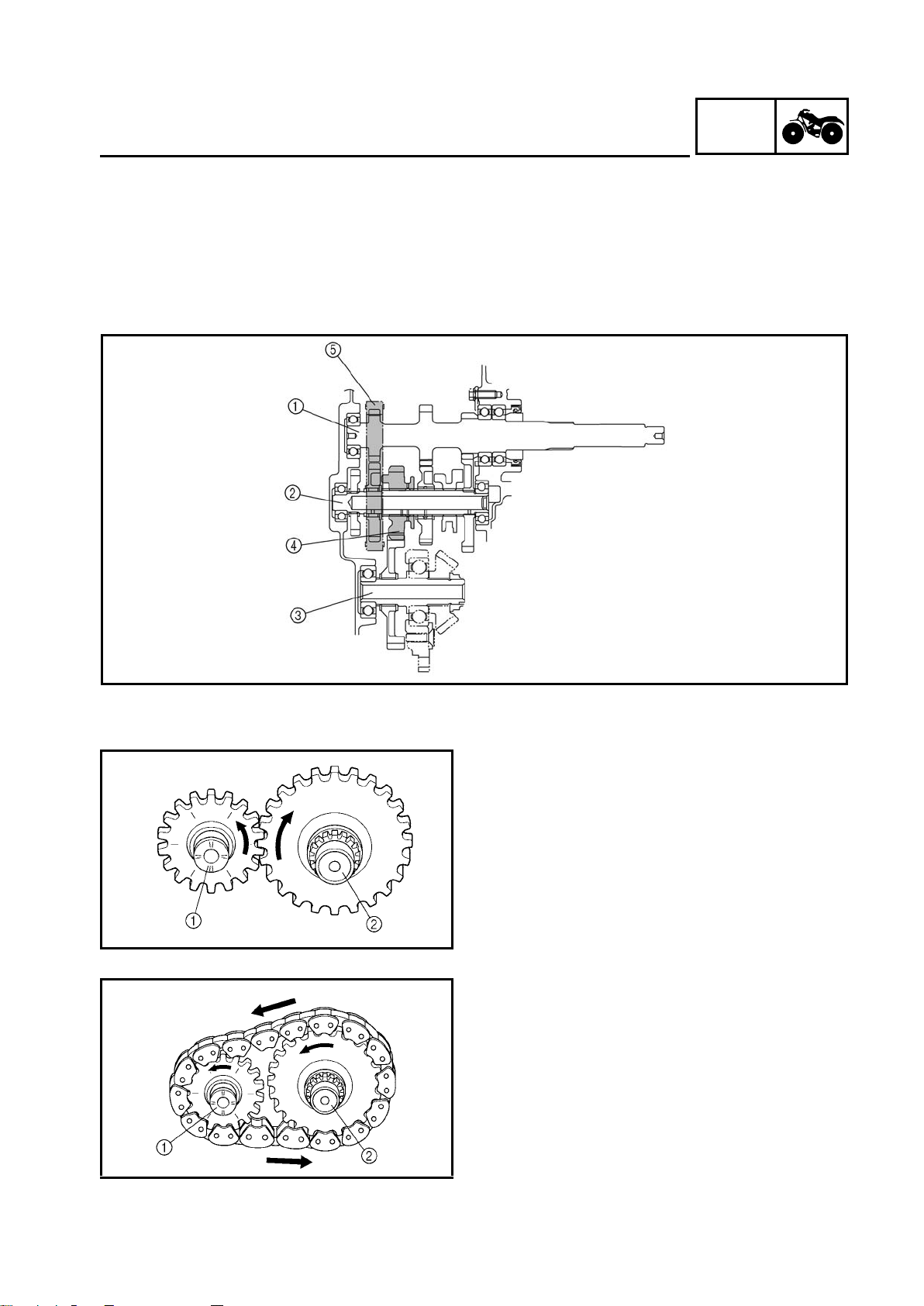
GEN
FEATURES
TRANSMISSION
To create a compact, 3-axle transmission, a chain drive has been adopted for the reverse transmission.
1 Secondary shaft
2 Drive axle
3 Middle drive shaft
4 Low wheel gear
5 Chain
INFO
1 Secondary shaft
2 Drive axle
L (Low) or H (High) mode
When the transmission is in either the low or
high mode, the drive axle is driven via the secondary shaft and gear. Therefore, the rotation
of the drive axle is the opposite of the secondary shaft.
R (Reverse) mode
When the transmission is in the reverse mode,
the drive axle is driven via the drive chain.
Therefore, the rotation of the drive axle is the
same as the secondary shaft. (As a result, the
rotation of the drive axle is opposite to that of
the low and high modes.)
1 - 9

IMPORTANT INFORMATION
EB101000
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
PREPARATION FOR REMOVAL
PROCEDURES
1.Remove all dirt, mud, dust and foreign material before removal and disassembly.
2.Use proper tools and cleaning equipment.
Refer to the “SPECIAL TOOLS” section.
3.When disassembling the machine, always
keep mated parts together. This includes
gears, cylinder, piston and other parts that
have been “mated” through normal wear.
Mated parts must always be reused or
replaced as an assembly.
4.During machine disassembly, clean all parts
and place them in trays in the order of disassembly. This will speed up assembly and
allow for the correct installation of all parts.
5.Keep all parts away from any source of fire.
GEN
INFO
EB101010
REPLACEMENT PARTS
1.Use only genuine Yamaha parts for all
replacements. Use oil and grease recommended by Yamaha for all lubrication jobs.
Other brands may be similar in function and
appearance, but inferior in quality.
EB101020
GASKETS, OIL SEALS AND O-RINGS
1.Replace all gaskets, seals and O-rings when
overhauling the engine. All gasket surfaces,
oil seal lips and O-rings must be cleaned.
2.Properly oil all mating parts and bearings
during reassembly. Apply grease to the oil
seal lips.
1 - 10

IMPORTANT INFORMATION
EB101030
LOCK WASHERS/PLATES AND COTTER
PINS
1.Replace all lock washers/plates 1 and cotter
pins after removal. Bend lock tabs along the
bolt or nut flats after the bolt or nut has been
tightened to specification.
EB101040
BEARINGS AND OIL SEALS
1.Install bearings and oil seals so that the
manufacturer’s marks or numbers are visible.
When installing oil seals, apply a light coating of lightweight lithium base grease to the
seal lips. Oil bearings liberally when installing, if appropriate.
1 Oil seal
GEN
INFO
CAUTION:
Do not use compressed air to spin the
bearings dry. This will damage the bearing
surfaces.
1 Bearing
EB101050
CIRCLIPS
1.Check all circlips carefully before reassembly. Always replace piston pin clips after one
use. Replace distorted circlips. When installing a circlip 1, make sure that the sharpedged corner 2 is positioned opposite the
thrust 3 it receives. See sectional view.
4 Shaft
1 - 11
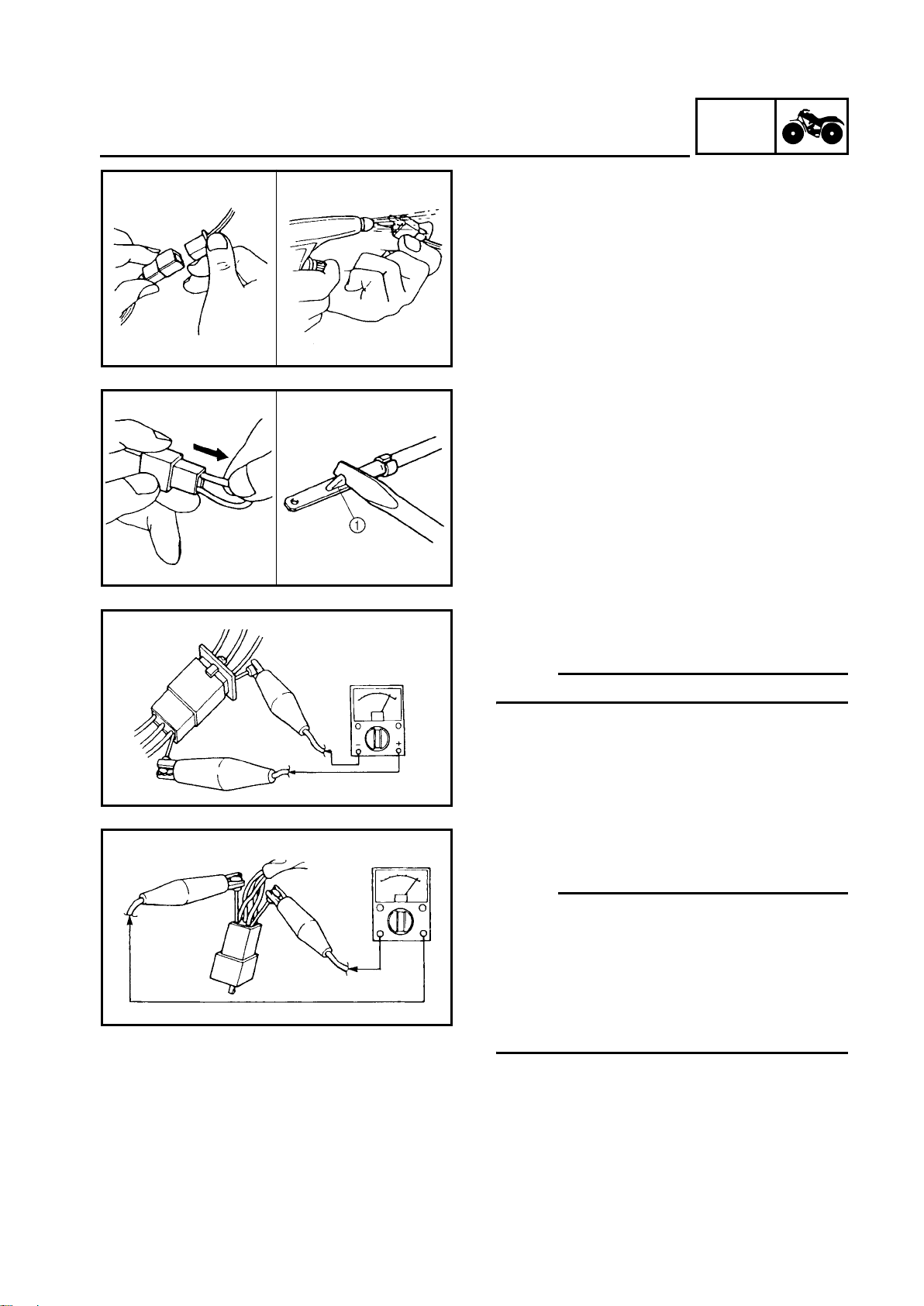
CHECKING OF CONNECTIONS
EB801000
CHECKING OF CONNECTIONS
Check the connectors for stains, rust, moisture, etc.
1.Disconnect:
Connector
●
2.Check:
Connector
●
Moisture → Dry each terminal with an air
blower.
Stains/rust → Connect and disconnect the
terminals several times.
3.Check:
Connector leads
●
Looseness → Bend up the pin 1 and connect the terminals.
GEN
INFO
4.Connect:
Connector terminals
●
OTE:
The two terminals “click” together.
5.Check:
Continuity (using a pocket tester)
●
OTE:
If there is no continuity, clean the terminals.
●
When checking the wire harness be sure to
●
perform steps 1 to 3.
As a quick remedy, use a contact revitalizer
●
available at most part stores.
Check the connector with a pocket tester as
●
shown.
1 - 12
 Loading...
Loading...