Yamaha RCX40 User Manual
User’s Manual
ENGLISH
E
YAMAHA 4-AXIS ROBOT CONTROLLER
E75-Ver. 12.00
RCX40


1
2
Introduction
Our sincere thanks for your purchase of this YAMAHA robot controller.
This manual explains how to install and operate the robot controller. Be sure to read this
manual carefully as well as related manuals and comply with their instructions for using
the YAMAHA robot controllers safely and correctly.
For details on robot programs, refer to the separate “Programming Manual”.

2
2
Safety precautions (Be sure to read before using)
Before using the YAMAHA robot controller, be sure to read this manual and related manuals, and follow their instructions to use the robot controller safely and correctly.
Warning and caution items listed in this manual relate to YAMAHA robot controllers.
When this robot controller is used in a robot controller system, please take appropriate
safety measures needed by the user’s individual system.
This manual classifies safety caution items and operating points into the following levels,
along with symbols for “WARNING”, “CAUITON” and “NOTE”.
w
WARNING
Failure to follow WARNING instructions could result in severe injury or death to the
operator, bystanders or persons inspecting or repairing the robot controller or robot.
c
CAUTION
Failure to follow CAUTION instructions may result in injury to the operator, bystanders or persons
inspecting or repairing the robot controller or robot, and may damage the robot controller or robot.
n
NOTE
Explains the key point in the operation in a simple and clear manner.
Note that the items classified into “CAUTION” might result in serious injury depending
on the situation or environmental conditions. So always comply with the CAUTION and
WARNING instructions as these are essential for safety.
Keep this manual carefully so that the operator can refer to it when needed. Also make
sure that this manual reaches the end user.
When installing the RCX40 robot controller, please take into account all the instructions
and precautions described in Chapter 3, "Installation".

3
2
[System design safety points]
w
WARNING
• Refer to this manual for details on the operating status of the robot controller and
related instruction manuals.
Design and configure the system including the robot controller so that it will
always work safely.
• The robot controller has an emergency stop terminal to trigger emergency stop.
Using this terminal, prepare a physical interlock circuit so that the system
including the robot controller will work safely.
c
CAUTION
• Do not bundle control lines or communication cables together or in close contact with the
robot controller main circuit or power lines. As a general rule, separate them by at least
100mm. Noise in the main circuit or power lines may cause faulty operation or malfunctions.
• Data (programs, point data, etc.) stored in the robot controller is not guaranteed to be
unchanged, so be sure to save it into an external storage device.
[Installation safety points]
w
WARNING
• Securely install the connectors into the robot controller, and when wiring the
connectors, make the crimp, press-contact or solder connections correctly, using
the tool specified by the manufacturer.
• Always shut off all phases of the power supply externally before starting
installation or wiring work. Failure to shut off all phases could lead to electric
shocks or product damage.
c
CAUTION
• Use the robot controller within the environment specifications listed in this manual.
Using the controller in an environment outside the specification range could lead to electric
shocks, fires, malfunctions, product damage or deteriorated performance.
• Tighten the screws on the robot controller firmly to make secure connections.
• Never directly touch the conductive sections or electronic parts other than the rotary switches
and DIP switches on the outside panel of the robot controller.
• Securely install each connection cable connector into the receptacles or sockets.
Poor connections will cause faulty operation or malfunctions.
[Wiring safety points]
w
WARNING
• Always shut off all phases of the power supply externally before starting
installation or wiring work. Failure to shut off all phases could lead to electric
shocks or product damage.
• Always attach the terminal cover (supplied) before turning on the power to the
robot controller after installation and wiring work are complete. Failure to attach
the terminal cover could lead to fire, electrical shock, product damage or
malfunctions.
c
CAUTION
• Tighten the terminal screws within the specified torque range.
A loose terminal screw could lead to short-circuit, faulty operation or malfunctions. In
contrast, if the terminal screw is too tight, short-circuit, faulty operation or malfunctions could
also occur due to screw damage.
• Make sure that foreign matter, such as cutting chips or wire scraps, do not enter the robot
controller.
• Always store the cables connected to the robot controller in a conduit or clamp them securely
in place.
If the cables are not stored in a conduit or properly clamped, excessive play or movement, or
mistakenly pulling on the cable may damage the connector or cables, and poor cable contact
may lead to faulty operation or malfunctions.
• When disconnecting the cable, detach by holding the connector itself and not by tugging on the
cable. Loosen the screws on the connector (if fastened with the screws), and then disconnect
the cable.
Detaching by pulling on the cable itself may damage the connector or cables, and poor cable
contact may lead to faulty operation or malfunctions.

4
2
[Start-up and maintenance safety points]
w
WARNING
• When operating the robot, only personnel trained in safety and robot operation
may operate it.
• Never allow anyone to enter the robot movement range when the robot controller
is turned on. Serious accident including fatal injury or death could otherwise
result.
• This robot controller is not designed for explosion-proof. Do not use it in locations
exposed to inflammable gases, gasoline or solvent that could cause explosion or
fire.
• Do not touch any electrical terminal while power is supplied to the robot
controller. This may cause electrical shocks, faulty operation or malfunctions.
• Always shut off all phases of the power supply externally before cleaning or
tightening the terminal screws.
Failure to shut off all phases could lead to electric shocks, product damage or
malfunctions.
A loose screw could lead to dropping, short circuit or malfunctions.
If the screw is too tight, short circuit or malfunctions could also occur due to
screw damage.
• Never disassemble or modify the robot controller.
This may lead to breakdowns, malfunctions, injury or fire.
• Always shut off all phases of the power supply externally before installing or
removing an option board.
Failure to shut off all phases could lead to breakdowns or malfunctions.
• When using ferrite cores for noise elimination, fit them to the power cable as close
to the robot controller as possible, to prevent faulty operation or malfunctions due
to noise.
• When performing maintenance of the robot controller under instructions from
YAMAHA or YAMAHA sales dealer, turn off the robot controller and wait for at least
30 minutes. Some parts in the robot controller may be hot or applied at a high
voltage shortly after operation, so burns or electrical shocks may occur if those
parts are touched.
[Precautions for disposal]
c
CAUTION
• When disposing of this product discard it as industrial waste.
[Other precautions]
c
CAUTION
• Please note that the state of California USA has legal restrictions on the handling of
manganese dioxide lithium batteries. See the following website for more information:
http://www.dtsc.ca.gov/hazardouswaste/perchlorate
This manual does not constitute a concession of rights or a guarantee of
industrial rights. Please acknowledge that we bear no liability whatsoever
for conflicts with industrial rights arising from the contents of this manual.
2007 YAMAHA MOTOR CO., LTD.

5
2
Before using the robot controller
(Be sure to read the following notes.)
Please be sure to perform the following tasks before using the robot controller.
Failing to perform these tasks will require absolute reset for origin position setting each
time the power is turned on or may cause abnormal operation (vibration, noise).
[1] When connecting the power supply to the robot controller
Always make a secure connection to the ground terminal on the robot controller to
ensure safety and prevent malfunctions due to noise.
[2] When connecting the battery cable to the robot controller
The absolute battery is fully charged when the robot controller is shipped to the
customer. However, it is left disconnected to prevent battery discharge. After installing
the controller, always be sure to connect the absolute battery while referring to “9.
Connecting the absolute battery” in Chapter 3 before connecting the robot cables.
An error (relating to absolute settings) is always issued if the robot controller power is
turned on without making the absolute battery connections, so the origin position is
not detected. This means the robot connected to this controller cannot be used as
absolute specifications.
[3] When connecting robot cables to the robot controller
Be sure to keep robot cables separate from the robot controller power connection
lines and other equipment power lines. Using in close contact with lines carrying
power may cause malfunctions or abnormal operation.
Reference
Absolute reset is always required when
the robot controller power is first
turned on after connecting the robot
cable to the robot controller. Perform
absolute reset while referring to “11.8
Absolute reset” in Chapter 4,
“Operation”.
Absolute reset is also required after the
robot cable was disconnected from the
robot controller and then reconnected.
Reference
Refer to “4. Connecting the power” in
Chapter 3, “Installation”.

6
2
Overview of the RCX series
The YAMAHA RCX series robot controllers were developed based on years of YAMAHA
experience and achievements in robotics and electronics. These controllers are specifically
designed to operate YAMAHA industrial robots efficiently and accurately.
Despite its compact size, the RCX series controllers serve as multi-axis controllers with a
variety of functions.
Major features and functions are:
1. Multi-task function
Up to 8 tasks* can be run simultaneously in a specified priority. (Low priority tasks
are halted while high priority tasks are run.)
I/O parallel processing and interrupt processing are also available, so that operational
efficiency of the total robot system including peripheral units is greatly improved.
(*: Refer to the programming manual for more details on multi-tasking.)
2. Robot language
The RCX series controller comes with a BASIC-like high-level robot language that
conforms to the industrial robot programming language SLIM*1. This robot language
allows easy programming even of complex movements such as multi-task operations
and uses a compiling method*2 for rapid execution of programs.
(*1: Standard Language for Industrial Manipulators)
(*2: This compiling method checks the syntax in a robot language program, converts
it into intermediate codes, and creates an execution file (object file) before actually
performing the program.)
3. Movement command
• Arch motion
Spatial movement during pick-and-place work can be freely set according to the
work environment. This is effective in reducing cycle time.
• Three-dimensional CP control
Three-dimensional interpolation control for linear and circular movements is
possible.
4. Maintenance
Software servo control provides unit standardization. This means compatibility with
most YAMAHA robot models, thus simplifying maintenance and adjustment.
5. CE marking*
As a product of YAMAHA robot series, the RCX series robot controller is designed to
conform to machinery directives, low-voltage directives and EMC (Electromagnetic
compatibility) directives. In this case, the robot controller is set to operate under SAFE
mode. (* For CE marking compatibility, see the CE marking compatibility manual.)
This manual explains how to handle and operate the YAMAHA robot controllers correctly
and effectively, as well as I/O interface connections.
Read this manual carefully before installing and using the robot controller. Also refer to
the separate “Programming Manual” and “Robot User’s Manual” as needed.

i
Contents
Chapter 1 Safety
1. Safety .........................................................................................1-1
1.1 Safety precautions during robot operation ........................................... 1-2
1.2 Safety precautions during maintenance ............................................... 1-2
1.3 Precautions for motor overload ........................................................... 1-2
1.4 Warning labels.................................................................................... 1-3
1.5 Warning marks ................................................................................... 1-3
2. Warranty ...................................................................................1-4
3. Operating environment .............................................................1-5
Chapter 2 System overview
1. System overview ........................................................................2-1
1.1 Main system configuration .................................................................. 2-1
1.2 Axis definition for the RCX40 .............................................................. 2-3
2. Part names and functions...........................................................2-4
2.1 RCX40 (Maximum number of axes: 4 axes) ......................................... 2-4
3. Controller system ......................................................................2-5
3.1 Basic configuration ............................................................................. 2-5
4. Optional devices........................................................................ 2-6
4.1 MPB programming device................................................................... 2-6
4.2 Expansion I/O board ........................................................................... 2-6
4.3 Regenerative unit ................................................................................ 2-6
Chapter 3 Installation
1. Unpacking .................................................................................3-1
1.1 Packing box ........................................................................................ 3-1
1.2 Unpacking .......................................................................................... 3-1
2. Installing the robot controller.................................................... 3-2
2.1 Installation .......................................................................................... 3-2
2.2 Installation methods ............................................................................ 3-3
3. Connectors ................................................................................3-5
4. Power connections ....................................................................3-6
4.1 AC200 to 230V single-phase specifications......................................... 3-6
4.2 Power capacity ................................................................................... 3-6
4.3 External leakage breaker installation ................................................... 3-8
4.4 Circuit protector installation................................................................ 3-8
4.5 Current control switch installation ...................................................... 3-8
5. Robot cable connections ...........................................................3-9
6. Connecting the MPB programming unit ..................................3-10
7. I/O connections....................................................................... 3-11
8. Connecting a host computer.................................................... 3-12

ii
9. Connecting the absolute battery ..............................................3-13
10. Replacing the absolute battery ................................................ 3-15
11. Connecting a regenerative unit................................................ 3-18
12. Precautions for cable routing and installation .........................3-19
12.1 Wiring methods ................................................................................ 3-19
12.2 Precautions for installation ................................................................ 3-19
12.3 Methods of preventing malfunctions ................................................. 3-19
13. Checking the robot controller operation .................................3-21
13.1 Cable connection.............................................................................. 3-21
13.2 Emergency stop input signal connection ........................................... 3-22
13.3 Operation check ............................................................................... 3-22
Chapter 4 Operation
1. Operation overview................................................................... 4-1
2. The RCX robot controller ..........................................................4-2
2.1 Part names .......................................................................................... 4-2
2.2 Main functions .................................................................................... 4-2
3. MPB programming unit .............................................................4-3
3.1 Part names .......................................................................................... 4-3
3.2 Main functions .................................................................................... 4-4
3.3 Connection to the robot controller ...................................................... 4-5
4. Turning power on and off .......................................................... 4-6
5. Operation keys ..........................................................................4-7
5.1 MPB screen......................................................................................... 4-7
5.2 Operation key layout .......................................................................... 4-8
5.3 Basic key operation............................................................................. 4-9
5.4 Function keys.................................................................................... 4-10
5.5 Control keys...................................................................................... 4-12
5.6 Data keys .......................................................................................... 4-14
5.7 Other keys ........................................................................................ 4-14
6. Emergency stop .......................................................................4-15
6.1 Emergency stop reset ........................................................................ 4-16
7. Mode configuration .................................................................4-18
7.1 Basic operation modes ...................................................................... 4-18
7.2 Other operation modes ..................................................................... 4-19
7.3 Mode hierarchy ................................................................................. 4-20
8. “SERVICE” mode .....................................................................4-24
8.1 Operation device .............................................................................. 4-24
8.2 Prohibition of “AUTO” mode operation ............................................ 4-24
8.3 Hold-to-Run function ........................................................................ 4-24
8.4 Limitations on robot operating speed ................................................ 4-24
9. “AUTO” mode.........................................................................4-25
9.1 Automatic operation ......................................................................... 4-28
9.2 Stopping the program........................................................................ 4-29

iii
9.3 Resetting the program ....................................................................... 4-30
9.4 Switching task display ....................................................................... 4-32
9.5 Switching the program ...................................................................... 4-33
9.6 Changing the automatic movement speed......................................... 4-34
9.7 Executing the point trace................................................................... 4-34
9.7.1 PTP motion mode ...........................................................................................4-36
9.7.2 ARCH motion mode ....................................................................................... 4-38
9.7.3 Linear interpolation motion mode ................................................................... 4-40
9.8 Direct command execution............................................................... 4-42
9.9 BREAK point ..................................................................................... 4-43
9.9.1 Break point setting .......................................................................................... 4-43
9.9.2 Break point deletion ....................................................................................... 4-44
9.10 STEP ................................................................................................. 4-45
9.11 SKIP .................................................................................................. 4-45
9.12 NEXT ................................................................................................ 4-45
10. “PROGRAM” mode .................................................................4-46
10.1 Program list scroll ............................................................................. 4-47
10.2 Program editing ................................................................................ 4-48
10.2.1 Cursor movement ........................................................................................... 4-50
10.2.2 Insert/Overwrite mode switching .................................................................... 4-50
10.2.3 Inserting a line ................................................................................................ 4-51
10.2.4 Deleting a character ....................................................................................... 4-51
10.2.5 Deleting a line ................................................................................................ 4-52
10.2.6 User function key display ............................................................................... 4-52
10.2.7 Quitting program editing ................................................................................ 4-53
10.2.8 Specifying the copy/cut lines .......................................................................... 4-53
10.2.9 Copying the selected lines .............................................................................. 4-53
10.2.10 Cutting the selected lines ................................................................................ 4-54
10.2.11 Pasting the data ............................................................................................... 4-54
10.2.12 Backspace ...................................................................................................... 4-54
10.2.13 Line jump ....................................................................................................... 4-55
10.2.14 Searching a character string ............................................................................ 4-56
10.3 Directory .......................................................................................... 4-57
10.3.1 Cursor movement ........................................................................................... 4-58
10.3.2 Registering a new program name ....................................................................4-58
10.3.3 Directory information display ......................................................................... 4-59
10.3.4 Copying a program ......................................................................................... 4-60
10.3.5 Erasing a program ........................................................................................... 4-61
10.3.6 Renaming a program ...................................................................................... 4-62
10.3.7 Changing the program attribute ...................................................................... 4-63
10.3.8 Displaying object program information ........................................................... 4-63
10.3.9 Creating a sample program automatically ....................................................... 4-64
10.4 Compiling ......................................................................................... 4-66
10.5 Line jump and character string search ............................................... 4-67
10.6 Registering user function keys ........................................................... 4-67
10.7 Resetting an error in the selected program ........................................ 4-70
11. “MANUAL” mode ................................................................... 4-71
11.1 Manual movement ............................................................................ 4-73
11.2 Displaying and editing point data ..................................................... 4-75
11.2.1 Point data input and editing ............................................................................4-76
11.2.1.1 Restoring point data ........................................................................................ 4-77
11.2.2 Point data input by teaching ........................................................................... 4-78
11.2.3 Point data input by direct teaching.................................................................. 4-82
11.2.4 Point jump display ..........................................................................................4-82

iv
11.2.5 Copying point data ......................................................................................... 4-83
11.2.6 Erasing point data ........................................................................................... 4-84
11.2.7 Point data trace ............................................................................................... 4-85
11.2.8 Point comment input and editing ....................................................................4-86
11.2.8.1 Point comment input and editing ..................................................................... 4-87
11.2.8.2 Point data input by teaching ............................................................................ 4-87
11.2.8.3 Jump to a point comment ................................................................................ 4-88
11.2.8.4 Copying a point comment ............................................................................... 4-89
11.2.8.5 Erasing point comments ................................................................................... 4-90
11.2.8.6 Point comment search ..................................................................................... 4-91
11.2.9 Point data error reset ....................................................................................... 4-92
11.3 Displaying, editing and setting pallet definitions ............................... 4-93
11.3.1 Editing pallet definitions ................................................................................. 4-95
11.3.1.1 Point setting in pallet definition ....................................................................... 4-96
11.3.1.1.1 Editing the point in pallet definition ................................................................... 4-97
11.3.1.1.2 Setting the point in pallet definition by teaching ................................................ 4-97
11.3.2 Pallet definition by teaching ............................................................................ 4-98
11.3.3 Copying a pallet definition ............................................................................ 4-100
11.3.4 Deleting a pallet definition ........................................................................... 4-101
11.4 Changing the manual movement speed .......................................... 4-102
11.5 Displaying, editing and setting shift coordinates.............................. 4-103
11.5.1 Editing shift coordinates ................................................................................4-106
11.5.1.1 Restoring shift coordinates .............................................................................4-107
11.5.2 Editing the shift coordinate range ..................................................................4-107
11.5.2.1 Restoring a shift coordinate range ..................................................................4-109
11.5.3 Shift coordinate setting method 1 .................................................................. 4-109
11.5.4 Shift coordinate setting method 2 .................................................................. 4-111
11.6 Displaying, editing and setting hand definitions .............................. 4-113
11.6.1 Editing hand definitions ................................................................................ 4-119
11.6.1.1 Restoring hand definitions ............................................................................. 4-120
11.6.2 Hand definition setting method 1 .................................................................. 4-120
11.7 Changing the display units .............................................................. 4-122
11.8 Absolute reset ................................................................................. 4-123
11.8.1 Checking absolute reset ................................................................................ 4-124
11.8.2 Axis absolute reset ........................................................................................ 4-125
11.8.3 Absolute reset on all axes ............................................................................. 4-129
11.9 Setting the standard coordinates...................................................... 4-133
11.9.1 Setting the standard coordinates by 4-point teaching .................................... 4-136
11.9.2 Setting the standard coordinate by 3-point teaching ...................................... 4-138
11.9.3 Setting the standard coordinates by simple teaching ..................................... 4-140
11.10 Executing the user function keys ..................................................... 4-142
12. “SYSTEM” mode ....................................................................4-143
12.1 Parameters ...................................................................................... 4-145
12.1.1 Robot parameters .......................................................................................... 4-147
12.1.2 Axis parameters ............................................................................................ 4-152
12.1.3 Other parameters ..........................................................................................4-168
12.1.4 Parameters for option boards......................................................................... 4-174
12.1.4.1 Option DIO setting ........................................................................................4-175
12.1.4.2 Serial I/O setting ............................................................................................4-176
12.2 Communication parameters ............................................................ 4-178
12.3 OPTION parameters ....................................................................... 4-184
12.3.1 Setting the area check output ........................................................................4-185
12.3.2 Setting the “SERVICE” mode ......................................................................... 4-189
12.3.2.1 Saving the “SERVICE” mode parameters ........................................................ 4-194
12.3.2.2 Help display in “SERVICE” mode ................................................................... 4-194
12.3.3 SIO settings ................................................................................................... 4-195
12.4 Initialization.................................................................................... 4-198
12.4.1 Initializing the parameters ............................................................................. 4-199

v
12.4.2 Initializing the memory .................................................................................4-200
12.4.3 Initializing the communication parameters ................................................... 4-201
12.4.4 Clock setting .................................................................................................4-202
12.4.5 System generation ......................................................................................... 4-203
12.5 Self diagnosis .................................................................................. 4-204
12.5.1 Controller check ........................................................................................... 4-204
12.5.2 Error history display ...................................................................................... 4-205
12.5.3 Absolute battery voltage display.................................................................... 4-206
12.5.4 System error details display ........................................................................... 4-206
12.6 Backup processes............................................................................ 4-207
12.6.1 Internal flash ROM ....................................................................................... 4-207
12.6.1.1 Loading files .................................................................................................. 4-208
12.6.1.2 Saving files .................................................................................................... 4-209
12.6.1.3 Initializing the files ........................................................................................ 4-209
13. “MONITOR” mode ............................................................... 4-210
14. “UTILITY” mode....................................................................4-212
14.1 Canceling emergency stop; Motor power and servo on/off .............. 4-213
14.1.1 Canceling emergency stop ............................................................................4-213
14.1.2 Motor power and servo on/off ....................................................................... 4-214
14.2 Enabling/disabling the sequence execution flag .............................. 4-215
14.3 Changing the arm type .................................................................... 4-216
14.4 Resetting the output ports................................................................ 4-217
14.5 Changing the execution level .......................................................... 4-218
14.5.1 Changing the execution level ........................................................................ 4-219
14.5.2 Displaying the Help message ........................................................................4-220
14.6 Changing the access level (operation level) ..................................... 4-221
14.6.1 Entering the password ...................................................................................4-221
14.6.2 Changing the access level .............................................................................4-222
14.6.3 Displaying the Help message ........................................................................4-222
Chapter 5 I/O interface
1. I/O interface overview ..............................................................5-1
1.1 Power supply ...................................................................................... 5-1
1.2 Connector I/O signals ......................................................................... 5-2
1.3 Connector pin numbers ...................................................................... 5-3
1.4 Typical I/O signal connection ............................................................. 5-4
1.5 Typical output signal connection ........................................................ 5-5
1.5.1 Dedicated outputs ............................................................................................ 5-5
1.5.2 General-purpose outputs .................................................................................. 5-6
1.6 Dedicated input signals....................................................................... 5-7
1.7 Dedicated output signals..................................................................... 5-9
1.8 Dedicated I/O signal timing chart ..................................................... 5-11
1.8.1 Controller power ON, servo ON and emergency stop..................................... 5-11
1.8.2 Absolute reset .................................................................................................5-12
1.8.3 Switching to AUTO mode, program reset and execution ................................. 5-13
1.8.4 Stopping due to program interlocks ................................................................ 5-14
1.9 General-purpose I/O signals.............................................................. 5-15
1.9.1 General-purpose input signals ........................................................................ 5-15
1.9.2 General-purpose output signal ........................................................................5-15
1.9.3 General-purpose output signal reset (off) ......................................................... 5-15
2. Option I/O interface overview ................................................5-16
2.1 ID settings ......................................................................................... 5-17
2.2 Power supply .................................................................................... 5-17

vi
2.3 Connector I/O signals ....................................................................... 5-18
2.4 Connector pin numbers .................................................................... 5-19
2.5 Typical input signal connection ........................................................ 5-20
2.6 Typical output signal connection ...................................................... 5-20
2.7 General-purpose I/O signals.............................................................. 5-20
2.7.1 General-purpose input signals ........................................................................ 5-20
2.7.2 General-purpose output signals ...................................................................... 5-20
2.7.3 General-purpose output signal reset (off) ......................................................... 5-21
3. Ratings .....................................................................................5-22
4. Caution items ..........................................................................5-23
Chapter 6 SAFETY I/O interface
1. SAFETY I/O interface overview ................................................. 6-1
1.1 Power ................................................................................................. 6-1
1.2 Connector I/O signal chart .................................................................. 6-1
1.3 Connector terminal numbers............................................................... 6-2
1.4 Emergency stop input signal connections ............................................ 6-3
1.5 Dedicated input signal connections .................................................... 6-6
1.6 Input signal description ....................................................................... 6-7
Chapter 7 RS-232C interface
1. Communication overview.......................................................... 7-1
2. Communication function overview............................................7-2
3. Communication specifications ...................................................7-3
3.1 Connector ........................................................................................... 7-3
3.2 Transmission mode and communication parameters ........................... 7-4
3.3 Communication flow control .............................................................. 7-5
3.3.1 Flow control during transmit .............................................................................7-5
3.3.2 Flow control during receive ..............................................................................7-5
3.4 Other caution items ............................................................................ 7-6
3.5 Character code table ........................................................................... 7-7
Chapter 8 Specifications
1. Controller basic specifications ...................................................8-1
2. Controller basic specifications ...................................................8-2
3. Robot controller external view ..................................................8-3
3.1 RXC40 external view .......................................................................... 8-3
4. MPB basic specifications and external view...............................8-4
Chapter 9 Troubleshooting
1. Error Messages...........................................................................9-1
1.1 Robot controller error messages .......................................................... 9-1
[ 0] Warnings and messages ............................................................................................9-3
[ 1] Warnings (Error history entry).................................................................................... 9-5
[ 2] Robot operating area errors....................................................................................... 9-5
[ 3] Program file operating errors..................................................................................... 9-8

vii
[ 4] Data entry and edit errors ....................................................................................... 9-10
[ 5] Robot language syntax (compiling) errors ............................................................... 9-11
[ 6] Robot programming execution errors ...................................................................... 9-18
[ 9] Memory errors ........................................................................................................9-22
[10] System setting or hardware errors. .......................................................................... 9-24
[12] I/O and option board errors .................................................................................... 9-26
[13] MPB errors ............................................................................................................. 9-29
[14] RS-232C communication errors ..............................................................................9-30
[15] Memory card errors ................................................................................................ 9-31
[17] Motor control errors................................................................................................ 9-34
[21] Major software errors .............................................................................................. 9-40
[22] Major hardware errors ............................................................................................ 9-42
1.2 MPB Error Messages.......................................................................... 9-45
2. Troubleshooting .......................................................................9-47
2.1 When trouble occurs ........................................................................ 9-47
2.2 Acquiring error information .............................................................. 9-48
2.2.1 Acquiring information from the MPB .............................................................. 9-48
2.2.2 Acquiring information from the RS-232C ........................................................ 9-48
2.3 Troubleshooting checkpoints............................................................. 9-49

viii
MEMO
Chapter 1 Safety
Contents
1. Safety ............................................................................................... 1-1
1.1 Safety precautions during robot operation ............................................... 1-2
1.2 Safety precautions during maintenance ................................................... 1-2
1.3 Precautions for motor overload ............................................................... 1-2
1.4 Warning labels ........................................................................................1-3
1.5 Warning marks ........................................................................................1-3
2. Warranty .......................................................................................... 1-4
3. Operating environment .................................................................... 1-5

MEMO

1-1
1
Safety
1. Safety
Please observe all safety rules and cautions to use the YAMAHA robot safely and correctly. Also,
please bear in mind that not all safety items can be listed in detail, so that an accurate judgment by the
operator or service personnel is essential to operate the robot and controller safely.
Industrial robots are highly programmable, mechanical devices that provide a large degree
of freedom for performing various manipulative tasks. To ensure correct and safe use of
YAMAHA industrial robots, carefully read this manual and FOLLOW THE WARNINGS,
CAUTIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS in this chapter. Failure to take necessary safety
measures or mishandling may result in trouble or damage to the robot and injury to
personnel (robot operator or service personnel) including fatal accidents.
Particularly important safety items and operation points are identified in this manual by
the following symbols.
w
WARNING
Failure to follow WARNING instructions could result in severe injury or death to the
operator, bystanders or persons inspecting or repairing the robot controller or robot.
c
CAUTION
Failure to follow CAUTION instructions may result in injury to the operator, bystanders or persons
inspecting or repairing the robot controller or robot, and may damage the robot controller or robot.
n
NOTE
Explains the key point in the operation in a simple and clear manner.
To install, operate or adjust the YAMAHA robot or controller safely and correctly, always
follow the instructions explained in this manual by using either of the following methods.
1. Install, operate or adjust the robot or controller while referring to the contents of this
manual.
2. Install, operate or adjust the robot or controller while viewing the contents of the CDROM version manual on your computer screen.
3. Install, operate or adjust the robot or controller while referring to a printout of the
necessary pages from the CD-ROM version manual.

1-2
Safety
1
1. Safety
1.1 Safety precautions during robot operation
a. The robot must be operated by a person who has received the proper training on safety
and operation from YAMAHA or an authorized YAMAHA sales dealer.
b. During operation of the robot, be sure to stay out of the working area of the robot
manipulator. Install a safeguard enclosure to keep anyone away from the working area
or provide a gate interlock using an area sensor that triggers emergency stop when
anyone enters the working area.
c. This robot controller is not designed for explosion-proof. Do not use the controller
and robot in locations exposed to inflammable gases, gasoline or solvent that could
cause explosion or fire.
1.2 Safety precautions during maintenance
a. Never disassemble the robot or controller. In cases where you have to replace or repair
parts used in the robot or controller, first consult with us and follow the instructions
we provide.
b. Before beginning maintenance for the robot or controller, be sure to turn off the power
to the controller. Even after turning off the controller, there are some parts in the
controller which are still hot or at a high voltage. Always wait for at least 30 minutes
after the controller is turned off.
1.3 Precautions for motor overload
Since abnormal operation (such as overload) of the motor is detected by software, the
controller parameters must be set correctly to match the motor type used in the robot
connected to the controller.
Prior to shipping, the controller parameters are preset to match the robot model to be
used. However, please check the robot model again when connecting it to the controller.
If any abnormality is found during operation, stop the controller and contact us for
corrective action.

1-3
1
Safety
1. Safety
1.4 Warning labels
The warning labels shown below are affixed to the controller. To use the YAMAHA robot
and controller safely and correctly, be sure to observe the instructions and caution on the
labels.
a. “Electric Hazard” label
!
CAUTION
ELECTRIC HAZARD
■ This label warns you of possible electrical shock. Do not touch the terminal strip and
connectors to avoid electrical shock.
b. “Read Instruction Manual” label
READ INSTRUCTION
MANUAL
■ This label means that important information you must know is described in the manual.
When in particular connecting a power supply to the robot controller, read this manual
carefully and follow the instructions. Connectors have an orientation, so insert each
connector in the correct direction.
1.5 Warning marks
The following warning marks are shown on the controller. To use the YAMAHA robot
and controller safely and correctly, be sure to observe the instructions and caution of the
marks.
a. “Electric Hazard” mark
■ This mark warns you of possible electrical shock. Do not touch the terminal block and
connectors to avoid electrical shock.
b. “Read Instruction Manual” mark
!
■ This mark indicates that important information you must know is described in the
manual.
When in particular connecting a power supply to the robot controller, read this
manual carefully and follow the instructions. Connectors have an orientation, so
insert each connector in the correct direction.

1-4
Safety
1
2. W arranty
The YAMAHA robot and/or related product you have purchased are warranted against the defects or
malfunctions as described below.
Warranty description:
If a failure or breakdown occurs due to defects in materials or workmanship in the genuine
parts constituting this YAMAHA robot and/or related product within the warranty period,
then YAMAHA will repair or replace those parts free of charge (hereafter called "warranty
repair").
Warranty Period:
The warranty period ends when any of the following applies:
(1) After 18 months (one and a half year) have elapsed from the date of shipment
(2) After one year has elapsed from the date of installation
(3) After 2,400 hours of operation
Exceptions to the Warranty:
This warranty will not apply in the following cases:
(1) Fatigue arising due to the passage of time, natural wear and tear occurring during
operation (natural fading of painted or plated surfaces, deterioration of parts subject
to wear, etc.)
(2) Minor natural phenomena that do not affect the capabilities of the robot and/or related
product (noise from computers, motors, etc.).
(3) Programs, point data and other internal data that were changed or created by the
ser.
Failures resulting from the following causes are not covered by warranty repair.
1) Damage due to earthquakes, storms, floods, thunderbolt, fire or any other natural or
man-made disasters.
2) Troubles caused by procedures prohibited in this manual.
3) Modifications to the robot and/or related product not approved by YAMAHA or
YAMAHA sales representatives.
4) Use of any other than genuine parts and specified grease and lubricants.
5) Incorrect or inadequate maintenance and inspection.
6) Repairs by other than authorized dealers.
YAMAHA MOTOR CO., LTD. MAKES NO OTHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY
OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THE WARRANTY SET FORTH
ABOVE IS EXCLUSIVE AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR WARRANTIES ARISING FROM A COURSE
OF DEALING OR USAGE OF TRADE.
YAMAHA MOTOR CO., LTD. SOLE LIABILITY SHALL BE FOR THE DELIVERY
OF THE EQUIPMENT AND YAMAHA MOTOR CO., LTD. SHALL NOT BE LIABLE
FOR ANY CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (WHETHER ARISING FROM
CONTRACT, WARRANTY, NEGLIGENCE OR STRICT LIABILITY). YAMAHA
MOTOR CO., LTD. MAKES NO WARRANTY WHATSOEVER WITH REGARD TO
ACCESSORIES OR PARTS NOT SUPPLIED BY YAMAHA MOTOR CO., LTD.

1-5
1
Safety
3. Operating environment
Operating temperature
The ambient temperature should be maintained within a range of 0 to 40°C during
operation. This is the range in which continuous operation of the robot controller is
guaranteed according to the initial specifications. If the robot controller is installed in a
narrow space, heat generated from the controller itself and from peripheral equipment
may drive the temperature above the allowable operating temperature range. This may
result in thermal runaway or malfunctions and may lower component performance along
with shortening their useful service life. So be sure to install the controller in locations
with a vent having a natural air flow. If this proves insufficient provide forced air-cooling.
Storage temperature
The controller should be stored in a location at an ambient temperature between -10 and
+65°C when not being used. If the robot controller is stored in a location at high
temperatures for extended periods, deterioration of the electronic components may occur
and the memory backup time may decrease.
Operating humidity
The ambient humidity of the robot controller should be 35% to 85% RH (no condensation)
in order to guarantee continuous operation within the initial specifications. Installing the
robot controller inside an air-conditioned or cooled housing is recommended when an
ambient humidity is higher than 85% or condensation occurs.
Storage humidity
The controller should be stored in a location at an ambient humidity below 95% RH (no
condensation) when not being used. If the robot controller is stored in a location at high
humidity for an extended period of time, rust may form on the electronic components.
Vibration and shock
Do not apply excessive shocks or constant vibrations to the robot controller. Install the
robot controller in a steady location not subject to vibrations.
Atmosphere (gas, etc.)
Do not install the robot controller in locations where conductive dust particles, hydrogen
sulfide gas or sulfurous acid gas are present. Such an atmosphere may cause the components
to erode or poor installation. If such dust particles or gases are generated at the current
location, then installing the robot controller in an air-conditioned or cooled housing is
recommended.
Installation location
Always install the robot controller indoors, at a height of less than 1000 meters above sea
level.

1-6
MEMO
Chapter 2 System overview
Contents
1. System overview .............................................................................. 2-1
1.1 Main system configuration ...................................................................... 2-1
1.2 Axis definition for the RCX40 .................................................................. 2-3
2. Part names and functions ................................................................. 2-4
2.1 RCX40 (Maximum number of axes: 4 axes) ............................................. 2-4
3. Controller system ............................................................................. 2-5
3.1 Basic configuration.................................................................................. 2-5
4. Optional devices .............................................................................. 2-6
4.1 MPB programming device .......................................................................2-6
4.2 Expansion I/O board ...............................................................................2-6
4.3 Regenerative unit .................................................................................... 2-6

MEMO
2-1
2
System overview
1. System overview
The RCX series controllers are designed for use with a SCARA robot or Cartesian robot, mainly for
assembly and pick-and-place applications. Applications also include various inspection instruments,
sealers and spray equipment utilizing linear and circular interpolation functions.
1.1 Main system configuration
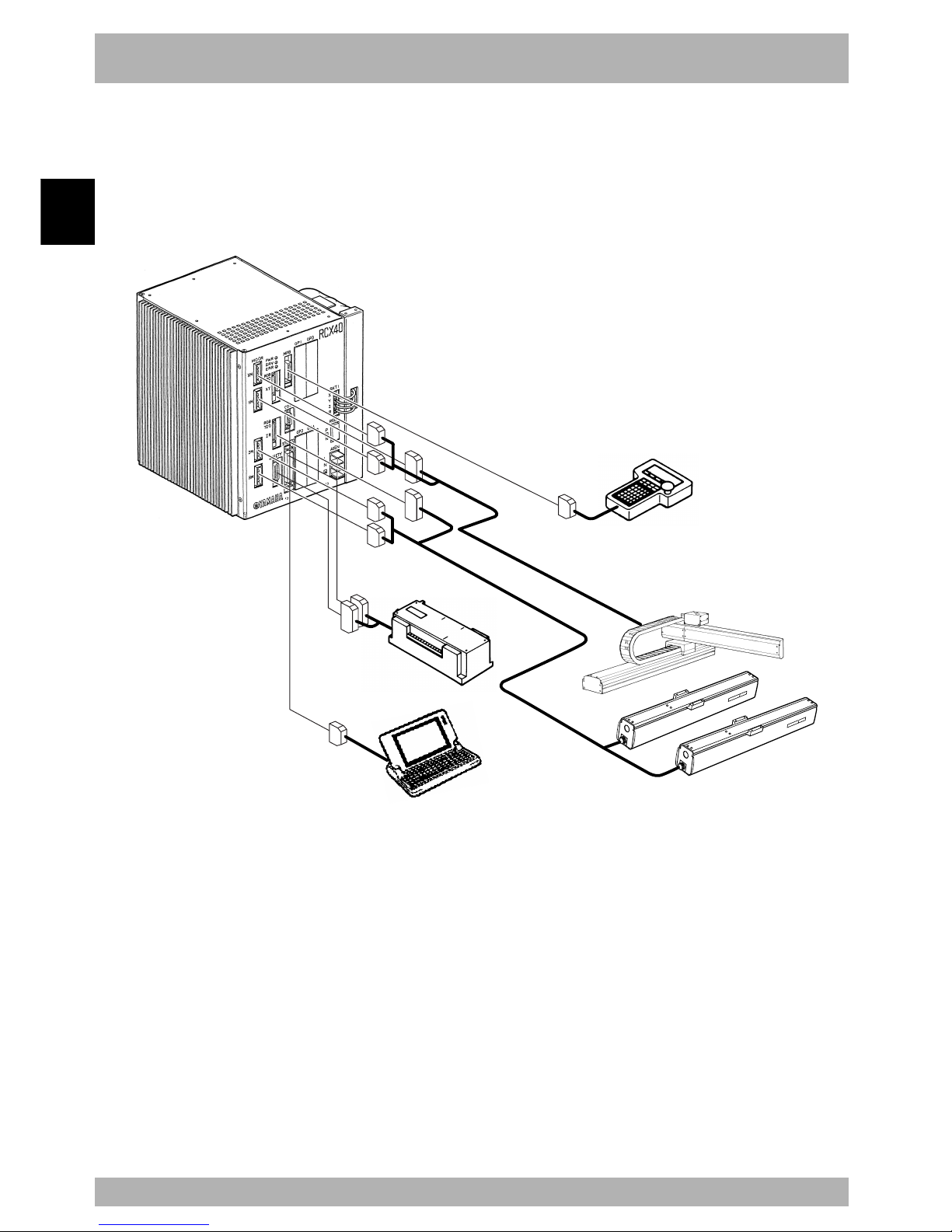
Configuration 1: System for controlling one robot
Example : YK400X
All the axes on the robot controller are used as the main robot axes.
Fig. 2-1-1 System for controlling one robot
PC
PLC
MPB
YAMAHA robot
2-2
System overview
2
1. System overview
Configuration 2: System for controlling one robot and auxiliary axes
Example: SXYx+T9+T9
Axes 1 and 2 on the robot controller are used as the main robot axes and
axes 3 and 4 are used as the main auxiliary axes.
Fig. 2-1-2 System for controlling one robot and auxiliary axes
PLC
MPB
PC
YAMAHA robot
2-3
2
System overview
1. System overview
1.2 Axis definition for the RCX40
Axis definitions for the YAMAHA RCX40 robot controller are shown below.
Robot
controller (RC)
Main robot axis (M?)
Main robot auxiliary axis (m?)
Sub robot axis (S?)
Sub robot auxiliary axis (s?)
Main robot (MR)
Sub robot (SR)
Main group (MG)
Subgroup (SG)
Robot controller ................ Indicates the entire robot controller and controls a
maximum of 4 axes.
The letters “RC” are displayed on the MPB.
Main group ........................ Indicates the main robot and main auxiliary axes and has a
maximum of 4 axes.
The letters “MG” are displayed on the MPB.
Main robot ......................... Indicates the robot name specified as a main robot, and
includes all axes of the main robot.
The letters “MR” are displayed on the MPB.
Main robot axes ................. Indicate the axes composing the main robot.
These can be moved with the robot language MOVE
command.
The letters “M?” are displayed on the MPB. (?=1 to 4)
Main auxiliary axes ........... Are the single axes composing the main group.
These cannot be moved with the robot language MOVE
command. Use the DRIVE command to move these axes.
The letters “m?” are displayed on the MPB. (?=1 to 4)
Sub group .......................... Indicates the sub robot and sub auxiliary axes, and has a
maximum of 2 axes.
The letters “SG” are displayed on the MPB.
Sub robot ........................... Indicates the robot name specified as a sub robot, and
includes all axes of the sub robot.
The letters “SR” are displayed on the MPB.
Sub robot axes ................... Indicate the axes composing the sub robot.
These can be moved with the robot language MOVE2
command.
The letters “S?” are displayed on the MPB. (?=1 to 2)
Sub auxiliary axes ............. Are the single axes composing the sub group.
These cannot be moved with the robot language MOVE2
command. Use the DRIVE2 command to move these axes.
The letters “s?” are displayed on the MPB. (?=1 to 2)
Normally, only main robot axes can be specified. Auxiliary axes and sub group settings
are for options made at the time of shipment.
2-4
System overview
2
2. Part names and functions
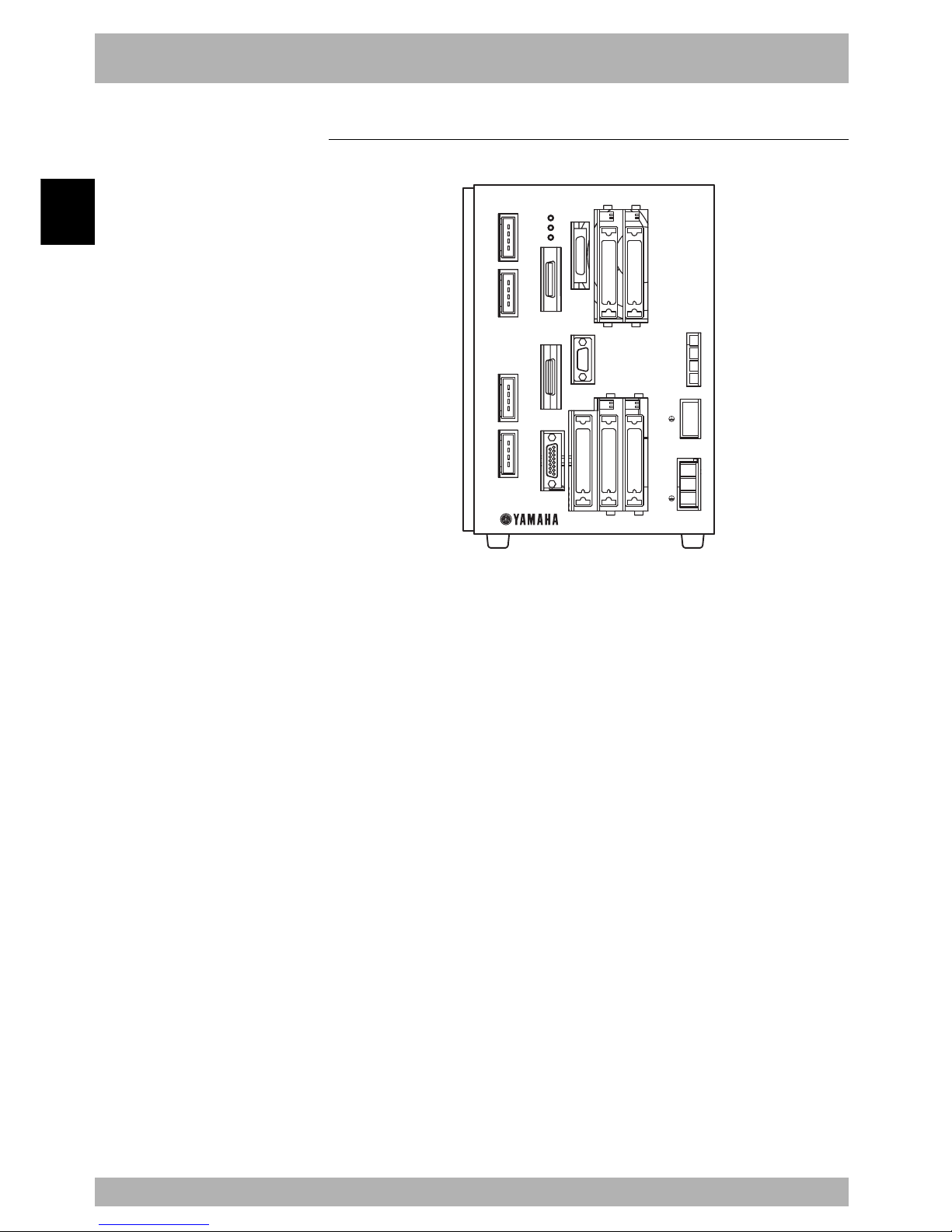
2.1 RCX40 (Maximum number of axes: 4 axes)
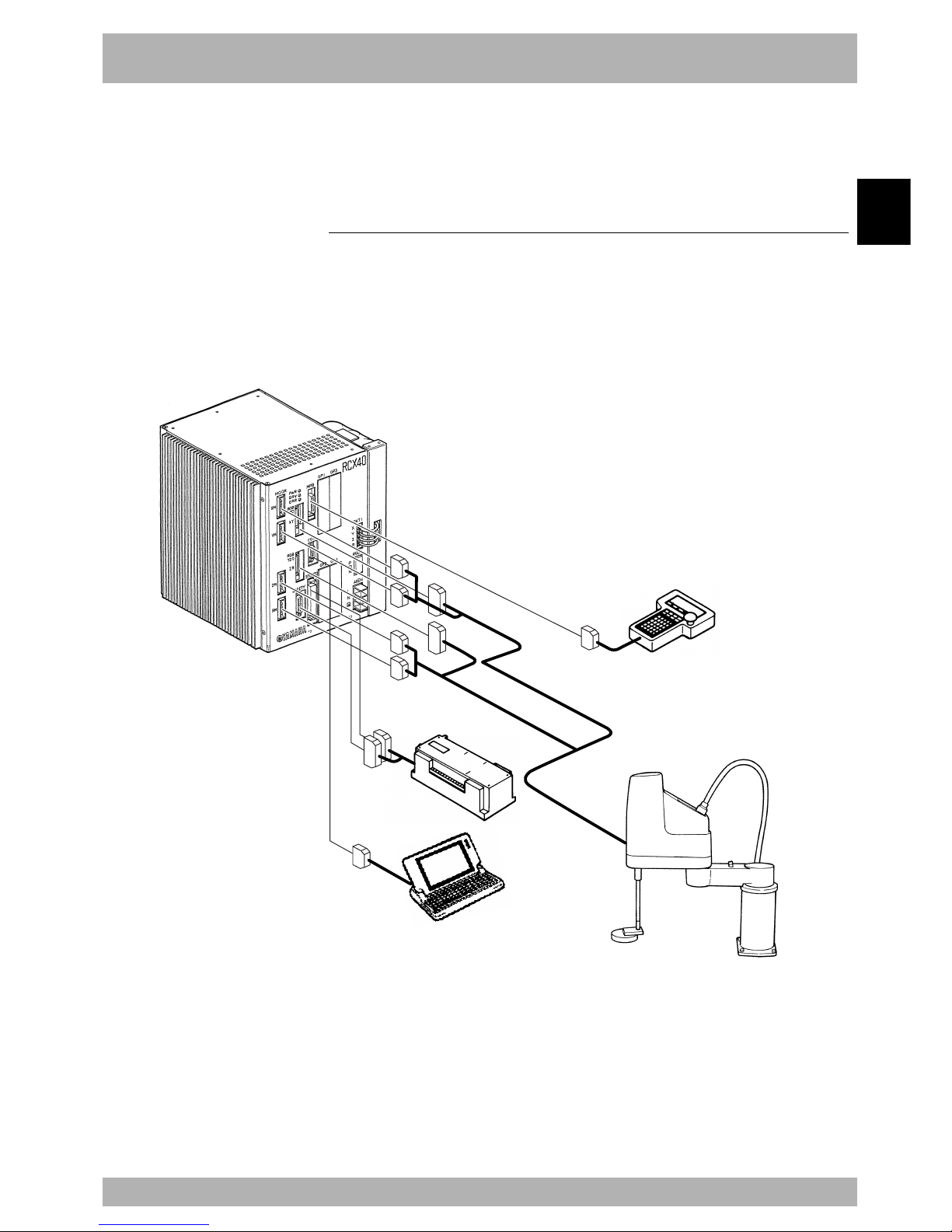
Fig. 2-2-1
RCX40
MOTOR
XM
YM
ZM
RM
PWR
SRV
ERR
SAFETY
MPB
COM
STD.DIO
BATT
RGEN
ACIN
X
Y
Z
R
P
N
L
N
ROB
I/O
XY
ROB
I/O
ZR
OP.1 OP.3
OP.2
OP.4
 Loading...
Loading...