Page 1

VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
4-8-8 Nakameguro, Meguro-Ku, Tokyo 153-8644, Japan
VERTEX STANDARD
US Headquarters
FM TRANSCEIVER
FT-1900R
Technical Supplement
©2009 VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD. EH023N91A
10900 Walker Street, Cypress, CA 90630, U.S.A.
YAESU UK LTD.
Unit 12, Sun Valley Business Park, Winnall Close
Winchester, Hampshire, SO23 0LB, U.K.
VERTEX STANDARD HK LTD.
Unit 5, 20/F., Seaview Centre, 139-141 Hoi Bun Road,
Kwun Tong, Kowloon, Hong Kong
VERTEX STANDARD (AUSTRALIA) PTY., LTD.
Normanby Business Park, Unit 14/45 Normanby Road
Notting Hill 3168, Victoria, Australia
Introduction
This manual provides technical information necessary for servicing the FT-1900R FM Transceiver.
Servicing this equipment requires expertise in handling surface-mount chip components. Attempts by non-
qualified persons to service this equipment may result in permanent damage not covered by the warranty,
and may be illegal in some countries.
Two PCB layout diagrams are provided for each double-sided circuit board in the Transceiver. Each side of
is referred to by the type of the majority of components installed on that side (“leaded” or “chip-only”). In
most cases one side has only chip components, and the other has either a mixture of both chip and leaded
components (trimmers, coils, electrolytic capacitors, ICs, etc.), or leaded components only.
While we believe the technical information in this manual to be correct, VERTEX STANDARD assumes no
liability for damage that may occur as a result of typographical or other errors that may be present. Your
cooperation in pointing out any inconsistencies in the technical information would be appreciated.
Important Note
The transceiver was assembled using Pb (lead) free solder, based on the RoHS specification.
Only lead-free solder (Alloy Composition: Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu) should be used for repairs performed on this appara-
tus. The solder stated above utilizes the alloy composition required for compliance with the lead-free specification,
and any solder with the above alloy composition may be used.
Contents
Specifications ...................................................... 2
Exploded View & Miscellaneous Parts ............ 3
Block Diagram .................................................... 5
Connection Diagram .......................................... 6
Circuit Description............................................. 7
Alignment ............................................................ 9
Board Unit (
MAIN Unit Circuit Diagram ................................. 13
MAIN Unit Parts Layout ...................................... 15
MAIN Unit Parts List............................................ 17
CNTL Unit Circuit Diagram .................................. 27
CNTL Parts Layout............................................... 28
CNTL Parts List .................................................... 29
Schematics, Layouts & Parts
)
1
Page 2

Specifications
General
Frequency Range: Tx 144 - 146 MHz or 144 - 148 MHz
Rx 144 - 146 MHz or 136 - 174 MHz
Channel Step: 5/10/12.5/15/20/25/50/100 kHz
Standard Repeater Shift: ±600 kHz
Frequency Stability: Better than ±10 ppm [–4 °F to +140 °F (–20 °C to +60 °C)]
Modes of Emission: F2D/F3E
Antenna Impedance: 50 Ohms, unbalanced
Supply voltage: 13.8 V DC ±15%, negative ground
Current Consumption (typical): Rx: less than 0.7 A, less than 0.3 A (squelched)
Tx: 10 A (55 W) /7 A (25 W) /5 A (10 W) /4 A (5 W)
Operating Temperature Range: –4° F to +140° F (–20° C to +60° C)
Case Size (WxHxD): 5.5” x 1.6” x 5.7” (140 x 40 x 146 mm) (w/o knobs)
Weight (Approx.): 2.6 lb (1.2 kg)
Transmitter
Output Power: 55 W/25 W/10 W/5 W
Modulation Type: Variable Reactance
Maximum Deviation: ±5 kHz/±2.5 kHz
Spurious Radiation: Better than –60 dB
Microphone Impedance: 2000 Ohms
Receiver
Circuit Type: Double Conversion Superheterodyne
Ifs: 21.7 MHz & 450 kHz
Sensitivity (for 12dB SINAD): Better than 0.2 µV
Selectivity (–6/–60dB): 12 kHz/28 kHz
IF Rejection: Better than 70 dB
Image Rejection: Better than 70 dB
Maximum AF Output: 3 W into 4 Ohms @10 % THD
Specifications subject to change without notice or obligation. Specifications guaranteed only within Amateur band.
Frequency ranges and functions will vary according to transceiver version; check with your dealer.
2
Page 3
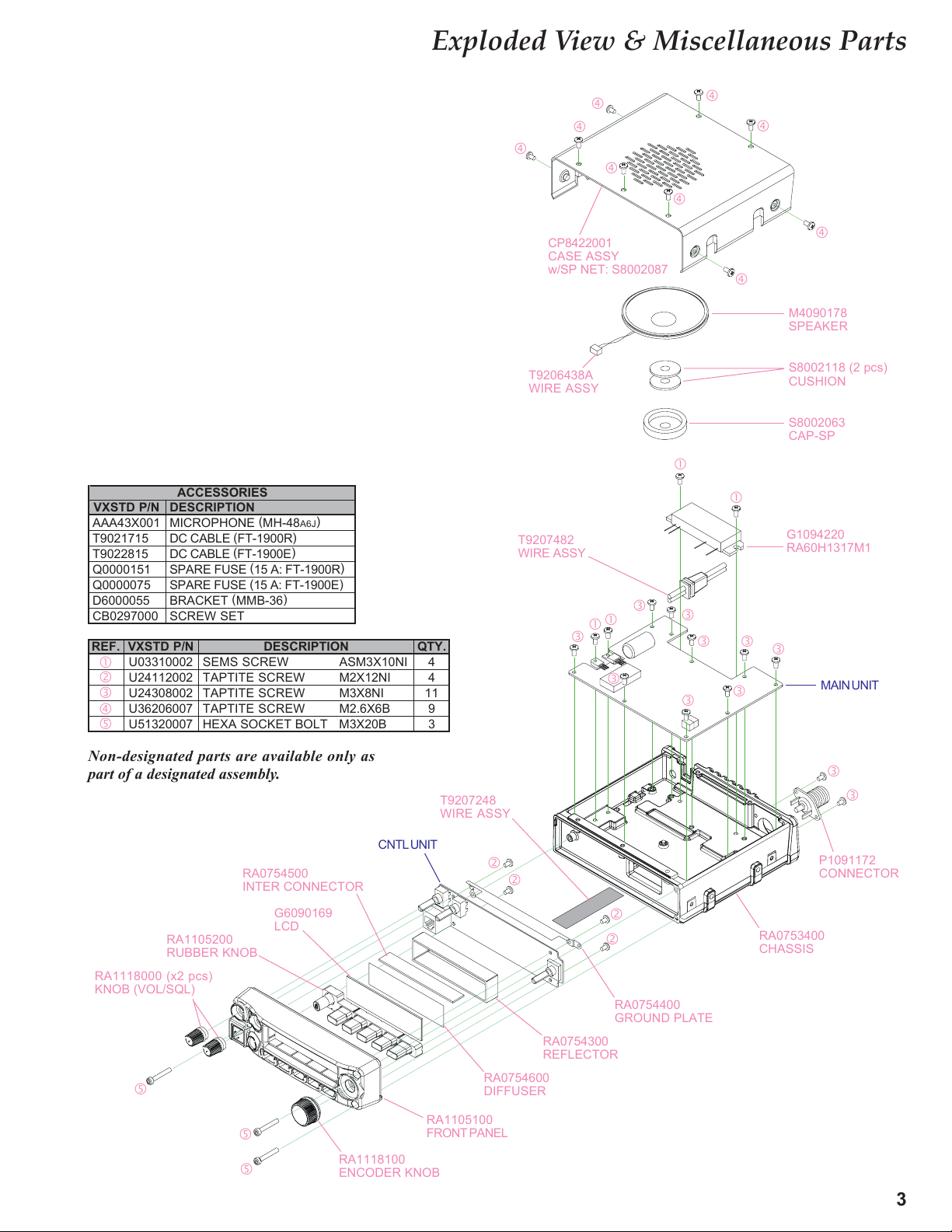
Exploded View & Miscellaneous Parts
VXSTD P/N
AAA43X001
T9021715
T9022815
Q0000151
Q0000075
D6000055
CB0297000
REF.
VXSTD P/N
U03310002
c
U24112002
d
U24308002
e
U36206007
f
U51320007
g
ACCESSORIES
DESCRIPTION
MICROPHONE (MH-48A6J
DC CABLE (FT-1900R
DC CABLE (FT-1900E
SPARE FUSE (15 A: FT-1900R
SPARE FUSE (15 A: FT-1900E
BRACKET (MMB-36
SCREW SET
DESCRIPTION
SEMS SCREW ASM3X10NI
TAPTITE SCREW M2X12NI
TAPTITE SCREW M3X8NI
TAPTITE SCREW M2.6X6B
HEXA SOCKET BOLT M3X20B
)
)
)
)
f
f
f
f
f
f
f
CP8422001
CASE ASSY
w/SP NET: S8002087
T9206438A
WIRE ASSY
f
f
M4090178
SPEAKER
S8002118 (2 pcs)
CUSHION
S8002063
CAP-SP
c
c
e
G1094220
RA60H1317M1
e
MAIN UNIT
T9207482
)
)
QTY.
4
4
11
9
3
WIRE ASSY
e
c
c
e
e
e
e
e
e
Non-designated parts are available only as
part of a designated assembly.
RA0754500
INTER CONNECTOR
G6090169
RA1105200
RUBBER KNOB
RA1118000 (x2 pcs)
KNOB (VOL/SQL)
LCD
g
g
g
RA1118100
ENCODER KNOB
CNTL UNIT
T9207248
WIRE ASSY
d
RA0754600
DIFFUSER
RA1105100
FRONT PANEL
d
d
RA0754300
REFLECTOR
e
e
P1091172
CONNECTOR
d
RA0753400
CHASSIS
RA0754400
GROUND PLATE
3
Page 4

Note
4
Page 5
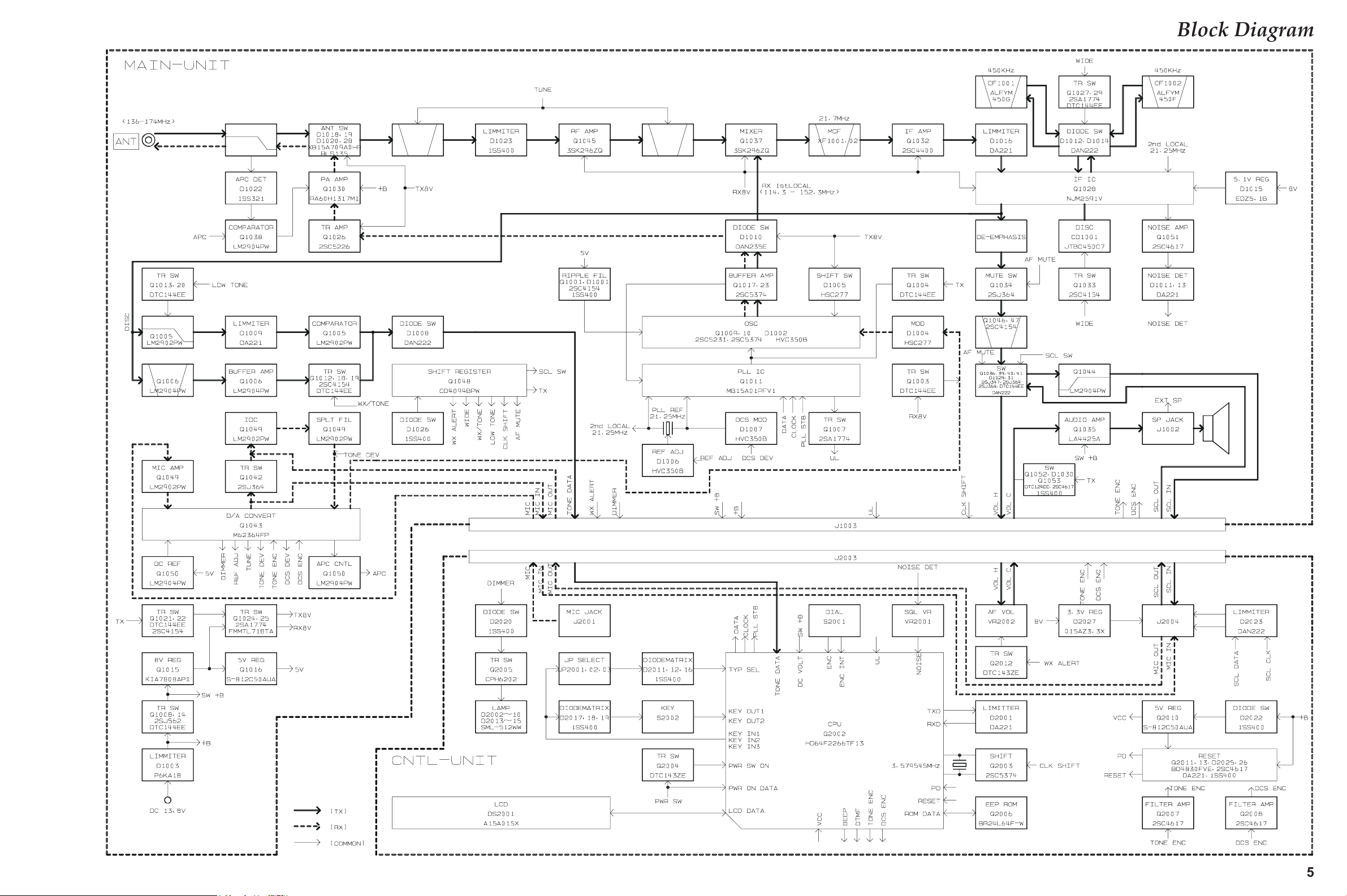
Block Diagram
5
Page 6
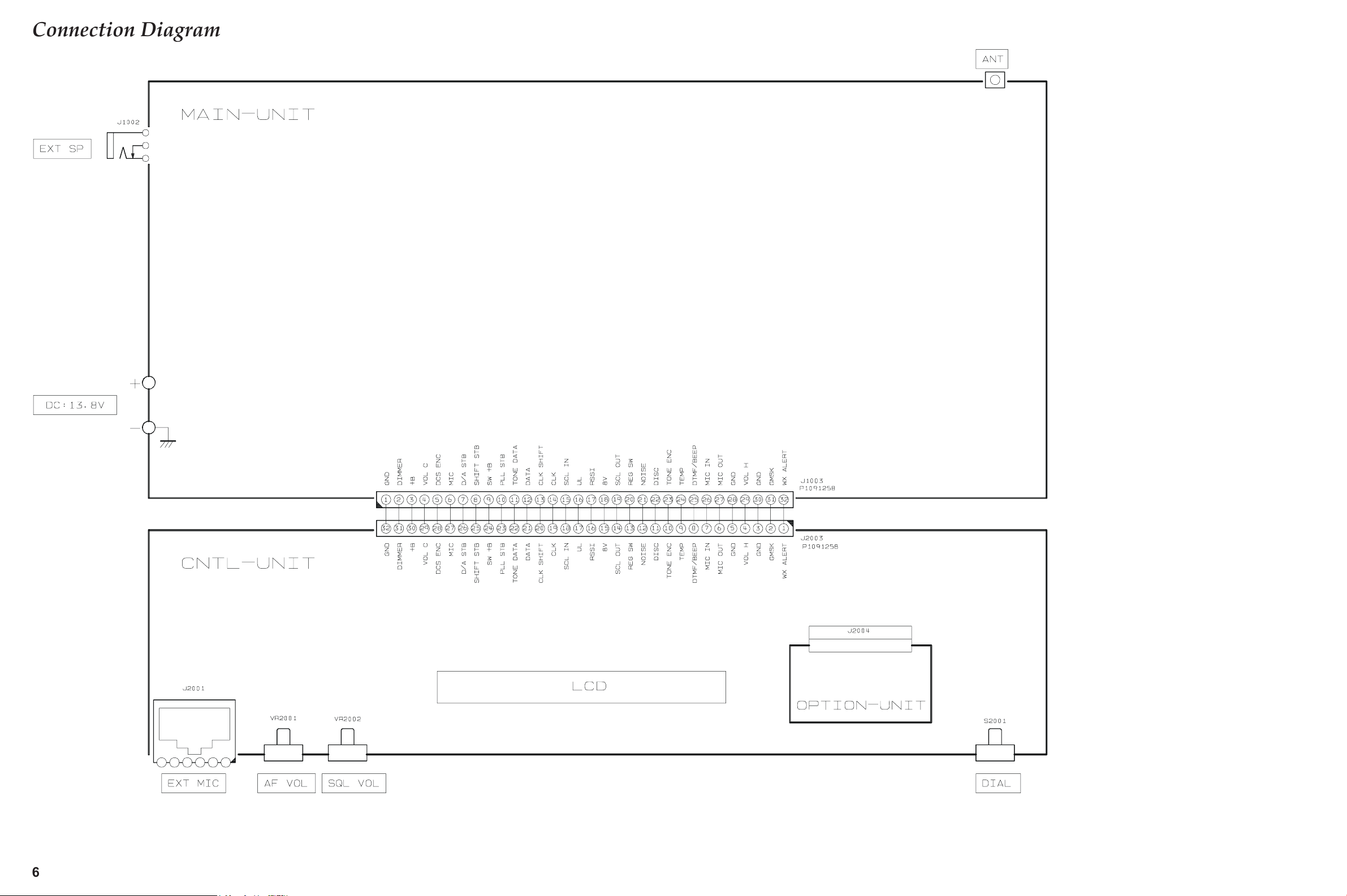
Connection Diagram
6
Page 7

Circuit Description
Receive Signal Path
Incoming RF signal is from the antenna jack is de-
livered to the Main Unit and passed through the low-
pass filter network consisting capacitors C1213,
C1236, C1239, & C1241 and coils L1017, L1018, &
L1019, antenna switching diode D1020 and D1028
(both RLS135), and varactor-tuned band-pass filter
consisting of capacitors C1248, C1249, C1250, C1251,
C1252, & C1268, coils L1020, L1021, & L1024, and
diodes D1024 and D1025 (both HVC350B), before
delivery to the RF amplifier Q1045 (3SK296ZQ). The
amplified RF signal is passed through the another
varactor-tuned band-pass filter consisting of capac-
itors C1198, 1199, 1200, & 1218, coils L1012 and L1015,
and diodes D1017 and D1021 (both HVC350B), then
applied to the 1st mixer Q1037 (3SK296ZQ) along
with the first local signal from the PLL circuit.
The first local signal is generated between 114.3 MHz
and 152.3 MHz by the VCO, which consists of Q1009
(2SC5231) and varactor diode D1002 (HVC350B)
according to the receiving frequency.
IF and Audio Circuits
The 21.7 MHz first IF signal is applied to the mono-
lithic crystal filters XF1001 and XF1002 which strip
away unwanted mixer products, and the IF signal is
applied to the first IF amplifier Q1032 (2SC4400).
The amplified first IF signal is then delivered to the
FM IF subsystem IC Q1028 (NJM2591V), which con-
tains the second mixer, limiter amplifier, noise am-
plifier, and FM detector.
The audio signal passes through a band-pass filter
consisting of Q1046 and Q1047 (both 2SC4154), and
the audio mute gate Q1039 (2SJ347), to the audio
VR which adjusts the audio sensitivity to compen-
sate for audio level variations. The adjusted audio
signal is delivered to the audio amplifier Q1035
(LA4425A) which provides up to 3 Watts, to the ex-
ternal speaker jack or a 4-Ohm loudspeaker.
Squelch Control
When no carrier received, the noise signal from
Q1028 (NJM2591V) is amplified by Q1051
(2SC4617), and is detected by D1011 and D1013
(both DA221). The resulting DC voltage passes
through the SQL knob to main CPU Q2002
(HD64F2266TF13). While no carrier is received,
main CPU Q2002 (HD64F2266TF13) control Q1048
(CD4094BPWR), thus, audio mute gate Q1034
(2SJ364) and Q1039 (2SJ347) turns “OFF” to dis-
able the audio output from the speaker.
Transmit Signal Path
The speech signal from the microphone is amplified
by Q1049 (LA2902PWR). The amplified speech sig-
nal is subjected to the low-pass filter network Q1049
(LA2902PWR) to deviation controlled by Q1043
(M62364FP).
The adjusted speech signal from Q1043 (M62364FP)
is delivered to VCO Q1009 (2SC5231) which fre-
quency modulates the transmitting VCO made up
of D1004 (HSC277).
The second local signal is generated by 21.25 MHz
crystal X1001, produces the 450 kHz second IF sig-
nal when mixed with first IF signal within Q1028
(NJM2591V).
The 450 kHz second IF signal is applied to the ce-
ramic filter CF1001 (for Narrow FM) or CF1002 (for
Wide FM) which strip away unwanted mixer prod-
ucts to the ceramic discriminator CD1001 which re-
moves any amplitude variations in the 450 kHz IF
signal before detection of speech.
The detected audio from the Q1028 (NJM2591V)
passes through the de-emphasis circuit consisting
of resistors R1082 & R1113, and capacitors C1120 &
C1122, to the audio mute gate Q1034 (2SJ364)
The modulated transmit signal passes through buff-
er amplifier Q1010 and Q1023 (both 2SC5374).
The transmit signal applied to the drive amplifier
Q1026 (2SC5226), then finally amplified by power
amplifier module Q1030 (RA60H1317M) up to 50
Watts. The APC circuit controls the Q1030
(RA60H1317M) power amplifier’s gain.
The 50 Watts RF signal passes through low-pass fil-
ter network consisting of Capacitors C1210 and
C1211 and coil L1013, antenna switch D1018 and
D1019 (both XB15A709), and another low-pass fil-
ter network consisting capacitors C1213, C1236,
C1239, & C1241 and coils L1017, L1018, & L1019, and
then deliver to the ANT jack.
7
Page 8

Circuit Description
TX APC Circuit
A portion of the power amplifier module output is
rectified by D1022 (1SS321), then delivered to APC
Q1038 (LM2904PWR), as a DC voltage which is pro-
portional to the output level of the power amplifier
module.
The APC Q1038 (LM2904PWR) is compared the rec-
tified DC voltage from the power amplifier module
and the reference voltage from the main CPU Q2002
(HD64F2266TF13), to produce a control voltage,
which regulates supply voltage to the power ampli-
fier module Q1030 (RA60H1317M), so as to main-
tain stable output power under varying antenna
loading condition.
PLL
A portion of the output from the VCO Q1009
(2SC5231) passes through the buffer amplifier
Q1010 and Q1017 (both 2SC5374), then delivered
to the programmable divider section of the PLL IC
Q1011 (MB15A01PFV1), which divided according
to the frequency dividing data that is associated with
the setting frequency input from the main CPU
Q2002 (HD64F2266TF13). It is then sent to the phase
comparator section of the PLL IC Q1011
(MB15A01PFV1).
The 21.25 MHz frequency of the reference oscillator
circuit made up of X1001 is divided by the reference
frequency divider section of Q1011 (MB15A01PFV1)
into 4250 or 3400 parts to become 5 kHz or 6.25 kHz
comparative reference frequencies, which are uti-
lized by the phase comparator section of Q1011
(MB15A01PFV1).
The phase comparator section of Q1011
(MB15A01PFV1) compares the phase between the
frequency-divided oscillation frequency of the VCO
circuit and comparative frequency and its output is
a pulse corresponding to the phase difference. This
pulse is integrated by the charge pump and loop fil-
ter into a control voltage (VCV) to control the oscil-
lation frequency of the VCO Q1009 (2SC5231).
8
Page 9

Alignment
Introduction
The FT-1900R is carefully aligned at the factory for
the specified performance across the amateur band.
Realignment should therefore not be necessary ex-
cept in the event of a component failure. Only an
authorized Vertex Standard representative should
perform all component replacement and service, or
the warranty policy may be void.
The following procedures cover the adjustments that
are not normally required once the transceiver has
left the factory. However, if damage occurs and some
parts subsequently are replaced, realignment may
be required. If a sudden problem occurs during nor-
mal operation, it is likely due to component failure;
realignment should not be done until after the faulty
component has been replaced.
We recommend that servicing be performed only
by authorized Vertex Standard service technicians
who are experienced with the circuitry and fully
equipped for repair and alignment. If a fault is sus-
pected, contact the dealer from whom the transceiver
was purchased for instructions regarding repair.
Authorized Vertex Standard service technicians re-
align all circuits and make complete performance
checks to ensure compliance with factory specifica-
tions after replacing any faulty components.
Those who do undertake any of the following align-
ments are cautioned to proceed at their own risk.
Problems caused by unauthorized attempts at re-
alignment are not covered by the warranty policy.
Also, Vertex Standard reserves the right to change
circuits and alignment procedures in the interest of
improved performance, without notifying owners.
Required Test Equipment
The following test equipment (and familiarity with
its use) is necessary for complete realignment. Cor-
rection of problems caused by misalignment result-
ing from use of improper test equipment is not cov-
ered under the warranty policy. While most steps
do not require all of the equipment listed, the inter-
actions of some adjustments may require that more
complex adjustments be performed afterwards.
Do not attempt to perform only a single step unless
it is clearly isolated electrically from all other steps.
Have all test equipment ready before beginning and,
follow all of the steps in a section in the order pre-
sented.
RF Signal Generator with calibrated output level
at 200 MHz
Deviation Meter (linear detector)
In-line Wattmeter with 5% accuracy at 200 MHz
50-Ohm 50-W RF Dummy Load
8-Ohm AF Dummy Load
Regulated DC Power Supply adjustable from 6
to 15 VDC, 10A
Frequency Counter: 0.2-ppm accuracy at 200 MHz
AF Signal Generator
AC Voltmeter
DC Voltmeter: high impedance
VHF Sampling Coupler
SINAD Meter
Under no circumstances should any alignment be
attempted unless the normal function and operation
of the transceiver are clearly understood, the cause
of the malfunction has been clearly pinpointed and
any faulty components replaced, and realignment
determined to be absolutely necessary.
9
Page 10

Alignment
Alignment Preparation & Precautions
A 50-Ohm RF load and in-line wattmeter must be
connected to the antenna jack in all procedures that
call for transmission; alignment is not possible with
an antenna. After completing one step, read the next
step to see if the same test equipment is required. If
not, remove the test equipment (except dummy load
and wattmeter, if connected) before proceeding.
Correct alignment requires that the ambient tem-
perature be the same as that of the transceiver and
test equipment, and that this temperature be held
constant between 68 °F ~ 86 °F (20 °C ~ 30 °C). When
the transceiver is brought into the shop from hot or
cold air, it should be allowed some time to come to
room temperature before alignment. Whenever pos-
sible, alignments should be made with oscillator
shields and circuit boards firmly affixed in place.
Also, the test equipment must be thoroughly
warmed up before beginning.
Note: Signal levels in dB referred to in the alignment
procedure are based on 0dBµ = 0.5µV.
Test Setup
Set up the test equipment as shown below for trans-
ceiver alignment.
Entering the Alignment Mode
Alignment of the FT-1900R is performed using a
front panel software-based procedure. To perform
alignment of the transceiver, it must first be placed
in the “Alignment Mode,” in which the adjustments
will be made and then stored into memory.
PLL Reference Frequency
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
B0201 rFB0201 rF
B0201 rF.”
B0201 rFB0201 rF
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “PLL Reference Frequency.”
Press the PTT switch to activate the transmitter,
adjust the DIAL knob so that the counter fre-
quency reading is 148.000 MHz (±100 Hz).
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
RF Front-end Tuning
Inject a 145.100 MHz signal at a level of –10 dBµ
(with 1 kHz modulation @±3.5 kHz deviation)
from the RF signal generator.
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
B0111 tnB0111 tn
B0111 tn.”
B0111 tnB0111 tn
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “RF Front-end Tuning.”
Adjust the DIAL knob so that the maximum
SINAD.
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
Squelch Threshold Level
Inject a 145.100 MHz signal at a level of –14 dBµ
(with 1 kHz modulation @±3.5 kHz deviation)
from the RF signal generator.
Rotate the SQL knob to the 10-o’clocl position.
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
B0111 tLB0111 tL
B0111 tL.”
B0111 tLB0111 tL
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “Squelch Threshold Level.”
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key three times.
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
To enter the Alignment mode:
1. Press and hold in the [MHz(SET)] key while turning
the radio on.
2. Press and hold in the [PWR
( )]
switch for 1/2 sec-
ond to turn the radio off.
3. To enter the Alignment mode, press and hold in the
[REV(DW)] and [D/MR(MW)] keys while turning the
radio on. Once the radio is on, release these two key.
The transceiver is now in the “Alignment Mode.”
10
50-Ohm
Dummy Load
Inline
Watt met er
Frequency
Counter
RF
Signal Generator
RF Sampling
Coupler
ANT
FT-1900R
MIC
AF
Signal Generator
TEST EQUIPMENT SETUP
DC INPUT
EXT SP
RF
Signal Generator
SINAD MeterDeviation Meter
GND +8V
MIC INPUT
PTT/CLONE
MIC SW1
MIC SW2
Page 11

Alignment
S-meter Level (S-1)
Inject a 145.100 MHz signal at a level of –5 dBµ
(with 1 kHz modulation @±3.5 kHz deviation)
from the RF signal generator.
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “S-meter Level (S-1).”
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key three times.
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
S-meter Level (S-9)
Inject a 145.100 MHz signal at a level of +20 dBµ
(with 1 kHz modulation @±3.5 kHz deviation)
from the RF signal generator.
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “S-meter Level (S-9).”
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key three times.
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
TX Power (High)
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “TX Power (High).”
Press the PTT switch to activate the transmitter,
adjust the DIAL knob so that the RF Power Meter
reading is 50 W (±2.0W).
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
TX Power (Low 3)
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “TX Power (Low 3).”
Press the PTT switch to activate the transmitter,
adjust the DIAL knob so that the RF Power Meter
reading is 25 W (±1.5 W).
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
B0111 S1B0111 S1
B0111 S1.”
B0111 S1B0111 S1
B0111 S9B0111 S9
B0111 S9.”
B0111 S9B0111 S9
B0101 HPB0101 HP
B0101 HP.”
B0101 HPB0101 HP
B0101 L3B0101 L3
B0101 L3.”
B0101 L3B0101 L3
TX Power (Low 2)
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “TX Power (Low 2).”
Press the PTT switch to activate the transmitter,
adjust the DIAL knob so that the RF Power Meter
reading is 10 W (±1.0 W).
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
TX Power (Low 1)
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “TX Power (Low 1).”
Press the PTT switch to activate the transmitter,
adjust the DIAL knob so that the RF Power Meter
reading is 5 W (±0.5 W).
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
TX Deviation
Inject a 1 kHz, 50 mV signal from the Audio Gen-
erator.
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “TX Deviation.”
Press the PTT switch to activate the transmitter,
adjust the DIAL knob so that the Deviation Meter
reading is 4.2 kHz (±0.1 kHz) (EXP version: 4.5
kHz ± 0.1 kHz).
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
CTCSS TX Deviation
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “CTCSS TX Deviation.”
Press the PTT switch to activate the transmitter,
adjust the DIAL knob so that the Deviation Meter
reading is 0.6 kHz (±0.05 kHz).
Press the [D/MR(MW
B0101 L2B0101 L2
B0101 L2.”
B0101 L2B0101 L2
B0101 L1B0101 L1
B0101 L1
B0101 L1B0101 L1
B0101 dUB0101 dU
B0101 dU.”
B0101 dUB0101 dU
B0101 100B0101 100
B0101 100.”
B0101 100B0101 100
)]
.”
key.
11
Page 12

Alignment
DCS TX Deviation
Rotate the DIAL knob to set the alignment pa-
rameter to “
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key to enable adjustment
of the “DCS TX Deviation.”
Press the PTT switch to activate the transmitter,
adjust the DIAL knob so that the Deviation Meter
reading is 0.6 kHz (±0.05 kHz).
Press the [D/MR(MW)] key.
B0101 dCB0101 dC
B0101 dC.”
B0101 dCB0101 dC
Closing the Alignment mode
1. Press the [DW(REV)] key to save the new setting and
exit to normal operation.
2. Press and hold in the [PWR
ond to turn the radio off.
3. Press and hold in the [MHz(SET)] key while turning
the radio on.
( )]
switch for 1/2 sec-
12
Page 13

MAIN Unit
Circuit Diagram
Ú1 Q1028
Pin RX TX
1 5.0 V 5.0 V
2 --- ---
3 3.0 V 0 V
4 5.0 V 0.6 V
5 5.0 V 0.5 V
6 5.0 V 0.5 V
7 --- ---
8 0.7 V 0 V
9 1.1 V 0 V
10 5.0 V 0.6 V
11 4.2 V 0.1 V
12 0.6 V 0 V
13 --- ---
14 --- ---
15 0 V 0 V
16 1.0 V 0 V
Ú2 Q1043 Pin 2
RX: 0.7 V
TX (LOW 1): 2.1 V
TX (LOW 2): 2.5 V
TX (LOW 3): 3.3 V
TX (HIGH): 4.3 V
4.3 V
0 V
RX: 7.9 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 13.8 V
TX: 12.4 V
RX: 1.4 V
TX: 1.7 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 4.9 V
RX: 2.1 V
TX: 0 V
0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 0.8 V
0 V
4.6 V
0 V
RX: 2.1 V
TX: 0.1 V
RX: 2.1 V
TX: 0 V
0 V
2.0 V
3.8 V
4.8 V
4.8 V
4.1 V
1.4 V
RX: 3.2 V
TX: 0 V
0 V
RX: 1.4 V
TX: 1.7 V
5.0 V
RX: 2.1 V
TX: 0 V
RX: 1.9 V
TX: 0 V
3.2 V
3.3 V
RX: 4.2 V
TX: 0.5 V
1.9 V
2.0 V2.0 V
0 V
RX: 0.6 V
TX: 0.5 V
0 V
RX: 2.2 V
TX: 0 V
RX: 1.9 V
TX: 0 V
5.0 V
8.0 V
5.0 V
RX: 7.8 V
TX: 0.1 V
0 V
RX: 0.7 V
TX: 0.1 V
RX: 0.5 V
TX: 0.6 V
RX: 3.0 V
TX: 0 V
RX: 0.1 V
TX: 8.0 V
RX: 6.1 V
TX: 4.2 V
0.7 V
0 V
RX: 7.2 V
TX: 8.0 V
RX: 0.6 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 1.4 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 3.4 V
TX: 0 V
RX: 7.8 V
TX: 7.2 V
RX: 4.8 V
TX: 0.2 V
RX: 7.9 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 5.0 V
RX: 6.9 V
TX: 0.5 V
2.3 V
RX: 5.4 V
TX: 0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 8.0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 2.0 V
RX: 2.9 V
TX: 0.4 V
Ú1
RX: 0.1 V
TX: 0 V
RX: 4.5 V
TX: 0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 6.9 V
0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 1.4 V
0 V
4.9 V
0.6 V
RX: 6.8 V
TX: 6.2 V
RX: 5.2 V
TX: 0.6 V
RX: 5.0 V
TX: 4.5 V
RX: 2.3 V
TX: 0.1 V
0 V
0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 5.0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 4.3 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 4.6 V
RX: 6.4 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 3.8 V
RX: 0.7 V
TX: 0.4 V
1.3 V
0 V
0 V
0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 4.8 V
RX: 0.8 V
TX: 0 V
RX: 2.5 V
TX: 0.8 V
0 V
RX: 2.1 V
TX: 0.7 V
0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 3.1 V
RX: 7.2 V
TX: 4.5 V
1.9 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 3.1 V
RX: 6.9 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 3.7 V
TX: 0.3 V
RX: 1.7 V
TX: 0.1 V
RX: 2.5 V
TX: 0.3 V
0 V
0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 1.6 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 0.8 V
0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 3.1 V
RX: 4.2 V
TX: 0.3 V
RX: 6.8 V
RX: 0.7 V
TX: 0 V
3.1 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 5.5 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 3.1 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 3.2 V
TX: 0.2 V
0.7 V
0.7 V
1.9 V
RX: 1.4 V
TX: 0.1 V
RX: 2.6 V
TX: 0.4 V
RX: 1.9 V
TX: 0.7 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 4.9 V
RX: 2.0 V
TX: 0.7 V
RX: 1.4 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 0.9 V
TX: 0 V
0 V
RX: 3.2 V
TX: 0 V
0 V
RX: 7.7 V
TX: 0.5 V
RX: 1.9 V
TX: 1.8 V
Ú2
2.8 V
RX: 1.9 V
TX: 0.7 V
RX: 2.5 V
TX: 0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 5.0 V
0 V
RX: 0 V
TX: 7.5 V
4.1 V
4.6 V
0 V
5.0 V
0 V
3.0 V
13
Page 14

MAIN Unit
Note
14
Page 15

MAIN Unit
Parts Layout (Side A)
BA DCEFHGI
RA60H1317M1
(Q1030)
2SA1774 (FR)
(Q1007)
CD4094BPWR
(Q1048)
MB15A01PFV1
(Q1011)
NJM2591V
(Q1028)
KIA7808API
(Q1015)
2SJ615
(Q1008)
3SK299 (U73)
(Q1037, 1045)
LA4425A
(Q1035)
2SC4081 (B)
(Q1033)
2SC4400 (RT4)
(Q1032)
2SC4617 (BR)
(Q1051, 1053)
2SC5226 (R22)
(Q1026)
2SC5231 (C9)
(Q1009)
2SC5374 (NA)
(Q1010, 1017, 1023)
1
2
3
4
DTC124EE (25)
(Q1052)
DA221 (26)
(D1011, 1013, 1016)
DTC144EE (26)
(Q1003, 1004, 1014)
5
DAN235E (M)
(D1010)
6
7
15
Page 16

MAIN Unit
Parts Layout (Side B)
ba dcefh
1
2
3
g
i
LM2904PWR
(Q1006, 1038,
1044, 1050)
2SA1774 (FR)
(Q1024, 2027, 1029)
2SC4081 (B)
(Q1001, 1012, 1021,
1046, 1047)
FMMTL718TA
(Q1025)
LM2902PWR
(Q1005, 1049)
2SJ347 (KS)
(Q1039)
DTC144EE (26)
(Q1013, 1018, 1019,
1020, 1031, 1040)
M62364FP
(Q1043)
2SJ364 (4M)
(Q1034, 1036,
1041, 1042)
S-812C50AUA
(Q1016)
4
5
DA221 (26)
(D1009)
1SS321 (F9)
(D1022)
DAN222 (N)
(D1008, 1012, 1014,
1029, 1031)
DTC143ZE (E23)
(Q1022)
6
7
16
Page 17

MAIN Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
PCB with Components CB3119006 CE:OFF, DST:USA2
CB3119007 CE:OFF, DST:EXP2
Printed Circuit Board AH023N000 FR013240E 1-
C 1001 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 1 0V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- B g5
C 1002 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 1 0V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- B g5
C 1003 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B g4
C 1004 CHIP CAP. 1uF 1 0V F GRM188F11A105ZA01D K22105001 1- B d5
C 1005 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50 V CH GRM1882C1H101JA01D K22174235 1- A B2
C 1006 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A A 2
C 1007 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 3300uF 16V UVR1C332MHD K40129106 1- A B2
C 1008 CHIP CAP. 0.5pF 50 V CK GRM1884C1HR50CZ01D K22174201 1- A C6
C 1009 CHIP CAP. 15pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H150JA01D K22174215 1- A C6
C 1011 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C7
C 1012 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C6
C 1013 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C6
C 1014 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C6
C 1015 CHIP TA.CAP. 0.22uF 20V TMCP1D224MTRF K78130069 1- A D7
C 1016 CHIP TA.CAP. 0.22uF 20V TMCP1D224MTRF K78130069 1- A D7
C 1017 CHIP TA.CAP. 3.3uF 6.3V TEESVP0J335M8R K78080052 1- A D6
C 1018 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A D7
C 1019 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 25 V B GRM188B11E473KA01D K22144811 1- A D6
C 1020 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A D6
C 1021 CHIP CAP. 0.0082uF 50V B GRM188B11H822KA01D K22174837 1- B d5
C 1022 CHIP CAP. 0.0082uF 50V B GRM188B11H822KA01D K22174837 1- B d5
C 1024 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 25 V TEESVA1E105M8R K78140013 1- B d5
C 1025 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B d5
C 1026 CHIP CAP. 0.0027uF 50V B GRM188B11H272KA01D K22174814 1- B d5
C 1027 CHIP TA.CAP. 1uF 25 V TEESVA1E105M8R K78140013 1- B d5
C 1029 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B g2
C 1030 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C3
C 1031 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A B3
C 1032 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C3
C 1033 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C5
C 1034 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C5
C 1035 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C6
C 1036 CHIP CAP. 18pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H180JA01D K22174217 1- A C6
C 1037 CHIP CAP. 20pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H200JZ01D K22174218 1- A C6
C 1038 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C6
C 1039 CHIP CAP. 1uF 1 0V F GRM188F11A105ZA01D K22105001 1- A C6
C 1040 CHIP CAP. 1.5pF 50 V CK GRM1884C1H1R5CZ01D K22174258 1- A C5
C 1041 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C5
C 1042 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 1 0V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- A D5
C 1043 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- A D6
C 1044 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A D5
C 1045 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A D6
C 1046 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 1 0V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- A D6
C 1047 CHIP CAP. 47pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H470JA01D K22174227 1- A D7
C 1048 CHIP CAP. 47pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H470JA01D K22174227 1- A D7
C 1049 CHIP CAP. 47pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H470JA01D K22174227 1- A D7
C 1050 CHIP CAP. 15pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H150JA01D K22174215 1- A D6
C 1051 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B d5
C 1052 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 50 V B GRM188B11H223KA01D K22174839 1- B e5
C 1053 CHIP CAP. 0.015uF 50 V B GRM188B11H153KA01D K22174838 1- B e5
C 1054 CHIP CAP. 150pF 50 V CH GRM1882C1H151JA01D K22174239 1- B d6
C 1055 CHIP CAP. 560pF 50 V B GRM188B11H561KA01D K22174806 1- B d6
C 1056 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 100uF 16V UVR1C101MDD K40129104 1- A B5
C 1057 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- A B4
C 1059 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B g5
C 1060 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B g5
C 1061 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 10uF 16V UVR1C100MDD K40129103 1- A B5
C 1062 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B g5
C 1063 CHIP CAP. 47pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H470JA01D K22174227 1- A C5
C 1064 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C4
C 1065 CHIP CAP. 5pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H5R0CZ01D K22174206 1- A C5
C 1066 CHIP CAP. 5pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H5R0CZ01D K22174206 1- A C5
C 1067 CHIP CAP. 5pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H5R0CZ01D K22174206 1- A C4
C 1068 CHIP CAP. 7pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H7R0DZ01D K22174208 1- A E6
C 1069 CHIP CAP. 47pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H470JA01D K22174227 1- A E6
C 1070 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50 V CH GRM1882C1H101JA01D K22174235 1- A E6
C 1071 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A E7
C 1072 CHIP CAP. 10pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H100JA01D K22174211 1- A E6
C 1073 CHIP CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V B JMK107BJ475MA-T K22084803 1- A E6
C 1074 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A E6
C 1076 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A E6
C 1077 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 50 V B GRM188B11H223KA01D K22174839 1- B e6
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
17
Page 18

MAIN Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
C 1078 CHIP CAP. 0.015uF 50 V B GRM188B11H153KA01D K22174838 1- B e6
C 1079 CHIP CAP. 150pF 50 V CH GRM1882C1H151JA01D K22174239 1- B e6
C 1080 CHIP CAP. 560pF 50 V CH GRM1882C1H561JA01D K22174273 1- B e6
C 1081 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B g4
C 1082 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 100uF 16V USR1C101MDD K40129110 1- A C4
C 1083 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B f 5
C 1084 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B f 4
C 1085 CHIP CAP. 22pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H220JA01D K22174219 1- A C4
C 1086 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B a6
C 1089 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- A H5
C 1090 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B b5
C 1091 CHIP CAP. 120pF 50 V CH GRM1882C1H121JA01D K22174237 1- A G5
C 1092 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B b5
C 1093 CHIP CAP. 120pF 50 V CH GRM1882C1H121JA01D K22174237 1- A G5
C 1094 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 25 V B GRM188B11E473KA01D K22144811 1- A G5
C 1096 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 25 V B GRM188B11E473KA01D K22144811 1- A G5
C 1098 CHIP CAP. 0.0047uF 50V B GRM188B11H472KA01D K22174817 1- A G5
C 1099 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 16 V B GRM39B473K16PT K22124804 1- B e6
C 1099 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 25 V B GRM188B11E473KA01D K22144811 1- B e6
C 1101 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174809 1- B g4
C 1101 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B g4
C 1102 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B g4
C 1103 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B f 5
C 1104 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B f 4
C 1105 CHIP CAP. 15pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H150JA01D K22174215 1- A C4
C 1106 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C4
C 1107 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A D4
C 1108 CHIP CAP. 15pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H150JA01D K22174215 1- A C4
C 1109 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C4
C 1110 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B f 4
C 1111 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- A H6
C 1112 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B a6
C 1113 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A H6
C 1114 CHIP CAP. 47pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H470JA01D K22174227 1- A G6
C 1115 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 1 0V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- A H6
C 1116 CHIP CAP. 47pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H470JA01D K22174227 1- A G6
C 1117 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- A G6
C 1118 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- A G6
C 1119 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B b5
C 1120 CHIP CAP. 0.033uF 16 V R GRM188R11C333KA01D K22124801 1- B a4
C 1121 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 25 V B GRM188B11E473KA01D K22144811 1- B b6
C 1122 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 50 V B GRM188B11H223KA01D K22174839 1- B a4
C 1123 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B a4
C 1124 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 10uF 16 V RE2-16V100ME3# K40129004 1- A A2
C 1125 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F7
C 1126 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F6
C 1127 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F7
C 1128 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F6
C 1129 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F7
C 1130 CHIP CAP. 47pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H470JA01D K22174227 1- A B6
C 1131 CHIP CAP. 33pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H330JA01D K22174223 1- A C3
C 1132 CHIP CAP. 33pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H330JA01D K22174223 1- A C3
C 1133 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A C3
C 1134 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A E3
C 1135 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A D3
C 1136 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A G6
C 1137 CHIP CAP. 39pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H390JA01D K22174225 1- A G6
C 1138 CHIP CAP. 43pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H430JZ01D K22174226 1- A G6
C 1139 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 25 V B GRM188B11E473KA01D K22144811 1- B b5
C 1140 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B h1
C 1141 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B h1
C 1142 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B h3
C 1143 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B g6
C 1144 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 470uF 16V UVR1C471MPD K40129108 1- A A4
C 1145 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B g6
C 1146 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B h6
C 1147 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 220uF 16V UVR1C221MED K40129105 1- A A7
C 1148 CHIP CAP. 47pF 5 0V CH GRM1552C1H470JZ01D K22178228 1- A F7
C 1149 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F6
C 1150 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F6
C 1151 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A F7
C 1152 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B c 6
C 1153 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A F7
C 1154 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F6
C 1155 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A F7
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
18
Page 19

MAIN Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
C 1156 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F6
C 1157 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- A E3
C 1158 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F3
C 1161 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 25 V B GRM188B11E473KA01D K22144811 1- B d4
C 1162 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B c 4
C 1163 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 10uF 16V UVR1C100MDD K40129103 1- A E3
C 1164 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 16V TAJA475M016Y K78120079 1- B c4
C 1165 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B c 4
C 1166 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- A G5
C 1167 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F4
C 1168 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- A F4
C 1170 CHIP CAP. 8pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H8R0DZ01D K22174209 1- A F5
C 1171 CHIP CAP. 1pF 5 0V CK GRM1884C1H1R0CZ01D K22174202 1- A F5
C 1173 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B c5
C 1174 CHIP CAP. 56pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H560JA01D K22174229 1- A F5
C 1175 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- A F5
C 1176 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B g6
C 1177 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B b7
C 1178 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 50 V B GRM188B11H223KA01D K22174839 1- B b7
C 1179 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A F7
C 1180 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F6
C 1181 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A G7
C 1182 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A G6
C 1183 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A G7
C 1184 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B b6
C 1185 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A G7
C 1186 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A G6
C 1187 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A G6
C 1188 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- A G4
C 1189 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 100V CH GRM31M2C2A102JZ01L K22201202 1- A F3
C 1190 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 1 0V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- A G4
C 1191 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A G4
C 1192 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A F4
C 1193 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B c4
C 1194 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B b4
C 1196 CHIP CAP. 22pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H220JA01D K22174219 1- A F4
C 1198 CHIP CAP. 43pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H430JZ01D K22174226 1- A F5
C 1199 CHIP CAP. 0.5pF 50 V CK GRM1884C1HR50BZ01D K22174265 1- A G4
C 1200 CHIP CAP. 5pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H5R0CZ01D K22174206 1- A G5
C 1201 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B c5
C 1202 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B b4
C 1203 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B c 5
C 1204 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 6.3V TAJA226M006Y K78080086 1- B c 5
C 1205 CHIP CAP. 470pF 50 V CH GRM1882C1H471JA01D K22174249 1- B b7
C 1206 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 50 V B GRM188B11H223KA01D K22174839 1- B b7
C 1207 CHIP CAP. 0.0047uF 50V B GRM188B11H472KA01D K22174817 1- B b7
C 1208 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B b7
C 1209 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B g6
C 1210 CHIP CAP. 18pF 500V CH CF316CH180J500AT K22271258 1- A G3
C 1211 CHIP CAP. 18pF 500V CH CF316CH180J500AT K22271258 1- A G3
C 1212 CHIP CAP. 27pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H270JA01D K22174221 1- A H4
C 1213 CHIP CAP. 22pF 500V CH CF316CH220J500AT K22271259 1- A G3
C 1214 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B b4
C 1215 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B b4
C 1216 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B a4
C 1217 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B a3
C 1218 CHIP CAP. 33pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H330JA01D K22174223 1- A G5
C 1220 CHIP CAP. 8pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H8R0DZ01D K22174209 1- A G4
C 1221 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A G5
C 1223 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A G5
C 1224 CHIP CAP. 10pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H100JA01D K22174211 1- A G4
C 1225 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1 - B c 6
C 1226 CHIP CAP. 0.0056uF 50V B GRM188B11H562KA01D K22174818 1- B c4
C 1227 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B c 5
C 1228 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B c5
C 1230 CHIP CAP. 5pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H5R0CZ01D K22174206 1- B b7
C 1231 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 1 0V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- B a6
C 1232 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B a7
C 1233 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B b7
C 1236 CHIP CAP. 33pF 500V CH CF316CH330J500AT K22271261 1- A G2
C 1237 CHIP CAP. 1pF 200V CK GRM2194C2D1R0CY21D K22230208 1- A H3
C 1239 CHIP CAP. 33pF 500V CH CF316CH330J500AT K22271261 1- A H2
C 1240 CHIP CAP. 1pF 200V CK GRM2194C2D1R0CY21D K22230208 1- A H3
C 1241 CHIP CAP. 7pF 500V CH CF316CH070D500AT K22271252 1 - A H2
C 1243 CHIP CAP. 3pF 5 0V CJ GRM1883C1H3R0CZ01D K22174204 1- B a3
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
19
Page 20

MAIN Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
C 1244 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A G4
C 1245 CHIP CAP. 10pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H100JA01D K22174211 1- A G5
C 1248 CHIP CAP. 39pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H390JA01D K22174225 1- A H5
C 1249 CHIP CAP. 2pF 5 0V CK GRM1884C1H2R0CZ01D K22174203 1- A H5
C 1250 CHIP CAP. 22pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H220JA01D K22174219 1- A H5
C 1251 CHIP CAP. 1pF 5 0V CK GRM1884C1H1R0BZ01D K22174267 1- A H4
C 1252 CHIP CAP. 39pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H390JA01D K22174225 1- A H5
C 1253 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B c 4
C 1254 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B c 4
C 1255 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B c5
C 1256 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B c 4
C 1257 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B c5
C 1258 CHIP CAP. 0.0022uF 50V B GRM188B11H222KA01D K22174813 1- B c5
C 1259 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 50 V B GRM188B11H103KA01D K22174823 1- B c5
C 1260 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B b6
C 1261 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B b7
C 1262 CHIP CAP. 27pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H270JA01D K22174221 1- B b6
C 1263 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- B b6
C 1264 CHIP CAP. 12pF 500V CH CF316CH120J500AT K22271256 1- A H1
C 1265 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 100V CH GRM31M2C2A102JZ01L K22201202 1- A H1
C 1266 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50 V CH GRM1882C1H101JA01D K22174235 1- A H5
C 1267 CHIP CAP. 4pF 5 0V CH GRM1882C1H4R0CZ01D K22174205 1- B a3
C 1268 CHIP CAP. 0.5pF 50 V CK GRM1884C1HR50BZ01D K22174265 1- A H5
C 1270 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 1 0V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- B c4
C 1273 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B a6
C 1274 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B a6
C 1275 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- A E7
C 1276 CHIP CAP. 1uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B g7
C 1277 CHIP CAP. 0.0022uF 50V B GRM188B11H222KA01D K22174813 1- A H5
C 1278 CHIP CAP. 0.0056uF 50V B GRM188B11H562KA01D K22174818 1- A H6
C 1279 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- A G5
C 1280 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 16 V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- A G5
C 1281 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1- A G7
C 1282 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 50 V B GRM188B11H102KA01D K22174821 1- A D6
C 1283 CHIP CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V B JMK107BJ475MA-T K22084803 1- A F6
CD1001 CERAMIC DISC JTBM450CX7 H7901520 1 - A G7
CF1001 CERAMIC FILTER ALFYM450G=K H3900534 1- A H6
CF1001 CERAMIC FILTER LTM450GW H3900573 1- A H6
CF1002 CERAMIC FILTER LTM450FW H3900572 1- A H5
D 1001 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B g5
D 1002 DIODE HVC350B-TRF-E G2070596 1- A C6
D 1003 SURGE ABSORBER P6KA18A-E3 Q9000721 1- A B2
D 1004 DIODE HSC277TRF-E G2070584 1- A C6
D 1005 DIODE HSC277TRF-E G2070584 1- A C6
D 1006 DIODE HVC350B-TRF-E G2070596 1- A E6
D 1007 DIODE HVC350B-TRF-E G2070596 1- A E6
D 1008 DIODE DAN222 TL G2070174 1- B c5
D 1009 DIODE DA221 TL G2070178 1- B e6
D 1010 DIODE DAN235E TL G2070612 1- A C4
D 1011 DIODE DA221 TL G2070178 1- A G5
D 1012 DIODE DAN222 TL G2070174 1- B a5
D 1013 DIODE DA221 TL G2070178 1- A H5
D 1014 DIODE DAN222 TL G2070174 1- B a6
D 1015 DIODE EDZ TE-61 5.1B G2070998 1- B b5
D 1016 DIODE DA221 TL G2070178 1- A G6
D 1017 DIODE HVC350B-TRF-E G2070596 1- A G5
D 1018 DIODE L709CER G2071124 1- A G3
D 1019 DIODE L709CER G2071124 1- A G3
D 1020 DIODE RLS135 TE-11 G2070128 1- A H4
D 1021 DIODE HVC350B-TRF-E G2070596 1- A G5
D 1022 DIODE 1SS321(TE85R.F) G2070076 1- B a3
D 1023 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A G5
D 1024 DIODE HVC350B-TRF-E G2070596 1- A H5
D 1025 DIODE HVC350B-TRF-E G2070596 1- A H5
D 1026 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A E7
D 1028 DIODE RLS135 TE-11 G2070128 1- A H4
D 1029 DIODE DAN222 TL G2070174 1- B b5
D 1030 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A F6
D 1031 DIODE DAN222 TL G2070174 1- B b5
FB1001 FERRITE BEADS SMB304729 L9190094 1- A A 1
FB1002 FERRITE BEADS SMB304729 L9190094 1- A B1
FB1003 FERRITE BEADS SMB304729 L9190094 1- A A 2
FB1004 FERRITE BEADS SMB304729 L9190094 1- A B1
FB1005 FERRITE BEADS SMB304729 L9190094 1- A B3
FB1006 FERRITE BEADS BK1608HS121-T L9190081 1- B h1
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
20
Page 21

MAIN Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
FB1007 FERRITE BEADS BK1608HS121-T L9190081 1- B h1
J 1001 CONNECTOR SC25-02WS P0090621 1- A A 3
J 1002 CONNECTOR HSJ0836-0105009 P1091085 1 - A A 1
J 1003 CONNECTOR 32FLT-SM2-TB(LF)(SN)(M) P1091258 1- A F6
L 1002 CHIP COIL 0.056uH LQW2BHN56NG03L L1690978 1 - A C6
L 1003 CHIP COIL 0.018uH 2% LQW18AN18NG00D L1690883 1 - A C6
L 1004 M.RFC 0.1uH TFL0816-100N L1690981 1- A C5
L 1005 M.RFC 0.047uH TFL0816-47 L1690499 1- B f4
L 1006 M.RFC 0.082uH TFL0816-82N L1690980 1- A C4
L 1007 M.RFC 0.047uH TFL0816-47 L1690499 1- A C3
L 1008 M.RFC 1uH LK1608 1R0K-T L1690687 1 - A G6
L 1009 M.RFC 1uH LK1608 1R0K-T L1690687 1 - A G6
L 1010 COIL 0.212uH AS051047-212N L0022834 1- A F4
L 1011 M.RFC 1uH ELJ-ND1R0JF L1690977 1- A F5
L 1012 CHIP COIL 0.1uH 2% LQW18ANR10G00D L1690892 1- A F5
L 1013 COIL 0.033uH AS1005-33NK L0022546 1 - A G3
L 1014 COIL 0.047uH AS0805-47NK L0022539 1 - A H4
L 1015 CHIP COIL 0.1uH 2% LQW18ANR10G00D L1690892 1- A G5
L 1016 M.RFC 1uH ELJ-ND1R0JF L1690977 1- A G4
L 1017 COIL 0.033uH AS1005-33NK L0022546 1 - A G3
L 1018 COIL 0.033uH AS1005-33NK L0022546 1 - A H2
L 1019 COIL 0.033uH AS1005-33NK L0022546 1 - A H2
L 1020 CHIP COIL 0.1uH 2% LQW18ANR10G00D L1690892 1- A G5
L 1021 CHIP COIL 0.022uH 2% LQW18AN22NG00D L1690884 1 - A H5
L 1022 COIL 0.012uH AS080336-12N L0022810 1- A H1
L 1024 CHIP COIL 0.082uH 2% LQW18AN82NG00D L1690891 1 - A H4
Q 1001 TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T106 R G3340818R 1- B g5
Q 1003 TRANSISTOR DTC144EE TL G3070075 1- A C6
Q 1004 TRANSISTOR DTC144EE TL G3070075 1- A D7
Q 1005 IC LM2902PWR G1094009 1- B e6
Q 1006 IC LM2904PWR G1094010 1- B d5
Q 1007 TRANSISTOR 2SA1774 TL R G3117748R 1- A D6
Q 1008 FET 2SJ615-TD-E G3706158 1 - A B4
Q 1009 TRANSISTOR 2SC5231C9-TL G3352318I 1- A C6
Q 1010 TRANSISTOR 2SC5374-TL G3353748 1- A C5
Q 1011 IC MB15A01PFV1-G-BND-EFE1 G1092545 1- A D6
Q 1012 TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T106 R G3340818R 1- B d6
Q 1013 TRANSISTOR DTC144EE TL G3070075 1- B d6
Q 1014 TRANSISTOR DTC144EE TL G3070075 1- A C4
Q 1015 IC KIA7808API G1093164 1- A A 5
Q 1016 IC S-812C50AUA-C3E-T2G G1093652 1- B g4
Q 1017 TRANSISTOR 2SC5374-TL G3353748 1- A C5
Q 1018 TRANSISTOR DTC144EE TL G3070075 1- B d5
Q 1019 TRANSISTOR DTC144EE TL G3070075 1- B d5
Q 1020 TRANSISTOR DTC144EE TL G3070075 1- B d6
Q 1021 TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T106 R G3340818R 1- B f 5
Q 1022 TRANSISTOR DTC143ZE TL G3070102 1 - B f 5
Q 1023 TRANSISTOR 2SC5374-TL G3353748 1- A C4
Q 1024 TRANSISTOR 2SA1774 TL R G3117748R 1- B f 4
Q 1025 TRANSISTOR FMMTL718TA G3070335 1 - B f4
Q 1026 TRANSISTOR 2SC5226-5-TL G3352268E 1 - A C4
Q 1027 TRANSISTOR 2SA1774 TL R G3117748R 1- B b6
Q 1028 IC NJM2591V-TE1 G1094024 1- A G6
Q 1029 TRANSISTOR 2SA1774 TL R G3117748R 1- B b5
Q 1030 IC RA60H1317M1 G1094220 1- A C2
Q 1031 TRANSISTOR DTC144EE TL G3070075 1- B b6
Q 1032 TRANSISTOR 2SC4400-4-TL G3344008D 1- A G5
Q 1033 TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T106 R G3340818R 1- A G6
Q 1034 FET 2SJ364-P(TX) G3703648P 1- B b4
Q 1035 IC LA4425A G1092241 1- A A6
Q 1036 FET 2SJ364-P(TX) G3703648P 1- B b5
Q 1037 FET 3SK299-T1(U73) G4802998 1- A F5
Q 1038 IC LM2904PWR G1094010 1- B b4
Q 1039 FET 2SJ347(TE85L.F) G3703477 1- B c5
Q 1040 TRANSISTOR DTC144EE TL G3070075 1- B c 5
Q 1041 FET 2SJ364-P(TX) G3703648P 1- B c5
Q 1042 FET 2SJ364-P(TX) G3703648P 1- B a7
Q 1043 IC M62364FP 600D G1093033 1- B g7
Q 1044 IC LM2904PWR G1094010 1- B c5
Q 1045 FET 3SK299-T1(U73) G4802998 1- A G4
Q 1046 TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T106 R G3340818R 1- B b4
Q 1047 TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T106 R G3340818R 1- B c 4
Q 1048 IC CD4094BPWR G1093866 1- A E7
Q 1049 IC LM2902PWR G1094009 1- B b7
Q 1050 IC LM2904PWR G1094010 1- B h7
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
21
Page 22

MAIN Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
Q 1051 TRANSISTOR 2SC4617 TL R G3346178R 1- A G5
Q 1052 TRANSISTOR DTC143EE TL G3070114 1- A F6
Q 1053 TRANSISTOR 2SC4617 TL R G3346178R 1- A F6
R 1001 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- B g5
R 1002 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A C6
R 1003 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A C6
R 1004 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A C6
R 1005 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 123JTH J24189038 1- A C6
R 1006 CHIP RES. 33 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 330JTH J24189007 1- A C6
R 1007 CHIP RES. 1.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 182JTH J24189028 1- A D7
R 1008 CHIP RES. 1.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 182JTH J24189028 1- A D6
R 1010 CHIP RES. 1.5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 152JTH J24189027 1- A D6
R 1011 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A D6
R 1012 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A D6
R 1013 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- A D6
R 1014 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B d5
R 1015 CHIP RES. 68 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 681JTH J24189023 1- B d5
R 1016 CHIP RES. 560k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 564JTH J24189058 1- B d5
R 1017 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- B d5
R 1018 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 154JTH J24189051 1- B d5
R 1019 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B d5
R 1020 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- B d6
R 1021 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B d5
R 1022 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B d5
R 1023 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- B e5
R 1025 CHIP RES. 18k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 183JTH J24189040 1- B d5
R 1026 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B d6
R 1027 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A B3
R 1028 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A C6
R 1029 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A C5
R 1030 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- A C5
R 1031 CHIP RES. 47 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- A C5
R 1032 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A C6
R 1033 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- A C6
R 1034 CHIP RES. 68 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 681JTH J24189023 1- A C6
R 1035 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A C5
R 1036 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A C5
R 1037 CHIP RES. 68 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 681JTH J24189023 1- A D6
R 1038 CHIP RES. 22 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 220JTH J24189005 1- A D6
R 1039 CHIP RES. 22 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 220JTH J24189005 1- A E6
R 1040 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A D6
R 1041 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A D6
R 1042 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A D6
R 1043 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A D6
R 1044 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B d5
R 1045 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B d5
R 1046 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B d5
R 1047 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- B e5
R 1048 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- B e5
R 1049 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- B e6
R 1050 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A C4
R 1051 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A C5
R 1052 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- A C5
R 1053 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A C4
R 1054 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A C4
R 1055 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- A C4
R 1056 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A E6
R 1057 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A E6
R 1058 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 105JTH J24189061 1- A E7
R 1059 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- A E7
R 1060 CHIP RES. 39k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 393JTH J24189044 1- A E6
R 1061 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A E6
R 1062 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- A E6
R 1063 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- A E6
R 1064 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- A E6
R 1065 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B d5
R 1066 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- B e6
R 1067 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- B e6
R 1068 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B f 5
R 1069 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A C4
R 1070 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B f 4
R 1071 CHIP RES. 47 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- A C4
R 1072 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A G5
R 1073 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A E7
R 1075 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b5
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
22
Page 23

MAIN Unit
Parts List
REF
R 1076 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1- A G5
R 1077 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A G5
R 1079 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A G5
R 1081 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A G5
R 1082 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A G6
R 1083 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A G5
R 1084 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B d6
R 1085 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B c6
R 1086 CHIP RES. 12k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 123JTH J24189038 1- B e6
R 1087 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B d6
R 1088 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B e5
R 1089 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B e6
R 1090 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- B f 4
R 1091 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- B f 4
R 1092 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- B f 4
R 1093 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B f4
R 1094 CHIP RES. 2.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 272JTH J24189030 1- A C4
R 1095 CHIP RES. 33 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 331JTH J24189019 1- A C3
R 1096 CHIP RES. 22 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 220JTH J24189005 1- A C4
R 1097 CHIP RES. 47 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1- A C4
R 1098 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a6
R 1099 CHIP RES. 1.5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 152JTH J24189027 1- A C4
R 1100 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a6
R 1101 CHIP RES. 33 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 330JTH J24189007 1- A C4
R 1102 CHIP RES. 22 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- B b5
R 1103 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B b6
R 1104 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B b6
R 1105 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b5
R 1106 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b5
R 1107 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A H6
R 1108 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b5
R 1109 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a6
R 1110 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A G6
R 1111 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 562JTH J24189034 1- A G6
R 1112 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b6
R 1113 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a4
R 1114 CHIP RES. 33 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 331JTH J24189019 1- A C3
R 1115 CHIP RES. 18 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 180JTH J24189004 1- A C3
R 1116 CHIP RES. 33 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 331JTH J24189019 1- A C3
R 1117 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A E3
R 1118 CHIP RES. 47 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 470JTH J24189009 1- B b5
R 1119 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A G5
R 1120 CHIP RES. 22 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A G6
R 1121 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- A G5
R 1122 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A G6
R 1123 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b4
R 1124 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B b5
R 1125 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b4
R 1126 CHIP RES. 1 1/10W 5 % RMC1/10T 1R0J J24205010 1- B i3
R 1127 CHIP RES. 10 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 100JTH J24189001 1- B g6
R 1128 CHIP RES. 0.33 1W 10% RMC1 R33KATE J24309001 1- A B6
R 1129 CHIP RES. 10 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 100JTH J24189001 1- B g6
R 1130 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B d4
R 1131 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B c4
R 1133 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B c4
R 1134 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B c4
R 1135 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B c4
R 1136 CHIP RES. 1.5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 152JTH J24189027 1- A G5
R 1137 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- A F5
R 1138 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A F5
R 1139 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B c5
R 1140 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- B c5
R 1141 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b5
R 1142 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B g6
R 1143 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B b7
R 1144 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B a7
R 1145 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A G4
R 1146 CHIP RES. 47 1 W 5 % RMC1 470JTE J24305470 1- A G4
R 1147 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- B b4
R 1148 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b4
R 1149 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A F4
R 1150 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A F4
R 1152 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- A G5
R 1153 CHIP RES. 82 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 820JTH J24189012 1- A F5
R 1154 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A F4
DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
23
Page 24

MAIN Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
R 1156 CHIP RES. 39k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 393JTH J24189044 1- A F5
R 1157 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B d5
R 1158 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B c 5
R 1159 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B c 5
R 1160 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- B b7
R 1161 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B a7
R 1162 CHIP RES. 2.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 225JTH J24189065 1- B b7
R 1163 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b7
R 1164 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 1% RMC1/16 103FTP J24183103 1- B b7
R 1165 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 1% RMC1/16 104FTP J24183104 1- B b7
R 1166 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B g7
R 1167 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B g7
R 1168 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B g7
R 1169 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b4
R 1170 CHIP RES. 15k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- B a4
R 1171 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- A G4
R 1172 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- A G5
R 1173 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- A G4
R 1174 CHIP RES. 22 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1- A G4
R 1175 CHIP RES. 33 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 331JTH J24189019 1- A G5
R 1177 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A G4
R 1178 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A G4
R 1179 CHIP RES. 68 0 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD6800 J24189360 1- B c5
R 1180 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- B b4
R 1181 CHIP RES. 2.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 272JTH J24189030 1- B b4
R 1182 CHIP RES. 1k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B b5
R 1183 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B c4
R 1184 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- B c4
R 1185 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD3302 J24189380 1- B c5
R 1186 CHIP RES. 33k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD3302 J24189380 1- B c5
R 1187 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B c5
R 1188 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD1003 J24189386 1 - B c5
R 1189 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD4702 J24189382 1- B c5
R 1190 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD4703 J24189332 1 - B c5
R 1191 CHIP RES. 2.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 225JTH J24189065 1- B b7
R 1192 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 1% RMC1/16 683FTP J24183683 1- B b7
R 1193 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 1% RMC1/16 472FTP J24183472 1 - B b7
R 1194 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 1% RMC1/16 472FTP J24183472 1 - B b7
R 1195 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 1% RMC1/16 103FTP J24183103 1- B a7
R 1196 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- B a7
R 1197 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- B a7
R 1198 CHIP RES. 10 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1- B g7
R 1199 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- B g7
R 1200 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD3303 J24189330 1 - B h7
R 1201 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD2203 J24189389 1 - B h7
R 1202 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD3303 J24189330 1 - B h7
R 1203 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD4703 J24189332 1 - B h7
R 1204 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD3303 J24189330 1 - B h7
R 1205 CHIP RES. 56k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD5602 J24189383 1- B h7
R 1206 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B a3
R 1208 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A I4
R 1209 CHIP RES. 47k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A G5
R 1210 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- A H5
R 1211 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- A H5
R 1212 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 154JTH J24189051 1- B c 4
R 1213 CHIP RES. 2.2M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 225JTH J24189065 1- B c 4
R 1214 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- B c4
R 1215 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B c4
R 1216 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- B c 4
R 1217 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD2202 J24189378 1- B c5
R 1218 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD1002 J24189374 1- B c5
R 1219 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b6
R 1220 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1- B b6
R 1221 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b7
R 1222 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b6
R 1223 CHIP RES. 68k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- B b6
R 1224 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b6
R 1225 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- A E7
R 1226 CHIP RES. 5.6k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 562JTH J24189034 1- B a3
R 1228 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B b6
R 1229 CHIP RES. 330k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 334JTH J24189055 1- B b6
R 1230 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- B b6
R 1231 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- B b6
R 1234 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- A G5
R 1235 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- A G5
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
24
Page 25

MAIN Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
R 1236 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- A G5
R 1237 CHIP RES. 68 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 681JTH J24189023 1- A G6
R 1238 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B b7
R 1239 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- B b6
R 1240 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a6
R 1241 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B b7
R 1242 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A E7
R 1243 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A E7
R 1244 CHIP RES. 150k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 154JTH J24189051 1- B c 5
R 1245 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1- B c 5
R 1246 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A D6
R 1247 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1- B b5
R 1248 CHIP RES. 10k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- A F6
R 1249 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A F6
R 1250 CHIP RES. 22k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- A E6
TH1001 THERMISTOR ERTJ1VV473J G9090122 1- A E7
TH1002 THERMISTOR ERTJ1VV473J G9090122 1- A E3
X 1001 XTAL S-6 21.25MHz 21.250MHZ H0103315 1- A E6
XF1001 XTAL FILTER 21.700MHZ H1102395 1- A F5
XF1002 XTAL FILTER 21.700MHZ H1102395 1- A F5
SHIELD CASE RA0515300 1-
LEAF SPRING R0140031 W/ CE LABEL 1-
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
25
Page 26

MAIN Unit
Note
26
Page 27

CNTL Unit
Circuit Diagram
5.0 V
RX: 4.8 V
TX: 0.6 V
RX: 4.8 V
TX: 0.6 V
4.8 V
4.0 V
8.0 V
5.0 V
3.9 V
5.0 V
3.6 V
3.4 V
0 V
0 V
0 V
5.0 V
0 V
2.3 V
2.6 V
0 V
2.6 V
5.0 V
0 V
5.0 V
2.5 V
1.8 V
0 V
5.0 V
Ú J2003
Pin RX TX
1 4.6 V 4.6 V
20 V 0 V
30 V 0 V
40 V 0 V
50 V 0 V
60 V 0 V
70 V 0 V
8 1.9 V 1.8 V
9 3.0 V 3.0 V
10 5.0 V 0.6 V
11 1.1 V 0 V
12 3.2 V 0 V
13 4.9 V 4.9 V
14 0 V 0 V
15 8.0 V 8.0 V
16 0.6 V 0 V
17 0 V 0 V
18 0 V 0 V
19 --- ---
20 5.0 V 5.0 V
21 --- ---
22 --- ---
23 --- ---
24 13.8 V 12.3 V
25 --- ---
26 --- ---
27 0 V 0 V
28 0 V 0 V
29 0 V 0 V
30 13.8 V 12.4 V
31 3.1 V 3.1 V
32 0 V 0 V
5.0 V
0 V
3.6 V
0 V
RX: 13.1 V
4.9 V
5.0 V
1.2 V
5.6 V
0.6 V
Ú
TX: 11.9 V
RX: 13.8 V
TX: 12.6 V
RX: 4.9 V
TX: 4.5 V
4.6 V
0 V
5.0 V
0 V
0 V
27
Page 28

CNTL Unit
Parts Layout (Side A)
BA DCEFHGI
1
CPH6202 (CB)
(Q2005)
DTC143ZE (E23)
(Q2004)
2
3
(Side A)
BA DCEFHGI
1
2SC4617 (BR)
(Q2007, 2008, 2013)
2SC5374 (NA)
(Q2003)
BD4830FVE
(Q2011)
2
S-812C50AUA
(Q2010)
DTC143ZE (E23)
(Q2012)
3
(Side B)
DAN222 (N)
(D2023)
HD64F2266TF13
(Q2002)
DA221 (26)
(D2001, 2025)
BR24L64
(Q2006)
28
Page 29

CNTL Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
PCB with Components CS2033409 CE:OFF, DST:USA2, TYP:A2
CS2033410 CE:OFF, DST:EXP2, TYP:A1
CS2033411 CE:OFF, DST:EXP2, TYP:A2
CS2033412 CE:OFF, DST:EXP2, TYP:A3
CS2033415 CE:OFF, DST:EXP2, TYP:B3
Printed Circuit Board FR013250D 1-
C 2001 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B i2
C 2002 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B i2
C 2003 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - A A 1
C 2004 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B h2
C 2005 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B i2
C 2006 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H101JD01D K22178236 1- B f1
C 2007 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H101JD01D K22178236 1- B f1
C 2008 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B b2
C 2009 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B b1
C 2010 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B f 2
C 2011 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B f 2
C 2012 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B f 2
C 2013 CHIP CAP. 6 pF 50 V CH GRM1552C1H6R0DZ01D K22178208 1- B d2
C 2015 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H180JZ01D K22178218 1- B e2
C 2016 CHIP CAP. 18pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H180JZ01D K22178218 1- B e2
C 2017 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B d2
C 2018 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B e1
C 2019 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- A B2
C 2020 CHIP CAP. 100pF 50V CH GRM1552C1H101JD01D K22178236 1- A B2
C 2021 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A473KA01D K22108801 1 - B e2
C 2022 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 1 6V B GRM155B11C223KA01D K22128806 1 - B d2
C 2023 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B d1
C 2024 CHIP CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V B JMK107BJ475MA-T K22084803 1- B a2
C 2025 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B a2
C 2026 CHIP CAP. 1 uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B a1
C 2027 CHIP CAP. 0.047uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A473KA01D K22108801 1 - B a1
C 2028 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B a1
C 2029 CHIP CAP. 0.0047uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H472KA01D K22178838 1 - B a1
C 2030 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B h2
C 2031 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- B h2
C 2032 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B e2
C 2033 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B d2
C 2034 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B a2
C 2035 CHIP CAP. 0.022uF 1 6V B GRM155B11C223KA01D K22128806 1 - B a2
C 2036 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B a2
C 2037 CHIP TA.CAP. 4.7uF 6.3V TEESVP0J475M8R K78080053 1- B a2
C 2038 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B a1
C 2039 CHIP CAP. 1 uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B a1
C 2040 CHIP TA.CAP. 10uF 10V TAJA106M010Y K78100072 1- B h2
C 2041 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B h2
C 2042 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B d2
C 2043 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B e2
C 2044 CHIP TA.CAP. 22uF 6.3V TAJA226M006Y K78080086 1- B d1
C 2045 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B b2
C 2046 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 10uF 1 6V UZS1C100MCL1GB K48120030 1- B b2
C 2047 CHIP CAP. 0.01uF 25 V B GRM155B11E103KA01D K22148834 1- B b2
C 2048 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 47uF 1 6V UZS1C470MCL1GB K48120031 1- B b1
C 2049 CHIP CAP. 1 uF 10 V F GRM188F11A105ZA01D K22105001 1- B b2
C 2050 CHIP CAP. 0.47uF 10 V BJ LMK107BJ474KA-T K22104803 1- B h1
C 2051 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B d1
C 2052 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B d1
C 2053 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B b2
C 2054 CHIP CAP. 1 uF 6.3V B GRM188B10J105KA01D K22084801 1- B b2
C 2055 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - B b2
C 2056 AL.ELECTRO.CAP. 100uF 1 6V UWX1C101MCL1GB K48120032 1- B b2
C 2057 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B b2
C 2058 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 1 0V B GRM155B11A104KA01D K22108802 1- B e2
C 2059 CHIP CAP. 0.1uF 1 6V B GRM188B11C104KA01D K22124805 1- B d2
C 2060 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - A G1
C 2061 CHIP CAP. 0.001uF 5 0V B GRM155B11H102KA01D K22178809 1 - A G1
C 2062 CHIP CAP. 1 uF 6.3V B GRM155B30J105KE18D K22088803 1-
D 2001 DIODE DA221 TL G2070178 1- B f1
D 2002 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A C1
D 2003 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A D1
D 2004 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A E1
D 2005 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A F1
D 2006 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A G1
D 2007 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A G1
D 2008 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A C2
LOT
SIDE
LAY ADR
29
Page 30

CNTL Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
D 2009 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A D2
D 2010 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A E2
D 2011 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B d1
D 2012 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B d1
D 2013 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A F2
D 2014 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A G2
D 2015 LED SML-512WWT86 G2071104 1- A H2
D 2016 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B d1
D 2017 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A F1
D 2018 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A F1
D 2019 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A F1
D 2020 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- A H2
D 2022 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B b2
D 2023 DIODE DAN222 TL G2070174 1- B h2
D 2025 DIODE DA221 TL G2070178 1- B b2
D 2026 DIODE 1SS400 TE61 G2070634 1- B b2
D 2027 DIODE 015AZ3.3X-TPH3 G2071078 1- B h2
DS2001 LCD AH023N A15A015X G6090169 1 - A E1
FB2001 FERRITE BEADS BK1608HS121-T L9190081 1- B i2
FB2002 FERRITE BEADS BK1608HS121-T L9190081 1- B i2
FB2003 FERRITE BEADS BK1608HS121-T L9190081 1- B i2
FB2004 FERRITE BEADS BK1608HS121-T L9190081 1- B i2
FB2005 FERRITE BEADS BK1608HS121-T L9190081 1- B i2
FB2006 FERRITE BEADS BK1608HS121-T L9190081 1- B i2
J 2001 CONNECTOR MJD0606KX06L P1091242 1- A A 2
J 2002 CONNECTOR 53398-1071 P0091391 1- B c1
J 2003 CONNECTOR 32FLT-SM2-TB(LF)(SN)(M) P1091258 1- B c2
J 2004 CONNECTOR AXK6F14345YJ P0091406 1- B g2
L 2001 M.RFC 150uH FLC32T-151J L1690229 1- B d2
L 2002 M.RFC 1uH LK1608 1R0K-T L1690687 1 - B d1
Q 2002 IC HD64F2266TF13V
Q 2003 TRANSISTOR 2SC5374-TL G3353748 1- B d2
Q 2004 TRANSISTOR DTC143ZE TL G3070102 1 - A B2
Q 2005 TRANSISTOR CPH6202-TL G3070265 1- A H2
Q 2006 IC BR24L64F-WE2 G1093876 1- B d1
Q 2007 TRANSISTOR 2SC4617 TL R G3346178R 1- B a1
Q 2008 TRANSISTOR 2SC4617 TL R G3346178R 1- B a2
Q 2010 IC S-812C50AUA-C3E-T2G G1093652 1- B a2
Q 2011 IC BD4830FVE-TR G1094121 1- B b2
Q 2012 TRANSISTOR DTC143ZE TL G3070102 1 - B i2
Q 2013 TRANSISTOR 2SC4617 TL R G3346178R 1- B b2
R 2003 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1 - B b1
R 2004 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1 - B b1
R 2005 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A D1
R 2006 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A D1
R 2007 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A D1
R 2008 CHIP RES. 1 k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B f 2
R 2009 CHIP RES. 1 k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B f 2
R 2010 CHIP RES. 1 k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B f 2
R 2011 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A F1
R 2012 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A G1
R 2013 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A G1
R 2014 CHIP RES. 2 2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- B c 1
R 2015 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1 - B d2
R 2016 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 105JTH J24189061 1- B d2
R 2017 CHIP RES. 3 3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 333JTH J24189043 1- A B2
R 2018 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A D1
R 2019 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A D2
R 2020 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A D2
R 2021 CHIP RES. 2 2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- B c 1
R 2022 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1 - B c1
R 2023 CHIP RES. 1 k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B e2
R 2024 CHIP RES. 1 k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B e2
R 2025 CHIP RES. 6 8k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD6802 J24189384 1 - B d 2
R 2026 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD3903 J24189331 1- B d2
R 2027 CHIP RES. 1 0k 1/16W 0.5% MCR01MZPD1002 J24189374 1 - B d 2
R 2028 CHIP RES. 1 k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B d2
R 2030 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1 - A B2
R 2031 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A H2
R 2032 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A H2
R 2033 CHIP RES. 1 0 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 101JTH J24189013 1 - A H2
R 2034 CHIP RES. 1 0 1W 5% RMC1 100JTE J24305100 1- A I2
R 2036 CHIP RES. 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S JPTH J24189070 1- A H2
R 2037 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1 - B a1
R 2038 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 682JTH J24189035 1- B a2
30
Ú
:
Please contact VERTEX STANDARD
Ú
LOT
SIDE
1- B e2
LAY ADR
Page 31

CNTL Unit
Parts List
REF DESCRIPTION VALUE V/W TOL. MFR'S DESIG VXSTD P/N VERS.
R 2039 CHIP RES. 6 8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- B a2
R 2040 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1 - B a2
R 2041 CHIP RES. 6.8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 682JTH J24189035 1- B a1
R 2042 CHIP RES. 6 8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- B a1
R 2043 CHIP RES. 6 8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- B a1
R 2044 CHIP RES. 1.5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 152JTH J24189027 1- B a1
R 2045 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- B a1
R 2046 CHIP RES. 3.3M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 335JTH J24189324 1- B e2
R 2047 CHIP RES. 1.8M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 185JTH J24189064 1- B d2
R 2048 CHIP RES. 6 8k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 683JTH J24189047 1- B a2
R 2049 CHIP RES. 1.5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 152JTH J24189027 1- B a2
R 2050 CHIP RES. 3.3k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 332JTH J24189031 1- B a2
R 2051 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 105JTH J24189061 1- B d2
R 2052 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 105JTH J24189061 1- B f 2
R 2053 CHIP RES. 1M 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 105JTH J24189061 1- B h2
R 2054 CHIP RES. 2 7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 273JTH J24189042 1- B b2
R 2055 CHIP RES. 1 5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- B b2
R 2056 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- B h2
R 2057 CHIP RES. 2.2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 222JTH J24189029 1- B h2
R 2058 CHIP RES. 2 2 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 221JTH J24189017 1 - B i2
R 2059 CHIP RES. 2 2 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 220JTH J24189005 1 - B d1
R 2060 CHIP RES. 2 2k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 223JTH J24189041 1- B b2
R 2061 CHIP RES. 390k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 394JTH J24189056 1 - B b2
R 2062 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1 - B h2
R 2063 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1 - B h2
R 2064 CHIP RES. 1 5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- B h1
R 2065 CHIP RES. 470k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 474JTH J24189057 1 - B i2
R 2066 CHIP RES. 1 5k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 153JTH J24189039 1- B b2
R 2067 CHIP RES. 1 0k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B f 1
R 2068 CHIP RES. 1 0k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b2
R 2069 CHIP RES. 1 0k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B b1
R 2070 CHIP RES. 4 7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B d1
R 2071 CHIP RES. 4 7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- B d1
R 2072 CHIP RES. 4 7 0 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 471JTH J24189021 1 - B h2
R 2073 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1 - B i2
R 2074 CHIP RES. 100k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 104JTH J24189049 1 - B i2
R 2075 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1 - B i2
R 2076 CHIP RES. 4 7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A F1
R 2077 CHIP RES. 4 7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A F1
R 2078 CHIP RES. 4 7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 473JTH J24189045 1- A F1
R 2079 CHIP RES. 1 k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 102JTH J24189025 1- B f 1
R 2080 CHIP RES. 220k 1/16W 5 % RMC1/16S 224JTH J24189053 1 - B c1
R 2081 CHIP RES. 4.7k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 472JTH J24189033 1- B a1
R 2082 CHIP RES. 1 0k 1/16W 5% RMC1/16S 103JTH J24189037 1- B a1
RB2001 BLOCK RES. MNR04M0ABJ102 J42900039 1- B e2
RB2002 BLOCK RES. MNR04M0ABJ102 J42900039 1- B e2
RB2003 BLOCK RES. MNR04M0ABJ102 J42900039 1- B e2
RB2004 BLOCK RES. MNR04M0ABJ102 J42900039 1- B e2
RB2005 BLOCK RES. MNR04M0ABJ102 J42900039 1- B d2
RB2006 BLOCK RES. MNR04M0ABJ102 J42900039 1- B d2
RB2007 BLOCK RES. MNR04M0ABJ102 J42900039 1- B d1
S 2001 ROTARY ENCODER EC12E2420401 Q9000749 1- A I2
VR2001 POT. WH9011-1B B20K 25/5 J60800288 1- A B1
VR2002 POT. WH9011-1B A20K 25/5 J60800287 1- A A 1
X 2001 XTAL U3B 3.579545MHz 3.579545MHZ H0103304 1- B e2
LOT
…
LAY ADR
31
Page 32

CNTL Unit
Note
32
Page 33

33
Page 34

Copyright 2009
VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
All rights reserved
No portion of this manual
may be reproduced without
the permission of
VERTEX STANDARD CO., LTD.
Printed in Japan.
34
 Loading...
Loading...