Volkswagen Phaeton 2003 User Manual

Self-Study Program
Course Number 891303
The Phaeton

Volkswagen of America, Inc.
Service Training
Printed in U.S.A.
Printed 08/2003
Course Number 891303
©2003 Volkswagen of America, Inc.
All rights reserved. All information contained
in this manual is based on the latest
information available at the time of printing
and is subject to the copyright and other
intellectual property rights of Volkswagen of
America, Inc., its affiliated companies and its
licensors. All rights are reserved to make
changes at any time without notice. No part
of this document may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted
in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, recording or
otherwise, nor may these materials be
modified or reposted to other sites without
the prior expressed written permission of
the publisher.
All requests for permission to copy and
redistribute information should be referred
to Volkswagen of America, Inc.
Always check Technical Bulletins and the
Volkswagen Worldwide Repair Information
System for information that may supersede
any information included in this booklet.
Trademarks: All brand names and product
names used in this manual are trade names,
service marks, trademarks, or registered
trademarks; and are the property of their
respective owners.

Table of Contents
Introduction ................................................................................................... 1
Volkswagen’s Flagship, The Phaeton Name,
Phaeton’s Place in Automotive History, The Transparent Factory,
Phaeton Technical Innovations, Specifications, Aerodynamics
Engines......................................................................................................... 10
The 4.2-Liter V8-5V Gasoline Engine,
The 6.0-Liter W12 Gasoline Engine
Fuel Supply .................................................................................................. 14
Fuel Delivery System
Transmissions.............................................................................................. 15
Automatic Transmissions
Running Gear............................................................................................... 26
Phaeton Chassis Overview
Body ............................................................................................................. 28
Body Structure, Body Attachments, Sound Silencers, Glass,
Power-Assisted Luggage Compartment Lid, Sunroof
Occupant Protection ................................................................................... 38
Overview, Airbag Systems, Seat Belt Systems,
Active Headrest System
Seats............................................................................................................. 44
Front Seats, Rear Seats
Air Conditioning System ............................................................................ 49
Four-Zone Climatronic, Air Distribution in the Vehicle,
System Overview
Electrical System......................................................................................... 54
Convenience Electronics, Adaptive Cruise Control,
Headlights, Fog Lights, Rear Lights, Battery, Phaeton Battery
Systems, Emergency Starting, Using the Front Information Display
Control Head J523 for Component Service, Infotainment System
Service.......................................................................................................... 74
Special Tools
Knowledge Assessment ............................................................................. 77
The Self-Study Program provides you with information
regarding designs and functions.
New !
Important/Note!
The Self-Study Program is not a Repair Manual.
For maintenance and repair work, always refer to the
current technical literature.
i


Volkswagen’s Flagship
Introduction
The introduction of the Volkswagen
Phaeton is the result of developments in
the international market for luxury cars.
Product quality alone is no longer sufficient
to guarantee success in highly-developed
markets. The prestige and value of the
brand are also decisive in influencing
purchasing decisions.
The increasing importance of customer
brand awareness spurred Volkswagen’s
entry into the luxury-class vehicle
market segment.
With the launch of the Phaeton, we are
introducing a product that both meets the
technical requirements demanded by our
customers, and also satisfies the value and
prestige demands being made on the
Volkswagen brand.
There are separate Self-Study
Programs on the following topics:
• The W Engine Concept
(821203)
• The Phaeton W12 Engine
Management System (892303)
• The Phaeton Heating and
Air Conditioning System
(894303)
• The Phaeton On-Board Power
Supply (895303)
• The Phaeton Convenience and
Safety Electronics (896303)
• The Phaeton Infotainment
System (897303)
• The Phaeton Air Suspension
(899303)
• The Phaeton Adaptive Cruise
Control (898303)
• The Phaeton Chassis (893303)
SSP270/241
1
Introduction
SSP270/150
The Phaeton Name
The name Phaeton (or Phaethon) originally
derives from Greek mythology. Phaeton
(the “incandescent”) was the son of the
sun god Helios, who was the owner of the
sun chariot.
Derived from this, the word “phaeton” also
refers to the four-wheeled horse-drawn
walking coaches that became popular in the
18th century.
These phaetons are open owner-driver
carriages, featuring a trestle seat for two
persons with or without a canopy top.
Behind the trestle seat there is a seat for
one or two passengers facing forward.
Even now, these phaetons are driven
at special events. Original examples
have become extremely coveted
collectors’ items.
At the onset of the 20th century, the
term “phaeton” was applied to touring
carriages with a fabric canopy and without
side windows.
The Phonetics of Phaeton
How is it pronounced?
Phaeton is pronounced as follows:
fay - ton
The ending is spoken with an unvoiced
“N,” comparable to the pronunciation of
the words Futon or Flacon.
2
SSP270/151

Phaeton’ s Place in Automotive History
Introduction
Since 1910, August Horch endowed some
of his models with the “Phaeton” suffix.
Some examples include the 1931 Horch
18/90 hp 450 Phaeton and the 1911 Horch
12/28 hp Phaeton, as well as the 1937
Horch 853A Parade Phaeton only three of
which were built, and the last remaining
model of which recently sold for $334,000.
The choice of the name “Phaeton” for
the Volkswagen flagship links this vehicle
to the tradition of employing superior
quality-control requirements in the
production phase to provide the ultimate
in exclusivity for each future owner
of a Phaeton.
Horch 18/90 hp 450 Phaeton, 1931-32
SSP270/169
Horch 12/28 hp Phaeton, 1910-11
Horch 853A Parade Phaeton, 1937
SSP270/170
SSP270/168
3

Introduction
The Transparent Factory
Concept
Not only has the advent of the exclusive
Phaeton led to the building of an
impressive production line in Dresden,
it has also engendered a polished and
precisely-functioning logistics concept.
The transparent factory represents a
significant milestone for V olkswagen’s
customer-oriented manufacturing
and delivery.
In addition to these outstanding technical
production details, purchasers of this
high-quality luxury-class automobile can
expect a perfectly-arranged vehicle transfer
with all of the pageantry suitable to such
a special event.
4
Production Line
Contrary to the popular opinion that
automobile manufacture is irrevocably
linked with dirt and oil, the vision of
manufacturing evident in Dresden depicts
production in an almost noble light.
The core of the manufacturing process
features overlapping conveyor belts floored
with fine wood parquet. The result is a
production line with an atmosphere like that
otherwise only seen in elite luxury sports
car plants.

Introduction
transported in glass elevators to a different
level, where they are joined into a complete
vehicle and the final assembly process
takes place.
Once the manufacturing process has been
completed, each Phaeton is once again
placed on the overlapping conveyor belt
before receiving its finishing touches and
its final check.
Delivery
An exclusive automobile cries out for the
appropriate stage-management of its
delivery. Customers are the center of
attention in the transparent factory’s
emotionally and technologically impressive
discovery area.
SSP270/130
Logistics
An automated system guides baskets
containing the individual components used
for the assembly of each vehicle through
the factory. Each basket accompanies its
corresponding vehicle throughout the
assembly stage. This reduces wasted
motion during assembly.
The chassis for a specific vehicle, including
the engine, transmission and exhaust
system, and the corresponding body are
simultaneously assembled on different
floors. These major subassemblies are then
Potential Phaeton owners are treated to a
birds-eye view of production via live video
image during a Virtual Production Tour.
5

Introduction
Phaeton Technical Innovations
This is an overview. Detailed descriptions of
the individual topics can be found in this
and other Phaeton Self-Study Programs.
• Rear window heated by practically
invisible tungsten threads.
• Fenders and spare tire recess made of
plastic.
• Extremely narrow body jointing,
PVC-free underbody protection.
• Doors, engine hood and luggage
compartment lid made of aluminum.
• Fully-galvanized body.
• Taillights with two-color
LED technology.
• Antennas invisibly
integrated in the
rear window.
• Superior paint, scratch resistant,
exceptional brilliancy .
• Air-conditioned 12- and 18-position
seats, keyless access function,
Adaptive Cruise Control,
multi-function steering wheel.
• Infotainment system with navigation
and radio/CD; CD changer in the
glove compartment; four-zone
air conditioning.
6
SSP270/053

Introduction
• Xenon headlights with automatic
headlight range control.
• Surrounding illumination with front, rear, and forward lighting
simplifies orientation when getting out of the car in the dark.
• Air suspension with automatic control.
• Electro-mechanical high-pressure nozzles for cleaning headlights.
• Side and rear windows made of twin-pane laminated safety glass.
SSP270/054
7

Introduction
Specifications
57.09 in
(1450 mm)
• Length
203.74 inches (5175 mm)
64.09 in
(1628 mm)
74.92 in
(1903 mm)
118.15 in
(3001 mm)
203.74 in
(5175 mm)
63.46 in
(1612 mm)
SSP270/118
• Rear track width
63.46 inches (1612 mm)
• Width
74.92 inches (1903 mm)
• Height
57.09 inches (1450 mm)
• Wheelbase
118.15 inches (3001 mm)
• Fuel tank capacity
23.8 gallons (90 liters)
• Front track width
64.09 inches (1628 mm)
8
• Permitted gross vehicle weight
5732 – 6592 pounds (2600 – 2990 kg)
(depending on the engine)
• Curb weight
4398 – 5320 pounds (1995 – 2413 kg)
(depending on the engine)
• Luggage compartment space
13 cubic feet (368 liters)
• Drag coefficient
0.32 C
D

Aerodynamics
Introduction
The Phaeton has a low drag coefficient of
0.32 CD.
This level was achieved by combining
several design elements:
• The underbody has an extremely
smooth design.
• The windshield wipers are recessed.
• The body gap dimensions are
very narrow.
• The front has an arrow-shaped design.
• The body is lowered at higher
vehicle speeds.
Small features such as the retractable
headlight cleaning nozzles, the
antenna-free body, and the smooth
body transitions are also responsible for
this low drag coefficient.
SSP270/047
9

Engines
The 4.2-Liter V8-5V Gasoline Engine
Emphasis was placed on the following
development objectives:
• Compliance with future
exhaust-emission regulations.
• Reduction of fuel consumption.
• Increase in torque and power.
• Improvement of comfort and
convenience.
• Reduction of engine weight.
• Increased use of shared components.
Alloys are used extensively:
• The cylinder heads and oil sump top
section are made of aluminum.
• The valve covers are die-cast magnesium
coated with a thin synthetic material to
prevent corrosion.
• The cylinder block is aluminum.
10
SSP217/055
Engines
Technical Data – 4.2-Liter V8-5V
Gasoline Engine
• Type
V8 engine with 90 degree V-angle,
five valves per cylinder, and variable
intake and exhaust valve timing
• Displacement
255 cu in (4172 cm3)
• Bore
3.32 in (84.5 mm)
• Stroke
3.66 in (93.0 mm)
• Compression ratio
11:1
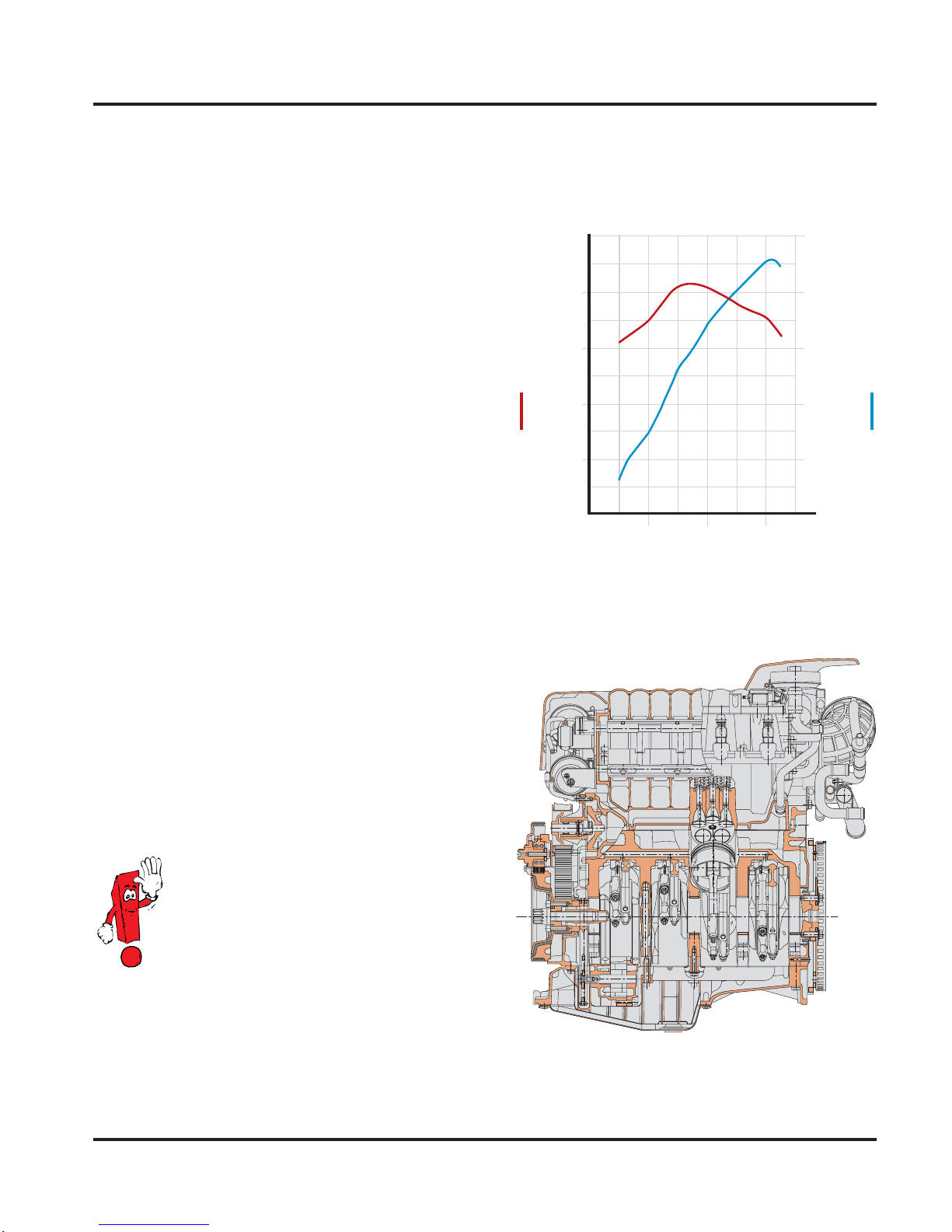
• Maximum power output
310 bhp (228 kW) @ 6200 rpm
• Maximum torque
302 lbs-ft (410 Nm) @ 3000 to 4000 rpm
lbs-ft Nm
369 500
332 450
295 400
258 350
221 300
184 250
Torque
148 200
111 150
74 100
37 50
hp kW
335 250
302 225
268 200
235 175
201 150
168 125
134 100
101 75
67 50
34 25
0
2000 4000 6000
Speed (rpm)
SSP297/072
Output
• Engine management
Motronic ME 7.1.1
• Firing sequence
1-5-4-8-6-3-7-2
• Fuel type recommendation
Premium unleaded gasoline (91 AKI)
The specified power data is
only possible if 91 AKI fuel is
used. A reduction in power
output must be expected if
lower grade fuel is used.
SSP 217/054
11

Engines
The 6.0-Liter W12 Gasoline Engine
With the W12 engine, Volkswagen is
offering a 12-cylinder engine in its lineup for
the first time ever. It is the most powerful
engine version available in the Phaeton.
Mechanical Innovations
• Cylinder block made of aluminum.
• Bottom crankshaft bearings in gray cast
iron bearing blocks.
• Oil pump driven by a chain.
• Very compact engine.
Engine Management
• Dual control module concept.
• Secondary air injection.
• Exhaust gas recirculation.
12
SSP270/300
Technical Data –
6.0-Liter W12 Gasoline Engine
Engines
• Type
W engine with four valves per cylinder
• Displacement
366 cu in (5998 cm3)
• Bore
3.31 in (84 mm)
• Stroke
3.55 in (90.186 mm)
• Compression ratio
10.75:1
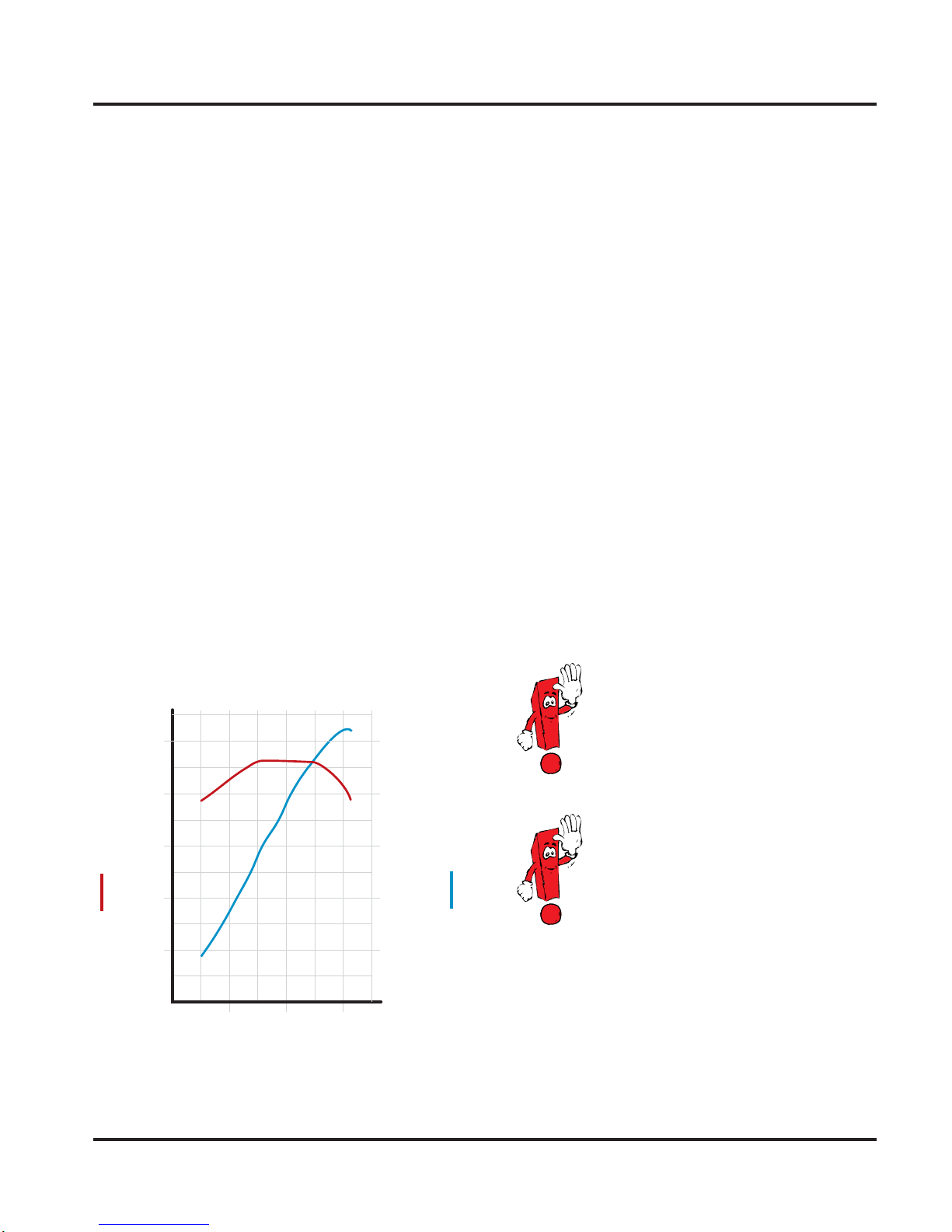
• Maximum power output
414 bhp (309 kW) @ 6000 rpm
lbs-ft Nm
487 660
443 600
398 540
354 480
310 420
266 360
Torque
221 300
177 240
133 180
89 120
44 60
0
2000 4000 6000
Speed (rpm)
hp kW
442 330
402 300
362 270
322 240
282 210
241 180
201 150
161 120
121 90
80 60
40 30
SSP270/172
Output
• Maximum torque
406 lbs-ft (550 Nm) @ 3500 rpm
• Engine management
Motronic ME 7.1.1
• Firing sequence
1-12-5-8-3-10-6-7-2-11-4-9
• Fuel type recommendation
Premium unleaded gasoline (91 AKI)
• Exhaust treatment
Three-way catalytic converters
The specified power data is
only possible if 91 AKI fuel is
used. A reduction in power
output must be expected if
lower grade fuel is used.
Please refer to
The W Engine Concept,
Self-Study Program Course
Number 821203 and
The Phaeton W12 Engine
Management System,
Self-Study Program Course
Number 892303 for more
detailed information on the
W engine concept.
13

Fuel Supply
Fuel Delivery System
Fuel Tank
The fuel tank is mounted on the vehicle
underbody close to the rear axle. It has a
capacity of 23.8 gallons (90 liters). Due to
its external shape, it consists of a main fuel
tank chamber and a secondary fuel tank
chamber.
Each fuel tank chamber has an electric fuel
pump and a suction jet fuel pump.
Reserve Fuel Tank
(only in vehicles with
gasoline engines)
Each electric fuel pump is assigned two
senders for fuel supply: a fuel sender and a
level sender.
The four senders for fuel supply transmit
their signals directly to the Control Module
with Indicator Unit in Instrument Panel
Insert J285.
Fuel Pump G6
Main
Fuel Tank
Chamber
Fuel Filter
Suction Jet Pump 1
Suction Jet Pump 2
Transfer
Fuel Pump
G23
Secondary
Fuel Tank
Chamber
SSP270/112
14
Automatic Transmissions
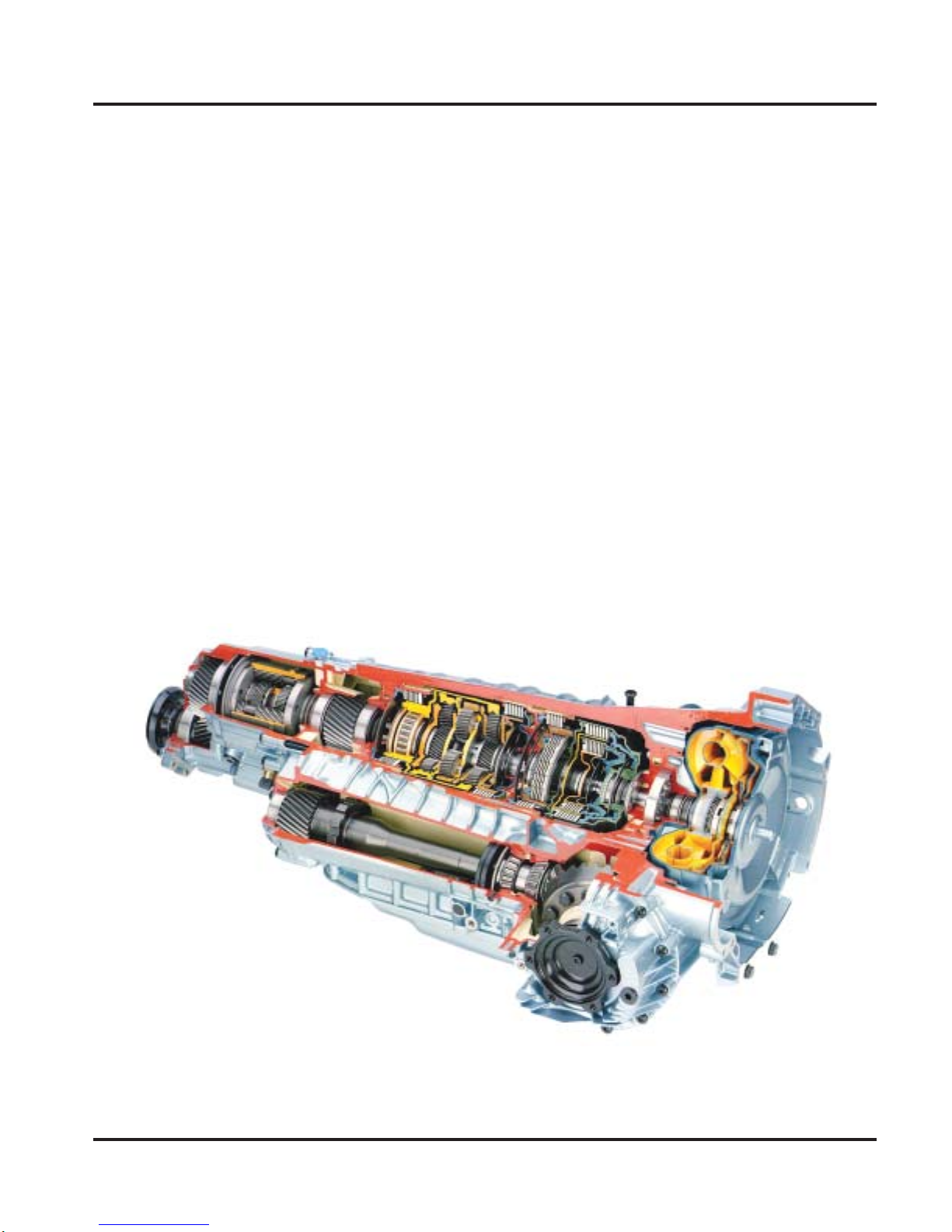
Transmissions
Depending on the engine application
and marketing area, the Volkswagen
Phaeton is available with a five-speed
automatic transmission or a six-speed
automatic transmission.
Both automatic transmissions are currently
already in use in other V olkswagen vehicles.
They have been modified and adapted for
installation in the Phaeton. An electrohydraulic system is used to control them.
The Transmission Control Module J217
registers operating conditions, driver input,
and external influences such as travelling
uphill or downhill. Gear selection is made
by the Transmission Control Module J217
based on all incoming data.
Five-speed automatic transmission features:
• Dynamic shift program and sport
shift program.
• Regulated torque converter
lockup clutch.
• Tiptronic shift program.
Five-Speed Automatic Transmission 01L
• Installed in the Phaeton equipped with
the 6.0-liter W12 engine.
• A Torsen center differential is integrated
in this transmission to distribute the
torque to all four wheels.
• Maximum torque transmission:
413 lbs-ft (560 Nm).
SSP270/105
15
Transmissions
Six-Speed Automatic Transmission 09F
This specially-developed automatic
transmission is used in Phaetons equipped
with the 4.2L V8-5V engine.
Compared with the five-speed automatic
transmissions, the six-speed automatic is
especially characterized by:
• Improved driving performance.
• Reduction of fuel consumption and
exhaust emissions.
• Mass reduction of approximately
30.9 pounds (14 kg).
• Reduction of the number of components
by approximately 30%.
• Excellent quality and highly
responsive shifting.
• Maximum input torque: 553 lbs-ft
(750 Nm).
Like the five-speed automatic, the
six-speed automatic transmission 09F
also has:
• Dynamic shift program and sport
shift program.
• Regulated torque converter
lockup clutch.
• Tiptronic shift program.
16
SSP270/135
Lepelletier gear set concept
Transmissions
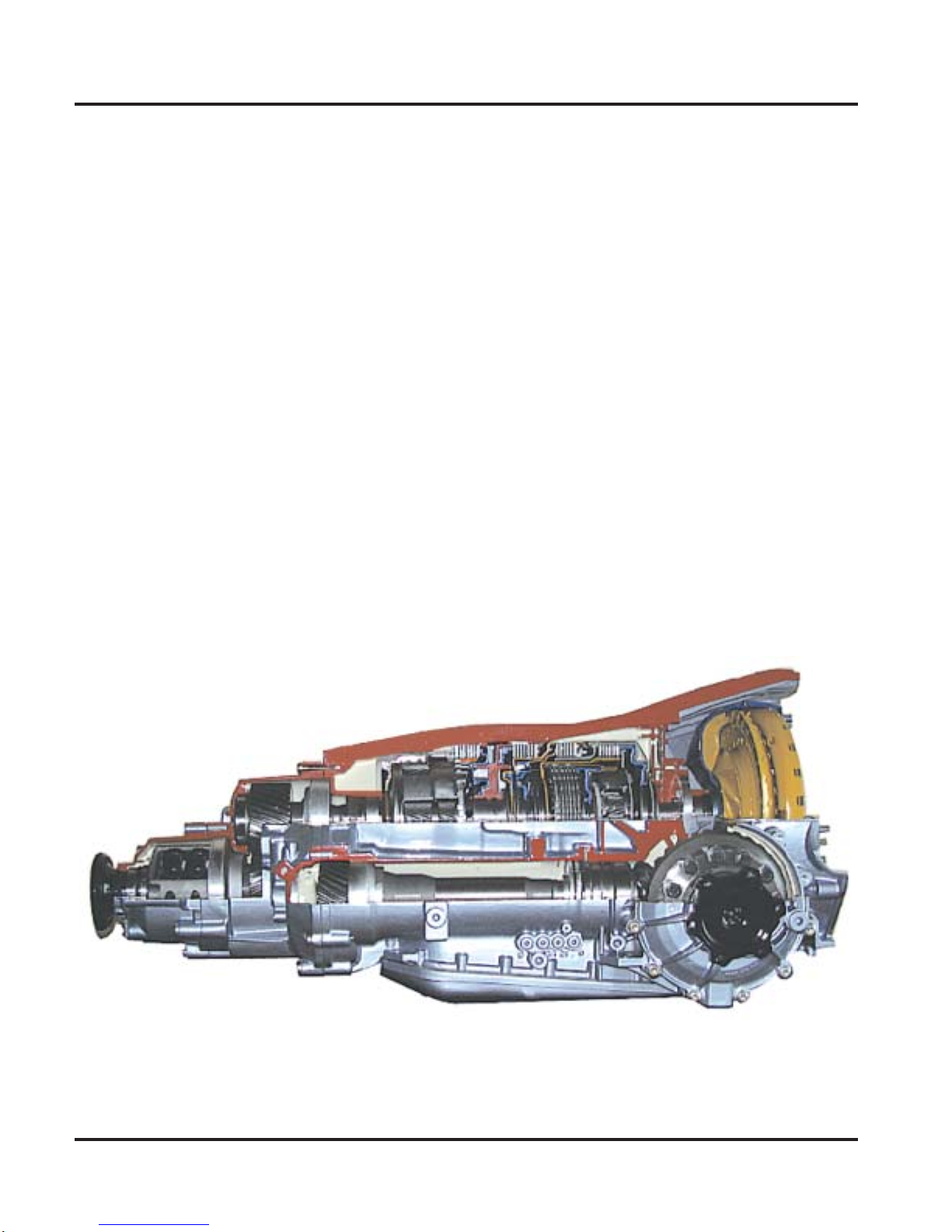
Lepelletier Gear Set
Simple Planetary
Gear Set
Internal Gear 1
The six automatic transmission gears are
shifted by a Ravigneaux planetary gear set
with a series-connected simple planetary
gear set.
This arrangement is known as the
Lepelletier gear set concept.
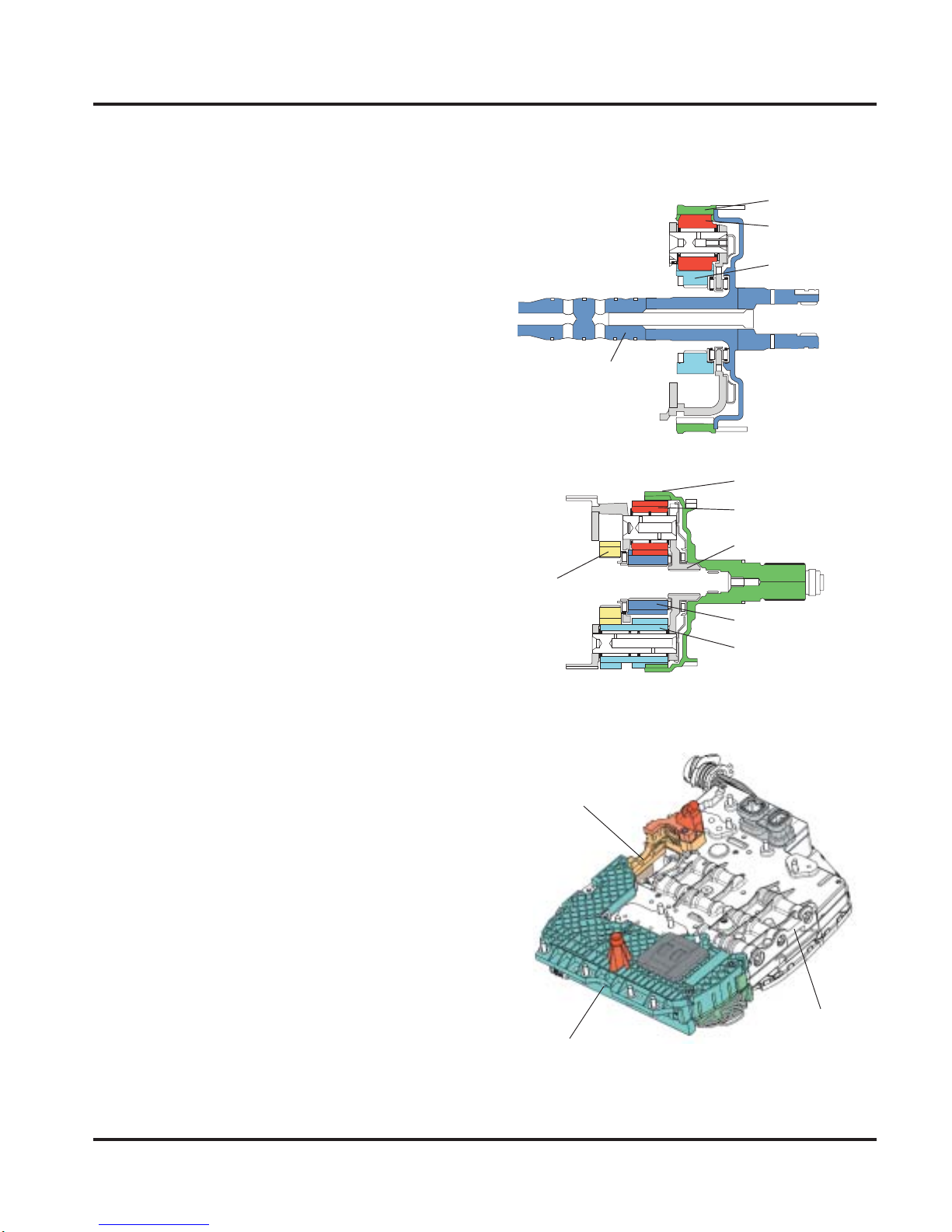
Mechatronics
Control of the six-speed automatic
transmission is effected by Mechatronics.
This is a combination of an electronic
Transmission Control Module J217
and a hydraulic control valve assembly
switching device.
Using Mechatronics, gear changes can be
controlled more precisely than before. This
provides drivers with an optimized shifting
quality and an increased level of driving
comfort. Using the incoming sensor
signals, the Transmission Control Module
J217 recognizes the current operating state
of the transmission and driver input,
reacting to these with adjusted shift points.
Turbine Shaft
Ravigneaux Planetary
Gear Set
Sun Gear 2
Multi-Function
Transmission
Range Switch
F125
Planet Gear
Sun Gear 1
SSP270/221a
Internal Gear 2
Short Planet Gear
Planet Carrier
Sun Gear 3
Long Planet Gear
SSP270/221b
Driver input ranging from an extremely
sporty to a very economical driving
style are recognized and taken into
consideration. Mechatronics components
are located on the control valve assembly
in the transmission.
Transmission
Control Module
J217
Hydraulic Control
Valve Assembly
Switching Device
SSP270/250
17
Transmissions
Automatic Transmission
Selector Lever Positions
The selector lever and Tiptronic functions
are the same in the five-speed automatic
transmissions and the six-speed
automatic transmission.
CLIMATE
RESET
FM
AM
MAP
VEHICLE
NAV
NAV SET
CD
AUDIO
TRIP DATA
SETTINGS
MANUAL
BAL/FADSCAN
ON/DARK
HELP
In order to move the selector lever from
the “P” position, the ignition must be
turned on and both the brake pedal and
the selector lever locking button must
be pressed.
R – Reverse
The brake pedal and the selector lever
locking button must be pressed in order to
shift to reverse gear.
N – Neutral
The transmission is idling in this
position. No power is being transmitted
to the wheels.
P – Parking
SSP270/106
D – Drive
When the selector lever is positioned at
“D,” gear change from gear 1 through 5 in
the five-speed, or gear 1 through 6 in the
six-speed, is effected automatically.
18
S – Sport
In this selector ever position, the
transmission shifts automatically according
to sporty characteristics. The shift points
occur at higher engine speeds resulting
in longer intervals in each gear and
brisker acceleration.
Shift Program and Gear Indicator on
Display Unit in Instrument Cluster Y24
In both the “D” and “S” automatic
shift programs, the engaged selector lever
position and the gear being currently
used are shown on Display Unit in
Instrument Cluster Y24.
Transmissions
P
R
N
D3
S
76.7 mi 54.1°F 76728 mi
SSP270/109
The gear being used is shown on the
display if the automatic transmission is in
the Tiptronic shift program.
P
R
3
D
S
76.7 mi 54.1°F 76728 mi
SSP270/108
19

Transmissions
Tiptronic
CLIMATE
RESET
FM
AM
MAP
VEHICLE
SCAN
NAV
NAV SET
CD
AUDIO
TRIP DATA
SETTINGS
MANUAL
AD
ON/DARK
HELP
On the Phaeton, Tiptronic gear selection
can be operated by the selector lever.
The automatic transmission is switched to
Tiptronic mode by moving the selector lever
to the right from the “D” position into the
Tiptronic notch.
Gear change must then be made by
moving the selector lever.
Moving the selector lever forward shifts
up a gear, moving the lever back shifts
down a gear.
SSP270/029
20
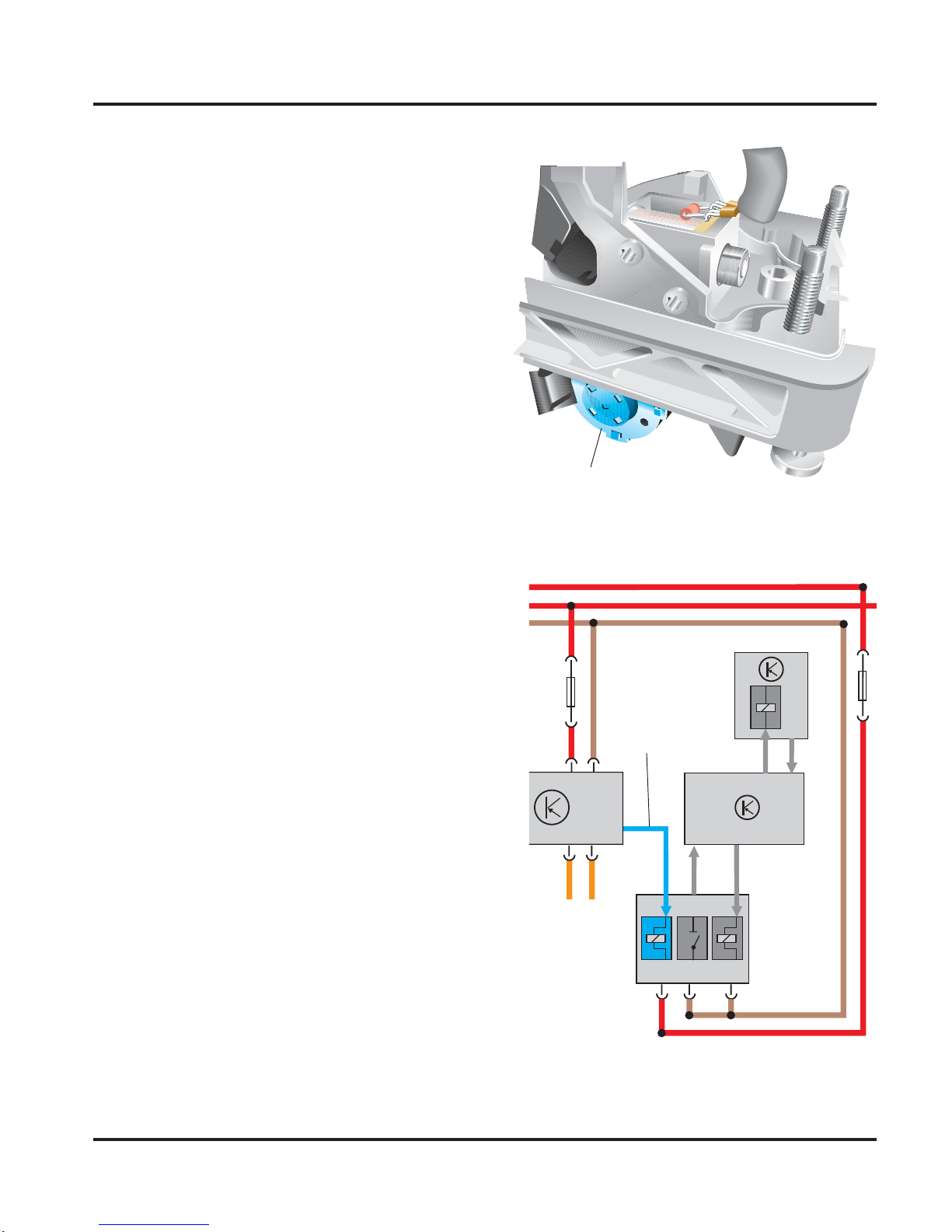
Shift Lock Solenoid N110
Shift Lock Solenoid N110 is located on the
selector lever frame below the selector
lever. It prevents the movement of the
selector lever from positions “P” and “N”
unless the brake pedal is pushed.
Transmissions
How it works
Once the ignition has been turned on, the
Shift Lock Solenoid N110 is activated by
the Transmission Control Module J217,
blocking the selector lever from movement.
If the Transmission Control Module J217
receives the signal “brake applied,” it cuts
off current to the Shift Lock Solenoid N110
and the selector lever can be moved.
Effects of failure
If one of these two signals fails or if the
Shift Lock Solenoid N110 is faulty, the
selector lever can be moved out of “P” or
“N” without applying the brake when the
ignition is turned on.
Shift Lock Solenoid N110
15
30
31
Control of
Shift Lock
Solenoid N110
CAN Data Bus
Signal “Brake
Applied”
N110
F319
SSP270/222
E415
N376
J518J217
N380
SSP270/224
21
 Loading...
Loading...