Page 1

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions
Administrator's and User's Guide
vSphere Big Data Extensions 2.3
This document supports the version of each product listed and
supports all subsequent versions until the document is
replaced by a new edition. To check for more recent editions
of this document, see http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
EN-TBD-00
Page 2

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware Web site at:
http://www.vmware.com/support/
The VMware Web site also provides the latest product updates.
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to:
docfeedback@vmware.com
Copyright © 2013 – 2015 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright and trademark information.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivs 3.0 United States License
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/3.0/us/legalcode).
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
2 VMware, Inc.
Page 3

Contents
About This Book 7
About VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions 9
1
Getting Started with Big Data Extensions 9
Big Data Extensions and Project Serengeti 10
About Big Data Extensions Architecture 11
About Application Managers 12
Installing Big Data Extensions 17
2
System Requirements for Big Data Extensions 17
Unicode UTF-8 and Special Character Support 20
The Customer Experience Improvement Program 21
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web Client 22
Install RPMs in the Serengeti Management Server Yum Repository 25
Install the Big Data Extensions Plug-In 26
Configure vCenter Single Sign-On Settings for the Serengeti Management Server 28
Connect to a Serengeti Management Server 28
Install the Serengeti Remote Command-Line Interface Client 29
Access the Serengeti CLI By Using the Remote CLI Client 30
Upgrading Big Data Extensions 33
3
Prepare to Upgrade Big Data Extensions 33
Upgrade the Big Data Extensions Virtual Appliance 34
Upgrade the Big Data Extensions Plug-in 35
Upgrade Big Data Extensions Clusters Using the Serengeti Command-Line Interface 36
Upgrade the Serengeti CLI 36
Add a Remote Syslog Server 37
VMware, Inc.
Managing Application Managers 39
4
Add an Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client 39
Modify an Application Manager by Using the Web Client 40
Delete an Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client 40
View Application Managers and Distributions by Using the Web Client 40
View Roles for Application Manager and Distribution by Using the Web Client 40
Managing Hadoop Distributions 43
5
Hadoop Distribution Deployment Types 43
Configure a Tarball-Deployed Hadoop Distribution by Using the Serengeti Command-Line
Interface 44
Configuring Yum and Yum Repositories 46
3
Page 4

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Managing Node Templates 63
6
Maintain a Customized Hadoop Template Virtual Machine 63
Create a Node Template Virtual Machine using RHEL Server 6.7 and VMware Tools 64
Support for Multiple Virtual Machine Templates 68
Managing the Big Data Extensions Environment 69
7
Add Specific User Names to Connect to the Serengeti Management Server 69
Change the Password for the Serengeti Management Server 70
Create a User Name and Password for the Serengeti Command-Line Interface 71
Authorize and Audit Commands Run as the Root User 72
Specify a Group of Users in Active Directory or LDAP to Use a Hadoop Cluster 72
Stop and Start Serengeti Services 73
Ports Used for Communication between Big Data Extensions and the vCenter Server 73
Verify the Operational Status of the Big Data Extensions Environment 75
Enter Maintenance Mode to Perform Backup and Restore with the Serengeti Command-Line
Interface Client 83
Backup and Restore the Big Data Extensions Environment 84
Managing vSphere Resources for Clusters 87
8
Add a Resource Pool with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface 87
Remove a Resource Pool with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface 88
Update Resource Pools with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface 88
Add a Datastore in the vSphere Web Client 89
Remove a Datastore in the vSphere Web Client 90
Update Datastores with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface 90
Add a Paravirtual SCSI Controller for System and Swap Disks 91
Add a Network in the vSphere Web Client 92
Modify the DNS Type in the vSphere Web Client 93
Reconfigure a Static IP Network in the vSphere Web Client 93
Remove a Network in the vSphere Web Client 94
Creating Hadoop and HBase Clusters 95
9
About Hadoop and HBase Cluster Deployment Types 97
Hadoop Distributions Supporting MapReduce v1 and MapReduce v2 (YARN) 97
About Cluster Topology 98
About HBase Database Access 98
Create a Big Data Cluster in the vSphere Web Client 99
Create an HBase Only Cluster in Big Data Extensions 102
Create a Cluster with an Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client 104
Create a Compute-Only Cluster with a Third Party Application Manager by Using vSphere Web
Client 105
Create a Compute Workers Only Cluster by Using the vSphere Web Client 105
Managing Hadoop and HBase Clusters 107
10
Stop and Start a Cluster in the vSphere Web Client 107
Delete a Cluster in the vSphere Web Client 108
Scale a Cluster in or out by using the vSphere Web Client 108
Scale CPU and RAM in the vSphere Web Client 109
4 VMware, Inc.
Page 5

Use Disk I/O Shares to Prioritize Cluster Virtual Machines in the vSphere Web Client 110
About vSphere High Availability and vSphere Fault Tolerance 110
Change the User Password on All of the Nodes of a Cluster 111
Reconfigure a Cluster with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface 111
Configure the Number of Data Disks Per Node Group 113
Recover from Disk Failure with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client 115
Log in to Hadoop Nodes with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client 115
Contents
Monitoring the Big Data Extensions Environment 117
11
Enable the Big Data Extensions Data Collector 117
Disable the Big Data Extensions Data Collector 118
View Serengeti Management Server Initialization Status 118
View Provisioned Clusters in the vSphere Web Client 119
View Cluster Information in the vSphere Web Client 120
Monitor the HDFS Status in the vSphere Web Client 121
Monitor MapReduce Status in the vSphere Web Client 121
Monitor HBase Status in the vSphere Web Client 122
Accessing Hive Data with JDBC or ODBC 123
12
Configure Hive to Work with JDBC 123
Configure Hive to Work with ODBC 125
Big Data Extensions Security Reference 127
13
Services, Network Ports, and External Interfaces 127
Big Data Extensions Configuration Files 129
Big Data Extensions Public Key, Certificate, and Keystore 130
Big Data Extensions Log Files 130
Big Data Extensions User Accounts 131
Security Updates and Patches 131
Troubleshooting 133
14
Log Files for Troubleshooting 134
Configure Serengeti Logging Levels 134
Collect Log Files for Troubleshooting 135
Troubleshooting Cluster Creation Failures 136
Big Data Extensions Virtual Appliance Upgrade Fails 142
Upgrade Cluster Error When Using Cluster Created in Earlier Version of Big Data Extensions 143
Unable to Connect the Big Data Extensions Plug-In to the Serengeti Server 143
vCenter Server Connections Fail to Log In 144
Management Server Cannot Connect to vCenter Server 144
SSL Certificate Error When Connecting to Non-Serengeti Server with the vSphere Console 145
Cannot Restart or Reconfigure a Cluster For Which the Time Is Not Synchronized 145
Cannot Restart or Reconfigure a Cluster After Changing Its Distribution 146
Virtual Machine Cannot Get IP Address and Command Fails 146
Cannot Change the Serengeti Server IP Address From the vSphere Web Client 147
A New Plug-In Instance with the Same or Earlier Version Number as a Previous Plug-In Instance
Does Not Load 147
Host Name and FQDN Do Not Match for Serengeti Management Server 148
VMware, Inc. 5
Page 6

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Serengeti Operations Fail After You Rename a Resource in vSphere 149
Big Data Extensions Server Does Not Accept Resource Names With Two or More Contiguous
White Spaces 149
Non-ASCII characters are not displayed correctly 149
MapReduce Job Fails to Run and Does Not Appear In the Job History 149
Cannot Submit MapReduce Jobs for Compute-Only Clusters with External Isilon HDFS 150
MapReduce Job Stops Responding on a PHD or CDH4 YARN Cluster 151
Cannot Download the Package When Using Downloadonly Plugin 151
Cannot Find Packages When You Use Yum Search 151
Remove the HBase Rootdir in HDFS Before You Delete the HBase Only Cluster 151
Index 153
6 VMware, Inc.
Page 7

About This Book
VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide describes how to install VMware
vSphere Big Data Extensions™ within your vSphere environment, and how to manage and monitor Hadoop
and HBase clusters using the Big Data Extensions plug-in for vSphere Web Client.
VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide also describes how to perform Hadoop
and HBase operations using the VMware Serengeti™ Command-Line Interface Client, which provides a
greater degree of control for certain system management and big data cluster creation tasks.
Intended Audience
This guide is for system administrators and developers who want to use Big Data Extensions to deploy and
manage Hadoop clusters. To successfully work with Big Data Extensions, you should be familiar with
VMware® vSphere® and Hadoop and HBase deployment and operation.
VMware Technical Publications Glossary
VMware Technical Publications provides a glossary of terms that might be unfamiliar to you. For definitions
of terms as they are used in VMware technical documentation, go to
http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs.
VMware, Inc.
7
Page 8

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
8 VMware, Inc.
Page 9

About VMware vSphere Big Data
Extensions 1
VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions lets you deploy and centrally operate big data clusters running on
VMware vSphere. Big Data Extensions simplifies the Hadoop and HBase deployment and provisioning
process, and gives you a real time view of the running services and the status of their virtual hosts. It
provides a central place from which to manage and monitor your big data cluster, and incorporates a full
range of tools to help you optimize cluster performance and utilization.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“Getting Started with Big Data Extensions,” on page 9
n
“Big Data Extensions and Project Serengeti,” on page 10
n
“About Big Data Extensions Architecture,” on page 11
n
“About Application Managers,” on page 12
n
Getting Started with Big Data Extensions
Big Data Extensions lets you deploy big data clusters. The tasks in this section describe how to set up
VMware vSphere® for use with Big Data Extensions, deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp, access the
VMware vCenter Server® and command-line interface (CLI) administrative consoles, and configure a
Hadoop distribution for use with Big Data Extensions.
VMware, Inc.
Prerequisites
Understand what Project Serengeti® and Big Data Extensions is so that you know how they fit into your
n
big data workflow and vSphere environment.
Verify that the Big Data Extensions features that you want to use, such as compute-only or data-
n
compute separated, are supported by Big Data Extensions for the Hadoop distribution that you want to
use.
Understand which features are supported by your Hadoop distribution.
n
Procedure
1 Do one of the following.
Install Big Data Extensions for the first time. Review the system requirements, install vSphere, and
n
install the Big Data Extensions components: Big Data Extensions vApp, Big Data Extensions plugin for vCenter Server, and Serengeti CLI Client.
Upgrade Big Data Extensions from a previous version. Perform the upgrade steps.
n
9
Page 10

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
2 (Optional) Install and configure a distribution other than Apache Bigtop for use with
Big Data Extensions.
Apache Bigtop is included in the Serengeti Management Server, but you can use any Hadoop
distribution that Big Data Extensions supports.
What to do next
After you have successfully installed and configured your Big Data Extensions environment, you can
perform the following additional tasks.
Stop and start the Serengeti services, create user accounts, manage passwords, and log in to cluster
n
nodes to perform troubleshooting.
Manage the vSphere resource pools, datastores, and networks that you use to create Hadoop and HBase
n
clusters.
Create, provision, and manage big data clusters.
n
Monitor the status of the clusters that you create, including their datastores, networks, and resource
n
pools, through the vSphere Web Client and the Serengeti Command-Line Interface.
On your Big Data clusters, run HDFS commands, Hive and Pig scripts , and MapReduce jobs, and
n
access Hive data.
If you encounter any problems when using Big Data Extensions, see Chapter 14, “Troubleshooting,” on
n
page 133.
Big Data Extensions and Project Serengeti
Big Data Extensions runs on top of Project Serengeti, the open source project initiated by VMware to
automate the deployment and management of Hadoop and HBase clusters on virtual environments such as
vSphere.
Big Data Extensions and Project Serengeti provide the following components.
Project Serengeti
Serengeti Management
Server
An open source project initiated by VMware, Project Serengeti lets users
deploy and manage big data clusters in a vCenter Server managed
environment. The major components are the Serengeti Management Server,
which provides cluster provisioning, software configuration, and
management services; and a command-line interface. Project Serengeti is
made available under the Apache 2.0 license, under which anyone can
modify and redistribute Project Serengeti according to the terms of the
license.
Provides the framework and services to run Big Data clusters on vSphere.
The Serengeti Management Server performs resource management, policybased virtual machine placement, cluster provisioning, software
configuration management, and environment monitoring.
10 VMware, Inc.
Page 11
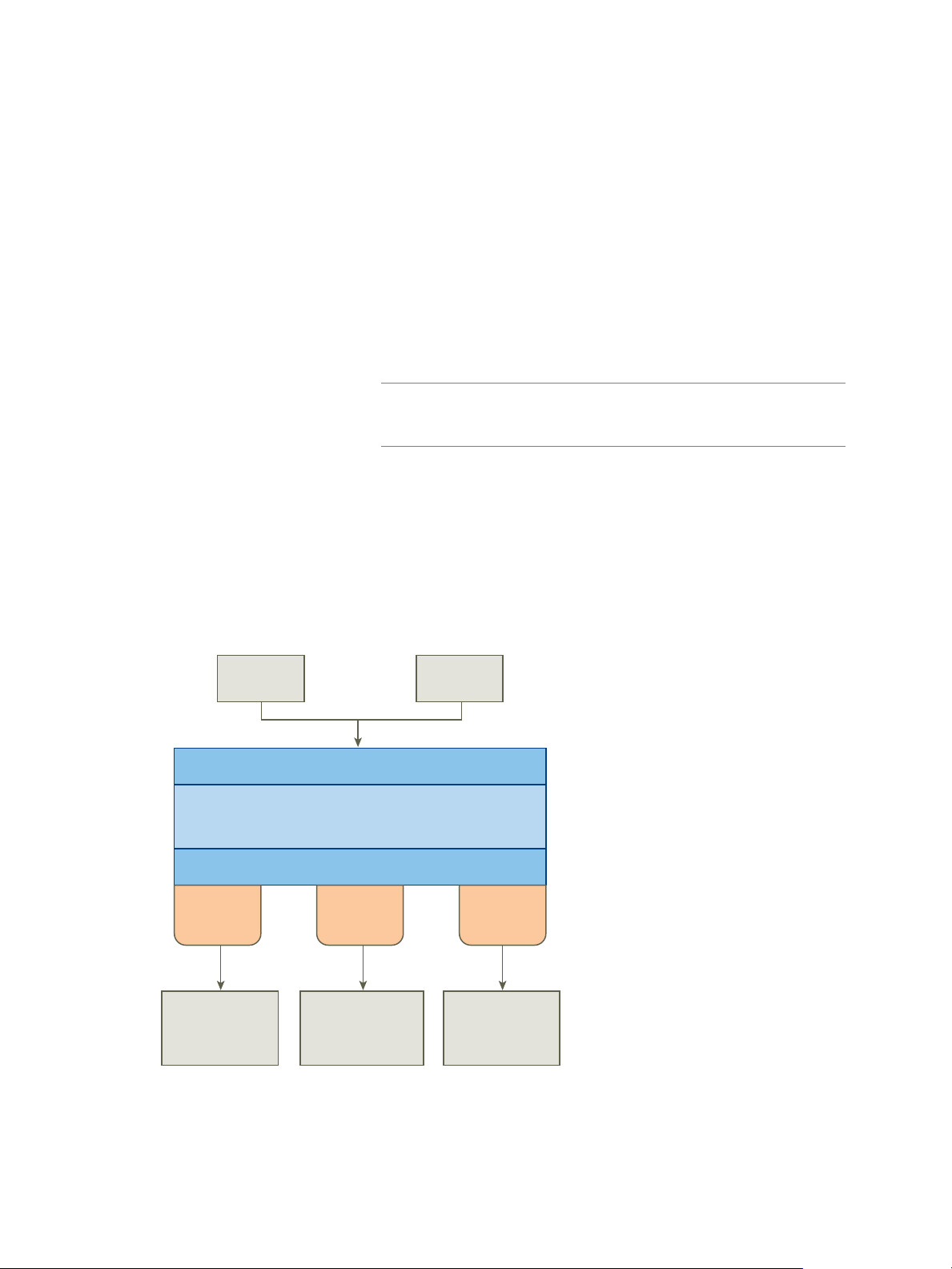
CLI GUI
Rest API
VM and Application
Provisioning Framework
Software Management SPI
Default
adapter
Cloudera
adapter
Ambari
adapter
Software
Management
Thrift Service
Cloudera
Manager
Server
Ambari
Server
Chapter 1 About VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions
Serengeti CommandLine Interface Client
The command-line interface (CLI) client provides a comprehensive set of
tools and utilities with which to monitor and manage your Big Data
deployment. If you are using the open source version of Serengeti without
Big Data Extensions, the CLI is the only interface through which you can
perform administrative tasks. For more information about the CLI, see the
VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Command-Line Interface Guide.
Big Data Extensions
The commercial version of the open source Project Serengeti from VMware,
Big Data Extensions, is delivered as a vCenter Server Appliance.
Big Data Extensions includes all the Project Serengeti functions and the
following additional features and components.
Enterprise level support from VMware.
n
Bigtop distribution from the Apache community.
n
NOTE VMware provides the Hadoop distribution as a convenience but
does not provide enterprise-level support. The Apache Bigtop
distribution is supported by the open source community.
The Big Data Extensions plug-in, a graphical user interface integrated
n
with vSphere Web Client. This plug-in lets you perform common
Hadoop infrastructure and cluster management administrative tasks.
About Big Data Extensions Architecture
The Serengeti Management Server and Hadoop Template virtual machine work together to configure and
provision big data clusters.
Figure 1‑1. Big Data Extensions Architecture
VMware, Inc. 11
Page 12

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Big Data Extensions performs the following steps to deploy a big data cluster.
1 The Serengeti Management Server searches for ESXi hosts with sufficient resources to operate the
cluster based on the configuration settings that you specify, and then selects the ESXi hosts on which to
place Hadoop virtual machines.
2 The Serengeti Management Server sends a request to the vCenter Server to clone and configure virtual
machines to use with the big data cluster.
3 The Serengeti Management Server configures the operating system and network parameters for the
new virtual machines.
4 Each virtual machine downloads the Hadoop software packages and installs them by applying the
distribution and installation information from the Serengeti Management Server.
5 The Serengeti Management Server configures the Hadoop parameters for the new virtual machines
based on the cluster configuration settings that you specify.
6 The Hadoop services are started on the new virtual machines, at which point you have a running
cluster based on your configuration settings.
About Application Managers
You can use Cloudera Manager, Apache Ambari, and the default application manager to provision and
manage clusters with VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions.
After you add a new Cloudera Manager or Ambari application manager to Big Data Extensions, you can
redirect your software management tasks, including monitoring and managing clusters, to that application
manager.
You can use an application manager to perform the following tasks:
List all available vendor instances, supported distributions, and configurations or roles for a specific
n
application manager and distribution.
Create clusters.
n
Monitor and manage services from the application manager console.
n
Check the documentation for your application manager for tool-specific requirements.
Restrictions
The following restrictions apply to Cloudera Manager and Ambari application managers:
To add an application manager with HTTPS, use the FQDN instead of the URL.
n
You cannot rename a cluster that was created with a Cloudera Manager or Ambari application
n
manager.
You cannot change services for a big data cluster from Big Data Extensions if the cluster was created
n
with Ambari or Cloudera Manager application manager.
To change services, configurations, or both, you must make the changes from the application manager
n
on the nodes.
If you install new services, Big Data Extensions starts and stops the new services together with old
services.
If you use an application manager to change services and big data cluster configurations, those changes
n
cannot be synced from Big Data Extensions. The nodes that you create with Big Data Extensions do not
contain the new services or configurations.
12 VMware, Inc.
Page 13

Chapter 1 About VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions
Services and Operations Supported by the Application Managers
If you use Cloudera Manager or Apache Ambari with Big Data Extensions, there are several additional
services that are available for your use.
Supported Application Managers and Distributions
Big Data Extensions supports certain application managers and Hadoop distributions. In some cases not all
features and operations are supported by certain versions of application mangers. The table below indicates
which features are available when using the listed application mangers.
Table 1‑1. Supported application managers and Hadoop distributions
Supported features
and operations Cloudera Manager
Supported Versions 5.3-5.4 2.0-2.1 1.7 2.3
Supported
Distributions
Automatic
Deployment
Cluster List, Stop,
Start, Export, and
Resume
vSphere High
Availability
vSphere Fault
Tolerance
Multiple Networks Multiple networks
Data-Compute
Combined
Data-Compute
Separation
Compute-only X Ambari can
Hbase Cluster X X X X
Hbase-only Not supported when
CDH 5.3-5.4, OneFS
7.1-7.2
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
X X X X
are not supported.
X X X X
X X X X
Hortonworks
Ambari Pivotal Ambari
HDP 2.2-2.3, OneFS*
7.1-7.2
Multiple networks
are not supported.
provision computeonly clusters when
using Isilon OneFS.
Refer to the EMC
Isilon Hadoop
Starter Kit for
Hortonworks
documentation for
information on
configuring Ambari
and Isilon OneFS.
PHD 3.0, OneFS*
7.1-7.2
Multiple networks
are not supported.
Ambari can
provision computeonly clusters when
using Isilon OneFS.
Refer to the EMC
Isilon Hadoop
Starter Kit for
Hortonworks
documentation for
information on
configuring Ambari
and Isilon OneFS.
Default Application
Manager
Bigtop 1.0, CDH
5.3-5.4, HDP 2.1, PHD
2.0-2.1, MapR 4.1-5.0,
and OneFS 7.1-7.2
Not supported when
using MapR.
Not supported when
using MapR.
using MapR.
VMware, Inc. 13
Page 14

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Table 1‑1. Supported application managers and Hadoop distributions (Continued)
Supported features
and operations Cloudera Manager
Hadoop
Topology/HVE
Hadoop Configuration Supported through
Hadoop Ecosystem
Components
X X X Topology is not
the Web interface of
the application
manager.
Full stack through
Cloudera Manager.
Hortonworks
Ambari Pivotal Ambari
Supported through
the Web interface of
the application
manager.
Full stack through
Ambari
Supported through
the Web interface of
the application
manager.
Full stack through
Ambari..
Default Application
Manager
supported when using
MapR.
HVE is only
supported when using
PHD.
Not supported when
using MapR.
Pig, Hive, Hive Server,
and Zookeeper.
Support for Hadoop Distributions in Isilon OneFS
If you wish to use Isilon OneFS, first verify if your Hadoop distribution is compatible with OneFS. See
Supported Hadoop Distributions in OneFS on the EMC Website.
NOTE Big Data Extensions does not natively support the provisioning of compute-only clusters with
Ambari Manager. However Ambari can provision compute-only clusters when using Isilon OneFS. Refer to
the EMC Isilon Hadoop Starter Kit for Hortonworks documentation for information on configuring Ambari
and Isilon OneFS.
Services Supported on Cloudera Manager and Ambari
Table 1‑2. Services supported on Cloudera Manager and Ambari
Service Name Cloudera Manager 5.3, 5.4 Ambari 1.6, 1.7
Falcon X
Flume X X
Ganglia X
HBase X X
HCatalog X
HDFS X X
Hive X X
Hue X X
Impala X
MapReduce X X
Nagios X
Oozie X X
Pig X
Sentry
Solr X
Spark X
Sqoop X X
Storm X
14 VMware, Inc.
Page 15

Chapter 1 About VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions
Table 1‑2. Services supported on Cloudera Manager and Ambari (Continued)
Service Name Cloudera Manager 5.3, 5.4 Ambari 1.6, 1.7
TEZ X
WebHCAT X
YARN X X
Zookeeper X X
About Service Level vSphere High Availability for Ambari
Ambari supports NameNode HA, however, you must configure NameNode HA for use with your Hadoop
deployment. See NameNode High Availability for Hadoop in the Hortonworks documentation.
About Service Level vSphere High Availability for Cloudera
The Cloudera distributions offer the following support for Service Level vSphere HA.
Cloudera using MapReduce v1 provides service level vSphere HA support for JobTracker.
n
Cloudera provides its own service level HA support for NameNode through HDFS2.
n
For information about how to use an application manager with the CLI, see the VMware vSphere Big Data
Extensions Command-Line Interface Guide.
VMware, Inc. 15
Page 16

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
16 VMware, Inc.
Page 17

Installing Big Data Extensions 2
To install Big Data Extensions so that you can create and provision big data clusters, you must install the
Big Data Extensions components in the order described.
What to do next
If you want to create clusters on any Hadoop distribution other than Apache Bigtop, which is included in
theSerengeti Management Server, install and configure the distribution for use with Big Data Extensions.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“System Requirements for Big Data Extensions,” on page 17
n
“Unicode UTF-8 and Special Character Support,” on page 20
n
“The Customer Experience Improvement Program,” on page 21
n
“Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 22
n
“Install RPMs in the Serengeti Management Server Yum Repository,” on page 25
n
“Install the Big Data Extensions Plug-In,” on page 26
n
“Configure vCenter Single Sign-On Settings for the Serengeti Management Server,” on page 28
n
“Connect to a Serengeti Management Server,” on page 28
n
“Install the Serengeti Remote Command-Line Interface Client,” on page 29
n
“Access the Serengeti CLI By Using the Remote CLI Client,” on page 30
n
System Requirements for Big Data Extensions
Before you begin the Big Data Extensions deployment tasks, your system must meet all of the prerequisites
for vSphere, clusters, networks, storage, hardware, and licensing.
Big Data Extensions requires that you install and configure vSphere and that your environment meets
minimum resource requirements. Make sure that you have licenses for the VMware components of your
deployment.
vSphere Requirements
VMware, Inc. 17
Before you install Big Data Extensions, set up the following VMware
products.
Install vSphere 5.5 (or later) Enterprise or Enterprise Plus.
n
Page 18

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
When you install Big Data Extensions on vSphere 5.5 or later, use
n
VMware® vCenter™ Single Sign-On to provide user authentication.
When logging in to vSphere 5.5 or later you pass authentication to the
vCenter Single Sign-On server, which you can configure with multiple
identity sources such as Active Directory and OpenLDAP. On successful
authentication, your user name and password is exchanged for a
security token that is used to access vSphere components such as
Big Data Extensions.
If your vCenter Server uses a FQDN, ensure you configure it correctly
n
when you install vCenter Server.
Configure all ESXi hosts to use the same Network Time Protocol (NTP)
n
server.
On each ESXi host, add the NTP server to the host configuration, and
n
from the host configuration's Startup Policy list, select Start and stop
with host. The NTP daemon ensures that time-dependent processes
occur in sync across hosts.
Cluster Settings
Network Settings
Configure your cluster with the following settings.
Enable vSphere HA and VMware vSphere® Distributed Resource
n
Scheduler™.
Enable Host Monitoring.
n
Enable admission control and set the policy you want. The default
n
policy is to tolerate one host failure.
Set the virtual machine restart priority to high.
n
Set the virtual machine monitoring to virtual machine and application
n
monitoring.
Set the monitoring sensitivity to high.
n
Enable vMotion and Fault Tolerance logging.
n
All hosts in the cluster have Hardware VT enabled in the BIOS.
n
The Management Network VMkernel Port has vMotion and Fault
n
Tolerance logging enabled.
Big Data Extensions can deploy clusters on a single network or use multiple
networks. The environment determines how port groups that are attached to
NICs are configured and which network backs each port group.
You can use either a vSwitch or vSphere Distributed Switch (vDS) to provide
the port group backing a Serengeti cluster. vDS acts as a single virtual switch
across all attached hosts while a vSwitch is per-host and requires the port
group to be configured manually.
When you configure your networks to use with Big Data Extensions, verify
that the following ports are open as listening ports.
Ports 8080 and 8443 are used by the Big Data Extensions plug-in user
n
interface and the Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client.
Port 5480 is used by vCenter Single Sign-On for monitoring and
n
management.
Port 22 is used by SSH clients.
n
18 VMware, Inc.
Page 19

Chapter 2 Installing Big Data Extensions
To prevent having to open a network firewall port to access Hadoop
n
services, log into the Hadoop client node, and from that node you can
access your cluster.
To connect to the internet (for example, to create an internal yum
n
repository from which to install Hadoop distributions), you may use a
proxy.
To enable communications, be sure that firewalls and web filters do not
n
block the Serengeti Management Server or other Serengeti nodes.
Direct Attached Storage
Do not use
Big Data Extensions in
conjunction with
vSphere Storage DRS
Migrating virtual
machines in vCenter
Server may disrupt the
virtual machine
placement policy
Attach and configure direct attached storage on the physical controller to
present each disk separately to the operating system. This configuration is
commonly described as Just A Bunch Of Disks (JBOD). Create VMFS
datastores on direct attached storage using the following disk drive
recommendations.
8-12 disk drives per host. The more disk drives per host, the better the
n
performance.
1-1.5 disk drives per processor core.
n
7,200 RPM disk Serial ATA disk drives.
n
Big Data Extensions places virtual machines on hosts according to available
resources, Hadoop best practices, and user defined placement policies prior
to creating virtual machines. For this reason, you should not deploy
Big Data Extensions on vSphere environments in combination with Storage
DRS. Storage DRS continuously balances storage space usage and storage I/O
load to meet application service levels in specific environments. If Storage
DRS is used with Big Data Extensions, it will disrupt the placement policies
of your Big Data cluster virtual machines.
Big Data Extensions places virtual machines based on available resources,
Hadoop best practices, and user defined placement policies that you specify.
For this reason, DRS is disabled on all the virtual machines created within
the Big Data Extensions environment. While this prevents virtual machines
from being automatically migrated by vSphere, it does not prevent you from
inadvertently moving virtual machines using the vCenter Server user
interface. This may break the Big Data Extensions defined placement policy.
For example, this may disrupt the number of instances per host and group
associations.
Resource Requirements
Resource pool with at least 27.5GB RAM.
n
for the vSphere
40GB or more (recommended) disk space for the management server
Management Server and
Templates
Resource Requirements
for the Hadoop Cluster
n
and Hadoop template virtual disks.
Datastore free space is not less than the total size needed by the Hadoop
n
cluster, plus swap disks for each Hadoop node that is equal to the
memory size requested.
Network configured across all relevant ESXi hosts, and has connectivity
n
with the network in use by the management server.
vSphere HA is enabled for the master node if vSphere HA protection is
n
needed. To use vSphere HA or vSphere FT to protect the Hadoop master
node, you must use shared storage.
VMware, Inc. 19
Page 20

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Hardware Requirements
for the vSphere and
Big Data Extensions
Environment
Host hardware is listed in the VMware Compatibility Guide. To run at optimal
performance, install your vSphere and Big Data Extensions environment on
the following hardware.
Dual Quad-core CPUs or greater that have Hyper-Threading enabled. If
n
you can estimate your computing workload, consider using a more
powerful CPU.
Use High Availability (HA) and dual power supplies for the master
n
node's host machine.
4-8 GBs of memory for each processor core, with 6% overhead for
n
virtualization.
Use a 1GB Ethernet interface or greater to provide adequate network
n
bandwidth.
Tested Host and Virtual
Machine Support
The maximum host and virtual machine support that has been confirmed to
successfully run with Big Data Extensions is 256 physical hosts running a
total of 512 virtual machines.
vSphere Licensing
You must use a vSphere Enterprise license or above to use VMware vSphere
HA and vSphere DRS.
Unicode UTF-8 and Special Character Support
Big Data Extensions supports internationalization (I18N) level 3. However, there are resources you specify
that do not provide UTF-8 support. You can use only ASCII attribute names consisting of alphanumeric
characters and underscores (_) for these resources.
Big Data Extensions Supports Unicode UTF-8
vCenter Server resources you specify using both the CLI and vSphere Web Client can be expressed with
underscore (_), hyphen (-), blank spaces, and all letters and numbers from any language. For example, you
can specify resources such as datastores labeled using non-English characters.
When using a Linux operating system, you should configure the system for use with UTF-8 encoding
specific to your locale. For example, to use U.S. English, specify the following locale encoding: en_US.UTF-8.
See your vendor's documentation for information on configuring UTF-8 encoding for your Linux
environment.
Special Character Support
The following vCenter Server resources can have a period (.) in their name, letting you select them using
both the CLI and vSphere Web Client.
portgroup name
n
cluster name
n
resource pool name
n
datastore name
n
The use of a period is not allowed in the Serengeti resource name.
20 VMware, Inc.
Page 21

Chapter 2 Installing Big Data Extensions
Resources Excluded From Unicode UTF-8 Support
The Serengeti cluster specification file, manifest file, and topology racks-hosts mapping file do not provide
UTF-8 support. When you create these files to define the nodes and resources for use by the cluster, use only
ASCII attribute names consisting of alphanumeric characters and underscores (_).
The following resource names are excluded from UTF-8 support:
cluster name
n
nodeGroup name
n
node name
n
virtual machine name
n
The following attributes in the Serengeti cluster specification file are excluded from UTF-8 support:
distro name
n
role
n
cluster configuration
n
storage type
n
haFlag
n
instanceType
n
groupAssociationsType
n
The rack name in the topology racks-hosts mapping file, and the placementPolicies field of the Serengeti
cluster specification file is also excluded from UTF-8 support.
The Customer Experience Improvement Program
You can configure Big Data Extensions to collect data to help improve your user experience with VMware
products. The following section contains important information about the VMware Customer Experience
Improvement Program.
The goal of the Customer Experience Improvement Program is to quickly identify and address problems
that might be affecting your experience. If you choose to participate in the Customer Experience
Improvement Program,Big Data Extensions will regularly send anonymous data to VMware. You can use
this data for product development and troubleshooting purposes.
Before collecting the data, VMware makes anonymous all fields that contain information that is specific to
your organization. VMware sanitizes fields by generating a hash of the actual value. When a hash value is
collected, VMware cannot identify the actual value but can detect changes in the value when you change
your environment.
VMware, Inc. 21
Page 22
VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Categories of Information in Collected Data
When you choose to participate in VMware’s Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP), VMware
will receive the following categories of data:
Configuration Data
Feature Usage Data
Performance Data
Data about how you have configured VMware products and information
related to your IT environment. Examples of Configuration Data include:
version information for VMware products; details of the hardware and
software running in your environment; product configuration settings, and
information about your networking environment. Configuration Data may
include hashed versions of your device IDs and MAC and Internet Protocol
Addresses.
Data about how you use VMware products and services. Examples of
Feature Usage Data include: details about which product features are used;
metrics of user interface activity; and details about your API calls.
Data about the performance of VMware products and services. Examples of
Performance Data include metrics of the performance and scale of VMware
products and services; response times for User Interfaces, and details about
your API calls.
Enabling and Disabling Data Collection
By default, enrollment in the Customer Experience Improvement Program is enabled during installation.
You have the option of disabling this service during installation. You can discontinue participation in the
Customer Experience Improvement Program at any time, and stop sending data to VMware. See“Disable
the Big Data Extensions Data Collector,” on page 118.
If you have any questions or concerns regarding the Customer Experience Improvement Program for Log
Insight, contact bde-info@vmware.com.
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web Client
Deploying the Big Data Extensions vApp is the first step in getting your cluster up and running with
Big Data Extensions.
Prerequisites
Install and configure vSphere.
n
Configure all ESXi hosts to use the same NTP server.
n
On each ESXi host, add the NTP server to the host configuration, and from the host configuration's
n
Startup Policy list, select Start and stop with host. The NTP daemon ensures that time-dependent
processes occur in sync across hosts.
When installing Big Data Extensions on vSphere 5.5 or later, use vCenter Single Sign-On to provide
n
user authentication.
Verify that you have one vSphere Enterprise license for each host on which you deploy virtual Hadoop
n
nodes. You manage your vSphere licenses in the vSphere Web Client or in vCenter Server.
Install the Client Integration plug-in for the vSphere Web Client. This plug-in enables OVF deployment
n
on your local file system.
NOTE Depending on the security settings of your browser, you might have to approve the plug-in
when you use it the first time.
22 VMware, Inc.
Page 23

Chapter 2 Installing Big Data Extensions
Download the Big Data Extensions OVA from the VMware download site.
n
Verify that you have at least 40GB disk space available for the OVA. You need additional resources for
n
the Hadoop cluster.
Ensure that you know the vCenter Single Sign-On Look-up Service URL for your
n
vCenter Single Sign-On service.
If you are installing Big Data Extensions on vSphere 5.5 or later, ensure that your environment includes
vCenter Single Sign-On. Use vCenter Single Sign-On to provide user authentication on vSphere 5.5 or
later.
Review the Customer Experience Improvement Program description, and determine if you wish to
n
collect data and send it to VMware help improve your user experience using Big Data Extensions. See
“The Customer Experience Improvement Program,” on page 21.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Web Client, select a select a top level resource pool, then select Actions > Deploy OVF
Template.
Select a top-level resource pool. Child resource pools are not supported by Big Data Extensions even
though you can select a child resource pool. If you select a child resource pool, you will not be able to
create Big Data clusters with Big Data Extensions.
2 Choose the location where the Big Data Extensions OVA resides and click Next.
Option Description
Deploy from File
Deploy from URL
Browse your file system for an OVF or OVA template.
Type a URL to an OVF or OVA template located on the internet. For
example: http://vmware.com/VMTN/appliance.ovf.
3 View the OVF Template Details page and click Next.
4 Accept the license agreement and click Next.
5 Specify a name for the vApp, select a target datacenter for the OVA, and click Next.
The only valid characters for Big Data Extensions vApp names are alphanumeric and underscores. The
vApp name must be < 60 characters. When you choose the vApp name, also consider how you will
name your clusters. Together the vApp and cluster names must be < 80 characters.
6 Select shared storage for the OVA and click Next.
If shared storage is not available, local storage is acceptable.
7 For each network specified in the OVF template, select a network in the Destination Networks column
in your infrastructure to set up the network mapping.
The first network lets the Management Server communicate with your Hadoop cluster. The second
network lets the Management Server communicate with vCenter Server. If your vCenter Server
deployment does not use IPv6, you can specify the same IPv4 destination network for use by both
source networks.
VMware, Inc. 23
Page 24

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
8 Configure the network settings for your environment, and click Next.
a Enter the network settings that let the Management Server communicate with your Hadoop
cluster.
Use a static IPv4 (IP) network. An IPv4 address is four numbers separated by dots as in
aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd, where each number ranges from 0 to 255. You must enter a netmask, such as
255.255.255.0, and a gateway address, such as 192.168.1.253.
If the vCenter Server or any ESXi host or Hadoop distribution repository is resolved using a fully
qualified domain name (FQDN), you must enter a DNS address. Enter the DNS server IP address
as DNS Server 1. If there is a secondary DNS server, enter its IP address as DNS Server 2.
NOTE You cannot use a shared IP pool with Big Data Extensions.
b (Optional) If you are using IPv6 between the Management Server and vCenter Server, select the
Enable Ipv6 Connection checkbox.
Enter the IPv6 address, or FQDN, of the vCenter Server. The IPv6 address size is 128 bits. The
preferred IPv6 address representation is: xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx where each x is
a hexadecimal digit representing 4 bits. IPv6 addresses range from
0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000 to ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff. For convenience, an IPv6
address may be abbreviated to shorter notations by application of the following rules.
Remove one or more leading zeroes from any groups of hexadecimal digits. This is usually
n
done to either all or none of the leading zeroes. For example, the group 0042 is converted to 42.
Replace consecutive sections of zeroes with a double colon (::). You may only use the double
n
colon once in an address, as multiple uses would render the address indeterminate. RFC 5952
recommends that a double colon not be used to denote an omitted single section of zeroes.
The following example demonstrates applying these rules to the address
2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:ff00:0042:8329.
Removing all leading zeroes results in the address 2001:db8:0:0:0:ff00:42:8329.
n
Omitting consecutive sections of zeroes results in the address 2001:db8::ff00:42:8329.
n
See RFC 4291 for more information on IPv6 address notation.
9 Verify that the Initialize Resources check box is selected and click Next.
If the check box is unselected, the resource pool, data store, and network connection assigned to the
vApp will not be added to Big Data Extensions.
If you do not add the resource pool, datastore, and network when you deploy the vApp, use the
vSphere Web Client or the Serengeti CLI Client to specify the resource pool, datastore, and network
information before you create a Hadoop cluster.
10 Run the vCenter Single Sign-On Lookup Service URL to enable vCenter Single Sign-On.
If you use vCenter 5.x, use the following URL: https://FQDN_or_IP_of_SSO_SERVER:
n
7444/lookupservice/sdk
If you use vCenter 6.0, use the following URL: https://FQDN_of_SSO_SERVER:
n
443/lookupservice/sdk
If you don't input the URL, vCenter Single Sign-On is disabled.
11 To disable the Big Data Extensions data collector, uncheck the Customer Experience Improvement
Program checkbox.
24 VMware, Inc.
Page 25
Chapter 2 Installing Big Data Extensions
12 (Optional) To disable the Big Data Extensions Web plug-in from automatically registering, uncheck the
enable checkbox.
By default the checkbox to enable automatic registration of the Big Data Extensions Web plug-in is
selected. When you first login to the Big Data Extensions Web client, it automatically connects to the
Serengeti management server.
13 Specify a remote syslog server, such as VMware vRealize Log Insight, to which Big Data Extensions can
send logging information to across the network.
Retention, rotation and the splitting of logs received and managed by a syslog server are controlled by
that syslog server. Big Data Extensions cannot configure or control log management on a remote syslog
server. For more information on log management, see the documentation for the syslog server.
Regardless of the additional syslog configuration specified with this option, logs continue to be placed
in the default locations of the Big Data Extensions environment.
14 Verify the vService bindings and click Next.
15 Verify the installation information and click Finish.
vCenter Server deploys the Big Data Extensions vApp. When deployment finishes, two virtual
machines are available in the vApp.
The Management Server virtual machine, management-server (also called the
n
Serengeti Management Server), which is started as part of the OVA deployment.
The Node Template virtual machine, node-template, is not powered on. Big Data Extensions clones
n
Hadoop nodes from this template when provisioning a cluster. Do not start or stop this virtual
machine without good reason. The template does not include a Hadoop distribution.
IMPORTANT Do not delete any files under the /opt/serengeti/.chef directory. If you delete any of these
files, such as the serengeti.pem file, subsequent upgrades to Big Data Extensions might fail without
displaying error notifications.
What to do next
Install the Big Data Extensions plug-in within the vSphere Web Client. See “Install the Big Data Extensions
Plug-In,” on page 26.
If the Initialize Resources check box is not selected, add resources to the Big Data Extensions server before
you create a Hadoop cluster.
Install RPMs in the Serengeti Management Server Yum Repository
Install the wsdl4j and mailx Red Hat Package Manager (RPM) packages within the internal Yum repository
of the Serengeti Management Server.
The wsdl4j and mailx RPM packages are not embedded withinBig Data Extensions due to licensing
agreements. For this reason you must install them within the internal Yum repository of the
Serengeti Management Server.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as the
user serengeti.
VMware, Inc. 25
Page 26
VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
2 Download and install the wsdl4j and mailx RPM packages.
If the Serengeti Management Server can connect to the Internet, run the commands as shown in the
n
example below to download the RPMs, copy the files to the required directory, and create a
repository.
umask 022
cd /opt/serengeti/www/yum/repos/centos/6/base/RPMS/
wget http://mirror.centos.org/centos/6/os/x86_64/Packages/mailx-12.4-8.el6_6.x86_64.rpm
wget http://mirror.centos.org/centos/6/os/x86_64/Packages/wsdl4j-1.5.2-7.8.el6.noarch.rpm
createrepo ..
If the Serengeti Management Server cannot connect to the Internet, you must run the following
n
tasks manually.
a Download the RPM files as shown in the example below.
http://mirror.centos.org/centos/6/os/x86_64/Packages/mailx-12.4-8.el6_6.x86_64.rpm
http://mirror.centos.org/centos/6/os/x86_64/Packages/wsdl4j-1.5.2-7.8.el6.noarch.rpm
b Copy the RPM files to /opt/serengeti/www/yum/repos/centos/6/base/RPMS/.
c Run the createrepo command to create a repository from the RPMs you downloaded.
umask 022
chmod a+r /opt/serengeti/www/yum/repos/centos/6/base/*.rpm
createrepo /opt/serengeti/www/yum/repos/centos/6/base/
Install the Big Data Extensions Plug-In
To enable the Big Data Extensions user interface for use with a vCenter Server Web Client, register the plugin with the vSphere Web Client. The Big Data Extensions graphical user interface is supported only when
you use vSphere Web Client 5.5 and later.
The Big Data Extensions plug-in provides a GUI that integrates with the vSphere Web Client. Using the
Big Data Extensions plug-in interface you can perform common Hadoop infrastructure and cluster
management tasks.
NOTE Use only the Big Data Extensions plug-in interface in the vSphere Web Client or the Serengeti CLI
Client to monitor and manage your Big Data Extensions environment. Performing management operations
in vCenter Server might cause the Big Data Extensions management tools to become unsynchronized and
unable to accurately report the operational status of your Big Data Extensions environment.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22.
By default, the Big Data Extensions Web plug-in automatically installs and registers when you deploy
n
the Big Data Extensions vApp. To install the Big Data Extensions Web plug-in after deploying the
Big Data Extensions vApp, you must has opted not to enable automatic registration of the Web plug-in
during deployment. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web Client,” on
page 22.
Ensure that you have login credentials with administrator privileges for the vCenter Server system with
n
which you are registering Big Data Extensions.
NOTE The user name and password you use to login cannot contain characters whose UTF-8 encoding
is greater than 0x8000.
26 VMware, Inc.
Page 27

Chapter 2 Installing Big Data Extensions
If you want to use the vCenter Server IP address to access the vSphere Web Client, and your browser
n
uses a proxy, add the vCenter Server IP address to the list of proxy exceptions.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser and go to the URL of vSphere Web Client 5.5 or later.
https://hostname-or-ip-address:port/vsphere-client
The hostname-or-ip-address can be either the DNS hostname or IP address of vCenter Server. By default
the port is 9443, but this might have changed during installation of the vSphere Web Client.
2 Enter the user name and password with administrative privileges that has permissions on
vCenter Server, and click Login.
3 Using the vSphere Web Client Navigator pane, locate the ZIP file on the Serengeti Management Server
that contains the Big Data Extensions plug-in to register to the vCenter Server.
You can find the Serengeti Management Server under the datacenter and resource pool to which you
deployed it.
4 From the inventory tree, select management-server to display information about the
Serengeti Management Server in the center pane.
Click the Summary tab in the center pane to access additional information.
5 Note the IP address of the Serengeti Management Server virtual machine.
6 Open a Web browser and go to the URL of the management-server virtual machine.
https://management-server-ip-address:8443/register-plugin
The management-server-ip-address is the IP address you noted in Step 5.
7 Enter the information to register the plug-in.
Option Action
Register or Unregister
vCenter Server host name or IP
address
User Name and Password
Big Data Extensions Package URL
Click Install to install the plug-in. Select Uninstall to uninstall the plug-in.
Enter the server host name or IP address of vCenter Server.
Do not include http:// or https:// when you enter the host name or IP
address.
Enter the user name and password with administrative privileges that you
use to connect to vCenter Server. The user name and password cannot
contain characters whose UTF-8 encoding is greater than 0x8000.
Enter the URL with the IP address of the management-server virtual
machine where the Big Data Extensions plug-in package is located:
https://management-server-ip-address/vcplugin/serengetiplugin.zip
8 Click Submit.
The Big Data Extensions plug-in registers with vCenter Server and with the vSphere Web Client.
9 Log out of the vSphere Web Client, and log back in using your vCenter Server user name and
password.
The Big Data Extensions icon appears in the list of objects in the inventory.
10 Click Big Data Extensions in the Inventory pane.
What to do next
Connect the Big Data Extensions plug-in to the Big Data Extensions instance that you want to manage by
connecting to the corresponding Serengeti Management Server. See “Connect to a Serengeti Management
Server,” on page 28.
VMware, Inc. 27
Page 28

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Configure vCenter Single Sign-On Settings for the Serengeti Management Server
If the Big Data Extensions Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication settings are not configured or if they change
after you install the Big Data Extensions plug-in, you can use the Serengeti Management Server
Administration Portal to enable SSO, update the certificate, and register the plug-in so that you can connect
to the Serengeti Management Server and continue managing clusters.
The SSL certificate for the Big Data Extensions plug-in can change for many reasons. For example, you
install a custom certificate or replace an expired certificate.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you know the IP address of the Serengeti Management Server to which you want to
n
connect.
Ensure that you have login credentials for the Serengeti Management Server root user.
n
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser and go the URL of the Serengeti Management Server Administration Portal.
https://management-server-ip-address:5480
2 Type root for the user name, type the password, and click Login.
3 Select the SSO tab.
4 Do one of the following.
Option Description
Update the certificate
Enable SSO for the first time
The Big Data Extensions and vCenter SSO server certificates are synchronized.
What to do next
Reregister the Big Data Extensions plug-in with the Serengeti Management Server. See “Connect to a
Serengeti Management Server,” on page 28.
Click Update Certificate.
Type the Lookup Service URL, and click Enable SSO.
Connect to a Serengeti Management Server
To use the Big Data Extensions plug-in to manage and monitor big data clusters and Hadoop distributions,
you must connect the Big Data Extensions plug-in to the Serengeti Management Server in your
Big Data Extensions deployment.
You can deploy multiple instances of the Serengeti Management Server in your environment. However, you
can connect the Big Data Extensions plug-in with only one Serengeti Management Server instance at a time.
You can change which Serengeti Management Server instance the plug-in connects to, and use the
Big Data Extensions plug-in interface to manage and monitor multiple Hadoop and HBase distributions
deployed in your environment.
IMPORTANT The Serengeti Management Server that you connect to is shared by all users of the
Big Data Extensions plug-in interface in the vSphere Web Client. If a user connects to a different
Serengeti Management Server, all other users are affected by this change.
28 VMware, Inc.
Page 29

Chapter 2 Installing Big Data Extensions
Prerequisites
Verify that the Big Data Extensions vApp deployment was successful and that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
Verify that the version of the Serengeti Management Server and the Big Data Extensions plug-in is the
n
same.
Ensure that vCenter Single Sign-On is enabled and configured for use by Big Data Extensions for
n
vSphere 5.5 and later.
Install theBig Data Extensions plug-in.
n
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
2 Select Big Data Extensions.
3 Click the Summary tab.
4 In the Connected Server pane, click the Connect Server link.
5 Navigate to the Serengeti Management Server virtual machine in the Big Data Extensions vApp to
which to connect, select it, and click OK.
The Big Data Extensions plug-in communicates using SSL with the Serengeti Management Server.
When you connect to a Serengeti server instance, the plug-in verifies that the SSL certificate in use by
the server is installed, valid, and trusted.
The Serengeti server instance appears as the connected server on the Summary tab of the
Big Data Extensions Home page.
What to do next
You can add resource pool, datastore, and network resources to your Big Data Extensions deployment, and
create big data clusters that you can provision for use.
Install the Serengeti Remote Command-Line Interface Client
Although theBig Data Extensions Plug-in for vSphere Web Client supports basic resource and cluster
management tasks, you can perform a greater number of the management tasks using the Serengeti CLI
Client.
Prerequisites
Verify that the Big Data Extensions vApp deployment was successful and that the Management Server
n
is running.
Verify that you have the correct user name and password to log into the Serengeti CLI Client. If you are
n
deploying on vSphere 5.5 or later, the Serengeti CLI Client uses your vCenter Single Sign-On
credentials.
Verify that the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is installed in your environment, and that its location is
n
in your PATH environment variable.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
2 Select Big Data Extensions.
3 Click the Getting Started tab, and click the Download Serengeti CLI Console link.
A ZIP file containing the Serengeti CLI Client downloads to your computer.
VMware, Inc. 29
Page 30

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
4 Unzip and examine the download, which includes the following components in the cli directory.
The serengeti-cli-version JAR file, which includes the Serengeti CLI Client.
n
The samples directory, which includes sample cluster configurations.
n
Libraries in the lib directory.
n
5 Open a command shell, and navigate to the directory where you unzipped the Serengeti CLI Client
download package.
6 Change to the cli directory, and run the following command to open the Serengeti CLI Client:
java -jar serengeti-cli-version.jar
What to do next
To learn more about using the Serengeti CLI Client, see the VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Commandline Interface Guide.
Access the Serengeti CLI By Using the Remote CLI Client
You can access the Serengeti Command-Line Interface (CLI) to perform Serengeti administrative tasks with
the Serengeti Remote CLI Client.
Prerequisites
Use the VMware vSphere Web Client to log in to the VMware vCenter Server® on which you deployed
n
the Serengeti vApp.
Verify that the Serengeti vApp deployment was successful and that the Management Server is running.
n
Verify that you have the correct password to log in to Serengeti CLI. See the VMware vSphere Big Data
n
Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide.
The Serengeti CLI uses its vCenter Server credentials.
Verify that the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is installed in your environment and that its location is
n
in your path environment variable.
Procedure
1 Download the Serengeti CLI package from the Serengeti Management Server.
Open a Web browser and navigate to the following URL: https://server_ip_address/cli/VMware-
Serengeti-CLI.zip
2 Download the ZIP file.
The filename is in the format VMware-Serengeti-cli-version_number-build_number.ZIP.
3 Unzip the download.
The download includes the following components.
The serengeti-cli-version_number JAR file, which includes the Serengeti Remote CLI Client.
n
The samples directory, which includes sample cluster configurations.
n
Libraries in the lib directory.
n
4 Open a command shell, and change to the directory where you unzipped the package.
30 VMware, Inc.
Page 31

Chapter 2 Installing Big Data Extensions
5 Change to the cli directory, and run the following command to enter the Serengeti CLI.
For any language other than French or German, run the following command.
n
java -jar serengeti-cli-version_number.jar
For French or German languages, which use code page 850 (CP 850) language encoding when
n
running the Serengeti CLI from a Windows command console, run the following command.
java -Dfile.encoding=cp850 -jar serengeti-cli-version_number.jar
6 Connect to the Serengeti service.
You must run the connect host command every time you begin a CLI session, and again after the 30
minute session timeout. If you do not run this command, you cannot run any other commands.
a Run the connect command.
connect --host xx.xx.xx.xx:8443
b At the prompt, type your user name, which might be different from your login credentials for the
Serengeti Management Server.
NOTE If you do not create a user name and password for the
Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client, you can use the default vCenter Server administrator
credentials. The Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client uses the vCenter Server login credentials
with read permissions on the Serengeti Management Server.
c At the prompt, type your password.
A command shell opens, and the Serengeti CLI prompt appears. You can use the help command to get help
with Serengeti commands and command syntax.
To display a list of available commands, type help.
n
To get help for a specific command, append the name of the command to the help command.
n
help cluster create
Press Tab to complete a command.
n
VMware, Inc. 31
Page 32

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
32 VMware, Inc.
Page 33

Upgrading Big Data Extensions 3
You can upgrade Big Data Extensions from earlier versions.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“Prepare to Upgrade Big Data Extensions,” on page 33
n
“Upgrade the Big Data Extensions Virtual Appliance,” on page 34
n
“Upgrade the Big Data Extensions Plug-in,” on page 35
n
“Upgrade Big Data Extensions Clusters Using the Serengeti Command-Line Interface,” on page 36
n
“Upgrade the Serengeti CLI,” on page 36
n
“Add a Remote Syslog Server,” on page 37
n
Prepare to Upgrade Big Data Extensions
As a prerequisite to upgrading Big Data Extensions, you must prepare your system to ensure that you have
all necessary software installed and configured properly, and that all components are in the correct state.
Data from non-working Big Data Extensions deployments is not migrated during the upgrade process. If
Big Data Extensions is not working and you cannot recover according to the troubleshooting procedures, do
not try to perform the upgrade. Instead, uninstall the previous Big Data Extensions components and install
the new version.
VMware, Inc.
IMPORTANT Do not delete any files in the /opt/serengeti/.chef directory. If you delete any of these files,
such as the sernegeti.pem file, subsequent upgrades to Big Data Extensions might fail without displaying
error notifications.
Prerequisites
Verify that your previous Big Data Extensions deployment is working normally.
n
Procedure
1 Log in to your pre-existing Serengeti Management Server.
2 Run the script /opt/serengeti/sbin/serengeti-maintenance.sh to place Big Data Extensions into
maintenance mode.
serengeti-maintenance.sh on
33
Page 34

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
3 Verify that Big Data Extensions is in maintenance mode.
When Big Data Extensions completes all jobs that have been submitted, the maintenance status will
enter safe mode. Run the serengeti-maintenance.sh with the status parameter repeatedly until it
returns the safe system status message.
serengeti-maintenance.sh status
safe
When the system returns the safe system status message, you can perform the system upgrade tasks.
What to do next
You can now upgrade to the new version of Big Data Extensions. See “Upgrade the Big Data Extensions
Virtual Appliance,” on page 34.
Upgrade the Big Data Extensions Virtual Appliance
You must perform several tasks to complete the upgrade of the Big Data Extensions virtual appliance.
Prerequisites
The new version of Big Data Extensions is successfully deployed in the same vCenter Server environment as
the version from which you are upgrading.
Procedure
1 Run the Big Data Extensions Upgrade Script on page 34
The upgrade script imports the configuration from the previous version of Big Data Extensions.
2 Upgrade Serengeti Management Server Using the Serengeti Management Server Administration
Portal on page 35
You can upgrade from your previous Big Data Extensions version to the latest version using the
Serengeti Management Server Administration Portal.
Run the Big Data Extensions Upgrade Script
The upgrade script imports the configuration from the previous version of Big Data Extensions.
Prerequisites
Deploy the new version of Big Data Extensions on the same vCenter Server instance as your previous
n
deployment. This allows the upgrade script to import your Big Data Extensions settings from your
previous deployment into the latest version.
You can only upgrade from version 2.2 to version 2.3 using this method. If you are upgrading from an
n
earlier version of Big Data Extensions, you must first upgrade to version 2.2.
If you use a customized Hadoop template, create a new Hadoop template for your environment prior to
n
upgrading to the new version of Big Data Extensions. See “Create a Node Template Virtual Machine
using RHEL Server 6.7 and VMware Tools,” on page 64
Have available the IP address for version 2.2 of the Serengeti Management Server.
n
Procedure
1 Open a command shell on the version of the Serengeti Management Server you are upgrading to
(version 2.3), and log in as the user serengeti.
34 VMware, Inc.
Page 35

Chapter 3 Upgrading Big Data Extensions
2 Run the /opt/serengeti/sbin/upgrade.py script.
Provide the IP address for version 2.2 of the Serengeti Management Server. The script prompts you to
enter the password for the serengeti user for version 2.2 of the Serengeti Management Server.
/opt/serengeti/sbin/upgrade.py ip_address_2.2
The upgrade process may take several minutes to complete. Informational messages alert you to the
progress of the upgrade as it proceeds.
3 Open a command shell on the Serengeti Management Server for version 2.3, and log in as the user
serengeti.
If the upgrade procedure returns an error, view the /opt/serengeti/logs/serengeti-upgrade.log file.
The log file tracks and records events when upgradingBig Data Extensions, and can be used to diagnose
problems that may occur.
What to do next
You can now upgrade the Serengeti Management Server. See “Upgrade Serengeti Management Server
Using the Serengeti Management Server Administration Portal,” on page 35 .
Upgrade Serengeti Management Server Using the Serengeti Management Server Administration Portal
You can upgrade from your previous Big Data Extensions version to the latest version using the
Serengeti Management Server Administration Portal.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser and go to the URL of the Serengeti Management Server Administration Portal for
Big Data Extensions 2.3.
https://management-server-ip-address:5480
2 Type root for the user name, type the password, and click Login.
3 Select the Upgrade tab.
4 Enter the IP addresses for the Big Data Extensions server from which you want to upgrade from, and
the password for the serengeti user, and click Upgrade.
Upgrade the Big Data Extensions Plug-in
You must use the same version of the Serengeti Management Server and the Big Data Extensions plug-in.
By default, the Big Data Extensions Web plug-in automatically installs and registers with the
Serengeti Management Server when you deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. If you chose not to install
and register the Big Data Extensions Web plug-in when installing the Big Data Extensions vApp, you must
perform this task to upgrade the plug-in.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser and go to the URL of the Serengeti Management Server plug-in manager service.
https://management-server-ip-address:8443/register-plugin
2 Select Uninstall and click Submit.
3 Select Install.
4 Enter the information to register the new plug-in, and click Submit.
VMware, Inc. 35
Page 36

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Upgrade Big Data Extensions Clusters Using the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
To enable the Serengeti Management Server to manage clusters created in a previous version of
Big Data Extensions, you must upgrade the components in the virtual machines of each cluster. The
Serengeti Management Server uses these components to control the cluster nodes.
When you upgrade from an earlier version of Big Data Extensions, clusters that you need to upgrade are
shown with an alert icon next to the cluster name. When you click the alert icon the error message Upgrade
the cluster to the latest version displays as a tool tip. See “View Provisioned Clusters in the vSphere
Web Client,” on page 119.
You can also identify clusters you need to upgrade using the cluster list command. When you run the
cluster list command, the message "Earlier" displays where the cluster version normally appears.
Prerequisites
You can upgrade any cluster created by Big Data Extensions 2.x to version 2.3. You do not need to
n
upgrade the cluster to version 2.2 prior to upgrading it to version 2.3.
Procedure
1 Log into the vSphere Web Client that is connected to vCenter Server and navigate to Hosts and
Clusters.
2 Select the resource pool of the cluster, select the Virtual Machines tab, and power on the cluster's
virtual machines.
IMPORTANT It may take up to five minutes for vCenter Server to assign valid IP addresses to the Big
Data cluster nodes. Do not perform the remaining upgrade steps until the nodes have received their IP
addresses. If a node does not have a valid IP address, it cannot be upgraded to the new version of
Big Data Extensions virtual machine tools.
3 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
4 Run the cluster upgrade command for each cluster that was created with a previous version of
Big Data Extensions.
5 If the upgrade fails for a node, make sure that the failed node has a valid IP address and then rerun the
cluster upgrade command.
You can rerun the command as many times as you need to upgrade all the nodes.
What to do next
Stop and restart your Big Data clusters.
Upgrade the Serengeti CLI
The Serengeti CLI must be the same version as your Big Data Extensions deployment. If you run the CLI
remotely to connect to the management server, you must upgrade the Serengeti CLI.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Web Client.
2 Select Big Data Extensions from the navigation panel.
3 Click the Summary tab.
4 In the Connected Server panel, click Connect Server.
36 VMware, Inc.
Page 37

Chapter 3 Upgrading Big Data Extensions
5 Select the Serengeti Management Server virtual machine in the Big Data Extensions vApp to which you
want to connect and click OK.
6 Click the Getting Started tab, and click Download Serengeti CLI Console.
A ZIP file containing the Serengeti CLI Client downloads to your computer.
7 Unzip and examine the ZIP file, which includes the following components in the CLI directory:
The serengeti-cli-version JAR file, which includes the Serengeti CLI Client.
n
The samples directory, which includes sample cluster configurations.
n
Libraries in the lib directory.
n
8 Open a command shell and navigate to the directory where you unzipped the Serengeti CLI Client
download package.
9 Change to the CLI directory, and run the following command to open the Serengeti CLI Client:
java -jar serengeti-cli-version.jar
What to do next
1 If your clusters are deployed with a Hadoop Template virtual machine that has a customized version of
the CentOS 6.x operating system that includes VMware Tools, you must customize a new CentOS 6.x
template to use after you upgrade Big Data Extensions.
2 To enable the Serengeti Management Server to manage clusters that you created in a previous version
of Big Data Extensions, you must upgrade each cluster.
Add a Remote Syslog Server
If you wish to use a remote syslog server after upgrading from earlier versions of Big Data Extensions, you
must manually specify the remote syslog server you wish to use.
The retention, rotation and splitting of logs received and managed by a syslog server are controlled by that
syslog server. Big Data Extensions cannot configure or control log management on a remote syslog server.
For more information on log management, see the documentation for your syslog server.
Prerequisites
Successfully upgrade to the current release of Big Data Extensions.
n
Have a remote syslog server within your environment that Big Data Extensions can send logging
n
information to.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as the
user serengeti.
2 Open the file /etc/rsyslog.d/20-base.conf in a text editor.
3 Edit the file to include the remote syslog service information.
*.* @syslog_ip_address:port_number
4 Restart the syslog service.
service rsyslog restart
VMware, Inc. 37
Page 38

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Your upgraded Big Data Extensions deployment will send logging information to the remote syslog service
you specify.
NOTE Regardless of the additional syslog configuration specified with this procedure, logs continue to be
placed in the default locations of the Big Data Extensions environment. See “Log Files for Troubleshooting,”
on page 134.
38 VMware, Inc.
Page 39

Managing Application Managers 4
A key to managing your Hadoop clusters is understanding how to manage the different application
managers that you use in your Big Data Extensions environment.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“Add an Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client,” on page 39
n
“Modify an Application Manager by Using the Web Client,” on page 40
n
“Delete an Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client,” on page 40
n
“View Application Managers and Distributions by Using the Web Client,” on page 40
n
“View Roles for Application Manager and Distribution by Using the Web Client,” on page 40
n
Add an Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client
To use either Cloudera Manager or Ambari application managers to manage clusters, you must add the
application manager and add server information to Big Data Extensions.
Application manager names can include only alphanumeric characters ([0-9, a-z, A-Z]) and the following
special characters; underscores, hyphens, and blank spaces.
VMware, Inc.
Procedure
1 On the Big Data Extensions navigation pane, click Application Managers.
2 Click the Add Application Manager icon (+) at the top of the page to open the New Application
Manager wizard.
3 Follow the prompts to complete the installation of the application manager.
You can use either http or https.
Option Action
Use http
Use https
The vSphere Web UI refreshes the Application Manager list and displays it in the List view.
Enter the server URL with http. The SSL certification text box is disabled.
Enter the FQDN instead of the URL. The SSL certification text box is
enabled.
39
Page 40

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Modify an Application Manager by Using the Web Client
You can modify the information for an application manager, for example, you can change the manager
server IP address if it is not a static IP, or you can upgrade the administrator account.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have at least one external application manager installed on your Big Data Extensions
environment.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Web Client, click Application Managers in the navigation menu.
2 From the Application Managers list, right-click the application manager to modify and select edit
settings.
3 In the Edit Application Manager dialog box, make the changes to the application manager and click
OK.
Delete an Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client
You can delete an application manager with the vSphere Web Client when you no longer need it.
The process fails if the application manager you want to delete contains clusters.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have at least one external application manager installed in your Big Data Extensions
environment.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Web Client, click Application Managers in the navigation pane.
2 Right-click the application manager to delete and select Delete.
The application manager is removed from the Application Managers list panel.
View Application Managers and Distributions by Using the Web Client
You can view a list of the application managers and distributions that are currently being used in your
Big Data Extensions environment.
Procedure
From Big Data Extensions, click Application Managers from the Inventory Lists.
u
A list opens that contains the distributions, descriptions, application managers, and how many clusters
are managed by your Big Data Extensions environment.
View Roles for Application Manager and Distribution by Using the Web Client
You can use the Application Managers pane to view a list and the details of the Hadoop roles for a specific
application manager and distribution.
Procedure
1 From Big Data Extensions, click Inventory Lists > Application Managers.
40 VMware, Inc.
Page 41

Chapter 4 Managing Application Managers
2 Select the application manager for which you want to view details.
The details pane opens that contains a list of supported distributions with the name, vendor, version
and roles of the distribution.
VMware, Inc. 41
Page 42

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
42 VMware, Inc.
Page 43

Managing Hadoop Distributions 5
The Serengeti Management Server includes the Apache Bigtop distribution, but you can add any supported
Hadoop distribution to your Big Data Extensions environment.
Procedure
1 Hadoop Distribution Deployment Types on page 43
You can choose which Hadoop distribution to use when you deploy a cluster. The type of distribution
you choose determines how you configure it for use with Big Data Extensions. When you deploy the
Big Data Extensions vApp, the Bigtop 1.0 distribution is included in the OVA that you download and
deploy.
2 Configure a Tarball-Deployed Hadoop Distribution by Using the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
on page 44
You can add and configure Hadoop distributions other than those included with the Big Data
Extensions vApp using the command line. You can configure multiple Hadoop distributions from
different vendors.
3 Configuring Yum and Yum Repositories on page 46
You can deploy Cloudera CDH4 and CDH5, Apache Bigtop, MapR, and Pivotal PHD Hadoop
distributions using Yellowdog Updater, Modified (yum). Yum enables automatic updates and
package management of RPM-based software distributions. To deploy a Hadoop distribution using
yum, you must create and configure a yum repository.
Hadoop Distribution Deployment Types
You can choose which Hadoop distribution to use when you deploy a cluster. The type of distribution you
choose determines how you configure it for use with Big Data Extensions. When you deploy the
Big Data Extensions vApp, the Bigtop 1.0 distribution is included in the OVA that you download and
deploy.
Depending on which Hadoop distribution you want to configure to use with Big Data Extensions, use either
a tarball or yum repository to install your distribution. The table lists the supported Hadoop distributions,
the distribution name, vendor abbreviation, and version number to use as input parameters when you
configure the distribution for use with Big Data Extensions.
Table 5‑1. Hadoop Deployment Types in Default Application Manager
Vendor
Hadoop Distribution Version Number
Bigtop 1.0 BIGTOP Yum No
Pivotal HD 2.0, 2.1 PHD Yum Yes
Hortonworks Data Platform 1.2, 2.1 HDP Yum No
VMware, Inc. 43
Abbreviation Deployment Type HVE Support?
Page 44

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Table 5‑1. Hadoop Deployment Types in Default Application Manager (Continued)
Hadoop Distribution Version Number
Cloudera 5.3, 5.4 CDH Yum No
MapR 4.1, 5.0 MAPR Yum No
Vendor
Abbreviation Deployment Type HVE Support?
About Hadoop
Virtualization
Extensions
Configure Hadoop 2.x
and Later Distributions
with DNS Name
Resolution
Hadoop Virtualization Extensions (HVE), developed by VMware, improves
Hadoop performance in virtual environments by enhancing Hadoop’s
topology awareness mechanism to account for the virtualization layer.
When you create clusters using Hadoop distributions based on Hadoop 2.0
and later, the DNS server in your network must provide forward and reverse
FQDN/IP resolution. Without valid DNS and FQDN settings, the cluster
creation process might fail, or the cluster is created but does not function.
Hadoop distributions based on Hadoop 2.x and later include Apache Bigtop,
Cloudera CDH4 and CDH5, Hortonworks HDP 2.x, and Pivotal PHD 1.1 and
later releases.
Configure a Tarball-Deployed Hadoop Distribution by Using the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
You can add and configure Hadoop distributions other than those included with the Big Data Extensions
vApp using the command line. You can configure multiple Hadoop distributions from different vendors.
Refer to your Hadoop distribution vendor's Web site to obtain the download URLs to use for the
components that you want to install. If you are behind a firewall, you might need to modify your proxy
settings to allow the download. Before you install and configure tarball-based deployments, ensure that you
have the vendor's URLs from which to download the different Hadoop components. Use these URLs as
input parameters to the config-distro.rb configuration utility.
If you have a local Hadoop distribution and your server does not have access to the Internet, you can
manually upload the distribution.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp.
n
Review the different Hadoop distributions so you know which distribution name abbreviation, vendor
n
name abbreviation, and version number to use as an input parameter, and whether the distribution
supports Hadoop Virtualization Extension (HVE).
(Optional) Set the password for the Serengeti Management Server.
n
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
44 VMware, Inc.
Page 45

Chapter 5 Managing Hadoop Distributions
2 Run the /opt/serengeti/sbin/config-distro.rb Ruby script.
config-distro.rb --name distro_name --vendor vendor_name --version version_number
--hadoop hadoop_package_url --pig pig_package_url --hive hive_package_url
--hbase hbase_package_url --zookeeper zookeeper_package_URL --hve {true | false} --yes
Option Description
--name
--vendor
--version
--hadoop
--pig
--hive
--hbase
--zookeeper
--hve {true | false}
--yes
Name to identify the Hadoop distribution that you are downloading. For
example, hdp for Hortonworks. This name can include alphanumeric
characters ([a-z], [A-Z], [0-9]) and underscores ("_").
Vendor name whose Hadoop distribution you want to use. For example,
HDP for Hortonworks.
Version of the Hadoop distribution that you want to use. For example,
1.3.
URL from which to download the Hadoop distribution tarball package
from the Hadoop vendor's Web site.
URL from which to download the Pig distribution tarball package from the
Hadoop vendor's Web site.
URL from which to download the Hive distribution tarball package from
the Hadoop vendor's Web site.
(Optional) URL from which to download the HBase distribution tarball
package from the Hadoop vendor's Web site.
(Optional) URL from which to download the ZooKeeper distribution
tarball package from the Hadoop vendor's Web site.
(Optional) Specifies whether the Hadoop distribution supports HVE
(Optional) Specifies that all confirmation prompts from the config-
distro.rb script are answered with a "yes" response.
The example downloads the tarball version of Hortonworks Data Platform (HDP), which consists of
Hortonworks Hadoop, Hive, HBase, Pig, and ZooKeeper distributions. Note that you must provide the
download URL for each of the software components you wish to configure for use with
Big Data Extensions.
config-distro.rb --name hdp --vendor HDP --version 1.3.2
--hadoop http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/centos6/1.x/updates/1.3.2.0/tars/
hadoop-1.2.0.1.3.2.0-111.tar.gz
--pig http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/centos6/1.x/updates/1.3.2.0/tars/
pig-0.11.1.1.3.2.0-111.tar.gz
--hive http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/centos6/1.x/updates/1.3.2.0/tars/
hive-0.11.0.1.3.2.0-111.tar.gz
--hbase http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/centos6/1.x/updates/1.3.2.0/tars/
hbase-0.94.6.1.3.2.0-111-security.tar.gz
--zookeeper http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/centos6/1.x/updates/1.3.2.0/tars/
zookeeper-3.4.5.1.3.2.0-111.tar.gz
--hve true
The script downloads the files.
VMware, Inc. 45
Page 46

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
3 When the download finishes, explore the /opt/serengeti/www/distros directory, which includes the
following directories and files.
Item Description
name
manifest
manifest.example
Directory that is named after the distribution. For example, apache.
The manifest file that is generated by config-distro.rb that is used to
download the Hadoop distribution.
Example manifest file. This file is available before you perform the
download. The manifest file is a JSON file with three sections: name,
version, and packages.
4 To enable Big Data Extensions to use the added distribution, restart the tomcat service.
sudo /sbin/service tomcat restart
The Serengeti Management Server reads the revised manifest file and adds the distribution to those
from which you can create a cluster.
5 Return to the Big Data Extensions Plug-in for vSphere Web Client, and click Hadoop Distributions to
verify that the Hadoop distribution is available to use to create a cluster.
The distribution and the corresponding role appear.
The distribution is added to the Serengeti Management Server, but is not installed in the Hadoop Template
virtual machine. The agent is preinstalled on each virtual machine that copies the distribution components
that you specify from the Serengeti Management Server to the nodes during the Hadoop cluster creation
process.
What to do next
You can add datastore and network resources for the Hadoop clusters that you create.
You can create and deploy big data clusters using your chosen Hadoop distribution.
Configuring Yum and Yum Repositories
You can deploy Cloudera CDH4 and CDH5, Apache Bigtop, MapR, and Pivotal PHD Hadoop distributions
using Yellowdog Updater, Modified (yum). Yum enables automatic updates and package management of
RPM-based software distributions. To deploy a Hadoop distribution using yum, you must create and
configure a yum repository.
Yum Repository Configuration Values on page 47
n
To create a local yum repository, you create a configuration file that identifies the file and package
names of a distribution to download and deploy. When you create the configuration file, you replace a
set of placeholder values with values that correspond to your Hadoop distribution. The yum
repositories are used to install or update Hadoop software on CentOS and other operating systems
that use Red Hat Package Manager (RPM).
Setup a Local Yum Repository for Apache Bigtop, Cloudera, Hortonworks, and MapR Hadoop
n
Distributions on page 50
Although publicly available yum repositories exist for Ambari, Apache Bigtop, Cloudera,
Hortonworks, and MapReduce distributions, creating your own yum repository can result in faster
download times and greater control over the repository.
46 VMware, Inc.
Page 47

Chapter 5 Managing Hadoop Distributions
Setup a Local Yum Repository for the Pivotal Hadoop Distribution on page 52
n
Pivotal does not provide a publicly accessible yum repository from which you can deploy and
upgrade the Pivotal Hadoop software distribution. Therefore, you might want to download the
Pivotal software tarballs and create your own yum repository for Pivotal which provides you with
better access and control over installing and updating your Pivotal HD distribution software.
Configure a Yum-Deployed Hadoop Distribution on page 54
n
You can install Hadoop distributions that use yum repositories (as opposed to tarballs) for use with
Big Data Extensions. When you create a cluster for a yum-deployed Hadoop distribution, the Hadoop
nodes download and install Red Hat Package Manager (RPM) packages from the official yum
repositories for a particular distribution or your local yum repositories.
Set Up a Local Yum Repository for Cloudera Manager Application Manager on page 55
n
When you create a new cluster with an external application manager, you must install agents and
distribution packages on each cluster node. If the installation downloads the agents and packages
from the Internet, the process might be slow. If you do not have an Internet connection, the cluster
creation process is not possible. To avoid these problems, you can create a local yum repository.
Set Up a Local Yum Repository for Ambari Application Manager on page 58
n
When you create a new cluster with an external application manager, you must install agents and
distribution packages on each cluster node. If the installation downloads the agents and packages
from the Internet, the process might be slow. If you do not have an Internet connection, the cluster
creation process is impossible. To avoid these problems, you can create a local yum repository.
Yum Repository Configuration Values
To create a local yum repository, you create a configuration file that identifies the file and package names of
a distribution to download and deploy. When you create the configuration file, you replace a set of
placeholder values with values that correspond to your Hadoop distribution. The yum repositories are used
to install or update Hadoop software on CentOS and other operating systems that use
Red Hat Package Manager (RPM).
The following tables list the values to use for the Ambari, Apache Bigtop, Cloudera, Hortonworks, MapR,
and Pivotal distributions.
NOTE If you copy-and-paste values from the table, be sure to include all required information. Some values
appear on two lines in the table, for example, "maprtech maprecosystem", and they must be combined into a
single line when you use them.
Apache Bigtop Yum Repository Configuration Values
Table 5‑2. Apache Bigtop Yum Repository Placeholder Values
Placeholder Value
repo_file_name bigtop.repo
package_info [bigtop]
name=Bigtop
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
type=NONE
baseurl=http://bigtop-repos.s3.amazonaws.com/releases/1.0.0/centos/6/x86_64
gpgkey=https://dist.apache.org/repos/dist/release/bigtop/KEYS
NOTE If you use a version other than 1.0.0, use the exact version number of your
Apache Bigtop distribution in the pathname.
mirror_cmds reposync -r bigtop
VMware, Inc. 47
Page 48

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Table 5‑2. Apache Bigtop Yum Repository Placeholder Values (Continued)
Placeholder Value
default_rpm_dir bigtop
target_rpm_dir bigtop
local_repo_info [bigtop]
name=Apache Bigtop
baseurl=http://ip_of_yum_repo_webserver/bigtop/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
Cloudera Yum Repository Configuration Values
Table 5‑3. Cloudera Yum Repository Placeholder Values
Placeholder Value
repo_file_name cloudera-cdh.repo
package_info If you use CDH4, use the values below.
[cloudera-cdh]
name=Cloudera's Distribution for Hadoop
http://archive.cloudera.com/cdh4/redhat/6/x86_64/cdh/4/
gpkey=http://archive.cloudera.com/cdh4/redhat/6/x86_64/cdh/RPM-GPG-KEY-cloudera
gpgcheck=1
If you use CDH5, use the values below.
[cloudera-cdh]
name=Cloudera's Distribution for Hadoop
baseurl=http://archive.cloudera.com/cdh5/redhat/6/x86_64/cdh/5/
gpgkey=http://archive.cloudera.com/cdh5/redhat/6/x86_64/cdh/RPM-GPG-KEY-cloudera
gpgcheck=1
mirror_cmds reposync -r cloudera-cdh4
default_rpm_dir cloudera-cdh/RPMS
target_rpm_dir cdh/version_number
local_repo_info [cloudera-cdh]
name=Cloudera's Distribution for Hadoop
baseurl=http://ip_of_yum_repo_webserver/cdh/version_number/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
48 VMware, Inc.
Page 49

Hortonworks Yum Repository Configuration Values
Table 5‑4. Hortonworks Yum Repository Placeholder Values
Placeholder Value
repo_file_name hdp.repo
package_info [hdp]
name=Hortonworks Data Platform Version - HDP-2.1.1.0
baseurl=http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/centos6/2.x/GA/2.1.1.0
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP/centos6/2.x/GA/2.1.1.0/RPM-GPGKEY/RPM-GPG-KEY-Jenkins
enabled=1
priority=1
NOTE If you use a version other than HDP 2.1.1.0, use the exact version number of your
Hortonworks distribution in the pathname.
mirror_cmds reposync -r hdp
default_rpm_dir hdp
target_rpm_dir hdp/2
local_repo_info [hdp]
name=Hortonworks Data Platform Version -HDP-2.1.1.0
baseurl=http://ip_of_yum_repo_webserver/hdp/2/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
Chapter 5 Managing Hadoop Distributions
MapR Yum Repository Configuration Values
Table 5‑5. MapR Yum Repository Placeholder Values
Placeholder Value
repo_file_name mapr.repo
package_info [maprtech]
name=MapR Technologies
baseurl=http://package.mapr.com/releases/3.1.0/redhat/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
protect=1
[maprecosystem]
name=MapR Technologies
baseurl=http://package.mapr.com/releases/ecosystem/redhat
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
protect=1
NOTE If you use a version other than 3.1.0, use the exact version number of your MapR
distribution in the pathname.
mirror_cmds reposync -r maprtech
reposync -r maprecosystem
default_rpm_dir maprtech maprecosystem
VMware, Inc. 49
Page 50

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Table 5‑5. MapR Yum Repository Placeholder Values (Continued)
Placeholder Value
target_rpm_dir mapr/3
local_repo_info [mapr]
name=MapR Version 3
baseurl=http://ip_of_yum_repo_webserver/mapr/3/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
protect=1
Pivotal Yum Repository Configuration Values
Table 5‑6. Pivotal Yum Repository Placeholder Values
Placeholder Value
repo_file_name phd.repo
package_info Not Applicable
mirror_cmds Not Applicable
default_rpm_dir pivotal
target_rpm_dir phd/1
local_repo_info [pivotalhd]
name=PHD Version 1.0
baseurl=http://ip_of_yum_repo_webserver/phd/1/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
Setup a Local Yum Repository for Apache Bigtop, Cloudera , Hortonworks, and MapR Hadoop Distributions
Although publicly available yum repositories exist for Ambari, Apache Bigtop, Cloudera, Hortonworks, and
MapReduce distributions, creating your own yum repository can result in faster download times and
greater control over the repository.
Prerequisites
High-speed Internet access.
n
CentOS 6.x 64-bit or Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 6.x 64-bit.
n
The node-template virtual machine in the Serengeti vApp contains CentOS 6.7 64-bit. You can clone the
node-template virtual machine to a new virtual machine and create the yum repository on it.
An HTTP server with which to create the yum repository. For example, Apache HTTP server.
n
If there is a firewall on your system, ensure that the firewall does not block the network port number
n
used by your HTTP server proxy. Typically, this is port 80.
Refer to the yum repository placeholder values to populate the variables required in the steps. See
n
“Yum Repository Configuration Values,” on page 47.
50 VMware, Inc.
Page 51

Chapter 5 Managing Hadoop Distributions
Procedure
1 If your yum repository server requires an HTTP proxy server, open a command shell, such as Bash or
PuTTY, log in to the yum repository server, and run the following commands to export the http_proxy
environment variable.
# switch to root user
sudo su
umask 002
export http_proxy=http://host:port
Option Description
host
port
The hostname or the IP address of the proxy server.
The network port number to use with the proxy server.
2 Install the HTTP server that you want to use as a yum server.
This example installs the Apache HTTP Server and enables the httpd server to start whenever the
machine is restarted.
yum install -y httpd
/sbin/service httpd start
/sbin/chkconfig httpd on
3 Install the yum-utils and createrepo packages.
The yum-utils package contains the reposync command.
yum install -y yum-utils createrepo
4 Synchronize the yum server with the official yum repository of your preferred Hadoop vendor.
a Using a text editor, create the file /etc/yum.repos.d/$repo_file_name.
b Add the package_info content to the new file.
c Mirror the remote yum repository to the local machine by running the mirror_cmds for your
distribution packages.
It might take several minutes to download the RPMs from the remote repository. The RPMs are
placed in the $default_rpm_dir directories.
5 Create the local yum repository.
a Move the RPMs to a new directory under the Apache HTTP Server document root.
The default document root is /var/www/html/.
doc_root=/var/www/html
mkdir -p $doc_root/$target_rpm_dir
mv $default_rpm_dir $doc_root/$target_rpm_dir/
For example, the mv command for the MapR Hadoop distribution is the following:
mv maprtech maprecosystem $doc_root/mapr/3/
b Create a yum repository for the RPMs.
cd $doc_root/$target_rpm_dir
createrepo .
c Create a new file, $doc_root/$target_rpm_dir/$repo_file_name, and include the local_repo_info.
d From a different machine, ensure that you can download the repository file from
http://ip_of_webserver target_rpm_dir//repo_file_name.
VMware, Inc. 51
Page 52

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
6 (Optional) Configure HTTP proxy.
If the virtual machines created by the Serengeti Management Server do not need an HTTP proxy to
connect to the local yum repository, skip this step.
On the Serengeti Management Server, edit the /opt/serengeti/conf/serengeti.properties file and add
the following content anywhere in the file or replace existing items:
# set http proxy server
serengeti.http_proxy = http://<proxy_server:port>
# set the FQDNs (or IPs if no FQDN) of the Serengeti Management Server and the
local yum repository servers for 'serengeti.no_proxy'.
The wildcard for matching multi IPs doesn't work.
serengeti.no_proxy = serengeti_server_fqdn_or_ip.
yourdomain.com, yum_server_fqdn_or_ip.
yourdomain.com
What to do next
Configure your Apache Bigtop, Cloudera, Hortonworks, or MapR deployment for use with
Big Data Extensions. See “Configure a Yum-Deployed Hadoop Distribution,” on page 54.
Setup a Local Yum Repository for the Pivotal Hadoop Distribution
Pivotal does not provide a publicly accessible yum repository from which you can deploy and upgrade the
Pivotal Hadoop software distribution. Therefore, you might want to download the Pivotal software tarballs
and create your own yum repository for Pivotal which provides you with better access and control over
installing and updating your Pivotal HD distribution software.
Pivotal does not provide a publicly accessible yum repository from which you can deploy and upgrade the
Pivotal Hadoop software distribution. You might want to download the Pivotal software tarballs, and create
your own yum repository from which to deploy and configure the Pivotal Hadoop software.
Prerequisites
High-speed Internet access.
n
CentOS 6.x 64-bit or Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 6.x 64-bit.
n
The node-template virtual machine in the Big Data Extensions vApp contains CentOS 6.7 64-bit. You
can clone the node-template virtual machine to a new virtual machine and create the yum repository on
it.
NOTE Because the Pivotal Hadoop distribution requires CentOS 6.2 64-bit version or 6.4 64-bit version
(x86_64), the yum server that you create to deploy the distribution must also use a CentOS 6.x 64-bit
operating system.
An HTTP server with which to create the yum repository. For example, Apache HTTP server.
n
If there is a firewall on your system, ensure that the firewall does not block the network port number
n
used by your HTTP server proxy. Typically, this is port 80.
52 VMware, Inc.
Page 53

Chapter 5 Managing Hadoop Distributions
Procedure
1 If your yum repository server requires an HTTP proxy server, open a command shell, such as Bash or
PuTTY, log in to the yum repository server, and run the following commands to export the http_proxy
environment variable.
# switch to root user
sudo su
umask 002
export http_proxy=http://host:port
Option Description
host
port
The hostname or the IP address of the proxy server.
The network port number to use with the proxy server.
2 Install the HTTP server that you want to use with a yum server.
This example installs the Apache HTTP Server and enables the httpd server to start whenever the
machine is restarted.
yum install -y httpd
/sbin/service httpd start
/sbin/chkconfig httpd on
3 Install the yum-utils and createrepo packages.
The yum-utils package includes the reposync command.
yum install -y yum-utils createrepo
4 Download the Pivotal HD 1.0 or 2.0 tarball from the Pivotal Web site.
5 Extract the tarball that you downloaded.
The tarball name might vary if you download a different version of Pivotal HD.
tar -xf phd_1.0.1.0-19_community.tar
6 Extract PHD_1.0.1_CE/PHD-1.0.1.0-19.tar to the default_rpm_dir directory.
For Pivotal Hadoop the default_rpm_dir directory is pivotal.
The version numbers of the tar that you extract might be different from those used in the example if an
update has occurred.
tar -xf PHD_1.0.1_CE/PHD-1.0.1.0-19.tar -C pivotal
7 Create and configure the local yum repository.
a Move the RPMs to a new directory under the Apache HTTP Server document root.
The default document root is /var/www/html/.
doc_root=/var/www/html
mkdir -p $doc_root/$target_rpm_dir
mv $default_rpm_dir $doc_root/$target_rpm_dir/
This example moves the RPMs for the Pivotal Hadoop distribution.
mv pivotal $doc_root/phd/1/
b Create a yum repository for the RPMs.
cd $doc_root/$target_rpm_dir
createrepo .
VMware, Inc. 53
Page 54

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
c Create a file, $doc_root/$target_rpm_dir/$repo_file_name, and include the local_repo_info.
d From a different machine, ensure that you can download the repository file from
http://ip_of_webserver/$target_rpm_dir/$repo_file_name.
8 (Optional) Configure an HTTP proxy.
If the virtual machines created by the Serengeti Management Server do not need an HTTP proxy to
connect to the local yum repository, skip this step.
On the Serengeti Management Server, edit the file/opt/serengeti/conf/serengeti.properties, and add
the following content anywhere in the file or replace existing items:
# set http proxy server
serengeti.http_proxy = http://<proxy_server:port>
# set the FQDNs (or IPs if no FQDN) of the Serengeti Management Server and the
local yum repository servers for 'serengeti.no_proxy'.
The wildcard for matching multi IPs doesn't work.
serengeti.no_proxy = serengeti_server_fqdn_or_ip.
yourdomain.com, yum_server_fqdn_or_ip.yourdomain.com
Configure a Yum-Deployed Hadoop Distribution
You can install Hadoop distributions that use yum repositories (as opposed to tarballs) for use with
Big Data Extensions. When you create a cluster for a yum-deployed Hadoop distribution, the Hadoop nodes
download and install Red Hat Package Manager (RPM) packages from the official yum repositories for a
particular distribution or your local yum repositories.
Prerequisites
Review the different Hadoop distributions so that you know which distribution name, vendor
n
abbreviation, and version number to use as an input parameter, and whether the distribution supports
Hadoop Virtualization Extensions.
Create a local yum repository for your Hadoop distribution. Creating your own repository can result in
n
better access and more control over the repository.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
2 Run the /opt/serengeti/sbin/config-distro.rb Ruby script.
config-distro.rb --name distro_name --vendor vendor_abbreviation --version ver_number
--repos http://url_to_yum_repo/name.repo
Option Description
--name
--vendor
--version
--repos
Name to identify the Hadoop distribution that you are downloading. For
example, chd4 for Cloudera CDH4. This name can include alphanumeric
characters ([a-z], [A-Z], [0-9]) and underscores ("_").
Abbreviation of vendor name whose Hadoop distribution you want to use.
For example, CDH.
Version of the Hadoop distribution that you want to use. For example,
4.6.0.
URL from which to download the Hadoop distribution yum package. This
URL can be a local yum repository that you create or a publicly accessible
yum repository hosted by the software vendor.
54 VMware, Inc.
Page 55

Chapter 5 Managing Hadoop Distributions
This example adds the Apache Bigtop Hadoop Distribution to Big Data Extensions.
config-distro.rb --name bigtop --vendor BIGTOP --version 0.8.0
--repos http://url_to_yum_repo/bigtop.repo
The example adds the Cloudera CDH4 Hadoop distribution to Big Data Extensions.
config-distro.rb --name cdh4 --vendor CDH --version 4.6.0 --repos
http://url_to_yum_repo/cloudera-cdh4.repo
NOTE The config-distro.rb script downloads files only for tarball-deployed distributions. No files are
downloaded for yum-deployed distributions.
This example adds the Hortonworks Hadoop Distribution to Big Data Extensions.
config-distro.rb --name hdp --vendor HDP --version 2.1.1
--repos http://url_to_yum_repo/hdp.repo
The example adds the MapR Hadoop distribution to Big Data Extensions.
config-distro.rb --name mapr --vendor MAPR --version 3.1.0 --repos
http://url_to_yum_repo/mapr.repo
This example adds the Pivotal Hadoop Distribution to Big Data Extensions.
config-distro.rb --name phd --vendor PHD --version 2.0
--repos http://url_to_yum_repo/phd.repo
3 To enable Big Data Extensions to use the new distribution, restart the Tomcat service.
sudo /sbin/service tomcat restart
The Serengeti Management Server reads the revised manifest file and adds the distribution to those
from which you can create a cluster.
4 Return to the Big Data Extensions Plug-in for vSphere Web Client, and click Hadoop Distributions to
verify that the Hadoop distribution is available.
What to do next
You can create Hadoop and HBase clusters.
Set Up a Local Yum Repository for Cloudera Manager Application Manager
When you create a new cluster with an external application manager, you must install agents and
distribution packages on each cluster node. If the installation downloads the agents and packages from the
Internet, the process might be slow. If you do not have an Internet connection, the cluster creation process is
not possible. To avoid these problems, you can create a local yum repository.
Prepare the Software Environment for the Local Repository for Cloudera Manager
The first step to create a local yum repository for Cloudera Manager is to prepare the software environment
by setting up necessary servers and directories.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have the following conditions in place.
High-speed Internet access.
n
CentOS 6.x 64-bit or Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 6.x 64-bit.
n
The node-template virtual machine in the Serengeti vApp contains CentOS 6.7 64-bit. You can clone the
node-template virtual machine to a new virtual machine and create the yum repository on it.
VMware, Inc. 55
Page 56

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
An HTTP server with which to create the yum repository. For example, Apache HTTP server.
n
If your system has a firewall, ensure that the firewall does not block the network port number that your
n
HTTP server proxy uses. Typically, this is port 80.
For more information about the yum repository placeholder values, see “Yum Repository
n
Configuration Values,” on page 47.
Procedure
1 If your yum repository server requires an HTTP proxy server, perform the steps:
a Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY.
b Log in to the yum repository server.
c Export the http_proxy environment variable.
# switch to root user
sudo su
umask 002
export http_proxy=http://host:port
Option Description
host
port
The hostname or the IP address of the proxy server.
The network port number to use with the proxy server.
2 Install the HTTP server to use as a yum server.
This example installs the Apache HTTP Server and enables the httpd server to start whenever the
machine restarts.
yum install -y httpd
/sbin/service httpd start
/sbin/chkconfig httpd on
3 Make the CentOS directory.
mkdir -p /var/www/html/yum/centos6
4 Make the Cloudera Manager directory.
mkdir -p /var/www/html/yum/cm
5 Install the createrepo RPM.
yum install -y createrepo
Set Up the Local CentOS Yum Repository
You must copy all the RPM packages from the CentOS 6 DVD ISO images to set up the local CentOS yum
repository.
Prerequisites
Verify that you prepared the software environment for the CentOS yum repository creation, including the
directories for CentOS and the application manager. Refer to your CentOS documentation.
Procedure
1 Download the CentOS-6.7-x86_64-bin-DVD1.iso and CentOS-6.7-x86_64-bin-DVD2.iso CentOS 6 DVD
ISO images from the CentOS official website.
2 Download the ISO images to the virtual machine servers.
56 VMware, Inc.
Page 57

Chapter 5 Managing Hadoop Distributions
3 Copy all of the CentOS RPM packages to /var/www/html/yum/centos6.
mkdir /mnt/centos6-1
mount -o loop CentOS-6.7-x86_64-bin-DVD1.iso /mnt/centos6-1
cp /mnt/centos6-1/Packages/* /var/www/html/yum/centos6
mkdir /mnt/centos6-2
mount -o loop CentOS-6.7-x86_64-bin-DVD2.iso /mnt/centos6-2
cp /mnt/centos6-2/Packages/* /var/www/html/yum/centos6
4 Create the CentOS 6 yum repository.
createrepo /var/www/html/yum/centos6
Download Packages for Cloudera Manager
After you set up the local CentOS yum repository, you must download the packages for Cloudera Manager.
Procedure
1 Download the cm5.4.8-centos6.tar.gz file.
wget http://archive-primary.cloudera.com/cm5/repo-as-tarball/5.4.8/cm5.4.8-centos6.tar.gz
For other versions of Cloudera Manager, the URLs used in the example might vary.
2 Extract the tarball.
tar xzf cm5.4.8-centos6.tar.gz -C /var/www/html/yum/cm/
For other versions of Cloudera Manager, the URLs used in the example might vary.
Configure the Yum Repository Server and the Local Parcel Repository
You must configure the yum repository server and the local parcel repository before you can distribute the
parcels file.
Procedure
1 Create the yum repository.
The repodata directory is created in /var/www/html/yum/cm/5.4.8.
createrepo /var/www/html/yum/cm/5.4.8
2 Ensure that you can access the URL http://yum_repo_server_ip/yum from a browser.
3 Create the Parcels directory.
mkdir -p /var/www/html/parcels
4 Change to the Parcels directory.
cd /var/www/html/parcels
5 Download the Parcels file.
wget http://archive-primary.cloudera.com/cdh5/parcels/5.4.8/CDH-5.4.8-1.cdh5.4.8.p0.4el6.parcel
6 Download the manifest.json file.
wget http://archive-primary.cloudera.com/cdh5/parcels/5.4.8/manifest.json
7 In the manifest.json file, remove all items except for CDH-5.4.8-1.cdh5.4.8.p0.4-el6.parcel
8 Open a browser, go to http://your_cloudera_manager_server:7180/cmf/parcel/status and click Edit
Settings.
VMware, Inc. 57
Page 58

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
9 Select one minute in the Parcel Update Frequency text box.
10 Remove the remote parcel repository URL that was replaced by the target parcel URL.
11 Add the URL http://yum_repo_server_ip/parcels.
You can now create clusters for the Cloudera Manager by using the local yum repository.
Set Up a Local Yum Repository for Ambari Application Manager
When you create a new cluster with an external application manager, you must install agents and
distribution packages on each cluster node. If the installation downloads the agents and packages from the
Internet, the process might be slow. If you do not have an Internet connection, the cluster creation process is
impossible. To avoid these problems, you can create a local yum repository.
Prepare the Software Environment for the Local Repository for Ambari
The first step to create a local yum repository for Ambari is to prepare the software environment.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have the following conditions in place.
High-speed Internet access.
n
CentOS 6.x 64-bit or Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 6.x 64-bit.
n
The node-template virtual machine in the Serengeti vApp contains CentOS 6.7 64-bit. You can clone the
hadoop-template virtual machine to a new virtual machine and create the yum repository on it.
An HTTP server with which to create the yum repository. For example, Apache HTTP server.
n
If your system has a firewall, ensure that the firewall does not block the network port number that your
n
HTTP server proxy uses. Typically, this is port 80.
For more information about the yum repository placeholder values, see “Yum Repository
n
Configuration Values,” on page 47.
Procedure
1 If your yum repository server requires an HTTP proxy server, open a command shell, such as Bash or
PuTTY, log in to the yum repository server, and export the http_proxy environment variable.
# switch to root user
sudo su
umask 002
export http_proxy=http://host:port
Option Description
host
port
The hostname or the IP address of the proxy server.
The network port number to use with the proxy server.
2 Install the HTTP server to use as a yum server.
This example installs the Apache HTTP Server and enables the httpd server to start whenever the
machine restarts.
yum install -y httpd
/sbin/service httpd start
/sbin/chkconfig httpd on
58 VMware, Inc.
Page 59

Chapter 5 Managing Hadoop Distributions
3 Make the CentOS directory.
mkdir -p /var/www/html/yum/centos6
4 Make the Ambari directory.
mkdir -p /var/www/html/yum/ambari
5 Install the createrepo RPM.
yum install -y createrepo
Set Up the Local CentOS Yum Repository
You must copy all the RPM packages from the CentOS 6 DVD ISO images to set up the local CentOS yum
repository.
Prerequisites
Verify that you prepared the software environment for the CentOS yum repository creation, including the
directories for CentOS and the application manager. Refer to your CentOS documentation.
Procedure
1 Download the CentOS-6.7-x86_64-bin-DVD1.iso and CentOS-6.7-x86_64-bin-DVD2.iso CentOS 6 DVD
ISO images from the CentOS official website.
2 Download the ISO images to the virtual machine servers.
3 Copy all of the CentOS RPM packages to /var/www/html/yum/centos6.
mkdir /mnt/centos6-1
mount -o loop CentOS-6.7-x86_64-bin-DVD1.iso /mnt/centos6-1
cp /mnt/centos6-1/Packages/* /var/www/html/yum/centos6
mkdir /mnt/centos6-2
mount -o loop CentOS-6.7-x86_64-bin-DVD2.iso /mnt/centos6-2
cp /mnt/centos6-2/Packages/* /var/www/html/yum/centos6
4 Create the CentOS 6 yum repository.
createrepo /var/www/html/yum/centos6
Download Packages for Ambari
After you set up the local CentOS yum repository, download the packages for the Ambari application
manager.
Procedure
1 Make /var/www/html/yum/ambari your working directory.
cd /var/www/html/yum/ambari
2 Download the Ambari agent.
wget http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/ambari/centos6/2.x/updates/2.1.2/AMBARI-2.1.2-377centos6.tar.gz
If you use other versions of Ambari, for example Ambari 2.1.1, the URL that you use might vary.
3 Download the HDP packages.
If you use other versions of HDP, for example HDP 2.2 or HDP 2.3, the URL you use may vary.
VMware, Inc. 59
Page 60

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
4 Download the HDP-UTILS packages.
wget http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/HDP-UTILS-1.1.0.20/repos/centos6/HDPUTILS-1.1.0.20-centos6.tar.gz
5 Extract all of the tarball files.
tar xzf AMBARI-2.1.2-377-centos6.tar.gz
tar xzf HDP-2.3.2.0-centos6-rpm.tar.gz
tar xzf HDP-UTILS-1.1.0.20-centos6.tar.gz
Configure the Ambari Repository File on the Ambari Server
To set up the local yum repository, you must configure the Ambari repository file.
Procedure
1 Log in to Ambari over SSH.
ssh username@ambari_server_ip_address
2 Stop the Ambari server..
ambari-server stop
3 Download the ambari.repo file.
cd /etc/yum.repos.d
wget http://public-repo-1.hortonworks.com/ambari/centos6/2.x/updates/2.1.2/ambari.repo
4 Edit the ambari.repo file.
a Replace the URLs with the yum repository server address.
b Remove the group check.
c Add a new section for CentOS.
Example: Configuring the Ambari Repository File on the Ambari Server
[centos]
name=centos6
baseurl=http://<yum_repo_server_ip>/yum/centos6/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
[Updates-ambari-2.1.2]
name=ambari-2.1.2 - Updates
baseurl=http://<yum_repo_server_ip>/yum/ambari/AMBARI-2.1.2/centos6/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
priority=1
Configure the HDP Repository on the Ambari Server
After you configure the Ambari repository on the Ambari server, you must configure the HDP repository on
the Ambari server.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have configured the ambari.repository on the Ambari server.
60 VMware, Inc.
Page 61

Chapter 5 Managing Hadoop Distributions
Procedure
1 Edit the following file:
/var/lib/ambari-server/resources/stacks/HDP/2.3/repos/repoinfo.xml
a Replace the version number 2.3 with your version number.
b Replace the baseurl in the os type="redhat6" with your local HDP repository URL, as shown in the
following example:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!- License section(not displayed here).
-->
<reposinfo>
<os family="redhat6">
<repo>
<baseurl>http://yum_repo_server_ip/yum/ambari/HDP/centos6/2.x/updates/2.3.0.0</baseurl>
<repoid>HDP-2.3</repoid>
<reponame>HDP</reponame>
</repo>
<repo>
<baseurl>http://yum_repo_server_ip/yum/ambari/HDPUTILS-1.1.0.20/repos/centos6</baseurl>
<repoid>HDP-UTILS-1.1.0.20</repoid>
<reponame>HDP-UTILS</reponame>
</repo>
</os>
</reposinfo>
2 Start the Ambari server.
ambari-server start
You are ready to create clusters for the Ambari server by using the local yum repository.
VMware, Inc. 61
Page 62

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
62 VMware, Inc.
Page 63

Managing Node Templates 6
You can manage templates.
Prerequisites
Procedure
u
Example:
What to do next
This chapter includes the following topics:
“Maintain a Customized Hadoop Template Virtual Machine,” on page 63
n
“Create a Node Template Virtual Machine using RHEL Server 6.7 and VMware Tools,” on page 64
n
“Support for Multiple Virtual Machine Templates,” on page 68
n
Maintain a Customized Hadoop Template Virtual Machine
You can modify or update the Hadoop Template virtual machine operating system. When you make
updates, you must remove the snapshot that is created by the virtual machine.
If you create a custom Hadoop Template virtual machine that uses a version of RHEL 6.x, or modify the
operating system, you must remove the serengeti-snapshot that Big Data Extensions creates. If you do not
remove the serengeti-snapshot, changes you made to the Hadoop Template virtual machine will not take
effect.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22.
Create a customized Hadoop Template virtual machine using RHEL 6.x. See “Create a Node Template
n
Virtual Machine using RHEL Server 6.7 and VMware Tools,” on page 64
.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
VMware, Inc.
63
Page 64

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
2 Power on the Hadoop Template virtual machine and apply changes or updates.
3 Remove the /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules file to prevent increasing the eth number
during the clone operation.
If you do not remove the file, virtual machines that are cloned from the template cannot get IP
addresses. If you power on the Hadoop template virtual machine to make changes, remove the file
before you shut down this virtual machine.
4 From the vSphere Web Client, shut down the Hadoop Template virtual machine.
5 Delete the snapshot labeled serengeti-snapshot from the customized Hadoop Template virtual machine.
a In the vSphere Web Client, right-click the Hadoop Template virtual machine and select Snapshot >
Snapshot Manager
b Select the serengeti-snapshot, and click Delete.
The generated snapshot is removed.
6 Synchronize the time on the Hadoop template virtual machine with vCenter Server.
a In the vSphere Web Client, right-click the Hadoop template virtual machine and select Edit
Settings.
b On the VM Options tab, click VMware Tools > Synchronize guest time with host.
Create a Node Template Virtual Machine using RHEL Server 6.7 and VMware Tools
You can create a Node Template virtual machine that has a customized version of the
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) Server 6.x operating system that includes VMware Tools. Although only a
few Hadoop distributions require a custom version of RHEL Server 6.7, you can customize RHEL Server 6.7
for any Hadoop distribution.
Before You Create a Node Template Virtual Machine using RHEL Server 6.7 and VMware Tools
Before you create a Node template virtual machine using the RHEL server 6.7 and VMware tools, you must
perform some prerequisite tasks and be familiar with some important information on the RHEL Server 6.1,
hostnames, disk partitioning, and creating Hadoop Template virtual machines with multiple cores per
socket.
You can create a Node Template virtual machine that uses RHEL Server 6.7 or later as the guest operating
system into which you can install VMware Tools for RHEL 6.7 in combination with a supported Hadoop
distribution. This allows you to create a Hadoop Template virtual machine that uses your organization's
operating system configuration. When you provision Big Data clusters using the customized Hadoop
template, the VMware Tools for RHEL 6.7 will be in the virtual machines that are created from the Hadoop
Template virtual machine.
If you create Hadoop Template virtual machines with multiple cores per socket, when you specify the CPU
settings for the virtual machine you must specify a multiple of cores per socket. For example, if the virtual
machine uses two cores per socket, the vCPU settings must be an even number. For example: 4, 8, or 12. If
you specify an odd number, the cluster provisioning or CPU resizing will fail.
IMPORTANT
You must use localhost.localdomain as the hostname when you install the RHEL template otherwise
n
the FQDN of the virtual machine cloned from the template may not be set correctly.
If you are performing disk partitioning, do not use the Linux Volume Manager (LVM).
n
64 VMware, Inc.
Page 65

Chapter 6 Managing Node Templates
Prerequisites
Deploy theBig Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22.
Obtain the IP address of the Serengeti Management Server.
n
Locate the VMware Tools version that corresponds to the ESXi version in your data center.
n
Create a Virtual Machine Template with a 20GB Thin Provisioned Disk and Install RHEL 6.7
You create a virtual machine template and install Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.7.
For more information on this procedure, see the Red Hat Enterprise Linux Installation Guide, available on the
Red Hat website.
Procedure
1 Download the RHEL Server 6.7 installation ISO from www.redhat.com to a datastore.
2 In vSphere Client, create a new virtual machine with a 20GB thin provision disk and select Red Hat
Enterprise Linux 6.7 (64-bit) as the Guest OS.
3 Right-click the virtual machine and click Edit Settings.
4 Select CD/DVD Device 0, and select the datastore ISO file for the RHEL ISO file.
5 Select SCSI controller 0 > Change Type > LSI Logic Parallel and click OK.
6 Under Device Status, select connected and connect at power on, and click OK.
7 From the console window of the virtual machine, install the RHEL Server 6.x operating system using
the default settings for all settings except the following items:
You can select the language and time zone you want the operating system to use
n
You can specify that the swap partition use a smaller size to save disk space (for example, 500MB)
n
You can reduce the size of the swap partition because it is not used by Big Data Extensions.
n
Select Minimal in the Package Installation Defaults screen.
n
Ensure the Virtual Machine has a Valid IP and Internet Connectivity
The Hadoop template virtual machine requires a valid IP address and an Internet connection.
Prerequisites
n
Procedure
Run the ifconfig command to ensure that the virtual machine has a valid IP and Internet connectivity.
u
This task assumes the use of Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
If IP address information appears in the output of the ifconfig command , see “Configure the
n
Network for the Hadoop Template Virtual Machine to use DHCP,” on page 66.
If no IP address information appears, see “Configure the Network for the Hadoop Template
n
Virtual Machine to use DHCP,” on page 66.
VMware, Inc. 65
Page 66

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Configure the Network for the Hadoop Template Virtual Machine to use DHCP
Procedure
1 Using a text editor open the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 file.
2 Locate the following parameters and specify the following configuration.
ONBOOT=yes
DEVICE=eth0
BOOTPROTO=dhcp
3 Save your changes and close the file.
4 Restart the network service.
sudo /sbin/service network restart
5 Run the ifconfig command to ensure that the virtual machine has a valid IP and Internet connectivity.
Install the JDK 7 RPM
Procedure
1 From the Oracle® Java SE 7 Downloads page, download the latest JDK 7 Linux x64 RPM and copy it to
the root folder of the virtual machine template.
2 Install the RPM.
rpm -Uvh jdk-7u91-linux-x64.rpm
3 Delete the RPM file.
rm -f jdk-7u91-linux-x64.rpm
4 Edit /etc/environment and add the following line: JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/default
Customize the Virtual Machine
Run the installation scripts to customize the virtual machine.
Procedure
1 Register the RHEL operating system to enable the RHEL yum repositories. This allows the installation
script to download packages from the yum repository. See "Registering from the Command Line" in the
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Deployment Guide, available on the Red Hat website.
2 Download the scripts from https://deployed_serengeti_server_IP/custos/custos.tar.gz.
3 Create the directory /tmp/custos, make this your working directory, and run tar xf to uncompress the
tar file.
mkdir /tmp/custos
cd /tmp/custos
tar xf /tmp/custos/custos.tar.gz
4 Run the installer.sh script specifying the /usr/java/default directory path.
./installer.sh /usr/java/default
You must use the same version of the installer.sh script as your Big Data Extensions deployment.
66 VMware, Inc.
Page 67

Chapter 6 Managing Node Templates
5 Remove the /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules file to prevent increasing the eth number
during the clone operation.
If you do not remove the file, virtual machines that are cloned from the template cannot get IP
addresses. If you power on the Hadoop template virtual machine to make changes, remove the file
before you shut down this virtual machine.
Install VMware Tools for RHEL 6.x
Procedure
1 Right-click the RHEL 6 virtual machine in vSphere Client, then select Guest > Install/Upgrade VMware
Tools.
2 Log in to the virtual machine and mount the CD-ROM to access the VMware Tools installation package.
mkdir /mnt/cdrom
mount /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom
mkdir /tmp/vmtools
cd /tmp/vmtools
3 Run the tar xf command to extract the VMware Tools package tar file.
tar xf /mnt/cdrom/VMwareTools-*.tar.gz
4 Make vmware-tools-distrib your working directory, and run the vmware-install.pl script.
cd vmware-tools-distrib
./vmware-install.pl
Press Enter to finish the installation.
5 Remove the vmtools temporary (temp) file that is created as an artifact of the installation process.
rm -rf /tmp/vmtools
6 Shut down virtual machine.
Synchronize the Time on the Hadoop Template Virtual Machine
Synchronize the time on the Hadoop template virtual machine with vCenter Server.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Web Client, right-click the Hadoop Template virtual machine and select Edit Settings.
2 On the VM Options tab, click VMware Tools > Synchronize guest time with host.
Complete the Process of Creating a Hadoop Template Virtual Machine
To use the customized Hadoop Template virtual machine you replace the original Hadoop Template virtual
machine and restart the Tomcat service to enable the custom RHEL virtual machine template.
Procedure
1 On the Virtual Hardware tab of the Edit Settings dialog, uncheck the Connected checkbox. If the
CD/DVD Device is connected to the ISO file, the clone virtual machine process fails.
2 Replace the original Hadoop Template virtual machine with the customized virtual machine that you
created. to do this, drag the new template virtual machine that you created into the vApp.
VMware, Inc. 67
Page 68

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
3 Log in to the Serengeti Management Server as the user serengeti, and restart the Tomcat service.
sudo /sbin/service tomcat restart
Restarting the Tomcat service enables the custom RHEL virtual machine template, making it your
Hadoop Template virtual machine.
Support for Multiple Virtual Machine Templates
You can configure multiple virtual machine templates and choose which one to use when you create a Big
Data cluster. This lets you satisfy customization requirements for different use cases.
Big Data Extensions support the use of multiple virtual machine templates. You can specify the Node
template from which to create a cluster in both the Serengeti CLI or vSphere Web Client.
To create a node template using an operating system variation other than the default, see “Maintain a
Customized Hadoop Template Virtual Machine,” on page 63.
68 VMware, Inc.
Page 69

Managing the Big Data Extensions
Environment 7
After you install Big Data Extensions, you can stop and start the Serengeti services, create user accounts,
manage passwords, update SSL certificates, and log in to cluster nodes to perform troubleshooting.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“Add Specific User Names to Connect to the Serengeti Management Server,” on page 69
n
“Change the Password for the Serengeti Management Server,” on page 70
n
“Create a User Name and Password for the Serengeti Command-Line Interface,” on page 71
n
“Authorize and Audit Commands Run as the Root User,” on page 72
n
“Specify a Group of Users in Active Directory or LDAP to Use a Hadoop Cluster,” on page 72
n
“Stop and Start Serengeti Services,” on page 73
n
“Ports Used for Communication between Big Data Extensions and the vCenter Server,” on page 73
n
“Verify the Operational Status of the Big Data Extensions Environment,” on page 75
n
“Enter Maintenance Mode to Perform Backup and Restore with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
n
Client,” on page 83
“Backup and Restore the Big Data Extensions Environment,” on page 84
n
Add Specific User Names to Connect to the Serengeti Management Server
You can add specific user names with which to login to the Serengeti Management Server. The user names
you add are the only users who can connect to the Serengeti Management Server using the Serengeti CLI or
the Big Data Extensions user interface for use with vSphere Web Client.
Passwords must be from 8 to 20 characters, use only visible lowerASCII characters (no spaces), and must
contain at least one uppercase alphabetic character (A - Z), at least one lowercase alphabetic character (a - z),
at least one digit (0 - 9), and at least one of the following special characters: _, @, #, $, %, ^, &, *
Prerequisites
Deploy the Serengeti vApp.
n
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
VMware, Inc.
69
Page 70

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Procedure
1 Right-click the Serengeti Management Server virtual machine and select Open Console.
The password for the Serengeti Management Server appears.
NOTE If the password scrolls off the console screen, press Ctrl+D to return to the command prompt.
2 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
Use the IP address that appears in the Summary tab and the current password.
3 Edit the /opt/serengeti/conf/Users.xml file to add additional user names.
vi /opt/serengeti/conf/Users.xml
4 Edit the <user name="*" /> attribute by replacing the asterisk (*) wildcard character with the user name
you wish to use. You can add multiple user names by adding a new <user name="name" /> attribute on
its own line. The User.xml file supports multiple lines.
<user name="jsmith" />
<user name="sjones" />
<user name="jlydon" />
5 Restart the Tomcat service.
/sbin/service tomcat restart
Only the user names you add to the User.xml file can be used to login to the Serengeti Management Server
using the Serengeti CLI or the Big Data Extensions user interface for use with vSphere Web Client.
Change the Password for the Serengeti Management Server
When you power on the Serengeti Management Server for the first time, it generates a random password
that is used for the root and serengeti users. If you want an easier to remember password, you can use the
virtual machine console to change the random password for the root and serengeti users.
NOTE You can change the password for the virtual machine of any node by using this procedure.
Passwords must be from 8 to 20 characters, use only visible lowerASCII characters (no spaces), and must
contain at least one uppercase alphabetic character (A - Z), at least one lowercase alphabetic character (a - z),
at least one digit (0 - 9), and at least one of the following special characters: _, @, #, $, %, ^, &, *
Prerequisites
Deploy the Serengeti vApp.
n
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the Serengeti Management
n
Server virtual machine is running.
Procedure
1 Right-click the Serengeti Management Server virtual machine and select Open Console.
The password for the Serengeti Management Server appears.
NOTE If the password scrolls off the console screen, press Ctrl+D to return to the command prompt.
2 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
Use the IP address that appears in the Summary tab and the current password.
70 VMware, Inc.
Page 71

Chapter 7 Managing the Big Data Extensions Environment
3 Use the /opt/serengeti/sbin/set-password command to change the password for the root user and the
serengeti user.
sudo /opt/serengeti/sbin/set-password -u
4 Enter a new password, and enter it again to confirm.
The next time you log in to the Serengeti Management Server, use the new password.
What to do next
You can create a new user name and password for the Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client.
Create a User Name and Password for the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
The Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client uses the vCenter Server login credentials with read
permissions on the Serengeti Management Server. If you do not create a user name and password for the
Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client, it will use the default vCenter Server administrator credentials.
However, for security reasons, it's best to create a user account specifically for use with the Serengeti
Command-Line Interface Client.
Passwords must be from 8 to 20 characters, use only visible lowerASCII characters (no spaces), and must
contain at least one uppercase alphabetic character (A - Z), at least one lowercase alphabetic character (a - z),
at least one digit (0 - 9), and at least one of the following special characters: _, @, #, $, %, ^, &, *
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22.
Install the Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client. See “Install the Serengeti Remote Command-Line
n
Interface Client,” on page 29.
Procedure
1 Open a Web browser and go to: https://vc-hostname:port/vsphere-client.
The vc-hostname can be either the DNS host name or IP address of vCenter Server. By default the port is
9443, but this can change during the installation of the vSphere Web Client.
2 Type the user name and password that has administrative privileges on vCenter Server, and click
Login.
NOTE vCenter Server 5.5 users must use a local domain to perform SSO related operations.
3 From the vSphere Web Client Navigator panel, select Administration, SSO Users and Groups.
4 Change the login credentials.
The login credentials are updated. The next time you access the Serengeti Command-Line Interface use the
new login credentials.
What to do next
You can change the password of the Serengeti Management Server. See “Change the Password for the
Serengeti Management Server,” on page 70.
VMware, Inc. 71
Page 72

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Authorize and Audit Commands Run as the Root User
You can customize the sudo command using pbrun. The pbrun command lets you execute commands with
the privileges of another user, typically the root user.
The pbrun command uses PowerBroker, a centralized server application, for the authorization and auditing
of commands run as the root user. PowerBroker let's you assign root user privileges to specific users, and
authorize and audit their use of the environment.
Prerequisites
To use PowerBroker or similar identity services, you must first configure your environment for use with
them.
Procedure
1 Log into the Serengeti management server.
2 Export the custom sudo command using pbrun to your environment.
"export SUDO_CMD=pbrun" >> /opt/serengeti/sbin/env.sh
3 Log into the cluster node, and run the following command sequence.
sed -i 's|^serengeti.sudo.command.*|serengeti.sudo.command =
pbrun|' /opt/serengeti/conf/serengeti.properties
Specify a Group of Users in Active Directory or LDAP to Use a Hadoop Cluster
You can specify an Active Directory or LDAP server for user authentication. This lets you manage users
from a central point.
By defaultBig Data Extensions is installed with authentication only for local user accounts. If you want to
use LDAP or Active Directory to authenticate users, you must configure Big Data Extensions for use with
your LDAP or Active Directory service.
Big Data Extensions lets you authenticate local users, those managed by LDAP or Active Directory server, or
a combination of these authentication methods.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22.
Use the Serengeti Management Server Administration Portal to enable SSO and update the certificate.
n
See “Configure vCenter Single Sign-On Settings for the Serengeti Management Server,” on page 28.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Clientto log in to vCenter Server.
2 Select Big Data Extensions and click the Manage tab.
3 Select User Mode and click Edit.
The Configure User dialog box appears.
72 VMware, Inc.
Page 73

Chapter 7 Managing the Big Data Extensions Environment
4 Choose the user authentication mode you wish to use for your Big Data Extensions environment.
Table 7‑1. User Authentication Modes
User Mode Description
Local Select Local to create and manage users and groups that are stored locally in your
Big Data Extensions environment. Local is the default user management solution.
LDAP user Select LDAP user to create and manage users and groups that are stored in your
organization's identity source, such as Active Directory or LDAP. If you choose LDAP user
you must configure Big Data Extensions to use an LDAP or Active Directory service.
Mixed mode Select Mixed mode to use a combination of both local users and users stored in an external
identity source. If you choose mixed mode you must configure Big Data Extensions to use
AD as LDAP mode.
5 If you choose to use LDAP or Mixed mode, configure Big Data Extensions to use an LDAP or Active
Directory service.
Table 7‑2. LDAP Connection Information
Base user DN Specify the base user DN.
Base group DN Specify the base group DN.
Primary server URL Specify the primary server URL of your Active Directory or LDAP server.
Secondary server URL Specify the secondary server URL of your Active Directory or LDAP server.
Username Type the username of the Active Directory or LDAP server administrator account.
Password Type the password of the Active Directory or LDAP server administrator account.
6 (Optional) Click Test to verify that user accounts are found.
Stop and Start Serengeti Services
You can stop and start Serengeti services to make a reconfiguration take effect, or to recover from an
operational anomaly.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
2 Run the serengeti-stop-services.sh script to stop the Serengeti services.
serengeti-stop-services.sh
3 Run the serengeti-start-services.sh script to start the Serengeti services.
serengeti-start-services.sh
Ports Used for Communication between Big Data Extensions and the vCenter Server
Big Data Extensions queries information from the vCenter Server, and uses the vCenter Server Single SignOn service.
Big Data Extensions Management Server
The table below shows the published port for the management server.
VMware, Inc. 73
Page 74

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Service Port Comments
Serengeti Rest API 8080, 8443 Open for Serengeti client and for BDE plugin
SSHD 22 Open for Serengeti client connection
Hadoop Ports
Serengeti deploys Hadoop and Hbase clusters using all default ports. The following lists all ports that are
used by the Hadoop or HBase service, the production network.
Daemon Default Port
HDFS Namenode Webpage 50070
Namenode RPC 8020
Datanode 50075
MapReduce JobTracker Webpage 50030
JobTracker RPC 8021
TaskTracker 50060
Yarn Resource Manager Webpage 8088
Resource Manager RPC 8030, 8031, 8032, 8033
Node Manager 8040, 8042
Hive N/A 1000
registration called by VC
50010
50020
Hbase Ports
The table below shows the ports used by HBase clusters, along with the default port numbers.
Service Property Name Port
ZooKeeper hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort 2181
Master hbase.master.port 60000
Master hbase.master.info.port 60010
Region server hbase.regionserver.port 60020
Region server hbase.regionserver.info.port 60030
REST server hbase.rest.port 8080
REST server hbase.rest.info.port 8085
Thrift server hbase.thrift.port 9090
Thrift server hbase.thrift.info.port 9095
MapR Ports
The table below defines the ports used by a MapR cluster, along with the default port numbers.
74 VMware, Inc.
Page 75

Service Port
CLDB 7222
CLDB JMX monitor port 7220
CLDB web port 7221
HBase Master 60000
HBase Master (for GUI) 60010
HBase RegionServer 60020
Hive Metastore 9083
JobTracker Webpage 50030
JobTracker RPC 8021
MFS server 5660
MySQL 3306
NFS 2049
NFS monitor (for HA) 9997
NFS management 9998
Port mapper 111
TaskTracker 50060
Web UI HTTPS 8443
ZooKeeper 5181
Chapter 7 Managing the Big Data Extensions Environment
Verify the Operational Status of the Big Data Extensions Environment
To successfully provision a Hadoop cluster, your Big Data Extensions environment must meet certain
criteria. You can verify that your environment meets these criteria prior to creating Hadoop clusters, as well
as troubleshoot cluster creation issues you may encounter.
Operational Status of Big Data Extensions Services
Big Data Extensions consists of several services that you can verify are running.
Big Data Extensions consists of the following services: Tomcat service, Yum server, Chef server, and
PostgreSQL server. You can verify that these services are running prior to creating Hadoop clusters.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Serengeti vApp.
n
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
VMware, Inc. 75
Page 76

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
2 Verify that the Tomcat service is running.
a Run the command pgrep -f org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap -l.
pgrep -f org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap -l
b Run the command wget https://bde_server_ip:8443 --no-check-certificate
wget https://bde_server_ip:8443 --no-check-certificate
3 Verify that the Yum server is running.
Run the command /sbin/service httpd status.
/sbin/service httpd status
If the Yum server is operating properly it responds with the status message running.
4 Verify that the Chef server is running.
Run the command sudo /chef-server-ctl status. The status subcommand displays the status of all
services available to the Chef server.
sudo /chef-server-ctl status
5 Verify that the PostgreSQL server is running.
a Run the command pgrep -f /opt/opscode/embedded/bin/postgres -l to verify that the postgres
process is running. The -l option lists the available databases.
pgrep -f /opt/opscode/embedded/bin/postgres -l
b Run the command echo "\dt" | psql -U serengeti to display the database tables created for
Big Data Extensions. The -dt option specifies the name of the database to connect to, and turns off
the display of the database column names in the resulting output. The -U option specifies the
username with which to connect to the database.
echo "\dt" | psql -U serengeti
If the databases available to PostgreSQL and the tables owned by the serengeti user display, your
PostgreSQL server is running as expected.
What to do next
If any of the above services is not running, you can view the initialization status of the
Serengeti Management Server services, view error messages to help troubleshoot problems, and recover
services that may not have successfully started using the Serengeti Management Server Administration
Portal. See “View Serengeti Management Server Initialization Status,” on page 118.
Verify Network Connectivity with vCenter Server
You can verify if your Big Data Extensions deployment can connect to vCenter Server, and identify possible
causes that may be preventing a successful network connection.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Serengeti vApp.
n
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
76 VMware, Inc.
Page 77

Chapter 7 Managing the Big Data Extensions Environment
2 Run the command wget https://vcenter_server_ip:9443 --no-check-certificate.
wget https://vcenter_server_ip:9443 --no-check-certificate
If this command retrieves the index.html file whose title is vSphere Web Client, vCenter Server is
running, and there is connectivity between Big Data Extensions and vCenter Server.
If running this command fails to retrieve the index.html file, see Step. 3.
3 If the command returns the error message Connecting to vcenter_server_ip:vcenter_server_port...
failed: Connection refused, the vCenter Server IP address you specified is reachable, but the vCenter
Server network port number is incorrect.
4 If the vCenter Server IP address and port number are correct, check your Big Data Extensions
deployment's network configuration and ensure that it is properly configured. For example, is
Big Data Extensions using a valid IP address and gateway?
What to do next
If you are unable to verify a network connection between Big Data Extensions and vCenter Server, and
cannot identify the cause of the problem, the troubleshooting topics provide solutions to problems you
might encounter when using Big Data Extensions. See Chapter 14, “Troubleshooting,” on page 133
Verify vCenter Server User Authentication
You can verify if your vCenter Server user authentication is working properly, and identify possible causes
that may be preventing a successful cluster creation.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Serengeti vApp.
n
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as the
user serengeti.
2 Type serengeti to start the Serengeti Command-Line Interface.
3 Run the command connect –host localhost:8443, and at the prompt type your username and
password, which might be different from your login credentials for the Serengeti Management Server.
If you can log into Big Data Extensions your vCenter Server user authentication is working correctly.
What to do next
Before creating new virtual machines on hosts, the time on the target hosts is checked against the time on
the Serengeti Management Server. If the time between the Serengeti Management Server and the hosts is not
synchronized, the virtual machine creation will fail. See “Check Time Synchronization Between Serengeti
Management Server and Hosts,” on page 77.
Check Time Synchronization Between Serengeti Management Server and Hosts
When you run the cluster create or cluster create ... --resume command, the command can fail if
there are time discrepancies in the environment. You can verify that the time is within allowable tolerances
and synchronize the time between the Serengeti Management Server and the other hosts within your
environment.
Before creating new virtual machines on hosts, the time on the target hosts is checked against the time on
the Serengeti Management Server. If the time between the Serengeti Management Server and the hosts is not
synchronized, the cluster creation might fail.
VMware, Inc. 77
Page 78

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Prerequisites
Deploy the Serengeti vApp.
n
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
2 Run the command date +%T to see the time on the Serengeti Management Server.
date +%T
3 From the vSphere Web Client, record the time of each host in the datacenter.
4 Compare the date and time from the Serengeti Management Server and each host to see if they are
greater than the Maximum-Threshold. If there is HBase service in the cluster, the Maximum-Threshold
is 20 seconds. Otherwise, the Maximum-Threshold is 4 minutes.
If the times between hosts are not synchronized, login to each host and view the /etc/ntp.conf file to
verify if the NTP configuration is correct.
5 From the vSphere Web Client, configure all ESXi hosts to synchronize their clocks with the same NTP
server.
What to do next
After you synchronize the time between the Serengeti Management Server and the other ESXi hosts within
your environment, try to create a cluster.
Verify Network Connectivity Between Compute Nodes and Isilon HDFS
If you are using EMC Isilon OneFS for your HDFS, you can verify the network connectivity from the
compute nodes to the Isilon OneFS filesystem.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
2 For each compute node (TaskTracker or NodeManager), login and run the command hadoop dfsadmin
-report to verify that the HDFS is running correctly. If the command returns the Configured Capacity
and Present Capacity, the worker node can successfully access the HDFS.
If the HDFS does not respond, see Step 3.
3 Ensure that the HDFS IP address and network port number is correct. Login to the Isilon Namenode
(which may require a different username and password) and verify that the HDFS service is listening
on port 8020.
If the HDFS is listening on the correct network port, see Step 4.
4 Check the fs.defaultFS entry in the Hadoop configuration file core-site.xml. Ensure that the IP
address, FQDN, and network port are configured to use the correct HDFS service.
78 VMware, Inc.
Page 79

Chapter 7 Managing the Big Data Extensions Environment
Check Which Users and User Groups Exist in the Isilon OneFS
If you use EMC Isilon OneFS as the external HDFS cluster, you must create and configure users and user
groups and prepare your Isilon OneFS environment. You can verify that you have created the correct users
and user groups, and check which users and groups exist in your Isilon OneFS environment.
Prerequisites
Prepare the Isilon OneFS for use as an external HDFS cluster. See “Prepare the EMC Isilon OneFS as the
External HDFS Cluster,” on page 103.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and SSH to the Isilon OneFS node.
2 Run the command isi auth users/groups list to list the existing Isilon OneFS users and user groups.
3 Run the command ls -al HDFS_ROOT_DIR to verify which users and user groups are using the HDFS.
When running the ls command in the Isilon filesystem, the -al option must come before the
HDFS_ROOT_DIR directory name. Otherwise, the -al option will be regarded as a directory name by the ls
command.
ls -al HDFS_ROOT_DIR
NOTE In the HDFS subdirectory there may be files and directories with permissions and ownership
assigned to users or groups other than those using Big Data Extensions.
Check Storage Capacity
To successfully deploy a cluster you must have enough storage capacity in your Big Data Extensions
environment.
The datastores you add to your Big Data Extensions environment are made available to the clusters you
create within Big Data Extensions. If you do not add enough storage capacity cluster creation will fail.
In addition to overall storage capacity, you must ensure that you have enough Shared and Local storage.
Shared stroage is recommended for master nodes, and enables you to use vMotion, HA, and Fault
Tolerance. Local storage is recommended for worker nodes.
Prerequisites
You must have added a datastore to your Big Data Extensions environment. See “Add a Datastore in the
vSphere Web Client,” on page 89
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as user
serengeti.
2 Run the command datastore list --detail to see which vCenter Server datastores are in use by
Big Data Extensions.
3 Using the configuration values specified in the cluster specification file, calculate how much storage
capacity the cluster will require.
4 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the datastores you identified as
belonging to Big Data Extensions have enough storage capacity for the clusters you want to create.
Additionally, ensure that the datastores are in an active state.
VMware, Inc. 79
Page 80

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
What to do next
If your Big Data Extensions environment does not have adequate storage capacity to create clusters, add
additional datastores. See “Add a Datastore in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 89.
Verify the Ambari Application Manager Installation
If you use Apache Ambari to manage your Hadoop cluster, you can verify that the Ambari service is
running, has a network connection, and valid user credentials with which to connect to your cluster.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
Add the Ambari application manager to your Big Data Extensions environment. See “Add an
n
Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client,” on page 39.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as the
user serengeti.
2 Run the curl command with the -u option to specify the username and password in use by the Ambari
service, and the -G option to specify the URL of the Ambari system check service:
http://ambari_server_ip:8080/api/v1/check
curl -u username:password -G http://ambari_server_ip:8080/api/v1/check
If the system returns RUNNING, the Ambari server is running. If you receive a system message
n
indicating that your Ambari service is not running, investigate the issue and confirm that you can
successfully start Ambari before proceeding.
If the system returns Bad credentials, the username and password are incorrect. Obtain the correct
n
username and password for your Ambari installation.
If the curl command hangs for 30 or more seconds, and the system returns the error message curl:
n
(7) Failed to connect to ambari_server_ip port port_number: Connection refused, the
IP/FQDN or port number is incorrect. Obtain the correct network address for your Ambari
installation.
This error message may also indicate that the Ambari server virtual machine in powered off. Verify
that the Ambari virtual machine is powered on, and that the Ambari server is running.
What to do next
If your Ambari installation is not responding, confirm that it is properly installed and configured. See
“Modify an Application Manager by Using the Web Client,” on page 40.
Verify Cloudera Manager Installation
If you use Cloudera Manager to manage your Hadoop cluster, you can verify that Cloudera Manager is
running, has a network connection, and valid user credentials with which to connect to your cluster.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22
80 VMware, Inc.
Page 81

Chapter 7 Managing the Big Data Extensions Environment
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
Add the Cloudera Manager application to your Big Data Extensions environment. See “Add an
n
Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client,” on page 39.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as the
user serengeti.
2 Run the curl command with the -u option to specify the username and password in use by
Cloudera Manager, and the -G option to specify the URL of the Cloudera ManagerAPI version number :
http://cloudera_manager_server_ip:7180/api/version
curl -u username:password -G http://cloudera_manager_server_ip:7180/api/version
Record the API version number returned by Cloudera Manager.
3 Run the curl command with the -u option to specify the username and password in use by
Cloudera Manager, and the -G option to specify the URL of the Cloudera Manager /tools/echo query:
http://cloudera_manager_server_ip:7180/api/cloudera_manager_api_version/tools/echo
curl -u username:password -G http://cloudera_manager_server_ip:
7180/api/cloudera_manager_api_version/tools/echo
This example specifies a Cloudera Manager installation using the username and password cloudera,
whose network address is 192.168.1.1 using API version v5.
curl -u cloudera:cloudera -G http://192.168.1.1:7180/api/v5/tools/echo
If the system returns Hello world!, Cloudera Manager is running. If you receive a system message
n
indicating that your Cloudera Manager is not running, investigate the issue and confirm that you
can successfully start Cloudera Manager before proceeding.
If the system returns Error 401 Bad credentials, the username and password are incorrect.
n
Obtain the correct username and password for your Cloudera Manager installation.
If the system returns the error message curl: (7) Failed to connect to
n
cloudera_manager_server_ip port 7180: No route to host, the IP address or FQDN is incorrect.
Obtain the correct network address for your Cloudera Manager installation.
This error message may also indicate that the Cloudera Manager virtual machine in powered off.
Verify that the Cloudera Manager virtual machine is powered on, and that Cloudera Manager is
running.
What to do next
If your Cloudera Manager installation is not responding, confirm that it is properly installed and
configured. See “Modify an Application Manager by Using the Web Client,” on page 40.
Check DNS Forward and Reverse Lookup
Big Data Extensions requires a properly configured network environment. You can verify that you have a
properly configured forward and reverse address lookup for you DNS.
Reverse DNS lookup determines the hostname associated with a given IP address. Forward DNS lookup
determines the determines the IP address associated with a given hostname.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22
VMware, Inc. 81
Page 82

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as the
user serengeti.
2 Run the echo command to retrieve the IP addresses in use by the cluster.
echo ipv4_address_from_network_interface | psql
Record the IP addresses for each network interface card in use by the cluster.
3 For each IP address you recorded in the previous step, run the host command to verify that DNS
reverse lookup returns the fully qualified domain name (FQDN). If the system responds with a FQDN
for each IP address, DNS reverse lookup is working.
host IP_address
Record the FQDN for each network address you check.
4 For each FQDN you recorded in the previous step, run the host command to verify that DNS forward
lookup returns the IP address associated with th FQDN. If the system responds with an IP address for
each FQDN, DNS forward lookup is working.
5 (Optional) If you are unable to resolve the IP addresses and FQDNs, open the file /etc/resolv.conf,
and confirm that a DNS name server has been configured for use with your environment.
If there is no name server configured for use with your environment, ask you administrator for the
n
correct DNS server name to use.
If a name server is configured, but your DNS does not provide forward or reverse lookup,
n
investigate the cause and configure your DNS as required. Possible causes preventing your DNS
from functioning correctly may include:
The name server cannot be reached due to an incorrect IP address.
n
The DNS service on that virtual machine may be shutdown, or unresponsive.
n
The virtual machine containing the DNS service may be shutdown.
n
What to do next
If your DNS is not functioning as expected, investigate the cause and make the necessary configuration or
operational changes until you are able to verify that you have a properly configured forward and reverse
address lookup for you DNS. See “Modify the DNS Type in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 93.
Verify the Network Connection Between Big Data Extensions and the Cluster Nodes
The Serengeti Management Server must be able to connect to each of the nodes in a Hadoop cluster. You can
verify that the Serengeti Management Server can contact each cluster node.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
Add a network for use by Big Data Extensions. See “Add a Network in the vSphere Web Client,” on
n
page 92.
82 VMware, Inc.
Page 83

Chapter 7 Managing the Big Data Extensions Environment
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as the
user serengeti.
2 Run the echo command to retrieve the IP addresses in use by the cluster.
echo "select ipv4_address_from_network_interface" | psql
Record the IP addresses for each network interface card in use by the cluster.
3 Run the ping command to contact each IP address and verify that the Serengeti Management Server can
contact each of the cluster nodes.
What to do next
If you are unable to establish a connection between the Serengeti Management Server and the Hadoop
cluster nodes, investigate the cause and make the necessary changes until you are able to verify that you
have a properly configured network.
Verify the Local Yum Repository
If you created a local yum repository from which to deploy your Hadoop distributions, you can verify that
the repository is working properly.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp. See “Deploy the Big Data Extensions vApp in the vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 22
Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server, and verify that the
n
Serengeti Management Server virtual machine is running.
You created a local Yum repository from which to deploy your Hadoop distributions. See “Configuring
n
Yum and Yum Repositories,” on page 46.
Procedure
1 Open a command shell, such as Bash or PuTTY, and log in to the Serengeti Management Server as the
user serengeti.
2 Run the command wget local_repository_url to download the local repository Web page.
3 You can open and view the local repository Web page with a Web browser inside your network to
verify that the local repository works.
What to do next
You can successfully create Hadoop clusters in your Big Data Extensions environment. See Chapter 9,
“Creating Hadoop and HBase Clusters,” on page 95
Enter Maintenance Mode to Perform Backup and Restore with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface Client
Before performing backup and restore operations, or other maintenance tasks, you must place
Big Data Extensions into maintenance mode.
Prerequisites
Deploy the Serengeti vApp.
n
Ensure that you have adequate resources allocated to run the Hadoop cluster.
n
VMware, Inc. 83
Page 84

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
To use any Hadoop distribution other than the default distribution, add one or more Hadoop
n
distributions. See the VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide.
Procedure
1 Log into the Serengeti Management Server.
2 Run the script /opt/serengeti/sbin/serengeti-maintenance.sh to place Big Data Extensions into
maintenance mode, or check maintenance status.
serengeti-maintenance.sh on | off | status
Option Description
on
off
status
Turns on maintenance mode. Upon entering maintenance mode,
Big Data Extensions continues executing jobs that have already been
started, but will not respond to any new requests.
Turn off maintenance mode, and returns Big Data Extensions to its normal
operating state.
Displays the maintenance status of Big Data Extensions.
n
n
n
To place your Big Data Extensions deployment into maintenance mode, run the serengeti-
maintenance.sh script with the on option.
A status of safe means it is safe to backup or perform other
maintenance tasks on your Big Data Extensions deployment.
A status of off means maintenance mode has been turned off, and it is
not safe to perform maintenance tasks such as backup and restore.
A status of on means Big Data Extensions has entered maintenance
mode, but it is not yet safe to perform back and restore operations. You
must wait until the system returns the safe status message.
serengeti-maintenance.sh on
3 Verify that Big Data Extensions is in maintenance mode.
When Big Data Extensions completes all jobs that have been submitted, the maintenance status will
enter safe mode. Run the serengeti-maintenance.sh with the status parameter repeatedly until it
returns the safe system status message.
serengeti-maintenance.sh status
safe
4 Perform the necessary system maintenance tasks.
5 Once you have completed the necessary system maintenance tasks, return Big Data Extensions to its
normal operating state by manually exiting maintenance mode.
serengeti-maintenance.sh off
Backup and Restore the Big Data Extensions Environment
You can recover Big Data Extensions from an abnormal operational status by performing a backup and
restore operation.
You can perform a backup and restore operation on the same Big Data Extensions instance, or on two
different Big Data Extensions servers deployed within the same vCenter Server environment.
Prerequisites
Prior to performing a backup and restore operation, place Big Data Extensions into maintenance mode. See
“Enter Maintenance Mode to Perform Backup and Restore with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
Client,” on page 83.
84 VMware, Inc.
Page 85

Chapter 7 Managing the Big Data Extensions Environment
Procedure
1 Backup your data to a file from the source Big Data Extensions server using
the /opt/serengeti/sbin/backup.sh script.
/opt/serengeti/sbin/backup.sh filename
2 Copy the bde-backup-xxxx.tar.gz file to the target Big Data Extensions server.
3 On the target Big Data Extensions, execute the /opt/serengeti/sbin/restore.sh bde-backup-
xxxx.tar.gz to restore the data from the first Big Data Extensions server.
When the restoration process completes, the target Big Data Extensions server will be ready for use.
VMware, Inc. 85
Page 86

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
86 VMware, Inc.
Page 87

Managing vSphere Resources for
Clusters 8
Big Data Extensions lets you manage the resource pools, datastores, and networks that you use in the
clusters that you create.
This chapter includes the following topics:
“Add a Resource Pool with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface,” on page 87
n
“Remove a Resource Pool with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface,” on page 88
n
“Update Resource Pools with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface,” on page 88
n
“Add a Datastore in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 89
n
“Remove a Datastore in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 90
n
“Update Datastores with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface,” on page 90
n
“Add a Paravirtual SCSI Controller for System and Swap Disks,” on page 91
n
“Add a Network in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 92
n
“Modify the DNS Type in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 93
n
“Reconfigure a Static IP Network in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 93
n
“Remove a Network in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 94
n
Add a Resource Pool with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
You add resource pools to make them available for use by Hadoop clusters. Resource pools must be located
at the top level of a cluster. Nested resource pools are not supported.
When you add a resource pool to Big Data Extensions it symbolically represents the actual vSphere resource
pool as recognized by vCenter Server. This symbolic representation lets you use the Big Data Extensions
resource pool name, instead of the full path of the resource pool in vCenter Server, in cluster specification
files.
NOTE After you add a resource pool to Big Data Extensions, do not rename the resource pool in vSphere. If
you rename it, you cannot perform Serengeti operations on clusters that use that resource pool.
Procedure
1 Access the Serengeti Command-Line Interface client.
VMware, Inc.
87
Page 88

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
2 Run the resourcepool add command.
The --vcrp parameter is optional.
This example adds a Serengeti resource pool named myRP to the vSphere rp1 resource pool that is
contained by the cluster1 vSphere cluster.
resourcepool add --name myRP --vccluster cluster1 --vcrp rp1
Remove a Resource Pool with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
You can remove resource pools from Serengeti that are not in use by a Hadoop cluster. You remove resource
pools when you do not need them or if you want the Hadoop clusters you create in the Serengeti
Management Server to be deployed under a different resource pool. Removing a resource pool removes its
reference in vSphere. The resource pool is not deleted.
Procedure
1 Access the Serengeti Command-Line Interface client.
2 Run the resourcepool delete command.
If the command fails because the resource pool is referenced by a Hadoop cluster, you can use the
resourcepool list command to see which cluster is referencing the resource pool.
This example deletes the resource pool named myRP.
resourcepool delete --name myRP
Update Resource Pools with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
You can update an existing cluster to use new resource pools. Do this when you expand your environment
by adding a new ESX cluster with new resource pools.
The cluster update command lets you add new resource pools to an existing cluster, as well as update the
resource pools already in use.
You can also add new resource pools to the already existing resource pools using the --append parameter.
This adds the new resource pool, but does not update those resource pools already in use by the cluster. If
your environment has a large number of resource pools, the --append parameter lets you add new resource
pools without having to explicitly list each resource pool in use.
Prerequisites
You must have an existing Big Data cluster whose resources you want to update with new or different
n
resource pools.
Run the cluster export command to verify which resource pools are currently in use by the cluster.
n
and note which of your resource pools are currently in use by the cluster you want to update with new
or additional resource pools.
Procedure
1 Login to the Serengeti CLI.
2 Add a new resource pool from an ESX cluster using the resourcepool add command.
This example adds a resource pool labeled myRP2 from the vSphere resource pool rp1 that is contained
by the vSphere cluster cluster1.
resourcepool add --name myRP2 --vccluster cluster1 --vcrp rp1
3 Use the cluster export command to verify which resource pools are currently in use by the cluster.
cluster export --name cluster_name
88 VMware, Inc.
Page 89

4 Update the resource pools for the cluster using the cluster update command.
cluster update --name cluster1 –-rpNames myRP,myRP2
The new resource pool, myRP2, is now available for use by the cluster labeled cluster1.
5 (Optional) You can append the new resource pool myRP2 to your existing resource pools with the --
append parameter. This adds the new resource pool, but does not update those resource pools already in
use by the cluster.
cluster update --name cluster1 --rpNames myPR2 --append
What to do next
Optionally, you can update the cluster to use new datastores. See “Update Datastores with the Serengeti
Command-Line Interface,” on page 90.
Add a Datastore in the vSphere Web Client
You can add datastores to Big Data Extensions to make them available to big data clusters.
Big Data Extensions supports both shared datastores and local datastores.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
Chapter 8 Managing vSphere Resources for Clusters
2 Select Big Data Extensions.
3 From the Inventory Lists, select Resources.
4 Expand the Inventory Lists, and select Datastores.
5 Click the Add (+) icon.
6 In the Name text box, type a name with which to identify the datastore in Big Data Extensions.
Passwords must be from 8 to 20 characters, use only visible lowerASCII characters (no spaces), and
must contain at least one uppercase alphabetic character (A - Z), at least one lowercase alphabetic
character (a - z), at least one digit (0 - 9), and at least one of the following special characters: _, @, #, $, %,
^, &, *
7 From the Type list, select the datastore type in vSphere.
Type Description
Shared
Local
Recommended for master nodes. Enables you to leverage vMotion, HA,
and Fault Tolerance.
NOTE If you do not specify shared storage and try to provision a cluster
using vMotion, HA, or Fault Tolerance, the provisioning fails.
Recommended for worker nodes. Throughput is scalable and the cost of
storage is lower.
8 Select one or more vSphere datastores to make available to the Big Data Extensions datastore that you
are adding.
9 Click OK to save your changes.
The vSphere datastores are available for use by big data clusters deployed within Big Data Extensions.
VMware, Inc. 89
Page 90

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Remove a Datastore in the vSphere Web Client
You remove a datastore from Big Data Extensions when you no longer want the Hadoop clusters you create
to use that datastore.
Prerequisites
Remove all Hadoop clusters associated with the datastore. See “Delete a Cluster in the vSphere Web Client,”
on page 108.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
2 Select Big Data Extensions.
3 From the Inventory Lists, select Resources.
4 Expand Resources, select Inventory Lists, and select Datastores.
5 Select the datastore that you want to remove, right-click, and select Remove.
6 Click Yes to confirm.
If you did not remove the cluster that uses the datastore, you receive an error message indicating that
the datastore cannot be removed because it is currently in use.
The datastore is removed from Big Data Extensions.
Update Datastores with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface
You can update an existing cluster to use new datastores. Do this when you expand your environment by
adding a new ESXi host with new datastores.
When you add datastores to an existing cluster, if the new datastore names match those of the datastores
already in use by the cluster, they will automatically be available for use by the cluster. If, however, the
current datastore names do not match those of the datastores on the new ESXi hosts, you must use the
datastore add and cluster update commands to update the datastores available to the cluster, specifying
both the current and new datastore names.
Prerequisites
You must have an existing Big Data cluster that you want to update with a new or different datastore. For
example, if you have added a new ESXi host to your environment and want to expand the resources
available to your Big Data Extensions environment.
Procedure
1 Login to the Serengeti CLI.
2 Add a new datastore from an ESXi host using the datastore add command, or the vSphere Web Client.
This example uses the Serengeti CLI to add a new, local storage datastore named newDS. The value of
the --spec parameter, local*, is a wildcard specifying a set of vSphere datastores. All vSphere datastores
whose names begin with "local" are added and managed as a whole by Big Data Extensions.
datastore add --name newDS --spec local* --type LOCAL
90 VMware, Inc.
Page 91

Chapter 8 Managing vSphere Resources for Clusters
3 Update the list of datastores available for use by the cluster with the cluster update command. When
you add datastores to an existing cluster, you must also specify those datastores currently in use by the
cluster. This example uses the labels currentDS and newDS to differentiate between the datastores being
newly added to the cluster (newDS), and those currently in use by the cluster (currentDS).
If you do not provide the names of those datastores already in use by the cluster with the --dsNames
parameter, a warning message cautions you that the cluster is using all available datastores, and that
the datastores being updated belong to a subset of these datastores. In such a case, some data may be
unavailable after the update, which can cause errors. The Serengeti CLI will prompt you to confirm that
you wish to continue the update by typing Y (yes), or to abort the update by typing N (no).
cluster update --name cluster1 –-dsNames currentDS,newDS
Both the current and new datastores are now available for use by the cluster labeled cluster1.
4 If you wish to add new datastores alongside those datastores already in use by the cluster, use the --
append parameter. Using --append lets you omit listing the datastores already in use by the cluster with
the --dsNames parameter.
cluster update --name cluster1 –-dsNames newDS --append
The new datastore is now available for use by the cluster labeled cluster1. Any datastores previously
in use by the cluster are unaffected.
What to do next
Optionally, you can update the cluster to use new resource pools. See “Update Resource Pools with the
Serengeti Command-Line Interface,” on page 88.
Add a Paravirtual SCSI Controller for System and Swap Disks
You can add a VMware Paravirtual SCSI (PVSCSI) high performance storage controller to provide greater
throughput and lower CPU utilization.
PVSCSI controllers are best suited for environments running I/O-intensive operations such as system and
swap disks. The PVSCSI controller provides greater throughput and lower CPU utilization.
NOTE By default, the controller type for data disks is set to PVSCSI . You can specify that the data disk use
the LSI Logic SAS controller by editing the parameter storage.data.disk.controller.type as described in
this procedure.
Prerequisites
Prior to adding the PVSCSI controller, shut down the Hadoop Template virtual machine.
Procedure
1 From the vSphere Web Client, shut down the Hadoop Template virtual machine.
2 Login to the Serengeti Management Server as the user serengeti.
3 Open the file /opt/serengeti/conf/serengeti.properties in a text editor.
4 Change the configuration value of the storage.system_swap.disk.controller.type= parameter to
ParaVirtualSCSIController.
storage.system_swap.disk.controller.type=ParaVirtualSCSIController
5 In the virtual machines and templates inventory tree, select the node-template virtual machine whose
disk controller setting you want to modify.
6 In the VM Hardware panel, click Edit Settings.
7 Click Virtual Hardware.
VMware, Inc. 91
Page 92

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
8 Click the triangle next to the SCSI device to expand the device options.
9 From the Change type drop-down menu, select VMware Paravirtual .
10 Click OK to save your changes and exit the dialog box.
11 Delete all existing snapshots of the node-template virtual machine.
Add a Network in the vSphere Web Client
You add networks to Big Data Extensions to make the IP addresses contained by those networks available to
big data clusters.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
2 Select Big Data Extensions.
3 From the Inventory Lists, select Resources.
4 Expand Resources, click Inventory Lists > Inventory Lists and select Networks.
5 Click the Add (+) icon.
6 In the Name text box, type a name with which to identify the network resource in Big Data Extensions.
7 From the Port group name list, select the vSphere port group that you want to add to Big Data
Extensions.
8 Select a DNS type.
Option Description
Normal
Dynamic
Others
The DNS server provides both forward and reverse FQDN to IP resolution.
Reverse DNS is IP address to domain name mapping. The opposite of
forward (normal) DNS which maps domain names to IP addresses.
Normal is the default DNS type.
Dynamic DNS (DDNS or DynDNS) is a method of automatically updating
a name server in the Domain Name System (DNS) with the active DNS
configuration of its configured hostnames, addresses or other information.
Big Data Extensions integrates with a Dynamic DNS server in its network
through which it provides meaningful host names to the nodes in a
Hadoop cluster. . The cluster will then automatically register with the DNS
server.
There is no DNS server in the VLAN, or the DNS server doesn't provide
normal DNS resolution or Dynamic DNS services. In this case, you must
add FQDN/IP mapping for all nodes in the /etc/hosts file for each node
in the cluster. Through this mapping of hostnames to IP addresses each
node can contact another node in the cluster.
9 Choose the type of addressing to use for the network: Use DHCP to obtain IP addresses or Use static
IP addresses.
10 (Optional) If you chose Use static IP addresses in Step 9, enter one or more IP address ranges.
11 Click OK to save your changes.
The IP addresses of the network are available to big data clusters that you create within Big Data Extensions.
92 VMware, Inc.
Page 93

Chapter 8 Managing vSphere Resources for Clusters
Modify the DNS Type in the vSphere Web Client
DHCP selects the IP address for the IP pool randomly. The FQDN and the IP address of the nodes in a
cluster are random. The Hadoop user or application cannot identify where the master nodes are unless they
do a query to Big Data Extensions. Even if the user knows the original address, the address might change
when the cluster is restarted. Therefore, it is difficult for the Hadoop user or application to access the cluster.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
2 Select Big Data Extensions.
3 From the Inventory Lists, select Resources.
4 Expand Resources, select Inventory Lists > Networks.
5 Select a single network to modify, right-click, and select Modify DNS Type.
6 Select a DNS type.
Option Description
Normal
Dynamic
Others
7 Click OK to save your changes.
The DNS server provides both forward and reverse FQDN to IP resolution.
Reverse DNS is IP address to domain name mapping. The opposite of
forward (normal) DNS which maps domain names to IP addresses.
Normal is the default DNS type.
Dynamic DNS (DDNS or DynDNS) is a method of automatically updating
a name server in the Domain Name System (DNS) with the active DNS
configuration of its configured hostnames, addresses or other information.
Big Data Extensions integrates with a Dynamic DNS server in its network
through which it provides meaningful host names to the nodes in a
Hadoop cluster. . The cluster will then automatically register with the DNS
server.
There is no DNS server in the VLAN, or the DNS server doesn't provide
normal DNS resolution or Dynamic DNS services. In this case, you must
add FQDN/IP mapping for all nodes in the /etc/hosts file for each node
in the cluster. Through this mapping of hostnames to IP addresses each
node can contact another node in the cluster.
Reconfigure a Static IP Network in the vSphere Web Client
You can reconfigure a Big Data Extensions static IP network by adding IP address segments to it. You might
need to add IP address segments so that there is enough capacity for a cluster that you want to create.
Prerequisites
If your network uses static IP addresses, be sure that the addresses are not occupied before you add the
network.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
2 Select Big Data Extensions.
3 From the Inventory Lists, select Resources.
4 Expand Resources, select Inventory Lists > Networks.
5 Select the static IP network to reconfigure, right-click, and select Add IP Range.
VMware, Inc. 93
Page 94

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
6 Click Add IP range, and enter the IP address information.
7 Click OK to save your changes.
IP address segments are added to the network.
Remove a Network in the vSphere Web Client
You can remove an existing network from Big Data Extensions when you no longer need it. Removing an
unused network frees the IP addresses for use by other services.
Prerequisites
Remove clusters assigned to the network. See “Delete a Cluster in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 108.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
2 Select Big Data Extensions.
3 From the Inventory Lists, click Resources.
4 Expand Resources, select Inventory Lists > Networks.
5 Select the network to remove, right-click, and select Remove.
6 Click Yes to confirm.
If you have not removed the cluster that uses the network, you receive an error message indicating that
the network cannot be removed because it is currently in use.
The network is removed, and the IP addresses are available for use.
94 VMware, Inc.
Page 95

Creating Hadoop and HBase Clusters 9
Big Data Extensions you can create and deploy Hadoop and HBase clusters. A big data cluster is a type of
computational cluster designed for storing and analyzing large amounts of unstructured data in a
distributed computing environment.
Restrictions
When you create an HBase only cluster, you must use the default application manager because the
n
other application managers do not support HBase only clusters.
You cannot rename a cluster that was created with Cloudera Manager or Ambari application manager.
n
Temporarily powering off hosts will cause Big Data clusters to fail during cluster creation.
n
When creating Big Data clusters, Big Data Extensions calculates virtual machine placement according to
available resources, Hadoop best practices, and user defined placement policies prior to creating the
virtual machines. When performing placement calculations, if some hosts are powered off or set to
stand-by, either manually, or automatically by VMware Distributed Power Management (VMware
DPM), those hosts will not be considered as available resources when Big Data Extensions calculates
virtual machine placement for use with a Big Data cluster.
If a host is powered off or set to stand-by after Big Data Extensions calculates virtual machine
placement, but before it creates the virtual machines, the cluster fails to create until you power on those
hosts. The following workarounds can help you both prevent and recover from this issue.
Disable VMware DPM on those vSphere clusters where you deploy and run Big Data Extensions.
n
Put hosts in maintenance mode before you power them off.
n
If a Big Data cluster fails to create due to its assigned hosts being temporarily unavailable, resume
n
the cluster creation after you power-on the hosts.
Requirements
The resource requirements are different for clusters created with the Serengeti Command-Line Interface and
the Big Data Extensions plug-in for the vSphere Web Client because the clusters use different default
templates. The default clusters created by using the Serengeti CLI are targeted for Project Serengeti users
and proof-of-concept applications, and are smaller than the Big Data Extensions plug-in templates, which
are targeted for larger deployments for commercial use.
VMware, Inc.
95
Page 96

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Some deployment configurations require more resources than other configurations. For example, if you
create a Greenplum HD 1.2 cluster, you cannot use the small size virtual machine. If you create a default
MapR or Greenplum HD cluster by using the Serengeti CLI, at least 550 GB of storage and 55 GB of memory
are recommended. For other Hadoop distributions, at least 350 GB of storage and 35 GB of memory are
recommended.
CAUTION When you create a cluster with Big Data Extensions, Big Data Extensions disables the virtual
machine automatic migration on the cluster. Although this prevents vSphere from automatically migrating
the virtual machines, it does not prevent you from inadvertently migrating cluster nodes to other hosts by
using the vCenter Server user interface. Do not use the vCenter Server user interface to migrate clusters.
Performing such management functions outside of the Big Data Extensions environment can make it
impossible for you to perform some Big Data Extensions operations, such as disk failure recovery.
Passwords must be from 8 to 20 characters, use only visible lowerASCII characters (no spaces), and must
contain at least one uppercase alphabetic character (A - Z), at least one lowercase alphabetic character (a - z),
at least one digit (0 - 9), and at least one of the following special characters: _, @, #, $, %, ^, &, *
This chapter includes the following topics:
“About Hadoop and HBase Cluster Deployment Types,” on page 97
n
“Hadoop Distributions Supporting MapReduce v1 and MapReduce v2 (YARN),” on page 97
n
“About Cluster Topology,” on page 98
n
“About HBase Database Access,” on page 98
n
“Create a Big Data Cluster in the vSphere Web Client,” on page 99
n
“Create an HBase Only Cluster in Big Data Extensions,” on page 102
n
“Create a Cluster with an Application Manager by Using the vSphere Web Client,” on page 104
n
“Create a Compute-Only Cluster with a Third Party Application Manager by Using vSphere Web
n
Client,” on page 105
“Create a Compute Workers Only Cluster by Using the vSphere Web Client,” on page 105
n
96 VMware, Inc.
Page 97

Chapter 9 Creating Hadoop and HBase Clusters
About Hadoop and HBase Cluster Deployment Types
With Big Data Extensions, you can create and use several types of big data clusters.
Basic Hadoop Cluster
HBase Cluster
Data and Compute
Separation Cluster
Compute Only Cluster
Compute Workers Only
Cluster
HBase Only Cluster
Simple Hadoop deployment for proof of concept projects and other smallscale data processing tasks. The Basic Hadoop cluster contains HDFS and the
MapReduce framework. The MapReduce framework processes problems in
parallel across huge datasets in the HDFS.
Runs on top of HDFS and provides a fault-tolerant way of storing large
quantities of sparse data.
Separates the data and compute nodes, or clusters that contain compute
nodes only. In this type of cluster, the data node and compute node are not
on the same virtual machine.
You can create a cluster that contain only compute nodes, for example
Jobtracker, Tasktracker, ResourceManager and NodeManager nodes, but not
Namenode and Datanodes. A compute only cluster is used to run
MapReduce jobs on an external HDFS cluster.
Contains only compute worker nodes, for example, Tasktracker and
NodeManager nodes, but not Namenodes and Datanodes. A compute
workers only cluster is used to add more compute worker nodes to an
existing Hadoop cluster.
Contains HBase Master, HBase RegionServer, and Zookeeper nodes, but not
Namenodes or Datanodes. Multiple HBase only clusters can use the same
external HDFS cluster.
Customized Cluster
Uses a cluster specification file to create clusters using the same
configuration as your previously created clusters. You can edit the cluster
specification file to customize the cluster configuration.
Hadoop Distributions Supporting MapReduce v1 and MapReduce v2 (YARN)
If you use either Cloudera CDH4 or CDH5 Hadoop distributions, which support both MapReduce v1 and
MapReduce v2 (YARN), the default Hadoop cluster configurations are different. The default hadoop cluster
configuration for CDH4 is a MapReduce v1 cluster. The default hadoop cluster configuration for CDH5 is a
MapReduce v2 cluster. All other distributions support either MapReduce v1 or MapReduce v2 (YARN), but
not both.
VMware, Inc. 97
Page 98
VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
About Cluster Topology
You can improve workload balance across your cluster nodes, and improve performance and throughput,
by specifying how Hadoop virtual machines are placed using topology awareness. For example, you can
have separate data and compute nodes, and improve performance and throughput by placing the nodes on
the same set of physical hosts.
To get maximum performance out of your big data cluster, configure your cluster so that it has awareness of
the topology of your environment's host and network information. Hadoop performs better when it uses
within-rack transfers, where more bandwidth is available, to off-rack transfers when assigning MapReduce
tasks to nodes. HDFS can place replicas more intelligently to trade off performance and resilience. For
example, if you have separate data and compute nodes, you can improve performance and throughput by
placing the nodes on the same set of physical hosts.
CAUTION When you create a cluster with Big Data Extensions, Big Data Extensions disables the virtual
machine automatic migration of the cluster. Although this prevents vSphere from migrating the virtual
machines, it does not prevent you from inadvertently migrating cluster nodes to other hosts by using the
vCenter Server user interface. Do not use the vCenter Server user interface to migrate clusters. Performing
such management functions outside of the Big Data Extensions environment might break the placement
policy of the cluster, such as the number of instances per host and the group associations. Even if you do not
specify a placement policy, using vCenter Server to migrate clusters can break the default ROUNDROBIN
placement policy constraints.
You can specify the following topology awareness configurations.
Hadoop Virtualization
Extensions (HVE)
RACK_AS_RACK
HOST_AS_RACK
None
Enhanced cluster reliability and performance provided by refined Hadoop
replica placement, task scheduling, and balancer policies. Hadoop clusters
implemented on a virtualized infrastructure have full awareness of the
topology on which they are running when using HVE.
To use HVE, your Hadoop distribution must support HVE and you must
create and upload a topology rack-hosts mapping file.
Standard topology for Apache Hadoop distributions. Only rack and host
information are exposed to Hadoop. To use RACK_AS_RACK, create and
upload a server topology file.
Simplified topology for Apache Hadoop distributions. To avoid placing all
HDFS data block replicas on the same physical host, each physical host is
treated as a rack. Because data block replicas are never placed on a rack, this
avoids the worst case scenario of a single host failure causing the complete
loss of any data block.
Use HOST_AS_RACK if your cluster uses a single rack, or if you do not have
rack information with which to decide about topology configuration options.
No topology is specified.
About HBase Database Access
Serengeti supports several methods of HBase database access.
Log in to the client node virtual machine and run hbase shell commands.
n
Log in to the client node virtual machine and run HBase jobs by using the hbase command.
n
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.PerformanceEvaluation –-nomapred randomWrite 3
98 VMware, Inc.
Page 99

Chapter 9 Creating Hadoop and HBase Clusters
The default Serengeti-deployed HBase cluster does not contain Hadoop JobTracker or Hadoop
TaskTracker daemons. To run an HBase MapReduce job, you must deploy a customized cluster that
includes JobTracker and TaskTracker nodes.
Use the client node Rest-ful Web Services, which listen on port 8080, by using the curl command.
n
curl –I http://client_node_ip:8080/status/cluster
Use the client node Thrift gateway, which listens on port 9090.
n
Create a Big Data Cluster in the vSphere Web Client
After you complete deployment of the Hadoop distribution, you can create big data clusters to process data.
You can create multiple clusters in your Big Data Extensions environment but your environment must meet
all prerequisites and have adequate resources.
Prerequisites
Start the Big Data Extensions vApp.
n
Install theBig Data Extensions plug-in.
n
Connect to a Serengeti Management Server.
n
Configure one or more Hadoop distributions.
n
Understand the topology configuration options that you want to use with your cluster.
n
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to vCenter Server.
2 Select Big Data Extensions > Big Data Clusters.
3 In the Objects tab, click New Big Data Cluster.
4 Follow the prompts to create the new cluster. The table describes the information to enter for the cluster
that you want to create.
Option Description
Hadoop cluster name
Application manager
Node template
Hadoop distro
Type a name to identify the cluster.
The only valid characters for cluster names are alphanumeric and
underscores. When you choose the cluster name, also consider the
applicable vApp name. Together, the vApp and cluster names must be < 80
characters.
Select an application manager. The list contains the default application
manager and the application managers that you added to your Big Data
Extensions environment. For example, Cloudera Manager and Ambari.
Select a node template. The list contains all templates available in the
Big Data Extensions vApp.
Select the Hadoop distribution. The list contains the default Apache Bigtop
distribution for Big Data Extensions and the distributions that you added
to your Big Data Extensions environment. The distribution names match
the value of the --name parameter that was passed to the config-
distro.rb script when the Hadoop distribution was configured. For
example, cdh5 and mapr.
NOTE To create an Apache Bigtop, Cloudera CDH4 and CDH5,
Hortonworks HDP 2.x, or Pivotal PHD 1.1 or later cluster, you must
configure a valid DNS and FQDN for the cluster's HDFS and MapReduce
network traffic. If the DNS server cannot provide valid forward and
reverse FQDN/IP resolution, the cluster creation process might fail or the
cluster is created but does not function.
VMware, Inc. 99
Page 100

VMware vSphere Big Data Extensions Administrator's and User's Guide
Option Description
Local repository URL
Type a local repository URL. This is an optional item for all of application
managers. If you specify a local repository URL, the Cloudera Manager or
Ambari application manager downloads the required Red Hat Package
Managers (RPMs) from the local repository that you specify instead of
from a remote repository, which could affect your system performance.
Deployment type
Select the type of cluster you want to create.
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
The type of cluster you create determines the available node group
selections.
If you select Customize, you can load an existing cluster specification file.
DataMaster Node Group
The DataMaster node is a virtual machine that runs the Hadoop
NameNode service. This node manages HDFS data and assigns tasks to
Hadoop TaskTracker services deployed in the worker node group.
Select a resource template from the drop-down menu, or select Customize
to customize a resource template.
For the master node, use shared storage so that you protect this virtual
machine with vSphere HA and vSphere FT.
ComputeMaster Node Group
The ComputeMaster node is a virtual machine that runs the Hadoop
JobTracker service. This node assigns tasks to Hadoop TaskTracker
services deployed in the worker node group.
Select a resource template from the drop-down menu, or select Customize
to customize a resource template.
For the master node, use shared storage so that you protect this virtual
machine with vSphere HA and vSphere FT.
HBaseMaster Node Group (HBase
cluster only)
The HBaseMaster node is a virtual machine that runs the HBase master
service. This node orchestrates a cluster of one or more RegionServer slave
nodes.
Select a resource template from the drop-down menu, or select Customize
to customize a resource template.
For the master node, use shared storage so that you protect this virtual
machine with vSphere HA and vSphere FT.
Worker Node Group
Worker nodes are virtual machines that run the Hadoop DataNode,
TaskTracker, and HBase HRegionServer services. These nodes store HDFS
data and execute tasks.
Select the number of nodes and the resource template from the drop-down
menu, or select Customize to customize a resource template.
For worker nodes, use local storage.
NOTE You can add nodes to the worker node group by using Scale Out
Cluster. You cannot reduce the number of nodes.
Client Node Group
A client node is a virtual machine that contains Hadoop client components.
From this virtual machine you can access HDFS, submit MapReduce jobs,
run Pig scripts, run Hive queries, and HBase commands.
Select the number of nodes and a resource template from the drop-down
menu, or select Customize to customize a resource template.
NOTE You can add nodes to the client node group by using Scale Out
Cluster. You cannot reduce the number of nodes.
Basic Hadoop Cluster
Basic HBase Cluster
Compute Only Hadoop Cluster
Compute Workers Only Cluster
HBase Only Cluster
Data/Compute Separation Hadoop Cluster
Customized
100 VMware, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...