Page 1

175i
TRANSMIG
MULTI PROCESS WELDING
INVERTER
Operating Manual
Revision: AD Issue Date: January 7, 2013 Manual No.: 0-5143
Operating Features:
A-09519
Page 2
WE APPRECIATE YOUR BUSINESS!
Congratulations on your new Cigweld product. We are proud
to have you as our customer and will strive to provide you with
the best service and reliability in the industry. This product
is backed by our extensive warranty and world-wide service
network. To locate your nearest distributor or service agency call
+1300 654 674, or visit us on the web at www.cigweld.com.au
This Operating Manual has been designed to instruct you on the
correct use and operation of your CIGWELD product. Your satisfaction
with this product and its safe operation is our ultimate concern.
Therefore please take the time to read the entire manual, especially
the Safety Precautions. They will help you to avoid potential hazards
that may exist when working with this product.
YOU ARE IN GOOD COMPANY!
The Brand of Choice for Contractors and Fabricators Worldwide.
CIGWELD is the Market Leading Brand of Arc Welding Products for
Victor Technologies International. We are a mainline supplier to major
welding industry sectors in the Asia Pacific and emerging global
markets including; Manufacturing, Construction, Mining, Automotive,
Engineering, Rural and DIY.
We distinguish ourselves from our competition through marketleading, dependable products that have stood the test of time. We
pride ourselves on technical innovation, competitive prices, excellent
delivery, superior customer service and technical support, together
with excellence in sales and marketing expertise.
Above all, we are committed to develop technologically advanced
products to achieve a safer working environment for industry
operators.
Page 3

!
WARNINGS
Read and understand this entire Manual and your employer’s safety practices before installing,
operating, or servicing the equipment.
While the information contained in this Manual represents the Manufacturer’s best judgement,
the Manufacturer assumes no liability for its use.
Operating Manual Number 0-5143 for:
Cigweld Transmig 175i Inverter Plant (South Pacific) Part Number W1005175
Cigweld Transmig 175i Inverter Power Source (packed) Part Number W1005177
Cigweld Transmig 175i Inverter Plant (Asia) Part Number W1005175M
Published by:
CIGWELD Pty Ltd.
71 Gower Street
Preston, Victoria, Australia, 3072
+61 3 9474 7400 +61 3 9474 7391
www.cigweld.com.au
Copyright 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 by
CIGWELD Pty Ltd.
All rights reserved.
Reproduction of this work, in whole or in part, without written permission of the
publisher is prohibited.
The publisher does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for any
loss or damage caused by any error or omission in this Manual, whether such error
results from negligence, accident, or any other cause.
Publication Date: July 21, 2010
Revision AD Date: January 7, 2013
Record the following information for Warranty purposes:
Where Purchased: ____________________________________
Purchase Date: ____________________________________
Equipment Serial #: ____________________________________
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1:ARC WELDING SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS.............................. 1-1
1.01 Arc Welding Hazards ....................................................................................... 1-1
1.02 Principal Safety Standards .............................................................................. 1-5
1.03 Declaration of Conformity ............................................................................... 1-6
SECTION 2:INTRODUCTION .............................................................................. 2-1
2.01 How To Use This Manual ................................................................................ 2-1
2.02 Equipment Identification ................................................................................. 2-1
2.03 Receipt Of Equipment ..................................................................................... 2-1
2.04 Symbol Chart .................................................................................................. 2-2
2.05 Description ..................................................................................................... 2-3
2.06 User Responsibility ......................................................................................... 2-3
2.07 Transporting Methods ..................................................................................... 2-3
2.08 Packaged Items .............................................................................................. 2-3
2.09 Duty Cycle ....................................................................................................... 2-4
2.10 Specifications ................................................................................................. 2-5
2.11 Options and Accessories ................................................................................ 2-6
SECTION 3:INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP ................................................. 3-1
3.01 Environment ................................................................................................... 3-1
3.02 Location .......................................................................................................... 3-1
3.03 Ventilation ....................................................................................................... 3-1
3.04 Mains Supply Voltage Requirements .............................................................. 3-1
3.05 Electromagnetic Compatibility ........................................................................ 3-1
3.06 Transmig 175i Power Source Controls, Indicators and Features ..................... 3-3
3.07 Attaching the Tweco Professional Fusion Mig Torch (Euro) ............................ 3-9
3.08 Installing Minispool (100mm diameter) ......................................................... 3-9
3.09 Installing Handispool (200mm diameter) ..................................................... 3-10
3.10 Inserting Wire into the Wire Feed Mechanism .............................................. 3-11
3.11 Feed Roller Pressure Adjustment .................................................................. 3-12
3.12 Changing the Feed Roll ................................................................................. 3-12
3.13 Wire Reel Brake ............................................................................................ 3-13
3.14 Shielding Gas Regulator Operating Instructions ........................................... 3-13
3.15 Setup for MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gas Shielded Mig Wire ...................... 3-16
3.16 Setup for MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gasless Mig Wire .............................. 3-17
3.17 Setup for TIG (GTAW) Welding ..................................................................... 3-17
3.18 Setup for Manual Arc (MMAW) Welding ..................................................... 3-19
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 4:BASIC WELDING GUIDE .................................................................... 4-1
4.01 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Basic Welding Technique ............................................... 4-1
4.02 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Welding Troubleshooting ............................................... 4-7
4.03 Stick (MMAW) Basic Welding Technique ...................................................... 4-10
4.04 Stick (MMAW) Welding Troubleshooting ...................................................... 4-22
4.05 TIG (GTAW) Basic Welding Technique .......................................................... 4-24
4.06 TIG (GTAW) Welding Problems ..................................................................... 4-27
SECTION 5:POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE REQUIREMENTS............. 5-1
5.01 Power Source Problems ................................................................................. 5-1
5.02 Routine Service and Calibration Requirements ............................................... 5-2
5.03 Cleaning the Welding Power Source ............................................................... 5-5
5.04 Cleaning the Feed Rolls ................................................................................... 5-5
SECTION 6:KEY SPARE PARTS ........................................................................... 6-1
6.01 Power Source ................................................................................................. 6-1
6.02 Tweco Fusion 250 Mig Torch ......................................................................... 6-2
APPENDIX: TRANSMIG 175i CIRCUIT DIAGRAM ...................................................... A-1
CIGWELD - LIMITED WARRANTY TERMS
TERMS OF WARRANTY – JULY 2010
WARRANTY SCHEDULE – JULY 2010
GLOBAL CUSTOMER SERVICE CONTACT INFORMATION ........................... Inside Rear Cover
Page 6

Page 7
TRANSMIG 175i
!
SECTION 1:
ARC WELDING SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. KEEP CHILDREN
AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS KEEP AWAY UNTIL CONSULTING YOUR DOCTOR. DO NOT LOSE THESE
INSTRUCTIONS. READ OPERATING/INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE INSTALLING, OPERATING OR
SERVICING THIS EQUIPMENT.
Welding products and welding processes can cause serious injury or death, or damage to other equipment or
property, if the operator does not strictly observe all safety rules and take precautionary actions.
Safe practices have developed from past experience in the use of welding and cutting. These practices must be
learned through study and training before using this equipment. Some of these practices apply to equipment
connected to power lines; other practices apply to engine driven equipment. Anyone not having extensive
training in welding and cutting practices should not attempt to weld.
Safe practices are outlined in the Australian Standard AS1674.2-2007 entitled: Safety in welding and allied
processes Part 2: Electrical. This publication and other guides to what you should learn before operating
this equipment are listed at the end of these safety precautions. HAVE ALL INSTALLATION, OPERATION,
MAINTENANCE, AND REPAIR WORK PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED PEOPLE.
1.01 Arc Welding Hazards
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Touching live electrical parts can cause
fatal shocks or severe burns. The electrode
and work circuit is electrically live whenever the output is on. The input power circuit and machine internal circuits are also
live when power is on. In semiautomatic
or automatic wire welding, the wire, wire
reel, drive roll housing, and all metal parts
touching the welding wire are electrically
live. Incorrectly installed or improperly
grounded equipment is a hazard.
1. Do not touch live electrical parts.
2. Wear dry, hole-free insulating gloves and body
protection.
3. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry
insulating mats or covers.
4. Disconnect input power or stop engine before
installing or servicing this equipment. Lock input
power disconnect switch open, or remove line
fuses so power cannot be turned on accidentally.
5. Properly install and ground this equipment according to its Owner’s Manual and national, state, and
local codes.
6. Turn off all equipment when not in use. Disconnect
power to equipment if it will be left unattended or
out of service.
7. Use fully insulated electrode holders. Never dip
holder in water to cool it or lay it down on the
ground or the work surface. Do not touch holders
connected to two welding machines at the same
time or touch other people with the holder or
electrode.
8. Do not use worn, damaged, undersized, or poorly
spliced cables.
9. Do not wrap cables around your body.
10. Ground the workpiece to a good electrical (earth)
ground.
11. Do not touch electrode while in contact with the
work (ground) circuit.
12. Use only well-maintained equipment. Repair or
replace damaged parts at once.
13. In confined spaces or damp locations, do not use a
welder with AC output unless it is equipped with a
voltage reducer. Use equipment with DC output.
14. Wear a safety harness to prevent falling if working
above floor level.
15. Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
Manual 0-5143 1-1 GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 8
TRANSMIG 175i
2. Wear approved safety glasses. Side shields recommended.
WARNING
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin; NOISE
can damage hearing.
Arc rays from the welding process produce
intense heat and strong ultraviolet rays
that can burn eyes and skin. Noise from
some processes can damage hearing.
1. Use a Welding Helmet or Welding Faceshield fitted
with a proper shade of filter (see ANSI Z49.1 and
AS 1674 listed in Safety Standards) to protect your
face and eyes when welding or watching.
Recommended Protective Filters for Electric Welding
Description of Process
Manual Metal Arc Welding - covered
electrodes (MMAW)
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GWAW)
(MIG) other than Aluminium and
Stainless Steel
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
(MIG) Aluminium and Stainless Steel
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
(TIG)
Flux-cored Arc Welding (FCAW) -with
or without shielding gas.
Air - Arc Gouging Less than or equal to 400 12
Plasma - Arc Cutting
Plasma - Arc Spraying
Plasma - Arc Welding
Submerged - Arc Welding
Resistance Welding
Approximate Range of
Welding Current in Amps
Less than or equal to 100 8
Greater than 400 13
Less than or equal to 150 10
Greater than 400 14
Less than or equal to 250 12
Less than or equal to 100 10
Greater than 350 14
Less than or equal to 300 11
Greater than 500 14
Less than or equal to 20 8
3. Use protective screens or barriers to protect others
from flash and glare; warn others not to watch the
arc.
4. Wear protective clothing made from durable,
flame-resistant material (wool and leather) and
foot protection.
5. Use approved ear plugs or ear muffs if noise level
is high.
6. Never wear contact lenses while welding.
Minimum Shade Number of
Filter(s)
100 to 200 10
200 to 300 11
300 to 400 12
150 to 250 11
250 to 300 12
300 to 400 13
250 to 350 13
100 to 200 11
200 to 250 12
250 to 350 13
300 to 400 12
400 to 500 13
50 to 100 10
100 to 400 12
400 to 800 14
—
20 to 100 10
100 to 400 12
400 to 800 14
—
—
Safety Spectacles or eye
15
2(5)
shield
Refer to standard AS/NZS 1338.1:1992 for comprehensive information regarding the above table.
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-2 Manual 0-5143
Page 9
WARNING
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous to
your health.
Welding produces fumes and gases.
Breathing these fumes and gases can be
hazardous to your health.
1. Keep your head out of the fumes. Do not breath
the fumes.
2. If inside, ventilate the area and/or use exhaust at
the arc to remove welding fumes and gases.
3. If ventilation is poor, use an approved air-supplied
respirator.
4. Read the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs)
and the manufacturer’s instruction for metals,
consumables, coatings, and cleaners.
5. Work in a confined space only if it is well ventilated, or while wearing an air-supplied respirator.
Shielding gases used for welding can displace air
causing injury or death. Be sure the breathing air
is safe.
6. Do not weld in locations near degreasing, cleaning,
or spraying operations. The heat and rays of the
arc can react with vapours to form highly toxic
and irritating gases.
TRANSMIG 175i
3. Remove all flammables within 35 ft (10.7 m) of the
welding arc. If this is not possible, tightly cover
them with approved covers.
4. Be alert that welding sparks and hot materials from
welding can easily go through small cracks and
openings to adjacent areas.
5. Watch for fire, and keep a fire extinguisher
nearby.
6. Be aware that welding on a ceiling, floor, bulkhead,
or partition can cause fire on the hidden side.
7. Do not weld on closed containers such as tanks
or drums.
8. Connect work cable to the work as close to the
welding area as practical to prevent welding current from travelling long, possibly unknown paths
and causing electric shock and fire hazards.
9. Do not use welder to thaw frozen pipes.
10. Remove stick electrode from holder or cut off
welding wire at contact tip when not in use.
WARNING
FLYING SPARKS AND HOT METAL can
cause injury.
Chipping and grinding cause flying metal.
As welds cool, they can throw off slag.
7. Do not weld on coated metals, such as galvanized,
lead, or cadmium plated steel, unless the coating
is removed from the weld area, the area is well
ventilated, and if necessary, while wearing an airsupplied respirator. The coatings and any metals
containing these elements can give off toxic fumes
if welded.
WARNING
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
Sparks and spatter fly off from the welding
arc. The flying sparks and hot metal, weld
spatter, hot workpiece, and hot equipment
can cause fires and burns. Accidental contact of electrode or welding wire to metal
objects can cause sparks, overheating,
or fire.
1. Protect yourself and others from flying sparks and
hot metal.
1. Wear approved face shield or safety goggles. Side
shields recommended.
2. Wear proper body protection to protect skin.
WARNING
CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under
high pressure. If damaged, a cylinder can
explode. Since gas cylinders are normally
part of the welding process, be sure to
treat them carefully.
1. Protect compressed gas cylinders from excessive
heat, mechanical shocks, and arcs.
2. Install and secure cylinders in an upright position
by chaining them to a stationary support or equipment cylinder rack to prevent falling or tipping.
3. Keep cylinders away from any welding or other
electrical circuits.
2. Do not weld where flying sparks can strike flammable material.
Manual 0-5143 1-3 GENERAL INFORMATION
4. Never allow a welding electrode to touch any
cylinder.
Page 10
TRANSMIG 175i
!
5. Use only correct shielding gas cylinders,
regulators, hoses, and fittings designed for the
specific application; maintain them and associated
parts in good condition.
6. Turn face away from valve outlet when opening
cylinder valve.
7. Keep protective cap in place over valve except
when cylinder is in use or connected for use.
8. Read and follow instructions on compressed
gas cylinders, associated equipment, and CGA
publication P-1 listed in Safety Standards.
WARNING
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
Moving parts, such as fans, rotors, and belts can cut
fingers and hands and catch loose clothing.
1. Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards closed
and securely in place.
2. Stop engine before installing or connecting unit.
a very large volume of scientific findings based on
experiments at the cellular level and from studies
with animals and people which clearly establish that
low frequency magnetic fields and interact with, and
produce changes in, biological systems. While most
of this work is of very high quality, the results are
complex. Current scientific understanding does not
yet allow us to interpret the evidence in a single coherent framework. Even more frustrating, it does not yet
allow us to draw definite conclusions about questions
of possible risk or to offer clear science-based advice
on strategies to minimize or avoid potential risks.”
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the
following procedures.
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping
them.
2. Arrange cables to one side and away from the
operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cable around the body.
4. Keep welding power source and cables as far away
from body as practical.
3. Have only qualified people remove guards or
covers for maintenance and troubleshooting as
necessary.
4. To prevent accidental starting during servicing,
disconnect negative (-) battery cable from battery.
5. Keep hands, hair, loose clothing, and tools away
from moving parts.
6. Reinstall panels or guards and close doors when
servicing is finished and before starting engine.
WARNING
This product, when used for welding or
cutting, produces fumes or gases which
contain chemicals know to the State of
California to cause birth defects and, in
some cases, cancer. (California Health &
Safety code Sec. 25249.5 et seq.)
NOTE
ABOUT PACEMAKERS:
The above procedures are among those
also normally recommended for pacemaker wearers. Consult your doctor for
complete information.
Considerations About Welding And The
Effects of Low Frequency Electric and
Magnetic Fields
The following is a quotation from the General Conclusions Section of the U.S. Congress, Office of
Technology Assessment, Biological Effects of Power
Frequency Electric & Magnetic Fields - Background
Paper, OTA-BP-E-63 (Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, May 1989): “...there is now
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-4 Manual 0-5143
Page 11

TRANSMIG 175i
1.02 Principal Safety Standards
Safety in Welding and Cutting, ANSI Standard Z49.1, from American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd.,
Miami, FL 33126.
Safety and Health Standards, OSHA 29 CFR 1910, from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government
Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402.
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and Cutting of Containers That Have Held
Hazardous Substances, American Welding Society Standard AWS F4.1, from American Welding Society, 550
N.W. LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL 33126.
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park,
Quincy, MA 02269.
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA Pamphlet P-1, from Compressed Gas Association,
1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Suite 501, Arlington, VA 22202.
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, CSA Standard W117.2, from Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 178 Rexdale Boulevard, Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3.
Safe Practices for Occupation and Educational Eye and Face Protection, ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American
National Standards Institute, 1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018.
Cutting and Welding Processes, NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch
Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
Safety in welding and allied processes Part 1: Fire Precautions, AS 1674.1-1997 from SAI Global Limited,
www.saiglobal.com.
Safety in welding and allied processes Part 2: Electrical, AS 1674.2-2007 from SAI Global Limited, www.
saiglobal.com.
Filters for eye protectors - Filters for protection against radiation generated in welding and allied operations
AS/NZS 1338.1:1992 from SAI Global Limited, www.saiglobal.com.
Manual 0-5143 1-5 GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 12

TRANSMIG 175i
1.03 Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer: CIGWELD
Address: 71 Gower St, Preston
Victoria 3072
Australia
Description of equipment: Welding Equipment (GMAW, FCAW, GTAW, MMAW) including, but not limited to
CIGWELD Transmig 175i Multi Process Welding Inverter and associated accessories.
Serial numbers are unique with each individual piece of equipment and details description, parts used to
manufacture a unit and date of manufacture.
The equipment conforms to all applicable aspects and regulations of the ‘Low Voltage Directive’ (Directive
73/23/EU, as recently changed in Directive 93/68/EU and to the National legislation for the enforcement of
the Directive.
National Standard and Technical Specifications
The product is designed and manufactured to a number of standards and technical requirements among them
are:
• IEC60974-10applicabletoIndustrialEquipment-genericemissionsandregulations.
• AS1674Safetyinweldingandalliedprocesses.
• AS60974.1/IEC60974-1applicabletoweldingequipmentandassociatedaccessories.
Extensive product design verification is conducted at the manufacturing facility as part of the routine design
and manufacturing process, to ensure the product is safe and performs as specified. Rigorous testing is incorporated into the manufacturing process to ensure the manufactured product meets or exceeds all design
specifications.
CIGWELD has been manufacturing and merchandising an extensive equipment range with superior performance,
ultra safe operation and world class quality for more than 30 years and will continue to achieve excellence.
GENERAL INFORMATION 1-6 Manual 0-5143
Page 13
SECTION 2:
!
INTRODUCTION
TRANSMIG 175i
2.01 How To Use This Manual
To ensure safe operation, read the entire manual,
including the chapter on safety instructions and
warnings.
Throughout this manual, the words WARNING,
CAUTION, and NOTE may appear. Pay particular attention to the information provided under these headings. These special annotations are easily recognized
as follows:
WARNING
A WARNING gives information regarding
possible personal injury.
CAUTION
A CAUTION refers to possible equipment
damage.
NOTE
A NOTE offers helpful information concerning certain operating procedures.
Additional copies of this manual may be purchased by
contacting Cigweld at the address and phone number
for your location listed in the inside back cover of this
manual. Include the Owner’s Manual number and
equipment identification numbers.
2.02 Equipment Identification
The unit’s identification number (specification or
part number), model, and serial number usually appear on a nameplate attached to the control panel. In
some cases, the nameplate may be attached to the
rear panel. Equipment which does not have a control
panel such as gun and cable assemblies is identified
only by the specification or part number printed on
the shipping container. Record these numbers on the
bottom of page i for future reference.
2.03 Receipt Of Equipment
When you receive the equipment, check it against
the invoice to make sure it is complete and inspect
the equipment for possible damage due to shipping.
If there is any damage, notify the carrier immediately
to file a claim. Furnish complete information concerning damage claims or shipping errors to the location
in your area listed in the inside back cover of this
manual.
Include all equipment identification numbers as
described above along with a full description of the
parts in error.
Move the equipment to the installation site before
un-crating the unit. Use care to avoid damaging the
equipment when using bars, hammers, etc., to uncrate the unit.
Manual 0-5143 2-1 INTRODUCTION
Page 14
TRANSMIG 175i
Gas Tungsten Arc
Welding (GTAW)
Air Carbon Arc
Cutting (CAC-A)
Constant Current
Constant Voltage
Or Constant Potential
High Te mperature
Fault Indication
Arc Force
Touch Start (GTAW)
Variable Inductance
Voltage Input
Single Phase
Three Phase
Three Phase Static
Frequency ConverterTransformer-Rectifier
Dangerous Voltage
Off
On
Panel/Local
Shielded Metal
Arc Welding (SMAW)
Gas Metal Arc
Welding (GMAW)
Increase/Decrease
Circuit Breaker
AC Auxiliary Power
Remote
Duty Cycle
Percentage
Amperage
Voltage
Hertz (cycles/sec)
Frequency
Negative
Positive
Direct Current (DC)
Protective Earth
(Ground)
Line
Line Connection
Auxiliary Power
Receptacle RatingAuxiliary Power
Art # A-04937
115V 15A
t
t1
t2
%
X
IPM
MPM
t
V
Fuse
Wire Feed Function
Wire Feed Towards
Workpiece With
Output Voltage Off.
Preflow Time
Postflow Time
Spot Time
Spot Weld Mode
Continuous Weld
Mode
Press to initiate wirefeed and
welding, release to stop.
Purging Of Gas
Inches Per Minute
Meters Per Minute
Disturbance In
Ground System
Welding Gun
Burnback Time
Press and hold for preflow, release
to start arc. Press to stop arc, and
hold for preflow.
4 Step Trigger
Operation
2 Step Trigger
Operation
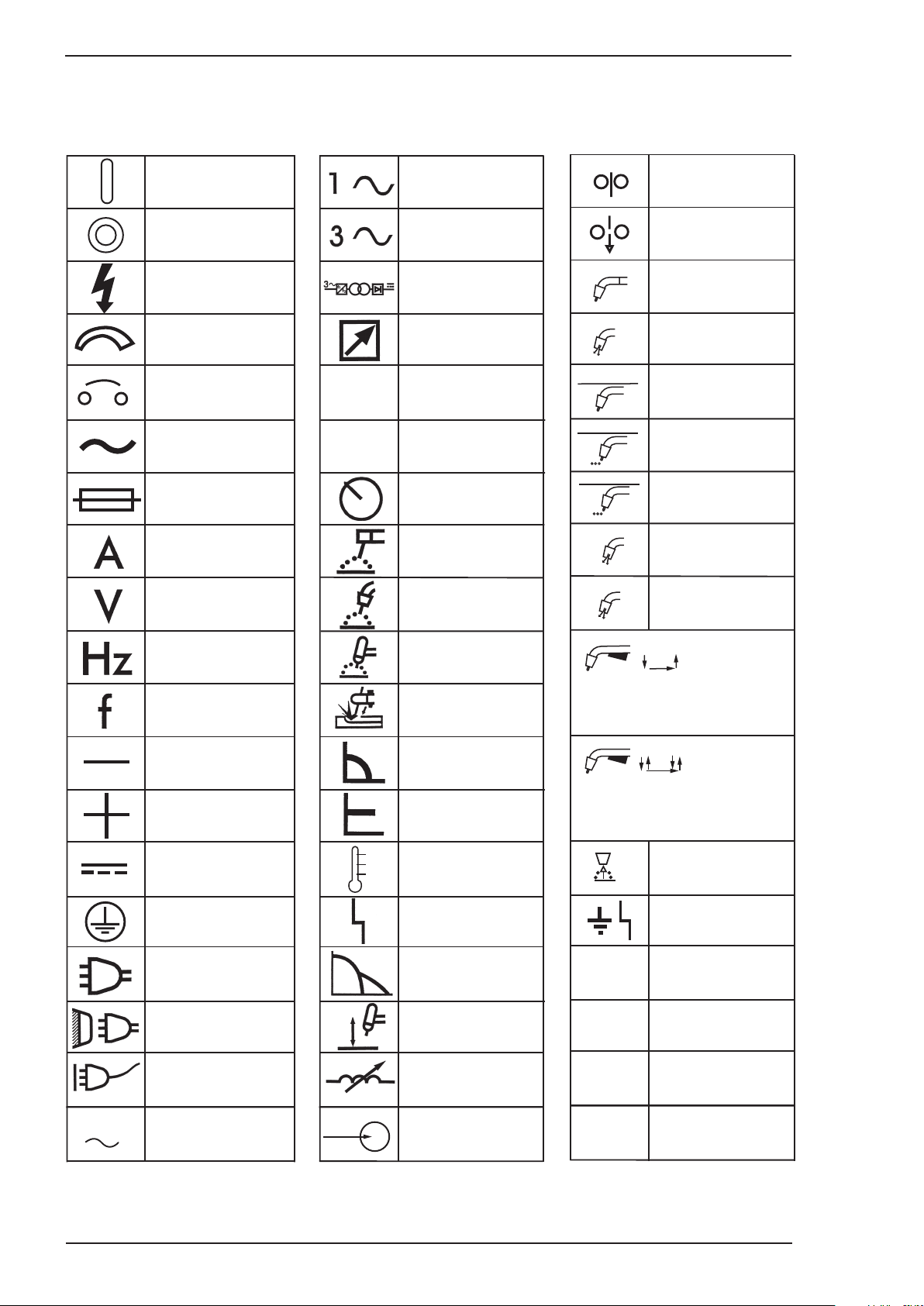
2.04 Symbol Chart
Note that only some of these symbols will appear on your model.
INTRODUCTION 2-2 Manual 0-5143
Page 15
TRANSMIG 175i
!
2.05 Description
The Cigweld Transmig 175i is a self contained single
phase multi process welding inverter that is capable
of performing GMAW/FCAW (MIG), MMAW (Stick)
and GTAW (Lift TIG) welding processes. The unit
is equipped with an integrated wire feed unit, voltage reduction device (VRD applicable in stick mode
only Note; VRD is not fitted to the Asia Version Plant
Part No W1005175M), digital voltage and amperage
meters, and a host of other features in order to fully
satisfy the broad operating needs of the modern welding professional. The unit is also fully compliant to
Australian Standard AS 60974.1 and IEC 60974.1.
The Transmig 175i MIG provides excellent welding
performance across a broad range of applications
when used with the correct welding consumables
and procedures. The following instructions detail how
to correctly and safely set up the machine and give
guidelines on gaining the best efficiency and quality
from the Power Source. Please read these instructions
thoroughly before using the unit.
2.06 User Responsibility
This equipment will perform as per the information
contained herein when installed, operated, maintained
and repaired in accordance with the instructions provided. This equipment must be checked periodically.
Defective equipment (including welding leads) should
not be used. Parts that are broken, missing, plainly
worn, distorted or contaminated, should be replaced
immediately. Should such repairs or replacements
become necessary, it is recommended that such repairs be carried out by appropriately qualified persons
approved by CIGWELD. Advice in this regard can
be obtained by contacting an Accredited CIGWELD
Distributor.
This equipment or any of its parts should not be altered from standard specification without prior written
approval of CIGWELD. The user of this equipment
shall have the sole responsibility for any malfunction
which results from improper use or unauthorized
modification from standard specification, faulty
maintenance, damage or improper repair by anyone
other than appropriately qualified persons approved
by CIGWELD.
2.07 Transporting Methods
This unit is equipped with a handle for carrying
purposes.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill. DO NOT TOUCH
live electrical parts. Disconnect input
power conductors from de-energized
supply line before moving the welding
power source.
WARNING
FALLING EQUIPMENT can cause serious
personal injury and equipment damage.
Lift unit with handle on top of case.
Use handcart or similar device of adequate capacity.
If using a fork lift vehicle, place and secure unit on a
proper skid before transporting.
2.08 Packaged Items
Transmig 175i Plant
• Transmig175iInverterPowerSource
• TwecoFusion250MIGTorch
• CometProfessionalArgonRegulator/Flowmeter
(Not included in Asia Version Plant Part No.
W1005175M)
• Feedrolls:0.6/0.8mmVGroove(tted);
1.0/1.2mm U Groove; 0.8/0.9mm V Knurled
• ContactTips:0.8mm(tted);0.6mm;0.9mm;
1.0mm
• ElectrodeHolderwith4mLead
• WorkClampwith4mLead
• ShieldingGasHoseAssembly
• ShieldingGasAdaptor(SuppliedinAsiaVersion
Part No. W1005175M only)
• ShoulderStrap
• ProductBag
• OperatingManual
Transmig 175i Power Source (Part No. W1005177)
(South Pacific Only)
• Transmig175iInverterPowerSource
• ShieldingGasHoseAssembly
• ShoulderStrap
• OperatingManual
Manual 0-5143 2-3 INTRODUCTION
Page 16
TRANSMIG 175i
A-09520
Duty Cycle (percentage)
Safe
Operating
Region
0
20 40 60
80
100
120 140 160 180
30
50
70
90
40
60
20
10
80 100
0
Welding Current (amps)
Stick (MMAW)
MIG (GMAW)
TIG (GTAW)
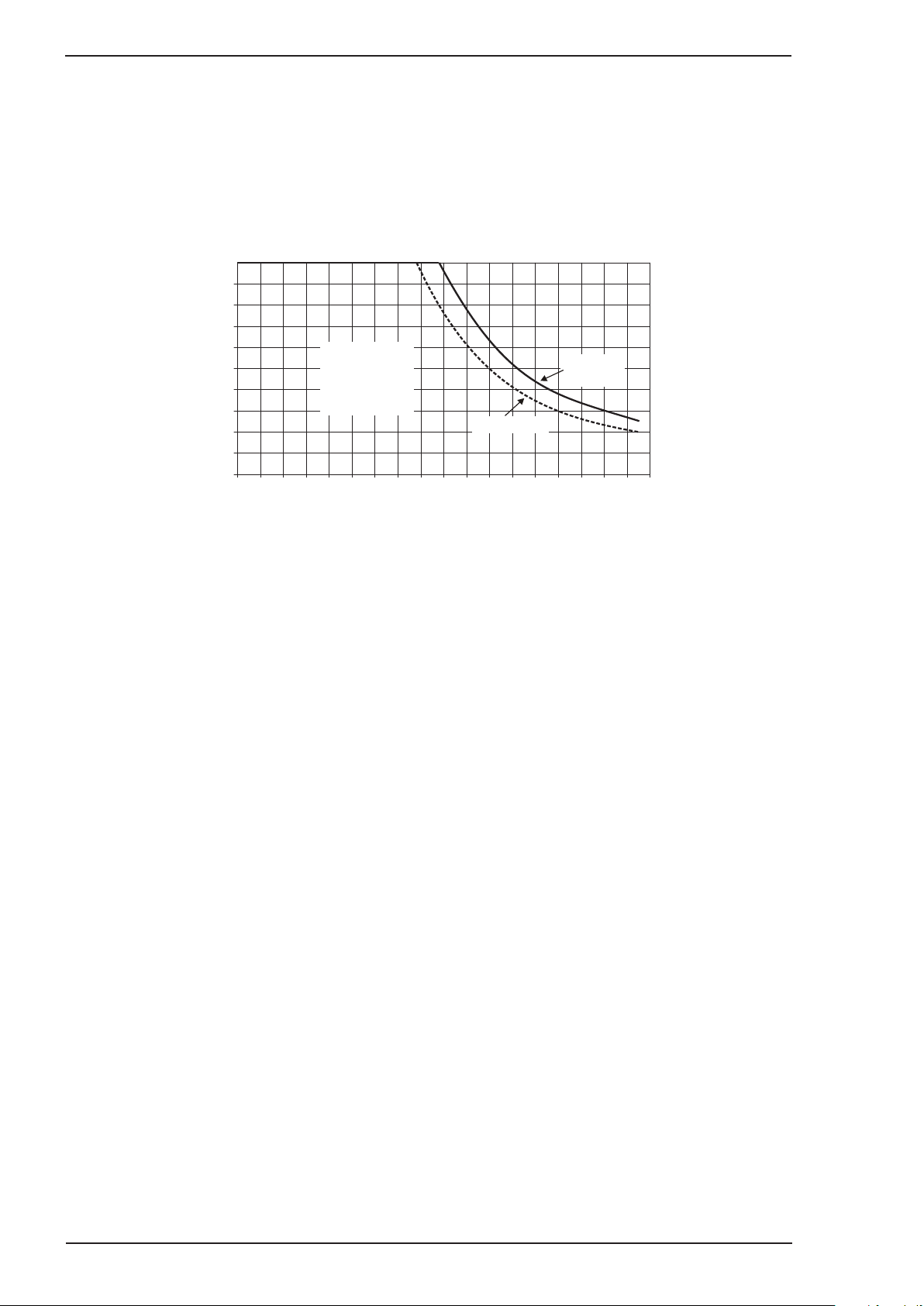
2.09 Duty Cycle
The rated duty cycle of a Welding Power Source, is a statement of the time it may be operated at its rated
welding current output without exceeding the temperature limits of the insulation of the component parts. To
explain the 10 minute duty cycle period the following example is used. Suppose a Welding Power Source is
designed to operate at a 15% duty cycle, 90 amperes at 23.6 volts. This means that it has been designed and
built to provide the rated amperage (90A) for 1.5 minutes, i.e. arc welding time, out of every 10 minute period
(15% of 10 minutes is 1.5 minutes). During the other 8.5 minutes of the 10 minute period the Welding Power
Source must idle and be allowed to cool.
Figure 2-1: Transmig 175i Duty Cycle
INTRODUCTION 2-4 Manual 0-5143
Page 17
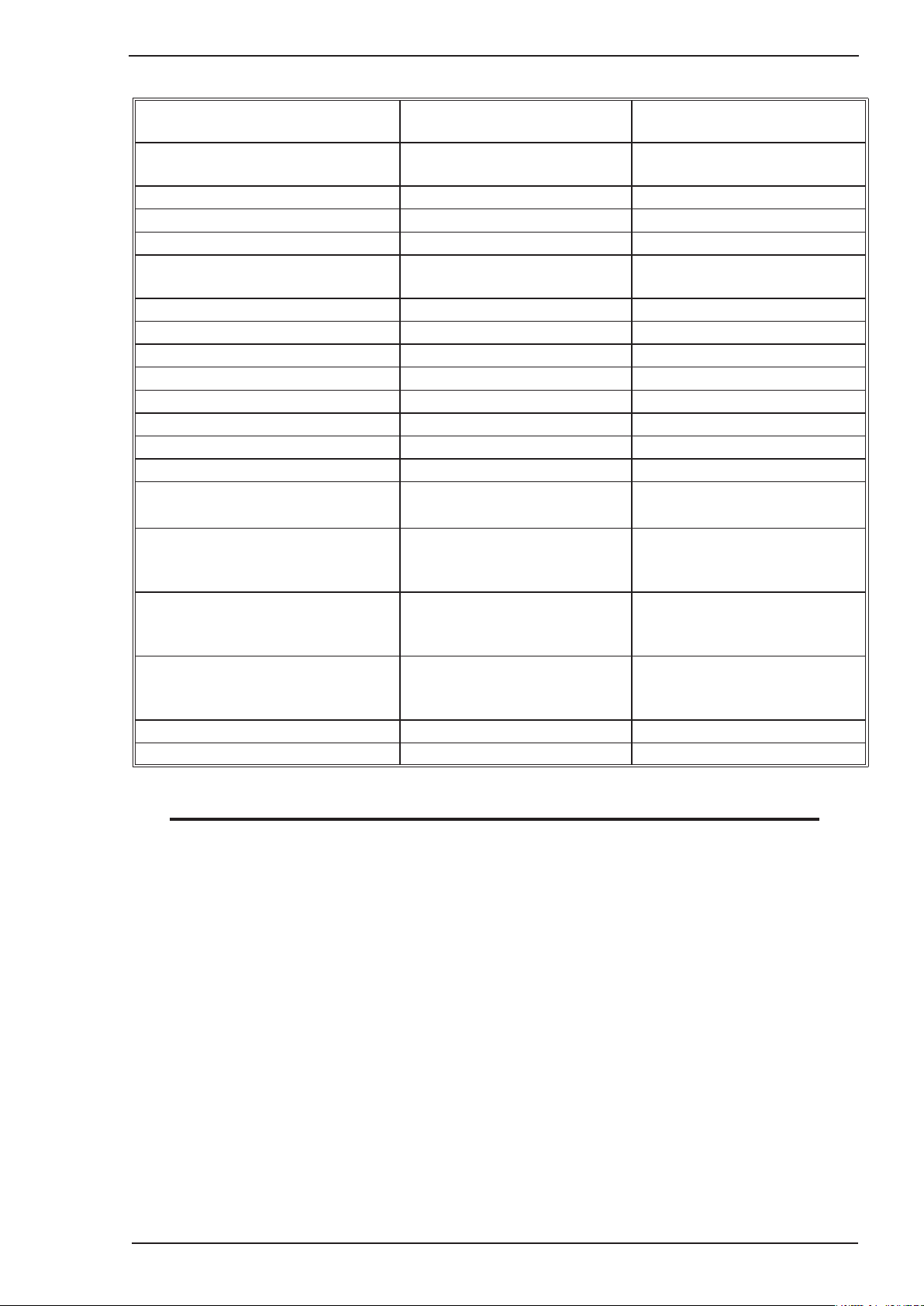
2.10 Specifications
TRANSMIG 175i
Description TRANSMIG 175i
Plant Part Number
Power Source (Packed) Part Number
(South Pacific Version)
W1005175
W1005176
TRANSMIG 175i
(Asia Version)
W1005175M
W1005176M
Power Source Dimensions H410mm x W210mm x D450mm H410mm x W210mm x D450mm
Power Source Mass 14.6kg 14.6kg
Cooling Fan Cooled Fan Cooled
Welder Type Multi Process Inverter Power
Source
Multi Process Inverter Power
Source
Australian Standard AS60974-1 / IEC60974-1 AS60974-1 / IEC60974-1
Number of Phases Single Phase Single Phase
Nominal Supply Voltage 240 VAC ± 15% 240 VAC ± 15%
Nominal Supply Frequency 50 / 60Hz 50 / 60Hz
Welding Current Range (MIG mode) 10 – 175A 10 – 175A
Factory Fitted Supply Plug Rating 15Amps Asian Style Input Plug
1
Effective Input Current (I
Maximum Input Current (I
Minimum Single Phase Generator
Recommendation (refer Note 3)
MIG (GMAW)
Welding Output, 40º C, 10 min.
STICK (MMAW)
Welding Output, 40º C, 10 min.
TIG (GTAW)
Welding Output, 40º C, 10 min.
) 15Amps 15Amps
1eff
) 35.5Amps 35.5Amps
1max
9kVA
[9kVA@0.8PowerFactor]
175A@25%,22.8V
113A @ 60%, 19.7V
88A@100%,18.4V
175A @ 20%, 27.0V
101A @ 60%, 24.0V
78A@100%,23.1V
175A @ 25%, 17.0V
113A @ 60%, 14.5V
88A@100%,13.5V
[9kVA@0.8PowerFactor]
175A@25%,22.8V
113A @ 60%, 19.7V
88A@100%,18.4V
175A @ 20%, 27.0V
101A @ 60%, 24.0V
78A@100%,23.1V
175A @ 25%, 17.0V
113A @ 60%, 14.5V
88A@100%,13.5V
9kVA
Open Circuit Voltage (VRD active) 65V 65V
Protection Class IP23S IP23S
Table 2-1: Transmig 175i Specification
NOTE
Note 1: The Effective Input Current should be used for the determination of cable size & supply
requirements.
Note 2: Motor start fuses or thermal circuit breakers are recommended for this application.
Check local requirements for your situation in this regard.
Note 3: Minimum Generator Recommendation at the Maximum Output Duty Cycle.
Due to large variations in performance and specifications of different brands and types of genera
tors, Cigweld cannot guarantee full welding output power or duty cycle on every brand or type of
generator.
Some small generators incorporate low cost circuit breakers on their outputs. These circuit break
ers usually will have a small reset button, and will trip much faster than a switchboard type circuit
breaker. This may result in not being able to achieve full output or duty cycle from the power source
/ generator combination. For this reason we recommend a generator that incorporates switchboard
type circuit breakers.
In some circumstances, long welds at high welding current may trip the circuit breaker on the
generator.
Cigweld recommends that when selecting a generator, that the particular power source / generator
combination be adequately trialled to ensure the combination performs to the users expectations.
Manual 0-5143 2-5 INTRODUCTION
Page 18
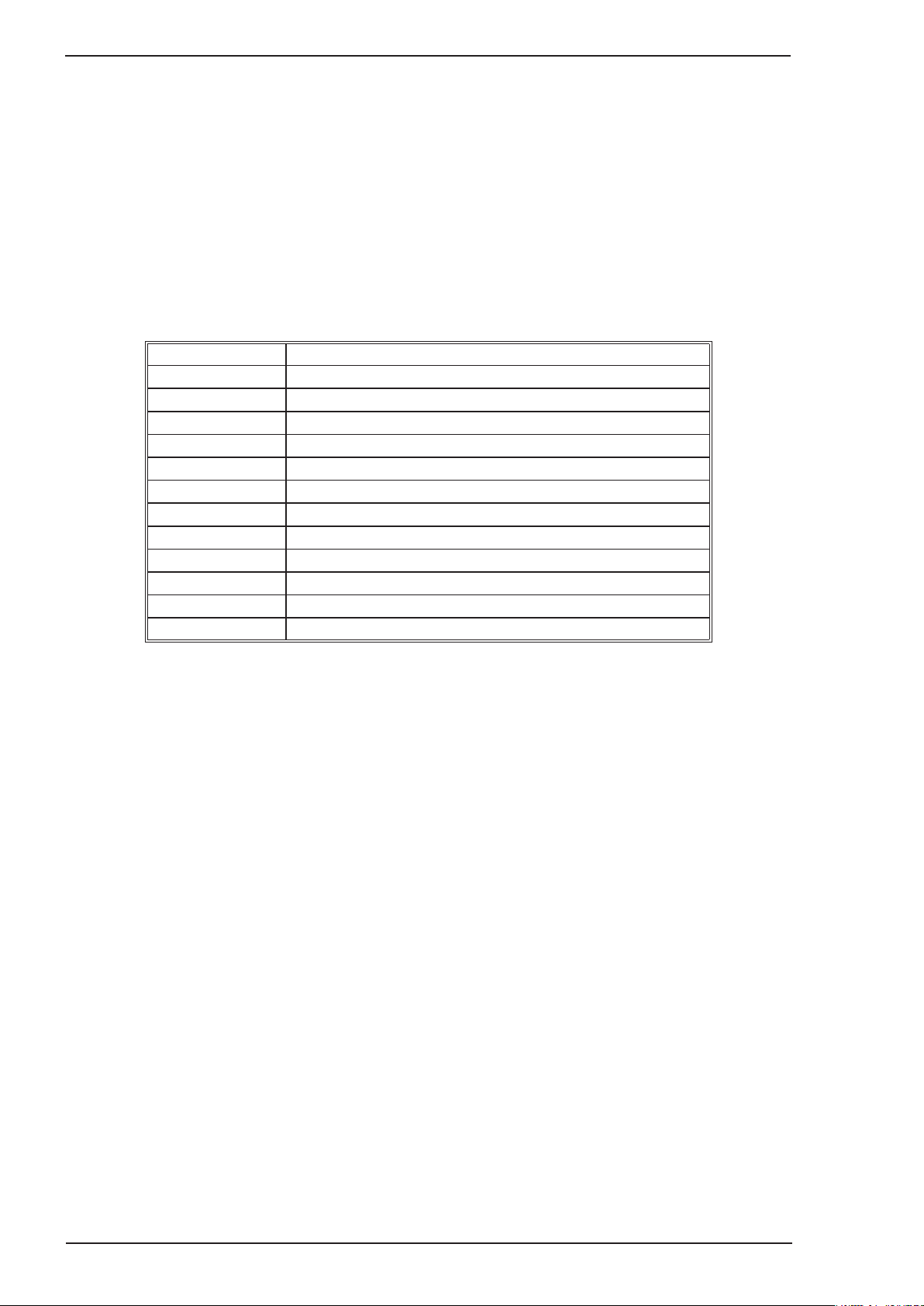
TRANSMIG 175i
Note 4: CIGWELD reserves the right to change product performance and specifications without
notice
Note 5: Transmig 175i Plant Part No. W1005175M (Asia Version) and Transmig 175i Power
Source Part No. W1005176M (Asia Version) are not fitted with a VRD. Additional safety precau
tions may be required when using unit in an environment with increased hazard of electric shock
. Please refer to relevant local standards for further information prior to using in such areas.
-
Note 6: Due to variations that can occur in manufactured products, claimed performance, volt
ages, ratings, all capacities, measurements, dimensions and weights quoted are approximate only.
Achievable capacities and ratings in use and operation will depend upon correct installation, use,
applications, maintenance and service.
2.11 Options and Accessories
Part Number Description
W4013701 Tweco professional Fusion 250A MIG Torch, 3.0 metre EURO
OTWX212/3035 TWECO #2, 250A MIG torch, 3.6 metre EURO
W4013801 TIG Torch 17V with 4m lead
W4013800 TIG Torch 17V with 4m lead and remote control
7977036 FeedRoll0.6/0.8mmVgroove(hard),(tted)
7977660 Feed Roll 0.9/1.2mm V groove (hard)
7977731 FeedRoll0.8/0.9mmUgroove(soft)
7977264 Feed Roll 1.0/1.2mm U groove (soft)
7977732 FeedRoll0.8/0.9mmVgrooveknurled(uxcored)
704277 FeedRoll1.2/1.6mmVgrooveknurled(uxcored)
W7004913 Shielding Gas Hose Assembly
WSPLIER MIG Pliers
Table 2-2: Transmig 175i Optional Accessories
-
INTRODUCTION 2-6 Manual 0-5143
Page 19
TRANSMIG 175i
!
SECTION 3:
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
3.01 Environment
These units are designed for use in environments
with increased hazard of electric shock as outlined in
AS 60974.1 and AS 1674.2. Note the Transmig 175i
Plant Part No. W1005175M (Asia Version) is not
fitted with VRD. Additional safety precautions may
be required when using unit in an environment with
increased hazard of electric shock. Please refer to
relevant local standards for further information prior
to using in such areas.
A. Examples of environments with increased hazard
of electric shock are:
1. In locations in which freedom of movement
is restricted, so that the operator is forced
to perform the work in a cramped (kneeling,
sitting or lying) position with physical contact
with conductive parts.
2. In locations which are fully or partially limited
by conductive elements, and in which there
is a high risk of unavoidable or accidental
contact by the operator.
3. In wet or damp hot locations where humidity
or perspiration considerable reduces the
skin resistance of the human body and the
insulation properties of accessories.
B. Environments with increased hazard of electric
shock do not include places where electrically
conductive parts in the near vicinity of the
operator, which can cause increased hazard, have
been insulated.
G. The enclosure design of this power source meets
the requirements of IP23S as outlined in AS60529.
This provides adequate protection against solid
objects (greater than 12mm), and direct protection
from vertical drops. Under no circumstances
should the unit be operated or connected in a
micro environment that will exceed the stated
conditions. For further information please refer
to AS 60529.
H. Precautions must be taken against the power
source toppling over. The power source must
be located on a suitable horizontal surface in the
upright position when in use.
3.03 Ventilation
Since the inhalation of welding fumes can be harmful,
ensure that the welding area is effectively ventilated.
3.04 Mains Supply Voltage Requirements
The Mains supply voltage should be within ± 15%
of the rated mains supply voltage. Too low a voltage
may cause poor welding performance. Too high a
supply voltage will cause components to overheat
and possibly fail.
The Welding Power Source must be:
• Correctlyinstalled,ifnecessary,byaqualied
electrician.
• Correctlyearthed (electrically)in accordance
with local regulations.
3.02 Location
Be sure to locate the welder according to the following
guidelines:
A. In areas, free from moisture and dust.
B. Ambient temperature between 0° C to 40° C.
C. In areas, free from oil, steam and corrosive
gases.
D. In areas, not subjected to abnormal vibration or
shock.
E. In areas, not exposed to direct sunlight or rain.
F. Place at a distance of 300mm or more from walls
or similar that could restrict natural air flow for
cooling.
Manual 0-5143 3-1 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
• Connectedtothecorrectsizepowerpointand
fuse as per the Specifications on page 2-5.
!
WARNING
Any electrical work must be carried out by
a qualified Electrical Tradesperson.
3.05 Electromagnetic Compatibility
WARNING
Extra precautions for Electromagnetic
Compatibility may be required when
this Welding Power Source is used in a
domestic situation.
Page 20

TRANSMIG 175i
A. Installation and Use - Users Responsibility
The user is responsible for installing and using the
welding equipment according to the manufacturer’s
instructions. If electromagnetic disturbances are
detected then it shall be the responsibility of
the user of the welding equipment to resolve
the situation with the technical assistance of
the manufacturer. In some cases this remedial
action may be as simple as earthing the welding
circuit, see NOTE below. In other cases it could
involve constructing an electromagnetic screen
enclosing the Welding Power Source and the work,
complete with associated input filters. In all cases,
electromagnetic disturbances shall be reduced to
the point where they are no longer troublesome.
NOTE
The welding circuit may or may nor be
earthed for safety reasons. Changing the
earthing arrangements should only be
authorised by a person who is competent
to assess whether the changes will
increase the risk of injury, e.g. by allowing
parallel welding current return paths which
may damage the earth circuits of other
equipment. Further guidance is given in
IEC 60974-13 Arc Welding Equipment Installation and use (under preparation).
B. Assessment of Area
Before installing welding equipment, the user shall
make an assessment of potential electromagnetic
problems in the surrounding area. The following
shall be taken into account
1. Other supply cables, control cables, signalling
and telephone cables; above, below and
adjacent to the welding equipment.
2. Radio and television transmitters and
receivers.
3. Computer and other control equipment.
4. Safety critical equipment, e.g. guarding of
industrial equipment.
5. The health of people around, e.g. the use of
pacemakers and hearing aids.
is compatible: this may require additional
protection measures.
The size of the surrounding area to be considered
will depend on the structure of the building
and other activities that are taking place. The
surrounding area may extend beyond the
boundaries of the premises.
C. Methods of Reducing Electromagnetic
Emissions
1. Mains Supply
Welding equipment should be connected to the
mains supply according to the manufacturer’s
recommendations. If interference occurs,
it may be necessary to take additional
precautions such as filtering of the mains
supply. Consideration should be given to
shielding the supply cable of permanently
installed welding equipment in metallic
conduit or equivalent. Shielding should be
electrically continuous throughout it’s length.
The shielding should be connected to the
Welding Power Source so that good electrical
contact is maintained between the conduit and
the Welding Power Source enclosure.
2. Maintenance of Welding Equipment
The welding equipment should be routinely
maintained according to the manufacturer’s
recommendations. All access and service
doors and covers should be closed and
properly fastened when the welding
equipment is in operation. The welding
equipment should not be modified in any way
except for those changes and adjustments
covered in the manufacturer’s instructions. In
particular, the spark gaps of arc striking and
stabilising devices should be adjusted and
maintained according to the manufacturer’s
recommendations.
3. Welding Cables
The welding cables should be kept as short
as possible and should be positioned close
together, running at or close to the floor
level.
6. Equipment used for calibration and
measurement.
7. The time of day that welding or other activities
are to be carried out.
8. The immunity of other equipment in the
environment: the user shall ensure that other
equipment being used in the environment
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-2 Manual 0-5143
4. Equipotential Bonding
Bonding of all metallic components in the
welding installation and adjacent to it should
be considered. However. Metallic components
bonded to the work piece will increase the
risk that the operator could receive a shock
by touching the metallic components and
Page 21
TRANSMIG 175i
the electrode at the same time. The operator should be insulated from all such bonded metallic
components.
5. Earthing of the Workpiece
Where the workpiece is not bonded to earth for electrical safety, nor connected to earth because of it’s
size and position, e.g. ship’s hull or building steelwork, a connection bonding the workpiece to earth
may reduce emissions in some, but not all instances. Care should be taken to prevent the earthing of
the workpiece increasing the risk of injury to users, or damage to other electrical equipment. Where
necessary, the connection of the workpiece to earth should be made by direct connection to the
workpiece, but in some countries where direct connection is not permitted, the bonding should be
achieved by suitable capacitance, selected according to national regulations.
6. Screening and Shielding
Selective screening and shielding of other cables and equipment in the surrounding area may alleviate
problems of interference. Screening the entire welding installation may be considered for special
applications.
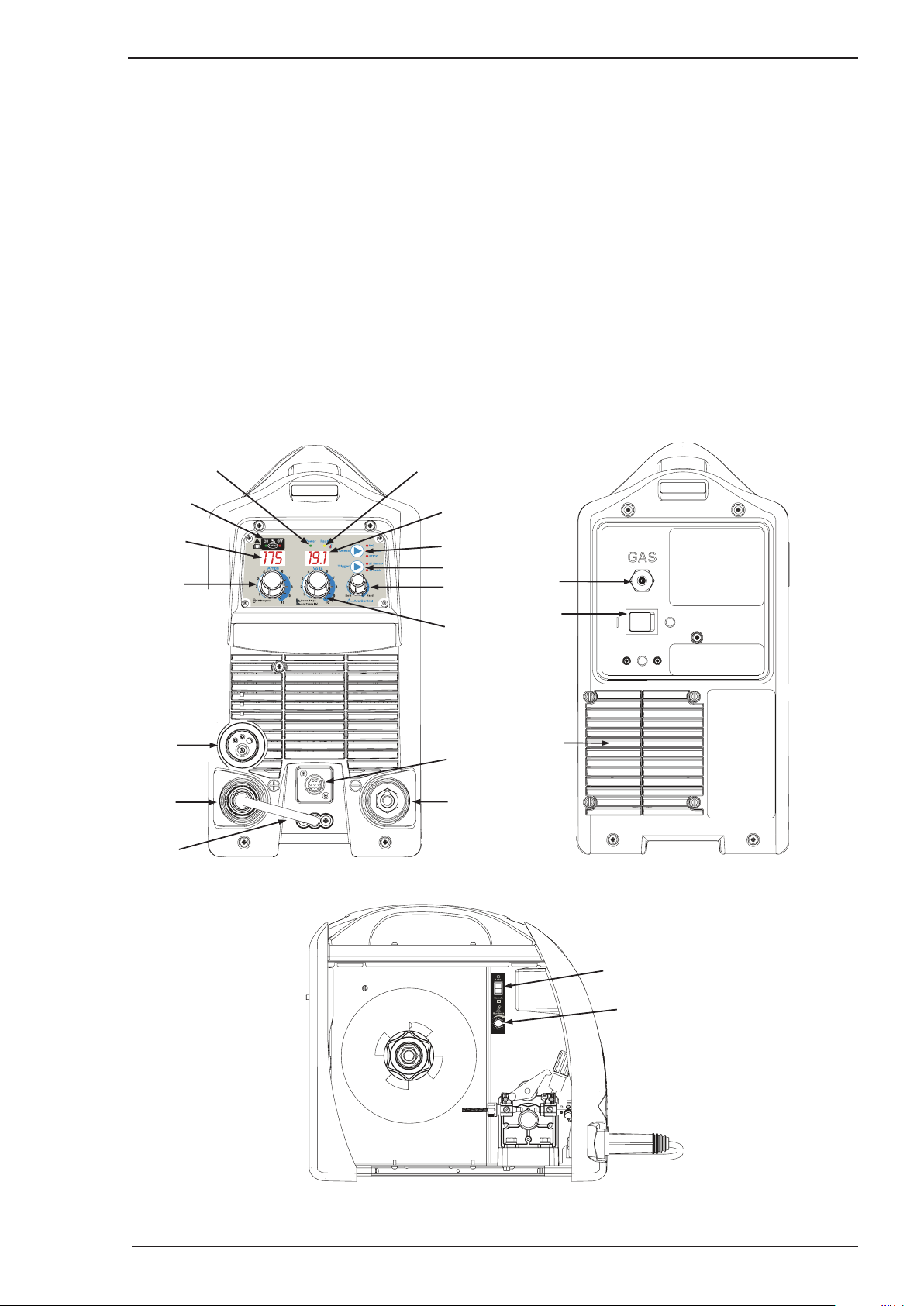
3.06 Transmig 175i Power Source Controls, Indicators and Features
A-09592
1
15
5
6
7
4
2
3
14
13
12
11
16
17
10
9
20
8
A-09591
Figure 3-1: Front Panel
Figure 3-2: Rear Panel
A-09593
18
19
Figure 3-3: Wire Feed Compartment Control
Manual 0-5143 3-3 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Page 22
TRANSMIG 175i
!
1. Power Indicator
The power indicator is illuminated when the correct mains power is applied to the power source and when
the ON/OFF switch located on the rear panel is in the ON position.
2. VRD ON/OFF Indicator Lights (South Pacific Version Only)
WARNING
VRD is NOT fitted to Transmig 175i (Asia Version) Plant Part No W1005175M.
A VRD (voltage reduction device) is a hazard reducing device designed to reduce electric shock hazards
present on the output of welding power source when operating in MMAW (stick) mode. Note that the
presence of VRD should not be used as a substitute for the use of appropriate safety practices as indicated
in section one of this manual.
Both the green and red indicator lights only operate in MMAW (stick) mode.
The green VRD ON light illuminates (red light is off) when the VRD is active. Under this condition the open
circuit voltage of the unit is limited to below 35V DC, thus reducing the potential of serious electric shock
(such as when changing electrodes).
The red VRD OFF light illuminates (green light is off) when the VRD is inactive. Under this condition the
output voltage of the unit will be at welding potential which in some cases may exceed 35V DC.
3. Digital Amps Meter
The digital amperage meter is used to display both the pre-set current (Stick and TIG modes only) and
actual output current (all modes) of the power source.
At times of non-welding, the amperage meter will display a pre-set (preview) value in both MMAW (Stick)
and GTAW (TIG) modes. This value can be adjusted by varying the amperage potentiometer (item 4). Note
that in GMAW/FCAW (MIG) mode, the amperage meter will not preview welding current and will display
zero.
When welding, the amperage meter will display actual welding current in all modes.
At the completion of welding, the amperage meter will hold the last recorded amperage value for a period
of approximately 10 seconds in all modes. The amperage meter will hold the value until; (1) any of the front
panel controls are adjusted in which case the unit will revert to preview mode, (2) welding is recommenced,
in which case actual welding amperage will be displayed, or (3) a period of 10 seconds elapses following
the completion of welding in which case the unit will return to preview mode.
4. Amperage Control (Wirespeed)
The amperage control knob adjusts the amount of welding current delivered by the power source. In
MMAW (stick) and GTAW (TIG) modes, the amperage control knob directly adjusts the power inverter to
deliver the desired level of output current. In GMAW/FCAW modes (MIG), the amperage knob adjusts the
speed of the wire feed motor (which in turn adjusts the output current by varying the amount of MIG wire
delivered to the welding arc). The optimum wire speed required will dependent on the type of welding
application. The setup chart on the inside of the wire feed compartment door provides a brief summary
of the required output settings for a basic range of MIG welding applications.
5. MIG Torch Adaptor (Euro Style)
The MIG torch adaptor is the connection point for the MIG welding torch. Connect the torch by pushing
the torch connector into the brass torch adaptor firmly and screwing the plastic torch nut clockwise to
secure in position. To remove the MIG Torch simply reverse these directions.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-4 Manual 0-5143
Page 23
TRANSMIG 175i
6. Positive Welding Output Terminal
The positive welding terminal is used to connect the welding output of the power source to the appropriate
welding accessory such as the MIG torch (via the MIG torch polarity lead), electrode holder lead or work
lead. Positive welding current flows from the power source via this heavy duty bayonet type terminal.
It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical
connection.
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused
in the bayonet terminal.
7. MIG Torch Polarity Lead
The polarity lead is used to connect the MIG torch to the appropriate positive or negative output terminal
(allowing polarity reversal for different welding applications). In general, the polarity lead should be
connected in to the positive welding terminal (+) when using steel, stainless steel or aluminium electrode
wire. When using gasless wire, the polarity lead is generally connected to the negative welding terminal (-).
If in doubt, consult the manufacturer of the electrode wire for the correct polarity. It is essential, however,
that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused
in the bayonet terminal.
8. Negative Welding Output Terminal
The negative welding terminal is used to connect the welding output of the power source to the appropriate
welding accessory such as the MIG torch (via the MIG torch polarity lead), TIG torch or work lead. Negative
welding current flows to the power source via this heavy duty bayonet type terminal. It is essential, however,
that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused
in the bayonet terminal.
Manual 0-5143 3-5 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Page 24
TRANSMIG 175i
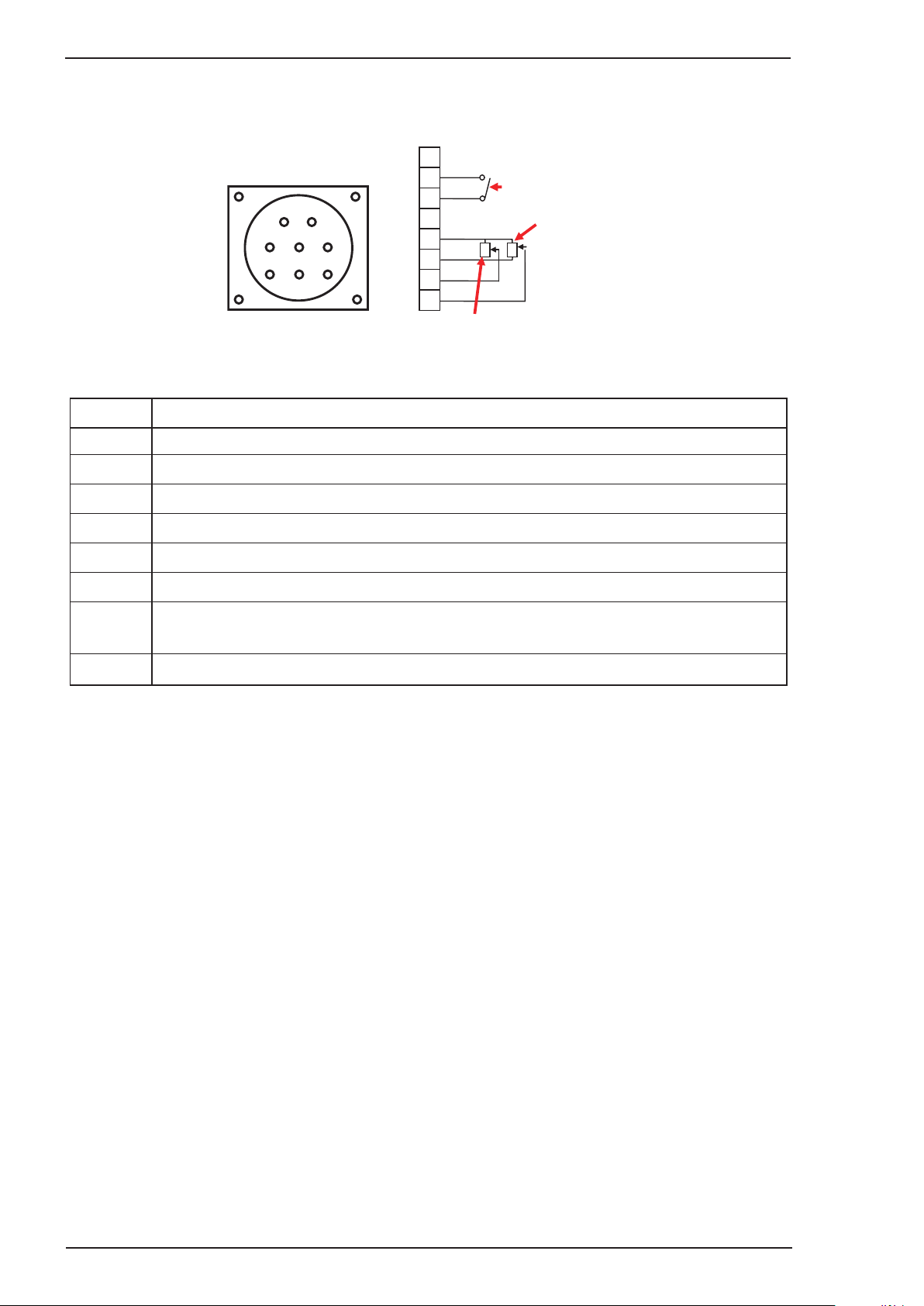
9. Remote Control Socket
The 8 pin Remote Control Socket is used to connect remote control devices to the welding power source.
To make connections, align keyway, insert plug, and rotate threaded collar fully clockwise.
1
A-09594
2
1
2
5
8
3
4
6
7
3
4
5
6
7
8
Figure 3-4: Remote Control Socket
Trigger Switch
W
V
Remote Wirespeed in GMAW mode
Remote Amps in GTAW mode
Remote Volts in
GMAW Mode
Socket Pin
Function
1 Not connected
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Trigger Switch Input
Trigger Switch Input
Not connected
5k ohm (maximum) connection to 5k ohm remote control potentiometer.
Zero ohm (minimum) connection to 5k ohm remote control potentiometer.
Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm remote control Wirespeed GMAW (MIG) mode potentiometer.
Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm remote control Amps GTAW (TIG) mode potentiometer.
Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm remote control Volts GMAW (MIG) mode potentiometer.
Table 3-1
Note that the remote local switch (item 18) located in the wirefeed compartment should be set to remote
for the amperage/voltage controls to be operative.
10. Multifunction Control - Voltage, Down Slope & Arc Force
The multifunction control knob is used to adjust three main parameters depending on the welding mode
selected.
When GMAW/FCAW (MIG) Mode is Selected
In this mode the control knob is used to adjust the output voltage of the unit. The welding voltage is
increased by turning the knob clockwise or decreased by turning the knob anti-clockwise. The optimum
voltage level required will dependent on the type of welding application. The setup chart on the inside
of the wire feed compartment door provides a brief summary of the required output settings for a basic
range of MIG welding applications.
When MMAW (Stick) Mode is Selected
In this mode the multifunction control knob is used to adjust arc force. Arc force control provides an
adjustable amount of welding force (or “dig”) control. This feature can be particularly beneficial in
providing the operator the ability to compensate for variability in joint fit-up in certain situations with
particular electrodes. In general increasing the arc force control toward ‘10’ (maximum arc force) allows
greater penetration control to be achieved. Arc force is increased by turning the control knob clockwise
or decreased by turning the knob anti-clockwise
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-6 Manual 0-5143
Page 25

TRANSMIG 175i
When TIG Mode is Selected
In this mode the multifunction control knob is used to adjust down slope. Down slope allows the user
to select the ramp down time at the completion of the weld. The main function of down slope is to allow
the welding current to be gradually reduced over a pre-set time frame such that the welding pool is given
time to cool sufficiently.
Note that when in 2T normal mode (refer item 12), the unit will enter down slope mode as soon as the
trigger switch is released (ie if the multifunction control knob is set to 5, the unit will ramp down from
the present welding current to zero over 5 seconds). If no down slope time is selected then the welding
output will cease immediately. If the unit is set to 4T latch mode, to enter down slope mode the trigger
must be held in for the selected time period (ie press and release trigger to commence welding, then press
and hold trigger again to enter down slope mode). Should the trigger be released during the down slope
phase (4T only), the output will cease immediately.
11. Arc Control (Inductance)
The arc control operates in GMAW (MIG) mode only and is used to adjust the intensity of the welding arc.
Lower arc control settings make the arc softer with less weld spatter. Higher arc control settings give a
stronger driving arc which can increase weld penetration.
12. Trigger Mode Control (MIG and TIG Mode only)
The trigger mode control is used to switch the functionality of the of the torch trigger between 2T (normal)
and 4T (latch mode)
2T Normal Mode
In this mode, the torch trigger must remain depressed for the welding output to be active. Press and hold
the torch trigger to activate the power source (weld). Release the torch trigger switch to cease welding.
4T Latch Mode
This mode of welding is mainly used for long welding runs to reduce operator fatigue. In this mode the
operator can press and release the torch trigger and the output will remain active. To deactivate the power
source, the trigger switch must again be depressed and realised, thus eliminating the need for the operator
to hold the torch trigger.
Note that when operating in GTAW (TIG mode), the power source will remain activated until the selected
downslope time has elapsed (refer Item 10).
13. Process Selection Control
The process selection control is used to select the desired welding mode. Three modes are available,
GMAW/FCAW (MIG), GTAW (Lift TIG) and (MMAW (Stick) modes. Refer to section 3.15 or 3.16 for
FCAW/GMAW (MIG) set up details, section 3.17 for GTAW (TIG) set-up details or section 3.18 for MMAW
(stick) set-up details.
Note that when the unit is powered off the mode selection control will automatically default to MIG mode.
This is necessary so as to prevent inadvertent arcing should an electrode holder be connected to the unit
and mistakenly be in contact with the work piece during power up.
14. Digital Voltage Meter
The digital voltage meter is used to display the both the pre-set voltage (Mig mode only) and actual output
voltage (all modes) of the power source.
At times of non-welding, the voltage meter will display a pre-set (preview) value in GMAW/FCAW (MIG)
modes. This value can be adjusted by varying the multifunction control knob (item 10). Note that in MMAW
(stick) and GTAW (TIG) modes, the voltage meter will not preview welding voltage and will display zero.
When welding, the voltage meter will display actual welding current in all modes.
Manual 0-5143 3-7 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Page 26

TRANSMIG 175i
!
At the completion of welding, the digital voltage meter will hold the last recorded voltage value for a period
of approximately 10 seconds in all modes. The voltage meter will hold the value until; (1) any of the front
panel controls are adjusted in which case the unit will revert to preview mode, (2) welding is recommenced,
in which case actual welding amperage will be displayed, or (3) a period of 10 seconds elapses following
the completion of welding in which case the unit will return to preview mode.
15. Thermal Overload Indicator
This welding power source is protected by a self resetting thermostat. The indicator will illuminate if the
duty cycle of the power source has been exceeded. Should the thermal overload indicator illuminate the
output of the power source will be disabled. Once the power source cools down this light will go OFF and
the over temperature condition will automatically reset. Note that the mains power switch should remain
in the on position such that the fan continues to operate thus allowing the unit to cool sufficiently. Do not
switch the unit off should a thermal overload condition be present.
16. Gas Inlet (MIG mode only)
The Gas Inlet connection is used to supply the appropriate MIG welding gas to the unit. Refer to section
3.15 or 3.16 for FCAW/GMAW (MIG) set up details.
WARNING
Only Inert Shielding Gases specifically designed for welding applications should be used.
17. On / Off Switch
This switch is used to turn the unit on/off.
18. Local / Remote Switch (located in wirefeed compartment)
The remote / local switch is used only when a remote control device (such as a TIG torch with remote
current control) is fitted to the unit via the remote control socket (item 9). When the local/remote switch is
in the remote position, the unit will detect a remote device and work accordingly. When in the local mode,
the unit will not detect the remote device and will operate from the power source controls only. Note that
the trigger will operate at all times on the remote control socket irrespective of the position of the local
remote switch (ie in both local and remote modes).
Should a remote device be connected and the remote/local switch set to remote, the maximum setting
of the power source will be determined by the respective front panel control, irrespective of the remote
control device setting. As an example, if the output current on the power source front panel is set to 50%
and the remote control device is set to 100%, the maximum achievable output from the unit will be 50%.
Should 100% output be required, the respective front panel control must be set to 100%, in which case
the remote device will then be able to control between 0-100% output.
19. Burnback Control (located in wirefeed compartment)
The burnback control is used to adjust the amount of MIG wire that protrudes from the MIG torch after
the completion of MIG welding (commonly referred to as stick out). To decrease the burnback time (or
lengthen the amount of wire protruding from the MIG torch at the completing of welding), turn the burnback
control knob anti clockwise. To increase the burnback time (or shorten the amount of wire protruding from
the torch at the completing of welding), turn the Burnback Control knob clockwise.
20. Fan on Demand
The Transmig 175i is fitted with a fan on demand feature. Fan on demand automatically switches the cooling
fan off when it is not required. This has two main advantages; (1) to minimize power consumption, and
(2) to minimise the amount of contaminants such as dust that are drawn into the power source.
Note that the fan will only operate when required for cooling purposes and will automatically switch off
when not required.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-8 Manual 0-5143
Page 27

TRANSMIG 175i
A-09521_AB
MIG Torch Adaptor
MIG Torch Connector
A-09522_AB
Friction Washer
100mm
Diameter spool
Nut with
Nylon Insert
Spring
Plastic Spacer
Brass Flat
Washer
Flat Washer
3.07 Attaching the Tweco Professional Fusion MIG Torch (Euro)
Fit the MIG Torch to the power source by pushing the MIG torch connector into the MIG torch adaptor and
screwing the plastic torch nut clockwise to secure the MIG torch to the MIG torch adaptor.
Figure 3-5: Attaching MIG Torch
3.08 Installing Minispool (100mm diameter)
As delivered from the factory, the unit is fitted with a Wire Spool Hub which accepts a Handispools of 200mm
diameter.
In order to fit a Minispool (100mm diameter) assemble parts in the sequence shown below in Figure 3-6.
Adjustment of the nut with nylon insert will control the Mig Wire Spool Brake. Clockwise rotation of this nut
with nylon insert tightens the brake. The brake is correctly adjusted when the spool stops within 10 to 20mm
(measured at the outer edge of the spool) after Mig Torch trigger is released. Wire should be slack without
becoming dislodged from the spool.
Overtension of brake will cause rapid wear of mechanical WIREFEED parts, overheating of electrical
componentry and possibly an increased incidence of electrode wire Burnback into contact tip.
CAUTION
Figure 3-6: 100mm Spool Installation
Manual 0-5143 3-9 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Page 28

TRANSMIG 175i
3.09 Installing Handispool (200mm diameter)
As delivered from the factory, the unit is set for a Handispool (200mm diameter).
In order to re-fit a 200mm spool assemble parts in the sequence shown below in Figure 3-7.
Adjustment of the nut with nylon insert will control the Mig Wire Spool Brake. Clockwise rotation of this nut
with nylon insert tightens the brake. The Brake is correctly adjusted when the spool stops within 10 to 20mm
(measured at the outer edge of the spool) after Mig Torch trigger is released. Wire should be slack without
becoming dislodged from the spool.
CAUTION
Overtension of brake will cause rapid wear of mechanical WIREFEED parts, overheating of electrical
componentry and possibly an increased incidence of electrode wire Burnback into contact tip.
Ensure that the alignment pin on the wire spool hub aligns with the hole allocated in the
Handispool.
NOTE
This alignment pin can be removed by unscrewing in an anticlockwise direction and locating in
the appropriate position.
200mm
diameter spool
Spool Hub Nut
Alignment pin
Alternate
Alignment Pin
Position
Plastic Spacer
Spring
Brass Flat
Washer
Wire Spool Hub
Friction
Washer
Flat Washer
Nut with
Nylon Insert
A-09523_AB
Figure 3-7: 200mm Handispool Installation
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-10 Manual 0-5143
Page 29

TRANSMIG 175i
w
m
MIG Welding Wire
3.10 Inserting Wire into the Wire Feed Mechanism
Release the tension from the pressure roller by turning the adjustable wire drive tension screw in an anticlockwise direction. Then to release the pressure roller arm push the tension screw toward the front of the
machine which releases the pressure roller arm (Figure 3-8). With the MIG welding wire feeding from the
bottom of the spool (Figure 3-9) pass the electrode wire through the inlet guide, between the rollers, through
the outlet guide and into the MIG torch. Re-secure the pressure roller arm and wire drive tension screw and
adjust the pressure accordingly (Figure 3-8). Remove the contact tip from the MIG torch. With the MIG Torch
lead reasonably straight, feed the wire through the torch by depressing the trigger switch. Fit the appropriate
contact tip.
!
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work make sure the mains power supply is switched
off.
The electrode wire will be at welding voltage potential while it is being feed through the system.
Keep Mig Torch away from eyes and face.
A-09581
Inlet Guide
Figure 3-8: Wire Drive Assembly Components
Wire Drive Tension Scre
Pressure Roller Ar
Outlet Guide
A-09582_AB
Figure 3-9: Mig Welding Wire - Installation
Manual 0-5143 3-11 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Page 30

TRANSMIG 175i
3.11 Feed Roller Pressure Adjustment
The pressure (top) roller applies pressure to the grooved feed roller via an adjustable pressure screw. These
devices should be adjusted to a minimum pressure that will provide satisfactory WIREFEED without slippage. If
slipping occurs, and inspection of the wire contact tip reveals no wear, distortion or burn back jam, the conduit
liner should be checked for kinks and clogging by metal flakes and swarf. If it is not the cause of slipping, the
feed roll pressure can be increased by rotating the pressure screw clockwise.
!
WARNING
Before changing the feed roller ensure that the mains supply to the power source is switched off.
CAUTION
The use of excessive pressure may cause rapid wear of the feed rollers, shafts and bearing.
3.12 Changing the Feed Roll
To change feed roll remove the feed roll retaining screw by turning in an anticlockwise direction. Once the feed
roll is removed then to replace feed roll simply reverse these directions.
A dual groove feed roller is supplied as standard. It can accommodate 0.6/0.8mm diameter hard wires. Select
the roller required with the chosen wire size marking facing outward.
GROOVE “B”GROOVE “A”
GROOVE “B” SIZE
GROOVE “A” SIZE
A-09583
Figure 3-10: Dual Groove Feed Roller
A-09584_AB
Feed Roll
Retaining Screw
Feed Roll
Figure 3-11: Changing the Feed Roll
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-12 Manual 0-5143
Page 31

TRANSMIG 175i
Wire Reel Brake Adjustment Nut
A-09585
3.13 Wire Reel Brake
The wire reel hub incorporates a friction brake which is adjusted during manufacture for optimum breaking.
If it is considered necessary, adjustment can be made by turning the large nut inside the open end of the
hub clockwise to tighten the brake. Correct adjustment will result in the wire reel circumference continuing
no further than 10-20mm after release of the trigger. The electrode wire should be slack without becoming
dislodged from wire spool.
CAUTION
Overtension of brake will cause rapid wear of mechanical WIREFEED parts, overheating of electrical
componentry and possibly an increased incidence of electrode wire Burnback into contact tip.
Figure 3-12: Wire Reel Brake
3.14 Shielding Gas Regulator Operating Instructions
!
WARNING
This equipment is designed for use with welding grade (Inert) shielding gases only.
NOTE
Shielding Gas Regulator not included in the Transmig 175i (Asia Version) Plant Part No
W1005175M.
Shielding Gas Regulator Safety
This regulator is designed to reduce and control high pressure gas from a cylinder or pipeline to the working
pressure required for the equipment using it.
If the equipment is improperly used, hazardous conditions are created that may cause accidents. It is the
users responsibility to prevent such conditions. Before handing or using the equipment, understand and
comply at all times with the safe practices prescribed in this instruction.
SPECIFIC PROCEDURES for the use of regulators are listed below.
1. NEVER subject the regulator to inlet pressure greater than its rated inlet pressure.
2. NEVER pressurize a regulator that has loose or damaged parts or is in a questionable condition. NEVER
loosen a connection or attempt to remove any part of a regulator until the gas pressure has been
relieved. Under pressure, gas can dangerously propel a loose part.
3. DO NOT remove the regulator from a cylinder without first closing the cylinder valve and releasing gas
in the regulator high and low pressure chambers.
Manual 0-5143 3-13 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Page 32

TRANSMIG 175i
4. DO NOT use the regulator as a control valve. When downstream equipment is not in use for extended
periods of time, shut off the gas at the cylinder valve and release the gas from the equipment.
5. OPEN the cylinder valve SLOWLY. Close after use.
User Responsibilities
This equipment will perform safely and reliable only when installed, operated and maintained, and repaired in
accordance with the instructions provided. Equipment must be checked periodically and repaired, replaced,
or reset as necessary for continued safe and reliable performance. Defective equipment should not be used.
Parts that are broken, missing, obviously worn, distorted, or contaminated should be replaced immediately.
The user of this equipment will generally have the sole responsibility for any malfunction, which results from
improper use, faulty maintenance, or by repair by anyone other than an accredited repairer.
CAUTION
Match regulator to cylinder. NEVER CONNECT a regulator designed for a particular gas or gases to
a cylinder containing any other gas.
Art: A-05087
Figure 3-13: Fit Regulator to Cylinder
Installation
1. Remove cylinder valve plastic dust seal. Clean the cylinder valve outlet of impurities that may clog
orifices and damage seats before connecting the regulator.
Crack the valve (open then close) momentarily, pointing the outlet away from people and sources of
ignition. Wipe with a clean lint free cloth.
2. Match regulator to cylinder. Before connecting, check that the regulator label and cylinder marking
agree and that the regulator inlet and cylinder outlet match. NEVER CONNECT a regulator designed
for a particular gas or gases to a cylinder containing any other gas.
3. Connect the regulator inlet connection to cylinder or pipeline and tighten it firmly but not excessively,
with a suitable spanner.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-14 Manual 0-5143
Page 33

TRANSMIG 175i
4. Connect and tighten the outlet hose firmly and attach down-stream equipment.
5. To protect sensitive down-stream equipment a separate safety device may be necessary if the regulator
is not fitted with a pressure relief device.
Operation
With the regulator connected to cylinder or pipeline, and the adjustment screw/knob fully disengaged, pressurize
as follows:
1. Stand to one side of regulator and slowly open the cylinder valve. If opened quickly, a sudden pressure
surge may damage internal regulator parts.
2. With valves on downstream equipment closed, adjust regulator to approximate working pressure. It is
recommended that testing for leaks at the regulator connection points be carried out using a suitable
leak detection solution or soapy water.
3. Purge air or other unwanted welding grade shielding gas from equipment connected to the regulator
by individually opening then closing the equipment control valves. Complete purging may take up to
ten seconds or more, depending upon the length and size of the hose being purged.
Adjusting Flow Rate
Art: A-05088_AB
Figure 3-14: Adjust Flow Rate
With the regulator ready for operation, adjust working flow rate as follows:
1. Slowly turn adjusting screw/knob in (clockwise) direction until the outlet gauge indicates the required
flow rate.
NOTE
It may be necessary to re-check the shielding gas regulator flow rate following the first weld sequence
due to back pressure present within shielding gas hose assembly.
2. To reduce flow rate, allow the welding grade shielding gas to discharge from regulator by opening the
downstream valve. Bleed welding grade shielding gas into a well ventilated area and away from any
ignition source. Turn adjusting screw counterclockwise, until the required flow rate is indicated on the
gauge. Close downstream valve.
Shutdown
Close cylinder valve whenever the regulator is not in use. To shut down for extended periods (more than 30
minutes).
1. Close cylinder or upstream valve tightly.
2. Open downstream equipment valves to drain the lines. Bleed gas into a well ventilated area and away
from any ignition source.
3. After gas is drained completely, disengage adjusting screw and close downstream equipment valves.
Manual 0-5143 3-15 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Page 34

TRANSMIG 175i
!
4. Before transporting cylinders that are not secured on a cart designed for such purposes, remove
regulators.
3.15 Setup for MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gas Shielded Mig Wire
A. Select MIG mode with the process selection control. (refer to Section 3.06.13 for further information)
B. Connect the Mig torch polarity lead to the positive welding terminal (+). If in doubt, consult the electrode
wire manufacturer. Welding current flows from the Power Source via heavy duty bayonet type terminals.
It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical
connection.
C. Fit the Mig Torch to the power source. (Refer to section 3.07 Attaching the Tweco Fusion Mig Torch).
D. Connect the work lead to the negative welding terminal (-). If in doubt, consult the electrode wire
manufacturer. Welding current flows from the Power Source via heavy duty bayonet type terminals. It
is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical
connection.
E. Fit the welding grade shielding gas regulator/flowmeter to the shielding gas cylinder (refer to Section 3.14)
then connect the shielding gas hose from the rear of the power source to the regulator/flowmeter outlet.
F. Refer to the Weld Guide located on the inside of the wirefeed compartment door for further information.
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work make sure the mains power supply is switched
off.
Secure the welding grade shielding gas cylinder in an upright position by chaining it to a suitable
stationary support to prevent falling or tipping.
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused
in the terminal.
Remove any packaging material prior to use. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear of the
Welding Power Source.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-16 Manual 0-5143
Page 35

TRANSMIG 175i
!
A-09586_AC
Positive Welding
Terminal (+)
MIG Torch
MIG Torch
Polarity Lead
Work Lead
Negative Welding
Terminal (-)
Shielding Gas Hose Fitted
with Quick
Connect
Supply Input Lead
Figure 3-15: Setup for Mig Welding with Gas Shielded Mig Wire
3.16 Setup for MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gasless Mig Wire
A. Select MIG mode with the process selection control (refer to Section 3.06.13 for further information).
B. Connect the Mig Torch polarity lead to the negative welding terminal (-). If in doubt, consult the electrode
wire manufacturer. Welding current flows from the power source via heavy duty bayonet type terminals.
It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical
connection.
C. Connect the work lead to the positive welding terminal (+). If in doubt, consult the electrode wire manufacturer.
Welding current flows from the power source via heavy duty bayonet type terminals. It is essential, however,
that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
D. Refer to the Weld Guide located on the inside of the wirefeed compartment door for further information.
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work make sure the mains power supply is switched
off.
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused
in the terminal.
Remove any packaging material prior to use. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear of the
Welding Power Source.
Manual 0-5143 3-17 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Page 36

TRANSMIG 175i
A-09587_AB
(+)
Positive Welding
Terminal
MIG Torch
MIG Torch
Polarity Lead.
Work Lead
Negative Welding
Terminal (-)
Figure 3-16: Setup for Mig Welding with Gasless Mig Wire
3.17 Setup for TIG (GTAW) Welding
A. Select Lift TIG mode with the process selection control (refer to Section 3.06.13 for further information).
B. Connect the TIG Torch to the negative welding terminal (-). Welding current flows from the power source
via heavy duty bayonet type terminals. It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned
securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
C. Connect the work lead to the positive welding terminal (+). Welding current flows from the Power Source
via heavy duty bayonet type terminals. It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned
securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
D. Connect the TIG torch trigger switch via the 8 pin socket located on the front of the power source as shown
below. The TIG torch will require a trigger switch to operate in Lift TIG Mode.
NOTE
If the TIG torch has a remote TIG torch current control fitted then it will require to be connected to
the 8 pin socket. (Refer to section 3.06.9 Remote Control Socket for further information).
E. Fit the welding grade shielding gas regulator/flowmeter to the shielding gas cylinder (refer to Section 3.14)
then connect the shielding gas hose from the TIG torch to the regulator/flowmeter outlet. Note that the TIG
torch shielding gas hose is connected directly to the regulator/flowmeter. The power source is not fitted
with a shielding gas solenoid to control the gas flow in TIG mode therefore the TIG torch will require a gas
valve.
!
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work and inserting the electrode in the TIG Torch make
sure the mains power supply is switched off.
Secure the welding grade shielding gas cylinder in an upright position by chaining it to a stationary
support to prevent falling or tipping.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-18 Manual 0-5143
Page 37

TRANSMIG 175i
""
(+)
CAUTION
Remove any packaging material prior to use. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear of the
Welding Power Source.
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused
in the terminal.
A-09588_AD
Positive welding
terminal
.
Connect to shielding gas
regulator/flowmeter
MIG Torch
polarity lead
not connected.
Work lead
TIG Torch
Note: This 8 pin
connection plug is for
TIG torch trigger
connection and remote
TIG torch current
control if applicable.
Negative welding
terminal (-).
Figure 3-17: Setup for TIG Welding
3.18 Setup for Manual Arc (MMAW) Welding
A. Connect the Electrode Holder lead to the positive welding terminal (+). If in doubt, consult the electrode
manufacturer. Welding current flows from the Power Source via heavy duty bayonet type terminals. It
is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical
connection.
B. Connect the work lead to the negative welding terminal (-). If in doubt, consult the electrode manufacturer.
Welding current flows from the power source via heavy duty bayonet type terminals. It is essential, however,
that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
!
WARNING
VRD is NOT fitted to Transmig 175i (Asia Version) Plant Part No W1005175M.
!
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work and inserting the electrode in the electrode holder
make sure the mains power supply is switched off.
Manual 0-5143 3-19 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Page 38

TRANSMIG 175i
A-09589_AB
Negative Welding
Terminal (-)
Positive Welding
Terminal
(+)
Work Lead
Electrode
Holder
MIG Torch
polarity lead
not connected.
CAUTION
Remove any packaging material prior to use. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear of the
Welding Power Source.
Figure 3-18: Setup for Manual Arc Welding.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-20 Manual 0-5143
Page 39

TRANSMIG 175i
Shielding Gas
SECTION 4:
BASIC WELDING GUIDE
4.01 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Basic Welding Technique
Two different welding processes are covered in this section (GMAW and FCAW), with the intention of providing
the very basic concepts in using the Mig mode of welding, where a welding gun is hand held, and the electrode
(welding wire) is fed into a weld puddle, and the arc is shielded by an inert welding grade shielding gas or inert
welding grade shielding gas mixture.
GAS METAL ARC WELDING (GMAW): This process, also known as MIG welding, CO
welding, Micro Wire
2
Welding, short arc welding, dip transfer welding, wire welding etc., is an electric arc welding process which
fuses together the parts to be welded by heating them with an arc between a solid continuous, consumable
electrode and the work. Shielding is obtained from an externally supplied welding grade shielding gas or welding
grade shielding gas mixture. The process is normally applied semi automatically; however the process may
be operated automatically and can be machine operated. The process can be used to weld thin and fairly thick
steels, and some non-ferrous metals in all positions.
Shielding Gas
Molten Weld Metal
Solidified
Weld Metal
GMAW Process
Nozzle
Electrode
Arc
Base Metal
Art # A-8991_AB
Figure 4-1
FLUX CORED ARC WELDING (FCAW): This is an electric arc welding process which fuses together the parts to
be welded by heating them with an arc between a continuous flux filled electrode wire and the work. Shielding
is obtained through decomposition of the flux within the tubular wire. Additional shielding may or may not be
obtained from an externally supplied gas or gas mixture. The process is normally applied semi automatically;
however the process may be applied automatically or by machine. It is commonly used to weld large diameter
electrodes in the flat and horizontal position and small electrode diameters in all positions. The process is used
to a lesser degree for welding stainless steel and for overlay work.
Slag
(Optional)
Molten Metal
Molten
Slag
Solidified
Weld Metal
FCAW Process
Figure 4-2
Nozzle
(Optional)
Flux Cored
Electrode
Arc
Base Metal
Art # A-08992_AB
Manual 0-5143 4-1 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 40

TRANSMIG 175i
Position of MIG Torch
The angle of MIG torch to the weld has an effect on the width of the weld.
Push
Vertical
Drag/Pull
Art # A-07185_AB
Figure 4-3
The welding gun should be held at an angle to the weld joint. (see Secondary Adjustment Variables below)
Hold the gun so that the welding seam is viewed at all times. Always wear the welding helmet with proper filter
lenses and use the proper safety equipment.
CAUTION
Do not pull the welding gun back when the arc is established. This will create excessive wire
extension (stick-out) and make a very poor weld.
The electrode wire is not energized until the gun trigger switch is depressed. The wire may therefore be placed
on the seam or joint prior to lowering the helmet.
5° to 15°
Longitudinal
Angle
Direction of
90°
Transverse
Angle
Travel
5° to 15°
Longitudinal Angle
Direction of
Travel
Figure 4-4
30° to 60°
Transverse Angle
Art # A-08994
Figure 4-5
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-2 Manual 0-5143
Page 41

TRANSMIG 175i
10° to 20° Longitudinal
Direction of Travel
10°
Longitudinal Angle
30° to 60°
Transverse
Angle
30° to 60°
Transverse Angle
Direction of Travel
Vertical Fillet Welds
Figure 4-6
Figure 4-7
Angle
30° to 60°
Transverse
Angle
Art # A-08995
5° to 15°
Longitudinal
Angle
Art # A-08996
Distance from the MIG Torch Nozzle to the Work Piece
The electrode wire stick out from the MIG Torch nozzle should be between 10mm to 20.0mm. This distance
may vary depending on the type of joint that is being welded.
Travel Speed
The speed at which the molten pool travels influences the width of the weld and penetration of the welding
run.
MIG Welding (GMAW) Variables
Most of the welding done by all processes is on carbon steel. The items below describe the welding variables
in short-arc welding of 24gauge (0.024”, 0.6mm) to ¼” (6.4mm) mild sheet or plate. The applied techniques
and end results in the GMAW process are controlled by these variables.
Preselected Variables
Preselected variables depend upon the type of material being welded, the thickness of the material, the welding
position, the deposition rate and the mechanical properties. These variables are:
• Type of electrode wire
• Size of electrode wire
• Type of gas (not applicable to self shielding wires FCAW)
• Gas flow rate (not applicable to self shielding wires FCAW)
Primary Adjustable Variables
These control the process after preselected variables have been found. They control the penetration, bead
width, bead height, arc stability, deposition rate and weld soundness. They are:
• Arc Voltage
• Welding current (wire feed speed)
• Travel speed
Manual 0-5143 4-3 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 42

TRANSMIG 175i
Electrode Stick-Out
Transverse
Direction of Gun Travel
Secondary Adjustable Variables
These variables cause changes in primary adjustable variables which in turn cause the desired change in the
bead formation. They are:
1. Stick-out (distance between the end of the contact tube (tip) and the end of the electrode wire). Maintain
at about 10mm stick-out
2. Wire Feed Speed. Increase in wire feed speed increases weld current, Decrease in wire feed speed
decreases weld current.
Gas Nozzle
Tip to
Work Distance
Average Arc Length
Contact Tip (Tube)
Electrode Wire
Actual Stick-out
Art # A-08997_AD
Figure 4-8
3. Nozzle Angle. This refers to the position of the welding gun in relation to the joint. The transverse angle
is usually one half the included angle between plates forming the joint. The longitudinal angle is the
angle between the centre line of the welding gun and a line perpendicular to the axis of the weld. The
longitudinal angle is generally called the Nozzle Angle and can be either trailing (pulling) or leading
(pushing). Whether the operator is left handed or right handed has to be considered to realize the
effects of each angle in relation to the direction of travel.
Angle
Longitudinal
Angle
Axis of Weld
Transverse and Longitudinal
Figure 4-9
Leading or “Pushing”
Angle
(Forward Pointing)
90°
Nozzle Angle, Right Handed Operator
Figure 4-10
Art # A-08998_AB
Trailing or “Pulling”
Angle
(Backward Pointing)
Art # A-08999_AC
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-4 Manual 0-5143
Page 43

TRANSMIG 175i
Establishing the Arc and Making Weld Beads
Before attempting to weld on a finished piece of work, it is recommended that practice welds be made on a
sample metal of the same material as that of the finished piece.
The easiest welding procedure for the beginner to experiment with MIG welding is the flat position. The
equipment is capable of flat, vertical and overhead positions.
For practicing MIG welding, secure some pieces of 16 or 18 gauge (0.06” 1.5mm or 0.08” 2.0mm) mild steel plate
6” x 6” (150 x 150mm). Use 0.030” (0.8mm) flux cored gasless wire or a solid wire with shielding gas.
Setting of the Power Source
Power source and Wirefeeder setting requires some practice by the operator, as the welding plant has two
control settings that have to balance. These are the Wirespeed control (refer to section 3.06.4) and the welding
Voltage Control (refer to section 3.06.10). The welding current is determined by the Wirespeed control, the
current will increase with increased Wirespeed, resulting in a shorter arc. Less wire speed will reduce the
current and lengthen the arc. Increasing the welding voltage hardly alters the current level, but lengthens the
arc. By decreasing the voltage, a shorter arc is obtained with a little change in current level.
When changing to a different electrode wire diameter, different control settings are required. A thinner electrode
wire needs more Wirespeed to achieve the same current level.
A satisfactory weld cannot be obtained if the Wirespeed and Voltage settings are not adjusted to suit the
electrode wire diameter and the dimensions of the work piece.
If the Wirespeed is too high for the welding voltage, “stubbing” will occur as the wire dips into the molten
pool and does not melt. Welding in these conditions normally produces a poor weld due to lack of fusion. If,
however, the welding voltage is too high, large drops will form on the end of the wire, causing spatter. The
correct setting of voltage and Wirespeed can be seen in the shape of the weld deposit and heard by a smooth
regular arc sound. Refer to the Weld Guide located on the inside of the wirefeed compartment door for setup
information.
Electrode Wire Size Selection
The choice of Electrode wire size and shielding gas used depends on the following
• Thicknessofthemetaltobewelded
• Typeofjoint
• CapacityofthewirefeedunitandPowerSource
• Theamountofpenetrationrequired
• Thedepositionraterequired
• Thebeadproledesired
• Thepositionofwelding
• Costofthewire
Manual 0-5143 4-5 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 44

TRANSMIG 175i
Cigweld MIG Wire Selection Chart
Table 4-1: Cigweld MIG Wire Selection Chart
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-6 Manual 0-5143
Page 45

TRANSMIG 175i
!
4.02 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Welding Troubleshooting
Solving Problems Beyond the Welding Terminals
The general approach to fix Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) problems is to start at the wire spool then
work through to the MIG torch. There are two main areas where problems occur with GMAW, Porosity and
Inconsistent wire feed
Solving Problems Beyond the Welding Terminals - Porosity
When there is a gas problem the result is usually porosity within the weld metal. Porosity always stems from
some contaminant within the molten weld pool which is in the process of escaping during solidification of
the molten metal. Contaminants range from no gas around the welding arc to dirt on the work piece surface.
Porosity can be reduced by checking the following points.
FAULT CAUSE
1Shielding gas cylinder contents
and flow meter.
2Gas leaks. Check for gas leaks between the regulator/cylinder connec-
3Internal gas hose in the Power
Source.
4Welding in a windy environment. Shield the weld area from the wind or increase the gas flow.
5Welding dirty, oily, painted,
oxidised or greasy plate.
6Distance between the MIG torch
nozzle and the work piece.
7Maintain the MIG torch in good
working order.
Table 4-2: Solving Problems beyond the Welding Terminals-Porosity
Ensure that the shielding gas cylinder is not empty and the
flow meter is correctly adjusted to 15 litres per minute.
tion and in the gas hose to the Power Source.
Ensure the hose from the solenoid valve to the torch adaptor
has not fractured and that it is connected to the torch adaptor.
Clean contaminates off the work piece.
Keep the distance between the MIG torch nozzle and the work
piece to a minimum. Refer to section 2.03
AEnsure that the gas holes are not blocked and gas is exiting
out of the torch nozzle.
BDo not restrict gas flow by allowing spatter to build up inside
the torch nozzle.
CCheck that the MIG torch O-rings are not damaged.
WARNING
Disengage the feed roll when testing for gas flow by ear.
Manual 0-5143 4-7 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 46

TRANSMIG 175i
Solving Problems Beyond the Welding Terminals - Inconsistent Wire Feed
Wire feeding problems can be reduced by checking the following points.
FAULT CAUSE
1Feed roller driven by motor in the
cabinet slipped.
2Wire spool unwinded and tangled. Wire spool brake is too loose.
3Worn or incorrect feed roller size AUse a feed roller matched to the size you are welding.
4Wire rubbed against the mis-aligned
guides and reduced wire feedability.
5Liner blocked with swarf AIncreased amounts of swarf are produced by the wire
6Incorrect or worn contact tip AThe contact tip transfers the weld current to the elec-
Wire spool brake is too tight.
BReplace feed roller if worn.
Mis-alignment of inlet/outlet guides
passing through the feed roller when excessive pressure is applied to the pressure roller adjuster.
BSwarf can also be produced by the wire passing
through an incorrect feed roller groove shape or size.
CSwarf is fed into the conduit liner where it accumu-
lates thus reducing wire feedability.
trode wire. If the hole in the contact tip is too large
then arcing may occur inside the contact tip resulting
in the wire jamming in the contact tip
BWhen using soft wire such as aluminium it may
become jammed in the contact tip due to expansion of
the wire when heated. A contact tip designed for soft
wires should be used.
7Poor work lead contact to work piece If the work lead has a poor electrical contact to the
work piece then the connection point will heat up and
result in a reduction of power at the arc.
8Bent liner This will cause friction between the wire and the liner
thus reducing wire feedability
Table 4-3: Wire Feeding Problems
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-8 Manual 0-5143
Page 47

Basic GMAW (MIG) Welding Troubleshooting
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
TRANSMIG 175i
1 Undercut A Welding arc voltage too
high.
B Incorrect torch angle B Adjust angle.
C Excessive heat input C Increase the torch travel speed and/or decrease
2 Lack of penetration A Welding current too low A Increase welding current by increasing wire feed
B Joint preparation too
narrow or gap too tight
C Shielding gas incorrect C Change to a gas which gives higher penetration.
3 Lack of fusion Voltage too low Increase voltage.
4 Excessive spatter A Voltage too high A Decrease voltage or increase the wirespeed
B Voltage too low B Increase the voltage or decrease wirespeed.
5 Irregular weld shape A Incorrect voltage and
current settings. Convex, voltage too low.
Concave, voltage too
high.
A Decrease voltage or increase the wire feed speed.
welding current by decreasing the voltage or
decreasing the wire feed speed.
speed and increasing voltage.
B Increase joint angle or gap.
control.
A Adjust voltage and current by adjusting the voltage
control and the wirespeed control.
B Wire is wandering. B Replace contact tip.
C Incorrect shielding gas C Check shielding gas.
D Insufficient or excessive
heat input
6 Weld cracking A Weld beads too small A Decrease travel speed
B Weld penetration narrow
and deep
C Excessive weld stresses C Increase weld metal strength or revise design
D Excessive voltage D Decrease voltage.
E Cooling rate too fast E Slow the cooling rate by preheating part to be
7 Cold weld puddle A Loose welding cable
connection.
B Low primary voltage B Contact supply authority.
C Fault in power source C Have an Accredited CIGWELD Service Provider to
D Adjust the wirespeed control or the voltage
control.
B Reduce current and voltage and increase Mig torch
travel speed or select a lower penetration shielding
gas.
welded or cool slowly.
A Check all welding cable connections.
test then replace the faulty component.
8 Arc does not have
a crisp sound that
short arc exhibits
when the wirefeed
speed and voltage
are adjusted correctly.
Manual 0-5143 4-9 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
The MIG torch has been
connected to the wrong
voltage polarity on the
front panel.
Table4-4: GMAW (MIG) Welding Problems
Connect the MIG torch to the positive (+) welding
terminal for solid wires and gas shielded flux cored
wires. Refer to the electrode wire manufacturer for
the correct polarity.
Page 48

TRANSMIG 175i
4.03 Stick (MMAW) Basic Welding Technique
Size of Electrode
The electrode size is determined by the thickness of metals being joined and can also be governed by the type
of welding machine available. Small welding machines will only provide sufficient current (amperage) to run
the smaller size electrodes.
For thin sections, it is necessary to use smaller electrodes otherwise the arc may burn holes through the job.
A little practice will soon establish the most suitable electrode for a given application.
Storage of Electrodes
Always store electrodes in a dry place and in their original containers.
Electrode Polarity
Electrodes are generally connected to the ELECTRODE HOLDER with the Electrode Holder connected positive
polarity. The WORK LEAD is connected negative polarity and is connected to the work piece. If in doubt consult
the electrode data sheet or your nearest Accredited CIGWELD Distributor.
Effects of Arc Welding Various Materials
A. High tensile and alloy steels
The two most prominent effects of welding these steels are the formation of a hardened zone in the weld
area, and, if suitable precautions are not taken, the occurrence in this zone of under-bead cracks may result.
Hardened zone and under-bead cracks in the weld area may be reduced by using the correct electrodes,
preheating, using higher current settings, using larger electrodes sizes, short runs for larger electrode
deposits or tempering in a furnace.
Hydrogen controlled Electrodes must be used for this application. Use Ferrocraft 61 or 16TXP for normal
strength (500 MPa) steels, and Alloycraft range for higher strength steels.
B. Austenitic manganese steels
The effect on manganese steel of slow cooling from high temperatures is to embrittle it. For this reason it
is absolutely essential to keep manganese steel cool during welding by quenching after each weld or skip
welding to distribute the heat. Suitable Electrode types are Cobalarc Austex or Cobalarc Mangcraft.
C. Cast Iron
Most types of cast iron, except white iron, are weldable. White iron, because of its extreme brittleness,
generally cracks when attempts are made to weld it. Trouble may also be experienced when welding whiteheart malleable, due to the porosity caused by gas held in this type of iron. Suitable Electrode types are
Castcraft 55 or Castcraft 100.
D. Copper and alloys
The most important factor is the high rate of heat conductivity of copper, making preheating of heavy
sections necessary to give proper fusion of weld and base metal. Suitable Electrode types are Bronzecraft
AC-DC electrodes.
Arc Welding Practice
The techniques used for arc welding are almost identical regardless of what types of metals are being joined.
Naturally enough, different types of electrodes would be used for different metals as described in the preceding
section.
Welding Position
The electrodes dealt with in this publication can be used in most positions, i.e. they are suitable for welding in
flat, horizontal, vertical and overhead positions. Numerous applications call for welds to be made in positions
intermediate between these. Some of the common types of welds are shown in Figures 4-15 through 4-22.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-10 Manual 0-5143
Page 49

Art # A-07687
Art # A-07688
Art # A-07689
Art # A-07690
Figure 4-11: Flat Position, Down Hand Butt Weld
Figure 4-12: Flat Position, Gravity Fillet Weld
TRANSMIG 175i
Figure 4-13: Horizontal Position, Butt Weld
Figure 4-14: Horizontal-Vertical (HV) Position
Art A-07691
Figure 4-15: Vertical Position, Butt Weld
Art # A-07692
Figure 4-16: Vertical Position, Fillet Weld
Manual 0-5143 4-11 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 50

TRANSMIG 175i
Open Square Butt
Single Vee Butt Joint
Not less than
Art# A-07693
Figure 4-17: Overhead Position, Butt Weld
Art # A-07694
Figure 4-18: Overhead Position, Fillet Weld
Joint Preparations
In many cases, it will be possible to weld steel sections without any special preparation. For heavier sections
and for repair work on castings, etc., it will be necessary to cut or grind an angle between the pieces being
joined to ensure proper penetration of the weld metal and to produce sound joints.
In general, surfaces being welded should be clean and free of rust, scale, dirt, grease, etc. Slag should be
removed from oxy-cut surfaces. Typical joint designs are shown in Figure 4-19.
Joint
Gap varies from
1.6mm (1/16”) to 4.8mm (3/16”)
depending on plate thickness
Single Vee Butt Joint
Lap Joint
Fillet Joint
Corner Weld
Not less than
45°
Double Vee Butt Joint
Tee Joints
(Fillet both sides of the
joint)
Edge Joint
1.6mm (1/16”)
1.6mm (1/16”)
70°
Not less than
70°
1.6mm (1/16” ) max
1.6mm (1/16”) max
Plug Weld Plug Weld
Art # A-07695_AE
Figure 4-19: Typical Joint Designs for Arc Welding
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-12 Manual 0-5143
Page 51

TRANSMIG 175i
Arc Welding Technique - A Word to Beginners
For those who have not yet done any welding, the simplest way to commence is to run beads on a piece of
scrap plate. Use mild steel plate about 6.0mm thick and a 3.2mm electrode. Clean any paint, loose scale or
grease off the plate and set it firmly on the work bench so that welding can be carried out in the downhand
position. Make sure that the work clamp is making good electrical contact with the work, either directly or
through the work table. For light gauge material, always clamp the work lead directly to the job, otherwise a
poor circuit will probably result.
The Welder
Place yourself in a comfortable position before beginning to weld. Get a seat of suitable height and do as
much work as possible sitting down. Don't hold your body tense. A taut attitude of mind and a tensed body
will soon make you feel tired. Relax and you will find that the job becomes much easier. You can add much to
your peace of mind by wearing a leather apron and gauntlets. You won't be worrying then about being burnt
or sparks setting alight to your clothes.
Place the work so that the direction of welding is across, rather than to or from, your body. The electrode
holder lead should be clear of any obstruction so that you can move your arm freely along as the electrode
burns down. If the lead is slung over your shoulder, it allows greater freedom of movement and takes a lot of
weight off your hand. Be sure the insulation on your cable and electrode holder is not faulty, otherwise you
are risking an electric shock.
Striking the Arc
Practice this on a piece of scrap plate before going on to more exacting work. You may at first experience
difficulty due to the tip of the electrode "sticking" to the work piece. This is caused by making too heavy a
contact with the work and failing to withdraw the electrode quickly enough. A low amperage will accentuate it.
This freezing-on of the tip may be overcome by scratching the electrode along the plate surface in the same
way as a match is struck. As soon as the arc is established, maintain a 1.6mm to 3.2mm gap between the
burning electrode end and the parent metal. Draw the electrode slowly along as it melts down.
Another difficulty you may meet is the tendency, after the arc is struck, to withdraw the electrode so far that
the arc is broken again. A little practice will soon remedy both of these faults.
20°
Art # A-07696_AB
1.6 mm (1/16”)
Figure 4-20: Striking an Arc
Arc Length
The securing of an arc length necessary to produce a neat weld soon becomes almost automatic. You will
find that a long arc produces more heat. A very long arc produces a crackling or spluttering noise and the
weld metal comes across in large, irregular blobs. The weld bead is flattened and spatter increases. A short
arc is essential if a high quality weld is to be obtained although if it is too short there is the danger of it being
blanketed by slag and the electrode tip being solidified in. If this should happen, give the electrode a quick
twist back over the weld to detach it. Contact or "touch-weld" electrodes such as Ferrocraft 21 do not stick in
this way, and make welding much easier.
Manual 0-5143 4-13 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 52

TRANSMIG 175i
20°-30°
Rate of Travel
After the arc is struck, your next concern is to maintain it, and this requires moving the electrode tip towards
the molten pool at the same rate as it is melting away. At the same time, the electrode has to move along the
plate to form a bead. The electrode is directed at the weld pool at about 20º from the vertical. The rate of travel
has to be adjusted so that a well-formed bead is produced.
If the travel is too fast, the bead will be narrow and strung out and may even be broken up into individual
globules. If the travel is too slow, the weld metal piles up and the bead will be too large.
Making Welded Joints
Having attained some skill in the handling of an electrode, you will be ready to go on to make up welded
joints.
A. Butt Welds
Set up two plates with their edges parallel, as shown in Figure 4-21, allowing 1.6mm to 2.4mm gap between
them and tack weld at both ends. This is to prevent contraction stresses from the cooling weld metal
pulling the plates out of alignment. Plates thicker than 6.0mm should have their mating edges bevelled to
form a 70º to 90º included angle. This allows full penetration of the weld metal to the root. Using a 3.2mm
Ferrocraft 21 electrode at 100 amps, deposit a run of weld metal on the bottom of the joint.
Do not weave the electrode, but maintain a steady rate of travel along the joint sufficient to produce a
well-formed bead. At first you may notice a tendency for undercut to form, but keeping the arc length
short, the angle of the electrode at about 20º from vertical, and the rate of travel not too fast, will help
eliminate this. The electrode needs to be moved along fast enough to prevent the slag pool from getting
ahead of the arc. To complete the joint in thin plate, turn the job over, clean the slag out of the back and
deposit a similar weld.
Electrode
Tack Weld
Tack Weld
Art # A-07697_AB
Figure 4-21: Butt Weld
Art # A-07698
Figure 4-22: Weld Build up Sequence
Heavy plate will require several runs to complete the joint. After completing the first run, chip the slag
out and clean the weld with a wire brush. It is important to do this to prevent slag being trapped by the
second run. Subsequent runs are then deposited using either a weave technique or single beads laid down
in the sequence shown in Figure 4-22. The width of weave should not be more than three times the core
wire diameter of the electrode. When the joint is completely filled, the back is either machined, ground or
gouged out to remove slag which may be trapped in the root, and to prepare a suitable joint for depositing
the backing run. If a backing bar is used, it is not usually necessary to remove this, since it serves a similar
purpose to the backing run in securing proper fusion at the root of the weld.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-14 Manual 0-5143
Page 53

TRANSMIG 175i
Art # A-07699_AB
B. Fillet Welds
These are welds of approximately triangular cross-section made by depositing metal in the corner of two
faces meeting at right angles. Refer to Figure 4-14.
A piece of angle iron is a suitable specimen with which to begin, or two lengths of strip steel may be
tacked together at right angles. Using a 3.2mm Ferrocraft 21 electrode at 100 amps, position angle iron
with one leg horizontal and the other vertical. This is known as a horizontal-vertical (HV) fillet. Strike the
arc and immediately bring the electrode to a position perpendicular to the line of the fillet and about 45º
from the vertical. Some electrodes require to be sloped about 20º away from the perpendicular position
to prevent slag from running ahead of the weld. Refer to Figure 4-23. Do not attempt to build up much
larger than 6.4mm width with a 3.2mm electrode, otherwise the weld metal tends to sag towards the
base, and undercut forms on the vertical leg. Multi-runs can be made as shown in Figure 4-24. Weaving
in HV fillet welds is undesirable.
45° from
vertical
60° - 70° from line
of weld
Figure 4-23: Electrode Position for HV Fillet Weld
Art # A-07700_AB
6
3
1
5
2
4
Figure 4-24: Multi-runs in HV Fillet Weld
Manual 0-5143 4-15 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 54

TRANSMIG 175i
C. Vertical Welds
1. Vertical Up
Tack weld a three feet length of angle iron to your work bench in an upright position. Use a 3.2mm
Ferrocraft 21 electrode and set the current at 100 amps. Make yourself comfortable on a seat in front
of the job and strike the arc in the corner of the fillet. The electrode needs to be about 10º from the
horizontal to enable a good bead to be deposited. Refer Figure 4-25. Use a short arc, and do not attempt
to weave on the first run. When the first run has been completed de-slag the weld deposit and begin
the second run at the bottom. This time a slight weaving motion is necessary to cover the first run and
obtain good fusion at the edges. At the completion of each side motion, pause for a moment to allow
weld metal to build up at the edges, otherwise undercut will form and too much metal will accumulate
in the centre of the weld. Figure 4-26 illustrates multi-run technique and Figure 4-27 shows the effects
of pausing at the edge of weave and of weaving too rapidly.
Art # A-07701
Figure 4-25: Single Run Vertical Fillet Weld
Art # A-07702
Figure 4-26: Multi Run Vertical Fillet Weld
Art # A-07703
Figure 4-27: Examples of Vertical Fillet Welds
2. Vertical Down
The Ferrocraft 21 electrode makes welding in this position particularly easy. Use a 3.2mm electrode at
100 amps. The tip of the electrode is held in light contact with the work and the speed of downward
travel is regulated so that the tip of the electrode just keeps ahead of the slag. The electrode should
point upwards at an angle of about 45º.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-16 Manual 0-5143
Page 55

TRANSMIG 175i
3. Overhead Welds
Apart from the rather awkward position necessary, overhead welding is not much more difficult that
downhand welding. Set up a specimen for overhead welding by first tacking a length of angle iron at
right angles to another piece of angle iron or a length of waste pipe. Then tack this to the work bench
or hold in a vice so that the specimen is positioned in the overhead position as shown in the sketch.
The electrode is held at 45º to the horizontal and tilted 10º in the line of travel (Figure 4-28). The tip of
the electrode may be touched lightly on the metal, which helps to give a steady run. A weave technique
is not advisable for overhead fillet welds. Use a 3.2mm Ferrocraft 12XP electrode at 100 amps, and
deposit the first run by simply drawing the electrode along at a steady rate. You will notice that the
weld deposit is rather convex, due to the effect of gravity before the metal freezes.
Art # A-07704
Figure 4-28: Overhead Fillet Weld
Manual 0-5143 4-17 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 56

TRANSMIG 175i
Upsetting
Distortion
Distortion in some degree is present in all forms of welding. In many cases it is so small that it is barely
perceptible, but in other cases allowance has to be made before welding commences for the distortion that will
subsequently occur. The study of distortion is so complex that only a brief outline can be attempted hear.
The Cause of Distortion
Distortion is caused by:
A. Contraction of Weld Metal:
Molten steel shrinks approximately 11 per cent in volume on cooling to room temperature. This means
that a cube of molten metal would contract approximately 2.2 per cent in each of its three dimensions. In
a welded joint, the metal becomes attached to the side of the joint and cannot contract freely. Therefore,
cooling causes the weld metal to flow plastically, that is, the weld itself has to stretch if it is to overcome
the effect of shrinking volume and still be attached to the edge of the joint. If the restraint is very great,
as, for example, in a heavy section of plate, the weld metal may crack. Even in cases where the weld
metal does not crack, there will still remain stresses "Locked-up" in the structure. If the joint material is
relatively weak, for example, a butt joint in 2.0mm sheet, the contracting weld metal may cause the sheet
to become distorted.
B. Expansion and Contraction of Parent Metal in the Fusion Zone:
While welding is proceeding, a relatively small volume of the adjacent plate material is heated to a very
high temperature and attempts to expand in all directions. It is able to do this freely at right angles to the
surface of the plate (i.e., "through the weld", but when it attempts to expand "across the weld" or "along the
weld", it meets considerable resistance, and to fulfil the desire for continued expansion, it has to deform
plastically, that is, the metal adjacent to the weld is at a high temperature and hence rather soft, and, by
expanding, pushes against the cooler, harder metal further away, and tends to bulge (or is "upset". When
the weld area begins to cool, the "upset" metal attempts to contract as much as it expanded, but, because
it has been "upset" it does not resume its former shape, and the contraction of the new shape exerts a
strong pull on adjacent metal. Several things can then happen.
The metal in the weld area is stretched (plastic deformation), the job may be pulled out of shape by the
powerful contraction stresses (distortion), or the weld may crack, in any case, there will remain "lockedup" stresses in the job. Figures 4-29 and 4- 30 illustrate how distortion is created.
Hot
Weld
Hot
Expansion with
compression
Cool
Art # A-07705_AB
Figure 4-29: Parent Metal Expansion
Art # A-07706_AB
Weld
Permanent Upset
Contraction
with tension
Figure 4-30: Parent Metal Contraction
Overcoming Distortion Effects
There are several methods of minimizing distortion effects.
A. Peening
This is done by hammering the weld while it is still hot. The weld metal is flattened slightly and because of
this the tensile stresses are reduced a little. The effect of peening is relatively shallow, and is not advisable
on the last layer.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-18 Manual 0-5143
Page 57

TRANSMIG 175i
B. Distribution of Stresses
Distortion may be reduced by selecting a welding sequence which will distribute the stresses suitably so
that they tend to cancel each other out. See Figures 4-30 through 4-33 for various weld sequences. Choice
of a suitable weld sequence is probably the most effective method of overcoming distortion, although an
unsuitable sequence may exaggerate it. Simultaneous welding of both sides of a joint by two welders is
often successful in eliminating distortion.
C. Restraint of Parts
Forcible restraint of the components being welded is often used to prevent distortion. Jigs, positions, and
tack welds are methods employed with this in view.
D. Presetting
It is possible in some cases to tell from past experience or to find by trial and error (or less frequently, to
calculate) how much distortion will take place in a given welded structure. By correct pre-setting of the
components to be welded, constructional stresses can be made to pull the parts into correct alignment.
A simple example is shown in Figure 4-31.
E. Preheating
Suitable preheating of parts of the structure other than the area to be welded can be sometimes used to
reduce distortion. Figure 4-32 shows a simple application. By removing the heating source from b and c as
soon as welding is completed, the sections b and c will contract at a similar rate, thus reducing distortion.
Art # A-07707
Figure 4-31: Principle of Presetting
Art # A-07708
B
Dotted lines show effect if no preheat is used
Weld
C
PreheatPreheat
Figure 4-32: Reduction of Distortion by Preheating
Art # A-07709
Figure 4-33: Examples of Distortion
Manual 0-5143 4-19 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 58

TRANSMIG 175i
1
Art # A-07710_AB
2
Block Sequence.
The spaces between the welds are
filled in when the welds are cool.
Figure 4-34: Welding Sequence
2
3
4
Figure 4-35: Step back Sequence
Art # A-07712
3
1
Figure 4-36: Chain Intermittent Welding
Art # A-07713_AB
Figure 4-37: Staggered Intermittent Welding
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-20 Manual 0-5143
Page 59

Electrode Selection Chart
CIGWELD Electrode Selection Chart
Description Diameter Pack Part No. Application
Satincraft 13
Ferrocraft
12XP
WeldSkill GP
Ferrocraft 16
Twincoat
Satincrome
308L-17
Satincrome
309Mo-17
Satincrome
316L-17
Weldall
Castcraft 55
Castcraft
100
2.5mm
2.5mm
3.2mm
3.2mm
4.0mm
2.0mm
2.0mm
2.5mm
2.5mm
3.2mm
3.2mm
4.0mm
2.0mm
2.0mm
2.5mm
2.5mm
2.5mm
3.2mm
3.2mm
3.2mm
4.0mm
2.5mm
3.2mm
4.0mm
2.5mm
3.2mm
4.0mm
2.5mm
3.2mm
4.0mm
2.0mm
2.5mm
3.2mm
2.5/3.2mm
4.0mm
2.5mm
3.2mm
2.5/3.2mm
4.0mm
3.2mm
4.0mm
2.5mm
3.2mm
Blisterpack
4.0mm
1kg
2.5kg
1kg
2.5kg
5kg
1kg
2.5kg
1kg
2.5kg
1kg
2.5kg
5kg
1 kg
2.5 kg
1 kg
2.5 kg
5 kg
1 kg
2.5 kg
5 kg
5 kg
5 kg
5 kg
5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
2,5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
Blisterpack
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
Blisterpack
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
2.5 kg
Blisterpack
2.5 kg
322135
612182
322136
612183
611184
322128
612231
322129
612232
322138
612233
611234
WEG1020
WEG2520
WEG1025
WEG2525
WEG5025
WEG1032
WEG2532
WEG5032
WEG5040
611752
611753
611754
611602
611603
611604
611692
611693
611694
611661
611662
611663
322215
611664
611702
611703
322216
611704
611723
611724
611732
611733
322217
611734
General purpose electrode suitable for all positional
welding and galvanised steel.
General purpose, Xtra performance electrode
recommended for all positional (inc. Vertical down)
welding of mild and galvanised steel.
User-friendly GP electrode for welding thin section mild
and galvanised steels. Excellent for vertical down fillet
welding applications.
Hydrogen Controlled type offering exceptional AC/DC
performance in all welding positions.
Stainless Steel type for 19Cr/10Ni stainless grades
including 201, 202, 301, 302, 303, 304, 304L, 305,
308, etc
Stainless Steel type for 309 and 309L grades. It is also
suitable for welding of dissimilar welding of other 300
series stainless steels.
Stainless Steel type for welding of matching Mo bearing
grades, 316 and 316L.
High alloy stainless steel type for welding of unknown
steels, repair of die or tool steels and for joining
dissimilar steels. (Not recommended for cast iron).
For repair and maintenance welding of S.G. cast iron,
meehanite and other cast irons. It produces high
strength weld than Castcraft 100.
Soft, Ductile Nickel type electrode for repair and
maintenance welding of a wide range of cast irons. It
has better “wetting” action than Castcraft 55.
Table 4-5: Cigweld Electrode Selection Chart
TRANSMIG 175i
Further information on CIGWELD electrodes can be found at the website www.cigweld.com.au
Manual 0-5143 4-21 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 60

TRANSMIG 175i
Art # A-05866_AC
4.04 Stick (MMAW) Welding Troubleshooting
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1 Welding current
varying
2 A gap is left by
failure of the weld
metal to fill the
root of the weld.
3 Non-metallic par-
ticles are trapped
in the weld metal.
ARC FORCE control knob
is set at a value that
causes the welding current
to vary excessively with
Reduce the ARC FORCE control knob until welding current is reasonably constant while prohibiting the electrode from sticking to the work piece
when you “dig” the electrode into the workpiece.
the arc length.
A Welding current too low A Increase welding current.
B Electrode too large for
B Use smaller diameter electrode.
joint.
C Insufficient gap. C Allow wider gap.
A Non-metallic particles may
be trapped in undercut
A If a bad undercut is present clean slag bout and
cover with a run from a smaller gauge electrode.
from previous run.
B Joint preparation too
restricted.
C Irregular deposits allow
B Allow for adequate penetration and room for
cleaning out the slag.
C If very bad, chip or grind out irregularities.
slag to be trapped.
D Lack of penetration with
slag trapped beneath weld
bead.
D Use smaller electrode with sufficient current to
give adequate penetration. Use suitable tools to
remove all slag from comers.
E Rust or mill scale is pre-
E Clean joint before welding.
venting full fusion.
F Wrong electrode for posi-
tion in which welding is
done.
Figure 1-Example of insufficient gap or incorrect sequence
Insufficient Gap
4 A groove has been
formed in the base
metal adjacent to
Incorrect Sequence
A Welding current is too
high.
B Welding arc is too long. B Reduce the length of the welding arc.
F Use electrodes designed for position in which
welding is done, otherwise proper control of slag
is difficult.
A Reduce welding current.
the toe of a weld
and has not been
filled by the weld
metal (undercut).
C Angle of the electrode is
incorrect.
D Joint preparation does not
allow correct electrode
C Electrode should not be inclined less than 45° to
the vertical face.
D Allow more room in joint for manipulation of the
electrode.
angle.
E Electrode too large for
E Use smaller gauge electrode.
joint.
F Insufficient deposit time at
edge of weave.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-22 Manual 0-5143
G Power source is set for
MIG (GMAW) welding.
F Pause for a moment at edge of weave to allow
weld metal buildup.
G Set power source to STICK (MMAW) mode.
Page 61

TRANSMIG 175i
Lack of fusion caused by dirt,
5 Portions of the
weld run do not
fuse to the surface
of the metal or
edge of the joint.
A Small electrodes used on
A Use larger electrodes and preheat the plate.
heavy cold plate.
B Welding current is too low. B Increase welding current.
C Wrong electrode angle. C Adjust angle so the welding arc is directed more
into the base metal.
D Travel speed of electrode
D Reduce travel speed of electrode.
is too high.
E Scale or dirt on joint
E Clean surface before welding.
surface.
electrode angle incorrect,
rate of travel too high
Figure 2: Example of Lack of Fusion
Art # A-05867_AC
Lack of side fusion,
scale dirt, small electrode,
amperage too low
6 Gas pockets or
voids in weld
metal (porosity)
Lack of
inter-run fusion
Lack of root fusion
A High levels of sulphur in
steel.
A Use an electrode that is designed for high sul-
phur steels.
B Electrodes are damp. B Dry electrodes before use.
C Welding current is too
C Reduce welding current.
high.
D Surface impurities such as
D Clean joint before welding.
oil, grease, paint, etc.
E Welding in a windy envi-
E Shield the weld area from the wind.
ronment.
7 Crack occurring in
weld metal soon
after solidification
commences
F Electrode damaged ie flux
coating incomplete.
A Rigidity of joint. A Redesign to relieve weld joint of severe stresses
B Insufficient throat thick-
ness.
F Discard damaged electrodes and only use elec-
trodes with a complete flux coating.
or use crack resistance electrodes.
B Travel slightly slower to allow greater build up in
throat.
C Weld current is too high. C Decrease welding current.
Slag
trapped in
Figure 3: Example of Slag Inclusion
Not cleaned,
or incorrect
electrode
undercut
Slag trapped in root
Art # A-05868_AC
Manual 0-5143 4-23 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Table 4-6: Welding Problems MMAW (Stick)
Page 62

TRANSMIG 175i
4.05 TIG (GTAW) Basic Welding Technique
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) as it is commonly referred to, is a welding
process in which fusion is produced by an electric arc that is established between a single tungsten (nonconsumable) electrode and the work piece. Shielding is obtained from a welding grade shielding gas or welding
grade shielding gas mixture which is generally Argon based. A filler metal may also be added manually in some
circumstances depending on the welding application.
A-09658_AB
Gas Cup
Either Ceramic,
Work Piece
Can Be Any Commercial
Metal
Welds Made With or Without
Addition of Filler Metal
High-lmpact or
Water Cooled
Metal
Tungsten Electrode
Non-Consumable
Inert Gas
Shields Electrode
and Weld Puddle
Figure 4-38: TIG Welding Application Shot
Tungsten Electrode Current Ranges
Electrode Diameter DC Current (Amps)
0.040” (1.0mm) 30-60
1/16” (1.6mm) 60-115
3/32” (2.4mm) 100-165
1/8” (3.2mm) 135-200
5/32” (4.0mm) 190-280
3/16” (4.8mm) 250-340
Table 4-7: Current Ranges for Various Tungsten Electrode Sizes
Guide for Selecting Filler Wire Diameter
Filler Wire Diameter DC Current Range (Amps)
1/16” (1.6mm) 20-90
3/32” (2.4mm) 65-115
1/8” (3.2mm) 100-165
3/16” (4.8mm) 200-350
Table 4-8: Filler Wire Selection Guide
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-24 Manual 0-5143
Page 63

Tungsten Electrode Types
TRANSMIG 175i
Electrode Type
(Ground Finish)
Thoriated 2%
Zirconated 1%
Ceriated 2%
Welding Application Features Colour Code
DC welding of mild
steel, stainless steel
and copper
High quality AC welding of aluminium,
magnesium and their
alloys.
AC & DC welding of
mild steel, stainless
steel, copper, aluminium, magnesium and
their alloys
Excellent arc starting,
Long life, High current
carrying capacity
Self cleaning, Long
life, Maintains balled
end, High current carrying capacity.
Longer life, More
stable arc, Easier
starting, Wider current
range, Narrower more
concentrated arc.
Table 4-9
NOTE
The Transmig 175i Inverter is not suited for AC Tig welding.
Red
White
Grey
Manual 0-5143 4-25 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 64

TRANSMIG 175i
TIG Welding Filler Rods
Comweld
Rod
LW1
LW1-6
Supersteel
CrMo1
CrMo2
308L
309L
316L
Base Metal
Thickness
0.040”
1.0mm
0.045”
1.2mm
Aust Std AWS Std Part No.
1.6mm
R4
R6
R2
RB2
RB3
R308L
R309L
R316L
DC Current
ER70S-4
ER70S-6
ER70S-2
ER80S-B2
ER90S-B3
for Mild
Steel
35-45
40-50
45-55
50-60
ER308L
ER309L
ER316L
DC Current
for Stainless
321411
321417
321370
—
—
321406
321403
321400
Steel
20-30
25-35
30-45
35-50
Part No.
2.4mm
—
—
—
321379
321383
321407
321404
321401
Table 4-10
Tungsten
Electrode
Diameter
0.040”
1.0mm
0.040”
1.0mm
Part No.
3.2mm
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Filler Rod
Diameter (if
required)
1/16”
1.6mm
1/16”
1.6mm
Type/Application
For mild-medium strength steels.
Pipes, tubing, roll cages, etc.
For welding of high strength Cr-Mo
steels used at elevated temperatures.
For stainless steels. Stainless pipes,
tubing, architectural uses, etc.
Argon Gas
Flow Rate
Litres/min
5-7 Butt/Corner
5-7 Butt/Corner
Joint Type
Lap/Fillet
Lap/Fillet
1/16”
1.6mm
1/8”
3.2mm
3/16”
4.8mm
1/4”
6.4mm
TIG Welding is generally regarded as a specialised process that requires operator competency. While many of
the principles outlined in the previous Arc Welding section are applicable a comprehensive outline of the TIG
Welding process is outside the scope of this Operating Manual. For further information please refer to www.
cigweld.com.au or contact Cigweld.
60-70
70-90
80-100
90-115
115-135
140-165
160-175
170-200
40-60
50-70
65-85
90-110
100-125
125-150
135-160
160-180
1/16”
1.6mm
1/16”
1.6mm
3/32”
2.4mm
1/8”
3.2mm
Table 4-11
1/16”
1.6mm
3/32”
2.4mm
1/8”
3.2mm
5/32”
4.0mm
7 Butt/Corner
Lap/Fillet
7 Butt/Corner
Lap/Fillet
10 Butt/Corner
Lap/Fillet
10 Butt/Corner
Lap/Fillet
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-26 Manual 0-5143
Page 65

4.06 TIG (GTAW) Welding Problems
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
TRANSMIG 175i
1 Excessive beard build up
or poor penetration or poor
fusion at edges of weld.
2 Weld bead too wide and
flat or undercut at edges
of weld or excessive burn
through.
3 Weld bead too small or
insufficient penetration or
ripples in bead are widely
spaced apart.
4 Weld bead too wide or
excessive bead build up or
excessive penetration in
butt joint.
5 Uneven leg length in fillet
joint
6 Electrode melts or oxidises
when an arc is struck.
Welding current is too
low
Welding current is too
high
Travel speed too fast Reduce travel speed.
Travel speed too slow Increase travel speed.
Wrong placement of
filler rod
A Torch lead connected
to positive welding
terminal.
Increase weld current and/or faulty joint
preparation.
Decrease weld current.
Re-position filler rod.
A Connect torch lead to negative welding
terminal.
B No gas flowing to weld-
ing region.
C Torch is clogged with
dust or dirt.
D Gas hose is cut. D Replace gas hose.
E Gas passage contains
impurities.
F Gas regulator turned
off.
G Torch valve is turned
off.
H The electrode is too
small for the welding
current.
I Power source is set for
MIG welding.
B Check the gas lines for kinks or breaks
and gas cylinder contents.
C Clean torch.
E Disconnect gas hose from the rear of
Power Source then raise gas pressure
and blow out impurities.
F Turn on.
G Turn on.
H Increase electrode diameter or reduce the
welding current.
I Set Power Source to Lift TIG mode.
Manual 0-5143 4-27 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
Page 66

TRANSMIG 175i
7 Dirty weld pool A Electrode contaminated
by contact with work
piece or filler rod material.
B Work piece surface has
foreign material on it.
C Gas contaminated with
air.
8 Poor weld finish Inadequate shielding
gas.
9 Arc start is not smooth. A Tungsten electrode is
too large for the welding current.
B The wrong electrode
is being used for the
welding job.
C Gas flow rate is too
high.
A Clean the electrode by grinding off the
contaminates.
B Clean surface.
C Check gas lines for cuts and loose fitting
or change gas cylinder.
Increase gas flow or check gas line for
gas flow problems.
A Select the right size electrode. Refer to
Table 4-7 Cigweld Electrode Selection
Chart.
B Select the right electrode type. Refer to
Table 4-9 Cigweld Electrode Selection
Chart.
C Select the right rate for the welding job.
Refer to Table 4-11.
10 Arc flutters during TIG
welding.
D Incorrect shielding gas
is being used.
E Poor work clamp con-
nection to work piece.
Tungsten electrode is
too large for the welding current.
Table 4-12: GTAW (TIG) Welding Problems
D Select the right shielding gas.
E Improve connection to work piece.
Select the right size electrode. Refer to
Table 4-7 Cigweld Electrode Selection
Chart.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-28 Manual 0-5143
Page 67

POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE
5.01 Power Source Problems
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1 Mains supply voltage is ON,
power indicator is illuminated however unit will not
commence welding when
the torch trigger switch is
depressed.
A Power source is not in the
B Faulty torch trigger. B Repair or replace torch trigger
SECTION 5:
REQUIREMENTS
correct mode of operation.
TRANSMIG 175i
A Set the power source to the cor-
rect mode of operation with the
process selection switch.
switch/lead.
2 Fault Indicator is illumi-
nated and unit will not
commence welding when
the torch trigger switch is
depressed.
3 Unit will not feed wire in
MIG mode.
4 Welding wire continues to
feed when torch trigger is
released.
5 Welding arc cannot be
established in MIG mode.
Duty cycle of power source
has been exceeded.
A Electrode wire stuck in
conduit liner or contact tip
(burn-back jam).
B Internal fault in power
source
A Trigger mode selection
switch is in 4T latch mode.
B Torch trigger leads shorted. B Repair or replace torch trigger
A MIG torch polarity lead is
not connected into a welding output terminal.
Leave the power source
switched ON and allow it to cool.
Note that fault indicator must
be extinguished prior to commencement of welding.
A Check for clogged / kinked MIG
torch conduit liner or worn
contact tip. Replace faulty components.
B Have an Accredited CIGWELD
Service Provider investigate the
fault.
A Change the trigger mode selec-
tion switch from 4T latch mode
to 2T normal mode.
switch/lead.
A Connect the MIG torch polar-
ity lead to either the positive
welding output terminal or the
negative welding output terminal
as required.
B Poor or no work lead
contact.
6 Inconsistent wire feed. A Worn or dirty contact tip. A Replace if necessary.
B Worn feed roll. B Replace.
C Excessive brake tension on
wire reel hub.
D Worn, kinked or dirty con-
duit liner
7 No gas flow in MIG mode. A Gas hose is damaged. A Replace or repair.
B Gas passage contains
impurities.
C Gas regulator turned off. C Turn on regulator.
D Empty gas cylinder. D Replace gas cylinder.
Manual 0-5143 5-1 POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE REQUIREMENTS
B Clean work clamp area and en-
sure good electrical contact.
C Reduce brake tension on spool
hub
D Clean or replace conduit liner
B Disconnect gas hose from
the rear of power source or
wirefeeder and blow out impurities.
Page 68

TRANSMIG 175i
!
8 Gas flow continues after
the torch trigger switch has
been released (MIG mode).
9 Power indicator will not
illuminate and welding arc
cannot be established.
10 TIG electrode melts when
arc is struck.
11 Arc flutters during TIG
welding.
Gas valve has jammed open
due to impurities in the gas
or the gas line.
The mains supply voltage
has exceeded voltage limits
of the power source.
TIG torch is connected to
the (+) VE terminal.
Tungsten electrode is too
large for the welding current.
Table 5-1
Have an accredited CIGWELD
service provider repair or replace gas valve.
Ensure that the mains supply
voltage is within 240VAC ± 15%.
Connect the TIG torch to the (-)
VE terminal.
Select the correct size of tungsten electrode. Refer to Table
4-7.
5.02 Routine Service and Calibration Requirements
WARNING
There are extremely dangerous voltage and power levels present inside this Inverter Power Source.
Do not attempt to open or repair unless you are an accredited CIGWELD Service Provider. Disconnect the Welding Power Source from the Mains Supply Voltage before disassembling.
Routine Inspection, Testing & Maintenance
The inspection and testing of the power source and associated accessories shall be carried out in accordance
with Section 5 of AS 1674.2 - 2007: Safety in Welding and Allied Processes-Part 2 Electrical. This includes an
insulation resistance test and an earthing test to ensure the integrity of the unit is compliant with Cigweld's
original specifications.
If equipment is to be used in a hazardous location or environments with a high risk of electrocution as outlined
in AS 1674.2 - 2007, then the above tests should be carried out prior to entering this location.
A. Testing Schedule
1. For transportable equipment, at least once every 3 months; and
2. For fixed equipment, at least once every 12 months.
The owners of the equipment shall keep a suitable record of the periodic tests and a system of tagging,
including the date of the most recent inspection.
A transportable power source is deemed to be any equipment that is not permanently connected and fixed
in the position in which it is operated.
POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE REQUIREMENTS 5-2 Manual 0-5143
Page 69

TRANSMIG 175i
!
B. Insulation Resistance
Minimum insulation resistance for in-service Cigweld Inverter Power Sources shall be measured at a voltage
of 500V between the parts referred to in Table 6-1below. Power sources that do not meet the insulation
resistance requirements set out below shall be withdrawn from service and not returned until repairs have
been performed such that the requirements outlined below are met.
Components to be Tested
Input circuit (including any connected control circuits) to welding circuit
(including any connected control circuits)
All circuits to exposed conductive parts
Welding circuit (including any connected control circuits) to any auxiliary
circuit which operates at a voltage exceeding extra low voltage
Welding circuit (including any connected control circuits) to any auxiliary
circuit which operates at a voltage not exceeding extra low voltage
Separate welding circuit to separate welding circuit
Table 5-2: Minimum Insulation Resistance Requirements: Cigweld Inverter Power Sources
C. Earthing
The resistance shall not exceed 1Ω between any metal of a power source where such metal is required
to be earthed, and -
1. The earth terminal of a fixed power source; or
2. The earth terminal of the associated plug of a transportable power source
Note that due to the dangers of stray output currents damaging fixed wiring, the integrity of fixed wiring
supplying Cigweld welding power sources should be inspected by a licensed electrical worker in accordance
with the requirements below -
Minimum Insulation
Resistance (MΩ)
5
2.5
10
1
1
1. For outlets/wiring and associated accessories supplying transportable equipment - at least once
every 3 months; and
2. For outlets/wiring and associated accessories supplying fixed equipment - at least once every 12
months.
D. Voltage Reduction Device (VRD)
WARNING
VRD is NOT fitted to Transmig 175i (Asia Version) Plant Part No W1005175M.
Units fitted with VRD's, shall have the periodic tests outlined in Table 6-2 below conducted by an accredited
CIGWELD service provider. Testing shall be conducted at intervals as outlined below -
1. For transportable equipment, at least once every 3 months; and
2. For fixed equipment, at least once every 12 months.
Description Required Parameters
VRD Open Circuit Voltage Less than 35V; at nominal input voltage
VRD Turn ON Resistance Less than 200 ohms
VRD Turn OFF Time Less than 0.3 seconds
Table 5-3: VRD Periodic Tests
Manual 0-5143 5-3 POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE REQUIREMENTS
Page 70

TRANSMIG 175i
E. General Maintenance Checks
Welding equipment should be regularly checked by an accredited Cigweld Service Provider to ensure
that:
1. Flexible cord is of the multi-core tough rubber or plastic sheathed type of adequate rating, correctly
connected and in good condition.
2. Welding terminals are in suitable condition and are shrouded to prevent inadvertent contact or short
circuit.
3. The Welding System is clean internally, especially from metal filing, slag, and loose material.
F. Accessories
Accessory equipment, including output leads, electrode holders, torches, wire feeders and the like shall be
inspected at least monthly by a competent person to ensure that the equipment is in a safe and serviceable
condition. All unsafe accessories shall not be used.
G. Repairs
If any parts are damaged for any reason, it is recommended that replacement be performed by an accredited Cigweld Service Provider.
Power Source Calibration
A. Schedule
Output testing of all Cigweld Inverter Power Sources and applicable accessories shall be conducted at regular
intervals to ensure they fall within specified levels. Calibration intervals shall be as outlined below -
1. For transportable equipment, at least once every 3 months; and
2. For fixed equipment, at least once every 12 months.
If equipment is to be used in a hazardous location or environments with a high risk of electrocution as
outlined in AS 1674.2 - 2007, then the above tests should be carried out prior to entering this location.
B. Calibration Requirements
Where applicable, the tests outlined in Table 6-3 below shall be conducted by an accredited CIGWELD
service agent.
Testing Requirements
Output current (A) to be checked to ensure it falls within applicable Cigweld power source specifications
Output Voltage (V) to be checked to ensure it falls within applicable Cigweld power source specifications
Motor Speed (RPM) of wire drive motors to be checked to ensure it falls within required Cigweld power
source / wire feeder specifications
Accuracy of digital meters to be checked to ensure it falls within applicable Cigweld power source specifications
Table 5-4: Calibration Parameters
Periodic calibration of other parameters such as timing functions are not required unless a specific fault
has been identified.
C. Calibration Equipment
All equipment used for Power Source calibration shall be in proper working condition and be suitable for
conducting the measurement in question. Only test equipment with valid calibration certificates (NATA
certified laboratories) shall be utilized.
POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE REQUIREMENTS 5-4 Manual 0-5143
Page 71

TRANSMIG 175i
!
5.03 Cleaning the Welding Power Source
WARNING
There are dangerous voltage and power levels present inside this product. Do not attempt to open
or repair unless you are a qualified electrical tradesperson. Disconnect the Welding Power Source
from the Mains Supply Voltage before disassembling.
To clean the Welding Power Source, open the enclosure and use a vacuum cleaner to remove any accumulated
dirt, metal filings, slag and loose material. Keep the shunt and lead screw surfaces clean as accumulated foreign
material may reduce the welders output welding current.
5.04 Cleaning the Feed Rolls
Clean the grooves in the drive rolls frequently. This can be done by using a small wire brush. Also wipe off, or
clean the grooves on the upper feed roll. After cleaning, tighten the feed roll retaining knobs.
CAUTION
Do not use compressed air to clean the Welding Power Source. Compressed air can force metal
particles to lodge between live electrical parts and earthed metal parts within the Welding Power
Source. This may result in arcing between this parts and their eventual failure.
Manual 0-5143 5-5 POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE REQUIREMENTS
Page 72

TRANSMIG 175i
This page is left blank intentionally.
POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE REQUIREMENTS 5-6 Manual 0-5143
Page 73

6.01 Power Source
Art # A-09657_AB
TRANSMIG 175i
SECTION 6:
KEY SPARE PARTS
Figure 6-1
TRANSMIG 175i POWER SOURCE SPARE PARTS
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 W7004900 PCB Power
2 W7004901 PCB Control
3 W7004902 PCB EMC Filter
4 W7004903 PCB Front Panel (Display)
5 W7004904 PCB Front Panel (Piggy-Back)
6 W7004905 Wiredrive Assembly
7 W7004906 Feed Roll Retaining Thumbscrew
8 7977036
9 W7004907 Fan Assembly
10 W7003010 Input Rectifier
11 W7004908 Gas Solenoid Valve Assembly
12 W7004909 Dinse Socket 50mm²
13 704461 Dinse Plug Male 50mm²
14 W7003036
15 W7004910 Input Supply Switch
16 W7004911 CT, Output
17 W7004912 Wire Hub Assembly
18 W7004913 Shielding Gas Hose Assembly (not shown)
19 W7005635 Latch, Door, Slide (not shown)
Manual 0-5143 6-1 KEY SPARE PARTS
Feed Roll 0.6/0.8mm V groove (fitted as standard)
(Refer to options and accessories table for other feed rolls available).
Control Socket 8 pin (Note that 8 pin control plug part number is
UOA706900).
Table 6-1
Page 74

TRANSMIG 175i
6.02 Tweco Fusion 250 Mig Torch
MIG Torch Part No: W4013701
21 43
55
767
8
Figure 6-1
TWECO FUSION MIG TORCH PARTS
ITEM PART NO. DESCRIPTION
A-09659
7
1
OTW22/50 Nozzle 13mm
OTW22/62 Nozzle 16mm
OTW14/23 Contact Tip 0.6mm
OTW14/30 Contact Tip 0.8mm
2
OTW14/35 Contact Tip 0.9mm
OTW14/40 Contact Tip 1.0mm
OTW14/45 Contact Tip 1.2mm
3 OTW32 Insulator
4 OTW52 Gas Diffuser
5 62J-45S Conductor Tube, 45 Degree
6 W7005001 Trigger Assembly
7 W7005000 Handle Mouldings
OTW42/3035 Liner 0.8-0.9mm Hard Wire
8
OTW42N/3545 Liner 0.9-1.2mm Soft Wire
Table 6-2
KEY SPARE PARTS 6-2 Manual 0-5143
Page 75

APPENDIX: TRANSMIG 175i CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Control Socket 8 Pin
W7003036
PCB EMC Filter
W7004902
W7004904
PCB Front Panel (Piggy Back)
Input Rectifier
W7003010
TRANSMIG 175i
W7004900 PCB Power
W7004907
Fan Assembly
PCB Front Panel (Display)
W7004903
W7004901
PCB Control
W7004911
CT Output
Wiredrive Assembly
W7004905
A-09596_AE
Manual 0-5143 A-1 APPENDIX
Page 76

CIGWELD - LIMITED WARRANTY TERMS
LIMITED WARRANTY: CIGWELD Pty Ltd, A Thermadyne Company, hereafter, “CIGWELD” warrants to customers of its authorized distributors hereafter “Purchaser” that its products will be free of defects in workmanship
or material. Should any failure to conform to this warranty appear within the time period applicable to the
CIGWELD products as stated below, CIGWELD shall, upon notification thereof and substantiation that the
product has been stored, installed, operated, and maintained in accordance with CIGWELD’s specifications,
instructions, recommendations and recognized standard industry practice, and not subject to misuse, repair,
neglect, alteration, or accident, correct such defects by suitable repair or replacement, at CIGWELD’s sole
option, of any components or parts of the product determined by CIGWELD to be defective.
CIGWELD MAKES NO OTHER WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. THIS WARRANTY IS EXCLUSIVE AND
IN LIEU OF ALL OTHERS, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: CIGWELD SHALL NOT UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL,
INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SUCH AS, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, LOST PROFITS AND BUSINESS
INTERRUPTION. The remedies of the Purchaser set forth herein are exclusive and the liability of CIGWELD
with respect to any contract, or anything done in connection therewith such as the performance or breach
thereof, or from the manufacture, sale, delivery, resale, or use of any goods covered by or furnished by CIGWELD whether arising out of contract, negligence, strict tort, or under any warranty, or otherwise, shall not,
except as expressly provided herein, exceed the price of the goods upon which such liability is based. No
employee, agent, or representative of CIGWELD is authorized to change this warranty in any way or grant any
other warranty.
PURCHASER’S RIGHTS UNDER THIS WARRANTY ARE VOID IF REPLACEMENT PARTS OR ACCESSORIES
ARE USED WHICH IN CIGWELD’S SOLE JUDGEMENT MAY IMPAIR THE SAFETY OR PERFORMANCE OF ANY
CIGWELD PRODUCT. PURCHASER’S RIGHTS UNDER THIS WARRANTY ARE VOID IF THE PRODUCT IS SOLD
TO PURCHASER BY NON-AUTHORIZED PERSONS.
The warranty is effective for the time stated below beginning on the date that the authorized distributor delivers
the products to the Purchaser. Notwithstanding the foregoing, in no event shall the warranty period extend
more than the time stated plus one year from the date CIGWELD delivered the product to the authorized
distributor.
Page 77

TERMS OF WARRANTY – JULY 2010
1. The Trade Practices Act 1974 (Commonwealth) and similar State Territory legislation relating to the supply
of goods and services, protects consumers’ interests by ensuring that consumers are entitled in certain
situations to the benefit of various conditions, warranties, guarantees, rights and remedies (including warranties as to merchantability and fitness for purpose) associated with the supply of goods and services.
A consumer should seek legal advice as to the nature and extent of these protected interests. In some
circumstances, the supplier of goods and services may legally stipulate that the said conditions, warranties, guarantees, rights and remedies are limited or entirely excluded. The warranties set out in Clause 2
shall be additional to any nonexcludable warranties to which the Customer may be entitled pursuant to any
statute.
2. Subject to Clause 3. CIGWELD gives the following warranties to the Customer:
Insofar as they are manufactured or imported by CIGWELD, goods will upon delivery be of merchantable
quality and reasonably fit for the purpose for which they are supplied by CIGWELD.
CIGWELD will repair or, at its option, replace those of the goods which, upon examination, are found by
CIGWELD to be defective in workmanship and/or materials.
CIGWELD reserves the right to request documented evidence of date of purchase.
3. The Warranty in Clause 2;
Is conditional upon:
The Customer notifying CIGWELD or our Accredited Distributor in writing of its claim within seven (7) days
of becoming aware of the basis thereof, and at its own expense returning the goods which are the subject
of the claim to CIGWELD or nominated Accredited Distributor/Accredited Service Provider. The goods being
used in accordance with the Manufacturer’s Operating Manuals, and under competent supervision.
Does not apply to:
Obsolete goods sold at auction, second-hand goods and prototype goods.
Breakdown or malfunction caused by accident, misuse or normal wear and tear.
Repairs or replacement made other than by CIGWELD or Accredited Service Providers, unless by prior
arrangement with CIGWELD.
Replacement parts or accessories which may affect product safety or performance and which are not
manufactured, distributed or approved by CIGWELD.
4. CIGWELD declares that, to the extent permitted by law, it hereby limits its liability in respect of the supply of
goods which are not of a kind ordinarily acquired for personal, domestic or household use or consumption
to any one or more of the following (the choice of which shall be at the option of CIGWELD).
The replacement of the goods or the supply of equivalent goods.
The repair of goods.
The payment of cost of replacing the goods or acquiring equivalent goods.
The payment of the cost of having goods repaired.
5. Except as provided in Clauses 2 to 4 above, to the extent permitted by statute, CIGWELD hereby excludes
all liability for any loss, damage, death or injury of any kind whatsoever occasioned to the Customer in
respect of the supply of goods including direct, indirect, consequential or incidental loss, damage or injury
of any kind.
Page 78

WARRANTY SCHEDULE – JULY 2010
These warranty periods relate to the warranty conditions in clause 2. All warranty periods are from date of
sale from the Accredited Distributor of the equipment. Notwithstanding the foregoing, in no event shall the
warranty period extend more than the time stated plus one year from the date CIGWELD delivered the product
to the Accredited Distributor. Unless otherwise stated the warranty period includes parts and labour. CIGWELD
reserves the right to request documented evidence of date of purchase.
TRANSMIG 175i POWER SOURCE
Original main power magnetics. 3 Years 2 Years
Original main power rectifiers, printed circuit boards and power switch
semiconductors.
All other circuits and components including, but not limited to, relays,
switches, contactors, solenoids, fans and electric motors.
ACCESSORIES WARRANTY PERIOD
MIG torch, electrode holder lead and work lead. 3 Months
MIG torch consumable items. NIL
Gas regulator/flowmeter (excluding seat assembly, pressure gauges, elastomer seals and “O” rings).
Regulator seat assemblies and pressure gauges. 6 Months
Elastomer seals and “O” rings used in the equipment. 3 Months
Please note that the information detailed in this statement supersedes any prior published data produced by
CIGWELD.
WARRANTY
PERIOD
2 Years 2 Years
1 Year 1 Year
1 Year
LABOUR
Page 79

GLOBAL CUSTOMER SERVICE CONTACT INFORMATION
CIGWELD, Australia
71 Gower Street
Preston, Victoria
Australia, 3072
Telephone: 61-3-9474-7400
Fax: 61-3-9474-7391
Email: enquiries@cigweld.com.au
Victor Technologies USA
2800 Airport Road
Denton, Tx 76207 USA
Telephone: (940) 566-2000
800-426-1888
Fax: 800-535-0557
Email: sales@thermalarc.com
Victor Technologies Canada
2070 Wyecroft Road
Oakville, Ontario
Canada, L6L5V6
Telephone: (905)-827-1111
Fax: 905-827-3648
Victor Technologies, China
No 100 Lao Hongjing Rd
Minhang District
Shanghai, PR, 200235
Telephone: 86-21-64072626
Fax: 86-21-64483032
Victor Technologies Asia Sdn Bhd
Lot 151, Jalan Industri 3/5A
Rawang Integrated Industrial Park - Jln Batu Arang
48000 Rawang Selangor Darul Ehsan
West Malaysia
Telephone: 603+ 6092 2988
Fax : 603+ 6092 1085
Victor Technologies Italy
OCIM, S.r.L.
Via Benaco, 3
20098 S. Giuliano
Milan, Italy
Tel: (39) 02-98 80320
Fax: (39) 02-98 281773
Victor Technologies Europe
Europe Building
Chorley North Industrial Park
Chorley, Lancashire
England, PR6 7Bx
Telephone: 44-1257-261755
Fax: 44-1257-224800
PT. Victor Technologies Utama Indonesia
Jl. Angsana II Blok AE No. 28
Delta Silicon I, Cikarang - Sukaresmi
Bekasi, 17550
Indonesia
Tel: +62 21 8990 6095
Fax: +62 21 8990 6096 / 1867
http://www.Victortechnologies.com
Victor Technologies International
2070 Wyecroft Road
Oakville, Ontario
Canada, L6L5V6
Telephone: (905)-827-9777
Fax: 905-827-9797
Page 80

Asia Pacific Regional Headquarters
www.cigweld.com.au
71 Gower Street
Preston, Victoria, Australia, 3072
Telephone: +61 3 9474 7400
FAX:
Email: enquiries@cigweld.com.au
+61 3 9474 7391
 Loading...
Loading...