Page 1

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Cover Page
Page 2

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Table of Contents
i
Contents
Product Overview ........................................................................... 1
Package Contents .......................................................................................................... 1
Features ......................................................................................................................... 1
Product Hardware Features........................................................................................... 2
Applications ................................................................................................................... 3
Switch Installation .......................................................................... 4
Basic Installation ............................................................................................................ 4
Connect additional devices to your switch .................................................................... 5
Configure your switch ..................................................................... 6
Access your switch management page .......................................................................... 6
System Info .................................................................................................................... 6
View your switch status information ................................................................... 6
Configure IP address settings ........................................................................................ 7
Set your switch IP address settings...................................................................... 7
Port Status ..................................................................................................................... 8
View Traffic Information Statistics ....................................................................... 8
VLAN .............................................................................................................................. 8
Add, modify, and remove VLANs ......................................................................... 8
Trunk/Link Aggregation ............................................................................................... 10
Configure port trunk settings ............................................................................ 10
Mirroring ...................................................................................................................... 10
QoS (Quality of Service) ............................................................................................... 11
Port-Based QoS .................................................................................................. 11
IEEE 802.1p QoS ................................................................................................. 11
Storm Control .............................................................................................................. 12
Configure Storm Control .................................................................................... 12
Rate Limiting ................................................................................................................ 13
Set Per Port Rate Limiting .................................................................................. 13
Loopback Detection & Prevention............................................................................... 13
Enable loopback prevention .............................................................................. 13
IGMP Snooping ............................................................................................................ 14
Configure IGMP Snooping Settings .................................................................... 14
PoE Configuration ........................................................................................................ 14
Configure PoE settings ....................................................................................... 15
Switch Maintenance ..................................................................... 16
Change administrator password.................................................................................. 16
Upgrade your switch firmware .................................................................................... 17
Backup and restore your switch configuration settings .............................................. 18
Backup/Restore ................................................................................................. 18
Reboot/Reset to factory defaults ................................................................................ 19
Technical Specifications ................................................................ 20
Troubleshooting ........................................................................... 22
Appendix ...................................................................................... 23
Configure port mirror settings ........................................................................... 10
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
1
Product Overview
Features
TRENDnet’s 8-Port Gigabit EdgeSmart PoE+ Switch, model TPE-TG44ES, is a costeffective switch solution for high-speed gigabit PoE+ applications. This EdgeSmart switch
features the most commonly used managed switch features, reducing unnecessary
switch complexity. The web-based management interface offers features for traffic
control, troubleshooting, access controls, and monitoring. TRENDnet’s TPE-TG44ES
provides four gigabit PoE+ and four gigabit non-PoE ports. The PoE+ standard supplies
up to 30W of power per port for devices such as high power wireless access points, PTZ
(Pan Tilt Zoom) Internet cameras, and VoIP telephony systems.
Ports
Four gigabit PoE+ ports and four gigabit ports provides a 16Gbps switching capacity
TPE-TG44ES
Package Contents
In addition to your switch, the package includes:
Quick Installation Guide
CD-ROM (Utility & User’s Guide)
Power adapter (55V DC, 1.3A)
If any package contents are missing or damaged, please contact the retail store, online
retailer, or reseller/distributor from which the product was purchased.
PoE Power
Supplies up to 30W of PoE+ power per PoE port with a 60W power
budget
Compact Design
With a compact and lightweight housing design this switch is well-suited for desktop
installations. Its fanless design is perfect for quiet environments that require silent
operation.
Network Management
A broad range of network configurations are supported by: 802.3ad link aggregation,
802.1Q VLAN, bandwidth controls, IGMP, loopback detection, port mirroring and 802.1p
(QoS).
Troubleshooting
Traffic statistics and a convenient cable diagnostic test aid in network troubleshooting.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 4
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
2
Housing
Compact wall mountable metal housing
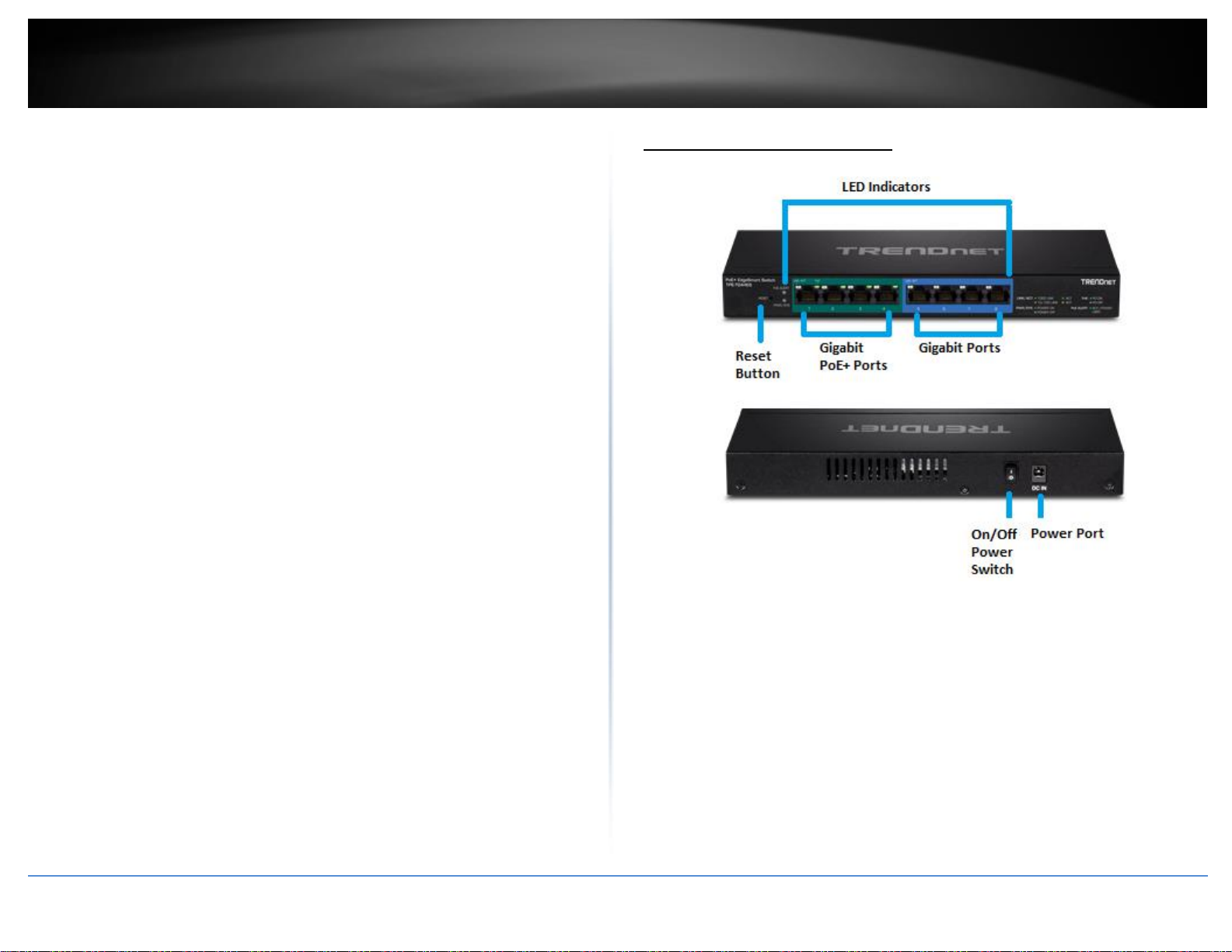
Product Hardware Features
LED Indicators
LED indicators convey port status
Reset Button – Press and hold this button for 10 seconds and release to
reset the switch to factory defaults.
PoE+ ports (1-4) – Ports 1-4 can supply power and Gigabit connectivity
to both PoE (802.3af) or PoE+ (802.3at) PoE devices.
PoE ports (5-8) – Ports 5-8 can provide Gigabit connectivity to network
non-PoE devices. (When using LACP, only ports 7 & 8 can be used for link
aggregation.)
On/Off Power Switch – Turns the switch on (|) or off (o).
Power Connector – Connect the included DC power adapter to the
connector and the other side of the power adapter to an available power
outlet.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 5

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
3
On
:
Indicates if 80% or more of the PoE power budget is used.
(equal or greater than 50W)
On
:
When the Power LED lights on, the device is powered and
on and ready.
Blinking
:
System boot up.
Off
:
When the Power LED light is off, the device is powered off
or power is not connected.
On (Green)
:
When the Green LED lights are on, the link is established
at Gigabit connectivity.
On
(Amber)
:
When the Amber LED lights are on, the link is established
at 10/100Mbps connectivity.
Blinking
:
When the LED is blinking, the port is transmitting or
receiving data.
Off The link is disconnected or not established.
On (Green)
:
When the Green LED lights are on, PoE power is being
supplied to the connected device.
Off PoE power is off and not supplying power to the
connected device.
PoE Alert
PWR/SYS LED
Gigabit Ports 1-8
Link/ACT LED
Applications
PoE
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 6
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
4
Switch Installation
Basic Installation
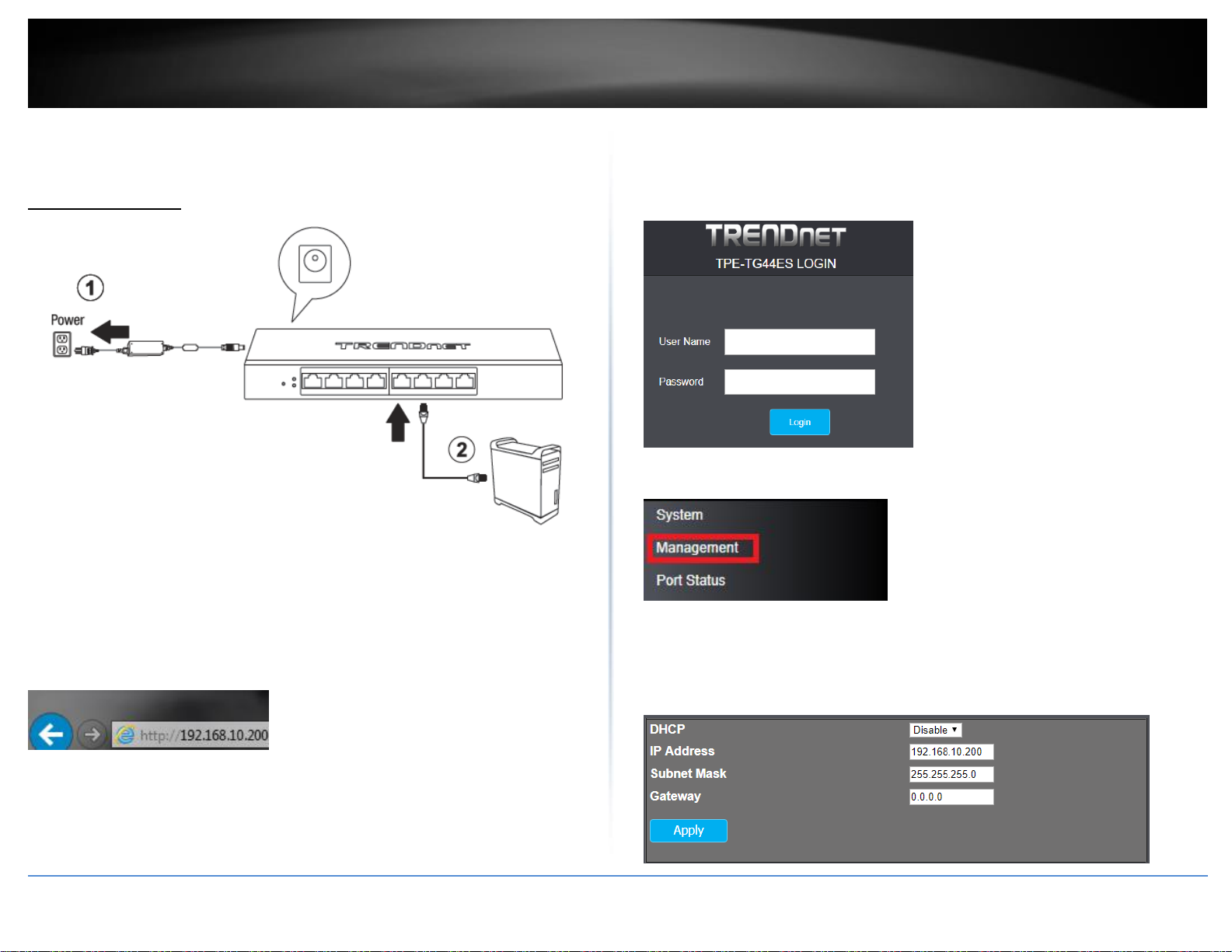
3. Push the power switch to the on (|) position.
4. Assign a static IP address to your computer’s network adapter in the subnet of
192.168.10.x (e.g. 192.168.10.25) and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
5. Open your web browser, and type the IP address of the switch in the address bar, and
then press Enter. The default IP address is 192.168.10.200.
6. Enter the User Name and Password, and then click Login. By default:
User Name: admin
Password: admin
Note: User name and password are case sensitive.
7. Click Management.
8. Configure the switch IP address settings to be within your network subnet, then click
Apply.
Note: You may need to modify the static IP address settings of your computer’s network
adapter to IP address settings within your subnet in order to regain access to the switch.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 7
5
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
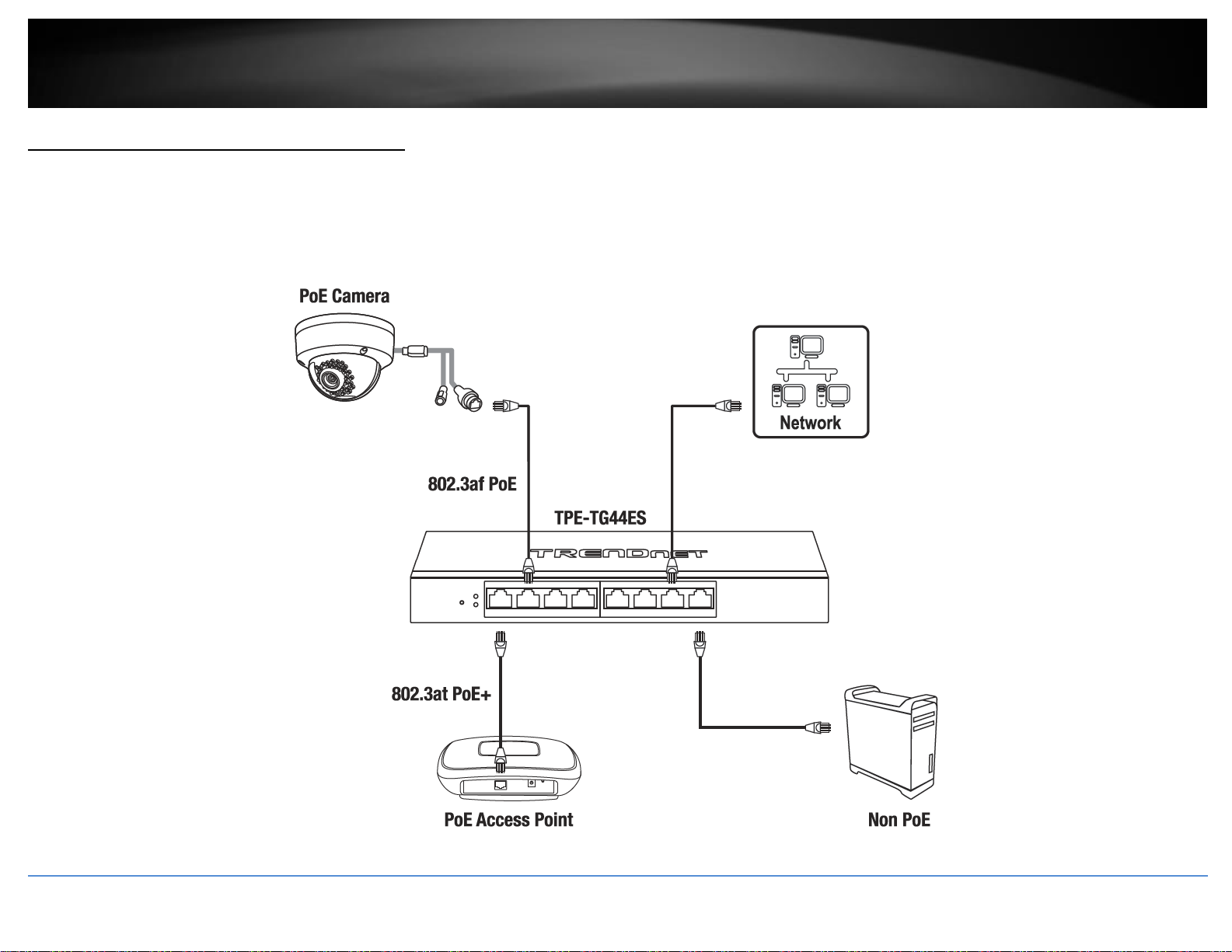
Connect additional devices to your switch
You can connect additional computers or other network devices PoE (Power over Ethernet) (Ports 1-4 PoE+/PoE, Ports 5-8) or non-PoE devices to your switch using Ethernet cables to
connect them to one of the available Gigabit Ports (1-8). Check the status of the LED indicators on the front panel of your switch to ensure the physical cable connection from your
computer or device.
Note: If you encounter issues connecting to your network, there may be a problem with your computer or device network settings. Please ensure that your computer or device network
settings (also called TCP/IP settings) are configured properly within the network subnet your switch is connected.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 8
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
6
Configure your switch
Access your switch management page
Note: Your switch default management IP address http://192.168.10.200 is accessed
through the use of your Internet web browser (e.g. Internet Explorer®, Firefox®,
Chrome™, Safari®, and Opera™) and will be referenced frequently in this User’s Guide.
1. Open your web browser and go to the IP address http://192.168.10.200. Your switch
will prompt you for a user name and password.
2. Enter the user name and password. By default:
User Name: admin
Password: admin
Note: User Name and Password are case sensitive.
System Info
View your switch status information
System
You may want to check the general system information of your switch such as firmware
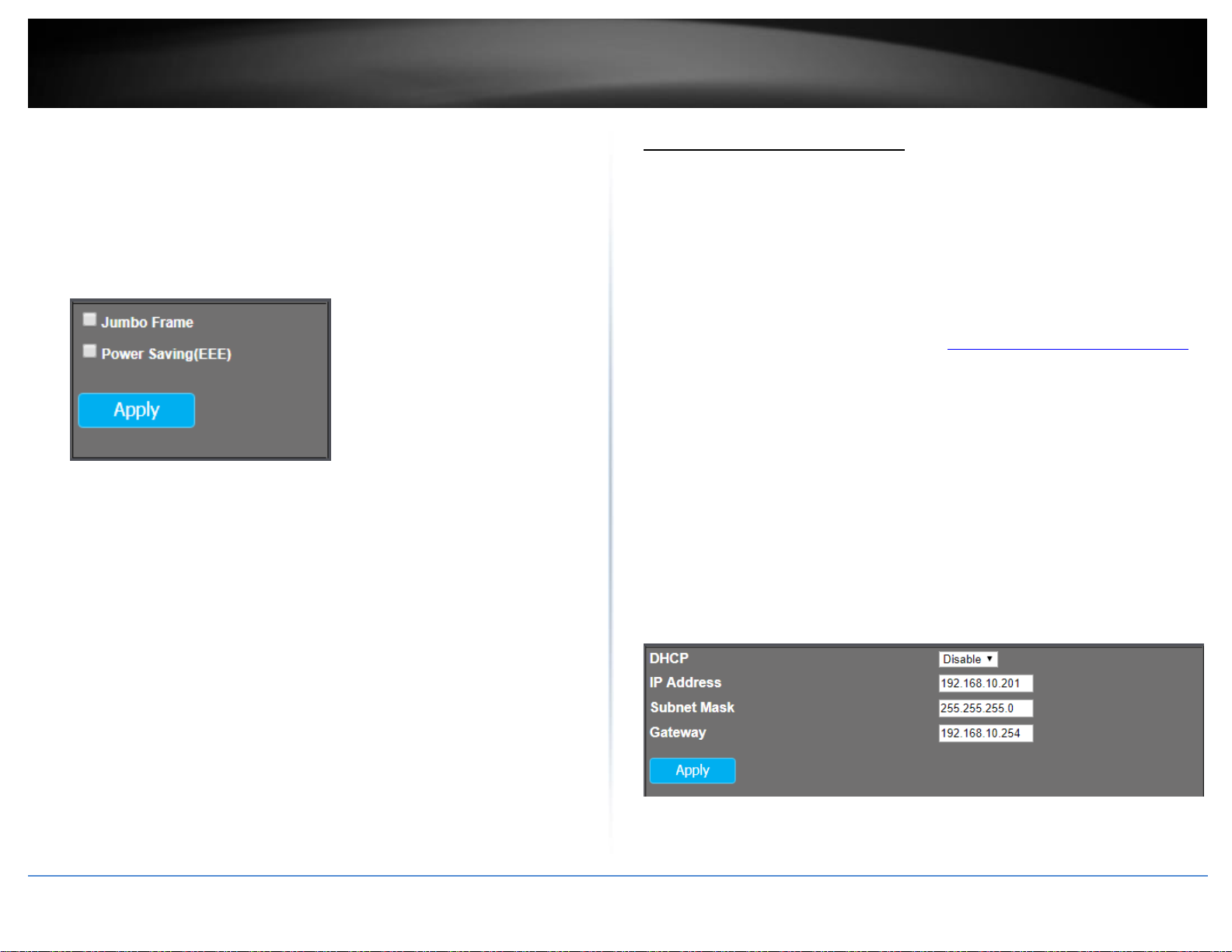
version, build date, and IP address information. You can also enable or disable jumbo
frames or power saving (EEE) features.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on System.
Mode Name: The model name of the switch.
Device Name: The current device name assigned to the switch. This can be
changed by clicking the TPE-TG44ES, entering new device name and clicking
Apply.
Firmware Version: The current software or firmware version your switch is
running.
Build Date: The build of the current software or firmware running on your switch.
MAC Address: Displays the switch system MAC address.
IPv4 Address: Displays the current IP address assigned to your switch.
Subnet Mask: Displays the current IP subnet mask assigned to your switch.
Gateway: Displays the current gateway address assigned to your switch.
Loop Status: If loopback prevention is enabled, displays if loops have been
detected on the network.
Note: You can also click Logout at the bottom of the left hand navigation to log out of
the switch management page.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 9
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
7
Jumbo Frame: Check the option and click Apply to enable jumbo frames. The
switch can support jumbo frames up to 9KB in size.
Power Saving (EEE): Check the option and click Apply to enable IEEE 802.3az
power saving.
The IEEE 802.3 EEE standard defines mechanisms and protocols intended to
reduce the energy consumption of network links during periods of low utilization,
by transitioning interfaces into a low-power state without interrupting the
network connection. The transmitted and received sides should be IEEE802.3az
EEE compliance.
Configure IP address settings
Set your switch IP address settings
Management
This section allows you to change your switch IP address settings. Typically, the IP
address settings should be changed to match your existing network subnet in order to
access the switch management page on your network.
Default Switch IP Address: 192.168.10.200
Default Switch IP Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Management.
3. Review the settings. When you have completed making changes, click Apply to save
the settings.
DHCP: Click the drop-down list and select Disable to manually specify your IP
address settings or DHCP to allow your switch to obtain IP address settings
automatically from a DHCP server on your network
IP Address: Enter the new switch IP address. (e.g. 192.168.200.200)
Subnet Mask: Enter the new switch subnet mask. (e.g. 255.255.255.0)
Gateway: Enter the default gateway IP address. (e.g. 192.168.200.1 or typically
your router/gateway to the Internet).
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 10

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
8
Port Status
Port status will display the link status/speed, and frame statistics of transmit and receive
for each port for troubleshooting purposes.
View Traffic Information Statistics
Port Status
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Port Status.
3. View the Traffic Information Statistics. Clicking the Clear Counters, will reset all of the
TX and RX information to 0 and restart the frame counters.
Port: Displays the port number.
Link Status: Displays the current link status and speed if connected.
TX: Displays the total amount of frames transmitted on the specified port.
RX: Displays the total amount of frames received on the specified port.
VLAN
Add, modify, and remove VLANs
VLAN
A VLAN is a group of ports that can be anywhere in the network, but communicate as
though they were in the same area.
VLANs can be easily organized to reflect department groups (such as R&D, Marketing),
usage groups (such as e-mail), or multicast groups (multimedia applications such as
video conferencing), and therefore help to simplify network management by allowing
users to move devices to a new VLAN without having to change any physical
connections.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on VLAN.
The PVID table displays the current port VLAN ID assignment.
Note: when untagged or VLAN-unaware ports are assigned to a VLAN, the port VLAN ID
should be assigned the same ID as the VLAN to be properly configured. (ex. If adding
ports 7 & 8 as untagged port members of VLAN ID 100, the PVID assignment for ports 7
& 8 should be set to 100.)
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 11

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
9
The VLAN table displays the current list of VLANs. By default, all ports are assigned as
untagged members of VLAN ID 1. The color code on each port indicates the type of
membership for each port assigned to a specific VLAN. Up to 32 VLANs can be created.
Untagged port member – Green
Tagged port member – Orange
Non- member or restricted port - Gray
VLAN ID – Displays the VLAN ID.
Modify – Click modify to edit the VLAN configuration. The default VLAN cannot
be modified.
Delete – Click delete to delete the VLAN. The default VLAN cannot be deleted.
Management VLAN – Click the drop-down list and select Enabled to allow
access to the switch management page through the new VLAN. If you want to
restrict management access through this VLAN, select Disabled.
Note: By default, the default VLAN VID 1 is set as the Management VLAN.
To create a new VLAN, click Create New VLAN.
Enter the VLAN ID to assign to the new VLAN. (ex. ID 100)
By default, all ports are set as tagged members of the new VLAN.
To change the port membership to untagged or non-member, click on the port box
multiple times to cycle through the port membership type based on the color code.
After you have assigned all the ports with the desired port membership to the new
VLAN, click Apply.
Note: when untagged or VLAN-unaware ports are assigned to a VLAN, the port VLAN ID
should be assigned the same ID as the VLAN to be properly configured. (ex. If adding
ports 7 & 8 as untagged port members of VLAN ID 100, the PVID assignment for ports 7
& 8 should be set to 100.)
Tagged/Untagged/Non-Member VLAN Ports
On a port, the tag information within a frame is examined when it is received to
determine if the frame is qualified as a member of a specific tagged VLAN. If it is, it is
eligible to be switched to other member ports of the same VLAN. If it is determined that
the frame’s tag does not conform to the tagged VLAN, the frame is discarded.
Since these VLAN ports are VLAN aware and able to read VLAN VID tagged information
on a frame and forward to the appropriate VLAN, typically tagged VLAN ports are used
for uplink and downlink to other switches to carry and forward traffic for multiple VLANs
across multiple switches. Tagged VLAN ports can be included as members for multiple
VLANs. Computers and other edge devices are not typically connected to tagged VLAN
ports unless the network interface on these device can be enabled to be VLAN aware.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 12

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
10
Trunk/Link Aggregation
Configure port trunk settings
Trunking/Link Aggregation
The trunking function enables the cascading of two or more ports for a combined larger
total bandwidth. Only a single trunk group can be created consisting of ports 7 & 8 only.
Only 802.3ad LACP dynamic trunking is supported.
Important Note: Do not connect the cables of a port trunk to the ports on the switch
until you have configured the ports on both sides of the trunk configured for link
aggregation. Connecting the cables prior to configuring the ports can create loops in
your network topology. Loops can result in broadcast storms which can severely limited
the effective bandwidth of your network.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Trunking/Link Aggregation.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
LACP Global State – Click the drop-down list and select Enable to enable LACP
trunking.
Link Aggregation Algorithm – Click the drop-down list and select the algorithm
to use for the trunk. The algorithm used should be the same on both sides of
the link aggregation trunk. (ex. If MAC SA & DA is configured on the switch,
then the device on the other end of the trunk should also be configured to use
the MAC SA & DA algorithm.)
o MAC SA & DA – MAC source and destination address
o MAC SA – MAC source address only.
o MAC DA – MAC destination address only.
Link Group Activity – Select Active mode for 802.3ad link aggregation.
Link Group Member - Only ports 7 & 8 may be used for link aggregation. The
ports will not be checked if a link aggregation trunk has not been established. If
a link aggregation trunk has been successfully established, ports 7 & 8 will
automatically be checked.
Mirroring
Configure port mirror settings
Mirror
Port mirroring allows you to monitor the ingress and egress traffic on a port by having
the traffic copied to another port where a computer or device can be set up to capture
the data for monitoring and troubleshooting purposes.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Mirror.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
Enable Mirror – Check the option to enable port mirroring.
Mirror Direction
o Ingress – Only mirror received frames on the selected ports.
o Egress – Only mirror transmitted frames on the selected ports.
o Both – Mirror both received and transmitted frames on the selected
ports.
Monitor Port – Click the drop-down to select the target port to send the
mirrored or copied frames. (ex. Computer or device with packet capture or data
analysis software.)
Mirrored Port List – Check which ports to mirror.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 13

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
11
QoS (Quality of Service)
When a port on an Ethernet switch becomes oversubscribed, its egress
queues contain more packets than the port can handle in a timely manner. In this
situation, the port may be forced to delay the transmission of some packets, resulting in
the delay of packets reaching their destinations. A port may be forced to delay
transmission of packets while it handles other traffic, and, in some situations, some
packets destined to be forwarded to an oversubscribed port from other switch ports
may be discarded.
Minor delays are often of no consequence to a network or its performance. But there
are applications, referred to as delay or time sensitive applications, which can be
impacted by packet delays. Voice transmission and video conferences are two examples.
If packets carrying data in either of these cases are delayed from reaching their
destination, the audio or video quality may suffer.
The switch supports port-based QoS or IEEE 802.1p QoS (CoS).
Port-Based QoS
QoS
The switch will assign priority to each queue per port based on the weight assignment
for each queue.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Port-Based QoS and when prompted to change the QoS mode, click OK.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
By default, queue configuration can be found at the bottom of the page, queue 0 being
the lowest priority and queue 3 being the highest.
1-8 – Indicates the port number. By default, all ports are assigned to the lowest
priority queue 0. This would require manually configuration to apply per port
priority.
Weight – The weight value indicates the queue priority value 1 being the
lowest and 32 being the highest. The higher the weight value assigned to a
specified queue, the higher the amount of packets from that queue are sent
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
IEEE 802.1p QoS
QoS
The switch will accept frames with specified 802.1p CoS priority tags from other
network devices and process and schedule according to the IEEE 802.1p QoS
configuration but will not add priority tags to new frames originating from the switch.
Supports passthrough 802.1p QoS only.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
2. Click on IEEE 802.1p QoS and when prompted to change the QoS mode, click OK.
out and processed before other lower priority queues. This can be adjusted
accordingly however default settings should be sufficient.
Strict Priority - Using this scheduling method, the port transmits all frames out
of higher priority queues before transmitting any from the lower priority
queues.
WFQ (Weighted Fair Queuing) – Using this scheduling method, the port
transmits a set number of bits from random queues, in a round robin fashion,
so that each has a chance to transmit traffic.
on page 6).
Page 14

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
12
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
By default, queue configuration can be found at the bottom of the page, queue 0 being
the lowest priority and queue 3 being the highest.
1-7 – Indicates the 802.1p CoS tag values, 1 being the lowest and 7 being the
highest. Based on the priority tag value identified on the incoming frame, the
frame will be assigned to the specified queue assigned for the priority tag
value. This can be adjusted accordingly however default settings should be
sufficient.
Weight – The weight value indicates the queue priority value 1 being the
lowest and 32 being the highest. The higher the weight value assigned to a
specified queue, the higher the amount of packets from that queue are sent
out and processed before other lower priority queues. This can be adjusted
accordingly however default settings should be sufficient.
Strict Priority - Using this scheduling method, the port transmits all frames out
of higher priority queues before transmitting any from the lower priority
queues.
WFQ (Weighted Fair Queuing) – Using this scheduling method, the port
transmits a set number of bits from random queues, in a round robin fashion,
so that each has a chance to transmit traffic.
Storm Control
Configure Storm Control
Broadcast Storm Control
The switch can set rate limits on broadcast, multicast, and unicast (DLF) traffic and drop
traffic once the configured rate threshold is reached. This feature can be useful more
specifically for broadcast storms.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Broadcast Storm Control.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
Broadcast – Click the drop-down list and select the speed threshold for
broadcast traffic which will be applied to the switch on all ports.
Multicast – Click the drop-down list and select the speed threshold for
multicast traffic which will be applied to the switch on all ports.
DLF (Destination Lookup Failure) – Click the drop-down list and select the
speed threshold for unicast (DLF) traffic which will be applied to the switch on
all ports.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 15

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
13
Rate Limiting
Set Per Port Rate Limiting
Rate Limiting
The switch allows you to set a rate or bandwidth limit per port both transmitting and
receiving.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Rate Limiting.
3. Review the settings for each port. Click Apply to save the settings.
Port – Indicates the port number.
Ingress rate – Click the drop-down list to select the rate or bandwidth limit for
received on a specific port.
Egress rate – Click the drop-down list to select the rate or bandwidth limit for
transmitted from a specific port.
Loopback Detection & Prevention
Enable loopback prevention
Loopback Prevention
The loopback detection and prevention feature allows the switch to detect and prevent
disruption from loops that occur on other switches directly connected to your switch.
Ex. A loop occurs on another switch that is connected to your switch on port 5. If
loopback detection and prevention is enabled on your switch, the switch will detect a
loop occurrence on port 5 and disable it until the loop issue is resolved.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Loopback Prevention.
3. To enable loopback detection and prevention on all ports, click the drop-down list and
select Loopback Prevention. Click Apply to save changes.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 16

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
14
Class
Maximum Power
Output
from a Switch Port
Power Ranges of the PDs
0
15.4W
0.44W to 12.95W
1
4.0W
0.44W to 3.84W
2
7.0W
3.84W to 6.49W
3
15.4W
6.49W to 12.95W
4
30W
12.95-25.50W
IGMP Snooping
Configure IGMP Snooping Settings
IGMP Snooping
The IGMP snooping feature filters multicast traffic sent across your switch only to the
multicast hosts and servers. This will prevent multicast traffic from flooding all ports of
the switch in order to prevent unnecessary switch processing and optimize switch
traffic. The switch supports IGMP 1/2/3 snooping.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on IGMP Snooping.
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save the settings.
Block Unknown Multicast – Enabling this option will prevent or drop multicast
traffic from an unknown multicast source address.
Enable IGMP Snooping – Check this option to enable IGMP snooping.
IGMP Static Router Port – IGMP snooping will automatically learn the ports of
the multicast server, you may statically set the port where the multicast server
is connected or linked from another switch.
The table will display the discovered multicast group address, multicast
server/router port, and VLAN ID.
PoE Configuration
The main advantage of PoE is that it can make installing a network easier. The selection
of a location for a network device is often limited by whether there is a power source
nearby. This constraint limits equipment placement or requires the added time and cost
of having additional electrical sources installed. However, with PoE, you can install PoE
compatible devices wherever they are needed without having to worry about whether
there is power source nearby.
Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE)
A device that provides PoE to other network devices is referred to as
power sourcing equipment (PSE). The Gigabit Web Smart PoE+ Switch is a PSE
device which provides DC power to the network cable and functions as a central power
source for other network devices.
Powered Device (PD)
A device that receives power from a PSE device is called a powered
device (PD). Examples include wireless access points, IP phones, webcams, and even
other Ethernet switches.
PD Classes PDs are grouped into five classes. The classes are based on the amount of
power that PDs require. The Gigabit Web Smart PoE+ Switch supports all five classes.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 17

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
15
Power Budget
Power budget is the maximum amount of power that the PoE switch can provide at one
time to the connected PDs.
Configure PoE settings
PoE Configuration
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on PoE.
3. Review the settings for each port. Next to each port entry, click Apply to save the
settings.
PSE Total Power – Displays the maximum PoE power budget in watts.
PSE MAX LED Power - Displays the threshold limit of PoE power usage when
the PoE Alert LED will turn on to indicate 80% of total PoE power used.
PSE IC MAX Temperature – Displays the maximum temperature allowable limit
of the PoE IC chip.
PSE Voltage – Displays the PoE voltage supplied to each PoE port.
Port – Displays the port number. You can manually enable or disable PoE on
the specified port by clicking the number and selecting Turn on or Turn off. By
default, PoE is enabled on all PoE ports.
Power Status – Displays the current status of the PoE port, whether PoE is
turned on or off.
Power Usage – Displays the current PoE power provided to PoE device or PDs
(Powered devices) in watts.
Temperature – Displays the current temperature of each port supplying PoE.
Turned On – Displays the total number of ports with PoE enabled.
Total Power – Displays the current amount of PoE power used by all PoE ports.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 18

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
16
Switch Maintenance
Change administrator password
Password
This section explains how to change the administrator password.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Password.
3. In the New Password and Confirm Password fields, enter the new password. Click
Confirm to save the settings.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 19

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
17
Upgrade your switch firmware
Management
TRENDnet may periodically release firmware upgrades that may add features or fix
problems associated with your TRENDnet switch model and version. To check if there is
a firmware upgrade available for your device, please check your TRENDnet model and
version using the link. http://www.trendnet.com/support/
In addition, it is also important to verify if the latest firmware version is newer than the
one your switch is currently running. To identify the firmware that is currently loaded on
your switch, log in to the switch, click on the System Info section or click on Tools and
click on Firmware Upgrade. The firmware used by the switch is listed as Runtime Image
or Image Version. If there is a newer version available, also review the release notes to
check if there were any new features you may want or if any problems were fixed that
you may have been experiencing.
1. If a firmware upgrade is available, download the firmware to your computer.
2. Unzip the file to a folder on your computer.
Please note the following:
Do not interrupt the firmware upgrade process. Do not turn off the device or
press the Reset button during the upgrade.
If you are upgrade the firmware using a laptop computer, ensure that the laptop
is connected to a power source or ensure that the battery is fully charged.
Disable sleep mode on your computer as this may interrupt the firmware upgrade
process.
Do not upgrade the firmware using a wireless connection, only using a wired
network connection.
Any interruptions during the firmware upgrade process may permanently
damage your switch.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Management.
3. Under the Firmware Upgrade section, click Upgrade. W
4. When prompted to enter Loader Mode, click OK.
5. Wait for the loader page to appear and click Browse or Choose File. Navigate to the
folder on your computer where the unzipped firmware file (.bin) is located and select
it.
6. Click Upgrade. If prompted, click Yes or OK. You may also click Reboot to cancel the
firmware upgrade.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 20

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
18
Backup and restore your switch configuration settings
Tools > Config File Backup/Restore
You may have added many customized settings to your switch and in the case that you
need to reset your switch to default, all your customized settings would be lost and
would require you to manually reconfigure all of your switch settings instead of simply
restoring from a backed up switch configuration file.
Backup/Restore
To backup your switch configuration:
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Management.
3. Under Configuration Restore / Backup, click Backup to save the configuration file
(switch_cfg.bin) to your local hard drive.
Note: If prompted, choose the location on your local hard drive. If you are not prompted,
the configuration file (switch_cfg.bin) will be saved to your default downloads folder.
To restore your switch configuration:
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Management.
3. Under Configuration Restore / Backup and mext to Select File, depending on your
web browser, click on Browse or Choose File.
4. A separate file navigation window should open.
5. Select the switch configuration file to restore and click Restore. (Default Filename:
switch_cfg.bin). If prompted, click Yes or OK.
6. Wait for the switch to restore settings.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 21

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
19
Administrator User Name
admin
Administrator Password
admin
Switch IP Address
192.168.10.200
Switch Subnet Mask
255.255.255.0
Reboot/Reset to factory defaults
Tools > Reboot
This section provides the procedures for rebooting or resetting the switch to factory
default settings.
To reboot your switch:
You may want to reboot your switch if you are encountering difficulties with your switch
and have attempted all other troubleshooting.
There are two methods that can be used to reboot your switch.
Hardware Method: Push the power on/off switch to the off (o) position then to
the on position (|) or disconnect the power adapter and reconnect.
Software Method (Switch Management Page):
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Management.
3. Under the section Reset to Default / Reboot, click the Reboot. When prompted to
Reboot System, click OK. Wait for the switch complete the rebooting process.
To reset your switch to factory defaults:
You may want to reset your switch to factory defaults if you are encountering difficulties
with your switch and have attempted all other troubleshooting. Before you reset your
switch to defaults, if possible, you should backup your switch configuration first, see
“Backup and restore your switch configuration settings” on page 77.
There are two methods that can be used to reset your switch to factory defaults.
Hardware Method: Using a paper clip, on the front panel of the switch, push
and hold the Reset button more than 10 seconds and release. Located on the
front panel of your switch, see “Product Hardware Features” on page 2. Use
this method if you are encountering difficulties with accessing your switch
management page.
Software Method (Switch Management Page):
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 6).
2. Click on Management.
3. Under the section Reset to Default / Reboot, click the Reboot. When prompted to
Reset System, click OK. Wait for the switch complete resetting the switch to factory
default settings.
The switch factory default settings are below.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 22

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
20
Technical Specifications
Standards
IEEE 802.1p
IEEE 802.1Q
IEEE 802.3
IEEE 802.3u
IEEE 802.3x
IEEE 802.3ab
IEEE 802.3ad
IEEE 802.3af (15.4 Watts/port)
IEEE 802.3at (30 Watts/port)
IEEE 802.3az
Device Interface
4 x Gigabit PoE+ ports (1-4)
4 x Gigabit ports (5-8)
LED indicators
Reset button
Data Transfer Rate
Ethernet: 10 Mbps (half duplex), 20 Mbps (full duplex)
Fast Ethernet: 100 Mbps (half duplex), 200 Mbps (full duplex)
Gigabit Ethernet: 2000 Mbps (full duplex)
Performance
Switch fabric: 16 Gbps
RAM buffer: 192 KB
MAC Address Table: 4K entries
Jumbo Frames: 9 KB
Forwarding rate: 11.9 Mpps (64-byte packet size)
Management
HTTP Web based GUI
Backup/Restore Configuration
Upload Firmware
Link Aggregation
802.3ad Dynamic LACP
Quality of Service (QoS)
Port-based QoS
802.1p Class of Service (CoS)
Bandwidth Control/Rate Limiting per port (Min. Limit: 512Kbps)
Queue Scheduling: Strict Priority (SP), Weighted Fair Queueing (WFQ)
VLAN
Port-based VLAN
802.1Q Tagged VLAN
Up to 32 VLAN groups, ID Range 1-4094
Multicast
IGMP Snooping v1/2/3
Block unknown multicast source
Up to 128 multicast groups
Port Mirror
One to one
Many to one
Access Control
Trusted Host/IP Access List
Storm Control
Broadcast (Min. Limit: 512Kbps)
Multicast (Min. Limit: 512Kbps)
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 23

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
21
Destination Lookup Failure (DLF) (Min. Limit: 512Kbps)
Loopback Detection
Special Features
PoE+ support
Enable/disable 802.3az Power Saving
Wall mountable
Power
Input: 100 - 240V AC, 50/60 Hz, 2.5A
Output: 55V DC, 1.3A external power adapter
Consumption: 65.28W (max.)
PoE
PoE budget: 60 W (max.)
802.3at: Up to 30 W per port (ports 1-4)
Mode A: Pins 1,2 for power(+) and pins 3,6 for power(-)
PD auto classification
Over current/short circuit protection
Fan / Acoustics
Fanless design
MTBF
1,089,244 hours
Operating Temperature
0 – 50°C (32 - 122°F)
Dimensions
240 x 105 x 27 mm (9.45 x 4.1 x 1.06 in.)
Wall mountable
Weight
576 g (20.3 oz.)
Certifications
CE
FCC
Operating Humidity
Max. 90% non-condensing
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 24

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
22
Troubleshooting
Q: I typed http://192.168.10.200 in my Internet Browser Address Bar, but an error
message says “The page cannot be displayed.” How can I access the switch
management page?
Answer:
1. Check your hardware settings again. See “Switch Installation” on page 8.
2. Make sure the Power and port Link/Activity and WLAN lights are lit.
3. Make sure your network adapter TCP/IP settings are set to Use the following IP
address or Static IP(see the steps below).
4. Make sure your computer is connected to one of the Ethernet switch ports.
5. Since the switch default IP address is 192.168.10.200, make sure there are no other
network devices assigned an IP address of 192.168.10.200
Windows 7/8/8.1/10
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Sharing Center.
b. Click Change Adapter Settings, right-click the Local Area Connection icon.
c. Then click Properties and click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and make sure to assign your
network adapter an IP address in the subnet of 192.168.10.x. Click OK
Windows Vista
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Internet.
b. Click Manage Network Connections, right-click the Local Area Connection
icon and click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol Version (TCP/IPv4) and then click Properties.
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and make sure to assign your
network adapter an IP address in the subnet of 192.168.10.x. Click OK
Windows XP/2000
a. Go into the Control Panel, double-click the Network Connections icon
b. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and the click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and make sure to assign your
network adapter an IP address in the subnet of 192.168.10.x. Click OK
Note: If you are experiencing difficulties, please contact your computer or operating
system manufacturer for assistance.
Q: If my switch IP address is different than my network’s subnet, what should I do?
Answer:
You should still configure the switch first. After all the settings are applied, go to the
switch configuration page, click on System, click IPv4 Setup and change the IP address of
the switch to be within your network’s IP subnet. Click Apply, then click OK. Then click
Save Settings to Flash (menu) and click Save Settings to Flash to save the IP settings to
the NV-RAM.
Q: I changed the IP address of the switch, but I forgot it. How do I reset my switch?
Answer:
Using a paper clip, push and hold the reset button on the front of the switch and release
after 15 seconds.
The default IP address of the switch is 192.168.10.200. The default user name and
password is “admin”.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 25

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
23
Appendix
How to find your IP address?
Note: Please note that although the following procedures provided to follow for your
operating system on configuring your network settings can be used as general
guidelines, however, it is strongly recommended that you consult your computer or
operating system manufacturer directly for assistance on the proper procedure for
configuring network settings.
Command Prompt Method
Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7/8/8.1/10
1. On your keyboard, press Windows Logo+R keys simultaneously to bring up the Run
dialog box.
2. In the dialog box, type cmd to bring up the command prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type ipconfig /all to display your IP address settings.
MAC OS X
1. Navigate to your Applications folder and open Utilities.
2. Double-click on Terminal to launch the command prompt.
3. In the command prompt, type ipconfig getifaddr <en0 or en1> to display the wired
or wireless IP address settings.
Note: en0 is typically the wired Ethernet and en1 is typically the wireless Airport
interface.
Graphical Method
MAC OS 10.6/10.5
1. From the Apple menu, select System Preferences.
2. In System Preferences, from the View menu, select Network.
3. In the Network preference window, click a network port (e.g., Ethernet, AirPort,
modem). If you are connected, you'll see your IP address settings under "Status:"
MAC OS 10.4
1. From the Apple menu, select Location, and then Network Preferences.
2. In the Network Preference window, next to "Show:", select Network Status. You'll see
your network status and your IP address settings displayed.
Note: If you are experiencing difficulties, please contact your computer or operating
system manufacturer for assistance.
How to configure your network settings to use a static IP address?
Note: Please note that although the following procedures provided to follow for your
operating system on configuring your network settings can be used as general
guidelines, however, it is strongly recommended that you consult your computer or
operating system manufacturer directly for assistance on the proper procedure for
configuring network settings.
Windows 7/8/8.1/10
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Sharing Center.
b. Click Change Adapter Settings, right-click the Local Area Connection icon.
c. Then click Properties and click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and assign your network adapter a
static IP address. Click OK
Windows Vista
a. Go into the Control Panel, click Network and Internet.
b. Click Manage Network Connections, right-click the Local Area Connection
icon and click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol Version (TCP/IPv4) and then click Properties.
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and assign your network adapter a
static IP address. Click OK
Windows XP/2000
a. Go into the Control Panel, double-click the Network Connections icon
b. Right-click the Local Area Connection icon and the click Properties.
c. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
d. Then click Use the following IP address, and assign your network adapter a
static IP address. Click OK
MAC OS 10.4/10.5/10.6
a. From the Apple, drop-down list, select System Preferences.
b. Click the Network icon.
c. From the Location drop-down list, select Automatic.
d. Select and view your Ethernet connection.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 26

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
24
In MAC OS 10.4, from the Show drop-down list, select Built-in
Ethernet and select the TCP/IP tab.
In MAC OS 10.5/10.6, in the left column, select Ethernet.
e. Configure TCP/IP to use a static IP.
In MAC 10.4, from the Configure IPv4, drop-down list, select Manually
and assign your network adapter a static IP address. Then click the
Apply Now button.
In MAC 10.5/10.6, from the Configure drop-down list, select Manually
and assign your network adapter a static IP address . Then click the
Apply button.
f. Restart your computer.
Note: If you are experiencing difficulties, please contact your computer or operating
system manufacturer for assistance.
How to find your MAC address?
In Windows 2000/XP/Vista/7/8.1/.10,
Your computer MAC addresses are also displayed in this window, however, you can type
getmac –v to display the MAC addresses only.
In MAC OS 10.4,
1. Apple Menu > System Preferences > Network
2. From the Show menu, select Built-in Ethernet.
3. On the Ethernet tab, the Ethernet ID is your MAC Address.
In MAC OS 10.5/10.6,
1. Apple Menu > System Preferences > Network
2. Select Ethernet from the list on the left.
3. Click the Advanced button.
3. On the Ethernet tab, the Ethernet ID is your MAC Address.
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 27

TRENDnet User’s Guide
TPE-TG44ES
25
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance
20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna
or transmitter.
Country Code selection feature to be disabled for products marketed to the US/CANADA
RoHS
This product is RoHS compliant.
Europe – EU Declaration of Conformity
Safety
EN 60950-1: 2011 + A2: 2013
EMC
EN 55032: 2015
EN 61000-3-2: 2014
EN 61000-3-3: 2013
EN 55024: 2010
AS/NZS CISPR 32: 2013
Directives:
Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
EMC Directive EN 2014/30/EU
RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU
WEEE Directive 2012/19/EU
REACH Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 28

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Limited Warranty
26
Limited Warranty
TRENDnet warrants only to the original purchaser of this product from a TRENDnet
authorized reseller or distributor that this product will be free from defects in material
and workmanship under normal use and service. This limited warranty is nontransferable and does not apply to any purchaser who bought the product from a
reseller or distributor not authorized by TRENDnet, including but not limited to
purchases from Internet auction sites.
Limited Warranty
TRENDnet warrants its products against defects in material and workmanship, under
normal use and service. Specific warranty periods are listed on each of the respective
product pages on the TRENDnet website.
AC/DC Power Adapter, Cooling Fan, and Power Supply carry a one-year
warranty.
Limited Lifetime Warranty
TRENDnet offers a limited lifetime warranty for all of its metal-enclosed network
switches that have been purchased in the United States/Canada on or after 1/1/2015.
Cooling fan and internal power supply carry a one-year warranty
To obtain an RMA, the ORIGINAL PURCHASER must show Proof of Purchase and return
the unit to the address provided. The customer is responsible for any shipping-related
costs that may occur. Replacement goods will be shipped back to the customer at
TRENDnet’s expense.
Upon receiving the RMA unit, TRENDnet may repair the unit using refurbished parts. In
the event that the RMA unit needs to be replaced, TRENDnet may replace it with a
refurbished product of the same or comparable model.
In the event that, after evaluation, TRENDnet cannot replace the defective product or
there is no comparable model available, we will refund the depreciated value of the
product.
If a product does not operate as warranted during the applicable warranty period,
TRENDnet shall reserve the right, at its expense, to repair or replace the defective
product or part and deliver an equivalent product or part to the customer. The
repair/replacement unit's warranty continues from the original date of purchase. All
products that are replaced become the property of TRENDnet. Replacement products
may be new or reconditioned. TRENDnet does not issue refunds or credit. Please
contact the point-of-purchase for their return policies.
TRENDnet shall not be responsible for any software, firmware, information, or memory
data of customer contained in, stored on, or integrated with any products returned to
TRENDnet pursuant to any warranty.
There are no user serviceable parts inside the product. Do not remove or attempt to
service the product by any unauthorized service center. This warranty is voided if (i) the
product has been modified or repaired by any unauthorized service center, (ii) the
product was subject to accident, abuse, or improper use, or (iii) the product was subject
to conditions more severe than those specified in the manual.
Warranty service may be obtained by contacting TRENDnet within the applicable
warranty period and providing a copy of the dated proof of the purchase. Upon proper
submission of required documentation, a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number
will be issued. An RMA number is required in order to initiate warranty service support
for all TRENDnet products. Products that are sent to TRENDnet for RMA service must
have the RMA number marked on the outside of return packages and sent to TRENDnet
prepaid, insured and packaged appropriately for safe shipment. International customers
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 29

TRENDnet User’s Guide
Limited Warranty
27
shipping from outside of the USA and Canada are responsible for any return shipping
and/or customs charges, including but not limited to, duty, tax, and other fees.
Refurbished product: Refurbished products carry a 90-day warranty after date of
purchase. Please retain the dated sales receipt with purchase price clearly visible as
evidence of the original purchaser's date of purchase. Replacement products may be
refurbished or contain refurbished materials. If TRENDnet, by its sole determination, is
unable to replace the defective product, we will offer a refund for the depreciated value
of the product.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE: IF THE TRENDNET PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS
WARRANTED ABOVE, THE CUSTOMER'S SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE, AT TRENDNET'S
OPTION, REPAIR OR REPLACE. THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE
EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED,
EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
TRENDNET NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR
IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, OR USE OF TRENDNET'S PRODUCTS.
TRENDNET SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND
EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THAT THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST
OR WAS CAUSED BY CUSTOMER'S OR ANY THIRD PERSON'S MISUSE, NEGLECT,
IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR OR
MODIFY, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED USE, OR BY
ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
CONTRACT OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), FOR INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR FOR LOSS OF REVENUE OR
PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATE, OR OTHER FINANCIAL
LOSS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION OF THE POSSIBILITY
OF SUCH DAMAGES, AND LIMITS ITS LIABILITY TO REPAIR, REPLACEMENT, OR REFUND
OF THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID, AT TRENDNET'S OPTION. THIS DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
FOR DAMAGES WILL NOT BE AFFECTED IF ANY REMEDY PROVIDED HEREIN SHALL FAIL
OF ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE.
Governing Law: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the state of
California.
Some TRENDnet products include software code written by third party developers.
These codes are subject to the GNU General Public License ("GPL") or GNU Lesser
General Public License ("LGPL").
Visit http://www.trendnet.com/gpl or the support section on
http://www.trendnet.com and search for the desired TRENDnet product to access to
the GPL Code or LGPL Code. These codes are distributed WITHOUT WARRANTY and are
subject to the copyrights of the developers. TRENDnet does not provide technical
support for these codes. Please visit http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.txt or
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl.txt for specific terms of each license.
PWP07172015v3 2017/08/02
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, TRENDNET ALSO
EXCLUDES FOR ITSELF AND ITS SUPPLIERS ANY LIABILITY, WHETHER BASED IN
© Copyright 2017 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
Page 30

 Loading...
Loading...