Page 1

Voyager™ II Rooftop units
Cooling only TKD/TKH 155 175 200 250
Reversible WKD/WKH 125 155 200
Gas-Fired YKD/YKH 155 175 200 250
R22 - R407C Refrigerant
Installation
Operation
Maintenance
RT-SVX19A-E4
Page 2

Foreword
These instructions are given as a
guide to good practice in the
installation, start-up, operation, and
maintenance by the user, of Trane
TKD/TKH, WKD/WKH and YKD/YKH
units. They do not contain full
service procedures necessary for
the continued successful operation
of this equipment. The services of a
qualified technician should be
employed through the medium of a
maintenance contract with a
reputable service company. Read
this manual thoroughly before unit
start-up.
TKD/TKH units are designed to
operate in cooling mode only, with
optional auxiliary heat (electric
heater or hot water coil).
WKD/WKH can operate in cooling
mode or heating mode by reversing
the refrigeration cycle with or
without auxiliary heat.
YKD/YKH units are designed to
operate In cooling mode and
equipped with a gas fired heating
module.
TKD/TKH, WKD/WKH and YKD/YKH
units are assembled, pressure
tested, dehydrated, charged and run
tested before shipment.
Warnings and cautions
Warnings and Cautions appear at
appropriate sections throughout
this manual. Your personal safety
and the proper operation of this
machine require that you follow
them carefully. The constructor
assumes no liability for installations
or servicing performed by
unqualified personnel.
WARNING! : Indicates a potentially
hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
CAUTION! : Indicates a potentially
hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury. It may also be
used to alert against unsafe
practices or for equipment or
property-damage-only accidents.
Safety recommendations
To avoid death, injury, equipment or
property damage, the following
recommendations should be
observed during maintenance and
service visits:
1. The maximum allowable
pressures for system leak testing
on low and high pressure side
are given in the chapter
"Installation". Always provide a
pressure regulator.
2. Disconnect the main power
supply before any servicing on
the unit.
3. Service work on the refrigeration
system and the electrical system
should be carried out only by
qualified and experienced
personnel.
Reception
On arrival, inspect the unit before
signing the delivery note.
In case of visible damage: The
consignee (or the site
representative) must specify any
damage on the delivery note,
legibly sign and date the delivery
note, and the truck driver must
countersign it. The consignee (or the
site representative) must notify
Trane Epinal Operations - Claims
team and send a copy of the
delivery note. The customer (or the
site representative) should send a
registered letter to the last carrier
within 3 days of delivery.
Reception in France only:
Concealed damage must be looked
for at delivery and immediately
treated as visible damage.
Reception in all countries except
France:
In case of concealed damage: The
consignee (or the site
representative) must send a
registered letter to the last carrier
within 7 days of delivery, claiming
for the described damage. A copy of
this letter must be sent to Trane
Epinal Operations - Claims team.
General information
RT-SVX19A-E42
Page 3

Warranty
Warranty is based on the general
terms and conditions of the
manufacturer. The warranty is void if
the equipment is repaired or
modified without the written
approval of the manufacturer, if the
operating limits are exceeded or if
the control system or the electrical
wiring is modified. Damage due to
misuse, lack of maintenance or
failure to comply with the
manufacturer's instructions or
recommendations is not covered by
the warranty obligation. If the user
does not conform to the rules of
this manual, it may entail
cancellation of warranty and
liabilities by the manufacturer.
Refrigerant
The refrigerant provided by the
manufacturer meets all the
requirements of our units. When
using recycled or reprocessed
refrigerant, it is advisable to ensure
its quality is equivalent to that of a
new refrigerant. For this, it is
necessary to have a precise analysis
made by a specialized laboratory. If
this condition is not respected, the
manufacturer warranty could be
cancelled.
Maintenance contract
It is strongly recommended that you
sign a maintenance contract with
your local Service Agency. This
contract provides regular
maintenance of your installation by
a specialist in our equipment.
Regular maintenance ensures that
any malfunction is detected and
corrected in good time and
minimizes the possibility that
serious damage will occur. Finally,
regular maintenance ensures the
maximum operating life of your
equipment. We would remind you
that failure to respect these
installation and maintenance
instructions may result in
immediate cancellation of the
warranty.
Storage
Take precautions to prevent
condensate formation inside the
unit's electrical components and
motors when:
1. The unit is stored before it is
installed; or,
2. The unit is set on the roof curb
and temporary auxiliary heat is
provided in the building.
Isolate all side panel service
entrances and base pan openings
(e.g., conduit holes, S/A and R/A
openings, and flue openings) to
minimize ambient air from entering
the unit until it is ready for start-up.
Do not use the unit's heater as
temporary heat without completing
the start-up procedures detailed
under "Unit Start-Up".
The Trane Company will not assume
responsibility for equipment
damage resulting from
accumulation of condensate on the
unit electrical components.
Training
To assist you in obtaining the best
use of it and maintaining it in
perfect operating condition over a
long period of time, the
manufacturer has at your disposal a
refrigeration and air conditioning
service school. The principal aim of
this is to give operators and
technicians a better knowledge of
the equipment they are using, or
that is under their charge. Emphasis
is particularly given to the
importance of periodic checks on
the unit operating parameters as
well as on preventive maintenance,
which reduces the cost of owning
the unit by avoiding serious and
costly breakdown.
General information
3RT-SVX19A-E4
Page 4

RT-SVX19A-E44
Contents
Foreword 2
Warnings and Cautions 2
Safety recommendations 2
Reception 2
Warranty 3
Refrigerant 3
Maintenance contract 3
Storage 3
Training 3
Installation 6
Reception of units 6
Roof curb installation 7
Dimensions/Weights/Clearances 8
Installing the unit 10
Connection of duct network 11
Condensate drain piping 12
Gas pipework installation 13
Filter installation 14
Supply fan adjustment 15
Component air pressure drops 17
Supply fan performances 20
Electrical connection 26
Controls 31
Control wiring 31
CO2sensors 33
Remote potentiometer 36
Fire thermostat 37
Clogged filter detector 38
Smoke detector 38
High temperature safety thermostat 38
Remote fault relay 38
Thermostats 38
Communication Interfaces 39
Page 5

Contents
5RT-SVX19A-E4
Unit Options 40
Hot water coil 40
Electric Heater 41
Soft Starter 41
0 - 25% fresh air hood 42
Barometric relief 43
Operation 44
Operation with a conventional thermostat 44
Setting the economizer 47
Test procedures 49
Test modes 50
Unit start-up 51
Cooling without an Economizer 54
Low Ambient Operation 55
Cooling with an Economizer 55
Economizer Set-Up 56
ReliaTel™ Control Heating Operation 56
Ignition Module 56
Final installation checklist 57
Maintenance 58
End user routine maintenance 58
Service technician maintenance 59
Troubleshooting 60
Page 6
Installation
RT-SVX19A-E46
General information :The
installation must conform to all
local standards and regulations.
Reception of units
Rooftop unit
The unit is supplied on a wooden
frame. It is recommended to check
the machine's condition upon
reception.
There are two ways to handle the
unit:
1. Use the openings in the wooden
frame to handle the machine
using a fork lift, in accordance
with applicable safety
regulations.
2. Use a lifting beam correctly
adjusted to fit the unit
(Figure 1a).
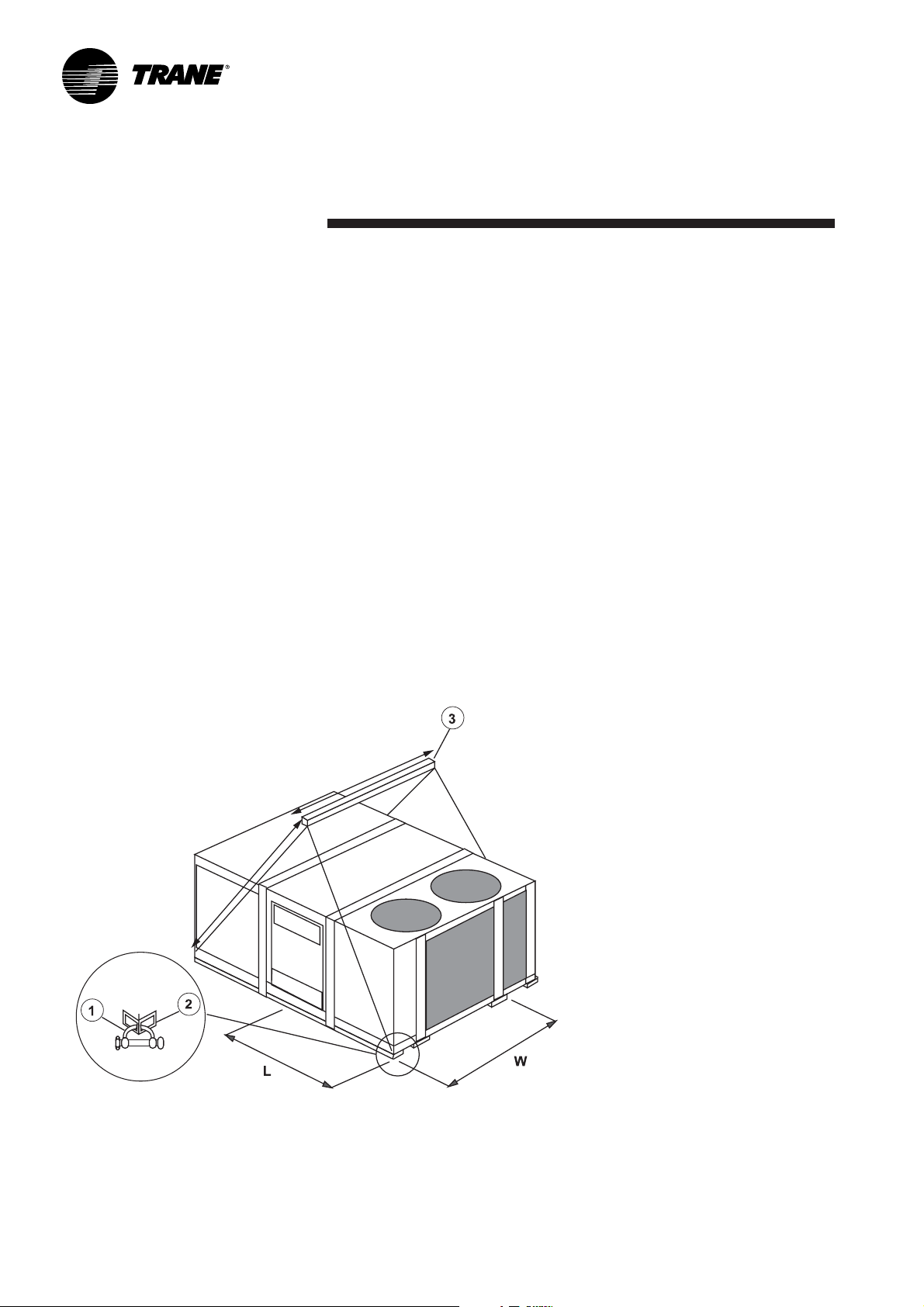
Unit handling
The units are supplied on the truck
but are not unloaded. An opening is
provided on each corner of the unit
base to facilitate handling.
4 shackles and 4 slings are required.
Use a lifting beam to prevent the
cables pressing too hard on top of
the unit during lifting.
Figure 1a indicates the position of
the center of gravity and the lifting
recommendations.
Important: For unit to fit on the
roof curb the fork lift pockets must
be removed.
Figure 1a - Unit handling
1 = Clevis
2 = Base Rail
3 = Spreader Bar
L = Length (Center of Gravity)
W = Width (Center of Gravity)
Refer to Table 2 for weights and center of gravity.
A
B
Page 7
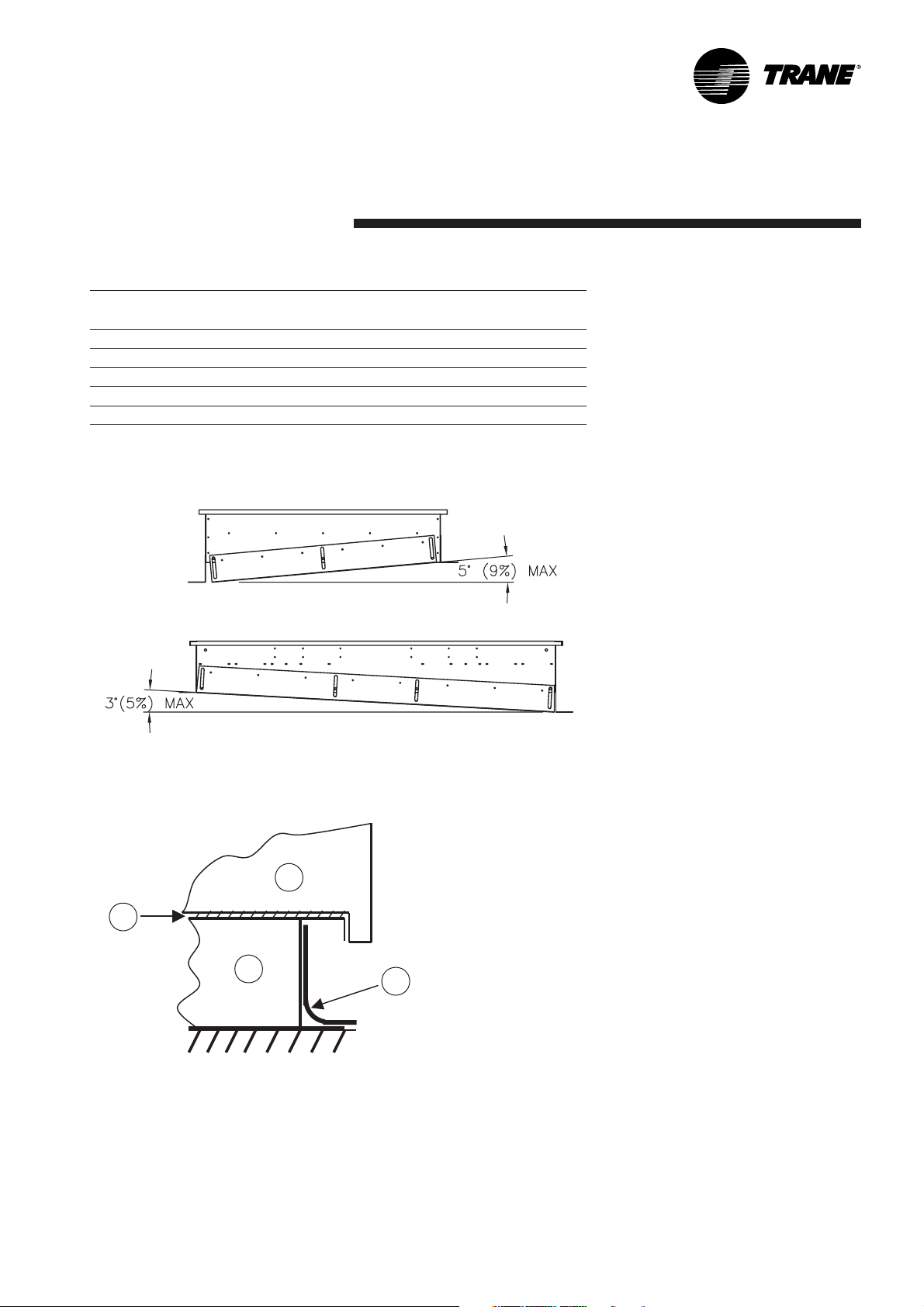
Roof curb Installation
(TKD-WKD-YKD
accessories)
Roof curbs are available as an
accessory for "downflow" units to
support the unit and ensure the
water tightness between the rooftop
and the roof. Two types of roof
curbs are available: The standard
version to allow the installation of
the unit on a flat roof and the
adjustable version for a sloped roof
installation. (See Figure 1b for the
maximum slope correction of
adjustable roofcurb.)
The adjustable roof curbs are
supplied pre-assembled on a skid.
Two types of self-adhesive seals are
provided separately. (40 mm wide
for the perimeter, 20 mm wide for
the cross pieces). Make sure they
are properly installed where
indicated to assure an adequate
curb to unit seal.
Instructions for the roof curb
assembly and installation with curb
dimensions are provided with each
roof curb kit.
Table 1 - Sling lengths and maximum unit weight
Figure 1b - Maximum slope correction of adjustable roof curb.
Figure 2 - Waterproofing
1 = Roofcurb
2 = Roof membrane
3 = Seal
4 = Rooftop
Unit size A (mm) B (mm)
Maximm weight
kg
125 3000 1900 644
155 3000 1900 773
175 3000 1900 810
400 3500 2200 1001
500 3500 2200 1027
Installation
7RT-SVX19A-E4
3
4
1
2
Page 8
Installation
RT-SVX19A-E48
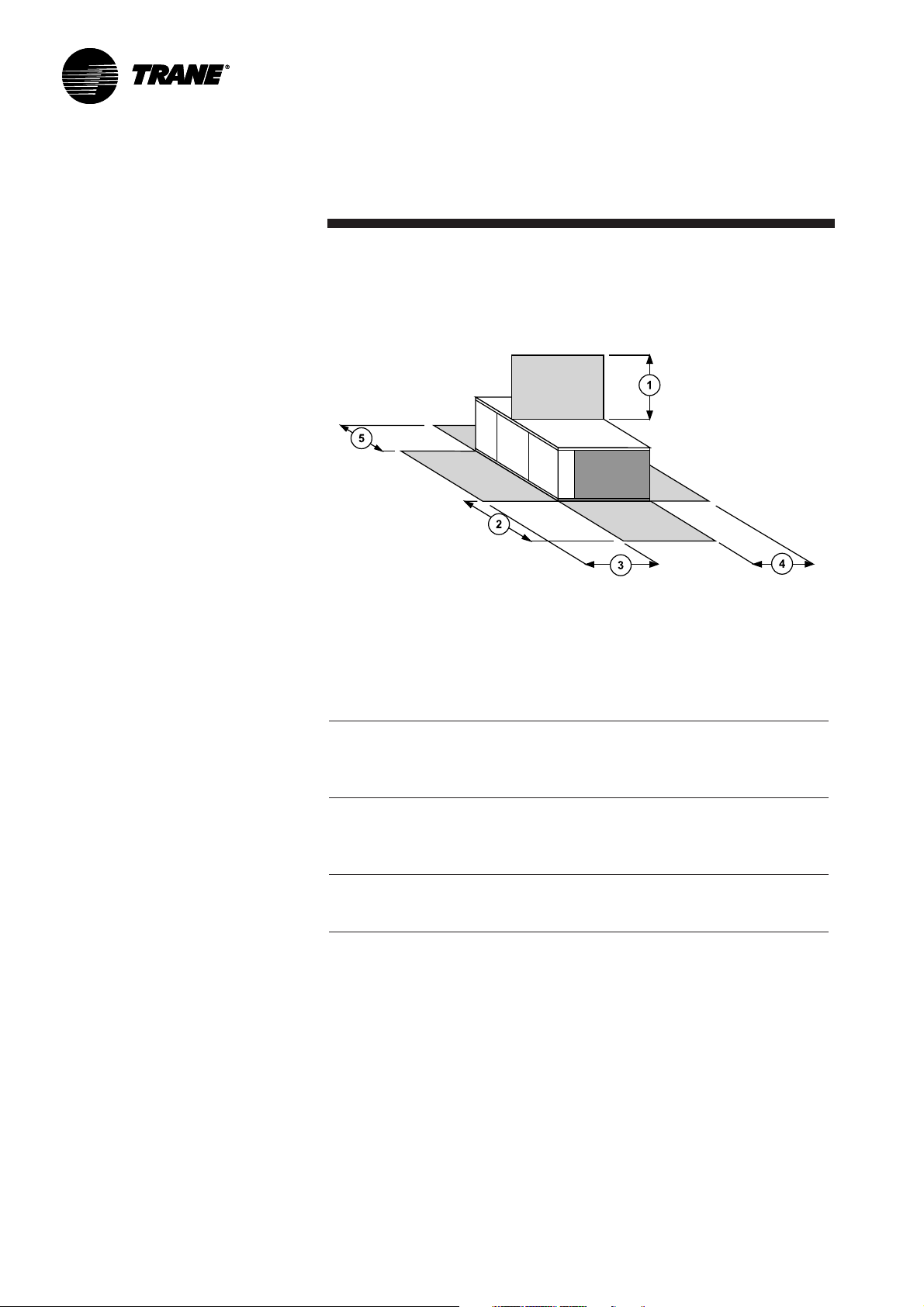
Dimensions/Weights/Clearances
Figure 3 - Minimum clearances
Table 2 - Minimum clearances (mm)
The structure accommodating the unit(s) must be designed to support the
equipment in operation, as a minimum. Refer to Table 3a and the space
requirement plan.
Minimum clearance
UNIT 1 2 3 4 5
YKD/YKH 155 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
YKD/YKH 175 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
YKD/YKH 200 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
YKD/YKH 250 1900 1800 1220 1000 130 0
TKD/TKH 155 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
TKD/TKH 175 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
TKD/TKH 200 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
TKD/TKH 250 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
WKD/WKH 125 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
WKD/WKH 155 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
WKD/WKH 200 1900 1800 1220 1000 1300
Page 9

Installation
9RT-SVX19A-E4
Installation
Table 3a - Weigths & center of gravity (Figure 1)
1. Corner weights are given for information only. All models must be supported continuously by a curb or equivalent frame support.
Table 3b - Weights of Options & accessories
Notes :
Net weight should be added to unit weight when ordering factory installed accessories.
To estimate shipping weight add 2.3 kg to net weight.
UNIT
Standard Roof
Curb
Adjustable Roof
Curb Economizer
Manual Outside
Air Damper
Motorized
Outside Air
Damper Electric heater Hot water coil
YKD 155 93 220 30 15 27
YKD 175 93 220 30 15 27
YKD 200 107 260 37 15 34
YKD 250 107 260 37 15 34
YKH 155 30 15 27
YKH 175 30 15 27
YKH 200 37 15 34
YKH 250 37 15 34
TKD 155 93 220 30 15 27 14 85
TKD 175 93 220 30 15 27 14 85
TKD 200 107 260 37 15 34 18 11 0
TKD 250 107 260 37 15 34 18 11 0
TKH 155 30 15 27 14
TKH 175 30 15 27 14
TKH 200 37 15 34 18
TKH 250 37 15 34 18
WKD 125 93 180 20 15 27 18 85
WKD 155 93 220 30 15 27 18 85
WKD 200 107 260 37 15 34 18 11 0
WKH 125 20 15 27 18
WKH 155 30 15 27 18
WKH 200 37 15 34 18
Maximum weight Corner Weight (1) Center of Gravity
Shipping Net A B C D Length (L) Width (W)
UNIT (kg) (kg) (kg) (kg) (kg) (kg) (mm) (mm)
YKD/YKH 155 866 698 243 176 118 162 11 43 737
YKD/YKH 175 902 735 251 188 127 169 116 8 737
YKD/YKH 200 112 8 920 324 242 151 203 1321 838
YKD/YKH 250 115 4 946 327 251 159 208 1346 838
TKD/TKH 155 790 623 219 159 10 3 142 114 3 711
TKD/TKH 175 827 660 227 17 2 112 149 11 68 711
TKD/TKH 200 1050 841 297 221 138 185 1321 838
TKD/TKH 250 1075 866 300 230 145 206 1346 838
WKD/WKH 125 792 625 218 159 10 5 144 114 3 711
WKD/WKH 155 809 642 228 162 10 5 147 114 3 711
WKD/WKH 200 1080 871 291 226 155 199 1346 889
Page 10

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E410
Installing the unit
1) Unit mounting on roof
Fix the rooftop curb on the joint
beam of the building's structure.
Make the rooftop curb's sealing
surface level using angle brackets
adjusted by screw bolts, located
around its perimeter. Place the
adhesive seals on the curb's sealing
surface (perimeter and cross
pieces). Make the rooftop leak-tight
around the curbs before installing
the unit, in compliance with current
construction standards.
Note: The unit must be installed
perfectly level to ensure
condensates flow from the
condensate tray.
The rooftop unit nests into the curb
and is supported by it. Position the
unit, taking care to comply with the
indicated directions: the unit's
discharge and intake openings must
match those of the curb.
2) Installing the unit on the ground
To install the unit on the ground, its
base must be level and supported
securely.
For horizontal discharge units, a
support is required such as a metal
or concrete slab whose height must
be determined according to the
amount of snow cover, to prevent
problems with condensation
drainage and obstruction of the
external coil. If necessary use an
anti-vibration material between the
rooftop unit's base and the support.
Note: Unit installation must comply
to local codes
Figure 4
1 = Frame
Figure 5
1 = Concrete slab
RT-SVX19A-E4
Page 11

Installation
11RT-SVX19A-E4RT-SVX19A-E4
Connection of duct
network
1) Downflow discharge units
(TKD,WKD,YKD)
Using the rooftop curb
• The rooftop curb must be
insulated on the outside walls at
the discharge and intake
openings to prevent
condensation in the ducts.
• The rims around the discharge
and intake openings make it
possible to attach the flanges on
the ends of the ducts. If you are
using rigid duct ends
recommended on the rooftop
curb plan, it is essential to fix
these components before
installing the unit.
• For the design of the duct
network, comply with
recommendations currently
applicable on the market, in
particular:
. Installation of a section of
flexible ducts to limit
transmission of the unit's
vibrations
. Use of movable vanes or
deflectors to reduce the sound
level.
2) Horizontal discharge units
(TKH,WKH,YKH)
• The intake and discharge ducts
must be insulated (thermal
insulation).
• The duct section located outside
must be leak-tight.
• Provide a flexible connector to
prevent transmission of the unit
vibrations. This flexible duct
must be installed inside the
building.
Note: In case of use of TKH, WKH or
YKH units with economizer option,
temperature and humidity sensors
must be installed in return duct.
Economizer linkage is factory
mounted but the damper position
must be adjusted on site.
Figure 6 - Condensate Drain location
1 = Condensate drain connection
A = TKH/YKH 155, 175, 200, 250 - WKH 125,155, 200
B = TKD/YKD 155, 175, 200, 250 - WKD 125,155,200
Page 12
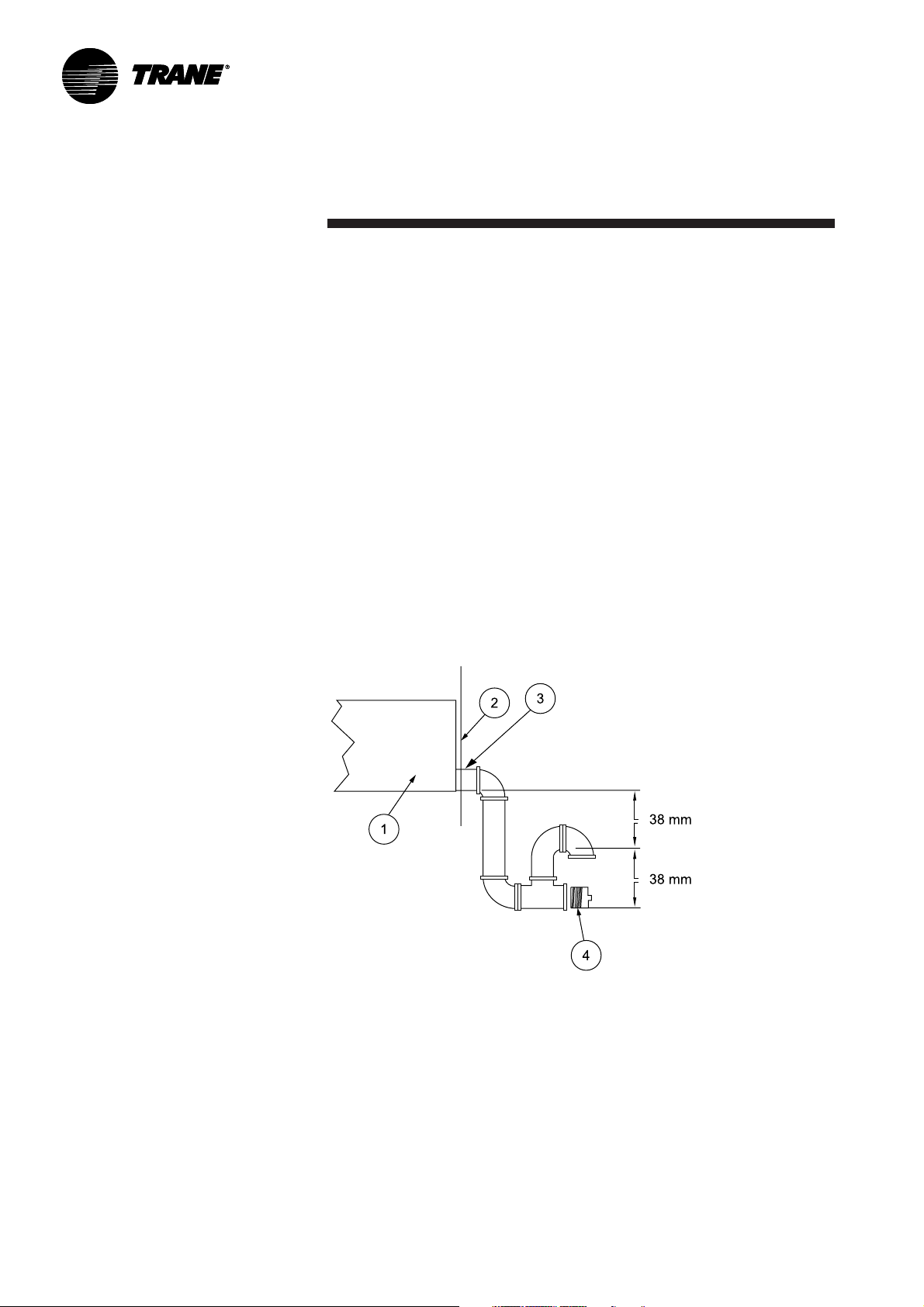
Installation
RT-SVX19A-E412
Figure 7 - Condensate drain line connection
1 = Static pressure drain pan
2 = Panel enclosure
3 = 42mm PVC drain
4 = Cleanout plug
RT-SVX19A-E4
Condensate drain piping
A 42mm PVC condensate drain
connection with P-trap is provided.
Follow local codes and standard
piping practices when running the
drain line. Install a trap and be sure
to fill with water before starting the
unit. Pitch the line downward, away
from the unit to avoid long, level,
horizontal runs. Refer to Figure 7.
Page 13
Installation
13RT-SVX19A-E4
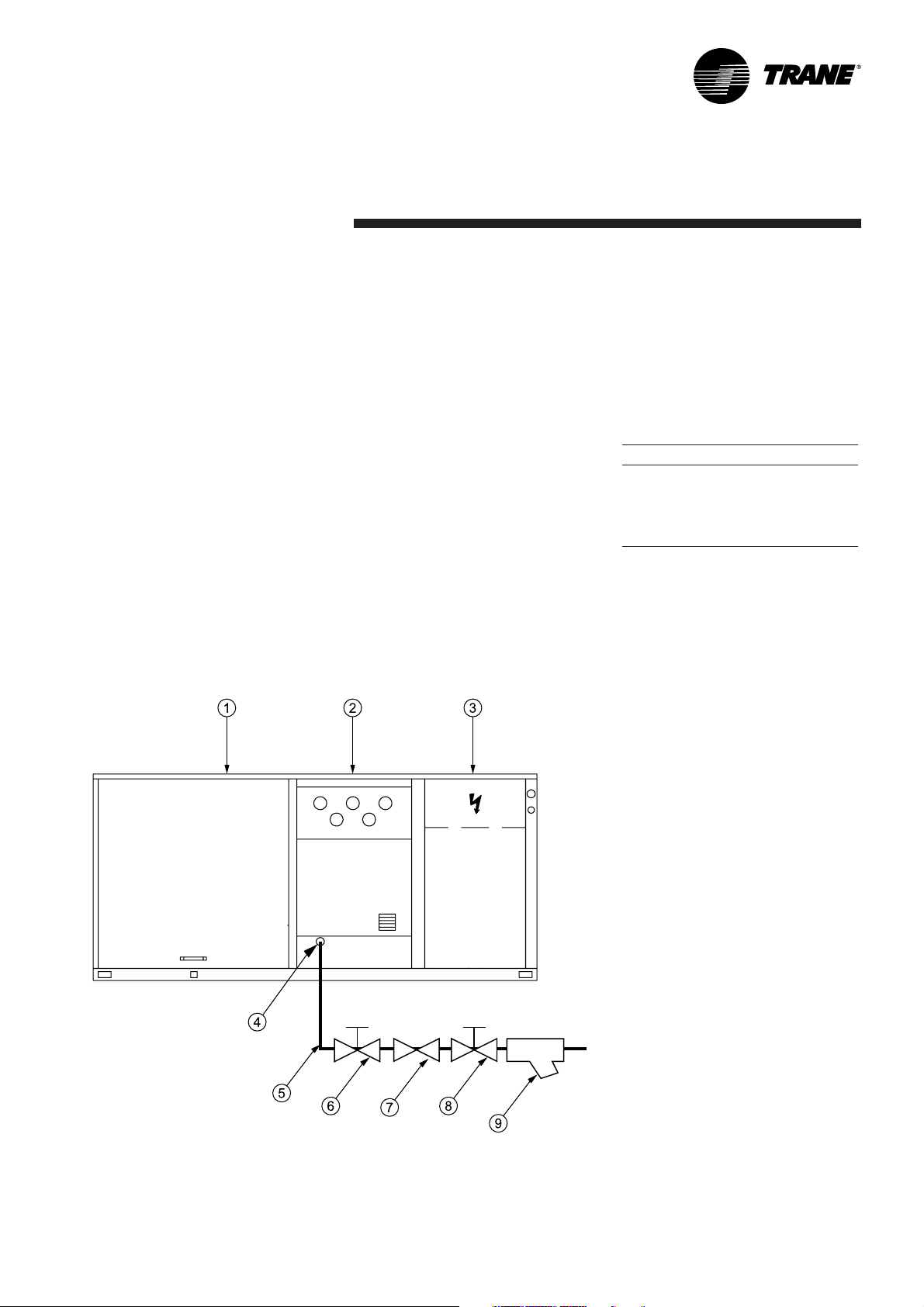
Gas pipework installation
The installation must conform to all
standards and regulations.
The gas supply pipework and gas
stop valve to be installed near the
unit must be sized so as to assure
the gas pressure is sufficient at the
unit inlet when operating at full
load.
CAUTION! Should the pressure at
the unit valve gas inlet be higher
than 0.035 bar, an expansion valve
must be installed.
The pipework must be selfsupporting and the final connection
to the burner must be made by a
flexible pipe. Provide a dust
protection (filter) upstream the unit
connection.
CAUTION!The gas pipework must
not exert any stress on the burner
gas connection.
Note: Expansion valve must be
adapted to the type of gas used:
• G 20 : 20 mb
• G 25 : 25 mb
• G 31 : (Propane): 37 or 50 mb
Table 4 - Gas burner models
See Table 38 for burner
performance.
Gas leak check procedure
1. Vent the gas line
2. Gas supply line pressure test:
close valve 4 and open valve 2
3. Leak-check the gas pipe
Look for gas pipe leaks using
"Typol", "1000 bulles" or a similar
product. Do not use soapy water.
WARNING! Never use an open
flame to check for gas leaks.
Required gas pressure at the unit
inlet connection are given in
Table 37.
Note:To operate with propane gas,
the burner is fitted with a pressure
limiter (supplied by Trane)
Unit Burner size
YKD/H 155 G350A
YKD/H 175 G350A
YKD/H 200 G350A
YKD/H 250 G350A
Figure 8 - Typical gas supply Pipework
1 = Evaporator section
2 = Gas burner section
3 = Condenser section
4 = Gas supply connection
5 = Gas supply line
6,8 = Gas stop valve (Field supplied)
7 = Expansion valve (Field supplied)
9 = Filter (Field supplied)
Page 14

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E414
CAUTION! Do not operate unit
without filters in place.
The maximum pressure drops
allowable on filters are:
EU2/G2: 120 Pa
EU4/G4: 150 Pa
Filter installation
To gain access to filters, remove the
supply fan access panel on
downflow units and the filter access
panel on the end for horizontal
units.
Each unit ships with 40 or 50 mm
thick filters. Number and size of
filters is determined by size and
configuration of the unit.
Table 5 - Filter arrangement
UNIT
EU2/G2 EU4/G4
Qty Size Qty Size
YKH/YKD 155
2 (508x508x50) 2 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
YKH/YKD 175
2 (508x508x50) 2 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
YKH 200 8 (508x635x50) 8 (500x625x50)
YKD 200
4 (508x508x50) 4 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
YKH 250 8 (508x635x50) 8 (500x625x50)
YKD 250
4 (508x508x50) 4 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
TKH/TKD 155
2 (508x508x50) 2 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
TKH/TKD 175
2 (508x508x50) 2 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
TKH 200 8 (508x635x50) 8 (500x625x50)
TKD 200
4 (508x508x50) 4 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
TKH 250 8 (508x635x50) 8 (500x625x50)
TKD 250
4 (508x508x50) 4 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
WKH/WKD 125
2 (508x508x50) 2 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
WKH/WKD 155
2 (508x508x50) 2 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
WKH 200 8 (508x635x50) 8 (500x625x50)
WKD 200
4 (508x508x50) 4 (498x498x40)
4 (508x635x50) 4 (500x625x50)
Page 15

Installation
15RT-SVX19A-E4
Supply fan adjustment
Use the following procedure to
determine the proper adjustment of
the supply fan for a specific
application.
1. Determine total external static
pressure about system and
accessories.
a. Obtain the design airflow rate
and the design external static
pressure drop through the
distribution system.
b. Add static pressure drop of the
accessories installed on the
unit. (Table 7,8 & 9)
c. Add the total accessory static
pressure drop (from step 1b) to
the design external static
pressure (from step 1a). The
sum of these two values is the
total system external static
pressure.
2. Using the Tables 10 through 20 to
find the external static pressure
that most closely approximates
total system external static
pressure. Then locate the
appropriate airflow rate for your
unit. The value obtained
represents the brake horsepower
for the supply fan motor and the
fan RPM.
3. Adjust motor sheave according
to Table 6.
Table 6 - Motor sheave / Fan speed
Fan Speed (RPM)
Standard Drive
6 turns 5 turns 4 turns 3 turns 2 turns 1 turns
UNIT Open Open Open Open Open Open Closed
YKD/YKH 155 566 601 637 672 708 74 3 N/A
YKD/YKH 175 724 76 9 815 860 906 951 N/A
YKD/YKH 200 513 550 586 623 659 696 N/A
YKD/YKH 250 588 619 650 681 712 74 3 N/A
TKD/TKH 155 566 601 637 672 708 74 3 N/A
TKD/TKH 175 724 769 815 860 906 951 N/A
TKD/TKH 200 513 550 586 623 659 696 N/A
TKD/TKH 250 588 619 650 681 712 74 3 N/A
WKD/WKH 125 533 566 600 633 667 700 N/A
WKD/WKH 155 566 601 637 672 708 74 3 N/A
WKD/WKH 200 513 550 586 623 659 696 N/A
Fan Speed (RPM)
Oversized Drive
6 turns 5 turns 4 turns 3 turns 2 turns 1 turns
UNIT Open Open Open Open Open Open Closed
YKD/YKH 155 672 714 756 798 840 882 N/A
YKD/YKH 175 791 840 890 939 989 1038 N/A
YKD/YKH 200 680 711 74 2 773 804 835 N/A
YKD/YKH 250 690 722 754 786 818 850 N/A
TKD/TKH 155 672 714 756 798 840 882 N/A
TKD/TKH 175 791 840 890 939 989 1038 N/A
TKD/TKH 200 680 711 74 2 773 804 835 N/A
TKD/TKH 250 690 722 754 786 818 850 N/A
WKD/WKH 125 724 76 9 815 860 906 951 N/A
WKD/WKH 155 513 550 586 623 659 696 N/A
WKD/WKH 200 588 619 650 681 712 74 3 N/A
Page 16

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E416
To increase airflow
Loosen variable sheave set screw
and turn sheave clockwise.
To decrease airflow
Loosen variable sheave set screw
and turn sheave counter-clockwise.
To increase belt tension
Loosen the nut (next to the idler
sheave) that secures the sheave in
place. With a wrench, apply
pressure clockwise on the outside
nut (round headed one), until
tension desired is reached. While
holding pressure with the tension
nut, retighten the nut next to the
idler sheave.
Figure 9 - Typical fan, motor, and sheave
assembly
A = Fan Housing
B = Terminal Block
C = Fan Sheave
D = Plastic Bushing
E = Belt Tension Adjustment Bolt
F = Idler Pulley
Table 6b - Belt tensioning
TK* / YK* /
WK*
Motor kW
Fan pulley
Ty p e /
diam. (mm)
Fan pulley
Ty p e /
diam. (mm)
Belt type
/ lengh (mm)
Belt
deflexion
(mm)
Deflexion
effort
mini kg
Deflexion
effort
maxi kg
Belt tension
mini
N
Belt tension
maxi
N
125 1,5 BK90 / 222 1VP44 / 105 BX68 / 1727 5,89 2,4 2,9 400 500
155 1,5 BK85 / 210 1VP44 / 105 BX68 / 1727 6 2,4 2,9 400 500
175 3 BK130 / 324 1VP44 / 105 BX75 / 1905 6,05 2,4 2,9 400 500
200 3 BK160 / 400 1VL40 / 95 BX90 / 2286 6,96 2,4 2,9 400 500
250 4,6 BK190 / 476 1VP50 / 121 BX96 / 2438 6,91 2,4 2,9 400 500
125 3 BK130 / 324 1VP44 / 105 BX75 / 1905 5,85 2,4 2,9 400 500
155 3 BK140 / 349 1VP44 / 105 BX77 / 1955 6,17 2,4 2,9 400 500
175 4,6 BK140 / 349 1VP56 / 136 BX75 / 1905 5,45 2,4 2,9 400 500
200 4,6 BK190 / 476 1VP56 / 136 BX96 / 2438 6,87 2,4 2,9 400 500
250 4,6 BK190 / 476 1VP56 / 136 BX96 / 2438 6,32 2,4 2,9 400 500
Page 17

Installation
17RT-SVX19A-E4
Component air pressure drops
Table 7 - YKD/YKH Pressure drop through accessories
Filter Filter Economizer Economizer
Airflow EU2/G2 EU4/G4
100%
outside air
100%
return air
YKD/YKH 155
6800 13 27 8 6
7650 16 30 10 7
8500 19 34 12 8
9350 22 37 14 9
10200 26 40 16 10
YKD/YKH 175
7870 17 30 10 7
8860 21 34 12 8
9850 25 38 15 9
10840 30 43 17 11
11830 35 47 20 12
YKD 200
8970 12 26 29 6
10090 15 30 37 8
112 10 19 33 45 9
12330 23 37 55 11
13450 27 41 65 13
YKH 200
8970 11 23 33 6
10090 14 26 41 8
112 10 17 29 51 9
12330 20 33 61 11
13450 23 36 72 13
YKD 250
11280 18 32 46 10
12690 24 36 58 12
14100 29 41 71 14
15510 36 46 86 17
16920 43 51 102 19
YKH 250
11280 17 30 52 10
12690 21 34 65 12
14100 26 38 80 14
15510 31 43 96 17
16920 36 47 11 4 19
Page 18

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E418
Table 8 - TKD/TKH Pressure drop through accessories
Filter Filter Economizer Economizer Electric Hot water coil
Airflow EU2/G2 EU4/G4
100%
outside air
100%
return air
heater Downflow only
TKD/TKH 155
6800 13 27 8 6 7 33
7650 16 30 10 7 9 40
8500 19 34 12 8 11 48
9350 22 37 14 9 13 56
10200 26 40 16 10 16 65
TKD/TKH 175
7870 17 30 10 7 10 42
8860 21 34 12 8 13 51
9850 25 38 15 9 16 61
10840 30 43 17 11 19 72
11830 35 47 20 12 23 83
TKD 200
8970 12 26 29 6 13 33
10090 15 30 37 8 17 40
112 10 19 33 45 9 21 48
12330 23 37 55 11 25 56
13450 27 41 65 13 30 65
TKH 200
8970 11 23 33 6 13 -
10090 14 26 41 8 17 -
112 10 17 29 51 9 21 12330 20 33 61 11 25 13450 23 36 72 13 30 -
TKD 250
11280 18 32 46 10 20 49
12690 24 36 58 12 25 59
14100 29 41 71 14 32 71
15510 36 46 86 17 38 82
16920 43 51 10 2 19 46 95
TKH 250
11280 17 30 52 10 19 12690 21 34 65 12 24 14100 26 38 80 14 29 15510 31 43 96 17 35 16920 36 47 114 19 42 -
Page 19

Installation
19RT-SVX19A-E4RT-SVX19A-E4
Table 9 - WKD/WKH Pressure drop through accessories
Airflow
Filter
EU2/G2
Filter
EU4/G4
Economizer
100%
outside air
Economizer
100%
return air
Electric
heater
Hot water coil
Downflow only
WKD/WKH 125
5720 9 21 6 5 4 37
6430 11 24 7 6 6 45
7140 14 27 9 6 7 53
7850 17 30 10 7 9 62
8560 20 33 12 8 12 72
WKD/WKH 155
6800 13 27 8 6 7 33
7650 16 30 10 7 9 40
8500 19 34 12 8 11 48
9350 22 37 14 9 13 56
10200 26 40 16 10 16 65
WKD 200
8970 12 26 29 6 13 33
10090 15 30 37 8 17 40
112 10 19 33 45 9 21 48
12330 23 37 55 11 25 56
13450 27 41 65 13 30 65
WKH 200
8970 11 23 33 6 13 -
10090 14 26 41 8 17 -
112 10 17 29 51 9 21 12330 20 33 61 11 25 13450 23 36 72 13 30 -
Page 20

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E420
Supply fan performances
Table 10 - YK 155 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
6800 699 1. 4 7 719 1. 5 5 739 1. 6 3 758 1. 7 1 777 1. 7 9 795 1. 8 6 813 1. 9 4 830 2.01 847 2.09 863 2.16
7650 729 1. 8 2 74 9 1. 9 2 76 8 2.01 787 2.1 806 2.19 824 2.28 841 2.37 858 2.46 875 2.55
8500 764 2.25 782 2.35 800 2.45 818 2.55
9350
10200
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
6800 564 1 587 1. 0 7 610 1. 15 633 1. 2 3 655 1. 3 1 677 1. 3 9
7650 560 1. 1 4 583 1. 2 3 605 1. 3 1 627 1. 3 9 648 1. 4 8 669 1. 5 6 690 1. 6 5 710 1. 74
8500 559 1. 3 1 584 1. 4 1 606 1. 5 628 1. 6 649 1. 6 9 669 1. 7 8 689 1. 8 7 708 1. 9 7 727 2.06 74 6 2.16
9350 610 1. 7 2 633 1. 8 3 654 1. 9 4 675 2.04 694 2.14 713 2.24 732 2.34 750 2.45 767 2.55 785 2.65
10200 661 2.21 683 2.33 703 2.45 722 2.56
Page 21

Installation
21RT-SVX19A-E4
Table 11 - YK 175 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
Table 12 - YK 200 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
8970 633 2.14 652 2.27 670 2.4 688 2.54 705 2.67 721 2.8 737 2.93 753 3.06 768 3.19 783 3.31
10090 660 2.6 679 2.75 697 2.91 714 3.06 731 3.21 74 7 3.35 76 3 3.5 778 3.65 793 3.8 808 3.95
112 10 690 3.16 707 3.31 724 3.47 74 1 3.64 757 3.81 773 3.98 789 4.14 804 4.31
12330 724 3.84 739 3.99 754 4.15 770 4.31
13450
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
8970 530 1. 5 551 1. 6 1 572 1. 74 593 1. 8 7 614 2
10090 529 1. 7 1 548 1. 8 3 567 1. 9 4 586 2.06 604 2.18 623 2.31 641 2.45
112 10 530 1. 9 9 551 2.12 570 2.24 588 2.36 606 2.48 623 2.61 640 2.74 657 2.87 673 3.01
12330 548 2.41 573 2.58 594 2.73 613 2.87 630 3 646 3.13 662 3.27 678 3.4 693 3.54 709 3.69
13450 593 3.1 617 3.29 638 3.46 656 3.61 672 3.76 688 3.9 703 4.05 718 4.19
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
7870 857 2.12 879 2.22 900 2.33 921 2.44 942 2.55 962 2.65 981 2.75 1000 2.86 1018 2.96 1036 3.06
8860 907 2.7 927 2.81 946 2.92 965 3.03 985 3.15
9850 964 3.42 981 3.53 998 3.64 1016 3.76 1033 3.88
10840 1024 4.29
11830
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
7870 726 1. 5 8 74 8 1. 6 6 770 1. 74 791 1. 8 3 813 1. 9 2 835 2.02
8860 751 1. 9 6 772 2.05 792 2.13 811 2.22 831 2.31 850 2.4 869 2.5 888 2.6
9850 779 2.41 801 2.52 822 2.62 841 2.72 859 2.82 877 2.91 895 3.01 912 3.11 929 3.21 947 3.31
10840 852 3.19 874 3.31 893 3.42 911 3.53 928 3.64 945 3.75 961 3.85 977 3.96 993 4.07 1009 4.18
11830 926 4.12 946 4.25
RT-SVX19A-E4
Page 22

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E422
Table 13 - YK 250 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
9870 662 1. 9 2 681 2.03 699 2.15 717 2.26 735 2.36 752 2.48 768 2.59 784 2.69 800 2.81 815 2.91
11280 702 2.48 718 2.59 734 2.70 750 2.82 76 7 2.94 783 3.08 800 3.20 815 3.33 831 3.46 846 3.59
12690 74 8 3.19 762 3.30 776 3.42 791 3.54 805 3.66 819 3.79 834 3.92 848 4.05
14100 797 4.05 810 4.17 823 4.30 836 4.43 849 4.55
15510 848 5.08
16920
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
9870 606 1. 6 2 625 1. 7 2 643 1. 8 2
11280 603 1. 8 8 620 1. 9 7 637 2.07 653 2.17 670 2.27 686 2.37
12690 602 2.18 622 2.30 640 2.41 657 2.52 673 2.63 688 2.74 704 2.85 719 2.96 733 3.08
14100 639 2.77 660 2.92 679 3.06 696 3.19 712 3.32 727 3.44 74 2 3.56 756 3.68 770 3.80 784 3.92
15510 699 3.65 719 3.82 736 3.98 753 4.13 76 8 4.27 782 4.40 796 4.54 810 4.67 823 4.81 836 4.94
16920 758 4.70 777 4.89 794 5.06 810 5.23 824 5.39 838 5.54
Table 14 - TK 155 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
6800 787 1. 2 8 815 1. 3 7 842 1. 4 6 868 1. 5 4
7650 808 1. 5 3 836 1. 6 3 862 1. 74
8500 833 1. 8 3 858 1. 9 3 883 2.04
9350 862 2.18 885 2.29 909 2.4
10200 894 2.58
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
6800 565 0.7 599 0.77 633 0.85 665 0.93 697 1. 0 2 728 1. 1 758 1. 1 9
7650 571 0.82 603 0.9 634 0.99 665 1. 0 7 694 1. 1 6 723 1. 2 5 752 1. 3 4 780 1. 4 4
8500 580 0.97 613 1. 0 7 643 1. 1 6 672 1. 2 5 700 1. 3 4 727 1. 4 3 754 1. 5 3 781 1. 6 3 807 1. 7 3
9350 590 1. 13 624 1. 2 4 656 1. 3 5 684 1. 4 6 711 1. 5 5 738 1. 6 5 763 1. 7 5 788 1. 8 6 813 1. 9 6 838 2.07
10200 637 1. 4 4 670 1. 5 7 699 1. 6 9 727 1. 8 1 753 1. 9 2 777 2.02 801 2.13 825 2.24 848 2.35 871 2.46
Page 23

Installation
23RT-SVX19A-E4
Table 15 - TK 175 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
7870 842 1. 7 9 869 1. 9 1 896 2.03 921 2.15 946 2.27 970 2.39 994 2.51 1016 2.63 1038 2.75
8860 877 2.19 901 2.31 925 2.43 949 2.56 973 2.69 997 2.83 1020 2.96 1043 3.1
9850 919 2.7 941 2.82 962 2.94 984 3.07 10 06 3.2 1027 3.33
10840 965 3.3 985 3.43 10 05 3.55 1025 3.68 1044 3.82
11830 1015 4.02 1033 4.15
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
7870 593 0.95 623 1. 0 3 651 1. 11 679 1. 1 9 706 1. 2 8 733 1. 3 7 761 1. 4 7 788 1. 5 7 815 1. 6 8
8860 623 1. 2 1 653 1. 3 1 680 1. 4 706 1. 4 9 731 1. 5 8 756 1. 6 7 780 1. 7 7 805 1. 8 7 829 1. 9 7 853 2.08
9850 687 1. 6 4 714 1. 7 5 739 1. 8 5 763 1. 9 5 786 2.05 809 2.15 831 2.25 853 2.36 875 2.47 897 2.58
10840 750 2.16 775 2.28 799 2.4 821 2.51 843 2.62 864 2.73 884 2.84 905 2.95 925 3.07 945 3.18
11830 814 2.78 837 2.92 860 3.05 881 3.17 901 3.29 921 3.41 940 3.53 959 3.65 978 3.77 996 3.89
Table 16 - TK 200 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
8970 710 1. 8 6 735 2 759 2.14 783 2.27 805 2.41 827 2.55
10090 729 2.2 753 2.35 777 2.5 800 2.66 823 2.81
112 10 752 2.6 774 2.75 797 2.92 819 3.08 841 3.25
12330 778 3.08 799 3.24 820 3.4 841 3.57
13450 808 3.64 828 3.81
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
8970 512 0.98 542 1. 0 9 571 1. 2 1 600 1. 3 3 629 1. 4 5 656 1. 5 8 684 1. 7 2
10090 519 1. 1 6 547 1. 2 8 575 1. 3 9 601 1. 5 1 627 1. 6 4 653 1. 7 7 679 1. 9 1 704 2.05
112 10 528 1. 3 6 557 1. 5 584 1. 6 3 610 1. 76 634 1. 8 9 658 2.02 682 2.16 705 2.3 729 2.44
12330 537 1. 5 8 568 1. 74 596 1. 9 622 2.05 647 2.19 670 2.33 692 2.47 714 2.62 735 2.77 757 2.92
13450 580 2.01 609 2.19 636 2.37 661 2.54 684 2.7 706 2.85 728 3.01 74 8 3.16 76 8 3.32 788 3.48
Page 24

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E424
Table 17 - TK 250 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
9870 714 1. 8 6 733 1. 9 4 751 2.02 769 2.1 786 2.17 802 2.25 818 2.32 834 2.39 849 2.46 864 2.53
11280 757 2.45 775 2.55 793 2.65 810 2.74 827 2.84 843 2.93 859 3.02 874 3.11 889 3.19 904 3.28
12690 803 3.14 820 3.26 837 3.38 853 3.49 869 3.61 885 3.72 901 3.83 916 3.93 931 4.04
14100 850 3.95 866 4.09 883 4.23 898 4.37
15510
16920
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
9870 585 1. 3 1 609 1. 4 2 632 1. 5 1 654 1. 6 675 1. 6 9 695 1. 7 8
11280 606 1. 6 3 633 1. 7 7 657 1. 9 679 2.02 700 2.13 720 2.24 739 2.35
12690 599 1. 8 628 1. 9 7 655 2.15 681 2.31 704 2.47 726 2.62 74 7 2.76 76 6 2.89 785 3.02
14100 631 2.2 654 2.38 679 2.57 705 2.76 729 2.96 752 3.14 774 3.32 795 3.49 814 3.65 832 3.8
15510 690 2.9 711 3.08 733 3.28 756 3.5 779 3.71 801 3.93 822 4.13 842 4.33
16920 74 9 3.73 768 3.92 788 4.14 809 4.36
Table 18 - WK 125 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
5720 772 1. 0 6 802 1. 15 830 1. 2 4 857 1. 3 3 883 1. 4 1 909 1. 5 933 1. 5 9 957 1. 6 8
6430 786 1. 2 3 815 1. 3 2 843 1. 4 2 871 1. 5 2 897 1. 6 2 922 1. 7 2 947 1. 8 2
7140 800 1. 4 829 1. 5 1 857 1. 6 2 884 1. 7 3 911 1. 8 4 936 1. 9 4 960 2.05
7850 816 1. 5 9 844 1. 7 872 1. 8 2 898 1. 9 4 925 2.06 950 2.18
8560 835 1. 8 2 862 1. 9 4 888 2.05 913 2.18 939 2.3
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
8970 562 0.55 601 0.63 639 0.71 675 0.8 709 0.89 74 1 0.98
10090 548 0.6 584 0.68 620 0.76 655 0.84 690 0.93 723 1. 0 3 755 1. 1 3
112 10 544 0.68 578 0.75 611 0.83 644 0.91 676 1 708 1. 0 9 739 1. 19 770 1. 2 9
12330 542 0.77 577 0.85 609 0.93 640 1. 0 1 670 1. 1 700 1. 1 9 730 1. 2 8 759 1. 3 8 788 1. 4 8
13450 541 0.85 578 0.96 612 1. 0 5 643 1. 1 4 671 1. 2 3 699 1. 3 2 727 1. 4 1 755 1. 5 1 782 1. 6 1 809 1. 7 1
Page 25

Installation
25RT-SVX19A-E4
Table 19 - WK 155 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
6800 787 1. 2 9 816 1. 3 8 843 1. 4 7
7650 807 1. 5 4 834 1. 6 4 861 1. 74
8500 832 1. 8 3 857 1. 9 4 882 2.04
9350 861 2.18 884 2.29
10200 893 2.58
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
6800 566 0.7 599 0.77 632 0.85 664 0.93 696 1. 0 2 727 1. 1 1 757 1. 2
7650 571 0.82 604 0.9 634 0.99 664 1. 0 7 694 1. 1 6 723 1. 2 5 751 1. 3 4 779 1. 4 4
8500 578 0.95 612 1. 0 5 644 1. 1 5 673 1. 2 5 700 1. 3 4 727 1. 4 3 754 1. 5 3 780 1. 6 3 806 1. 7 3
9350 586 1. 0 9 622 1. 2 2 655 1. 3 3 685 1. 4 4 712 1. 5 5 739 1. 6 5 764 1. 7 5 788 1. 8 6 813 1. 9 6 837 2.07
10200 633 1. 3 9 667 1. 5 3 698 1. 6 6 726 1. 7 8 753 1. 9 778 2.02 803 2.13 826 2.24 848 2.35 871 2.47
Table 20 - WK 200 External static pressure
Standard drive
Oversized drive
External Static Pressure (Pa)
275 300 325 350 375 400 425 450 475 500
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
8970 717 1. 9 74 2 2.04 766 2.17 789 2.31 811 2.45 833 2.58
10090 737 2.25 761 2.4 785 2.56 808 2.71 830 2.87
112 10 761 2.66 784 2.82 806 2.98 828 3.15
12330 789 3.16 810 3.32 831 3.49
13450 820 3.75 840 3.91
14570
15690
16810
External Static Pressure (Pa)
25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
m3/h RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW) RPM (kW)
8970 521 1. 0 1 550 1. 1 2 579 1. 2 4 608 1. 3 6 636 1. 4 9 664 1. 6 2 691 1. 76
10090 529 1. 2 557 1. 3 2 584 1. 4 4 610 1. 5 6 636 1. 6 8 662 1. 8 2 687 1. 9 5 712 2.1
112 10 540 1. 4 2 569 1. 5 6 595 1. 6 9 621 1. 8 2 645 1. 9 5 669 2.08 692 2.22 715 2.36 738 2.51
12330 552 1. 6 6 582 1. 8 2 610 1. 9 8 635 2.13 659 2.27 681 2.41 704 2.55 725 2.7 74 7 2.85 768 3
13450 597 2.11 625 2.3 651 2.47 675 2.64 698 2.8 720 2.95 74 1 3.11 76 1 3.26 781 3.42 801 3.58
14570 638 2.59 666 2.8 692 3.01 716 3.2 74 0 3.39 762 3.58 783 3.75 803 3.92
15690 677 3.1 707 3.37 735 3.61 761 3.85
16810 715 3.66 74 8 3.98
Page 26

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E426
Electrical connection
The electric panel is located in the
unit compressor section. Remove
the compressor access panel. The
unit is designed to run with 400 V
+/- 5%/50 Hz/ 3 ph.
Factory supplied Disconnect switch
(Option)
The disconnect switch is factory
mounted. It is located on the side of
the Electrical panel and equipped
with fuses as standard.
Over current protection
The branch circuit feeding the unit
must be protected in accordance
with national or local codes and
max unit amps indicated in Table 21
to 28.
Power wiring
The unit power supply must be
provided by 4-wire cable with crosssectional areas complying with
legislation.
The power supply cables must be
laid in leak-tight pipes and pass
through the bottom of the electric
panel. The cables must not be taut.
Appropriate connectors must be
provided. Flexible pipe supports are
required to prevent noise
transmission in the building
structure. Ensure all the connections
are tightened.
Note:
1. earthing must be executed in
accordance with local legislation.
2. the machines are designed for a
short-circuit current of 10 kA. In
the event of a higher application,
contact your Trane sales office.
Figure 10 - Power supply
TKD/TKH, WKD/WKH units:
YKD/YKH units:
1 = Power supply from the bottom or from the side.
Page 27

Installation
27RT-SVX19A-E4
Scroll compressors
Compressor electrical phasing
Proper phasing of the electrical
power wiring is critical for proper
operation and reliability of the scroll
compressor and fans.
Proper rotation of the scroll
compressor must be established
before the unit is started. This is
accomplished by confirming that
the electrical phase sequence of the
power supply is correct. The motor
is internally connected for clockwise
rotation with the inlet power supply
phased A, B, C.
The direction of rotation may be
reversed by interchanging any two
of the line wires. It is this possible
interchange of wiring that makes a
phase sequence indicator necessary
if the operator is to quickly
determine the phase rotation of the
compressor motor.
The "ABC" indicator on the face of
the phase indicator will glow if
phase is ABC for terminals L1, L2,
L3.
CAUTION! After completion of
wiring, check all electrical
connections, and ensure all
connections are tight. Replace and
secure all electrical box covers and
access doors before leaving unit or
connecting power to circuit
supplying unit.
CAUTION! Units with Scroll
compressors are not equipped with
crankcase heaters.
WARNING !
Disconnect all power,including
remote disconnects, and discharge
all capacitors before servicing.
Follow proper lockout/tagout
procedures to ensure the power
cannot be inadvertently energized.
After power is removed, allow
4 minutes for capacitors to
discharge. Verify with an
appropriate voltmeter that all
capacitors have discharged. Failure
to disconnect power and/or
discharge capacitors before
servicing could result in death or
serious injury. For additional
information regarding the safe
discharge of capacitors, see Trane
Service Bulletin PROD-SVB06A.
Table 21 - Electrical data - YKD/YKH Unit Wiring
Electrical Characteristics Unit amps
UNIT MPS
Standard Evaporator
Fan Motor
Oversized Evaporator
Fan Motor
Minimum
Circuit
Ampacity
Maximum
Overcurrent
Protective
Device (Fuse
or Circuit
Breaker)
Minimum
circuit
ampacity
Maximum
Overcurrent
Protective
Device (Fuse
or Circuit
Breaker)
Without Electric heat option
TKD/H 155 400/3/50 35 50 36.9 50
TKD/H 175 400/3/50 41 50 41.9 50
TKD/H 200 400/3/50 44 63 44.5 63
TKD/H 250 400/3/50 46.4 63 - WKD/H 125 400/3/50 31.9 40 33.8 40
WKD/H 155 400/3/50 35.1 50 37 50
WKD/H 200 400/3/50 50.4 63 50.9 63
YKD/H 155 400/3/50 35.6 50 37.5 50
YKD/H 175 400/3/50 42.3 50 43.2 50
YKD/H 200 400/3/50 44.6 63 45.1 63
YKD/H 250 400/3/50 46.4 63 - -
With Electric heat
TKD/H 155 400/3/50 41 63 43 63
TKD/H 175 400/3/50 43 63 43 63
TKD/H 200 400/3/50 61 80 61 80
TKD/H 250 400/3/50 62 80 - WKD/H 125 400/3/50 68 80 69.9 80
WKD/H 155 400/3/50 71.2 80 73.1 80
WKD/H 200 400/3/50 104.5 125 105 125
Page 28

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E428
Table 22 - Electrical data - TKD/TKH Compressor motor and condenser motor
(1) At Eurovent rating conditions : Indoor return Air (27°C DB / 19°C WB) - Ambiant 35°C
(2) per motor
Table 23 - Electrical data - YKD/YKH Compressor motor and condenser motor
(1) At Eurovent rating conditions : Indoor return Air (27°C DB / 19°C WB) - Ambiant 35°C
(2) per motor
TKD/H TKD/H TKD/H TKD/H
155 175 200 250
Compressor
Number 2 2 2 2
Ty pe Scroll Scroll Scroll Scroll
Model 9T / 5T 10T / 6.7T 9T / 9T 10T / 10T
Rated Amps (1) (A) 15.0 / 8.5 15.1 / 11.4 14.7 / 14.7 15.3 / 15.3
Locked rotor Amps (2) (A) 118 / 65.5 118 / 101 118 / 118 118 / 118
Outdoor Fan
Nominal Airflow (m3/h) 15350 19750 21000 23500
Ty pe Axial Axial Axial Axial
Diameter (mm) 660 660 710 710
Drive type Direct Direct Direct Direct
Number 2 2 2 2
Motor HP (kW) 0.25 0.25 0.56 0.56
Motor Rated Amps (1) (A) 1. 6 1. 6 2.3 2.3
Motor Locked rotor Amps (2) (A) 3.8 3.8 5.8 5.8
Motor RPM (rpm) 925 925 925 925
YKD/H YKD/H YKD/H YKD/H
155 175 200 250
Compressor
Number 2 2 2 2
Ty pe Scroll Scroll Scroll Scroll
Model 9T / 5T 10T / 6.7T 9T / 9T 10T / 10T
Nominal Amps (1) (A) 15.0 / 8.5 15.1 / 11.4 14.7 / 14.7 15.3 / 15.3
Locked rotor Amps (2) (A) 118 / 65.5 118 / 101 118 / 118 118 / 118
Outdoor Fan
Nominal Airflow (m3/h) 15350 19750 21000 23500
Ty pe Axial Axial Axial Axial
Diameter (mm) 660 660 710 710
Drive type Direct Direct Direct Direct
Number / Voltage 2 2 2 2
Motor HP (kW) 0.25 0.25 0.56 0.56
Motor Rated Amps (1) (A) 1. 6 1. 6 2.3 2.3
Motor Locked rotor Amps (2) (A) 3.8 3.8 5.8 5.8
Motor RPM (rpm) 925 925 925 925
Page 29

Installation
29RT-SVX19A-E4
Table 24 - Electrical data - WKD/WKH Compressor motor and condenser motor
(1) At Eurovent rating conditions : Indoor return Air (27°C DB / 19°C WB) - Ambiant 35°C
(2) per motor
Table 25 - Electrical data - TKD/TKH Supply fan motor
(4) At the nominal airflow with standard drive
(5) At the nominal airflow with oversized drive when available
YKD/H YKD/H YKD/H YKD/H
155 175 200 250
Indoor Fan
Nominal Airflow (m3/h) 8500 9850 11 21 0 14100
Static pressure available (4) (Pa) 150 75 17 5 75
Maximum static pressure available (5) (Pa) 350 375 450 375
Ty pe FC Centrifugal FC Centrifugal FC Centrifugal FC Centrifugal
Diameter / Width (in / in) 15" / 15" 15" / 15" 18" / 18" 18" / 18"
Drive type Belt Belt Belt Belt
Number # 1 1 1 1
Motor HP (Standard/Oversized) (kW) 2.2 / 3.0 3.0 / 4.6 3.0 / 4.6 4.6 / Motor Rated Amps (Standard/Oversized) (A) 4.6 / 6.5 6.5 / 9.0 6.5 / 9.0 9 / Motor Locked rotor Amps (Standard/Oversized) (A) 36.4 / 57 57 / 71.9 57 / 71.9 71.9 / Motor RPM (Standard/Oversized) (rpm) 1450 / 2870 2870 / 2900 2870 / 2900 2900 / -
WKD/H WKD/H WKD/H
125 155 200
Compressor
Number 2 2 2
Ty pe Scroll Scroll Scroll
Model 6T / 6T 7.5T /7.5T 10T / 10T
Rated Amps (1) (A) 10.0 / 10.0 12.1 / 12.1 17.5 / 17.5
Locked rotor Amps (2) (A) 74 / 74 79 / 79 98 / 98
Outdoor Fan
Nominal Airflow (m3/h) 15300 15850 23600
Ty pe Axial Axial Axial
Diameter (mm) 660 660 710
Drive type Direct Direct Direct
Number 2 2 2
Motor HP (kW) 0.25 0.25 0.56
Motor Rated Amps (1) (A) 1. 6 1. 6 2.3
Motor Locked rotor Amps (2) (A) 3.8 3.8 5.8
Motor RPM (rpm) 925 925 950
Page 30

Installation
RT-SVX19A-E430
Table 26 - Electrical data - YKD/YKH Supply fan motor
(4) At the nominal airflow with standard drive
(5) At the nominal airflow with oversized drive when available
Table 27 - Electrical data - WKD/WKH Supply fan motor
(4) At the nominal airflow with standard drive
(5) At the nominal airflow with oversized drive when available
Table 28 - Electrical data - Combustion Blower Motorr
YKD/H YKD/H YKD/H YKD/H
155 175 200 250
Gas burner
Heating Models G350 G350 G350 G350
Heating Input (G20) (kW) 77 77 77 77
Heating Output (kW) 69.3 69.3 69.3 69.3
Steady State Efficiency (%) 90 90 90 90
No. Burners 1 1 1 1
No. Stages 2 2 2 2
Gas Connection Pipe Size 3/4" NPT 3/4" NPT 3/4" NPT 3/4" NPT
WKD/H WKD/H WKD/H
125 155 200
Indoor Fan
Nominal Airflow (m3/h) 7140 8500 112 10
Static pressure available (4) (Pa) 200 17 5 200
Maximum static pressure available (5) (Pa) 425 325 350
Ty pe FC Centrifugal FC Centrifugal FC Centrifugal
Diameter / Width (in / in) 15" / 15" 15" / 15" 18" / 18"
Drive type Belt Belt Belt
Number # 1 1 1
Motor HP (Standard/Oversized) (kW) 2.2 / 3.0 2.2 / 3.0 3.0 / 4.6
Motor Rated Amps (Standard/Oversized) (A) 4.6 / 6.5 4.6 / 6.5 6.5 / 9.0
Motor Locked rotor Amps (Standard/Oversized) (A) 36.4 / 57 36.4 / 57 57 / 71.9
Motor RPM (Standard/Oversized) (rpm) 1450 / 2870 1450 / 2870 2870 / 2900
TKD/H TKD/H TKD/H TKD/H
155 175 200 250
Indoor Fan
Nominal Airflow (m3/h) 8500 9850 11 21 0 14100
Static pressure available (4) (Pa) 175 250 200 125
Maximum static pressure available (5) (Pa) 325 400 375 350
Ty pe FC Centrifugal FC Centrifugal FC Centrifugal FC Centrifugal
Diameter / Width (in / in) 15" / 15" 15" / 15" 18" / 18" 18" / 18"
Drive type Belt Belt Belt Belt
Number # 1 1 1 1
Motor HP (Standard/Oversized) (kW) 2.2 / 3.0 3.0 / 4.6 3.0 / 4.6 4.6 / Motor Rated Amps (Standard/Oversized) (A) 4.6 / 6.5 6.5 / 9.0 6.5 / 9.0 9 / Motor Locked rotor Amps (Standard/Oversized) (A) 36.4 / 57 57 / 71.9 57 / 71.9 71.9 / Motor RPM (Standard/Oversized) (rpm) 1450 / 2870 2870 / 2900 2870 / 2900 2900 / -
Page 31

Controls
31RT-SVX19A-E4
Control wiring
The control circuit is 24 V AC. Unit
includes a 400/24 V transformer.
WARNING!The unit disconnect
switch must be opened and locked
open. Risk of injury and
electrocution.
CAUTION!The unit 24 V transformer
must not be used to power
accessories mounted on site, other
than those proposed by Trane.
Unit controlled by thermostat
Figure 11 - Thermostat wiring
Trane THS01,THS02, THP01 and
THP02 Thermostats are directly
connected to RTRM board
(J7 connector). TRANE THS02 and
THP03 thermostats are directly
connected to RTRM board
(J6 connector).
Install the electrical link between the
thermostat (thermostat terminal
strip) and the unit (J6 or J7
connector) in compliance with the
interconnection diagram. The low
voltage wiring must not be laid in
the same pipes as the power cables.
The sizes and lengths of the
thermostat connection wires are
given in Table 29. The total
resistance of these control cables
must not exceed 5 ohms. If the
resistance exceeds this value the
thermostat may not operate with
the same precision.
Table 29 - Zone sensor wire size and
maximum length
Maximum length
Zone sensor wire size
Wire
size
(mm²)
Maximum
wire lengh
(m)
THS/THP 03
0.33 45
0.5 76
0.75 115
1. 3 185
2 300
Conventionnal
thermostat
THS/THP 01-02
0.33 10
0.5 15
0.75 23
1. 3 37
2 60
RTRM
3J6
7
7
8
8
9
9
10
10
11
11
12
12
14
14
RTRM
3J6
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
9
10
10
11
11
12
12
14
14
RTRM
3J7
0
W1
G
Y1
Y2
R
COM
RTRM
3J7
W1
W2
G
Y1
Y2
R
COM
SR6
1
2
THS02
4239070
THP02
4240530
THS01
4239060
THP01
4240520
7
7
THP03
8
8
9
S2
9
10
S1
10
11
11
12
12
14
14
1
SR6
1
2
(WH)
(GN)
(RD)
THA01
(BK)
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
THS03
1
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
9
10
10
11
12
14
0
W1
G
Y1
Y2
R
24V
24V(C)
W1
W2
G
Y1
Y2
R
24V
24V(C)
Page 32

Controls
RT-SVX19A-E432
Unit controlled by BAS
Each unit must be equipped with a
TCI-R board. A communication bus
(twisted shielded pair) must link
each TCI-R to the Trane Roof Top
Manager (RTM) or to the
communication gateway (in the
case of an external BAS). Connect
one temperature sensor to each
unit. LonTalk
®
communication
interface LTCl-R board allows ICS
communication between a
ReliaTel™ unit and LonTalk
®
communication applications.
Unit controlled by Tracker™
supervisor
The units must also be equipped
with the TCI-R communication
board. One remote sensor is
required on each unit for a constant
flow volume. In the case of a
variable flow installation
(VariTrac™) these sensors must not
be installed. A twisted shielded pair
must be used for the
communication link. The main
functions of the Tracker™ supervisor
are control of setpoints, timetable
management (Programming) and
display of faults. For more details
refer to the supervisor
documentation.
Page 33

Controls
33RT-SVX19A-E4
CO2sensors
Wall-mounted and duct-mounted
CO
2
sensors
Table 30 - Specifications
WaII-mounted Duct-mounted
Measuring range CO
2
0-200 ppm
Accuracy at 25°C
<+/- [40 ppm CO2+
3%
of reading]
(included repeatability
and calibration
uncertainty)
<+/- [30 ppm CO
2
+ 2%
of reading]
(included
repeatability and
caiibration
uncertainty)
Non-linearity <1.0% full scale
Ternperature dependence
of output
0.3% full scale/°C
Long-term stability
<5.0% fulI scale /
5years
Recomrnended
calibration interval
5 years
Response time 1 minute (0-63%)
Operating temperature 15-35°C - 5-45°C
Storage temperature -20-70°C
Humidity range
0-85% relative
humidity
Airflow range 0-10 m/s)
Output signals (jumper
selectable)
0-10Vdc
Resolution of anaIog
outputs
10 ppm CO2
Recomrnended external
load
Current output:
max 500
Voltage output:
min. 1000
Power supply Nominal 24Vac
Power consumption <5 VA
Warm-up time <15 minutes
Dimensions (mm) 108 x 80 x 36 80 x 80 x 200
Page 34

Controls
RT-SVX19A-E434
Power supply requirements
CAUTION! Make sure that you
connect the power wire only to the
24V terminal. Connecting the power
wire to the output terminal may
result in equipment damage.
The CO
2
sensor is designed to
operate with a nominal 24 Vac
supply. The power supply should
maintain the voltage between 20 to
26 Vac.
Table 31 - CO2 sensor wire size
Wiring the wall-mounted CO
2
sensor
DVC setpoint potentiometer on
economizer module can be adjusted
as follows:
0% - 500ppm, 50% - 1000 ppm,
100% - 1500ppm
The outside air damper will
modulate from minimum position
setting to up to 100% while
attempting to maintain the CO
2
setpoint.
To connect the wall mounted CO
2
sensor, Refer to the wiring diagram
provided in the unit.
Cross
section
Maximum wire
Iength
(mm2) (mn)
0.25 50
0.5 100
1 200
Wiring the duct-mounted CO
2
sensor
1. Connect the DCV signal lwire to
the connector DCV of the ECA
2. Connect the power according to
the guidelines in Power supply
requirements.
To connect the wall mounted CO
2
sensor, Refer to the wiring diagram
provided in the unit.
Mounting the wall-mounted sensor
1. Select a proper location in the
room to mount the CO
2
sensor.
Look for an interior wall with
good air circulation,
approximately 1.4 m from the
floor.
2. Remove the back plate from the
sensor and thread the power
wires and output signal wire
through the hole in the back
plate.
For surface wiring, make cutouts with pliers to the thinner
section of the upper or lower
edge of the back plate and to
thread the wires through.
3. Mount the back plate to the wall
with screws. Note that the arrow
on the back plate shows the
mounting direction.
Figure 12 - Jumper settings
OUTPUT
SELECTION
JUMPERS
Page 35

Controls
35RT-SVX19A-E4
Mounting the duct-mounted CO
2
sensor
1. Select a proper location on the
duct to mount the CO
2
sensor.
2. Drill a 22-25 mm hole in the
mounting surface for sensor
insertion (Figure 13).
3. Attach the mounting plate to the
duct wall with four screws.
4. Insert the sensor through the
mounting plate, adjusting the
depth for optimal air sensing.
Figure 13 - Duct-mounted CO2sensor
Figure 14 - Duct-mounted CO
2
insertion depth
CO2 sensor maintenance
This CO
2
sensor has excellent
stability and requires no
maintenance. In most environments
the recommended calibration
interval is five years. A trained
service technician can use a
portable CO
2
meter to certify sensor
calibration. If, when checking the
sensor, the reading differs too much
from the reference value, the sensor
can be recalibrated in the field. A
calibration kit, software, and
calibration gases are required. If
certified accuracy is required, the
sensor must be calibrated against
accurate and traceable calibration
gases in a laboratory. Consult Trane
BAS for further details.
15/8 in. ( 42 mm)
7
/8 in. (2 2 mm)
5
/8 in.
1
(42 mm)
21/2 in. (64 mm) 31/8 -51/2 in. (80 - 140 mm)
Page 36

Note:This potentiometer allows to
adjust the permanent fresh air
intake from 0 to 50%.
0 W corresponds to closed fresh air
damper.
270 W corresponds to 50% open
fresh air damper.
Controls
RT-SVX19A-E436
Remote potentiometer
To install the remote potentiometer,
cut the jumper WL on the
economizer ECA board, and connect
the wires to P and P1.
Note:This potentiometer allows to
adjust the permanent fresh air
intake from 0 to 50%.
0 W corresponds to closed fresh air
damper.
270 W corresponds to 50% open
fresh air damper.
Figure 15 - Remote potentiometer dimensions
Figure 16 - Remote potentiometer wiring
1 = Remote potentiometer
2 = ECA Board
WH = White wire
RD = Red Wire
BU = Blue wire
_____ Factory wiring
-------- Field wiring
P
P
Page 37

Controls
37RT-SVX19A-E4
Fire thermostat
There are two sensors in the fire
thermostat Kit: Sensor X1310004001 is factory-set to open at 57°C.
Sensor X13100040-02 is set to open
at 115°C.
Sensors are mounted directly in the
ductwork. They should be installed
where elements can respond quickly
to air temperature changes. If not
possible, the sensor may be
installed on a suitable bracket so
the air is drawn across the element.
Sensor X13100040-01 has to be
mounted in the return air duct.
Sensor X13100040-02 has to be
mounted in the supply air duct.
Note: Do not permit element guard
to touch internal parts. Do not
locate sensor where the air
circulation is restricted by baffles.
Connection of the fire thermostat
with TCI board : Refer to the wiring
diagram provided in the unit.
Connection without TCI board
Connect according to the standard
wiring diagram provided on the
unit.
Remove sensor cover and fasten
control securely with screws. Loads
connected must not exceed 2 amps,
30V Ac.
Figure 17 - Duct mounting of fire thermostat
1 = Fire thermostat
2 = Hole in the duct
Page 38

Controls
RT-SVX19A-E438
Clogged filter detector
This device is mounted in the filter
section. The sensor measures the
difference in pressure before and
after the filter section. The
information is sent to the THP03
thermostat, to a Tracker™ or to a
BMS.
Smoke detector
This device is used to detect smoke
in the air stream. It includes a
factory mounted detector connected
to a central panel, both fitted in the
fan section.
When smoke is detected, it shuts off
the unit. A dry contact is available
on the control panel for a remote
default.
High temperature safety
thermostat
This additional safety device is a
manual reset thermostat for gas
fired units (YKD/YKH), required
mainly by the French ERP
regulation. It is located in the gas
burner section. It stops the gas
burner and the supply air fan when
the supply air temperature rises to
120°C.
Remote fault relay
This is a factory mounted relay used
to send alarm signals (dry contact)
to a local BMS or a local control
panel. With this relay, the
compressor, heating, fan and power
supply alarm output signals from
the controller are reported to a
single dry contact.
Thermostats
6 thermostats are available:
THS01/THP01, THS02/THP02 and
THS03/THP03.
"THS" are non programmable
thermostats, "THP" are
programmable.
01 and 02 series are conventional
thermostat, 03 series are dedicated
to the controller.
Table 32 - Thermostats features
*some important features are lost while using the CTI card.
Note: thermostats are powered up by the rooftop control (24V)
THS01 THP01 THS02 THP02 THS03 THP03
non-programmable X - X - X -
programmable - X - X - X
electronic X X X X X X
unit control type design electromech. electromech. electromech. electromech. Reliatel Reliatel
interface card needed CTI* CTI* CTI* CTI* none none
for Cooling Only units X X - - X X
for Heat Pump units - - X X X X
for Gas Fired units X X - - X X
Cooling stages 2 2 2 2 2 2
auxiliary heating stages
(elec. heater, HWC )
2 2 1 1 2 2
heating stages
(heat pump mode)
none none 1 1 1 1
liquid crystal display
X X X X - X
Page 39

Controls
39RT-SVX19A-E4
Other accessories available
Remote temperature sensor to be
used with THS/THP 01-02
TZS01: Remote room temperature
sensor to be used with THS/THP 03,
Tracker or Varitrac systems.
DTS: Duct temperature sensor to be
used with THS/THP 03
TZS02: Remote room temperature
sensor with adjustable thumwheel
setpoint to be used with Tracker or
Varitrac systems
TZS04: Room temperature sensor
with adjustable thumbwheel and
override button, to be used with
Tracker or Varitrac systems
Refer to separate documentation for
more information.
Communication Interfaces
TRANE Communication Interface
(TCI-R) board
This is an electronic board, factorymounted in the main control panel,
needed to allow communication
between a TRANE Integrated
Comfort system (TRACKER or
Varitrac CCP2) and the unit. (COM3COM4)
LON Communication Interface
(LCI-R) board
This is an electronic board, factorymounted in the main control panel,
needed to allow communication on
a LonTalk
®
Network at the unit level.
LonTalk
®
. Communication Interface
(LCI-R) board
This interface board allows Voyager
units to communicate on a LonTalk
®
Network at the unit level. Network
variables are based on the
LonMark®. Space Comfort Controller
Functional Profile Template. The LCIV uses a Free Topology transceiver
FTT-10A. The FTT-10A transceiver
supports non-polarity sensitive, free
topology wiring, allowing the
system installer to use star, bus,
and loop architecture. The LCI-V can
also be connected to an optional
High Temperature Limit Switch if
installed with the rooftop unit. For
more information, see attached
manual LTCI-IN-1.
Page 40

Unit Options
RT-SVX19A-E440
Hot water coil
(Down flow units only)
In order to prevent water to freeze
up in the coil during unoccupied
period or shutdown limited period,
a thermostat opens when there is a
risk of freeze-up. The services of a
water treatment specialist are
recommended if water used can
cause scaling deposits or erosion.
Insulate all the water piping likely to
be exposed to freezing
temperatures in order to avoid
freeze up of the coil and heat losses.
The water distribution network must
be fitted with vents in places where
air is likely to be trapped.
The hot water coil is factory
mounted in the discharge section.
Two holes are provided to connect
the hot water coil. They are located
at the base of the unit. Remove the
central panel to access the coil,
using an 8 mm wrench (the bolts
are located on the bottom part of
the panels). The tubes for entering
and leaving water are equipped
with a threaded female connector.
Water connection inlet/outlet: 1 ¼"
ISO R7.
Hot water coil: Installation and
connection
In order to prevent water to freeze
up in the coil during unoccupied
period or shutdown limited period,
it is recommended to use ethylene
glycol. The services of a water
treatment specialist are
recommended if water used can
cause scaling deposits or erosion.
Insulate all the water piping likely to
be exposed to freezing
temperatures in order to avoid
freeze up of the coil and heat losses.
The water distribution network must
be fitted with vents in places where
air is likely to be trapped.
Table 33 - Ethylene glycol percentage
Ethylene glycol
percentage
Freezing point
(%) (°C)
10 -4
20 -10
Figure 18 - Hot water coil connections
Page 41

Unit Options
41RT-SVX19A-E4
Electric Heater
Electric heaters are fitted on the fan
discharge.
Heaters have two heating stages
and provided with two types of
overheat thermostats:
• Automatic reset thermostats
which stop the electric heater
when the air temperature rises to
76°C. Automatic reset at 60°C. No
alarm output available.
• The manual reset thermostat
which stop the unit when the air
temperature rises to 120°C. No
alarm output available.
Soft Starter
The soft starter is used to achieve a
progressive supply fan start and a
reduced starting current as well as
the motor starting torque. This
option is well adapted for textile
duct applications. It is factory
installed in the main control panel.
The soft starter gradually increases
the voltage of the supply fan motor
until it reaches full line voltage.
The starting time can be adjusted
from 0 to 64 seconds but the soft
starter is factory set to the
maximum starting time value,
64 seconds.
Figure 19 - Soft starter
1 = Three phase mains connections
2 = Motor connections
3 = Settings
4 = Status outputs
5 = Controls
6 = LEDs
INITAL
TORQ UE
Time(s)
Motor
Softstarter
Stop / Load
Start / Line
Supply
Urg.
Stop
Ctrl
Byp.
Diag.
3
6
5
4
1
2
Page 42

Unit Options
RT-SVX19A-E442
0 - 25% fresh air hood
The 0-25% fresh air hood allows to
introduce fresh air into the unit.
This is a manual device fitted on the
back of the unit, sized for a
maximum of 25% of the nominal
rooftop air flow.
This option includes for the hood
itself, a wire mesh and a slidable
damper.
The slidable damper has to be
adjusted manually by removing the
screws and sliding it off up or down
(Figure 20).
The amount of fresh air introduced
is then permanently fixed.
Figure 20 - 0-25% manual fresh air hood
1 = Intake hood
2 = Wire mesh
3 = Slidable damper
H
5
8
5
210
1
3
4
8
5
2
Page 43

This option includes exhaust hoods
and gravity dampers located in the
return air section (Figure 22). When
the pressure of the building
increase, the gravity dampers open
and relieve air to the outside.
If the return air duct pressure drop
is higher than the building
overpressure, the gravity dampers
will not open.
If the return air duct pressure drop
is lower than the building
overpressure, the gravity dampers
will open and releive air outside of
the building.
Unit Options
43RT-SVX19A-E4
Barometric relief
The barometric relief allows to
minimize overpressure in the
building caused by the introduction
of fresh air. This option is typically
installed when fresh air intake is
below 25% of the nominal air flow
and when the return air pressure
drop is below 25Pa.
Figure 21 - Economizer flow chart with barometric relief
Downflow version Horizontal flow version
R = return
S = supply
F = fresh air
E = exhaust
S
R
F
S
R
E
F
Page 44

Operation
RT-SVX19A-E444
Operation with a
conventional thermostat
The ReliaTel module has
conventional thermostat
connections as well as Zone Sensor
Module connections. When a
conventional thermostat is
controlling the unit, operation
differs as follows.
• Supply Air Tempering feature is
not available. If outdoor air is
being introduced through the
equipment, discharge air
temperature may be cold when
not actively heating.
• Proportional Integral (PI) control
is not available.
• Zone Sensor Diagnostics are
only available on the RTRM
module on the J6 terminals,
instead of at the Zone Sensor in
the space.
• Intelligent Fall-Back is not
available. If a failure occurs in
the device controlling the
equipment, operation will cease.
• Heat Pump Smart Recovery and
Smart Staging is not available.
Heat Pump operation becomes
more costly unless the generic
control being applied can
accomplish this.
• Remote Sensing Capabilities are
not available on most
mechanical thermostats.
• Space Temperature Averaging
capabilities are not available on
most mechanical thermostats.
• 27½ to 50 VAV – Conventional
thermostat input terminals are
inactive.
• Built in Night Set Back and
Unoccupied Functions function
differently with a conventional
mechanical thermostat.
• A built-in algorithm which allows
for automatic reset of the
discharge air temperature while
economizing is not available.
The terminal strip for attaching the
thermostat wires is located on the
RTRM module in the control
compartment.
The purpose of each terminal is
discussed in the next section.
Customers occasionally require
operation with a conventional
thermostat rather than a zone
sensor. In some cases there is a
preference for a specific thermostat
model, and in others there is
reluctance to adopt newer
technology that may not be as well
understood as conventional
thermostats. In addition, non-Trane
Building Controllers typically
provide an interface to HVAC
equipment based on a conventional
thermostat interface. Units applied
with this type of controller need to
accept conventional thermostat
inputs.
Conventional thermostat signals
represent direct calls for unit
functions. In their simplest
applications, thermostat contacts
directly control contactors or other
load switching devices. This function
provides inputs for the thermostat
signals and processing to enhance
reliability and performance.
Compressor protection and
reliability enhancement functions
(HPC, LPC, Minimum On/Off timers,
etc.). All operate the same whether
applied with zone sensors or a
conventional thermostat.
Logic is also provided to cause
appropriate unit functions when
inappropriate thermostat signals are
provided. Simultaneous calls for
heating and cooling will be ignored,
and the fan will be turned on with a
call for heating or cooling even if
the fan request is not detected.
If the thermostat is immediately
changed from a heating to a cooling
call, or vice versa, there will be a
five minute delay before the new
call will initiate.
COM
T
X2
Y2
W2
G
W1/0
Y1
R
Page 45

Operation
45RT-SVX19A-E4
Thermostat signals are as follows:
R 24VAC power to thermostat
Y1 Call for compressor 1 or first
stage cooling
Y2 Call for compressor 2 or 2nd
stage cooling
G Call for supply fan
W1 Call for heat 1
W2 Call for heat 2
Heat pump only:
X2 Call for emergency heat
O Switchover valve On = cooling,
Off = heating
T Bias for heat anticipation for those
mechanical thermostats that use
this function
Conventional thermostat –
Gas/ Electric, Electric Heat:
Input/connection
Function when
energized :
G (fan) Fan runs continuously
except during
unoccupied mode
(see next page)
Y1 (compressor 1
or economizer)
Compressor #1 runs
or economizer
operates
Y2 (compressor 2
or compressor 1
while economizing)
Compressor #2 also
runs, or #1
compressor runs
while economizing
W1 (gas / electric
heat first stage)
1st stage heat
W2 (gas / electric
heat 2nd stage)
2nd stage heat (if
available)
Conventional thermostat –
Heat Pump
T (provides heat anticipation signal for
those mechanical thermostats that use this
feature. If the thermostat used does not
have a “T” terminal, disregard this
terminal.
Input/connection
Function when
energized
Cooling mode:
G (fan) Fan runs continuously
except during
unoccupied mode
(see next page)
O (reversing valve
during cooling)
Reversing valve in
cool mode
Y1 + O
(first stage cooling)
Compressor #1 runs
or economizer
operates
Y1 + Y2 + O
(2nd stage cool)
Compressor #2 also
runs, or #1
compressor runs
while economizing.
Heating mode:
G (fan) Fan runs continuously
except during
unoccupied mode
(see below)
Y1 (both
compressors 1st
stage heat)
Both compressors
run
Y2 (during heating
– nothing happens)
No change
W2 (electric heat
2nd stage)
2nd stage (electric)
heat
X2 (electric heat
only)
Electric heat only –
no compressors
Page 46

Operation
RT-SVX19A-E446
Unoccupied mode:
If the thermostat being used is
programmable, it will have its own
strategy for unoccupied mode and
will control the unit directly. If a
mechanical thermostat is being
used, a field applied time clock with
relay contacts connected to J6-11
and J6-12 can initiate an
unoccupied mode as follows:
• Contacts open: Normal occupied
operation.
• Contacts closed: Unoccupied
operation as follows - Fan in
auto mode regardless of fan
switch position. Economizer
closes except while economizing
regardless of minimum position
setting.
Cooling/Economizer Operation:
If unit does not have an economizer,
the Cool/Econ Stage 1 and Stage 2
will call directly for mechanical
cooling (compressor) stages. If the
unit has an economizer, the
Cool/Econ stages will function as
follows.
Table 34 - Cooling/Economizer Operation with Thermostat1,2
OK to
Economize?
ThermostatY1ThermostatY2Call for Economizer
Cooling
Compressor Staging
Request
No On Off Inactive Compressor Output 1
No Off On Inactive Compressor Output 2
No On On Inactive
Compressor
Outputs 1 & 2
Ye s On Off Active Off
Ye s Off On Active Compressor off
Ye s On On Active Compessor
Page 47

Operation
47RT-SVX19A-E4
Setting the economizer
or 0-50% motorized hood
(option)
The ECA board is mounted on the
damper actuator. To access the ECA
board on economizers:
• Remove the access panel located
on the economizer section.
• The electrical power must be
disconnected to set the
minimum position and check the
economizer.
• Disconnect the power supply,
put the thermostat fan selector
to "ON" and the "HEAT/COOL"
selector to "OFF". This puts the
damper in the minimum
ventilation position.
• To set the required minimum
ventilation air position, turn the
dial on the ECA clockwise to
increase ventilation, or anticlockwise to decrease ventilation.
The damper will open at this
setting whenever the fan circuit
is powered up.
• When the arrow on the dial
adjustment screw is pointing to 8
o'clock, the minimum position is
roughly 0%. When the dial is
pointing to 12 o'clock it is
roughly 25%, and when the dial
is pointing to 4 o'clock it is
roughly 50%
To check the damper is functioning
correctly, the ECA is equipped with
an indicator light in the middle of
the board. This light operates as in
Table 35.
Table 35 - ECA board LED
While setting the minimum position
the damper may move toward the
new setting in several small steps.
Once the damper has remained in
the same position for 10 to
15 seconds it can be assumed it is
in the new position.
OFF: No Power or Failure
ON: Normal, OK to Economize
Slow Flash: Normal, Not OK to
Economize
Fast Flash: Communications Failure
Pulse Flash: Error Code:
1 Flash: Actuator Fault
2 Flashes: C02Sensor
3 Flashes: RA Humidity Sensor
4 Flashes RATemp Sensor
5 Flashes: OA Quality Sensor
6 Flashes: OA Humidity Sensor
7 Flashes: OATernp Sensor
8 Flashes: MATemp Sensor
9 Flashes: RAM Fault
10 Flashes: ROM Fault
11 Flashes: EEPROM Fault
Page 48

Operation
RT-SVX19A-E448
Figure 22 - Minimum fresh air adjustment
1 = ECA board
EXF
AH
DCV
2-10 VDC
FEED
INPUT
2-10 VDC
ONT
OUTPUT
MIN POS.
SETPOINT
0-50%
ABCD
TING
O2 "PU
SETPOINT
ADJUS
MEN
500-1500 PPM
GREEN
LED
WER EXH
MIXED AIR SENSOR INPUT
OMMO
OMMO
OHS INPUT
T USED-
T I
ONNECTED
A INPU
OMMO
OMMO
RHS INPUT
O2 SENSOR INPU
OMMO
P1
REM
MINIMUM
TENTIOMETE
SHO
TED=C
OSE
OPEN=ON B
ARD P
270 omega = 50%
WHT
RED
MOD
OMMO
24
+
POWER EXHAUST
CONTACTS
MIXED AIR SENSOR
INPUT COMMON
COMMON
OHS INPUT
NOT USED-OAT IS
CONNECTED TO
RA INPUT
COMMON
COMMON
RHS INPUT
CO
2
SENSOR INPUT
COMMON
SHORTED=CLOSED
OPEN=ON CARD POT.
270 omega = 50%
REMOTE
MINIMUM
POTENTIOMETER
CO2 “PURGE”
SETPOINT
ADJUSTMENT
500-1500 PPM
GREEN
LED
COMMON
24VAC
MODBUS
2-10 VDC
CONTROL
OUTPUT
2-10 VDC
FEEDBACK
INPUT
MIN POS.
SETPOINT
0-50%
ABCD
SETTINGS
WHT
RED
BLUE
2-10 VDC
POWER EXH
AUSUST
CONONTACTS
MIXED AIR SENSOR INPUT
COMMO
N
N
COMMO
OHS INPUT
NOT USED-
OAT I
TO O RTRTRM
RA INPU
COMMO
COMMO
RHS INPUT
COMMO
D
OT.
R
WHT
S
T
N
N
T
N
RED
BLUE
CONNECTED
CO2 SENSOR INPU
SHO
RTED=C
LOSE
OPEN=ON B
OARD P
270 omega = 50%
REM
OTE
MINIMUM
POTENTIOMETE
1
EXF
2
1
MAT
2
1
/
OAH
2
OAE
1
OAT
2
1
RAT
2
1
RAHAH/
2
RAE
1
DCV
2
P
P1
FEED
BACK
INPUT
2-10 VDC
CONT
OUTPUT
MIN POS.
SETPOINT
0-50%
ABCD
SESETTING
S
RGEGE"
CO2 "PU
SETPOINT
ADJUS
TMEN
500-1500 PPM
1234
ROL
T
+
-
+
-
GREEN
LED
-
MOD
BUS
+
COMMO
VAC
24
1
N
Page 49

Operation
49RT-SVX19A-E4
Test procedures
Operating checklist before start-up
• Unit is level, with sufficient
clearance all round
• Duct network is correctly sized
according to the unit
configuration, insulated, and
water-tight
• Condensate drainage line is
correctly sized, equipped with a
trap, and sloped
• Filters are in position, of correct
size and quantity and clean
• Wiring is correctly sized and
connected in accordance with
wiring diagrams
• Power supply lines are protected
by recommended fuses and
correctly earthed
• Thermostat is correctly wired
and positioned
• Unit is checked for refrigerant
charge and leaks
• Indoor and outdoor fans rotate
freely and are fixed on shafts
• Supply fan rotation speed is set
• Access panels and doors are
replaced to prevent air entering
and risks of injury
• Checking of the gas heating
section, in accordance with
above procedure
WARNING! If any operating checks
must be performed with the unit
operating, it is the technician's
responsibility to recognize any
possible hazards and proceed in a
safe manner. Failure to do so could
result in severe personal injury or
death due to electrical shock or
contact with moving parts.
Power-up initialization
CAUTION! Before proceeding with
any test procedure or operation,
make sure that crankcase heaters
have been energized for at least 8
hours.
Units equipped with Scroll
compressors do not have crankcase
heaters.
Note:
Upon power initialization, the RTRM
performs self-diagnostic checks to
insure that all internal controls are
functional. It also checks the
configuration parameters against
the components connected to the
system. The Liteport LED located on
the RTRM module is turned "On"
within 1 second of power-up if
internal operation is okay.
Test mode procedure at the
ReliaTel™ control board
Operating the unit from the roof
using the test mode at the
ReliaTel™ control board.
CAUTION! Before proceeding with
the following test procedures, make
sure that thermostat or zone sensor
is off.
CAUTION! Use one of the following
"Test" procedures to bypass some
time delays and to start the unit at
the control panel.
Each step of unit operation can be
activated individually by
temporarily shorting across the
"Test" terminals for two to three
seconds. The Liteport LED located
on the RTRM module will blink
when the test mode has been
initiated. The unit can be left in any
"Test" step for up to one hour
before it will automatically
terminate, or it can be terminated
by opening the main power
disconnect switch. Once the test
mode has been terminated, the
Liteport LED will glow continuously
and the unit will revert to the
"System" control.
Page 50

Operation
RT-SVX19A-E450
Test modes
There are 2 methods in which the
"Test" mode can be cycled with the
test button:
1. Step Test Mode
This method initiates the different
components of the unit, one at a
time, by temporarily shorting across
the two test terminals for two to
three seconds. For the initial startup of the unit, this method allows
the technician to cycle a component
"On" and have up to 1 hour to
complete the check.
2. Auto Test Mode
This method is not recommended
for start-up due to the short timing
between individual component
steps. This method initiates the
different components of the unit,
one at a time, when a jumper is
installed across the test terminals.
The unit will start the first test step
and change to the next step every
30 seconds. At the end of the test
mode, control of the unit will
automatically revert to the applied
"System" control method.
For unit test steps and test modes,
values to cycle the various
components, refer to Table 36.
Table 36 - Service Test Guide for Component Operation on gas-fired units
* With Optional Accessory
** "Off" If temperature falls below 16° (±1°)°C, "On" if temperature rises above 18°(±1°)°C.
Note: Steps for optional accessories and modes not present in unit will be skipped.
Step Mode
Indoor
Fan
Economizer
Compressor 1Compressor
2
Heat 1 Heat 2 Outdoor 1 Outdoor 2
1 Fan On On Min Off Off Off Off Off Off
2* Econ. On Open Off Off Off Off Off Off
3 CooI1 On Min On Off Off Off On **
4 CooI2 On Min On On Off Off On **
5 Heat1 On Min Off Off On Off Off Off
6 Heat2 On Min Off Off On On Off Off
Page 51

Operation
51RT-SVX19A-E4
Unit start-up
Verification of gas valve settings (Reserved for the qualified gas
technician)
WARNING! Improper gas valve
setting may lead to burner
destruction and people injury.
Note: Unit factory-set for G20.
Figure 23 - Gas valve
1 = Negative pressure controller
2 = Safety solenoid valve
3 = Gas injector
4 = Air inlets
5 = To the burner
6 = Fan
7 = Gas unit
8 = Minimum gas pressure cut-out
Note: Unit to be installed outside
only.
Note: Expansion valve must be
adapted to the type of gas used:
• G 20: 20 mb
• G 25: 25 mb
• G 31 (Propane): 37 or 50 mb
Page 52

Operation
RT-SVX19A-E452
Table 37 - Marking category of the gas section in different countries
Table 38 - Gas burner data
Country FR CH+ES-GB-IE-PT IT NL BE LU-DE AT-DK-Fl-SE
Category II2E+3P II2H3P II2H3+ II2L3P I2E+ & I3P I2E & I3P I2H
Type of gas Pressure in mbar
G20 20 20 20 - 20 20 20
G25 25 - - 25 25 20 G31 37 37 37 30 37 50 -
Burner G350
Natural Gas G20 (20mbar) 34.02 MJ/m3(15°C-1013)
Gas Flow (15 C-1013 mbar) (m3/h)
Nominal rate 8.1
Reduced rate 8.13
Heating Capacity (kW)
Nominal rate 69.3
Reduced rate 69.1
Heating Rate
(kW)
Nominal rate 77
Reduced rate 76. 8
Efficiency %
Nominal rate 90
Reduced rate 90
Smoke analysis
G20 - 20mbar
@ 400V-3-50Hz
CO % < 0.001%
Nox ppm 9 ppm
CO2%
9.7%
G350
YK* 155-175-200-225 1
Burner G350
Natural Gas G25 (20 ou 25 mbar) 29.30 MJ/m3(15°C-1013)
Gas Flow (15 C-1013 mbar) (m3/h)
Nominal rate 8.8
Reduced rate 8.21
Heating Capacity (kW)
Nominal rate 62.9
Reduced rate 59.5
Heating Rate (kW)
Nominal rate 71.5
Reduced rate 66.8
Efficiency %
Nominal rate 88
Reduced rate 89
Smoke analysis
G25 - 25mbar
@ 400V-3-50Hz
CO % < 0.001%
Nox ppm CO2%
7. 4 %
Burner G350
Propane Gas G31 (30, 37ou 50 mbar) 88.00 MJ/m3(15 C-1013)
Gas Flow (15 C-1013 mbar) (m3/h)
Nominal rate 2.7
Reduced rate 2.56
Gas Flow (15 C-1013 mbar) (kg/h)
Nominal rate 5.1
Reduced rate 4.9
Heating Capacity (kW)
Nominal rate 57.5
Reduced rate 55.3
Heating Rate (kW)
Nominal rate 65.3
Reduced rate 62.6
Efficiency
%
Nominal rate 88
Reduced rate 88.3
Combustion Air Flow
(Avec E=25%)
(m3/h)
Nominal rate 98
Reduced rate 93
Smoke analysis
G31 - 37mbar
@ 400V-3-50Hz
CO % < 0.001%
Nox ppm CO2%
8.9%
Page 53

Operation
53RT-SVX19A-E4
Starting the unit in cooling mode
Before start-up, ensure that all
power cables are tightened.
Verify that the unit airflow rate is
adjusted according to the
information provided in the "Supply
fan adjustment" section of this
manual.
To start the unit in cooling mode:
• Place the zone sensor system
switch in the "COOL" position.
• Position the cooling setpoint
approximately 10° below room
temperature and place the fan
switch in the "AUTO" or "ON"
position.
• Turn on unit main power supply.
The condenser fan motor,
compressor and supply fan motor
should operate automatically.
There will be a delay of up to
5 minutes before the unit starts in
cooling mode.
Operating pressures
After the unit has operated in
cooling mode for a short period of
time, install pressure gauges on the
gauge ports of the discharge and
suction line valves.
Note:To bypass time delays and
verify the operation of this unit from
the roof, use the "Test procedure"
section in this manual. Check the
suction and discharge pressures.
Note: Always route refrigerant
hoses through the port hole
provided and ensure that the
compressor access panel is in place.
Cooling shutdown
To exit the test mode, disconnect
unit power for 3-5 seconds and
reapply. When running the unit
using the zone sensor as the
control, position the selector switch
to "OFF".
There may be a delay of up to
3 minutes before compressors shut
down and an additional one minute
before the fan shuts down in this
setting.
Do not de-energize main power
disconnect except when unit is to
be serviced. Power is required to
keep the compressor crankcase
warm and boil off refrigerant in the
oil (except on units with Scroll
compressors).
Final installation checklist
• Are all power cables tightened?
Check torque of power
cables contact !
• Is the condenser fan and indoor
blower operating correctly, i.e.
correct rotation and without
undue noise?
• Are the compressors operating
correctly and has the system
been checked for leaks?
• Have the voltage and running
currents been checked to
determine if they are within
limits?
• Have the air discharge grilles
been adjusted to balance the
system?
• Has the ductwork been checked
for air leaks and any
condensation?
• Has the air temperature rise
been checked?
• Has the indoor airflow been
checked and adjusted if
necessary?
• Has the unit been checked for
tubing and sheet metal rattles or
any unusual noises?
• Are all covers and panels in
place and properly fastened?
Page 54

Operation
RT-SVX19A-E454
ReliaTel™ is a microelectronic
control feature, which provides
operating functions that are
significantly different from
conventional electro-mechanical
units. The master module is the
ReliaTel™ Refrigeration Module
(RTRM).
The RTRM provides compressor
antishort cycle timing functions
through minimum "Off" and "On"
timing to increase reliability,
performance and to maximize unit
efficiency.
Upon power initialization, the RTRM
performs self-diagnostic checks to
insure that all internal controls are
functioning. It checks the
configuration parameters against
the components connected to the
system.
The LED located on the RTRM
module is turned "On" within one
second after power-up if all internal
operations are okay.
Cooling without an
Economizer
When the system switch is set to
the "Cool" position and the zone
temperature rises above the cooling
setpoint controlband, the RTRM
energizes the (K9) relay coil located
on the RTRM. When the K9 relay
contacts close, the compressor
contactor (CC1) coil is energized
provided the low pressure control
(LPC1) and high pressure control
(HPC1) are closed. When the CC1
contacts close, compressor (CPR1)
and the outdoor fan motor (ODM)
start to maintain the zone
temperature to within ± 2 F of the
sensor setpoint at the sensed
location.
If the first stage of cooling can not
satisfy the cooling requirement, the
RTRM energizes the (K10) relay coil
located on the RTRM. When the
(K10) relay contacts close, the
compressor contactor (CC2) coil is
energized provided the low
pressure control (LPC2) and high
pressure control (HPC2) are closed.
When the CC2 contacts close,
compressor (CPR2) starts to
maintain the zone temperature to
within ± 2 F of the sensor setpoint
at the sensed location.
Evaporator Fan Operation
When the fan selection switch is set
to the "Auto" position, the RTRM
energizes the (K6) relay coil
approximately one second after
energizing the compressor
contactor coil (CC1) in the cooling
mode. In heating mode, the RTRM
energizes the (K6) relay coil
approximately 45 seconds after gas
ignition. Closing the K6 contacts on
the RTRM energizes the supply fan
relay (F) coil to start the supply fan
motor (IDM).
The RTRM de-energizes the fan
relay (F) approximately 60 seconds
after the cooling requirement has be
satisfied to enhance unit efficiency.
When the heating cycle is
terminated, the supply fan relay (F)
coil is de-energized approximately
90 seconds after the heating
requirement.
When the fan selection switch is set
to the "On" position, the RTRM
keeps the supply fan relay coil (F)
energized for continuous fan motor
operation.
When the unit is equipped with the
optional clogged filter switch, wired
between terminals J7-3 and J7-4 on
the ReliaTel™ Options Module
(RTOM), the RTRM produces an
analog output if the clogged filter
switch (CFS) closes for two minutes
after a request for fan operation.
When the system is connected to a
remote panel, the "SERVICE" LED
will be turned on when this failure
occurs.
Page 55

Operation
55RT-SVX19A-E4
Low Ambient Operation
During low ambient operation,
outside air temperature below 13ºC,
the RTRM will cycle the compressor
and outdoor fan motor "Off" for
approximately three minutes after
every 10 minutes of accumulated
compressor run time. The supply
fan motor (IDM) will continue to
operate during this evaporator
defrost cycle (EDC) and the
compressor and outdoor fan will
return to normal operation once the
defrost cycle has terminated and
the compressor "Off" time delay has
been satisfied.
Cooling with an
Economizer
The economizer is utilized to control
the zone temperature providing the
outside air conditions are suitable.
Outside air is drawn into the unit
through modulating dampers. When
cooling is required and economizing
is possible, the RTRM sends the
cooling request to the unit
economizer actuator (ECA) to open
the economizer damper. The RTRM
tries to cool the zone utilizing the
economizer to slightly below the
zone temperature setpoint. If the
mixed air sensor (MAS) senses that
the mixed air temperature is below
53ºF, the damper modulates toward
the closed position. If the zone
temperature continues to rise above
the zone temperature setpoint
controlband and the economizer
damper is full open, the RTRM
energizes the compressor contactor
(CC1). If the zone temperature
continues to rise above the zone
temperature setpoint controlband
and the economizer damper is fully
open, the RTRM energizes the
compressor contactor (CC2).
The ECA continues to modulate the
economizer damper open/closed to
keep the mixed air temperature that
is calculated by the RTRM.
If economizing is not possible, the
ECA drives the damper to the
minimum position setpoint when
the supply fan relay (F) is energized
and allows mechanical cooling
operation. When the unit is
equipped with the optional fan
failure switch, wired between
terminals J7-5 and J7-6 on the
RTOM, the RTRM will stop all
cooling functions and produce an
analog output if the fan failure
switch (FFS) does not open within
40 seconds after a request for fan
operation. When the system is
connected to a remote panel, the
"SERVICE" LED will flash when this
failure occurs.
Page 56

Economizer Set-Up
Adjusting the minimum position
potentiometer located on the unit
economizer Actuator (ECA) sets the
required amount of ventilation air.
Two of the three methods for
determining the suitability of the
outside air can be selected utilizing
the enthalpy potentiometer on the
ECA, as described below:
1. Ambient Temperature controlling the economizing
cycle by sensing the outside air
dry bulb temperature. The Table
below lists the selectable dry
bulb values by potentiometer
setting.
2. Reference Enthalpy - controlling
the economizer cycle by sensing
the outdoor air humidity. The
Table below lists the selectable
enthalpy values by
potentiometer setting.
If the outside air enthalpy value
is less than the selected value,
the economizer is allowed to
operate.
Operation
RT-SVX19A-E456
Ignition Module
Two Stage (IGN) runs self-check
(including verification that the gas
valve is de-energized). (IGN) checks
the high-limit switches (TC01 &
TC02) for normally closed contacts.
With 115 VAC power supplied to the
ignition module (IGN), the hot
surface ignition probe (IP) is
preheated for approximately
45 seconds. The gas valve (GV) is
energized for approximately
7 seconds for trial for ignition, to
ignite the burner.
Once the burner is ignited, the hot
surface ignition probe (IP) is deenergized by the ignition module
(IGN) and functions as the flame
sensing device.
If the burner fails to ignite, the
ignition module will make two more
attempts before locking out. The
green LED will indicate a lock out by
two fast flashes. An ignition lockout
can be reset by:
1. Opening for 3 seconds and
closing the main power
disconnect switch
2. By switching the "Mode" switch
on the zone sensor to "OFF" and
then to the desired position
3. Allowing the ignition control
module to reset automatically
after one hour.
3. Comparative Enthalpy - By
utilizing a humidity sensor and a
temperature sensor in both the
return air stream and the
outdoor air stream, the unit
control processor (RTRM) will be
able to establish which
conditions are best suited for
maintaining the zone
temperature, i.e. indoor
conditions or outdoor conditions.
The potentiometer located on
the ECA is non-functional when
both the temperature and
humidity sensors are installed.
Table 39 - Potentiometer Setting
*Factory Setting
ReliaTel™ Control Heating
Operation
When the system switch is set to
the "Heat" position and the zone
temperature falls below the heating
setpoint controlband, a heat cycle is
initiated when the RTRM
communicates ignition information
to the Ignition module (IGN).
Potentiometer
Setting
Dry BuIb Enthalpy
(°C) (KJ/kg)
A 23* 63
B 21 58
C 19 53
D 17 51
Page 57

Final installation checklist
• Is the condenser fan and indoor
blower operating correctly, i.e.:
correct rotation and without
undue noise?
• Are the compressors operating
correctly and has the system
charge been checked?
• Has the gas module been
installed as per the procedure in
this manual?
• Have the voltage and running
currents been checked to
determine if they are with in
limits?
• Have the air discharge grilles
been adjusted to balance the
system?
• Has the ductwork been checked
for air leaks and any
condensation?
• Has the heating air temperature
rise been checked?
• Has the indoor airflow been
checked and adjusted if
necessary?
• Has the unit been checked for
tubing and sheet metal rattles
orany unusual noises?
• Are all covers and panels in
placeand properly fastened?
To keep the unit operating safely
and efficiently, the manufacturer
recommends that a qualified service
technician check the entire system
at least once each year, or more
frequently if conditions warrant.
Operation
57RT-SVX19A-E4
Refer to the ignition control module
diagnostics section for the LED
diagnostic definitions.
When the fan selection switch is set
to the "Auto" position, the RTRM
energizes the supply fan relay (F)
coil approximately 30 second after
initiating the heating cycle to start
the supply fan motor (IDM).
The automatic reset high limit
(TCO1), located in the bottom right
corner of the burner compartment,
protects against abnormally high
leaving air temperatures.
The automatic reset fan fail limit
(TCO2), located in the upper middle
section of the supply fan board,
protects against abnormally high
heat buildup which could occur
because of extended cycling of the
high limit (TCO1) or if the supply
fan motor (IDM) fails to operate.
Should TCO2 open, the RTRM will
energize the supply fan relay (F) in
an attempt to start the fan motor.
The RTRM signals that a heat failure
has occurred by flashing the "Heat"
LED on the zone sensor.
There is a Green LED located in the
Ignition Control Module. The table
below lists the diagnostics and the
status of the LED during the various
operating states.
Table 40 -LED status
Diagnostics Green LED Red LED
1. Powered but no heat dernand Off Off
2. Heat demand without fault Flash ing Off
3. No flame detection on ignition - or signal detected
and then lost
Off Flashing
4. Gas unit incorrectly wired or flame signal detected on
a heat demand
Steady Flashing
5. Internal fault Off Steady
Page 58

Maintenance
RT-SVX19A-E458
To keep the unit operating safely
and efficiently, the manufacturer
recommends that a qualified service
technician check the entire system
at least once each year, or more
frequently if conditions warrant it.
End user routine
maintenance
Some of the periodic maintenance
functions for the unit can be
undertaken by the end user. This
includes replacing (disposable) or
cleaning (permanent) air filters,
cleaning unit cabinet, cleaning the
condenser coil, and carrying out a
general unit inspection on a regular
basis.
WARNING! Disconnect the power
supply before removing access
panels to service the unit. Failure to
disconnect power before attempting
any servicing can result in severe
injury or death.
Air filters
It is very important for the central
duct system air filters to be kept
clean.
These should be inspected at least
once a month when the system is in
constant operation (in new
buildings, the filters should be
checked every week for the first four
weeks). If disposable-type filters are
used, they should only be replaced
with ones of the same type and size.
Table 41 - Refrigerant charge
Note: Refrigerant charges are given for information only. Check unit nameplate for exact values.
Unit model and size Number of circuits
Refrigerant charge
(kg) (R22/R407C)
YSD/YSH 060 1 3.5
YSD/YSH 072 1 3.7
YSD/YSH 090 1 4.5
YSD/YSH 102 2 3.7/2.1
YSD/YSH 120 2 3.5/3.0
Page 59

Note: Do not attempt to clean
disposable filters. Permanent filters
can be cleaned by washing with a
mild detergent and water. Ensure
that the filters are thoroughly dry
before reinstalling them in the unit
(or duct system).
Note: Replace permanent filters
annually if washing fails to clean
them, or they show signs of
deterioration. Be sure to use the
same type and size as were
originally installed.
Condenser coil
Unfiltered air circulates through the
unit's condenser coil and can cause
the coil's surface to become
clogged with dust, dirt, etc. To clean
the coil, brush the coil surface in the
direction of the fins with a soft
bristled brush.
Keep all vegetation away from the
condenser coil area.
Hot water coil (option)
Stop the unit. Do not disconnect the
main supply to the unit. This will
permit the anti-frost protection to
continue to operate, and avoid
water to freeze-up in the coil.
Service technician
maintenance
Before the cooling season, your
service technician may examine the
following areas of your unit:
• Filters, for cleaning or
replacement
• Motors and drives system
components
• Economizer gaskets, for
replacement if necessary
• Condenser coils, for cleaning
• Safety controls, for mechanical
cleaning
• Electrical components and
wiring, for replacement and
tightening of connections as
necessary
• Condensate drain, for cleaning
• Unit duct connections, to ensure
they are physically sound and
sealed to the unit casing
• Unit mounting support, to
ensure that it is sound
• The unit, to ensure there is no
obvious deterioration
Before the heating season, your
service technician may examine the
following areas of your unit:
• The unit, to ensure that the
condenser coil can receive the
required airflow (that the
condenser fan grille is not
obstructed)
• The control panel wiring, to
verify that all electrical
connections are tight, and that
wire insulation is intact
• Clean burner area, verify the gas
heat system operates properly.
Maintenance
59RT-SVX19A-E4
Page 60

System Status Checkout Procedure
"System Status" is checked by using
one of the following two methods:
Method 1
If the Zone Sensor Module (ZSM) is
equipped with a remote panel with
LED status indication, you can check
the unit within the space. If the ZSM
does not have LED's, use Method 2.
THS/P03 have the remote panel
indication feature. The LED
descriptions are listed below:
LED 1 (System) "On" during
normal operation. "Off" if a system
failure occurs or the LED fails.
"Flashing" indicates test mode.
LED 2 (Heat) "On" when the heat
cycle is operating. "Off" when the
heat cycle terminates or the LED
fails. "Flashing" indicates a heating
failure.
LED 3 (Cool) "On" when the
cooling cycle is operating. "Off"
when the cooling cycle terminates
or the LED fails. "Flashing" indicates
a cooling failure.
LED 4 (Service) "On" indicates a
clogged filter. "Off" during normal
operation. "Flashing" indicates an
supply fan failure.
Maintenance
RT-SVX19A-E460
Troubleshooting
The RTRM has the ability to provide
the service personnel with some
unit diagnostics and system status
information. Before turning the
main power disconnect switch "Off",
follow the steps below to check the
ReliaTel™
Refrigeration Module (RTRM). All
diagnostics & system status
information stored in the RTRM will
be lost when the main power is
turned "Off".
1. Verify that the Liteport LED on
the RTRM is burning
continuously. If the LED is lit, go
to Step 3.
2. If the LED is not lit, verify that
24 VAC is present between J1-1
and J1-2. If 24 VAC is present,
proceed to Step 3. If 24 VAC is
not present, check the unit main
power supply, check transformer
(TNS1). Proceed to Step 3 if
necessary.
3. Utilizing "Method 1" or
"Method 2" in the system status
diagnostic section, check the
following: System status,
Heating status, Cooling status. If
a System failure is indicated,
proceed to Step 4. If no failures
are indicated, proceed to Step 5.
4. If a System failure is indicated,
recheck Steps 1 and 2. If the LED
is not lit in Step 1, and 24 VAC is
present in Step 2, the RTRM has
failed. Replace the RTRM.
5. If no failures are indicated, use
one of the TEST mode
procedures described in the unit
"Start-Up" section to start the
unit. This procedure will allow
you to check all of the RTRM
outputs, and all of the external
controls (relays, contactors, etc.)
that the RTRM outputs energize,
for each respective mode.
Proceed to Step 6.
6. Step the system through all of
the available modes, and verify
operation of all outputs, controls,
and modes. If a problem in
operation is noted in any mode,
you may leave the system in that
mode for up to one hour while
troubleshooting. Refer to the
sequence of operations for each
mode, to assist in verifying
proper operation. Make the
necessary repairs and proceed to
Steps 7 and 8.
7. If no abnormal operating
conditions appear in the test
mode, exit the test mode by
turning the power "Off" at the
main power disconnect switch.
8. Refer to the individual
component test procedures if
other microelectronic
components are suspect.
Page 61

Maintenance
61RT-SVX19A-E4
Below is the complete listing of
failure indication causes:
System failure
Check the voltage between
terminals 6 and 9 on J6, it should
read approximately 32 VDC. If no
voltage is present, a system failure
has occurred. Refer to Step 4 in the
previous section for the
recommended troubleshooting
procedure.
Heating Failure
Verify Heat Failure by Ignition
Module (IGN) LED indicator:
OFF: No Power or Failure
ON: Normal
Slow Flash: Normal, Heat Call
Fast Flash: Error Code:
1 Flash: Communication Failure
2 Flashes: System Lockout
3 Flashes: Pressure Switch Fail
4 Flashes TC01 or TC02 Open
5 Flashes: Flame w/o Gas Valve
6 Flashes: Flame Rollout Open
Cooling Failure
1. Cooling and heating set point
(slide pot) on the zone sensor
has failed. Refer to the "Zone
Sensor Test Procedure" section.
2. Zone temperature thermistor
ZTEMP on ZTS failed. Refer to
the "Zone Sensor Test Procedure"
section.
3. CC1 or CC2 24 VAC control circuit
has opened, check CC1 & CC2
coils, and any of the controls
below that apply to the unit
(HPC1, HPC2).
4. LPC1 has opened during the
3 minute minimum "on time"
during 4 consecutive compressor
starts, check LPC1 or LPC2 by
testing voltage between the J1-8
& J3-2 terminals on the RTRM
and ground. If 24 VAC is present,
the LPC's has not tripped. If no
voltage is present, LPC's has
tripped.
Service Failure
1. If the supply fan proving switch
has closed, the unit will not
operate (when connected to
RTOM), check the fan motor,
belts, and proving switch.
2. Clogged filter switch has closed,
check the filters.
Simultaneous Heat and Cool Failure
1. Emergency Stop is activated
Method 2
The second method for determining
system status is done by checking
voltage readings at the RTRM (J6).
The system indication descriptions
and the approximate voltages are
listed below.
System Failure
Measure the voltage between
terminals J6-9 & J6-6.
Normal Operation = approximately
32 VDC
System Failure = less than 1 VDC,
approximately 0.75 VDC
Test Mode = voltage alternates
between 32 VDC & 0.75 VDC
Heat Failure
Measure the voltage between
terminals J6-7 & J6-6.
Heat Operating = approximately
32 VDC
Heat Off = less than 1 VDC,
approximately 0.75 VDC
Heating Failure = voltage alternates
between 32 VDC & 0.75 VDC
Cool Failure
Measure the voltage between
terminals J6-8 & J6-6.
Cool Operating = approximately
32 VDC
Cool Off = less than 1 VDC,
approximately 0.75 VDC
Cooling Failure = voltage alternates
between 32 VDC & 0.75 VDC
Page 62

Zone Temperature Sensor (ZTS)
Service Indicator
The ZSM SERVICE LED is a generic
indicator that will signal the closing
of a Normally Open switch at any
time, providing the Indoor Motor
(IDM) is operating. This indicator is
usually used to indicate a clogged
filter, or an air side fan failure.
The RTRM will ignore the closing of
this Normally Open switch for 2 (±1)
minutes. This helps prevent
nuisance SERVICE LED indications.
The exception is the LED will flash
40 seconds after the fan is turned
"On" if the Fan Proving Switch is not
made.
Clogged Filter Switch
This LED will remain lit the entire
time that the Normally Open switch
is closed. The LED will be turned off
immediately after resetting the
switch (to the Normally Open
position), or any time that the IDM
is turned "Off".
If the switch remains closed, and
the IDM is turned "On", the SERVICE
LED will be turned "On" again after
the 2 (±1) minute ignore delay.
This LED being turned "On", will
have no other affect on unit
operation. It is an indicator only.
Fan Failure Switch
When the "Fan Failure" switch is
wired to the RTOM, the LED will
remain flashing the entire time the
fan proving switch is closed,
indicating a fan failure, and it will
shut the unit operations down.
Maintenance
RT-SVX19A-E462
Service Failure
Measure the voltage between
terminals J6-10 & J6-6.
Clogged Filter = Approximately
32 VDC.
Normal = Less than 1 VDC,
approximately 0.75 VDC
Fan Failure = voltage alternates
between 32 VDC & 0.75 VDC.
To use LED's for quick status
information at the unit, purchase a
ZSM and connect wires with
alligator clamps to terminals 6
through 10.
Connect each respective terminal
wire (6 through 10) from the Zone
Sensor to the unit J6 terminals 6
through 10.
Note: If the system is equipped
with a programmable zone sensor
THS03, the LED indicators will not
function while the ZSM is
connected.
Resetting Cooling and Ignition
Lockouts
Cooling Failures and Ignition
Lockouts are reset in an identical
manner. Method 1 explains
resetting the system from the space,
Method 2 explains resetting the
system at the unit.
Note: Before resetting Cooling
Failures and Ignition Lockouts,
check the Failure Status Diagnostics
by the methods previously
explained.
Diagnostics will be lost when the
power to the unit is disconnected.
Method 1
To reset the system from the zone,
turn the "Mode" selection switch at
the zone sensor to the "Off"
position.
After approximately 30 seconds,
turn the "Mode" selection switch to
the desired mode, i.e. Heat, Cool or
Auto.
Method 2
To reset the system at the unit,
cycle the unit power by turning the
disconnect switch "Off" and then
"On".
Lockouts can be cleared through the
building management system. Refer
to the building management system
instructions for more information.
Page 63

Maintenance
63RT-SVX19A-E4
Zone Temperature Sensor (ZTS) Test
Note:These procedures are not for
programmable or digital models
and are conducted with the Zone
Sensor
Module electrically removed from
the system.
Test 1
Zone Temperature Thermistor
(ZTEMP)
This component is tested by
measuring the resistance between
terminals 1 and 2 on the Zone
Temperature Sensor.
Table 42 - Thermistor Resistance /
Temperature Chart
Temperature/resistance coefficient is
negative.
Temperature Resistance
(°C) (kOhms)
-21 103
-15 74 . 6 5
-9 54.66
-7 46.94
-4 40.4
-1 34.85
2 30.18
4 26.22
7 22.85
10 19.96
13 17. 47
16 15.33
18 13.49
21 11. 89
24 10.5
27 9.297
29 8.247
32 7. 3 3
35 6.528
38 5.824
Page 64

Literature order number RT-SVX19A-E4
Date 0805
Supersedes RT-SVX04A and RT-SVX05A
Literature stocking location Europe
Trane has a policy of continuous product and product data improvement and reserves the right to
change design and specifications without notice. Only qualified technicians should perform the
installation and servicing of equipment referred to in this publication.
A business of American Standard
Companies www.trane.com
For more information, contact your local Trane
sales office or e-mail us at comfort@trane.com
American Standard Europe BVBA
Registered Office: 1789 Chaussée de Wavre, 1160 Brussels - Belgium
 Loading...
Loading...