Page 1

Installation
Operation
Maintenance
Series R Air-Cooled Helical Rotary
Liquid Chillers
Preliminary
© American Standard Inc. 2006
Models
RTAC 140-500 ton units (60 Hz)
RTAC 140-400 ton units (50 Hz)
January 2006 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 2

NOTICE: Warnings and Cautions appear at appropriate sections throughout this literature. Read these carefully.
WARNING: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury. It may also be used to
alert against unsafe practices.
CAUTION: Indicates a situation that may result in equipment or propertydamage only accidents.
Important
Environmental Concerns!
Scientific research has shown that certain man-made chemicals can
affect the earth’s naturally occurring stratospheric ozone layer when
released to the atmosphere. In particular, several of the identified
chemicals that may affect the ozone layer are refrigerants that contain
Chlorine, Fluorine and Carbon (CFCs) and those containing Hydrogen,
Chlorine, Fluorine and Carbon (HCFCs). Not all refrigerants containing
these compounds have the same potential impact to the environment.
Trane advocates the responsible handling of all refrigerants—including
industry replacements for CFCs such as and HCFCs and HFCs.
Responsible Refrigerant Practices!
Trane believes that responsible refrigerant practices are important to the
environment, our customers, and the air conditioning industry. All
technicians who handle refrigerants must be certified. The Federal Clean
Air Act (Section 608) sets forth the requirements for handling,
reclaiming, recovering and recycling of certain refrigerants and the
equipment that is used in these service procedures. In addition, some
states or municipalities may have additional requirements that must
also be adhered to for responsible management of refrigerants. Know
the applicable laws and follow them.
WARNING
Contains Refrigerant!
System contains oil and refrigerant under high pressure. Recover
refrigerant to relieve pressure before opening the system. See unit
nameplate for refrigerant type. Do not use non-approved refrigerants,
refrigerant substitutes, or refrigerant additives.
Failure to follow proper procedures or the use of non-approved
refrigerants, refrigerant substitutes, or refrigerant additives could result
in death or serious injury or equipment damage.
2 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 3

Table of Contents
General Information ............................................................................................. 7
Literature History.................................................................................................... 7
Unit Identification - Nameplates ............................................................................. 7
Unit Inspection ....................................................................................................... 8
Inspection Checklist ............................................................................................... 8
Loose Parts Inventory ............................................................................................ 8
Unit Description...................................................................................................... 8
Installation - Mechanical..................................................................................... 28
Installation Responsibilities ................................................................................... 28
Nameplates ........................................................................................................... 28
Outdoor Unit Nameplate ....................................................................................... 28
Compressor Nameplate ........................................................................................ 28
Storage .................................................................................................................. 29
General .................................................................................................................. 29
Location Requirements ......................................................................................... 29
Setting the Unit ..................................................................................................... 29
Isolation and Sound Emission ............................................................................... 36
Noise Considerations ............................................................................................ 37
Foundation............................................................................................................. 38
Clearances ............................................................................................................. 38
Unit Isolation and Leveling .................................................................................... 41
Neoprene Isolator Installation................................................................................ 41
Drainage ................................................................................................................ 41
Evaporator Water Piping........................................................................................ 41
Evaporator Piping .................................................................................................. 41
Entering Chilled Water Piping................................................................................ 42
Leaving Chilled Water Piping................................................................................. 42
Evaporator Drain .................................................................................................... 42
Evaporator Flow Switch......................................................................................... 42
Evaporator Water Pressure Drop RTAC 140 - 250 Ton ......................................... 43
Evaporator Water Pressure Drop RTAC 250 - 500 Ton ......................................... 44
Water Pressure Gauges ........................................................................................ 45
Water Pressure Relief Valves ................................................................................ 46
Freeze Protection .................................................................................................. 46
Low Evaporator Refrigerant Cutout and % Glycol Recommendations ................. 46
Procedure .............................................................................................................. 46
Important ............................................................................................................... 47
Specials ................................................................................................................. 47
Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option ................................................................................ 49
Line Sizing ............................................................................................................. 53
Liquid Line Sizing Steps ........................................................................................ 54
Example Liquid Line Sizing .................................................................................... 55
Suction Line Sizing Steps ...................................................................................... 56
Example Suction Line Sizing.................................................................................. 56
Suction Accumulator Sizing ................................................................................... 57
Example of Suction Accumulator Line Sizing ........................................................ 57
Piping Installation Procedures ............................................................................... 57
Refrigerant Sensors............................................................................................... 58
Refrigerant Pressure Relief Valve Venting............................................................. 58
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 3
Page 4

Table of Contents
Leak Test and Evacuation ..................................................................................... 58
Refrigerant and Additional Oil Charge .................................................................. 60
Refrigerant Charge Determination........................................................................ 60
Oil Charge Determination ..................................................................................... 61
Installation - Electrical........................................................................................ 62
General Recommendations .................................................................................. 62
Installer-Supplied Components............................................................................. 75
Power Supply Wiring ............................................................................................ 75
Control Power Supply ........................................................................................... 76
Heater Power Supply and Convenience Outlet (Packaged Units Only) ................ 76
Water Pump Power Supply .................................................................................. 77
Interconnecting Wiring ......................................................................................... 77
Chilled Water Flow (Pump) Interlock .................................................................... 77
Chilled Water Pump Control ................................................................................. 77
Alarm and Status Relay Outputs (Programmable Relays)..................................... 78
Relay Assignments Using TechView.................................................................... 79
Low Voltage Wiring .............................................................................................. 79
Emergency Stop ................................................................................................... 79
External Auto/Stop................................................................................................ 80
External Circuit Lockout – Circuit #1 and Circuit #2.............................................. 80
Ice Building Option ............................................................................................... 80
External Chilled Water Setpoint (ECWS) Option................................................... 81
External Current Limit Setpoint (ECLS) Option..................................................... 81
Chilled Water Reset (CWR) .................................................................................. 82
Communications Interface options....................................................................... 84
Optional Tracer Communications Interface .......................................................... 84
LonTalk Communications Interface for Chillers (LCI-C) ........................................ 84
Operating Principles ........................................................................................... 86
Refrigeration Cycle ............................................................................................... 86
Refrigerant R134a................................................................................................. 88
Compressor .......................................................................................................... 88
Condenser and Subcooler .................................................................................... 88
Expansion Valve.................................................................................................... 89
Evaporator ............................................................................................................ 89
Oil System ............................................................................................................ 89
Controls Interface ............................................................................................... 91
CH530 Communications Overview ...................................................................... 91
Controls Interface ................................................................................................. 91
DynaView Interface .............................................................................................. 91
Key Functions ....................................................................................................... 92
Radio Buttons ....................................................................................................... 92
Spin Value Buttons ............................................................................................... 92
Action Buttons ...................................................................................................... 92
Hot Links .............................................................................................................. 92
File Folder Tabs .................................................................................................... 92
Display Screens .................................................................................................... 93
Basic Screen Format ............................................................................................ 93
Front Panel Lockout Feature ................................................................................ 94
Front Panel Display During Cold Ambients........................................................... 94
4 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 5

Table of Contents
Modes Screen ....................................................................................................... 95
Chiller Screen ....................................................................................................... 101
Compressor Screen.............................................................................................. 101
Refrigerant Screen ............................................................................................... 102
Setpoint Screen .................................................................................................... 103
Diagnostic Screen ................................................................................................ 104
Power-Up ............................................................................................................. 105
Display Formats.................................................................................................... 105
Units ..................................................................................................................... 105
Languages ............................................................................................................ 105
TechView ............................................................................................................ 106
Minimum PC requirements to install and operate TechView ............................... 107
Unit View .............................................................................................................. 107
Compressor Service View .................................................................................... 109
Status View .......................................................................................................... 110
Setpoint View ....................................................................................................... 113
Diagnostics View .................................................................................................. 117
Software View ...................................................................................................... 122
Binding View ........................................................................................................ 123
Replacing or Adding Devices................................................................................ 124
Software Download.............................................................................................. 124
Instructions for First Time TechView Users ......................................................... 124
Diagnostics ......................................................................................................... 126
Legend to Diagnostics Table ................................................................................ 126
Pre-Start Checkout ............................................................................................. 137
Installation Checklist............................................................................................. 137
Receiving .............................................................................................................. 137
Unit Location and Mounting ................................................................................. 137
Unit Piping ............................................................................................................ 137
Electrical Wiring.................................................................................................... 138
General ................................................................................................................. 139
Unit Voltage Power Supply................................................................................... 140
Unit Voltage Imbalance ........................................................................................ 141
Unit Voltage Phasing ............................................................................................ 141
Water System Flow Rates.................................................................................... 142
Water System Pressure Drop............................................................................... 142
CH530 Set-Up ...................................................................................................... 143
Unit Start-Up Procedures .................................................................................. 144
Daily Unit Start-Up ................................................................................................ 144
General ................................................................................................................. 144
Seasonal Unit Start-Up Procedure ........................................................................ 145
System Restart After Extended Shutdown .......................................................... 146
Unit Shutdown Procedures ............................................................................... 147
Temporary Shutdown And Restart ....................................................................... 147
Extended Shutdown Procedure ........................................................................... 147
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 5
Page 6

Table of Contents
Periodic Maintenance........................................................................................ 149
Weekly Maintenance ........................................................................................... 149
Maintenance Procedures .................................................................................. 155
Refrigerant and Oil Charge Management ............................................................ 155
R134a Field Charging Procedure ......................................................................... 156
Factory (initial) Refrigerant Charging Procedure .................................................. 156
Field Refrigerant Charging Procedure .................................................................. 156
Adding charge:..................................................................................................... 157
Charge Isolation in the high or low side of system.............................................. 157
High side charge isolation procedure: ................................................................. 157
Returning unit to running condition: .................................................................... 158
Low side charge isolation procedure: .................................................................. 158
Refrigerant Filter Replacement Procedure .......................................................... 159
Lubrication System .............................................................................................. 159
Oil Charging Procedure........................................................................................ 159
Factory (initial) Oil Charging Procedure................................................................ 161
Evaporator tube replacement .............................................................................. 163
Compressor Replacement ................................................................................... 163
Unit Wiring ......................................................................................................... 165
6 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 7
General Information
Literature History
RTAC-SVX001-EN (December 2000)
New manual.
RTAC-SVX01B-EN (September 2001)
New manual describes installation, operation, and maintenance of RTAC units and the
remote evaporator option.
RTAC-SVX01C-EN (February 2002)
Revised manual includes additional RTAC units to size 500 tons, new installation and
maintenance material, and expanded CH530 diagnostics.
RTAC-SVX01D-EN (July 2003)
Revised manual for new evaporator design for 2 compressor units. Design Sequence
H0 and later.
RTAC-SVX01E-EN (July 2004)
Revised manual for new evaporator design for 3 and 4 compressor units. Design
Sequence J0 and later.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN (January 2006)
Revised manual for new control panel design.
Unit Identification - Nameplates
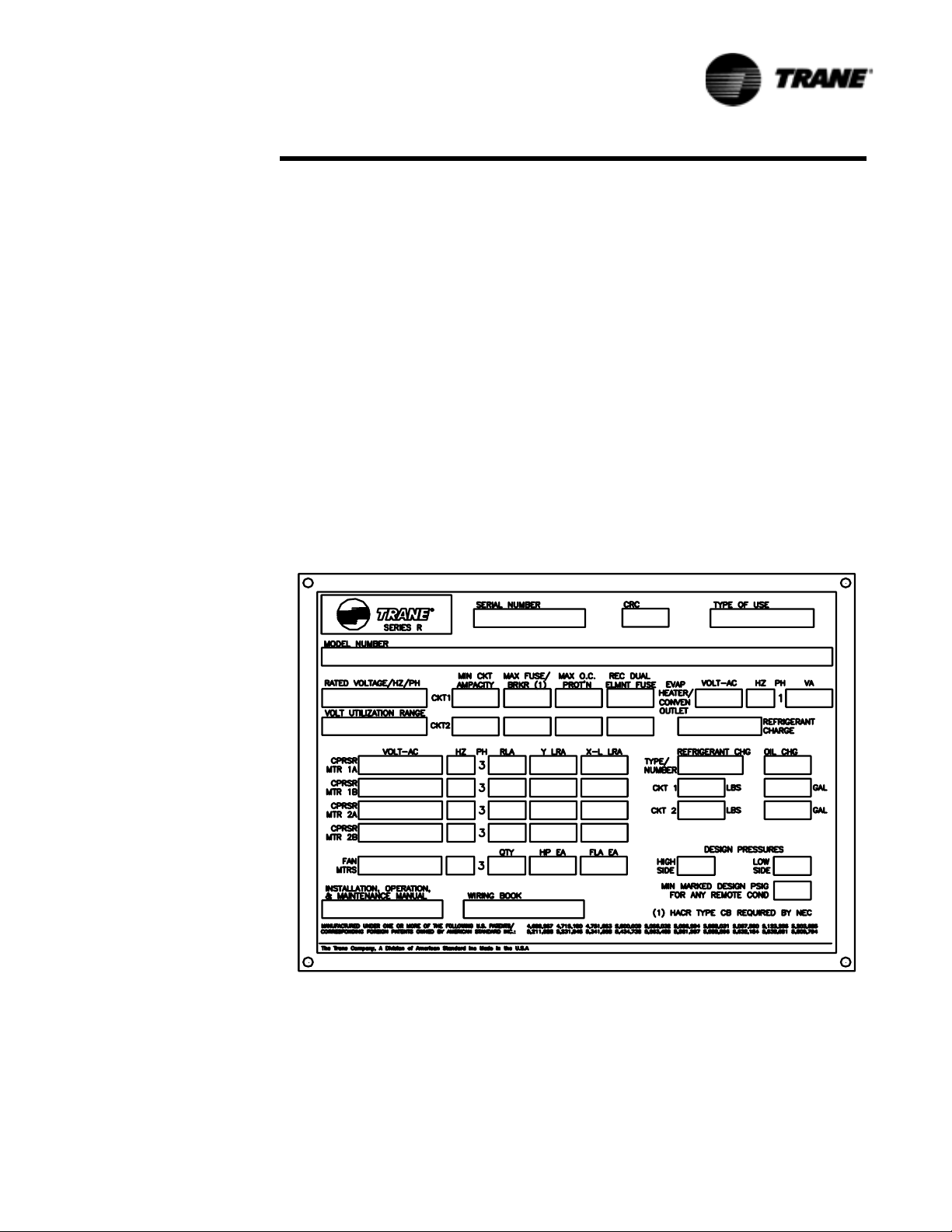
When the unit arrives, compare all nameplate data with ordering, submittal, and shipping information. A typical unit nameplate is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Typical Unit Nameplate
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 7
Page 8

General information
Unit Inspection
When the unit is delivered, verify that it is the correct unit and that it is properly
equipped. Compare the information which appears on the unit nameplate with the
ordering and submittal information.
Inspect all exterior components for visible damage. Report any apparent damage or
material shortage to the carrier and make a “unit damage” notation on the carrier’s
delivery receipt. Specify the extent and type of damage found and notify the appropri
ate Trane Sales Office. Do not proceed with installation of a damaged unit without
sales office approval.
Inspection Checklist
To protect against loss due to damage incurred in transit, complete the following
checklist upon receipt of the unit.
• Inspect the individual pieces of the shipment before accepting the unit. Check for
obvious damage to the unit or packing material.
• Inspect the unit for concealed damage as soon as possible after delivery and
before it is stored. Concealed damage must be reported within 15 days.
• If concealed damage is discovered, stop unpacking the shipment. Do not remove
damaged material from the receiving location. Take photos of the damage, if pos
sible. The owner must provide reasonable evidence that the damage did not
occur after delivery.
• Notify the carrier’s terminal of the damage immediately, by phone and by mail.
Request an immediate, joint inspection of the damage with the carrier and the
consignee.
• Notify the Trane sales representative and arrange for repair. Do not repair the unit,
however, until damage is inspected by the carrier’s representative.
-
-
Loose Parts Inventory
Check all the accessories and loose parts which are shipped with the unit against the
shipping list. Included in these items will be water vessel drain plugs, rigging and
electrical diagrams, and service literature, which are placed inside the control panel
and/or starter panel for shipment.
Unit Description
The 140 - 500 ton Model RTAC units are helical-rotary type, air-cooled liquid chillers
designed for installation outdoors. The compressor circuits are completely assem
bled, hermetic packages that are factory-piped, wired, leak-tested, dehydrated, and
tested for proper control operation before shipment.
NOTE: Packaged units are factory charged with refrigerant and oil.
Figure 2 shows a typical RTAC packaged unit and its components.
Table 1 through Table 5 contain general RTAC mechanical specifications for all unit
sizes.
-
8 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 9

General Information
.
Figure 2 Typical RTAC Unit
Chilled water inlet and outlet openings are covered for shipment. Each compressor
has a separate compressor motor starter. The RTAC series features Trane’s exclusive
Adaptive Control ™ logic, which monitors the control variables that govern the opera
tion of the chiller unit. Adaptive Control logic can adjust capacity variables to avoid
chiller shutdown when necessary, and keep producing chilled water. The units feature
two independent refrigerant circuits. Compressor unloaders are solenoid actuated
and oil pressure operated. Each refrigerant circuit is provided with filter, sight glass,
electronic expansion valve, and charging valves. The shell-and-tube type evaporator is
manufactured in accordance with ASME standards or other international codes. Each
evaporator is fully insulated and is equipped with water drain and vent connections.
Packaged units have heat tape protection to - 20°F (-28.9°C) as standard. As an
option, a convenience outlet can be supplied.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 9
-
Page 10
General information
Table 1 General Data — 140-250 Ton 60 Hz Units - Standard Efficiency
Size 140 155 170 185 200 225 250
Type STD STD STD STD STD STD STD
Compressor
Quantity 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
Nominal
Size
Water Storage (gallons) 29 32 33 35 39 38 42
Min. Flow (gpm) 193 214 202 217 241 217 241
Max. Flow (gpm) 709 785 741 796 883 796 883
Quantity of Coils 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
Coil Length (inches) 156/156 180/156 180/180 216/180 216/216 252/216 252/252
Coil Height (inches) 42 42 42 42 42 42 42
Fins/Ft 192 192 192 192 192 192 192
Number of Rows 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
Quantity 4/4 5/4 5/5 6/5 6/6 7/6 7/7
Diameter (inches) 30 30 30 30 30 30 30
Total Airflow (cfm) 77000 84542 92087 101296 110506 119725 128946
Nominal Fan
Speed
Tip Speed (ft/min) 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954
Std Unit (Deg F) 25 25 25 25 25 25 25
Low Ambient (Deg F) 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0,0 0.0 0.0
Refrigerant HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a
No. of Independent
Refrigerant Circuits
% Min . lo ad 15 15 15 15 15 15 15
Refrigerant
Charge
Oil Charge (gallons) 1.5/1.5 1.5/1.5 1.5/1.5 2.1/1.5 2.1/2.1 2.1/2.1 2.1/2.1
Base Length (feet) 15 15 15 18 18 21 21
1. Data containing information on two circuits shown as follows: CKT1/CKT 2.
2. Minimum start-up/operating ambient based on a 5 mph wind across the condenser.
(tons) 70/70 85/70 85/85 100/85 100/100 120/100 120/120
Evaporator
(liters) 111 121 127 134 146 145 158
(l/sec) 12 14 13 14 15 14 15
(l/sec) 45 50 47 50 56 50 56
Condenser
(mm) 3962/3962 4572/3962 4572/4572 5486/4572 5486/5486 6401/5486 6401/6401
(mm) 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067
Condenser Fans
(m m) 762 762 762 762 76 2 76 2 762
3
(m
/hr) 130811 143623 156441 172086 187732 203394 219059
(rpm ) 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140
(rps) 19 19 19 19 19 19 19
(m/s) 45 45 45 45 45 45 45
Min Starting/Operating Ambient
(Deg C) -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9
(Deg C) -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8
General Unit
22 22222
(lb) 165/165 175/165 175/175 215/210 215/215 225/215 225/225
(kg) 75/75 79/75 79/79 98/95 98/98 102/98 102/102
(liters) 6/6 6/6 6/6 8/6 8/8 8/8 8/8
10 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 11

General Information
Table 2 General Data — 275- 500 Ton 60 Hz Units - Standard Efficiency
Size 275 300 350 400 450 500
Type STD STD STD STD STD STD
Compressor
Quantity 3 3 3 4 4 4
Nominal
Size
Water Storage (gallons) 60 65 70 81 84 89
Min. Flow (gpm) 309 339 375 404 422 461
Max. Flow (gpm) 1134 1243 1374 1483 1548 1690
Quantity of Coils 8 8 8 8 8 8
Coil Length (inches) 180/108 216/108 252/108 216/216 252/216 252/252
Coil Height (inches) 42 42 42 42 42 42
Fins/Ft 192 192 192 192 192 192
Number of Rows 3 3 3 3 3 3
Quantity 10/6 12/6 14/6 12/12 14/12 14/14
Diameter (inches) 30 30 30 30 30 30
Total Airflow (cfm) 147340 165766 184151 221016 239456 257991
Nominal Fan Speed (rpm) 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140
Tip Speed (ft/min) 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954
Std Unit (Deg F) 25 25 25 25 25 25
Low Ambient (Deg F) 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Refrigerant HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a
No. of Independent
Refrigerant Circuits
% Min. load 15 15 15 15 15 15
Refrigerant Charge (lb) 365/200 415/200 460/200 415/415 460/415 460/460
Oil Charge (gallons) 4.6/2.1 5.0/2.1 5.0/2.1 5.0/5.0 5.0/5.0 5.0/5.0
Base Length (feet) 30 36 36 39 45 45
1. Data containing information on two circuits shown as follows: CKT1/CKT 2.
2. Minimum start-up/operating ambient based on a 5 mph wind across the condenser.
(tons) 85/85
100
100 /100
100
120/12 0
100
100/10 0
100/10 0
120/120
100 /100
120/120
120/120
Evaporator
(liters) 229 245 264 306 316 337
(l/sec) 20 21 24 26 27 29
(l/sec) 72 78 87 94 98 107
Condenser
(mm) 4572/2743 5486/2743 6401/4572 5486/5486 6401/5486 6401/6401
(mm) 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067
Condenser Fans
(mm) 762 762 762 762 762 762
3
(m
/hr) 250307 281610 312843 375471 406797 438285
(rps) 19 19 19 19 19 19
(m/s) 45 45 45 45 45 45
Min Starting/Oper Ambient
(Deg C) -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9
(Deg C) -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8
General Unit
222222
(kg) 166/91 188/91 209/91 188/188 209/188 209/209
(liters) 17.4/8 19/8 19/8 19/19 19/19 19/19
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 11
Page 12

General information
Table 3 General Data — 140-400 Ton 60 Hz Units - High Efficiency
Size 140 155 170 185 200 225 250 275 300 350 400
Type HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH
Compressor
Quantity 22222223344
Nominal
Size
Water
Storage
Min. Flow (gpm) 202 217 241 217 241 241 241 375 375 404 461
Max. Flow (gpm) 741 796 883 796 883 883 883 1374 1374 1483 1690
Quantity of
Coils
Coil Length (inches) 180/180 216/180 216/216 252/216 252//252 144/144 180/108 216/144 252/144 216/216 252/252
Coil Height (inches)4242424242424242424242
Fins/Ft 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192
Number of Rows33333333333
Quantity 5/5 6/5 6/6 7/6 7/7 8/6 8/8 12/6 14/6 12/12 14/14
Diameter (inches)3030303030303030303030
To ta l
Airflow
Nominal
Fan Speed
Tip Speed (ft/min) 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954 8954
Std Unit (Deg F) 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25
Low
Ambient
Refrigerant HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a
No. of Independent
Refrigerant Circuits
% Min . lo ad 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15
Refrigerant
Charge
Oil Charge (gallons) 1.5/1.5 1.5/1.5 1.5/1.5 2.1/1.5 2.1/2.1 2.1/2.1 2.1/2.1 4.6/2.2 5.0/2.2 4.6/4.6 5.0/5.0
Base
Length
1. Data containing information on two circuits shown as follows: CKT 1/CKT 2
2. Minimum start-up/operating ambient based on a 5 mph wind across the condenser
(tons) 70/70 85/70 85/85 100/85 100/100 120/100 120/120 85/85
100
100/10 0
100
85/85
85/85
100/10 0
100/10 0
Evaporator
(gallons)3335393842424270708189
(liters) 127 134 146 145 158 158 158 264 264 306 337
(l/sec)1314151415151524242629
(l/sec) 47 50 56 50 56 56 56 87 87 94 107
Condenser
44444888888
(mm) 4572/
4572
(mm) 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067
5486/
4572
5486/
5486
6401/
5486
6401/
6401
3658/
3658
4572/
2743
5486/
3658
6401/
3658
5486/
5486
6401/
6401
Condenser Fans
(m m) 762 76 2 762 762 762 762 762 762 762 76 2 762
(cfm) 91993 101190 110387 119598 128812 136958 147242 173733 192098 220778 257626
3
(m
/hr) 156281 171906 187530 203178 218831 232670 250141 295145 326344 375066 437665
(rpm ) 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140 1140
(rps)1919191919191919191919
(m/s)4545454545454545454545
Min Starting/Oper Ambient
(Deg C) -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9
(Deg F) 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
(Deg C) -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8
General Unit
22222222222
(lb) 175/175 215/205 215/215 225/215 225/225 235/235 235/235 415/200 460/200 415/415 460/460
(kg) 79/79 98/93 98/98 102/98 102/102 107/107 107/107 188/91 209/91 188/188 209/209
(liters) 6/6 6/6 6/6 8/6 8/8 8/8 8/8 17/8 19/8 17/17 19/19
(feet) 15 18 18 21 21 30 30 36 39 39 45
12 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 13

General Information
Table 4 General Data - 120-400 Ton 50 Hz Units-Standard Efficiency
Size 140 155 170 185 200 250 275 300 350 375 400
Type STD STD STD STD STD STD STD STD STD STD STD
Compressor
Quantity 22222333444
Nominal
Size
(tons) 70/70 85/70 85/85 100/85 100/100 70-70/100 85-85/100 100-100/
100
85-85/85-85100-10 0/
85-85
100-10 0/
100-10 0
Evaporator
Water
Storage
Min. Flow (gpm) 192 221 200 215 239 262 307 336 384 377 401
Max. Flow (gpm) 702 778 735 789 875 962 1124 1232 1275 1383 1470
(gallons)29 32 33 35 38 546064737780
(liters) 110 120 126 133 145 203 227 243 275 291 304
(l/sec)1213131415171921222425
(l/sec) 44 49 46 50 55 61 72 78 80 87 93
Condenser
Quantity of
Coils
Coil Length (inches) 156/156 180/156 180/180 216/180 216/216 156/108 180/108 216/108 180/180 216/180 252/216
(mm) 3962/
Coil Height (inches) 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42
(mm) 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067
Fins/Ft 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192
Number of Rows33333333333
44444888888
3962
4512/
3962
4572/
4512
5486/
4572
5486/
5486
3962/
4512
4572/
2743
5486/
2743
4572/
4572
5486/
4572
6401/
5486
Condenser Fans
Quantity 4/4 5/4 5/5 6/5 6/6 8/6 10/6 12/6 10/10 12/10 12/12
Diameter (inches) 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30
(m m) 76 2 762 762 76 2 762 76 2 762 762 76 2 762 76 2
To t al
Airflow
Nominal
Fan Speed
Tip Speed (ft/min) 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461 7451 7461 7461 7461
(cfm) 63346 69507 75671 83236 90803 108698 121056 136210 151332 166467 181611
3
/hr) 107615 118081 128553 141405 154260 184661 205655 231399 257089 282801 308528
(m
(rpm) 950 950 950 950 950 950 950 950 950 950 950
(rps) 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8
(m/s)38 38 38 38 38 383838383838
Min Starting/Oper Ambient
Std Unit (Deg F) 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25
(Deg C) -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9 -3.9
Low
Ambient
(Deg F)00000000000
(Deg C) -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8 -17.8
General Unit
Refrigerant HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a
No. of Independent
Refrigerant Circuits
% Min. load 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15
Refrigerant
Charge
Oil
Charge
Base
Length
1. Data containing information on two circuits shown as follows: CKT 1/CKT 2
2. Minimum start-up/operating ambient based on a 5 mph wind across the condenser
(lb) 165/165 175/165 175/175 215/210 215/215 335/200 365/200 415/200 365/365 415/365 415/415
(kg) 75/75 79/75 79/79 98/95 98/98 152/91 166/91 188/91 166/166 188/166 188/188
(gallons) 1.5/1.5 1.5/1.5 1.5/1.5 2.1/1.5 2.1/2.1 4.6/2.1 4.6/2.1 5.0/2.1 4.6/4.6 5.0/4.6 5.0/5.0
(liters) 6/6 6/6 6/6 8/6 8/8 17.4/8 17.4/8 19.0/8 17.4/17.4 19.0/17.4 19.0/19.0
(feet)15 15 15 18 18 303036393939
22222222222
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 13
Page 14
General information
Table 5 General Data - 120-400 Ton 50 Hz Units-High Efficiency
Size 140 155 170 185 200 250 275 300 350 375 400
Type HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH
Compressor
Quantity 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 4
Nominal Size (tons) 7 0/70 85/70 85/8 5 100/85 100/100 70-70/
100
Evaporator
Water
Storage
Min. Flow (gpm) 200 215 239 215 239 336 371 371 401 419 457
Max. Flow (gpm) 735 789 875 789 875 1232 1362 1362 1470 1535 1675
(gallons)33 353838416469 6980 83 89
(liters) 126 133 145 145 157 243 262 262 304 314 335
(l/sec) 13 14 15 14 15 21 23 23 25 26 29
(l/sec) 46 50 55 50 55 78 86 86 93 97 106
Condenser
Qty of Coils 4 444488 88 8 8
Coil Length (inches) 180/180 216/180 216/216 252/216 252/252 180/108 216/144 252/144 216/216 252/216 252/252
(mm) 4572/
Coil Height (inches) 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42 42
(mm) 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067 1067
Fins/Ft 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192 192
Number of Rows 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
4572
5486/
4572
5486/
5486
6401/
5486
6401/
6401
4572/
2743
Condenser Fans
Quantity 5/5 6/5 6/6 7/6 7/7 10/6 12/6 14/6 12/12 14/12 14/14
Diameter in. (mm) 30 (762) 30 (762) 30 (762) 30 (762) 30 (762) 30 (762) 30 (762) 30 (762) 30 (762) 30 (762) 30 (762)
Total Airflow (cfm) 75575 83130 90687 98256 105826 120971 142969 158112 181371 194731 211648
Nominal Fan
Speed
Tip Speed (ft/min) 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461 7461
3
/hr) 128390 141225 154063 166921 179781 205510 242881 268607 308120 330817 359556
(m
(rpm) 950 950 950 950 950 950 950 950 950 950 950
(rps) 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8
(m/s) 38 38 38 38 38 38 38 38 38 38 38
Min Starting/Oper Ambient
Std Unit Deg F
Low
Ambient
(C)
Deg F
(C)
25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9) 25 (-3.9)
0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8) 0 (-17.8)
General Unit
Refrigerant HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a HFC-134a
No. of Independent
Refrigerant Circuits
% Min. load 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15
Refrigerant
Charge
Oil Charge (gallons) 1.5/1.5 1.5/1.5 1.5/1.5 2.1/1.5 2.1/2.1 4.6/2.1 4.6/2.1 5.0/2.1 4.6/4.6 5.0/5.0 5.0/5.0
Base Length (feet) 15 18 18 21 21 30 36 39 39 45 45
1. Data containing information on two circuits shown as follows CKT 1/CKT 2
2. Minimum start-up/operating ambient based on a 5 mph wind across the condenser
(lb) 175/175 215/205 215/215 225/215 225/225 365/200 415/200 460/200 415/415 460/415 460/460
(kg) 79/79 98/93 98/98 102/98 102/102 166/91 188/91 209/91 188/188 209/188 209/209
(liters) 6/6 6/6 6/6 8/6 8/8 17.4/8 17.4/8 19.0/8 17.4/17.4 19.0/19.0 19.0/19.0
22222222222
85-85/
100
5486/3658 6401/
100-10 0/
100
3658
85-85/
85-85
5486/5486 6401/5486 6401/
100-10 0/
85-85
100-10 0/
100-10 0
6401
14 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 15

General Information
Figure 3 Unit Dimensions 185-200 Ton Standard Efficiency, 60 Hz and 155, 170 Ton, High Efficiency, 50 and 60 Hz
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 15
Page 16
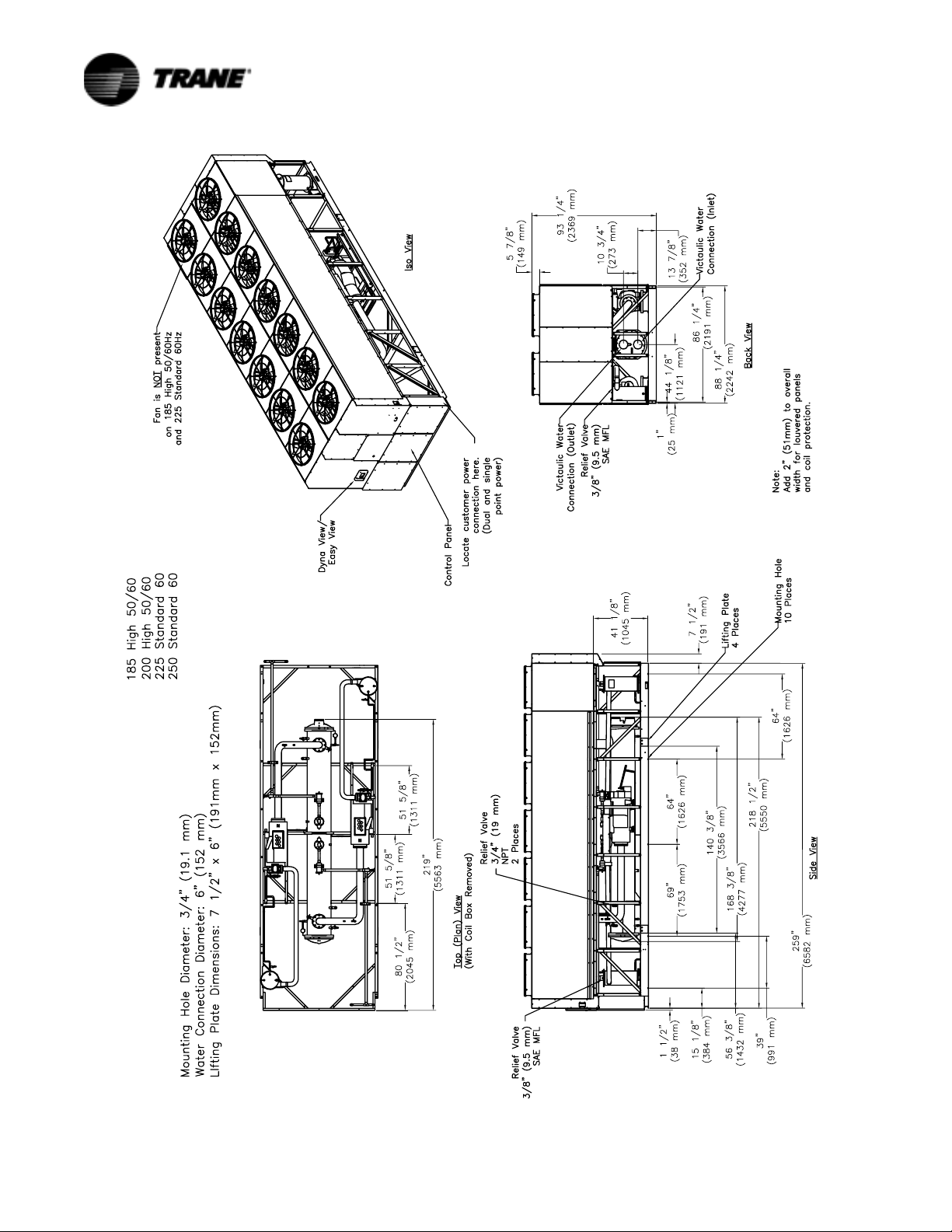
Figure 4 Unit Dimensions 225-250 Ton Standard Efficiency, 60 Hz and 185-200 Ton, High Efficiency, 50 and 60 Hz
16 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 17
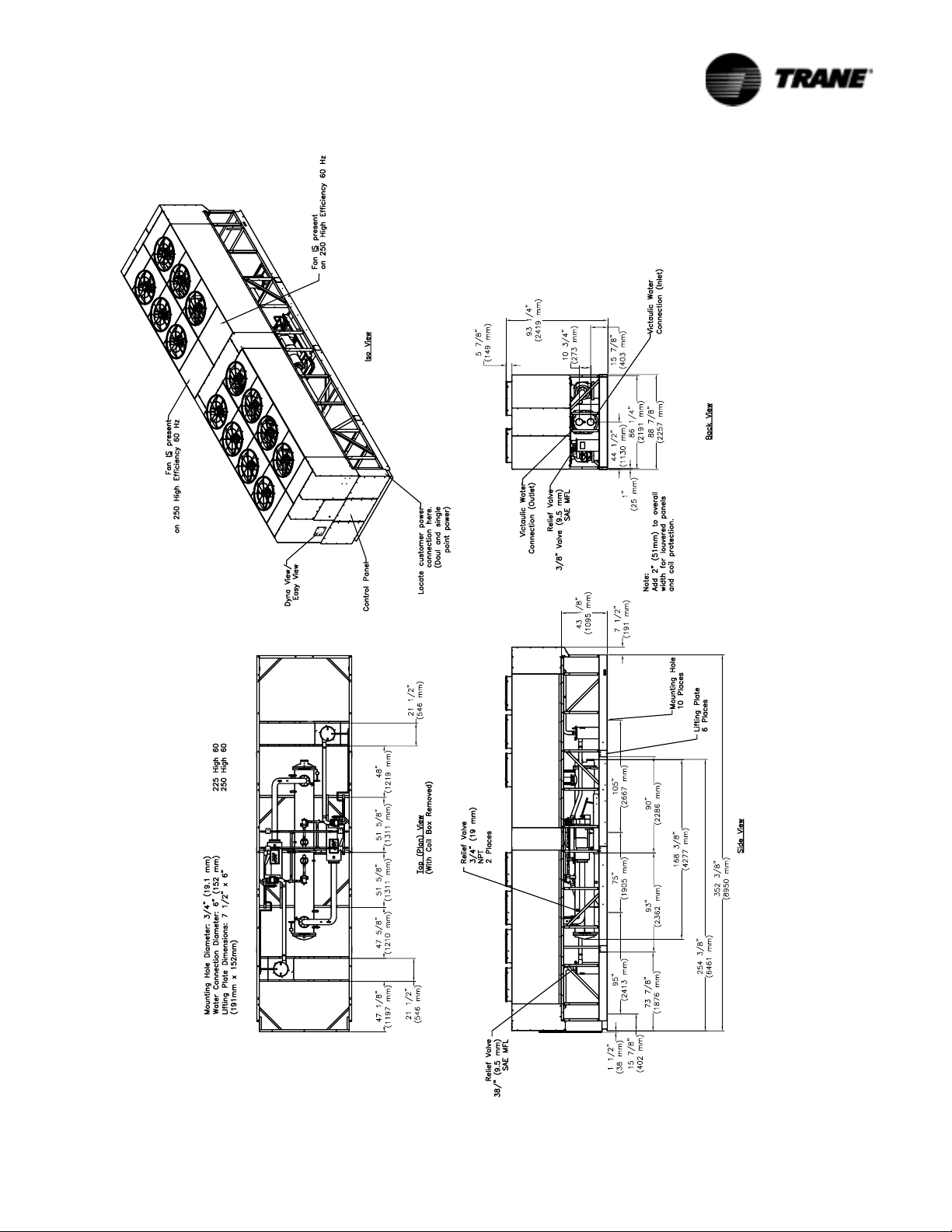
Figure 5 Unit Dimensions 225-250 Ton High Efficiency, 60 Hz
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 17
Page 18

Figure 6 Unit Dimensions 250-275 Ton Standard Efficiency, 50 Hz and 250 Ton High Efficiency, 50 Hz and 275 Ton
Standard Efficiency, 60 Hz
18 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 19
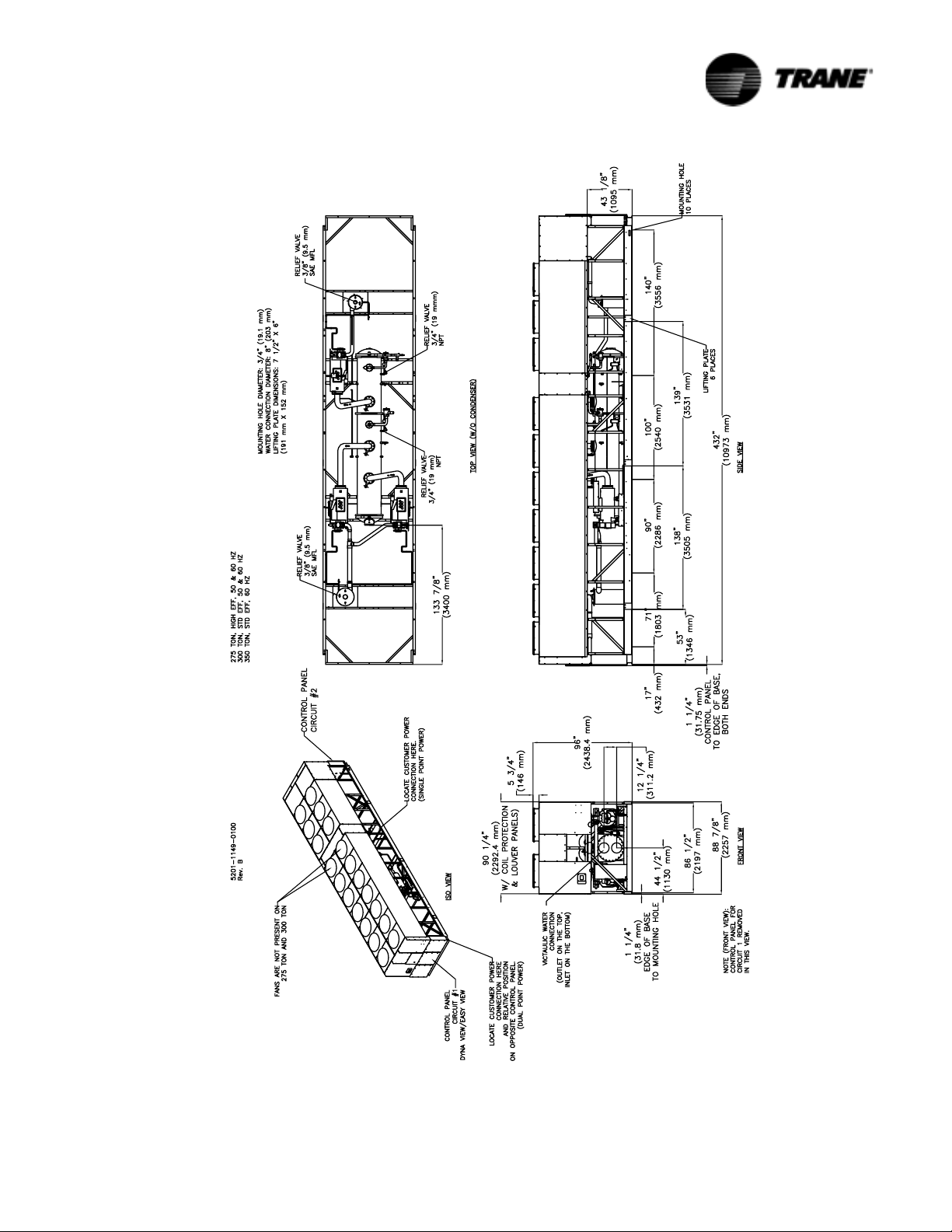
Figure 7 Unit Dimensions 275 Ton High Efficiency, 50 and 60 Hz; 300 Ton, Standard Efficiency, 50 and 60 Hz and 350
Ton, Standard Efficiency 60 Hz
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 19
Page 20
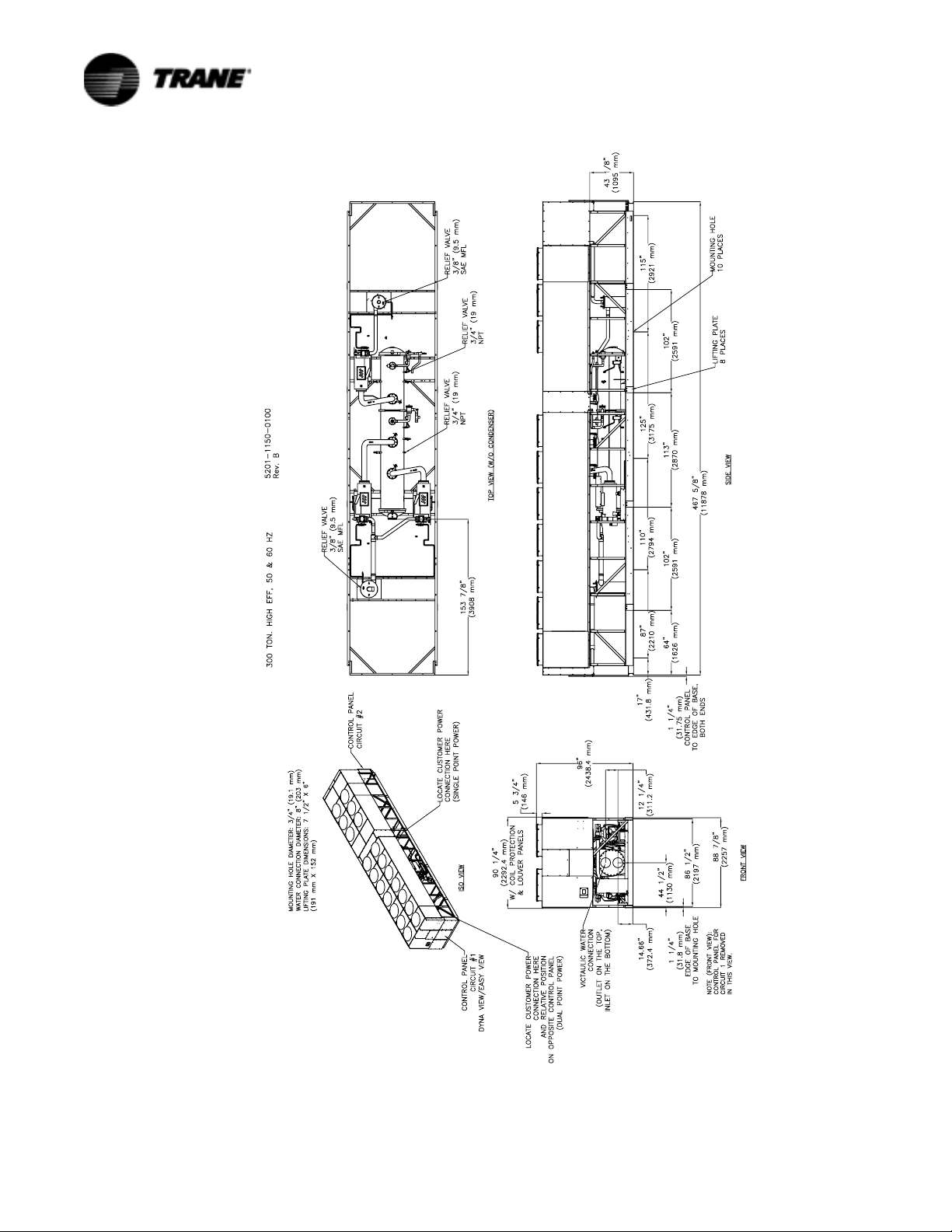
Figure 8 Unit Dimensions 300 Ton High Efficiency, 50 and 60 Hz
20 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 21

Figure 9 Unit Dimensions 350-400 Ton Standard Efficiency, Hz and 400 Ton, Standard Efficiency, 60 Hz and 350 Ton
High Efficiency, 50 and 60Hz
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 21
Page 22
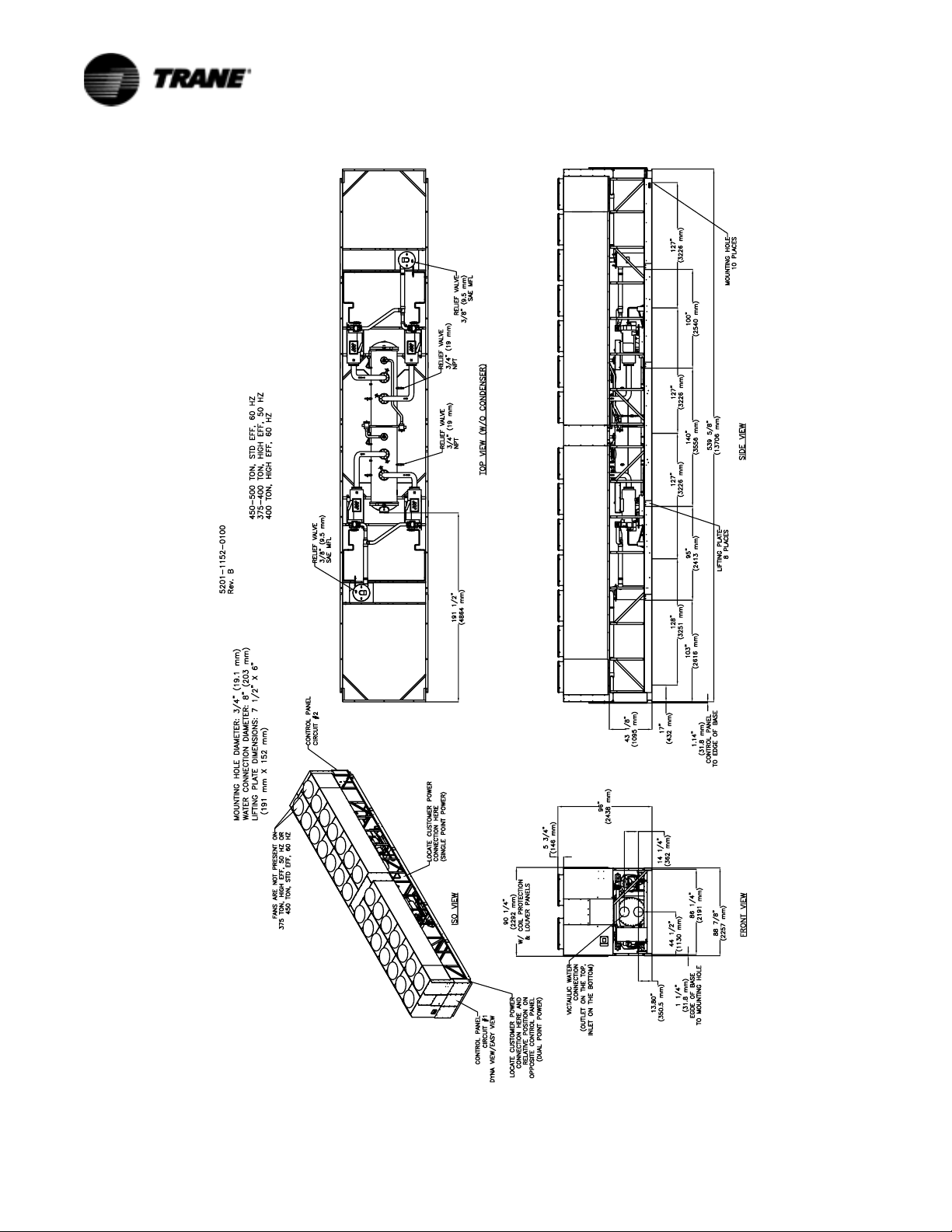
Figure 10 Unit Dimensions 450-500 Ton Standard Efficiency, 60 Hz and 375-400 Ton, High Efficiency, 50 Hz and 400 Ton
High Efficiency, 60 Hz
22 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 23
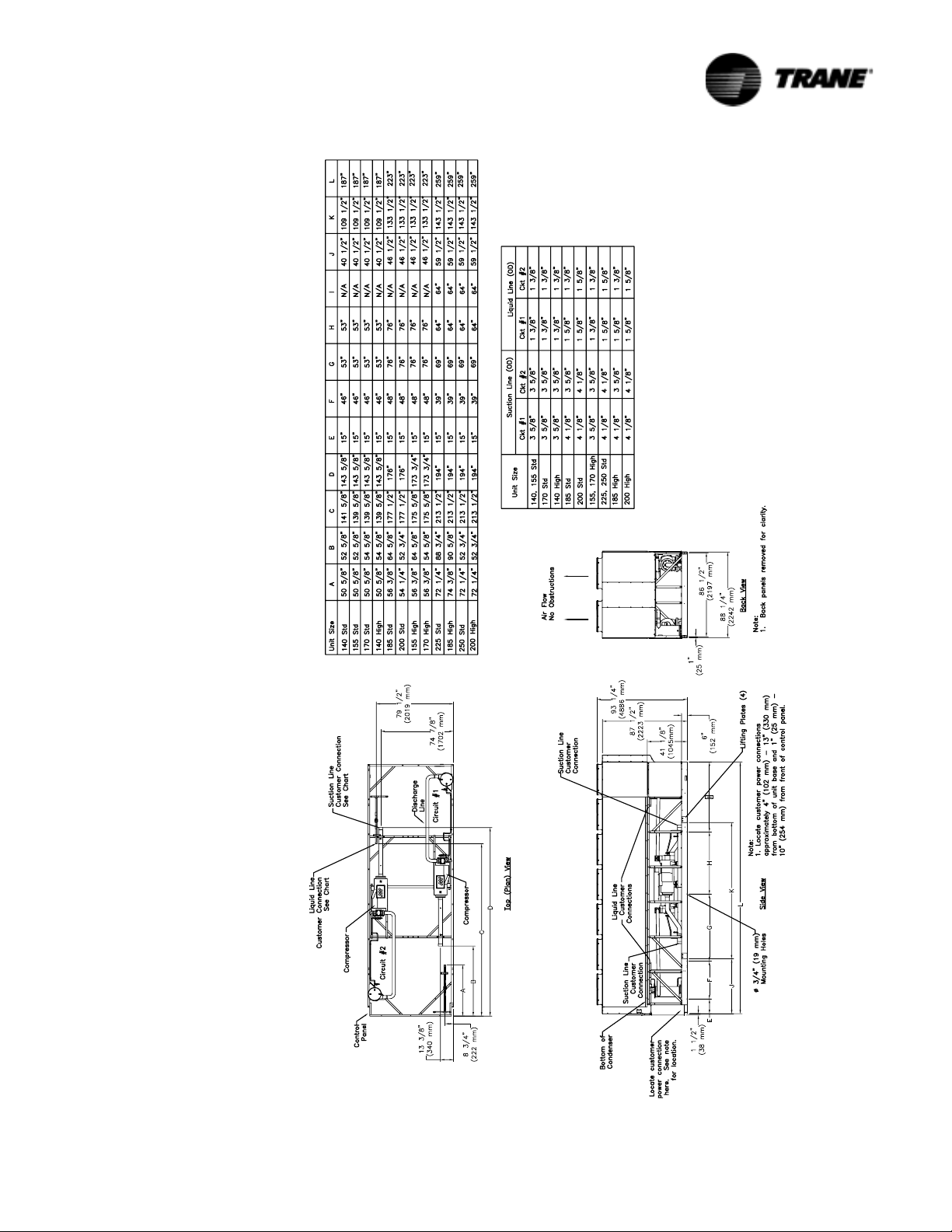
Figure 11 Unit Dimensions of Condenser/Compressor Unit for Remote Evaporator Option
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 23
Page 24
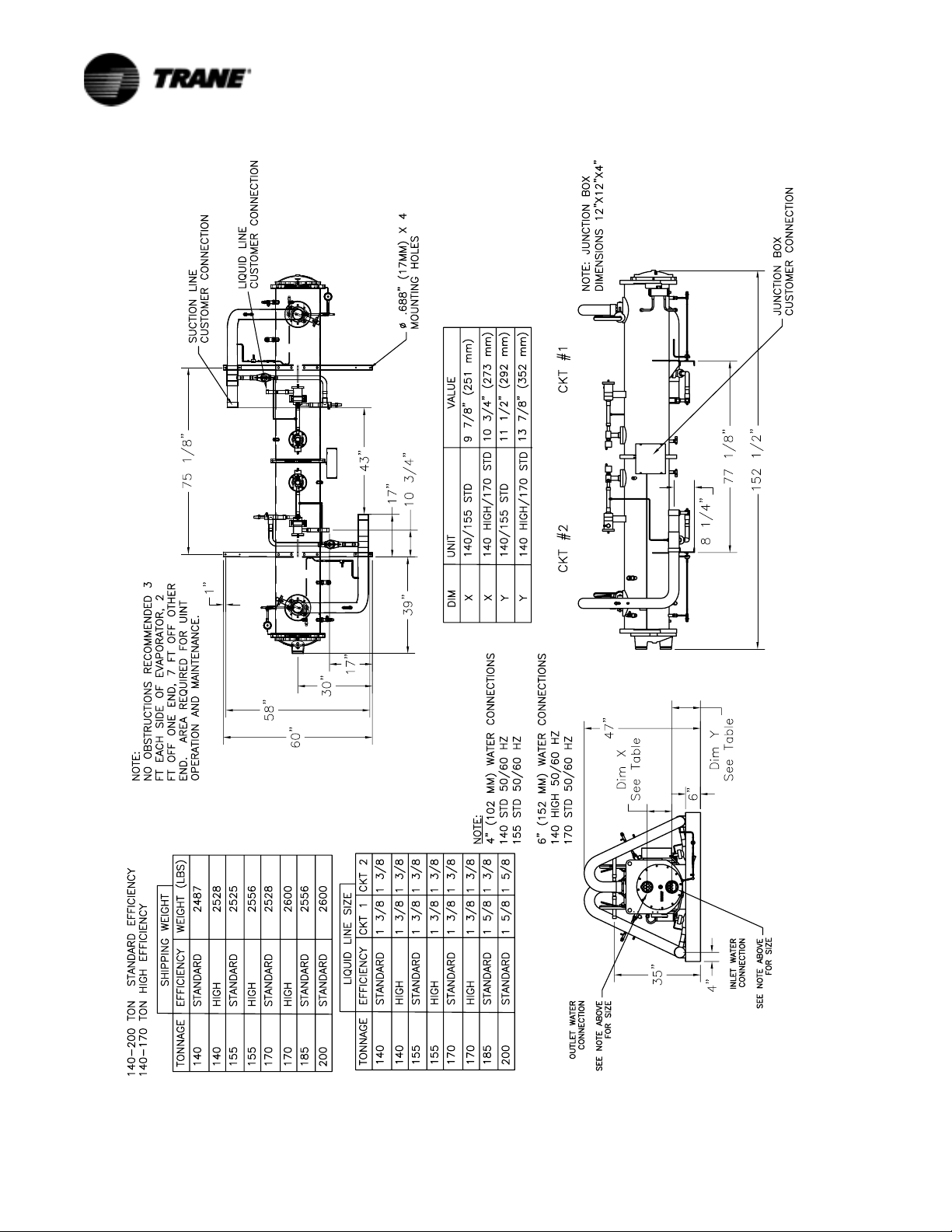
Figure 12 Unit Dimensions for Remote Evaporator 140-170 Ton Standard Efficiency and 140 Ton High Efficiency
24 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 25

Figure 13 Unit Dimensions for Remote Evaporator185-250 Ton Standard Efficiency and 155-200 Ton High Efficiency
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 25
Page 26

Model Number Coding System
The model numbers for the unit and the starter are composed of numbers and letters
that represent features of the equipment. Shown in the following table is a sample of
typical unit model number and the coding system for each.
Each position, or group of positions, in the model number is used to represent a feature. For example, in the first table, position 08 of the unit model number, Unit Voltage, contains the number “4”. A 4 in this position means that the unit voltage is 460/
60/3.
Unit Model Number
An example of a typical unit model number (M/N) is:
RTAC 350A UA0N NAFN N1NX 1TEN NN0N N01N
Model number digits are selected and assigned in accordance with the following defi-
nitions using the model number example shown above.
26 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 27

Digit 1-4
Unit Model
RTAC Air Cooled Series R® chiller
Digit 5-7
Unit Nominal Capacity
140 140 Nominal Tons
155 155 Nominal Tons
170 170 Nominal Tons
185185 Nominal Tons
200 200 Nominal Tons
225 225 Nom inal Tons
250 250 Nom inal Tons
275 275 Nom inal Tons
300 300 Nominal Tons
350 350 Nom inal Tons
375 375 Nom inal Tons
400 400 Nominal Tons
450 450 Nom inal Tons
500 500 Nominal Tons
Digit 8
Unit Voltage
A 200V/60Hz/3Ph power
K 220V/50Hz/3 Ph power
C 230V/60Hz/3Ph power
J380V/60Hz/3Ph power
D 400V/50Hz/3Ph power
4 460V/60Hz/3Ph power
5 575V/60Hz/3Ph power
Digit 9
Manufacturing Location
U Pueblo
ECharmes
Digit 10-11
Design Sequence
XX Factory/ABU Assigned
Digit 12
Unit Type
N Std. Efficiency/Performance
H High Efficiency/Performance
Digit 13
Agency Listing
N No agency listing
U C/UL listing
Digit 14
Pressure Vessel Code
A ASME pressure vessel code
C Canadian code
D Australian code
L Chinese code
R Vietanamese code
S Special
Digit 15
Evaporator Temperature Range &
Application Type
F Standard Temp. with Frz Prot
RRem Evap, Std. Temp, No Frz
Prot
G Low Temp, with Frz Prot
Digit 16
Evaporator Configuration
N Standard pass arrangement,
insulated
Digit 17
Condenser Temperature Range
N Standard ambient range
25-115 deg F
H High ambient capability
25-125 deg F
LLow ambient capability
0-115 deg F
WWide ambient capability
0-125 deg F
Digit 18
Condenser Fin Material
1 Standard aluminum slit fins
2 Copper fins, non-slit fins
4Complete Coat aluminum fins
Digit 19
Condenser Fan/Motor Configuration
N Condenser fans with ODP
motors
W Low Noise fans
T Condenser fans with TEAO
motors
Digit 20
Compressor Motor Starter Type
X Across-the-line starters
Y Wye-delta closed transition
starters
Digit 21
Incoming Power Line Connection
1 Single point power connection
2 Dual point power connection (1/
ckt)
Digit 22
Power Line Connection Type
TTerminals only
D Non-fused disconnect
switch(es)
C Circuit Breaker(s), HACR-rated
Digit 23
Unit Operator Interface
E Easy-View operator interface
D Dyna-View operator interface
Digit 24
Remote Interface
N No remote interface
C Tracer Comm 3 interface
LLon Talk Communication interface
(LCI)
Digit 25
Control Input Accessories/Options
N No remote input
RRemote leaving water temp stpt
CRemote current limit setpoint
BRemote lvg. temp.setpoint and
remote current limit setpoint
Digit 26
COOP 26
Control Output Accessories/Options
N No output options
AAlarm relay
CIcemaking
DIcemaking and alarm relay
Digit 27
Short Circuit Rating
0 No short circuit withstand rating
5 10000A SCR
4 35000A SCR
6 65000A SCR
Digit 28
Electrical Accessories and Export
Packing
N No flow switches
F NEMA-1 flow switch - 150 psi
E Vapor Proof FS - 150 psi
Digit 29
Control Panel Accessories
N No convenience outlet
A 15A 115V convenience outlet
(60HZ)
Digit 30
Refrigerant Service Valves
1 Suction service valves
Digit 31
Compressor Sound Attenuator
Option
0 No sound attenuator
1 Factory installed sound attenuator
Digit 32
Appearance Options
N No appearance options
A Architectural louvered panels
CHalf Louvers
G Access guards
B Access guards and half louvers
P Painted unit
L Painted unit with full louvered
panels
H Painted unit with half louvered
panels
K Painted unit with access guards
W Painted w/access guards and half
louvers
Digit33
Installation Accessories
N No installation accessories
R Neoprene isolators
F Flanged water connection kit
G Neoprene isolators and flange
wtr conn kit
Digit 34
Factory Test
0 No factory run test
P Performance test
WWitness test
Digit 35
Label, and Literature Language
EEnglish
G Chinese
Digit 36
Special Order
X Standard catalog configuration
S Unit has special order feature
Digit 37
Safety Devices
N None
X Standard
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 27
Page 28

Installation - Mechanical
Installation Responsibilities
Generally, the contractor must do the following when installing an RTAC unit:
• Install unit on a flat foundation, level (within 1/4” [6 mm] across the length and
width of the unit), and strong enough to support unit loading.
• Install unit per the instructions contained in the Installation-Mechanical and
Installation-Electrical sections of this manual.
• Install any optional sensors and make electrical connections at the CH530.
• Where specified, provide and install valves in water piping upstream and
downstream of evaporator water connections to isolate the evaporator for
maintenance, and to balance/trim system.
• Furnish and install flow switch to prove chilled water flow.
• Furnish and install pressure gauges in inlet and outlet piping of the evaporator.
• Furnish and install a drain valve to the bottom of the evaporator waterbox.
• Supply and install a vent cock to the top of the evaporator waterbox.
• Furnish and install strainers ahead of all pumps and automatic modulating valves,
and at inlet of evaporator.
• Provide and install field wiring.
• Install heat tape and insulate the chilled water lines and any other portions of the
system, as required, to prevent sweating under normal operating conditions or
freezing during low ambient temperature conditions.
• Install evaporator drain plug. The plug ships in unit control panel.
• Start unit under supervision of a qualified service technician.
Nameplates
The RTAC outdoor unit nameplates (Figure 1) are applied to the exterior of the Control
Panel. A compressor nameplate is located on each compressor.
Outdoor Unit Nameplate
The outdoor unit nameplate provides the following information:
– Unit model and size description.
– Unit serial number.
– Identifies unit electrical requirements.
– Lists correct operating charges of R-134a and refrigerant oil (Trane OIL00048).
– Lists unit test pressures.
– Identifies installation, operation and maintenance and service data literature
(Pueblo).
– Lists drawing numbers for unit wiring diagrams (Pueblo).
Compressor Nameplate
The compressor nameplate provides following information:
– Compressor model number.
– Compressor serial number.
– Compressor electrical characteristics.
– Utilization range.
– Recommended refrigerant.
28 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 29
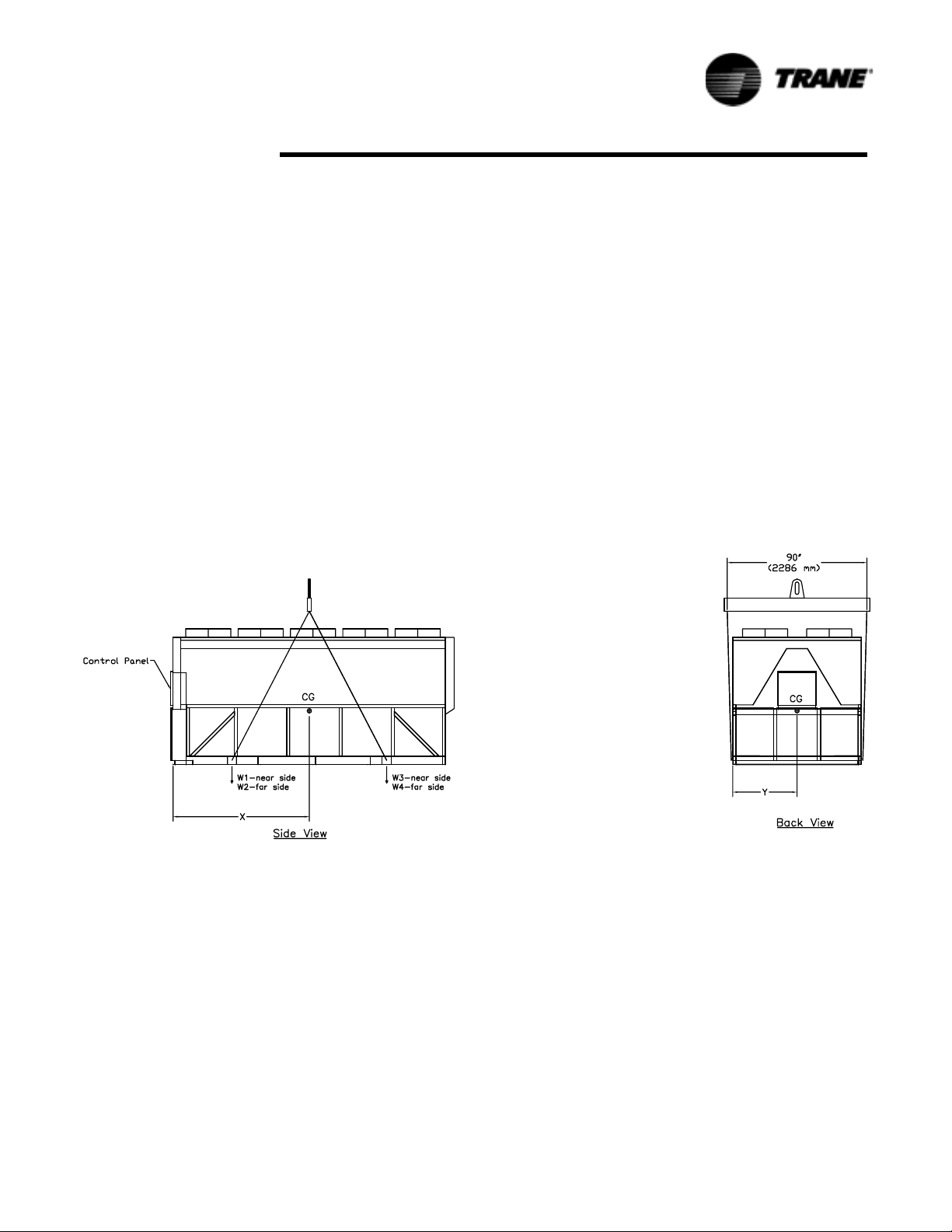
Installation - Mechanical
Storage
Extended storage of the outdoor unit prior to installation requires the following precautionary measures:
1. Store the outdoor unit in a secure area.
2. At least every three months (quarterly), check the pressure in the refrigerant circuits to verify that the refrigerant charge is intact. If it is not, contact a qualified
service organization and the appropriate Trane sales office.
3. Close the discharge and liquid line isolation valves.
General
Report any damage incurred during handling or installation to the Trane sales office
immediately.
Location Requirements
Setting the Unit
A base or foundation is not required if the selected unit location is level and strong
enough to support the unit’s operating weight as listed in
the General Information section.
See Table 6 for lifting weights and center of gravity (CG) dimensions.
Tab l e 1 through Tab l e 5 in
1. Lifting chains/cables will not
be the same length. Adjust to keep unit level while lifting.
2. Do not fork lift unit.
3. Weights are typical for units with R-134a charge.
Figure 14 Lifting the Unit (Package and Remote) 15-21-foot Base
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 29
Page 30
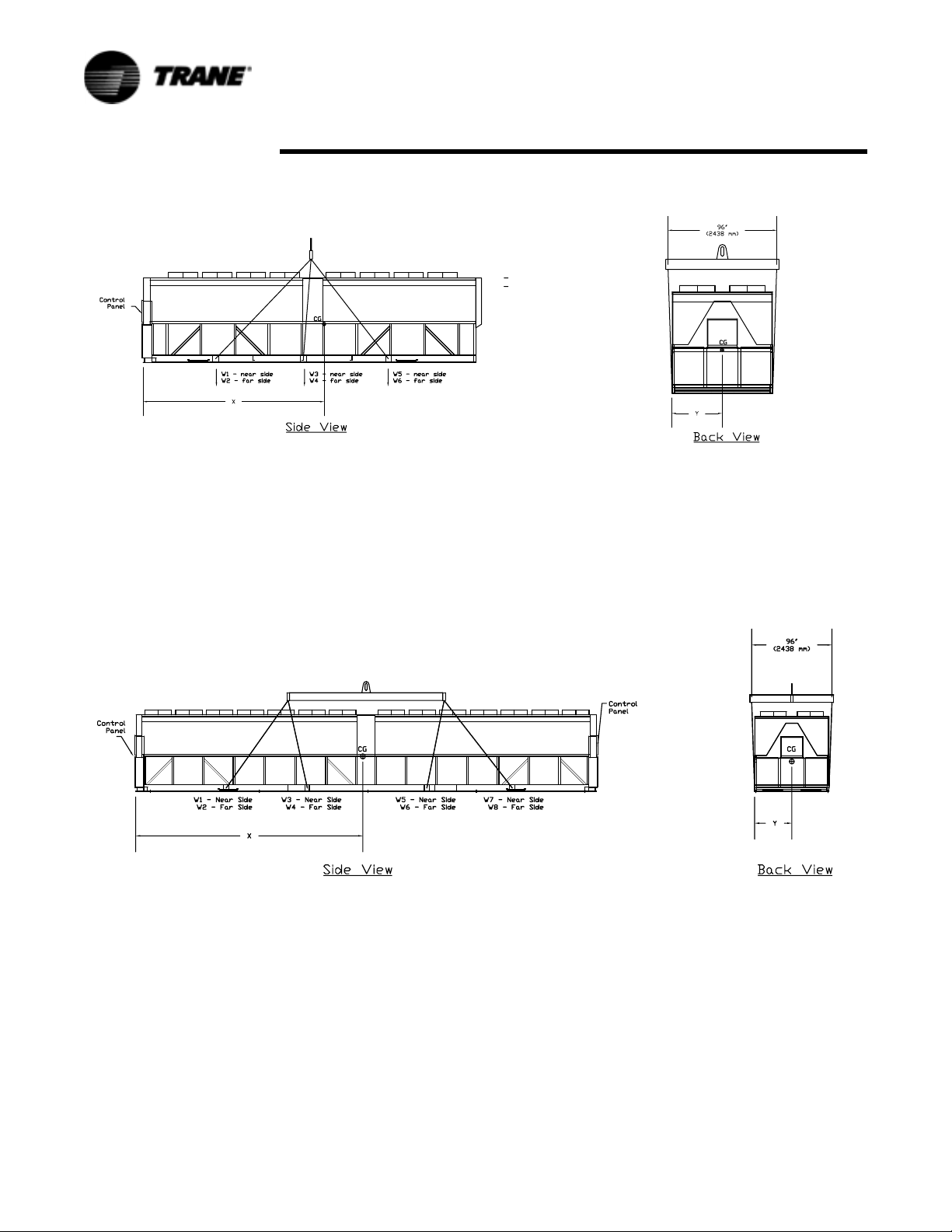
Installation - Mechanical
1. Lifting chains/cables will not be the same length. Adjust to
keep unit level while lifting.
2. Do not fork lift unit.
3. Weights are typical for units with R-134a charge.
Figure 15 Lifting the Unit (Package and Remote) 30-36-foot Base
1. Lifting chains/cables will not be the same length. Adjust to
keep unit level while lifting.
2. Do not fork lift unit.
3. Weights are typical for units with R-134a charge.
Figure 16 Lifting the Unit 39-45-foot Base
30 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 31

Installation - Mechanical
Table 6 Lifting Weights and CG Dimensions (Refer to Figure 14 - Figure 15)
:
W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 W7 W8 Shipping
Xcg Ycg
Weight
Unit
140 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 2499 2874 2686 3019 NA NA NA NA 11077 88 45
140 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2488 2859 2668 3000 NA NA NA NA 11015 88 45
140 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 2495 2869 2680 3013 NA NA NA NA 11057 88 45
140 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2484 2855 2662 2994 NA NA NA NA 10995 88 45
155 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3281 3588 2747 3055 NA NA NA NA 12671 106 44
155 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2601 2882 2794 3033 NA NA NA NA 11309 88 44
155 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3168 3562 2604 2998 NA NA NA NA 12332 106 45
155 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2493 2862 2675 3004 NA NA NA NA 11034 88 45
170 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3308 3721 2760 3173 NA NA NA NA 12962 106 45
170 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2598 2990 2838 3177 NA NA NA NA 11603 89 45
170Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3186 3586 2623 3024 NA NA NA NA 12418 106 45
170 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2498 2873 2684 3018 NA NA NA NA 11073 88 45
185 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3650 4199 3113 3662 NA NA NA NA 14624 124 45
185 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3342 3763 2745 3166 NA NA NA NA 13015 106 45
185 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3526 4117 2990 3581 NA NA NA NA 14214 124 46
185 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3296 3635 2707 3047 NA NA NA NA 12685 106 44
200 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3778 4252 3175 3649 NA NA NA NA 14853 124 45
200 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3370 3789 2828 3247 NA NA NA NA 13234 106 45
200 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3719 4187 3110 3578 NA NA NA NA 14593 124 45
200 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3340 3756 2796 3212 NA NA NA NA 13104 106 45
225 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3711 4229 3114 3632 NA NA NA NA 14687 124 45
250 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3778 4252 3175 3649 NA NA NA NA 14853 124 45
250 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3360 2930 3390 2959 3430 3000 NA NA 19069 177 41
250 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2951 2522 3238 2809 3430 3000 NA NA 17949 182 41
275 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3403 2997 3689 3283 3977 3571 NA NA 20920 202 42
kg
1134 1303 1218 1369 5025 2245 1140
1128 1297 1210 1361 4996 2245 1140
1132 1301 12 16 13 67 5015 22 45 1140
1127 1295 1208 1358 4987 2243 1140
1488 1628 1246 1386 5748 2695 1123
1180 1307 1267 1376 5130 2243 1120
1437 1616 1181 1360 5594 2682 1140
1131 1298 1213 1362 5005 2245 1138
1501 1688 1252 1439 5880 2695 1140
1179 1356 1287 1441 5263 2256 1138
1445 1627 1190 1371 5633 2685 1140
1133 1303 1218 1369 5023 2245 1140
1655 1905 1412 1661 6633 3160 1153
1516 1707 1245 1436 5904 2682 1140
1600 1867 1356 1624 6447 3157 1161
1495 1649 1228 1382 5754 2680 1128
1714 1928 1440 1655 6737 3147 1140
1529 1719 1283 1473 6003 2697 1138
1687 1899 1411 1623 6619 3142 1140
1515 1704 1268 1457 5944 2697 1138
1683 1918 1413 1648 6662 3147 1148
1714 1928 1440 1655 6737 3147 1140
1526 1330 1539 1344 1557 1362 8657 4483 1052
1340 1145 1470 1275 1557 1362 8149 4623 1046
1545 1361 1675 1491 1805 1621 9498 5128 1064
lbs
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
Aluminum Fins
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs kglbs
kg
in
mm
in
mm
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 31
Page 32

Installation - Mechanical
Table 6 Lifting Weights and CG Dimensions (Refer to Figure 14 - Figure 15)
W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 W7 W8 Shipping
Xcg Ycg
Weight
Unit
275 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3668 3194 3478 3004 3356 2877 NA NA 19577 172 41
1665 1450 1579 1364 1524 1306 NA NA 8888 4376 1046
275 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3251 2863 3571 3183 3894 3505 NA NA 20266 203 42
1476 1300 1621 1445 1768 1591 9201 515 9 1064
275 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3345 2936 3351 2942 3356 2947 NA NA 18876 176 42
1518 1333 1521 1336 1523 1338 8570 4473 1057
300 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 2955 2628 2892 2565 2822 2495 2759 2432 21548 222 42
1342 1193 1313 1164 1281 1133 1253 1104 9783 5644 1059
300 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3328 2917 3564 3153 3802 3393 NA NA 20314 201 42
1511 1394 1618 1431 1726 1540 9222 5100 1059
300 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 2955 2628 2892 2565 2782 2495 2759 2432 21508 222 42
1342 1193 1313 1165 1263 1133 1253 1104 9765 5641 1062
300 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3456 3074 3615 3233 3774 3393 NA NA 19572 199 42
1569 1396 1641 1468 1713 1540 8886 5044 1067
350 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3278 3258 3179 3159 3075 3055 2977 2957 24936 234 44
1488 1479 1443 1434 1396 1387 1352 1342 11321 5951 1125
350 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3018 2998 2933 2914 2844 2824 2760 2740 23031 235 44
1370 1361 1332 1323 1291 1282 1253 1244 10456 5956 1125
350 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3140 3123 3038 3020 2930 2912 2828 2811 23803 234 44
1426 1418 1379 1371 1330 1322 1284 1276 10806 5941 1125
350 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3374 2998 3772 3367 4172 3767 NA NA 21450 205 42
1532 1361 1712 1529 1894 1710 9738 5197 1064
375 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3393 3372 3278 3257 3108 3086 2986 2965 25444 266 44
1541 1531 1488 1478 1411 1401 1356 1346 11552 6754 1125
375 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3328 3296 3116 3083 2892 2859 2681 2649 23903 229 44
1511 1496 1414 1400 1313 1298 1217 1202 10852 5827 1123
400 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3345 3271 3377 3303 3425 3350 3458 3384 26912 274 44
1519 1485 1533 1499 1555 1521 1570 1536 12218 6957 1115
400 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3299 3279 3201 3180 3098 3077 3001 2939 25073 234 44
1498 1488 1453 1444 1406 1397 1362 1334 11383 5951 1125
400 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3345 3271 3377 3303 3425 3350 3458 3384 26913 274 44
1519 1485 1533 1500 1555 1521 1570 1536 12219 6955 1118
400 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3299 3279 3201 3180 3098 3077 3001 2939 25074 234 44
1498 1489 1453 1444 1406 1397 1362 1334 11383 5951 1125
450 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3423 3402 3307 3286 3137 3116 3015 2994 25678 266 44
1554 1544 1501 1492 1424 1414 1369 1359 11658 6754 1125
500 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3363 3289 3395 3321 3442 3368 3476 3402 27056 274 44
1527 1493 1541 1508 1563 1529 1578 1544 12283 6955 1115
140 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 2972 3464 3410 3805 NA NA NA NA 13651 90 45
1348 1571 1547 1726 6192 2289 1140
140 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2961 3450 3392 3786 NA NA NA NA 13589 90 45
1343 1565 1539 1717 6164 2286 1140
140 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 2969 3460 3404 3799 NA NA NA NA 13631 90 45
1347 1569 1544 1723 6183 2289 1140
140 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2957 3445 3386 3780 NA NA NA NA 13569 90 45
1341 1563 1536 1715 6155 2286 1140
155 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4027 4454 3591 4018 NA NA NA NA 16091 108 44
1827 2020 1629 1823 7299 2743 1128
155 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3074 3472 3518 3819 NA NA NA NA 13883 90 44
1394 1575 1596 1732 6297 2286 1125
155 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3915 4428 3448 3961 NA NA NA NA 15752 108 45
1776 2009 1564 1797 7145 2736 1140
kg
lbs kglbs
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
Copper Fins
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs kglbs
kg
lbs
kg
in
mm
in
mm
32 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 33

Installation - Mechanical
Table 6 Lifting Weights and CG Dimensions (Refer to Figure 14 - Figure 15)
W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 W7 W8 Shipping
Xcg Ycg
Weight
Unit
155 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2967 3453 3399 3790 NA NA NA NA 13608 90 45
170 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4055 4587 3604 4136 NA NA NA NA 16382 108 45
170 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3071 3581 3562 3963 NA NA NA NA 14177 90 45
170Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3932 4452 3467 3987 NA NA NA NA 15838 108 45
170 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2972 3463 3409 3804 NA NA NA NA 13647 90 45
185 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4585 5283 4161 4860 NA NA NA NA 18889 126 45
185 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 4088 4629 3589 4129 NA NA NA NA 16435 108 45
185 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 4462 5201 4039 4778 NA NA NA NA 18479 126 46
185 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4042 4501 3551 4010 NA NA NA NA 16105 108 45
200 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4713 5336 4223 4846 NA NA NA NA 19118 126 45
200 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 4116 4654 3672 4211 NA NA NA NA 16654 108 45
200 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 4654 5271 4158 4775 NA NA NA NA 18858 126 45
200 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4087 4622 3640 4175 NA NA NA NA 16524 108 45
225 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4646 5313 4163 4830 NA NA NA NA 18952 126 45
250 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4713 5336 4223 4846 NA NA NA NA 19118 126 45
250 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4303 3872 4188 3756 4111 3679 NA NA 23909 174 42
250 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3534 3104 3918 3488 4174 3744 NA NA 21962 183 42
275 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4366 3959 4618 4211 4872 4465 NA NA 26492 200 42
275 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 4611 4136 4276 3801 4057 3577 NA NA 24458 171 42
275 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 4214 3877 4501 4111 4789 4399 NA NA 25891 201 42
275 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4287 3877 4149 3739 4057 3647 NA NA 23758 174 42
300 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3836 3508 3689 3360 3526 3197 3379 3050 27544 220 42
300 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 4360 3948 4476 4064 4593 4182 NA NA 25623 197 42
300 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3799 3508 3689 3360 3526 3197 3379 3050 27508 219 42
300 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4488 4105 4527 4144 4593 4182 NA NA 26039 195 43
350 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4173 4152 4053 4032 3927 3905 3808 3787 31836 235 44
kg
1346 1566 1542 1719 6173 2286 1140
1839 2081 1635 1876 7431 2743 1140
1393 1624 1616 1798 6431 2296 1140
1784 2019 1573 1808 7184 2738 1140
1348 1571 1546 1725 6190 2289 1140
2080 2396 1888 2204 8568 3211 1151
1854 2100 1628 1873 7455 2733 1140
2024 2359 1832 2167 8382 3211 1158
1834 2042 1611 1819 7305 2733 1133
2138 2420 1916 2198 8672 3200 1140
1867 2111 1666 1910 7554 2746 1140
2111 2391 1886 2166 8554 3198 1140
1854 2097 1651 1894 7495 2746 1140
2108 2410 1888 2191 8597 3200 1146
2138 2420 1916 2198 8672 3200 1140
1954 1758 1901 1705 1866 1670 10855 4422 1067
1605 1409 1779 1583 1895 1700 9971 4638 1062
1982 1797 2097 1912 2212 2027 12027 5070 1077
2093 1878 1941 1725 1842 1624 11104 4338 1062
1913 1760 2043 1866 2174 1997 11754 5093 1077
1946 1760 1884 1698 1842 1656 10786 4415 1069
1742 1592 1675 1526 1601 1451 1534 1385 12505 5575 1074
1980 1792 2032 1845 2085 1899 11633 4999 1074
1725 1593 1675 1525 1601 1451 1534 1385 12489 5573 1074
2038 1864 2055 1881 2085 1899 11822 4956 1080
1895 1885 1840 1830 1783 1773 1729 1719 14453 5956 1125
lbs
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs kglbs
kg
lbs
kg
in
mm
in
mm
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 33
Page 34

Installation - Mechanical
Table 6 Lifting Weights and CG Dimensions (Refer to Figure 14 - Figure 15)
W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 W7 W8 Shipping
Xcg Ycg
Weight
Unit
350 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3778 3757 3675 3654 3566 3545 3465 3444 28882 235 44
1715 1705 1668 1659 1619 1610 1573 1563 13113 5961 1125
350 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 4036 4017 3912 3893 3782 3763 3660 3641 30703 234 44
1832 1824 1776 1767 1717 1708 1661 1653 13939 5949 1125
350 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4283 3877 4754 4348 5229 4823 NA NA 27315 204 43
1944 1760 2158 1974 2374 2190 12401 5179 1080
375 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4502 4479 4244 4221 3863 3841 3592 3569 32311 261 44
2044 2034 1927 1916 1754 1744 1631 1620 14669 6632 1125
375 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 4332 4298 3984 3950 3618 3584 3274 3240 30279 227 44
1967 1951 1809 1793 1643 1627 1486 1471 13747 5761 1123
400 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4341 4265 4367 4291 4406 4330 4433 4357 34791 273 44
1971 1936 1983 1948 2000 1966 2013 1978 15795 6939 1118
400 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 4195 4173 4075 4053 3950 3928 3832 3810 32014 235 44
1904 1894 1850 1840 1793 1783 1740 1730 14534 5956 1125
400 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 4341 4265 4367 4291 4406 4330 4433 4357 34790 273 44
1971 1936 1983 1948 2000 1966 2013 1978 15795 6939 1120
400 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4195 4173 4075 4053 3950 3928 3832 3810 32016 234 44
1905 1895 1850 1840 1793 1783 1740 1730 14535 5954 1125
450 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4532 4509 4273 4251 3892 3870 3621 3598 32545 261 44
2057 2047 1940 1930 1767 1757 1644 1633 14775 6634 1125
500 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4359 4283 4385 4309 4424 4348 4451 4375 34935 273 44
1979 1945 1991 1956 2008 1974 2021 1986 15860 6939 1118
140 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 2033 2292 1972 2244 NA NA NA NA 8542 86 45
922 1040 895 1018 3875 2179 1138
140 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2030 2287 1967 2238 NA NA NA NA 8522 86 45
921 1038 892 1015 3866 2177 1138
140 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 2030 2288 1967 2238 NA NA NA NA 8522 86 45
921 1038 892 1015 3866 2177 1138
140 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2026 2283 1961 2232 NA NA NA NA 8502 86 45
919 1036 889 1013 3857 2177 1138
155 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 2725 2944 2119 2337 NA NA NA NA 10125 104 44
1236 1335 961 1060 4593 2637 1115
155 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2139 2305 2087 2265 NA NA NA NA 8795 86 44
970 1046 947 1027 3989 2177 1113
155 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 2612 2918 1975 2281 NA NA NA NA 9786 103 45
1185 1323 896 1034 4439 2619 1138
155 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2031 2285 1968 2236 NA NA NA NA 8520 86 45
921 1037 893 1014 3865 2177 1135
170 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 2749 3073 2128 2451 NA NA NA NA 10400 104 45
1247 1394 965 1112 4717 2637 1138
170 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2138 2415 2133 2411 NA NA NA NA 9097 87 45
970 1096 967 1094 4126 2197 1135
170Ton 60 Hz High Eff 2626 2938 1990 2302 NA NA NA NA 9856 103 45
1191 1332 903 1044 4471 2621 1138
170 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2033 2291 1971 2243 NA NA NA NA 8538 86 45
922 1039 894 1018 3873 2179 1138
185 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3034 3485 2423 2875 NA NA NA NA 11817 122 45
1376 1581 1099 1304 5360 3106 1153
185 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2786 3118 2116 2449 NA NA NA NA 10469 103 45
12 6 4 14 1 4 9 6 0 1111 4 749 2621 1138
185 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 2911 3403 2300 2793 NA NA NA NA 11407 122 46
1320 1544 1043 1267 5174 3101 1166
kg
lbs kglbs
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
Remote Evaporator Aluminum Fins
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs kglbs
kg
lbs
kg
in
mm
in
mm
34 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 35

Installation - Mechanical
Table 6 Lifting Weights and CG Dimensions (Refer to Figure 14 - Figure 15)
W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 W7 W8 Shipping
Xcg Ycg
Weight
Unit
185 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2740 2991 2079 2329 NA NA NA NA 10139 103 44
200 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3156 3531 2478 2853 NA NA NA NA 12019 122 45
200 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2811 3140 2196 2525 NA NA NA NA 10672 104 45
200 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3097 3466 2413 2782 NA NA NA NA 11759 121 45
200 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2781 3108 2163 2490 NA NA NA NA 10542 104 45
225 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3096 3516 2425 2845 NA NA NA NA 11880 122 45
250 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3156 3531 2478 2853 NA NA NA NA 12019 122 45
140 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 2506 2883 2697 3031 NA NA NA NA 11116 88 45
140 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2503 2878 2691 3025 NA NA NA NA 11096 88 45
140 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 2503 2878 2691 3025 NA NA NA NA 11096 88 45
140 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2499 2874 2685 3019 NA NA NA NA 11076 88 45
155 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3472 3810 2963 3301 NA NA NA NA 13545 107 44
155 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2612 2896 2811 3051 NA NA NA NA 11369 88 44
155 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3359 3783 2819 3244 NA NA NA NA 13206 106 45
155 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2505 2876 2692 3022 NA NA NA NA 11094 88 45
170 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3496 3938 2972 3414 NA NA NA NA 13820 107 45
170 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 2611 3006 2857 3198 NA NA NA NA 11671 89 45
170Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3373 3803 2834 3265 NA NA NA NA 13276 106 45
170 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 2506 2882 2695 3030 NA NA NA NA 11112 88 45
185 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 3969 4570 3471 4072 NA NA NA NA 16082 125 45
185 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3532 3984 2960 3412 NA NA NA NA 13889 106 45
185 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 3846 4487 3349 3990 NA NA NA NA 15672 125 46
185 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3487 3857 2923 3293 NA NA NA NA 13559 106 45
200 Ton 50 Hz High Eff 4092 4615 3527 4050 NA NA NA NA 16284 125 45
200 Ton 50 Hz Std Eff 3557 4006 3040 3489 NA NA NA NA 14092 107 45
200 Ton 60 Hz High Eff 4033 4551 3462 3979 NA NA NA NA 16024 125 45
kg
1243 1357 943 1057 4599 2619 1123
1432 1602 1124 1294 5452 3091 1138
1275 1424 996 1146 4841 2644 1138
1405 1572 1095 1262 5334 3084 1138
1262 1410 981 1129 4782 2639 1138
1404 1595 1100 1290 5389 3091 1148
1432 1602 1124 1294 5452 3091 1138
1137 1308 1223 1375 5042 2245 1140
1135 1305 1221 1372 5033 2245 1140
1135 1306 1221 1372 5033 2245 1140
1134 1303 1218 1369 5024 2245 1140
1575 1728 1344 1497 6144 2710 1123
1185 1313 1275 1384 5157 2243 1120
1524 1716 1279 1471 5990 2700 1140
1136 1305 1221 1371 5032 2245 1138
1586 1786 1348 1549 6269 2708 1140
1184 1363 1296 1450 5294 2258 1138
1530 1725 1286 1481 6022 2700 1140
1137 1307 1223 1374 5040 2245 1140
1800 2073 1575 1847 7295 3180 1151
1602 1807 1343 1548 6300 2697 1140
1745 2035 1519 1810 7109 3178 1161
1581 1749 1326 1494 6150 2697 1130
1856 2094 1600 1837 7386 3167 1140
1613 1817 1379 1583 6392 2713 1140
1829 2064 1570 1805 7269 3165 1140
lbs
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
Remote Evaporator Copper Fins
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs kglbs
kg
lbs
kg
in
mm
in
mm
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 35
Page 36

Installation - Mechanical
Table 6 Lifting Weights and CG Dimensions (Refer to Figure 14 - Figure 15)
W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6 W7 W8 Shipping
Xcg Ycg
Weight
Unit
200 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 3528 3974 3007 3453 NA NA NA NA 13962 107 45
1600 1802 1364 1566 6333 2710 1140
225 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4031 4600 3473 4042 NA NA NA NA 16145 125 45
1828 2086 1575 1833 7323 3167 1148
250 Ton 60 Hz Std Eff 4092 4615 3527 4050 NA NA NA NA 16284 125 45
1856 2094 1600 1837 7386 3167 1140
kg
lbs kglbs
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs
kg
lbs kglbs
kg
lbs
kg
in
mm
Table 7 Remote Evaporator Lifting Weights
Standard Eff Premium Eff
To n n a g e
lbs
Kg
140 155 170 185 200 225 250 140 155 170 185 200
2487
2525
2528
2556
112 8
114 5
114 6
115 9
2600
117 9
2797
1268
2846
1291
2528
114 6
2556
115 9
2600
117 9
2797
1268
Isolation and Sound Emission
The most effective form of isolation is to locate the unit away from any sound sensitive area. Structurally transmitted sound can be reduced by elastomeric vibration eliminators. Spring isolators are not recommended. Consult an acoustical engineer in
critical sound applications.
For maximum isolation effect, isolate water lines and electrical conduit. Wall sleeves
and rubber isolated piping hangers can be used to reduce the sound transmitted
through water piping. To reduce the sound transmitted through electrical conduit, use
flexible electrical conduit.
State and local codes on sound emissions should always be considered. Since the
environment in which a sound source is located affects sound pressure, unit place
ment must be carefully evaluated. Sound power levels for Trane air-cooled Series R®
chillers are available on request.
in
mm
2846
1291
-
5NITSWITH#OMPRESSORS
5NITSWITHORMORE#OMPRESSORS
Figure 17 Unit Isolator Locations
36 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 37

Table 8 Unit Isolators
Installation - Mechanical
Tonnage Efficiency Frequency Unit Type Condenser
Fin Material
140 Std/High 50/60 Packaged AL X10140305620 8
140 Std/High 50/60 Remote AL X10140305610 8
140 Std/High 50/60 Packaged/Remote Cu X10140305620 8
155 Std/High 50/60 Packaged AL X10140305620 8
155 Std/High 50/60 Remote AL X10140305610 8
155 Std/High 50/60 Packaged/Remote Cu X10140305620 8
170 Std/High 50/60 Packaged AL X10140305620 8
170 Std/High 50/60 Remote AL X10140305610 8
170 Std/High 50/60 Packaged/Remote Cu X10140305620 8
185 Std 50/60 Packaged AL X10140305620 8
185 High 50/60 Packaged AL X10140305620 10
185 Std 50/60 Remote AL X10140305610 8
185 High 50/60 Remote AL X10140305610 10
185 Std 50/60 Packaged Cu X10140305620 8
185 High 50/60 Packaged Cu X10140305620 10
185 Std 50/60 Remote Cu X10140305620 8
185 High 50/60 Remote Cu X10140305620 10
200 Std 50/60 Packaged AL X10140305620 8
200 High 50/60 Packaged AL X10140305620 10
200 Std 50/60 Remote AL X10140305610 8
200 High 50/60 Remote AL X10140305610 10
200 Std 50/60 Packaged Cu X10140305620 8
200 High 50/60 Packaged Cu X10140305620 10
200 Std 50/60 Remote Cu X10140305620 8
200 High 50/60 Remote Cu X10140305620 10
225 Std 50/60 Packaged AL X10140305620 10
225 Std 50/60 Remote AL X10140305610 10
225 Std 50/60 Packaged/Remote Cu X10140305620 10
225 High 60 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305620 10
250 Std 50/60 Packaged AL X10140305620 10
250 Std 50/60 Remote AL X10140305610 10
250 Std 50/60 Packaged/Remote Cu X10140305620 10
250 High 60 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305620 10
250 Std 50 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305630 10
250 High 50 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
275 Std/High 50/60 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
300 Std/High 50/60 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
350 Std 60 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
350 Std 50 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
350 High 50/60 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
375 Std/High 50 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
400 Std/High 50/60 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
450 Std/High 60 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
500 Std 60 Packaged Al/Cu X10140305640 10
Isolator Part
Number
Quantity
Noise Considerations
Locate the outdoor unit away from sound sensitive areas. If required, install rubber
vibration isolators in all water piping and use flexible electrical conduit. Consult an
acoustical engineer for critical applications. Also refer to Trane Engineering Bulletins
for application information on RTAC chillers.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 37
Page 38

Installation - Mechanical
Foundation
Provide rigid, non-warping mounting pads or a concrete foundation of sufficient
strength and mass to support the outdoor unit operating weight (i.e., including com
pleted piping, and full operating charges of refrigerant, oil and water). Refer to Tabl e 1
though Tabl e 5 in the General Information section for unit operating weights. Once in
place, the outdoor unit must be level within 1/ 4" (6 mm) over its length and width.
The Trane Company is not responsible for equipment problems resulting from an
improperly designed or constructed foundation.
NOTE: To allow for cleaning under the condensing coil, it is recommended that an
opening be left between the unit base and the concrete pad.
Clearances
Provide enough space around the outdoor unit to allow the installation and maintenance personnel unrestricted access to all service points. Refer to submittal drawings
for the unit dimensions. A minimum of 4 feet (1.2 m) is recommended for compressor
service. Provide sufficient clearance for the opening of control panel doors. Refer to
Figure 18 through Figure 19 for minimum clearances. In all cases, local codes which
require additional clearances will take precedence over these recommendations.
-
Figure 18 Recommended Unit Clearances 15-foot bases
38 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 39

Installation - Mechanical
Figure 19 Recommended Unit Clearances 18-21 foot bases
Figure 20 Recommended Unit Clearances 30-45 foot bases
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 39
Page 40

Installation - Mechanical
Figure 21 Recommended Remote Evaporator Unit Clearances 15-30 foot bases
Figure 22 Recommended Evaporator Clearance
Unobstructed flow of condenser air is essential to maintain chiller capacity and operating efficiency. When determining unit placement, give careful consideration to
assuring a sufficient flow of air across the condenser heat transfer surface. Two detri
mental conditions are possible and must be avoided if optimum performance is to be
achieved: warm air recirculation and coil starvation.
Warm air recirculation occurs when discharge air from the condenser fans is recycled
back to the condenser coil inlet. Coil starvation occurs when free airflow to (or from)
the condenser is restricted.
Both warm air recirculation and coil starvation cause reduction in unit efficiency and
capacity due to the increased head pressures.
-
40 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 41

Installation - Mechanical
Debris, trash, supplies etc. should not be allowed to accumulate in the vicinity of the
unit. Supply air movement may draw debris into the condenser coil, blocking spaces
between coil fins and causing coil starvation. Special consideration should be given to
low ambient units. Condenser coils and fan discharge must be kept free of snow or
other obstructions to permit adequate airflow for satisfactory unit operation.
In situations where equipment must be installed with less clearance than recommended, such as frequently occurs in retrofit and rooftop applications, restricted airflow is common. The Main Processor will direct the unit to make as much chilled
water as possible given the actual installed conditions. Consult your Trane sales engi
neer for more details.
NOTE: If the outdoor unit configuration requires a variance to the clearance dimensions, contact your Trane Sales Office Representative. Also refer to Trane Engineering
Bulletins for application information on RTAC chillers.
Unit Isolation and Leveling
For additional reduction of sound and vibration, install the optional neoprene isolators.
Construct an isolated concrete pad for the unit or provide concrete footings at the unit
mounting points. Mount the unit directly to the concrete pads or footings.
Level the unit using the base rail as a reference. The unit must be level within 1/4-in (6
mm) over the entire length and width. Use shims as necessary to level the unit.
Neoprene Isolator Installation
1. Secure the isolators to the mounting surface using the mounting slots in the isolator base plate. Do not fully tighten the isolator mounting bolts at this time.
2. Align the mounting holes in the base of the unit with the threaded positioning
pins on the top of the isolators.
3. Lower the unit onto the isolators and secure the isolator to the unit with a nut.
Maximum isolator deflection should be 1/4 inch (6 mm).
4. Level the unit carefully. Fully tighten the isolator mounting bolts.
-
Drainage
Provide a large capacity drain for water vessel drain-down during shutdown or repair.
The evaporator is provided with a drain connection. All local and national codes apply.
The vent on the top of the evaporator waterbox is provided to prevent a vacuum by
allowing air into the evaporator for complete drainage.
Evaporator Water Piping
Thoroughly flush all water piping to the unit before making the final piping connections to the unit.
Evaporator Piping
Components and layout will vary slightly, depending on the location of connections
and the water source.
CAUTION
Evaporator Damage!
The chilled water connections to the evaporator are to be “victaulic”
type connections. Do not attempt to weld these connections, as the
heat generated from welding can cause microscopic and macroscopic
fractures on the cast iron waterboxes that can lead to premature failure
of the waterbox. To prevent damage to chilled water components, do
not allow evaporator pressure (maximum working pressure) to exceed
150 psig (10.5 bar).
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 41
Page 42

Installation - Mechanical
Provide shutoff valves in lines to the gauges to isolate them from the system when
they are not in use. Use rubber vibration eliminators to prevent vibration transmission
through the water lines. If desired, install thermometers in the lines to monitor enter
ing and leaving water temperatures. Install a balancing valve in the leaving water line
to control water flow balance. Install shutoff valves on both the entering and leaving
water lines so that the evaporator can be isolated for service.
CAUTION
Use Piping Strainers!
To prevent evaporator damage, pipe strainers must be installed in the
water supplies to protect components from water born debris. Trane is
not responsible for equipment-only-damage caused by water born
debris.
“Piping components” include all devices and controls used to provide proper water
system operation and unit operating safety. These components and their general loca
tions are given below.
Entering Chilled Water Piping
• Air vents (to bleed air from system).
• Water pressure gauges with shutoff valves.
• Vibration eliminators.
• Shutoff (isolation) valves. Thermometers (if desired).
• Clean-out tees.
• Pipe strainer.
-
-
Leaving Chilled Water Piping
• Air vents (to bleed air from system).
• Water pressure gauges with shutoff valves. Vibration eliminators.
• Shutoff (isolation) valves.
• Thermometers.
• Clean-out tees.
• Balancing valve.
• Flow Switch
Evaporator Drain
A1/2 inch drain connection is located under the outlet end of the evaporator waterbox.
This may be connected to a suitable drain to permit evaporator drainage during unit
servicing. A shutoff valve must be installed on the drain line.
Evaporator Flow Switch
Specific connection and schematic wiring diagrams are shipped with the unit. Some
piping and control schemes, particularly those using a single water pump for both
chilled and hot water, must be analyzed to determine how and or if a flow sensing
device will provide desired operation.
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for selection and installation procedures. General guidelines for flow switch installation are outlined below
1. Mount the switch upright, with a minimum of 5 pipe diameters of straight horizontal run on each side. Do not install close to elbows, orifices or valves.
NOTE: The arrow on the switch must point in the direction of flow.
42 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 43

100
Installation - Mechanical
2. To prevent switch fluttering, remove all air from the water system.
NOTE: The CH530 provides a 6-second time delay after a “loss-of-flow” diagnostic
before shutting the unit down. Contact a qualified service representative if nuisance
machine shutdowns persist.
3. Adjust the switch to open when water flow falls below the minimum flow rate.
Evaporator data is given in the General Information section. Flow switch contacts
are closed on proof of water flow.
4. Install a pipe strainer in the entering evaporator water line to protect components
from waterborne debris.
Evaporator Water Pressure Drop RTAC 140 - 250 Ton
Evaporator Water Pressure Drop
250S, 200H,
225H, 250H
(60Hz)
225S, 185H
10
Pressure Drop (ft H2O)
1
100 1000
Figure 23 Evaporator Water Pressure Drop
200S, 170H
185S, 155H
170S, 140H
155S
140S
Flow Rate (GPM)
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 43
Page 44

100.0
Installation - Mechanical
Evaporator Water Pressure Drop RTAC 250 - 500 Ton
Water-Side Pressure Drop vs Flow Rate
250S (50Hz)
275S
300S, 250H (50Hz)
350S (60 Hz), 275H, 300H
10.0
Pressure Drop (ft H2O)
1.0
100 1000 10000
Flow Rate (GPM)
Figure 24 Evaporator Water Pressure Drop
CAUTION
Proper Water Treatment!
The use of untreated or improperly treated water in a unit may result in
scaling, erosion, corrosion, algae or slime. It is recommended that the
services of a qualified water treatment specialist be engaged to
determine what water treatment, if any, is required. Trane assumes no
responsibility for equipment failures which result from untreated or
improperly treated water, or saline or brackish water.
350S (50Hz)
375S (50Hz)
400S, 350H
450S (60Hz), 375H (50Hz)
500S (60Hz), 400H
If using an acidic commercial flushing solution, construct a temporary
bypass around the unit to prevent damage to internal components of the
evaporator.
Dirt, scale, products of corrosion and other foreign material will adversely affect heat
transfer between the water and system components. Foreign matter in the chilled
water system can also increase pressure drop and, consequently, reduce water flow.
Proper water treatment must be determined locally, depending on the type of system
and local water characteristics.
44 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 45

Installation - Mechanical
Neither salt nor brackish water is recommended for use in Trane air-cooled Series R®
chillers. Use of either will lead to a shortened life to an indeterminable degree. The
Trane Company encourages the employment of a reputable water treatment special
ist, familiar with local water conditions, to assist in this determination and in the
establishment of a proper water treatment program.
Using untreated or improperly treated water in these units may result in inefficient
operation and possible tube damage. Consult a qualified water treatment specialist to
determine whether treatment is needed. The following disclamatory label is provided
on each RTAC unit:
NOTE: The use of improperly treated or untreated water in this equipment may
result in scaling, erosion, corrosion, algae or slime. The services of a qualified water
treatment specialist should be engaged to determine what treatment, if any, is
advisable. The Trane Company warranty specifically excludes liability for corrosion,
erosion or deterioration of Trane equipment.
Water Pressure Gauges
Install field-supplied pressure components as shown in Figure 25. Locate pressure
gauges or taps in a straight run of pipe; avoid placement near elbows, etc. Be sure to
install the gauges at the same elevation on each shell if the shells have opposite-end
water connections.
-
Figure 25 Suggested Piping for Typical RTAC Evaporator
NOTE: Once the unit is installed at a site, one vertical or one diagonal unit support
can be permanently removed if it creates an obstruction for water piping.
To read manifolded pressure gauges, open one valve and close the other (depending
upon the reading desired). This eliminates errors resulting from differently calibrated
gauges installed at unmatched elevations.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 45
Page 46

Installation - Mechanical
Water Pressure Relief Valves
CAUTION
Shell Damage!
To prevent shell damage, install pressure relief valves in the evaporator
water system.
Install a water pressure relief valve in the evaporator inlet piping between the evaporator and the inlet shutoff valve, as shown in Figure 25. Water vessels with close-coupled shutoff valves have a high potential for hydrostatic pressure buildup on a water
temperature increase. Refer to applicable codes for relief valve installation guidelines.
Freeze Protection
If the unit will remain operational at subfreezing ambient temperatures, the chilled
water system must be protected from freezing. Heaters are factory-installed on the
packaged unit evaporator and will help protect it from freezing in ambient tempera
tures down to -20°F (-29°C).
Install heat tape on all water piping, pumps, water box nozzles and other components
that may be damaged if exposed to freezing temperatures. Heat tape must be
designed for low ambient temperature applications. Heat tape selection should be
based on the lowest expected ambient temperature.
Add a non-freezing, low temperature, corrosion inhibiting, heat transfer fluid may also
be added to the chilled water system. The solution must be strong enough to provide
protection against ice formation at the lowest anticipated ambient temperature. Refer
to
Tabl e 1 through Ta bl e 5 in the General Information section for evaporator water
storage capacities.
-
NOTE: Use of glycol type antifreeze reduces the cooling capacity of the unit and
must be considered in the design of the system specifications.
CAUTION
Evaporator Damage!
ALL unit chilled water pumps must be controlled by the Trane CH530 to
avoid catastrophic damage to the evaporator due to freezing. Refer to
RLC-PRB012-EN.
Low Evaporator Refrigerant Cutout and % Glycol Recommendations
1. Solution freeze point is 4 deg F below operating point saturation temperature.
2. LRTC is 4 deg F below freeze point.
Procedure
1. Is operating condition contained within Tab l e 9 ? If no see “Special” below.
2. For leaving fluid temperatures greater than 40 deg F, use settings for 40 deg F.
3. Select operating conditions from Ta b le 9.
4. Read off recommended % glycol.
5. Go to Ta b le 10. From the % glycol.
46 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 47

Installation - Mechanical
Important
1. Additional glycol beyond the recommendations will adversely effect unit performance. The unit efficiency will be reduced and the saturated evaporator temperature will be reduced. For some operating conditions this effect can be significant.
2. If additional glycol is used, then use the actual % glycol to establish the low
refrigerant cutout setpoint.
3. The minimum low refrigerant cutout setpoint allowed is -5 deg F. The minimum is
established by the solubility limits of the oil in the refrigerant.
Specials
The following constitute a special that must be calculated by engineering:
1. Freeze inhibitor other than Ethylene Glycol or Propylene Glycol.
2. Fluid delta T outside the range 4 to 16 deg F.
3. Unit configuration other than Standard, Standard with extra pass, and Premium.
4. % Glycol greater than maximum in column in Ta bl e 10 .
Special should all be calculated by engineering. The purpose of calculating is to make
sure that design saturation temperature is greater than 3 deg F. Additionally, the calcu
lation must verify that the fluid freeze point is a minimum of 4 deg. F lower that the
design saturation temperature. The low evaporator temperature cutout will be 4 deg F
below the freeze point or -5 deg F, whichever is greater.
-
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 47
Page 48

Installation - Mechanical
Table 9 Glycol Recommendations
Ethylene Glycol Propylene Glycol
DT
4 6 8 10 12 14 16 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
[F]
[C] -15 -14 -13 -12 -11 -10 -9 -15 -14 -13 -12 -11 -10 -9
38
--55556----66778--
3
34
-- 11 11 11 12 -- -- -- 13 13 15 17 -- --
1
30
-- 15 16 17 18 -- -- -- 19 21 -- -- -- --
-1
28
-- 18 18 19 -- -- -- -- 22 -- -- -- -- --
-2
26
-- 20 21 22 -- -- -- -- 25 -- -- -- -- --
-3
24
-- 22 23 26 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
-4
22
-- 24 26 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
-6
20
-- 26 30 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
-7
18
-- 29 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
-8
16
Leaving Water Temperature (F/C)
These tables represent the MINIMUM RECOMMENDED glycol percentages for each operating condition
Operation is not recommended at certain operating conditions as some chillers may not satisfy maximum or
minimum velocity requirements or minimum performance requirements. Contact Trane Sales Representative
for more information regarding the operating limits of a particular chiller.
-- 31
-9
14
30 -- -- --
-10
12
32 -- -- --
-11
10. 4
34 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
-12
-- -- -- -- --
-- -- --
-- -- --
-- -- -- -- -- -- --
-- -- -- -- -- -- --
-- -- -- -- -- -- --
Table 10 Recommended Low Evaporator Refrigerant Cutout and % Glycol
Ethylene Glycol Propylene Glycol
% Glycol
Low Refrig. Temp Cutout Solution Freeze Point Low Refrig. Temp Cutout Solution Freeze Point
°F °C °F °C °F °C °F °C
0 28.0 -2.2 32 0 28.0 -2.2 32.0 0
5 25.0 -3.9 29 -1.7 25.3 -3.7 29.3 -1.5
10 21.5 -5.8 25.5 -3.6 22.4 -5.3 26.4 -3.1
15 17.5 -8.1 21.5 -5.8 19.1 -7.2 23.1 -4.9
20 12.8 -10.7 16.8 -8.4 15.3 -9.3 19.3 -7.1
25 7.4 -13.7 11.4 -11.4 10.8 -11.8 14.8 -9.6
30 1.1 -17.2 5.1 -15.0 5.3 -14.8 9.3 -12.6
35 -5.0 -20.6 -2.3 -19.1 -1.3 -19.5 2.7 -16.3
40 -5.0 -20.6 -10.8 -23.8 -5.0 -20.6 -5.2 -20.7
45 -5.0 -20.6 -20.7 -29.3 -5.0 -20.6 -14.6 -25.9
50 -5.0 -20.6 -32.1 -35.6 -5.0 -20.6 -25.8 -32.1
54 -5.0 -20.6 -42.3 -41.3 -5.0 -20.6 -36.1 -37.8
Chilled Water Temperature Cutout should be set to 5
°F below the lowest allowable Chilled Water Set Point bases on the %Glycol.
48 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 49

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
The RTAC 140-250 ton outdoor unit with the Remote Evaporator option is shipped as two
pieces: the outdoor unit (condensing) and the evaporator. Short suction line connections
are provided with the outdoor condensing unit. The remote evaporator is shipped com
plete, with factory-mounted electronic expansion valves, water temperature sensors, suction pressure transducers, liquid level control sensors, all factory wired to a ribbon cable.
Solenoid valves and drain valves are wired to a relay board in the terminal box. The install
ing contractor is required to provide and install the following:
• 2-wire, twisted shielded communication line between the remote evaporator terminal
box and the Condensing Unit’s control panel
• 115 VAC single phase power supply to the remote evaporator terminal box
• 2 liquid lines
• 2 suction lines
• Suction accumulator as specified
NOTE: A unit ordered as a remote evaporator must also be ordered with either the wide
or low ambient option. The fan inverters are necessary for proper control.
System Configuration and Interconnecting Refrigerant Piping
The system may be configured in any of the four arrangements shown in Figure 26. The
configurations and their associated elevations, along with the total distance between the
remote evaporator and the compressor/condenser section, play a critical role in determining suction and liquid line sizes. This will also affect field refrigerant and oil charges. Consequently, there are physical limits which must not be violated if the system is to operate as
designed. Please note the following requirements for field installation:
1. The remote evaporator MUST be matched with its respective outdoor condensing unit.
2. The circuit number on the outdoor condensing unit must match the circuit number on
the evaporator, i.e. circuit #1 on the outdoor condensing unit must be connected with
circuit # 1 on the remote evaporator and likewise for circuit #2. RTAC Circuit Capacities
are shown in General Data Tables.
-
-
CAUTION
Equipment Damage!
If the circuits are crossed, serious equipment damage may occur.
3. Piping between the evaporator and outdoor unit can not exceed 200 actual feet and/or
an equivalent length of 300 feet.
NOTE: The latter includes the equivalent length of all associated field installed fittings,
4. Horizontal portions of suction lines must be downward sloping toward the compressor
5. Suction lines must be insulated.
6. The line sizes defined are to be used only for 40-60 F leaving water temperature and/or
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 49
valves, accessories and straight lengths of interconnecting piping.
at least 1/2 inch for each 10 feet run. This promotes the movement of oil in the direc
tion of gas flow.
full load ice-making applications.
-
Page 50

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
7. Figure 26, drawing 1 depicts an installation where the remote evaporator elevation is the same as that of the outdoor condensing unit. The suction and liquid
lines are horizontal or down flowing only.
The suction and liquid lines can be put under ground or in a trench. The
temperature of the suction lines must never exceed the temperature of the
compressor. The line can be below the compressors a maximum of 15 ft.
8. Figure 26, drawing 2 shows a variation to drawing 1. The remote evaporator and
outdoor condensing unit are at the same elevation but interconnecting piping may
be installed up to 15 feet above the base elevation. Refer to
the required length of the suction accumulator line. A full size suction accumulator is required at the evaporator and 50% of the value is required at the condensing unit.
9. A refrigerant drain valve is installed at the bottom of the evaporator for freeze protection. This drain valve is a normally open, pilot operated valve which remains
closed unless there is a potential freezing situation detected via low evap temper
atures or low water temperatures or a power failure. If the drain valve is opened
the installed suction accumulator must be capable of holding the entire evapora
tor charge. Refer to Tab l e 13 for sizing.
10. For installations where the remote evaporator is at a lower elevation than the outdoor condensing unit as shown in Figure 26, drawing 3, the elevation difference is
not to exceed 100 feet. An inverted liquid line trap at the condensing unit is
required to prevent unwanted free cooling. The apex of the liquid line trap should
be at a height above the condenser coils. A suction accumulator must be installed
at the evaporator. Refer to
11. When the elevation of the remote evaporator exceeds that of the outdoor condensing unit as shown in Figure 26, drawing 4, the elevation difference is determined by Tabl e 11. The suction accumulator line must be installed according to
Table 13. It is very important, for proper control and operation of the chiller, that
the elevation requirements given in Table 11 are not exceeded. It should also be
noted that in this configuration the suction accumulator is installed at the condensing section.
Note: The height is limited by the available subcooling.
12. Compressor & oil separator heaters must be on at least 24 hours prior to compressor start.
Tabl e 13 for sizing.
Tab l e 13 to determine
-
-
50 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 51

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
Figure 26 Remote Evaporator Installations
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 51
Page 52

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
Figure 27 Circuit Identification
52 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 53

Installation - Mechanical
40-50F
50-60F
40-50F
40-50F
50-60F
40-50F
50-60F
50-60F
Remote Evaporator Option
Lvg. Water
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
275
300
Total Equiv. Length (ft)
Lvg. Water
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
275
300
Total Equiv. Length (ft)
Lvg. Water
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
275
300
Total Equiv. Length (ft)
Lvg. Water
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
275
300
Total Equiv. Length (ft)
RTAC 140-250 Ton Remote Evaporator
Liquid Line Sizes
0 1 to 5 6 to 10 11 to 15 16 to 20 21 to 25 26 to 30 31 to 35 0 1 to 5 6 to 10 11 to 15 16 to 20 21 to 25 26 to 30
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 1.625 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 N/A N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 1.625 N/A N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 1.625 N/A N/A N/A
0 1 to 5 6 to 10 11 to 15 16 to 20 21 to 25 26 to 30 31 to 35 0 1 to 5 6 to 10 11 to 15 16 to 20 21 to 25 26 to 30
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 2.125 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A N/A
1.375 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A
1.375 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A
0 1 to 5 6 to 10 11 to 15 16 to 20 21 to 25 26 to 30 31 to 35 0 1 to 5 6 to 10 11 to 15 16 to 20 21 to 25 26 to 30
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 N/A
0 1 to 5 6 to 10 11 to 15 16 to 20 21 to 25 26 to 30 31 to 35 0 1 to 5 6 to 10 11 to 15 16 to 20 21 to 25 26 to 30
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A
1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A
1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A
Heig ht (ft)
Heig ht (ft) Heig ht (ft)
Heig ht (ft)
Heig ht (ft) Heig ht (ft)
70-ton Circuit
85-ton Circuit
100-ton Circuit
120-ton Circuit
Lvg. Water
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
275
300
Total Equiv. Length (ft)
Lvg. Water
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
275
300
Total Equiv. Length (ft)
Lvg. Water
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
275
300
Total Equiv. Length (ft)
Lvg. Water
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
275
300
Total Equiv. Length (ft)
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 2.125
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 2.125
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 2.125 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A
1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A
1.375 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 N/A
1.375 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 N/A
Heig ht (ft)
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.375 2.125 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.375 1.625 2.125 N/A N/A
1.375 1.375 1.625 1.625 N/A N/A N/A
1.375 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A N/A N/A
1.375 1.625 1.625 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A N/A N/A
1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A N/A
1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A N/A
1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A N/A
1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A N/A
1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A N/A
2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 N/A N/A N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125
1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625
1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625
1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625
N/A N/A N/A
Heig ht (ft)
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.625 N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A
1.625 1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A
1.625 1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A
1.625 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A
2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A
2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A N/A
2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A N/A
2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A N/A
2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.625 N/A N/A
Table 11 Liquid Line Sizes for Remote Evaporators (typical type L copper O.D.)
Line Sizing
To determine the appropriate outside diameter for field installed liquid and suction
lines, it is first necessary to establish the equivalent length of pipe for each line. It is
also necessary to know the capacity (tons) of each circuit. Circuit capacities for each
RTAC unit are listed in the General Data Tables in Section1.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 53
Page 54

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
Table 12 Equivalent Lengths of Non-Ferrous Valves and Fittings (feet)
Line Size Inches ODGlobe Valve Short Angle
Val ve
1-1/887292.71.9
1-3/8 102 33 3.2 2.2
1-5/8 115 34 3.8 2.6
2-1/8 141 39 5.2 3.4
2-5/8 159 44 6.5 4.2
3-1/8 185 53 8 5.1
3-5/8 216 66 10 6.3
4-1/8 248 76 12 7.3
Liquid Line Sizing Steps
The steps to compute liquid line size are as follows:
1. Compute the actual length of field installed piping.
2. Multiply the length from step # 1 by 1.5 to estimate the equivalent length.
3. Refer to Table 11 to determine the outside diameter that corresponds to the
equivalent length computed in step # 2 for the height and leaving water temperature of interest.
Note: If the condenser is at the same elevation or above the evap, use the 0 ft.
column.
4. With the outside diameter found in step # 3, use Tab l e 12 to determine the equivalent lengths of each fitting in the field installed piping.
5. Sum the equivalent lengths of all the field installed elbows and valves.
6. Add the length found in step # 5 to the actual length from step # 1. This is your
new equivalent line length.
7. U s i n g Ta ble 11 again, find the outside diameter that corresponds to the new
equivalent line length from step # 6. If it is the same as step #3, this is the final
equivalent length. Otherwise, proceed to the next step.
8. Using Tab le 12 and the new outside diameter found in step # 7, find the equivalent
line length of each valve and fitting, and sum them.
9. Add the length found in step # 8 to the actual length from step # 1. This is the new
equivalent line length.
10. With the equivalent line length found in step # 9, use Table 11 to select the proper
outside diameter for the liquid lines. If the same as in step #7, this is your final
equivalent line length. Otherwise, repeat step #7.
Short Radius
ELL
Long Radius
ELL
54 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 55

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
Required Length in Feet of Field Installed Suction Line Accumulator
(1)
1 3/8" O.D.
Actu al ft
of field
installed
liquid line
100 56 62 75 64 70 83 57 68 81 66 76 89
110 58 64 79 66 72 87 59 70 85 67 79 93
120 59 66 82 67 74 90 60 73 89 69 81 97
130 61 68 85 69 76 93 62 75 93 70 84 101
140 62 70 89 70 78 97 63 78 97 72 86 105
150 64 72 92 72 80 100 65 81 101 73 89 109
160 65 74 95 73 82 103 67 83 105 75 92 113
170 66 76 99 75 84 107 68 86 108 76 94 117
180 68 78 102 76 86 110 70 88 112 78 97 121
190 69 79 105 77 88 113 71 91 116 80 99 125
200 71 81 109 79 90 117 73 94 120 81 102 129
Installed
Liquid Line
10 43 44 45 52 52 53 43 44 46 52 53 54
20 45 46 49 53 54 57 45 47 50 53 55 58
30 46 48 52 54 56 60 46 49 53 55 58 62
40 48 50 55 56 58 63 48 52 57 56 60 66
50 49 52 59 57 60 67 49 55 61 58 63 70
60 51 54 62 59 62 70 51 57 65 59 66 74
70 52 56 65 60 64 73 53 60 69 61 68 78
80 53 58 69 62 66 77 54 62 73 62 71 81
90 55 60 72 63 68 80 56 65 77 64 73 85
(1) Note: Circuit 2 (M1) of 155 Ton Premium Unit requires an additional 10 feet of Suction Accumulator length.
1 5/8" O.D.
Field
Field
Installed
Liquid Line
Length of 3 5/8"
Suction Accumulator
2 1/8" O.D.
Field
Installed
Liquid Line
1 3/8" O.D.
Liquid Line
85 Ton Circuit
1 5/8" O.D.
Field
Installed
Field
Installed
Liquid Line
Length of 3 5/8"
Suction Accumulator
2 1/8" O.D.
Field
Installed
Liquid Line
1 5/8" O.D.
Installed
Liquid Line
2 1/8" O.D.
Field
Installed
Liquid Line
Length of 4 1/8"
Suction Accumulator
Field
2 5/8" O.D.
Field
Installed
Liquid Line
120 Ton Circuit100 Ton Circuit70 Ton Circuit
1 5/8" O.D.
Installed
Liquid Line
2 1/8" O.D.
Field
Installed
Liquid Line
Length of 4 1/8"
Suction Accumulator
Field
2 5/8" O.D.
Field
Installed
Liquid Line
Table 13 Required Length of Field Installed Suction Accumulator
NOTE: Location and quantity of suction accumulator is dependent upon the unit
configuration.
Example Liquid Line Sizing
Figure 28 Liquid Line Sizing Example
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 55
Page 56

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
For this example, refer to Tab le 11 , Table 12 and Figure 28. Assume a 70 ton circuit
and a leaving water temperature of 49 degrees F.
1. F r o m Figure 28, the actual length of field installed piping is:
80 + 8 + 8 + 21 = 117 feet
2. Estimate equivalent line length:
117 feet x 1.5 = 175 feet
3. From Table 11 for a 70 ton circuit, for 175 equivalent feet the OD is 1.375 inches.
Note: use the 0 ft. column since the condenser is above the evap
4. In Figure 28 there are six long-radius elbows. From Tab le 12 , for 1.375 inch
elbows, the equivalent feet is:
6 elbows x 2.2 feet = 13.2 feet
5. Adding equivalent feet from step #4 to step #1 gives:
13.2 feet + 117 feet = 130.2 feet
6. From Table 11, for a 70 ton circuit, for 125 equivalent feet (nearest to 130.2), the
O.D. is 1- 3/8 inches.
Liquid Line size = 1-3/8 inches
Suction Line Sizing Steps
Table 14 Suction Line Sizes
Vertical/Upflow and Horizontal/Downflow Suction Lines O.D. (Type L Copper)
LWT (F) 70 ton circuit 85ton circuit 100 ton circuit 120 ton circuit
40 - 60 3 5/8” 3 5/8” 4 1/8” 4 1/8”
The steps to compute suction line size are as follows:
1. Break the suction line into it's Vertical/Upflow and Horizontal/Downflow components.
2. From Table 14, select the appropriate Vertical/Upflow suction line outside diame-
ter according to the circuit tonnage. This is the diameter of the upflow suction line
and any fittings in the upflow line.
3. From Table 14, select the appropriate Horizontal/Downflow suction line outside
diameter according to the circuit tonnage. This is the diameter of the upflow suction line and any fittings in the upflow line.
NOTE: The diameters of the upflow, and horizontal or downflow portions of the
suction line may differ depending on the application.
Example Suction Line Sizing
For this example, refer to Tab le 14 and Figure 28 assume a 70 ton circuit and a leaving
water temperature of 49 degrees F.
1. F r o m Table 14, the vertical/upflow suction line is: 3 5/8” O.D.
2. From Table 14, the horizontal/downflow line is: 3 5/8” O.D.
NOTE: In this example, the horizontal line is pitched downward in the direction of
flow.
56 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 57

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
Suction Accumulator Sizing
Use Tab l e 13 to calculate length and size of the required suction accumulator(s).
Example of Suction Accumulator Line Sizing
Use Figure 28 and the same assumptions from the liquid line sizing example to calculate the suction accumulator line size and length.
In this case the accumulator is installed at the evaporator.
1. Use the 70 ton circuit column.
2. From the liquid line sizing example, use a field installed liquid line of:
1.375 (1 3/8”) inches
3. The actual feet of liquid line installed is: 117 feet
4. The size of the suction accumulator is: 3 5/8 inches
5. The length of the suction line accumulator is: 59 feet
Piping Installation Procedures
The outdoor unit and the evaporator are shipped with a 25 psig holding pressure of
dry nitrogen. Do not relieve this pressure until field installation of the refrigerant pip
ing is to be accomplished. This will require the removal of the temporary pipe caps.
NOTE: Use Type L refrigerant-grade copper tubing only.
-
The refrigerant lines must be isolated to prevent line vibration from being transferred
to the building. Do not secure the lines rigidly to the building at any point.
All horizontal suction lines should be pitched downward, in the direction of flow, at a
slope of 1/2 inch per 10 feet of run.
Do not use a saw to remove end caps, as this may allow copper chips to contaminate
the system. Use a tubing cutter or heat to remove the end caps.
When sweating copper joints, flow dry nitrogen through the system. This prevents
scale formation and the possible formation of an explosive mixture of R-134a and air.
This will also prevent the formation of toxic phosgene gas, which occurs when refrig
erant is exposed to open flame.
WARNING
Hazardous Gas!
To prevent injury or death, due to explosion and/or inhalation of
phosgene gas, purge the system thoroughly with dry nitrogen while
sweating connections. Use a pressure regulator in the line between the
unit and the high pressure nitrogen cylinder to avoid over-pressurization
and possible explosion.Failure to use a nitrogen purge and pressure
regulator could result in death or serious injury or equipment damage.
-
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 57
Page 58

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
Refrigerant Sensors
All necessary refrigerant devices, transducers and solenoids are factory installed and
wired to the evaporator terminal box.
Refrigerant Pressure Relief Valve Venting
WARNING
Hazardous Gases!
Consult local regulations for any special relief line requirements.
Refrigerant vented into a confined equipment room could displace
available oxygen to breathe, causing possible asphyxiation or other
serious health risks. Failure to follow these recommendations could
result in death or serious injury.
Vent pipe size must conform to the ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 15 for vent pipe sizing. All
federal, state, and local codes take precedence over any suggestions stated in this
manual.
All relief valve venting is the responsibility of the installing contractor.
All RTAC remote evaporator units use evaporator pressure relief valves (Figure 29)
that must be vented to the outside of the building.
Relief valve connection sizes and locations are shown in the unit submittals. Refer to
local codes for relief valve vent line sizing information.
Caution
Equipment Damage!
Do not exceed vent piping code specifications. Failure to comply with
specifications may result in capacity reduction, unit damage and/or relief
valve damage.
Relief valve discharge setpoints and capacities rates are given in Table 12. Once the
relief valve has opened, it will re-close when pressure is reduced to a safe level.
Once opened, relief valves may have a tendency to leak and must be replaced.
Pressure relief valve discharge capacities will vary with shell diameter and length and
also compressor displacement. Discharge venting capacity should be calculated as
required by ASHRAE Standard 15-94. Do not adjust relief valve setting in the field.
Table 15 Pressure Relief Valve Data
Valve Location Discharge
Setpoint
(psi)
Evap 200 2 28.9 3/4 7/8 - 14
Leak Test and Evacuation
After installation of the refrigerant piping, thoroughly test the system for leaks. Pressure test the system at pressures required by local codes.
Number of
Va lv es
Rated Capacity
per Relief Valve
(lba/min.)
Field Connection
Pipe Size (in NPT)
Factory
Shell Side
Connection (in)
58 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 59

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
WARNING
Hazard of Explosion!
Use only dry nitrogen with a pressure regulator for pressurizing unit. Do
not use acetylene, oxygen or compressed air or mixtures containing
them for pressure testing. Do not use mixtures of a hydrogen containing
refrigerant and air above atmospheric pressure for pressure testing as
they may become flammable and could result in an explosion.
Refrigerant, when used as a trace gas should only be mixed with dry
nitrogen for pressurizing units. Failure to follow these recommendations
could result in death or serious injury or equipment or property-only
damage.
For field evacuation, use a rotary-type vacuum pump capable of pulling a vacuum of
500 microns or less. Follow the pump manufacturer's instructions for proper use of
the pump. The line used to connect the pump to the system should be copper and be
the largest diameter that can be practically used. A larger line size with minimum flow
resistance can significantly reduce evacuation time.
Use the ports on the suction service valves and the liquid line shutoff valves for
access to the system for evacuation. Ensure that the suction service valve, the liquid
line shutoff valve, the oil line shutoff valve and any field installed valves are open in
the proper position before evacuating.
Insulate the entire suction line and the suction accumulator line. Where the line is
exposed to the weather, wrap it with weatherproof tape and seal with weatherproof
compound.
Figure 29 Remote Evaporator
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 59
Page 60

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
Figure 30 Field Wiring between Remote Evaporator and Condensing Unit
Refrigerant and Additional Oil Charge
Refrigerant Charge Determination
The approximate amount of refrigerant charge required by the system must be determined by referring to Table 16 and must be verified by running the system and check-
ing subcooling.
Table 16 Field Installed Piping Charge
Pipe O.D. (in)
1-3/8 N/A 62.4
1-5/8 N/A 88.3
2-1/8 N/A 153.6
2-5/8 N/A 236.9
3-1/8 5.0 N/A
3-5/8 6.8 N/A
4-1/8 8.8 N/A
60 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Suction Line
lbs of R134a per 100ft
Liquid Line
lbs of R134a per 100ft
Page 61

Installation - Mechanical
Remote Evaporator Option
1. To determine the appropriate charge, first refer to the General Data Tables in Section 1 to establish the required charge without the field-installed piping.
2. Next, determine the charge required for the field-installed piping by referring to
Tab l e 16.
3. Sum the values of step 1 and step 2 to determine the circuit charge.
NOTE: The amounts of refrigerant listed in Tab le 16 are per 100 feet of pipe.
Requirements will be in direct proportion to the actual length of piping.
Oil Charge Determination
The unit is factory charged with the amount of oil required by the system, without the
field-installed piping. The amount of the additional oil required is dependent upon the
amount of refrigerant that is added to the system for the field installed piping.
Use the following formula to calculate the amount of oil to be added:
Pints of Oil = [lbs of R-134a added for field-installed piping]/100
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 61
Page 62

Installation - Electrical
General Recommendations
All wiring must comply with local codes and the National Electric Code. Typical field
wiring diagrams are included at the end of the manual. Minimum circuit ampacities
and other unit electrical data are on the unit nameplate and in
19. See the unit order specifications for actual electrical data. Specific electrical
schematics and connection diagrams are shipped with the unit.
WARNING
Hazardous Voltage w/Capacitors!
Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before
servicing. Follow proper lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power
cannot be inadvertently energized. For variable frequency drives or other
energy storing components provided by Trane or others, refer to the
appropriate manufacturer’s literature for allowable waiting periods for
discharge of capacitors. Verify with an appropriate voltmeter that all
capacitors have discharged. Failure to disconnect power and discharge
capacitors before servicing could result in death or serious injury.
Note: For additional information regarding the safe discharge of
capacitors, see PROD-SVB06A-EN or PROD-SVB06A-FR
Tab l e 17 though Table
CAUTION
Use Copper Conductors Only!
Unit terminals are not designed to accept other types of conductors.
Failure to use copper conductors may result in equipment damage.
Important!
Do not allow conduit to interfere with other components, structural members or
equipment. Control voltage (115V) wiring in conduit must be separate from
conduit carrying low voltage (<30V) wiring.
Caution: To prevent control malfunctions, do not run low voltage wiring (<30V)
in conduit with conductors carrying more than 30 volts.
62 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 63

Installation - Electrical
Table 17 Unit Electrical Data for Std. Efficiency at All Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
# of
Unit
Rated
Size
Vol ta ge
200/60/3 1 660 800 800 2 270-270 1498-1498 487-487 8 1.5 6.5 0.83
RTAC
140
200/60/3 2 364/364 600/600 450/450 2 270/270 1498/1498 487/487 4/4 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 581 800 700 2 235-235 1314-1314 427-427 8 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 320/320 500/500 400/400 2 235/235 1314/1314 427/427 4/4 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 348 450 400 2 142-142 801-801 260-260 8 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 192/192 300/300 250/250 2 142/142 801/801 260/260 4/4 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 290 400 350 2 118-118 652-652 212-212 8 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 160/160 250/250 200/200 2 118/118 652/652 212/212 4/4 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 232 300 300 2 94-94 520-520 172-172 8 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 128/128 200/200 175/175 2 94/94 520/520 172/172 4/4 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 333 450 400 2 138-138 774-774 259-259 8 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 184/184 300/300 250/250 2 138/138 774/774 259/259 4/4 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 730 1000 1000 2 320-270 1845-1498 600-701 9 1.5 6.5 0.83
RTAC
155
200/60/3 2 433/364 700/600 600/450 2 320/270 1845/1498 600/701 5/4 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 641 800 800 2 278-235 1556-1314 506-571 9 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 380/320 600/500 450/400 2 278/235 1556/1314 506/571 5/4 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 380 500 450 2 168-142 973-801 316-260 9 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 228/192 350/300 300/250 2 168/142 973/801 316/260 5/4 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 319 450 400 2 139-118 774-652 252-212 9 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 189/160 300/250 225/200 2 139/118 774/652 252/212 5/4 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 255 350 300 2 111-94 631-528 205-172 9 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 152/128 250/200 200/175 2 111/94 631/528 205/172 5/4 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 373 500 450 2 168-138 896-796 291-259 9 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 224/184 350/300 300/250 2 168/138 896/796 291/259 5/4 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 785 1000 1000 2 320-320 1845-1845 600-600 10 1.5 6.5 0.83
RTAC
170
200/60/3 2 433/433 700/700 600/600 2 320/320 1845/1845 600/600 5/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 691 800 800 2 278-278 1556-1556 506-506 10 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 380/380 600/600 450/450 2 278/278 1556/1556 506/506 5/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 413 500 500 2 168-168 973-973 316-316 10 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 228/228 350/350 300/300 2 168/168 973/973 316/316 5/5 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 343 450 400 2 139-139 774-774 252-252 10 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 189/189 300/300 225/225 2 139/139 774/774 252/252 5/5 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 275 350 350 2 111-111 631-631 205-205 10 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 152/152 250/250 200/200 2 111/111 631/631 205/205 5/5 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 406 500 450 2 168-168 896-896 291-291 10 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 224/224 350/350 300/300 2 168/168 896/896 291/291 5/5 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 874 1200 1000 2 386-320 2156-1845 701-600 11 1.5 6.5 0.83
RTAC
185
200/60/3 2 522/433 800/700 700/600 2 386/320 2156/1845 701/600 6/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 770 1000 1000 2 336-278 1756-1556 571-506 11 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 459/380 700/600 600/450 2 336/278 1756/1556 571/506 6/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 460 600 600 2 203-168 1060-973 345-316 11 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 275/228 450/350 350/300 2 203/168 1060/973 345/316 6/5 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 382 500 450 2 168-139 878-774 285-252 11 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 228/189 350/300 300/225 2 168/139 878/774 285/252 6/5 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 306 400 350 2 134-111 705-631 229-205 11 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 183/152 300/250 225/200 2 134/111 705/631 229/205 6/5 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 446 600 500 2 198-168 1089-896 354-291 11 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 264/224 450/350 350/300 2 198/168 1089/896 354/291 6/5 0.9 2.8 0.83
Power
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or
RDE (4)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
Control
VA ( 7 )
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 63
Page 64

Installation - Electrical
Table 17 Unit Electrical Data for Std. Efficiency at All Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
# of
Unit
Rated
Size
Vo lt ag e
200/60/3 1 947 1200 1200 2 386-386 2156-2156 701-701 12 1.5 6.5 0.83
RTAC
200
200/60/3 2 522/522 800/800 700/700 2 386/386 2156/2156 701/701 6/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 834 1000 1000 2 336-336 1756-1756 571-571 12 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 459/459 700/700 600/600 2 336/336 1756/1756 571/571 6/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 499 700 600 2 203-203 1060-1060 345-345 12 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 275/275 450/450 350/350 2 203/203 1060/1060 345/345 6/6 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 414 500 500 2 168-168 878-878 285-285 12 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 228/228 350/350 300/300 2 168/168 878/878 285/285 6/6 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 323 450 400 2 134-134 705-705 229-229 12 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 183/183 300/300 225/225 2 134/134 705/705 229/229 6/6 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 479 600 600 2 198-198 1089-1089 354-354 12 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 264/264 450/450 350/350 2 198/198 1089/1089 354/354 6/6 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 1045 1200 1200 2 459-386 2525-2156 821-701 13 1.5 6.5 0.83
RTAC
225
200/60/3 2 620/522 1000/800 800/700 2 459/386 2525/2156 821/701 7/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 920 1200 1200 2 399-336 2126-1756 691-571 13 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 545/459 800/700 700/600 2 399/336 2126/1756 691/571 7/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 551 700 700 2 242-203 1306-1060 424-345 13 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 327/275 500/450 400/350 2 242/203 1306/1060 424/345 7/6 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 457 600 600 2 200-168 1065-878 346-285 13 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 271/228 450/350 350/300 2 200/168 1065/878 346/285 7/6 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 367 500 450 2 160-134 853-705 277-229 13 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 218/183 350/300 300/225 2 160/134 853/705 277/229 7/6 1.5 2.5 0.83
200/60/3 1 1124 1200 1200 2 459-459 2525-2525 821-821 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
RTAC
250
200/60/3 2 620/620 1000/1000 800/800 2 459/459 2525/2525 821/821 7/7 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 989 1200 1200 2 399-399 2126-2126 691-691 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 545/545 800/800 700/700 2 399/399 2126/2126 691/691 7/7 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 594 800 700 2 242-242 1306-1306 424-424 14 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 327/327 500/500 400/400 2 242/242 1306/1306 424/424 7/7 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 492 600 600 2 200-200 1065-1065 346-346 14 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 271/271 450/450 350/350 2 200/200 1065/1065 346/346 7/7 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 395 500 500 2 160-160 853-853 277-277 14 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 218/218 350/350 300/300 2 160/160 853/853 277/277 7/7 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 563 700 700 3 138-138-198 796-796-1089 259-259-354 14 0.9 2.8 1.2
400/50/3 2 333/265 450/450 400/350 3 138/138/198 796/796/1089 259/259/354 8/6 0.9 2.8 1.2
200/60/3 1 NA
RTAC
275
200/60/3 2 785/522 1000/800 1000/700 3 320/320/386 1845/1845/2156 600/600/701 10/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 681/459 800/700 800/600 3 278/278/336 1556/1556/1756 506/506/571 10/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 413/275 500/450 500/350 3 168/168/203 973/973/1060 316/316/345 10/6 1.5 3.5 1.2
460/60/3 1 536 700 600 3 139-139-168 774-774-878 252-252-285 16 1.5 3.0 1.2
460/60/3 2 343/228 450/350 400/300 3 139/139/168 774/774/878 252/252/285 10/6 1.5 3.0 1.2
575/60/3 1 430 500 500 3 111-111-134 631-631-705 205-205-229 16 1.5 2.5 1.2
575/60/3 2 275/183 350/300 350/225 3 111-111/134 631/631/705 205/205/229 10/6 1.5 2.5 1.2
400/50/3 1 629 800 700 3 168-168-198 896-896-1089 291-291-354 16 0.9 2.8 1.2
400/50/3 2 406/265 500/450 450/350 3 168/168/198 896/896/1089 291/291/254 10/6 0.9 2.8 1.2
Power
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or
RDE (4)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
Control
VA (7)
64 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 65

Installation - Electrical
Table 17 Unit Electrical Data for Std. Efficiency at All Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
# of
Unit
Rated
Size
Vol ta ge
200/60/3 1 NA
RTAC
300
200/60/3 2 947/522 1200/800 1200/700 3 386/386/386 2156/2156/2156 701/701/701 12/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 834/459 1000/700 1000/600 3 336/336/336 1756/1756/1756 571/571/571 12/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 499/275 700/450 600/350 3 203/203/203 1060/1060/1060 345/345/345 12/6 1.5 3.5 1.2
460/60/3 1 600 700 700 3 168-168-168 878-878-878 285-285-285 18 1.5 3.0 1.2
460/60/3 2 414/228 500/350 500/300 3 168/168/168 878/878/878 285/285/285 12/6 1.5 3.0 1.2
575/60/3 1 481 600 600 3 134-134-134 705-705-705 229-229-229 18 1.5 2.5 1.2
575/60/3 2 332/183 450/300 400/225 3 134/134/134 705/705/705 229/229/229 12/6 1.5 2.5 1.2
400/50/3 1 694 800 800 3 198-198-198 1089-1089-1089 354-354-354 18 0.9 2.8 1.2
400/50/3 2 480/265 600/450 600/350 3 198/198/198 1089/1089/1089 354/354/354 12/6 0.9 2.8 1.2
200/60/3 1 NA
RTAC
350
200/60/3 2 1124/522 1200/800 1200/700 3 459/459/386 1845/1845/1845/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 989/459 1200/700 1200/600 3 399/399/336 1556/1556/1556/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 594/275 800/450 700/350 3 242/242/203 973/973/973/973 424/424/345 14/6 1.5 3.5 1.2
460/60/3 1 678 800 800 3 200-200-168 774-774-774-774 346-346-285 20 1.5 3.0 1.2
460/60/3 2 492/228 600/350 600/300 3 200/200/168 774/774/774/774 346/346/285 14/6 1.5 3.0 1.2
575/60/3 1 544 700 600 3 160-160-134 631-631-631-631 277-277-229 20 1.5 2.5 1.2
575/60/3 2 395/183 500/300 450/225 3 160/160/134 631/631/631/631 277/277/229 14/6 1.5 2.5 1.2
400/50/3 1 770 800 800 4 168-168-168-
400/50/3 2 406/406 500/500 450/450 4 168/168/168/
400/50/3 1 844 1000 1000 4 198-198-168-
RTAC
375
400/50/3 2 480/406 600/500 600/450 4 198/198/168/
200/60/3 1 NA
RTAC
400
200/60/3 2 947/947 1200/1200 1200/1200 4 386/386/386/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 834/834 1000/1000 1000/1000 4 336/336/336/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 499/499 700/700 600/600 4 203/203/203/
460/60/3 1 786 800 800 4 168-168-168-
460/60/3 2 414/414 500/500 500/500 4 168/168/168/
575/60/3 1 630 700 700 4 134-134-134-
575/60/3 2 332/332 450/450 400/400 4 134/134/134/
400/50/3 1 909 1000 1000 4 198-198-198-
400/50/3 2 480/480 600/600 600/600 4 198/198/198/
Power
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or
RDE (4)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
168
168
168
168
386
336
203
168
168
134
134
198
198
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
1845
1556
896-896-896-896 291-291-291-
896/896/896/896 291/291/291/
1089-1089-896-896 354-354-291-
1089/1089/896/896 354/354/291/
2156/2156/2156/
2156
1756/1756/1756/
1756
1060/1060/1060/
1060
878-878-878-878 285-285-285-
878/878/878/878 285/285/285/
705-705-705-705 229-229-229-
705/705/705/705 229/229/229/
1089-1089-10891089
1089/1089/1089/
1089
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
821/821/701 14/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
691/691/571 14/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
291
291
291
291
701/701/701/
701
571/571/571/
571
345/345/345/
345
285
285
229
229
354-354-354-
354
354/354/354/
354
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
20 0.9 2.8 1.59
10/10 0.9 2.8 1.59
22 0.9 2.8 1.59
12/10 0.9 2.8 1.59
14/14 1.5 6.5 1.59
14/14 1.5 6.5 1.59
14/14 1.5 3.5 1.59
2 8 1. 5 3 . 0 1. 5 9
14/14 1.5 3.0 1.59
2 8 1. 5 2 . 5 1. 5 9
14/14 1.5 2.5 1.59
28 0.9 2.8 1.59
14/14 0.9 2.8 1.59
Control
VA ( 7 )
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 65
Page 66

Installation - Electrical
Table 17 Unit Electrical Data for Std. Efficiency at All Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
# of
Unit
Rated
Size
Vo lt ag e
200/60/3 1 NA
RTAC
450
200/60/3 2 1124/947 1200/1200 1200/1200 4 459/459/386/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 989/834 1200/1000 1200/1000 4 399/399/336/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 594/499 800/700 700/600 4 242/242/203/
460/60/3 1 864 1000 1000 4 200-200-168-
460/60/3 2 492/414 600/500 600/500 4 200/200/168/
575/60/3 1 693 800 800 4 160-160-134-
575/60/3 2 395/332 500/450 450/400 4 160/160/134/
200/60/3 1 NA
RTAC
500
200/60/3 2 1124/1124 1200/1200 1200/1200 4 459/459/459/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 989/989 1200/1200 1200/1200 4 399/399/399/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 594/594 800/800 700/700 4 242/242/242/
460/60/3 1 929 1000 1000 4 200-200-200-
460/60/3 2 490/490 600/600 600/600 4 200/200/200/
575/60/3 1 745 800 800 4 160-160-160-
575/60/3 2 393/393 500/500 450/450 4 160/160/160/
Power
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or
RDE (4)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Notes:
1. As standard, 140-250 ton (60 Hz) units and 140-200 ton (50Hz) units have a single point power connection. Optional dual point power connections
are available. As standard, 275-500 ton (60Hz) units and 250-400 ton (50Hz) units have dual point power connections. Optional single point power
connections are available on 380V, 460V 575V/50 Hz and 400V/50 Hz units.
2. Max Fuse or HACR type breaker = 225 percent of the largest compressor RLA plus 100 percent of the second compressor RLA, plus the sum of the
condenser fan FLA per NEC 440-22. (Use FLA per circuit, NOT FLA for the entire unit).
3. MCA - Minimum Circuit Ampacity - 125 percent of largest compressor RLA plus 100 percent of the second compressor RLA plus the sum of the
condenser fans FLAs per NEC 440-33.
4. RECOMMENDED TIME DELAY OR DUAL ELEMENT (RDE) FUSE SIZE: 150 percent of the largest compressor RLA plus 100 percent of the second
compressor RLA and the sum of the condenser fan FLAs.
5. RLA - Rated Load Amps - rated in accordance with UL Standard 1995.
6. Local codes may take precedence.
7. Control VA includes operational controls only. Does not include evaporator heaters.
8. XLRA - Locked Rotor Amps - based on full winding (x-line) start units. YLRA for wye-delta starters is ~1/3 of LRA of x-line units.
9. Voltage Utilization Range:
Rated Voltage 200/60/3 230/60/3 380/60/3 460/60/3 575/60/3 400/50/3
Use Range 180-220 208-254 342-418 414-506 516-633 360-440
10. A separate 115/60/1, 20 amp or 220/50/1, 15 amp customer provided power connection is required to power the evaporator heaters (1640 watts).
11. If factory circuit breakers are supplied with the chiller, then these values represent Maximum Overcurrent Protection (MOP).
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
386
336
203
168
168
134
134
459
399
242
200
200
160
160
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
2525/2525/2156/
2156
2126/2126/1756/
1756
1306/1306/1060/
1060
1065-1065-878-878 346-346-285-
1065/1065/878/878 346/346/285/
853-853-705-705 277-277-229-
853/853/705/705 277/277/229/
2525/2525/2525/
2525
2126/2126/2126/
2126
1306/1306/1306/
1306
1065-1065-10651065
1065/1065/1065/
1065
853-853-853-853 277-277-277-
853/853/853/853 277/277/277/
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
821/821/701/
701
691/691/571/
571
424/424/345/
345
285
285
229
229
821/821/821/
821
691/691/691/
691
424/424/424/
424
346-346-346346
346/346/346/
346
277
277
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
14/12 1.5 6.5 1.59
14/12 1.5 6.5 1.59
14/12 1.5 3.5 1.59
26 1.5 3.0 1.59
14/12 1.5 3.0 1.59
26 1.5 2.5 1.59
14/12 1.5 2.5 1.59
14/14 1.5 6.5 1.59
14/14 1.5 6.5 1.59
14/14 1.5 3.5 1.59
28 1.5 3.0 1.59
14/14 1.5 3.0 1.59
28 1.5 2.5 1.59
14/14 1.5 2.5 1.59
Control
VA (7)
66 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 67

Installation - Electrical
Table 18 Unit Electrical Data for High Efficiency at Std. Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
Unit
Size
RTAC
140
RTAC
155
RTAC
170
RTAC
185
# of
Power
Rated
Vo lt ag e
200/60/3 1 648 800 800 2 259-259 1498-1498 487-487 10 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 356/356 600/600 450/450 2 259/259 1498/1498 487/487 5/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 572 700 700 2 225-225 1314-1314 427-427 10 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 314/314 500/500 400/400 2 225/225 1314/1314 427/427 5/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 341 450 400 2 136-136 801-801 260-260 10 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 188/188 300/300 225/225 2 136/136 801/801 260/260 5/5 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 285 350 350 2 113-113 652-652 212-212 10 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 157/157 250/250 200/200 2 113/113 652/652 212/212 5/5 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 228 300 250 2 90-90 520-520 172-172 10 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 125/125 200/200 150/150 2 90/90 520/520 172/172 5/5 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 325 450 400 2 132-132 774-774 259-259 10 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 179/179 300/300 225/225 2 132/132 774/774 259/259 5/5 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 712 1000 800 2 305-259 1845-1498 600-487 11 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 421/356 700/600 500/450 2 305/259 1845/1498 600/487 6/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 628 800 700 2 265-225 1556-1314 506-427 11 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 371/314 600/500 450/400 2 265/225 1556/1314 506/427 6/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 376 500 416 2 161-136 973-801 316-260 11 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 222/188 350/300 300/225 2 161/136 973/801 316/260 6/5 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 313 400 350 2 133-113 774-652 252-212 11 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 185/157 300/250 225/200 2 133/113 774/652 252/212 6/5 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 250 350 300 2 106-90 631-528 205-172 11 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 148/125 250/200 175/150 2 106/90 631/528 205/172 6/5 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 363 500 450 2 160-132 896-796 291-259 11 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 217/179 350/300 300/225 2 160/132 896/796 291/259 6/5 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 765 1000 1000 2 305-305 1845-1845 600-600 12 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 421/421 700/700 500/500 2 305/305 1845/1845 600/600 6/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 675 800 800 2 265-265 1556-1556 506-506 12 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 371/371 600/600 450/450 2 265/265 1556/1556 506/506 6/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 404 500 450 2 161-161 973-973 316-316 12 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 222/222 350/350 300/300 2 161/161 973/973 316/316 6/6 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 336 450 400 2 133-133 774-774 252-252 12 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 185/185 300/300 225/225 2 133/133 774/774 252/252 6/6 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 269 350 300 2 106-106 631-631 205-205 12 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 148/148 250/250 175/175 2 106/106 631/631 205/205 6/6 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 394 500 450 2 160-160 896-896 291-291 12 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 217/217 350/350 300/300 2 160/160 896/896 291/291 6/6 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 856 1200 1000 2 373-305 2156-1845 701-600 13 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 512/421 800/700 700/500 2 373/305 2156/1845 701/600 7/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 755 1000 1000 2 324-265 1756-1556 571-506 13 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 451/371 700/600 600/450 2 324/265 1756/1556 571/506 7/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 452 600 500 2 196-161 1060-973 345-316 13 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 270/222 450/350 350/300 2 196/161 1060/973 345/316 7/6 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 375 500 450 2 162-133 878-774 285-252 13 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 224/185 350/300 300/225 2 162/133 878/774 285/252 7/6 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 301 400 350 2 130-106 705-631 229-205 13 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 180/148 300/250 225/175 2 130/106 705/631 229/205 7/6 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 433 600 500 2 189-160 1089-896 354-291 13 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 256/217 400/350 350/300 2 189/160 1089/896 354/291 7/6 0.9 2.8 0.83
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/
Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or
RDE (4)
Ckt1/Ckt 2
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
Control
VA ( 7 )
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 67
Page 68

Installation - Electrical
Table 18 Unit Electrical Data for High Efficiency at Std. Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
Unit
Size
RTAC
200
RTAC
225
RTAC
250
RTAC
275
# of
Power
Rated
Vo lt ag e
200/60/3 1 931 1200 1200 2 373-373 2156-2156 701-701 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 512/512 800/800 700/700 2 373/373 2156/2156 701/701 7/7 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 820 1000 1000 2 324-324 1756-1756 571-571 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 451/451 700/700 600/600 2 324/324 1756/1756 571/571 7/7 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 490 600 600 2 196-196 1060-1060 345-345 14 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 270/270 450/450 350/350 2 196/196 1060/1060 345/345 7/7 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 407 500 450 2 162-162 878-878 285-285 14 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 224/224 350/350 300/300 2 162/162 878/878 285/285 7/7 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 328 450 400 2 130-130 705-705 229-229 14 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 180/180 300/300 225/225 2 130/130 705/705 229/229 7/7 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 464 600 600 2 189-189 1089-1089 354-354 14 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 256/256 400/400 350/350 2 189/189 1089/1089 354/354 7/7 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 1023 1200 1200 2 447-373 2525-2156 821-701 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 611/506 1000/800 800/600 2 447/373 2525/2156 821/701 8/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 900 1200 1000 2 388-224 2126-1756 691-571 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 537/544 800/700 700/600 2 388/324 2126/1756 691/571 8/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 539 700 600 2 235-196 1306-1060 424-345 14 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 322/266 500/450 400/350 2 235/196 1306/1060 424/345 8/6 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 447 600 500 2 194-162 1065-878 346-285 14 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 267/221 450/350 350/300 2 194/162 1065/878 346/285 8/6 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 359 500 400 2 155-130 853-705 277-229 14 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 214/178 350/300 300/225 2 155/130 853/705 277/229 8/6 1.5 2.5 0.83
200/60/3 1 1110 1200 1200 2 447-447 2525-2525 821-821 16 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 611/611 1000/1000 800/800 2 447/447 2525/2525 821/821 8/8 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 977 1200 1200 2 388-388 2126-2126 691-691 16 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 537/537 800/800 700/700 2 388/388 2126/2126 691/691 8/8 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 585 800 700 2 235-235 1306-1306 424-424 16 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 322/322 500/500 400/400 2 235/235 1306/1306 424/424 8/8 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 485 600 600 2 194/-194 1065-1065 346-346 16 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 267/267 450/450 350/350 2 194/194 1065/1065 346/346 8/8 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 389 500 450 2 155-155 853-853 277-277 7/4 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 214/214 350/350 300/300 2 155/155 853/853 277/277 8/8 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 546 700 600 3 132-132-189 796-796-1089 259-259-354 16 0.9 2.8 1.2
400/50/3 2 325/254 450/400 400/350 3 132/132/189 796/796/1089 259/259/354 10/6 0.9 2.8 1.2
200/60/3 1 NA
200/60/3 2 765/506 1000/800 1000/600 3 305/305/373 1845/1845/2156 600/600/701 12/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 675/444 800/700 800/600 3 265/265/324 1556/1556/1756 506/506/571 12/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 405/266 500/450 450/350 3 161/161/196 973/973/1060 316/316/345 12/6 1.5 3.5 1.2
460/60/3 1 523 600 600 3 133-133-162 774-774-878 252-252-285 18 1.5 3.0 1.2
460/60/3 2 336/221 450/350 400/300 3 133/133/162 77/-774/878 252/252/285 12/6 1.5 3.0 1.2
575/60/3 1 420 500 450 3 106-106-130 631-631-705 205-205-229 18 1.5 2.5 1.2
575/60/3 2 269/178 350/300 300/225 3 106/106/130 631/631/705 205/205/229 12/6 1.5 2.5 1.2
400/50/3 1 607 700 700 3 160-160-189 896-896-1089 291-291-354 18 0.9 2.8 1.2
400/50/3 2 394/254 500/400 450/350 3 160/160/189 896/896/1089 291/291/254 12/6 0.9 2.8 1.2
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/
Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or
RDE (4)
Ckt1/Ckt 2
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
Control
VA (7)
68 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 69

Installation - Electrical
Table 18 Unit Electrical Data for High Efficiency at Std. Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
Unit
Size
RTAC
300
RTAC
350
RTAC
375
# of
Power
Rated
Vo lt ag e
200/60/3 1 NA
200/60/3 2 931/506 1200/800 1200/600 3 373/373/373 2156/2156/2156 701/701/701 14/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 820/444 1000/700 1000/600 3 324/324/324 1756/1756/1756 571/571/571 14/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 490/266 600/450 600/350 3 196/196/196 1060/1060/1060 345/345/345 14/6 1.5 3.5 1.2
460/60/3 1 587 700 700 3 162-162 - 162 878-878-878 285-285-285 20 1.5 3.0 1.2
460/60/3 2 407/221 500/350 450/300 3 162/162/162 878/878/878 285/285/285 14/6 1.5 3.0 1.2
575/60/3 1 473 500 500 3 130-130-130 705-705-705 229-229-229 20 1.5 2.5 1.2
575/60/3 2 328/178 450/300 400/225 3 130/130/130 705/705/705 229/229/229 14/6 1.5 2.5 1.2
400/50/3 1 671 800 800 3 189-189-189 1089-1089-1089 354-354-354 20 0.9 2.8 1.2
400/50/3 2 465/254 600/400 600/350 3 189/189/189 1089/1089/1089 354/354/354 14/6 0.9 2.8 1.2
200/60/3 1 NA
200/60/3 2 765/765 1000/1000 1000/1000 4 305/305/305/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 675/675 800/800 800800 4 265/265/265/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 405/405 500/500 450/450 4 161/161/161/
460/60/3 1 638 700 700 4 133-133-133-
460/60/3 2 336/336 450/450 400/400 4 133/133/133/
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/
Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or
RDE (4)
Ckt1/Ckt 2
575/60/3 1 511 600 600 4 106-106-
575/60/3 2 269/269 350/350 300/300 4 106/106/
400/50/3 1 748 800 800 4 160-160-
400/50/3 2 394/394 500/500 450/450 4 160/160/
400/50/3 1 819 1000 1000 4 189-189-
400/50/3 2 465/394 600/500 600/450 4 189/189/
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
305
265
161
133
133
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
1845/1845/
1845/1845
1556/1556/
1556/1556
973/973/973/
973
774-774-774-774 252-252-252-
774/774/774/774 252/252/252/
631-631-631-
106 -106
631
631/631/631/
106 /106
631
896-896-896-
160-160
896
896/896/896/
160/160
896
1089-1089-
160-160
896-896
1089/1089/
160/160
896/896
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
600/600/
600/600
506/506/506/
506
316/316/316/
316
252
252
205-205-
205-205
205/205/
205/205
291-291-
291-291
291/291/
291/291
354-354-
291-291
254/254/
291/291
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
12/12 1.5 6.5 1.2
12/12 1.5 6.5 1.2
12/12 1.5 3.5 1.2
24 1.5 3.0 1.2
12/12 1.5 3.0 1.2
1. 5 2 . 5
24
24
26
1. 5 2 . 5
0.9 2.8
0.9 2.8
0.9 2.8
0.9 2.8
12/12
12/12
14/12
Control
VA ( 7 )
1. 2
1. 2
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 69
Page 70

Installation - Electrical
Table 18 Unit Electrical Data for High Efficiency at Std. Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or
RDE (4)
Ckt1/Ckt 2
Unit
Size
RTAC
400
# of
Power
Rated
Vo lt ag e
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/
Ckt2
200/60/3 1 NA
200/60/3 2 931/931 1200/1200 1200/1200 4 373/373/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 820/820 1000/1000 1000/1000 4 324/324/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 490/490 600/600 600/600 4 196/196/
460/60/3 1 773 800 800 4 162-162-
460/60/3 2 407/407 500/500 450/450 4 162/162/
575/60/3 1 623 700 700 4 130-130-
575/60/3 2 328/328 450/450 400/400 4 130/130/
400/50/3 1 882 1000 1000 4 189-189-
400/50/3 2 465/465 600/600 600/600 4 189/189/
Notes:
1. As standard, 140-250 ton (60 Hz) units and 140-200 ton (50Hz) units have a single point power connection. Optional dual point power connections
are available. As standard, 275-500 ton (60Hz) units and 250-400 ton (50Hz) units have dual point power connections. Optional single point power
connections are available on 380V, 460V 575V/50 Hz and 400V/50 Hz units.
2. Max Fuse or HACR type breaker = 225 percent of the largest compressor RLA plus 100 percent of the second compressor RLA, plus the sum of the
condenser fan FLA per NEC 440-22. (Use FLA per circuit, NOT FLA for the entire unit).
3. MCA - Minimum Circuit Ampacity - 125 percent of largest compressor RLA plus 100 percent of the second compressor RLA plus the sum of the
condenser fans FLAs per NEC 440-33.
4. RECOMMENDED TIME DELAY OR DUAL ELEMENT (RDE) FUSE SIZE: 150 percent of the largest compressor RLA plus 100 percent of the second
compressor RLA and the sum of the condenser fan FLAs.
5. RLA - Rated Load Amps - rated in accordance with UL Standard 1995.
6. Local codes may take precedence.
7. Control VA includes operational controls only. Does not include evaporator heaters.
8. XLRA - Locked Rotor Amps - based on full winding (x-line) start units. YLRA for wye-delta starters is ~1/3 of LRA of x-line units.
9. Voltage Utilization Range:
Rated Voltage 200/60/3 230/60/3 380/60/3 460/60/3 575/60/3 400/50/3
Use Range 180-220 208-254 342-418 414-506 516-633 360-440
10. A separate 115/60/1, 20 amp or 220/50/1, 15 amp customer provided power connection is required to power the evaporator heaters (1640 watts).
11. If factory circuit breakers are supplied with the chiller, then these values represent Maximum Overcurrent Protection (MOP).
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
373/373
324/324
196/196
162-162
162/162
130-130
130/130
189- 189
189/ 189
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
2156/2156/
2156/2156
1756/1756/
1756/1756
1060/1060/
1060/1060
878-878-878-
878
878/878/878/
878
705-705-705-
705
705/705/705/
705
1089-1089-
1089-1089
1089/1089/
1089/1089
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
701/701/
701/701
571/571/
571/571
345/345/
345/345
285-285285-285
285/285/
285/285
229-229229-229
229/229/
229/229
354-354354-354
354/354/
354/354
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
14/14
14/14
14/14
28
14/14
28
14/14
28
14/14
1. 5 6 . 5
1. 5 6 . 5
1. 5 3 . 5
1. 5 3 . 0
1. 5 3 . 0
1. 5 2 . 5
1. 5 2 . 5
0.9 2.8
0.9 2.8
Control
VA (7)
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
1. 5 9
70 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 71

Installation - Electrical
Table 19 Unit Electrical Data for High Efficiency at High Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
Unit
Size
RTAC
140
RTAC
155
RTAC
170
RTAC
185
# of
Rated
Vol ta ge
200/60/3 1 673 800 800 2 270-270 1498-1498 487-487 10 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 370/370 600/600 450/450 2 270/270 1498/1498 487/487 5/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 594 700 700 2 235-235 1314-1314 427-427 10 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 327/327 500/500 400/400 2 235/235 1314/1314 427/427 5/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 355 400 400 2 142-142 801-801 260-260 10 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 195/195 300/300 250/250 2 142/142 801/801 260/260 5/5 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 296 400 350 2 118-118 652-652 212-212 10 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 163/163 250/250 200/200 2 118/118 652/652 212/212 5/5 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 237 300 300 2 94-94 520-520 172-172 10 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 130/130 200/200 175/175 2 94/94 520/520 172/172 5/5 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 339 450 400 2 138-138 774-774 259-259 10 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 187/187 300/300 225/225 2 138/138 774/774 259/259 5/5 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 742 1000 1000 2 320-270 1845-1498 600-487 11 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 439/370 700/600 600/450 2 320/270 1845/1498 600/487 6/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 654 800 800 2 278-235 1556-1314 506-427 11 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 387/327 600/500 500/400 2 278/235 1556/1314 506/427 6/5 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 391 500 450 2 168-142 973-801 316-260 11 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 231/195 350/300 300/250 2 168/142 973/801 316/260 6/5 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 325 450 400 2 139-118 774-652 252-212 11 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 192/163 300/250 225/200 2 139/118 774/652 252/212 6/5 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 261 350 300 2 111-94 631-528 205-172 11 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 154/130 250/200 200/175 2 111/94 631/528 205/172 6/5 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 379 500 450 2 168-138 896-796 291-259 11 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 227/187 350/300 300/225 2 168/138 896/796 291/259 6/5 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 798 1000 1000 2 320-320 1845-1845 600-600 12 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 439/439 700/700 600/600 2 320/320 1845/1845 600/600 6/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 704 800 800 2 278-278 1556-1556 506-506 12 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 387/387 600/600 500/500 2 278/278 1556/1556 506/506 6/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 420 500 500 2 168-168 973-973 316-316 12 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 231/231 350/350 300/300 2 168/168 973/973 316/316 6/6 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 349 450 400 2 139-139 774-774 252-252 12 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 192/192 300/300 225/225 2 139/139 774/774 252/252 6/6 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 280 350 350 2 111-111 631-631 205-205 12 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 154/154 250/250 200/200 2 111/111 631/631 205/205 6/6 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 412 500 500 2 168-168 896-896 291-291 12 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 227/227 350/350 300/300 2 168/168 896/896 291/291 6/6 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 887 1200 1000 2 386-320 2156-1845 701-600 13 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 528/439 800/700 700/600 2 386/320 2156/1845 701/600 7/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 783 1000 1000 2 336-278 1756-1556 571-506 13 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 466/387 800/600 600/500 2 336/278 1756/1556 571/506 7/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 467 600 600 2 203-168 1060-973 345-316 13 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 278/231 450/350 350/300 2 203/168 1060/973 345/316 7/6 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 388 500 450 2 168-139 878-774 285-252 13 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 231/192 350/300 300/225 2 168/139 878/774 285/252 7/6 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 311 450 350 2 134-111 705-631 229-205 13 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 185/154 300/250 225/200 2 134/111 705/631 229/205 7/6 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 445 600 500 2 198-168 1089-896 354-291 13 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 267/227 450/350 350/300 2 198/168 1089/896 354/291 7/6 0.9 2.8 0.83
Power
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or RDE
(4)
Ckt1/Ckt 2
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
Control
VA (7)
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 71
Page 72

Installation - Electrical
Table 19 Unit Electrical Data for High Efficiency at High Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
Unit
Size
RTAC
200
RTAC
225
RTAC
250
RTAC
275
# of
Rated
Vo lt ag e
200/60/3 1 960 1200 1200 2 386-386 2156-2156 701-701 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 528/528 800/800 700/700 2 386/386 2156/2156 701/701 7/7 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 847 1000 1000 2 336-336 1756-1756 571-571 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 466/466 800/800 600/600 2 336/336 1756/1756 571/571 7/7 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 506 700 600 2 203-203 1060-1060 345-345 14 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 278/278 450/450 350/350 2 203/203 1060/1060 345/345 7/7 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 420 500 500 2 168-168 878-878 285-285 14 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 231/231 350/350 300/300 2 168/168 878/878 285/285 7/7 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 337 450 400 2 134-134 705-705 229-229 14 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 185/185 300/300 225/225 2 134/134 705/705 229/229 7/7 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 485 600 600 2 198-198 1089-1089 354-354 14 0.9 2.8 0.83
400/50/3 2 267/267 450/450 350/350 2 198/198 1089/1089 354/354 7/7 0.9 2.8 0.83
200/60/3 1 1051 1200 1200 2 459-358 2525-2156 821-701 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 626/522 1000/800 800/700 2 459/358 2525/2156 821/701 8/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 926 1200 1200 2 399-336 2126-1756 691-571 14 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 551/459 800/700 700/600 2 399/336 2126/1756 691/571 8/6 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 555 700 700 2 242-203 1306-1060 424-345 14 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 331/275 500/450 400/350 2 242/203 1306/1060 424/345 8/6 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 460 600 600 2 200-168 1065-878 346-285 14 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 274/228 450/350 350/300 2 200/168 1065/878 346/285 8/6 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 369 500 450 2 160-134 853-705 277-229 14 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 220/183 350/300 300/225 2 160/134 853/705 277/229 8/6 1.5 2.5 0.83
200/60/3 1 1137 1200 1200 2 459-459 2525-2525 821-821 16 1.5 6.5 0.83
200/60/3 2 626/626 1000/1000 800/800 2 459/459 2525/2525 821/821 8/8 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 1 1002 1200 1200 2 399-399 2126-2126 691-691 16 1.5 6.5 0.83
230/60/3 2 551/551 800/800 700/700 2 399/399 2126/2126 691/691 8/8 1.5 6.5 0.83
380/60/3 1 601 800 700 2 242-242 1306-1306 424-424 16 1.5 3.5 0.83
380/60/3 2 331/331 500/500 400/400 2 242/242 1306/1306 424/424 8/8 1.5 3.5 0.83
460/60/3 1 498 600 600 2 200-200 1065-1065 346-346 16 1.5 3.0 0.83
460/60/3 2 274/274 450/450 350/350 2 200/200 1065/1065 346/346 8/8 1.5 3.0 0.83
575/60/3 1 400 500 450 2 160-160 853-853 277-277 16 1.5 2.5 0.83
575/60/3 2 220/220 350/350 300/300 2 160/160 853/853 277/277 8/8 1.5 2.5 0.83
400/50/3 1 569 700 700 3 138-138-198 796-796-1089 259-259-354 16 0.9 2.8 1.2
400/50/3 2 339/265 450/450 400/350 3 138/138/198 796/796/1089 259/259/354 10/6 0.9 2.8 1.2
200/60/3 1 NA
200/60/3 2 798/522 1000/800 1000/700 3 320/320/386 1845/1845/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 704/459 800/700 800/600 3 278/278/336 1556/1556/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 420/275 500/450 500/350 3 168/168/203 973/973/1060 316/316/345 12/6 1.5 3.5 1.2
460/60/3 1 542 700 600 3 139-139-168 774-774-878 252-252-285 18 1.5 3.0 1.2
460/60/3 2 349/228 450/350 400/300 3 139/139/168 774/774/878 252/252/285 12/6 1.5 3.0 1.2
575/60/3 1 435 500 500 3 111-111-134 631-631-705 205-205-229 18 1.5 2.5 1.2
575/60/3 2 280/183 350/300 350/225 3 111/111/134 631/631/705 205/205/229 12/6 1.5 2.5 1.2
400/50/3 1 634 800 700 3 168-168-168 896-896-1089 291-291-354 18 0.9 2.8 1.2
400/50/3 2 412/265 500/450 500/350 3 168/168/168 896/896/1089 291/291/254 12/6 0.9 2.8 1.2
Power
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or RDE
(4)
Ckt1/Ckt 2
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
2156
1756
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
600/600/701 12/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
506/506/571 12/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
Control
VA (7)
72 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 73

Installation - Electrical
Table 19 Unit Electrical Data for High Efficiency at High Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
Unit
Size
RTAC
300
RTAC
350
RTAC
375
# of
Rated
Vol ta ge
200/60/3 1 NA
200/60/3 2 960522 1200/800 1200/700 3 386/386/386 2156/2156/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 847/459 1000/700 1000/600 3 336/336/336 1756/1756/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 506/275 700/450 600/350 3 203/203/203 1060/1060/
460/60/3 1 606 700 700 3 168-168-168 878-878-878 285-285-285 20 1.5 3.0 1.2
460/60/3 2 420/228 500/350 500/300 3 168/168/168 878/878/87/ 285/285/285 14/6 1.5 3.0 1.2
575/60/3 1 486 600 600 3 134-134-134 705-705-705 229-229-229 20 1.5 2.5 1.2
575/60/3 2 337/183 450/300 400/225 3 134/134/134 705/705/705 229/229/229 14/6 1.5 2.5 1.2
400/50/3 1 700 800 800 3 198-198-198 1089-1089-
400/50/3 2 485/265 600/450 600/350 3 198/198/198 1089/1089/
200/60/3 1 NA
200/60/3 2 798/798 10001000 10001000 4 320/320/320/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 704/704 800/800 800/800 4 278/278/278/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 420/420 500/500 500/500 4 168/168/168/
460/60/3 1 663 700 700 4 139-139-139-
460/60/3 2 349/349 450/450 400/400 4 139/139/139/
575/60/3 1 532 600 600 4 111-111-111-
575/60/3 2 280/280 350/350 350/350 4 111/111/111/
400/50/3 1 782 800 800 4 168-168-168-
400/50/3 2 412/412 500/500 500/500 4 168/168/168/
400/50/3 1 855 1000 1000 4 198-198-168-
400/50/3 2 485/412 600/500 600/500 4 198/198/168/
Power
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or RDE
(4)
Ckt1/Ckt 2
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
320
278
168
139
139
111
111
168
168
168
168
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
2156
1756
1060
1089
1089
1845/1845/
1845/1845
1556/1556/
1556/1556
973/973/973/
973
774-774-774774
774/774/774/
774
631-631-631631
631/631/631/
631
896-896-896896
896/896/896/
896
1089-1089896-896
1089/1089/
896/896
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
701/701/701 14/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
571/571/571 14/6 1.5 6.5 1.2
345/345/345 14/6 1.5 3.5 1.2
354-354-354 20 0.9 2.8 1.2
354/354/354 14/6 0.9 2.8 1.2
600/600/600/
600
506/506/506/
506
316/316/316/
316
252-252-252252
252/252/252/
252
205-205-205205
205/205/205/
205
291-291-291291
291/291/291/
291
354-354-291291
254/254/291/
291
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
12/12 1.5 6.5 1.2
12/12 1.5 6.5 1.2
12/12 1.5 3.5 1.2
2 4 1. 5 3 . 0 1. 2
12/12 1.5 3.0 1.2
2 4 1. 5 2 . 5 1. 2
12/12 1.5 2.5 1.2
24 0.9 2.8 1.59
12/12 0.9 2.8 1.59
26 0.9 2.8 1.59
14/12 0.9 2.8 1.59
Control
VA (7)
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 73
Page 74

Installation - Electrical
Table 19 Unit Electrical Data for High Efficiency at High Ambient Operation
Unit Wiring Motor Data
Max. Fuse,
HACR
Breaker or
MOP (11)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Rec. Time
Delay or RDE
(4)
Ckt1/Ckt 2
Unit
Size
RTAC
400
# of
Rated
Vo lt ag e
200/60/3 1 NA
200/60/3 2 960/960 1200/1200 12001200 4 386/386/386/
230/60/3 1 NA
230/60/3 2 847/847 1000/1000 1000/1000 4 336/336/336/
380/60/3 1 NA
380/60/3 2 505/506 700/700 600/600 4 203/203/203/
460/60/3 1 798 800 800 4 168-168-168-
460/60/3 2 420/420 500/500 500/500 4 168/168/168/
575/60/3 1 640 700 700 4 134-134-134-
575/60/3 2 337/337 450/450 400/400 4 134/134/134/
400/50/3 1 920 1000 1000 4 198-198-198-
400/50/3 2 485/485 600/600 600/600 4 198/198/198/
Power
Conns
(1)
MCA (3)
Ckt1/Ckt2
Notes:
1. As standard, 140-250 ton (60 Hz) units and 140-200 ton (50Hz) units have a single point power connection. Optional dual point power connections are
available. As standard, 275-500 ton (60Hz) units and 250-400 ton (50Hz) units have dual point power connections. Optional single point power connections are available on 380V, 460V 575V/50 Hz and 400V/50 Hz units.
2. Max Fuse or HACR type breaker = 225 percent of the largest compressor RLA plus 100 percent of the second compressor RLA, plus the sum of the
condenser fan FLA per NEC 440-22. (Use FLA per circuit, NOT FLA for the entire unit).
3. MCA - Minimum Circuit Ampacity - 125 percent of largest compressor RLA plus 100 percent of the second compressor RLA plus the sum of the
condenser fans FLAs per NEC 440-33.
4. RECOMMENDED TIME DELAY OR DUAL ELEMENT (RDE) FUSE SIZE: 150 percent of the largest compressor RLA plus 100 percent of the second
compressor RLA and the sum of the condenser fan FLAs.
5. RLA - Rated Load Amps - rated in accordance with UL Standard 1995.
6. Local codes may take precedence.
7. Control VA includes operational controls only. Does not include evaporator heaters.
8. XLRA - Locked Rotor Amps - based on full winding (x-line) start units. YLRA for wye-delta starters is ~1/3 of LRA of x-line units.
Voltage Utilization Range:
Rated Voltage 200/60/3 230/60/3 380/60/3 460/60/3 575/60/3 400/50/3
Use Range 180-220 208-254 342-418 414-506 516-633 360-440
9. A separate 115/60/1, 20 amp or 220/50/1, 15 amp customer provided power connection is required to power the evaporator heaters (1640 watts).
10. If factory circuit breakers are supplied with the chiller, then these values represent Maximum Overcurrent Protection (MOP).
Compressor (Each) Fans (Each)
Qty
RLA (5)
Ckt1/Ckt2
386
336
203
168
16/
134
134/
198
198
XLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
2156/2156/
2156/2156
1756/1756/
1756/1756
1060/1060/
1060/1060
878-878-878878
878/878/878/
878
705-705-705705
705/705/705/
705
1089-10891089-1089
1089/1089/
108 9
YLRA (8)
Ckt1/Ckt2
701/701/701/
701
571/571/571/
571
345/345/345/
345
285-285-285285
285/285/285/
285
229-229-229229
229/229/229/
229
354-354-354354
354/354/354/
354
Qty.
Ckt1/Ckt2 kW FLA
14/14 1.5 6.5 1.59
14/14 1.5 6.5 1.59
14/14 1.5 3.5 1.59
2 8 1. 5 3 . 0 1. 5 9
14/14 1.5 3.0 1.59
2 8 1. 5 2 . 5 1. 5 9
14/14 1.5 2.5 1.59
28 0.9 2.8 1.59
14/14 0.9 2.8 1.59
Control
VA (7)
74 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 75

Installation - Electrical
Installer-Supplied Components
Customer wiring interface connections are shown in the electrical schematics and
connection diagrams that are shipped with the unit. The installer must provide the
following components if not ordered with the unit:
• Power supply wiring (in conduit) for all field-wired connections.
• All control (interconnecting) wiring (in conduit) for field supplied devices.
• Fused-disconnect switches or circuit breakers.
• Power factor correction capacitors. (optional)
Power Supply Wiring
All power supply wiring must be sized and selected accordingly by the project
engineer in accordance with NEC Table 310-16.
WARNING
Hazardous Voltage w/Capacitors!
Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before
servicing. Follow proper lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power
cannot be inadvertently energized. For variable frequency drives or other
energy storing components provided by Trane or others, refer to the
appropriate manufacturer’s literature for allowable waiting periods for
discharge of capacitors. Verify with an appropriate voltmeter that all
capacitors have discharged. Failure to disconnect power and discharge
capacitors before servicing could result in death or serious injury.
Note: For additional information regarding the safe discharge of
capacitors, see PROD-SVB06A-EN or PROD-SVB06A-FR
All wiring must comply with local codes and the National Electrical Code. The
installing (or electrical) contractor must provide and install the system interconnecting
wiring, as well as the power supply wiring. It must be properly sized and equipped
with the appropriate fused disconnect switches.
The type and installation location(s) of the fused disconnects must comply with all
applicable codes.
CAUTION
Use Copper Conductors Only!
Unit terminals are not designed to accept other types of conductors.
Failure to use copper conductors may result in equipment damage.
Cut holes into the sides of the control panel for the appropriately-sized power wiring
conduits. The wiring is passed through these conduits and connected to the terminal
blocks, optional unit-mounted disconnects, or HACR type breakers. Refer to
31.
To provide proper phasing of 3-phase input, make connections as shown in field
wiring diagrams and as stated on the WARNING label in the starter panel. For
additional information on proper phasing, refer to “Unit Voltage Phasing.” Proper
equipment ground must be provided to each ground connection in the panel (one for
each customer-supplied conductor per phase).
Figure
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 75
Page 76

Knockouts for 30 volt
115 volt
field wiring
Installation - Electrical
115 volt field-provided connections (either control or power) are made through
knockouts on the lower left side of the panel (
required for each 115 volt power supply to the unit. Green lugs are provided for 115V
customer wiring.
Figure 31). Additional grounds may be
Cut holes for power
wiring THIS AREA
Figure 31 Starter Panel
Control Power Supply
The unit is equipped with a control power transformer; it is not necessary to provide
additional control power voltage to the unit.
All units are factory-connected for appropriate labeled voltages except for the 400V/
50Hz units which need the control power transformer (1T1) reconnected as noted
below.
NOTE: Important! As shipped, a normal 400 volt unit control power transformer is
wired on the 400 volt tap (H3). Reconnect the appropriate transformer wire lead 126A
to the tap (H2) for 380V/50Hz power supply or lead 126A to the tap H4 for the 415V/
50 Hz power supply. It is also necessary to adjust the “unit voltage” setting using
TechView (Configuration-Custom Tab).
Heater Power Supply and Convenience Outlet (Packaged Units Only)
The evaporator shell is insulated from ambient air and protected from freezing
temperatures by two thermostatically-controlled immersion heaters and two strip
heaters. Whenever the water temperature drops to approximately 37°F (2.8°C), the
thermostat energizes the heaters. The heaters will provide protection from ambient
temperatures down to -20°F (-29°C).
It is required to provide an independent power source (115V 60Hz-20 amp, 220V
50Hz-15 amp), with a fused-disconnect. The heaters are factory-wired back to the unit
control panel.
76 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 77

Installation - Electrical
CAUTION
Heat Tape!
Control panel main processor does not check for loss of power to the
heat tape nor does it verify thermostat operation. A qualified technician
must verify power to the heat tape and confirm operation of the heat
tape thermostat to avoid catastrophic damage to the evaporator.
A convenience outlet is also optional, which shares the same power supply as the
heaters on 140-250 ton units. Be aware that when the heater is operating, the
convenience outlet amperage draw will be reduced accordingly.
NOTE: The convenience outlet is optional. The heaters are required.
Interconnecting Wiring
Chilled Water Flow (Pump) Interlock
The Model RTAC Series R® chiller requires a field-supplied control voltage contact
input through a flow proving switch 5S1 and an auxiliary contact 5K1 AUX. Connect
the proving switch and auxiliary contact to 1TB5-8 and 1U11 J3-2. Refer to the field
wiring for details. The auxiliary contact can be BAS signal, starter contactor auxiliary.
or any signal which indicates the pump is running. A flow switch is still required and
cannot be omitted.
Chilled Water Pump Control
An evaporator water pump output relay closes when the chiller is given a signal to go
into the Auto mode of operation from any source. The contact is opened to turn off
the pump in the event of most machine level diagnostics to prevent the build up of
pump heat.
CAUTION
Evaporator Damage!
IMPORTANT: ALL unit chilled water pumps must be controlled by the
Trane CH530 to avoid catastrophic damage to the evaporator due to
freezing. Refer to RLC-PRB012-EN.
The relay output from 1U10 is required to operate the Evaporator Water Pump (EWP)
contactor. Contacts should be compatible with 115/240 VAC control circuit. The EWP
relay operates in different modes depending on CH530 or Tracer commands, if
available, or service pumpdown (See maintenance section). Normally, the EWP relay
follows the AUTO mode of the chiller. Whenever the chiller has no diagnostics and is
in the AUTO mode, regardless of where the auto command is coming from, the
normally open relay is energized. When the chiller exits the AUTO mode, the relay is
timed open for an adjustable (using TechView) 0 to 30 minutes. The non-AUTO modes
in which the pump is stopped, include Reset (88), Stop (00), External Stop (100),
Remote Display Stop (600), Stopped by Tracer (300), Low Ambient Run Inhibit (200),
and Ice Building complete (101).
Regardless of whether the chiller is allowed to control the pump on a full-time basis, if
the MP calls for a pump to start and water does not flow, the evaporator may be
damaged catastrophically. It is the responsibility of the installing contractor and/or
the customer to ensure that a pump will start when called upon by the chiller
controls.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 77
Page 78

Installation - Electrical
Table 20 Pump Relay Operation
Chiller Mode Relay Operation
Auto Instant close
Ice Building Instant close
Tracer Override Close
Stop TImed Open
Ice Complete Instant Open
Diagnostics Instant Open
NOTE: Exceptions are listed below.
When going from Stop to Auto, the EWP relay is energized immediately. If evaporator
water flow is not established in 4 minutes and 15 sec., the CH530 de-energizes the
EWP relay and generates a non-latching diagnostic. If flow returns (e.g. someone else
is controlling the pump), the diagnostic is cleared, the EWP is re-energized, and
normal control resumed.
If evaporator water flow is lost once it had been established, the EWP relay remains
energized and a non-latching diagnostic is generated. If flow returns, the diagnostic is
cleared and the chiller returns to normal operation.
In general, when there is either a non-latching or latching diagnostic, the EWP relay is
turned off as though there was a zero time delay. Exceptions (see above table)
whereby the relay continues to be energized occur with:
A Low Chilled Water Temp. diagnostic (non-latching) (unless also accompanied by an
Evap Leaving Water Temperature Sensor Diagnostic)
or
A starter contactor interrupt failure diagnostic, in which a compressor continues to
draw current even after commanded to have shutdown
or
A Loss of Evaporator Water Flow diagnostic (non-latching) and the unit is in the AUTO
mode, after initially having proven evaporator water flow.
Alarm and Status Relay Outputs (Programmable Relays)
A programmable relay concept provides for enunciation of certain events or states of
the chiller, selected from a list of likely needs, while only using four physical output
relays, as shown in the field wiring diagram. The four relays are provided (generally
with a Quad Relay Output LLID) as part of the Alarm Relay Output Option. The relay’s
contacts are isolated Form C (SPDT), suitable for use with 120 VAC circuits drawing
up to 2.8 amps inductive, 7.2 amps resistive, or 1/3 HP and for 240 VAC circuits
drawing up to 0.5 amp resistive.
The list of events/states that can be assigned to the programmable relays can be
found in
Table 21 Alarm and Status Relay Output Configuration Table
Description
Alarm - Latching This output is true whenever there is any active diagnostic that requires a manual reset to clear, that
affects either the Chiller, the Circuit, or any of the Compressors on a circuit. This classification does not
include informational diagnostics.
Alarm - Auto Reset This output is true whenever there is any active diagnostic that could automatically clear, that affects
either the Chiller, the Circuit, or any of the Compressors on a circuit. This classification does not include
informational diagnostics.
Alarm This output is true whenever there is any diagnostic affecting any component, whether latching or auto-
matically clearing. This classification does not include informational diagnostics
Table 21. The relay will be energized when the event/state occurs.
78 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 79

Installation - Electrical
Table 21 Alarm and Status Relay Output Configuration Table
Description
Alarm Ckt 1 This output is true whenever there is any diagnostic effecting Refrigerant Circuit 1, whether latching or
Alarm Ckt 2 This output is true whenever there is any diagnostic affecting Refrigerant Circuit 2 whether latching or
Chiller Limit Mode
(with a 20 minute filter)
Circuit 1 Running This output is true whenever any compressors are running (or commanded to be running) on Refrigerant
Circuit 2 Running This output is true whenever any compressors are running (or commanded to be running) on Refrigerant
Chiller Running This output is true whenever any compressors are running (or commanded to be running) on the chiller
Maximum Capacity
(software 18.0 or
later)
automatically clearing, including diagnostics affecting the entire chiller. This classification does not
include informational diagnostics.
automatically clearing, including diagnostics effecting the entire chiller. This classification does not
include informational diagnostics.
This output is true whenever the chiller has been running in one of the Unloading types of limit modes
(Condenser, Evaporator, Current Limit or Phase Imbalance Limit) continuously for the last 20 minutes.
Circuit 1, and false when no compressors are commanded to be running on that circuit.
Circuit 2, and false when no compressors are commanded to be running on that circuit.
and false when no compressors are commanded to be running on the chiller.
This output is true whenever the chiller has reached maximum capacity or had reached its maximum
capacity and since that time has not fallen below 70% average current relative to the rated ARI current
for the chiller. The output is false when the chiller falls below 70% average current and, since that time,
had not reestablished maximum capacity.
Relay Assignments Using TechView
CH530 Service Tool (TechView) is used to install the Alarm and Status Relay Option
package and assign any of the above list of events or status to each of the four relays
provided with the option. The relays to be programmed are referred to by the relay’s
terminal numbers on the LLID board 1U12.
The default assignments for the four available relays of the RTAC Alarm and Status
Package Option are:
Table 22 Default Assignments
Relay
Relay 1 Terminals J2 -12,11,10: Alarm
Relay 2 Terminals J2 - 9,8,7: Chiller Running
Relay 3 Terminals J2-6,5,4: Maximum Capacity (software 18.0 or later)
Relay 4 Terminals J2-3,2,1: Chiller Limit
If any of the Alarm/Status relays are used, provide electrical power, 115 VAC with
fused-disconnect to the panel and wire through the appropriate relays (terminals on
1U12 (EUR=A4-5)). Provide wiring (switched hot, neutral, and ground connections) to
the remote annunciation devices. Do not use power from the chiller’s control panel
transformer to power these remote devices. Refer to the field diagrams which are
shipped with the unit.
Low Voltage Wiring
The remote devices described below require low voltage wiring. All wiring to and
from these remote input devices to the Control Panel must be made with shielded,
twisted pair conductors. Be sure to ground the shielding only at the panel.
To prevent control malfunctions, do not run low voltage wiring (<30 V) in
conduit with conductors carrying more than 30 volts.
Emergency Stop
CH530 provides auxiliary control for a customer specified/installed latching trip out.
When this customer-furnished remote contact 5K14 is provided, the chiller will run
normally when the contact is closed. When the contact opens, the unit will trip on a
manually resettable diagnostic. This condition requires manual reset at the chiller
switch on the front of the control panel.
Connect low voltage leads to terminal strip locations on 1U4. Refer to the field
diagrams that are shipped with the unit.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 79
Page 80

Installation - Electrical
Silver or gold-plated contacts are recommended. These customer-furnished contacts
must be compatible with 24 VDC, 12 mA resistive load.
External Auto/Stop
If the unit requires the external Auto/Stop function, the installer must provide leads
from the remote contacts 5K15 to the proper terminals of the LLID 1U4 on the control
panel.
The chiller will run normally when the contacts are closed. When either contact
opens, the compressor(s), if operating, will go to the RUN:UNLOAD operating mode
and cycle off. Unit operation will be inhibited. Closure of the contacts will permit the
unit to return to normal operation.
Field-supplied contacts for all low voltage connections must be compatible with dry
circuit 24 VDC for a 12 mA resistive load. Refer to the field diagrams that are shipped
with the unit.
External Circuit Lockout – Circuit #1 and Circuit #2
CH530 provides auxiliary control of a customer specified or installed contact closure,
for individual operation of either Circuit #1 or #2. If the contact is closed, the
refrigerant circuit will not operate 1K15 and 1K16.
Upon contact opening, the refrigerant circuit will run normally. This feature is used to
restrict total chiller operation, e.g. during emergency generator operations.
Connections to 1U5 are shown in the field diagrams that are shipped with the unit.
These customer-supplied contact closures must be compatible with 24 VDC, 12 mA
resistive load. Silver or gold plated contacts are recommended.
Ice Building Option
CH530 provides auxiliary control for a customer specified/installed contact closure for
ice building if so configured and enabled. This output is known as the Ice Building
Status Relay. The normally open contact will be closed when ice building is in
progress and open when ice building has been normally terminated either through Ice
Termination setpoint being reached or removal of the Ice Building command. This
output is for use with the ice storage system equipment or controls (provided by
others) to signal the system changes required as the chiller mode changes from “ice
building” to “ice complete”. When contact 5K18 is provided, the chiller will run
normally when the contact is open.
CH530 will accept either an isolated contact closure (External Ice Building command)
or a Remote Communicated input (Tracer) to initiate and command the Ice Building
mode.
CH530 also provides a “Front Panel Ice Termination Setpoint”, settable through
TechView, and adjustable from 20 to 31°F (-6.7 to -0.5°C) in at least 1°F (1°C)
increments.
NOTE: When in the Ice Building mode, and the evaporator entering water temperature drops below the ice termination setpoint, the chiller terminates the Ice Building
mode and changes to the Ice Building Complete Mode.
CAUTION
Evaporator Damage!
Freeze inhibitor must be adequate for the leaving water temperature.
Failure to do so will result in damage to system components.
Techview must also be used to enable or disable Ice Machine Control. This setting
does not prevent the Tracer from commanding Ice Building mode.
Upon contact closure, the CH530 will initiate an ice building mode, in which the unit
runs fully loaded at all times. Ice building shall be terminated either by opening the
contact or based on the entering evaporator water temperature. CH530 will not
80 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 81

Installation - Electrical
permit the ice building mode to be reentered until the unit has been switched out of
ice building mode (open 5K18 contacts) and then switched back into ice building
mode (close 5K18 contacts.)
In ice building, all limits (freeze avoidance, evaporator, condenser, current) will be
ignored. All safeties will be enforced.
If, while in ice building mode, the unit gets down to the freeze stat setting (water or
refrigerant), the unit will shut down on a manually resettable diagnostic, just as in
normal operation.
Connect leads from 5K18 to the proper terminals of 1U7. Refer to the field diagrams
which are shipped with the unit.
Silver or gold-plated contacts are recommended. These customer furnished contacts
must be compatible with 24 VDC, 12 mA resistive load.
External Chilled Water Setpoint (ECWS) Option
The CH530 provides inputs that accept either 4-20 mA or 2-10 VDC signals to set the
external chilled water setpoint (ECWS). This is not a reset function. The input defines
the set point. This input is primarily used with generic BAS (building automation
systems). The chilled water setpoint set via the DynaView or through digital
communication with Tracer (Comm3). The arbitration of the various chilled water
setpoint sources is described in the flow charts at the end of the section.
The chilled water setpoint may be changed from a remote location by sending either a
2-10 VDC or 4-20 mA signal to the 1U6, terminals 5 and 6 LLID. 2-10 VDC and 4-20
mA each correspond to a 10 to 65°F (-12 to 18°C) external chilled water setpoint.
The following equations apply:
Voltage Signal Current Signal
As generated from external
source
As processed by CH530 ECWS=6.875*(VDC)-3.75 ECWS=3.4375(mA)-3.75
VDC=0.1455*(ECWS)+0.5454 mA=0.2909(ECWS)+1.0909
If the ECWS input develops an open or short, the LLID will report either a very high or
very low value back to the main processor. This will generate an informational
diagnostic and the unit will default to using the Front Panel (DynaView) Chilled Water
Setpoint.
TechView Service Tool is used to set the input signal type from the factory default of
2-10 VDC to that of 4-20 mA. TechView is also used to install or remove the External
Chilled Water Setpoint option as well as a means to enable and disable ECWS.
External Current Limit Setpoint (ECLS) Option
Similar to the above, the CH530 also provides for an optional External Current Limit
Setpoint that will accept either a 2-10 VDC (default) or a 4-20 mA signal. The Current
Limit Setting can also be set via the DynaView or through digital communication with
Tracer (Comm 3). The arbitration of the various sources of current limit is described in
the flow charts at the end of this section. The External Current Limit Setpoint may be
changed from a remote location by hooking up the analog input signal to the 1 U6
LLID terminals 2 and 3. Refer to the following paragraph on Analog Input Signal
Wiring Details. The following equations apply for ECLS:
Voltage Signal Current Signal
As generated from external
source
As processed by UCM %=7.5*(VDC)+45.0 %=3.75*(mA)+45.0
VDC+0.133*(%)-6.0 mA=0.266*(%)-12.0
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 81
Page 82

Installation - Electrical
If the ECLS input develops an open or short, the LLID will report either a very high or
very low value back to the man processor. This will generate an informational
diagnostic and the unit will default to using the Front Panel (DynaView) Current Limit
Setpoint.
The TechView Service Tool must be used to set the input signal type from the factory
default of 2-10 VDC to that of 4-20 mA current. TechView must be also be used to
install or remove the External Current Limit Setpoint Option for field installation, or
can be used to enable or disable the feature (if installed).
ECLS and ECWS Analog Input Signal Wiring Details:
Both the ECWS and ECLS can be connected and setup as either a 2-10 VDC (factory
default), 4-20 mA, or resistance input (also a form of 4-2OmA) as indicated below.
Depending on the type to be used, the TechView Service Tool must be used to
configure the LLID and the MP for the proper input type that is being used. This is
accomplished by a setting change on the Custom Tab of the Configuration View
within TechView.
The J2-3 and J2-6 terminal is chassis grounded and terminal J2- 1 and J2-4 can be
used to source 12 VDC. The ECLS uses terminals J2-2 and J2-3. ECWS uses
terminals J2-5 and J2-6. Both inputs are only compatible with high-side current
sources.
Figure 32 Wiring Examples for ECLS and ECWS
Chilled Water Reset (CWR)
CH530 resets the chilled water temperature set point based on either return water
temperature, or outdoor air temperature. Return Reset is standard, Outdoor Reset is
optional.
The following shall be selectable:
• One of three Reset Types: None, Return Water Temperature Reset, Outdoor Air
Temperature Reset, or Constant Return Water Temperature Reset.
• Reset Ratio Set Points.
For outdoor air temperature reset there shall be both positive and negative reset
ratio's.
82 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 83

Installation - Electrical
• Start Reset Set Points.
• Maximum Reset Set Points.
The equations for each type of reset are as follows:
Return
CWS' = CWS + RATIO (START RESET - (TWE - TWL))
and CWS' > or = CWS
and CWS' - CWS < or = Maximum Reset
Outdoor
CWS' = CWS + RATIO * (START RESET - TOD)
and CWS' > or = CWS
and CWS' - CWS < or = Maximum Reset
where
CWS' is the new chilled water set point or the "reset CWS"
CWS is the active chilled water set point before any reset has occurred, e.g. normally
Front Panel, Tracer, or ECWS
RESET RATIO is a user adjustable gain
START RESET is a user adjustable reference
TOD is the outdoor temperature
TWE is entering evap. water temperature
TWL is leaving evap. water temperature
MAXIMUM RESET is a user adjustable limit providing the maximum amount of reset.
For all types of reset, CWS' - CWS < or = Maximum Reset.
Reset Type Reset Ratio
Range
Return: 10 to 120% 4 to 30 F 0 to 20 F 1% 1% 50%
Outdoor 80 to -80% 50 to 130 F 0 to 20 F 1% 1% 10%
Start Reset
Range
(2.2 to 16.7 C) (0.0 to 11.1 C)
(10 to 54.4 C) (0.0 to 11.1 C)
Maximum Reset
Range
Increment
English Units
Increment
SI Units
Factory Default
Va lu e
In addition to Return and Outdoor Reset, the MP provides a menu item for the
operator to select a Constant Return Reset. Constant Return Reset will reset the
leaving water temperature set point so as to provide a constant entering water
temperature. The Constant Return Reset equation is the same as the Return Reset
equation except on selection of Constant Return Reset, the MP will automatically set
Ratio, Start Reset, and Maximum Reset to the following.
RATIO = 100%
START RESET = Design Delta Temp.
MAXIMUM RESET = Design Delta Temp.
The equation for Constant Return is then as follows:
CWS' = CWS + 100% (Design Delta Temp. - (TWE - TWL))
and CWS' > or = CWS
and CWS' - CWS < or = Maximum Reset
When any type of CWR is enabled, the MP will step the Active CWS toward the
desired CWS' (based on the above equations and setup parameters) at a rate of 1
degree F every 5 minutes until the Active CWS equals the desired CWS'. This
applies when the chiller is running.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 83
Page 84

Installation - Electrical
When the chiller is not running the CWS is reset immediately (within one minute) for
Return Reset and at a rate of 1 degree F every 5 minutes for Outdoor Reset. The
chiller will start at the Differential to Start value above a fully reset CWS or CWS' for
both Return and Outdoor Reset.
Communications Interface options
Optional Tracer Communications Interface
This option allows the Tracer CH530 controller to exchange information (e.g. operating
setpoints and Auto/Standby commands) with a higher-level control device, such as a
Tracer Summit or a multiple-machine controller. A shielded, twisted pair connection
establishes the bi-directional communications link between the Tracer CH530 and the
building automation system.
To prevent control malfunctions, do not run low voltage wiring (<30 V) in
conduit with conductors carrying more than 30 volts.
Field wiring for the communication link must meet the following requirements:
• All wiring must be in accordance with the NEC and local codes.
• Communication link wiring must be shielded, twisted pair wiring (Belden 8760 or
equivalent). See the table below for wire size selection:
Table 23 Wire Size
Wire Size Maximum Length of Communication Wire
14 AWG (2.5 mm2) 5,000 FT (1525 m)
16 AWG (1.5 mm
18 AWG (1.0 mm
2
) 2,000 FT (610 m)
2
) 1,000 FT (305 m)
• The communication link cannot pass between buildings.
• All units on the communication link can be connected in a “daisy chain”
configuration.
LonTalk Communications Interface for Chillers (LCI-C)
CH530 provides an optional LonTalk Communication Interface (LCI-C) between the
chiller and a Building Automation System (BAS). An LCI-C LLID shall be used to
provide "gateway" functionality between a LonTalk compatible device and the Chiller.
The inputs/outputs include both mandatory and optional network variables as
established by the LonMark Functional Chiller Profile 8040.
Installation Recommendations
• 22 AWG Level 4 unshielded communication wire recommended for most LCI-C
installations
• LCI-C link limits: 4500 feet, 60 devices
• Termination resistors are required
– 105 ohms at each end for Level 4 wire
– 82 ohms at each end for Trane "purple" wire
• LCI-C topology should be daisy chain
• Zone sensor communication stubs limited to 8 per link, 50 feet each (maximum)
• One repeater can be used for an additional 4500 feet, 60 devices, 8
communication stubs
84 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 85

Installation - Electrical
Table 24 LonTalk Points List
LonTalk Communications Interface
Inputs Variable type SNVT_Type
Chiller Enable/Disable binary start(1)/stop(0) SNVT_switch
Chilled Water Setpoint analog temperature SNVT_temp_p
Current Limit Setpoint analog % current SNVT_lev_percent
Chiller Mode Note 1 SNVT_hvac_mode
Outputs Variable type SNVT_Type
Outputs Variable type SNVT_Type
Chiller On/Off binary on(1)/off(0) SNVT_switch
Active Chilled Water Setpoint analog temperature SNVT_temp_p
Percent RLA analog % current SNVT_lev_percent
Active Current Limit Setpoint analog % current SNVT_lev_percent
Leaving Chilled Water Temperature analog temperature SNVT_temp_p
Entering Chilled Water Temperature analog temperature SNVT_temp_p
Entering Condenser Water Temperature analog temperature SNVT_temp_p
Leaving Condenser Water Temperature analog temperature SNVT_temp_p
Alarm Description Note 2 SNVT_str_asc
Chiller Status Note 3 SNVT_chlr_status
Note 1: Chiller Mode is used to place the chiller into an alternate mode; Cool or Ice Build
Note 2: Alarm Description denotes alarm severity and target.
Severity: no alarm, warning, normal shutdown, immediate shutdown
Target: Chiller, Platform, Ice Building (Chiller is refrigerant circuit and Platform is control circuit)
Note 3: Chiller Status describes Chiller Run Mode and Chiller Operating Mode.
Run Modes: Off, Starting, Running, Shutting Down
Operating Modes: Cool, Ice Build
States: Alarm, Run Enabled, Local Control, Limited, CHW Flow, Cond Flow
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 85
Page 86

Operating Principles
This section contains an overview of the operation and maintenance of RTAC units
equipped with CH530 control systems. It describes the overall operating principles of
the RTAC design.
Refrigeration Cycle
The refrigeration cycle of the RTAC chiller is similar to that of the RTAA air cooled
water chiller. The exception is that the evaporating and condensing temperatures have
been increased to allow for optimization of the chiller and reduced foot print. The
refrigeration cycle is represented in the pressure enthalpy diagram in
state points are indicated on the figure. The cycle for the full load ARI design point is
represented in the plot.
Figure 33. Key
3
39 F
R134a
106 F
(4 C)
126 F
(41 C)
137 F
(52 C)
600
500
200
3b
P (psia)
100
50
30
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
4b
4
h (btu/lb)
Figure 33 Pressure Enthalpy (P-h) diagram of RTAC chiller
The RTAC chiller uses a shell and tube evaporator design with refrigerant evaporating
on the shell side and water flowing inside tubes having enhanced surfaces (states 4
to 1). The suction lines and bolt pads are designed to minimize pressure drop.(states
1 to 1b). The compressor is a twin-rotor helical rotary compressor designed similarly
to the compressors offered in other Trane Screw Compressor Based Chillers (states
1b to 2). The discharge lines include a highly efficient oil separation system that
virtually removes all oil from the refrigerant stream going to the heat exchangers
(states 2 to 2b). De-superheating, condensing and sub-cooling is accomplished in a fin
and tube air cooled heat exchanger where refrigerant is condensed in the tube (states
2b to 3b). Refrigerant flow through the system is balanced by an electronic expansion
valve (states 3b to 4).
(58 C)
2
2b
1
1b
86 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 87

Operating Principles
Figure 34 System Schematic
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 87
Page 88

Operating Principles
Refrigerant R134a
The RTAC chiller uses environmentally friendly R134a. Trane believes that responsible
refrigerant practices are important to the environment, our customers, and the air
conditioning industry. All technicians who handle refrigerants must be certified. The
Federal Clean Air Act (Section 608) sets forth the requirements for handling,
reclaiming, recovering and recycling of certain refrigerants and the equipment that is
used in these service procedures. In addition, some states or municipalities may have
additional requirements that must also be adhered to for responsible management of
refrigerants. Know the applicable laws and follow them.
R134a is a medium pressure refrigerant. It may not be used in any condition that
would cause the chiller to operate in a vacuum without a purge system. RTAC is not
equipped with a purge system. Therefore, the RTAC chiller may not be operated in a
condition that would result in a saturated condition in the chiller of –15°F (-26°C) or
lower.
R134a requires the use of specific POE oils as designated on the unit nameplate.
Important! The RTAC units must only operate with R-134a and Trane Oil 00048.
Compressor
The compressor is a semi-hermetic, direct-drive rotary type compressor. Each
compressor has only four moving parts: two rotors that provide compression and
male and female load-control valves. The male rotor is attached to the motor and the
female rotor is driven by the male rotor. The rotors and motor are supported by
bearings.
The helical rotary compressor is a positive displacement device. Refrigerant vapor
from the evaporator is drawn into the suction opening of the compressor (state 1b),
through a suction strainer screen across the motor (which provides motor cooling)
and into the intake of the compressor rotors. The gas is then compressed and
discharged through a check valve and into the discharge line (state 2).
There is no physical contact between the rotors and the compressor housing. The
rotors contact each other at the point where the driving action between the male and
female rotors occurs. Oil is injected into the rotors of the compressor, coating the
rotors and the compressor housing interior. Although this oil does provide rotor
lubrication, its primary purpose is to seal the clearance spaces between the rotors
and compressor housing. A positive seal between these internal parts enhances
compressor efficiency by limiting leakage between the high pressure and low
pressure cavities.
Capacity control is accomplished by means of a female step load-control valve and a
male control valve. The female step valve is the first stage of loading after the
compressor starts and the last stage of unloading before the compressor shuts
down. The male control valve is positioned by a piston cylinder along the length of the
male rotor. Compressor capacity is dictated by the position of the loading valve
relative to the rotors. When the valve slides toward the discharge end of the rotors
compressor capacity is reduced.
Condenser and Subcooler
The condenser and subcooler are similar to the condenser used in RTAA chillers. The
heat exchanger consists of 3/8” tubes that contain the refrigerant, large fins that are
in the air flow and fans that draw air through the fins. Heat is transferred from the
refrigerant through the tubes and fins to the air.
High pressure gas from the compressor enters the tubes of the condenser through a
distribution header (state 2b). As refrigerant flows through the tubes, the heat of
compression and cooling load are rejected to the air. In this process the refrigerant is
de-superheated, condensed (states 2b to 3) and finally subcooled (states 3 to 3b) to a
temperature slightly above the ambient air temperature. The subcooled liquid
refrigerant is collected in the leaving header where it is transferred to the liquid line
(state 3b).
A controls algorithm always runs as many fans as possible without reducing the
differential pressure (discharge minus suction) below the setpoint (60 psid or 4.2 bar).
If a warm enough ambient is sensed, all the fans will run. If the ambient is cooler,
88 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 89

Operating Principles
some fans are shut off to maintain the pressure differential. Fan staging depends on
the chiller load, evaporator pressure, condenser effectiveness, ambient temperature,
and numbers and sizes of fans installed on the circuit.
The algorithm pre-starts fans (based on ambient and water temperatures) when a
circuit starts the compressor. (For rare conditions such as during some pull-downs, a
steady fan state would either violate the 60 psid (4.2 bar) setpoint or cause a high
pressure cut-out; in those conditions a fan will cycle on and off.)
For up to two minutes after chiller start-up, the setpoint is 35 psi (2.45 bar) difference,
and then before the controls adjust gradually over half a minute up to 60 psi (4.2 bar).
Expansion Valve
Pressure drop occurs in an electronic expansion valve. The unit controller (CH530)
uses the valve to regulate the flow through the liquid line to match the flow produced
by the compressor. The valve has a variable orifice that is modulated by a stepper
motor.
High pressure, subcooled liquid refrigerant enters the expansion valve from the liquid
line. As refrigerant passes through the valve the pressure is dropped substantially,
which results in vaporization of some of the refrigerant. The heat of vaporization is
supplied by the two phase mixture resulting in low temperature low pressure
refrigerant which is supplied to the evaporator (state 4) to provide cooling.
Evaporator
The evaporator is composed of a liquid-vapor distributor and falling film evaporator.
A liquid-vapor refrigerant mixture enters the distributor (state 4). The mixture is
distributed over the length of the evaporator tubes (state 4b). Liquid is evenly
distributed over the length of the evaporator tubes by the two-phase distribution
system. A portion of the liquid boils as it falls by gravity from tube to tube, wetting all
the tubes of the evaporator. To ensure that the tubes at the bottom of the evaporator
do not experience “dry out,” a liquid pool is maintained in the bottom few inches of
the bundle. Tubes located in the bottom of the evaporator will evaporate the liquid
refrigerant by boiling (pool boiling).
Heat is transferred from the water or glycol inside the tubes to the liquid refrigerant
as the film of refrigerant evaporates on the surface of the tube. Thin film heat transfer
requires a smaller temperature difference for a given amount of heat transfer than
nucleate boiling, which is the heat transfer process used in flooded evaporators.
Hence, efficiency is enhanced by the use of falling film evaporation. Additionally, the
evaporator requires less refrigerant than a comparable flooded evaporator and the
evaporator boils the entire refrigerant supply at constant pressure. Refrigerant vapor
exits the evaporator through the suction line (state 1).
Oil System
Screw compressors require large quantities of oil for lubricating and sealing the rotors
and lubricating the bearings. This oil is mixed with refrigerant at the discharge of the
compressor. To enhance the performance of the heat exchanger surfaces an oil
separation system is placed into the discharge line. The oil separator is located
between the compressor and the condenser. It separates oil using highly efficient
centrifugal force. Approximately 99.5% of the oil is removed from the refrigerant in
the separator.
Oil that is removed from the refrigerant falls by gravity into the oil sump. This oil is
directed back to the compressor through the oil lines. Internal to the compressor is a
high efficiency filter to clean the oil before it is delivered to the rotors and bearings.
Once oil is injected into the compressor rotors it mixes with the refrigerant again and
is delivered back to the discharge line.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 89
Page 90

Operating Principles
Oil that gets past the oil separators flows through the condenser, subcooler and
expansion valve into the evaporator. This oil is collected in the pool of refrigerant that
is maintained in the bottom of the evaporator. A small amount of oil and refrigerant
from this pool (state 4b) is returned through a line that is connected to the
compressor down stream of the motor. This oil and refrigerant mixes with the
refrigerant vapor that was drawn out of the evaporator, prior to injection into the
compressor rotors.
C o n d e n s e r
E v a p o r a t o r
R e f r i g e r a n t
P r e s s u r e
T r a n s d u c e r
P
E
E v a p o r a t o r
O i l R e t u r n L i n e F i l t e r
E v a p o r a t o r
E X V
C o n d e n s e r
R e f r i g e r a n t
P r e s s u r e
T r a n s d u c e r
P
C
B e a r i n g a n d R o t o r
R e s t r i c t o r s a n d
O i l i n j e c t i o n
K E Y
R e f r i g e r a n t w i t h
s m a l l a m o u n t o f O i l
R e f r i g e r a n t & O i l M i x t u r e
( r e f r i g e r a n t v a p o r a n d o i l )
O i l R e c o v e r y S y s t e m
i g e r a n t a n d o i l )
( l i q u i d r e f r
P r i m a r y O i l S y s t e m
Figure 35 RTAC Oil System
C o m p r e s s o r
I n t e r m e d i a t e
O i l P r e s s u r e
T r a n s d u c e r
C o m p r e s s o r
H e a t e r
I n t e r n a l
C o m p r e s s o r
O i l F i l t e r
C o m p r e s s o r O i l
T e m p e r a t u r e S e n s o r
P
I
S e p a r a t o r
M a n u a l
S e r v i c e
V a l v e
O i l
O i l S e p a r a t o r
S u m p H e a t e r
O p t i o n a l O i l
C o o l e r
90 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 91

Controls Interface
CH530 Communications Overview
The Trane CH530 control system that runs the chiller consists of several elements:
• The main processor collects data, status, and diagnostic information and communicates commands to the starter module and the LLID (for Low Level Intelligent
Device) bus. The main processor has an integral display (DynaView).
• Higher level modules (e.g. starter) exist only as necessary to support system level
control and communications. The starter module provides control of the starter
when starting, running, and stopping the chiller motor. It also processes its own
diagnostics and provides motor and compressor protection.
• Low level intelligent device (LLID) bus. The main processor communicates to
each input and output device (e.g. temperature and pressure sensors, low voltage
binary inputs, analog input/output) all connected to a four-wire bus, rather than
the conventional control architecture of signal wires for each device.
• The communication interface to a building automation system (BAS).
• A service tool to provide all service/maintenance capabilities.
Main processor and service tool (TechView) software is downloadable from
www.Trane.com. The process is discussed later in this section under TechView Interface.
DynaView provides bus management. It has the task of restarting the link, or filling in
for what it sees as “missing” devices when normal communications has been
degraded. Use of TechView may be required.
The CH530 uses the IPC3 protocol based on RS485 signal technology and communicating at 19.2 Kbaud to allow 3 rounds of data per second on a 64-device network. A
typical four-compressor RTAC will have around 50 devices.
Most diagnostics are handled by the DynaView. If a temperature or pressure is
reported out of range by a LLID, the DynaView processes this information and calls
out the diagnostic. The individual LLIDs are not responsible for any diagnostic func
tions. The only exception to this is the Starter module.
-
NOTE: It is imperative that the CH530 Service Tool (TechView) be used to facilitate
the replacement of any LLID or reconfigure any chiller component. TechView is
discussed later in this section.
Controls Interface
Each chiller is equipped with a DynaView interface. The DynaView has the capability
to display information to the operator including the ability to adjust settings. Multiple
screens are available and text is presented in multiple languages as factory-ordered or
can be easily downloaded from www.trane.com.
TechView can be connected to either the DynaView module and provides further data,
adjustment capabilities, diagnostics information using downloadable software.
DynaView Interface
The DynaView share the same enclosure design: weatherproof and durable plastic for
use as a stand-alone device on the outside of the unit or mounted nearby.
The display on DynaView is a 1/4 VGA display with a resistive touch screen and an
LED backlight. The display area is approximately 4 inches wide by 3 inches high
(102mm x 60mm).
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 91
Page 92

Controls Interface
Figure 36 DynaView
Key Functions
In this touch screen application, key functions are determined completely by software
and change depending upon the subject matter currently being displayed. The basic
touch screen functions are outlined below.
Radio Buttons
Radio buttons show one menu choice among two or more alternatives, all visible. (It is
the AUTO button in
old-fashioned radios to select stations. When one is pressed, the one that was previously pressed “pops out” and the new station is selected. In the DynaView model
the possible selections are each associated with a button. The selected button is dark
ened, presented in reverse video to indicate it is the selected choice. The full range of
possible choices as well as the current choice is always in view.
Spin Value Buttons
Spin values are used to allow a variable setpoint to be changed, such as leaving water
setpoint. The value increases or decreases by touching the increment (+) or decre
ment (-) arrows.
Action Buttons Action buttons appear temporarily and provide the user with a choice such as Enter or Cancel.
Hot Links
Hot links are used to navigate from one view to another view.
File Folder Tabs
File folder tabs are used to select a screen of data. Just like tabs in a file folder, these
serve to title the folder/screen selected, as well as provide navigation to other
screens. In DynaView, the tabs are in one row across the top of the display. The folder
tabs are separated from the rest of the display by a horizontal line. Vertical lines sepa
rate the tabs from each other. The folder that is selected has no horizontal line under
Figure 36.) The radio button model mimics the buttons used on
-
-
-
92 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 93

Controls Interface
its tab, thereby making it look like a part of the current folder (as would an open folder
in a file cabinet). The user selects a screen of information by touching the appropriate
tab.
Display Screens
Basic Screen Format
The basic screen format appears as
:
File folder
Tabs
Radio buttons
Page scroll
(up)
Page scroll
(down)
Line scroll
(up/down)
Tab navigator
Auto Stop Alarms
Contrast control (lighter)
The file folder tabs across the top of the screen are used to select the various display
screens.
Scroll arrows are added if more file tabs (choices) are available. When the tabs are at
the left most position, the left navigator will not show and only navigation to the right
will be possible. Likewise when the right most screen is selected, only left navigation
will be possible.
The main body of the screen is used for description text, data, setpoints, or keys
(touch sensitive areas). The Chiller Mode is displayed here.
The double up arrows cause a page-by-page scroll either up or down. The single
arrow causes a line by line scroll to occur. At the end of the page, the appropriate
scroll bar will disappear.
A double arrow pointing to the right indicates more information is available about the
specific item on that same line. Pressing it will bring you to a subscreen that will
present the information or allow changes to settings.
The bottom of the screen (Fixed Display) is present in all screens and contains the following functions. The left circular area is used to reduce the contrast/viewing angle
of the display. The right circular area is used to increase the contrast/viewing angle
of the display. The contrast may require re-adjustment at ambient temperatures sig
nificantly different from those present at last adjustment.
The other functions are critical to machine operation. The AUTO and STOP keys are
used to enable or disable the chiller. The key selected is in black (reverse video). The
chiller will stop when the STOP key is touched and after completing the Run Unload
mode.
Touching the AUTO key will enable the chiller for active cooling if no diagnostic is
present. (A separate action must be taken to clear active diagnostics.)
The AUTO and STOP keys, take precedence over the Enter and Cancel keys. (While a
setting is being changed, AUTO and STOP keys are recognized even if Enter or Cancel
has not been pressed.)
Contrast control (darker)
-
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 93
Page 94

Controls Interface
The ALARMS button appears only when an alarm is present, and blinks (by alternating
between normal and reverse video) to draw attention to a diagnostic condition. Press
ing the ALARMS button takes you to the corresponding tab for additional information.
Front Panel Lockout Feature
Display and Touch Screen are Locked
Enter Password to Unlock
-
1
4
7
Enter 0 Cancel
NOTE: The DynaView display and Touch Screen Lock screen is shown below. This
screen is used if the Display and touch screen and lock feature is enabled. Thirty
minutes after the last keystroke, this screen is displayed and the Display and Touch
Screen is locked out until the sequence “159 <ENTER>” is pressed.
Until the proper password is entered, there will be no access to the DynaView
screens including all reports, setpoints, and Auto/Stop/Alarms/Interlocks.
The password “159” is not programmable from either DynaView or TechView.
2
5
8
3
6
9
Front Panel Display During Cold Ambients
Display and Touch Screen are Locked
Enter 159 to Unlock
1
4
7
Enter 0 Cancel
94 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
2
5
8
3
6
9
Page 95

Controls Interface
If the Display and Touch Screen Lock feature is disabled, the following screen is automatically displayed if the DynaView Temperature is below freezing and has been 30
minutes after the last keystroke. Note: This feature is provided to avoid unintended
actuations of the keypad, which can occur due to ice build-up on the DynaView’s exte
rior surfaces. Also be aware that at extremes of temperatures, the LCD display
screen will change its contrast from the optimal adjustment made at more normal
temperatures. It can appear washed out or blacked out. Simply pressing the lower
right contrast control on the screen will return the display to readable condition.
NOTE: All screens shown in this section are typical. Some screens show all display
options available, only one of which may appear on a line.
Modes Screen
The Mode Screen is only found on software revisions 18 and later. This screen provides a display for the top level operating mode for each of the components and subcomponents of the chiller (i.e. Chiller, Circuits, and Compressors) that exist on the
Chiller as it is configured. The modes are displayed as text only without the hex
codes.
In software revisions 17.0 and earlier, the top level mode and the sub mode for each
component was displayed on the respective component tab on the first two lines.
The mode display of the first three lines of the Compressor and Chiller Screen tabs is
eliminated with the addition of the Mode Screen
-
Modes
Chiller Mode:
Circuit 1 Mode:
Cprsr 1A Mode:
Cprsr 1B Mode:
Circuit 2 Mode:
Cprsr 2A Mode:
Cprsr 2B Mode:
Chiller Compressor
Running
Running - Limit
Running
Running
Run Inhibit
Stopped
Stopped
Auto Stop
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 95
Page 96

Controls Interface
Table 25 Chiller Modes
Chiller Modes Description
Top Level Mode
Sub-modes
Stopped The chiller is not running and cannot run without inter-
vention. Further information is provided by the submode:
Local Stop Chiller is stopped by DynaView Stop button command-
cannot be remotely overridden.
Panic Stop Chiller is stopped by the DynaView Panic Stop (by
pressing Stop button twice in succession) - previous
shutdown was manually commanded to shutdown
immediately without a run-unload or pumpdown cycle cannot be remotely overridden.
Diagnostic Shutdown - Manual Reset The chiller is stopped by a diagnostic that requires
manual intervention to reset.
Other sub-modes are possible in conjunction with at least
one of the above modes - See items below for their
descriptions:
Diagnostic Shutdown - Auto Reset
Start Inhibited by Low Cond Temp
Start Inhibited by Low Ambient Temp
Start Inhibited by External Source
Start Inhibited by BAS
Waiting for BAS Communications
Ice Building to Normal Transition
Ice Building is Complete
Design Note: Maximum Capacity was eliminated as a
annunciated mode prior to any release
Run Inhibit The chiller is currently being inhibited from starting (and
running), but may be allowed to start if the inhibiting or
diagnostic condition is cleared. Further information is
provided by the sub-mode:
Diagnostic Shutdown - Auto Reset The entire chiller is stopped by a diagnostic that may
automatically clear.
Start Inhibited by Low Cond Temp The chiller is inhibited from starting by Low Condenser
Temperature- Inhibit is active below either 25°F (can be
disabled with proper freeze protection) or 0°F (limit set by
design, cannot be disabled). As an exception, this will not
stop a chiller already running.
Start Inhibited by Low Ambient Temp The chiller is inhibited from starting (and running) by an
outdoor air ambient temperature lower than a specified
temperature - per user adjustable settings and can be
disabled.
Start Inhibited by External Source The chiller is inhibited from starting (and running) by the
"external stop" hardwired input.
96 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 97

Controls Interface
Table 25 Chiller Modes
Chiller Modes Description
Top Level Mode
Sub-modes
Start Inhibited by BAS The chiller is inhibited from starting (and running) by
command from a Building Automation System via the
digital communication link (com 3 or com 5).
Waiting for BAS Communications This is a transient mode - 15-min. max, and is only
possible if the chiller is in the Auto - Remote command
mode. After a power up reset, it is necessary to wait for
valid communication from a Building Automation System
(Tracer) to know whether to run or stay inhibited. Either
valid communication will be received from the Building
Automation System (e.g. Tracer), or a communication
diagnostic ultimately will result. In the latter case the
chiller will revert to Local control.
Ice Building to Normal Transition The chiller is inhibited from running for a brief period of
time if it is commanded from active ice building mode
into normal cooling mode via the ice building hardwired
input or Tracer. This allows time for the external system
load to "switchover" from an ice bank to the chilled water
loop, and provides for a controlled pull down of the
loop's warmer temperature. This mode is not seen if the
ice making is automatically terminated on return brine
temperature per the mode below.
Ice Building is Complete The chiller is inhibited from running as the Ice Building
process has been normally terminated on the return brine
temperature. The chiller will not start unless the ice
building command (hardwired input or Building
Automation System command) is removed or cycled.
Auto The chiller is not currently running but can be expected to
start at any moment given that the proper conditions and
interlocks are satisfied. Further information is provided
by the sub-mode:
Waiting For Evap Water Flow The chiller will wait up to 4 minutes in this mode for
evaporator water flow to be established per the flow
switch hardwired input.
Waiting for Need to Cool The chiller will wait indefinitely in this mode, for an
evaporator leaving water temperature higher than the
Chilled Water Setpoint plus the Differential to Start.
Starting The chiller is going through the necessary steps to allow
the lead circuit and lead compressor to start.
No Sub Modes
Running At least one circuit and one compressor on the chiller are
currently running. Further information is provided by the
sub-mode:
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 97
Page 98

Controls Interface
Table 25 Chiller Modes
Chiller Modes Description
Top Level Mode
Sub-modes
Unit is Building Ice The chiller is running in the Ice Building Mode, and either
at or moving towards full capacity available. Ice mode is
terminated either with the removal of the ice mode
command or with the return brine temperature falling
below the Ice Termination Setpoint.
Running - Limited At least one circuit and one compressor on the chiller are
currently running, but the operation of the chiller as a
whole is being actively limited by the controls.
Capacity Limited by
High Evap Water Temp
This mode will occur if both the OA temperature is above
40°F and the Evap Leaving Water Temperature is above
75°F as is often the case in a high temperature pull-down.
While in this mode, no compressors will be allowed to
load past their minimum load capacity step, but it will not
inhibit compressor staging. This mode is necessary to
prevent nuisance trips due to Compressor Overcurrent or
High Pressure Cutout. Reasonable pull-down rates can
still be expected despite this limit.
Table 26 Circuit Modes
Circuit Modes Description
Top Level Mode
Sub-modes
Stopped The given circuit is not running and cannot run without intervention.
Front Panel Lockout The circuit is manually locked out by the circuit lockout setting - the
Diagnostic Shutdown - Manual Reset The circuit has been shutdown on a latching diagnostic.
Other sub-modes are possible in conjunction with at least one of
the above modes - See items below for their descriptions:
Diagnostic Shutdown - Auto Reset
Start Inhibited by External Source
Start Inhibited by BAS
Run Inhibit The given circuit is currently being inhibited from starting (and run-
Diagnostic Shutdown - Auto Reset The circuit has been shutdown on a diagnostic that may clear auto-
Start Inhibited by External Source The circuit is inhibited from starting (and running) by its "external cir-
Start Inhibited by BAS The circuit is inhibited from starting (and running) by command
Further information is provided by the sub-mode:
nonvolatile lockout setting is accessible through either the DynaView or TechView.
ning), but may be allowed to start if the inhibiting or diagnostic condition is cleared. Further information is provided by the sub-mode:
matically.
cuit lockout" hardwired input.
from a Building Automation System via the digital communication
link (com 3 or com 5).
98 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
Page 99

Controls Interface
Table 26 Circuit Modes
Circuit Modes Description
Top Level Mode
Sub-modes
Auto The given circuit is not currently running but can be expected to
No Sub Modes
Starting The given circuit is going through the necessary steps to allow the
No Sub Modes
Running At least one compressor on the given circuit is currently running.
Establishing Min. Cap - Low Diff pressure The circuit is experiencing low system differential pressure and is
Running - Limited At least one compressor on the given circuit is currently running,
Capacity Limited by High Cond Press The circuit is experiencing condenser pressures at or near the con-
Capacity Limited by Low Evap Rfgt Temp The circuit is experiencing saturated evaporator temperatures at or
Capacity Limited by Low Liquid Level The circuit is experiencing low refrigerant liquid levels and the EXV
Shutting Down The given circuit is still running but shutdown is imminent. The cir-
Operational Pumpdown The circuit is in the process shutting down by performing an opera-
Front Panel Lockout The circuit has been manually locked out by the circuit lockout set-
Diagnostic Shutdown - Manual Reset The circuit is in the process of shutdown due to a latching diagnos-
Diagnostic Shutdown - Auto Reset The circuit is in the process of shutdown due to a diagnostic that
Start Inhibited by External Source The circuit is in the process of shutdown due to a command from
Start Inhibited by BAS The circuit is in the process of shutdown due to a command from
Service Override The given circuit is in a Service Override mode
Service Pumpdown The circuit is running with fan control, via a manual command to
start at any moment given that the proper conditions and interlocks
are satisfied.
lead compressor on that circuit to start.
Further information is provided by the sub-mode:
being force loaded, irregardless Chilled Water Temperature Control,
to develop pressure sooner.
but the capacity of the circuit is being actively limited by the controls. Further information is provided by the sub-mode:
denser limit setting. Compressors on the circuit will be unloaded to
prevent exceeding the limits.
near the Low Refrigerant Temperature Cutout setting. Compressors on the circuit will be unloaded to prevent tripping.
is at or near full open. The compressors on the circuit will be
unloaded to prevent tripping.
cuit is going through either a compressor run-unload mode or a circuit operational pumpdown to dry out the evaporator (cold OA
ambient only). Shutdown is necessary due to one (or more) of the
following sub-modes:
tional pumpdown just prior to stopping the last running compressor. The EXV is commanded closed. Pumpdown will terminate
when both the liquid level and the evap pressure
ting and is in the process of shutting down - the nonvolatile lockout
setting is accessible through either the DynaView or TechView.
tic.
may automatically clear.
the external circuit lockout hardwired input.
the Building Automation System (e.g. Tracer)
perform a Service Pumpdown. Its respective EXV is being held
wide open, but the manual liquid line service valve should be
closed.
RTAC-SVX01F-EN 99
Page 100

Controls Interface
Table 27 Compressor Modes
Compressor Modes Description
Top Level Mode
Sub-modes
Stopped The given compressor is not running and cannot run without inter-
Diagnostic Shutdown - Manual Reset The compressor has been shutdown on a latching diagnostic.
Service Tool Lockout The compressor has been shutdown due to a command from the
Other sub-modes are possible in conjunction with at least one of
the above modes - See items below for their descriptions:
Diagnostic Shutdown - Auto Reset
Restart Inhibit
Run Inhibit The given compressor is currently being inhibited from starting (and
Diagnostic Shutdown - Auto Reset The compressor has been shutdown on a diagnostic that may clear
Restart Inhibit The compressor is currently unable to start due to its restart inhibit
Auto The given compressor is not currently running but can be expected
No Sub Modes
Starting The given compressor is going through the necessary steps to
No Sub Modes
Running The given compressor is currently running. Further information is
Establishing Min. Capacity - High Oil Temp The compressor is running and is being forced loaded to its step
Running - Limited The given compressor is currently running, but its capacity is being
Capacity Limited by High Current The compressor is running and its capacity is being limited by high
Capacity Limited by Phase Unbalance The compressor is running and its capacity is being limited by
Shutting Down The given compressor is still running but shutdown is imminent.
Diagnostic Shutdown - Manual Reset The compressor is in the process of shutdown due to a latching
vention. Further information is provided by the sub-mode:
TechView Service Tool to be "locked out" and inoperative. This setting is nonvolatile and operation can only be restored by using TechView to "unlock" it.
running*), but may be allowed to start if the inhibiting or diagnostic
condition is cleared. Further information is provided by the submode:
automatically.
timer. A given compressor is not allowed to start until 5 minutes
has expired since its last start.
to start at any moment given that the proper conditions occur.
allow it to start. (This mode is short and transitory)
provided by the sub-mode:
load point, without regard to the leaving water temperature control,
to prevent tripping on high oil temperature.
actively limited by the controls. Further information is provided by
the sub-mode:
currents. The current limit setting is 120% RLA (to avoid overcurrent trips) or lower as set by the compressor's "share" of the active
current limit (demand limit) setting for the entire chiller.
excessive phase current unbalance.
The compressor is going through either a run-unload mode or is the
active compressor in the operational pumpdown cycle for its circuit.
Shutdown is either normal (no sub-mode displayed) or due the following sub-modes:
diagnostic.
100 RTAC-SVX01F-EN
 Loading...
Loading...