
User Guide
1910012722 REV3.1.0
October 2020

CONTENTS
About This Guide
Intended Readers ................................................................................................................................................................1
Conventions ...........................................................................................................................................................................1
More Information .................................................................................................................................................................2
Accessing the Switch
Overview ................................................................................................................................................................................4
Web Interface Access ........................................................................................................................................................5
Login .................................................................................................................................................................................................................5
Save Config Function ..............................................................................................................................................................................6
Disable the Web Server .........................................................................................................................................................................7
Configure the Switch's IP Address and Default Gateway ...................................................................................................7
Command Line Interface Access ............................................................................................................................... 10
Console Login (only for switch with console port) ...............................................................................................................10
Telnet Login ...............................................................................................................................................................................................12
SSH Login ...................................................................................................................................................................................................13
Disable Telnet login ...............................................................................................................................................................................18
Disable SSH login ...................................................................................................................................................................................18
Copy running-config startup-config ............................................................................................................................................19
Change the Switch's IP Address and Default Gateway .....................................................................................................19
Managing System
System .................................................................................................................................................................................. 22
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................................................................22
Supported Features ..............................................................................................................................................................................22
System Info Configurations .......................................................................................................................................... 23
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................................23
Viewing the System Summary ...........................................................................................................................................23
Configuring the Device Description ...............................................................................................................................26
Configuring the System Time ............................................................................................................................................27
Configuring the Daylight Saving Time ...........................................................................................................................28
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................29
Viewing the System Summary ...........................................................................................................................................29
Configuring the Device Description ...............................................................................................................................30

Configuring the System Time ............................................................................................................................................31
Configuring the Daylight Saving Time ...........................................................................................................................34
User Management Configurations ............................................................................................................................. 36
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................................36
Creating Accounts ...................................................................................................................................................................36
Configuring Enable Password ............................................................................................................................................37
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................38
Creating Accounts ...................................................................................................................................................................38
Configuring Enable Password ............................................................................................................................................40
System Tools Configurations ...................................................................................................................................... 43
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................................43
Configuring the Boot File ......................................................................................................................................................43
Restoring the Configuration of the Switch .................................................................................................................44
Backing up the Configuration File ....................................................................................................................................45
Upgrading the Firmware ........................................................................................................................................................46
Rebooting the switch ..............................................................................................................................................................47
Reseting the Switch .................................................................................................................................................................48
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................48
Configuring the Boot File ......................................................................................................................................................48
Restoring the Configuration of the Switch .................................................................................................................50
Backing up the Configuration File ....................................................................................................................................50
Upgrading the Firmware ........................................................................................................................................................51
Rebooting the Switch .............................................................................................................................................................51
Reseting the Switch .................................................................................................................................................................53
EEE Configuration ............................................................................................................................................................. 54
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................54
SDM Template Configuration ....................................................................................................................................... 56
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................................56
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................57
Time Range Configuration ............................................................................................................................................. 59
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................................59
Adding Time Range Entries .................................................................................................................................................59
Configuring Holiday .................................................................................................................................................................61
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................62
Adding Time Range Entries .................................................................................................................................................62
Configuring Holiday .................................................................................................................................................................63
Appendix: Default Parameters ..................................................................................................................................... 65

Managing Physical Interfaces
Physical Interface ............................................................................................................................................................. 68
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................................................................68
Supported Features ..............................................................................................................................................................................68
Basic Parameters Configurations ............................................................................................................................... 69
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................................69
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................70
Port Isolation Configurations ....................................................................................................................................... 73
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................................73
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................74
Loopback Detection Configuration ........................................................................................................................... 76
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................................76
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................78
Configuration Examples ................................................................................................................................................. 80
Example for Port Isolation ..................................................................................................................................................................80
Network Requirements ..........................................................................................................................................................80
Configuration Scheme ...........................................................................................................................................................80
Using the GUI ...............................................................................................................................................................................80
Using the CLI ...............................................................................................................................................................................82
Example for Loopback Detection..................................................................................................................................................83
Network Requirements ..........................................................................................................................................................83
Configuration Scheme ...........................................................................................................................................................83
Using the GUI ...............................................................................................................................................................................84
Using the CLI ...............................................................................................................................................................................85
Appendix: Default Parameters ..................................................................................................................................... 86
Configuring LAG
LAG ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 88
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................................................................88
Supported Features ..............................................................................................................................................................................88
LAG Configuration ............................................................................................................................................................ 89
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................................90
Configuring Load-balancing Algorithm ........................................................................................................................90
Configuring Static LAG or LACP.......................................................................................................................................91
Using the CLI .............................................................................................................................................................................................93
Configuring Load-balancing Algorithm ........................................................................................................................93
Configuring Static LAG or LACP.......................................................................................................................................94

Configuration Examples ................................................................................................................................................. 98
Example for Static LAG .......................................................................................................................................................................98
Network Requirements ..........................................................................................................................................................98
Configuration Scheme ...........................................................................................................................................................98
Using the GUI ...............................................................................................................................................................................98
Using the CLI ...............................................................................................................................................................................99
Example for LACP ...............................................................................................................................................................................100
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................100
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................100
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................101
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................101
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................105
Managing MAC Address Table
MAC Address Table .......................................................................................................................................................107
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................107
Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................107
MAC Address Configurations ....................................................................................................................................108
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................108
Adding Static MAC Address Entries ..........................................................................................................................108
Modifying the Aging Time of Dynamic Address Entries...................................................................................110
Adding MAC Filtering Address Entries.......................................................................................................................111
Viewing Address Table Entries .......................................................................................................................................111
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................112
Adding Static MAC Address Entries ..........................................................................................................................112
Modifying the Aging Time of Dynamic Address Entries...................................................................................113
Adding MAC Filtering Address Entries.......................................................................................................................114
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................116
Configuring 802.1Q VLAN
Overview ...........................................................................................................................................................................118
802.1Q VLAN Configuration .......................................................................................................................................119
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................119
Configuring the PVID of the Port ...................................................................................................................................119
Configuring the VLAN ..........................................................................................................................................................120
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................121
Creating a VLAN .....................................................................................................................................................................121

Configuring the Port .............................................................................................................................................................122
Adding the Port to the Specified VLAN .....................................................................................................................123
Configuration Example .................................................................................................................................................125
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................125
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................125
Network Topology ...............................................................................................................................................................................126
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................126
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................129
Appendix: Default Parameters ..................................................................................................................................131
Configuring MAC VLAN
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................133
MAC VLAN Configuration ............................................................................................................................................134
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................134
Configuring 802.1Q VLAN ................................................................................................................................................134
Binding the MAC Address to the VLAN .....................................................................................................................134
Enabling MAC VLAN for the Port ...................................................................................................................................135
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................136
Configuring 802.1Q VLAN ................................................................................................................................................136
Binding the MAC Address to the VLAN .....................................................................................................................136
Enabling MAC VLAN for the Port ...................................................................................................................................137
Configuration Example ................................................................................................................................................138
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................138
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................138
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................139
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................142
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................145
Configuring Protocol VLAN
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................147
Protocol VLAN Configuration.....................................................................................................................................148
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................148
Configuring 802.1Q VLAN ................................................................................................................................................148
Creating Protocol Template ............................................................................................................................................149
Configuring Protocol VLAN .............................................................................................................................................150
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................151
Configuring 802.1Q VLAN ................................................................................................................................................151

Creating a Protocol Template .........................................................................................................................................151
Configuring Protocol VLAN ..............................................................................................................................................152
Configuration Example ................................................................................................................................................154
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................154
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................154
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................155
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................160
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................165
Configuring GVRP
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................167
GVRP Configuration .......................................................................................................................................................168
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................169
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................170
Configuration Example .................................................................................................................................................173
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................173
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................173
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................174
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................178
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................182
Configuring Layer 2 Multicast
Layer 2 Multicast .............................................................................................................................................................184
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................184
Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................186
IGMP Snooping Configuration ...................................................................................................................................187
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................187
Configuring IGMP Snooping Globally .........................................................................................................................187
Configuring IGMP Snooping for VLANs ....................................................................................................................188
Configuring IGMP Snooping for Ports ........................................................................................................................192
Configuring Hosts to Statically Join a Group .........................................................................................................192
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................193
Configuring IGMP Snooping Globally .........................................................................................................................193
Configuring IGMP Snooping for VLANs ....................................................................................................................195
Configuring IGMP Snooping for Ports ........................................................................................................................200
Configuring Hosts to Statically Join a Group .........................................................................................................201
MLD Snooping Configuration .....................................................................................................................................203

Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................203
Configuring MLD Snooping Globally ...........................................................................................................................203
Configuring MLD Snooping for VLANs ......................................................................................................................204
Configuring MLD Snooping for Ports .........................................................................................................................207
Configuring Hosts to Statically Join a Group .........................................................................................................207
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................208
Configuring MLD Snooping Globally ...........................................................................................................................208
Configuring MLD Snooping for VLANs ......................................................................................................................209
Configuring MLD Snooping for Ports .........................................................................................................................214
Configuring Hosts to Statically Join a Group .........................................................................................................215
MVR Configuration .........................................................................................................................................................217
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................217
Configuring 802.1Q VLANs ..............................................................................................................................................217
Configuring MVR Globally ..................................................................................................................................................218
Adding Multicast Groups to MVR ..................................................................................................................................219
Configuring MVR for the Port ..........................................................................................................................................220
(Optional) Adding Ports to MVR Groups Statically .............................................................................................221
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................222
Configuring 802.1Q VLANs ..............................................................................................................................................222
Configuring MVR Globally ..................................................................................................................................................222
Configuring MVR for the Ports .......................................................................................................................................224
Multicast Filtering Configuration ...............................................................................................................................227
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................227
Creating the Multicast Profile ..........................................................................................................................................227
Configure Multicast Filtering for Ports .......................................................................................................................229
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................230
Creating the Multicast Profile ..........................................................................................................................................230
Binding the Profile to Ports ...............................................................................................................................................233
Viewing Multicast Snooping Information ...............................................................................................................237
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................237
Viewing IPv4 Multicast Table ...........................................................................................................................................237
Viewing IPv4 Multicast Statistics on Each Port .....................................................................................................238
Viewing IPv6 Multicast Table ...........................................................................................................................................239
Viewing IPv6 Multicast Statistics on Each Port .....................................................................................................240
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................241
Viewing IPv4 Multicast Snooping Information .......................................................................................................241
Viewing IPv6 Multicast Snooping Configurations ................................................................................................241
Configuration Examples ...............................................................................................................................................242

Example for Configuring Basic IGMP Snooping .................................................................................................................242
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................242
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................242
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................243
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................245
Example for Configuring MVR ......................................................................................................................................................247
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................247
Network Topology .................................................................................................................................................................247
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................248
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................248
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................251
Example for Configuring Unknown Multicast and Fast Leave ....................................................................................254
Network Requirement ..........................................................................................................................................................254
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................255
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................255
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................257
Example for Configuring Multicast Filtering ..........................................................................................................................258
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................258
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................258
Network Topology .................................................................................................................................................................259
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................259
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................263
Appendix: Default Parameters ..................................................................................................................................266
Default Parameters for IGMP Snooping .................................................................................................................................266
Default Parameters for MLD Snooping ...................................................................................................................................267
Default Parameters for MVR ..........................................................................................................................................................268
Default Parameters for Multicast Filtering .............................................................................................................................268
Configuring Spanning Tree
Spanning Tree ..................................................................................................................................................................270
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................270
Basic Concepts ....................................................................................................................................................................................270
STP/RSTP Concepts ............................................................................................................................................................270
MSTP Concepts .....................................................................................................................................................................274
STP Security ...........................................................................................................................................................................................275
STP/RSTP Configurations ...........................................................................................................................................278
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................278

Configuring STP/RSTP Parameters on Ports .........................................................................................................278
Configuring STP/RSTP Globally .....................................................................................................................................280
Verifying the STP/RSTP Configurations ....................................................................................................................282
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................284
Configuring STP/RSTP Parameters on Ports .........................................................................................................284
Configuring Global STP/RSTP Parameters .............................................................................................................286
Enabling STP/RSTP Globally ............................................................................................................................................288
MSTP Configurations ....................................................................................................................................................290
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................290
Configuring Parameters on Ports in CIST ................................................................................................................290
Configuring the MSTP Region ........................................................................................................................................293
Configuring MSTP Globally ...............................................................................................................................................297
Verifying the MSTP Configurations .............................................................................................................................299
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................300
Configuring Parameters on Ports in CIST ................................................................................................................300
Configuring the MSTP Region .......................................................................................................................................303
Configuring Global MSTP Parameters .......................................................................................................................306
Enabling Spanning Tree Globally...................................................................................................................................308
STP Security Configurations ......................................................................................................................................310
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................310
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................311
Configuring the STP Security ..........................................................................................................................................311
Configuration Example for MSTP .............................................................................................................................314
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................314
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................314
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................315
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................321
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................328
Configuring LLDP
LLDP .....................................................................................................................................................................................331
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................331
Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................331
LLDP Configurations .....................................................................................................................................................332
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................332
Configuring LLDP Globally ................................................................................................................................................332
Configuring LLDP For the Port .......................................................................................................................................334

Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................335
Global Config ............................................................................................................................................................................335
Port Config .................................................................................................................................................................................337
LLDP-MED Configurations ..........................................................................................................................................340
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................340
Configuring LLDP Globally ...............................................................................................................................................340
Configuring LLDP-MED Globally ...................................................................................................................................340
Configuring LLDP-MED for Ports ..................................................................................................................................341
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................343
Global Config ............................................................................................................................................................................343
Port Config .................................................................................................................................................................................344
Viewing LLDP Settings..................................................................................................................................................347
Using GUI ..................................................................................................................................................................................................347
Viewing LLDP Device Info .................................................................................................................................................347
Viewing LLDP Statistics .....................................................................................................................................................351
Using CLI ..................................................................................................................................................................................................352
Viewing LLDP-MED Settings ......................................................................................................................................353
Using GUI ..................................................................................................................................................................................................353
Using CLI ..................................................................................................................................................................................................356
Configuration Examples ...............................................................................................................................................357
Configuration Example for LLDP.................................................................................................................................................357
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................357
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................357
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................357
Using CLI .....................................................................................................................................................................................358
Example for LLDP-MED ...................................................................................................................................................................364
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................364
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................364
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................364
Using CLI .....................................................................................................................................................................................367
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................370
Configuring Layer 3 Interfaces
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................372
Layer 3 Interface Configurations ..............................................................................................................................373
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................373
Creating an Layer 3 Interface ..........................................................................................................................................373

Configuring IPv4 Parameters of the Interface .......................................................................................................375
Configuring IPv6 Parameters of the Interface .......................................................................................................376
Viewing Detail Information of the Interface .............................................................................................................379
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................380
Creating an Layer 3 Interface ..........................................................................................................................................380
Configuring IPv4 Parameters of the Interface .......................................................................................................382
Configuring IPv6 Parameters of the Interface .......................................................................................................383
Configuration Example ..................................................................................................................................386
Network Requirement ................................................................................................................................... 386
Configuration Scheme .................................................................................................................................. 386
Using the GUI .................................................................................................................................................... 386
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................387
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................389
Configuring Routing
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................391
IPv4 Static Routing Configuration ............................................................................................................................392
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................392
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................393
IPv6 Static Routing Configuration ............................................................................................................................394
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................394
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................394
Viewing Routing Table ..................................................................................................................................................396
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................396
Viewing IPv4 Routing Table ..............................................................................................................................................396
Viewing IPv6 Routing Table ..............................................................................................................................................397
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................397
Viewing IPv4 Routing Table ..............................................................................................................................................397
Viewing IPv6 Routing Table ..............................................................................................................................................398
Example for Static Routing ..........................................................................................................................................399
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................399
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................399
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................399
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................401
Configuring DHCP Service
DHCP ...................................................................................................................................................................................405

Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................405
Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................405
DHCP Server Configuration ........................................................................................................................................410
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................410
Enabling DHCP Server ........................................................................................................................................................410
Configuring DHCP Server Pool ......................................................................................................................................412
Configuring Manual Binding .............................................................................................................................................413
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................414
Enabling DHCP Server ........................................................................................................................................................414
Configuring DHCP Server Pool ......................................................................................................................................417
Configuring Manual Binding .............................................................................................................................................420
DHCP Relay Configuration ..........................................................................................................................................422
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................422
Enabling DHCP Relay and Configuring Option 82 ...............................................................................................422
Configuring DHCP Interface Relay ...............................................................................................................................424
Configuring DHCP VLAN Relay ......................................................................................................................................424
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................426
Enabling DHCP Relay ...........................................................................................................................................................426
(Optional) Configuring Option 82 ..................................................................................................................................427
Configuring DHCP Interface Relay ...............................................................................................................................429
Configuring DHCP VLAN Relay ......................................................................................................................................430
DHCP L2 Relay Configuration ....................................................................................................................................433
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................433
Enabling DHCP L2 Relay ....................................................................................................................................................433
Configuring Option 82 for Ports ....................................................................................................................................434
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................435
Enabling DHCP L2 Relay ....................................................................................................................................................435
Configuring Option 82 for Ports ....................................................................................................................................436
Configuration Examples ...............................................................................................................................................439
Example for DHCP Server ...............................................................................................................................................................439
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................439
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................439
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................439
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................441
Example for DHCP Interface Relay ............................................................................................................................................441
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................441
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................442
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................443

Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................449
Example for DHCP VLAN Relay ...................................................................................................................................................451
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................451
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................452
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................453
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................456
Example for Option82 in DHCP Relay .....................................................................................................................................458
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................458
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................459
Configuring the DHCP Relay Switch............................................................................................................................460
Configuring the DHCP Server .........................................................................................................................................462
Example for DHCP L2 Relay ..........................................................................................................................................................464
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................464
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................464
Configuring the DHCP Relay Switch............................................................................................................................465
Configuring the DHCP Server .........................................................................................................................................468
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................470
Configuring ARP
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................474
Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................474
ARP Configurations ........................................................................................................................................................476
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................476
Viewing the ARP Entries .....................................................................................................................................................476
Adding Static ARP Entries Manually ............................................................................................................................477
Configuring Gratuitous ARP .............................................................................................................................................477
Configuring Proxy ARP ........................................................................................................................................................478
Configuring Local Proxy ARP ..........................................................................................................................................479
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................480
Configuring the ARP Entry ................................................................................................................................................480
Configuring the Gratuitous ARP ...................................................................................................................................482
Configuring Proxy ARP ......................................................................................................................................................484
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................487
Configuring QoS
QoS .......................................................................................................................................................................................489
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................489

Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................489
Class of Service Configuration ..................................................................................................................................491
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................492
Configuring Port Priority .....................................................................................................................................................492
Configuring 802.1p Priority ..............................................................................................................................................494
Configuring DSCP Priority .................................................................................................................................................496
Specifying the Scheduler Settings ..............................................................................................................................499
Using CLI ..................................................................................................................................................................................................500
Configuring Port Priority .....................................................................................................................................................500
Configuring 802.1p Priority ..............................................................................................................................................502
Configuring DSCP Priority .................................................................................................................................................505
Specifying the Scheduler Settings ..............................................................................................................................510
Bandwidth Control Configuration .............................................................................................................................512
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................512
Configuring Rate Limit .........................................................................................................................................................512
Configuring Storm Control ...............................................................................................................................................513
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................514
Configuring Rate Limit .........................................................................................................................................................514
Configuring Storm Control ...............................................................................................................................................515
Voice VLAN Configuration ..........................................................................................................................................518
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................518
Configuring OUI Addresses .............................................................................................................................................518
Configuring Voice VLAN Globally .................................................................................................................................519
Adding Ports to Voice VLAN ...........................................................................................................................................520
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................521
Auto VoIP Configuration ..............................................................................................................................................524
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................524
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................525
Configuration Examples ...............................................................................................................................................529
Example for Class of Service ........................................................................................................................................................529
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................529
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................529
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................530
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................532
Example for Voice VLAN .................................................................................................................................................................534
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................534
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................535
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................535

Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................539
Example for Auto VoIP ......................................................................................................................................................................542
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................542
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................542
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................543
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................548
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................552
Configuring Access Security
Access Security ..............................................................................................................................................................557
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................557
Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................557
Access Security Configurations ...............................................................................................................................558
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................558
Configuring the Access Control Feature ..................................................................................................................558
Configuring the HTTP Function .....................................................................................................................................561
Configuring the HTTPS Function ..................................................................................................................................563
Configuring the SSH Feature ..........................................................................................................................................566
Configuring the Telnet Function ....................................................................................................................................567
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................568
Configuring the Access Control ....................................................................................................................................568
Configuring the HTTP Function .....................................................................................................................................569
Configuring the HTTPS Function ..................................................................................................................................571
Configuring the SSH Feature ..........................................................................................................................................574
Configuring the Telnet Function ....................................................................................................................................576
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................577
Configuring AAA
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................580
AAA Configuration ..........................................................................................................................................................581
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................582
Adding Servers ........................................................................................................................................................................582
Configuring Server Groups ...............................................................................................................................................584
Configuring the Method List ............................................................................................................................................584
Configuring the AAA Application List .........................................................................................................................586
Configuring Login Account and Enable Password .............................................................................................586
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................587

Adding Servers ........................................................................................................................................................................587
Configuring Server Groups ...............................................................................................................................................590
Configuring the Method List ............................................................................................................................................591
Configuring the AAA Application List .........................................................................................................................592
Configuring Login Account and Enable Password .............................................................................................595
Configuration Example .................................................................................................................................................598
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................598
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................598
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................599
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................601
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................604
Configuring 802.1x
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................607
802.1x Configuration .....................................................................................................................................................608
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................608
Configuring the RADIUS Server .....................................................................................................................................608
Configuring 802.1x Globally .............................................................................................................................................611
Configuring 802.1x on Ports ............................................................................................................................................612
View the Authenticator State ..........................................................................................................................................614
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................615
Configuring the RADIUS Server .....................................................................................................................................615
Configuring 802.1x Globally .............................................................................................................................................617
Configuring 802.1x on Ports ............................................................................................................................................619
Viewing Authenticator State ............................................................................................................................................621
Configuration Example .................................................................................................................................................623
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................623
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................623
Network Topology ...............................................................................................................................................................................623
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................624
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................626
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................629
Configuring Port Security
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................632
Port Security Configuration ........................................................................................................................................633
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................633

Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................634
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................637
Configuring ACL
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................639
ACL Configuration ..........................................................................................................................................................640
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................640
Configuring Time Range ..................................................................................................................................................640
Creating an ACL ......................................................................................................................................................................640
Configuring ACL Rules ........................................................................................................................................................641
Configuring MAC ACL Rule ..............................................................................................................................641
Configuring IP ACL Rule .....................................................................................................................................645
Configuring Combined ACL Rule ..................................................................................................................649
Configuring the IPv6 ACL Rule .......................................................................................................................654
Configuring ACL Binding ....................................................................................................................................................658
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................660
Configuring Time Range ..................................................................................................................................................660
Configuring ACL .....................................................................................................................................................................660
Configuring Policy ..................................................................................................................................................................668
Configuring ACL Binding ....................................................................................................................................................670
Viewing ACL Counting ........................................................................................................................................................671
Configuration Examples ...............................................................................................................................................672
Configuration Example for MAC ACL .......................................................................................................................................672
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................672
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................672
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................673
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................679
Configuration Example for IP ACL ..............................................................................................................................................680
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................680
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................681
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................681
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................687
Configuration Example for Combined ACL ...........................................................................................................................689
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................689
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................689
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................690
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................694

Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................696
Configuring IPv4 IMPB
IPv4 IMPB ...........................................................................................................................................................................699
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................699
Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................699
IP-MAC Binding Configuration ...................................................................................................................................700
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................700
Binding Entries Manually ....................................................................................................................................................700
Binding Entries via ARP Scanning .................................................................................................................................701
Binding Entries via DHCP Snooping ............................................................................................................................703
Viewing the Binding Entries ..............................................................................................................................................705
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................706
Binding Entries Manually ....................................................................................................................................................706
Binding Entries via DHCP Snooping ............................................................................................................................707
Viewing Binding Entries ......................................................................................................................................................709
ARP Detection Configuration .....................................................................................................................................710
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................710
Adding IP-MAC Binding Entries .....................................................................................................................................710
Enabling ARP Detection .....................................................................................................................................................710
Configuring ARP Detection on Ports ..........................................................................................................................711
Viewing ARP Statistics ........................................................................................................................................................712
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................713
Adding IP-MAC Binding Entries .....................................................................................................................................713
Enabling ARP Detection .....................................................................................................................................................713
Configuring ARP Detection on Ports ..........................................................................................................................714
Viewing ARP Statistics ........................................................................................................................................................716
IPv4 Source Guard Configuration .............................................................................................................................717
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................717
Adding IP-MAC Binding Entries .....................................................................................................................................717
Configuring IPv4 Source Guard .....................................................................................................................................717
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................718
Adding IP-MAC Binding Entries .....................................................................................................................................718
Configuring IPv4 Source Guard .....................................................................................................................................718
Configuration Examples ...............................................................................................................................................720
Example for ARP Detection ...........................................................................................................................................................720
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................720

Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................720
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................721
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................723
Example for IP Source Guard ........................................................................................................................................................725
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................725
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................725
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................725
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................727
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................728
Configuring IPv6 IMPB
IPv6 IMPB ...........................................................................................................................................................................731
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................731
Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................731
IPv6-MAC Binding Configuration ..............................................................................................................................733
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................733
Binding Entries Manually ....................................................................................................................................................733
Binding Entries via ND Snooping ...................................................................................................................................734
Binding Entries via DHCPv6 Snooping.......................................................................................................................736
Viewing the Binding Entries ..............................................................................................................................................737
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................738
Binding Entries Manually ....................................................................................................................................................738
Binding Entries via ND Snooping ...................................................................................................................................740
Binding Entries via DHCPv6 Snooping.......................................................................................................................741
Viewing Binding Entries ......................................................................................................................................................742
ND Detection Configuration .......................................................................................................................................743
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................743
Adding IPv6-MAC Binding Entries ................................................................................................................................743
Enabling ND Detection ........................................................................................................................................................743
Configuring ND Detection on Ports .............................................................................................................................744
Viewing ND Statistics ...........................................................................................................................................................744
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................745
Adding IPv6-MAC Binding Entries ................................................................................................................................745
Enabling ND Detection ........................................................................................................................................................745
Configuring ND Detection on Ports .............................................................................................................................746
Viewing ND Statistics ...........................................................................................................................................................747
IPv6 Source Guard Configuration .............................................................................................................................748

Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................748
Adding IPv6-MAC Binding Entries ................................................................................................................................748
Configuring IPv6 Source Guard .....................................................................................................................................748
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................749
Adding IPv6-MAC Binding Entries ................................................................................................................................749
Configuring IPv6 Source Guard .....................................................................................................................................749
Configuration Examples ...............................................................................................................................................751
Example for ND Detection ..............................................................................................................................................................751
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................751
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................751
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................752
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................754
Example for IPv6 Source Guard ..................................................................................................................................................755
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................755
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................756
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................756
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................757
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................759
Configuring DHCP Filter
DHCP Filter ........................................................................................................................................................................762
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................762
Supported Features ...........................................................................................................................................................................762
DHCPv4 Filter Configuration ......................................................................................................................................764
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................764
Configuring the Basic DHCPv4 Filter Parameters ...............................................................................................764
Configuring Legal DHCPv4 Servers ............................................................................................................................766
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................766
Configuring the Basic DHCPv4 Filter Parameters ...............................................................................................766
Configuring Legal DHCPv4 Servers ............................................................................................................................768
DHCPv6 Filter Configuration ......................................................................................................................................770
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................770
Configuring the Basic DHCPv6 Filter Parameters ...............................................................................................770
Configuring Legal DHCPv6 Servers ............................................................................................................................771
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................772
Configuring the Basic DHCPv6 Filter Parameters ...............................................................................................772
Configuring Legal DHCPv6 Servers ............................................................................................................................773

Configuration Examples ...............................................................................................................................................775
Example for DHCPv4 Filter .............................................................................................................................................................775
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................775
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................775
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................776
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................777
Example for DHCPv6 Filter .............................................................................................................................................................778
Network Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................778
Configuration Scheme ........................................................................................................................................................779
Using the GUI ............................................................................................................................................................................779
Using the CLI ............................................................................................................................................................................780
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................782
Configuring DoS Defend
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................784
DoS Defend Configuration ..........................................................................................................................................785
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................785
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................786
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................789
Monitoring the System
Overview ...........................................................................................................................................................................791
Monitoring the CPU .......................................................................................................................................................792
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................792
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................792
Monitoring the Memory ................................................................................................................................................794
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................794
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................794
Monitoring Traffic
Traffic Monitor .................................................................................................................................................................797
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................797
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................801
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................802
Mirroring Traffic
Mirroring .............................................................................................................................................................................804

Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................804
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................806
Configuration Examples ...............................................................................................................................................808
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................808
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................808
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................808
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................809
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................811
Configuring DLDP
Overview ...........................................................................................................................................................................813
DLDP Configuration .......................................................................................................................................................814
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................814
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................816
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................818
Configuring SNMP & RMON
SNMP ...................................................................................................................................................................................820
Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................................................820
Basic Concepts ....................................................................................................................................................................................820
SNMP Configurations ....................................................................................................................................................824
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................824
Enabling SNMP ........................................................................................................................................................................824
Creating an SNMP View......................................................................................................................................................825
Creating SNMP Communities (For SNMP v1/v2c) ..............................................................................................826
Creating an SNMP Group (For SNMP v3)..................................................................................................................827
Creating SNMP Users (For SNMP v3) .........................................................................................................................828
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................829
Enabling SNMP ........................................................................................................................................................................829
Creating an SNMP View......................................................................................................................................................831
Creating SNMP Communities (For SNMP v1/v2c) ..............................................................................................832
Creating an SNMP Group (For SNMPv3) ...................................................................................................................833
Creating SNMP Users (For SNMPv3) ..........................................................................................................................835
Notification Configurations .........................................................................................................................................837
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................837
Configuring the Information of NMS Hosts .............................................................................................................837
Enabling SNMP Traps ..........................................................................................................................................................839

Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................841
Configuring the NMS Host ................................................................................................................................................841
Enabling SNMP Traps ..........................................................................................................................................................843
RMON ..................................................................................................................................................................................850
RMON Configurations ...................................................................................................................................................851
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................851
Configuring the Statistics Group ...................................................................................................................................851
Configuring History Group ................................................................................................................................................852
Configuring Event Group ...................................................................................................................................................853
Configuring Alarm Group ...................................................................................................................................................854
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................856
Configuring Statistics ..........................................................................................................................................................856
Configuring History ...............................................................................................................................................................858
Configuring Event ..................................................................................................................................................................859
Configuring Alarm ..................................................................................................................................................................860
Configuration Example .................................................................................................................................................863
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................863
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................864
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................864
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................869
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................875
Diagnosing the Device & Network
Diagnosing the Device ..................................................................................................................................................880
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................880
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................881
Diagnosing the Network ...............................................................................................................................................882
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................882
Troubleshooting with Ping Testing ..............................................................................................................................882
Troubleshooting with Tracert Testing ........................................................................................................................883
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................884
Configuring the Ping Test ..................................................................................................................................................884
Configuring the Tracert Test ...........................................................................................................................................885
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................886
Configuring System Logs
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................................888

System Logs Configurations ......................................................................................................................................889
Using the GUI .........................................................................................................................................................................................890
Configuring the Local Logs ..............................................................................................................................................890
Configuring the Remote Logs.........................................................................................................................................890
Backing up the Logs ............................................................................................................................................................891
Viewing the Log Table .........................................................................................................................................................892
Using the CLI ..........................................................................................................................................................................................893
Configuring the Local Logs ..............................................................................................................................................893
Configuring the Remote Logs.........................................................................................................................................894
Configuration Example .................................................................................................................................................896
Network Requirements .....................................................................................................................................................................896
Configuration Scheme .....................................................................................................................................................................896
Using the GUI ........................................................................................................................................................................................896
Using the CLI .........................................................................................................................................................................................897
Appendix: Default Parameters ...................................................................................................................................898

About This Guide Intended Readers
About This Guide
This User Guide provides information for managing T1700X-16TS. Please read this guide
carefully before operation.
Intended Readers
This Guide is intended for network managers familiar with IT concepts and network
terminologies.
Conventions
When using this guide, notice that features available in JetStream Switches may vary by
model and software version. Availability of JetStream Switches may also vary by region or
ISP. All images, steps, and descriptions in this guide are only examples and may not reflect
your actual experience.
Some models featured in this guide may be unavailable in your country or region. For local
sales information, visit https://www.tp-link.com.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has
been made in the preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but
all statements, information, and recommendations in this document do not constitute
the warranty of any kind, express or implied. Users must take full responsibility for their
application of any products.
In this Guide, the following conventions are used:
The symbol
make better use of your device.
■ For GUI:
Menu Name > Submenu Name > Tab page indicates the menu structure. System >
System Info > System Summary means the System Summary page under the System Info
menu option that is located under the System menu.
Bold font indicates a button, a toolbar icon, menu or menu item.
stands for
Note
. Notes contains suggestions or references that helps you
■ For CLI:
Bold Font An unalterable keyword.
For example: show logging
User Guide 1

About This Guide More Information
Normal Font A constant (several options are enumerated and only one can be
selected).
For example: no bandwidth {all | ingress | egress}
{} Items in braces { } are required.
[] Items in square brackets [ ] are optional.
| Alternative items are grouped in braces and separated by vertical bars |.
For example: speed {10 | 100 | 1000}
Italic Font
Common combination:
{[ ][ ][ ]} A least one item in the square brackets must be selected.
A variable (an actual value must be assigned).
For example: bridge aging-time
For example: bandwidth {[ingress
]}
rate
This command can be used on three occasions:
bandwidth ingress
bandwidth.
bandwidth egress
bandwidth.
bandwidth ingress
restrict ingress and egress bandwidth.
ingress-rate
egress-rate
ingress-rate
aging-time
ingress-rate
is used to restrict ingress
is used to restrict egress
egress
egress-rate
] [egress
More Information
egress-
is used to
■
The latest software and documentations can be found at Download Center at
https://www.tp-link.com/support.
■
The Installation Guide (IG) can be found where you find this guide or inside the package
of the switch.
■
Specifications can be found on the product page at https://www.tp-link.com. To ask
questions, find answers, and communicate with TP-Link users or engineers, please visit
https://community.tp-link.com to join TP-Link Community.
■
Our Technical Support contact information can be found at the Contact Technical
Support page at https://www.tp-link.com/support.
User Guide 2

Part 1
Accessing the Switch
CHAPTERS
1. Overview
2. Web Interface Access
3. Command Line Interface Access

Accessing the Switch Overview
1
Overview
You can access and manage the switch using the GUI (Graphical User Interface, also called
web interface in this text) or using the CLI (Command Line Interface). There are equivalent
functions in the web interface and the command line interface, while web configuration is
easier and more visual than the CLI configuration. You can choose the method according
to their available applications and preference.
User Guide 4
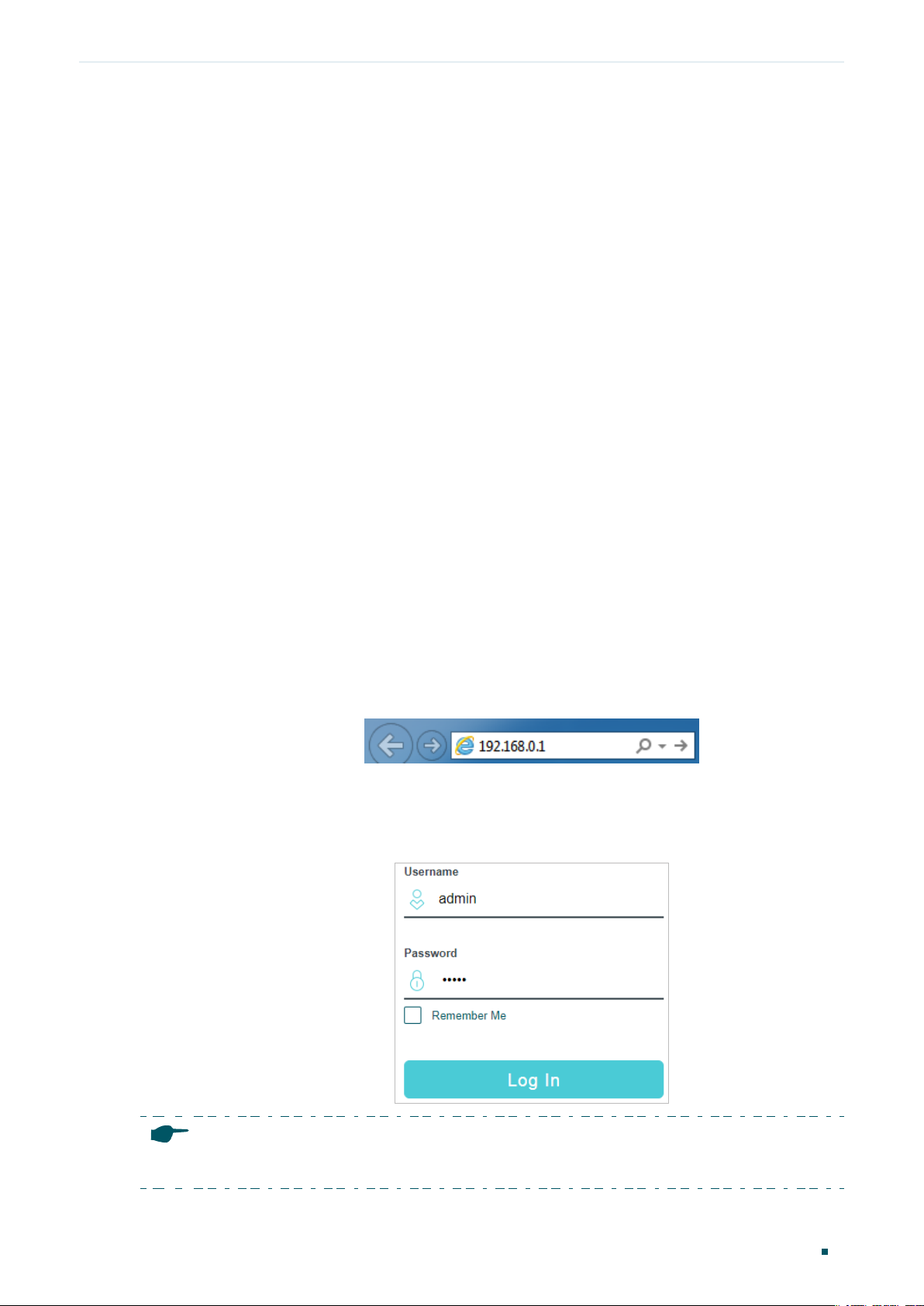
Accessing the Switch Web Interface Access
2
Web Interface Access
You can access the switch’s web interface through the web-based authentication.
The switch uses two built-in web servers, HTTP server and HTTPS server, for user
authentication.
The following example shows how to login via the HTTP server.
2.1 Login
To manage your switch through a web browser in the host PC:
1) Make sure that the route between the host PC and the switch is available.
2) Launch a web browser. The supported web browsers include, but are not limited to, the
following types:
● IE 8.0, 9.0, 10.0, 11.0
● Firefox 26.0, 27.0
● Chrome 32.0, 33.0
3) Enter the switch’s IP address in the web browser’s address bar. The switch’s default IP
address is 192.168.0.1.
Figure 2-1 Enter the switch's IP addresss in the browser
4) Enter the username and password in the pop-up login window. Use admin for both
username and password in lower case letters.
Figure 2-2 Login authentication
Note:
The first time you log in, change the password to better protect your network and devices.
User Guide
5

Accessing the Switch Web Interface Access
5) The typical web interface displays below. You can view the switch’s running status and
configure the switch on this interface.
Figure 2-3 Web interface
2.2 Save Config Function
The switch’s configuration files fall into two types: the running configuration file and the
start-up configuration file.
After you perform configurations on the sub-interfaces and click Apply, the modifications
will be saved in the running configuration file. The configurations will be lost when the
switch reboots.
If you need to keep the configurations after the switch reboots, please use the Save
function on the main interface to save the configurations in the start-up configuration file.
User Guide 6

Accessing the Switch Web Interface Access
Figure 2-4 Save the Configuration
2.3 Disable the Web Server
You can shut down the HTTP server and HTTPS server to block any access to the web
interface.
SECURITY > Access Security > HTTP Config, disable the HTTP server and click Apply.
Go to
Figure 2-5 Shut down HTTP server
Go to
SECURITY > Access Security > HTTPS Config
Apply.
Figure 2-6 Disbale the HTTPS Server
, disable the HTTPS server and click
2.4 Configure the Switch's IP Address and Default Gateway
If you want to access the switch via a specified port (hereafter referred to as the access
port), you can configure the port as a routed port and specify its IP address, or configure
the IP address of the VLAN which the access port belongs to.
User Guide
7

Accessing the Switch Web Interface Access
■ Change the IP Address
By default, all the ports belong to VLAN 1 with the VLAN interface IP 192.168.0.1.
The following example shows how to change the switch’s default access IP address
192.168.0.1.
1) Go to
L3 FEATURES > Interface
. The default access IP address in VLAN 1 in the
Interface List. Click Edit IPv4 to modify VLAN1’s IP address.
Figure 2-7 Change VLAN1's IP address
2) Choose the IP Address Mode as Static. Enter the new access address in the IP
Address field and click Apply. Make sure that the route between the host PC and the
switch’s new IP address is available.
Figure 2-8 Specify the IP address
3) Enter the new IP address in the web browser to access the switch.
4) Click
to save the settings.
■ Configure the Default Gateway
The following example shows how to configure the switch’s gateway. By default, the switch
has no default gateway.
User Guide 8

Accessing the Switch Web Interface Access
1) Go to page
L3 FEATURES > Static Routing > IPv4 Static Routing
. Click to load
the following page and configure the parameters related to the switch’s gateway. Then
click Create.
Figure 2-9 Configure the default gateway
Destination Specify the destination as 0.0.0.0.
Subnet Mask Specify the subnet mask as 0.0.0.0.
Next Hop Configure your desired default gateway as the next hop’s IP address.
Distance Specify the distance as 1.
2) Click to save the settings.
3) Check the routing table to verify the default gateway you configured. The entry marked
in red box displays the valid default gateway.
Figure 2-10 View the default gateway
User Guide
9

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
3
Command Line Interface Access
Users can access the switch's command line interface through the console (only for switch
with console port), Telnet or SSH connection, and manage the switch with the command
lines.
Console connection requires the host PC connecting to the switch’s console port directly,
while Telnet and SSH connection support both local and remote access.
The following table shows the typical applications used in the CLI access.
Table 3-1 Method list
Method Using Port Typical Applications
Console Console port (connected
directly)
Telnet RJ-45 port CMD
SSH RJ-45 port Putty
Hyper Terminal
3.1 Console Login (only for switch with console port)
Follow these steps to log in to the switch via the Console port:
1) Connect the PC or terminal to the Console port on the switch with the serial cable.
2) Start the terminal emulation program (such as the Hyper Terminal) on the PC and
configure the terminal emulation program as follows:
● Baud Rate: 38400bps
● Data Bits: 8
● Parity: None
● Stop Bits: 1
● Flow Control: None
3) Type the User name and Password in the Hyper Terminal window. The default value
for both of them is admin. Press Enter in the main window and Switch> will appear,
indicating that you have successfully logged in to the switch and you can use the CLI
now.
User Guide 10

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
Figure 3-1 CLI Main Window
Note:
The first time you log in, change the password to better protect your network and devices.
4) Enter enable to enter the User EXEC Mode to further configure the switch.
Figure 3-2 User EXEC Mode
Note:
In Windows XP, go to Start > All Programs > Accessories > Communications > Hyper Terminal to
open the Hyper Terminal and configure the above settings to log in to the switch.
User Guide
11

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
3.2 Telnet Login
The switch supports Login Local Mode for authentication by default.
Login Local Mode: Username and password are required, which are both admin by default.
The following steps show how to manage the switch via the Login Local Mode:
1) Make sure the switch and the PC are in the same LAN (Local Area Network). Click Start
and type in cmd in the Search bar and press Enter.
Figure 3-3 Open the cmd Window
2) Type in telnet 192.168.0.1 in the cmd window and press Enter.
Figure 3-4 Log In to the Switch
3) Type in the login username and password (both admin by default). Press Enter and you
will enter User EXEC Mode.
Figure 3-5 Enter User EXEC Mode
Note:
The first time you log in, change the password to better protect your network and devices.
4) Type in enable command and you will enter Privileged EXEC Mode. By default no
password is needed. Later you can set a password for users who want to access the
Privileged EXEC Mode.
User Guide 12

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
Figure 3-6 Enter Privileged EXEC Mode
Now you can manage your switch with CLI commands through Telnet connection.
Figure 3-7 Enter Privileged EXEC Mode
Now you can manage your switch with CLI commands through Telnet connection.
3.3 SSH Login
SSH login supports the following two modes: Password Authentication Mode and Key
Authentication Mode. You can choose one according to your needs:
■ Password Authentication Mode: Username and password are required, which are both
admin by default.
■ Key Authentication Mode (Recommended): A public key for the switch and a private key
for the client software (PuTTY) are required. You can generate the public key and the
private key through the PuTTY Key Generator.
User Guide
13

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
Before logging in via SSH, follow the steps below to enable SSH on the terminal emulation
program:
Figure 3-8 Enable SSH
Password Authentication Mode
1) Open PuTTY and go to the Session page. Enter the IP address of the switch in the Host
Name field and keep the default value 22 in the Port field; select SSH as the Connection
type. Click Open.
Figure 3-9 Configurations in PuTTY
2) Enter the login username and password to log in to the switch, and you can continue to
configure the switch.
User Guide 14

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
Figure 3-10 Log In to the Switch
Note:
The first time you log in, change the password to better protect your network and devices.
Key Authentication Mode
1) Open the PuTTY Key Generator. In the Parameters section, select the key type and
enter the key length. In the Actions section, click Generate to generate a public/private
key pair. In the following figure, an SSH-2 RSA key pair is generated, and the length of
each key is 1024 bits.
Figure 3-11 Generate a Public/Private Key Pair
Note:
● The key length should be between 512 and 3072 bits.
● You can accelerate the key generation process by moving the mouse quickly and randomly in
the Key section.
2) After the keys are successfully generated, click Save public key to save the public key
to a TFTP server; click Save private key to save the private key to the host PC.
User Guide
15

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
Figure 3-12 Save the Generated Keys
3) On Hyper Terminal, download the public key file from the TFTP server to the switch as
shown in the following figure:
Figure 3-13 Download the Public Key to the Switch
Note:
● The key type should accord with the type of the key file. In the above CLI, v1 corresponds to
SSH-1 (RSA), and v2 corresponds to SSH-2 RSA and SSH-2 DSA.
● The key downloading process cannot be interrupted.
4) After the public key is downloaded, open PuTTY and go to the Session page. Enter the
IP address of the switch and select SSH as the Connection type (keep the default value
in the Port field).
User Guide 16

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
Figure 3-14 Configure the Host Name and Connection Type
5) Go to Connection > SSH > Auth. Click Browse to download the private key file to
PuTTY. Click Open to start the connection and negotiation.
Figure 3-15 Download the Private Key to PuTTY
6) After negotiation is completed, enter the username to log in. If you can log in without
entering the password, the key authentication completed successfully.
User Guide
17

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
Figure 3-16 Log In to the Switch
3.4 Disable Telnet login
You can shut down the Telnet function to block any Telnet access to the CLI interface.
■
Using the GUI:
Go to
Apply.
Figure 3-17 Disable Telnet login
SECURITY > Access Security > Telnet Config, disable the Telnet function and click
■
Using the CLI:
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#telnet disable
3.5 Disable SSH login
You can shut down the SSH server to block any SSH access to the CLI interface.
■
Using the GUI:
SECURITY > Access Security > SSH Config, disable the SSH server and click Apply.
Go to
User Guide 18

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
Figure 3-18 Shut down SSH server
■
Using the CLI:
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#no ip ssh server
3.6 Copy running-config startup-config
The switch’s configuration files fall into two types: the running configuration file and the
start-up configuration file.
After you enter each command line, the modifications will be saved in the running
configuration file. The configurations will be lost when the switch reboots.
If you need to keep he configurations after the switch reboots, please user the command
copy running-config startup-config to save the configurations in the start-up
configuration file.
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
3.7 Change the Switch's IP Address and Default Gateway
If you want to access the switch via a specified port (hereafter referred to as the access
port), you can configure the port as a routed port and specify its IP address, or configure
the IP address of the VLAN which the access port belongs to.
■ Change the IP Address
By default, all the ports belong to VLAN 1 with the VLAN interface IP 192.168.0.1/24. In
the following example, we will show how to replace the switch’s default access IP address
192.168.0.1/24 with 192.168.0.10/24.
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#interface vlan 1
User Guide
19

Accessing the Switch Command Line Interface Access
Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.10 255.255.255.0
The connection will be interrupted and you should telnet to the switch's new IP address
192.168.0.10.
C:\Users\Administrator>telnet 192.168.0.10
User:admin
Password:admin
Switch>enable
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
■ Configure the Default Gateway
In the following example, we will show how to configure the switch’s gateway as
192.168.0.100. By default, the switch has no default gateway.
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.100 1
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide 20

Part 2
Managing System
CHAPTERS
1. System
2. System Info Configurations
3. User Management Configurations
4. System Tools Configurations
5. EEE Configuration
66. SDM Template Configuration
77. Time Range Configuration
88. Appendix: Default Parameters

Managing System System
1
System
1.1 Overview
In System module, you can view the system information and configure the system
parameters and features of the switch.
1.2 Supported Features
System Info
You can view the switch’s port status and system information, and configure the device
description, system time, and daylight saving time.
User Management
You can manage the user accounts for login to the switch. There are multiple user types
which have different access levels, and you can create different user accounts according
to your need.
System Tools
You can configure the boot file of the switch, backup and restore the configurations,
update the firmware, reset the switch, and reboot the switch.
EEE
EEE (Energy Efficient Ethernet) is used to save power consumption of the switch during
periods of low data activity. You can simply enable this feature on ports to allow power
reduction.
SDM Template
SDM (Switch Database Management) Template is used to prioritize hardware resources for
certain features. The switch provides three templates which allocate different hardware
resources for different usage, and you can choose one according to your need.
Time Range
With this feature, you can configure a time range and bind it to a n ACL rule.
User Guide 22

Managing System System Info Configurations
2
System Info Configurations
With system information configurations, you can:
■
View the System Summary
■
Configure the Device Description
■
Configure the System Time
■
Configure the Daylight Saving Time
2.1 Using the GUI
2.1.1 Viewing the System Summary
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Info > System Summary to load the System
Summary page. You can view the port status and system information of the switch.
Viewing the Port Status
In the Port Status section, you can view the status and bandwidth utilization of each port.
Figure 2-1 Viewing the System Summary
The following table introduces the meaning of each port status:
Port Status Indication
Indicates that the corresponding 10Gbps port is not connected to a device.
Indicates that the corresponding 10Gbps port is at the speed of 1000Mbps.
Indicates that the corresponding 10Gbps port is at the speed of 1000Mbps or
100Mbps.
Indicates that the corresponding SFP+ port is not connected to a device.
Indicates the SFP+ port is at the speed of 10Gbps.
Indicates the SFP+ port is at the speed of 1000Mbps.
You can move your cursor to a port to view the detailed information of the port.
User Guide
23

Managing System System Info Configurations
Figure 2-2 Port Information
Port Information Indication
Port Displays the port number.
Type Displays the type of the port.
Speed Displays the maximum transmission rate and duplex mode of the port.
Status Displays the connection status of the port.
You can click a port to view the bandwidth utilization on this port.
Figure 2-3 Bnadwidth Utilization
RX Displays the bandwidth utilization of receiving packets on this port.
TX Displays the bandwidth utilization of sending packets on this port.
User Guide 24

Managing System System Info Configurations
Viewing the System Information
In the System Info section, you can view the system information of the switch.
Figure 2-4 System Information
System
Description
Device Name Displays the name of the switch. You can edit it on the Device Description page.
Device Location Displays the location of the switch. You can edit it on the Device Description page.
Contact
Information
Hardware
Version
Firmware
Version
Boot Loader
Version
Displays the system description of the switch.
Displays the contact information of the switch. You can edit it on the Device
Description page.
Displays the hardware version of the switch.
Displays the firmware version of the switch.
Displays the boot loader version of the switch.
User Guide
25

Managing System System Info Configurations
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the switch.
System Time Displays the system time of the switch.
Running Time Displays the running time of the switch.
Serial Number Displays the serial number of the switch.
Jumbo Frame Displays whether Jumbo Frame is enabled. You can click Settings to jump to the
Jumbo Frame configuration page.
SNTP Displays whether the switch gets system time from NTP Server. You can click
Settings to jump to the System Time configuration page.
IGMP Snooping Displays whether IGMP Snooping is enabled. You can click Settings to jump to the
IGMP Snooping configuration page.
SNMP Displays whether SNMP is enabled. You can click Settings to jump to the SNMP
configuration page.
Spanning Tree Displays whether Spanning Tree is enabled. You can click Settings to jump to the
Spanning Tree configuration page.
DHCP Relay Displays whether DHCP Relay is enabled. You can click Settings to jump to the DHCP
Relay configuration page.
802.1x Displays whether Jumbo Frame is enabled. You can click Settings to jump to the
Jumbo Frame configuration page.
HTTP Server Displays whether HTTP server is enabled. You can click Settings to jump to the HTTP
configuration page.
Telnet Displays whether Telnet is enabled. You can click Settings to jump to the Telnet
configuration page.
SSH Displays whether SSH is enabled. You can click Settings to jump to the SSH
configuration page.
2.1.2 Configuring the Device Description
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Info > Device Description to load the following
page.
Figure 2-5 Configuring the Device Description
1) Configure the following parameters.
User Guide 26

Managing System System Info Configurations
Device Name Specify a name for the switch.
Device Location Enter the location of the switch.
System Contact Enter the contact information.
2) Click Apply.
2.1.3 Configuring the System Time
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Info > System Time to load the following page.
Figure 2-6 Configuring the System Time
In the Time Info section, you can view the current time information of the switch.
Current System
Time
Current Time
Source
Displays the current date and time of the switch.
Displays how the switch gets the current time.
In the Time Config section, follow these steps to configure the system time:
1) Choose one method to set the system time and specify the related parameters.
Manual Set the system time manually.
Date: Specify the date of the system.
Time: Specify the time of the system.
User Guide
27

Managing System System Info Configurations
Get Time from
NTP Server
Synchronize
with PC’s Clock
Get the system time from an NTP server. Make sure the NTP server is accessible
on your network. If the NTP server is on the internet, connect the switch to the
internet first.
Time Zone: Select your local time zone.
Primary Server: Enter the IP Address of the primary NTP server.
Secondary Server: Enter the IP Address of the secondary NTP server. Once the
primary NTP server is down, the EAP can get the system time from the secondary
NTP server.
Update Rate: Specify the interval the switch fetching time from NTP server, which
ranges from 1 to 24 hours.
Synchronize the system time with the clock of your currently logged-in host.
2) Click Apply.
2.1.4 Configuring the Daylight Saving Time
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Info > Daylight Saving Time to load the following
page.
Figure 2-7 Configuring the Daylight Saving Time
Follow these steps to configure Daylight Saving Time:
1) In the DST Config section, enable the Daylight Saving Time function.
2) Choose one method to set the Daylight Saving Time and specify the related
parameters.
Predefined
Mode
If you select Predefined Mode, choose a predefined DST schedule for the switch.
USA: Select the Daylight Saving Time of the USA. It is from 2: 00 a.m. on the
Second Sunday in March to 2:00 a.m. on the First Sunday in November.
Australia: Select the Daylight Saving Time of Australia. It is from 2:00 a.m. on the
First Sunday in October to 3:00 a.m. on the First Sunday in April.
Europe: Select the Daylight Saving Time of Europe. It is from 1: 00 a.m. on the Last
Sunday in March to 1:00 a.m. on the Last Sunday in October.
New Zealand: Select the Daylight Saving Time of New Zealand. It is from 2: 00 a.m.
on the Last Sunday in September to 3:00 a.m. on the First Sunday in April.
User Guide 28

Managing System System Info Configurations
Recurring Mode If you select Recurring Mode, specify a cycle time range for the Daylight Saving
Time of the switch. This configuration will be used every year.
Offset: Specify the time to set the clock forward by.
Start Time: Specify the start time of Daylight Saving Time. The interval between
start time and end time should be more than 1 day and less than 1 year(365 days).
End Time: Specify the end time of Daylight Saving Time. The interval between
start time and end time should be more than 1 day and less than 1 year (365 days).
Date Mode If you select Date Mode, specify an absolute time range for the Daylight Saving
Time of the switch. This configuration will be used only one time.
Offset: Specify the time to set the clock forward by.
Start Time: Specify the start time of Daylight Saving Time. The interval between
start time and end time should be more than 1 day and less than 1 year(365 days).
End Time: Specify the end time of Daylight Saving Time. The interval between
start time and end time should be more than 1 day and less than 1 year (365 days).
3) Click Apply.
2.2 Using the CLI
2.2.1 Viewing the System Summary
On privileged EXEC mode or any other configuration mode, you can use the following
commands to view the system information of the switch:
show interface status [ fastEthernet
View status of the interface.
port
: Enter the number of the Ethernet port.
show system-info
View the system information including System Description, Device Name, Device Location, System
Contact, Hardware Version, Firmware Version, System Time, Run Time and so on.
The following example shows how to view the interface status and the system information
of the switch.
port
| gigabitEthernet
port
| ten-gigabitEthernet
port
]
Switch#show interface status
Port Status Speed Duplex FlowCtrl Jumbo Active-Medium
------- ----------- ----- ------ -------- --------- -------------
Te1/0/1 LinkDown N/A N/A N/A Disable Copper
Te1/0/2 LinkDown N/A N/A N/A Disable Copper
User Guide
29

Managing System System Info Configurations
Te1/0/3 LinkUp 1000M Full Disable Disable Copper
...
Switch#show system-info
System Description - JetStream 12-Port 10GBase-T Smart Switch with 4 10G SFP+ Slots
System Name - T1700X-16TS
System Location - SHENZHEN
Contact Information - www.tp-link.com
Hardware Version - T1700X-16TS 3.0
Software Version - 3.0.0 Build 20180413 Rel.37790(s)
Bootloader Version - TP-LINK BOOTUTIL(v1.0.0)
Mac Address - 00-0A-EB-13-12-FF
Serial Number -
System Time - 2006-01-07 03:40:54
Running Time - 5 day - 19 hour - 42 min - 1 sec
2.2.2 Configuring the Device Description
Follow these steps to configure the device description:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 hostname [
Specify the system name of the switch.
hostname
default, it is the model name of the switch.
Step 3 location [
Specify the system location of the switch.
hostname
: Enter the device name. The length of the name ranges from 1 to 32 characters. By
location
]
]
location
it is “SHENZHEN”.
Step 4 contact-info [
Specify the system contact Information.
contact-info
By default, it is “www.tp-link.com”.
: Enter the device location. It should consist of no more than 32 characters. By default,
: Enter the contact information. It should consist of no more than 32 characters.
contact-info
]
User Guide 30

Managing System System Info Configurations
Step 5 show system-info
Verify the system information including system Description, Device Name, Device Location,
System Contact, Hardware Version, Firmware Version, System Time, Run Time and so on.
Step 6 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 7 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
The following example shows how to set the device name as Switch_A, set the location as
BEIJING and set the contact information as http://www.tp-link.com.
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#hostname Switch_A
Switch(config)#location BEIJING
Switch(config)#contact-info http://www.tp-link.com
Switch(config)#show system-info
System Description -JetStream 12-Port 10GBase-T Smart Switch with 4 10G SFP+ Slots
System Name - Switch_A
System Location - BEIJING
Contact Information - http://www.tp-link.com
...
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
2.2.3 Configuring the System Time
Follow these steps to configure the system time:
Note:
The mode of Synchronize with PC’s Clock does not support CLI command.
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
User Guide
31

Managing System System Info Configurations
Step 2 Use the following command to set the system time manually:
system-time manual
Configure the system time manually.
time
: Specify the date and time manually in the format of MM/DD/YYYY-HH:MM:SS. The valid
value of the year ranges from 2000 to 2037.
Use the following command to set the system time by getting time from the NTP server.
Ensure the NTP server is accessible. If the NTP server is on the internet, connect the switch to
the internet first.
system-time ntp {
timezone
The detailed information of each time-zone are displayed as follows:
UTC-12:00 —— TimeZone for International Date Line West.
UTC-11:00 —— TimeZone for Coordinated Universal Time-11.
UTC-10:00 —— TimeZone for Hawaii.
UTC-09:00 —— TimeZone for Alaska.
UTC-08:00 —— TimeZone for Pacific Time (US Canada).
UTC-07:00 —— TimeZone for Mountain Time (US Canada).
UTC-06:00 —— TimeZone for Central Time (US Canada).
: Enter your local time-zone, which ranges from UTC-12:00 to UTC+13:00.
time
timezone
} {
ntp-server
} {
backup-ntp-server
} {
fetching-rate
}
UTC-05:00 —— TimeZone for Eastern Time (US Canada).
UTC-04:30 —— TimeZone for Caracas.
UTC-04:00 —— TimeZone for Atlantic Time (Canada).
UTC-03:30 —— TimeZone for Newfoundland.
UTC-03:00 —— TimeZone for Buenos Aires, Salvador, Brasilia.
UTC-02:00 —— TimeZone for Mid-Atlantic.
UTC-01:00 —— TimeZone for Azores, Cape Verde Is.
UTC —— TimeZone for Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London.
UTC+01:00 —— TimeZone for Amsterdam, Berlin, Bern, Rome, Stockholm, Vienna.
UTC+02:00 —— TimeZone for Cairo, Athens, Bucharest, Amman, Beirut, Jerusalem.
UTC+03:00 —— TimeZone for Kuwait, Riyadh, Baghdad.
UTC+03:30 —— TimeZone for Tehran.
UTC+04:00 —— TimeZone for Moscow, St.Petersburg, Volgograd, Tbilisi, Port Louis.
UTC+04:30 —— TimeZone for Kabul.
UTC+05:00 —— TimeZone for Islamabad, Karachi, Tashkent.
User Guide 32

Managing System System Info Configurations
UTC+05:30 —— TimeZone for Chennai, Kolkata, Mumbai, New Delhi.
UTC+05:45 —— TimeZone for Kathmandu.
UTC+06:00 —— TimeZone for Dhaka,Astana, Ekaterinburg.
UTC+06:30 —— TimeZone for Yangon (Rangoon).
UTC+07:00 —— TimeZone for Novosibrisk, Bangkok, Hanoi, Jakarta.
UTC+08:00 —— TimeZone for Beijing, Chongqing, Hong Kong, Urumqi, Singapore.
UTC+09:00 —— TimeZone for Seoul, Irkutsk, Osaka, Sapporo, Tokyo.
UTC+09:30 —— TimeZone for Darwin, Adelaide.
UTC+10:00 —— TimeZone for Canberra, Melbourne, Sydney, Brisbane.
UTC+11:00 —— TimeZone for Solomon Is., New Caledonia, Vladivostok.
UTC+12:00 —— TimeZone for Fiji, Magadan, Auckland, Welington.
UTC+13:00 —— TimeZone for Nuku’alofa, Samoa.
ntp-server
backup-ntp-server
fetching-rate
Step 3 Use the following command to verify the system time information.
show system-time
Verify the system time information.
Use the following command to verify the NTP mode configuration information.
show system-time ntp
Verify the system time information of NTP mode.
Step 4 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 5 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
: Specify the IP address of the primary NTP server.
: Specify the IP address of the backup NTP server.
: Specify the interval fetching time from the NTP server.
The following example shows how to set the system time by Get Time from NTP Server and
set the time zone as UTC+08:00, set the NTP server as 133.100.9.2, set the backup NTP
server as 139.78.100.163 and set the update rate as 11.
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#system-time ntp UTC+08:00 133.100.9.2 139.78.100.163 11
Switch(config)#show system-time ntp
Time zone : UTC+08:00
Prefered NTP server: 133.100.9.2
Backup NTP server: 139.78.100.163
Last successful NTP server: 133.100.9.2
User Guide
33

Managing System System Info Configurations
Update Rate: 11 hour(s)
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
2.2.4 Configuring the Daylight Saving Time
Follow these steps to configure the Daylight Saving Time:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 Use the following command to select a predefined Daylight Saving Time configuration:
system-time dst predefined [ USA | Australia | Europe | New-Zealand ]
Specify the Daylight Saving Time using a predefined schedule.
USA | Australia | Europe | New-Zealand: Select one mode of Daylight Saving Time.
USA: 02:00 a.m. on the Second Sunday in March ~ 02:00 a.m. on the First Sunday in November.
Australia: 02:00 a.m. on the First Sunday in October ~ 03:00 a.m. on the First Sunday in April.
Europe: 01:00 a.m. on the Last Sunday in March ~ 01:00 a.m. on the Last Sunday in October.
New Zealand: 02:00 a.m. on the Last Sunday in September ~ 03:00 a.m. on the First Sunday in
April.
Use the following command to set the Daylight Saving Time in recurring mode:
system-time dst recurring {
etime
} [
offset
]
Specify the Daylight Saving Time in Recuring mode.
sweek
: Enter the start week of Daylight Saving Time. There are 5 values showing as follows:
first, second, third, fourth, last.
sday
: Enter the start day of Daylight Saving Time. There are 7 values showing as follows: Sun,
Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat.
smonth
Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec.
stime
eweek
first, second, third, fourth, last.
: Enter the start month of Daylight Saving Time. There are 12 values showing as follows:
: Enter the start time of Daylight Saving Time,in the format of HH:MM.
: Enter the end week of Daylight Saving Time. There are 5 values showing as follows:
sweek
} {
sday
} {
smonth
} {
stime
} {
eweek
} {
eday
} {
emonth
} {
eday
: Enter the end day of Daylight Saving Time. There are 7 values showing as follows: Sun,
Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat.
emonth
Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec.
etime
offset
: Enter the end month of Daylight Saving Time. There are 12 values showing as follows:
: Enter the end time of Daylight Saving Time,in the format of HH:MM.
: Enter the offset of Daylight Saving Time. The default value is 60.
User Guide 34

Managing System System Info Configurations
Use the following command to set the Daylight Saving Time in date mode:
system-time dst date {
offset
]
Specify the Daylight Saving Time in Date mode.
smonth
Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec.
sday
stime
syear
emonth
Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, Dec.
eday
etime
eyear
offset
Step 3 show system-time dst
Verify the DST information of the switch.
Step 4 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
: Enter the start month of Daylight Saving Time. There are 12 values showing as follows:
: Enter the start day of Daylight Saving Time, which ranges from 1 to 31.
: Enter the start time of Daylight Saving Time,in the format of HH:MM.
: Enter the start year of Daylight Saving Time.
: Enter the end month of Daylight Saving Time. There are 12 values showing as follows:
: Enter the end day of Daylight Saving Time, which ranges from 1 to 31.
: Enter the end time of Daylight Saving Time,in the format of HH:MM.
: Enter the end year of Daylight Saving Time.
: Enter the offset of Daylight Saving Time. The default value is 60.
smonth
} {
sday
} {
stime
} {
syear
} {
emonth
} {
eday
} {
etime
} {
eyear
} [
Step 5 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
The following example shows how to set the Daylight Saving Time by Date Mode. Set the
start time as 01:00 August 1st, 2017, set the end time as 01:00 September 1st,2017 and
set the offset as 50.
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#system-time dst date Aug 1 01:00 2017 Sep 1 01:00 2017 50
Switch(config)#show system-time dst
DST starts at 01:00:00 on Aug 1 2017
DST ends at 01:00:00 on Sep 1 2017
DST offset is 50 minutes
DST configuration is one-off
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide
35

Managing System User Management Configurations
3
User Management Configurations
With User Management, you can create and manage the user accounts for login to the
switch.
3.1 Using the GUI
There are four types of user accounts with different access levels: Admin, Operator, Power
User and User.
■ There is a default Admin account which cannot be deleted. The default username and
password of this account are both admin. You can also create more Admin accounts.
■ If you create Operator, Power User or User accounts, you need go to the AAA section
to create an Enable Password. If needed, these types of users can use the Enable
Password to change their access level to Admin.
3.1.1 Creating Accounts
Choose the menu SYSTEM > User Management > User Config to load the following page.
Figure 3-1 User Config Page
By default, there is a default Admin account in the table. You can click to edit this Admin
account but you cannot delete it.
You can create new user accounts. Click
and the following window will pop up.
User Guide 36

Managing System User Management Configurations
Figure 3-2 Adding Account
Follow these steps to create a new user account.
1) Configure the following parameters:
Username Specify a username for the account. It contains 16 characters at most,
composed of digits, English letters and symbols. No spaces, question
marks and double quotation marks are allowed.
Access Level Select the access level. There are four options provided:
Admin: Admin can edit, modify and view all the settings of different
functions.
Operator: Operator can edit, modify and view most of the settings of
different functions.
Power User: Power User can edit, modify and view some of the settings of
different functions.
User: User can only view the settings without the right to edit or modify.
Password Specify a password for the account. It contains 6–31 alphanumeric
characters (case-sensitive) and symbols. No spaces are allowed.
Confirm
Password
Retype the password.
2) Click Create.
3.1.2 Configuring Enable Password
Choose the menu SECURITY > AAA > Global Config to load the following page.
Figure 3-3 Configure Enable Password
User Guide
37

Managing System User Management Configurations
Follow these steps to configure Enable Password:
1) Select Set Password and specify the Enable Password in the Password field. It should
be a string with 31 characters at most, which can contain only English letters (case
sensitive) digits and 17 kinds of special characters. The special characters are !$%’()*,-
./[]_{|}.
2) Click Apply.
Tips:
The logged-in users can enter the Enable Password on this page to get the administrative
privileges.
3.2 Using the CLI
There are four types of user accounts with different access levels: Admin, Operator, Power
User and User.
■ There is a default Admin account which cannot be deleted. The default username and
password of this account are both admin. You can also create more Admin accounts.
■ If you create Operator, Power User or User accounts, you need go to the AAA section
to create an Enable Password. If needed, these types of users can use the Enable
Password to change their access level to Admin.
3.2.1 Creating Accounts
Follow these steps to create an account:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
User Guide 38

Managing System User Management Configurations
Step 2 Use the following command to create an account unencrypted or symmetric encrypted.
user name
7
encrypted-password
name
digits, English letters and symbols. No spaces, question marks and double quotation marks are
allowed.
admin | operator | power_user | user: Specify the access level for the user. Admin can edit,
modify and view all the settings of different functions. Operator can edit, modify and view
mostly the settings of different functions. Power User can edit, modify and view some the
settings of different functions. User only can view the settings without the right to edit and
modify.
0: Specify the encryption type. 0 indicates that the password you entered is unencrypted, and
the password is saved to the configuration file unencrypted. By default, the encryption type is 0.
password
or symbols. The password is case sensitive, allows digits, English letters (case sensitive),
underlines and sixteen special characters.
7: Specify the encryption type. 7 indicates that the password you entered is symmetric
encrypted, and the password is saved to the configuration file symmetric encrypted.
encrypted-password
copy from another switch’s configuration file. After the encrypted password is configured, you
should use the corresponding unencrypted password to reenter this mode.
name
{ privilege admin | operator | power_user | user } password { [ 0 ]
}
: Enter a user name for users’ login. It contains 16 characters at most, composed of
: Enter a password for users’ login. It is a string from 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters
: Enter a symmetric encrypted password with fixed length, which you can
password
|
Use the following command to create an account MD5 encrypted.
user name
encrypted-password
Create an account whose access level is Admin.
name
digits, English letters and symbols. No spaces, question marks and double quotation marks are
allowed.
admin | operator | power_user | user: Specify the access level for the user. Admin can edit,
modify and view all the settings of different functions. Operator can edit, modify and view
mostly the settings of different functions. Power User can edit, modify and view some the
settings of different functions. User only can view the settings without the right to edit and
modify.
0: Specify the encryption type. 0 indicates that the password you entered is unencrypted, but
the password is saved to the configuration file MD5 encrypted. By default, the encryption type
is 0.
password
or symbols. The password is case sensitive, allows digits, English letters (case sensitive),
underlines and sixteen special characters.
5: Specify the encryption type. 5 indicates that the password you entered is MD5 encrypted,
and the password is saved to the configuration file MD5 encrypted.
name
{ privilege admin | operator | power_user | user } secret { [ 0 ]
}
: Enter a user name for users’ login. It contains 16 characters at most, composed of
: Enter a password for users’ login. It is a string from 1 to 32 alphanumeric characters
password
| 5
encrypted-password
from another switch’s configuration file.
Step 3 show user account-list
Verify the information of the current users.
: Enter a MD5 encrypted password with fixed length, which you can copy
User Guide
39

Managing System User Management Configurations
Step 4 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 5 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
3.2.2 Configuring Enable Password
Follow these steps to create an account of other type:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 Use the following command to create an enable password unencrypted or symmetric
encrypted.
enable admin password { [ 0 ]
Create an Enable Password. It can change the users’ access level to Admin. By default, it is
empty.
0: Specify the encryption type. 0 indicates that the password you entered is unencrypted, and
the password is saved to the configuration file unencrypted. By default, the encryption type is 0.
password
sensitive), digits and 17 kinds of special characters. The special characters are !$%’()*,-./[]_{|}.
7: Specify the encryption type. 7 indicates that the password you entered is symmetric
encrypted, and the password is saved to the configuration file symmetric encrypted.
encrypted-password
copy from another switch’s configuration file. After the encrypted password is configured, you
should use the corresponding unencrypted password to reenter this mode.
Use the following command to create an enable password unencrypted or MD5 encrypted.
enable admin secret { [ 0 ]
Create an Enable Password. It can change the users’ access level to Admin. By default, it is
empty.
0: Specify the encryption type. 0 indicates that the password you entered is unencrypted, but
the password is saved to the configuration file MD5 encrypted. By default, the encryption type
is 0.
: It is a string with 31 characters at most, which can contain only English letters (case-
: Enter a symmetric encrypted password with fixed length, which you can
password
password
| 7
encrypted-password
| 5
encrypted-password
}
}
password
sensitive), digits and 17 kinds of special characters. The special characters are !$%’()*,-./[]_{|}.
5: Specify the encryption type. 5 indicates that the password you entered is MD5 encrypted,
and the password is saved to the configuration file MD5 encrypted.
encrypted-password
from another switch’s configuration file. After the encrypted password is configured, you
should use the corresponding unencrypted password to reenter this mode.
Step 3 show user account-list
Verify the information of the current users.
: It is a string with 31 characters at most, which can contain only English letters (case-
: Enter a MD5 encrypted password with fixed length, which you can copy
User Guide 40

Managing System User Management Configurations
Step 4 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 5 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
Tips:
The logged-in users can enter the enable-admin command and the Enable Password to get
the administrative privileges.
The following example shows how to create a uesr with the access level of Operator, set
the username as user1 and password as 123, and set the enable password as abc123.
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#user name user1 privilege operator password 123
Switch(config)#enable admin password abc123
Switch(config)#show user account-list
Index User-Name User-Type
----- --------- ---------
1 user1 Operator
2 admin Admin
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
Tips:
The logged-in users can enter the Enable Password on this page to get the administrative
privileges.
The following example shows how to create a uesr with the access level of Operator, set
the username as user1 and password as 123, enable AAA function and set the enable
password as abc123.
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#user name user1 privilege operator password 123
Switch(config)#aaa enable
Switch(config)#enable admin password abc123
Switch(config)#show user account-list
Index User-Name User-Type
----- --------- ---------
User Guide
41

Managing System User Management Configurations
1 user1 Operator
2 admin Admin
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide 42

Managing System System Tools Configurations
4
System Tools Configurations
With System Tools, you can:
■
Configure the boot file
■
Restore the configuration of the switch
■
Back up the configuration file
■
Upgrade the firmware
■
Reboot the switch
■
Reset the switch
4.1 Using the GUI
4.1.1 Configuring the Boot File
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Tools > Boot Config to load the following page.
Figure 4-1 Configuring the Boot File
User Guide
43

Managing System System Tools Configurations
Follow these steps to configure the boot file:
1) In the Boot Table section, select one or more units and configure the relevant
parameters.
Unit Displays the number of the unit.
Current Startup
Image
Next Startup
Image
Backup Image Select the backup image. When the switch fails to start up with the next startup
Current Startup
Config
Next Startup
Config
Backup Config Specify the backup configuration. When the switch fails to start up with the next
Displays the current startup image.
Select the next startup image. When the switch is powered on, it will try to start up
with the next startup image. The next startup image and backup image should not
be the same.
image, it will try to start up with the backup image. The next startup and backup
image should not be the same.
Displays the current startup configuration.
Specify the next startup configuration. When the switch is powered on, it will try
to start up with the next startup configuration. The next startup configuration and
backup configuration should not be the same.
startup configuration, it will try to start up with the backup configuration. The next
startup and backup configuration should not be the same.
2) Click Apply.
In the Image Table, you can view the information of the current startup image, next startup
image and backup image. The displayed information is as follows:
Image Name Displays the name of the image.
Software
Version
Flash Version Displays the flash version of the image.
Displays the software version of the image.
4.1.2 Restoring the Configuration of the Switch
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Tools > Restore Config to load the following page.
User Guide 44

Managing System System Tools Configurations
Figure 4-2 Restoring the Configuration of the Switch
Follow these steps to restore the current configuration of the switch:
1) In the Restore Config section, select the unit to be restored.
2) Click Browse and select the desired configuration file to be imported.
3) Choose whether to reboot the switch after restoring is completed. Only after the switch
is rebooted will the imported configuration take effect.
4) Click Import to import the configuration file.
Note:
It will take some time to restore the configuration. Please wait without any operation.
4.1.3 Backing up the Configuration File
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Tools > Backup Config to load the following page.
Figure 4-3 Backing up the Configuration File
In the Config Backup section, select one unit and click Export to export the configuration
file.
Note:
It will take some time to export the configuration. Please wait without any operation.
User Guide
45

Managing System System Tools Configurations
4.1.4 Upgrading the Firmware
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Tools > Firmware Upgrade to load the following
page.
Figure 4-4 Upgrading the Firmware
You can view the current firmware information on this page:
Firmware Version Displays the current firmware version of the system.
Hardware Version
Image Name Displays the image to upgrade. The operation will only affect the image displayed
Displays the current hardware version of the system.
here.
Follow these steps to upgrade the firmware of the switch:
1) Click Browse and select the proper firmware upgrade file.
2) Choose whether to reboot the switch after upgrading is completed. Only after the
switch is rebooted will the new firmware take effect.
3) Click Upgrade to upgrade the system.
Note:
● It will take some time to upgrade the switch. Please wait without any operation.
● It is recommended to backup your configuration before upgrading.
User Guide 46

Managing System System Tools Configurations
4.1.5 Rebooting the switch
There are two methods to reboot the switch: manually reboot the switch and configure
reboot schedule to automatically reboot the switch.
Manually Rebooting the Switch
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Tools > System Reboot > System Reboot to load
the following page.
Figure 4-5 Manually Rebooting the Switch
Follow these steps to reboot the switch:
1) In the System Reboot section, select the desired unit.
2) Choose whether to save the current configuration before reboot.
3) Click Reboot.
Configuring Reboot Schedule
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Tools > System Reboot > Reboot Schedule to load
the following page.
Figure 4-6 Configuring the Reboot Schedule
Follow these steps to configure the reboot schedule:
1) Enable Reboot Schedule, and select one time schedule for the switch to reboot.
Time Interval Specify a period of time. The switch will reboot after this period. Valid values are
from 1 to 43200 minutes.
To make this schedule recur, you need to click
or enable the option Save the current configuration before reboot.
to save current configuration
User Guide
47

Managing System System Tools Configurations
Special Time Specify the date and time for the switch to reboot.
Month/Day/Year: Specify the date for the switch to reboot.
Time (HH:MM): Specify the time for the switch to reboot, in the format of HH:MM.
2) Choose whether to save the current configuration before the reboot.
3) Click Apply.
4.1.6 Reseting the Switch
Choose the menu SYSTEM > System Tools > System Reset to load the following page.
Figure 4-7 Reseting the Switch
Follow these steps to reset the switch:
1) In the System Reset section, select the desired unit.
2) Choose whether to maintain the IP address of selected unit when resetting.
3) Click Reset.
After reset, all congurations of the switch will be reset to the factory defaults.
4.2 Using the CLI
4.2.1 Configuring the Boot File
Follow these steps to configure the boot file:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 boot application filename { image1 | image2 } { startup | backup }
Specify the configuration of the boot file. By default, image1.bin is the startup image and
image2.bin is the backup image.
image1 | image2: Select the image file to be configured.
startup | backup: Select the property of the image file.
User Guide 48

Managing System System Tools Configurations
Step 3 boot config filename { config1 | config2 } { startup | backup }
Specify the configuration of the boot file. By default, config1.cfg is the startup configuration
file and config2.cfg is the backup configuration file.
config1 | config2: Select the configuration file to be configured.
startup | backup: Specify the property of the configuration file.
Step 4 show boot
Verify the boot configuration of the system.
Step 5 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 6 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
The following example shows how to set the next startup image as image1, the
backup image as image2, the next startup configuration file as config1 and the backup
configuration file as config2.
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#boot application filename image1 startup
Switch(config)#boot application filename image2 backup
Switch(config)#boot config filename config1 startup
Switch(config)#boot config filename config2 backup
Switch(config)#show boot
Boot config:
Current Startup Image - image2.bin
Next Startup Image - image1.bin
Backup Image - image2.bin
Current Startup Config - config2.cfg
Next Startup Config - config1.cfg
Backup Config - config2.cfg
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide
49

Managing System System Tools Configurations
4.2.2 Restoring the Configuration of the Switch
Follow these steps to restore the configuration of the switch:
Step 1 enable
Enter privileged mode.
Step 2 copy tftp startup-config ip-address
Download the configuration file to the switch from TFTP server.
ip-addr
name
: Specify the IP address of the TFTP server. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are
supported.
: Specify the name of the configuration file to be downloaded.
ip-addr
filename
name
Note:
It will take some time to restore the configuration. Please wait without any operation.
The following example shows how to restore the configuration file named file1 from the
TFTP server with IP address 192.168.0.100.
Switch>enable
Switch#copy tftp startup-config ip-address 192.168.0.100 filename file1
Start to load user config file...
Operation OK! Now rebooting system...
4.2.3 Backing up the Configuration File
Follow these steps to back up the current configuration of the switch in a file:
Step 1 enable
Enter privileged mode.
Step 2 copy startup-config tftp ip-address
Back up the configuration file to TFTP server.
ip-addr
name
The following example shows how to backup the configuration file named file2 to TFTP
server with IP address 192.168.0.100.
Switch>enable
Switch#copy startup-config tftp ip-address 192.168.0.100 filename file2
Start to backup user config file...
: Specify the IP address of the TFTP server. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are
supported.
: Specify the name of the configuration file to be saved.
ip-addr
filename
name
User Guide 50

Managing System System Tools Configurations
Backup user config file OK.
4.2.4 Upgrading the Firmware
Follow these steps to upgrade the firmware:
Step 1 enable
Enter privileged mode.
Step 2 firmware upgrade tftp ip-address
Upgrade the switch’s backup image via TFTP server. To boot up with the new firmware, you
need to choose to reboot the switch with the backup image.
ip-addr
name
Step 3 Enter Y to continue and then enter Y to reboot the switch with the backup image.
: Specify the IP address of the TFTP server. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are
supported.
: Specify the name of the desired firmware file.
ip-addr
filename
name
The following example shows how to upgrade the firmware using the configuration file
named file3.bin. The TFTP server is 190.168.0.100.
Switch>enable
Switch#firmware upgrade tftp ip-address 192.168.0.100 filename file3.bin
It will only upgrade the backup image. Continue? (Y/N):Y
Operation OK!
Reboot with the backup image? (Y/N): Y
4.2.5 Rebooting the Switch
Manually Rebooting the Switch
Follow these steps to reboot the switch:
Step 1 enable
Enter privileged mode.
Step 2 reboot
Reboot the switch.
Configuring Reboot Schedule
Follow these steps to configure the reboot schedule:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
User Guide
51

Managing System System Tools Configurations
Step 2 Use the following command to set the interval of reboot:
reboot-schedule in
(Optional) Specify the reboot schedule.
interval
time
date
: Specify a period of time. The switch will reboot after this period. The valid values are
from 1 to 43200 minutes.
save_before_reboot: Save the configuration file before the switch reboots. To make this
schedule recur, you can add this part to the command.
Use the following command to set the special time of reboot:
reboot-schedule at
(Optional) Specify the reboot schedule.
: Specify the time for the switch to reboot, in the format of HH:MM.
: Specify the date for the switch to reboot, in the format of DD/MM/YYYY. The date should
be within 30 days.
save_before_reboot: Save the configuration file before the switch reboots.
If no date is specified, the switch will reboot according to the time you have set. If the time you
set is later than the time that this command is executed, the switch will reboot later the same
day; otherwise the switch will reboot the next day.
interval
time
[
[ save_before_reboot ]
date
] [ save_before_reboot ]
Step 3 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 4 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
The following example shows how to set the switch to reboot at 12:00 on 15/08/2017.
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#reboot-schedule at 12:00 15/08/2017 save_before_reboot
Reboot system at 15/08/2017 12:00. Continue? (Y/N): Y
Reboot Schedule Settings
---------------------------
Reboot schedule at 2017-08-15 12:00 (in 25582 minutes)
Save before reboot: Yes
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide 52

Managing System System Tools Configurations
4.2.6 Reseting the Switch
Follow these steps to reset the switch:
Step 1 enable
Enter privileged mode.
Step 2 reset [ except-ip ]
Reset the switch, and all configurations of the switch will be reset to the factory defaults.
except-ip: To maintain the IP address when resetting the switch, add this part to the command
Follow these steps to disable the reset function of console port or reset button:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 service reset-disable
Disable the reset function of console port or reset button. By default, the reset function is
enabled.
Note: use the no service reset-disable command to enable the reset function of console port.
User Guide
53

Managing System EEE Configuration
5
EEE Configuration
Choose the menu SYSTEM > EEE to load the following page.
Figure 5-1 Configuring EEE
Follow these steps to configure EEE:
1) In the EEE Config section, select one or more ports to be configured.
2) Enable or disable EEE on the selected port(s).
3) Click Apply.
5.1 Using the CLI
Follow these steps to configure EEE:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 interface { fastEthernet
gigabitEthernet
Enter interface configuration mode.
Step 3 eee
Enable EEE on the port.
port-list
port
| range fastEthernet
| ten-gigabitEthernet
port-list
port
| gigabitEthernet
| range ten-gigabitEthernet
port
| range
port-list
}
User Guide 54

Managing System EEE Configuration
Step 4 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 5 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
The following example shows how to enable the EEE feature on port 1/0/1.
Switch#config
Switch(config)#interface ten-gigabitEthernet 1/0/1
Switch(config-if)#eee
Switch(config-if)#show interface eee
Port EEE status
Te1/0/1 Enable
Te1/0/2 Disable
...
Switch(config-if)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide
55

Managing System SDM Template Configuration
6
SDM Template Configuration
6.1 Using the GUI
Choose the menu SYSTEM > SDM Template to load the following page.
Figure 6-1 Configuring SDM Template
In SDM Template Config section, select one template and click Apply. The setting will be
effective after the switch is rebooted.
Current Template Displays the template currently in effect.
Next Template Displays the template that will be effective after the reboot.
Select Next
Template
The Template Table displays the resources allocation of each template.
SDM Template Displays the name of the templates.
IP ACL Rules Displays the number of IP ACL Rules including Layer 3 ACL Rules and Layer 4 ACL
Select the template that will be effective after the next reboot.
Default: Select the template of default. It gives balance to the IP ACL rules and MAC
ACL rules.
EnterpriseV4: Select the template of enterpriseV4. It maximizes system resources
for IP ACL rules and MAC ACL rules.
EnterpriseV6: Select the template of enterpriseV6. It allocates resources to IPv6
ACL rules.
Rules.
User Guide 56

Managing System SDM Template Configuration
MAC ACL Rules Displays the number of Layer 2 ACL Rules.
Combined ACL
Rules
IPv6 ACL Rules Displays the number of IPv6 ACL rules.
IPv4 Source
Guard Entries
IPv6 Source
Guard Entries
6.2 Using the CLI
Follow these steps to configure the SDM template:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 show sdm prefer { used | default | enterpriseV4 | enterpriseV6 }
View the template table. It will help you determine which template is suitable for your network.
Displays the number of Combined ACL rules.
Displays the number of IPv4 source guard entries.
Displays the number of IPv6 source guard entries.
used: Displays the resource allocation of the current template.
default: Displays the resource allocation of the default template.
enterpriseV4: Displays the resource allocation of the enterpriseV4 template.
enterpriseV6: Displays the resource allocation of the enterpriseV6 template.
Step 3 sdm prefer { default | enterpriseV4 | enterpriseV6 }
Select the template that will be effective after the switch is rebooted.
default: Select the template of default. It gives balance to the IP ACL rules and MAC ACL.
enterpriseV4: Select the template of enterpriseV4. It maximizes system resources for IP ACL
rules and MAC ACL rules.
enterpriseV6: Select the template of enterpriseV4. It allocates resources to IPv6 ACL rules.
Step 4 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 5 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
The following example shows how to set the SDM template as enterpriseV4.
Switch#config
Switch(config)#show sdm prefer enterpriseV4
User Guide
57

Managing System SDM Template Configuration
“enterpriseV4” template:
number of IP ACL Rules : 360
number of MAC ACL Rules : 100
number of Combined ACL Rules : 50
number of IPV6 ACL Rules : 0
number of IPV6 Source Guard Entries : 0
Switch(config)#sdm prefer enterpriseV4
Switch to “enterpriseV4” tempale.
Changes to the running SDM preferences have been stored, but cannot take effect until
reboot the switch.
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide 58

Managing System Time Range Configuration
7
Time Range Configuration
To complete Time Range configuration, follow these steps:
1) Add time range entries.
2) Configure Holiday time range.
7.1 Using the GUI
7.1.1 Adding Time Range Entries
Choose the menu SYSTEM > Time Range > Time Range Config and click to load
the following page.
Figure 7-1 Configuring Time Range
Follow these steps to add time range entries:
1) In the Time-Range Config section, specify a name for the entry and select the Holiday
mode.
Name Specify a name for the entry.
Holiday Select to include or exclude the holiday in the time range.
Exclude: The time range will not take effect on holiday.
Include: The time range will not be affected by holiday.
To configure Holiday, refer to
2) In the Period Time Config section, click and the following window will pop up.
Configuring Holiday
.
User Guide
59

Managing System Time Range Configuration
Figure 7-2 Adding Period Time
Configure the following parameters and click Create:
Date Specify the start date and end date of this time range.
Time Specify the start time and end time of a day.
Day of Week Select days of a week as the period of this time range.
3) Similarly, you can add more entries of period time according to your needs. The final
period time is the sum of all the periods in the table. Click Create.
User Guide 60

Managing System Time Range Configuration
Figure 7-3 View Configruation Result
7.1.2 Configuring Holiday
Choose the menu SYSTEM > Time Range > Holiday Config and click to load the
following page.
Figure 7-1 Configuring Holiday
Configure the following parameters and click Create to add a Holiday entry.
Holiday Name Specify a name for the entry.
Start Date Specify the start date of the Holiday time range.
End Date Specify the end date of the Holiday time range.
Similarly, you can add more Holiday entries. The final Holiday time range is the sum of all
the entries.
User Guide
61

Managing System Time Range Configuration
7.2 Using the CLI
7.2.1 Adding Time Range Entries
Follow these steps to add time range entries:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 time-range
Create a time-range entry.
name
Step 3 holiday { exclude | include }
Include or exclude the holiday in the time range.
exclude: The time range will not take effect on holiday.
include: The time range will not be affected by holiday.
To configure Holiday, refer to
Step 4 absolute from
Specify the start date and end date of this time range.
start-date
end-date
Step 5 periodic { [start
Specify days of a week as the period of this time range.
name
: Specify a name for the entry.
start-date
: Specify the start date in the format MM/DD/YYYY.
: Specify the end date in the format MM/DD/YYYY.
start-time
Configuring Holiday
to
end-date
] [ end
end-time
.
] [day-of-the-week
week-day
] }
start-time
end-time
week-day
represent Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday and Sunday.
Step 6 show time-range
View the configuration of Time Range.
Step 7 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 8 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
: Specify the start end time of a day in the format HH:MM.
: Specify the end time and end time of a day in the format HH:MM.
: Specify the days of week in the format of 1-3, 7. The numbers 1-7 respectively
User Guide 62

Managing System Time Range Configuration
The following example shows how to create a time range entry and set the name as time1,
holiday mode as exclude, absolute time as 10/01/2017 to 10/31/2017 and periodic time as
8:00 to 20:00 on every Monday and Tuesday:
Switch#config
Switch(config)#time-range time1
Switch(config-time-range)#holiday exclude
Switch(config-time-range)#absolute from 10/01/2017 to 10/31/2017
Switch(config-time-range)#periodic start 08:00 end 20:00 day-of-the-week 1,2
Switch(config-time-range)#show time-range
Time-range entry: 12 (Inactive)
Time-range entry: time1 (Inactive)
holiday: exclude
number of time slice: 1
01 - 10/01/2017 to 10/31/2017
- 08:00 to 20:00 on 1,2
Switch(config-time-range)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
7.2.2 Configuring Holiday
Follow these steps to configure Holiday time range:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 holiday
Create a holiday entry.
name
start-date
name
start-date
: Specify a name for the entry.
: Specify the start date in the format MM/DD.
start-date
end-date
end-date
end-date
Step 3 show holiday
View the configuration of Holiday.
Step 4 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
: Specify the end date in the format MM/DD.
User Guide
63

Managing System Time Range Configuration
Step 8 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
The following example shows how to create a holiday entry and set the entry name as
holiday1 and set start date and end date as 07/01 and 09/01:
Switch#config
Switch(config)#holiday holiday1 start-date 07/01 end-date 09/01
Switch(config)#show holiday
Index Holiday Name Start-End
----- ------------ ---------
1 holiday1 07.01-09.01
Switch(config)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide 64

Managing System Appendix: Default Parameters
8
Appendix: Default Parameters
Default settings of System Info are listed in the following tables.
Table 8-1 Default Settings of Device Description Configuration
Parameter Default Setting
Device Name The model name
of the switch.
Device Location SHENZHEN
System Contact www.tp-link.com
Table 8-2 Default Settings of System Time Configuration
Parameter Default Setting
Time Source Manual
Table 8-3 Default Settings of Daylight Saving Time Configuration
Parameter Default Setting
DST status Disabled
Default settings of User Management are listed in the following table.
Table 8-4 Default Settings of User Configuration
Parameter Default Setting
User Name admin
Password admin
Access Level Admin
Default settings of System Tools are listed in the following table.
Table 8-5 Default Settings of Boot Configuration
Parameter Default Setting
Current Startup Image image1.bin
Next Startup Image image1.bin
Backup Image image2.bin
Current Startup Config config1.cfg
Next Startup Config config1.cfg
User Guide
65

Managing System Appendix: Default Parameters
Parameter Default Setting
Backup Config config2.cfg
Default setting of EEE is listed in the following table.
Table 8-6 Default Settings of EEE Configuration
Parameter Default Setting
Status Disabled
Default settings of SDM Template are listed in the following table.
Table 8-7 Default Settings of SDM Template Configuration
Parameter Default Setting
Current Template ID Default
Next Template ID Default
Default settings of Time Range are listed in the following table.
Table 8-8 Default Settings of Time Range Configuration
Parameter Default Setting
Holiday Include
User Guide 66

Part 3
Managing Physical Interfaces
CHAPTERS
1. Physical Interface
2. Basic Parameters Configurations
3. Port Isolation Configurations
4. Loopback Detection Configuration
5. Configuration Examples
6. Appendix: Default Parameters

Managing Physical Interfaces Physical Interface
1
Physical Interface
1.1 Overview
Interfaces are used to exchange data and interact with interfaces of other network devices.
Interfaces are classified into physical interfaces and layer 3 interfaces.
■ Physical interfaces are the ports on the switch panel. They forward packets based on
MAC address table.
■ Layer 3 interfaces are used to forward IPv4 and IPv6 packets using static or dynamic
routing protocols. You can use Layer 3 interfaces for IP routing and inter-VLAN routing.
This chapter introduces the configurations for physical interfaces.
1.2 Supported Features
The switch supports the following features about physical interfaces:
Basic Parameters
You can configure port status, speed mode, duplex mode, flow control and other basic
parameters for ports.
Port Isolation
You can use this feature to restrict a specific port to send packets to only the ports in the
forwarding port list that you configure.
Loopback Detection
This function allows the switch to detect loops in the network. When a loop is detected on
a port or VLAN, the switch will display an alert on the management interface and block the
corresponding port or VLAN according to your configurations.
User Guide 68

Managing Physical Interfaces Basic Parameters Configurations
2
Basic Parameters Configurations
2.1 Using the GUI
Choose the menu L2 FEATURES > Switching > Port > Port Config to load the following
page.
Figure 2-1 Configuring Basic Parameters
Follow these steps to configure basic parameters for the ports:
1) Configure the MTU size of jumbo frames for all the ports, then click Apply.
Jumbo Configure the size of jumbo frames. By default, it is 1518 bytes.
Generally, the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) size of a normal frame is 1518
bytes. If you want the switch supports to transmit frames of which the MTU size is
greater than 1518 bytes, you can configure the MTU size manually here.
2) Select one or more ports to configure the basic parameters. Then click Apply.
UNIT/LAGS Click the UNIT number to configure physical ports. Click LAGS to configure LAGs.
Type Displays the port type. Copper indicates an Ethernet port, and Fiber indicates an
SFP port.
User Guide
69

Managing Physical Interfaces Basic Parameters Configurations
Description (Optional) Enter a description for the port.
Status With this option enabled, the port forwards packets normally. Otherwise, the port
cannot work. By default, it is enabled.
Speed Select the appropriate speed mode for the port. When Auto is selected, the
port automatically negotiates speed mode with the neighbor device. The default
setting is Auto. It is recommended to select Auto if both ends of the link support
auto-negotiation.
Duplex Select the appropriate duplex mode for the port. There are three options: Half,
Full and Auto. The default setting is Auto.
Half: The port can send and receive packets, but only one-way at a time.
Full: The port can send and receive packets simultaneously.
Auto: The port automatically negotiates duplex mode with the peer device.
Flow Control With this option enabled, when a device gets overloaded it will send a PAUSE
frame to notify the peer device to stop sending data for a specified period
of time, thus avoiding the packet loss caused by congestion. By default, it is
disabled.
Note:
We recommend that you set the ports on both ends of a link as the same speed and duplex mode.
2.2 Using the CLI
Follow these steps to set basic parameters for the ports.
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 jumbo-size
Change the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) size to support jumbo frames. The default
MTU size for frames received and sent on all ports is 1518 bytes. To transmit jumbo
frames, you can manually configure MTU size of frames up to 9216 bytes.
size
: Configure the MTU size of jumbo frames. The value ranges from 1518 to 9216bytes.
Step 3 interface { fastEthernet
gigabitEthernet
port-channel
Enter interface configuration mode.
size
port-list
port-channel
port
| range fastEthernet
| ten-gigabitEthernet
| range port-channel
port-list
port
port-channel-list
| gigabitEthernet
| ten-range gigabitEthernet
|}
port
| range
port-list
|
User Guide 70

Managing Physical Interfaces Basic Parameters Configurations
Step 4 Configure basic parameters for the port:
description
Give a port description for identification.
string
shutdown
no shutdown
Use shutdown to disable the port, and use no shutdown to enable the port. When the
status is enabled, the port can forward packets normally, otherwise it will discard the
received packets. By default, all ports are enabled.
speed { 10 | 100 | 1000 | 10000 | auto }
Set the appropriate speed mode for the port.
10 | 100 | 1000 | 10000 | auto: Speed mode of the port. The options are subject to your
actual product. The device connected to the port should be in the same speed and duplex
mode with the port. When auto is selected, the speed mode will be determined by autonegotiation.
string
: Content of a port description, ranging from 1 to 16 characters.
duplex { auto | full | half }
Set the appropriate duplex mode for the port.
auto | full | half: Duplex mode of the port. The device connected to the port should be in the
same speed and duplex mode with the port. When auto is selected, the duplex mode will be
determined by auto-negotiation.
flow-control
Enable the switch to synchronize the data transmission speed with the peer device,
avoiding the packet loss caused by congestion. By default, it is disabled.
Step 5 show interface configuration [ fastEthernet
gigabitEthernet
Verify the configuration of the port or LAG.
Step 6 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 7 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
port
| port-channel
port-channel-id
port
| gigabitEthernet
]
port
| | ten-
The following example shows how to implement the basic configurations of port1/0/1,
including setting a description for the port, configuring the jumbo frame, making the port
automatically negotiate speed and duplex with the neighboring port, and enabling the flowcontrol:
Switch#configure
Switch#jumbo-size 9216
Switch(config)#interface ten-gigabitEthernet 1/0/1
Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
User Guide
71

Managing Physical Interfaces Basic Parameters Configurations
Switch(config-if)#description
router connection
Switch(config-if)#speed auto
Switch(config-if)#duplex auto
Switch(config-if)#flow-control
Switch(config-if)#show interface configuration ten-gigabitEthernet 1/0/1
Port State Speed Duplex FlowCtrl Description
-------- ----- -------- ------ -------- -----------
Te1/0/1 Enable Auto Auto Enable router connection
Switch(config-if)#show jumbo-size
Global jumbo size : 9216
Switch(config-if)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide 72

Managing Physical Interfaces Port Isolation Configurations
3
Port Isolation Configurations
3.1 Using the GUI
Port Isolation is used to limit the data transmitted by a port. The isolated port can only send
packets to the ports specified in its Forwarding Port List.
Choose the menu L2 FEATURES > Switching > Port > Port Isolation to load the following
page.
Figure 3-1 Port Isolation List
The above page displays the port isolation list. Click to configure Port Isolation on
the following page.
User Guide
73

Managing Physical Interfaces Port Isolation Configurations
Figure 3-2 Port Isolation
Follow these steps to configure Port Isolation:
1) In the Port section, select one or multiple ports to be isolated.
2) In the Forwarding Port List section, select the forwarding ports or LAGs which the
isolated ports can only communicate with. It is multi-optional.
3) Click Apply.
3.2 Using the CLI
Follow these steps to configure Port Isolation:
Step 1 configure
Enter global configuration mode.
Step 2 interface { fastEthernet
gigabitEthernet
port-channel
Specify the port to be isolated and enter interface configuration mode.
Step 3 port isolation { [fa-forward-list
forward-list
Add ports or LAGs to the forwarding port list of the isolated port. It is multi-optional.
fa-forward-list / te-forward-list / te-forward-list
po-forward-list:
port
| range fastEthernet
port-list
port-channel
te-forward-list
Specify the forwarding LAGs.
| ten-gigabitEthernet
| range port-channel
fa-forward-list
] [ po-forward-list
port-list
port
port-channel-list
] [te-forward-list
po-forward-list
: Specify the forwarding Ethernet ports.
| gigabitEthernet
| ten-range gigabitEthernet
|}
te-forward-list
] }
port
] [te-
| range
port-list
|
User Guide 74

Managing Physical Interfaces Port Isolation Configurations
Step 4 show port isolation interface { fastEthernet
gigabitEthernet
Verify the Port Isolation configuration of the specified port.
Step 5 end
Return to privileged EXEC mode.
Step 6 copy running-config startup-config
Save the settings in the configuration file.
port
| port-channel
port-channel
port
| gigabitEthernet
}
port
| ten-
The following example shows how to add ports 1/0/1-3 and LAG 4 to the forwarding list of
port 1/0/5:
Switch#configure
Switch(config)#interface ten-gigabitEthernet 1/0/5
Switch(config-if)#port isolation te-forward-list 1/0/1-3 po-forward-list 4
Switch(config-if)#show port isolation interface ten-gigabitEthernet 1/0/5
Port LAG Forward-List
---- --- -----------------------
Te1/0/5 N/A Te1/0/1-3,Po4
Switch(config-if)#end
Switch#copy running-config startup-config
User Guide
75
 Loading...
Loading...