
FOREWORD
This manual has been prepared to familiarize you with the new features of the 1990 model year vehicles, with the
exception of the new Celica.
MR2 and Van are not contained in this manual because 1990 models of these vehicles will not be produced.
For new features of the Celica and for detailed service specifications and repair procedures of each 1990 model year
vehicle, refer to the following manuals:
Manual Name Pub. No.
1990 Celica New Car Features
1990 model Repair Manuals
1990 model Electrical Wiring Diagram Manuals
This information is the most up–to–date at the time of publication. However, Toyota reserves the right to make changes
without prior notice.
NCF056U
Refer to the
}
respective
located
Pub. No.
1989 TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION
All rights reserved. This book may not be reproduced
or copied, in whole or in part, without the written
permission of Toyota Motor Corporation.
TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION

General 1990 Features
Page
DESCRIPTION 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
FRONT SEAT BELT 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT SYSTEM 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DOOR LOCK CONTROL SYSTEM 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
T
l
C
C
C
Toyota
Truck/
Land
GENERAL 1990 FEATURES
GENERAL 1990 FEATURES
DESCRIPTION
The following changes are made simultaneously in some models for the 1990 model year.
(1) : Door–mounted automatic belts with manual lap belts are made standard equipment for front seat belts for the U.S.
(2) : For Canada, a daytime running light system, which lights the headlights and taillights during daylight hours, is used
to improve vehicle visibility from the outside during the daytime.
(3) : In vehicles which were previously equipped with the electronically controlled door lock control system, in which
all the doors were unlocked by operating the key in the lock of the driver ’s door, the system is changed to the
2–operation type system used in the Cressida. In this system, operating the driver’s door lock one time unlocks only
the driver ’s door, while operating the driver ’s door lock twice in succession unlocks the other doors.
Models in which the above changes have been made are shown in the following table.
Model
Item
(1) — — — —
(2) —
(3) — * — —
*: Use of the 2–operation type unlock system was begun in the Cressida for the 1990 model year.
Information of Type and Application of Passive Restraint System (Only for U.S.A.)
Model Tercel Corolla Camry Cressida
’90 Model M M E*
’89 Model — — E E — — —
M: Mechanical Type (Driver and Passenger) E*1: Vehicle speed signal from August ’89
E: Electronic Type (Driver and Passenger) E*2: Vehicle speed signal from January ’90
A: SRS Airbag (Driver)
erce
orolla
amry
ressida
1
E*
2
Toyota Truck/ Land
Supra
Toyota
Supra
A — —
4Runner
Truck/
4Runner
Cruiser
Land
Cruiser
FRONT SEAT BELT
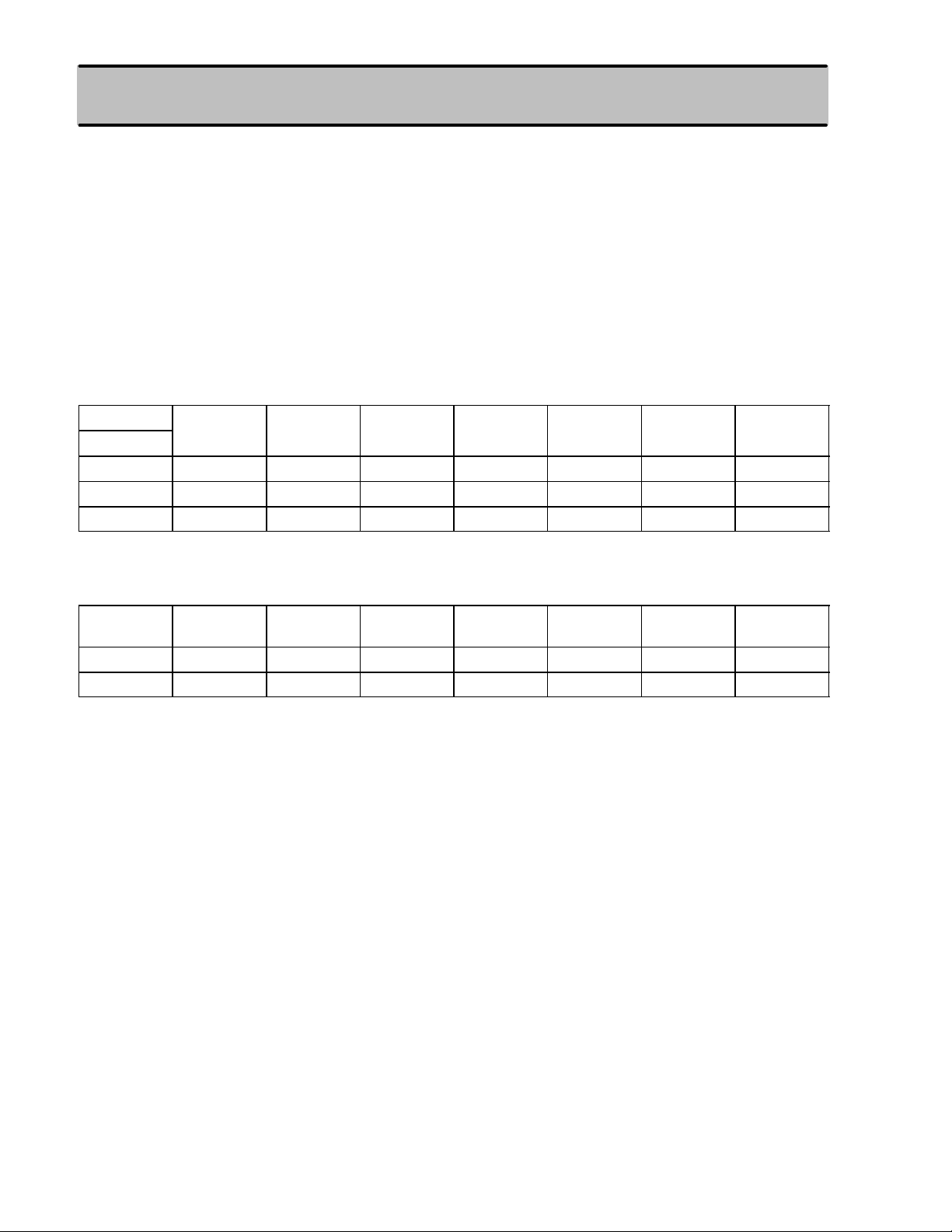
Door mounted automatic belts with manual lap belt are standard equipment in all Tercel and Corolla models for the U.S.
The shoulder belts are two–point ELR (Emergency Locking Retractor) belts. The shoulder belt retractors are mounted
in the bottom of the rear console box. The shoulder belt anchorages are mounted on the door frames and the shoulder
belts can be connected or disconnected using the buckles. A bracket is provided in each of the center pillars which assures
the rigidity of the shoulder belt anchorages.
The manual lap belts are two–point ALR (Automatic Locking Retractor) belts. The belt retractors are located at the bottom
of the center pillars in the rocker inner panel. The lap belt buckles slide fore and aft with the seats.
Construction
GENERAL 1990 FEATURES
3
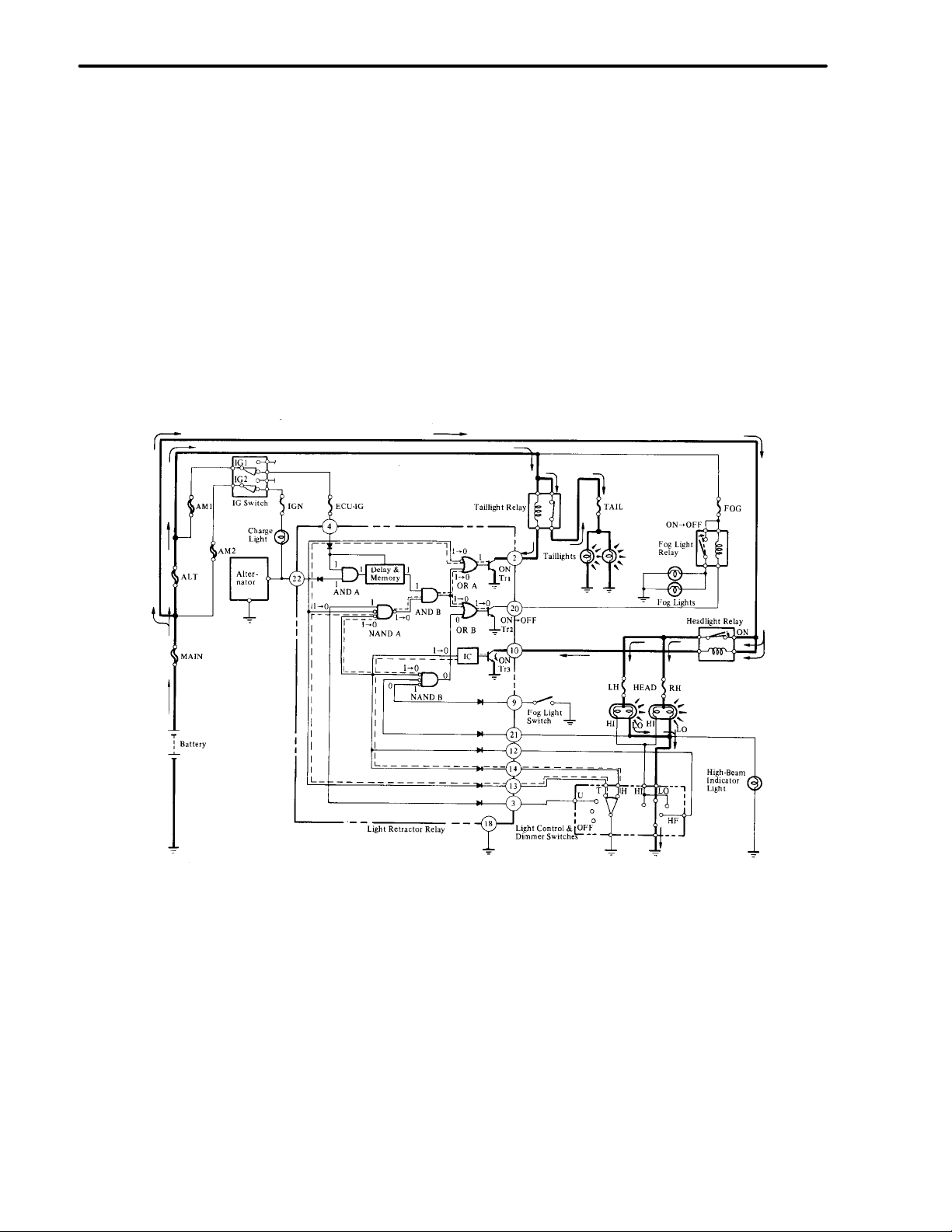
DAYTIME RUNNING LIGHT SYSTEM (Only for Canada)
GENERAL
The daytime running light system, in which the headlights and taillights are turned on automatically when the engine
is started, is standard in all models for Canada. However, in the Toyota Supra, the front fog lights light up instead
of the headlights and in the Corolla 2–door coupe, exclusive daytime lights light up.
4
Ignition
l
Dimmer
Fog Light
Tailligh
F
*
1
OFF
TAIL
LOW
GENERAL 1990 FEATURES
FUNCTION
The daytime running light system operates when the ignition switch is turned to the ON position and the engine is
started, with the operation of each switch turning the lights on and off as shown in the table below. (The lights do not
go on when the ignition switch is in the ON position only. The lights also stay on in the event that the engine stalls
after the engine is started.)
: Light on as daytime running light, : Lighted up, X : Off
Ignition
Switch
ON
Light
Contro
Switch
OFF,
HOLD
Dimmer Fog Light*
Switch
LOW, HIGH ON , X*
,
HF*
4
Switch
1
ON X
LOW, HIGH ON , X*
4
HF*
ON X
t
Headlight
Low High
3
3
ON X X X
HEAD
HIGH, HF*
4
ON X X
ON X X X
*1: Toyota Supra only
*2: Corolla 2–Door Coupe only
*3: Toyota Supra and Corolla 2–Door Coupe only
*4: High Flash
OPERATION
NOTE: Operation of the system is described using the Toyota Supra as an example.
1. Ignition Switch Turned ON (Before Starting Engine)
Daytime*
og Light
1
Running
Light
X
X
2
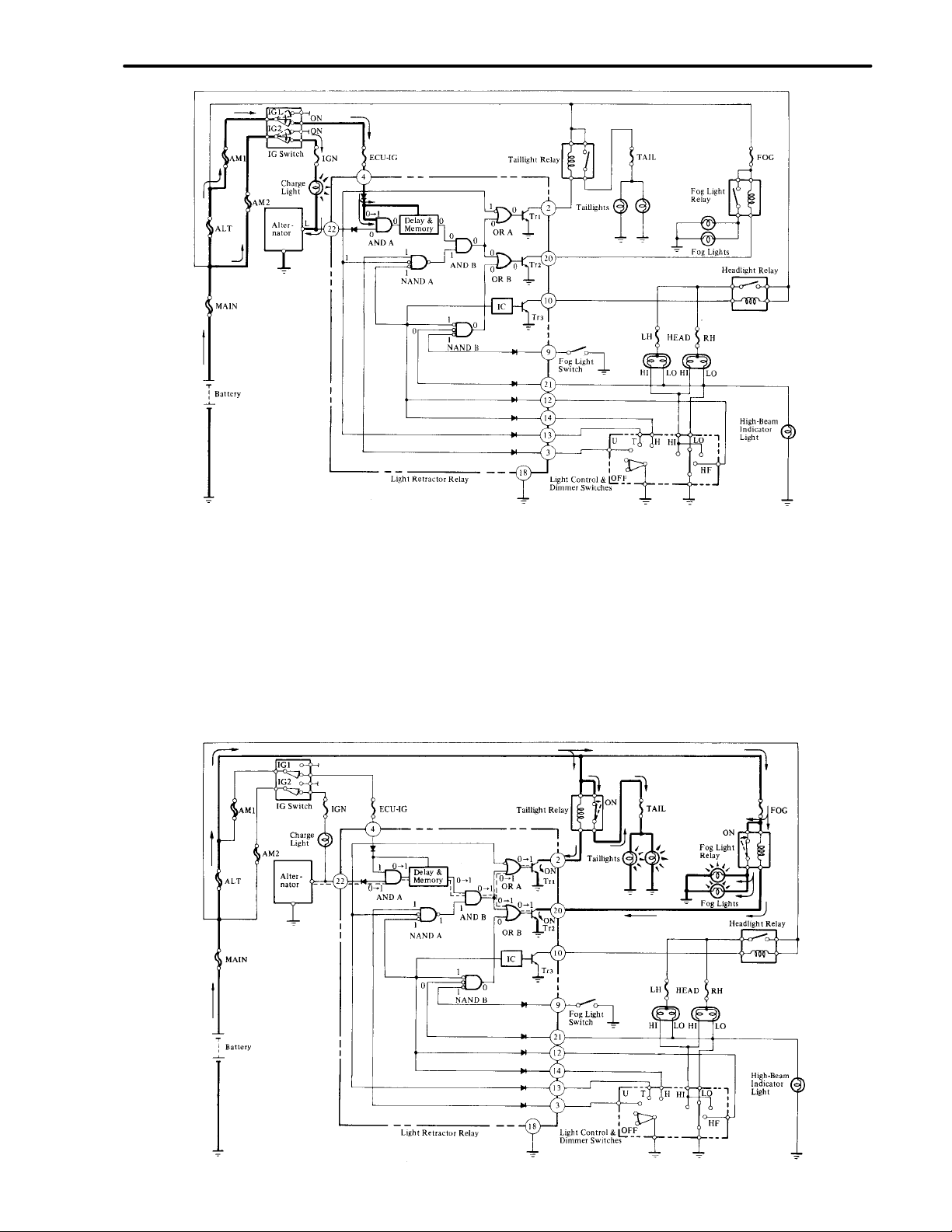
When the ignition switch is turned off, input and output signals at gates are in the condition shown on the next
page.
If the ignition switch is turned on in this condition, the voltage at terminal (4) goes high and the input to AND
gate A changes from “0” to “1”.
The electric current passing the charge light is grounded via the alternator and the voltage at terminal (22) is held
low. Therefore, the output from the AND gate A remains unchanged and the system remains inoperative.
If engine stalls after starting, lights stay on until ignition key is turned off.
GENERAL 1990 FEATURES
5
2. After Engine Starting
When the engine is started, the alternator begins charging and the voltage at terminal (22) goes high and the input
to AND gate A changes from “0” to “1”. Therefore, the output also changes from “0” to “1”.
When the “1” signal from AND gate A continues for 0.5 seconds or longer, the delay and memory circuit judges
that the engine has started and sends “1” to AND gate B.
Since the output from AND gate B changes from “0” to “1”, the output from OR gates A and B also changes from
“0” to “1” and causes Tr1 and Tr2 to go on respectively. Therefore, the taillight relay and fog light relay are turned
on and the daytime running lights are turned on as a result.
6
GENERAL 1990 FEATURES
3. Headlight (Low Beam) Turned ON
When the light control switch is put in the head position and the dimmer switch is put in low position while the
daytime running lights are turned on, the input to NAND gate A from light control switch terminals T and H
changes from “1” to “0”.
At the same time, the input signal to IC (Integrated Circuit) changes from “1” to “0”, so the IC then turns Tr
As a result, the headlight relay is turned on and the headlights (low beam) are turned on.
3
on.
When the input to NAND gate A changes to “0”, output changes from “1” to “0” and the output of AND gate B
also changes from “1” to “0”.
Since the output from OR gate B changes from “1” to “0” and causes Tr
and the fog lights (daytime running lights) go off automatically.
to go off, the fog light relay goes off
2
The “0” signal from AND gate B is also supplied to OR gate A. Since the “0” signal from the light control switch
(terminal T) is supplied to the other terminal, OR gate A maintains the output “1” and the taillights remain on
as a result.
NOTE: Fog lights can be turned on by turning the fog light switch on in this condition.

GENERAL 1990 FEATURES
1
2nd Ti
7
DOOR LOCK CONTROL SYSTEM
The method of unlocking all the doors when the driver’s door lock is operated by the key in models with the electronically
controlled door lock control system is changed. Previously, one operation of the driver’s door lock with the key unlocked
all the doors together with the driver’s door, but this has been changed to the method used in the current Cressida, in which
the only driver’s door is unlocked mechanically when the driver’s door lock is operated once. Operating driver’s door lock
twice in succession unlocks the other doors electronically. Operating the door lock on the passenger side once unlocks
all the doors as before. This change is made through changes in the operation of the door lock control relay.
Unlock Operation
Item
Key Cylinder
Unlock Door Driver ’s Door Only Other Doors
Control Mechanically Electrically
st Time
me

8
– MEMO –

64
CAMRY—OUTLINE OF NEW FEATURES
CAMRY
OUTLINE OF NEW FEATURES
The Toyota Camry is a compact class passenger car with a wealth of model variations which is evaluated highly by
customers. The following improvements are made for the 1990 model year to raise the Camry’s product appeal.
1. 3S–FE Engine
Plastic region tightening is used for the cylinder head bolts for good axial tension. Refer to the 1990 Camry Repair
Manual (Pub. No. RM151U) for the plastic region tightening method.
2. 2VZ–FE Engine
A knock prevention correction function, which controls the ignition timing according to engine knocking
conditions, is added to the ESA (Electronic Spark Advance) system to improve engine output and torque.
A fuel pressure control system, which raises the fuel pressure when the engine is restarted while hot, helps to
maintain restartability.
3. Drive Shaft
The inboard joint tulip of the drive shafts and the differential side gear shaft are integrated in models equipped with
the S51 manual transaxle in order to reduce the number of parts and weight.
4. Brake
The front disc brake rotor diameter in models equipped with the 2VZ–FE engine with A.B.S. (Anti–Lock Brake
System) is changed from 10.04 in. (255 mm) to 10.91 in. (277 mm) to improve the braking performance of the front
brakes.
5. Others (see GENERAL 1990 FEATURES for details)
For Canada, a daytime running light system, which lights up the headlights and taillights during daylight hours,
is used to improve a vehicle’s visibility from the outside during the daytime.
In models with power windows, the door unlock control system is changed from a system where a single key
operation of the driver’s door lock opened all the doors to the system used in the Cressida where the driver’s door
is unlocked with one operation of the driver’s door lock, and all the doors are unlocked if the driver’s door lock
is operated two times in succession.

CAMRY—OUTLINE OF NEW FEATURES
65

66
(2)
(4)
(8)
CAMRY—MODEL CODE
MODEL CODE
VZV21 L G – U W P N K A
(1)(2)(3)(4)(5)(6)(7)(8)(9)
BASIC MODEL CODE
SV21 : FWD with 3S–FE Engine
(1)
SV25 : All–Trac/4WD with 3S–FE Engine
VZV21 : FWD with 2VZ–FE Engine
STEERING WHEEL POSITION
L : Left–Hand Drive
BODY TYPE
(3)
Blank : Sedan
G : Wagon
MODEL NAME
U : Camry
BODY TYPE
(5)
E : Sedan
W : Wagon
GEARSHIFT TYPE
(6)
M : 5–Speed Manual
P : 4–Speed Automatic
GRADE
B : STD
(7)
D : DLX
N : LE
ENGINE SPECIFICATION
K : EFI and DOHC
DESTINATION
(9)
A : U.S.A.
K : Canada

MODEL LINE–UP
CAMRY—MODEL LINE–UP
67

68
CAMRY—NEW FEATURES
NEW FEATURES
2VZ–FE ENGINE
1. Description
The 2.5 liter, V–6, 24–valve, DOHC 2VZ–FE engine is liked by customers because of its quietness and good
performance.
The following improvements are made in the engine for the 1990 model year.
Modification Purpose Contents
Improve Performance
Maintain Restartability
A knock prevention correction function is added to the ESA to control the
ignition timing according to engine knocking conditions.
A fuel pressure control system is used to raise the fuel pressure when the
engine is restarted while hot.

CAMRY—NEW FEATURES
NewP
2. Engine Specifications and Performance Curve
69
Engine
Item
No. of Cyls. & Arrangement 6–Cylinder, V Type ←
Valve Mechanism
Combustion Chamber Pentroof Type ←
Manifold Cross–flow ←
Displacement cu. in. (cc) 153.0 (2508) ←
Bore x Stroke in. (mm) 3.44 x 2.74 (87.5 x 69.5) ←
Compression Ratio 9.0 : 1 ←
Max. Output (SAE–NET) 156 HP @ 5600 rpm 153 HP @ 5600 rpm
Max. Torque (SAE–NET) 160 ft.lbs @ 4400 rpm 155 ft.lbs @ 4400 rpm
Fuel Octane Number (RON) 96 91
4 Valves, DOHC, Belt
& Gear Drive
revious
←

70
NewP
CAMRY—NEW FEATURES
3. TCCS (TOYOTA Computer–Controlled System)
The following table is a comparison of the TCCS engine control systems between the new 2VZ–FE engine and
previous 2VZ–FE engine.
Engine
System
EFI
(Electronic Fuel
Injection)
Cold Start
Injector Control
ESA
(Electronic Spark
Advance)
ISC
(Idle Speed Control)
Oxygen Sensor
Heater Control
Air Conditioner
Control
Fuel Pressure
Control
An L–type EFI system is used, which
directly detects the intake air volume
with a vane type air flow meter.
The fuel injection system is a 3–group
type.
When the coolant temperature is between
71.6°F and 95°F (22°C and 35°C), the
injection duration of the cold start injector
is controlled by the ECU. At 71.6°F
(22°C) or lower, it is controlled by the
start injector time switch and the ECU.
Ignition timing is determined by the ECU
based on signals from various sensors.
In vehicles equipped with automatic
transaxle, the torque control
compensation during gear shifting is
used to provide smooth engagement of
brakes and clutches.
Corrects ignition timing in response to
engine knocking.
( Page 72)
A step motor type ISC is used, which
controls the fast idle and idle speeds.
Maintains the temperature of the oxygen
sensor at an appropriate level to increase
accuracy of detection of the oxygen
concentration in the exhaust gas.
By controlling the air conditioner
compressor in accordance with the
throttle valve opening angle and the
vehicle speed, drivability is maintained.
Maintains restartability by controlling the
fuel pressure.
( Page 72)
revious
←
←
←
←
←
N.A.
←
←
←
N.A.
Diagnosis
Fail–Safe
When a malfunction occurs, the ECU
diagnoses and stores code in memory.
17 diagnostic items (19 for California)
are monitored by the ECU.
( Page 73)
When a malfunction occurs, the ECU
stops or controls the engine according to
the data stored in memory.
15 diagnostic items (17 for California)
are monitored by the ECU.
←

CAMRY—NEW FEATURES
System Construction
The TCCS is the same as in the previous model with the exception of the items indicated.
71
*1: Applicable only to California specification vehicles.
*2: Applicable only to automatic transaxle models.

72
ESA (Electronic Spark Advance)
A knock sensor is mounted between the right and
left banks of the cylinder block in the new 2VZ–FE
engine.
This sensor detects if the engine is knocking or not
and also detects the strength of the knocking from
the vibrations of the cylinder block.
This ESA includes a knock prevention correction
function which corrects the ignition timing
according to the engine knocking conditions. This
correction prevents excessive knocking while at the
same time improving engine performance and
providing good fuel economy.
The construction and operation of the knock sensor
as well as the contents of knock prevention
correction control are the same as for the 3S–GTE
engine. However, fuel judgment is not included. For
details, see the Celica All–Trac/4WD New Car
Features (Pub. No. NCF033U).
CAMRY—NEW FEATURES
Fuel Pressure Control
1) General
This system is the same as that used in the 4A–GE engine for the Corolla. It includes a VSV in the vacuum line
from the intake manifold to the pressure regulator to control the fuel pressure in accordance with whether or not
intake manifold vacuum or atmospheric pressure is acting on the diaphragm chamber of the pressure regulator.
When the coolant temperature and intake air temperature are higher than predetermined levels during starting,
the ECU turns on the VSV and increases the fuel pressure to prevent the fuel percolation, which maintains engine
restartability and idling stability.

2) General
od of time or adaptive control value is not renewed for a certain period
When the coolant temperature is 203°F (95°C)
or higher and the intake air temperature is
140°F (60°C) or higher and the engine is
cranked, the ECU turns on the VSV. When the
VSV goes on, atmospheric air is introduced
into the diaphragm chamber of the pressure
regulator and the fuel pressure becomes higher
by the amount of the intake manifold vacuum
than the fuel pressure under normal engine
operating conditions.
The VSV is turned off when the air–fuel ratio becomes too thin and when the vehicle speed reaches 12.4 mph
(20 km/h) or more.
Self–Diagnosis
Due to the use of the knock sensor, diagnostic codes No. 52 and No. 53 have been added. Code No. 11 is also deleted.
Diagnostic codes in the new 2VZ–FE engine are as shown in the table below.
Code
No.
12 RPM Signal
13 RPM Signal No “Ne” signal to ECU when the engine speed is above 1000 rpm.
14 Ignition Signal No “IGf” signal to ECU 6–8 times in succession.
16
21
22
24
25*
26*
Item Diagnosis Trouble Area
No “Ne” or “G” signal to ECU within 2 seconds after the engine has been
cranked.
ECT Control
Signal in ECU
Oxygen Sensor
Signal
Oxygen Sensor
Heater Signal
Water Temp.
Sensor Signal
Intake Air
Temp. Sensor
Signal
Air–Fuel
1
Ratio Lean
Malfunction
Air–Fuel
2
Ratio Rich
Malfunction
ECT control in ECU faulty.
Deterioration of the main oxygen sensor.
Open or short circuit in main oxygen sensor heater signal (HT).
Open or short circuit in water temp. sensor signal (THW).
Open or short circuit in intake air temp. sensor signal (THA).
(1) When feedback frequency of air–fuel ratio feedback correction or
adaptive control is abnormally high during feedback condition.
(2) When air–fuel ratio feedback correction value or adaptive control val-
ue continues at the upper (lean) or lower (rich) limit for a certain period of time or adaptive control value is not renewed for a certain period
of time.
(3) Open or short circuit in oxygen sensor signal.
CAMRY—NEW FEATURES
Distributor circuit
Distributor
Starter signal circuit
ECU
Distributor circuit
Distributor
ECU
Igniter and ignition coil circuit
Igniter and ignition coil
ECU
ECU
Main oxygen sensor circuit
Main oxygen sensor
Main oxygen sensor heater circuit
Main oxygen sensor heater
ECU
Water temp. sensor circuit
Water temp. sensor
ECU
Intake air temp. sensor circuit
Intake air temp. sensor
ECU
Injector circuit
Injector
Fuel line pressure
Ignition system
Oxygen sensor circuit
Oxygen sensor
Air flow meter
Water temp. sensor
ECU
Injector circuit
Injector
Fuel line pressure
Cold start injector
Air flow meter
Water temp. sensor
ECU
ON
73
“CHECK ENGINE”
Lamp
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
ON
(Calif. Only)
ON
(Calif. Only)
ON
(Calif. Only)

74
CAMRY—NEW FEATURES
Code
No.
2
27*
31
32
41
42
43 Starter Signal
Item Diagnosis Trouble Area
Sub–oxygen
Sensor Signal
Air Flow
Meter Signal
Air Flow
Meter Signal
Throttle Position
Sensor Signal
Vehicle Speed
Sensor Signal
Open or short circuit in sub–oxygen
sensor signal (Ox2).
Open circuit in Vc signal or short
circuit between Vs and E2when idle
contacts are closed.
Open circuit in E2 or short circuit
between Vc and Vs.
Open or short circuit in throttle
position sensor signal (VTA).
No “SP1” signal to ECU for 8
seconds when engine speed is
between 2550 rpm and 4500 rpm
and coolant temp. is above 158
°C) except when racing the
(70
engine.
No “ST A” signal to ECU until
engine speed reaches 800 rpm with
vehicle not moving.
°F
Sub–oxygen sensor circuit
Sub–oxygen sensor
ECU
Air flow meter circuit
Air flow meter
ECU
Air flow meter circuit
Air flow meter
ECU
Throttle position sensor circuit
Throttle position sensor
ECU
No. 1 vehicle speed sensor circuit
No. 1 vehicle speed sensor
ECU
Ignition switch circuit
Ignition switch
ECU
“CHECK
ENGINE” Lamp
ON
ON
ON
ON
(Calif. Only)
OFF
OFF
Knock sensor circuit
Knock sensor
ECU
ECU
EGR system
EGR gas temp. sensor circuit
EGR gas temp. sensor
ECU
ON
OFF
ON
52
53
71*
2
Knock Sensor
Signal
Knock Control
Signal in ECU
EGR System
Malfunction
Open or short circuit in knock
sensor signal (KNK).
Knock control in ECU faulty.
EGR gas temp. below
predetermined level during EGR
operation.
Open circuit in EGR gas temp.
sensor signal (THG).
A/C amplifier
A/C switch circuit
Neutral start switch circuit
Switch Condition
51
Signal
No “IDL” signal or No “NSW” or
“A/C” signal to ECU, with the
check terminals E1 and T shorted.
Neutral start switch
Throttle position sensor circuit
OFF
Throttle position sensor
Accelerator pedal and cable
ECU
*1: No. (1) and (2) in the diagnostic contents of codes No. 25 and 26 apply to California specification vehicles only,
while (3) applies to all models.
*2: Applicable only to California specification vehicles.
Fail–Safe
The following two items are added to the previous items.
1) ECT Control System Malfunction
If trouble develops in the ECT control system in the ECU, the transmission will not operate properly. At this
time, the ECU prevents engine torque control correction by the ESA.
2) Knock Sensor or Knock Control System Malfunction
If the knock sensor circuit becomes open or shorted, or if trouble develops in the knock control system in the
ECU, the ECU corrects ignition timing to the maximum retard condition of the knock prevention correction to
prevent knocking.

CAMRY—NEW FEATURES
O
DRIVE SHAFT
The inboard joint in models equipped with the S51 manual transaxle is changed from the flange type, with separate
joint tulip and differential side gear shaft to the flangeless type, in which these parts are integrated. This design helps
to simplify the parts and reduce weight. Furthermore, the combination of the slidable tripod type inboard joint and
rzeppa type outboard joint is not changed.
75
BRAKE
The front brake disc rotor in models equipped with
the 2VZ–FE engine with A.B.S. (Anti–Lock Brake
System) is made larger.
The sizes of the disc brake caliper and disc pad are
unchanged from the previous model.
Disc Rotor Specifications
Item
Model
New 10.91 in. (277 mm)
Previous 10.01 in. (255 mm)
uter Diameter

142
Turn ng D ameter
Overall
Curb Weight
Gross V ehicle Weight
APPENDIX—CAMRY
CAMRY
Item Area U.S.A.
Engine Type 3S–FE ← ← ←
Valve Mechanism 4 Valves, DOHC ← ← ←
Bore x Stroke in. (mm) 3.39 x 3.39 (86 x 86) ← ← ←
Displacement cu.in (cc) 121.9 (1,998) ← ← ←
Compression Ratio 9.3 ← ← ←
Engine
Carburetor Type EFI ← ← ←
Research Octane No. RON 91 ← ← ←
Max. Output (SAE–NET) HP @ rpm (kW / rpm) 115 @ 5,200 (86/5,200) ← ← ←
Max. Torque (SAE–NET) ft–lbs @ rpm (N.m / rpm) 124 @ 4,400 (168/4,400) ← ← ←
Battery Capacity (5HR) Voltage & Amp. hr. 12–40, 12–48
Alternator Output Watts 840 ← ← ←
Starter Output kW 1.0, 1.4
Engine
Electrical
Max. Speed mph (km/h) 112 (180) ← 112 (180) ←
Max. Cruising Speed mph (km/h) 96 (155) 90 (145) 96 (155) 90 (145)
Acceleration
Max. Permissible Speed
Performance
Turning Diameter
(Outside Front)
Fuel Tank Capacity U.S. gal (L, Imp.gal.)
Clutch Type DST — DST ←
Transmission Type S51 A140L S51 A140E
Transmission Gear Ratio
Counter Gear Ratio — 0.945 — 0.945
Defferential Gear Ratio (FWD) 3.736 ← ← ←
Center Differential Gear Ratio (4WD) — — — —
Transfer and REar Drifferential Gear Ratio (4WD) — — — —
Rear Differential Gear Size (4WD) in. — — — —
Chassis
Suspension Type
Stabilizer Bar
Brake Type
Parking Brake Type L.T. Drum ← ← ←
Brake Booster Type and Size in. Tandem, 8” + 9” ← ← ←
Steering Gear Type Rack & Pinion ← ← ←
Steering Gear Ratio (Overall) 17.4 ← ← ←
Power Steering Type Integral Valve ← ← ←
Overall
Wheel Base in. (mm)
Tread
Effective Head Room
Effective Leg Room
Shoulder Room
Overhang
Min. Running Ground Clearance in. (mm) 5.3 (135) ← ← ←
Angle of Approach degree 21°00’ ← ← ←
Angle of Departure degree 14°3 0’ ← ← ←
Major Dimenstions & Vehicle Weights
Curb Weight
Gross Vehicle Weight
Luggage Compartment Capacity cu. ft. (m3) — — — —
*1: Set Option with Cold Area Spec., *2: Set Option without Cold Area Spec., *3: With Moon Roof (Option)
Body Type
Vehicle Grade STD DLX
Model Code SV21L–UEMBKA SV21L–UEPBKA SV21L–UEMDKA SV21L–UEPDKA
*1
*1
0 to 100 km/h
sec.
0 to 400 m sec. 17.5 18.0 17.5 18.0
1st Gear mph (km/h) 39 (49) 40 (65) 30 (49) 40 (65)
2nd Gear mph (km/h) 55 (89) 74 (119) 55 (89) 74 (119)
3rd Gear mph (km/h) 86 (139) — 86 (139) —
4th Gear mph (km/h) — — — —
Wall to Wall ft. (m)
Curb to Curb ft. (m)
In First 3.538 2.810 3.538 2.810
In Second 1.960 1.549 1.960 1.549
In Third 1.250 1.000 1.250 1.000
In Fourth 0.945 0.706 0.945 0.706
In Fifth 0.731 — 0.731 —
In Reverse 3.153 2.296 3.153 2.296
Front Mac Pherson Strut ← ← ←
Rear Mac Pherson Strut ← ← ←
Front STD ← ← ←
Rear — — STD ←
Front Ventilated Disc ← ← ←
Rear L.T. Drum ← ← ←
Length in. (mm) 182.1 (4,625) ← ← ←
Width in. (mm) 66.5 (1,690) ← 67.3 (1,710) ←
Height in. (mm) 54.1 (1,375) ← ← ←
Front in. (mm) 58.1 (1,475) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 56.9 (1,445) ← ← ←
Front in. (mm) 38.2 (970), 36.9 (937)
Rear in. (mm) 37.0 (939), 35.9 (911)
Front in. (mm) 42.9 (1,090) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 34.1 (866.1) ← ← ←
Front in. (mm) 54.3 (1,378) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 53.7 (1,363) ← ← ←
Front in. (mm) 36.4 (925) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 43.3 (1,100) ← ← ←
Front lb (kg) 1,642 (745) 1,698 (770) 1,665 (755) 1,720 (780)
Rear lb (kg) 1,047 (475) — 1,069 (485) ←
Total lb (kg) 2,689 (1,220) 2,745 (1,245) 2,734 (1,240) 2,789 (1,265)
Front lb (kg) — — — —
Rear lb (kg) — — — —
Total lb (kg) 3,880 (1,760) ← ← ←
11.0 13.0 11.0 13.0
— — — —
34.8 (10.6) ← ← ←
15.9 (60, 13.2) ← ← ←
102.4 (2,600) ← ← ←
*3
*3
← 12–48, 12–40
← 1.4, 1.0
← ← ←
← ← ←
Sedan
*2
*2
←
←

APPENDIX—CAMRY
U.S.A.
VZV21L–UEMDKA VAV21L–UEPDKA SV25L–UEMDKA SV25L–UEPDKA SV21L–UEPNKA VAV21L–UEPNKA
DLX LE
2VZ–FE ← 3S–FE ← ← 2VZ–FE
← ← ← ← ← ←
3.44 x 2.74 (87.5 x 69.5) ← 3.39 x 3.39 (86 x 86) ← ← 3.44 x 2.74 (87.5 x 69.5)
153.0 (2,508) ← 121.9 (1,998) ← ← 153.0 (2,508)
9.0 ← 9.3 ← ← 9.0
← ← ← ← ← ←
96 ← 91 ← ← 96
156 @ 5,600 (116/5,600) ← 115 @ 5,200 (86/5,200) ← ← 156 @ 5,600 (116/5,600)
160 @ 4,400 (217/4,400) ← 124 @ 4,400 (168/4,400) ← ← 160 @ 4,400 (217/4,400)
12–48 ← 12–48, 12–40
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
127 (205) 121 (195) 112 (180) 109 (175) 112 (180) 121 (195)
109 (175) 103 (165) 96 (155) 90 (145) ←
9.2 10.2 12.6 13.9 13.0 10.2
17.0 17.5 18.1 19.9 18.0 17.5
33 (52) 40 (64) 28 (45) 32 (52) 40 (65) 40 (64)
52 (83) 72 (116) 48 (78) 60 (96) 74 (119) 72 (116)
79 (127) 111 (179) 75 (120) 93 (149) — 111 (179)
109 (175) ← — — — —
— ← — — — —
35.4 (10.8) ← 34.8 (10.6) ← 35.4 (10.8)
← ← ← ← ← ←
DST — DST — — —
E52 A540E E56F5 A540H A140E A540E
3.230 2.810 3.538 2.810 ← ←
2.045 1.549 2.045 1.549 ← ←
1.333 1.000 1.333 1.000 ← ←
0.972 0.734 1.028 0.734 0.706 0.734
0.820 — 0.820 — — —
3.583 2.296 3.583 2.296 ← ←
— 1.027 — 1.027 0.945 1.027
3.933 3.625 — — 3.736 3.625
— — 4.235 4.285 — —
— ← 2.928 ← — —
— ← 6.7 ← ← —
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
Solid Disc ← ← ← L.T. Drum Solid Disc
Duo Servo ← ← ← L.T. Drum Duo Servo
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
57.9 (1,470) ← 58.1 (1,475) ← ← 57.9 (1,470)
56.7 (1,440) ← ← ← 56.9 (1,445) 56.7 (1,440)
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← — ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← — —
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← — —
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← 5.4 (136) ← 5.3 (135) ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
1,863 (845) 1,896 (860) 1,775 (805) 1,841 (835) 1,720 (780) 1.951 (885)
1,102 (500) 1,124 (510) 1,312 (595) ← 1,091 (495) 1,136 (515)
2,965 (1,345) 3,020 (1,370) 3,087 (1.400) 3,153 (1,430) 2.811 (1,275) 3,087 (1,400)
— — — — — —
— — — — — —
4,123 (1,870) ← 4,266 (1,935) ← 3,880 (1,760) 4,123 (1,870)
— — — — — —
Sedan
*2
← ← 12–48
←
143
103 (165)

144
T
O
ll
Curb Weight
Gross V ehicle Weight
APPENDIX—CAMRY
Item Area U.S.A.
Engine Type 3S–FE ← 2VZ–FE ←
Valve Mechanism 4 Valves, DOHC ← ← ←
Bore x Stroke in. (mm) 3.39 x 3.39 (86 x 86) ← 3.44 x 2.74 (87.5 x 69.5) ←
Displacement cu.in. (cc) 121.9 (1,998) ← 153.0 (2508) ←
Compression Ratio 9.3 ← 9.0 ←
Engine
Carburetor Type EFI ← ← ←
Research Octane No. RON 91 ← 96 ←
Max. Output (SAE–NET) HP @ rpm (kW / rpm) 115 @ 5,200 (86/5,200) ← 156 @ 5,600 (116/5,600) ←
Max. Torque (SAE–NET) ft–lbs @ rpm (N.m / rpm) 124 @ 4,400 (168/4,400) ← 160 @ 4,400 (217/4,400) ←
Battery Capacity (5HR) Voltage & Amp. hr. 12–48, 12–40
Alternator Output Watts 840 ← ← ←
Engine
Electrical
Starter Output kW 1.4, 1.0
Max. Speed mph (km/h) 109 (175) 112 (180) 124 (200) 118 (190)
Max. Cruising Speed mph (km/h) 90 (145) 87 (140) 106 (170) 99 (160)
Acceleration
Max. Permissible Speed
Performance
Turning Diameter
urning Diameter
(Outside Front)
Fuel Tank Capacity U.S. gal (L, Imp.gal) 15.9 (60, 13.2) ← ← ←
Clutch Type — — — —
Transmission Type A540H A140E A540E ←
Transmission Gear Ratio
Counter Gear Ratio 1.027 0.945 1.027 ←
Differential Gear Ratio (FWD) — 3.736 3.625 ←
Center Differential Gear Ratio (4WD) 4.285 — — —
Transfer and Rear Differential Gear Ratio (4WD) 2.928 — — —
Rear Differential Gear Size (4WD) in. 6.7 — — —
Chassis
Suspension Type
Stabilizer Bar
Brake Type
Parking Brake Type Duo Servo L.T. Drum Duo Servo ←
Brake Booster Type and Size in. Tandem, 8” + 9” ← ← ←
Steering Gear Type Rack & Pinion ← ← ←
Steering Gear Ratio (Overall) 17.4 ← ← ←
Power Steering Type Integral Valve ← ← ←
Overall
vera
Wheel Base in. (mm) 102.4 (2,600) ← ← ←
Tread
Effective Head Room
Effective Leg Room
Shoulder Room
Overhang
Min. Running Ground Clearance in. (mm) 5.4 (136) 5.3 (135) ← ←
Angle of Approach degree 21°00’ ← ← ←
Angle of Departure degree 14°30’ 12°30’ ← ←
Major Dimenstions & Vehicle Weights
Curb Weight
Gross Vehicle Weight
Luggage Compartment Capacity cu. ft. (m3) — — — —
Body Type
Vehicle Grade LE DLX LE
Model Code SV25L–UEPNKA SV21LG–UWPDKA VZV21LG–UWPDKA VAV2LG–UWPNKA
0 to 100 km/h sec. 13.9 13.5 9.5 10.5
0 to 400 m sec. 19.9 18.7 17.2 17.7
1st Gear mph (km/h) 32 (52) 40 (65) 40 (64) ←
2nd Gear mph (km/h) 60 (96) 74 (119) 72 (116) ←
3rd Gear mph (km/h) 93 (149) — 111 (179) ←
4th Gear mph (km/h) — — — —
Wall to Wall ft. (m) — — — —
Curb to Curb ft. (m) 34.8 (10.6) ← 35.4 (10.8) ←
In First 2.810 ← ← ←
In Second 1.549 ← ← ←
In Third 1.000 ← ← ←
In Fourth 0.734 0.706 0.734 ←
In Fifth — — — —
In Reverse 2.296 2.296 ← ←
Front Mac Pherson Strut ← ← ←
Rear Mac Pherson Strut ← ← ←
Front STD ← ← ←
Rear STD ← ← ←
Front Ventilated Disc ← ← ←
Rear Solid Disc L.T. Drum Solid Disc ←
Length in. (mm) 182.1 (4,625) 183.1 (4,650) ← ←
Width in. (mm) 67.3 (1,710) ← ← ←
Height in. (mm) 54.1 (1,375) 54.5 (1,385) ← ←
Front in. (mm) 58.1 (1,475) ← 57.9 (1,470) ←
Rear in. (mm) 56.7 (1,440) 56.9 (1,445) 56.7 (1,440) ←
Front in. (mm) 38.2 (970), 36.9 (937)
Rear in. (mm) 37.0 (939), 35.9 (911)
Front in. (mm) 42.9 (1,090) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 34.1 (866.1) 34.4 (873) ← ←
Front in. (mm) 54.3 (1,378) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 53.7 (1,363) ← ← ←
Front in. (mm) 36.4 (925) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 43.3 (1,100) 44.3 (1,125) ← ←
Front lb (kg) 1,841 (835) 1,686 (765) 1,874 (850) 1,929 (875)
Rear lb (kg) 1,334 (605) 1,224 (555) 1,257 (570) 1,268 (575)
Total lb (kg) 3,175 (1,440) 2,910 (1,835) 3,131 (1,420) 3,197 (1,450)
Front lb (kg) — — — —
Rear lb (kg) — — — —
Total lb (kg) 4,266 (1,935) 4,045 (1,835) 4,288 (1.945) ←
Sedan Wagon
*1
*1
*2
*2
← ← ←
← ← ←
38.3 (972), 37.1 (943)
37.7 (958), 36.1 (917)
*2
*2
← ←
← ←
*1 Set Option without Cold Area Spec.,*2 With Moon Roof.

APPENDIX—CAMRY
Canada
SV21L–UEMDKK SV21L–UEPDKK SV25L–UEMDKK SV25L–UEPDKK SV21–UEMNKK SV21L–UEPNKK
3S–FE ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
3.39 x 3.39 (86 x 86) ← ← ← ← ←
121.9 (1,998) ← ← ← ← ←
9.3 ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
91 ← ← ← ← ←
115 @ 5,200 (86/5,200) ← ← ← ← ←
124 @ 4,400 (168/4,400) ← ← ← ← ←
12–48 ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
1.4 ← ← ← ← ←
112 (180) ← ← 109 (175) 112 (180) ←
109 (155) ← ← 90 (145) 96 (155) 90 (145)
11.0 13.0 12.6 13.9 11.0 13.0
17.5 18.0 18.1 19.9 17.5 18.0
30.5 (49) 40.4 (65) 28 (45) 32 (52) 30 (49) 40 (65)
55.1 (89) 74.0 (119) 48 (78) 60 (96) 55 (89) 74 (119)
86.4 (139) ← 75 (120) 93 (149) 86 (139) —
— — — — — —
— — — — — —
34.8 (10.6) ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
DST — DST — DST —
S51 A140E E56F5 A540H S51 A140E
3.538 2.810 3.538 2.810 3.538 2.810
1.960 1.549 2.045 1.549 1.960 1.549
1.250 1.000 1.333 1.000 1.250 1.000
0.945 0.706 1.028 0.734 0.945 0.706
0.731 — 0.820 — 0.731 —
3.153 2.296 3.583 2.296 3.153 2.296
— 0.945 — 1.027 — 0.945
3.736 ← — — 3.736 ←
— — 4.235 4.285 — —
— — 2.928 ← — —
— — 6.7 ← — —
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← Venitlated Disc ← ← ←
L.T. Drum ← Solid Disk ← L.T. Drum ←
L.T. Drum ← Duo Servo ← L.T. Drum ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
182.1 (4,625) ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
54.1 (1,375) ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
58.1 (1,475) ← ← ← ← ←
56.9 (1,445) ← 56.7 (1,440) ← 56.9 (1,445) ←
3.82 (970), 36.9 (937)
37.0 (939), 35.9 (911)
34.1 (866.1) ← ← ← ← ←
43.4 (1,100) ← ← ← ← ←
14°30’ ← ← ← ← ←
1,642 (745) 1,698 (770) 1,753 (795) 1,819 (825) 1,642 (745) 1,698 (770)
1,069 (485) ← 1,301 (590) ← 1,080 (490) ←
2,712 (1,230) 2,767 (1,255) 3,035 (1,385) 3,120 (1,415) 2,722 (1,235) 2,778 (1,260)
3,880 (1,760) ← 4,266 (1,935) ← 3,880 (1760) ←
*3
*3
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
← ← 5.4 (136) ← 5.3 (135) ←
← ← ← ← ← ←
— — — — — —
— — — — — —
— — — — — —
DLX LE
← ← ← ← ←
← ← ← ← ←
Sedan
145

146
Turn ng D ameter
Overall
Curb Weight
Gross V ehicle Weight
APPENDIX—CAMRY
Item Area Canada
Engine Type 2VZ–FE ← 3S–FE ←
Valve Mechanism 4 Valves, DOHC ← ← ←
Bore x Stroke in. (mm) 3.44 x 2.74 (87.5 x 69.5) ← 3.39 x 3.39 (86 x 86) ←
Displacement cu.in (cc) 153.0 (2,508) ← 121.9 (1,993) ←
Compression Ratio 9.0 ← 9.3 ←
EngineChassisMajor Dimenstions & Vehicle Weights
Carburetor Type EFI ← ← ←
Research Octane No. RON 96 ← 91 ←
Max. Output (SAE–NET) HP @ rpm (kW / rpm) 156 @ 5,600 (116/5,600) ← 115 @ 5,200 (86 x 86) ←
Max. Torque (SAE–NET) ft–lbs @ rpm (N.m / rpm) 160 @ 4,400 (217/4,400) ← 124 @ 4,400 (168/4,400) ←
Battery Capacity (5HR) Voltage & Amp. hr. 12–48 ← ← ←
Alternator Output Watts 840 ← ← ←
Engine
Electrical
Starter Output kW 1.4 ← ← ←
Max. Speed mph (km/h) 127 (205) 121 (195) 109 (175) 112 (180)
Max. Cruising Speed mph (km/h) 109 (175) 103 (165) 90 (145) 93 (150)
Acceleration
Max. Permissible Speed
Performance
Turning Diameter
(Outside Front)
Fuel Tank Capacity U.S. gal (L, Imp.gal.)
Clutch Type DST — — ←
Transmission Type E52 A540E A540H S51
Transmission Gear Ratio
Counter Gear Ratio — 1.027 ← —
Defferential Gear Ratio (FWD) 3.933 3.625 — 3.736
Center Differential Gear Ratio (4WD) — — 4.285 —
Transfer and REar Drifferential Gear Ratio (4WD) — — 2.928 —
Rear Differential Gear Size (4WD) in. — — 6.7 —
Suspension Type
Stabilizer Bar
Brake Type
Parking Brake Type Duo Servo ← ← ←
Brake Booster Type and Size in. Tandem, 8” + 9” ← ← ←
Steering Gear Type Rack & Pinion ← ← ←
Steering Gear Ratio (Overall) 17.4 ← ← ←
Power Steering Type Integral Valve ← ← ←
Overall
Wheel Base in. (mm)
Tread
Effective Head Room
Effective Leg Room
Shoulder Room
Overhang
Min. Running Ground Clearance in. (mm) 5.3 (135) ← 5.4 (136) 5.3 (135)
Angle of Approach degree 21°00’ ← ← ←
Angle of Departure degree 14°3 0’ ← ← 12°30’
Curb Weight
Gross Vehicle Weight
Luggage Compartment Capacity cu. ft. (m3) — — — —
Body Type
Vehicle Grade LE DLX
Model Code VZV21L–UEMNKK VZV21L–UEPNKK XV25L–UEPNKK SV21LG–UWMDKK
0 to 100 km/h
sec.
0 to 400 m sec. 17.0 17.5 19.9 17.7
1st Gear mph (km/h) 32 (52) 40 (64) 32 (52) 30 (49)
2nd Gear mph (km/h) 52 (83) 72 (116) 60 (96) 55 (89)
3rd Gear mph (km/h) 79 (127) 111 (179) 93 (149) 86 (139)
4th Gear mph (km/h) 109 (175) — — —
Wall to Wall ft. (m)
Curb to Curb ft. (m)
In First 3.230 2.810 ← 3.538
In Second 2.045 1.549 ← 1.960
In Third 1.333 1.000 ← 1.250
In Fourth 0.972 0.734 ← 0.945
In Fifth 0.820 — — 0.731
In Reverse 3.583 2.296 ← 3.153
Front Mac Pherson Strut ← ← ←
Rear Mac Pherson Strut ← ← ←
Front STD ← ← ←
Rear STD ← ← L.T. Drum
Front Ventilated Disc ← ← L.T. Drum
Rear Solid Disc ← ← ←
Length in. (mm) 182.1 (4,625) ← ← 183.1 (4,650)
Width in. (mm) 67.3 (1,710) ← ← ←
Height in. (mm) 54.1 (1,375) ← ← 54.5 (1,385)
Front in. (mm) 57.9 (1,470) ← 58.1 (1,475) ←
Rear in. (mm) 56.7 (1,440) ← ← 56.7 (1,445)
Front in. (mm) 38.2 (970), 36.9 (937)
Rear in. (mm) 37.0 (939), 35.9 (911)
Front in. (mm) 42.9 (1,090) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 34.1 (866.1) ← ← 34.4 (873)
Front in. (mm) 54.3 (1,378) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 53.7 (1,378) ← ← ←
Front in. (mm) 36.4 (925) ← ← ←
Rear in. (mm) 43.3 (1,100) ← ← 44.3 (1,125)
Front lb (kg) 1,896 (860) 1,929 (875) 1,819 (825) 1,609 (730)
Rear lb (kg) 1,102 (500) 1,124 (510) 1,323 (600) 1,213 (550)
Total lb (kg) 2,998 (1,360) 3,053 (1,385) 3,142 (1,425) 2,822 (1,280)
Front lb (kg) — — — —
Rear lb (kg) — — — —
Total lb (kg) 4,090 (1,855) ← 4,266 (1,935) 4,045 (1,835)
9.2 10.2 13.9 11.5
— — — —
35.4 (10.8) ← 34.8 (10.6) ←
15.9 (60, 13.2) ← ← ←
102.4 (2,600) ← ← ←
*1
*1
Sedan Wagon
← ← 38.3 (972), 37.1 (943)
← ← 37.7 (958), 36.1 (917)
*1: With Moon Roof
*1
*1

APPENDIX—CAMRY
Canada
DLX LE
SV21LG–UWPDKK SV21LG–UWPNKK VZV21LG–UWPNKK
← ← 2VZ–FE
← ← ←
← ← 3.44 X 2.74 (87.5 X 69.5)
← ← 153.0 (2,508)
← ← 9.0
← ← ←
← ← 96
←
←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← 118 (190)
87 (140) ← 99 (160)
13.5 ← 10.5
18.7 ← 17.7
40 (65) ← 40 (64)
74 (119) ← 72 (116)
— — 111 (179)
— — —
— — —
← ← 35.4 (10.8)
← ← ←
— — —
A140E ← A540E
2.810 ← 2.810
1.549 ← ←
1.000 ← ←
0.706 ← 0.734
— — —
2.296 ← ←
0.945 ← 1.027
← ← 3.625
— — —
— — —
— — —
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← Solid Disc
← ← Duo Servo
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← 57.9 (1,470)
← ← 56.7 (1,440)
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← ←
← ← 5.3 (135)
← ← ←
← ← ←
1,664 (755) 1,675 (760) 1,907 (865)
← ← 1,259 (570)
2,877 (1,305) 2,888 (1,310) 3,164 (1,435)
— — —
— — —
← ← 4,266 (1,935)
— — —
Wagon
← 156 @ 5,600 (116/5,600)
← 160 @ 4,400 (217/4,400)
147
 Loading...
Loading...