Texas Instruments TPS2202IDFR, TPS2202IDFLE, TPS2202IDBR, TPS2202IDBLE Datasheet
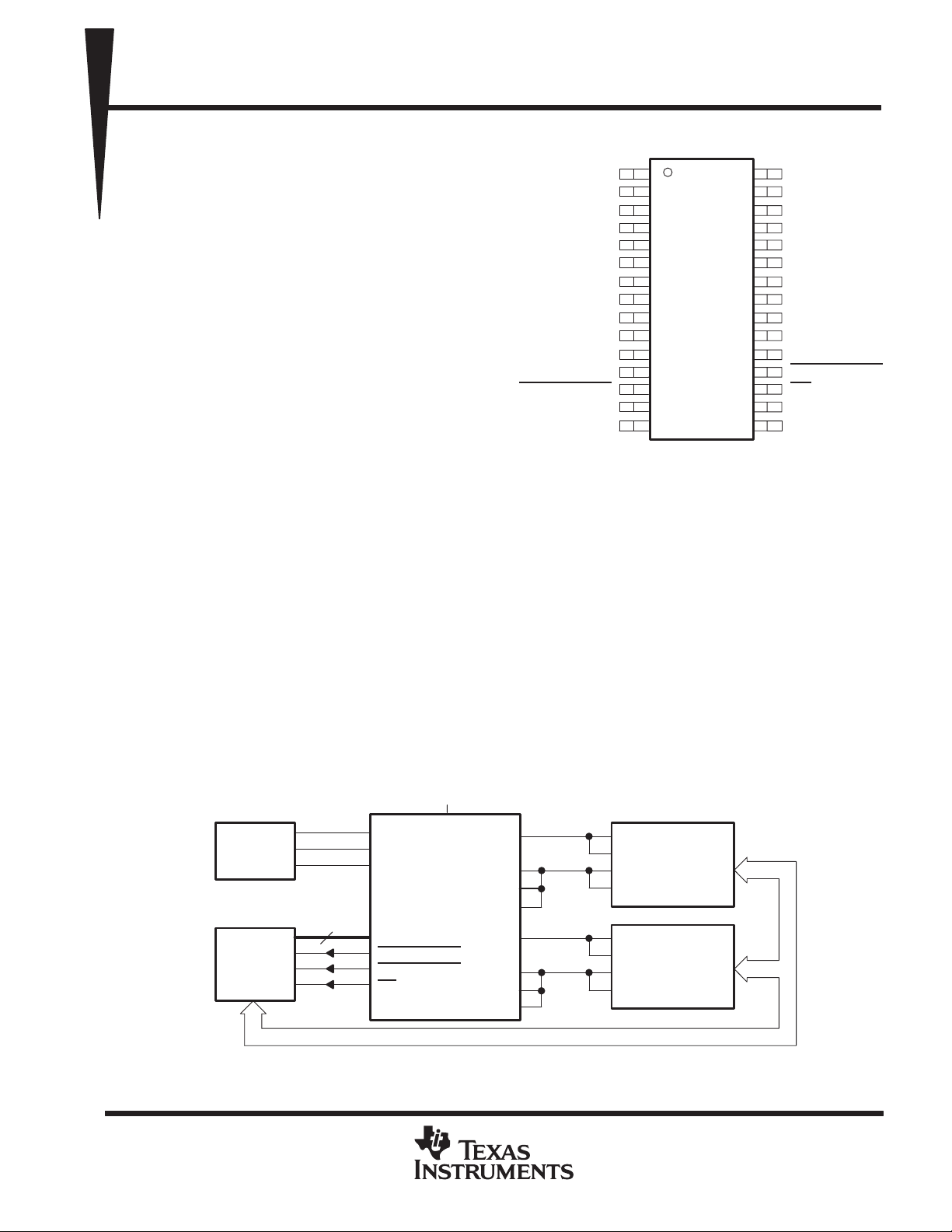
TPS2202, TPS2202Y
DUAL-SLOT PC CARD POWER-INTERFACE SWITCHES
FOR SERIAL PCMCIA CONTROLLERS
SLVS103A – DECEMBER 1994 – REVISED AUGUST 1995
• Fully Integrated V
and Vpp Switching for
CC
Dual-Slot PC Card Interface
• Saves PCMCIA Controller I/O Leads by
Utilizing 3-Lead Serial Interface
• Meets PCMCIA Standards
• Internal Charge Pump (No External
Capacitors Required) – 12-V Supply Can Be
Disabled Except for Flash Programming
• Short Circuit and Thermal Protection
• Space-Saving 30-Pin SSOP(DB) Package
• Compatible With 3.3-V, 5-V and 12-V PC
Cards
• Power Saving I
• Low r
DS(on)
= 83 µA Typ, IQ = 1 µA
DD
(160-mΩ VCC Switch)
• Break-Before-Make Switching
• ESD Protection Up to 2 kV Per
Mil-STD-883C, Method 3015
DATA
CLOCK
LA TCH
NC
12V
A VPP
A VCC
A VCC
A VCC
GND
APWR_GOOD
NC
NC – No internal connection
DB OR DF PACKAGE
5V
5V
3V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
(TOP VIEW)
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
5V
NC
NC
NC
NC
V
12V
BVPP
BVCC
BVCC
BVCC
BPWR_GOOD
OC
3V
3V
description
The TPS2202 PC Card (PCMCIA) power-interface switch provides an integrated power-management solution
for two PC Cards. All of the discrete power MOSFETs, a logic section, current limiting, thermal protection, and
power-good reporting for PC Card control are combined on a single integrated circuit (IC), using Texas
Instruments LinBiCMOS process. The circuit allows the distribution of 3-V, 5-V, and/or 12-V card power by
means of a reduced I/O serial interface. The current-limiting feature eliminates the need for fuses, which reduces
component count and improves reliability; current-limit reporting can help the user isolate a system fault to a
bad card.
DD
The TPS2202 maximizes battery life by using an internal charge pump to generate its own switch-drive voltage.
Therefore, the 12-V supply can be powered down and only brought out of standby when flash memory needs
to be written to or erased. End equipment for the TPS2202 includes notebook computers, desktop computers,
personal digital assistants (PDAs), digital cameras, handiterminals, and bar-code scanners.
typical PC-card power-distribution application
V
Power Supply
12 V
5 V
3 V
3
PCMCIA
Controller
LinBiCMOS is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
12V
5V
3V
Serial Interface
APWR_GOOD
BPWR_GOOD
OC
DD
TPS2202
AVPP
AVCC
AVCC
AVCC
BVPP
BVCC
BVCC
BVCC
V
pp1
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
pp2
CC
CC
pp1
pp2
CC
CC
PC
Card A
PC
Card B
Copyright 1995, Texas Instruments Incorporated
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
6–1
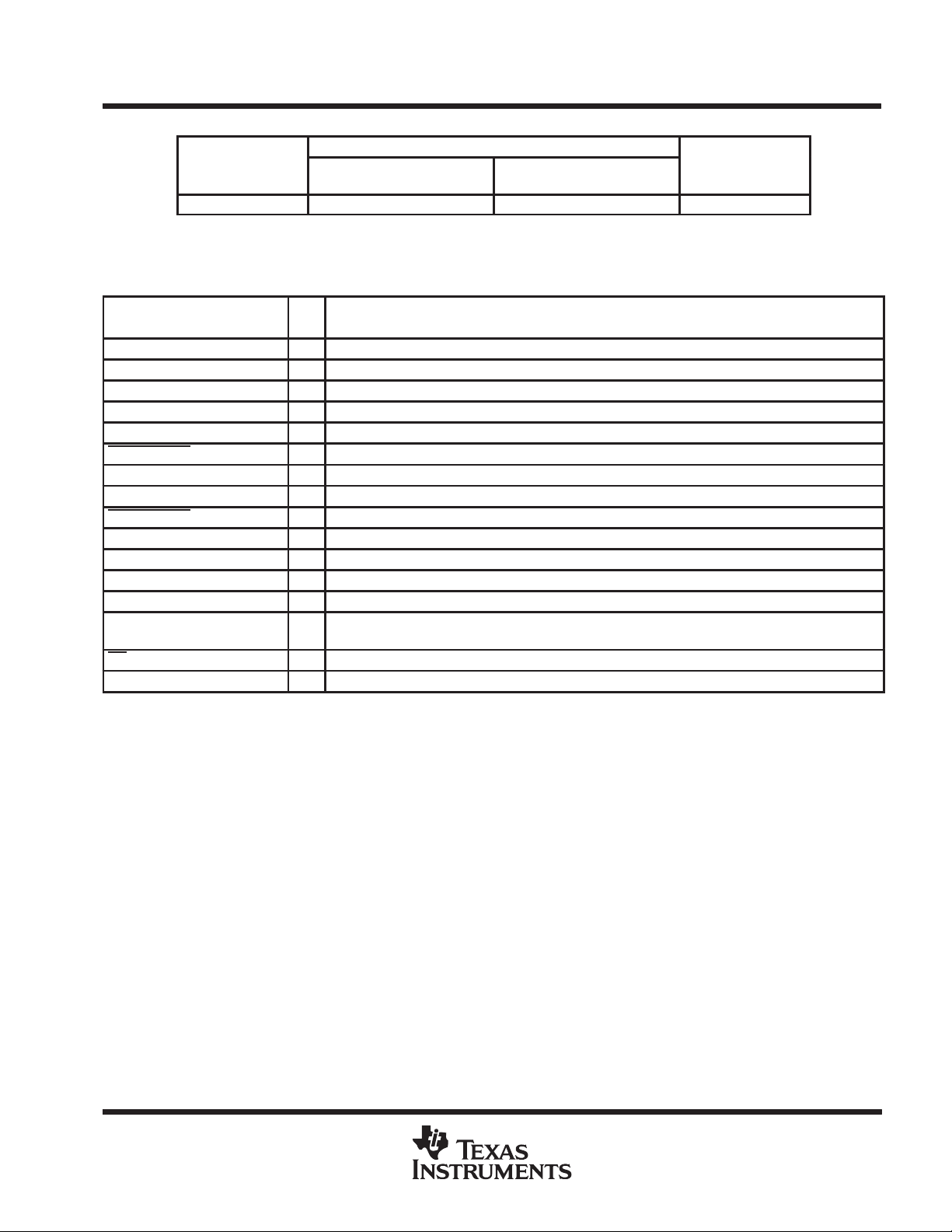
TPS2202, TPS2202Y
CHIP FORM
I/O
DESCRIPTION
DUAL-SLOT PC CARD POWER-INTERFACE SWITCHES
FOR SERIAL PCMCIA CONTROLLERS
SLVS103A – DECEMBER 1994 – REVISED AUGUST 1995
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGED DEVICES
T
J
–40°C to 150°C TPS2202IDB TPS2202IDF TPS2202Y
†
The DF package is only available left-end taped and reeled (indicated by the LE suffix on the device type; e.g.,
TPS2202IDFLE).
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
3V 15, 16, 17 I 3-V VCC input for card power
5V 1, 2, 30 I 5-V VCC input for card power
12V 7, 24 I 12-V VPP input for card power
AVCC 9, 10, 11 O Switched output that delivers 0 V , 3.3 V, 5 V, or high impedance
AVPP 8 O Switched output that delivers 0 V, 3.3 V, 5 V, 12 V, or high impedance
APWR_GOOD 13 O Logic-level power-ready output that stays low as long as AVPP is within limits.
BVCC 20, 21, 22 O Switched output that delivers 0 V, 3.3 V, 5 V, or high impedance
BVPP 23 O Switched output that delivers 0 V, 3.3 V, 5 V, 12 V, or high impedance
BPWR_GOOD 19 O Logic-level power-ready output that stays low as long as BVPP is within limits.
CLOCK 4 I Logic-level clock for serial data word
DATA 3 I Logic-level serial data word
GND 12 Ground
LATCH 5 I Logic-level latch for serial data word
NC 6, 14, 26,
OC 18 O Logic-level overcurrent reporting output that goes low when an overcurrent condition exists.
V
DD
27, 28, 29
25 5-V power to chip
SHINK SMALL-OUTLINE
(DB)
Terminal Functions
No internal connection
SMALL-OUTLINE
(DF)
(Y)
6–2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
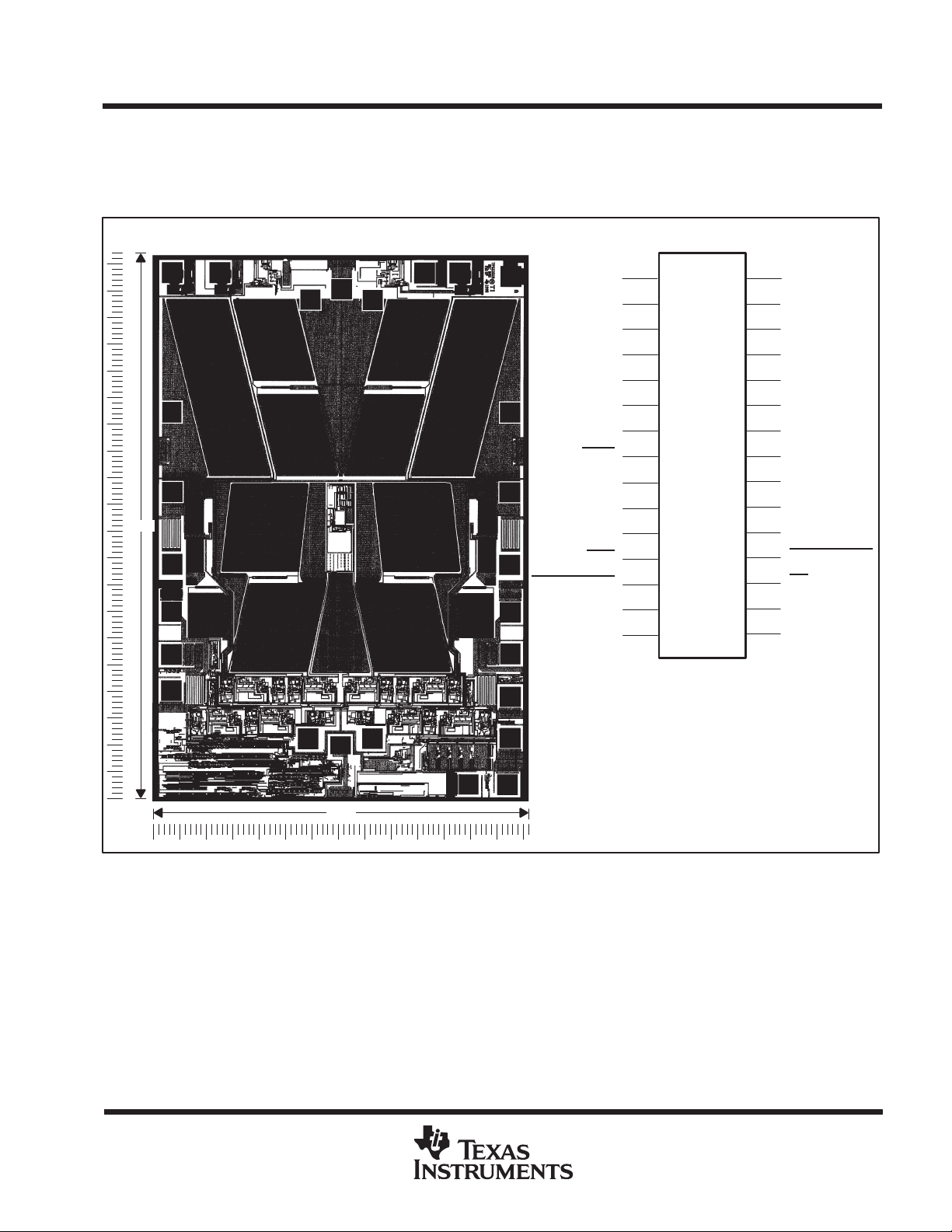
TPS2202, TPS2202Y
DUAL-SLOT PC CARD POWER-INTERFACE SWITCHES
FOR SERIAL PCMCIA CONTROLLERS
SLVS103A – DECEMBER 1994 – REVISED AUGUST 1995
TPS2202Y chip information
This chip, when properly assembled, displays characteristics similar to the TPS2202. Thermal compression or
ultrasonic bonding may be used on the doped aluminum bonding pads. The chips may be mounted with
conductive epoxy or a gold-silicon preform.
BONDING PAD ASSIGNMENTS
204
(19)
(20)
(21)
(22)
(23)
(24)
(25)
(18)
(17)
(30)
(16)
(1)
142
(15)
(2)
(13)
(3) (4)
(12)
(11)
(10)
(9)
APWR_GOOD
(8)
(7)
(5)
(1)
(2)
5V
(3)
DATA
CLOCK
LATCH
(5)
(6)
NC
(7)
12V
(8)
AVPP
(9)
AVCC
(10)
AVCC
(11)
AVCC
(12)
GND
(13)
(14)
NC
(15)
3V
CHIP THICKNESS: 15 MILS TYPICAL
BONDING PADS: 4 × 4 MILS MINIMUM
TJmax = 150°C
TOLERANCES ARE ±10%
ALL DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILS
TERMINALS 6, 14, 26, 27, 28, AND 29
ARE NOT CONNECTED
TPS2201Y
(30)
(29)
(28)
(27)(4)
(26)
(25)
(24)
(23)
(22)
(21)
(20)
(19)
(18)
(17)
(16)
5V5V
NC
NC
NC
NC
V
DD
12V
BVPP
BVCC
BVCC
BVCC
BPWR_GOOD
OC
3V
3V
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
6–3
TPS2202, TPS2202Y
Output current, I
DUAL-SLOT PC CARD POWER-INTERFACE SWITCHES
FOR SERIAL PCMCIA CONTROLLERS
SLVS103A – DECEMBER 1994 – REVISED AUGUST 1995
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage range, V
Input voltage range for card power: V
–0.3 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DD
–0.3 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
I(5V)
V
–0.3 V to V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
I(3V)
V
–0.3 V to 14 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
I(12V)
†
Logic input voltage –0.3 V to 7 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous total power dissipation See Dissipation Rating Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output current (each card): I
O(xVCC)
I
O(xVPP)
Operating virtual junction temperature range, T
Operating free-air temperature range, T
Storage temperature range, T
stg
internally limited. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
internally limited. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–40°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J
–40°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
–55°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds 260°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE
DB 1024 mW 8.2 mW/°C 655 mW 532 mW
DF 1158 mW 9.26 mW/°C 741 mW 602 mW
‡
Maximum values are calculated using a derating factor based on R
These devices are mounted on an FR4 board with no special thermal considerations.
TA ≤ 25°C
POWER RATING
DERATING FACTOR
ABOVE TA = 25°C
‡
TA = 70°C
POWER RATING
θJA
TA = 85°C
POWER RATING
= 108°C/W for the package.
I(5V)
recommended operating conditions
Supply voltage, V
Input voltage range, V
p
Clock frequency, f
Operating virtual junction temperature, T
†
V
should not be taken above V
I(3V)
O
DD
clock
V
I(5V)
I(5V)
V
I(3V)
V
I(12V)
I
O(xVCC)
I
O(xVPP)
J
.
I
MIN MAX UNIT
4.75 5.25 V
0 5.25 V
I(5V)
†
V
0 V
0 13.5 V
at 25°C 1 A
at 25°C 150 mA
0 2.5 MHz
–40 125 °C
6–4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
TPS2202, TPS2202Y
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNIT
mΩ
†
IppHigh-impedance state
Leakage current
A
ICCHigh-impedance state
Input current
Short-circuit output-current limit
J
,
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNIT
t
Output rise time
ms
t
Output fall time
ms
LATCH↑ to V
ms
t
Propagation delay (see Figure 1§)
LATCH↑ t
VCC (3 V)
ms
LATCH↑ to xVCC (5 V)
ms
DUAL-SLOT PC CARD POWER-INTERFACE SWITCHES
FOR SERIAL PCMCIA CONTROLLERS
SLVS103A – DECEMBER 1994 – REVISED AUGUST 1995
electrical characteristics, TA = 25°C, VDD = 5 V (unless otherwise noted)
dc characteristics
TPS2202
MIN TYP MAX
5 V to xVCC 160
3 V to xVCC 225
Switch resistances
Clamp low voltage Ipp at 10 mA 0.8 V
Clamp low voltage ICC at 10 mA 0.8 V
p
Power-ready threshold, PWR_GOOD 10.72 11.05 11.4 V
Power-ready hysteresis, PWR_GOOD (12-V mode) 50 mV
p
†
Pulse-testing techniques maintain junction temperature close to ambient temperature; thermal effects must be taken into account separately.
switching characteristics
r
f
pd
‡
Refer to Parameter Measurement Information
§
Propagation delays are with CL = 100 µF.
p
p
p
5 V to xVPP 6
3 V to xVPP 6
12 V to xVPP 1
p
p
I
DD
IDD in shutdown
I
O(xVCC)
I
O(xVPP)
TA = 25°C 1 10
TA = 85°C 50
TA = 25°C 1 10
TA = 85°C 50
V
O(AVCC)
V
O(AVPP)
V
O(BVCC)
T
Output powered up into a short to GND
= 85°C,
= V
= V
= V
= V
O(BVCC)
O(BVPP)
O(AVCC)
O(BVPP)
= 5 V,
= 12 V
= V
O(AVPP)
= high Z
83 150 µA
0.75 1.3 1.9 A
120 200 400 mA
‡
TPS2202
MIN TYP MAX
V
O(xVCC)
V
O(xVPP)
V
O(xVCC)
V
O(xVPP)
o x
O(xVPP)
t
on
t
off
t
on
t
off
t
on
t
off
1.2
5
10
14
5.8
18
5.8
28
4
30
µ
1 µA
Ω
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
6–5
TPS2202, TPS2202Y
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNIT
I
1 mA
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNIT
Leakage current
A
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
UNIT
t
Output rise time
ms
t
Output fall time
ms
LATCH↑ to V
ms
t
Propagation delay (see Figure 1‡)
LATCH↑ t
VCC
ms
LATCH↑ to xVCC
ms
DUAL-SLOT PC CARD POWER-INTERFACE SWITCHES
FOR SERIAL PCMCIA CONTROLLERS
SLVS103A – DECEMBER 1994 – REVISED AUGUST 1995
electrical characteristics, TA = 25°C, VDD = 5 V (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
logic section
TPS2202
MIN MAX
Logic input current 1 µA
Logic input high level 2.7 V
Logic input low level 0.8 V
Logic output high level
Logic output low level
=
O
dc characteristics
IppHigh-impedance state 1
ICCHigh-impedance state 1
V
Input current I
Power-ready threshold, PWR_GOOD 11.05 V
Power-ready hysteresis, PWR_GOOD (12-V mode) 50 mV
DD
O(AVCC)
V
O(AVPP)
= V
= V
O(BVCC)
O(BVPP)
= 5 V,
= 12 V
VDD–0.4 V
0.4 V
TPS2202Y
MIN TYP MAX
83 µA
µ
switching characteristics
r
f
pd
†
Refer to Parameter Measurement Information
‡
Propagation delays are with CL = 100 µF.
p
p
p
†
V
O(xVCC)
V
O(xVPP)
V
O(xVCC)
V
O(xVPP)
o x
O(xVPP)
TPS2202Y
MIN TYP MAX
1.2
5
10
14
t
on
t
off
t
on
t
off
t
on
t
off
5.8
18
5.8
28
4
30
6–6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
DUAL-SLOT PC CARD POWER-INTERFACE SWITCHES
FOR SERIAL PCMCIA CONTROLLERS
SLVS103A – DECEMBER 1994 – REVISED AUGUST 1995
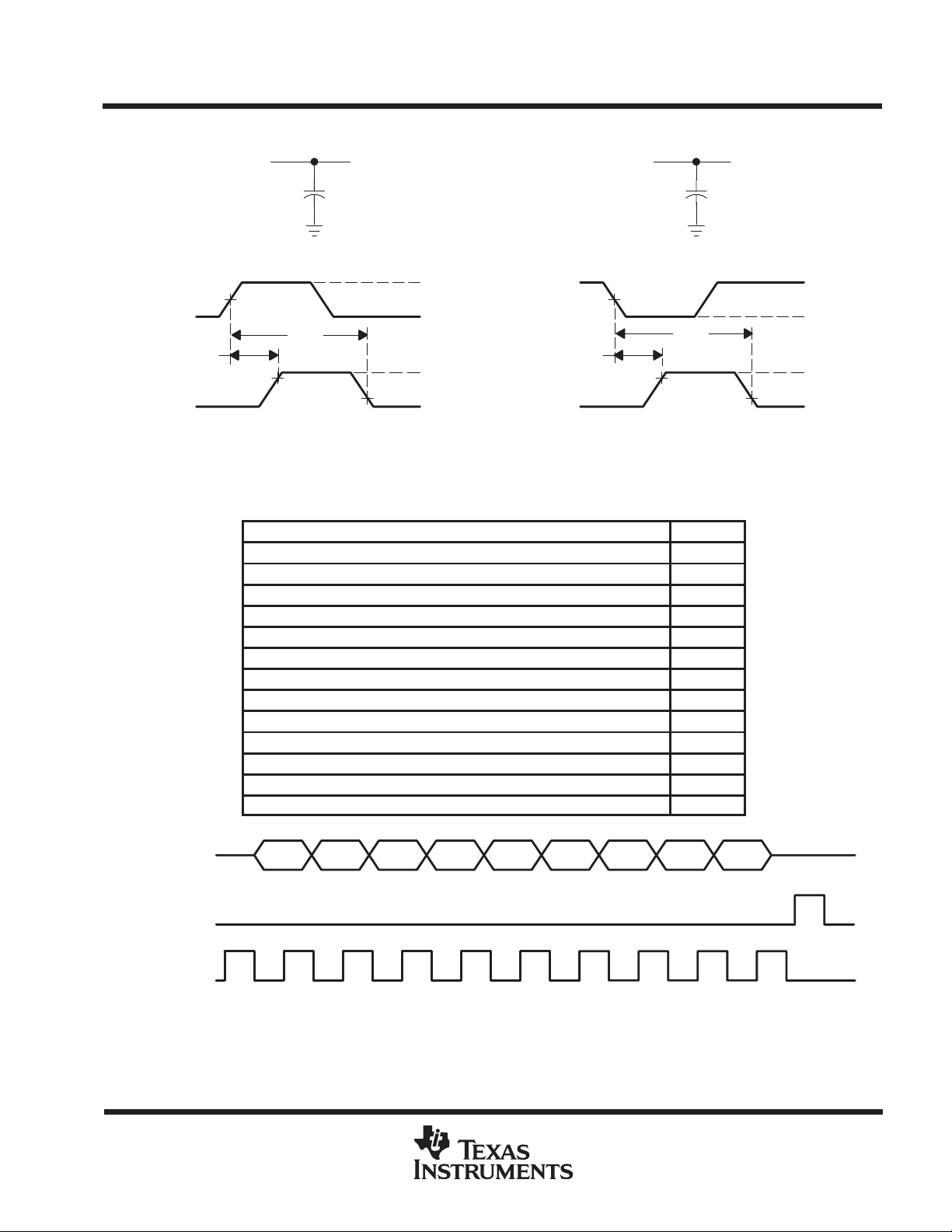
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
TPS2202, TPS2202Y
LATCH
V
O(xVPP)
V
pp
LOAD CIRCUIT
50%
t
on
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
Serial-Interface Timing 2
xVCC Propagation Delay and Rise Times With 1-µF Load, 3-V Switch 3
xVCC Propagation Delay and Fall Times With 1-µF Load, 3-V Switch 4
xVCC Propagation Delay and Rise Times With 100-µF Load, 3-V Switch 5
xVCC Propagation Delay and Fall Times With 100-µF Load, 3-V Switch 6
xVCC Propagation Delay and Rise Times With 1-µF Load, 5-V Switch 7
xVCC Propagation Delay and Fall Times With 1-µF Load, 5-V Switch 8
xVCC Propagation Delay and Rise Times With 100-µF Load, 5-V Switch 9
xVCC Propagation Delay and Fall Times With 100-µF Load, 5-V Switch 10
xVPP Propagation Delay and Rise Times With 1-µF Load, 12-V Switch 11
xVPP Propagation Delay and Fall Times With 1-µF Load, 12-V Switch 12
xVPP Propagation Delay and Rise Times With 100-µF Load, 12-V Switch 13
xVPP Propagation Delay and Fall Times With 100-µF Load, 12-V Switch 14
C
L
V
t
off
90%
10%
DD
GND
V
I(12V)
GND
LATCH
V
O(xVCC)
t
on
Figure 1. Test Circuits and Voltage Waveforms
Table of Timing Diagrams
V
CC
C
L
LOAD CIRCUIT
50%
t
off
90%
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
FIGURE
10%
V
DD
GND
V
I(5V)
GND
DATA
LATCH
CLOCK
NOTE A. Data is clocked in on the a positive leading edge of the clock. The latch should occur before next positive leading edge of
the clock. For definition of D0–D8, see control logic table.
D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Figure 2. Serial-Interface Timing
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
6–7
 Loading...
Loading...