Page 1

Reference Guide
This guidebook applies to TI-Nspire™ software version 1.4. To obtain the
latest version of the documentation, go to education.ti.com/guides.
Page 2

Important Information
Except as otherwise expressly stated in the License that accompanies a
program, Texas Instruments makes no warranty, either express or
implied, including but not limited to any implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, regarding any
programs or book materials and makes such materials available solely on
an "as-is" basis. In no event shall Texas Instruments be liable to anyone
for special, collateral, incidental, or consequential damages in connection
with or arising out of the purchase or use of these materials, and the sole
and exclusive liability of Texas Instruments, regardless of the form of
action, shall not exceed the amount set forth in the license for the
program. Moreover, Texas Instruments shall not be liable for any claim of
any kind whatsoever against the use of these materials by any other
party.
License
Please see the complete license installed in C:\Program Files\TI
Education\TI-Nspire.
© 2008 Texas Instruments Incorporated
Macintosh®, Windows®, Excel®, Vernier EasyLink®, EasyTemp®,
Go!®Link, Go!®Motion, and Go!®Temp are trademarks of their
respective owners.
ii
Page 3

Contents
Expression templates
Fraction template ........................................ 1
Exponent template ......................................1
Square root template .................................. 1
Nth root template ........................................1
e exponent template ................................... 1
Log template ................................................ 2
Piecewise template (2-piece) .......................2
Piecewise template (N-piece) ......................2
Absolute value template .............................2
dd°mm’ss.ss’’ template ................................2
Matrix template (2 x 2) ................................3
Matrix template (1 x 2) ................................3
Matrix template (2 x 1) ................................3
Matrix template (m x n) .............................. 3
Sum template (G) ......................................... 3
Product template (Π) ...................................4
Alphabetical listing
A
abs() ..............................................................5
amortTbl() .................................................... 5
and ................................................................5
angle() ..........................................................6
ANOVA .........................................................6
ANOVA2way ................................................ 7
Ans ................................................................8
approx() ........................................................9
approxRational() .......................................... 9
augment() .....................................................9
avgRC() ....................................................... 10
B
bal() .............................................................10
4Base2 .........................................................10
4Base10 .......................................................11
4Base16 .......................................................11
binomCdf() ................................................. 11
binomPdf() ................................................. 12
C
ceiling() .......................................................12
char() ...........................................................12
2
2way ........................................................12
c
2
Cdf() .........................................................13
c
2
GOF ......................................................... 13
c
2
Pdf() .........................................................13
c
ClearAZ .......................................................13
ClrErr ...........................................................14
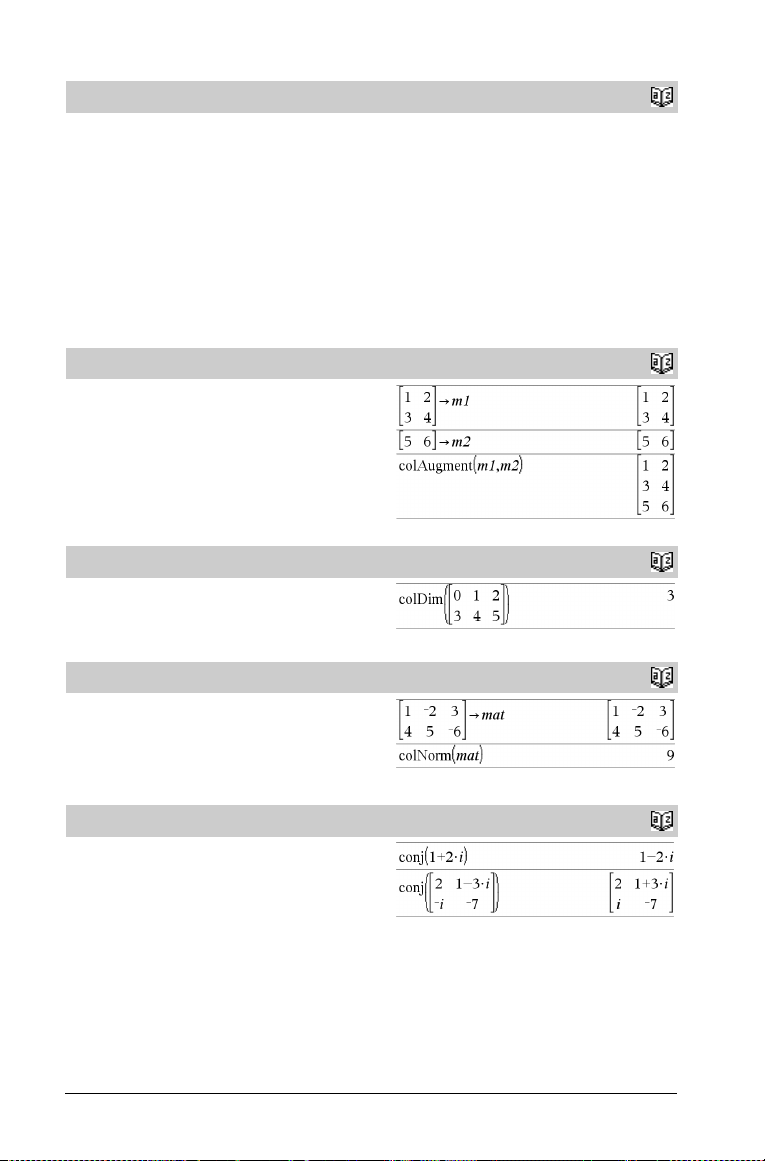
colAugment() ............................................. 14
colDim() ......................................................14
colNorm() ....................................................14
conj() ...........................................................14
constructMat() ............................................ 15
CopyVar ...................................................... 15
corrMat() ....................................................15
cos() .............................................................16
cosê() ...........................................................17
cosh() .......................................................... 17
coshê() ........................................................ 17
cot() ............................................................ 18
cotê() .......................................................... 18
coth() .......................................................... 18
cothê() ........................................................ 18
count() ........................................................ 19
countif() ..................................................... 19
crossP() ....................................................... 19
csc() ............................................................. 20
cscê() ........................................................... 20
csch() ........................................................... 20
cschê() ......................................................... 20
CubicReg .................................................... 21
cumSum() ................................................... 21
Cycle ........................................................... 22
4Cylind ........................................................ 22
D
dbd() ........................................................... 22
4DD ............................................................. 23
4Decimal ..................................................... 23
Define ......................................................... 23
Define LibPriv ............................................ 24
Define LibPub ............................................ 24
DelVar ........................................................ 25
det() ............................................................ 25
diag() .......................................................... 25
dim() ........................................................... 26
Disp ............................................................. 26
4DMS ........................................................... 26
dotP() .......................................................... 26
E
e^() ............................................................. 27
eff() ............................................................. 27
eigVc() ........................................................ 27
eigVl() ......................................................... 28
Else ............................................................. 28
ElseIf ........................................................... 28
EndFor ........................................................ 28
EndFunc ...................................................... 28
EndIf ........................................................... 28
EndLoop ..................................................... 28
EndPrgm ..................................................... 28
EndTry ........................................................ 28
EndWhile .................................................... 29
Exit .............................................................. 29
exp() ........................................................... 29
expr() .......................................................... 29
ExpReg ....................................................... 30
F
factor() ....................................................... 30
FCdf() ......................................................... 31
Fill ............................................................... 31
FiveNumSummary ...................................... 31
floor() ......................................................... 32
For .............................................................. 32
format() ...................................................... 32
iii
Page 4

fPart() ..........................................................33
FPdf() ..........................................................33
freqTable4list() ............................................33
frequency() .................................................33
FTest_2Samp ..............................................34
Func .............................................................34
G
gcd() ............................................................35
geomCdf() ...................................................35
geomPdf() ...................................................35
getDenom() ................................................35
getLangInfo() .............................................36
getMode() ...................................................36
getNum() ....................................................37
getVarInfo() ................................................37
Goto ............................................................38
4Grad ...........................................................38
I
identity() .....................................................38
If ..................................................................39
ifFn() ............................................................40
imag() ..........................................................40
Indirection ..................................................40
inString() .....................................................40
int() .............................................................41
intDiv() ........................................................41
2
() .........................................................41
invc
invF() ...........................................................41
invNorm() ....................................................41
invt() ............................................................41
iPart() ..........................................................41
irr() ..............................................................42
isPrime() ......................................................42
L
Lbl ...............................................................42
lcm() ............................................................43
left() ............................................................43
libShortcut() ................................................43
LinRegBx .....................................................44
LinRegMx ....................................................44
LinRegtIntervals .........................................45
LinRegtTest .................................................46
@List() ..........................................................47
list4mat() .....................................................47
ln() ...............................................................47
LnReg ..........................................................48
Local ............................................................49
log() .............................................................49
Logistic ........................................................50
LogisticD .....................................................50
Loop ............................................................51
LU ................................................................52
M
mat4list() .....................................................52
max() ...........................................................52
mean() .........................................................53
median() .....................................................53
MedMed .....................................................53
mid() ............................................................54
min() ........................................................... 54
mirr() ........................................................... 55
mod() .......................................................... 55
mRow() ....................................................... 55
mRowAdd() ................................................ 55
MultReg ...................................................... 55
MultRegIntervals ....................................... 56
MultRegTests ............................................. 56
N
nCr() ............................................................ 58
nDeriv() ....................................................... 58
newList() ..................................................... 58
newMat() .................................................... 58
nfMax() ....................................................... 59
nfMin() ....................................................... 59
nInt() ........................................................... 59
nom() .......................................................... 59
norm() ......................................................... 60
normCdf() ................................................... 60
normPdf() ................................................... 60
not .............................................................. 60
nPr() ............................................................ 61
npv() ........................................................... 61
nSolve() ....................................................... 61
O
OneVar ....................................................... 62
or ................................................................ 63
ord() ............................................................ 63
P
P4Rx() .......................................................... 63
P4Ry() .......................................................... 64
PassErr ........................................................ 64
piecewise() ................................................. 64
poissCdf() .................................................... 64
poissPdf() .................................................... 64
4Polar .......................................................... 65
polyEval() .................................................... 65
PowerReg ................................................... 65
Prgm ........................................................... 66
Product (PI) ................................................. 66
product() .................................................... 66
propFrac() ................................................... 67
Q
QR ............................................................... 68
QuadReg .................................................... 68
QuartReg .................................................... 69
R
R4Pq() .......................................................... 70
R4Pr() ........................................................... 70
4Rad ............................................................ 70
rand() .......................................................... 70
randBin() .................................................... 71
randInt() ..................................................... 71
randMat() ................................................... 71
randNorm() ................................................ 71
randPoly() ................................................... 71
randSamp() ................................................. 71
RandSeed ................................................... 72
iv
Page 5

real() ...........................................................72
4Rect ............................................................72
ref() .............................................................73
remain() ......................................................73
Return .........................................................73
right() ..........................................................73
root() ...........................................................74
rotate() .......................................................74
round() ........................................................75
rowAdd() ....................................................75
rowDim() ....................................................75
rowNorm() ..................................................75
rowSwap() ..................................................75
rref() ............................................................76
S
sec() .............................................................76
sec/() ...........................................................76
sech() ...........................................................76
sechê() ......................................................... 77
seq() ............................................................77
setMode() ................................................... 77
shift() ..........................................................78
sign() ...........................................................79
simult() ........................................................79
sin() .............................................................80
sinê() ...........................................................80
sinh() ...........................................................81
sinhê() .........................................................81
SinReg .........................................................81
SortA ...........................................................82
SortD ...........................................................82
4Sphere ....................................................... 83
sqrt() ...........................................................83
stat.results .................................................. 83
stat.values ...................................................84
stDevPop() .................................................. 84
stDevSamp() ............................................... 85
Stop .............................................................85
Store ...........................................................85
string() ........................................................85
subMat() .....................................................86
Sum (Sigma) ...............................................86
sum() ...........................................................86
sumIf() .........................................................87
system() .......................................................87
T
T (transpose) ...............................................87
tan() ............................................................88
tanê() ..........................................................88
tanh() ..........................................................89
tanhê() ........................................................89
tCdf() ...........................................................90
Then ............................................................90
tInterval ......................................................90
tInterval_2Samp .........................................90
tPdf() ...........................................................91
trace() .........................................................91
Try ...............................................................91
tTest ............................................................92
tTest_2Samp ...............................................93
tvmFV() .......................................................93
tvmI() .......................................................... 93
tvmN() ........................................................ 93
tvmPmt() .................................................... 94
tvmPV() ....................................................... 94
TwoVar ....................................................... 94
U
unitV() ........................................................ 96
V
varPop() ...................................................... 96
varSamp() ................................................... 96
W
when() ........................................................ 96
While .......................................................... 97
“With” ........................................................ 97
X
xor .............................................................. 97
Z
zInterval ..................................................... 98
zInterval_1Prop .......................................... 98
zInterval_2Prop .......................................... 99
zInterval_2Samp ........................................ 99
zTest ......................................................... 100
zTest_1Prop .............................................. 100
zTest_2Prop .............................................. 101
zTest_2Samp ............................................ 101
Symbols
+ (add) ...................................................... 102
N(subtract) ................................................ 102
·(multiply) ............................................... 103
à (divide) .................................................. 103
^ (power) .................................................. 104
2
(square) ................................................ 104
x
.+ (dot add) .............................................. 105
.. (dot subt.) ............................................. 105
·(dot mult.) ............................................ 105
.
. / (dot divide) .......................................... 105
.^ (dot power) .......................................... 105
ë(negate) .................................................. 106
% (percent) .............................................. 106
= (equal) ................................................... 107
ƒ (not equal) ............................................ 107
< (less than) .............................................. 107
{ (less or equal) ........................................ 108
> (greater than) ....................................... 108
| (greater or equal) ................................. 108
! (factorial) ............................................... 108
& (append) ............................................... 108
‡() (square root) ...................................... 109
Π() (product) ............................................ 109
G() (sum) ................................................... 109
GInt() ......................................................... 110
GPrn() ........................................................ 111
# (indirection) .......................................... 111
í (scientific notation) .............................. 111
g (gradian) ............................................... 112
ô(radian) ................................................... 112
¡ (degree) ................................................. 112
v
Page 6

¡, ', '' (degree/minute/second) .................112
(angle) ...................................................113
10^() ..........................................................113
^ê (reciprocal) ...........................................113
| (“with”) ...................................................114
& (store) ...................................................114
:= (assign) ..................................................114
© (comment) ............................................115
0b, 0h ........................................................115
Error codes and messages
Texas Instruments Support and
Service
vi
Page 7
TI-Nspire™
This guide lists the templates, functions, commands, and operators available for evaluating
math expressions.
Reference Guide
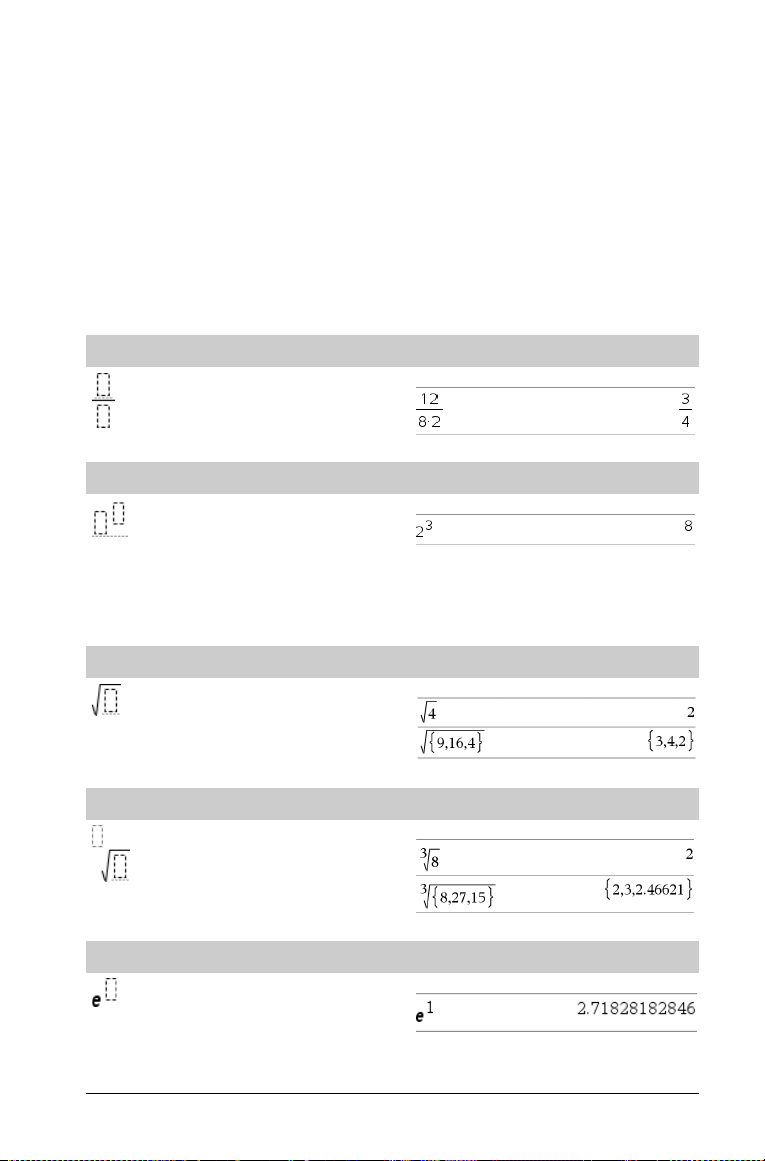
Expression templates
Expression templates give you an easy way to enter math expressions in standard mathematical
notation. When you insert a template, it appears on the entry line with small blocks at positions
where you can enter elements. A cursor shows which element you can enter.
Use the arrow keys or press
value or expression for the element. Press
Fraction template
Note: See also / (divide), page 103.
e to move the cursor to each element’s position, and type a
· or /· to evaluate the expression.
/p keys
Example:
Exponent template
Note: Type the first value, press l, and then type the
exponent. To return the cursor to the baseline, press right arrow (¢).
Note: See also ^ (power), page 104.
Square root template
Note: See also
Nth root template
Note: See also root(), page 74.
e exponent template
Natural exponential e raised to a power
Note: See also e^(), page 27.
‡
() (square root), page 109.
l key
Example:
/q keys
Example:
/l keys
Example:
u keys
Example:
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 1
Page 8
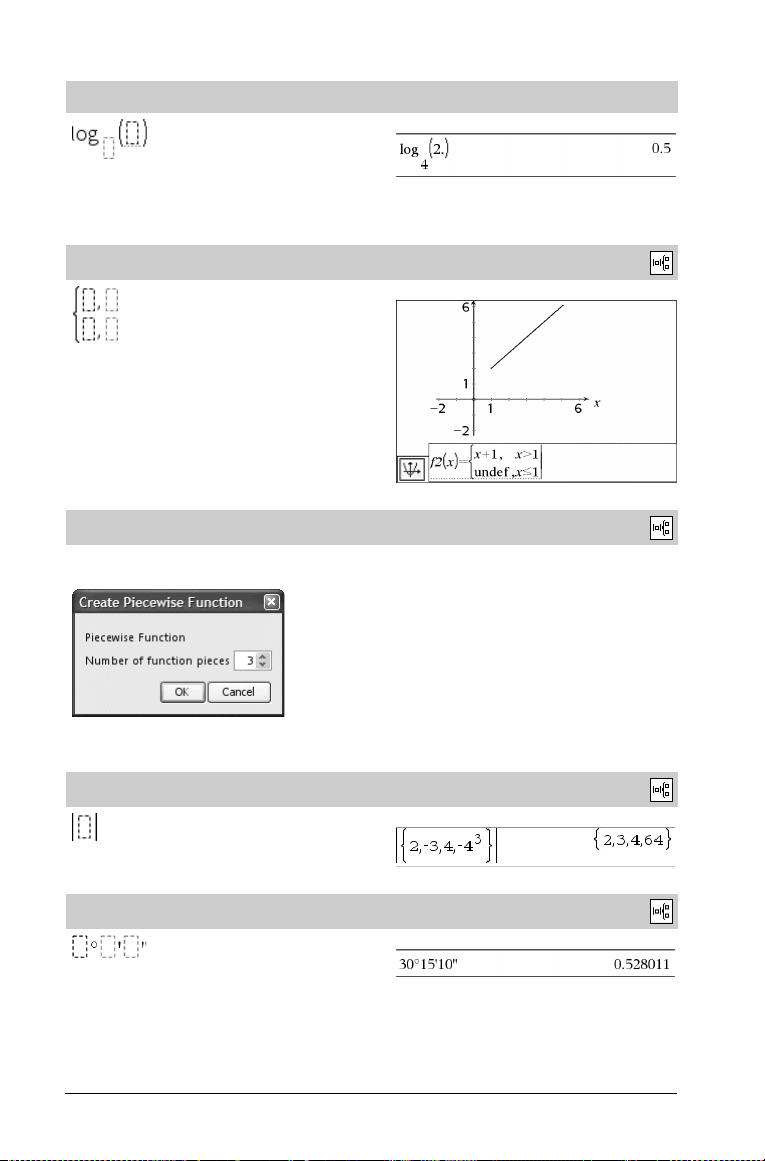
Log template
Calculates log to a specified base. For a default of base 10, omit the
base.
Note: See also log(), page 49.
/s key
Example:
Piecewise template (2-piece)
Lets you create expressions and conditions for a two-piece piecewise
function. To add a piece, click in the template and repeat the
template.
Note: See also piecewise(), page 64.
Piecewise template (N-piece)
Lets you create expressions and conditions for an N-piece piecewise
function. Prompts for N.
Note: See also piecewise(), page 64.
Absolute value template
Note: See also abs(), page 5.
Catalog >
Example:
Catalog >
Example:
See the example for Piecewise template (2-piece).
Catalog >
Example:
dd°mm’ss.ss’’ template
Lets you enter angles in dd°mm’ss.ss’’ format, where dd is the
number of decimal degrees, mm is the number of minutes, and ss.ss
is the number of seconds.
Example:
Catalog >
2 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 9
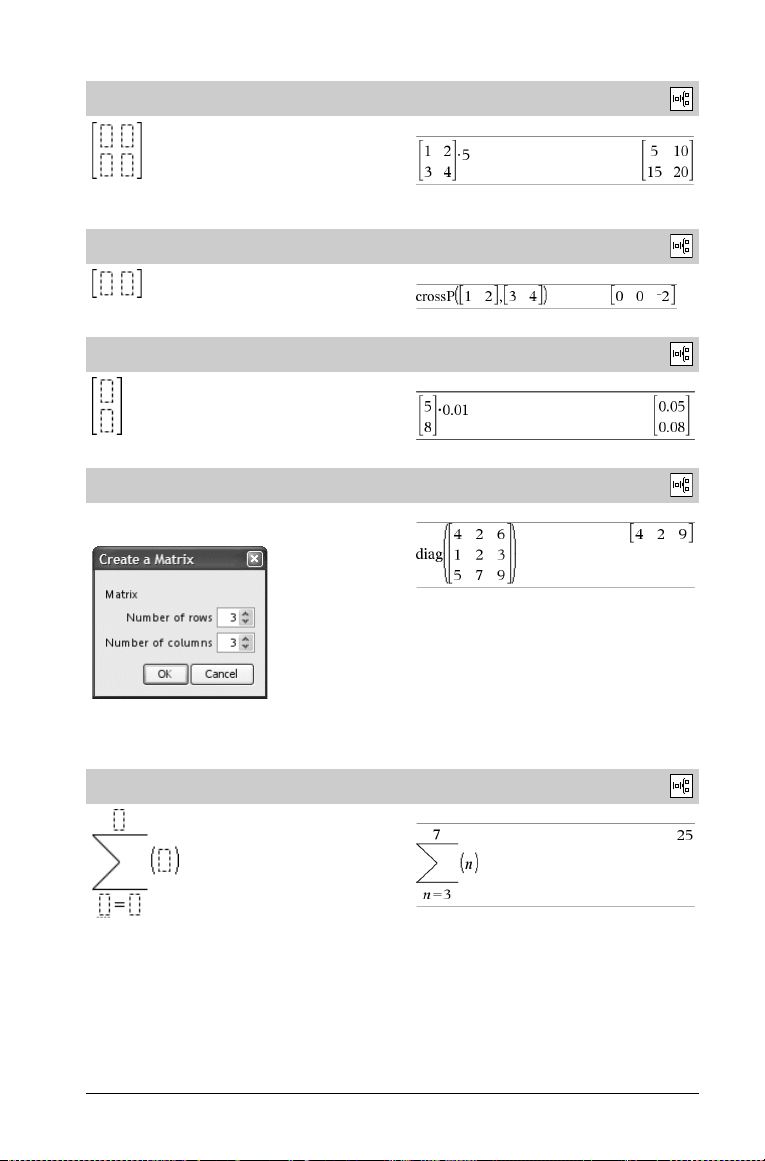
Matrix template (2 x 2)
Creates a 2 x 2 matrix.
Catalog >
Example:
Matrix template (1 x 2)
.
Matrix template (2 x 1)
Matrix template (m x n)
The template appears after you are prompted to specify the number
of rows and columns.
Note: If you create a matrix with a large number of rows and
columns, it may take a few moments to appear.
Sum template (G)
Catalog >
Example:
Catalog >
Example:
Catalog >
Example:
Catalog >
Example:
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 3
Page 10

Product template (Π)
Note: See also Π() (product), page 109.
Catalog >
Example:
4 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 11

Alphabetical listing
Items whose names are not alphabetic (such as +, !, and >) are listed at the end of this section,
starting on page 102. Unless otherwise specified, all examples in this section were performed
in the default reset mode, and all variables are assumed to be undefined.
A
abs()
abs(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
abs(
List1) ⇒ list
abs(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns the absolute value of the argument.
Note: See also Absolute value template, page 2.
If the argument is a complex number, returns the number’s modulus.
amortTbl()
amortTbl(NPmt,N,I,PV, [Pmt], [FV], [PpY], [CpY], [PmtAt],
roundValue]) ⇒ matrix
[
Amortization function that returns a matrix as an amortization table
for a set of TVM arguments.
NPmt is the number of payments to be included in the table. The
table starts with the first payment.
N, I, PV, Pmt, FV, PpY, CpY, and PmtAt are described in the table
of TVM arguments, page 94.
• If you omit Pmt, it defaults to
Pmt=tvmPmt(N,I,PV,FV,PpY,CpY,PmtAt).
• If you omit FV, it defaults to FV=0.
• The defaults for PpY, CpY, and PmtAt are the same as for the
TVM functions.
roundValue specifies the number of decimal places for rounding.
Default=2.
The columns in the result matrix are in this order: Payment number,
amount paid to interest, amount paid to principal, and balance.
The balance displayed in row n is the balance after payment n.
You can use the output matrix as input for the other amortization
functions GInt() and GPrn(), page 110, and bal(), page 10.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
and
BooleanExpr1 and BooleanExpr2 ⇒ Boolean expression
BooleanList1 and BooleanList2 ⇒ Boolean list
BooleanMatrix1 and BooleanMatrix2 ⇒ Boolean matrix
Returns true or false or a simplified form of the original entry.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 5
Page 12

and
Integer1 and Integer2 ⇒ integer
Compares two real integers bit-by-bit using an
Internally, both integers are converted to signed, 64-bit binary
numbers. When corresponding bits are compared, the result is 1 if
both bits are 1; otherwise, the result is 0. The returned value
represents the bit results, and is displayed according to the Base
mode.
You can enter the integers in any number base. For a binary or
hexadecimal entry, you must use the 0b or 0h prefix, respectively.
Without a prefix, integers are treated as decimal (base 10).
If you enter a decimal integer that is too large for a signed, 64-bit
binary form, a symmetric modulo operation is used to bring the value
into the appropriate range.
and operation.
Catalog
>
In Hex base mode:
Important: Zero, not the letter O.
In Bin base mode:
In Dec base mode:
Note: A binary entry can have up to 64 digits (not counting the
0b prefix). A hexadecimal entry can have up to 16 digits.
angle()
angle(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
Returns the angle of the argument, interpreting the argument as a
complex number.
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
angle(List1) ⇒ list
angle(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns a list or matrix of angles of the elements in List1 or Matrix1,
interpreting each element as a complex number that represents a
two-dimensional rectangular coordinate point.
ANOVA
ANOVA List1,List2[,List3,...,List20][,Flag]
Performs a one-way analysis of variance for comparing the means of
two to 20 populations. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
Flag=0 for Data, Flag=1 for Stats
Output variable Description
stat.F Value of the F statistic
stat.PVal Smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected
stat.df Degrees of freedom of the groups
stat.SS Sum of squares of the groups
stat.MS Mean squares for the groups
stat.dfError Degrees of freedom of the errors
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
6 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 13
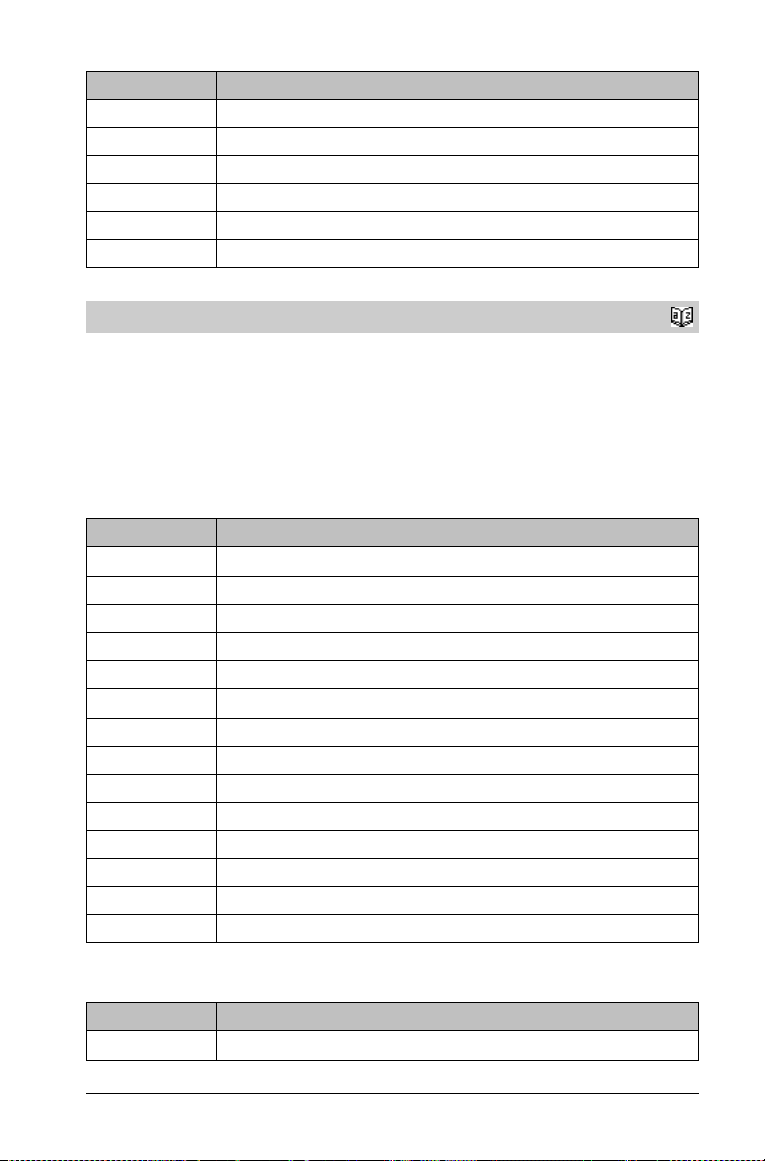
Output variable Description
stat.SSError Sum of squares of the errors
stat.MSError Mean square for the errors
stat.sp Pooled standard deviation
stat.xbarlist Mean of the input of the lists
stat.CLowerList 95% confidence intervals for the mean of each input list
stat.CUpperList 95% confidence intervals for the mean of each input list
ANOVA2way
ANOVA2way List1,List2[,List3,…,List20][,levRow]
Computes a two-way analysis of variance for comparing the means of
two to 20 populations. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
LevRow=0 for Block
LevRow=2,3,...,Len-1, for Two Factor, where
Len=length(List1)=length(List2) = … = length(List10) and
Len / LevRow ∈ {2,3,…}
Outputs: Block Design
Output variable Description
stat.FF statistic of the column factor
stat.PVal Smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected
stat.df Degrees of freedom of the column factor
stat.SS Sum of squares of the column factor
stat.MS Mean squares for column factor
stat.FBlock F statistic for factor
stat.PValBlock Least probability at which the null hypothesis can be rejected
stat.dfBlock Degrees of freedom for factor
stat.SSBlock Sum of squares for factor
stat.MSBlock Mean squares for factor
stat.dfError Degrees of freedom of the errors
stat.SSError Sum of squares of the errors
stat.MSError Mean squares for the errors
stat.s Standard deviation of the error
Catalog
>
COLUMN FACTOR Outputs
Output variable Description
stat.Fcol F statistic of the column factor
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 7
Page 14
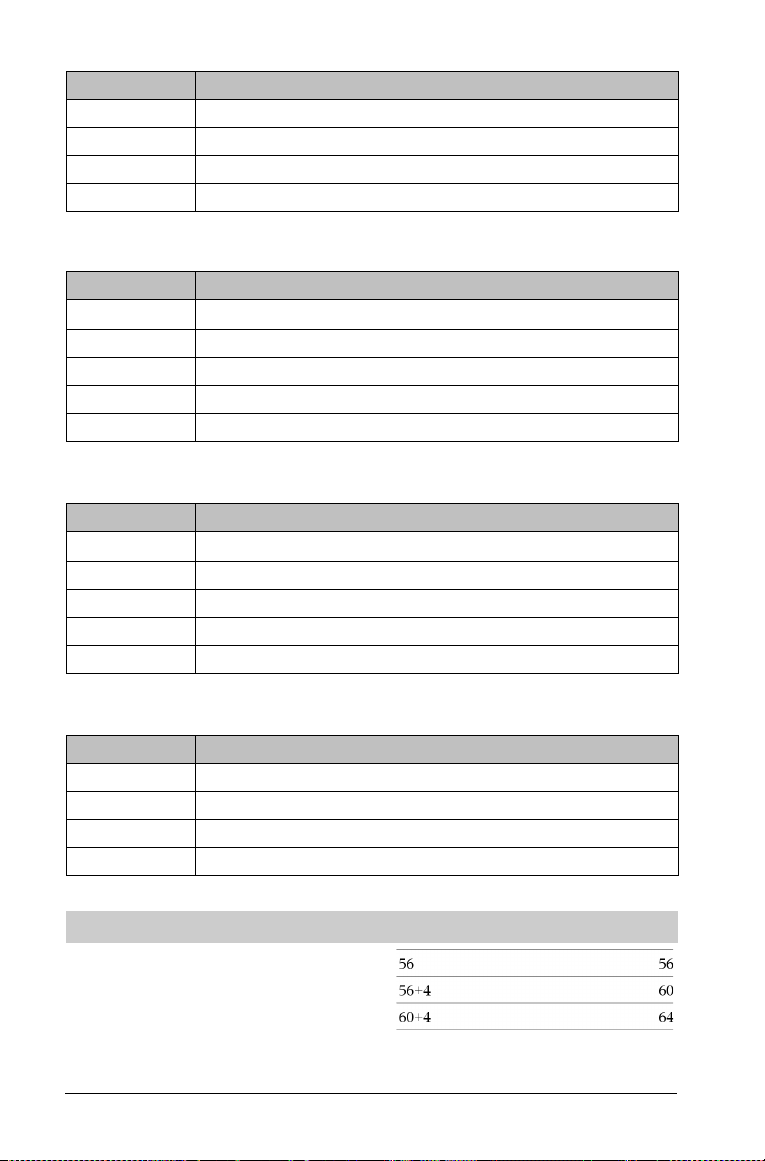
Output variable Description
stat.PValCol Probability value of the column factor
stat.dfCol Degrees of freedom of the column factor
stat.SSCol Sum of squares of the column factor
stat.MSCol Mean squares for column factor
ROW FACTOR Outputs
Output variable Description
stat.FRow F statistic of the row factor
stat.PValRow Probability value of the row factor
stat.dfRow Degrees of freedom of the row factor
stat.SSRow Sum of squares of the row factor
stat.MSRow Mean squares for row factor
INTERACTION Outputs
Output variable Description
stat.FInteract F statistic of the interaction
stat.PValInteract Probability value of the interaction
stat.dfInteract Degrees of freedom of the interaction
stat.SSInteract Sum of squares of the interaction
stat.MSInteract Mean squares for interaction
ERROR Outputs
Output variable Description
stat.dfError Degrees of freedom of the errors
stat.SSError Sum of squares of the errors
stat.MSError Mean squares for the errors
s Standard deviation of the error
Ans
Ans ⇒ value
Returns the result of the most recently evaluated expression.
/v
keys
8 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 15
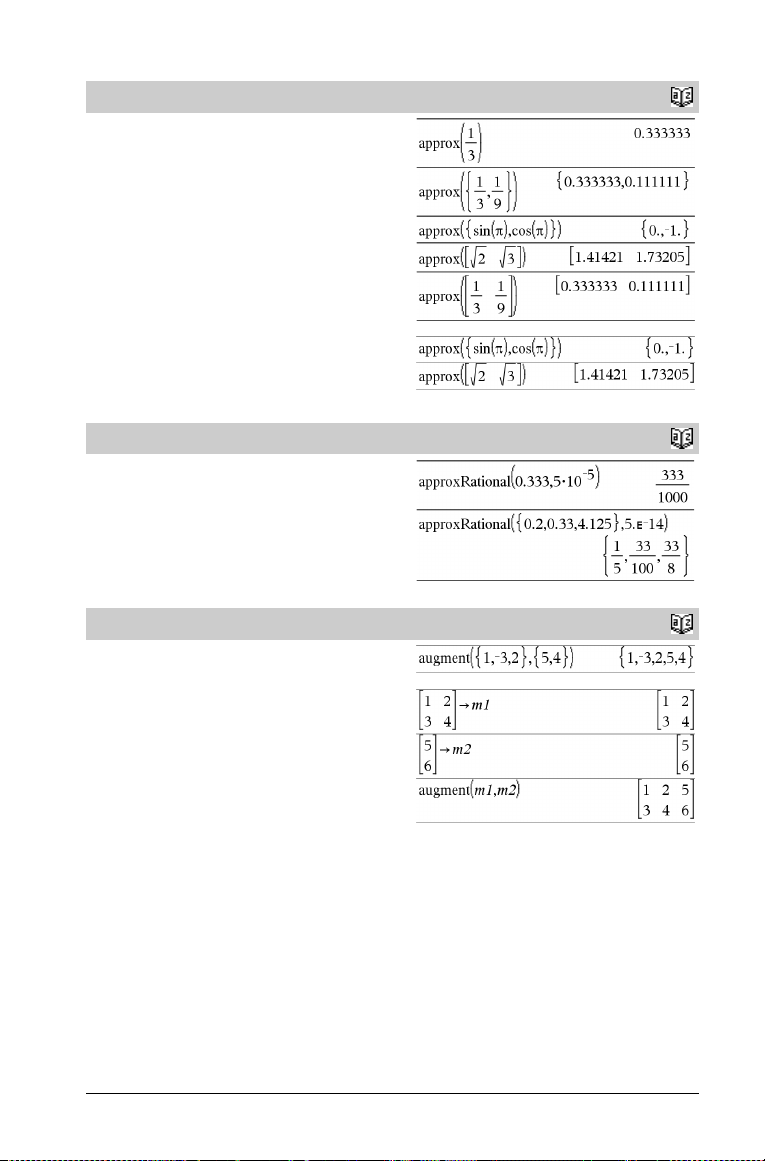
approx()
approx(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ number
Returns the evaluation of the argument as an expression containing
decimal values, when possible, regardless of the current Auto or
Approximate
This is equivalent to entering the argument and pressing
·
approx(List1) ⇒ list
approx(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns a list or matrix where each element has been evaluated to a
decimal value, when possible.
mode.
/
.
Catalog
>
approxRational()
approxRational(Expr[, tol]) ⇒ expression
approxRational(List[, tol]) ⇒ list
approxRational(Matrix[, tol]) ⇒ matrix
Returns the argument as a fraction using a tolerance of tol. If tol is
omitted, a tolerance of 5.E-14 is used.
augment()
augment(List1, List2) ⇒ list
Returns a new list that is List2 appended to the end of List1.
augment(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns a new matrix that is Matrix2 appended to Matrix1. When
the “,” character is used, the matrices must have equal row
dimensions, and Matrix2 is appended to Matrix1 as new columns.
Does not alter Matrix1 or Matrix2.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 9
Page 16
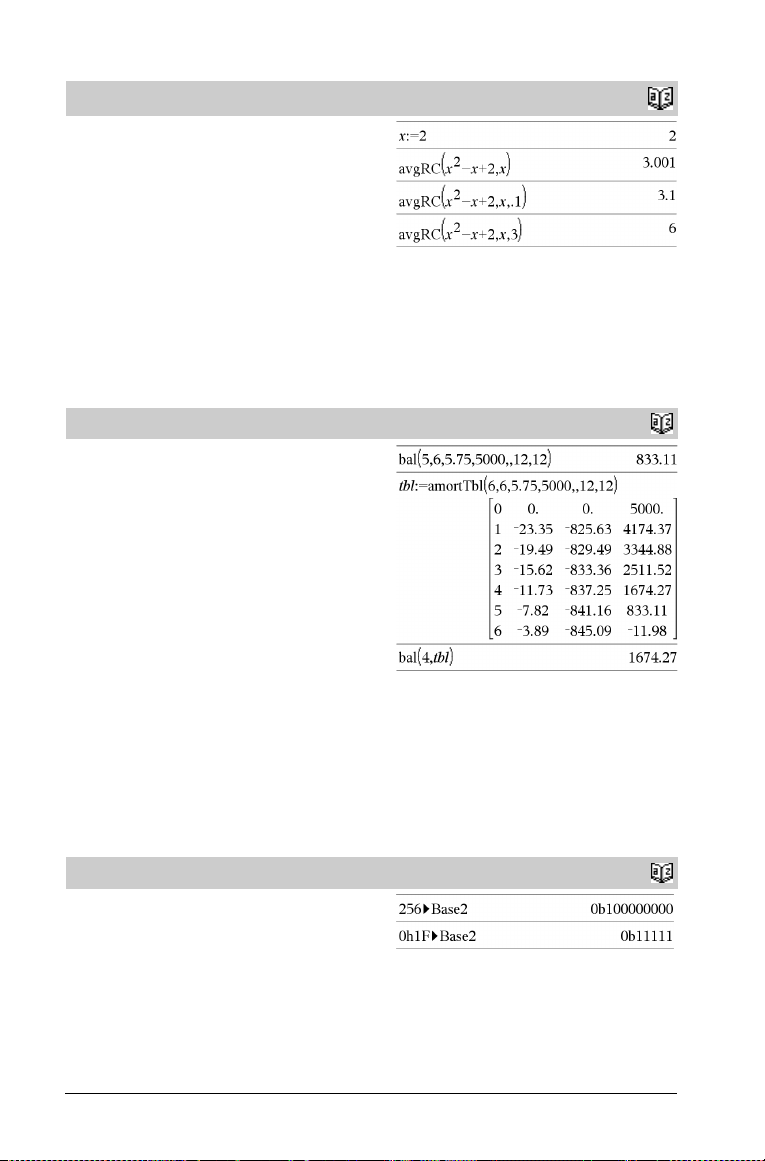
avgRC()
avgRC(Expr1, Va r [=Value] [, H]) ⇒ expression
avgRC(Expr1, Va r [=Value] [, List1]) ⇒ list
avgRC(List1, Va r [=Value] [, H]) ⇒ list
avgRC(Matrix1, Var [=Value] [, H]) ⇒ matrix
Returns the forward-difference quotient (average rate of change).
Expr1 can be a user-defined function name (see Func).
When value is specified, it overrides any prior variable assignment or
any current “such that” substitution for the variable.
H is the step value. If H is omitted, it defaults to 0.001.
Note that the similar function nDeriv() uses the central-difference
quotient.
B
Catalog
>
bal()
bal(NPmt,N,I,PV ,[Pmt], [FV], [PpY], [CpY], [PmtAt],
roundValue]) ⇒ value
[
bal(NPmt,amortTable) ⇒ value
Amortization function that calculates schedule balance after a
specified payment.
N, I, PV, Pmt, FV, PpY, CpY, and PmtAt are described in the table
of TVM arguments, page 94.
NPmt specifies the payment number after which you want the data
calculated.
N, I, PV, Pmt, FV, PpY, CpY, and PmtAt are described in the table
of TVM arguments, page 94.
• If you omit Pmt, it defaults to
Pmt=tvmPmt(N,I,PV,FV,PpY,CpY,PmtAt).
• If you omit FV, it defaults to FV=0.
• The defaults for PpY, CpY, and PmtAt are the same as for the
TVM functions.
roundValue specifies the number of decimal places for rounding.
Default=2.
bal(NPmt,amortTable) calculates the balance after payment
number NPmt, based on amortization table amortTable. The
amortTable argument must be a matrix in the form described under
amortTbl(), page 5.
Note: See also GInt() and GPrn(), page 110.
4
Base2
Integer1 4Base2 ⇒ integer
Converts Integer1 to a binary number. Binary or hexadecimal
numbers always have a 0b or 0h prefix, respectively.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
10 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 17

4
Base2
0b binaryNumber
0h hexadecimalNumber
Zero, not the letter O, followed by b or h.
A binary number can have up to 64 digits. A hexadecimal number can
have up to 16.
Without a prefix, Integer1 is treated as decimal (base 10). The result
is displayed in binary, regardless of the Base mode.
If you enter a decimal integer that is too large for a signed, 64-bit
binary form, a symmetric modulo operation is used to bring the value
into the appropriate range.
4
Base10
Integer1 4Base10 ⇒ integer
Converts Integer1 to a decimal (base 10) number. A binary or
hexadecimal entry must always have a 0b or 0h prefix, respectively.
0b binaryNumber
0h hexadecimalNumber
Zero, not the letter O, followed by b or h.
A binary number can have up to 64 digits. A hexadecimal number can
have up to 16.
Without a prefix, Integer1 is treated as decimal. The result is
displayed in decimal, regardless of the Base mode.
4
Base16
Integer1 4Base16 ⇒ integer
Converts Integer1 to a hexadecimal number. Binary or hexadecimal
numbers always have a 0b or 0h prefix, respectively.
0b binaryNumber
0h hexadecimalNumber
Zero, not the letter O, followed by b or h.
A binary number can have up to 64 digits. A hexadecimal number can
have up to 16.
Without a prefix, Integer1 is treated as decimal (base 10). The result
is displayed in hexadecimal, regardless of the Base mode.
If you enter a decimal integer that is too large for a signed, 64-bit
binary form, a symmetric modulo operation is used to bring the value
into the appropriate range.
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
binomCdf()
binomCdf(n,p,lowBound,upBound) ⇒ number if lowBound
and
upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and upBound are
lists
binomCdf(
list if upBound is a list
Computes a cumulative probability for the discrete binomial
distribution with n number of trials and probability p of success on
each trial.
For P(X upBound), set lowBound=0
n,p,upBound) ⇒ number if upBound is a number,
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 11
Page 18
binomPdf()
binomPdf(n,p) ⇒ number
binomPdf(n,p,XVal) ⇒ number if XVal is a number, list if
XVal is a list
Computes a probability for the discrete binomial distribution with n
number of trials and probability p of success on each trial.
C
Catalog
>
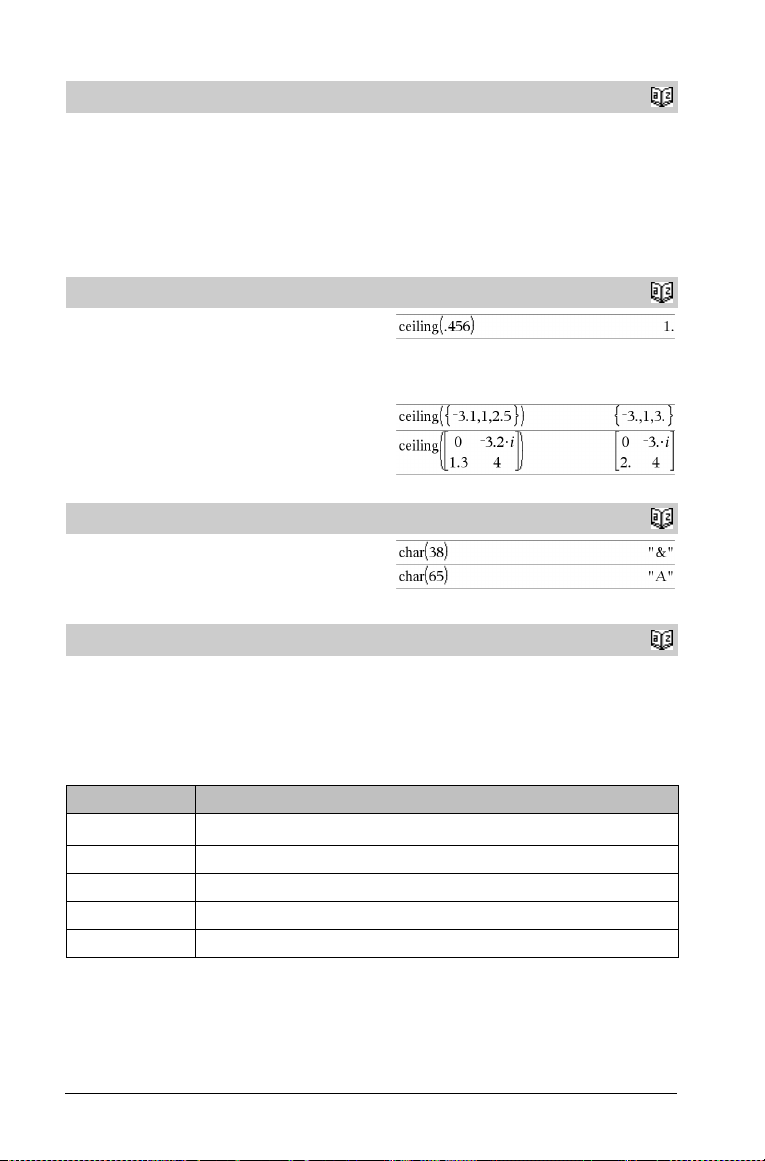
ceiling()
ceiling(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
Returns the nearest integer that is ‚ the argument.
The argument can be a real or a complex number.
Note: See also floor().
ceiling(List1) ⇒ list
ceiling(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns a list or matrix of the ceiling of each element.
char()
char(Integer) ⇒ character
Returns a character string containing the character numbered Integer
from the handheld character set. The valid range for Integer is 0–
65535.
2
c
2way
2
c
2way obsMatrix
chi22way obsMatrix
Computes a c2 test for association on the two-way table of counts in
the observed matrix obsMatrix. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
Output variable Description
stat.c2 Chi square stat: sum (observed - expected)2/expected
stat.PVal Smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected
stat.df Degrees of freedom for the chi square statistics
stat.ExpMat Matrix of expected elemental count table, assuming null hypothesis
stat.CompMat Matrix of elemental chi square statistic contributions
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
12 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 19

2
c
Cdf()
2
c
Cdf(lowBound,upBound,df) ⇒ number if lowBound and
upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and upBound are lists
chi2Cdf(
lowBound,upBound,df) ⇒ number if lowBound and
upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and upBound are lists
Computes the c2 distribution probability between lowBound and
upBound for the specified degrees of freedom df.
upBound), set lowBound = 0.
For P(X
2
c
GOF
2
c
GOF obsList,expList,df
chi2GOF obsList,expList,df
Performs a test to confirm that sample data is from a population that
conforms to a specified distribution. obsList is a list of counts and
must contain integers. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
Output variable Description
stat.c2 Chi square stat: sum((observed - expected)2/expected
stat.PVal Smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected
stat.df Degrees of freedom for the chi square statistics
stat.CompList Elemental chi square statistic contributions
2
c
Pdf()
2
c
Pdf(XVal,df) ⇒ number if XVal is a number, list if XVal is a
list
chi2Pdf(
XVal,df) ⇒ number if XVal is a number, list if XVal is
a list
Computes the probability density function (pdf) for the c2 distribution
at a specified XVal value for the specified degrees of freedom df.
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
ClearAZ
ClearAZ
Catalog
>
Clears all single-character variables in the current problem space.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 13
Page 20
ClrErr
ClrErr
Clears the error status and sets system variable errCode to zero.
Else clau se of the Try...Else...EndTry block should use ClrErr
The
or
PassErr. If the error is to be processed or ignored, use ClrErr. If
what to do with the error is not known, us e
next error handler. If there are no more pendin g Try...Else...EndTry
error handlers, the error dialog box will be displayed as normal.
Note: See also PassErr, page 64, and Try , page 91.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
PassErr to send i t to the
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
For an example of
command, page 92.
Catalog
ClrErr, See Example 2 under the Try
>
colAugment()
colAugment(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns a new matrix that is Matrix2 appended to Matrix1. The
matrices must have equal column dimensions, and Matrix2 is
appended to Matrix1 as new rows. Does not alter Matrix1 or
Matrix2.
colDim()
colDim(Matrix) ⇒ expression
Returns the number of columns contained in Matrix.
Note: See also rowDim() .
colNorm()
colNorm(Matrix) ⇒ expression
Returns the maximum of the sums of the absolute values of the
elements in the columns in Matrix.
Note: Undefined matrix elements are not allowed. See also
rowNorm().
conj()
conj(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
conj(List1) ⇒ list
conj(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns the complex conjugate of the argument.
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
>
14 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 21
constructMat()
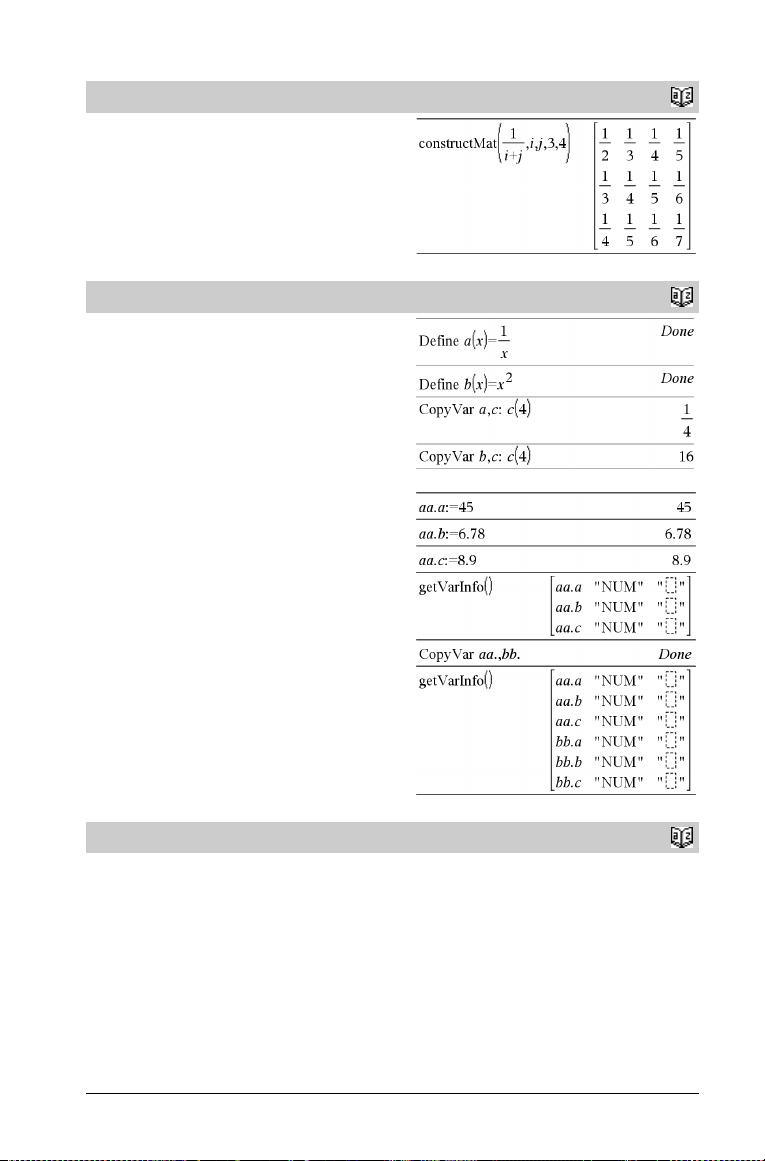
constructMat(Expr,Var 1 ,Var 2 ,numRows,numCols)
⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix based on the arguments.
Expr is an expression in variables Va r 1 and Va r 2 . Elements in the
resulting matrix are formed by evaluating Expr for each incremented
value of Var 1 and Va r 2.
Var 1 is automatically incremented from
each row, Va r2 is incremented from 1 through numCols.
1 through numRows. Within
Catalog
>
CopyVar
CopyVar Var 1 , Va r 2
CopyVar Var 1 ., Va r2 .
CopyVar Var 1 , Va r2 copies the value of variable Va r 1 to variable
Var 2 , creating Va r 2 if necessary. Variable Va r1 must have a value.
If Var 1 is the name of an existing user-defined function, copies the
definition of that function to function Va r 2. Function Va r 1 must be
defined.
Var 1 must meet the variable-naming requirements or must be an
indirection expression that simplifies to a variable name meeting the
requirements.
CopyVar Var 1 ., Va r 2. copies all members of the Va r 1 . variable
group to the Var 2 . group, creating Var 2 . if necessary.
Var 1 . must be the name of an existing variable group, such as the
statistics stat.nn results, or variables created using the
LibShortcut() function. If Var 2 . already exists, this command
replaces all members that are common to both groups and adds the
members that do not already exist. If a simple (non-group) variable
named Va r2 exists, an error occurs.
corrMat()
corrMat(List1,List2[,…[,List20]])
Computes the correlation matrix for the augmented matrix [List1,
List2, ..., List20].
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 15
Page 22
cos()
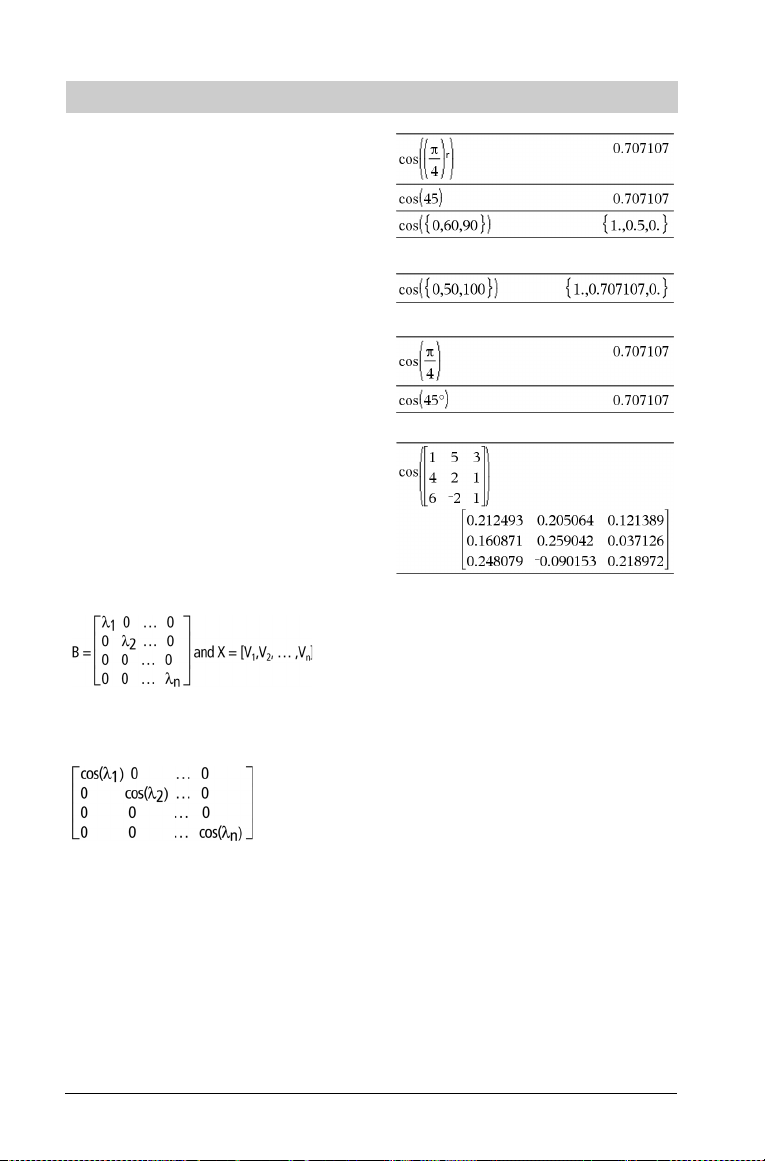
cos(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
cos(List1) ⇒ list
cos(Val u e 1 ) returns the cosine of the argument as a value.
cos(List1) returns a list of the cosines of all elements in List1.
Note: The argument is interpreted as a degree, gradian or radian
angle, according to the current angle mode setting. You can us e ó,G,
or ôto override the angle mode temporarily.
n key
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
cos(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix cosine of squareMatrix1. This is not the same as
calculating the cosine of each element.
When a scalar function f(A) operates on squareMatrix1 (A), the
result is calculated by the algorithm:
Compute the eigenvalues (li) and eigenvectors (Vi) of A.
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. Also, it cannot have symbolic
variables that have not been assigned a value.
Form the matrices:
Then A = X B Xêand f(A) = X f(B) Xê. For example, cos(A) = X cos(B)
Xê where:
cos(B) =
All computations are performed using floating-point arithmetic.
In Radian angle mode:
16 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 23
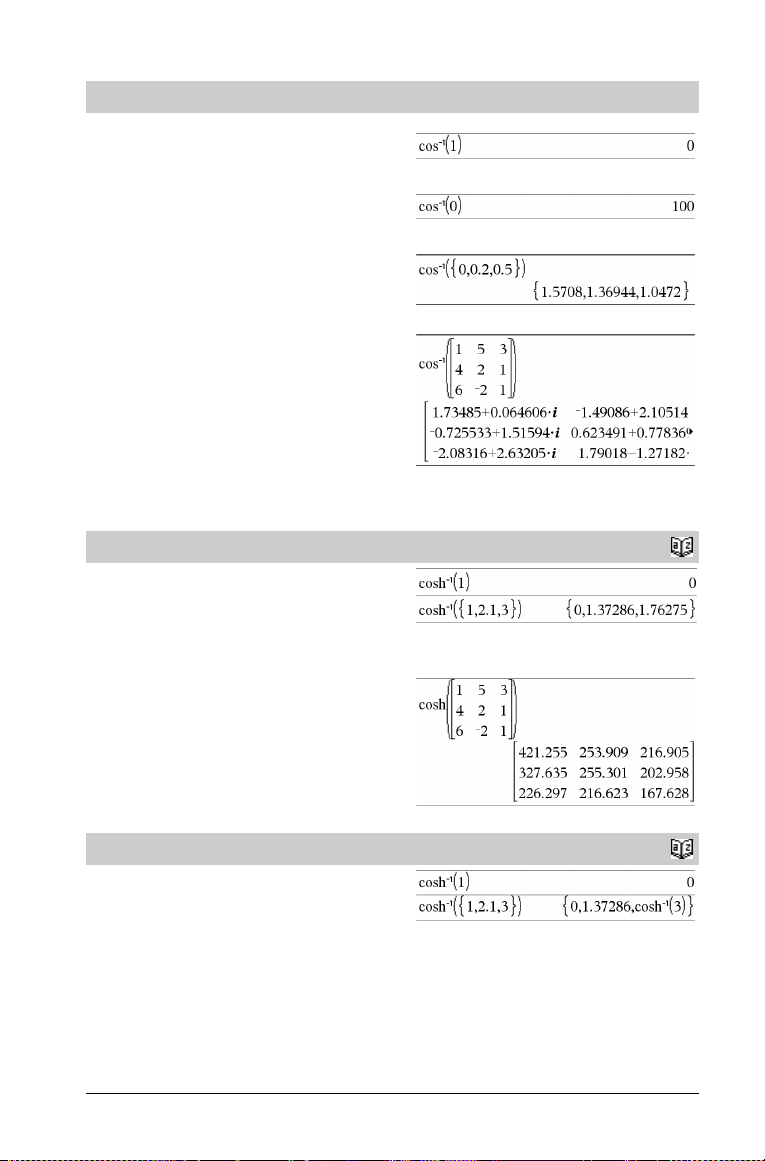
cosê()
cosê(Va lu e 1 ) ⇒ value
cosê(List1) ⇒ list
/n keys
In Degree angle mode:
cosê(Va lu e 1 ) returns the angle whose cosine is Va lu e 1 .
cosê(List1) returns a list of the inverse cosines of each element of
List1.
Note: The result is returned as a degree, gradian or radian angle,
according to the current angle mode setting.
cosê(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix inverse cosine of squareMatrix1. This is not the
same as calculating the inverse cosine of each element. For
information about the calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
cosh()
cosh(Va lu e 1 ) ⇒ value
cosh(List1) ⇒ list
cosh(Va lu e 1 ) returns the hyperbolic cosine of the argument.
cosh(List1) returns a list of the hyperbolic cosines of each element o f
List1.
cosh(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix hyperbolic cosine of squareMatrix1. This is not
the same as calculating the hyperbolic cosine of each element. For
information about the calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular Complex Format:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
Catalog
>
In Radian angle mode:
coshê()
coshê(Va lu e 1 ) ⇒ value
coshê(List1) ⇒ list
ê
cosh
(Va lu e 1 ) returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of the
argument.
ê
cosh
(List1) returns a list of the inverse hyperbolic cosines of each
element of List1.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 17
Page 24

coshê()
coshê(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix inverse hyperbolic cosine of squareMatrix1. This
is not the same as calculating the inverse hyperbolic cosine of each
element. For information about the calculation method, refer to
cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
Catalog
>
In Radian angle mode and In Rectangular Complex Format:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
cot()
cot(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
cot(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the cotangent of Val u e1 or returns a list of the cotangents of
all elements in List1.
Note: The argument is interpreted as a degree, gradian or radian
angle, according to the current angle mode setting. You can us e ó,G,
orôto override the angle mode temporarily.
cotê()
cotê(Va lu e 1 ) ⇒ value
cotê(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the angle whose cotangent is Va l ue 1 or returns a list
containing the inverse cotangents of each element of List1.
Note: The result is returned as a degree, gradian or radian angle,
according to the current angle mode setting.
coth()
coth(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
coth(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the hyperbolic cotangent of Va l ue 1 or returns a list of the
hyperbolic cotangents of all elements of List1.
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
cothê()
cothê(Va lu e 1 ) ⇒ value
cothê(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the inverse hyperbolic cotangent of Va l u e1 or returns a list
containing the inverse hyperbolic cotangents of each element of
List1.
Catalog
>
18 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 25

count()
count(Val u e 1 or L i s t1 [,Value2orList2 [,...]]) ⇒ value
Returns the accumulated count of all elements in the arguments that
evaluate to numeric values.
Each argument can be an expression, value, list, or matrix. You can
mix data types and use arguments of various dimensions.
For a list, matrix, or range of cells, each element is evaluated to
determine if it should be included in the count.
Within the Lists & Spreadsheet application, you can use a range of
cells in place of any argument.
Catalog
>
countif()
countif(List,Criteria) ⇒ value
Returns the accumulated count of all elements in List that meet the
specified Criteria.
Criteria can be:
• A value, expression, or string. For example, 3 counts only those
elements in List that simplify to the value 3.
• A Boolean expression containing the symbol ? as a placeholder
for each element. For example, ?<5 counts only those elements
in List that are less than 5.
Within the Lists & Spreadsheet application, you can use a range of
cells in place of List.
Note: See also sumIf(), page 87, and frequency(), page 33.
crossP()
crossP(List1, List2) ⇒ list
Returns the cross product of List1 and List2 as a list.
List1 and List2 must have equal dimension, and the dimension must
be either 2 or 3.
crossP(Vector1, Vector2) ⇒ vector
Returns a row or column vector (depending on the arguments) that is
the cross product of Vector1 and Vector2.
Both Vector1 and Vector2 must be row vectors, or both must be
column vectors. Both vectors must have equal dimension, and the
dimension must be either 2 or 3.
Counts the number of elements equal to 3.
Counts the number of elements equal to “def.”
Counts 1 and 3.
Counts 3, 5, and 7.
Counts 1, 3, 7, and 9.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 19
Page 26
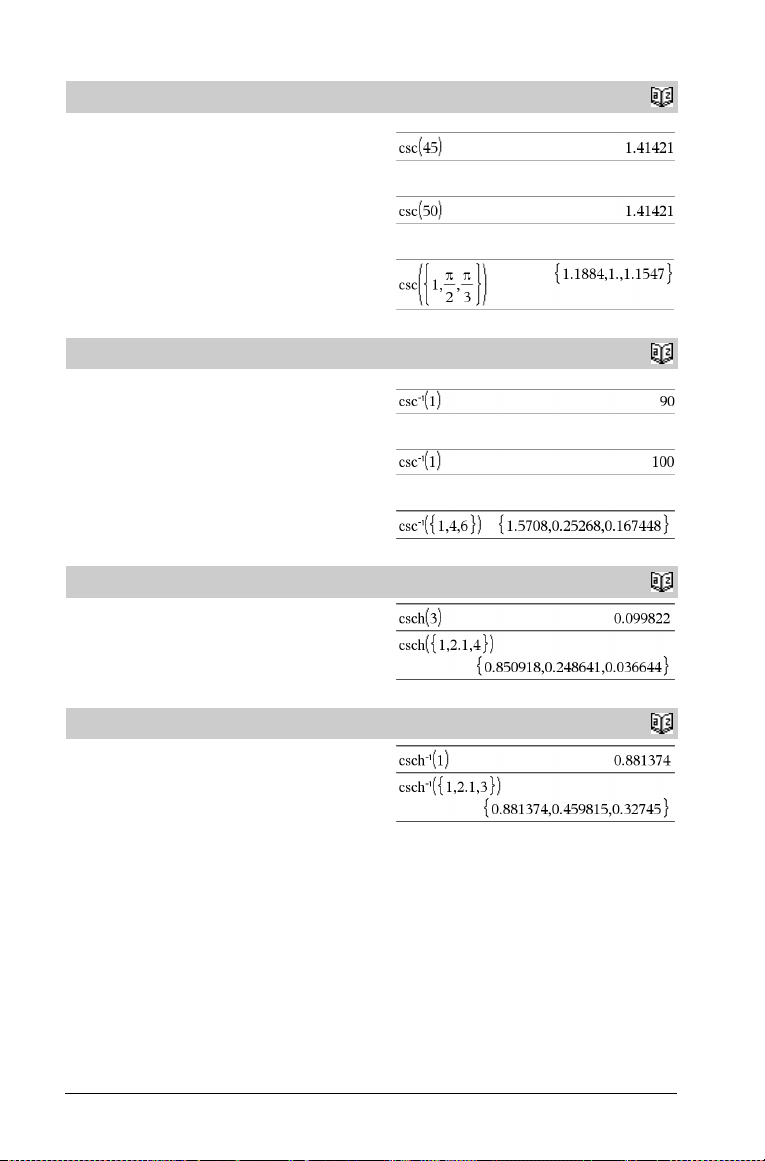
csc()
csc(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
csc(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the cosecant of Va lu e 1 or returns a list containing the
cosecants of all elements in List1.
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
>
cscê()
cscê(Va l ue 1 ) ⇒ value
cscê(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the angle whose cosecant is Va l ue 1 or returns a list
containing the inverse cosecants of each element of List1.
Note: The result is returned as a degree, gradian or radian angle,
according to the current angle mode setting.
csch()
csch(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
csch(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the hyperbolic cosecant of Va lu e 1 or returns a list of the
hyperbolic cosecants of all elements of List1.
cschê()
cschê(Val u e ) ⇒ value
cschê(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosecant of Va l u e1 or returns a list
containing the inverse hyperbolic cosecants of each element of List1.
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
20 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 27
CubicReg
CubicReg X, Y[, [Freq] [, Category, Include]]
Catalog
Computes the cubic polynomial regression y = a·x3+b·
x2+c·x+d on lists X and Y with frequency Freq. A summary of
results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.a, stat.b, stat.c,
stat.d
2
stat.R
Regression equation: a·x3+b·x2+c·x+d
Regression coefficients
Coefficient of determination
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
>
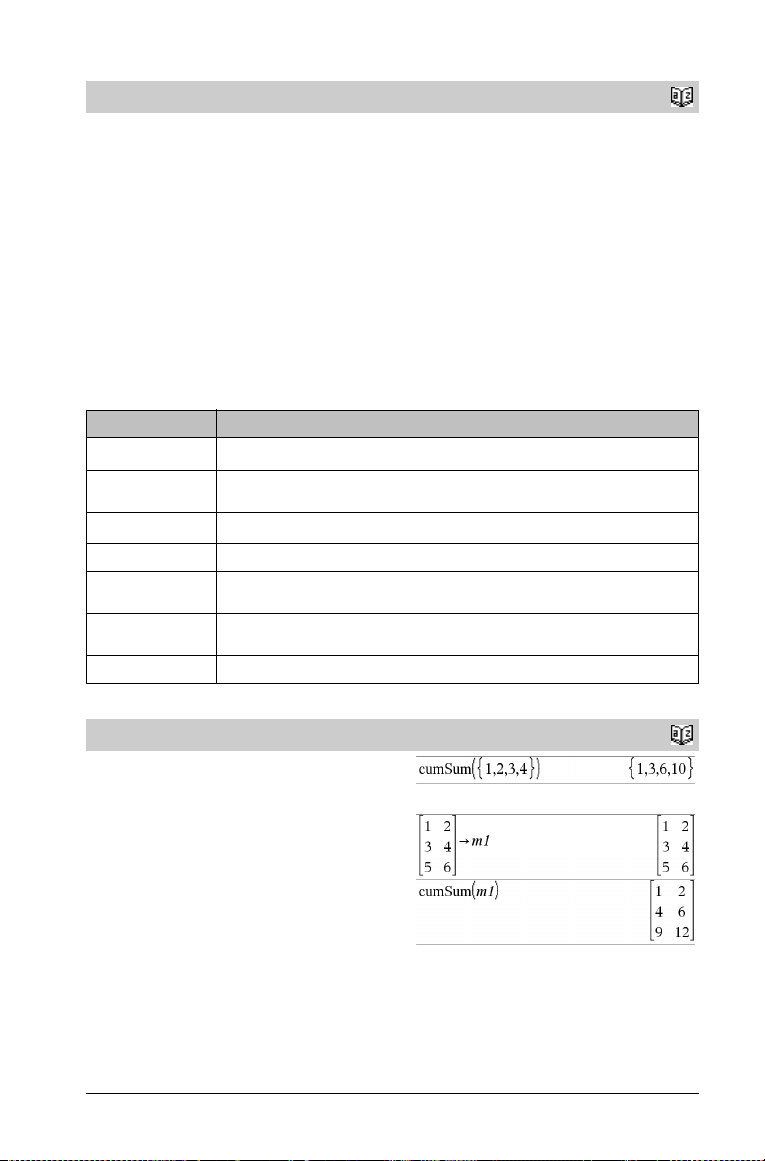
cumSum()
cumSum(List1) ⇒ list
Returns a list of the cumulative sums of the elements in List1,
starting at element 1.
cumSum(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix of the cumulative sums of the elements in Matrix1.
Each element is the cumulative sum of the column from top to
bottom.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 21
Page 28

Cycle
Cycle
Transfers control immediately to the next iteration of t he current loop
For, While, or Loop).
(
Cycle is not allowed outside the three looping structures (For,
While, or Loop).
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator
application on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by
pressing @ instead of · at the end of each line. On the
computer keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Catalog
>
Function listing that sums the integers from 1 to 100 skipping
50.
4Cylind
Vec t o r 4Cylind
Displays the row or column vector in cylindrical form [r,q, z].
Vec t o r must have exactly three elements. It can be either a row or a
column.
D
dbd()
dbd(date1,date2) ⇒ value
Returns the number of days between date1 and date2 using the
actual-day-count method.
date1 and date2 can be numbers or lists of numbers within the range
of the dates on the standard calendar. If both date1 and date2 are
lists, they must be the same length.
date1 and date2 must be between the years 1950 through 2049.
You can enter the dates in either of two formats. The decimal
placement differentiates between the date formats.
MM.DDYY (format used commonly in the United States)
DDMM.YY (format use commonly in Europe)
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
22 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 29

4DD
4DD ⇒ value
Expr1
List1 4DD ⇒ list
Matrix1
4DD ⇒ matrix
Returns the decimal equivalent of the argument expresse d in degrees.
The argument is a number, list, or matrix that is interpreted by the
Angle mode setting in gradians, radians or degrees.
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
>
4Decimal
4Decimal
Number1
4Decimal
List1
4
Decimal
Matrix1
Displays the argument in decimal form. This operator can be used
only at the end of the entry line.
Define
Define Var = Expression
Define Function(Param1, Param2, ...) = Expression
Defines the variable Var or the user-defined function Function.
Parameters, such as Param1, provide placeholders for passing
arguments to the function. When calling a user-defined function, you
must supply arguments (for example, values or variables) that
correspond to the parameters. When called, the function evaluates
Expression using the supplied arguments.
Var and Function cannot be the name of a system variable or built -in
function or command.
Note: This form of Define is equivalent to executing the
expression: expression & Function(Param1,Param2).
⇒ value
⇒ value
⇒ value
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 23
Page 30

Define
Define Function(Param1, Param2, ...) = Func
Block
EndFunc
Program(Param1, Param2, ...) = Prgm
Define
Block
EndPrgm
In this form, the user-defined function or program can execute a block
of multiple statements.
Block can be either a single statement or a series of statements on
separate lines. Block also can include expressions and instructions
(such as If, Then, Else, and For).
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Note: See also Define LibPriv, page 24, and Define LibPub,
page 24.
Catalog
>
Define LibPriv
Define LibPriv Var = Expression
Define LibPriv Function(Param1, Param2, ...) = Expression
Define LibPriv Function(Param1, Param2, ...) = Func
Block
EndFunc
Define LibPriv
EndPrgm
Operates the same as Define, except defines a private library
variable, function, or program. Private functions and progr ams do not
appear in the Catalog.
Note: See also Define, page 23, and Define LibPub, page 24.
Program(Param1, Param2, ...) = Prgm
Block
Define LibPub
Define LibPub Var = Expression
Define LibPub Function(Param1, Param2, ...) = Expression
Define LibPub Function(Param1, Param2, ...) = Func
Block
EndFunc
Define LibPub
EndPrgm
Operates the same as Define, except defines a public library
variable, function, or program. Public functions and programs appear
in the Catalog after the library has been saved and refreshed.
Note: See also Define, page 23, and Define LibPriv, page 24.
Program(Param1, Param2, ...) = Prgm
Block
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
24 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 31

DelVar
DelVar Var 1 [, Va r 2] [, Va r 3 ] ...
DelVar Var .
Deletes the specified variable or variable group from memory.
DelVar Var . deletes all members of the Va r . variable group (such as
the statistics stat.nn results or variables created using the
LibShortcut() function). The dot (.) in this form of the DelVar
command limits it to deleting a variable group; the simple variable
Var is not affected.
Catalog
>
det()
det(squareMatrix[, Tolerance]) ⇒ expression
Returns the determinant of squareMatrix.
Optionally, any matrix element is treated as zero if its absolute value
is less than Tolerance. This tolerance is used only if the matrix has
floating-point entries and does not contain any symbolic variables
that have not been assigned a value. Otherwise, Tolerance is
ignored.
• If you use
•If Tolerance is omitted or not used, the default tolerance is
diag()
diag(List) ⇒ matrix
diag(rowMatrix) ⇒ matrix
diag(columnMatrix) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix with the values in the argument list or matrix in its
main diagonal.
diag(squareMatrix) ⇒ rowMatrix
Returns a row matrix containing the elements from the main diagonal
of squareMatrix.
squareMatrix must be square.
/
mode to Approximate, computations are done using floatingpoint arithmetic.
calculated as:
5EM14 ·max(dim(squareMatrix))·
rowNorm(squareMatrix)
· or set the Auto or Approximate
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 25
Page 32

dim()
dim(List) ⇒ integer
Returns the dimension of List.
dim(Matrix) ⇒ list
Returns the dimensions of matrix as a two-element list {rows,
columns}.
dim(Strin g) ⇒ integer
Returns the number of characters contained in character string
Strin g.
Catalog
>
Disp
Disp [exprOrString1] [, exprOrString2] ...
Displays the arguments in the Calculator history. The arguments are
displayed in succession, with thin spaces as separators.
Useful mainly in programs and functions to ensure the display of
intermediate calculations.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
4DMS
Val u e 4DMS
List 4DMS
Matrix 4DMS
Interprets the argument as an angle and displays the equivalent DMS
(DDDDDD¡MM'SS.ss'') number. See ¡, ', '' on page 112 for DMS
(degree, minutes, seconds) format.
Note: 4DMS will convert from radians to degrees when used in
radian mode. If the input is followed by a degree symbol ¡ , no
conversion will occur. You can use 4DMS only at the en d of an entry
line.
In Degree angle mode:
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
dotP()
dotP(List1, List2) ⇒ expression
Returns the “dot” product of two lists.
dotP(Vector1, Vector2) ⇒ expression
Returns the “dot” product of two vectors.
Both must be row vectors, or both must be column vectors.
Catalog
>
26 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 33

E
e^()
e^(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
Returns e raised to the Val u e 1 power.
Note: See also e exponent template, page 1.
Note: Pressing u to display
character E on the keyboard.
You can enter a complex number in re
form in Radian angle mode only; it causes a Domain error in Degree
or Gradian angle mode.
e^(List1) ⇒ list
Returns e raised to the power of each element in List1.
e^(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix exponential of squareMatrix1. This is not the
same as calculating e raised to the power of each element. For
information about the calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
eff()
eff(nominalRate,CpY) ⇒ value
Financial function that converts the nominal interest rate
nominalRate to an annual effective rate, given CpY as the number of
compounding periods per year.
nominalRate must be a real number, and CpY must be a real number
> 0.
Note: See also nom(), page 59.
eigVc()
eigVc(squareMatrix) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix containing the eigenvectors for a real or complex
squareMatrix, where each column in the result corresponds to an
eigenvalue. Note that an eigenvector is not unique; it may be scaled
by any constant factor. The eigenvectors are normalized, meaning
that if V = [x1, x2, … , xn], then:
2
2
+ … + x
2
n
x
+x
1
2
squareMatrix is first balanced with similarity transformations until
the row and column norms are as close to the same va lue as possible.
The squareMatrix is then reduced to upper Hessenberg form and the
eigenvectors are computed via a Schur factorization.
= 1
e
^( is different from pressing the
i q
polar form. However, use this
u key
Catalog
>
Catalog
>
In Rectangular Complex Format:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 27
Page 34

eigVl()
eigVl(squareMatrix) ⇒ list
Returns a list of the eigenvalues of a real or complex squareMatrix.
squareMatrix is first balanced with similarity transformations until
the row and column norms are as close to the same va lue as possible.
The squareMatrix is then reduced to upper Hessenberg form and the
eigenvalues are computed from the upper Hessenberg matrix.
Else See If, page 39.
In Rectangular complex format mode:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
Catalog
>
ElseIf
If BooleanExpr1 Then
Block1
ElseIf BooleanExpr2 Then
Block2
©
ElseIf BooleanExprN Then
BlockN
EndIf
©
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
Catalog
>
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
EndFor See For, page 32.
EndFunc See Func, page 34.
EndIf See If, page 39.
EndLoop See Loop, page 51.
EndPrgm See Prgm, page 66.
EndTry See Try, page 91.
28 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 35

EndWhile See While, page 97.
Exit
Exit
Exits the current For, While, or Loop block.
Exit is not allowed outside the three looping structures (For,
While, or Loop).
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
exp()
exp(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
Returns e raised to the Val u e 1 power.
Note: See also e exponent template, page 1.
You can enter a complex number in re
form in Radian angle mode only; it causes a Domain error in Degree
or Gradian angle mode.
exp(List1) ⇒ list
Returns e raised to the power of each element in List1.
exp(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix exponential of squareMatrix1. This is not the
same as calculating e raised to the power of each element. For
information about the calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
i q
polar form. However, use this
Function listing:
Catalog
u key
>
expr()
expr(Stri ng) ⇒ expression
Returns the character string contained in Stri ng as an expression and
immediately executes it.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 29
Page 36

ExpReg
ExpReg X, Y [, [Freq] [, Category, Include]]
Computes the exponential regression y = a·(b)xon lists X and Y
with frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.a, stat.b Regression coefficients
2
stat.r
stat.r Correlation coefficient for transformed data (x, ln(y))
stat.Resid Residuals associated with the exponential model
stat.ResidTrans Residuals associated with linear fit of transformed data
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
Regression equation: a·(b)
Coefficient of linear determination for transformed data
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
x
Catalog
>
F
factor()
factor(rationalNumber) returns the rational number factored into
primes. For composite numbers, the computing time grows
exponentially with the number of digits in the second-largest factor.
For example, factoring a 30-digit integer could take more than a day,
and factoring a 100-digit number could take more than a century.
Note: To stop (break) a computation, press w.
If you merely want to determine if a number is prime, use isPrime()
instead. It is much faster, particularly if rationalNumber is not prime
and if the second-largest factor has more than five digits.
30 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Catalog
>
Page 37

FCdf()
FCdf(lowBound,upBound,dfNumer,dfDenom) ⇒ number if
lowBound and upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and
upBound are lists
FCdf(lowBound,upBound,dfNumer,dfDenom) ⇒ number if
lowBound and upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and
upBound are lists
Computes the F distribution probability between lowBound and
upBound for the specified dfNumer (degrees of freedom) and
dfDenom.
upBound), set lowBound = 0.
For P(X
Catalog
>
Fill
Fill Value, matrixVar ⇒ matrix
Replaces each element in variable matrixVar with Val u e.
matrixVar must already exist.
Fill Value, listVar ⇒ list
Replaces each element in variable listVar with Val u e.
listVar must already exist.
FiveNumSummary
FiveNumSummary X[,[Freq][,Category,Include]]
Provides an abbreviated version of the 1-variable statistics on list X.
A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page
83.)
X represents a list containing the data.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X value.
The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
values.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.MinX Minimum of x values.
stat.Q1X 1st Quartile of x.
stat.MedianX Median of x.
stat.Q3X 3rd Quartile of x.
stat.MaxX Maximum of x values.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 31
Page 38

floor()
floor(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ integer
Returns the greatest integer that is { the argument. This function is
identical to int().
The argument can be a real or a complex number.
floor(List1) ⇒ list
floor(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns a list or matrix of the floor of each element.
Note: See also ceiling() and int().
Catalog
>
For
For Var , Low, High [, St ep]
Block
EndFor
Executes the statements in Block iteratively for each value of Va r ,
from Low to High, in increments of Step.
Var must not be a system variable.
Step can be positive or negative. The default value is 1.
Block can be either a single statement or a series of statements
separated with the “:” character.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
format()
format(Val u e [, formatString]) ⇒ string
Returns Val u e as a character string based on the format template.
formatString is a string and must be in the form: “F[n]”, “S[n]”,
“E[n]”, “G[n][c]”, where [ ] indicate optional portions.
F[n]: Fixed format. n is the number of digits to display after the
decimal point.
S[n]: Scientific format. n is the number of digits to display after the
decimal point.
E[n]: Engineering format. n is the number of digits after the first
significant digit. The exponent is adjusted to a multiple of three, and
the decimal point is moved to the right by zero, one, or two digits.
G[n][c]: Same as fixed format but also separates digits to the left of
the radix into groups of three. c specifies the group separator
character and defaults to a comma. If c is a period, the radix will be
shown as a comma.
[Rc]: Any of the above specifiers may be suffixed with the Rc radix
flag, where c is a single character that specifies what to substitute for
the radix point.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
32 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 39

fPart()
fPart(Expr1) ⇒ expression
fPart(List1) ⇒ list
fPart(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns the fractional part of the argument.
For a list or matrix, returns the fractional parts of the elements.
The argument can be a real or a complex number.
Catalog
>
FPdf()
FPdf(XVal,dfNumer,dfDenom) ⇒ number if XVal is a number,
list if XVal is a list
Computes the F distribution probability at XVal for the
specified dfNumer (degrees of freedom) and dfDenom.
freqTable4list()
freqTable4list(List1,freqIntegerList) ⇒ list
Returns a list containing the elements from List1 expanded according
to the frequencies in freqIntegerList. This function can be used for
building a frequency table for the Data & Statistics application.
List1 can be any valid list.
freqIntegerList must have the same dimension as List1 and must
contain non-negative integer elements only. Each element specifies
the number of times the corresponding List1 element will be
repeated in the result list. A value of zero excludes the corresponding
List1 element.
frequency()
frequency(List1,binsList) ⇒ list
Returns a list containing counts of the elements in List1. The counts
are based on ranges (bins) that you define in binsList.
If binsList is {b(1), b(2), …, b(n)}, the specified ranges are {?{b(1),
b(1)<?{b(2),…,b(n-1)<?{b(n), b(n)>?}. The resulting list is one
element longer than binsList.
Each element of the result corresponds to the number of elements
from List1 that are in the range of that bin. Expressed in terms of the
countIf() function, the result is { countIf(list, ?{b(1)), countIf(list,
b(1)<?{b(2)), …, countIf(list, b(n-1)<?{b(n)), countIf(list, b(n)>?)}.
Elements of List1 that cannot be “placed in a bin” are ignored.
Within the Lists & Spreadsheet application, you can use a range of
cells in place of both arguments.
Note: See also countIf(), page 19.
Catalog
>
Catalog
>
Catalog
>
Explanation of result:
2 elements from Datalist are {2.5
4 elements from Datalist are >2.5 and {4.5
3 elements from Datalist are >4.5
The element "hello" is a string and cannot be placed in any of
the defined bins.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 33
Page 40

FTest_2Samp
FTest_2Samp List1,List2[,Freq1[,Freq2[,Hypoth]]]
FTest_2Samp
(Data list input)
List1,List2[,Freq1[,Freq2[,Hypoth]]]
FTest_2Samp sx1,n1,sx2,n2[,Hypoth]
FTest_2Samp
(Summary stats input)
Performs a two-sample
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
For Ha: s1 > s2, set Hypoth>0
For Ha: s1 ƒ s2 (default), set Hypoth =0
For Ha: s1 < s2, set Hypoth<0
Output variable Description
stat.F
stat.PVal Smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected
stat.dfNumer numerator degrees of freedom = n1-1
stat.dfDenom denominator degrees of freedom = n2-1
stat.sx1, stat.sx2 Sample standard deviations of the data sequences in List 1 and List 2
stat.x1_bar
stat.x2_bar
stat.n1, stat.n2 Size of the samples
sx1,n1,sx2,n2[,Hypoth]
F test. A summary of results is stored in the
Calculated ó statistic for the data sequence
Sample means of the data sequences in List 1 and List 2
Catalog
>
Func
Func
Block
EndFunc
Template for creating a user-defined function.
Block can be a single statement, a series of statements separated
with the “:” character, or a series of statements on separate lines.
The function can use the Return instruction to return a specific
result.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Define a piecewise function:
Result of graphing g(x)
Catalog
>
34 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 41

G
gcd()
gcd(Number1, Number2) ⇒ expression
Returns the greatest common divisor of the two arguments. The
of two fractions is the gcd of their numerators divided by the lcm of
their denominators.
In Auto or Approximate mode, the gcd of fractional floating-point
numbers is 1.0.
gcd(List1, List2) ⇒ list
Returns the greatest common divisors of the corresponding elements
in List1 and List2.
gcd(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns the greatest common divisors of the corresponding elements
in Matrix1 and Matrix2.
geomCdf()
geomCdf(p,lowBound,upBound) ⇒ number if lowBound and
upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and upBound are lists
geomCdf(
p,upBound) ⇒ number if upBound is a number, list
upBound is a list
if
Computes a cumulative geometric probability from lowBound to
upBound with the specified probability of success p.
For P(X upBound), set lowBound = 1.
geomPdf()
geomPdf(p,XVal) ⇒ number if XVal is a number, list if XVal
is a list
Computes a probability at XVal, the number of the trial on which the
first success occurs, for the discrete geometric distribution with the
specified probability of success p.
gcd
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
getDenom( )
getDenom(Fraction1) ⇒ value
Transforms the argument into an expression having a reduced
common denominator, and then returns its denominator.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 35
Page 42

getLangInfo( )
getLangInfo() ⇒ string
Returns a string that corresponds to the short name of the currently
active language. You can, for example, use it in a program or function
to determine the current language.
English = "en"
Danish = "da"
German = "de"
Finnish = "fi"
French = "fr"
Italian = "it"
Dutch = "nl"
Belgian Dutch = "nl_BE"
Norwegian = "no"
Portuguese = "pt"
Spanish = "es"
Swedish = "sv"
Catalog
>
getMode()
getMode(ModeNameInteger) ⇒ value
getMode(0) ⇒ list
getMode(ModeNameInteger) returns a value representing the
current setting of the ModeNameInteger mode.
getMode(0) returns a list containing number pairs. Each pair
consists of a mode integer and a setting integer.
For a listing of the modes and their settings, refer to the table below.
If you save the settings with getMode(0) & var, you can use
setMode(var) in a function or program to temporarily restore the
settings within the execution of the function or program only. See
setMode(), page 77.
Mode
Name
Display Digits
Angle
Exponential Format
Real or Complex
Auto or Approx.
Vector Format
Base
Mode
IntegerSetting Integers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
=Float, 2=Float1, 3=Float2, 4=Float3, 5=Float4, 6=Float5, 7=Float6, 8=Float7,
9=Float8, 10=Float9, 11=Float10, 12=Float11, 13=Float12, 14=Fix0, 15=Fix1,
16=Fix2, 17=Fix3, 18=Fix4, 19=Fix5, 20=Fix6, 21=Fix7, 22=Fix8, 23=Fix9, 24=Fix10,
25=Fix11, 26=Fix12
1
=Radian, 2=Degree, 3=Gradian
1
=Normal, 2=Scientific, 3=Engineering
1
=Real, 2=Rectangular, 3=Polar
1
=Auto, 2=Approximate
1
=Rectangular, 2=Cylindrical, 3=Spherical
1
=Decimal, 2=Hex, 3=Binary
Catalog
>
36 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 43

getNum()
getNum(Fraction1) ⇒ value
Transforms the argument into an expression having a reduced
common denominator, and then returns its numerator.
Catalog
>
getVarInfo()
getVarInfo() ⇒ matrix or string
getVarInfo(LibNameString) ⇒ matrix or string
getVarInfo() returns a matrix of information (variable name, type,
and library accessibility) for all variables and library objects defined in
the current problem.
If no variables are defined, getVarInfo() returns the string
"NONE".
getVarInfo(LibNameString) returns a matrix of information for
all library objects defined in library LibNameString. LibNameString
must be a string (text enclosed in quotation marks) or a string
variable.
If the library LibNameString does not exist, an error occurs.
Note the example to the left, in which the result of getVarInfo() is
assigned to variable vs. Attempting to display row 2 or row 3 of vs
returns an “Invalid list or matrix” error because at least one of
elements in those rows (variable b, for example) revaluates to a
matrix.
This error could also occur when using Ans to reevaluate a
getVarInfo() result.
The system gives the above error because the current version of the
software does not support a generalized matrix structure where an
element of a matrix can be either a matrix or a list.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 37
Page 44

Goto
Goto labelName
Transfers control to the label labelName.
labelName must be defined in the same function using a
instruction.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
Lbl
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Catalog
>
4Grad
Expr1 4 Grad ⇒ expression
Converts Expr1 to gradian angle measure.
I
identity()
identity(Integer) ⇒ matrix
Returns the identity matrix with a dimension of Integer.
Integer must be a positive integer.
In Degree angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
38 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 45

If
If BooleanExpr Statement
If BooleanExpr Then
Block
EndIf
If BooleanExpr evaluates to true, executes the single statement
Statement or the block of statements Block before continuing
execution.
If BooleanExpr evaluates to false, continues execution without
executing the statement or block of statements.
Block can be either a single statement or a sequence of statements
separated with the “:” character.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
If BooleanExpr Then
Block1
Else
Block2
EndIf
If BooleanExpr evaluates to true, executes Block1 and then skips
Block2.
If BooleanExpr evaluates to false, skips Block1 but executes
Block2.
Block1 and Block2 can be a single statement.
If BooleanExpr1 Then
Block1
ElseIf
BooleanExpr2 Then
Block2
©
BooleanExprN Then
ElseIf
BlockN
EndIf
Allows for branching. If BooleanExpr1 evaluates to true, executes
Block1. If BooleanExpr1 evaluates to false, evaluates
BooleanExpr2, etc.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 39
Page 46

ifFn()
ifFn(BooleanExpr,Value_If_true [,Value_If_false
Value_If_unknown]]) ⇒ expression, list, or matrix
[,
Evaluates the boolean expression BooleanExpr (or each element
from BooleanExpr ) and produces a result based on the following
rules:
• BooleanExpr can test a single value, a list, or a matrix.
• If an element of BooleanExpr evaluates to true, returns the
corresponding element from Value_If_true.
• If an element of BooleanExpr evaluates to false, returns the
corresponding element from Value_If_false. If you omit
Value_If_false, returns undef.
• If an element of BooleanExpr is neither true nor false, returns
the corresponding element Value_If_unknown. If you omit
Value_If_unknown, returns undef.
• If the second, third, or fourth argument of the
a single expression, the Boolean test is applied to every position
in BooleanExpr.
Note: If the simplified BooleanExpr statement involves a list or
matrix, all other list or matrix arguments must have the same
dimension(s), and the result will have the same dimension(s).
ifFn() function is
Catalog
>
Test va lue o f 1 is less than 2.5, so its corresponding
Value_If_True element of 5 is copied to the result list.
Test va lue o f 2 is less than 2.5, so its corresponding
Value_If_True element of 6 is copied to the result list.
Test va lue o f 3 is not less than 2.5, so its corresponding
Value_If_False element of 10 is copied to the result list.
Value_If_true is a single value and cor responds to any selected
position.
Value_If_false is not specified. Undef is used.
One element selected from Value_If_true. One element
selected from Value_If_unknown.
imag()
imag(Va l ue 1 ) ⇒ value
Catalog
>
Returns the imaginary part of the argument.
imag(List1) ⇒ list
Returns a list of the imaginary parts of the elements.
imag(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix of the imaginary parts of the elements.
Indirection See #(), page 111.
inString()
inString(srcString, subString[, Start]) ⇒ integer
Returns the character position in string srcString at which the first
occurrence of string subString begins.
Start, if included, specifies the character position within srcString
where the search begins. Default = 1 (the first character of srcString).
If srcString does not contain subString or Start is > the length of
srcString, returns zero.
Catalog
>
40 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 47

int()
int(Va l ue ) ⇒ integer
int(List1) ⇒ list
int(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns the greatest integer that is less than or equal to the
argument. This function is identical to
floor().
The argument can be a real or a complex number.
For a list or matrix, returns the greatest integer of each of the
elements.
Catalog
>
intDiv()
intDiv(Number1, Number2) ⇒ integer
intDiv(List1, List2) ⇒ list
intDiv(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns the signed integer part of (Number1 ÷ Number2).
For lists and matrices, returns the signed integer part of
(argument 1 ÷ argument 2) for each element pair.
invc2()
invc2(Area,df)
Area,df)
invChi2(
Computes the Inverse cumulative c2 (chi-square) probability function
specified by degree of freedom, df for a given Area under the curve.
invF()
invF(Area,dfNumer,dfDenom)
Area,dfNumer,dfDenom)
invF(
computes the Inverse cumulative F distribution function specified by
dfNumer and dfDenom for a given Area under the curve.
invNorm()
invNorm(Area[,m[,s]])
Computes the inverse cumulative normal distribution function for a
given Area under the normal distribution curve specified by m and s.
invt()
invt(Area,df)
Computes the inverse cumulative student-t probability function
specified by degree of freedom, df for a given Area under the curve.
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
>
>
iPart()
iPart(Number) ⇒ integer
iPart(List1) ⇒ list
iPart(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Catalog
>
Returns the integer part of the argument.
For lists and matrices, returns the integer part of each element.
The argument can be a real or a complex number.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 41
Page 48

irr()
irr(CF0,CFList [,CFFreq]) ⇒ value
Financial function that calculates internal rate of return of an
investment.
CF0 is the initial cash flow at time 0; it must be a real number.
CFList is a list of cash flow amounts after the initial cash flow CF0.
CFFreq is an optional list in which each element specifies the
frequency of occurrence for a grouped (consecutive) cash flow
amount, which is the corresponding element of CFList. The default is
1; if you enter values, they must be positive integers < 10,000.
Note: See also mirr(), page 55.
Catalog
>
isPrime()
isPrime(Number) ⇒ Boolean constant expression
Returns true or false to indicate if number is a whole number ‚ 2 that
is evenly divisible only by itself and 1.
If Number exceeds about 306 digits and has no factors {1021,
isPrime(Number) displays an error message.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
L
Lbl
Lbl labelName
Defines a label with the name labelName within a function.
You can use a Goto labelName instruction to transfer control to the
instruction immediately following the label.
labelName must meet the same naming requirements as a variable
name.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Catalog
Function to find the next prime after a specified number:
Catalog
>
>
42 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 49

lcm()
lcm(Number1, Number2) ⇒ expression
lcm(List1, List2) ⇒ list
lcm(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns the least common multiple of the two arguments. The
two fractions is the lcm of their numerators divided by the gcd of
their denominators. The
their product.
For two lists or matrices, returns the least common multiples of the
corresponding elements.
lcm of fractional floating-point numbers is
lcm of
Catalog
>
left()
left(sourceString[, Num]) ⇒ string
Returns the leftmost Num characters contained in character string
sourceString.
If you omit Num, returns all of sourceString.
left(List1[, Num]) ⇒ list
Returns the leftmost Num elements contained in List1.
If you omit Num, returns all of List1.
left(Comparison) ⇒ expression
Returns the left-hand side of an equation or inequality.
libShortcut()
libShortcut(LibNameString, ShortcutNameString
[, LibPrivFlag]) ⇒ list of variables
Creates a variable group in the current problem that contains
references to all the objects in the specified library document
libNameString. Also adds the group members to the Variables menu.
You can then refer to each object using its ShortcutNameString.
Set LibPrivFlag=0 to exclude private library objects (default)
Set LibPrivFlag=1 to include private library objects
To copy a variable group, see CopyVar on page 15.
To delete a variable group, see DelVar on page 25.
Catalog
>
Catalog
>
This example assumes a properly stored and refreshed library
document named linalg2 that contains objects defined as
clearmat, gauss1, and gauss2.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 43
Page 50

LinRegBx
LinRegBx X,Y[,[Freq][,Category,Include]]
Computes the linear regression y = a+b·x on lists X and Y with
frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results
variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.a, stat.b Regression coefficients
2
stat.r
stat.r Correlation coefficient
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.FreqReg and stat.YReg
Regression Equation: a+b·x
Coefficient of determination
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
Catalog
>
LinRegMx
LinRegMx X,Y[,[Freq][,Category,Include]]
Computes the linear regression y = m·x+b on lists X and Y with
frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results
variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Catalog
>
44 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 51

Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.m, stat.b Regression coefficients
2
stat.r
stat.r Correlation coefficient
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
Regression Equation: m
Coefficient of determination
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
·x+b
LinRegtIntervals
LinRegtIntervals X,Y[,Freq[,0[,CLev]]]
For Slope. Computes a level C confidence interval for the slope.
LinRegtIntervals X,Y[,Freq[,1,Xval[,CLev]]]
For Response. Computes a predicted y-value, a level C prediction
interval for a single observation, and a level C confidence interval for
the mean response.
A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page
83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.a, stat.b Regression coefficients
stat.df Degrees of freedom
2
stat.r
stat.r Correlation coefficient
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
For Slope type only
Regression Equation: a+b·x
Coefficient of determination
Catalog
>
Output variable Description
[stat.CLower,
stat.CUpper]
Confidence interval for the slope
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 45
Page 52

Output variable Description
stat.ME Confidence interval margin of error
stat.SESlope Standard error of slope
stat.s Standard error about the line
For Response type only
Output variable Description
[stat.CLower,
stat.CUpper]
stat.ME Confidence interval margin of error
stat.SE Standard error of mean response
[stat.LowerPred ,
stat.UpperPred]
stat.MEPred Prediction interval margin of error
stat.SEPred Standard error for prediction
stat.y
Confidence interval for the mean response
Prediction interval for a single observation
a + b·XVal
LinRegtTest
LinRegtTest X,Y[,Freq[,Hypoth]]
Computes a linear regression on the X and Y lists and a t test on the
value of slope b and the correlation coefficient r for the equation
y=a+bx. It tests the null hypothesis H0:b=0 (equivalently, r=0)
against one of three alternative hypotheses.
All the lists must have equal dimension.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Hypoth is an optional value specifying one of three alternative
hypotheses against which the null hypothesis (H0:b=r=0) will be
tested.
For Ha: bƒ0 and rƒ0 (default), set Hypoth=0
For Ha: b<0 and r<0, set Hypoth<0
For Ha: b>0 and r>0, set Hypoth>0
A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page
83.)
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.t t-Statistic for significance test
stat.PVal Smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected
Regression equation: a + b·x
Catalog
>
46 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 53

Output variable Description
stat.df Degrees of freedom
stat.a, stat.b Regression coefficients
stat.s Standard error about the line
stat.SESlope Standard error of slope
2
stat.r
stat.r Correlation coefficient
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
Coefficient of determination
@List()
@List(List1) ⇒ list
Returns a list containing the differences between consecutive
elements in List1. Each element of List1 is subtracted from the next
element of List1. The resulting list is always one element shorter than
the original List1.
list4mat()
list4mat(List [, elementsPerRow]) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix filled row-by-row with the elements from List.
elementsPerRow, if included, specifies the number of elements per
row. Default is the number of elements in List (one row).
If List does not fill the resulting matrix, zeros are added.
ln()
ln(Va l u e1 ) ⇒ value
ln(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the natural logarithm of the argument.
For a list, returns the natural logarithms of the elements.
If complex format mode is Real:
If complex format mode is Rectangular:
Catalog
Catalog
/u
>
>
keys
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 47
Page 54

ln()
ln(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix natural logarithm of squareMatrix1. This is not
the same as calculating the natural logarithm of each element. For
information about the calculation method, refer to cos() on.
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
/u
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular complex format:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
keys
LnReg
LnReg X, Y[, [Freq] [, Category, Include]]
Computes the logarithmic regression y = a+b·ln(x) on lists X and Y
with frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.a, stat.b Regression coefficients
2
stat.r
stat.r Correlation coefficient for transformed data (ln(x), y)
stat.Resid Residuals associated with the logarithmic model
stat.ResidTrans Residuals associated with linear fit of transformed data
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
Regression equation: a+b·ln(x)
Coefficient of linear determination for transformed data
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
Catalog
>
48 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 55

Local
Local Var 1 [, Va r 2] [, Va r 3 ] ...
Declares the specified vars as local variables. Those variables exist
only during evaluation of a function and are deleted when the
function finishes execution.
Note: Local variables save memory because they only exist
temporarily. Also, they do not disturb any existing global variable
values. Local variables must be used for
temporarily saving values in a multi-line function since modifications
on global variables are not allowed in a function.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
For loops and for
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Catalog
>
log()
log(Val u e 1 [,Val u e 2 ]) ⇒ value
log(List1[,Va l ue 2 ]) ⇒ list
Returns the base-Value2 logarithm of the first argument.
Note: See also Log template, page 2.
For a list, returns the base-Value2 logarithm of the elements.
If the second argument is omitted, 10 is used as the base.
log(squareMatrix1[,Val u e ]) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix base-Val u e logarithm of squareMatrix1. This is
not the same as calculating the base-Va lu e logarithm of each
element. For information about the calculation method, refer to
cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
If the base argument is omitted, 10 is used as base.
s
/
If complex format mode is Real:
If complex format mode is Rectangular:
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular complex format:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
keys
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 49
Page 56

Logistic
Logistic X, Y[, [Freq] [, Category, Include]]
Computes the logistic regression y = (c/(1+a·e
with frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
-bx
)) on lists X and Y
Catalog
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
Regression equation: c/(1+a·e
-bx
)
stat.a, stat.b, stat.c Regression coefficients
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
>
LogisticD
LogisticD X, Y [ , [Iterations] , [Freq] [, Category, Include] ]
Computes the logistic regression y = (c/(1+a·e
Y with frequency Freq, using a specified number of Iterations. A
summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page
83.)
-bx
)+d) on lists X and
Catalog
>
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Iterations is an optional value that specifies the maximum number of
times a solution will be attempted. If omitted, 64 is used. Typically,
larger values result in better accuracy but longer exe cution times, and
vice versa.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
50 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 57

Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.a, stat.b, stat.c,
stat.d
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
Regression equation: c/(1+a·e
Regression coefficients
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
-bx
)+d)
Loop
Loop
Block
EndLoop
Repeatedly executes the statements in Block. Note that the loop will
be executed endlessly, unless a Goto or Exit instruction is executed
within Block.
Block is a sequence of statements separated with the “:” character.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 51
Page 58

LU
LU Matrix, lMatName, uMatName, pMatName[, Tol ]
Calculates the Doolittle LU (lower-upper) decomposition of a real or
complex matrix. The lower triangular matrix is stored in lMatName,
the upper triangular matrix in uMatName, and the permutation
matrix (which describes the row swaps done during the calculation) in
pMatName.
lMatName · uMatName = pMatName · matrix
Optionally, any matrix element is treated as zero if its absolute value
is less than Tol . This tolerance is used only if the matrix has floatingpoint entries and does not contain any symbolic variables that have
not been assigned a value. Otherwise, To l is ignored.
• If you use
•If Tol is omitted or not used, the default tolerance is calculated
The LU factorization algorithm uses partial pivoting with row
interchanges.
/
mode to Approximate, computations are done using floatingpoint arithmetic.
as:
5EM14 ·max(dim(Matrix)) ·rowNorm(Matrix)
· or set the Auto or Approximate
M
Catalog
>
mat4list()
mat4list(Matrix) ⇒ list
Returns a list filled with the elements in Matrix. The elements are
copied from Matrix row by row.
max()
max(Va l ue 1 , Va l ue 2 ) ⇒ expression
max(List1, List2) ⇒ list
max(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns the maximum of the two arguments. If the arguments are
two lists or matrices, returns a list or matrix containing the maximum
value of each pair of corresponding elements.
max(List) ⇒ expression
Returns the maximum element in list.
max(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns a row vector containing the maximum element of each
column in Matrix1.
Note: See also min().
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
52 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 59

mean()
mean(List[, freqList]) ⇒ expression
Returns the mean of the elements in List.
Each freqList element counts the number of consecutive occurrences
of the corresponding element in List.
mean(Matrix1[, freqMatrix]) ⇒ matrix
Returns a row vector of the means of all the columns in Matrix1.
Each freqMatrix element counts the number of consecutive
occurrences of the corresponding element in Matrix1.
In Rectangular vector format:
Catalog
>
median()
median(List) ⇒ expression
Returns the median of the elements in List.
median(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns a row vector containing the medians of the columns in
Matrix1.
Note: All entries in the list or matrix must simplify to numbers.
MedMed
MedMed X,Y [, Freq] [, Category, Include]]
Computes the median-median line y = (m·x+b) on lists X and Y
with frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
Median-median line equation: m·x+b
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 53
Page 60

Output variable Description
stat.m, stat.b Model coefficients
stat.Resid Residuals from the median-median line
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
mid()
mid(sourceString, Start[, Count]) ⇒ string
Returns Count characters from character string sourceString,
beginning with character number Star t.
If Count is omitted or is greater than the dimension of sourceString,
returns all characters from sourceString, beginning with character
number Start.
Count must be ‚ 0. If Count = 0, returns an empty string.
mid(sourceList, Start [, Count]) ⇒ list
Returns Count elements from sourceList, beginning with element
number Start.
If Count is omitted or is greater than the dimension of sourceList,
returns all elements from sourceList, beginning with element number
Start.
Count must be ‚ 0. If Count = 0, returns an empty list.
mid(sourceStringList, Start[, Count]) ⇒ list
Returns Count strings from the list of strings sourceStringList,
beginning with element number Start.
min()
min(Val u e 1, Va l u e 2) ⇒ expression
min(List1, List2) ⇒ list
min(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns the minimum of the two arguments. If the arguments are two
lists or matrices, returns a list or matrix containing the minimum
value of each pair of corresponding elements.
min(List) ⇒ expression
Returns the minimum element of List.
min(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns a row vector containing the minimum element of each
column in Matrix1.
Note: See also max().
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
54 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 61

mirr()
mirr(financeRate,reinvestRate,CF0,CFList[,CFFreq])
Financial function that returns the modified internal rate of return of
an investment.
financeRate is the interest rate that you pay on the cash flow
amounts.
rein vestRa te is the interest rate at which the cash flows are
reinvested.
CF0 is the initial cash flow at time 0; it must be a real number.
CFList is a list of cash flow amounts after the initial cash flow CF0.
CFFreq is an optional list in which each element specifies the
frequency of occurrence for a grouped (consecutive) cash flow
amount, which is the corresponding element of CFList. The default is
1; if you enter values, they must be positive integers < 10,000.
Note: See also irr(), page 42.
Catalog
>
mod()
mod(Va lu e 1 , Val u e 2 ) ⇒ expression
mod(List1, List2) ⇒ list
mod(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns the first argument modulo the second argument as defined
by the identities:
mod(x,0) = x
mod(x,y) = x -ìy floor(x/y)
When the second argument is non-zero, the result is periodic in that
argument. The result is either zero or has the same sign as the second
argument.
If the arguments are two lists or two matrices, returns a list or matrix
containing the modulo of each pair of corresponding elements.
Note: See also remain(), page 73
mRow()
mRow(Va lu e , Matrix1, Index) ⇒ matrix
Returns a copy of Matrix1 with each element in row Index of
Matrix1 multiplied by Va lu e .
mRowAdd()
mRowAdd(Val u e , Matrix1, Index1, Index2) ⇒ matrix
Returns a copy of Matrix1 with each element in row Index2 of
Matrix1 replaced with:
Val u e · row Index1 + row Index2
MultReg
MultReg Y, X1[,X2[,X3,…[,X10]]]
Calculates multiple linear regression of list Y on lists X1, X2, …, X10.
A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page
83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension.
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 55
Page 62

Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.b0, stat.b1, ... Regression coefficients
2
stat.R
stat.yList yList = b0+b1·x1+ ...
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
Regression Equation: b0+b1
Coefficient of multiple determination
·x1+b2·x2+ ...
MultRegIntervals
MultRegIntervals Y, X1[,X2[,X3,…[,X10]]],XValList[,CLevel]
Computes a predicted y-value, a level C prediction interval for a single
observation, and a level C confidence interval for the mean response.
A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page
83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.y A point estimate: y = b0 + b1 · xl + ... for XValList
stat.dfError Error degrees of freedom
stat.CLower, stat.CUpper Confidence interval for a mean response
stat.ME Confidence interval margin of error
stat.SE Standard error of mean response
stat.LowerPred,
stat.UpperrPred
stat.MEPred Prediction interval margin of error
stat.SEPred Standard error for prediction
stat.bList List of regression coefficients, {b0,b1,b2,...}
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
Regression Equation: b0+b1·x1+b2·x2+ ...
Prediction interval for a single observation
Catalog
>
MultRegTests
MultRegTests Y, X1[,X2[,X3,…[,X10]]]
Multiple linear regression test computes a multiple linear regression
on the given data and provides the global F test statistic and t test
statistics for the coefficients.
A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page
83.)
Catalog
>
56 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 63

Outputs
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.F Global F test statistic
stat.PVal P-value associated with global F statistic
2
stat.R
2
stat.AdjR
stat.s Standard deviation of the error
stat.DW Durbin-Watson statistic; used to determine whether first-order auto correlation is present in the model
stat.dfReg Regression degrees of freedom
stat.SSReg Regression sum of squares
stat.MSReg Regression mean square
stat.dfError Error degrees of freedom
stat.SSError Error sum of squares
stat.MSError Error mean square
stat.bList {b0,b1,...} List of coefficients
stat.tList List of t statistics, one for each coefficient in the bList
stat.PList List P-values for each t statistic
stat.SEList List of standard errors for coefficients in bList
stat.yList yList = b0+b1·x1+...
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
stat.sResid Standardized residuals; obtained by dividing a residual by its standard deviation
stat.CookDist Cook’s distance; measure of the influence of an observation based on the residual and leverage
stat.Leverage Measure of how far the values of the independent variable are from their mean values
Regression Equation: b0+b1·x1+b2·x2+ ...
Coefficient of multiple determination
Adjusted coefficient of multiple determination
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 57
Page 64

N
nCr()
nCr(Va l u e1 , Va l ue 2 ) ⇒ expression
For integer Va l ue 1 and
the number of combinations of Va lu e 1 things taken Va l ue 2 at a time.
(This is also known as a binomial coefficient.)
nCr(Va lu e , 0) ⇒ 1
Va l ue , negInteger) ⇒ 0
nCr(
Va l ue , posInteger) ⇒ Va l ue ·(Va l u eN1)...
nCr(
Val u e NposInteger+1)/ posInteger!
(
Va l ue , nonInteger) ⇒ expression!/
nCr(
((
Val u e NnonInteger)!·nonInteger!)
nCr(
List1, List2) ⇒ list
Returns a list of combinations based on the corresponding element
pairs in the two lists. The arguments must be the same size list.
nCr(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix of combinations based on the corresponding
element pairs in the two matrices. The arguments must be the same
size matrix.
nDeriv()
nDeriv(Expr1, Va r [=Value] [, H]) ⇒ expression
nDeriv(Expr1, Va r [, H] | Var = Va lu e ) ⇒ expression
nDeriv(Expr1, Va r [=Value], List) ⇒ list
nDeriv(List1, Va r [=Value] [, H]) ⇒ list
nDeriv(Matrix1, Va r [=Value] [, H]) ⇒ matrix
Returns the numerical derivative as an expression. Uses the central
difference quotient formula.
When Val u e is specified, it overrides any prior variable assignment or
any current “such that” substitution for the variable.
H is the step value. If H is omitted, it defaults to 0.001.
When using List1 or Matrix1, the operation gets mapped across the
values in the list or across the matrix elements.
Note: See also avgRC().
Va lu e 2 with Val u e 1 ‚ Val u e 2 ‚ 0, nCr() is
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
newList()
newList(numElements) ⇒ list
Returns a list with a dimension of numElements. Each element is
zero.
newMat()
newMat(numRows, numColumns) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix of zeros with the dimension numRows by
numColumns.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
58 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 65

nfMax()
nfMax(Expr, Va r) ⇒ value
nfMax(Expr, Va r, lowBound) ⇒ value
nfMax(Expr, Va r, lowBound, upBound) ⇒ value
nfMax(Expr, Var) | lowBound<Va r <upBound ⇒ value
Returns a candidate numerical value of variable Va r where the local
maximum of Expr occurs.
If you supply lowBound and upBound, the function looks between
those values for the local maximum.
Catalog
>
nfMin()
nfMin(Expr, Va r) ⇒ value
nfMin(Expr, Va r, lowBound) ⇒ value
nfMin(Expr, Va r, lowBound, upBound) ⇒ value
nfMin(Expr, Var) | lowBound<Var <upBound ⇒ value
Returns a candidate numerical value of variable Va r where the local
minimum of Expr occurs.
If you supply lowBound and upBound, the function looks between
those values for the local minimum.
nInt()
nInt(Expr1, Var, Lower, Upper) ⇒ expression
If the integrand Expr1 contains no variable other than Va r , and if
Lower and Upper are constants, positive ˆ, or negative ˆ, then
nInt() returns an approximation of ‰(Expr1, Va r , Lower, Upper).
This approximation is a weighted average of some sample values of
the integrand in the interval Lower<Va r <Upper.
The goal is six significant digits. The adaptive algorithm terminates
when it seems likely that the goal has been achieved, or when it
seems unlikely that additional samples will yield a worthwhile
improvement.
A warning is displayed (“Questionable accuracy”) when it seems that
the goal has not been achieved.
Nest nInt() to do multiple numeric integration. Integration limits can
depend on integration variables outside them.
nom()
nom(effectiveRate,CpY) ⇒ value
Financial function that converts the annual effective interest rate
effectiveRate to a nominal rate, given CpY as the number of
compounding periods per year.
effectiveRate must be a real number, and CpY must be a real number
> 0.
Note: See also eff(), page 27.
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 59
Page 66

norm()
norm(Matrix) ⇒ expression
norm(Ve c to r ) ⇒ expression
Returns the Frobenius norm.
Catalog
>
normCdf()
normCdf(lowBound,upBound[,m[,s]]) ⇒ number if lowBound
upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and upBound are
and
lists
Computes the normal distribution probability between lowBound
and upBound for the specified m (default=0) and s (default=1).
For P(X upBound), set lowBound = .9E999.
normPdf()
normPdf(XVal[,m[,s]]) ⇒ number if XVal is a number, list if
XVal is a list
Computes the probability density function for the normal distribution
at a specified XVal value for the specified m and s.
not
not BooleanExpr ⇒ Boolean expression
Returns true, false, or a simplified form of the argument.
not Integer1 ⇒ integer
Returns the one’s complement of a real integer. Internally, Integer1 is
converted to a signed, 64-bit binary number. The value of each bit is
flipped (0 becomes 1, and vice versa) for the one’s complement.
Results are displayed according to the Base mode.
You can enter the integer in any number base. For a binary or
hexadecimal entry, you must use the 0b or 0h prefix, respectively.
Without a prefix, the integer is treated as decimal (base 10).
If you enter a decimal integer that is too large for a signed, 64-bit
binary form, a symmetric modulo operation is used to bring the value
into the appropriate range.
In Hex base mode:
Important: Zero, not the letter O.
In Bin base mode:
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
Note: A binary entry can have up to 64 digits (not counting the
0b prefix). A hexadecimal entry can have up to 16 digits.
60 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 67

nPr()
nPr(Va l ue 1 , Va l ue 2 ) ⇒ expression
For integer Va l ue 1 and
the number of permutations of Va lu e 1 things taken Va l u e2 at a time.
nPr(Val u e , 0) ⇒ 1
Val u e , negInteger) ⇒ 1/((Va l ue +1)·(Va l u e +2)...
nPr(
(
Val u e NnegInteger))
nPr(
Val u e , posInteger) ⇒ Va l ue ·(Va l u eN1)...
Val u e NposInteger+1)
(
Val u e , nonInteger) ⇒ Va l ue ! / (Va l ue NnonInteger)!
nPr(
nPr(
List1, List2) ⇒ list
Returns a list of permutations based on the corresponding element
pairs in the two lists. The arguments must be the same size list.
nPr(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix of permutations based on the corresponding
element pairs in the two matrices. The arguments must be the same
size matrix.
Va lu e 2 with Val u e 1 ‚ Val u e 2 ‚ 0, nPr() is
Catalog
>
npv()
npv(InterestRate,CFO,CFList[,CFFreq])
Financial function that calculates net present value; the sum of the
present values for the cash inflows and outflows. A positive result for
npv indicates a profitable investment.
InterestRate is the rate by which to discount the cash flows (the cost
of money) over one period.
CF0 is the initial cash flow at time 0; it must be a real number.
CFList is a list of cash flow amounts after the initial cash flow CF0.
CFFreq is a list in which each element specifies the frequency of
occurrence for a grouped (consecutive) cash flow amount, which is
the corresponding element of CFList. The default is 1; if you enter
values, they must be positive integers < 10,000.
nSolve()
nSolve(Equation,Var [=Guess]) ⇒ number or error_string
nSolve(Equation,Var [=Guess],lowBound)
⇒ number or error_string
nSolve(Equation,Var [=Guess],lowBound,upBound)
⇒ number or error_string
nSolve(Equation,Var [=Guess]) | lowBound<Va r <upBound
⇒ number or error_string
Iteratively searches for one approximate real numeric solution to
Equation for its one variable. Specify the variable as:
variable
– or –
variable = real number
For example, x is valid and so is x=3.
Catalog
>
Catalog
>
Note: If there are multiple solutions, you can use a guess to
help find a particular solution.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 61
Page 68

nSolve()
nSolve() attempts to determine either one point where the residual
is zero or two relatively close points where the residual has opposite
signs and the magnitude of the residual is not excessive. If it cannot
achieve this using a modest number of sample points, it returns the
string “no solution found.”
O
Catalog
>
OneVar
OneVar [1,]X[,[Freq][,Category,Include]]
OneVar [
n,]X1,X2[X3[,…[,X20]]]
Calculates 1-variable statistics on up to 20 lists. A summary of results
is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
The X arguments are data lists.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X value.
The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
values.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.v
stat.Gx
2
stat.Gx
stat.sx Sample standard deviation of x
stat.ssssx Population standard deviation of x
stat.n Number of data points
stat.MinX Minimum of x values
stat.Q1X 1st Quartile of x
stat.MedianX Median of x
stat.Q3X 3rd Quartile of x
stat.MaxX Maximum of x values
stat.SSX Sum of squares of deviations from the mean of x
Mean of x values
Sum of x values
Sum of x2 values
Catalog
>
62 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 69

or
BooleanExpr1 or BooleanExpr2
⇒ Boolean expression
Returns true or false or a simplified form of the original entry.
Returns true if either or both expressions simplify to true. Returns
false only if both expressions evaluate to false.
Note: See xor.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Integer1 or Integer2 ⇒ integer
Compares two real integers bit-by-bit using an or operation.
Internally, both integers are converted to signed, 64-bit binary
numbers. When corresponding bits are compared, the result is 1 if
either bit is 1; the result is 0 only if both bits are 0. The returned value
represents the bit results, and is displayed according to the Base
mode.
You can enter the integers in any number base. For a binary or
hexadecimal entry, you must use the 0b or 0h prefix, respectively.
Without a prefix, integers are treated as decimal (base 10).
If you enter a decimal integer that is too large for a signed, 64-bit
binary form, a symmetric modulo operation is used to bring the value
into the appropriate range.
Note: See xor.
Catalog
>
In Hex base mode:
Important: Zero, not the letter O.
In Bin base mode:
Note: A binary entry can have up to 64 digits (not counting the
0b prefix). A hexadecimal entry can have up to 16 digits.
ord()
ord(Str ing) ⇒ integer
ord(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the numeric code of the first character in character string
Strin g, or a list of the first characters of each list element.
Catalog
>
P
P4Rx()
P4Rx(rExpr, qExpr) ⇒ expression
P4Rx(rList, qList) ⇒ list
P4Rx(rMatrix, qMatrix) ⇒ matrix
Returns the equivalent x-coordinate of the
(r, q) pair.
Note: The q argument is interpreted as either a degree, gradian or
radian angle, according to the current angle mode. If the argument is
an expression, you can use ó,G or ôto override the angle mode
setting temporarily.
In Radian angle mode:
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 63
Catalog
>
Page 70

P4Ry()
P4Ry(rValue, qVal u e ) ⇒ value
P4Ry(rList, qList) ⇒ list
P4Ry(rMatrix, qMatrix) ⇒ matrix
Returns the equivalent y-coordinate of the (r, q) pair.
Note: The q argument is interpreted as either a degree, radian or
gradian angle, according to the current angle mode.
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
>
PassErr
PassErr
Passes an error to the next level.
If system variable errCode is zero, PassErr does not do anything.
The Else clause of the Try...Else...EndTry block should use ClrErr
or PassErr. If the error is to be processed or ignored, use ClrErr. If
what to do with the error is not known, use PassErr to send it to the
next error handler. If there are no more pending
Try...Else...EndTry error handlers, the error dialog box will be
displayed as normal.
Note: See also ClrErr, page 14, and Try, page 91.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
piecewise()
piecewise(Expr1 [, Cond1 [, Expr2 [, Cond2 [, … ]]]])
Returns definitions for a piecewise function in the form of a list. You
can also create piecewise definitions by using a template.
Note: See also Piecewise template, page 2.
poissCdf()
poissCdf(l,lowBound,upBound) ⇒ number if lowBound and
upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and upBound are lists
poissCdf(
l,upBound) (for P(0XupBound) ⇒ number if
upBound is a number, list if upBound is a list
Computes a cumulative probability for the discrete Poisson
distribution with specified mean l.
For P(X upBound), set lowBound=0
Catalog
For an example of PassErr, See Example 2 under the Try
command, page 92.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
poissPdf()
poissPdf(l,XVal) ⇒ number if XVal is a number, list if XVal is
a list
Computes a probability for the discrete Poisson distribution with the
specified mean l.
Catalog
>
64 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 71

4Polar
4Polar
Vec t o r
Displays vector in polar form [r q]. The vector must be of
dimension 2 and can be a row or a column.
Note: 4Polar is a display-format instruction, not a conversion
function. You can use it only at the end of an entry line, and it does
not update ans.
Note: See also 4Rect, page 72.
complexValue 4Polar
Displays complexVector in polar form.
• Degree angle mode returns (rq).
• Radian angle mode returns reiq.
complexValue can have any complex form. However, an reiq entry
causes an error in Degree angle mode.
Note: You must use the parentheses for an (rq) polar entry.
In Radian angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Degree angle mode:
Catalog
>
polyEval()
polyEval(List1, Expr1) ⇒ expression
polyEval(List1, List2) ⇒ expression
Interprets the first argument as the coefficient of a descending-degree
polynomial, and returns the polynomial evaluated for the value of the
second argument.
PowerReg
PowerReg X,Y [, Freq] [, Category, Include]]
Computes the power regression y = (a·(x)b) on lists X and Y with
frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results
variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
Regression equation: a·(x)
b
stat.a, stat.b Regression coefficients
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 65
Page 72

Output variable Description
2
stat.r
stat.r Correlation coefficient for transformed data (ln(x), ln(y))
stat.Resid Residuals associated with the power model
stat.ResidTrans Residuals associated with linear fit of transformed data
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
Coefficient of linear determination for transformed data
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
Prgm
Prgm
Block
EndPrgm
Template for creating a user-defined progra m. Must be used with the
Define, Define LibPub, or Define LibPriv command.
Block can be a single statement, a series of statements separated
with the “:” character, or a series of statements on separate lines.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Product (PI)
product()
product(List[, Start[, End]]) ⇒ expression
Returns the product of the elements contained in List. Start and End
are optional. They specify a range of elements.
Calculate GCD and display intermediate results.
See Π(), page 109.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
66 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 73

product()
product(Matrix1[, Start[, End]]) ⇒ matrix
Returns a row vector containing the products of the elements in the
columns of Matrix1. Start and end are optional. They specify a range
of rows.
Catalog
>
propFrac()
propFrac(Va l ue 1 [, Va r ]) ⇒ value
propFrac(rational_number) returns rational_number as the sum
of an integer and a fraction having the same sign and a greater
denominator magnitude than numerator magnitude.
propFrac(rational_expression,Var ) returns the sum of proper
ratios and a polynomial with respect to Va r . The degree of Va r in the
denominator exceeds the degree of Va r in the numerator in each
proper ratio. Similar powers of Va r are collected. The terms and their
factors are sorted with Var as the main variable.
If Var is omitted, a proper fraction expansion is done with respect to
the most main variable. The coefficients of the polynomial part are
then made proper with respect to their most main variable first and so
on.
You can use the propFrac() function to represent mixed fractions
and demonstrate addition and subtraction of mixed fractions.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 67
Page 74

Q
QR
QR Matrix, qMatrix, rMatrix[, Tol ]
Calculates the Householder QR factorization of a real or complex
matrix. The resulting Q and R matrices are stored to the specified
Matrix. The Q matrix is unitary. The R matrix is upper triangular.
Optionally, any matrix element is treated as zero if its absolute value
is less than Tol . This tolerance is used only if the matrix has floatingpoint entries and does not contain any symbolic variables that have
not been assigned a value. Otherwise, To l is ignored.
/
• If you use
mode to Approximate, computations are done using floating-
point arithmetic.
•If Tol is omitted or not used, the default tolerance is calculated
as:
5Eë14 ·max(dim(Matrix)) ·rowNorm(Matrix)
The QR factorization is computed numerically using Householder
transformations. The symbolic solution is computed using GramSchmidt. The columns in qMatName are the orthonormal basis
vectors that span the space defined by matrix.
QuadReg
QuadReg X,Y [, Freq] [, Category, Include]]
Computes the quadratic polynomial regression y = a·x2+b·x+c on
lists X and Y with frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in
the stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
· or set the Auto or Approximate
Catalog
The floating-point number (9.) in m1 causes results to be
calculated in floating-point form.
Catalog
>
>
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.a, stat.b, stat.c Regression coefficients
2
stat.R
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
Regression equation: a·x2+b·x+c
Coefficient of determination
Category List, and Include Categories
68 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 75

stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
Category List, and Include Categories
QuartReg
QuartReg X,Y [, Freq] [, Category, Include]]
Computes the quartic polynomial regression
y = a·x4+b·x3+c· x2+d·x+e on lists X and Y with frequency
Freq. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See
page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.a, stat.b, stat.c,
stat.d, stat.e
2
stat.R
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
Regression equation: a·x4+b·x3+c· x2+d·x+e
Regression coefficients
Coefficient of determination
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 69
Page 76

R
R4Pq()
R4Pq (xValue, yValue) ⇒ value
R4Pq (xList, yList) ⇒ list
R4Pq (xMatrix, yMatrix) ⇒ matrix
Returns the equivalent q-coordinate of the
(x,y) pair arguments.
Note: The result is returned as a degree, gradian or radian angle,
according to the current angle mode setting.
R4Pr()
R4Pr (xValue, yValue) ⇒ value
R4Pr (xList, yList) ⇒ list
R4Pr (xMatrix, yMatrix) ⇒ matrix
Returns the equivalent r-coordinate of the (x,y) pair arguments.
4Rad
Val u e 1 4Rad ⇒ value
Converts the argument to radian angle measure.
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
In Degree angle mode:
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
In Gradian angle mode:
rand()
rand() ⇒ expression
rand(#Trials) ⇒ list
rand() returns a random value between 0 and 1.
rand(#Trials) returns a list containing #Trials random values
between 0 and 1.
Sets the random-number seed.
Catalog
>
70 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 77

randBin()
randBin(n, p) ⇒ expression
randBin(n, p, #Trials) ⇒ list
randBin(n, p) returns a random real number from a specified
Binomial distribution.
randBin(n, p, #Trials) returns a list containing #Trials random real
numbers from a specified Binomial distribution.
Catalog
>
randInt()
randInt(lowBound,upBound) ⇒ expression
randInt(lowBound,upBound ,#Trials) ⇒ list
randInt(lowBound,upBound) returns a random integer within the
range specified by lowBound and upBound integer bounds.
randInt(lowBound,upBound ,#Trials) returns a list containing
#Trials random integers within the specified range.
randMat()
randMat(numRows, numColumns) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix of integers between -9 and 9 of the specified
dimension.
Both arguments must simplify to integers.
randNorm()
randNorm(m, s) ⇒ expression
randNorm(m, s, #Trials) ⇒ list
randNorm(m, s) returns a decimal number from the specified
normal distribution. It could be any real number but will be heavily
concentrated in the interval [mN3·s, m+3·s].
randNorm(m, s, #Trials) returns a list containing #Trials decimal
numbers from the specified normal distribution.
randPoly()
randPoly(Va r , Order) ⇒ expression
Returns a polynomial in Va r of the specified Order. The coefficients
are random integers in the range ë9 through 9. The leading
coefficient will not be zero.
Order must be 0–99.
Catalog
>
Catalog
>
Note: The value s in this matr ix will change each time you press
·.
Catalog
>
Catalog
>
randSamp()
randSamp(List,#Trials[,noRepl]) ⇒ list
Returns a list containing a random sample of #Trials trials from List
with an option for sample replacement (noRepl=0), or no sample
replacement (noRepl=1). The default is with sample replacement.
Catalog
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 71
Page 78

RandSeed
RandSeed Number
If Number = 0, sets the seeds to the factory defaults for the randomnumber generator. If Number
which are stored in system variables seed1 and seed2.
ƒ 0, it is used to generate two seeds,
Catalog
>
real()
real(Va l ue 1 ) ⇒ value
Returns the real part of the argument.
real(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the real parts of all elements.
real(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
Returns the real parts of all elements.
4Rect
Vec t o r 4Rect
Displays Vec t o r in rectangular form [x, y, z]. The vector must be of
dimension 2 or 3 and can be a row or a column.
Note: 4Rect is a display-format instruction, not a conversion
function. You can use it only at the end of an entry line, and it does
not update ans.
Note: See also 4Polar, page 65.
complexValue 4Rect
Displays complexValue in rectangular form a+bi. The complexValue
can have any complex form. However, an reiq entry causes an error in
Degree angle mode.
Note: You must use parentheses for an (rq) polar entry.
In Radian angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
In Degree angle mode:
Note: To type , select it from the symbol list in the Catalog.
72 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 79

ref()
ref(Matrix1[, To l]) ⇒ matrix
Returns the row echelon form of Matrix1.
Optionally, any matrix element is treated as zero if its absolute value
is less than Tol . This tolerance is used only if the matrix has floatingpoint entries and does not contain any symbolic variables that have
not been assigned a value. Otherwise, To l is ignored.
• If you use
•If Tol is omitted or not used, the default tolerance is calculated
Note: See also rref(), page 76.
/
mode to Approximate, computations are done using floatingpoint arithmetic.
as:
5Eë14 ·max(dim(Matrix1)) ·rowNorm(Matrix1)
· or set the Auto or Approximate
Catalog
>
remain()
remain(Va lu e 1 , Val u e 2 ) ⇒ value
remain(List1, List2) ⇒ list
remain(Matrix1, Matrix2) ⇒ matrix
Returns the remainder of the first argument with respect to the
second argument as defined by the identities:
remain(x,0) x
remain(x,y) xNy·iPart(x/y)
As a consequence, note that remain(Nx,y) Nremain(x,y). The
result is either zero or it has the same sign as the first argument.
Note: See also mod(), page 55.
Return
Return [Expr]
Returns Expr as the result of the function. Use within a
Func...EndFunc block.
Note: Use Return without an argument within a
Prgm...EndPrgm block to exit a program.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
right()
right(List1[, Num]) ⇒ list
Returns the rightmost Num elements contained in List1.
If you omit Num, returns all of List1.
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 73
Page 80

right()
right(sourceString[, Num]) ⇒ string
Returns the rightmost Num characters contained in character string
sourceString.
If you omit Num, returns all of sourceString.
right(Comparison) ⇒ expression
Returns the right side of an equation or inequality.
Catalog
>
root()
root(Val u e ) ⇒ root
root(Val u e 1 , Val u e 2 ) ⇒ root
root(Val u e ) returns the square root of Val u e.
root(Val u e 1 , Val u e 2 ) returns the Val u e2 root of Va l u e 1. Va l u e1
can be a real or complex floating point constant or an integer or
complex rational constant.
Note: See also Nth root template, page 1.
rotate()
rotate(Integer1[,#ofRotations]) ⇒ integer
Rotates the bits in a binary integer. You can enter Integer1 in any
number base; it is converted automatically to a signed, 64-bit binary
form. If the magnitude of Integer1 is too large for this form, a
symmetric modulo operation brings it within the range.
If #ofRotations is positive, the rotation is to the left. If #ofRotations
is negative, the rotation is to the right. The default is ë1 (rotate right
one bit).
For example, in a right rotation:
Each bit rotates right.
0b00000000000001111010110000110101
Rightmost bit rotates to leftmost.
produces:
0b10000000000000111101011000011010
The result is displayed according to the Base mode.
rotate(List1[,#ofRotations]) ⇒ list
Returns a copy of List1 rotated right or left by #of Rotations
elements. Does not alter List1.
If #ofRotations is positive, the rotation is to the left. If #of Rotations
is negative, the rotation is to the right. The default is ë1 (rotate right
one element).
rotate(String1[,#ofRotations]) ⇒ string
Returns a copy of String1 rotated right or left by #ofRotations
characters. Does not alter String1.
If #ofRotations is positive, the rotation is to the left. If #ofRotations
is negative, the rotation is to the right. The default is ë1 (rotate right
one character).
Catalog
>
Catalog
>
In Bin base mode:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
In Hex base mode:
Important: To enter a binary or hexadecimal number, always
use the 0b or 0h prefix (zero, not the letter O).
In Dec base mode:
74 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 81

round()
round(Va l ue 1 [, digits]) ⇒ value
Returns the argument rounded to the specified number of digits after
the decimal point.
digits must be an integer in the range 0–12. If digits is not included,
returns the argument rounded to 12 significant digits.
Note: Display digits mode may affect how this is displayed.
round(List1[, digits]) ⇒ list
Returns a list of the elements rounded to the specified number of
digits.
round(Matrix1[, digits]) ⇒ matrix
Returns a matrix of the elements rounded to the specified number of
digits.
Catalog
>
rowAdd()
rowAdd(Matrix1, rIndex1, rIndex2) ⇒ matrix
Returns a copy of Matrix1 with row rIndex2 replaced by the sum of
rows rIndex1 and rIndex2.
rowDim()
rowDim(Matrix) ⇒ expression
Returns the number of rows in Matrix.
Note: See also colDim(), page 14.
rowNorm()
rowNorm(Matrix) ⇒ expression
Returns the maximum of the sums of the absolute values of the
elements in the rows in Matrix.
Note: All matrix elements must simplify to numbers. See also
colNorm(), page 14.
rowSwap()
rowSwap(Matrix1, rIndex1, rIndex2) ⇒ matrix
Returns Matrix1 with rows rIndex1 and rIndex2 exchanged.
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 75
Page 82

rref()
rref(Matrix1[, To l]) ⇒ matrix
Returns the reduced row echelon form of Matrix1.
Optionally, any matrix element is treated as zero if its absolute value
is less than Tol . This tolerance is used only if the matrix has floatingpoint entries and does not contain any symbolic variables that have
not been assigned a value. Otherwise, To l is ignored.
• If you use
•If Tol is omitted or not used, the default tolerance is calculated
Note: See also ref(), page 73.
/
mode to Approximate, computations are done using floatingpoint arithmetic.
as:
5Eë14 ·max(dim(Matrix1)) ·rowNorm(Matrix1)
· or set the Auto or Approximate
S
Catalog
>
sec()
sec(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
sec(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the secant of Va lu e 1 or returns a list containing the secants
of all elements in List1.
Note: The argument is interpreted as a degree, gradian or radian
angle, according to the current angle mode setting. You can us e ó,G,
orôto override the angle mode temporarily.
sec/()
sec/(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
sec/(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the angle whose secant is Va l u e1 or returns a list containing
the inverse secants of each element of List1.
Note: The result is returned as a degree, gradian or radian angle,
according to the current angle mode setting.
sech()
sech(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
sech(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the hyperbolic secant of Va lu e 1 or returns a list containing
the hyperbolic secants of the List1 elements.
In Degree angle mode:
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
76 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 83

sechê()
sechê(Va l u e1 ) ⇒ value
sechê (List1) ⇒ list
Returns the inverse hyperbolic secant of Va l ue 1 or returns a list
containing the inverse hyperbolic secants of each element of List1.
Catalog
In Radian angle and Rectangular complex mode:
>
seq()
seq(Expr, Va r, Low, High[, St ep]) ⇒ list
Increments Va r from Low through High by an increment of Step ,
evaluates Expr, and returns the results as a list. The original contents
of Var are still there after seq() is completed.
Var cannot be a system variable.
The default value for Ste p = 1.
setMode()
setMode(modeNameInteger, settingInteger) ⇒ integer
setMode(list) ⇒ integer list
Valid only within a function or program.
setMode(modeNameInteger, settingInteger) temporarily sets
mode modeNameInteger to the new setting settingInteger, and
returns an integer corresponding to the original setting of that
mode. The change is limited to the duration of the program/
function’s execution.
modeNameInteger specifies which mode you want to set. It must
be one of the mode integers from the table below.
settingInteger specifies the new setting for the mode. It must be
one of the setting integers listed below for the specific mode you
are setting.
setMode(list) lets you change multiple settings. list contains
pairs of mode integers and setting integers. setMode(list)
returns a similar list whose integer pairs represent the original
modes and settings.
If you have saved all mode settings with getMode(0) & var,
you can use setMode(var) to restore those settings until the
function or program exits. See getMode(), page 36.
Note: The current mode settings are passed to called
subroutines. If any subroutine changes a mode setting, the mode
change will be lost when control returns to the calling routine.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator
application on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions
by pressing @ instead of · at the end of each line. On
the computer keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Catalog
>
Press Ctrl+Enter /· to evaluate:
Catalog
>
Display approximate value of p using the default setting for Display
Digits, and then display p with a setting of Fix2. Check to see that
the default is restored after the program executes.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 77
Page 84

Mode
Name
Display Digits
Angle
Exponential Format
Real or Complex
Auto or Approx.
Vector Format
Base
Mode
Integer Setting Integers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
=Float, 2=Float1, 3=Float2, 4=Float3, 5=Float4, 6=Float5, 7=Float6, 8=Float7,
9=Float8, 10=Float9, 11=Float10, 12=Float11, 13=Float12, 14=Fix0, 15=Fix1,
16=Fix2, 17=Fix3, 18=Fix4, 19=Fix5, 20=Fix6, 21=Fix7, 22=Fix8, 23=Fix9, 24=Fix10,
25=Fix11, 26=Fix12
1
=Radian, 2=Degree, 3=Gradian
1
=Normal, 2=Scientific, 3=Engineering
1
=Real, 2=Rectangular, 3=Polar
1
=Auto, 2=Approximate
1
=Rectangular, 2=Cylindrical, 3=Spherical
1
=Decimal, 2=Hex, 3=Binary
shift()
shift(Integer1[,#ofShifts]) ⇒ integer
Shifts the bits in a binary integer. You can enter Integer1 in any
number base; it is converted automatically to a signed, 64-bit binary
form. If the magnitude of Integer1 is too large for this form, a
symmetric modulo operation brings it within the range.
If #ofShifts is positive, the shift is to the left. If #ofShifts is negative,
the shift is to the right. The default is ë1 (shift right one bit).
In a right shift, the rightmost bit is dropped and 0 or 1 is inserted to
match the leftmost bit. In a left shift, the leftmost bit is dropped and 0
is inserted as the rightmost bit.
For example, in a right shift:
Each bit shifts right.
0b0000000000000111101011000011010
Inserts 0 if leftmost bit is 0,
or 1 if leftmost bit is 1.
produces:
0b00000000000000111101011000011010
The result is displayed according to the Base mode. Lea ding zeros are
not shown.
shift(List1 [,#ofShifts]) ⇒ list
Returns a copy of List1 shifted right or left by #ofShifts elements.
Does not alter List1.
If #ofShifts is positive, the shift is to the left. If #ofShifts is negative,
the shift is to the right. The default is ë1 (shift right one element).
Elements introduced at the beginning or end of list by th e shift are set
to the symbol “undef”.
shift(String1 [,#ofShifts]) ⇒ string
Returns a copy of String1 shifted right or left by #ofShifts characters.
Does not alter String1.
If #ofShifts is positive, the shift is to the left. If #ofShifts is negative,
the shift is to the right. The default is ë1 (shift right one character).
Characters introduced at the beginning or end of string by the shift
are set to a space.
Catalog
>
In Bin base mode:
In Hex base mode:
Important: To enter a binary or hexadecimal number, always
use the 0b or 0h prefix (zero, not the letter O).
In Dec base mode:
78 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 85

sign()
sign(Va l ue 1 ) ⇒ value
sign(List1) ⇒ list
sign(Matrix1) ⇒ matrix
For real and complex Val u e1 , returns Va lu e 1 /
Val u e 1 ƒ 0.
abs(Val u e 1 ) when
Returns 1 if Val u e 1 is positive.
Returns ë1 if Val u e 1 is negative.
sign(0) returns „1 if the complex format mode is Real; otherwise, it
returns itself.
sign(0) represents the unit circle in the complex domain.
For a list or matrix, returns the signs of all the elements.
If complex format mode is Real:
Catalog
>
simult()
simult(coeffMatrix, constVector[, Tol ]) ⇒ matrix
Returns a column vector that contains the solutions to a system of
linear equations.
coeffMatrix must be a square matrix that contains the coefficients of
the equations.
constVector must have the same number of rows (same dimension)
as coeffMatrix and contain the constants.
Optionally, any matrix element is treated as zero if its absolute value
is less than Tol . This tolerance is used only if the matrix has floatingpoint entries and does not contain any symbolic variables that have
not been assigned a value. Otherwise, To l is ignored.
• If you set the Auto or Approximate mode to Approximate,
computations are done using floating-point arithmetic.
•If Tol is omitted or not used, the default tolerance is calculated
as:
5Eë14 ·max(dim(coeffMatrix)) ·rowNorm(coeffMatrix)
simult(coeffMatrix, constMatrix[, To l]) ⇒ matrix
Solves multiple systems of linear equations, where each system has
the same equation coefficients but different constants.
Each column in constMatrix must contain the constants for a system
of equations. Each column in the resulting matrix contains the
solution for the corresponding system.
Catalog
>
Solve for x and y:
x + 2y = 1
3x + 4y = ë1
The solution is x=ë3 and y=2.
Solve:
ax + by = 1
cx + dy = 2
Solve:
x + 2y = 1
3x + 4y = ë1
x + 2y = 2
3x + 4y = ë3
For the first system, x=ë3 and y=2. For the second system,
x=ë7 and y=9/2.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 79
Page 86

sin()
sin(Va l ue 1 ) ⇒ value
sin(List1) ⇒ list
sin(Val u e 1 ) returns the sine of the argument.
sin(List1) returns a list of the sines of all elements in List1.
Note: The argument is interpreted as a degree, gradian or radian
angle, according to the current angle mode. You can us e ó,G, or ô to
override the angle mode setting temporarily.
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
m
key
sin(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix sine of squareMatrix1. This is not the same as
calculating the sine of each element. For information about the
calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
sinê()
sinê(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
sinê(List1) ⇒ list
sinê(Val u e 1 ) returns the angle whose sine is Va l ue 1 .
sinê(List1) returns a list of the inverse sines of each element of
List1.
Note: The result is returned as a degree, gradian or radian angle,
according to the current angle mode setting.
sinê(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix inverse sine of squareMatrix1. This is not the
same as calculating the inverse sine of each element. For information
about the calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
In Radian angle mode:
/m
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular complex format mode:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
keys
80 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 87

sinh()
sinh(Numver1) ⇒ value
sinh(List1) ⇒ list
sinh (Val u e 1 ) returns the hyperbolic sine of the argument.
sinh (List1) returns a list of the hyperbolic sines of each element of
List1.
sinh(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix hyperbolic sine of squareMatrix1. This is not the
same as calculating the hyperbolic sine of each element. For
information about the calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
>
sinhê()
sinhê(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
sinhê(List1) ⇒ list
sinhê(Val u e 1 ) returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of the argument.
sinhê(List1) returns a list of the inverse hyperbolic sines of each
element of List1.
sinhê(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix inverse hyperbolic sine of squareMatrix1. This is
not the same as calculating the inverse hyperbolic sine of each
element. For information about the calculation method, refer to
cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
SinReg
SinReg X, Y [ , [Iterations] ,[ Period] [, Category, Include] ]
Computes the sinusoidal regression on lists X and Y. A summary of
results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Iterations is a value that specifies the maximum number of times (1
through 16) a solution will be attempted. If omitted, 8 is used.
Typically, larger values result in better accuracy but longer execution
times, and vice versa.
Period specifies an estimated period. If omitted, the difference
between values in X should be equal and in sequential order. If you
specify Period, the differences between x values can be unequal.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
The output of SinReg is always in radians, regardless of the angle
mode setting.
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 81
Page 88

Output variable Description
stat.RegEqn
stat.a, stat.b, stat.c,
stat.d
stat.Resid Residuals from the regression
stat.XReg List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.YReg List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq,
stat.FreqReg List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg
Regression Equation: a
Regression coefficients
Category List, and Include Categories
Category List, and Include Categories
·sin(bx+c)+d
SortA
SortA List1[, List2] [, List3] ...
SortA
Vector1[, Vector2] [, Vector3] ...
Sorts the elements of the first argument in ascending order.
If you include additional arguments, sorts the elements of each so
that their new positions match the new positions of the elements in
the first argument.
All arguments must be names of lists or vectors. All arguments must
have equal dimensions.
SortD
SortD List1[, List2] [, List3] ...
SortD
Vector1[,Vector2] [,Vector3] ...
Identical to SortA, except SortD sorts the elements in descending
order.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
82 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 89

4Sphere
4Sphere
Vec t o r
Displays the row or column vector in spherical form [r q f].
Vec t o r must be of dimension 3 and can be either a row or a column
vector.
Note: 4Sphere is a display-format instruction, not a conversion
function. You can use it only at the end of an entry line.
Catalog
>
Z
(ρ,θ,φ)
φ
ρ
Y
θ
X
sqrt()
sqrt(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
sqrt(List1) ⇒ list
Returns the square root of the argument.
For a list, returns the square roots of all the elements in List1.
Note: See also
Square
root template
, page 1.
stat.results
stat.results
Displays results from a statistics calculation.
The results are displayed as a set of name-value pairs. The specific
names shown are dependent on the most recently evaluated statistics
function or command.
You can copy a name or value and paste it into other locations.
Note: Avoid defining variables that use the same names as those
used for statistical analysis. In some cases, an error condition could
occur. Variable names used for statistical analysis are listed in the
table below.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 83
Page 90

stat.a
stat.AdjR²
stat.b
stat.b0
stat.b1
stat.b2
stat.b3
stat.b4
stat.b5
stat.b6
stat.b7
stat.b8
stat.b9
stat.b10
stat.bList
stat.c²
stat.c
stat.CLower
stat.CLowerList
stat.CompList
stat.CompMatrix
stat.CookDist
stat.CUpper
stat.CUpperList
stat.d
Note: Each time the Lists & Spreadsheet application calculates stati stical results, it copies the "stat." group variables to a "stat #."
group, where # is a number that is incremented automatically. This lets you maintain previous results while performing multiple
calculations.
stat.dfDenom
stat.dfBlock
stat.dfCol
stat.dfError
stat.dfInteract
stat.dfReg
stat.dfNumer
stat.dfRow
stat.DW
stat.e
stat.ExpMatrix
stat.F
stat.FBlock
stat.Fcol
stat.FInteract
stat.FreqReg
stat.Frow
stat.Leverage
stat.LowerPred
stat.LowerVal
stat.m
stat.MaxX
stat.MaxY
stat.ME
stat.MedianX
stat.MedianY
stat.MEPred
stat.MinX
stat.MinY
stat.MS
stat.MSBlock
stat.MSCol
stat.MSError
stat.MSInteract
stat.MSReg
stat.MSRow
stat.n
stat.Ç
stat.Ç1
stat.Ç2
stat.ÇDiff
stat.PList
stat.PVal
stat.PValBlock
stat.PValCol
stat.PValInteract
stat.PValRow
stat.Q1X
stat.Q1Y
stat.Q3X
stat.Q3Y
stat.r
stat.r²
stat.RegEqn
stat.Resid
stat.ResidTrans
stat.
sx
sy
stat.
stat.sx1
stat.
sx2
Gx
stat.
stat.Gx²
stat.Gxy
stat.Gy
stat.Gy²
stat.s
stat.SE
stat.SEList
stat.SEPred
stat.sResid
stat.SEslope
stat.sp
stat.SS
stat.SSBlock
stat.SSCol
stat.SSX
stat.SSY
stat.SSError
stat.SSInteract
stat.SSReg
stat.SSRow
stat.tList
stat.UpperPred
stat.UpperVal
stat.v
stat.v1
v2
stat.
stat.vDiff
stat.vList
stat.XReg
stat.XVal
stat.XValList
stat.w
stat.y
stat.yList
stat.YReg
stat.values
stat.values
Displays a matrix of the values calculated for the most recently
evaluated statistics function or command.
Unlike stat.results, stat.values omits the names associated with
the values.
You can copy a value and paste it into other locations.
stDevPop()
stDevPop(List[, freqList]) ⇒ expression
Returns the population standard deviation of the elements in List.
Each freqList element counts the number of consecutive occurrences
of the corresponding element in List.
Note: List must have at least two elements.
stDevPop(Matrix1[, freqMatrix]) ⇒ matrix
Returns a row vector of the population standard deviations of the
columns in Matrix1.
Each freqMatrix element counts the number of consecutive
occurrences of the corresponding element in Matrix1.
Note: Matrix1 must have at least two rows.
See the stat.results example.
In Radian angle and auto modes:
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
84 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 91

stDevSamp()
stDevSamp(List[, freqList]) ⇒ expression
Returns the sample standard deviation of the elements in List.
Each freqList element counts the number of consecutive occurrences
of the corresponding element in List.
Note: List must have at least two elements.
stDevSamp(Matrix1[, freqMatrix]) ⇒ matrix
Returns a row vector of the sample standard deviations of the
columns in Matrix1.
Each freqMatrix element counts the number of consecutive
occurrences of the corresponding element in Matrix1.
Note: Matrix1 must have at least two rows.
Catalog
>
Stop
Stop
Programming command: Terminates the program.
Stop is not allowed in functions.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Store
string()
string(Expr) ⇒ string
Simplifies Expr and returns the result as a character string.
See
Catalog
& (store)
Catalog
>
, page 114.
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 85
Page 92

subMat()
subMat(Matrix1[, startRow] [, startCol] [, endRow] [, endCol])
⇒ matrix
Returns the specified submatrix of Matrix1.
Defaults: startRow=1, startCol=1, endRow=last row, endCol=last
column.
Catalog
>
Sum (Sigma)
sum()
sum(List[, Start[, End]]) ⇒ expression
Returns the sum of the elements in List.
Start and End are optional. They specify a range of elements.
sum(Matrix1[, Start[, End]]) ⇒ matrix
Returns a row vector containing the sums of the elements in the
columns in Matrix1.
Start and End are optional. They specify a range of rows.
See G(), page 109.
Catalog
>
86 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 93

sumIf()
sumIf(List,Criteria[, SumList]) ⇒ value
Returns the accumulated sum of all elements in List that meet the
specified Criteria. Optionally, you can specify an alternate list,
sumList, to supply the elements to accumulate.
List can be an expression, list, or matrix. SumList, if specified, must
have the same dimension(s) as List.
Criteria can be:
• A value, expression, or string. For example, 34 accumulates only
those elements in List that simplify to the value 34.
• A Boolean expression containing the symbol ? as a placeholder
for each element. For example, ?<10 accumulates only those
elements in List that are less than 10.
When a List element meets the Criteria, the element is added to the
accumulating sum. If you include sumList, the corresponding eleme nt
from sumList is added to the sum instead.
Within the Lists & Spreadsheet application, you can use a range of
cells in place of List and sumList.
Note: See also countIf(), page 19.
Catalog
>
system()
system(Val u e 1 [, Val u e 2 [, Val u e 3 [, ...]]])
Returns a system of equations, formatted as a list. You can also
create a system by using a template.
T
T
(transpose)
T
Matrix1
⇒ matrix
Returns the complex conjugate transpose of Matrix1.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 87
Page 94

tan()
tan(Va l ue 1 ) ⇒ value
tan(List1) ⇒ list
tan(Val u e 1 ) returns the tangent of the argument.
tan(List1) returns a list of the tangents of all elements in List1.
Note: The argument is interpreted as a degree, gradian or radian
angle, according to the current angle mode. You can use ó,G orôto
override the angle mode setting temporarily.
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
o
key
tan(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix tangent of squareMatrix1. This is not the same as
calculating the tangent of each element. For information about the
calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
tanê()
tanê(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
tanê(List1) ⇒ list
tanê(Val u e 1 ) returns the angle whose tangent is Va l u e1 .
tanê(List1) returns a list of the inverse tangents of each ele ment of
List1.
Note: The result is returned as a degree, gradian or radian angle,
according to the current angle mode setting.
In Radian angle mode:
In Degree angle mode:
In Gradian angle mode:
In Radian angle mode:
/o
keys
88 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 95

tanê()
tanê(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix inverse tangent of squareMatrix1. This is not the
same as calculating the inverse tangent of each element. For
information about the calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
In Radian angle mode:
/o
keys
tanh()
tanh(Va l ue 1 ) ⇒ value
tanh(List1) ⇒ list
tanh(Val u e 1 ) returns the hyperbolic tangent of the argument.
tanh(List1) returns a list of the hyperbolic tangents of each element
of List1.
tanh(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix hyperbolic tangent of squareMatrix1. This is not
the same as calculating the hyperbolic tangent of each element. For
information about the calculation method, refer to cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
tanhê()
tanhê(Val u e 1 ) ⇒ value
tanhê(List1) ⇒ list
tanhê(Val u e 1 ) returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of the
argument.
tanhê(List1) returns a list of the inverse hyperbolic tangents of
each element of List1.
tanhê(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix
Returns the matrix inverse hyperbolic tangent of squareMatrix1. This
is not the same as calculating the inverse hyperbolic tangent of each
element. For information about the calculation method, refer to
cos().
squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains
floating-point numbers.
Catalog
>
In Radian angle mode:
Catalog
>
In Rectangular complex format:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular complex format:
To see the entire result, press £ and then use ¡ and ¢ to
move the cursor.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 89
Page 96

tCdf()
tCdf(lowBound,upBound,df) ⇒ number if lowBound and
upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and upBound are lists
Computes the Student-t distribution probability between lowBound
and upBound for the specified degrees of freedom df.
Catalog
>
For P(X upBound), set lowBound = .9E999.
Then See If, page 39.
tInterval
tInterval List[,Freq[,CLevel]]
(Data list input)
tInterval v,sx,n[,CLevel]
(Summary stats input)
Computes a t confidence interval. A summary of results is stored in
the stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
Output variable Description
stat.CLower, stat.CUpper Confidence interval for an unknown population mean
stat.x
Sample mean of the data sequence from the normal random distribution
stat.ME Margin of error
stat.df Degrees of freedom
stat.sx
Sample standard deviation
stat.n Length of the data sequence with sample mean
tInterval_2Samp
tInterval_2Samp
List1,List2[,Freq1[,Freq2[,CLevel[,Pooled]]]]
(Data list input)
tInterval_2Samp v1,sx1,n1,v2,sx2,n2[,CLevel[,Pooled]]
(Summary stats input)
Computes a two-sample t confidence interval. A summary of results is
stored in the stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
Pooled=1 pools variances; Pooled=0 does not pool variances.
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
Output variable Description
stat.CLower, stat.CUpper Confidence interval containing confidence level probability of distribution
stat.x1-x2
Sample means of the data sequences from the normal random distribution
stat.ME Margin of error
90 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 97

Output variable Description
stat.df Degrees of freedom
stat.x1, stat.x2
stat.sx1, stat.sx2
stat.n1, stat.n2 Number of samples in data sequences
stat.sp The pooled standard deviation. Calculated when Pooled =YES
Sample means of the data sequences from the normal random distribution
Sample standard deviations for List 1 and List 2
tPdf()
tPdf(XVal,df) ⇒ number if XVal is a number, list if XVal is a
list
Computes the probability density function (pdf) for the Student-t
distribution at a specified x value with specified degrees of freedom
df.
trace()
trace(squareMatrix) ⇒ value
Returns the trace (sum of all the elements on the main diagonal) of
squareMatrix.
Try
Try
block1
Else
block2
EndTry
Executes block1 unless an error occurs. Program execution transfers
to block2 if an error occurs in block1. System variable errCode
contains the error code to allow the program to perform error
recovery. For a list of error codes, see "Error codes and messages,"
page 116.
block1 and block2 can be either a single statement or a series of
statements separated with the “:” character.
Note for entering the example: In the Calculator application
on the handheld, you can enter multi-line definitions by pressing
@ instead of · at the end of each line. On the computer
keyboard, hold down Alt and press Enter.
Catalog
Catalog
Catalog
>
>
>
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 91
Page 98

Try
Example 2
To see the commands Try , ClrErr, and PassErr in operation, enter
the eigenvals() program shown at the right. Run the program by
executing each of the following expressions.
Note: See also ClrErr, page 14, and PassErr, page 64.
Catalog
Define eigenvals(a,b)=Prgm
© Program eigenvals(A,B) displays eigenvalues of A·B
Try
Disp "A= ",a
Disp "B= ",b
Disp " "
Disp "Eigenvalues of A·B are:",eigVl(a*b)
Else
If errCode=230 Then
Disp "Error: Product of A·B must be a square matrix"
ClrErr
Else
PassErr
EndIf
EndTry
EndPrgm
>
tTest
tTest m0,List[,Freq[,Hypoth]]
(Data list input)
tTest m0,x,sx,n,[Hypoth]
(Summary stats input)
Performs a hypothesis test for a single unknown population mean m
when the population standard deviation s is unknown. A summary of
results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
Test H0: m = m0, against one of the following:
For Ha: m < m0, set Hypoth<0
For Ha: m ƒ m0 (default), set Hypoth=0
For Ha: m > m0, set Hypoth>0
Output variable Description
stat.t
stat.PVal Smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected
stat.df Degrees of freedom
stat.x
stat.sx Sample standard deviation of the data sequence
stat.n Size of the sample
(x N m0) / (stdev / sqrt(n))
Sample mean of the data sequence in List
Catalog
>
92 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
Page 99

tTest_2Samp
tTest_2Samp List1,List2[,Freq1[,Freq2[,Hypoth[,Pooled]]]]
(Data list input)
tTest_2Samp v1,sx1,n1,v2,sx2,n2[,Hypoth[,Pooled]]
(Summary stats input)
Computes a two-sample t test. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
Test H0: m1 = m2, against one of the following:
For Ha: m1< m2, set Hypoth<0
For Ha: m1ƒ m2 (default), set Hypoth=0
For Ha: m1> m2, set Hypoth>0
Pooled=1 pools variances
Pooled=0 does not pool variances
Output variable Description
stat.t Standard normal value computed for the difference of means
stat.PVal Smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected
stat.df Degrees of freedom for the t-statistic
stat.x1, stat.x2
Sample means of the data sequences in List 1 and List 2
stat.sx1, stat.sx2 Sample standard deviations of the data sequences in List 1 and List 2
stat.n1, stat.n2 Size of the samples
stat.sp The pooled standard deviation. Calculated when Pooled=1.
Catalog
>
tvmFV()
tvmFV(N,I,PV,Pmt,[PpY],[CpY],[PmtAt]) ⇒ value
Catalog
>
Financial function that calculates the future value of money.
Note: Arguments used in the TVM functions are described in the
table of TVM arguments, page 94. See also amortTbl(), page 5.
tvmI()
tvmI(N,PV,Pmt,FV,[PpY],[CpY],[PmtAt]) ⇒ value
Catalog
>
Financial function that calculates the interest rate per year.
Note: Arguments used in the TVM functions are described in the
table of TVM arguments, page 94. See also amortTbl(), page 5.
tvmN()
tvmN(I,PV,Pmt,FV,[PpY],[CpY],[PmtAt]) ⇒ value
Catalog
>
Financial function that calculates the number of payment periods.
Note: Arguments used in the TVM functions are described in the
table of TVM arguments, page 94. See also amortTbl(), page 5.
TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide 93
Page 100

tvmPmt()
tvmPmt(N,I,PV,FV,[PpY],[CpY],[PmtAt]) ⇒ value
Financial function that calculates the amount of each payment.
Note: Arguments used in the TVM functions are described in the
table of TVM arguments, page 94. See also
amortTbl(), page 5.
Catalog
>
tvmPV()
tvmPV(N,I,Pmt,FV,[PpY],[CpY],[PmtAt]) ⇒ value
Catalog
>
Financial function that calculates the present value.
Note: Arguments used in the TVM functions are described in the
table of TVM arguments, page 94. See also amortTbl(), page 5.
TVM
argument*
Description Data type
N Number of payment periods real number
I Annual interest rate real number
PV Present value real number
Pmt Payment amount real number
FV Future value real number
PpY Payments per year, default=1 integer > 0
CpY Compounding periods per year, default=1 integer > 0
PmtAt Payment due at the end or beginning of each period, default=end integer (0=end,
* These time-value-of-money argument names are similar to the TVM variable names (such as tvm.pv and tvm.pmt) that are used
by the Calculator application’s finance solver. Financial functions, however, do not store their argument values or results to the TVM
variables.
TwoVar
TwoVar X, Y[, [Freq] [, Category, Include]]
Calculates the TwoVar statistics. A summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 83.)
1=beginning)
Catalog
>
All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include.
X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables.
Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq
specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y
data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers | 0.
Category is a list of numeric category codes for the corresponding X
and Y data.
Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data
items whose category code is included in this list are included in the
calculation.
94 TI-Nspire™ Reference Guide
 Loading...
Loading...