TC237
680- × 500-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS044B – JUNE 1994 – REVISED JUNE 1996
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
D
Very High-Resolution, 1/3-in Solid-State
Image Sensor for NTSC Black and White
Applications
D
340,000 Pixels per Field
D
Frame Memory
D
658 (H) × 496 (V) Active Elements in Image
Sensing Area Compatible With Electronic
Centerin
D
Multimode Readout Capability
– Progressive Scan
– Interlaced Scan
– Dual-Line Readout
– Image-Area Line Summing
– Smear Subtraction
D
Fast Single-Pulse Clear Capability
D
Continuous Electronic Exposure Control
From 1/60 – 1/50,000 s
D
7.4-µm Square Pixels
D
Advanced Lateral-Overflow-Drain
Antiblooming
D
Low Dark Current
D
High Dynamic Range
D
High Sensitivity
D
High Blue Response
D
Solid-State Reliability With No Image
Burn-In, Residual Imaging, Image
Distortion, Image Lag, or
Microphonics
description
The TC237 is a frame-transfer, charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensor designed for use in single-chip
black and white NTSC TV, computer, and special-purpose applications requiring low cost and small size.
The image-sensing area of the TC237 is configured into 500 lines with 680 elements in each line. Twenty-two
elements are provided in each line for dark reference. The blooming-protection feature of the sensor is based
on an advanced lateral-overflow-drain concept. The sensor can be operated in a true-interlace mode as a
658(H) × 496(V) sensor with a very low dark current. One important feature of the TC237 very high-resolution
sensor is the ability to capture a full 340,000 pixels per field. The image sensor also provides high-speed imagetransfer capability. This capability allows for a continuous electronic exposure control without the loss of
sensitivity and resolution inherent in other technologies. The charge is converted to signal voltage at 20 µV per
electron by a high-performance structure with a reset and a voltage-reference generator. The signal is further
buffered by a low-noise, two-stage, source-follower amplifier to provide high output-drive capability.
The TC237 is built using TI-proprietary advanced virtual-phase (A VP) technology , which provides devices with
high blue response, low dark signal, good uniformity, and single-phase clocking. The TC237 is characterized
for operation from –10°C to 45°C.
This MOS device contains limited built-in gate protection. During storage or handling, the device leads should be shorted together
or the device should be placed in conductive foam. In a circuit, unused inputs should always be connected to VSS. Under no
circumstances should pin voltages exceed absolute maximum ratings. Avoid shorting OUT to VSS during operation to prevent
damage to the amplifier. The device can also be damaged if the output terminals are reverse-biased and an excessive current is
allowed to flow. Specific guidelines for handling devices of this type are contained in the publication
Guidelines for Handling
Electrostatic-Discharge-Sensitive (ESDS) Devices and Assemblies
available from Texas Instruments.
Copyright 1996, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
DUAL-IN-LINE PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
ODB 1
IAG2 2
SUB 3
ADB 4
OUT1 5
OUT2 6
12 IAG1
11 SAG
10 SAG
9 SUB
8 SRG
7 RST
TC237
680- × 500-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS044B – JUNE 1994 – REVISED JUNE 1996
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
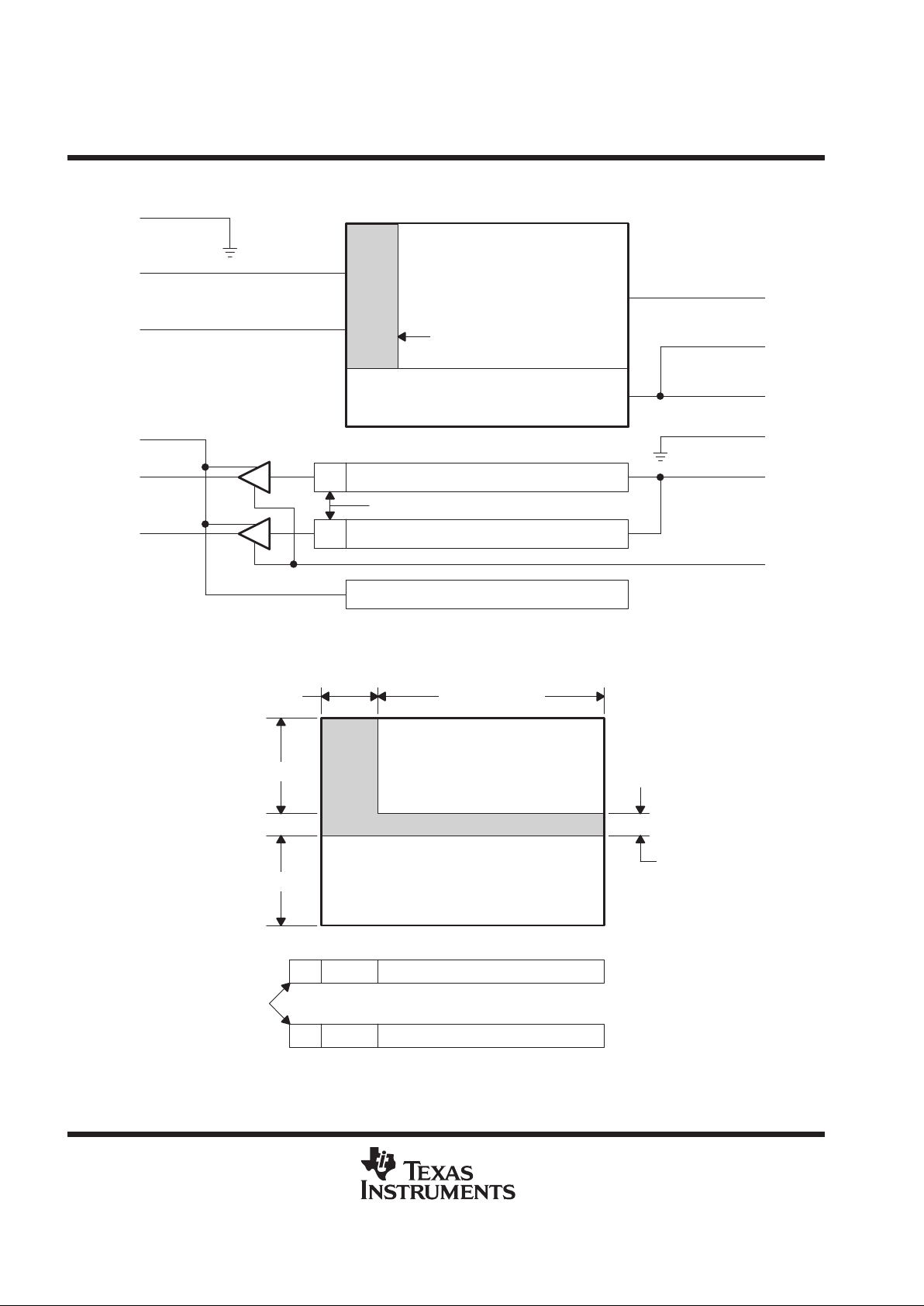
functional block diagram
Image Area With
Blooming Protection
Dark Reference Elements
Storage Area
Clearing Drain
3
1
2
4
6
5
SUB
ODB
IAG2
ADB
OUT2
OUT1
Amplifiers
4 Dummy Elements
9
8
7
10
12
11
IAG1
SAG
SAG
SUB
SRG
RST
sensor topology diagram
Single-Phase Storage Area
Two-Phase Image-Sensing Area
422
Optical Black
(OPB)
4 22 658 Active Pixels
Dummy Pixels
658 Active Pixels
4 Dark Lines
22 Dark Reference Pixels
658 Active Pixels
496 Lines
500 Lines
TC237
680- × 500-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS044B – JUNE 1994 – REVISED JUNE 1996
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
I/O
DESCRIPTION
ADB 4 I Supply voltage for amplifier-drain bias
IAG1 12 I Image-area gate 1
IAG2 2 I Image-area gate 2
ODB 1 I Supply voltage overflow-drain antiblooming bias
OUT1 5 O Output signal 1
OUT2 6 O Output signal 2
RST 7 I Reset gate
SAG 10, 11 I Storage-area gate
SRG 8 I Serial-register gate
SUB 3, 9 Substrate
detailed description
The TC237 consists of four basic functional blocks: the image-sensing area, the image-storage area, the serial
register gates, and the low-noise signal processing amplifier block with charge-detection nodes and
independent resets. The location of each of these blocks is identified in the functional block diagram.
image-sensing and storage areas
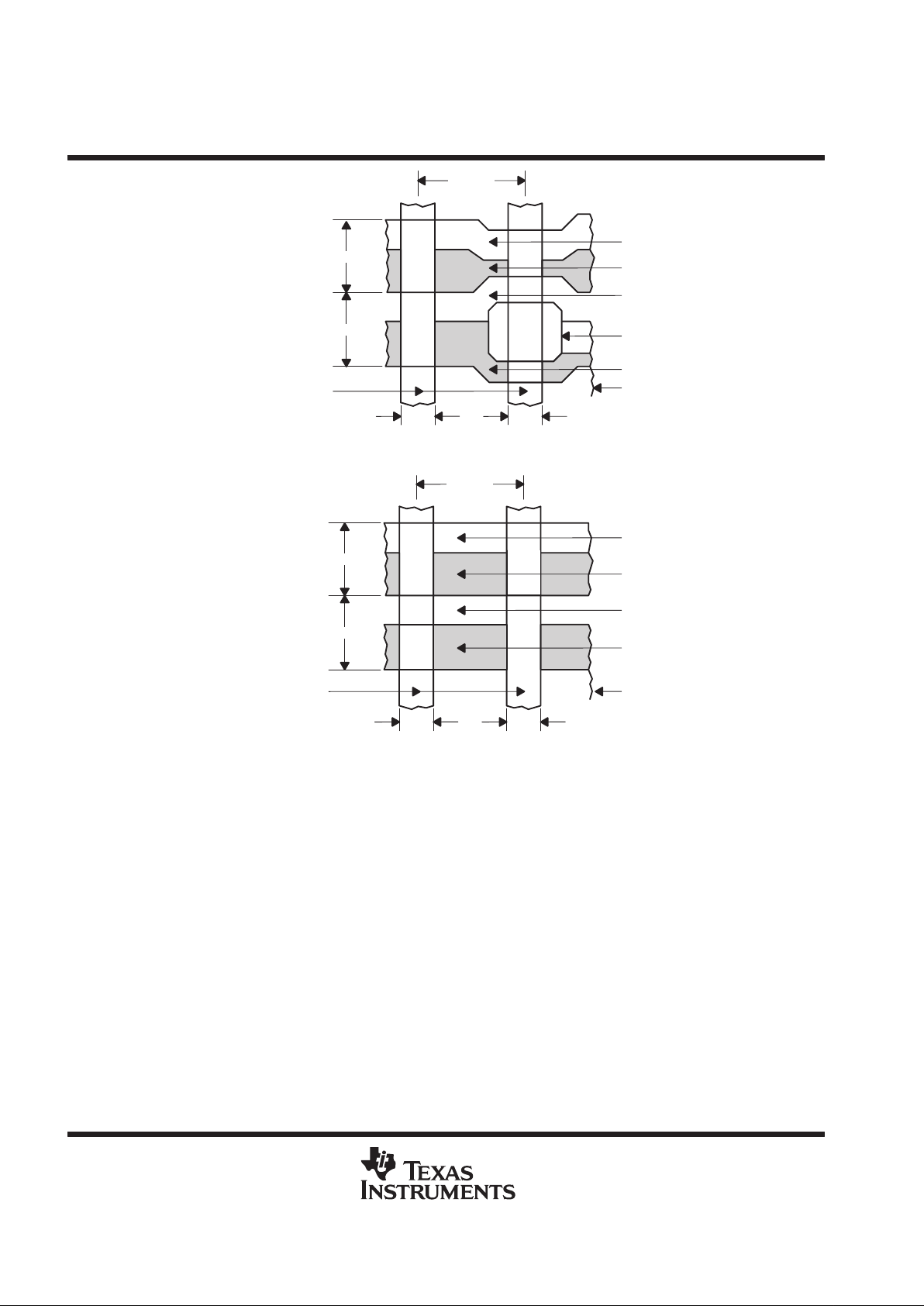
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show cross sections with potential-well diagrams and top views of the image-sensing and
storage-area elements. As light enters the silicon in the image-sensing area, free electrons are generated and
collected in the wells of the sensing elements. Blooming protection is provided by applying a dc bias to the
overflow-drain bias pin. If it is necessary to clear the image before beginning a new integration time (for
implementation of electronic fixed shutter or electronic auto-iris), it is possible to do so by applying a pulse at
least 1 µs in duration to the overflow-drain bias. After integration is complete, the charge is transferred into the
storage area; the transfer timing is dependent on whether the readout mode is interlace or progressive scan.
If the progressive-scan readout mode is selected, the readout may be performed normally by utilizing one serial
register or high speed by using both serial registers (see Figure 3 through Figure 5). A line-summing operation
(which is useful in off-chip smear subtraction) may be implemented before the parallel transfer (see Figure 6
for line-summing timing).
There are 22 columns at the left edge of the image-sensing area that are shielded from incident light; these
elements provide the dark reference used in subsequent video-processing circuits to restore the video black
level. There are also four dark lines between the image-sensing and the image-storage area that prevent charge
leakage from the image-sensing area into the image-storage area.
TC237
680- × 500-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS044B – JUNE 1994 – REVISED JUNE 1996
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
3.8 µm
3.6 µm
7.4 µm
1.6 µm
1.6 µm
Channel Stops
Including Metal Bus Lines
Clocked Barrier
Clocked Well
Virtual Barrier
Antiblooming
Device
Virtual Well
Clocked Gate
Figure 1. Image-Area Pixel Structure
3.5 µm
3.5 µm
7.4 µm
1.6 µm
Clocked Barrier
Clocked Well
Virtual Barrier
Virtual Well
Clocked Gate
1.6 µm
Channel Stops
Including Metal Bus Lines
Figure 2. Storage-Area Pixel Structure
TC237
680- × 500-PIXEL CCD IMAGE SENSOR
SOCS044B – JUNE 1994 – REVISED JUNE 1996
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Expanded Section of
Parallel Transfer
IAG1, 2
SAG
SRG
1 µs Minimum
684 Pulses
684 Pulses
†
†
†
‡
ODB
IAG1, 2
SAG
SRG
RST
Clear Integrate Transfer to Memory Readout
250 Cycles
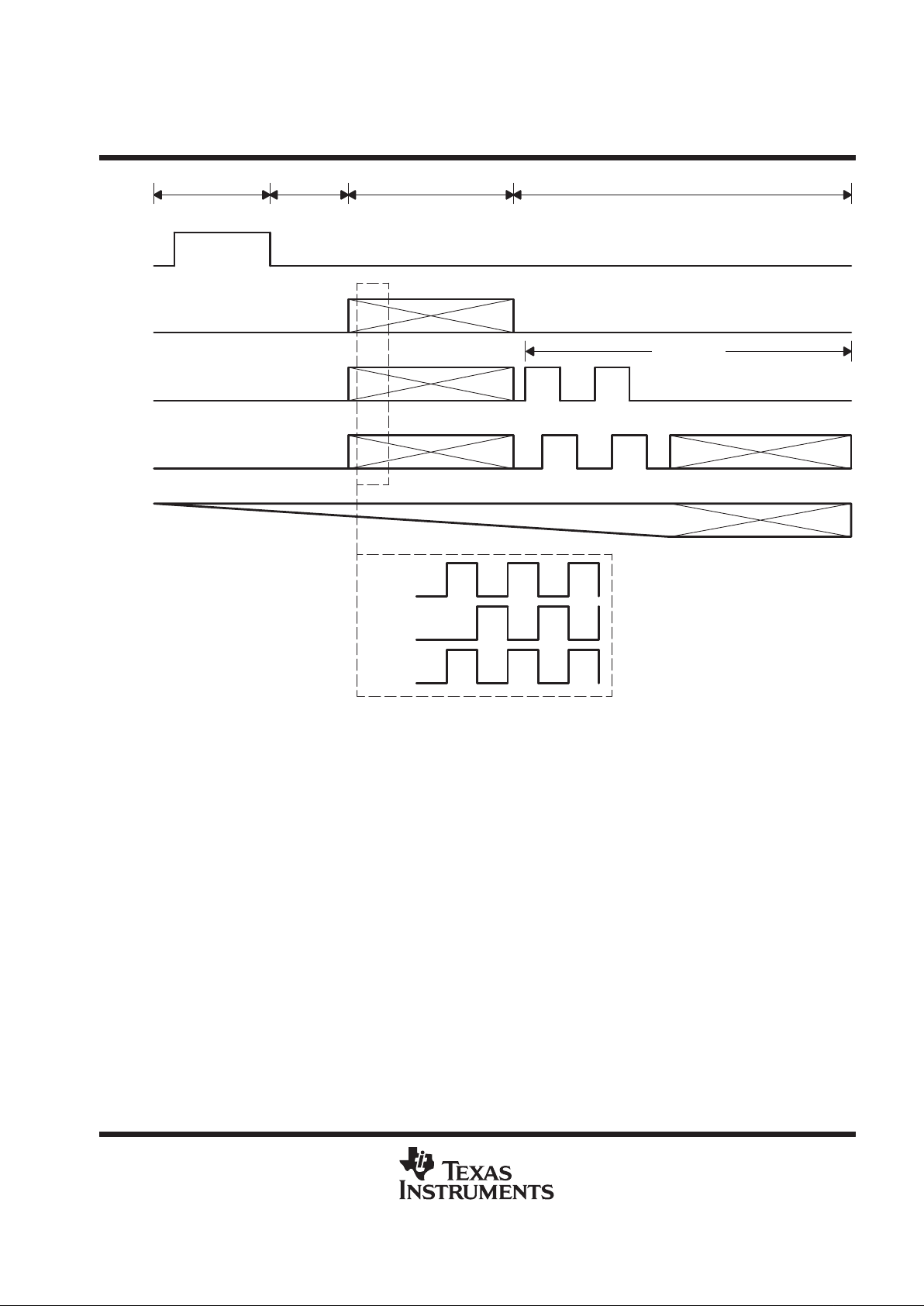
Figure 3. Interlace Timing
†
The number of parallel transfer pulses is field dependent. Field 1 has 500 pulses of IAG1, IAG2, SAG, and SRG with appropriate phasing. Field 2
has 501 pulses.
‡
The readout is from register 2.
 Loading...
Loading...